Essay On Women Rights
500 words essay on women rights.
Women rights are basic human rights claimed for women and girls all over the world. It was enshrined by the United Nations around 70 years ago for every human on the earth. It includes many things which range from equal pay to the right to education. The essay on women rights will take us through this in detail for a better understanding.


Importance of Women Rights
Women rights are very important for everyone all over the world. It does not just benefit her but every member of society. When women get equal rights, the world can progress together with everyone playing an essential role.
If there weren’t any women rights, women wouldn’t have been allowed to do something as basic as a vote. Further, it is a game-changer for those women who suffer from gender discrimination .
Women rights are important as it gives women the opportunity to get an education and earn in life. It makes them independent which is essential for every woman on earth. Thus, we must all make sure women rights are implemented everywhere.
How to Fight for Women Rights
All of us can participate in the fight for women rights. Even though the world has evolved and women have more freedom than before, we still have a long way to go. In other words, the fight is far from over.
First of all, it is essential to raise our voices. We must make some noise about the issues that women face on a daily basis. Spark up conversations through your social media or make people aware if they are misinformed.
Don’t be a mute spectator to violence against women, take a stand. Further, a volunteer with women rights organisations to learn more about it. Moreover, it also allows you to contribute to change through it.
Similarly, indulge in research and event planning to make events a success. One can also start fundraisers to bring like-minded people together for a common cause. It is also important to attend marches and protests to show actual support.
History has been proof of the revolution which women’s marches have brought about. Thus, public demonstrations are essential for demanding action for change and impacting the world on a large level.
Further, if you can, make sure to donate to women’s movements and organisations. Many women of the world are deprived of basic funds, try donating to organizations that help in uplifting women and changing their future.
You can also shop smartly by making sure your money is going for a great cause. In other words, invest in companies which support women’s right or which give equal pay to them. It can make a big difference to women all over the world.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conclusion of the Essay on Women Rights
To sum it up, only when women and girls get full access to their rights will they be able to enjoy a life of freedom . It includes everything from equal pay to land ownerships rights and more. Further, a country can only transform when its women get an equal say in everything and are treated equally.
FAQ of Essay on Women Rights
Question 1: Why are having equal rights important?
Answer 1: It is essential to have equal rights as it guarantees people the means necessary for satisfying their basic needs, such as food, housing, and education. This allows them to take full advantage of all opportunities. Lastly, when we guarantee life, liberty, equality, and security, it protects people against abuse by those who are more powerful.
Question 2: What is the purpose of women’s rights?
Answer 2: Women’s rights are the essential human rights that the United Nations enshrined for every human being on the earth nearly 70 years ago. These rights include a lot of rights including the rights to live free from violence, slavery, and discrimination. In addition to the right to education, own property; vote and to earn a fair and equal wage.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

138 Women’s Rights Research Questions and Essay Topics
🏆 best topics related to women’s rights, ⭐ simple & easy essay topics on women’s issues, 📌 most interesting research topics on women’s issues, 👍 good women’s rights research paper topics, ❓ research questions about women’s rights.
Women’s rights essays are an excellent way to learn about the situation of the female gender throughout the world and demonstrate your knowledge.
You can cover historical women’s rights essay topics, such as the evolution of girl child education in various countries and regions or the different waves of the feminism movement.
Alternatively, you can study more current topics, such as the status of women in Islam or the debate about whether women’s rights apply to transgender women.
In either case, there is a multitude of ideas that you can express and discuss in your paper to make it engaging and thought-provoking. However, you should not neglect the basic aspects of writing an essay, especially its structure and presentation.
The thesis statement is critical to your essay’s structure, as it has to be at the center of each point you make. It should state the overall message or question of your paper comprehensively but concisely at the same time.
Afterwards, every point you make should directly or indirectly support the claim or answer the question, and you should make the relationship explicit for better clarity.
It is good practice to make the thesis a single sentence that does not rely on context, being fully self-sufficient, but avoids being excessively long.
As such, writing a good thesis is a challenging task that requires care and practice. Do not be afraid to spend additional time writing the statement and refining it.
It is beneficial to have a framework of how you will arrange topics and formulate your points so that they flow into one another and support the central thesis before you begin writing.
The practice will help you arrange transitional words and make the essay more coherent and connected as opposed to being an assortment of loosely associated statements.
To that end, you should write an outline, which deserves a separate discussion. However, the basics are simple: write down all of the ideas you want to discuss, discard the worst or fold them into other, broader topics until you have a handful left, and organize those in a logical progression.
Here are some additional tips for your structuring process:
- Frame the ideas in your outline using self-explanatory and concise women’s rights essay titles. You can then use them to separate different points in your essay with titles that correspond to outline elements. The outline itself will effectively become a table of contents, saving you time if one is necessary.
- Try to keep the discussion of each topic self-contained, without much reference to other matters you discussed in the essay. If there is a significant relationship, you should devote a separate section to it.
- Do not forget to include an introduction and a conclusion in your paper. The introduction familiarizes the reader with the topic and ends with your thesis statement, setting the tone and direction of the essay. The conclusion sums up what you have written and adds some concluding remarks to finish. The introduction should not contain facts and examples beyond what is common knowledge in the field. The conclusion may not introduce new information beyond what has been stated in the essay.
You can find excellent women’s rights essay examples, useful samples, and more helpful tips on writing your essay at IvyPanda, so visit whenever you are having trouble or would like advice!
- The Success of Women’s Rights Movement They sought the equal treatment of women and men by law and fought for voting rights. The women’s rights movement was successful because they were united, had a strong ideological foundation, and organized campaigns on […]
- Women’s Rights in the 21st Century: Education and Politics The lack of equity in the specified areas affect women’s lives on range of levels, depriving them of the opportunities that they are supposed to be entitled to and posing a tangible threat to the […]
- The Women of the Veil: Gaining Rights and Freedoms The author chides the activities of the Western colonies in Afghanistan in restoring the rights of the women of the veil.
- What Causes Women’s Rights Violation? Most women have been abused in modern societies due to illiteracy and lack of exposure to their rights. Most developing nations are struggling to adopt democratic policies and forget that women deserve the right to […]
- Shirin Ebadi’s Perspective on Women’s Human Rights Activism and Islam It is worth noting that Shirin Ebadi’s self-identity as an Iranian woman and a Muslim empowers her experience and perspective in women’s rights activism.
- Women’s Rights and Gender Inequality in Saudi Arabia Indeed, it is crucial to understand the importance of women’s rights, see the connections between the past, the present, the local, and the global, and realize how political and media discourse represents the social issue […]
- “Women’s Rights Are Human Rights” by Hillary Clinton Hillary Clinton’s speech about women’s rights effectively convinces her audience that women rights are an indispensable part of human rights through the use of logical argument, repetition, historical facts, and emotional stories.
- The Role of African American Women in the Civil Right Movement The role of women in the Civil Rights Movement started to change in the 1960s. Women in the Civil Rights Movement: Trailblazers and Torchbearers.
- Women’s Rights and the Advancement of Democracy The degree of citizen involvement in the political process, including the participation of various social groups in political parties and decision-making bodies, determines the quality of democracy in addition to the structure of current political […]
- Women in New France: Rights, Freedoms and Responsibilities However, the development of New France was quite distinct due to peculiarities of the gender roles in the North America and France.
- Invisible Southern Black Women Leaders in the Civil Rights Movement Based on 36 personal interviews and multiple published and archived sources, the author demonstrates that black women in the South have played a prominent role in the struggle for their rights.
- Foot Binding in China in Terms of Women’s Rights The practice of foot binding in China can be traced back to the Sung Dynasty that prevailed between 960-1280 AD, supposedly as an imitation of an imperial concubine who was required to perform a dance […]
- African-American Women and the Civil Rights Movement The key factors that left the Black women unrecognized or led to recognition of just a few of them as leaders are class, race and gender biases.
- Planned Parenthood and Women’s Rights It took decades for the government to acknowledge the necessity of the services offered in these clinics and even longer for the public to accept a woman’s right to reproductive health care, the establishment of […]
- Utilitarian Permissive Concept for Women’s Right to Choose Abortion Utilitarians believe that the right to choose abortion should be protected under the law as a matter of justice since a woman should have the right to make decisions concerning her own body and health.
- Women’s Rights: Democratic Perceptions Therefore, it is proper to claim that women would not be able to exercise their rights and freedoms as frequently without the efforts of Democrats.
- Abolition, Women’s Rights, and Temperance Movements Analysis Movements for the abolition of slavery, women’s rights, or the temperance movement were reflecting the current social problems, were enriched through the participation of women, and were generally based on the Christian values of diligence, […]
- Judith Jarvis Thomson on Women’s Right to Abortion The most serious objection to Thompson’s argument might be the one addressing abortion as a killing of a child, given that the fetus is considered a human being from the moment of conception.
- Abortion and Women’s Right to Control Their Bodies However, the decision to ban abortions can be viewed as illegal, unethical, and contradicting the values of the 21st century. In such a way, the prohibition of abortion is a serious health concern leading to […]
- The Women’s Rights Movement and Indigenous People In this article, the author addresses the differences between the Euro-American and Native American societies and the role of women in them.
- The Texas Abortion Law: A Signal of War on Women’s Rights and Bodies The purpose of this paper is to examine the structure and implications of the Texas Abortion Law in order to demonstrate its flaws.
- Women’s Rights and Reform Impulses The reform impulses altered women’s place in society, making them equal to men in the ability to speak publicly, pursue their liberty, and attain their goals.
- The Evolution of Women’s Rights Through American History From the property-owning women of the late 18th century to the proponents of the women’s liberation in the 1960s, women always succeeded in using the influential political theories of their time to eventually make feminist […]
- Injustices Women Faced in Quest for Equal Rights The source Alice Paul depicts the numerous contributions that she and her fellow suffragists made to the new rights of women.
- Sojourner Truth – A Women’s Rights Activist and Abolitionist Sojourner Truth believed in truth, justice, and equality for all people, which made her escape slavery and advocate for women’s rights.
- Catharine Beecher and Women’s Rights Catharine Beecher’s “An Appeal to American Women” is a discussion kind of piece that considers the power of women in office and how the issue should be approached.
- The Aftermath of the Progression of Women’s Rights Period At the end of the 1800s and the beginning of 1900s, women’s organizations and women struggled for social reforms, to gain the right to vote, and for diverse political and economic equality.
- Lucy Parsons as a Women’s Rights Advocate and Her Beliefs She was a believer in anarchism and thought that it was the means to liberty and freedom. She wanted the constitution to be amended to say that men and women are equal in all aspects.
- Women in Islam: Some Rights, No Equality Notwithstanding the principles of equality of men and women in Islamic tradition, women’s low status should be attributed not to the ideals set in the Quran but to the cultural norms of the patriarchal society.
- Primary Source on Women’s Voting Rights The combination of statements that degrade the image of suffragettes and suffrage and quotes of leaders’ opinions is a way for the editor to influence the audience.
- Syrian Conflict and Women Rights: Way to Equality or Another Discrimination The main reason for a low percentage of women in the workforce is Syrian social norms, which stereotypically reflect the role of women in homes serving their husbands and in the private sector.
- Movement for Women’s Rights in Great Britain and the United States This essay analytically explores some of the conditions which helped bring about movement for women’s right in Great Britain and United States before the close of the last century. In addition, the most significant demand […]
- Women in Colonial America: Fight for Rights Wives that happily accepted their role and conformed to Puritan societal standards were openly referred to and addressed as ‘goodwife.’ However, the authoritative figure in the family and throughout all facets of Puritan society was […]
- Women’s Involvement and Their Rights in Nationalist Ireland The beginning of the seventeenth century and the eighteenth century saw the struggle of the Irish women for the struggle to attaining freedom.
- Women’s Fight for Their Rights Maybe, but lots of researchers are coming to various conclusions: women are not selecting to stay out of the workforce due to a change in approaches, the state.
- Women in the Struggle for Civil Rights In other instants, women in the struggle for civil rights can also file a case in a court of law demanding the lawmakers to enact some policies of which they feel when passed will protect […]
- Refugee Women and Their Human Rights According to the researches have been made by UNHCR, 1998, found that 80% of the refugees immigrating to the United States and other countries of second asylum are women or children.
- Women’s Rights Movement in the 19th Century In this paper, the peculiarities of women’s suffrage, its political and social background, and further reactions will be discussed to clarify the worth and impact of the chosen event.
- Advocating for Women’s Employment Rights in the UAE and Saudi Arabia The position of women in the societies of the UAE and Saudi Arabia is a cause for endless controversy. Public relations between women and men are limited in the given countries, and women are required […]
- Women Rights: New Data and Movements For example, whereas the women’s health rights movement is a global affair, the fact that events related to the movement are mainly held in the US means that other countries do not feel the impact […]
- Women’s Rights in the United States History The leading cause of poverty in developing countries is the lack of skills and education to enable people to get employment.
- Women’s Rights in Palestine and Neighboring Countries In a review of relevant literature, women’s rights in Palestine can be compared to women’s rights in three neighboring countries Jordan, Egypt, and Israel from the perspective of violence and discrimination, and specific differences, including […]
- Understanding Women’s Right in Islamic World The role of women in the Islamic society during and soon after the death of Prophet Mohammed was similar to that of men.
- Saudi Arabian Women’s Right to Drive: Pros and Cons The objective of this paper is to present the arguments from both sides of the discussion on the issue of whether women should be able to drive legally in Saudi Arabia.
- Arab Spring’s Impact on Women’s Rights and Security The aim of the research is to define the effects that the Arab Spring has had on the perception of women in the Arab society.
- Women’s Rights Since Pre-History to 1600 A.D In this regard, most women from the medieval times could determine their social and political destiny, but the responsibility to others mainly rested on the men.
- Women’s Fight for Equal Human Rights According to the readings assigned, the term feminist could be used to refer to people who fought for the rights of women.
- Women’s Family and Social Responsibilities and Rights The uniqueness of Addams and Sanger’s approach to discussing the rights of females is in the fact that these authors discuss any social responsibilities of women as the key to improving their roles in the […]
- Women’s Rights in the Great Depression Period The pursuit of the workplace equality and the protection of women from unfair treatment by the employers were quite unsuccessful and slow due to the major division in the opinions.
- Women’s Roles and Rights in the 18-19th Century America We can only do the simplest work; we cannot have a good job because that is the men’s domain, and they have the necessary training to do it.
- Debate Over Women’s Rights At times, the problem is that there is bias and discrimination about the strength of the woman and no chance has ever been given to them to prove if the allegation is wrong.
- Hip-Hop Music and the Role of Women in It: Fight for Women’s Rights in Society While looking at the various roles of women in hip hop and rap, it is also important to note that the way women are presented has various effects on society.
- Gender Studies: Women’s Rights in Saudi Arabia This paper will review the a issue of women’s rights in Saudi Arabia from the perspective of four different groups including the modern Saudi women, traditional Saudi women, Government officials, and international women’s rights organizations.
- Temperance, Women’s Rights, Education, Antislavery and Prison Reform: New Objectives, New Concerns Among the most memorable reforms of that time, the innovations in the system of treating the convicts and the prisoners must be the reform that reflected the very essence of the XIX-century social ideas.
- The Opportunity to Succeed as Women Entrepreneurs in Saudi Arabia Compared With UK In addition, it is through the small businesses that new products and services are being developed to meet the growing needs of the population in the entire Kingdom.
- Women’s Rights – Contribution of E. Cady Stanton and S.B. Anthony The first significant and most important move was made by Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony, on the other hand, was born in a Quaker family and her father was also quite a successful […]
- Oppression of Women’s Rights Affects the Economy of the Middle East For instance in Iceland, the high level of quality of life and health is one of the factors that lead to a GDP per capita of $54,291 On the contrary, there are situations where women […]
- Reform-Women’s Rights and Slavery The colonizers felt that the movement was threatening their business and status in the society and began to ridicule and attack the families of the abolitionists.
- Women’s Role in Contemporary Korea The effort of women to work in professional and high positions in different sectors, the government decided to boost their effort and maintain their morale.
- Non Governmental Organization of Women’s Learning Partnership for Rights Development and Peace In most cases the rights of women which are mainly suppressed include the right to own property, the right to work or hold a public office, the right of receiving education, the right to vote […]
- The Development of Women’s Rights However, she cannot agree to such distribution of the roles, and she calls upon all people to look again at the situation, connected to women’s rights, and provide all women with a chance to participate […]
- Jane Cunningham Croly: Fighting for Women Rights The problem of women inequality with men had been considered in the society and Jane Cunningham Croly was one of those who wanted to contribute to the movement, and her journalistic activity was that measure.
- Women’s Suffrage Discussion The entrenchment of equal rights of women and men and more noticeably the right of every American woman to vote came into being after the enactment of the nineteenth amendment.
- Disclosing the Aspects of Female Authorship as Presented in Woolf’s Professions for Women and Wollstonecraft’s A Vindication of the Right of Woman In their works called A Vindication of the Right of Woman and Professions of Women respectively, they express their vigorous desire to liberate women from the professional taboos to enter female authorship imposed by the […]
- Power of Women’s Rights How the Anti-Slavery Movement Challenge Established Notions of Manhood and Womanhood Kathryn Kish Sklar’s general idea in the book is to enlighten people on the role of women in the society during the 19th century, […]
- Women’s Rights in the Muslim World Ahmed first focuses on the gender pattern in the Middle East prior to the emergence of the Islam in order to gain ground to describe the Islamic doctrine on women that were practiced in the […]
- Afghan Women and Violation of Their Rights It is for this reason that the Taliban have been the party mostly blamed for the mistreatment of women in the country. The U.S.has the necessary resources to ensure that this is achieved therefore guaranteeing […]
- Did Flappers Have a Positive Effect on Women’s Rights in America in the 1920s?
- Abigail Adams’ Inspiring Rebellion for Women’s Rights
- The Power of the Internet and Women’s Rights in Guatemala
- Pencils and Bullets Women’s Rights in Afghanistan
- Women’s Rights in Supreme Court Decisions of the 1960’s and 1970’s
- Women’s Rights: A Path into the Society to Achieve Social Liberation
- The Taliban: Deprivers of Women’s Rights in Afghanistan
- Henrik Ibsen’s Description of Women’s Rights as Depicted in His Play, A Doll’s House
- Perceptions on The Islamic Practice of Veiling: Relevance to the Quest for Women’s Rights
- The Effects of Christianity on Women’s Rights in China
- Women’s Rights in the 1920’s and Examples in F. Scott Fitzgerald’s The Great Gatsby
- Pornography and Feminist Fight for Women’s Rights
- The Progression of Women’s Rights from the Early 20th Century
- Islamic Head Scarf: Women’s Rights and Cultural Sensibilities
- The Women’s Rights Movement in England: 18th Century and Beyond
- Comparing Cultures: the Development of Women’s Rights in China and Saudi Arabia
- Mary Wollstonecraft and the Early Women’s Rights Movement
- The Progression of Women’s Rights in the Middle East
- Elizabeth Stanton’s Impact on Women’s Rights Movement
- Women’s Rights in Latin America and the Caribbean
- Women’s Rights and Their Importance to the Development of True Democracy
- Women’s Rights Within A Thousand Splendid Suns by Khaled Hosseini
- Every Woman Has Her Day: The Women’s Rights Movement in 19th Century
- Evolution of Women’s Rights Since 19th Century
- Integrating Equality – Globalization, Women’s Rights, Son Preference and Human Trafficking
- Analysis of the View of Opinions of Authors Advocating for Women’s Rights
- Abolition of Slavery is Conducive to Women’s Rights Movement
- Women’s Rights Violations in Afghanistan
- Feminism and Women’s Rights in Post Colonial Africa and France
- Social Justice in America: Women’s Rights
- Horace Walpole and Samuel Johnson, Champions of Women’s Rights
- Muslims Women’s Rights to Practice Their Religion
- Women’s Rights and Hills Like White Elephants
- Rhetorical Analysis of Hillary Clinton’s Speech, Women’s Rights Are Human Rights
- Euripides Support of Women’s Rights
- Women’s Rights in Afghanistan 1996 to the Present
- Women’s Rights & Their Impact on the Development of Iran
- Women’s Rights Between 1750 and 1914
- Exploring The Women’s Rights Movement With Good Man Is Hard to Find by Flannery O´Conner
- Progressive Era: The Era of Immigration, Race, and Women’s Rights
- Women’s Rights in the United States in the 1700s
- Which Countries Violate Women’s Rights?
- What Was the Aim of the Women’s Movement?
- How Did the Anti-Slavery Movement Contribute to the Women’s Rights Movement?
- Who Were the 4 Main Leaders of the Women’s Rights Movement?
- How Does Gender Inequality Affect Women’s Rights?
- Who Fought for Women’s Right to Work?
- What Was the Biggest Women’s Rights Movement?
- What Are the Colors for Women’s Rights?
- Why Women’s Rights Lost Ground at the End of World War Two?
- What Is the Role of Lesbians in the Women’s Movement?
- How Far Women’s Rights Have Come?
- What Laws Help Women’s Rights?
- How Were the Abolition and Women’s Rights Movements Similar?
- What Are the Most Important Events in Women’s Rights History?
- Who Is Responsible for Women’s Rights?
- What Is the History of Women’s Rights?
- What Were 3 Major Events in the Women’s Rights Movement?
- How Margaret Fuller and Fanny Fern Used Writing as a Weapon for Women’s Rights?
- How Did Race Impact African American Women’s Experiences During the Women’s Suffrage Movement?
- What Was the Cause of the First Woman’s Rights Convention?
- Why Is Education Important for Women’s Rights?
- How Are Women’s Rights Linked to Economic Development?
- When Did the Women’s Rights Movement Start and End?
- Why Did the Women’s Rights Movement Emerge in the USA During the 1950S and 1960S?
- What Are Women’s Cultural Rights?
- Who Was the First Black Women’s Rights Activist?
- When Was the First Female Vote?
- What Was the Movement for Women’s Rights in the 1800S?
- Who Was the Black Woman Who Fought for Women’s Rights?
- Who Was the Biggest Women’s Rights Activist?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 1). 138 Women’s Rights Research Questions and Essay Topics. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/womens-rights-essay-examples/
"138 Women’s Rights Research Questions and Essay Topics." IvyPanda , 1 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/womens-rights-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '138 Women’s Rights Research Questions and Essay Topics'. 1 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "138 Women’s Rights Research Questions and Essay Topics." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/womens-rights-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "138 Women’s Rights Research Questions and Essay Topics." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/womens-rights-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "138 Women’s Rights Research Questions and Essay Topics." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/womens-rights-essay-examples/.
- Women’s Movement Questions
- Feminism Questions
- Women’s Role Essay Topics
- Discrimination Essay Titles
- Activist Essay Titles
- Equality Topics
- Human Rights Essay Ideas
- Civil Rights Movement Questions
- Gender Inequality Research Topics
- Women’s Suffrage Essay Ideas
- Childbirth Titles
- Gender Discrimination Research Topics
- Motherhood Ideas
- Personal Identity Paper Topics
- Reproductive Health Essay Titles

Essay on Women’s Rights
Students are often asked to write an essay on Women’s Rights in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Women’s Rights
Introduction.
Women’s rights are fundamental human rights that everyone should respect. They include the right to live free from violence, to be educated, to vote, and to earn a fair wage.
History of Women’s Rights
The fight for women’s rights began in the 1800s. Women protested for the right to vote, work, and receive equal pay. Their efforts led to significant changes.
Importance of Women’s Rights
Women’s rights are vital for equality. When women have the same rights as men, societies are fairer and more balanced.
There is still work to be done to ensure women’s rights worldwide. Everyone should strive to promote and protect these rights.
250 Words Essay on Women’s Rights
Women’s rights are the fundamental human rights that were enshrined by the United Nations for every human being on the planet nearly 70 years ago. These rights include the right to live free from violence, slavery, and discrimination; to be educated; to own property; to vote; and to earn a fair and equal wage.
The Historical Context
The fight for women’s rights has been a long-standing struggle. From the suffragettes of the early 20th century who fought for women’s right to vote, to the women’s liberation movement of the 1960s which sought economic and social equality, women’s rights have been a contentious issue throughout history.
Current Status
Despite significant progress, gender inequality persists in many parts of the world. Women are still underrepresented in political and corporate leadership, they are more likely to live in poverty, and they face higher levels of violence and discrimination.
Challenges and Solutions
The path to gender equality is fraught with obstacles, including deeply entrenched societal norms and institutions. However, change is possible. Education, legislation, and societal shifts in attitudes towards gender can play a significant role in promoting women’s rights.
The fight for women’s rights is a fight for human rights. As society evolves, it is crucial to continue advocating for gender equality, not just for the benefit of women, but for the betterment of society as a whole.
500 Words Essay on Women’s Rights
Women’s rights, a subject that has been at the forefront of social and political discussions for centuries, is a complex and multifaceted issue. It encompasses a wide range of topics, from the right to vote and work to reproductive rights and gender equality. This essay aims to delve into the evolution of women’s rights, the current state of these rights, and the challenges that remain.
The Evolution of Women’s Rights
Historically, women were typically relegated to roles within the domestic sphere, with limited access to education, political participation, and economic independence. The first wave of feminism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries challenged these norms, with suffragettes fighting for women’s right to vote. The second wave in the 1960s and 70s broadened the debate to include issues such as workplace equality and reproductive rights. The third wave in the 1990s and beyond has continued to challenge traditional gender norms and has expanded the conversation to include intersectionality and the rights of women in marginalized communities.
Current State of Women’s Rights
The progress made in the past century is undeniable. Women have achieved significant strides in political representation, educational attainment, and economic participation. However, the fight for equality is far from over. Globally, women still earn less than men, are underrepresented in positions of power, and are more likely to experience violence and discrimination.
Challenges and the Way Forward
The struggle for women’s rights faces numerous challenges. These include deeply entrenched patriarchal norms, religious and cultural beliefs, and structural inequalities that disadvantage women. To overcome these obstacles, it is essential to continue advocating for policy changes that promote gender equality, such as equal pay legislation, paid parental leave, and laws to prevent and punish gender-based violence.
However, policy changes alone are not enough. There must also be a cultural shift towards recognizing and valifying women’s rights. This includes challenging harmful stereotypes, promoting positive representations of women in media, and fostering a culture of respect and equality.
In conclusion, while significant progress has been made in the fight for women’s rights, there is still much work to be done. The struggle for gender equality is not just a women’s issue; it is a human issue that affects us all. By continuing to advocate for policy changes and cultural shifts, we can create a world where all women have the opportunity to live free from discrimination and violence, and to realize their full potential.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Autumn Season
- Essay on Architecture
- Essay on Apple Fruit
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

5 Women Empowerment Essays Everybody Should Read
What does “women’s empowerment” mean? It refers to the process of giving women control over their choices and access to the opportunities and resources that allow them to thrive. While there’s been progress, gender inequality remains a persistent issue in the world. Empowering women politically, socially, economically, educationally, and psychologically helps narrow the gap. Here are five essays about women’s empowerment that everyone should read:
Women’s Movements and Feminist Activism (2019)
Amanda Gouws & Azille Coetzee
This editorial from the “Empowering women for gender equity” issue of the journal Agenda explores the issue’s themes. It gives a big picture view of the topics within. The issue is dedicated to women’s movements and activism primarily in South Africa, but also other African countries. New women’s movements focus on engaging with institutional policies and running campaigns for more female representation in government. Some barriers make activism work harder, such as resistance from men and funding, If you’re interested in the whole issue, this editorial provides a great summary of the main points, so you can decide if you want to read further.
Agenda is an African peer-viewed academic journal focusing on feminism. It was established in 1987. It publishes articles and other entries, and tutors young writers.
5 Powerful Ways Women Can Empower Other Women (2020)
Pavitra Raja
Originally published during Women’s History Month, this piece explores five initiatives spearheaded by women in the Schwab Foundation for Social Entrepreneurship community. Created by women for women, these innovations demonstrate what’s possible when women harness their skills and empower each other. The initiatives featured in this article embrace technology, education, training programs, and more.
Pavitra Raja is the Community Manager for social entrepreneurs in Europe, North America, and Latin America. She’s consulted with the UN Economic Commission for Europe and also has experience in legal affairs and policy in the private and public sectors.
The Key to Improving Women’s Health in Developing Countries (2019)
Because of gender inequality, women’s health is affected around the world. Factors like a lower income than men, more responsibilities at home, and less education impact health. This is most clear in developing countries. How can this be addressed? This essay states that empowerment is the key. When giving authority and control over their own lives, women thrive and contribute more to the world. It’s important that programs seeking to end gender inequality focus on empowerment, and not “rescue.” Treating women like victims is not the answer.
Axa is a leading global insurer, covering more than 100 million customers in 57 countries. On their website, they say they strive for the collective good by working on prevention issues, fighting climate change, and prioritizing protection. The company has existed for over 200 years.
Empowering Women Is Smart Economics (2012)
Ana Revenga and Sudhir Shetty
What are the benefits of women’s empowerment? This article presents the argument that closing gender gaps doesn’t only serve women, it’s good for countries as a whole. Gender equality boosts economic productivity, makes institutions more representative, and makes life better for future generations. This piece gives a good overview of the state of the world (the data is a bit old, but things have not changed significantly) and explores policy implications. It’s based on the World Bank’s World Development Report in 2012 on gender equality and development.
Ana Revenga and Sudhir Shetty both worked at the World Bank at the time this article was originally published. Revenga was the Sector Director of Human Development, Europe and Central Asia. Shetty (who still works at the World Bank in a different role) was the Sector Director, Poverty Reduction and Economic Management, East Asia and Pacific.
The Side Of Female Empowerment We Aren’t Talking About Enough (2017)
Tamara Schwarting
In this era of female empowerment, women are being told they can do anything, but can they? It isn’t because women aren’t capable. There just aren’t enough hours in the day. As this article says, women have “more to do but no more time to do it.” The pressure is overwhelming. Is the image of a woman who can “do it all” unrealistic? What can a modern woman do to manage a high-stakes life? This essay digs into some solutions, which include examining expectations and doing self-checks.
Tamara Schwarting is the CEO of 1628 LTD, a co-working community space of independent professionals in Ohio. She’s also an executive-level consultant in supply chain purchasing and business processes. She describes herself as an “urbanist” and has a passion for creative, empowering work environments.
You may also like

15 Examples of Gender Inequality in Everyday Life

11 Approaches to Alleviate World Hunger

15 Facts About Malala Yousafzai

12 Ways Poverty Affects Society

15 Great Charities to Donate to in 2024

15 Quotes Exposing Injustice in Society

14 Trusted Charities Helping Civilians in Palestine

The Great Migration: History, Causes and Facts

Social Change 101: Meaning, Examples, Learning Opportunities

Rosa Parks: Biography, Quotes, Impact

Top 20 Issues Women Are Facing Today

Top 20 Issues Children Are Facing Today
About the author, human rights careers.
Human Rights Careers (HRC) provides information about online courses, jobs, paid internships, masters degrees, scholarships and other opportunities in the human rights sector and related areas.
The Fight for Women's Rights in the Past and Present
Understanding How the Treatment of Women Has Changed Over Time
- History Of Feminism
- Important Figures
- Women's Suffrage
- Women & War
- Laws & Womens Rights
- Feminist Texts
- American History
- African American History
- African History
- Ancient History and Culture
- Asian History
- European History
- Latin American History
- Medieval & Renaissance History
- Military History
- The 20th Century
United Nations Convention on Rights of Women
The now statement of purpose, the 1855 marriage protest.
- Seneca Falls Women's Rights Convention
- Women's Rights in the 1700s
Treatment of Women in the Ancient World
- B.A., Mundelein College
- M.Div., Meadville/Lombard Theological School
The meaning of "women's rights" has varied through time and across cultures. Today, there is still a lack of consensus about what constitutes women's rights. Some would argue a woman's ability to control family size is a fundamental women's right. Others would argue women's rights fall under workplace equality or the chance to serve in the military in the same ways that men do. Many would argue that all of the above should be deemed women's rights.
The term typically refers to whether women are treated as men's equals, but sometimes it specifically refers to special circumstances that affect women, such as job protection when they take time off for maternity leave, though men in the U.S. are increasingly taking paternity leave. While men and women may both be victims of social ills and violence related to human trafficking and rape, protection against these crimes is often described as beneficial to women's rights.
The implementation of various laws and policies over the years paints a historical picture of the benefits that were considered to be "women's rights" at one time. Societies in the ancient, classical, and medieval worlds show how women's rights, even if not referred to by that term, differed from culture to culture.
The 1979 Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women, signed by many United Nations member states, asserts that women's rights belong to the "political, economic, social, cultural, civil" realms. According to the convention text, which became an international treaty in 1981 :
"Any distinction, exclusion or restriction made on the basis of sex which has the effect or purpose of impairing or nullifying the recognition, enjoyment or exercise by women, irrespective of their marital status, on a basis of equality of men and women, of human rights and fundamental freedoms in the political, economic, social, cultural, civil or any other field."
The declaration specifically addresses eliminating prejudice in public education, giving women full political rights to vote and run for public office, as well as marriage and divorce rights that equal men's. The document also called for the elimination of child marriage and sex trafficking while also mentioning equality for women in the criminal justice system and in the workplace.
In 1966, the National Organization for Women (NOW) formed and wrote a statement of purpose that summarizes key women's rights issues of that time. The rights outlined were based on the idea of equality as an opportunity for women to "develop their fullest human potentials" and to put women into the "mainstream of American political, economic and social life." The women's rights issues identified included those in these areas of employment and economics, education, family, political participation, and racial justice.
In their 1855 marriage ceremony , women's rights advocates Lucy Stone and Henry Blackwell refused to honor laws that interfered with the rights of married women in particular. They advocated for wives to be able to legally exist outside of a husband's control, to inherit and own real estate , and have the right to their own wages. Stone and Blackwell also campaigned for wives to be able to choose their own names and place of residence and to sign contracts. They demanded that married mothers be granted custody of their children and be able to sue in court as well.
Seneca Falls Women's Rights Convention
In 1848, the first known women's rights convention in the world took place in Seneca Falls, New York. There, organizers of the convention declared that "men and women are created equal." As such, the feminists gathered demanded that women immediately be given the rights and privileges due to them as U.S. citizens.
In their " Declaration of Sentiments ," the Seneca Falls participants insisted that women should be able to vote, have property rights , including the right to the income they earned, and to pursue higher education and a variety of professions, such as theology, medicine, and law.
Women's Rights in the 1700s
In the 1700s, influential women also spoke out about women's rights from time to time. Abigail Adams , the wife of U.S. founding father and second President John Adams, asked her husband to " remember the ladies " in a letter in which she discussed disparities in women's and men's education.
Hannah Moore, Mary Wollstonecraft , and Judith Sargent Murray focused especially on women's right to an adequate education. They used their writing to advocate for women having influence over social, religious, moral, and political decisions. In "A Vindication of the Rights of Woman" (1791–1792), Wollstonecraft called for women to be educated, have equality in marriage, and have control over family size.
In 1791 during the French Revolution , Olympe de Gouges wrote and published the "Declaration of the Rights of Woman and of the Citizen." In this document, she called for women to have free speech, including the right to name the father of their children and equality for out-of-wedlock children, a demand that suggested that women had the same right as men to have sexual relationships outside of marriage.
In the ancient, classical, and medieval world, women's rights differed somewhat from culture to culture. In some cases, women were essentially regarded as enslaved adults or children under the authority of their husbands or fathers. Women were largely confined to the home and lacked the right to come and go as they pleased. They also had been deprived of the right to choose or refuse marriage partners or end a marriage. Whether women could dress as they liked was an issue during this time as well.
A number of these concerns and others continued to be problems for women in the centuries that followed. They included a lack of custodial rights over children, especially after a divorce; the inability of women to own property, run businesses, and control their own wages, income, and wealth. Women in the ancient, classical, and medieval world also faced employment discrimination, barriers to education, a lack of voting rights, and the inability to represent themselves in lawsuits and court actions.
In the centuries since, women have advocated for these rights and more, but the struggle for equality hasn't ended. Women still face employment discrimination and barriers to healthcare, while single mothers are at great risk of falling into poverty.
- Biography of Lucy Stone, Abolitionist and Women's Rights Reformer
- A History of the Seneca Falls 1848 Women's Rights Convention
- Seneca Falls Declaration of Sentiments: Women's Rights Convention 1848
- The Best Quotes From 19th Century Feminist Lucy Stone
- National Woman's Rights Conventions
- We Now Demand Our Right to Vote (1848)
- Seneca Falls Resolutions: Women's Rights Demands in 1848
- Frederick Douglass Quotes on Women's Rights
- Top 20 Influential Modern Feminist Theorists
- Top 10 Women's Suffrage Activists
- A Short History of Women's Equality Day
- Biography of Olympe de Gouges, French Women's Rights Activist
- Biography of Lucretia Mott
- Biography of Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Women's Suffrage Leader
- 15 Surprising Facts About Susan B. Anthony
- Profile of Amelia Bloomer

Women’s Rights
By Bastian Herre, Pablo Arriagada, Esteban Ortiz-Ospina, Hannah Ritchie, Joe Hasell and Max Roser
Women’s rights are human rights that all women have. But in practice, these rights are often not protected to the same extent as the rights of men.
Among others, women’s rights include: physical integrity rights, such as being free from violence and making choices over their own body; social rights, such as going to school and participating in public life; economic rights, such as owning property, working a job of their choice, and being paid equally for it; and political rights, such as voting for and holding public office.
The protection of these rights allows women to live the lives they want and to thrive in them.
On this page, you can find data and visualizations on how the protection of women’s rights has changed over time, and how it differs across countries.
Research & Writing
Women have made major advances in politics — but the world is still far from equal
Women have gained the right to vote and sit in parliament almost everywhere. But they remain underrepresented, especially in the highest offices.
Bastian Herre

If we can make maternal deaths as rare as they are in the healthiest countries, we can save almost 300,000 mothers each year
Maternal mortality was much more common in the past. Today, it is much lower — but there are still large inequalities across the world.
Hannah Ritchie

Interactive Charts on Women’s Rights
Cite this work.
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this topic page, please also cite the underlying data sources. This topic page can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.

History of the Women’s Rights Movement
Living the Legacy: The Women’s Rights Movement (1848-1998)
“ Never doubt that a small group of thoughtful, committed citizens can change the world. Indeed, it’s the only thing that ever has. ” That was Margaret Mead’s conclusion after a lifetime of observing very diverse cultures around the world. Her insight has been borne out time and again throughout the development of this country of ours. Being allowed to live life in an atmosphere of religious freedom, having a voice in the government you support with your taxes, living free of lifelong enslavement by another person. These beliefs about how life should and must be lived were once considered outlandish by many. But these beliefs were fervently held by visionaries whose steadfast work brought about changed minds and attitudes. Now these beliefs are commonly shared across U.S. society.
Another initially outlandish idea that has come to pass: United States citizenship for women. 1998 marked the 150th Anniversary of a movement by women to achieve full civil rights in this country. Over the past seven generations, dramatic social and legal changes have been accomplished that are now so accepted that they go unnoticed by people whose lives they have utterly changed. Many people who have lived through the recent decades of this process have come to accept blithely what has transpired. And younger people, for the most part, can hardly believe life was ever otherwise. They take the changes completely in stride, as how life has always been.
The staggering changes for women that have come about over those seven generations in family life, in religion, in government, in employment, in education – these changes did not just happen spontaneously. Women themselves made these changes happen, very deliberately. Women have not been the passive recipients of miraculous changes in laws and human nature. Seven generations of women have come together to affect these changes in the most democratic ways: through meetings, petition drives, lobbying, public speaking, and nonviolent resistance. They have worked very deliberately to create a better world, and they have succeeded hugely.
Throughout 1998, the 150th anniversary of the Women’s Rights Movement is being celebrated across the nation with programs and events taking every form imaginable. Like many amazing stories, the history of the Women’s Rights Movement began with a small group of people questioning why human lives were being unfairly constricted.
A Tea Launches a Revolution The Women’s Rights Movement marks July 13, 1848 as its beginning. On that sweltering summer day in upstate New York, a young housewife and mother, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, was invited to tea with four women friends. When the course of their conversation turned to the situation of women, Stanton poured out her discontent with the limitations placed on her own situation under America’s new democracy. Hadn’t the American Revolution had been fought just 70 years earlier to win the patriots freedom from tyranny? But women had not gained freedom even though they’d taken equally tremendous risks through those dangerous years. Surely the new republic would benefit from having its women play more active roles throughout society. Stanton’s friends agreed with her, passionately. This was definitely not the first small group of women to have such a conversation, but it was the first to plan and carry out a specific, large-scale program.
Today we are living the legacy of this afternoon conversation among women friends. Throughout 1998, events celebrating the 150th Anniversary of the Women’s Rights Movement are looking at the massive changes these women set in motion when they daringly agreed to convene the world’s first Women’s Rights Convention.
Within two days of their afternoon tea together, this small group had picked a date for their convention, found a suitable location, and placed a small announcement in the Seneca County Courier. They called “A convention to discuss the social, civil, and religious condition and rights of woman.” The gathering would take place at the Wesleyan Chapel in Seneca Falls on July 19 and 20, 1848.
In the history of western civilization, no similar public meeting had ever been called.
A “Declaration of Sentiments” is Drafted These were patriotic women, sharing the ideal of improving the new republic. They saw their mission as helping the republic keep its promise of better, more egalitarian lives for its citizens. As the women set about preparing for the event, Elizabeth Cady Stanton used the Declaration of Independence as the framework for writing what she titled a “Declaration of Sentiments.” In what proved to be a brilliant move, Stanton connected the nascent campaign for women’s rights directly to that powerful American symbol of liberty. The same familiar words framed their arguments: “We hold these truths to be self-evident; that all men and women are created equal; that they are endowed by their Creator with certain inalienable rights; that among these are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.”
In this Declaration of Sentiments, Stanton carefully enumerated areas of life where women were treated unjustly. Eighteen was precisely the number of grievances America’s revolutionary forefathers had listed in their Declaration of Independence from England.
Stanton’s version read, “The history of mankind is a history of repeated injuries and usurpations on the part of man toward woman, having in direct object the establishment of an absolute tyranny over her. To prove this, let facts be submitted to a candid world.” Then it went into specifics:
- Married women were legally dead in the eyes of the law
- Women were not allowed to vote
- Women had to submit to laws when they had no voice in their formation
- Married women had no property rights
- Husbands had legal power over and responsibility for their wives to the extent that they could imprison or beat them with impunity
- Divorce and child custody laws favored men, giving no rights to women
- Women had to pay property taxes although they had no representation in the levying of these taxes
- Most occupations were closed to women and when women did work they were paid only a fraction of what men earned
- Women were not allowed to enter professions such as medicine or law
- Women had no means to gain an education since no college or university would accept women students
- With only a few exceptions, women were not allowed to participate in the affairs of the church
- Women were robbed of their self-confidence and self-respect, and were made totally dependent on men
Strong words… Large grievances… And remember: This was just seventy years after the Revolutionary War. Doesn’t it seem surprising to you that this unfair treatment of women was the norm in this new, very idealistic democracy? But this Declaration of Sentiments spelled out what was the status quo for European-American women in 1848 America, while it was even worse for enslaved Black women.
Elizabeth Cady Stanton’s draft continued: “Now, in view of this entire disenfranchisement of one-half the people of this country, their social and religious degradation, — in view of the unjust laws above mentioned, and because women do feel themselves aggrieved, oppressed, and fraudulently deprived of their most sacred rights, we insist that they have immediate admission to all the rights and privileges which belong to them as citizens of these United States.”
That summer, change was in the air and Elizabeth Cady Stanton was full of hope that the future could and would be brighter for women.
The First Women’s Rights Convention The convention was convened as planned, and over the two-days of discussion, the Declaration of Sentiments and 12 resolutions received unanimous endorsement, one by one, with a few amendments. The only resolution that did not pass unanimously was the call for women’s enfranchisement. That women should be allowed to vote in elections was almost inconceivable to many. Lucretia Mott, Stanton’s longtime friend, had been shocked when Stanton had first suggested such an idea. And at the convention, heated debate over the woman’s vote filled the air.
Today, it’s hard for us to imagine this, isn’t it? Even the heartfelt pleas of Elizabeth Cady Stanton, a refined and educated woman of the time, did not move the assembly. Not until Frederick Douglass, the noted Black abolitionist and rich orator, started to speak, did the uproar subside. Woman, like the slave, he argued, had the right to liberty. “Suffrage,” he asserted, “is the power to choose rulers and make laws, and the right by which all others are secured.” In the end, the resolution won enough votes to carry, but by a bare majority.
The Declaration of Sentiments ended on a note of complete realism: “In entering upon the great work before us, we anticipate no small amount of misconception, misrepresentation, and ridicule; but we shall use every instrumentality within our power to effect our object. We shall employ agents, circulate tracts, petition the State and national Legislatures, and endeavor to enlist the pulpit and the press in our behalf. We hope this Convention will be followed by a series of Conventions, embracing every part of the country.”
The Backlash Begins Stanton was certainly on the mark when she anticipated “misconception, misrepresentation, and ridicule.” Newspaper editors were so scandalized by the shameless audacity of the Declaration of Sentiments, and particularly of the ninth resolution — women demanding the vote!– that they attacked the women with all the vitriol they could muster. The women’s rights movement was only one day old and the backlash had already begun!
In ridicule, the entire text of the Declaration of Sentiments was often published, with the names of the signers frequently included. Just as ridicule today often has a squelching effect on new ideas, this attack in the press caused many people from the Convention to rethink their positions. Many of the women who had attended the convention were so embarrassed by the publicity that they actually withdrew their signatures from the Declaration. But most stood firm. And something the editors had not anticipated happened: Their negative articles about the women’s call for expanded rights were so livid and widespread that they actually had a positive impact far beyond anything the organizers could have hoped for. People in cities and isolated towns alike were now alerted to the issues, and joined this heated discussion of women’s rights in great numbers!
The Movement Expands The Seneca Falls women had optimistically hoped for “a series of conventions embracing every part of the country.” And that’s just what did happen. Women’s Rights Conventions were held regularly from 1850 until the start of the Civil War. Some drew such large crowds that people actually had to be turned away for lack of sufficient meeting space!
The women’s rights movement of the late 19th century went on to address the wide range of issues spelled out at the Seneca Falls Convention. Elizabeth Cady Stanton and women like Susan B. Anthony, Lucy Stone, and Sojourner Truth traveled the country lecturing and organizing for the next forty years. Eventually, winning the right to vote emerged as the central issue, since the vote would provide the means to achieve the other reforms. All told, the campaign for woman suffrage met such staunch opposition that it took 72 years for the women and their male supporters to be successful.
As you might imagine, any 72-year campaign includes thousands of political strategists, capable organizers, administrators, activists and lobbyists. The story of diligent women’s rights activism is a litany of achievements against tremendous odds, of ingenious strategies and outrageous tactics used to outwit opponents and make the most of limited resources. It’s a dramatic tale, filled with remarkable women facing down incredible obstacles to win that most basic American civil right – the vote.
Among these women are several activists whose names and and accomplishments should become as familiar to Americans as those of Thomas Jefferson, Abraham Lincoln and Martin Luther King, Jr.
- Elizabeth Cady Stanton, of course. And Susan B. Anthony. Matilda Joslyn Gage. Lucy Stone. They were pioneer theoreticians of the 19th-century women’s rights movement.
- Esther Morris, the first woman to hold a judicial position, who led the first successful state campaign for woman suffrage, in Wyoming in 1869. Abigail Scott Duniway, the leader of the successful fight in Oregon and Washington in the early 1900s.
- Ida B. Wells-Barnett and Mary Church Terrell, organizers of thousands of African-American women who worked for suffrage for all women.
- Harriot Stanton Blatch, daughter of Elizabeth Cady Stanton, and Alice Stone Blackwell, Lucy Stone’s daughter, who carried on their mothers’ legacy through the next generation.
- Anna Howard Shaw and Carrie Chapman Catt, leaders of the National American Woman Suffrage Association in the early years of the 20th century, who brought the campaign to its final success.
- Alice Paul, founder and leader of the National Woman’s Party, considered the radical wing of the movement.
- Ruth Bader Ginsburg, now a Supreme Court Justice, learned the story of the Women’s Rights Movement. Today she says, “I think about how much we owe to the women who went before us – legions of women, some known but many more unknown. I applaud the bravery and resilience of those who helped all of us – you and me – to be here today.”
After the Vote was Won After the vote was finally won in 1920, the organized Women’s Rights Movement continued on in several directions. While the majority of women who had marched, petitioned and lobbied for woman suffrage looked no further, a minority – like Alice Paul – understood that the quest for women’s rights would be an ongoing struggle that was only advanced, not satisfied, by the vote.
In 1919, as the suffrage victory drew near, the National American Woman Suffrage Association reconfigured itself into the League of Women Voters to ensure that women would take their hard-won vote seriously and use it wisely.
In 1920, the Women’s Bureau of the Department of Labor was established to gather information about the situation of women at work, and to advocate for changes it found were needed. Many suffragists became actively involved with lobbying for legislation to protect women workers from abuse and unsafe conditions.
In 1923, Alice Paul, the leader of the National Woman’s Party, took the next obvious step. She drafted an Equal Rights Amendment for the United States Constitution. Such a federal law, it was argued, would ensure that “Men and women have equal rights throughout the United States.” A constitutional amendment would apply uniformly, regardless of where a person lived.
The second wing of the post-suffrage movement was one that had not been explicitly anticipated in the Seneca Falls “Declaration of Sentiments.” It was the birth control movement, initiated by a public health nurse, Margaret Sanger, just as the suffrage drive was nearing its victory. The idea of woman’s right to control her own body, and especially to control her own reproduction and sexuality, added a visionary new dimension to the ideas of women’s emancipation. This movement not only endorsed educating women about existing birth control methods. It also spread the conviction that meaningful freedom for modern women meant they must be able to decide for themselves whether they would become mothers, and when. For decades, Margaret Sanger and her supporters faced down at every turn the zealously enforced laws denying women this right. In 1936, a Supreme Court decision declassified birth control information as obscene. Still, it was not until 1965 that married couples in all states could obtain contraceptives legally.
The Second Wave So it’s clear that, contrary to common misconception, the Women’s Rights Movement did not begin in the 1960s. What occurred in the 1960s was actually a second wave of activism that washed into the public consciousness, fueled by several seemingly independent events of that turbulent decade. Each of these events brought a different segment of the population into the movement.
First: Esther Peterson was the director of the Women’s Bureau of the Dept. of Labor in 1961. She considered it to be the government’s responsibility to take an active role in addressing discrimination against women. With her encouragement, President Kennedy convened a Commission on the Status of Women, naming Eleanor Roosevelt as its chair. The report issued by that commission in 1963 documented discrimination against women in virtually every area of American life. State and local governments quickly followed suit and established their own commissions for women, to research conditions and recommend changes that could be initiated.
Then: In 1963, Betty Friedan published a landmark book, The Feminine Mystique. The Feminine Mystique evolved out of a survey she had conducted for her 20-year college reunion. In it she documented the emotional and intellectual oppression that middle-class educated women were experiencing because of limited life options. The book became an immediate bestseller, and inspired thousands of women to look for fulfillment beyond the role of homemaker.
Next: Title VII of the 1964 Civil Rights Act was passed, prohibiting employment discrimination on the basis of sex as well as race, religion, and national origin. The category “sex” was included as a last-ditch effort to kill the bill. But it passed, nevertheless. With its passage, the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission was established to investigate discrimination complaints. Within the commission’s first five years, it received 50,000 sex discrimination complaints. But it was quickly obvious that the commission was not very interested in pursuing these complaints. Betty Friedan, the chairs of the various state Commissions on the Status of Women, and other feminists agreed to form a civil rights organization for women similar to the NAACP. In 1966, the National Organization for Women was organized, soon to be followed by an array of other mass-membership organizations addressing the needs of specific groups of women, including Blacks, Latinas, Asians-Americans, lesbians, welfare recipients, business owners, aspiring politicians, and tradeswomen and professional women of every sort.
During this same time, thousands of young women on college campuses were playing active roles within the anti-war and civil rights movement. At least,that was their intention. Many were finding their efforts blocked by men who felt leadership of these movements was their own province, and that women’s roles should be limited to fixing food and running mimeograph machines. It wasn’t long before these young women began forming their own “women’s liberation” organizations to address their role and status within these progressive movements and within society at large.
New Issues Come to the Fore These various elements of the re-emerging Women’s Rights Movement worked together and separately on a wide range of issues. Small groups of women in hundreds of communities worked on grassroots projects like establishing women’s newspapers, bookstores and cafes. They created battered women’s shelters and rape crisis hotlines to care for victims of sexual abuse and domestic violence. They came together to form child care centers so women could work outside their homes for pay. Women health care professionals opened women’s clinics to provide birth control and family planning counseling — and to offer abortion services — for low-income women. These clinics provided a safe place to discuss a wide range of health concerns and experiment with alternative forms of treatment.
With the inclusion of Title IX in the Education Codes of 1972, equal access to higher education and to professional schools became the law. The long-range effect of that one straightforward legal passage beginning “Equal access to education programs…,” has been simply phenomenal. The number of women doctors, lawyers, engineers, architects and other professionals has doubled and doubled again as quotas actually limiting women’s enrollment in graduate schools were outlawed. Athletics has probably been the most hotly contested area of Title IX, and it’s been one of the hottest areas of improvement, too. The rise in girls’ and women’s participation in athletics tells the story: One in twenty-seven high school girls played sports 25 years ago; one in three do today. The whole world saw how much American women athletes could achieve during the last few Olympic Games, measured in their astonishing numbers of gold, silver, and bronze medals. This was another very visible result of Title IX.
In society at large, the Women’s Rights Movement has brought about measurable changes, too. In 1972, 26% of men and women said they would not vote for a woman for president. In 1996, that sentiment had plummeted to just over 5% for women and to 8% for men. The average age of women when they first marry has moved from twenty to twenty-four during that same period.
But perhaps the most dramatic impact of the women’s rights movement of the past few decades has been women’s financial liberation. Do you realize that just 25 years ago married women were not issued credit cards in their own name? That most women could not get a bank loan without a male co-signer? That women working full time earned fifty-nine cents to every dollar earned by men?
Help-wanted ads in newspapers were segregated into “Help wanted – women” and “Help wanted- men.” Pages and pages of jobs were announced for which women could not even apply. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission ruled this illegal in 1968, but since the EEOC had little enforcement power, most newspapers ignored the requirement for years. The National Organization for Women (NOW), had to argue the issue all the way to the Supreme Court to make it possible for a woman today to hold any job for which she is qualified. And so now we see women in literally thousands of occupations which would have been almost unthinkable just one generation ago: dentist, bus driver, veterinarian, airline pilot, and phone installer, just to name a few.
Many of these changes came about because of legislation and court cases pushed by women’s organizations. But many of the advances women achieved in the 1960s and ’70s were personal: getting husbands to help with the housework or regularly take responsibility for family meals; getting a long-deserved promotion at work; gaining the financial and emotional strength to leave an abusive partner.
The Equal Rights Amendment Is Re-Introduced Then, in 1972, the Equal Rights Amendment, which had languished in Congress for almost fifty years, was finally passed and sent to the states for ratification. The wording of the ERA was simple: “Equality of rights under the law shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any state on account of sex.” To many women’s rights activists, its ratification by the required thirty-eight states seemed almost a shoo-in.
The campaign for state ratification of the Equal Rights Amendment provided the opportunity for millions of women across the nation to become actively involved in the Women’s Rights Movement in their own communities. Unlike so many other issues which were battled-out in Congress or through the courts, this issue came to each state to decide individually. Women’s organizations of every stripe organized their members to help raise money and generate public support for the ERA. Marches were staged in key states that brought out hundreds of thousands of supporters. House meetings, walk-a-thons, door-to-door canvassing, and events of every imaginable kind were held by ordinary women, many of whom had never done anything political in their lives before. Generous checks and single dollar bills poured into the campaign headquarters, and the ranks of NOW and other women’s rights organizations swelled to historic sizes. Every women’s magazine and most general interest publications had stories on the implications of the ERA, and the progress of the ratification campaign.
But Elizabeth Cady Stanton proved prophetic once again. Remember her prediction that the movement should “anticipate no small amount of misconception, misrepresentation, and ridicule”? Opponents of the Equal Rights Amendment, organized by Phyllis Schlafly, feared that a statement like the ERA in the Constitution would give the government too much control over our personal lives. They charged that passage of the ERA would lead to men abandoning their families, unisex toilets, gay marriages, and women being drafted. And the media, purportedly in the interest of balanced reporting, gave equal weight to these deceptive arguments just as they had when the possibility of women winning voting rights was being debated. And, just like had happened with woman suffrage, there were still very few women in state legislatures to vote their support, so male legislators once again had it in their power to decide if women should have equal rights. When the deadline for ratification came in 1982, the ERA was just three states short of the 38 needed to write it into the U.S. constitution. Seventy-five percent of the women legislators in those three pivotal states supported the ERA, but only 46% of the men voted to ratify.
Despite polls consistently showing a large majority of the population supporting the ERA, it was considered by many politicians to be just too controversial. Historically speaking, most if not all the issues of the women’s rights movement have been highly controversial when they were first voiced. Allowing women to go to college? That would shrink their reproductive organs! Employ women in jobs for pay outside their homes? That would destroy families! Cast votes in national elections? Why should they bother themselves with such matters? Participate in sports? No lady would ever want to perspire! These and other issues that were once considered scandalous and unthinkable are now almost universally accepted in this country.
More Complex Issues Surface Significant progress has been made regarding the topics discussed at the Seneca Falls Convention in 1848. The people attending that landmark discussion would not even have imagined the issues of the Women’s Rights Movement in the 1990s. Much of the discussion has moved beyond the issue of equal rights and into territory that is controversial, even among feminists. To name a few:
- Women’s reproductive rights. Whether or not women can terminate pregnancies is still controversial twenty-five years after the Supreme Court ruling in Roe v. Wade affirmed women’s choice during the first two trimesters.
- Women’s enrollment in military academies and service in active combat. Are these desirable?
- Women in leadership roles in religious worship. Controversial for some, natural for others.
- Affirmative action. Is help in making up for past discrimination appropriate? Do qualified women now face a level playing field?
- The mommy track. Should businesses accommodate women’s family responsibilities, or should women compete evenly for advancement with men, most of whom still assume fewer family obligations?
- Pornography. Is it degrading, even dangerous, to women, or is it simply a free speech issue?
- Sexual harassment. Just where does flirting leave off and harassment begin?
- Surrogate motherhood. Is it simply the free right of a woman to hire out her womb for this service?
- Social Security benefits allocated equally for homemakers and their working spouses, to keep surviving wives from poverty as widows.
Today, young women proudly calling themselves “the third wave” are confronting these and other thorny issues. While many women may still be hesitant to call themselves “feminist” because of the ever-present backlash, few would give up the legacy of personal freedoms and expanded opportunities women have won over the last 150 years. Whatever choices we make for our own lives, most of us envision a world for our daughters, nieces and granddaughters where all girls and women will have the opportunity to develop their unique skills and talents and pursue their dreams.
1998: Living the Legacy In the 150 years since that first, landmark Women’s Rights Convention, women have made clear progress in the areas addressed by Elizabeth Cady Stanton in her revolutionary Declaration of Sentiments. Not only have women won the right to vote; we are being elected to public office at all levels of government. Jeannette Rankin was the first woman elected to Congress, in 1916. By 1971, three generations later, women were still less than three percent of our congressional representatives. Today women hold only 11% of the seats in Congress, and 21% of the state legislative seats. Yet, in the face of such small numbers, women have successfully changed thousands of local, state, and federal laws that had limited women’s legal status and social roles.
In the world of work, large numbers of women have entered the professions, the trades, and businesses of every kind. We have opened the ranks of the clergy, the military, the newsroom. More than three million women now work in occupations considered “nontraditional” until very recently.
We’ve accomplished so much, yet a lot still remains to be done. Substantial barriers to the full equality of America’s women still remain before our freedom as a Nation can be called complete. But the Women’s Rights Movement has clearly been successful in irrevocably changing the circumstances and hopes of women. The remaining injustices are being tackled daily in the courts and conference rooms, the homes and organizations, workplaces and playing fields of America.
Women and girls today are living the legacy of women’s rights that seven generations of women before us have given their best to achieve. Alice Paul, that intrepid organizer who first wrote out the Equal Rights Amendment in 1923, said, “I always feel the movement is sort of a mosaic. Each of us puts in one little stone, and then you get a great mosaic at the end.” Women, acting together, adding their small stones to the grand mosaic, have increased their rights against all odds, nonviolently, from an initial position of powerlessness. We have a lot to be proud of in this heroic legacy, and a great deal to celebrate on the occasion of the 150th Anniversary of the founding of the Women’s Rights Movement.
© By Bonnie Eisenberg and Mary Ruthsdotter, the National Women’s History Alliance. 1998
Background Essay: Shall Women Have the Right to Vote (1866-1890)

Directions:
Keep these discussion questions in mind as you read the background essay, making marginal notes as desired. Respond to the reflection and analysis questions at the end of the essay.
Discussion Questions
- How had the work of women to end slavery helped them develop skills that would ultimately be useful in the women’s suffrage struggle?
- What might be meant by the term, “the conscience of the nation,” and how did the fight against slavery help demonstrate that concept?
- What arguments might have been made against women’s suffrage?
- Why were Western states the first to grant suffrage to women?
Introduction
After the Civil War, the nation was finally poised to extend the promise of liberty expressed in the Declaration of Independence to newly emancipated African Americans. But the women’s suffrage movement was split: Should women push to be included in the Fifteenth Amendment? Should they wait for the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments to be adopted before turning to women’s suffrage, or should they seize the moment and demand the vote now? Not content to wait, Susan B. Anthony and other workers in the movement engaged in civil disobedience to wake the conscience of a nation. Meanwhile, railroads opened the West to settlement, and Western territories tried to boost population by offering votes for women.
Life for women in the mid-nineteenth century was as diverse as it is now. What was considered socially appropriate behavior for women varied widely across the country, based on region, social class, and other factors. Branches of the women’s suffrage movement disagreed regarding tactics, and some women (and many men) did not even believe women’s suffrage was appropriate or necessary. Ideals of the Cult of Domesticity, in which women were believed to possess the natural virtues of piety, purity, domesticity, and submissiveness, were still a powerful influence on culture. An important debate and split in the women’s suffrage movement between a state and national strategy emerged during this period.
The Cult of True Womanhood
The Cult of Domesticity, also known as the Cult of True Womanhood, affirmed the idea that natural differences between the sexes meant women, especially those of the upper and middle classes, were too delicate for work outside the home. According to this view, such women were more naturally suited to parenting, teaching, and making homes, which were their natural “sphere,” happy and peaceful for their families. In other words, it was unnatural and unladylike for women to work outside the home.
Educator and political activist Catharine Beecher wrote in 1871, “Woman’s great mission is to train immature, weak, and ignorant creatures [children] to obey the laws of God . . . first in the family, then in the school, then in the neighborhood, then in the nation, then in the world.” For Beecher and other writers, the role of homemaker was held up as an honored and dignified position for women, worthy of high esteem. Their contribution to public life would include managing the home in a manner that would support their husbands. According to this conception of the roles of men and women, men were considered to be exhausted, soiled, and corrupted by their participation in work and politics, and needed a peaceful, pure home life to enable them to recover their virtue.
Increasingly, women found their political voice through their work in social reform movements. Jane Addams, co-founder with Helen Gates Starr of Hull House and pioneer of social work in America, wrote in 1902, “The sphere of morals is the sphere of action . . . It is well to remind ourselves, from time to time, that ‘Ethics’ is but another word for ‘righteousness . . . ’” She noted that, to solve problems related to the needs of children, public health, and other social concerns that affected the home, women needed the vote.
In keeping with the feminine ideals of piety and purity, many women continued work within the temperance movement to campaign against the excesses of drunkenness. This cause was considered a socially permissible moral effort through which women could participate in public life, because of the damaging effects of alcohol abuse on the family. Annie Wittenmyer, a social reformer and war widow from Ohio who had reported on terrible hospital conditions during the Civil War, founded the Woman’s Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) in 1874 to build support for the idea of abstaining from alcohol use.
According to the tradition of Republican Motherhood, education should prepare girls to become mothers who raised educated citizens for the republic. In a challenge to the Cult of Domesticity, the latter half of the nineteenth century saw an expansion of broader academic opportunities for upper class females of college age in the United States. In the Northeast, liberal arts schools modeled after Wesleyan College (1836) in Macon, Georgia, opened. In 1844, Hillsdale College opened in Michigan, one of the first American colleges whose charter prohibited any discrimination based on race, religion, or sex. Vassar College in Poughkeepsie, New York, founded in 1861, and Wellesley College in Wellesley, Massachusetts, founded in 1875, also expanded educational opportunities for women. Teaching was among the first professions women entered in large numbers. During and after the Civil War, new opportunities also developed for women to become nurses.

New York City — The sewing-room at A.T. Stewart’s, between Ninth and Tenth Streets, Broadway and Fourth Avenue / Hyde, 1875. Library of Congress.

The Changing Roles of Women
While these career options did not radically challenge the cultural ideal of traditional womanhood, the work landscape of America was changing. As the United States economy grew to provide more options, people began to see themselves as consumers as well as producers. Indeed, mass consumerism drove new manufacturing methods. During the second industrial revolution, the United States started moving from an agricultural economy toward incorporating new modes of production, manufacturing, and consumer behavior.
Young working-class women worked in the same laundries, factories, and textile mills as poor and immigrant men, often spending twelve hours a day, seven days a week, in hot, dangerous conditions. Also, women found work as store clerks in the many new department stores that opened to sell factory-made clothing and other mass-produced items.
The Suffrage Movement Grows
Women continued to work to secure their right to vote. The Civil War ended in April of 1865 and the Thirteenth Amendment was ratified eight months later, banning slavery throughout the United States. A burning question remained: How would the rights of former slaves be protected? As the nation’s attention turned to civil rights and voting with the debates surrounding the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments, many women hoped to seize the opportunity to gain the vote alongside African American men.
The Civil War had forced women’s suffrage advocates to pause their efforts toward winning the vote, but in 1866 they came together at the eleventh National Women’s Rights Convention in New York. The group voted to call itself the American Equal Rights Association and work for the rights of all Americans. Appealing to the Cult of Domesticity, they argued that giving women the vote would improve government by bringing women’s virtues of piety and purity into politics, resulting in a more civilized, “maternal commonwealth.”
The Movement Splits
The American Equal Rights Association seemed poised for success with such well-known leaders as Lucretia Mott, Lucy Stone, and Frederick Douglass. But internal divisions soon became clear. Whose rights should be secured first? Some, especially former abolitionist leaders, wanted to wait until newly emancipated African American men had been given the vote before working to win it for women. Newspaper editor Horace Greeley urged, “This is a critical period for the Republican Party and the life of our Nation . . . I conjure you to remember that this is ‘the negro’s hour,’ and your first duty now is to go through the State and plead his claims.” Lucy Stone, Henry Blackwell, and Julia Ward Howe agreed.
But for Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton, the time for women also was now. Along with many others, they saw the move to put the cause of women’s suffrage on hold as a betrayal of both the principles of equality and republicanism. Frederick Douglass, who saw suffrage for African American men as a matter of life or death, challenged Anthony on this question, asking whether she believed granting women the vote would truly do anything to change the inequality under law between the sexes. Without missing a beat, Anthony responded:
“ It will change the nature of one thing very much, and that is the dependent condition of woman. It will place her where she can earn her own bread, so that she may go out into the world an equal competitor in the struggle for life.”
In the wake of this bitter debate, not one but two national organizations for women’s suffrage were established in 1869. Stone and Blackwell founded the American Woman Suffrage Association (AWSA). Worried that the Fifteenth Amendment would not pass if it included votes for women, the AWSA put their energy into convincing the individual states to give women the vote in their state constitutions. Anthony and Stanton founded the National Woman Suffrage Association (NWSA). They worked to win votes for women via an amendment to the U.S. Constitution at the same time as it would protect the right of former slaves to vote. Anthony and Stanton started the NWSA’s newspaper, The Revolution, in 1868. Its motto was, “Men, their rights, and nothing more; women, their rights, and nothing less.”
The NWSA was a broad coalition that included some progressives who questioned the fitness of African Americans and immigrants to vote because of the prevailing views of Social Darwinism. The racism against black males voting was especially prevalent in the South where white women supported women’s suffrage as a means of preserving white supremacy. In addition, throughout the country strong sentiment reflected the view that any non-white or immigrant individual was racially inferior and too ignorant to vote. In this vein, Anthony and Stanton used racially charged language in advocating for an educational requirement to vote. Unfortunately for many, universal suffrage challenged too many of their assumptions about the prevailing social structure.

Photograph of Lucy Stone between 1840 and 1860. Library of Congress.

The New Departure: Testing the Fourteenth Amendment
But there was another amendment which interested NWSA: the Fourteenth. In keeping with NWSA’s more confrontational approach, Anthony decided to test the meaning of the newly ratified Fourteenth Amendment. The Amendment stated in part, “No state shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States…” Anthony thought it was clear that this language protected the right of women to vote. After all, wasn’t voting a privilege of citizens?
The Fourteenth Amendment went on to state that representation in Congress would be reduced for states which denied the vote to male inhabitants over 21. In other words, states could choose to deny men over 21 the vote, but they would be punished with proportionally less representation (and therefore less power) in Congress. So in the end, the Fourteenth Amendment encouraged states to give all men over 21 the vote, but did not require it. The Fifteenth Amendment, ratified in 1870, banned states from denying the vote based on race, color, or having been enslaved in the past.
Susan B. Anthony on Trial
It was the Fourteenth Amendment’s protection of “privileges or immunities” that Anthony decided to test. On November 5, 1872, she and two dozen other women walked into the local polling place in Rochester, New York, and cast a vote in the presidential election. (Anthony voted for Ulysses S. Grant.) She was arrested and charged with voting in a federal election “without having a lawful right to vote.”
Before her trial, 52-year-old Anthony traveled all over her home county giving a speech entitled “Is it a Crime for a Citizen of the United States to Vote?” In it, she called on all her fellow citizens, from judges to potential jurors, to support equal rights for women.
At her trial, Anthony’s lawyer pointed out the unequal treatment under the law:
“ If this same act [voting] had been done by her brother, it would have been honorable. But having been done by a woman, it is said to be a crime . . . I believe this is the first instance in which a woman has been arraigned [accused] in a criminal court merely on account of her sex.”
The judge refused to let Anthony testify in her own defense, found her guilty of voting without the right to do so, and ordered her to pay a $100 fine. Anthony responded:
“ In your ordered verdict of guilty, you have trampled underfoot every vital principle of our government. My natural rights, my civil rights, my political rights, my judicial rights are all alike ignored . . . I shall never pay a dollar of your unjust penalty. And I shall earnestly and persistently continue to urge all women.” She concluded by quoting Thomas Jefferson: “Resistance to tyranny is obedience to God.”
Anthony’s case did not make it all the way to the Supreme Court. However, the Court did rule three years later in a different case, Minor v. Happersett (1875), that voting was not among the privileges or immunities of citizens and the Fourteenth Amendment did not protect a woman’s right to vote.

A caricature of Susan B. Anthony that appeared in a New York newspaper right before her trial. Thomas Wust, June 5, 1873. Library of Congress.

Suffrage in the West
While Anthony and other suffragists were agitating in the Northeast, railroads had helped open up the Great Plains and the American West to settlement. The Gold Rush of 1849 had enticed many thousands of settlers to the rugged West, and homesteading pioneers continued to push the frontier. These territories (and later states), were among the first to give women the right to vote: Wyoming Territory in 1869, followed by Utah Territory (1870), and Washington Territory (1883).
These territories had many reasons for extending suffrage to women, most related to the need to increase population. They would need to meet minimum population requirements to apply for statehood, and the free publicity they would get for giving women the vote might bring more people. And they did not just need more people—they needed women: There were six males for every female in some places. Some were motivated to give white women the vote to offset the influence of African American votes. And finally, there were, of course, those who genuinely believed that giving women the vote was the right thing to do.
Though several western legislatures had considered proposals to give women the vote since the 1850s, in 1869 Wyoming became the first territory to give women full political rights, including voting and eligibility to hold public office. In 1870, Louisa Garner Swain was the first woman in Wyoming to cast a ballot, and a life-sized statue honors her memory in Laramie.
Under territorial government, Wyoming’s population had grown slowly and most people lived on ranches or in small towns. Territorial leaders believed Wyoming would be more attractive to newcomers once statehood was achieved, as had been the case in other western states. The territory came close to reaching the threshold of 60,000 people for statehood, but many doubted whether that number had actually been reached.
Territorial Governor Francis E. Warren refused to wait for more people to move there. He set in motion the plans for a constitutional convention. Though they had the right to do so, no women ran for seats at the Wyoming constitutional convention. Borrowing passages from other state constitutions, delegates quickly drafted the constitution in September 1889. The new element of this constitution is that it enshrined the protections of women’s political rights by simply stating that equality would exist without reference to gender. Only one delegate, Louis J. Palmer, objected to women’s suffrage. Wyoming voters approved the document in November, and the territory applied for statehood.
In the House of Representatives there was some opposition, mostly from Democrats, because the territory was known to lean Republican. Debate did not openly center on party affiliation, but on a combination of doubts about whether Wyoming had truly achieved the required population and on reluctance to admit a state where women had political rights. In response, Wyoming’s legislature sent a telegram: “We will remain out of the Union a hundred years rather than come in without our women!” Wyoming officially joined the union in 1890, becoming the 44th state. Anthony praised Wyoming for its adherence to the nation’s Founding principles: “Wyoming is the first place on God’s green earth which could consistently claim to be the land of the free!”

Representative Women, seven prominent figures of the suffrage and women’s rights movement. Clockwise from the top: Lucretia Mott, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Mary Livermore, Lydia Marie Child, Susan B. Anthony, Grace Greenwood, and Anna E. Dickinson (center). L. Schamer; L. Prang & Co. publisher, 1870. Library of Congress.

REFLECTION AND ANALYSIS QUESTIONS
- What was the Cult of True Womanhood, or Cult of Domesticity?
- How did the Industrial Revolution challenge the notion that upper- and middle-class women’s bodies were too delicate for work outside the home?
- Describe the events leading to the split in the women’s movement in 1869.
- What are some actions in which Susan B. Anthony worked for the cause of women’s suffrage in a very personal way?
- The Fourteenth Amendment is ratified
- Susan B. Anthony is jailed for voting
- Western territories give women the vote
- Other (explain)
- Principles: equality, republican/representative government, popular sovereignty, federalism, inalienable rights, freedom of speech/press/assembly
- Virtues: perseverance, contribution, moderation, resourcefulness, courage, respect, justice

Ten ways to prevent violence against women and girls
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to E-mail

Violence against women and girls is one of the most pervasive human rights violations in the world, affecting one in three women. Addressing and eradicating it requires more than just reacting to violence when it happens; it mandates proactive and innovative solutions.
A key to these solutions lies in investing in and empowering women’s rights organizations. They possess the knowledge, tools, and determination to reshape societies to be safer, more inclusive, and just.
Recognizing this potential, the UN Trust Fund to End Violence against Women (UN Trust Fund), a global inter-agency grantmaking mechanism managed by UN Women on behalf of the UN system, distilled lessons from its archive and worked with 70 civil society organizations worldwide and to identify Ten pathways to prevent violence against women and girls :
Empowering women to break the silence on violence
Mobilizing women to become change agents emerged as vital to address violence. When projects mobilize women as community facilitators and create safe spaces, they can better reach particularly marginalized communities and make prevention initiatives more effective.
In Nepal, The Story Kitchen held “storytelling workshops”, where community facilitators who were survivors of the country’s civil war interviewed other women about their experiences of violence, offering them a chance to own their personal narratives to break the cycle of intergenerational violence. The Story Kitchen conceived of such spaces, not only as “safe spaces”, but also as “brave spaces”.
Community mobilization
Grassroots organizations are pivotal in mobilizing communities and building trust, which is critical to avoid backlash against or distancing from prevention programmes.
- Raising Voices has pioneered the SASA! approach, which combines identifying power imbalances within communities, a phased roll-out of initiatives, reaching community members at different levels including police and health care workers, and reinforcing the positive benefits of non-violence.
- In Nicaragua, MADRE , in partnership with Wangki Tangni, mobilized communities to create action plans whereby communities collectively identified key issues and priority actions for addressing violence against women.
Considering women’s diverse realities
Adopting an intersectional perspective when addressing gender-based violence is essential. Understanding how different women’s realities overlap and influence their experiences of violence allows for more effective strategies and prevents overlooking vulnerabilities.
- HelpAge Moldova found that gender-based violence services were unaware of violence experienced by older women in their homes and addressed this gap through its programme.
- In Colombia, Fundación Mundubat empowered Afro-Colombian and Indigenous women in rural and poverty-stricken areas by focusing on prevention and care to challenge community systems of patriarchy, racism, and classism.
Transformative learning
Effective prevention requires training for behaviour change. Tools like manuals, apps, and websites are vital to reinforce best practices and strengthen institutional knowledge.
- Physicians for Human Rights trained clinicians, police, and legal experts on documenting sexual violence forensically. They also introduced a medical glossary to enhance understanding of sexual violence crimes.
- Breakthrough Trust in India draws heavily from multimedia and social media in interventions. The initiative’s youth activists received training on core gender and human rights concepts, as well as on executing digital campaigns.
Engaging religious and community leaders
Faith-based and traditional figures play a pivotal role in violence prevention, acting as cultural gatekeepers and shaping social norms, either supporting or hindering initiatives.
- In Togo, many women and girls are forced to engage in harmful traditional widow cleansing practices for fear of reprisals. Alafia , an NGO working to end this harmful practice, found local communities were more receptive to changing their practices when human rights laws were put in the context of their traditional beliefs.
Navigating inaction and backlash
Organizations tackling violence against women frequently face resistance, including legal gaps, denial of gender-based violence, and inaction. More aggressive, or active, forms of pushback occur when certain groups try to obstruct changes, or when vulnerable groups face discrimination and violence from those in power.
- Serbia’s Association Roma Novi Bečej found that despite Roma leaders showing an increased awareness of early and forced marriage, their support was nominal and did not result in changing practices. The organization focused on boosting public awareness of the issue to garner broad support for policy improvements.
- In Turkey, the AÇEV Mother Child Education Foundation ’s partnership with a state ministry crumbled, severely disrupting its program. This challenge spurred a shift to a grassroots model by engaging with local communities and partners.
Adaptive programming
Women’s rights organizations often face unstable conditions, complex partnerships, and shifting sociopolitical landscapes. Knowledge gathering, flexible funding, and adaptive approaches are crucial to address changing circumstances.
- The Institute for Young Women’s Development in Zimbabwe holds monthly meetings with an activist committee to review, adjust and evaluate its strategy to guarantee programme success.
- The Women’s Justice Initiative in Guatemala met local leader resistance but adapted its programme by holding more explanatory meetings and boosting leader participation.
Empowering youth
Adolescence, especially for girls, is a critical stage for early interventions to prevent violence. Many projects chose to empower young people as agents of change to enhance the outcome of prevention interventions.
- Plan International Viet Nam applied a whole-school approach to empower adolescents to form peer support groups and raise awareness for violence prevention.
- In Nepal, Restless Development empowered adolescent girls and civil society organizations to campaign against chhaupadi, a practice that prohibits young girls and women from participating in normal activities while menstruating. They rallied national leaders and media to secure the government’s focus to enforce a 2008 directive against the harmful practice.
Survivor-centered responses
Gender-based violence prevention initiatives must center on survivors, involve them in the design process, and prioritize their needs.
- World Hope International in Cambodia enhances service providers and multisectoral systems aiding victims.
- Al Shehab in Egypt provides direct survivor-centred support to survivors, including medical, legal, and psychological services.
Institutionalizing prevention
To effectively implement gender-based violence prevention laws and policies the police and government ministries need proper training and mindset shifts. Civil society organizations can play a key role in fostering these changes and connecting communities with formal mechanisms.
- In Palestine, the Women’s Centre for Legal Aid and Counselling gave young female sharia lawyers training in violence prevention.
- Pragya in India established community kiosks offering legal guidance and government service connections, staffed by informed volunteers.

How funding women’s organizations prevents violence against women

What is gender-responsive budgeting?

16 Days of Activism Against Gender-Based Violence 2023
- Ending violence against women and girls
Related content

Speech: ‘Until we make it clear there are consequences for rape—real, dire consequences—we will never turn the tide of it’

“I want to build a network of powerful Roma women and girls” – Anzhelika Bielova on Roma women’s activism and leadership in Ukraine

Photo essay: A glimpse into the lives of Afghan women
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Women's Rights — Cultural Relativism And Women’s Rights
Cultural Relativism and Women's Rights
- Categories: Gender Equality Gender Inequality Women's Rights
About this sample

Words: 1984 |
10 min read
Published: Feb 8, 2022
Words: 1984 | Pages: 4 | 10 min read
Table of contents
The global south, women as victims, women's voice.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
4 pages / 1612 words
6 pages / 2671 words
2 pages / 702 words
3 pages / 1545 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Women's Rights
Judy Brady's essay, "Why I Want a Wife," is a thought-provoking piece that challenges societal norms and gender roles. Originally published in Ms. Magazine in 1972, Brady's essay is a satirical take on the expectations placed on [...]
Women's reproductive rights essay encompass a critical aspect of gender equality and public health. Access to comprehensive reproductive healthcare is a fundamental human right that intersects with broader issues of social [...]
In the tapestry of human rights and gender equality, the freedom to choose one's attire emerges as a crucial thread. This essay delves into the importance of women's autonomy over their clothing choices, asserting the [...]
Throughout history, the journey towards achieving women's reproductive rights has been marked by significant milestones and struggles. This essay explores the evolution of women's reproductive rights, highlighting the societal [...]
Feminism is the “belief that women should have economic, political, and social equality with men”(Gustafson). Many inspirational feminists have “challenged the traditional gender roles and demanded more opportunities for women [...]
Feminism can mean a lot of things but what it mostly comes down to is gender equality, being able to control your own life and live the choices you make. It is not about hating men or thinking that women are superior. In this [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Gender pay gap in U.S. hasn’t changed much in two decades
The gender gap in pay has remained relatively stable in the United States over the past 20 years or so. In 2022, women earned an average of 82% of what men earned, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of median hourly earnings of both full- and part-time workers. These results are similar to where the pay gap stood in 2002, when women earned 80% as much as men.
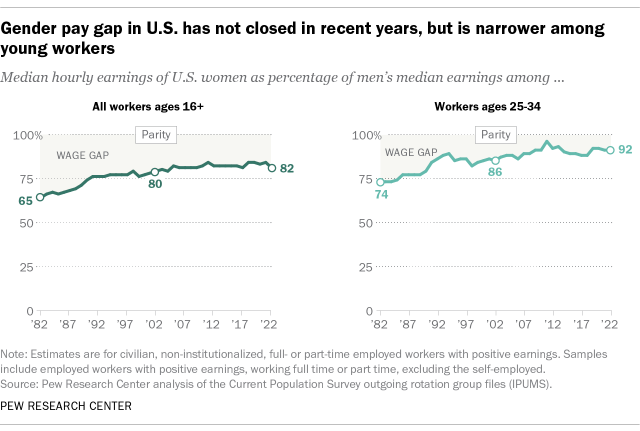
As has long been the case, the wage gap is smaller for workers ages 25 to 34 than for all workers 16 and older. In 2022, women ages 25 to 34 earned an average of 92 cents for every dollar earned by a man in the same age group – an 8-cent gap. By comparison, the gender pay gap among workers of all ages that year was 18 cents.
While the gender pay gap has not changed much in the last two decades, it has narrowed considerably when looking at the longer term, both among all workers ages 16 and older and among those ages 25 to 34. The estimated 18-cent gender pay gap among all workers in 2022 was down from 35 cents in 1982. And the 8-cent gap among workers ages 25 to 34 in 2022 was down from a 26-cent gap four decades earlier.
The gender pay gap measures the difference in median hourly earnings between men and women who work full or part time in the United States. Pew Research Center’s estimate of the pay gap is based on an analysis of Current Population Survey (CPS) monthly outgoing rotation group files ( IPUMS ) from January 1982 to December 2022, combined to create annual files. To understand how we calculate the gender pay gap, read our 2013 post, “How Pew Research Center measured the gender pay gap.”
The COVID-19 outbreak affected data collection efforts by the U.S. government in its surveys, especially in 2020 and 2021, limiting in-person data collection and affecting response rates. It is possible that some measures of economic outcomes and how they vary across demographic groups are affected by these changes in data collection.
In addition to findings about the gender wage gap, this analysis includes information from a Pew Research Center survey about the perceived reasons for the pay gap, as well as the pressures and career goals of U.S. men and women. The survey was conducted among 5,098 adults and includes a subset of questions asked only for 2,048 adults who are employed part time or full time, from Oct. 10-16, 2022. Everyone who took part is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used in this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology .
The U.S. Census Bureau has also analyzed the gender pay gap, though its analysis looks only at full-time workers (as opposed to full- and part-time workers). In 2021, full-time, year-round working women earned 84% of what their male counterparts earned, on average, according to the Census Bureau’s most recent analysis.
Much of the gender pay gap has been explained by measurable factors such as educational attainment, occupational segregation and work experience. The narrowing of the gap over the long term is attributable in large part to gains women have made in each of these dimensions.
Related: The Enduring Grip of the Gender Pay Gap
Even though women have increased their presence in higher-paying jobs traditionally dominated by men, such as professional and managerial positions, women as a whole continue to be overrepresented in lower-paying occupations relative to their share of the workforce. This may contribute to gender differences in pay.
Other factors that are difficult to measure, including gender discrimination, may also contribute to the ongoing wage discrepancy.
Perceived reasons for the gender wage gap
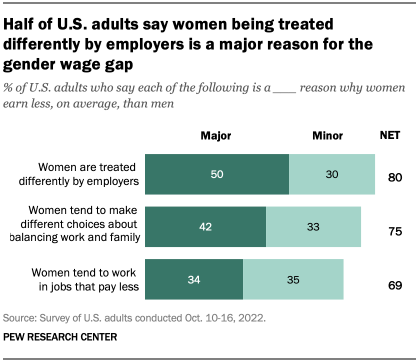
When asked about the factors that may play a role in the gender wage gap, half of U.S. adults point to women being treated differently by employers as a major reason, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in October 2022. Smaller shares point to women making different choices about how to balance work and family (42%) and working in jobs that pay less (34%).
There are some notable differences between men and women in views of what’s behind the gender wage gap. Women are much more likely than men (61% vs. 37%) to say a major reason for the gap is that employers treat women differently. And while 45% of women say a major factor is that women make different choices about how to balance work and family, men are slightly less likely to hold that view (40% say this).
Parents with children younger than 18 in the household are more likely than those who don’t have young kids at home (48% vs. 40%) to say a major reason for the pay gap is the choices that women make about how to balance family and work. On this question, differences by parental status are evident among both men and women.
Views about reasons for the gender wage gap also differ by party. About two-thirds of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (68%) say a major factor behind wage differences is that employers treat women differently, but far fewer Republicans and Republican leaners (30%) say the same. Conversely, Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say women’s choices about how to balance family and work (50% vs. 36%) and their tendency to work in jobs that pay less (39% vs. 30%) are major reasons why women earn less than men.
Democratic and Republican women are more likely than their male counterparts in the same party to say a major reason for the gender wage gap is that employers treat women differently. About three-quarters of Democratic women (76%) say this, compared with 59% of Democratic men. And while 43% of Republican women say unequal treatment by employers is a major reason for the gender wage gap, just 18% of GOP men share that view.
Pressures facing working women and men
Family caregiving responsibilities bring different pressures for working women and men, and research has shown that being a mother can reduce women’s earnings , while fatherhood can increase men’s earnings .
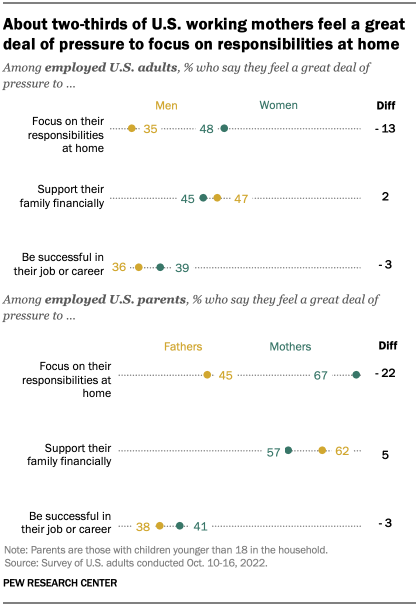
Employed women and men are about equally likely to say they feel a great deal of pressure to support their family financially and to be successful in their jobs and careers, according to the Center’s October survey. But women, and particularly working mothers, are more likely than men to say they feel a great deal of pressure to focus on responsibilities at home.
About half of employed women (48%) report feeling a great deal of pressure to focus on their responsibilities at home, compared with 35% of employed men. Among working mothers with children younger than 18 in the household, two-thirds (67%) say the same, compared with 45% of working dads.
When it comes to supporting their family financially, similar shares of working moms and dads (57% vs. 62%) report they feel a great deal of pressure, but this is driven mainly by the large share of unmarried working mothers who say they feel a great deal of pressure in this regard (77%). Among those who are married, working dads are far more likely than working moms (60% vs. 43%) to say they feel a great deal of pressure to support their family financially. (There were not enough unmarried working fathers in the sample to analyze separately.)
About four-in-ten working parents say they feel a great deal of pressure to be successful at their job or career. These findings don’t differ by gender.
Gender differences in job roles, aspirations
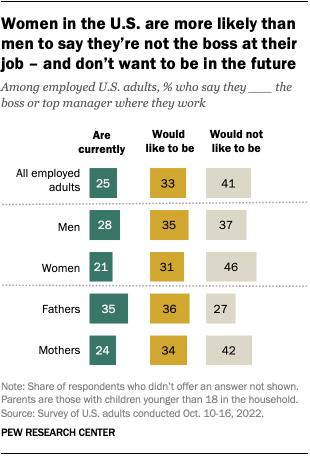
Overall, a quarter of employed U.S. adults say they are currently the boss or one of the top managers where they work, according to the Center’s survey. Another 33% say they are not currently the boss but would like to be in the future, while 41% are not and do not aspire to be the boss or one of the top managers.
Men are more likely than women to be a boss or a top manager where they work (28% vs. 21%). This is especially the case among employed fathers, 35% of whom say they are the boss or one of the top managers where they work. (The varying attitudes between fathers and men without children at least partly reflect differences in marital status and educational attainment between the two groups.)
In addition to being less likely than men to say they are currently the boss or a top manager at work, women are also more likely to say they wouldn’t want to be in this type of position in the future. More than four-in-ten employed women (46%) say this, compared with 37% of men. Similar shares of men (35%) and women (31%) say they are not currently the boss but would like to be one day. These patterns are similar among parents.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published on March 22, 2019. Anna Brown and former Pew Research Center writer/editor Amanda Barroso contributed to an earlier version of this analysis. Here are the questions used in this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology .
What is the gender wage gap in your metropolitan area? Find out with our pay gap calculator
- Gender & Work
- Gender Equality & Discrimination
- Gender Pay Gap
- Gender Roles

Carolina Aragão is a research associate focusing on social and demographic trends at Pew Research Center
Women have gained ground in the nation’s highest-paying occupations, but still lag behind men
Diversity, equity and inclusion in the workplace, the enduring grip of the gender pay gap, more than twice as many americans support than oppose the #metoo movement, women now outnumber men in the u.s. college-educated labor force, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Answer 2: Women's rights are the essential human rights that the United Nations enshrined for every human being on the earth nearly 70 years ago. These rights include a lot of rights including the rights to live free from violence, slavery, and discrimination. In addition to the right to education, own property; vote and to earn a fair and ...
Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie is one of the most influential voices in women's rights writing. Her book, We Should All Be Feminists, is a great exploration of 21st-century feminism. In this essay from Elle, Adichie takes a seemingly "small" topic about fashion and makes a big statement about independence and a woman's right to wear whatever ...
This paper will review the a issue of women's rights in Saudi Arabia from the perspective of four different groups including the modern Saudi women, traditional Saudi women, Government officials, and international women's rights organizations. Temperance, Women's Rights, Education, Antislavery and Prison Reform: New Objectives, New Concerns.
500 Words Essay on Women's Rights Introduction. Women's rights, a subject that has been at the forefront of social and political discussions for centuries, is a complex and multifaceted issue. It encompasses a wide range of topics, from the right to vote and work to reproductive rights and gender equality. This essay aims to delve into the ...
This essay states that empowerment is the key. When giving authority and control over their own lives, women thrive and contribute more to the world. It's important that programs seeking to end gender inequality focus on empowerment, and not "rescue.". Treating women like victims is not the answer. Axa is a leading global insurer ...
Welcome to this first edition of Essays on Equality, a new publication from the Global Institute for Women's Leadership. Written by GIWL researchers, members of our Advisory Council and leading researchers and campaigners, this essay collection provides research-informed reflections on the fight for women's equality.
Shelby Ostergaard. The author describes how Eleanor Roosevelt transformed the role of First Lady by advocating for women and speaking out against racial injustice. 9th Grade. Biography. 1070L. Study the history of women's rights with articles, texts, and speeches from CommonLit. Read to learn more about the fight for women's equality.
NCpedia - ANCHOR - The Women's Movement (Apr. 19, 2024) women's rights movement, diverse social movement, largely based in the United States, that in the 1960s and '70s sought equal rights and opportunities and greater personal freedom for women. It coincided with and is recognized as part of the "second wave" of feminism.
We promote women and girls' equal enjoyment of all human rights, including freedom from violence, sexual and reproductive rights, access to justice, socio-economic equality, and participation in decision-making. We do this by monitoring and advocating for women's rights, building capacity of stakeholders, and providing technical advice.
By examining the topic of women's rights in an essay, we contribute to raising awareness, challenging existing norms, and fostering a more inclusive and equitable society for all. Related Resources . 1. Bunch, C. (1990). Women's rights as human rights: Toward a re-vision of human rights. Human rights quarterly, 12(4), 486-498.
Here is an example of an introduction paragraph for women's rights essay. Title: Intimate Partner Violence. One of the most common forms of violence against women is intimate partner violence. For more than a century ago, it was considered more of a normal thing to beat a woman. In many countries it's still common.
Women s Rights are Human Rights Women s Rights are Human Rights Designed and Printed at United Nations, Geneva 1404379 (E) - November 2014 - 3,350 - HR/PUB/14/2 United Nations publication Sales No. E.14.XIV.5 ISBN 978-92-1-154206-2 . i New York and Geneva, 2014 Women's Rights are Human Rights ...
We are all entitled to human rights. These include the right to live free from violence and discrimination; to enjoy the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health; to be educated; to own property; to vote; and to earn an equal wage. But across the globe many women and girls still face discrimination on the basis of sex and gender.
You can also find more Essay Writing articles on events, persons, sports, technology and many more. Long and Short Essays on Women's Rights for Students and Kids in English. We are providing students with samples of essay on an extended piece of 500 words and short writing of 150 words on the topic "Women's Rights Essay" for reference.
Essay on Women Rights; Essay on Women Rights. Sort By: Page 1 of 50 - About 500 essays. Decent Essays. Women's Rights Of Women And Political Rights. 905 Words; 4 Pages ... Women's Rights is an extremely ethical topic that is surrounded by ethical theories and has a lot of history. While some of the theoretical systems in ethics have helped to ...
The NOW Statement of Purpose . In 1966, the National Organization for Women (NOW) formed and wrote a statement of purpose that summarizes key women's rights issues of that time. The rights outlined were based on the idea of equality as an opportunity for women to "develop their fullest human potentials" and to put women into the "mainstream of American political, economic and social life."
Women's rights are human rights that all women have. But in practice, these rights are often not protected to the same extent as the rights of men. Among others, women's rights include: physical integrity rights, such as being free from violence and making choices over their own body; social rights, such as going to school and participating ...
Women's rights is an issue that still persists to this day. However, this issue has made great progress partly due to a revolutionary speech made by the forty-second First Lady of the United States. In 1995, Hillary Rodham Clinton delivered a speech entitled "Women's Rights are Human Rights" at the UN Fourth World Conference on Women.
The definition of women's rights is legal, political, and social rights for women equal to those of men. A common idea that is associated with being a feminist is destroying the status in the esteem of men to build up women, or being a "feminazi". Feminists aim for equality not for the superiority of women over men.
Living the Legacy: The Women's Rights Movement (1848-1998) "Never doubt that a small group of thoughtful, committed citizens can change the world. Indeed, it's the only thing that ever has." That was Margaret Mead's conclusion after a lifetime of observing very diverse cultures around the world. Her insight has been borne out time and again […]
The first document to emerge from an organized women's rights collective in the United States was the Declaration of Sentiments, which was drafted using the Declaration of Independence as a model and ratified at the first convention of women's rights advocates in Seneca Falls, New York, in 1848. Historians trace the origins of the movement for ...
On November 5, 1872, she and two dozen other women walked into the local polling place in Rochester, New York, and cast a vote in the presidential election. (Anthony voted for Ulysses S. Grant.) She was arrested and charged with voting in a federal election "without having a lawful right to vote.".
Since its creation in 1996, the UN Trust Fund to End Violence against Women has invested USD 215 million to 646 initiatives led by women's rights organizations in 140 countries and territories. In 2022 alone, the Fund partnered with 186 civil society organizations across five regions, providing them with USD 87.8 million in grants to prevent ...
Cultural relativism is one of the most prominent threats when it comes to the fulfilment of the rights of women in different parts of the world. The concept assumes that there are many various cultures, each with their own set of traditions and each is to be judged according to their values . The term is often used in discussion regarding the ...
Women (66%) are more likely than men (57%) to say abortion should be legal in most or all cases, according to the survey conducted after the court's ruling. More than half of U.S. adults - including 60% of women and 51% of men - said in March that women should have a greater say than men in setting abortion policy. Just 3% of U.S. adults ...
The gender gap in pay has remained relatively stable in the United States over the past 20 years or so. In 2022, women earned an average of 82% of what men earned, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of median hourly earnings of both full- and part-time workers. These results are similar to where the pay gap stood in 2002, when women earned 80% as much as men.
Biden 'undoing decades of women's rights' with changes to Title IX law New rules stop short of protecting the right of transgender athletes to compete, but still anger US Republicans