Essay on Life for Students and Children
500+ words essay on life.
First of all, Life refers to an aspect of existence. This aspect processes acts, evaluates, and evolves through growth. Life is what distinguishes humans from inorganic matter. Some individuals certainly enjoy free will in Life. Others like slaves and prisoners don’t have that privilege. However, Life isn’t just about living independently in society. It is certainly much more than that. Hence, quality of Life carries huge importance. Above all, the ultimate purpose should be to live a meaningful life. A meaningful life is one which allows us to connect with our deeper self.


Why is Life Important?
One important aspect of Life is that it keeps going forward. This means nothing is permanent. Hence, there should be a reason to stay in dejection. A happy occasion will come to pass, just like a sad one. Above all, one must be optimistic no matter how bad things get. This is because nothing will stay forever. Every situation, occasion, and event shall pass. This is certainly a beauty of Life.
Many people become very sad because of failures . However, these people certainly fail to see the bright side. The bright side is that there is a reason for every failure. Therefore, every failure teaches us a valuable lesson. This means every failure builds experience. This experience is what improves the skills and efficiency of humans.
Probably a huge number of individuals complain that Life is a pain. Many people believe that the word pain is a synonym for Life. However, it is pain that makes us stronger. Pain is certainly an excellent way of increasing mental resilience. Above all, pain enriches the mind.
The uncertainty of death is what makes life so precious. No one knows the hour of one’s death. This probably is the most important reason to live life to the fullest. Staying in depression or being a workaholic is an utter wastage of Life. One must certainly enjoy the beautiful blessings of Life before death overtakes.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
How to Improve Quality of Life?
Most noteworthy, optimism is the ultimate way of enriching life. Optimism increases job performance, self-confidence, creativity, and skills. An optimistic person certainly can overcome huge hurdles.
Meditation is another useful way of improving Life quality. Meditation probably allows a person to dwell upon his past. This way one can avoid past mistakes. It also gives peace of mind to an individual. Furthermore, meditation reduces stress and tension.
Pursuing a hobby is a perfect way to bring meaning to life. Without a passion or interest, an individual’s life would probably be dull. Following a hobby certainly brings new energy to life. It provides new hope to live and experience Life.
In conclusion, Life is not something that one should take for granted. It’s certainly a shame to see individuals waste away their lives. We should be very thankful for experiencing our lives. Above all, everyone should try to make their life more meaningful.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Essays About Life: Top 5 Examples Plus 7 Prompts
Life envelops various meanings; if you are writing essays about life, discover our comprehensive guide with examples and prompts to help you with your essay.
What is life? You can ask anyone; I assure you, no two people will have the same answer. How we define life relies on our beliefs and priorities. One can say that life is the capacity for growth or the time between birth and death. Others can share that life is the constant pursuit of purpose and fulfillment. Life is a broad topic that inspires scholars, poets, and many others. It stimulates discussions that encourage diverse perspectives and interpretations.
5 Essay Examples
1. essay on life by anonymous on toppr.com, 2. the theme of life, existence and consciousness by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 3. compassion can save life by anonymous on papersowl.com, 4. a life of consumption vs. a life of self-realization by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 5. you only live once: a motto for life by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 1. what is the true meaning of life, 2. my life purpose, 3. what makes life special, 4. how to appreciate life, 5. books about life, 6. how to live a healthy life, 7. my idea of a perfect life.
“…quality of Life carries huge importance. Above all, the ultimate purpose should be to live a meaningful life. A meaningful life is one which allows us to connect with our deeper self.”
The author defines life as something that differentiates man from inorganic matter. It’s an aspect that processes and examines a person’s actions that develop through growth. For some, life is a pain because of failures and struggles, but it’s temporary. For the writer, life’s challenges help us move forward, be strong, and live to the fullest. You can also check out these essays about utopia .
“… Kafka defines the dangers of depending on art for life. The hunger artist expresses his dissatisfaction with the world by using himself and not an external canvas to create his artwork, forcing a lack of separation between the artist and his art. Therefore, instead of the art depending on the audience, the artist depends on the audience, meaning when the audience’s appreciation for work dwindles, their appreciation for the artist diminishes as well, leading to the hunger artist’s death.”
The essay talks about “ A Hunger Artist ” by Franz Kafka, who describes his views on life through art. The author analyzes Kafka’s fictional main character and his anxieties and frustrations about life and the world. This perception shows how much he suffered as an artist and how unhappy he was. Through the essay, the writer effectively explains Kafka’s conclusion that artists’ survival should not depend on their art.
“Compassion is that feeling that we’ve all experienced at some point in our lives. When we know that there is someone that really cares for us. Compassion comes from that moment when we can see the world through another person’s eyes.”
The author is a nurse who believes that to be professional, they need to be compassionate and treat their patients with respect, empathy, and dignity. One can show compassion through small actions such as talking and listening to patients’ grievances. In conclusion, compassion can save a person’s life by accepting everyone regardless of race, gender, etc.
“… A life of self-realization is more preferable and beneficial in comparison with a life on consumption. At the same time, this statement may be objected as person’s consumption leads to his or her happiness.”
The author examines Jon Elster’s theory to find out what makes a person happy and what people should think and feel about their material belongings. The essay mentions a list of common activities that make us feel happy and satisfied, such as buying new things. The writer explains that Elster’s statement about the prevalence of self-realization in consumption will always trigger intense debate.
“Appreciate the moment you’ve been given and appreciate the people you’ve been given to spend it with, because no matter how beautiful or tragic a moment is, it always ends. So hold on a little tighter, smile a little bigger, cry a little harder, laugh a little louder, forgive a little quicker, and love a whole lot deeper because these are the moments you will remember when you’re old and wishing you could rewind time.”
This essay explains that some things and events only happen once in a person’s life. The author encourages teenagers to enjoy the little things in their life and do what they love as much as they can. When they turn into adults, they will no longer have the luxury to do whatever they want.
The author suggests doing something meaningful as a stress reliever, trusting people, refusing to give up on the things that make you happy, and dying with beautiful memories. For help with your essays, check out our round-up of the best essay checkers .
7 Prompts for Essays About Life

Life encompasses many values and depends on one’s perception. For most, life is about reaching achievements to make themselves feel alive. Use this prompt to compile different meanings of life and provide a background on why a person defines life as they do.
Take Joseph Campbell’s, “Life has no meaning. Each of us has meaning, and we bring it to life. It is a waste to be asking the question when you are the answer,” for example. This quote pertains to his belief that an individual is responsible for giving life meaning.
For this prompt, share with your readers your current purpose in life. It can be as simple as helping your siblings graduate or something grand, such as changing a national law to make a better world. You can ask others about their life purpose to include in your essay and give your opinion on why your answers are different or similar.
Life is a fascinating subject, as each person has a unique concept. How someone lives depends on many factors, such as opportunities, upbringing, and philosophies. All of these elements affect what we consider “special.”
Share what you think makes life special. For instance, talk about your relationships, such as your close-knit family or best friends. Write about the times when you thought life was worth living. You might also be interested in these essays about yourself .
Life in itself is a gift. However, most of us follow a routine of “wake up, work (or study), sleep, repeat.” Our constant need to survive makes us take things for granted. When we endlessly repeat a routine, life becomes mundane. For this prompt, offer tips on how to avoid a monotonous life, such as keeping a gratitude journal or traveling.
Many literary pieces use life as their subject. If you have a favorite book about life, recommend it to your readers by summarizing the content and sharing how the book influenced your outlook on life. You can suggest more than one book and explain why everyone should read them.
For example, Paulo Coelho’s “The Alchemist” reminds its readers to live in the moment and never fear failure.

To be healthy doesn’t only pertain to our physical condition. It also refers to our mental, spiritual, and emotional well-being. To live a happy and full life, individuals must strive to be healthy in all areas. For this prompt, list ways to achieve a healthy life. Section your essay and present activities to improve health, such as eating healthy foods, talking with friends, etc.
No one has a perfect life, but describe what it’ll be like if you do. Start with the material things, such as your house, clothes, etc. Then, move to how you connect with others. In your conclusion, answer whether you’re willing to exchange your current life for the “perfect life” you described and why. See our essay writing tips to learn more!

Maria Caballero is a freelance writer who has been writing since high school. She believes that to be a writer doesn't only refer to excellent syntax and semantics but also knowing how to weave words together to communicate to any reader effectively.
View all posts

Modern Life Changes the Brain. Here's How to Change It Back
What is "frontal fatigue" and how do we treat it.
Posted June 6, 2022 | Reviewed by Devon Frye
- The demands of modern life are relentless and can have negative effects on our brain's prefrontal cortex (PFC).
- A weakened PFC can make us more vulnerable to mental disorders and poor well-being.
- I call this weakened and vulnerable state "frontal fatigue," and argue that most people in the modern world have it to some degree.
- There are ways to minimize frontal fatigue and protect ourselves from its effects.

Suicide . Depression . Anxiety . Medication . Psychiatric hospitalizations.
The signs are everywhere. Across the industrialized world, urban and rural, east and west, our mental states seem to only get worse by the year. The biggest commonality in this passage of time is that our societies become increasingly more modern and more technological. In spite of the many priceless benefits of modernity, it is also true that for any group, the more modern they become, the more mental illness and less emotional well-being they tend to have.
In a recent article , I explored ways to understand our modern predicament. Modern life is a constant flood of choices, decisions, and tasks, each more complex and abstract than the last. The most common and the most momentous parts of our lives are equalized by calendar reminders. Many cultures and traditions that formerly guided us in the work of living are now the stuff of nostalgia . Meanwhile, social media can distort our identities into cartoon versions, often depressed and alone.
How did we build such a world? In my last post, I argued that we built the modern world to run on the sizeable power of the human prefrontal cortex (PFC). We use our mighty PFCs to manage our current world, often enough with success. However, there’s a chink in the armor. The incessant and stressful demands we put on the PFC tend to weaken it. Weakened, it fails at its work while releasing vulnerabilities to mental illness and negative emotions.
This weakened, tired PFC is what I call "frontal fatigue" and describe in my book, Frontal Fatigue. The Impact of Modern Life and Technology on Mental Illness. Frontal fatigue is the vulnerability we all carry due to the demands of the modern world, our dearth of personal connections, and the effects all this has on our brains.
Unfortunately, the pace of modern life’s demands shows no sign of slowing down—in fact, they are escalating. Any individual person can, however, take steps to moderate the effects of this assault on their brain. Unplugging and leaving stress behind are not options for most of us. For those of us who must remain plugged in, there is still much we can do to attend to the health of our PFCs, and thus our minds.
3 Steps to Take Care of Your PFC
In the middle of the 20th century, it became obvious that, for the first time in human history, we had to exercise and diet to have a healthy body. A similar time has come for our minds. Disciplines such as meditation and yoga are wonderful but take considerable practice. I believe a more targeted approach affords control and relief without such efforts.
There are three methods I recommend to address this broad personal project. These are different from general stress reduction. They are aimed more directly at the PFC by supplying both outlets and control over these brain functions and hopefully restore some balance to our lives.
These three categories summarize my approach.
- Know when the PFC is strained. This is different from just stress or fatigue, and we need to recognize it.
- Have reliable ways to disconnect not just from technology, but from engaging the world only through the PFC.
- Because much of the time we will remain stuck in our own minds, and thus PFCs, we need to be greater masters of our thoughts and feelings.
These approaches are not intended to reinvigorate us so we can jump back into the thick of things. Instead, we should strive for a better sense of balance and control over how our lives and PFCs interact. If, as you examine these plans, they seem like one more thing to add to your to-do list, then you may not have time available. Rest may be what you need the most. Otherwise, focus on and practice the tasks that resonate with you.

1. Know the signs of PFC strain.
- Do you strain to maintain attention ? Especially reading difficult material or repetitive data such as numbers in a column—do you often need caffeine to continue?.
- Do you forget words and small things? Where you put things; what you thought a moment ago; the word you are looking for, often a name or a word you uncommonly use? This is a breakdown of working memory .
- Do you struggle to multi-task? This is really rapid-shifting as in cooking multiple dishes or managing multiple tasks simultaneously by jumping from one to the next.
- Do you let emotions slip through? Usually irritability. Or, do you say emotionally charged things you would not normally say?
When these signs appear, it likely means your PFC is at its limit due to stress, fatigue, or overuse. If you can, disengage from what you’re doing. Do something simpler, or nothing at all. The PFC is the only part of the brain that actually fatigues like a muscle with overuse. As with muscles, rest is essential.
2. Disconnect.
We need to engage with the world in ways other than just our PFCs. The PFC is always working, but we can use other brain systems to directly engage with life. There are no tricks or unusual techniques to learn here. These are fully human activities. Your body and mind will feel at home with their practice. We did these things every day in pre-modern societies:
- Engage life with your hands. Do crafts, cooking, art, play an instrument, garden, or take on a DIY project. Physical (as opposed to virtual) experience brings a level of care and easy focus.
- Engage life with your senses. We are starved for common beauty. Enrich your senses. See, smell, hear, and taste what life offers. Investigate new foods, art, music, and especially nature. Whatever pulls you in via a sense door, follow it (within reason). Green environments are very important in this endeavor. More and more, research finds them to be calming, restorative, and necessary for a healthy mind.
- Engage life with others. Talk with, question, greet, or chat with others—and not just those close to you, but people you see, work with, pass by, and wait in line with. People love to talk about themselves. Let them and hear their stories. I do not believe that chit-chat is mindless and trivial. Connecting dilutes the minor struggles of the day: the weather, traffic. It relieves stress by spreading out concerns among more people. Participate in some chit-chat even if it’s not your concern at the moment.
3. Better manage your thoughts and feelings.
As I mentioned above, you will not always be able to get out of your head and away from PFC-based activities. So, you must cultivate certain skills to use on an ongoing basis. These are not intended to conquer the mind or any similar grand spiritual goals . Rather, they give you more options when the effects of frontal fatigue build up.
- Practice a way to quiet your mind. You can hear, see, and feel the mind. You want it quiet sometimes such as before bed, but it can be so during the day. This need not be meditation, which can require practice and skill—although breathing exercises are easier and can accomplish this goal. Most people commonly quiet their minds with diversion. I have taken up landscape painting. Others use sports, crafts, or long walks. Learn to listen in on your mind to see how noisy it is. You will find things that quiet it down. Practice these.
- Read deeply. This is western meditation. It focuses, engages, and slows the mind all at once. Find something to read that intrigues or entertains you, but with a challenge. In other words, not page-turners. We have become skim readers due to the amount we digest from the internet’s constant flow. Read slowly on purpose.
- Begin to own your emotions. Observe that you are not irritat ed , but rather, irrit able . This halts the arguments in your mind and the search for blame. I mention this, of all the ways we can explore our inner selves, because it allows you to reassert control over emotions that the PFC has lost. This is a large project in itself. Begin with one pair of feelings, contrasting an external and internal source then owning the internal one. Irritated/irritable is a good choice for most (other choices are: angered and nearly angry; saddened and already sad).
Lastly, disconnect from tech and social media whenever you can. This will enhance the effects of all the tools listed above. As we further develop our understanding of how modernity fits into our lives, we can better refine what a mentally healthy life means for each of us.

Mark Rego, M.D., is a psychiatrist and a clinical assistant professor at the Yale School of Medicine.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Get the latest content and program updates from Life Time.
Unsubscribe
The Better Good Life: An Essay on Personal Sustainability

Imagine a cherry tree in full bloom, its roots sunk into rich earth and its branches covered with thousands of blossoms, all emitting a lovely fragrance and containing thousands of seeds capable of producing many more cherry trees. The petals begin to fall, covering the ground in a blanket of white flowers and scattering the seeds everywhere.
Some of the seeds will take root, but the vast majority will simply break down along with the spent petals, becoming part of the soil that nourishes the tree — along with thousands of other plants and animals.
Looking at this scene, do we shake our heads at the senseless waste, mess and inefficiency? Does it look like the tree is working too hard, showing signs of strain or collapse? Of course not. But why not?
Well, for one thing, because the whole process is beautiful, abundant and pleasure producing: We enjoy seeing and smelling the trees in bloom, we’re pleased by the idea of the trees multiplying (and producing delicious cherries ), and everyone for miles around seems to benefit in the process.
The entire lifecycle of the cherry tree is rewarding, and the only “waste” involved is an abundant sort of nutrient cycling that only leads to more good things.
The entire lifecycle of the cherry tree is rewarding, and the only “waste” involved is an abundant sort of nutrient cycling that only leads to more good things. Best of all, this show of productivity and generosity seems to come quite naturally to the tree. It shows no signs of discontent or resentment — in fact, it looks like it could keep this up indefinitely with nothing but good, sustainable outcomes.
The cherry-tree scenario is one model that renowned designer and sustainable-development expert William McDonough uses to illustrate how healthy, sustainable systems are supposed to work. “Every last particle contributes in some way to the health of a thriving ecosystem,” he writes in his essay (coauthored with Michael Braungart), “The Extravagant Gesture: Nature, Design and the Transformation of Human Industry” (available at).
Rampant production in this scenario poses no problem, McDonough explains, because the tree returns all of the resources it extracts (without deterioration or diminution), and it produces no dangerous stockpiles of garbage or residual toxins in the process. In fact, rampant production by the cherry tree only enriches everything around it.
In this system and most systems designed by nature, McDonough notes, “Waste that stays waste does not exist. Instead, waste nourishes; waste equals food.”
If only we humans could be lucky and wise enough to live this way — using our resources and energy to such good effect; making useful, beautiful, extravagant contributions; and producing nothing but nourishing “byproducts” in the process.
If only we humans could be lucky and wise enough to live this way — using our resources and energy to such good effect; making useful, beautiful, extravagant contributions ; and producing nothing but nourishing “byproducts” in the process. If only our version of rampant production and consumption produced so much pleasure and value and so little exhaustion, anxiety, depletion and waste.
Well, perhaps we can learn. More to the point, if we hope to create a decent future for ourselves and succeeding generations, we must. After all, a future produced by trends of the present — in which children are increasingly treated for stress, obesity, high blood pressure and heart disease, and in which our chronic health problems threaten to bankrupt our economy — is not much of a future.
We need to create something better. And for that to happen, we must begin to reconsider which parts of our lives contribute to the cherry tree’s brand of healthy vibrance and abundance, and which don’t.
The happy news is, the search for a more sustainable way of life can go hand in hand with the pursuit of a healthier, more rewarding life. And isn’t that the kind of life most of us are after?
In Search of Sustainability and Satisfaction
McDonough’s cherry-tree model represents several key principles of sustainability — including lifecycle awareness, no-waste nutrient cycling and a commitment to “it’s-all-connected” systems thinking (see “ See the Connection “). And it turns out that many of these principles can be usefully applied not just to natural resources and ecosystems, but to all systems — from frameworks for economic and industrial production to blueprints for individual and collective well-being.
For example, when we look at our lives through the lens of sustainability, we can begin to see how unwise short-term tradeoffs (fast food, skipped workouts, skimpy sleep, strictly-for-the-money jobs) produce waste (squandered energy and vitality, unfulfilled personal potential, excessive material consumption) and toxic byproducts (illness, excess weight , depression, frustration, debt).
We can also see how healthy choices and investments in our personal well-being can produce profoundly positive results that extend to our broader circles of influence and communities at large.
Conversely, we can also see how healthy choices and investments in our personal well-being can produce profoundly positive results that extend to our broader circles of influence and communities at large. When we’re feeling our best and overflowing with energy and optimism, we tend to be of greater service and support to others. We’re clearer of mind, meaning we can identify opportunities to reengineer the things that aren’t working in our lives. We can also more fully appreciate and emphasize the things that are (as opposed to feeling stuck in a rut , down in the dumps, unappreciated or entitled to something we’re not getting).
When you look at it this way, it’s not hard to see why sustainability plays such an important role in creating the conditions of a true “ good life ”: By definition, sustainability principles discourage people from consuming or destroying resources at a greater pace than they can replenish them. They also encourage people to notice when buildups and depletions begin occurring and to correct them as quickly as possible.
As a result, sustainability-oriented approaches tend to produce not just robust, resilient individuals , but resilient and regenerative societies — the kind that manage to produce long-term benefits for a great many without undermining the resources on which those benefits depend. (For a thought-provoking exploration of how and why this has been true historically, read Jared Diamond’s excellent book Collapse: How Societies Choose to Fail or Succeed .)
The Good Life Gone Bad
So, what exactly is a “good life”? Clearly, not everyone shares the same definition, but most of us would prefer a life filled with experiences we find pleasing and worthwhile and that contribute to an overall sense of well-being.
We’d prefer a life that feels good in the moment, but that also lays the ground for a promising future — a life, like the cherry tree’s, that contributes something of value and that benefits and enriches the lives of others, or at least doesn’t cause them anxiety and harm.
Unfortunately, historically, our pursuit of the good life has focused on increasing our material wealth and upgrading our socioeconomic status in the short term (learn more at “ What Is Affluenza? “). And, in the big picture, that approach has not turned out quite the way we might have hoped.
For too many, the current version of “the good life” involves working too-long hours and driving too-long commutes. It has us worrying and running ourselves ragged.
For too many, the current version of “the good life” involves working too-long hours and driving too-long commutes. It has us worrying and running ourselves ragged, overeating to soothe ourselves, watching TV to distract ourselves, binge-shopping to sate our desire for more, and popping prescription pills to keep troubling symptoms at bay. This version of “the good life” has given us only moments a day with the people we love, and virtually no time or inclination to participate as citizens or community members.
It has also given us anxiety attacks; obesity; depression ; traffic jams; urban sprawl; crushing daycare bills; a broken healthcare system; record rates of addiction, divorce and incarceration; an imploding economy; and a planet in peril.
From an economic standpoint, we’re more productive than we’ve ever been. We’ve focused on getting more done in less time. We’ve surrounded ourselves with technologies designed to make our lives easier, more comfortable and more amusing.
Yet, instead of making us happy and healthy, all of this has left a great many of us feeling depleted, lonely, strapped, stressed and resentful. We don’t have enough time for ourselves, our loved ones, our creative aspirations or our communities. And in the wake of the bad-mortgage-meets-Wall-Street-greed crisis, much of the so-called value we’ve been busy creating has seemingly vanished before our eyes, leaving future generations of citizens to pay almost inconceivably huge bills.
The conveniences we’ve embraced to save ourselves time have reduced us to an unimaginative, sedentary existence that undermines our physical fitness and mental health and reduces our ability to give our best gifts.
Meanwhile, the quick-energy fuels we use to keep ourselves going ultimately leave us feeling sluggish, inflamed and fatigued. The conveniences we’ve embraced to save ourselves time have reduced us to an unimaginative, sedentary existence that undermines our physical fitness and mental health and reduces our ability to give our best gifts. (Not sure what your best gift is? See “ Play to Your Strengths ” for more.)
Our bodies and minds are showing the telltale symptoms of unsustainable systems at work — systems that put short-term rewards ahead of long-term value. We’re beginning to suspect that the costs we’re incurring could turn out to be unacceptably high if we ever stop to properly account for them, which some of us are beginning to do.
Accounting for What Matters
Defining the good life in terms of productivity, material rewards and personal accomplishment is a little like viewing the gross domestic product (GDP) as an accurate measurement of social and economic progress.
In fact, the GDP is nothing more than a gross tally of products and services bought and sold, with no distinctions between transactions that enhance well-being and transactions that diminish it, and no accounting for most of the “externalities” (like losses in vitality, beauty and satisfaction) that actually have the greatest impact on our personal health and welfare.
We’d balk if any business attempted to present a picture of financial health by simply tallying up all of its business activity — lumping income and expense, assets and liabilities, and debits and credits together in one impressive, apparently positive bottom-line number (which is, incidentally, much the way our GDP is calculated).
Yet, in many ways, we do the same kind of flawed calculus in our own lives — regarding as measures of success the gross sum of the to-dos we check off, the salaries we earn, the admiration we attract and the rungs we climb on the corporate ladder.
But not all of these activities actually net us the happiness and satisfaction we seek, and in the process of pursuing them, we can incur appalling costs to our health and happiness. We also make vast sacrifices in terms of our personal relationships and our contributions to the communities, societies and environments on which we depend.
This is the essence of unsustainability , the equivalent of a cherry tree sucking up nutrients and resources and growing nothing but bare branches, or worse — ugly, toxic, foul-smelling blooms. So what are our options?
Asking the Right Questions
In the past several years, many alternative, GDP-like indexes have emerged and attempted to more accurately account for how well (or, more often, how poorly) our economic growth is translating to quality-of-life improvements.
Measurement tools like the Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI), developed by Redefining Progress, a nonpartisan public-policy and economic think tank, factor in well-being and quality-of-life concerns by considering both positive and negative impacts of various products and services. They also measure more impacts overall (including impacts on elements of “being” and “doing” vs. just “having”). And they evaluate whether various financial expenditures represent a net gain or net loss — not just in economic terms, but also in human, social and ecological ones (see “Sustainable Happiness,” below).
Perhaps it’s time to consider our personal health and well-being in the same sort of broader context — distinguishing productive activities from destructive ones, and figuring the true costs and unintended consequences of our choices into the assessment of how well our lives are working.
To that end, we might begin asking questions like these:
- Where, in our rush to accomplish or enjoy “more” in the short run, are we inadvertently creating the equivalent of garbage dumps and toxic spills (stress overloads, health crises, battered relationships, debt) that will need to be cleaned up later at great (think Superfund) effort and expense?
- Where, in our impatience to garner maximum gains in personal productivity, wealth or achievement in minimum time, are we setting the stage for bailout scenarios down the road? (Consider the sacrifices endured by our families, friends and colleagues when we fall victim to a bad mood, much less a serious illness or disabling health condition.)
- Where, in an attempt to avoid uncertainty, experimentation or change , are we burning through our limited and unrenewable resource of time (staying at jobs that leave us depleted, for example), rather than striving to harness our bottomless stores of purpose-driven enthusiasm (by, say, pursuing careers or civic duties of real meaning)?
- Where are we making short-sighted choices or non-choices (about our health, for example) that sacrifice the resources we need (energy, vitality, clear focus) to make progress and contributions in other areas of our lives?
In addition to these assessments, we can also begin imagining what a better alternative would look like:
- What might be possible if we embraced a different version of the good life — the kind of good life in which the vast majority of our choices both feel good and do good?
- What if we took a systems view of our life , acknowledging how various inputs and outputs play out (for better or worse) over time? What if we fully considered how those around us are affected by our choices now and in the long term?
- What if we embraced more choices that honor our true nature, that gave us more opportunities to use our talents and enthusiasms in the service of a higher purpose?
One has to wonder how many of our health and fitness challenges would evaporate under such conditions — how many compensatory behaviors (overeating, hiding out, numbing out) would simply no longer have a draw.
How many health-sustaining behaviors would become easy and natural choices if each of us were driven by a strong and joyful purpose , and were no longer saddled with the stress and dissatisfaction inherent in the lives we live now?
Think about the cherry-tree effect implicit in such a scenario: each of us getting our needs met, fulfilling our best potential, living at full vitality, and contributing to healthy, vital, sustainable communities in the process.
If it sounds a bit idealistic, that’s probably because it describes an ideal distant enough from our current reality to provoke a certain amount of hopelessness. But that doesn’t mean it’s entirely unrealistic. In fact, it’s a vision that many people are increasingly convinced is the only kind worth pursuing.
Turning the Corner
Maybe it has something to do with how many of our social, economic and ecological systems are showing signs of extreme strain. Maybe it’s how many of us are sick and tired of being sick and tired — or of living in a culture where everyone else seems sick and tired. Maybe it’s the growing realization that no matter how busy and efficient we are, if our efforts don’t feed us in a deep way, then all that output may be more than a little misguided. Whatever the reason, a lot of us are asking: If our rampant productivity doesn’t make us happy, doesn’t allow for calm and creativity, doesn’t give us an opportunity to participate in a meaningful way — then, really, what’s the point?
These days, it seems that more of us are taking a keen interest in seeking out better ways, and seeing the value of extending the lessons of sustainability beyond the natural world and into our own perspectives on what the good life is all about.
In her book MegaTrends 2010: The Rise of Conscious Capitalism , futurist Patricia Aburdene describes a hopeful collection of social and economic trends shaped by a large and influential subset of the American consuming public. What these 70 million individuals have in common, she explains, are some very specific values-driven behaviors — most of which revolve around seeking a better, deeper, more meaningful and sustainable quality of life (discover the four pillars or meaning at “ How to Build a Meaningful Life “).
[“Conscious Consumers” balance] short-term desires and conveniences with long-term well-being — not just their own, but that of their local and larger communities, and of the planet as a whole.
These “Conscious Consumers,” as Aburdene characterizes them, are more carefully weighing material and economic payoffs against moral and spiritual ones. They are balancing short-term desires and conveniences with long-term well-being — not just their own, but that of their local and larger communities, and of the planet as a whole. They are acting, says Aburdene, out of a sort of “enlightened self-interest,” one that is deeply rooted in concerns about sustainability in all its forms.
“Enlightened self-interest is not altruism,” she explains. “It’s self-interest with a wider view. It asks: If I act in my own self-interest and keep doing so, what are the ramifications of my choices? Which acts — that may look fine right now — will come around and bite me and others one year from now? Ten years? Twenty-five years?”
In other words, Conscious Consumers are not merely consumers, but engaged and concerned individuals who think in terms of lifecycles, who perceive the subtleties and complexities of interconnected systems .
As John Muir famously said: “When one tugs at a single thing in nature, he finds it attached to the rest of the world.” Just as the cherry tree is tethered in a complex ecosystem of relationships, so are we.
Facing Reality
When we live in a way that diminishes us or weighs us down — whether as the result of poor physical health and fitness, excess stress and anxiety, or any compromise of our best potential — we inevitably affect countless other people and systems whose well-being relies on our own.
For example, if we don’t have the time and energy to make food for ourselves and our families, we end up eating poorly, which further diminishes our energy, and may also result in our kids having behavior or attention problems at school, undermining the quality of their experience there, and potentially creating problems for others.
As satisfaction and well-being go down, need and consumption go up.
If we skimp on sleep and relaxation in order to “get more done,” we court illness and depression, risking both our own and others’ productivity and happiness in the process and diminishing the creativity with which we approach challenges.
At the individual level, unsustainable choices create strain and misery. At the collective level, they do the same thing, with exponential effect. Because, when not enough of us are living like thriving cherry trees, cycles of scarcity (rather than abundance) ensue. Life gets harder for everyone. As satisfaction and well-being go down, need and consumption go up. Our sense of “enough” becomes distorted.
Taking Full Account
The basic question of sustainability is this: Can you keep doing what you’re doing indefinitely and without ill effect to yourself and the systems on which you depend — or are you (despite short-term rewards you may be enjoying now, or the “someday” relief you’re hoping for) on a likely trajectory to eventual suffering and destruction?
When it comes to the ecology of the planet, this question has become very pointed in recent years. But posed in the context of our personal lives, the question is equally instructive: Are we living like the cherry tree — part of a sustainable and regenerative cycle — or are we sucking up resources, yet still obsessed with what we don’t have? Are we continually generating new energy, vitality, generosity and personal potential , or wasting it?
We can work just so hard and consume just so much before we begin to experience both diminishing personal returns and increasing degenerative costs.
The human reality, in most cases, isn’t quite as pretty as the cherry tree in full bloom. We can work just so hard and consume just so much before we begin to experience both diminishing personal returns and increasing degenerative costs. And when enough of us are in a chronically diminished state of well-being, the effect is a sort of social and moral pollution — the human equivalent of the greenhouse gasses that threaten our entire ecosystem.
Accounting for these soft costs, or even recognizing them as relevant externalities, is not something we’ve been trained to do well. But all that is changing — in part, because many of us are beginning to realize that much of what we’ve been sold in the name of “progress” is now looking like anything but. And, in part, because we’re starting to believe that not only might there be a better way, but that the principles for creating it are staring us right in the face.
By making personal choices that respect the principles of sustainability, we can interrupt the toxic cycles of overconsumption and overexertion. Ultimately, when confronted with the possibility of a better quality of life and more satisfying expression of our potential, the primary question becomes not just can we continue living the way we have been, but perhaps just as important, why would we even want to ?
If the approach we’ve been taking appears likely to make us miserable (and perhaps extinct), then it makes sense to consider our options. How do we want to live for the foreseeable and sustainable future, and what are the building blocks for that future? What would it be like to live in a community where most people were overflowing with vitality and looking for ways to be of service to others?
While no one expert or index or council claims to have all the answers to that question, when it comes to discerning the fundamentals of the good life, nature conveniently provides most of the models we need. It suggests a framework by which we can better understand and apply the principles of sustainability to our own lives. Now it’s up to us to apply them.
Make It Sustainable
Here are some right-now changes you can make to enhance and sustain your personal well-being:
1. Rethink Your Eating.
Look beyond meal-to-meal concerns with weight. Aim to eat consciously and selectively in keeping with the nourishment you want to take in, the energy and personal gifts you want to contribute, and the influence you want to have on the world around you.
To that end, you might start eating less meat, or fewer packaged foods, or you might start eating regularly so that you have enough energy to exercise (and so that your low blood sugar doesn’t negatively affect your mood and everyone around you).
You also might start packing your lunch, suggests money expert Vicki Robin: Not only will you have more control over what and how you eat, but the money you’ll save over the course of a career can amount to a year’s worth of work. “Bringing your lunch saves you a year of your life,” she says.
2. Set a Regular Bedtime
Having a target bedtime can help you get the sleep you need to be positive and productive, and to avoid becoming depleted and depressed. Research confirms that adequate sleep is essential to clear thinking, balanced mood, healthy metabolism, strong immunity, optimal vitality and strong professional performance.
Research also shows that going to bed earlier provides a higher quality of rest than sleeping in, so get your hours at the start of the night. By taking care of yourself in this simple way, you lay the groundwork for all kinds of regenerative (vs. depleting) cycles.
3. Own Your Outcomes
If there are parts of your life you don’t like — parts that feel toxic, frustrating or wasteful to you — be willing to trace the outcomes back to their origins, including your choices around self-care , seeking help, balancing priorities and sticking to your core values.
Also examine the full range of outputs and impacts: What waste or damage is occurring as a result of this area of unresolved challenge? Who else and what else in your life might be paying too-high a price for the scenario in question? If you’re unsure about whether or not a choice or an activity you’re involved in is sustainable, ask yourself the following questions:
- Given the option, would I do or choose this again? Would I do it indefinitely?
- How long can I keep this up, and at what cost — not just to me, but to the other people and systems I care about?
- What have I sacrificed to get here; what will it take for me to continue? Are the rewards worth it, even if the other areas of my life suffer?
Sustainable Happiness
Not all growth and productivity represent progress, particularly if you consider happiness and well-being as part of the equation. The growing gap between our gross domestic product and Genuine Progress Indicator (as represented below) suggests we could be investing our resources with far happier results.
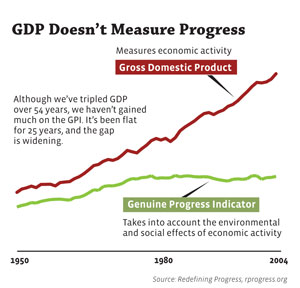
Data source: Redefining Progress, rprogress.org . Chart graphic courtesy of Yes! magazine.
Learn more about the most reliable, sustainable sources of happiness and well-being in the Winter 2009 issue of Yes! magazine, available at www.yesmagazine.org .
Learning From Nature
What can we learn from ecological sustainability about the best ways to balance and sustain our own lives? Here are a few key lessons:
- Everything is in relationship with everything else. So overdrawing or overproducing in one area tends to negatively affect other areas. An excessive focus on work can undermine your relationship with your partner or kids. Diminished physical vitality or low mood can affect the quality of your work and service to others.
- What comes around goes around. Trying to “cheat” or “skimp” or “get away with something” in the short term generally doesn’t work because the true costs of cheating eventually become painfully obvious. And very often the “cleanup” costs more and takes longer than it would have to simply do the right thing in the first place.
- Waste not, want not. Unpleasant accumulations or unsustainable drains represent opportunities for improvement and reinvention. Nature’s models of nutrient cycling show us that what looks like waste can become food for a process we simply haven’t engaged yet: Anxiety may be nervous energy that needs to be burned off, or a nudge to do relaxation and self-inquiry exercises that will churn up new insights and ideas. Excess fat may be fuel for enjoyable activities we’ve resisted doing or haven’t yet discovered — or a clue that we’re hungry for something other than food. The clutter in our homes may represent resources that we haven’t gotten around to sharing. Look for ways to put waste and excess to work, and you may discover all kinds of “nutrients” just looking for attention. (See “ The Emotional Toll of Clutter “.)
The Sustainable Self
Connie Grauds, RPh, is a pharmacist who combines her Western medical training with shamanic teachings, and in her view, we get caught in wearying patterns primarily because of fear . “Energy-depleting thoughts and feelings underlie energy-depleting habits,” Grauds writes in her book The Energy Prescription , cowritten with Doug Childers. She says that we often burn ourselves out because we’re unconsciously afraid of what will happen if we don’t.
Grauds uses the shamanic term “susto” to describe our anxious response to external situations we can’t control — the traffic jam, the work deadline, the pressure to buy stuff we don’t really need. “Susto” triggers the body’s fight-or-flight response, which encourages short-term, unconscious reactions to stress. When we shift to a more internal focus, tuning in to our body’s physical and emotional signals more reflectively, we act from what Grauds calls our “sustainable self.” She says the sustainable self can be accessed anytime with a simple four-step process:
- Take a deep breath ;
- Feel your body;
- Notice your thoughts, and then;
- Recognize that you are connected to a larger network of energy .
“A sustainable self recognizes and embraces its interdependent relationship to life,” she says, explaining that when we get our energy from controlling external circumstances we’re bound to collapse eventually, but when we’re connected to our internal reserves, we can be much more effective. “By consistently doing things that replenish us and not doing things that needlessly deplete us,” Grauds writes, “we access and conduct the energy we need to make and sustain positive changes and function at peak levels.”
Thoughts to share?
This Post Has 0 Comments
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
ADVERTISEMENT
More Like This

How to Develop a ‘Stretch’ Mindset
Working with what you have can be the key to more sustainable success. Adopting a “stretch” mindset can help.

The Power of Intention: Learning to Co-Create Your World Your Way
Thought-provoking takeaways from Wayne Dyer’s classic guide to conscious living.

6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy Life
A functional-medicine pioneer explains how to make small choices that build lasting well-being.

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Life for Students in English: 100 Words, 200 Words, 350 Words
- Updated on
- Apr 12, 2024

Life is a culmination of moments, a blend of laughter and tears, victory and challenges. From the moment we take our first breath to the day, we draw our last. It is a journey filled with countless experiences, lessons, and emotions. From the tiniest of creatures to the tallest of trees, every living being is a part of this incredible journey. In this blog, we will explore the multifaceted essence of life through three unique essays.
Also Read : Essay on My Aim in Life
Table of Contents
- 1 Sample Essay on Life in 100 words
- 2 Sample Essay on Life in 200 words
- 3 Sample Essay on Life in 350 words
Sample Essay on Life in 100 words
Life is a collection of stories etched in time, each page filled with lessons that have been learned. The journey of life is a rollercoaster, with peaks of joy and valleys of despair. It teaches us self-reliance, adaptability, and the importance of cherishing every passing second.
As we navigate through unknown paths, we discover the true essence of our being – the passions that fuel us and the relationships that sustain us. Life is a gift, a canvas upon which we paint our purpose. Let us embrace each passing day, for they collectively make the masterpiece that is our life.
Sample Essay on Life in 200 words
Life is a river that flows with an ever-changing current, carrying us through seasons of growth and moments of introspection. It presents us with opportunities to evolve, to change ourselves, and emerge as a new. Life is a precious gift that surrounds us with wonders every day. We wake up to the warmth of the sun, the chirping of birds, and the love of our family. Each moment teaches us something valuable – to be kind, to learn, and to grow.
As we play, study, and share, we make memories that become the colours of our life’s canvas. Life is about enjoying the little things – a smile, a hug, a blooming flower. The challenges we face are sometimes difficult but are also stepping stones that move and motivate us toward self-discovery. Life’s journey is not about reaching a destination, but about following the purpose and the richness of the path itself.
Also Read: Essay on My Hobby
Sample Essay on Life in 350 words
Life is a journey of discovery, where we encounter moments both big and small that shape our identity. From the joyful laughter of childhood to the trials of adolescence, each phase of life imparts unique lessons.
Each chapter unveils a new facet of our identity, inviting us to delve deeper into the essence of who we are. As we grow, we learn that life isn’t just about happiness; it’s about resilience in the face of difficulties. Challenges, like puzzles, help us develop problem-solving skills and the ability to adapt. Friends and family accompany us on this journey, providing companionship, support, and love.
Life, a masterpiece painted by time, is about making choices, experiences, and opportunities. In the early years, life is a playground of curiosity, where we explore the world with wonder-filled eyes. Learning becomes our companion, and mistakes are stepping stones to growth.
Adolescence brings a whirlwind of change – physical, emotional, and psychological. It’s a time of self-discovery, as we unfold our passions, talents, and values. Amidst this transformation, friendships blossom, leaving an indelible mark on our hearts. Responsibilities increase, and we navigate through the maze of choices, from careers to relationships. Life becomes full of ambitions , dreams, setbacks, and achievements. Failures and successes become part of our narrative, driving us to strive harder and reach higher.
In the sunset years, life’s pace may slow, but its essence deepens. Memories become treasures, and experiences turn into life lessons. Family becomes a stronghold of support, and the wisdom garnered over the years becomes a guiding light. Reflection becomes a companion, and gratitude fills our hearts as we look back on the incredible journey we’ve travelled.
In conclusion, life is a journey that encompasses the spectrum of human existence. From the innocence of childhood to the wisdom of old age, every phase contributes to our growth and understanding. Through challenges and triumphs, connections, and solitude, we weave a tale unique to ours. So, let’s embrace life’s twists and turns, for they shape us into the individuals we are meant to be.
Also Read: 100+ Rumi Quotes on Love, Life, Nature & the Universe
Ans. When children and students write a life essay, they have the opportunity to contemplate the wonder and significance of their being.
Ans. The pursuit of happiness is so connected in entirety that it is woven into our life, as we seek fulfillment. It is in the phase of low that we often find the strength to rise, and in the quiet moments of being ourselves, we hear our truest desires.
Ans. A life story is a valuable personal account of both personal and professional experiences that are shared by the individual.
Related Reads
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Rajshree Lahoty
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out

Essay on Internet and Modern Life
Students are often asked to write an essay on Internet and Modern Life in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Internet and Modern Life
Introduction.
Internet has revolutionized our lives. It has become an essential part of our daily routine, impacting our lifestyle significantly.
Education and the Internet
Internet has transformed education. It offers vast resources for learning, making education more accessible and enjoyable.
Communication and the Internet
Internet has made communication faster and easier. We can connect with anyone, anywhere, anytime using various applications.
Entertainment and the Internet
Internet provides endless entertainment. From music, movies, to games, there’s something for everyone.
In conclusion, the Internet has brought immense changes to our lives, making it more convenient and enjoyable.
250 Words Essay on Internet and Modern Life
The internet: a catalyst for modern life.
The internet, a revolutionary technology, has dramatically transformed our lifestyle, making it an inextricable part of modern life. It has not only reshaped communication but also significantly influenced education, business, and entertainment.
Revolutionizing Communication
The internet has revolutionized communication, enabling instant, global connections. Social media platforms, emails, and video conferencing have made it possible to interact with anyone, anywhere, anytime, thus shrinking the world into a global village. This has fostered cultural exchange and global understanding, making the world more interconnected.
Transforming Education
Education has been significantly impacted by the internet. Traditional classroom learning has evolved into e-learning, where students can access a wealth of knowledge at their fingertips. Online courses, virtual classrooms, and digital libraries have democratized education, making it accessible to all, irrespective of geographical boundaries.
Driving Business Innovation
The internet has also driven business innovation. E-commerce, digital marketing, and remote work have redefined the business landscape. Companies can now reach global markets, offer personalized customer experiences, and operate more efficiently, thanks to the internet.
Entertainment in the Digital Age
Entertainment has also been revolutionized by the internet. Streaming platforms have replaced traditional media, offering a plethora of choices to consumers. The internet has also given rise to new forms of entertainment like online gaming and social media.
In conclusion, the internet has profoundly influenced modern life, reshaping various aspects of our existence. It is a powerful tool that, when used wisely, can unlock limitless possibilities and opportunities. As we continue to innovate and evolve, the role of the internet in shaping our future cannot be overstated.
500 Words Essay on Internet and Modern Life
The advent of the internet.
The internet, the digital universe of information, has drastically revolutionized the modern world. It has woven itself into the fabric of our lives, becoming an indispensable tool for communication, information, entertainment, and business. The inception of the internet was a turning point in human history, marking the dawn of the information age.
Internet and Communication
One of the most significant impacts of the Internet is on communication. It has transformed the way we connect with each other, making it possible to interact with people from any part of the globe instantly. Social media platforms, emails, and video conferencing have not only made communication faster but also more efficient. They have broken geographical barriers, fostering global connections and collaborations.
Internet and Information
The internet has democratized access to information. Search engines, digital libraries, and online databases have made it possible to acquire knowledge on virtually any subject with just a few keystrokes. This has transformed education, making learning more accessible, flexible, and personalized. It has also changed the dynamics of news dissemination, making it instantaneous and interactive.
Internet and Entertainment
The entertainment industry has also been reshaped by the internet. Streaming platforms have revolutionized the way we consume music, movies, and television shows, offering on-demand entertainment. Online gaming and social media platforms have also become significant sources of amusement. These changes have not only altered the nature of entertainment but also its economics, giving rise to new business models.
Internet and Business
The internet has also had a profound impact on business. E-commerce has transformed the way we shop, making it possible to purchase anything from anywhere at any time. It has also enabled businesses to reach a global audience, opening up new markets. Moreover, the internet has given rise to a new generation of digital businesses, including social media platforms, search engines, and streaming services.
The Dark Side of the Internet
However, the internet is not without its downsides. It has given rise to new forms of crime, such as cyberbullying, identity theft, and online fraud. It has also led to concerns about privacy and the misuse of personal data. Moreover, the internet has been blamed for spreading misinformation and fake news, which can have serious societal implications.
In conclusion, the internet has profoundly transformed modern life. It has revolutionized communication, democratized access to information, reshaped entertainment, and transformed business. However, it has also brought new challenges that we must address. As we continue to navigate the digital age, it is crucial to harness the potential of the internet while mitigating its risks.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Internet Addiction
- Essay on Evolution of Internet
- Essay on Life Without Internet
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Modern Technology’s Impact on Society Essay
Introduction, disadvantages and advantages of technology.
Modern technology has changed the world beyond recognition. Thanks to technology in the twentieth and twenty-first centuries, advances have been made that have revolutionized our lives. Modern man can hardly imagine his life without machines. Every day, new devices either appear, or existing ones are improved. Technology has made the world a better place, bringing people additional conveniences and opportunities for healthy living through advances in science. I believe that the changes that technology has brought to our lives are incredibly positive in many areas.
One of the fields where computing and the Web have introduced improvements is education. Machines can keep large volumes of information in a tiny space, reducing entire library shelves of literature to a single CD-ROM of content (Garsten & Wulff, 2020). The Web also acts as a huge learning tool, linking together data sites and enabling inquisitive individuals to seek out just about any subject conceivable. A single personal computer can hold hundreds of instructional programs, visual and audio tutorials, and provide learners with exposure to an immense quantity of content. In the classroom, virtual whiteboards are replacing conventional whiteboards, allowing teachers to provide interactive content for students and play instructional movies without the need for a projector.
Advanced technology has also dramatically and favorably changed the medical care sector. Developments in diagnostic instruments allow doctors to detect hidden diseases, improving the likelihood of successful therapy and saving lives. Advances in drugs and vaccines have been extremely influential, nearly eradicating diseases such as measles, diphtheria, and smallpox, which once caused massive epidemics (Garsten & Wulff, 2020). Modern medicine allows patients to treat chronic diseases that were once debilitating and life-threatening, such as diabetes and hypertension. Technological advances in medicine have helped improve the lives of people around the world. In addition, the latest technology has dramatically increased the productivity of various techniques.
The computers’ capability to resolve complicated mathematical calculations enables them to accelerate any problem that involves metrics or other calculations. Simulating physical processes on a computer can save time and money in any production situation, giving engineers the ability to simulate any design. Modern technology in transportation allows large distances to be traveled quickly. Electric trains, airplanes, cars, and even rockets are used for this purpose (Garsten & Wulff, 2020). In this way, technology brings positive change for people who love to travel.
Despite all the positive changes, there are also disadvantages to the active development of technology. For example, more and more people are becoming dependent on the computer, TV, or cell phone. They ignore their household chores, studies, or work and spend all their time in front of a laptop or TV screen (Garsten & Wulff, 2020). Because of this, people may become inactive and less willing to work, hoping that technology will do everything for them.
In conclusion, I believe that despite some of the disadvantages, the advantages of gadgets are much more significant. Modern technology saves time and allows people to enjoy life. Moreover, new technologies in medicine also contribute to a longer life expectancy of the population and the cure of diseases that were previously beyond the reach of doctors. In addition to medicine, technology has brought significant positive changes to the fields of communication, education, and engineering. Therefore, I believe that the positive impact of technological progress on human lives cannot be denied.
Garsten, C., & Wulff, H. (2020). New technologies at work: People, screens, and social virtuality . Routledge. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, May 30). Modern Technology's Impact on Society. https://ivypanda.com/essays/modern-technologys-impact-on-society/
"Modern Technology's Impact on Society." IvyPanda , 30 May 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/modern-technologys-impact-on-society/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Modern Technology's Impact on Society'. 30 May.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Modern Technology's Impact on Society." May 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/modern-technologys-impact-on-society/.
1. IvyPanda . "Modern Technology's Impact on Society." May 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/modern-technologys-impact-on-society/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Modern Technology's Impact on Society." May 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/modern-technologys-impact-on-society/.
- Interactive Whiteboard Use During a Meeting
- Interactive Whiteboards in Teachers' Perception
- Interactive Whiteboard Technology
- The Use of Interactive Whiteboards in Guided Inquiry-Based Learning in Early Childhood Education
- Saudi Primary Teachers and Interactive Whiteboards
- Interactive Whiteboards in Saudi Arabian Schools
- The Whiteboard App Marketing and Advertising Models
- Interactive Smartboard: Advantages & Disadvantages
- Quality Improvement Initiative
- Integration of the Modern Technological Solutions Into the Academic Field
- The Covid-19 Registry Importance
- Impact of Computer Technology on Economy and Social Life
- Technology Effect on the Disappearance of Specific Jobs
- Modern Communication Impacted by Technology
- Human Existence in Age of Informational Knowledge Work
Asteroid Mining: A New Space Race
The dictatorship of free choice: identities among algorithms, openmind books, scientific anniversaries, why do we tan, featured author, latest book, how the internet has changed everyday life, what happened.
The Internet has turned our existence upside down. It has revolutionized communications, to the extent that it is now our preferred medium of everyday communication. In almost everything we do, we use the Internet. Ordering a pizza, buying a television, sharing a moment with a friend, sending a picture over instant messaging. Before the Internet, if you wanted to keep up with the news, you had to walk down to the newsstand when it opened in the morning and buy a local edition reporting what had happened the previous day. But today a click or two is enough to read your local paper and any news source from anywhere in the world, updated up to the minute.
The Internet itself has been transformed. In its early days—which from a historical perspective are still relatively recent—it was a static network designed to shuttle a small freight of bytes or a short message between two terminals; it was a repository of information where content was published and maintained only by expert coders. Today, however, immense quantities of information are uploaded and downloaded over this electronic leviathan, and the content is very much our own, for now we are all commentators, publishers, and creators.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the Internet widened in scope to encompass the IT capabilities of universities and research centers, and, later on, public entities, institutions, and private enterprises from around the world. The Internet underwent immense growth; it was no longer a state-controlled project, but the largest computer network in the world, comprising over 50,000 sub-networks, 4 million systems, and 70 million users.
The emergence of web 2.0 in the first decade of the twenty-first century was itself a revolution in the short history of the Internet, fostering the rise of social media and other interactive, crowd-based communication tools.
The Internet was no longer concerned with information exchange alone: it was a sophisticated multidisciplinary tool enabling individuals to create content, communicate with one another, and even escape reality. Today, we can send data from one end of the world to the other in a matter of seconds, make online presentations, live in parallel “game worlds,” and use pictures, video, sound, and text to share our real lives, our genuine identity. Personal stories go public; local issues become global.
The rise of the Internet has sparked a debate about how online communication affects social relationships. The Internet frees us from geographic fetters and brings us together in topic-based communities that are not tied down to any specific place. Ours is a networked, globalized society connected by new technologies. The Internet is the tool we use to interact with one another, and accordingly poses new challenges to privacy and security.
Information technologies have wrought fundamental change throughout society, driving it forward from the industrial age to the networked era. In our world, global information networks are vital infrastructure—but in what ways has this changed human relations? The Internet has changed business, education, government, healthcare, and even the ways in which we interact with our loved ones—it has become one of the key drivers of social evolution.
The changes in social communication are of particular significance. Although analogue tools still have their place in some sectors, new technologies are continuing to gain ground every day, transforming our communication practices and possibilities—particularly among younger people. The Internet has removed all communication barriers. Online, the conventional constraints of space and time disappear and there is a dizzyingly wide range of communicative possibilities. The impact of social media applications has triggered discussion of the “new communication democracy.”
The development of the Internet today is being shaped predominantly by instant, mobile communications. The mobile Internet is a fresh revolution. Comprehensive Internet connectivity via smartphones and tablets is leading to an increasingly mobile reality: we are not tied to any single specific device, and everything is in the cloud.
People no longer spend hours gazing at a computer screen after work or class; instead, they use their mobile devices to stay online everywhere, all the time.
Anyone failing to keep abreast of this radical change is losing out on an opportunity.
Communication Opportunities Created by the Internet
The Internet has become embedded in every aspect of our day-to-day lives, changing the way we interact with others. This insight struck me when I started out in the world of social media. I created my first social network in 2005, when I was finishing college in the United States—it had a political theme. I could already see that social media were on the verge of changing our way of communicating, helping us to share information by opening up a new channel that cuts across conventional ones.
That first attempt did not work out, but I learned from the experience.I get the feeling that in many countries failure is punished too harshly—but the fact is, the only surefire way of avoiding failure is to do nothing at all. I firmly believe that mistakes help you improve; getting it wrong teaches you how to get it right. Creativity, hard work, and a positive attitude will let you achieve any goal.
In 2006, after I moved to Spain, I created Tuenti. Tuenti (which, contrary to widespread belief, has nothing to do with the number 20; it is short for “tu entidad,” the Spanish for “your entity”) is a social communication platform for genuine friends. From the outset, the idea was to keep it simple, relevant, and private. That’s the key to its success.
I think the real value of social media is that you can stay in touch from moment to moment with the people who really matter to you. Social media let you share experiences and information; they get people and ideas in touch instantly, without frontiers. Camaraderie, friendship, and solidarity—social phenomena that have been around for as long as humanity itself—have been freed from the conventional restrictions of space and time and can now thrive in a rich variety of ways.
Out of all the plethora of communication opportunities that the Internet has opened up, I would highlight the emergence of social media and the way they have intricately melded into our daily lives. Social media have changed our personal space, altering the way we interact with our loved ones, our friends, and our sexual partners; they have forced us to rethink even basic daily processes like studying and shopping; they have affected the economy by nurturing the business startup culture and electronic commerce; they have even given us new ways to form broad-based political movements.
The Internet and Education
The Internet has clearly impacted all levels of education by providing unbounded possibilities for learning. I believe the future of education is a networked future. People can use the Internet to create and share knowledge and develop new ways of teaching and learning that captivate and stimulate students’ imagination at any time, anywhere, using any device. By connecting and empowering students and educators, we can speed up economic growth and enhance the well-being of society throughout the world. We should work together, over a network, to build the global learning society.
The network of networks is an inexhaustible source of information. What’s more, the Internet has enabled users to move away from their former passive role as mere recipients of messages conveyed by conventional media to an active role, choosing what information to receive, how, and when. The information recipient even decides whether or not they want to stay informed.
We have moved on from scattergun mass communication to a pattern where the user proactively selects the information they need.
Students can work interactively with one another, unrestricted by physical or time constraints. Today, you can use the Internet to access libraries, encyclopedias, art galleries, news archives, and other information sources from anywhere in the world: I believe this is a key advantage in the education field. The web is a formidable resource for enhancing the process of building knowledge.
I also believe the Internet is a wonderful tool for learning and practicing other languages—this continues to be a critical issue in many countries, including Spain, and, in a globalized world, calls for special efforts to improve.
The Internet, in addition to its communicative purposes, has become a vital tool for exchanging knowledge and education; it is not just an information source, or a locus where results can be published, it is also a channel for cooperating with other people and groups who are working on related research topics.
The Internet and Privacy and Security
Another key issue surrounding Internet use is privacy. Internet users are becoming more sensitive to the insight that privacy is a must-have in our lives.
Privacy has risen near the top of the agenda in step with an increasing awareness of the implications of using social media. Much of the time, people started to use social media with no real idea of the dangers, and have wised up only through trial and error—sheer accident, snafus, and mistakes. Lately, inappropriate use of social media seems to hit the headlines every day. Celebrities posting inappropriate comments to their profiles, private pictures and tapes leaked to the Internet at large, companies displaying arrogance toward users, and even criminal activities involving private-data trafficking or social media exploitation.
All this shows that—contrary to what many people seem to have assumed—online security and privacy are critical, and, I believe, will become even more important going forward. And, although every user needs privacy, the issue is particularly sensitive for minors—despite attempts to raise their awareness, children still behave recklessly online.
I have always been highly concerned about privacy. On Tuenti, the default privacy setting on every user account is the highest available level of data protection. Only people the user has accepted as a “friend” can access their personal details, see their telephone number, or download their pictures. This means that, by default, user information is not accessible to third parties. In addition, users are supported by procedures for reporting abuse. Any user can report a profile or photograph that is abusive, inappropriate, or violates the terms of use: action is taken immediately. Security and privacy queries are resolved within 24 hours.
We need to be aware that different Internet platforms provide widely different privacy experiences. Some of them are entirely open and public; no steps whatsoever are taken to protect personal information, and all profiles are indexable by Internet search engines.
On the other hand, I think the debate about whether social media use should be subject to an age requirement is somewhat pointless, given that most globally active platforms operate without age restrictions. The European regulatory framework is quite different from the United States and Asian codes. Companies based in Europe are bound by rigorous policies on privacy and underage use of social media. This can become a competitive drawback when the ground rules do not apply equally to all players—our American and Japanese competitors, for instance, are not required to place any kind of age constraint on access.
Outside the scope of what the industry or regulators can do, it is vital that users themselves look after the privacy of their data. I believe the information is the user’s property, so the user is the only party entitled to control the collection, use, and disclosure of any information about him or herself. Some social networks seem to have forgotten this fact—they sell data, make it impossible to delete an account, or make it complex and difficult to manage one’s privacy settings. Everything should be a lot simpler and more transparent.
Social networks should continue to devote intense efforts to developing self-regulation mechanisms and guidelines for this new environment of online coexistence to ensure that user information is safe: the Internet should be a space for freedom, but also for trust. The main way of ensuring that social media are used appropriately is awareness. But awareness and user education will be of little use unless it becomes an absolute requirement that the privacy of the individual is treated as a universal value.

The Internet and Culture
As in the sphere of education, the development of information and communication technologies and the wide-ranging effects of globalization are changing what we are, and the meaning of cultural identity. Ours is a complex world in which cultural flows across borders are always on the rise. The concepts of space, time, and distance are losing their conventional meanings. Cultural globalization is here, and a global movement of cultural processes and initiatives is underway.
Again, in the cultural arena, vast fields of opportunity open up thanks to online tools. The possibilities are multiplied for disseminating a proposal, an item of knowledge, or a work of art. Against those doomsayers who warn that the Internet is harming culture, I am radically optimistic. The Internet is bringing culture closer to more people, making it more easily and quickly accessible; it is also nurturing the rise of new forms of expression for art and the spread of knowledge. Some would say, in fact, that the Internet is not just a technology, but a cultural artifact in its own right.
In addition to its impact on culture itself, the Internet is enormously beneficial for innovation, which brings progress in all fields of endeavor—the creation of new goods, services, and ideas, the advance of knowledge and society, and increasing well-being.
The Internet and Personal Relationships
The Internet has also changed the way we interact with our family, friends, and life partners. Now everyone is connected to everyone else in a simpler, more accessible, and more immediate way; we can conduct part of our personal relationships using our laptops, smart phones, and tablets.
The benefits of always-online immediate availability are highly significant. I would find a long-distance relationship with my life partner or my family unthinkable without the communication tools that the network of networks provides me with. I’m living in Madrid, but I can stay close to my brother in California. For me, that is the key plus of the Internet: keeping in touch with the people who really matter to me.
As we have seen, the Internet revolution is not just technological; it also operates at a personal level, and throughout the structure of society. The Internet makes it possible for an unlimited number of people to communicate with one another freely and easily, in an unrestricted way.
Just a century ago, this was unimaginable. An increasing number of couples come together, stay together, or break up with the aid—or even as a consequence—of social communication tools. There are even apps and social networks out there that are purposely designed to help people get together for sex.
Of course, when compared to face-to-face communication, online communication is severely limited in the sense impressions it can convey (an estimated 60 to 70 percent of human communication takes place nonverbally), which can lead to misunderstandings and embarrassing situations—no doubt quite a few relationships have floundered as a result. I think the key is to be genuine, honest, and real at all times, using all the social media tools and their many advantages. Let’s just remember that a liar and a cheat online is a liar and a cheat offline too.
The Internet and Social and Political Activism
Even before the emergence of social media, pioneering experiments took place in the political sphere—like Essembly , a project I was involved in. We started to create a politically themed platform to encourage debate and provide a home for social and political causes; but the social networks that have later nurtured activism in a new way were not as yet in existence.
Research has shown that young people who voice their political opinions on the Internet are more inclined to take part in public affairs. The better informed a citizen is, the more likely they will step into the polling booth, and the better they will express their political liberties. The Internet has proved to be a decisive communication tool in the latest election campaigns. It is thanks to the Internet that causes in the social, welfare, ideological, and political arenas have been spoken up for and have won the support of other citizens sharing those values—in many cases, with a real impact on government decision making.
The Internet and Consumer Trends
New technologies increase the speed of information transfer, and this opens up the possibility of “bespoke” shopping. The Internet offers an immense wealth of possibilities for buying content, news, and leisure products, and all sorts of advantages arise from e-commerce, which has become a major distribution channel for goods and services. You can book airline tickets, get a T-shirt from Australia, or buy food at an online grocery store. New applications support secure business transactions and create new commercial opportunities.
In this setting, it is the consumer who gains the upper hand, and the conventional rules and methods of distribution and marketing break down. Consumers’ access to information multiplies, and their reviews of their experience with various products and services take center stage. Access to product comparisons and rankings, user reviews and comments, and recommendations from bloggers with large followings have shaped a new scenario for consumer behavior, retail trade, and the economy in general.
The Internet and the Economy
The Internet is one of the key factors driving today’s economy. No one can afford to be left behind. Even in a tough macroeconomic framework, the Internet can foster growth, coupled with enhanced productivity and competitiveness.
The Internet provides opportunities for strengthening the economy: How should we tackle them? While Europe—and Spain specifically—are making efforts to make the best possible use of the Internet, there are areas in which their approach needs to improve. Europe faces a major challenge, and risks serious failure if it lets the United States run ahead on its own. The European Commission, in its “Startup Manifesto,” suggests that the Old World be more entrepreneur-friendly—the proposal is backed by companies like Spotify and Tuenti. Europe lacks some of the necessary know-how. We need to improve in financial services and in data privacy, moving past the obsolete regulatory framework we now have and making a bid to achieve a well-connected continent with a single market for 4G mobile connections. We need to make it easier to hire talent outside each given country.
The use of e-commerce should be encouraged among small and medium-sized enterprises so that growth opportunities can be exploited more intensely. Following the global trend of the Internet, companies should internalize their online business. And much more emphasis should be placed on new technologies training in the academic and business spheres.
Modern life is global, and Spain is competing against every other country in the world. I do not believe in defeatism or victim culture. Optimism should not translate into callousness, but I sincerely believe that if you think creatively, if you find a different angle, if you innovate with a positive attitude and without fear of failure, then you can change things for the better. Spain needs to seize the moment to reinvent itself, grasping the opportunities offered up by the online world. We need to act, take decisions, avoid “paralysis through analysis.” I sometimes feel we are too inclined to navel-gazing: Spain shuts itself off, fascinated with its own contradictions and local issues, and loses its sense of perspective. Spain should open up to the outside, use the crisis as an opportunity to do things differently, in a new way—creating value, underlining its strengths, aspiring to be something more.
In the United States, for instance, diving headfirst into a personal Internet-related startup is regarded as perfectly normal. I’m glad to see that this entrepreneurial spirit is beginning to take hold here as well. I believe in working hard, showing perseverance, keeping your goals in view, surrounding yourself with talent, and taking risks. No risk, no success. We live in an increasingly globalized world: of course you can have a Spain-based Internet startup, there are no frontiers.
We need to take risks and keep one step ahead of the future. It is precisely the most disruptive innovations that require radical changes in approach and product, which might not even find a market yet ready for them—these are the areas providing real opportunities to continue being relevant, to move forward and “earn” the future, creating value and maintaining leadership. It is the disruptive changes that enable a business, product, or service to revolutionize the market—and, particularly in the technology sector, such changes are a necessity.
The Future of Social Communications, Innovation, Mobile Technologies, and Total Connectivity in Our Lives
The future of social communications will be shaped by an always-online culture. Always online is already here and will set the trend going forward. Total connectivity, the Internet you can take with you wherever you go, is growing unstoppably. There is no turning back for global digitalization.
Innovation is the driving force of growth and progress, so we need to shake up entrenched processes, products, services, and industries, so that all of us together—including established businesses, reacting to their emerging competitors—can move forward together.
Innovation is shaping and will continue to shape the future of social communications. It is already a reality that Internet connections are increasingly mobile. A survey we conducted in early 2013 in partnership with Ipsos found that 94 percent of Tuenti users aged 16 to 35 owned cell phones, 84 percent of users connected to the Internet using their phones, and 47 percent had mobile data subscriptions for connecting to the Internet. A total of 74 percent of users reported connecting to the Internet from their phone on a daily basis, while 84 percent did so at least weekly. Only 13 percent did not use their phones to connect to the Internet, and that percentage is decreasing every day.
Mobile Internet use alters the pattern of device usage; the hitherto familiar ways of accessing the Internet are changing too. The smartphone activities taking up the most time (over three hours a day) include instant messaging (38%), social media use (35%), listening to music (24%), and web browsing (20%). The activities taking up the least time (under five minutes a day) are: SMS texting (51%), watching movies (43%), reading and writing e-mail (38%), and talking on the phone (32%). Things are still changing.
Smartphones are gaining ground in everyday life. Many of the purposes formerly served by other items now involve using our smartphones. Some 75 percent of young people reported having replaced their MP3 player with their phone, 74 percent use their phone as an alarm clock, 70 percent use it as their camera, and 67 percent use it as their watch.
We have been observing these shifts for a while, which is why we decided to reinvent ourselves by placing smartphones at the heart of our strategy. I want to use this example as a showcase of what is happening in the world of social communication and the Internet in general: mobile connectivity is bringing about a new revolution. Tuenti is no longer just a social network, and social media as a whole are becoming more than just websites. The new Tuenti provides native mobile apps for Android, iPhone, Blackberry, Windows Phone, as well as the Firefox OS app and the mobile version of the website, m.tuenti.com. Tuenti is now a cross-platform service that lets users connect with their friends and contacts from wherever they may be, using their device of choice. A user with a laptop can IM in real time with a user with a smartphone, and switch from one device to another without losing the thread of the conversation. The conversations are in the cloud, so data and contacts are preserved independently of the devices being used. This means the experience has to be made uniform across platforms, which sometimes involves paring down functionalities, given the processing and screen size limitations of mobile devices. Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, and so on are all evolving to become increasingly cross-platform experiences. But Tuenti is the first social network that has also developed its own Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO)—the company is an Internet service provider over the mobile network. Tuenti is an MVNO with a social media angle, and this may be the future path of telecommunications.
Social media are evolving to become something more, and innovation must be their hallmark if they are to continue being relevant. Tuenti now embraces both social communications and telecom services provision, offering value added by letting you use the mobile app free of charge and without using up your data traffic allowance, even if you have no credit on your prepaid card—this is wholly revolutionary in the telecom sector. The convergence of social media with more traditional sectors is already bringing about a new context for innovation, a new arena for the development and growth of the Internet.
Just about everything in the world of the Internet still lies ahead of us, and mobile communications as we know them must be reinvented by making them more digital. The future will be shaped by innovation converging with the impact of mobility. This applies not just to social media but to the Internet in general, particularly in the social communications field. I feel that many people do not understand what we are doing and have no idea of the potential development of companies like ours at the global level. Right now, there may be somebody out there, in some corner of the world, developing the tool that will turn the Internet upside down all over again. The tool that will alter our day-to-day life once more. Creating more opportunities, providing new benefits to individuals, bringing more individual and collective well-being. Just ten years ago, social media did not exist; in the next ten years, something else radically new will emerge. There are many areas in which products, processes, and services can be improved or created afresh. The future is brimming with opportunities, and the future of the Internet has only just begun.
Related publications
- The Impact of the Internet on Society: A Global Perspective
- Implications of the Revolution in Work and Family
- Vision 2020+: A Future to Be Built
Download Kindle
Download epub, download pdf, more publications related to this article, more about technology, artificial intelligence, digital world, visionaries, comments on this publication.
Morbi facilisis elit non mi lacinia lacinia. Nunc eleifend aliquet ipsum, nec blandit augue tincidunt nec. Donec scelerisque feugiat lectus nec congue. Quisque tristique tortor vitae turpis euismod, vitae aliquam dolor pretium. Donec luctus posuere ex sit amet scelerisque. Etiam sed neque magna. Mauris non scelerisque lectus. Ut rutrum ex porta, tristique mi vitae, volutpat urna.
Sed in semper tellus, eu efficitur ante. Quisque felis orci, fermentum quis arcu nec, elementum malesuada magna. Nulla vitae finibus ipsum. Aenean vel sapien a magna faucibus tristique ac et ligula. Sed auctor orci metus, vitae egestas libero lacinia quis. Nulla lacus sapien, efficitur mollis nisi tempor, gravida tincidunt sapien. In massa dui, varius vitae iaculis a, dignissim non felis. Ut sagittis pulvinar nisi, at tincidunt metus venenatis a. Ut aliquam scelerisque interdum. Mauris iaculis purus in nulla consequat, sed fermentum sapien condimentum. Aliquam rutrum erat lectus, nec placerat nisl mollis id. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
Nam nisl nisi, efficitur et sem in, molestie vulputate libero. Quisque quis mattis lorem. Nunc quis convallis diam, id tincidunt risus. Donec nisl odio, convallis vel porttitor sit amet, lobortis a ante. Cras dapibus porta nulla, at laoreet quam euismod vitae. Fusce sollicitudin massa magna, eu dignissim magna cursus id. Quisque vel nisl tempus, lobortis nisl a, ornare lacus. Donec ac interdum massa. Curabitur id diam luctus, mollis augue vel, interdum risus. Nam vitae tortor erat. Proin quis tincidunt lorem.
The Way of the Dodo
Do you want to stay up to date with our new publications.
Receive the OpenMind newsletter with all the latest contents published on our website
OpenMind Books
- The Search for Alternatives to Fossil Fuels
- View all books
About OpenMind
Connect with us.
- Keep up to date with our newsletter
Quote this content
Home — Essay Samples — Philosophy — Meaning of Life — The Meaning of Life in Modern Society
The Meaning of Living in a Modern Society
- Categories: Meaning of Life Society
About this sample

Words: 1103 |
Published: Aug 10, 2018
Words: 1103 | Pages: 2 | 6 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Philosophy Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
4 pages / 1873 words
1 pages / 636 words
2 pages / 923 words
2 pages / 768 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Meaning of Life
Smith, Adam. 'The Theory of Moral Sentiments.' 1759.
The question of the meaning of life has been a timeless and profound inquiry that has intrigued philosophers, thinkers, and individuals throughout history. In this essay, we will delve into the philosophical exploration of the [...]
In the hustle and bustle of modern life, we often find ourselves caught in the whirlwind of the present moment, constantly seeking the next thrill or distraction. However, there is a profound and often overlooked potential in [...]
Oscar Wilde said that “Life is too important to be taken seriously.” It’s true, the line said that you don’t have to waste your life, as there are many important things that you have to finish in your life. There are many [...]
Albert Camus studied the philosophy of the absurd and decided that, to him, the most important philosophical question was “why not commit suicide?” In “The Myth of Sisyphus: An Absurd reasoning” (1942), he discusses his thoughts [...]
Life is not as hard as we sometimes make it to be. All fingers are not equal and some were born more fortunate than some others. Bearing this in mind, we should learn to cut our coats according to our coat. Social media has got [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essays Examples >
- Essay Topics
Essays on Modern Life
31 samples on this topic
Our essay writing service presents to you an open-access directory of free Modern Life essay samples. We'd like to emphasize that the showcased papers were crafted by proficient writers with proper academic backgrounds and cover most various Modern Life essay topics. Remarkably, any Modern Life paper you'd find here could serve as a great source of inspiration, valuable insights, and content organization practices.
It might so happen that you're too pressed for time and cannot allow yourself to waste another minute browsing Modern Life essays and other samples. In such a case, our service can offer a time-saving and very practical alternative solution: an entirely unique Modern Life essay example crafted particularly for you according to the provided instructions. Get in touch today to learn more about effective assistance opportunities offered by our buy an essay service in Modern Life writing!
Conception Of An Urban Modernism: Free Sample Essay To Follow
Art & Architecture
A-Level Essay On The Idea Of Commons And Communing For Free Use
The Idea of Commons and Communing
Essay On A Rose For Emily
Free biological and social aspects of sex differences essay: top-quality sample to follow, essays that wow - family traditions, good queer theory-paris is burning course work example.
Questions for Women and Cinema
1. Transgender It is a state in which an individual’s gender is not matching his or her assigned sex responsibility. It refers to the trans-genders, such as homosexual, bisexuals, heterosexual. In the Paris burning film, the issue of Transgender is explored using various characters men and women. For instance, Trans women used as members of the club to show realness. The women are sued to enhance transgender in the film, this shows that as much as they are women they can also compete men and become real (Besnier and Kalissa 34).
‘name’ Term Paper Samples
‘Instructor’s Name’
Free Exercise Of Human Agency Through Collective Efficacy Essay Example
Sample critical thinking on the key to happiness & unhappiness: shantideva & einstein – a critique, civilization and its discontents in a modern context essay examples, example of dream theories research paper, good example of plan of investigation essay.
Introduction:
Good Essay On Are We Too Dependent On Computers
Good essay about lightness, abdullah alshaib essay samples.
The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock” by Eliot
Making Informed Decisions For A Future Happy Life Business Plan Samples
Good literature review on the love song of j. alfred prufrock by eliot.
Introduction
Free Research Paper On Human And Society Nature Disconnection
Jazz education and its impact on child behavior research paper examples.
Jazz Music and the Modern Society
Good Example Of Essay On Sedentary Life And Colon Cancer
Mid term integration paper essay example.
Mid Term Integration Paper Mid Term Integration Paper
Good Essay About Stress Management
Stress management
Poetry Or A Song Essays Example
Literary Criticism of T. S. Eliot’s Love Song of J Alfred Prufrock
Example Of Thesis On The Secret Life Of Walter Mitty
Article review on sociology, free essay on campbells soup by andy warhol, essay on protestant reformation, free essay on existential crisis hemingways use of prose and the ambiguity of.
Modern Life
Course Work On Critique Of News Report
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
Baudelaire: The Painter of Modern Life
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 18 April 2018
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Jeremy Tambling 2
399 Accesses
The Painter of Modern Life written by Charles Baudelaire (1821–1867) in the winter of 1859–1860 and published in 1863 as a series of newspaper pieces ( feuilletons ) in the November 26 and 28 and December 3 editions of the Figaro makes essential and seminal reading, for several reasons. It has profound implications for art criticism (turning it away from the tourist’s study of acknowledged masterpieces), and for discussions of beauty – the existence of which, and perception of which, becomes a kind of transgressiveness, rather than a Platonic ideal – and for analysis of modernity. Further, it gives a sense of a shift which has happened in ways of living and of seeing the city, which has implications for how a person perceives his or her own identity: it produces a new kind of “self-fashioning.” A significant influence on Walter Benjamin in the Arcades Project , the essay rethinks the topics of absolute values in art versus the modern, where values are fleeting, nature and art, and throughout, the relationship between beauty and fashion.
Download reference work entry PDF
Similar content being viewed by others

‘What is fashionably termed ennui’: Maria Edgeworth Represents the Clinically Bored

The Birth of Modernism: How the Science of Aesthetics Created One of the Most Popular Periods of Art
- Walter Benjamin
- Edgar Allan Poe
- Prostitution
- Constantin Guys
The artist he considers is Constantin Guys (1802–1892), whom he introduces in the third section, noting his modesty and desire not to be called an artist, more someone “who takes an interest in everything the world over” (Baudelaire 1972 : 397). Guys remained obscure and unknown, though he was photographed by Nadar (Mayne 1964 : 10), and his use in the essay confirms the sense that modernity works with what may often be ignored or thought of as a minority interest. This article uses Charvet’s translation of Baudelaire, with some modifications.
Beauty, Fashion, and Happiness
Baudelaire had a reputation as an art critic as well as being the author of the poems Les Fleurs du Mal : he had reviewed the various Paris “Salons” (exhibitions of art) in 1845, 1846, and 1859, and he deeply admired Eugène Delacroix (1798–1863). These Salons were held at the Louvre, until 1857, when they began to be held at the Palais de l’Industrie, in the Champs Elysées, where the 1855 Exposition Universelle had been held. He wrote, too, on caricaturists, French and English, on whom he was an authority. (It should be said that Guys was not a caricaturist. If caricature starts by having a sense of what it wants to present, and what it thinks of its subject, Guys, as Baudelaire presents him, is much more open, suggesting possibilities in his work, not showing something complete.) Baudelaire begins with discussion of those who think that the Louvre enshrines the eternal values of art and who go to museums to fact-check recognized masterpieces. He contrasts this with a series of fashion plates, popular images, which encourage thinking about the historical differences which changes in fashion show up, changes, for example, since the French Revolution. Such changes indicate that while beauty has always been desired, ideas of what is beautiful change, so we need “a rational and historical theory of beauty” as well as the sense of “a unique and absolute beauty” (392). He argues that these two things, this “duality of art,” respond to the duality of man; further he quotes Stendhal (Henri Beyle, 1783–1842), from his study L’Amour (“Love,” 1822), saying that “the beautiful is the promise of happiness”: in other words, there is nothing disinterested within the perception of beauty (as Kant claimed, the issue is developed by Nietzsche, using Stendhal ( 1996 : 83)). For Baudelaire, the need for both types of beauty is satisfying, and the beautiful is not an add-on in art but essential in any approach to it.
This leads Baudelaire in the second section, “Manners and Modes,” to a second point, that a contemporary “speed of movement” imposes on the artist an equivalent “speed of execution.” Lithography, an invention at the end of the eighteenth century, enabled speed in reproduction (it will be noted that Baudelaire never discusses photography, which obviously gives speed in capturing manners and modes in everyday life). He mentions Gavarni and Daumier as supplementing the presentation of such manners in Balzac’s Comédie humaine , the novel being another way of capturing such speed. The artist of modern life, as opposed to things of an eternal nature, such as heroic or religious subjects, will be an observer of the present and a flâneur .
Artist, Man of the World, Man of Crowds, and Child
Constantin Guys, impoverished and obscure, presents himself as “a man of the world,” rather than calling himself an “artist,” which would separate him from the world, or from certain parts of it (“if he [i.e., the artist] lives in the Bréda quarter [of Paris], he knows nothing of what goes on in the Faubourg Saint-Germain”) (397). The then new Bréda quarter was “the upper end of the Faubourg Montmartre, around the then new church of Notre-Dame-de-Lorette, today divided between the Rue Henri-Monnier and Rue Clauzel” (Hazan 2010 : 143–144). It was then an area of prostitution, so that a “lorette” became slang for a prostitute. The Faubourg Saint-Germain was, of course, the aristocratic part of the Left Bank. Baudelaire respects his desire for anonymity, which he notes Thackeray, another caricaturist about whom Baudelaire was interested in, had not; and he simply calls him M.G. (i.e., Monsieur G). Baudelaire thinks that M.G. did not start drawing and making watercolors until 1847: he associates, then, with the changes in France which belong with the post-1848 failed year of revolutions.
According to Baudelaire, M.G. starts his work with his curiosity, seen here in relation to the urban, and here Baudelaire discusses Poe’s story, “The Man of the Crowd,” to speculate on the significance of the flâneur being a convalescent, convalescence being a liminal state, so that for the convalescent reality appears in brighter, more sudden forms, and there is a forgetting of the past. M.G. is like the perpetual convalescent, and Baudelaire compares that state with childhood, for “the child sees everything as a novelty ( en nouveauté ); the child is always ‘drunk’” (398). Childhood and convalescence consist in not only a sense of “congestion” – a point which Baudelaire emphasizes, to indicate that experiences – particularly urban ones, cannot be processed, but also in shock-experiences: “every sublime thought is accompanied by more or less vigorous nervous impulse that reverberates in the cerebral cortex” (398). There is a vulnerability connected with being at large in this urban world, where colors and sensations appear overly bright. Here, too, is a justification for the place of the child, since for the latter, “no edge of life is blunted” (399). The significance of children in Romanticism and Dickens and Dostoevsky come to mind here.
The type of artist M.G. epitomizes is not a dandy, for that implies being blasé , and the crowd is his domain. Here Baudelaire characterizes the urban writer, or artist in ideal terms, in language which breaks new ground. As the “lover of universal life,” he moves into the crowd (recalling Poe), “as though into an enormous reservoir of electricity” (400). As a mirror of that crowd, he is a “kaleidoscope endowed with consciousness” displaying constantly changing patterns of life, as the ego in search of the nonego (400). OED gives 1817 for the first use of “kaleidoscope,” from the Greek words “ kalos ” (beautiful) and “eidos” (form). A kaleidoscope was an optical instrument which, as it was rotated, would show numerous, and always changing, reflections of colored glass. Not just external reality, but the “artist” is in perpetual change; each illuminates the other. The clue is the crowd: Baudelaire quotes M.G. saying with an intense gaze and eloquence of gesture, “tout homme qui n’est pas accablé par un des chagrins d’une nature trop positive pour ne pas absorber toutes les facultés, et qui s’ennuie au sein de la multitude, est un sot! Un sot! Et je le méprise!” (Baudelaire 1976 : 2.692): “any man who is not overwhelmed by some worry of a nature too strong not to absorb all the faculties, and who is bored in the midst of the crowd, is a fool! A fool! And I despise him!” (400). The artist cannot stand off from life, nor from the stimulation provided by the crowd, which produces a reaction which looks akin to the apparently exaggerated power of melodrama and affords a way of thinking about novelists’ responses to the city and its multitudes. The city becomes, for M.G., a place for seeing “the landscapes of the great city, landscapes of stone, caressed by mist or hit by the buffets of the sun” (400–401), and Baudelaire goes through the times of the day as the artist sees them, followed by the time of rendering those images, where everything is rendered in more bright reality, called a “fantasmagorie” (Baudelaire 1976 : 2.694).
La Modernité
The artist, the flâneur , is in search of what Baudelaire calls “modernity,” which may then be defined as trying to extract from fashion the poetry within its historical envelope, to extract the eternal from the transitory. The alliance between being of the “mode” (i.e., fashionable, and literally “of the day,” which is what “modern” means) and modernity implies that for the first time, in the urban experience, the absolutely new may be seen to contain a poetry and beauty within it. Artists had previously ignored this by dressing people in pictures in fashions from the past, such as in Roman or Biblical models. Modernity is “le transitoire, le fugitif, le contingent” (Baudelaire 1976 : 2.695) – the transitory, the fleeting, the contingent – i.e., dependent on chance, and the other half of art, which is eternal and immovable. To capture present-day fashion is the responsibility of the artist of modernity, and if any form of modernity (i.e., of modern fashion) is going to pass into antiquity, i.e., be recognized after its time is gone, then the “mysterious beauty that human life unintentionally puts into it must have been extracted from it” (Baudelaire 1972 : 404). For fashions, however modish, are not just that; they bring out something that survives after they have gone and, in that statement, lies much of Benjamin’s fascination with Baudelaire, and with what may be extracted from outmoded forms. We can see Benjamin’s refusal to let anything be lost to history. Baudelaire criticizes anyone who would go back to outmoded forms, such as the fashionable forms of a Van Dyck, for a standard of beauty: the past cannot offer that. That will require seeing the fantastic reality of life in the present. Here, and in the following section “Mnemonic Art,” Baudelaire thinks of M.G.’s active and evocative memory, in recalling what he has seen and making it speak again, “His memory says to every object: ‘Lazarus arise’” (408). That is, it makes the dead, the forgotten, speak. And there is the sense that his paintbrush or pencil is intoxicated, which returns to Baudelaire’s emphasis on speed, in order to grasp the gestures and attitudes, solemn or grotesque, of humans and “their luminous explosion in space” (409). The need for an active memory is itself a huge subject for modernity: it is Baudelaire’s subject in his poetry, and Proust’s, and Benjamin’s, and it derives from the other half of the stress on fashion, which is the tendency for everything to be forgotten as soon as it has had its moment.
The following section looks at renderings of war (Bulgaria, Turkey, the Crimea, and Spain), and now it becomes clear that Baudelaire is using M.G. as a type of the artist he has in mind, the “painter of modern life”; many artists dispatched sketches of the war front to journals such as The Illustrated London News , a weekly which began circulation in 1842, which would then make an engraving for the magazine. Guys himself worked for The Illustrated London News , particularly during the Crimea, and here, and in the next sections are the only times when Baudelaire discusses his actual work, noting, for instance, his interest in those on the fringes of society – the forgotten and the dying on the battlefields, and in the hospitals. Journalism, then, is part of “modern life,” as a new perception of the instantaneity of things. So too, in the following section, “Pomp and Ceremony,” heavy with Orientalist detail, is the perception of sexual ambiguity in noting members of “the third sex,” i.e., homosexuals (414). In Sect. 8, “The Soldier,” the subject that the artist is said to like best is “the pomp of life,” as it appears in “the capitals of the civilized world, the pageantry of military life, or high life, of loose life” (416). The artist likes especially the soldier because of “the showy apparel his profession clothes him in” and because of his mixture of calm and daring, indifference and enthusiasm, qualities which associate him with what Baudelaire finds valuable in the dandy, and which differentiate him from the bourgeoisie (416).
The Dandy and Women
Section 9 is on renderings of “the dandy,” “the man who has no profession other than elegance” and for whom delight in clothes and material elegance is “no more than the symbol of the aristocratic superiority of his mind” (419). He defines another type important for the city, as the person with the desire to create a personal form of originality, resisting the tendency toward anonymity and standardization also associated with city-life, and yet having a “blasé” attitude; the dandy is possible when “aristocracy is only partially weakened” and democracy is not yet all-powerful (421). The antithesis to the dandy is the woman (Sect. 19) who is spoken about in terms decidedly addressed to men, in terms of her beauty and as “an invitation to happiness” which recalls the terms of Stendhal. And she is seen as indistinguishable from her apparel, with which she forms an indivisible whole. Baudelaire is fascinated by clothing as a part of fashion, and as a way of self-stylizing: it is not intended to be seen as a trivialization of women. Baudelaire thinks of ornament, which produces the second distinction working throughout the essay: between nature and art. Hence Sect. 11 is called “Eloge du Maqillage” – “In Praise of Make-Up.” The argument rejects Nature as any kind of guide; hence Baudelaire reacts away from the eighteenth-century sense of Nature, as rational, and with it, Romanticism itself which depends on the “naturalness” of Nature as a guide to life. Instead, “everything that is beautiful and noble is the product of reason and calculation, and virtue is artificial. Crime is the product of nature” (425). Hence women are right to aspire toward an ideal through fashion, and makeup, to create a sense of surprise, and to fascinate. And this is not to embellish ugliness but to serve beauty. At that point, Baudelaire writes: “who would dare assign to art the sterile function of imitating nature?” (428). With this, he dismisses the idea that art represents nature; the rejection of mimesis as sterile implies the rejection of realism and frees art from the task of being like photography, representing what is there. (Something of this rejection of realism shows with Baudelaire’s lack of discussion of Courbet, though Courbet actually painted Baudelaire.) This movement from realism implies the course that modernist art takes, and Baudelaire leads toward it and justifies it. It also means that, given a distinction between depth and surface, and since makeup belongs to the latter category, art may be seen as presenting what is on the surface, not as studying depth of character, this latter being what realism does. And it means that if depth of character is to be set aside, what emerges is a new way of thinking, broadly called postmodern, wherein the primary duty is to “self-stylize” the life – a term associated with the late work of Michel Foucault. To think in terms of self-fashioning, rather than believing that there is some deep truth informing a person’s identity, Foucault, considering Baudelaire’s essay, identifies with dandyism (Foucault 1997 : 303–319).
“Les Femmes et les Filles”
Section 12 on women and courtesans begins with how many different types of women, in differing social situations, M.G. has portrayed, including the courtesan, and the actress as a creature “of show.” In this “extensive gallery of London and Paris life,” he says, there are many types of unattached women, and he goes through a list (428–233). There are women of “the highest social circles” (428); there are actresses from the “suburban theaters,” women seen at a café door; contemplating the crowd; women in the amusement halls; women who show “the varied image of the shadier type of beauty” which “either displays an alluring and barbaric form of elegance of her own invention, or she apes, more or less successfully, the simplicity current in higher circles” (430). Women are identified here, throughout, with art, not with nature, and all, including the highest circles, are theatrical: but this is, of course, a compliment in Baudelaire; “She has a kind of beauty, which comes to her from sin (“Mal”); always lacing spirituality, but at times tinged with fatigue masquerading as melancholy” (430). Baudelaire shows that he has been talking about the courtesan, a category which T.J. Clark says was a created category, constructed by the bourgeoisie, who could not represent prostitution to themselves (Clark 1984 : 109). Baudelaire speaks of “the woman in revolt at every level”; women of the town; women “confined in hovels, often enough decorated like cafés,” with “nothing they can call their own, not even the eccentric adornments that act as condiment to their beauty” (431). But they include the woman “in whom an innocent yet monstrous sort of fatuity is only too apparent,” women who “carry in their faces and in their eyes, which look you brazenly in the face, the evident joy of being alive” (431). The type appears in Manet’s “Olympia” (1865), analyzed by Clark (79–146), where the perhaps high-class prostitute looks back at the presumably male gaze. This is part of an analysis where the woman’s eyes are said to be cast toward the horizon (430), which Benjamin discusses in the Arcades Project : saying that Guys is fascinated by backgrounds (compare Baudelaire 1972 : 409). But “because these pictures … are to be viewed from close up, the magic of distance is cancelled for the viewer without his having to renounce the judgment of distance” (Benjamin 1999 : J47,4). There is, in other words, nothing of the “aura” in the presentation of the woman, no sense of a beauty which is ideal or traditionally “artistic.”
Baudelaire continues the list of different types of women, concluding with the consumptive and “gruesome nymphs and living dolls” (432). But beauty takes no part in morality, and to find that true is to state a point about modernity: it is the opposite to what Plato believed. The types have all been portrayed by M.G. and illustrate “the beauty peculiar to evil, the beautiful in the horrible” (432). To associate beauty with evil of course takes it outside traditional Platonism where it points to the ideal and immaterial world. It makes beauty something other than what looking at masterpieces would suggest; it makes it a challenge to find, and to accept, perhaps; it makes its origins material, of the city; and contestatory, not part of what may be easily accepted and recognized because it is on display. It is apparent here that beauty, which emerges in situations where it would not be expected to be found, is dual, as he has said at the beginning, both real and ideal and at the same time contesting that ideality, because if it did not “the first element would be indigestible, tasteless, unadapted, and inappropriate to human nature. I challenge anyone to find any sample whatsoever of beauty that does not contain these two elements” (392). It may be said that beauty as dual, and confronting and challenging expectations, is an insight inseparable from city-existence. It is, then, not that there are two types of beauty, the eternal and the fleeting, so much as that beauty comprises both, and that makes it so difficult to locate, but that the urban allows the possibility for looking for it.
The essay winds to a close with a last section on “Carriages,” as seen in any park in big cities, where coaches and carriages, containing women, derive, from the fact of motion, “a mysterious and complex gracefulness which is very difficult to note down” (434). With urban civilization, art is bound toward representation of the fleeting. Every detail M.G. presents of coachwork “is correct, every detail is in its right place, and does not need to be gone over again. In whatever position it is drawn, at whatever speed it may be going, a carriage, like a vessel, derives, from the fact of motion, a mysterious and complex gracefulness which is very difficult to note down in shorthand. The pleasure that the artist’s eye gets from it comes apparently from the series of geometrical figures that the object … describes successively in space” (434–435). Paul de Man ( 1983 : 160–161) discusses this passage to think of the shorthand, and the way that movement can only be rendered in geometrical forms as containing Baudelaire’s acceptance that writing cannot record the present, that modernity must rest content with allegory, being unable to capture the present as it is (another rejection of realism, of course). Beauty, then, can never be realized fully, nor modernity be captured, but it remains the project for art, and literature, confronted with the city.
Baudelaire, Charles. 1972. Selected writings on art and artists . Trans. P.E. Charvet. Harmondsworth: Penguin.
Google Scholar
Baudelaire, Charles. 1976. In Oeuvres completes , ed. Claude Pichois. Paris: Gallimard.
Benjamin, Walter. 1999. The Arcades project . Trans. Howard Eiland and Kevin McLoughlin. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Clark, T.J. 1984. The painting of modern life: Paris in the art of Manet and his followers . London: Thames and Hudson.
de Man, Paul. 1983. Literary history and literary modernity. In Blindness and insight: Essays in the rhetoric of contemporary criticism , 2nd ed. London: Routledge.
Foucault, Michel. 1997. What is enlightenment? In Michel Foucault: Essential works of Foucault 1954–1984: vol 1 – Ethics , ed. Paul Rabinow. London: Penguin.
Hazan, Eric. 2010. The invention of Paris: A history in footsteps . Trans. David Fernbach. London: Verso.
Hiddleston, J.A. 1999. Baudelaire and the art of memory . Oxford: Clarendon Press.
Book Google Scholar
Holme, C. Geoffrey. 1930. The painter of Victorian life: A study of constantin guys with an introduction and a translation of Baudelaire’s Peintre de la Vie Moderne by P.G. Konody . London: The Studio ltd..
Mayne, Jonathan, ed. 1964. The painter of modern life and other essays . London: Phaidon.
Nietzsche, Friedrich. 1996. On the genealogy of morals . Trans. Douglas Smith. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Raser, Jonathan. 1989. A poetics of art criticism: The case of Baudelaire . Chapel Hill: North Carolina Studies in the Romance Languages and Literatures.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Jeremy Tambling
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jeremy Tambling .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
London, United Kingdom
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Tambling, J. (2018). Baudelaire: The Painter of Modern Life . In: Tambling, J. (eds) The Palgrave Encyclopedia of Urban Literary Studies. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62592-8_83-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62592-8_83-1
Received : 23 March 2018
Accepted : 23 March 2018
Published : 18 April 2018
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-62592-8
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-62592-8
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Literature, Cultural and Media Studies Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Humanities
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- Literature & Fiction
- History & Criticism

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.
Buy new: $28.00 $28.00 FREE delivery: Tuesday, April 23 on orders over $35.00 shipped by Amazon. Ships from: Amazon.com Sold by: Amazon.com
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method
Buy used: $16.01
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a service we offer sellers that lets them store their products in Amazon's fulfillment centers, and we directly pack, ship, and provide customer service for these products. Something we hope you'll especially enjoy: FBA items qualify for FREE Shipping and Amazon Prime.
If you're a seller, Fulfillment by Amazon can help you grow your business. Learn more about the program.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

Follow the author

The Writer of Modern Life: Essays on Charles Baudelaire Paperback – November 15, 2006
Purchase options and add-ons.
Walter Benjamin's essays on the great French lyric poet Charles Baudelaire revolutionized not just the way we think about Baudelaire, but our understanding of modernity and modernism as well. In these essays, Benjamin challenges the image of Baudelaire as late-Romantic dreamer, and evokes instead the modern poet caught in a life-or-death struggle with the forces of the urban commodity capitalism that had emerged in Paris around 1850. The Baudelaire who steps forth from these pages is the flâneur who affixes images as he strolls through mercantile Paris, the ragpicker who collects urban detritus only to turn it into poetry, the modern hero willing to be marked by modern life in its contradictions and paradoxes. He is in every instance the modern artist forced to commodify his literary production: "Baudelaire knew how it stood with the poet: as a flâneur he went to the market; to look it over, as he thought, but in reality to find a buyer." Benjamin reveals Baudelaire as a social poet of the very first rank. The introduction to this volume presents each of Benjamin's essays on Baudelaire in chronological order. The introduction, intended for an undergraduate audience, aims to articulate and analyze the major motifs and problems in these essays, and to reveal the relationship between the essays and Benjamin's other central statements on literature, its criticism, and its relation to the society that produces it.
- Print length 320 pages
- Language English
- Publisher Belknap Press: An Imprint of Harvard University Press
- Publication date November 15, 2006
- Dimensions 5.5 x 0.87 x 8.25 inches
- ISBN-10 0674022874
- ISBN-13 978-0674022874
- See all details

Frequently bought together

Customers who viewed this item also viewed

Editorial Reviews
About the author, product details.
- Publisher : Belknap Press: An Imprint of Harvard University Press; n edition (November 15, 2006)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 320 pages
- ISBN-10 : 0674022874
- ISBN-13 : 978-0674022874
- Item Weight : 14.9 ounces
- Dimensions : 5.5 x 0.87 x 8.25 inches
- #113 in German Literary Criticism (Books)
- #2,492 in Essays (Books)
- #2,668 in Literary Criticism & Theory
About the author
Walter benjamin.
Walter Bendix Schonflies Benjamin (1892 -- 1940) was a German-Jewish Marxist literary critic, essayist, translator, and philosopher. He was at times associated with the Frankfurt School of critical theory and was also greatly inspired by the Marxism of Bertolt Brecht and Jewish mysticism as presented by Gershom Scholem.
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
Top reviews from other countries
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
- Share full article

Why the World Still Needs Immanuel Kant
Unlike in Europe, few in the United States will be celebrating the philosopher’s 300th birthday. But Kant’s writing shows that a free, just and moral life is possible — and that’s relevant everywhere.
Supported by
By Susan Neiman
The philosopher Susan Neiman is the director of the Einstein Forum in Potsdam, Germany.
- April 17, 2024
When I arrived in Berlin in 1982, I was writing a dissertation on Kant’s conception of reason. It was thrilling to learn that the apartment I’d sublet turned out to be located near Kantstrasse, though at the time I wondered in frustration: Why was there no James Street — Henry or William — in the Cambridge, Mass., I’d left behind; no streets honoring Emerson or Eliot? Were Americans as indifferent to culture as snooty Europeans supposed? It didn’t take long before I, too, could walk down Kantstrasse and turn right on Leibniz without a thought.
It’s harder to ignore the way Germany, like other European nations, sets aside entire years to honor its cultural heroes. This century has already seen an Einstein Year , a Beethoven Year , a Luther Year and a Marx Year , each commemorating some round-numbered anniversary of the hero in question. Federal and local governments provide considerable sums for events that celebrate the thinkers in question and debate their contemporary relevance.
Years before Immanuel Kant’s 300th birthday on April 22, 2024, the Academy of Science in Berlin, to which he once belonged, organized a conference to begin preparations for his tercentennial. A second conference published a report of the proceedings, but when I urged colleagues to use the occasion to create programs for a wider audience, I was met with puzzled silence. Reaching a wider audience is not a talent philosophy professors normally cultivate, but conversations with other cultural institutions showed this case to be especially thorny.
It wasn’t just uneasiness about celebrating “another dead white man,” as one museum director put it. The problems became deeper as the zeitgeist changed. “ Immanuel Kant: A European Thinker ” was a good title for that conference report in 2019, when Brexit seemed to threaten the ideal of European unification Germans supported. Just a few years later, “European” has become a slur. At a time when the Enlightenment is regularly derided as a Eurocentric movement designed to support colonialism, who feels comfortable throwing a yearlong birthday party for its greatest thinker?
Nonetheless, this year’s ceremonies will officially commence on April 22 with a speech by Chancellor Scholz and a memorial lunch that has taken place on the philosopher’s birthday every year since 1805. Two days earlier, President Frank-Walter Steinmeier of Germany will open an exhibit at the presidential palace devoted to Kant’s writing on peace.
The start of the year saw special Kant editions of four prominent German magazines. A Kant movie made for television premiered on March 1, and another is in production. Four exhibits on Kant and the Enlightenment will open in Bonn, Lüneburg, Potsdam and Berlin. The conferences will be numerous, including one organized by the Divan, Berlin’s house for Arab culture.
But why celebrate the Kant year at all?
The philosopher’s occasional autobiographical remarks provide a clue to the answer. As the son of a saddle maker, Kant would have led a workman’s life himself, had a pastor not suggested the bright lad deserved some higher education. He came to love his studies and to “despise the common people who knew nothing,” until “Rousseau set me right,” he wrote. Kant rejected his earlier elitism and declared his philosophy would restore the rights of humanity — otherwise they would be more useless than the work of a common laborer.
Chutzpah indeed. The claim becomes even more astonishing if you read a random page of his texts. How on earth, you may ask, are human rights connected with proving our need to think in categories like “cause” or “substance?” The question is seldom raised, and the autobiographical remarks usually ignored, for traditional readings of Kant focus on his epistemology, or theory of knowledge.
Before Kant, it’s said, philosophers were divided between Rationalists and Empiricists, who were concerned about the sources of knowledge. Does it come from our senses, or our reason? Can we ever know if anything is real? By showing that knowledge requires sensory experience as well as reason, we’re told, Kant refuted the skeptics’ worry that we never know if anything exists at all.
All this is true, but it hardly explains why the poet Heinrich Heine found Kant more ruthlessly revolutionary than Robespierre. Nor does it explain why Kant himself said only pedants care about that kind of skepticism. Ordinary people do not fret over the reality of tables or chairs or billiard balls. They do, however, wonder if ideas like freedom and justice are merely fantasies. Kant’s main goal was to show they are not.
The point is often missed, because Kant was as bad a writer as he was a great philosopher. By the time he finishes proving the existence of the objects of ordinary experience and is ready to show how they differ from ideas of reason, the semester is nearly over. Long-windedness is not, however, the only reason his work is often misinterpreted. Consider the effects of a bad review.
Had Kant died before his 57th birthday, he’d be remembered by a few scholars for some short, early texts. He withdrew from writing them in 1770 to conceive and compose his great “Critique of Pure Reason .” After what scholars call his “silent decade,” Kant pulled the text together in six months and finally published in 1781. For a year and a half, Kant waited for responses. When one finally appeared, it was a hatchet job accusing him of being a Berkeleyan solipsist: someone who denies the existence of ordinary objects.
Any author can imagine Kant’s dismay, and most likely his rage. In haste to refute the distortion of his life’s work, Kant wrote a second edition of the “Critique of Pure Reason,” and more fatefully, the “Prolegomena .” Since the latter is much shorter than the main book, it’s read far more often, and this has skewed the interpretation of Kant’s work as a whole. If the major problem of philosophy were proving the world’s existence, then Kant surely solved it. (Richard Rorty argued that he did, and that philosophy has little more to offer.)
In fact Kant was driven by a question that still plagues us: Are ideas like freedom and justice utopian daydreams, or are they more substantial? Their reality can’t be proven like that of material objects, for those ideas make entirely different claims on us — and some people are completely impervious to their claims. Could philosophy show that acting morally, if not particularly common, is at least possible?
A stunning thought experiment answers that question in his next book, the “Critique of Practical Reason .” Kant asks us to imagine a man who says temptation overwhelms him whenever he passes “a certain house.” (The 18th century was discrete.) But if a gallows were constructed to insure the fellow would be hanged upon exiting the brothel, he’d discover he can resist temptation very well. All mortal temptations fade in the face of threats to life itself.
Yet the same man would hesitate if asked to condemn an innocent man to death, even if a tyrant threatened him to execute him instead. Kant always emphasized the limits of our knowledge, and none of us know if we would crumble when faced with death or torture. Most of us probably would. But all of us know what we should do in such a case, and we know that we could .
This experiment shows we are radically free. Not pleasure but justice can move human beings to deeds that overcome the deepest of animal desires, the love of life. We want to determine the world, not only to be determined by it. We are born and we die as part of nature, but we feel most alive when we go beyond it: To be human is to refuse to accept the world we are given.
At the heart of Kant’s metaphysics stands the difference between the way the world is and the way the world ought to be. His thought experiment is an answer to those who argue that we are helpless in the face of pleasure and can be satisfied with bread and circuses — or artisanal chocolate and the latest iPhone. If that were true, benevolent despotism would be the best form of government.
But if we long, in our best moments, for the dignity of freedom and justice, Kant’s example has political consequences. It’s no surprise he thought the French Revolution confirmed our hopes for moral progress — unlike the followers of his predecessor David Hume, who thought it was dangerous to stray from tradition and habit.
This provides an answer to contemporary critics whose reading of Kant’s work focuses on the ways in which it violates our understanding of racism and sexism. Some of his remarks are undeniably offensive to 21st-century ears. But it’s fatal to forget that his work gave us the tools to fight racism and sexism, by providing the metaphysical basis of every claim to human rights.
Kant argued that each human being must be treated as an end and not as a means — which is why he called colonialism “evil” and congratulated the Chinese and Japanese for denying entry to European invaders. Contemporary dismissals of Enlightenment thinkers forget that those thinkers invented the concept of Eurocentrism, and urged their readers to consider the world from non-European perspectives. Montesquieu put his criticisms of French society in the mouths of fictitious Persians; Lahontan attacked European politics through dialogues with a Native American.
At a time when the advice to “be realistic” is best translated as the advice to decrease your expectations, Kant’s work asks deep questions about what reality is. He insisted that when we think morally, we should abstract from the cultural differences that divide us and recognize the potential human dignity in every human being. This requires the use of our reason. Contrary to trendy views that see reason as an instrument of domination, Kant saw reason’s potential as a tool for liberation.
He also argued that political and social relations must aim toward justice rather than power, however often those may be confused in practice. We’ve come to better understand how racism and sexism can preclude genuine universalism. Should we discard Kant’s commitment to universalism because he did not fully realize it himself — or rather celebrate the fact that we can make moral progress, an idea which Kant would wholeheartedly applaud?
In Germany, it’s now common to hear that the Enlightenment was at very best ambivalent. While it may have been an age of reason, it was also an age of slavery and colonialism: This argument ignores the fact that, like progressive intellectuals everywhere, Enlightenment thinkers did not win all their battles. It also neglects the fact that they fought for them anyway, despite the risks of censorship, exile and even death.
Significantly, many contemporary intellectuals from formerly colonized countries reject those arguments. Thinkers like the Ghanaian Ato Sekyi-Otu, the Nigerian Olufemi Taiwo, the Chilean Carlos Peña, the Brazilian Francisco Bosco or the Indian Benjamin Zachariah are hardly inclined to renounce Enlightenment ideas as Eurocentric.
The problem with ideas like universal human rights is not that they come from Europe, but that they were not realized outside of it. Perhaps we should take a lesson from the Enlightenment and listen to non-Western standpoints?
Arts and Culture Across Europe
A reimagining of Andrew Lloyd Webber’s “Sunset Boulevard,” starring Nicole Scherzinger as Norma Desmond, the long forgotten silent movie star who descends into madness, was the big winner at this year’s Olivier Awards .
New productions of “Macbeth” and “Hamlet” in Paris follow a French tradition of adapting familiar works . The results are innovative, and sometimes cryptic.
The internet latched on to 16-year-old Felicia Dawkins’ performance as The Unknown at a shambolic Willy Wonka-inspired event . Now she’s heading to a bigger and scarier stage in London.
When activists urged Tate Britain in London to take an offensive artwork off its walls, the institution commissioned Keith Piper to create a response instead. The result recently went on display.
The new National Holocaust Museum in Amsterdam has been in the works for almost 20 years. It is the first institution to tell the full story of the persecution of Dutch Jews during World War II.
At a retrospective of John Singer Sargent’s portraits in London, where the American expatriate fled after creating a scandal in Paris, clothes offer both armor and self-expression .
Advertisement
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
6 Common Leadership Styles — and How to Decide Which to Use When
- Rebecca Knight

Being a great leader means recognizing that different circumstances call for different approaches.
Research suggests that the most effective leaders adapt their style to different circumstances — be it a change in setting, a shift in organizational dynamics, or a turn in the business cycle. But what if you feel like you’re not equipped to take on a new and different leadership style — let alone more than one? In this article, the author outlines the six leadership styles Daniel Goleman first introduced in his 2000 HBR article, “Leadership That Gets Results,” and explains when to use each one. The good news is that personality is not destiny. Even if you’re naturally introverted or you tend to be driven by data and analysis rather than emotion, you can still learn how to adapt different leadership styles to organize, motivate, and direct your team.
Much has been written about common leadership styles and how to identify the right style for you, whether it’s transactional or transformational, bureaucratic or laissez-faire. But according to Daniel Goleman, a psychologist best known for his work on emotional intelligence, “Being a great leader means recognizing that different circumstances may call for different approaches.”
- RK Rebecca Knight is a journalist who writes about all things related to the changing nature of careers and the workplace. Her essays and reported stories have been featured in The Boston Globe, Business Insider, The New York Times, BBC, and The Christian Science Monitor. She was shortlisted as a Reuters Institute Fellow at Oxford University in 2023. Earlier in her career, she spent a decade as an editor and reporter at the Financial Times in New York, London, and Boston.
Partner Center
Tradwives, stay-at-home girlfriends and the dream of feminine leisure
Some young women see patriarchy as a solution, not a problem. what in ‘the feminine mystique’ is going on here.

I t’s always inspiring when citizens of the vast and disparate internet find something to unite them, and in late March, the unifying force was hatred for an essay, published in the Cut, called “ The Case for Marrying an Older Man .” It was written by a woman who had done just that: Grazie Sophia Christie spent her undergraduate years at Harvard sneaking into receptions for MBA candidates where she hoped to bag a more established male before her “fiercest advantage” — her youth — disappeared and rendered her common. After some trial and error, at the age of 20, she made off with a 30-year-old whose defining characteristics seemed to be that he was French and rich.
The essay’s alleged offenses ranged from the kind that would irritate Greta Thunberg — the casual way Christie’s byline notes that she lives in “Miami and London” — to the kind that would irritate Gloria Steinem. “I’ll never forget it,” the author writes, “how he showed me around our first place like he was introducing me to myself: This is the wine you’ll drink, where you’ll keep your clothes, we vacation here, this is the other language we’ll speak, you’ll learn it.”
Christie was taking a cosseted, retro archetype — the gold digger — and presenting it as something intellectual and liberated. She hadn’t wanted to marry a fixer-upper, she writes, citing her younger brother who still left his towels on the floor. She wanted a man that some other woman had already fixed up, and who could, in turn, fix her. Not a partner, she writes, but a “mentor.” Specifically, one who could fulfill a promise that feminism had allegedly failed to deliver: “I had grown bored of discussions of fair and unfair, equal or unequal,” writes Christie, “and preferred instead to consider a thing called ease.”
A thing called ease.
That last sentence was the only one in the whole piece that made me stop in my tracks. It was breathtaking in its transparency: I’m not doing this out of principle or based on a worldview. I’m doing this because life seemed hard and this seemed easy.
You could argue, as many did, that if your relationship is predicated on you being young, it might get considerably less easy when you age. But castigating Christie’s essay was actually the least interesting way to engage with it, because, at heart, it was dealing with bigger themes than even she seemed to know what to do with: The elusiveness of female contentment in the modern era. The elusiveness of rest — for everyone — in the modern era. The concept of romantic relationships as the ultimate life hack, and the resigned idea that the only way to move forward is by moving backward.
Perhaps you’ve been seeing the term “tradwife” lately, a modern coinage for a TikTok-fluent married woman who keeps house, extols “traditional” values and yields to her husband. Perhaps you’ve even seen the term “stay-at-home girlfriends,” the influencer community’s true prophets of female ease. Unlike stay-at-home moms, whose days might be filled with school drop-offs and toddler-wrangling, the childless SAHG’s days are filled mostly with home care and self care: elaborate skin, fitness and food routines that keep their bodies beautiful and their lives serene for the boyfriends who are, after all, funding the whole shebang.
In one SAHG video, I watched a platinum blonde explain that her boyfriend agreed to pay for all of their travel if she would do all of the packing. The rest of the video was dedicated to the most meticulous suitcase job you’ve ever seen — sunglasses nestled in shoes, a rainbow of rolled shirts — which appeared to take her the better part of an afternoon.
Another video featured a young woman in a negligee patiently curling her hair while an overlay of text read: “People used to ask me, ‘what’s your dream job?’ I never knew the answer. I realized it’s because I don’t dream of labor. I dream of living a soft, feminine life.” The video was captioned, “I dream of feminine leisure,” which I soon realized was a sort of motto among this set.
“I dream of feminine leisure,” wrote a lovely brunette as she sauntered to the pool in a floaty coverup.
“I dream of feminine leisure,” wrote another lovely brunette as she applied a fresh coat of lip gloss at her vanity.
The comments on these types of videos abound with wistful envy: heart emoji, lipstick kiss emoji, green juice, vacuum.
W hat is feminine leisure, exactly? Is it a set of prescribed activities? An aesthetic? A vibe?
The simple answer is that it’s a solution — maybe not a good solution, but a conceivable one — to a problem. A problem some young women have diagnosed in the landscape of modern adulthood.
A frantic mother of a 16-year-old wrote into Slate’s Care and Feeding advice column a few months ago to say that her formerly go-getter daughter had announced that she wanted to skip the rigors of college and instead focus on maintaining her appearance for a future husband. “She’s now talking about how great the ‘patriarchy’ is,” wrote the alarmed mom, “and how she can’t wait for someone to come and take care of her.”
From Christie to tradwives to SAHGs to the Patriarchy Daughter, the common thread seems to be the concept that liberation is overrated. That women raised on the virtues of female independence have been sold a bill of goods. Yes, we are allowed to have successful careers. But nobody had decreased the amount of laundry or errands that still needed to be run. Nobody had added any more hours onto the clock.
The Wall Street Journal recently detailed a new paper to be published in the journal Social Indicators Research that found that, “regardless of how the question is asked or what measure is used, women say they are more anxious, more depressed, more tired and more pessimistic than men,” the Journal said. At the same time, though, women are also more likely “to say they are happy and satisfied with their lives.”
It’s a phenomenon known as the “female happiness paradox,” and researchers can’t really explain it.
One guess cited in the article is that the measuring stick itself is off: Men, after all, are the ones who die more often by suicide, drug overdoses and alcoholism. So maybe it’s not that they are less anxious and depressed than women, but that, conditioned to be taciturn, they are less likely to report it. Another guess is that the things that stress women out — children, relationship-building, achieving work-life balance — are also the things that give them the most satisfaction.
Regardless of how to interpret the data, the facts of the matter remain that women are either miserable but happy or happy but miserable. And if scientific researchers can’t figure out what to do about this paradox, can 20-year-old women? Why knock yourself over trying? Crash the MBA reception. Curl your hair. Pack the suitcase. Choose ease.
I’ll pause to note that, generally, we see and hear much less from the men in these relationships than from their influencer wives and girlfriends; their voices are missing from this discourse. Maybe it’s because the mutual arrangement is working for them, but they’re afraid of being labeled sexist for admitting it. Maybe they don’t want to hurt their girlfriend’s feelings by explaining that they truly could not care less if their shirts are rolled. Maybe it’s just because they’re at their offices when all the lovely content is being made.
Whatever the case: I can imagine a lot of men would like to have a stay-at-home partner, not because they are misogynists but because it’s a relief when someone else has already done the grocery shopping — and I can imagine a lot of women would feel the same way. I can also imagine that a lot of men would like to saunter toward a pool in the middle of a Tuesday, or spend their days as Christie describes in the Cut: “Mostly I get to read, to walk central London and Miami and think in delicious circles.” So far, TikTok has not spun off an equivalent stay-at-home-boyfriend aesthetic.
The fact of the matter is that almost nobody who works for a living has the time they wish they did to look, feel or be their best, much less to cultivate a highly aesthetic relationship with a thing called ease .
What if the problem is not feminism but capitalism — specifically the American version, where work-life balance is a punchline? What if instead of 11 paid vacation days , as the average American gets, these women got the full month that is standard in the United Kingdom? What if instead of five (or six or seven) days a week, they worked the four days that countries such as South Africa and Belgium are piloting? Would that allow enough time to do a full skin-care regimen and pack a great suitcase? If college weren’t so ghastly expensive here, maybe that one lady’s daughter wouldn’t be so keen on the patriarchy as a route to leisure that bypasses the long, uphill road to financial independence.
It wasn’t fair when women had no choice to stay home. It’s not fair if women are working but are still doing the work of maintaining a home. It’s not fair if both men and women are trying to juggle it together and are still finding that there aren’t enough hours or dollars in a day.
Who wouldn’t dream of feminine leisure?
A few months ago, I decided to reread Ottessa Moshfegh’s brilliant novel “My Year of Rest and Relaxation.” It’s about a young woman struggling so much with her grown-up life that she embarks on a plan to sleep through an entire year via a steady influx of prescription narcotics. The ending is ambiguous — but, the way I read it, happy: By the end of the experiment, she has finally rested enough to rejoin the world, which she does with a rejuvenated and more optimistic perspective than she had before.
I mentioned this to a friend, who looked at me funny.
“Oh,” my friend said. “I thought she died.”
W hile writing this, I learned that a colleague and I were both obsessed with an influencer with a tradwife aesthetic who made elaborate pastries while wearing a placid, unchanging expression that made her look like a high-functioning lobotomy patient. In 2024, was this satire, or serious?
The same co-worker had been served the SAHG skinfluencer videos that also populated my social media feeds. Could you imagine, we asked one another, spending 30 minutes a day washing your face?
Then I went home and started thinking about the most satisfying day I’d had in recent months: A bundle of accrued comp time had allowed me to take a paid day off work on a random Wednesday. I went to yoga, bought a fancy sandwich, booked summer travel, researched preschools and made a dinner that was, for once, assembled patiently and attractively and not after desperately Googling “15-minute dinner can of beans and one potato?”
There was a good amount of leisure in there — even a good amount of feminine leisure.
But here’s the thing: The day hadn’t felt satisfying because I had achieved harmony with my feminine destiny; it felt satisfying because I, like most other adult humans of any gender, have a long list of necessary tasks, and almost never enough time to get through them. American culture is not conducive to helping to-do lists get shorter. Workweeks are long, vacation is limited, preschools are not universal and must therefore be researched.
And dreams? Dreams are dreams.
I wondered about the women who seemed to be seeking a relationship solution to the societal and existential problem of unrest. Did they really want to have no control over their own finances? To have to ask for an allowance? How would they feel about themselves and the choices they had made in five, 10, 20 years? When their skin was going to get wrinkles no matter how well they had cared for it. When they had run out of ways to film their get-ready-with-me mornings.
Cosmopolitan ran a story last month about some women who had once identified as stay-at-home girlfriends but who don’t anymore. “If he is paying for your whole life and you don’t have any income at all, there will start to be resentment,” influencer Bella Greenlee was quoted as saying, later adding: “I would clean the house more than I had to, just to keep myself entertained. I didn’t really have a lot to do, so I was kind of going crazy.”
The solution to this messy moment in the history of gender and work is not to dream backward, to the way the middle class used to do it — women as pretty property and men as forced breadwinners — and decide that if today isn’t working, yesterday must have been. The solution is to wonder what we might do about tomorrow.
A few days after the “Case for Marrying an Older Man” essay came out, the New Yorker published an article that received much less vitriol and attention. It was a story about a woman named Alena Kate Pettitt , who had gained fame four years ago as one of the original tradwife influencers. Since childhood, she’d prized the idea of a well-kept home and well-set table, and, after marrying and getting pregnant, she quit her job to make such a life a reality. She ironed. She sewed. She took pictures of herself making banana bread and getting dolled up in 1950s-style clothes, and she posted them to Instagram.
Then, gradually and for a lot of reasons, she got tired of being an influencer. She didn’t like how her lifestyle, which she’d pursued out of genuine interest, had slowly become symbolic and politicized. She noted how her content had become an ouroboros: If she tried to post pictures of herself being domestic in jeans and a T-shirt, the reaction was “muted,” according to the New Yorker, while the dolled-up photos of retro housedresses went “through the roof,” she said. So she wore more dresses, and got more followers, and wore more dresses, and what she was doing started to seem progressively more like a myth than real life.
It was lacking, shall we say, ease. Even wrapping herself in a retro bubble hadn’t protected her from having to make difficult choices, engage in self-introspection, work hard, live life. Being a public-facing tradwife turned out to be just as false of a promise as having it all.
Last year, Pettitt made the radical decision to leave Instagram. Her son was about to start high school, and her family was planning a transcontinental move. It seemed like a good time to consider all of her life choices, she said. She’d always wanted to own a coffee shop. She thought she might go back to work.
- Nicole Brown Simpson’s cries for help are still hard to hear April 13, 2024 Nicole Brown Simpson’s cries for help are still hard to hear April 13, 2024
- Meet the ‘pursuer of nubile young females’ who helped pass Arizona’s 1864 abortion law April 10, 2024 Meet the ‘pursuer of nubile young females’ who helped pass Arizona’s 1864 abortion law April 10, 2024
- Tradwives, stay-at-home girlfriends and the dream of feminine leisure April 10, 2024 Tradwives, stay-at-home girlfriends and the dream of feminine leisure April 10, 2024

The Huge Risks From AI In an Election Year
On the eve of New Hampshire’s primary election, a flood of robocalls exhorted Democratic voters to sit out a write-in campaign supporting President Joe Biden during the state’s presidential primary. An AI-generated voice on the line matched the uncanny cadence and signature catchphrase— (“malarkey!”)—characteristic to Biden. From that call to fake creations envisioning a cascade of calamities under Biden’s watch to AI deepfakes of a Slovakian candidate for country leader pondering vote rigging and raising beer prices, AI is making its mark on elections worldwide. Against this backdrop, governments and several tech companies are taking some steps to mitigate risks—European lawmakers just approved a watershed law, and as recently as February tech companies signed a pledge at the Munich Security Conference. But much more needs to be done to protect American democracy.
In Munich, companies including OpenAI, Apple, Meta, Microsoft, TikTok, Google, X, and others announced a compact to undertake measures to protect elections as America and other countries go to the polls in 2024. The companies pledged to help audiences track the origin of AI-generated and authentic content, to try to detect deceptive AI media in elections, and to deploy “reasonable precautions” to curb risks from AI-fueled election trickery. While not unwelcome, the success of the compact will depend on how its commitments are executed. They were couched in slippery language—“proportionate responses,” “where appropriate and technically feasible,” “attempting to,” and so on—that give latitude to companies to do very little if they so choose. While some are taking further steps, of course, the urgency of the situation demands stronger and more universal action.
This year is the first national American election since AI developments will allow fraudsters to produce phony but close-to-perfect pictures, video, or audio of candidates and officials doing or saying almost anything with minimal time, little to no cost, and on a widespread basis. And the technology underlying generative AI chatbots lets hoaxers spoof election websites or spawn pretend news sites in a matter of seconds and on a mammoth scale. It also gives bad actors— foreign and domestic—the ability to conduct supercharged, hard-to-track interactive influence campaigns.
As generative AI is integrated into common search engines and voters converse with chatbots, people seeking basic information about elections have at times been met with misinformation, pure bunkum, or links to fringe websites. A recent study by AI Democracy Projects and Proof News indicated that popular AI tools—including Google’s Gemini, OpenAI’s GPT-4, and Meta’s Llama 2— “ performed poorly on accuracy ” when fed certain election questions. The more traditional, non-generative AI could fuel mass challenges to thousands of voters’ eligibility, risking wrongful purges from voter rolls and burdening election offices. As election officials consider using new AI tools in their day-to-day tasks, the lack of meaningful regulation risks putting some voting access in harm’s way even as AI unlocks time-saving opportunities for short-staffed offices.
Before the Munich conference the world’s premier generative AI operation, OpenAI, had recently announced a slate of company policies designed to curtail election harms as America votes in 2024. These include forbidding users from building custom AI chatbots that impersonate candidates, barring users from deploying OpenAI tools to spread falsehoods about when and how to vote, and encrypting images with digital codes that will help observers figure out whether OpenAI’s Dall-E made an image that is multiplying in the wild.
But these actions—while more robust than those of some other major AI companies to date—fall short in important ways and underscore the limitations of what we may see in future months as OpenAI and other tech giants make gestures towards honoring the commitments made in Munich. First: the company’s public-facing policies do not call out several core false narratives and depictions that have haunted prior election cycles and are likely to be resurrected in new guises this year. For example, they do not expressly name fakeries that supposedly show election officials interfering with the vote count, fabrications of unreliable or impaired voting machines, or baseless claims that widespread voter fraud has occurred. (According to Brennan Center tracking , these rank among the most common false narratives promoted by election deniers in the 2022 midterm elections.) While OpenAI policies addressing misleading others and intentional deception arguably cover some, or all, such content, specifically naming these categories as being barred from creation and spread would give more clarity to users and protection to voters. Since election procedures— and the occasional fast-resolved Election Day glitch—vary from county to county, the company should have conduits for the sharing of information between local election officials and OpenAI staff in the months leading up to the election.
Perhaps most importantly, the tech wunderkind needs to do more to curb the risks of working with third party developers—that is, the companies that license OpenAI’s technology and integrate its models into their own services and products . For instance, if a user enters basic election questions into a third-party search engine that cannibalizes OpenAI models, the answers can be rife with errors, outdated facts, and other blunders. (WIRED reporting on Microsoft Copilot last December revealed several issues at that time with the search engine—which uses OpenAI technology— though some of those problems may have since been addressed.) To better protect voters this election season, the company must create and enforce stricter requirements for its partnerships with developers that integrate OpenAI models into search engines—or any digital platform where voters may go to seek information on the ABCs of voting and elections. While the accord signed in Munich was targeted to intentionally deceptive content, voters can also be harmed by AI “hallucinations”—fabrications spit out by systems’ algorithms—or other hiccups that AI creators and service providers have failed to prevent.
But, OpenAI can’t go it alone. Other tech titans must release their own election policies for generative AI tools, unmasking any behind-the-scenes tinkering and opening internal practices to public scrutiny and knowledge. As a first step, more major tech companies—including Apple, ByteDance, Samsung, and X—should sign onto the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity ’s open standard for embedding content with digital markers that help prove that it is AI-generated or authentic as it travels through the online ether. (While Apple and X committed to consider attaching similar signals to their content in Munich, a consistent standard would improve detection and coordination across the board.) The markers, meanwhile, should be made more difficult to remove. And social media companies must act swiftly to address deepfakes and bot accounts that mimic human activity, as well as instituting meaningful account verification processes for election officials and bonafide news organizations to help voters find accurate information in feeds flush with misinformation, impersonators, and accounts masquerading as real news.
One company’s—or a handful of companies’ —steps to address election harms, while important, are not enough in a landscape awash with unsecured, open-source AI models where systems’ underlying code and the mathematical instructions that make them tick are publicly available, downloadable, and manipulatable. Companies as prominent as Meta and Stability AI have released unsecured AI systems, and other players have rapidly churned out many more. Anyone who wishes to interfere in elections today has a suite of AI technology to choose from to bolster their efforts, and multiple ways to deploy it. That means that governments at all levels must also take urgent action to protect voters.
Congress, agencies, and states have a plethora of options at hand to blunt AI’s risks ahead of the 2024 election. Congress and states should regulate deepfakes—particularly those spread by campaigns, political action committees, and paid influencers—by requiring disclaimers on deceptive and digitally manipulated images, video, and audio clips that could suppress votes, or that misrepresent candidates’ and election officials’ words and actions. Lawmakers should also require campaigns and political action committees to clearly label a subset of content produced by the technology underlying generative AI chatbots, particularly where politicos deploy the technology to engage in continuous conversations with voters or to deceptively impersonate humans to influence elections. Policymakers should protect voters against frivolous challenges to their voting eligibility by setting constraints on the evidence that may be used to substantiate a challenge — including evidence unearthed or created through AI.
Federal agencies should act quickly to publish guidance for certifying the authenticity and provenance of government content—as envisioned by the executive order on AI issued by the administration last year—and state and local election officials should apply similar practices to their official content. Longer term, federal and state governments should also create guidance and benchmarks that help election officials evaluate AI systems before purchasing them, checking for reliability, accuracy, biases, and transparency.
These steps are all pivotal to dealing with challenges that arise specifically from AI technology. But the election risks that AI amplifies—disinformation, vote suppression, election security hazards, and so on—long predate the advent of the generative-AI boom. To fully protect voting and elections, lawmakers must also pass reforms like the Freedom to Vote Act—a set of wide-ranging provisions that stalled in the U.S. Senate. It also means updating political ad disclosure requirements for the 21 st century. And it means maintaining an expansive vision for democracy that is impervious to age-old and persistent efforts to subvert it.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- The Revolution of Yulia Navalnaya
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- Stop Looking for Your Forever Home
- If You're Dating Right Now , You're Brave: Column
- The AI That Could Heal a Divided Internet
- Fallout Is a Brilliant Model for the Future of Video Game Adaptations
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Modern Lifestyle Essay. The modern lifestyle has a number of advantages which includes easing peoples life, saving hundreds of peoples lives by the new development of medicine and vaccines. On the other hand different modern life style patterns have negative effects on health physically, psychologically, and socially.
500+ Words Essay on Life. First of all, Life refers to an aspect of existence. This aspect processes acts, evaluates, and evolves through growth. Life is what distinguishes humans from inorganic matter. Some individuals certainly enjoy free will in Life.
Each of us has meaning, and we bring it to life. It is a waste to be asking the question when you are the answer," for example. This quote pertains to his belief that an individual is responsible for giving life meaning. 2. My Life Purpose. For this prompt, share with your readers your current purpose in life.
The Illusion of Abundance. One of the most insidious aspects of food waste is the perception of abundance. In developed nations, supermarkets overflow with produce, obscuring the reality of limited global resources. The illusion of endless supply.... Read More. View our collection of modern life essays. Find inspiration for topics, titles ...
The PFC is the only part of the brain that actually fatigues like a muscle with overuse. As with muscles, rest is essential. 2. Disconnect. We need to engage with the world in ways other than just ...
Becoming Modern. People use the term "modern" in a variety of ways, often very loosely, with a lot of implied associations of new, contemporary, up-to-date, and technological. We know the difference between a modern society and one that remains tied to the past and it usually has less to do with art and more to do with technology and ...
Modern life may increase the risk of some physical and mental health problems, but striking a balance between online and real-world social relationships, going forward, may help to keep our mental ...
Technology is a vital component of life in the modern world. People are so dependent on technology that they cannot live without it. Technology is important and useful in all areas of human life today. It has made life easy and comfortable by making communication and transport faster and easier (Harrington, 2011, p.35).
1. Rethink Your Eating. Look beyond meal-to-meal concerns with weight. Aim to eat consciously and selectively in keeping with the nourishment you want to take in, the energy and personal gifts you want to contribute, and the influence you want to have on the world around you.
Sample Essay on Life in 350 words. Life is a journey of discovery, where we encounter moments both big and small that shape our identity. From the joyful laughter of childhood to the trials of adolescence, each phase of life imparts unique lessons. Each chapter unveils a new facet of our identity, inviting us to delve deeper into the essence of ...
500 Words Essay on Internet and Modern Life The Advent of the Internet. The internet, the digital universe of information, has drastically revolutionized the modern world. It has woven itself into the fabric of our lives, becoming an indispensable tool for communication, information, entertainment, and business. The inception of the internet ...
Therefore, modern life was about social mixing, social mobility, frequent journeys from the city to the country and back, and a generally faster pace which has accelerated ever since. ... In 1863 the poet and art critic Charles Baudelaire published an essay entitled "The Painter of Modern Life," which declared that the artist must be of his ...
Introduction. Modern technology has changed the world beyond recognition. Thanks to technology in the twentieth and twenty-first centuries, advances have been made that have revolutionized our lives. Modern man can hardly imagine his life without machines. Every day, new devices either appear, or existing ones are improved.
Walter Benjamin's essays on the great French lyric poet Charles Baudelaire revolutionized not just the way we think about Baudelaire, but our understanding of modernity and modernism as well. In these essays, Benjamin challenges the image of Baudelaire as late-Romantic dreamer, and evokes instead the modern poet caught in a life-or-death struggle with the forces of the urban commodity ...
"The Painter of Modern Life" (French: "Le Peintre de la vie moderne") is an essay written by French poet, essayist, and art critic Charles Baudelaire (1821-1867). It was composed sometime between November 1859 and February 1860, and was first published in three installments in the French morning newspaper Le Figaro in 1863: first on November 26, and then on the 28th, and finally on December 3.
The Internet has become embedded in every aspect of our day-to-day lives, changing the way we interact with others. This insight struck me when I started out in the world of social media. I created my first social network in 2005, when I was finishing college in the United States—it had a political theme.
Other life events that increase stress are outlined in the Holmes-Rahe Life Stress Inventory, and include the death of a life partner, divorce, major personal injury, retirement, and pregnancy. Daily hassles - ordinary challenges we face in daily - can also cause stress. These include having too much to do, cost of living, and conflict at work.
The meaning of life has changed from experiencing to capturing, editing, posting and reposting. Life has become a blatant excuse to oppress the already poor while subjecting the human race to a culture of following. The meaning of life has become the fellowship of the followers. This essay was reviewed by.
Essay On A Rose For Emily. "A rose for Emily" is a short story written by William Faulkner. The story is mainly focused on the character of Emily Grierson who may be considered as the protagonist of the story. Miss Emily may be described as a mysterious character that has a rather difficult life.
The Painter of Modern Life written by Charles Baudelaire (1821-1867) in the winter of 1859-1860 and published in 1863 as a series of newspaper pieces (feuilletons) in the November 26 and 28 and December 3 editions of the Figaro makes essential and seminal reading, for several reasons. It has profound implications for art criticism (turning it away from the tourist's study of acknowledged ...
In these essays, Benjamin challenges the image of Baudelaire as late-Romantic dreamer, and evokes instead the modern poet caught in a life-or-death struggle with the forces of the urban commodity capitalism that had emerged in Paris around 1850.
Wednesday, April 10, 2024. More podcasts. Washington Post Live brings The Post's newsroom to life. Some women are retreating to stereotypical, retro gender roles that embrace the patriarchy ...
Guest Essay. An Essential Part of Modern Life That Armies Should Never Attack Again. April 15, 2024, 5:04 a.m. ET. A Ukrainian power plant heavily damaged by recent Russian missile strikes.
Technology in Modern Life Persuasive Essay. Technology has played an important role in the modern workplace. Gone are the days of using paper and pencil to keep track of revenue, cash received, and other vital business statistics. Work that previously required human labor such as answering the phone has now been replaced with automated machines ...
Today, Perel reads one of the most provocative Modern Love essays ever published: " What Sleeping With Married Men Taught Me About Infidelity ," by Karin Jones. In her 2018 essay, Jones wrote ...
A Few Words About Nests. April 15, 2024. Margaret Renkl. Share full article. 20. By Margaret Renkl. Ms. Renkl is a contributing Opinion writer who covers flora, fauna, politics and culture in the ...
Unlike in Europe, few in the United States will be celebrating the philosopher's 300th birthday. But Kant's writing shows that a free, just and moral life is possible — and that's relevant ...
Much has been written about common leadership styles and how to identify the right style for you, whether it's transactional or transformational, bureaucratic or laissez-faire. But according to ...
The essay's alleged offenses ranged from the kind that would irritate Greta Thunberg — the casual way Christie's byline notes that she lives in "Miami and London" — to the kind that ...
These steps are all pivotal to dealing with challenges that arise specifically from AI technology. But the election risks that AI amplifies—disinformation, vote suppression, election security ...