- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free


Getting Started with Essay Writing
This course is part of Academic English: Writing Specialization
Taught in English
Some content may not be translated

Instructors: Tamy Chapman +1 more
Instructors
Instructor ratings.
We asked all learners to give feedback on our instructors based on the quality of their teaching style.
Financial aid available
227,299 already enrolled

(3,162 reviews)
Details to know

Add to your LinkedIn profile
See how employees at top companies are mastering in-demand skills

Build your subject-matter expertise
- Learn new concepts from industry experts
- Gain a foundational understanding of a subject or tool
- Develop job-relevant skills with hands-on projects
- Earn a shareable career certificate

Earn a career certificate
Add this credential to your LinkedIn profile, resume, or CV
Share it on social media and in your performance review

There are 5 modules in this course
Course 2: Getting Started with Essay Writing
This is the second course in the Academic English: Writing specialization. By introducing you to three types of academic essays, this course will especially help prepare you for work in college classes, but anyone who wants to improve his or her writing skills can benefit from this course. After completing this course, you will be able to: - create effective thesis statements for your essays - plan and write compare/contrast, cause/effect, and argument essays - write well-developed body paragraphs Note: The lectures and practice activities are available for free, but you must upgrade to the pay version in order to take the quizzes and get feedback on writing assignments.
Course Introduction
This is the second course in the Academic English: Writing specialization. In the last course, you reviewed sentence types and punctuation. You'll use that information in this course to make your writing great. In this course, you'll learn all about academic essay writing and, specifically, how to write three types of essays: compare/contrast, cause/effect, and argument. To pass this course, you need to pass all four quizzes and pass all three writing assignments. When you finish one activity, you can continue to the next one. Enjoy!
What's included
2 videos 2 readings 1 peer review
2 videos • Total 2 minutes
- Course Introduction Video • 0 minutes • Preview module
- Academic Integrity Video Lecture • 2 minutes
2 readings • Total 20 minutes
- Pre-Course Survey • 10 minutes
- Message about Opinions • 10 minutes
1 peer review • Total 60 minutes
- Introductions • 60 minutes
Essay Writing
In this module, you'll start learning about essay structure and some other important tools for good writing. There's a lot of information in this module, but it's all necessary for writing well. Make sure you take notes so you will remember these tools when you write your essays. Note to learners: this course is designed for learners of English with intermediate English writing skills. The sample essays in this course are aimed at that level. However, the principles discussed in the lessons are practical for writers of any level. If you're at a lower level, do the best you can. If you are a more advanced writer, feel free to write more developed and complex essays than the ones in the examples. Just make sure you follow the structures introduced.
6 videos 8 readings 2 quizzes 1 peer review
6 videos • Total 50 minutes
- What is an Essay? Video Lecture • 9 minutes • Preview module
- Introduction Paragraphs Video Lecture • 12 minutes
- Body Paragraphs Video Lecture • 9 minutes
- Paragraph Basics Video Lecture • 10 minutes
- Conclusion Paragraphs Video Lecture • 3 minutes
- The Writing Process Video Lecture • 4 minutes
8 readings • Total 80 minutes
- Learning Objectives • 10 minutes
- Thesis Statement Practice • 10 minutes
- Topic Sentences Practice • 10 minutes
- Sample Essay • 10 minutes
2 quizzes • Total 60 minutes
- Essay Writing Practice Quiz • 30 minutes
- Essay Writing • 30 minutes
- Academic Essay Discussion • 60 minutes
Writing Compare/Contrast Essays
Now, you're ready to write your first type of academic essay--the compare/contrast essay. In this module, you'll learn what this type of essay is and how to structure it. Then, you'll look at some examples and practice writing your own compare/contrast essay. Remember the sample essays in the lesson are typical for an intermediate-level student. Write a compare/contrast essay that fits your own writing ability. Good luck!
3 videos 6 readings 2 quizzes 2 peer reviews
3 videos • Total 12 minutes
- Introduction to Writing Compare/Contrast Essays • 0 minutes • Preview module
- Compare/Contrast Essay Video Lecture • 6 minutes
- Teacher Discusses a Compare/Contrast Essay • 5 minutes
6 readings • Total 60 minutes
- Compare/Contrast Practice • 10 minutes
- Compare/Contrast Writing Assignment • 10 minutes
- Sample Compare/Contrast Essay • 10 minutes
- Links to Other Resources • 10 minutes
- Quiz Instructions • 10 minutes
- Compare/Contrast Essays Practice Quiz • 30 minutes
- Writing Compare/Contrast Essays • 30 minutes
2 peer reviews • Total 180 minutes
- Compare/Contrast Essay Discussion • 120 minutes
- Compare/Contrast Essay Peer Review • 60 minutes
Writing Cause/Effect Essays
Now, you'll learn about writing the cause/effect essay. This is another type of academic essay that you might be asked to write in your college classes. For this type of essay you'll think about reasons why something happens or the effects of something. The sample essays in this module are also representative of an intermediate-level writer. Write a cause/effect essay appropriate for your own English level. Just remember to follow the advice given in the lessons.
3 videos 7 readings 2 quizzes 2 peer reviews
- Introduction to Writing Cause/Effect Essays • 0 minutes • Preview module
- Cause/Effect Video Lecture • 6 minutes
- Teacher Discusses a Cause/Effect Essay • 5 minutes
7 readings • Total 70 minutes
- Cause/Effect Practice • 10 minutes
- Cause/Effect Writing Assignment • 10 minutes
- Sample Cause/Effect Essay • 10 minutes
- Learn More! • 10 minutes
- Cause/Effect Essays Practice Quiz • 30 minutes
- Writing Cause/Effect Essays • 30 minutes
2 peer reviews • Total 120 minutes
- Cause/Effect Essay Discussion • 60 minutes
- Cause/Effect Essay Peer Review • 60 minutes
Writing Argument Essays
In this last module, you'll learn how to write the most common type of college essay. The argument essay is probably the most fun essay to write too. In this one, you will try to convince your reader to believe your argument or position on some controversial topic. You have to think of good reasons to support your position. Remember to write an argument essay that is to the best of your own abilities.
3 videos • Total 13 minutes
- Introduction to Writing Argument Essays • 0 minutes • Preview module
- Argument Essays Video Lecture • 8 minutes
- Teacher Discusses an Argument Essay • 4 minutes
- Debatable vs Non-Debatable Practice • 10 minutes
- Argument Practice • 10 minutes
- Argument Writing Assignment • 10 minutes
- Sample Argument Essay • 10 minutes
- Argument Essay Practice Quiz • 30 minutes
- Argument Essays • 30 minutes
- Argument Essay Discussion • 60 minutes
- Argument Essay Peer Review • 60 minutes

Since 1965, the University of California, Irvine has combined the strengths of a major research university with the bounty of an incomparable Southern California location. UCI’s unyielding commitment to rigorous academics, cutting-edge research, and leadership and character development makes the campus a driving force for innovation and discovery that serves our local, national and global communities in many ways.
Recommended if you're interested in Music and Art

University of California, Irvine
Advanced Writing

Introduction to Research for Essay Writing

Project: Writing a Research Paper

Academic English: Writing
Specialization
Why people choose Coursera for their career

Learner reviews
Showing 3 of 3162
3,162 reviews
Reviewed on Jul 6, 2020
I am very happy that I have completed the course. It was indeed priceless learning experience. I would like to thank all the instructors for their valuable inputs on different types of essays.
Reviewed on Jul 19, 2020
This course really helped me a lot , by doing this course i got full of ideas of the compare and contrast , Argumentative Essay in order to write essay. Thank you Coursera Team.
Reviewed on May 3, 2020
It is a very good course on Essay Writing. Since it started with the basics, it helped me a lot to start from level zero. It was extremely helpful to go ahead with the future course in Writing.

Open new doors with Coursera Plus
Unlimited access to 7,000+ world-class courses, hands-on projects, and job-ready certificate programs - all included in your subscription
Advance your career with an online degree
Earn a degree from world-class universities - 100% online
Join over 3,400 global companies that choose Coursera for Business
Upskill your employees to excel in the digital economy
Frequently asked questions
When will i have access to the lectures and assignments.
Access to lectures and assignments depends on your type of enrollment. If you take a course in audit mode, you will be able to see most course materials for free. To access graded assignments and to earn a Certificate, you will need to purchase the Certificate experience, during or after your audit. If you don't see the audit option:
The course may not offer an audit option. You can try a Free Trial instead, or apply for Financial Aid.
The course may offer 'Full Course, No Certificate' instead. This option lets you see all course materials, submit required assessments, and get a final grade. This also means that you will not be able to purchase a Certificate experience.
What will I get if I subscribe to this Specialization?
When you enroll in the course, you get access to all of the courses in the Specialization, and you earn a certificate when you complete the work. Your electronic Certificate will be added to your Accomplishments page - from there, you can print your Certificate or add it to your LinkedIn profile. If you only want to read and view the course content, you can audit the course for free.
What is the refund policy?
If you subscribed, you get a 7-day free trial during which you can cancel at no penalty. After that, we don’t give refunds, but you can cancel your subscription at any time. See our full refund policy Opens in a new tab .
Is financial aid available?
Yes. In select learning programs, you can apply for financial aid or a scholarship if you can’t afford the enrollment fee. If fin aid or scholarship is available for your learning program selection, you’ll find a link to apply on the description page.
More questions
- The Open University
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
Essay and report writing skills

Course description
Course content, course reviews.
Writing reports and assignments can be a daunting prospect. Learn how to interpret questions and how to plan, structure and write your assignment or report. This free course, Essay and report writing skills, is designed to help you develop the skills you need to write effectively for academic purposes.
Course learning outcomes
After studying this course, you should be able to:
- understand what writing an assignment involves
- identify strengths and weaknesses
- understand the functions of essays and reports
- demonstrate writing skills.
First Published: 10/08/2012
Updated: 26/04/2019
Rate and Review
Rate this course, review this course.
Log into OpenLearn to leave reviews and join in the conversation.
Create an account to get more
Track your progress.
Review and track your learning through your OpenLearn Profile.
Statement of Participation
On completion of a course you will earn a Statement of Participation.
Access all course activities
Take course quizzes and access all learning.
Review the course
When you have finished a course leave a review and tell others what you think.
For further information, take a look at our frequently asked questions which may give you the support you need.
About this free course
Become an ou student, download this course, share this free course.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Understanding Writing Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
How to Decipher the Paper Assignment
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing.
- Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
- Underline or circle the portions that you absolutely must know. This information may include due date, research (source) requirements, page length, and format (MLA, APA, CMS).
- Underline or circle important phrases. You should know your instructor at least a little by now - what phrases do they use in class? Does he repeatedly say a specific word? If these are in the prompt, you know the instructor wants you to use them in the assignment.
- Think about how you will address the prompt. The prompt contains clues on how to write the assignment. Your instructor will often describe the ideas they want discussed either in questions, in bullet points, or in the text of the prompt. Think about each of these sentences and number them so that you can write a paragraph or section of your essay on that portion if necessary.
- Rank ideas in descending order, from most important to least important. Instructors may include more questions or talking points than you can cover in your assignment, so rank them in the order you think is more important. One area of the prompt may be more interesting to you than another.
- Ask your instructor questions if you have any.
After you are finished with these steps, ask yourself the following:
- What is the purpose of this assignment? Is my purpose to provide information without forming an argument, to construct an argument based on research, or analyze a poem and discuss its imagery?
- Who is my audience? Is my instructor my only audience? Who else might read this? Will it be posted online? What are my readers' needs and expectations?
- What resources do I need to begin work? Do I need to conduct literature (hermeneutic or historical) research, or do I need to review important literature on the topic and then conduct empirical research, such as a survey or an observation? How many sources are required?
- Who - beyond my instructor - can I contact to help me if I have questions? Do you have a writing lab or student service center that offers tutorials in writing?
(Notes on prompts made in blue )
Poster or Song Analysis: Poster or Song? Poster!
Goals : To systematically consider the rhetorical choices made in either a poster or a song. She says that all the time.
Things to Consider: ah- talking points
- how the poster addresses its audience and is affected by context I'll do this first - 1.
- general layout, use of color, contours of light and shade, etc.
- use of contrast, alignment, repetition, and proximity C.A.R.P. They say that, too. I'll do this third - 3.
- the point of view the viewer is invited to take, poses of figures in the poster, etc. any text that may be present
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing I'll cover this second - 2.
- ethical implications
- how the poster affects us emotionally, or what mood it evokes
- the poster's implicit argument and its effectiveness said that was important in class, so I'll discuss this last - 4.
- how the song addresses its audience
- lyrics: how they rhyme, repeat, what they say
- use of music, tempo, different instruments
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing
- emotional effects
- the implicit argument and its effectiveness
These thinking points are not a step-by-step guideline on how to write your paper; instead, they are various means through which you can approach the subject. I do expect to see at least a few of them addressed, and there are other aspects that may be pertinent to your choice that have not been included in these lists. You will want to find a central idea and base your argument around that. Additionally, you must include a copy of the poster or song that you are working with. Really important!
I will be your audience. This is a formal paper, and you should use academic conventions throughout.
Length: 4 pages Format: Typed, double-spaced, 10-12 point Times New Roman, 1 inch margins I need to remember the format stuff. I messed this up last time =(
Academic Argument Essay
5-7 pages, Times New Roman 12 pt. font, 1 inch margins.
Minimum of five cited sources: 3 must be from academic journals or books
- Design Plan due: Thurs. 10/19
- Rough Draft due: Monday 10/30
- Final Draft due: Thurs. 11/9
Remember this! I missed the deadline last time
The design plan is simply a statement of purpose, as described on pages 40-41 of the book, and an outline. The outline may be formal, as we discussed in class, or a printout of an Open Mind project. It must be a minimum of 1 page typed information, plus 1 page outline.
This project is an expansion of your opinion editorial. While you should avoid repeating any of your exact phrases from Project 2, you may reuse some of the same ideas. Your topic should be similar. You must use research to support your position, and you must also demonstrate a fairly thorough knowledge of any opposing position(s). 2 things to do - my position and the opposite.
Your essay should begin with an introduction that encapsulates your topic and indicates 1 the general trajectory of your argument. You need to have a discernable thesis that appears early in your paper. Your conclusion should restate the thesis in different words, 2 and then draw some additional meaningful analysis out of the developments of your argument. Think of this as a "so what" factor. What are some implications for the future, relating to your topic? What does all this (what you have argued) mean for society, or for the section of it to which your argument pertains? A good conclusion moves outside the topic in the paper and deals with a larger issue.
You should spend at least one paragraph acknowledging and describing the opposing position in a manner that is respectful and honestly representative of the opposition’s 3 views. The counterargument does not need to occur in a certain area, but generally begins or ends your argument. Asserting and attempting to prove each aspect of your argument’s structure should comprise the majority of your paper. Ask yourself what your argument assumes and what must be proven in order to validate your claims. Then go step-by-step, paragraph-by-paragraph, addressing each facet of your position. Most important part!
Finally, pay attention to readability . Just because this is a research paper does not mean that it has to be boring. Use examples and allow your opinion to show through word choice and tone. Proofread before you turn in the paper. Your audience is generally the academic community and specifically me, as a representative of that community. Ok, They want this to be easy to read, to contain examples I find, and they want it to be grammatically correct. I can visit the tutoring center if I get stuck, or I can email the OWL Email Tutors short questions if I have any more problems.
- Utility Menu
- Writing Center
- Writing Program
- Designing Essay Assignments
by Gordon Harvey
Students often do their best and hardest thinking, and feel the greatest sense of mastery and growth, in their writing. Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount:
1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it
However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you’re inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit. Having satisfied yourself, as you should, that what you’re asking is doable, with dignity, by writers just learning the material, try to anticipate in your prompt or discussions of the assignment the following queries:
- What is the purpose of this? How am I going beyond what we have done, or applying it in a new area, or practicing a key academic skill or kind of work?
- To what audience should I imagine myself writing?
- What is the main task or tasks, in a nutshell? What does that key word (e.g., analyze, significance of, critique, explore, interesting, support) really mean in this context or this field?
- What will be most challenging in this and what qualities will most distinguish a good paper? Where should I put my energy? (Lists of possible questions for students to answer in a paper are often not sufficiently prioritized to be helpful.)
- What misconceptions might I have about what I’m to do? (How is this like or unlike other papers I may have written?) Are there too-easy approaches I might take or likely pitfalls? An ambitious goal or standard that I might think I’m expected to meet but am not?
- What form will evidence take in my paper (e.g., block quotations? paraphrase? graphs or charts?) How should I cite it? Should I use/cite material from lecture or section?
- Are there some broad options for structure, emphasis, or approach that I’ll likely be choosing among?
- How should I get started on this? What would be a helpful (or unhelpful) way to take notes, gather data, discover a question or idea? Should I do research?
2. Take time in class to prepare students to succeed at the paper
Resist the impulse to think of class meetings as time for “content” and of writing as work done outside class. Your students won’t have mastered the art of paper writing (if such a mastery is possible) and won’t know the particular disciplinary expectations or moves relevant to the material at hand. Take time in class to show them:
- discuss the assignment in class when you give it, so students can see that you take it seriously, so they can ask questions about it, so they can have it in mind during subsequent class discussions;
- introduce the analytic vocabulary of your assignment into class discussions, and take opportunities to note relevant moves made in discussion or good paper topics that arise;
- have students practice key tasks in class discussions, or in informal writing they do in before or after discussions;
- show examples of writing that illustrates components and criteria of the assignment and that inspires (class readings can sometimes serve as illustrations of a writing principle; so can short excerpts of writing—e.g., a sampling of introductions; and so can bad writing—e.g., a list of problematic thesis statements);
- the topics of originality and plagiarism (what the temptations might be, how to avoid risks) should at some point be addressed directly.
3. Build in process
Ideas develop over time, in a process of posing and revising and getting feedback and revising some more. Assignments should allow for this process in the following ways:
- smaller assignments should prepare for larger ones later;
- students should do some thinking and writing before they write a draft and get a response to it (even if only a response to a proposal or thesis statement sent by email, or described in class);
- for larger papers, students should write and get response (using the skills vocabulary of the assignment) to a draft—at least an “oral draft” (condensed for delivery to the class);
- if possible, meet with students individually about their writing: nothing inspires them more than feeling that you care about their work and development;
- let students reflect on their own writing, in brief cover letters attached to drafts and revisions (these may also ask students to perform certain checks on what they have written, before submitting);
- have clear and firm policies about late work that nonetheless allow for exception if students talk to you in advance.
- Pedagogy Workshops
- Responding to Student Writing
- Commenting Efficiently
- Vocabulary for Discussing Student Writing
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- HarvardWrites Instructor Toolkit
- Additional Resources for Teaching Fellows

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Assignments
Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine

Introduction
Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing assignments at university.
- You may be returning to study after a break
- You may have come from an exam based assessment system and never written an assignment before
- Maybe you have written assignments but would like to improve your processes and strategies
This chapter has a collection of resources that will provide you with the skills and strategies to understand assignment requirements and effectively plan, research, write and edit your assignments. It begins with an explanation of how to analyse an assignment task and start putting your ideas together. It continues by breaking down the components of academic writing and exploring the elements you will need to master in your written assignments. This is followed by a discussion of paraphrasing and synthesis, and how you can use these strategies to create a strong, written argument. The chapter concludes with useful checklists for editing and proofreading to help you get the best possible mark for your work.
Task Analysis and Deconstructing an Assignment
It is important that before you begin researching and writing your assignments you spend sufficient time understanding all the requirements. This will help make your research process more efficient and effective. Check your subject information such as task sheets, criteria sheets and any additional information that may be in your subject portal online. Seek clarification from your lecturer or tutor if you are still unsure about how to begin your assignments.
The task sheet typically provides key information about an assessment including the assignment question. It can be helpful to scan this document for topic, task and limiting words to ensure that you fully understand the concepts you are required to research, how to approach the assignment, and the scope of the task you have been set. These words can typically be found in your assignment question and are outlined in more detail in the two tables below (see Table 19.1 and Table 19.2 ).
Table 19.1 Parts of an Assignment Question
Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the task word requires you to address.
Table 19.2 Task words
The criteria sheet , also known as the marking sheet or rubric, is another important document to look at before you begin your assignment. The criteria sheet outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required.
The task or criteria sheet will also include the:
- Word limit (or word count)
- Referencing style and research expectations
- Formatting requirements
Task analysis and criteria sheets are also discussed in the chapter Managing Assessments for a more detailed discussion on task analysis, criteria sheets, and marking rubrics.
Preparing your ideas
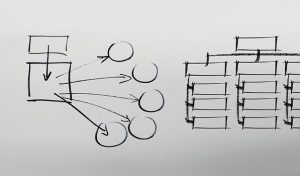
Brainstorm or concept map: List possible ideas to address each part of the assignment task based on what you already know about the topic from lectures and weekly readings.
Finding appropriate information: Learn how to find scholarly information for your assignments which is
See the chapter Working With Information for a more detailed explanation .
What is academic writing?
Academic writing tone and style.
Many of the assessment pieces you prepare will require an academic writing style. This is sometimes called ‘academic tone’ or ‘academic voice’. This section will help you to identify what is required when you are writing academically (see Table 19.3 ). The best way to understand what academic writing looks like, is to read broadly in your discipline area. Look at how your course readings, or scholarly sources, are written. This will help you identify the language of your discipline field, as well as how other writers structure their work.
Table 19.3 Comparison of academic and non-academic writing
Thesis statements.
Essays are a common form of assessment that you will likely encounter during your university studies. You should apply an academic tone and style when writing an essay, just as you would in in your other assessment pieces. One of the most important steps in writing an essay is constructing your thesis statement. A thesis statement tells the reader the purpose, argument or direction you will take to answer your assignment question. A thesis statement may not be relevant for some questions, if you are unsure check with your lecturer. The thesis statement:
- Directly relates to the task . Your thesis statement may even contain some of the key words or synonyms from the task description.
- Does more than restate the question.
- Is specific and uses precise language.
- Let’s your reader know your position or the main argument that you will support with evidence throughout your assignment.
- The subject is the key content area you will be covering.
- The contention is the position you are taking in relation to the chosen content.
Your thesis statement helps you to structure your essay. It plays a part in each key section: introduction, body and conclusion.
Planning your assignment structure

When planning and drafting assignments, it is important to consider the structure of your writing. Academic writing should have clear and logical structure and incorporate academic research to support your ideas. It can be hard to get started and at first you may feel nervous about the size of the task, this is normal. If you break your assignment into smaller pieces, it will seem more manageable as you can approach the task in sections. Refer to your brainstorm or plan. These ideas should guide your research and will also inform what you write in your draft. It is sometimes easier to draft your assignment using the 2-3-1 approach, that is, write the body paragraphs first followed by the conclusion and finally the introduction.
Writing introductions and conclusions
Clear and purposeful introductions and conclusions in assignments are fundamental to effective academic writing. Your introduction should tell the reader what is going to be covered and how you intend to approach this. Your conclusion should summarise your argument or discussion and signal to the reader that you have come to a conclusion with a final statement. These tips below are based on the requirements usually needed for an essay assignment, however, they can be applied to other assignment types.
Writing introductions

Most writing at university will require a strong and logically structured introduction. An effective introduction should provide some background or context for your assignment, clearly state your thesis and include the key points you will cover in the body of the essay in order to prove your thesis.
Usually, your introduction is approximately 10% of your total assignment word count. It is much easier to write your introduction once you have drafted your body paragraphs and conclusion, as you know what your assignment is going to be about. An effective introduction needs to inform your reader by establishing what the paper is about and provide four basic things:
- A brief background or overview of your assignment topic
- A thesis statement (see section above)
- An outline of your essay structure
- An indication of any parameters or scope that will/ will not be covered, e.g. From an Australian perspective.
The below example demonstrates the four different elements of an introductory paragraph.
1) Information technology is having significant effects on the communication of individuals and organisations in different professions. 2) This essay will discuss the impact of information technology on the communication of health professionals. 3) First, the provision of information technology for the educational needs of nurses will be discussed. 4) This will be followed by an explanation of the significant effects that information technology can have on the role of general practitioner in the area of public health. 5) Considerations will then be made regarding the lack of knowledge about the potential of computers among hospital administrators and nursing executives. 6) The final section will explore how information technology assists health professionals in the delivery of services in rural areas . 7) It will be argued that information technology has significant potential to improve health care and medical education, but health professionals are reluctant to use it.
1 Brief background/ overview | 2 Indicates the scope of what will be covered | 3-6 Outline of the main ideas (structure) | 7 The thesis statement
Note : The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing conclusions
You should aim to end your assignments with a strong conclusion. Your conclusion should restate your thesis and summarise the key points you have used to prove this thesis. Finish with a key point as a final impactful statement. Similar to your introduction, your conclusion should be approximately 10% of the total assignment word length. If your assessment task asks you to make recommendations, you may need to allocate more words to the conclusion or add a separate recommendations section before the conclusion. Use the checklist below to check your conclusion is doing the right job.
Conclusion checklist
- Have you referred to the assignment question and restated your argument (or thesis statement), as outlined in the introduction?
- Have you pulled together all the threads of your essay into a logical ending and given it a sense of unity?
- Have you presented implications or recommendations in your conclusion? (if required by your task).
- Have you added to the overall quality and impact of your essay? This is your final statement about this topic; thus, a key take-away point can make a great impact on the reader.
- Remember, do not add any new material or direct quotes in your conclusion.
This below example demonstrates the different elements of a concluding paragraph.
1) It is evident, therefore, that not only do employees need to be trained for working in the Australian multicultural workplace, but managers also need to be trained. 2) Managers must ensure that effective in-house training programs are provided for migrant workers, so that they become more familiar with the English language, Australian communication norms and the Australian work culture. 3) In addition, Australian native English speakers need to be made aware of the differing cultural values of their workmates; particularly the different forms of non-verbal communication used by other cultures. 4) Furthermore, all employees must be provided with clear and detailed guidelines about company expectations. 5) Above all, in order to minimise communication problems and to maintain an atmosphere of tolerance, understanding and cooperation in the multicultural workplace, managers need to have an effective knowledge about their employees. This will help employers understand how their employee’s social conditioning affects their beliefs about work. It will develop their communication skills to develop confidence and self-esteem among diverse work groups. 6) The culturally diverse Australian workplace may never be completely free of communication problems, however, further studies to identify potential problems and solutions, as well as better training in cross cultural communication for managers and employees, should result in a much more understanding and cooperative environment.
1 Reference to thesis statement – In this essay the writer has taken the position that training is required for both employees and employers . | 2-5 Structure overview – Here the writer pulls together the main ideas in the essay. | 6 Final summary statement that is based on the evidence.
Note: The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing paragraphs
Paragraph writing is a key skill that enables you to incorporate your academic research into your written work. Each paragraph should have its own clearly identified topic sentence or main idea which relates to the argument or point (thesis) you are developing. This idea should then be explained by additional sentences which you have paraphrased from good quality sources and referenced according to the recommended guidelines of your subject (see the chapter Working with Information ). Paragraphs are characterised by increasing specificity; that is, they move from the general to the specific, increasingly refining the reader’s understanding. A common structure for paragraphs in academic writing is as follows.
Topic Sentence
This is the main idea of the paragraph and should relate to the overall issue or purpose of your assignment is addressing. Often it will be expressed as an assertion or claim which supports the overall argument or purpose of your writing.
Explanation/ Elaboration
The main idea must have its meaning explained and elaborated upon. Think critically, do not just describe the idea.
These explanations must include evidence to support your main idea. This information should be paraphrased and referenced according to the appropriate referencing style of your course.
Concluding sentence (critical thinking)
This should explain why the topic of the paragraph is relevant to the assignment question and link to the following paragraph.
Use the checklist below to check your paragraphs are clear and well formed.
Paragraph checklist
- Does your paragraph have a clear main idea?
- Is everything in the paragraph related to this main idea?
- Is the main idea adequately developed and explained?
- Do your sentences run together smoothly?
- Have you included evidence to support your ideas?
- Have you concluded the paragraph by connecting it to your overall topic?
Writing sentences
Make sure all the sentences in your paragraphs make sense. Each sentence must contain a verb to be a complete sentence. Avoid sentence fragments . These are incomplete sentences or ideas that are unfinished and create confusion for your reader. Avoid also run on sentences . This happens when you join two ideas or clauses without using the appropriate punctuation. This also confuses your meaning (See the chapter English Language Foundations for examples and further explanation).
Use transitions (linking words and phrases) to connect your ideas between paragraphs and make your writing flow. The order that you structure the ideas in your assignment should reflect the structure you have outlined in your introduction. Refer to transition words table in the chapter English Language Foundations.
Paraphrasing and Synthesising
Paraphrasing and synthesising are powerful tools that you can use to support the main idea of a paragraph. It is likely that you will regularly use these skills at university to incorporate evidence into explanatory sentences and strengthen your essay. It is important to paraphrase and synthesise because:
- Paraphrasing is regarded more highly at university than direct quoting.
- Paraphrasing can also help you better understand the material.
- Paraphrasing and synthesising demonstrate you have understood what you have read through your ability to summarise and combine arguments from the literature using your own words.
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is changing the writing of another author into your words while retaining the original meaning. You must acknowledge the original author as the source of the information in your citation. Follow the steps in this table to help you build your skills in paraphrasing (see Table 19.4 ).
Table 19.4 Paraphrasing techniques
Example of paraphrasing.
Please note that these examples and in text citations are for instructional purposes only.
Original text
Health care professionals assist people often when they are at their most vulnerable . To provide the best care and understand their needs, workers must demonstrate good communication skills . They must develop patient trust and provide empathy to effectively work with patients who are experiencing a variety of situations including those who may be suffering from trauma or violence, physical or mental illness or substance abuse (French & Saunders, 2018).
Poor quality paraphrase example
This is a poor example of paraphrasing. Some synonyms have been used and the order of a few words changed within the sentences however the colours of the sentences indicate that the paragraph follows the same structure as the original text.
Health care sector workers are often responsible for vulnerable patients. To understand patients and deliver good service , they need to be excellent communicators . They must establish patient rapport and show empathy if they are to successfully care for patients from a variety of backgrounds and with different medical, psychological and social needs (French & Saunders, 2018).
A good quality paraphrase example
This example demonstrates a better quality paraphrase. The author has demonstrated more understanding of the overall concept in the text by using the keywords as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up to see how much the structure has changed from the original text.
Empathetic communication is a vital skill for health care workers. Professionals in these fields are often responsible for patients with complex medical, psychological and social needs. Empathetic communication assists in building rapport and gaining the necessary trust to assist these vulnerable patients by providing appropriate supportive care (French & Saunders, 2018).
The good quality paraphrase example demonstrates understanding of the overall concept in the text by using key words as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up, which indicates how much the structure has changed from the original text.
What is synthesising?
Synthesising means to bring together more than one source of information to strengthen your argument. Once you have learnt how to paraphrase the ideas of one source at a time, you can consider adding additional sources to support your argument. Synthesis demonstrates your understanding and ability to show connections between multiple pieces of evidence to support your ideas and is a more advanced academic thinking and writing skill.
Follow the steps in this table to improve your synthesis techniques (see Table 19.5 ).
Table 19.5 Synthesising techniques
Example of synthesis
There is a relationship between academic procrastination and mental health outcomes. Procrastination has been found to have a negative effect on students’ well-being (Balkis, & Duru, 2016). Yerdelen, McCaffrey, and Klassens’ (2016) research results suggested that there was a positive association between procrastination and anxiety. This was corroborated by Custer’s (2018) findings which indicated that students with higher levels of procrastination also reported greater levels of the anxiety. Therefore, it could be argued that procrastination is an ineffective learning strategy that leads to increased levels of distress.
Topic sentence | Statements using paraphrased evidence | Critical thinking (student voice) | Concluding statement – linking to topic sentence
This example demonstrates a simple synthesis. The author has developed a paragraph with one central theme and included explanatory sentences complete with in-text citations from multiple sources. Note how the blocks of colour have been used to illustrate the paragraph structure and synthesis (i.e., statements using paraphrased evidence from several sources). A more complex synthesis may include more than one citation per sentence.
Creating an argument
What does this mean.
Throughout your university studies, you may be asked to ‘argue’ a particular point or position in your writing. You may already be familiar with the idea of an argument, which in general terms means to have a disagreement with someone. Similarly, in academic writing, if you are asked to create an argument, this means you are asked to have a position on a particular topic, and then justify your position using evidence.
What skills do you need to create an argument?
In order to create a good and effective argument, you need to be able to:
- Read critically to find evidence
- Plan your argument
- Think and write critically throughout your paper to enhance your argument
For tips on how to read and write critically, refer to the chapter Thinking for more information. A formula for developing a strong argument is presented below.
A formula for a good argument
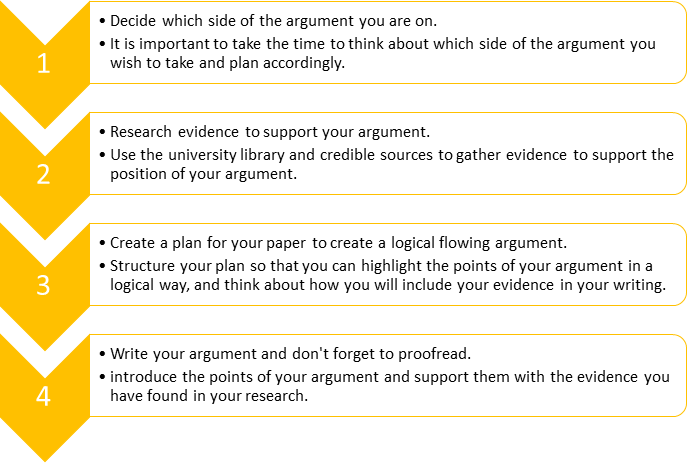
What does an argument look like?
As can be seen from the figure above, including evidence is a key element of a good argument. While this may seem like a straightforward task, it can be difficult to think of wording to express your argument. The table below provides examples of how you can illustrate your argument in academic writing (see Table 19.6 ).
Table 19.6 Argument
Editing and proofreading (reviewing).
Once you have finished writing your first draft it is recommended that you spend time revising your work. Proofreading and editing are two different stages of the revision process.
- Editing considers the overall focus or bigger picture of the assignment
- Proofreading considers the finer details
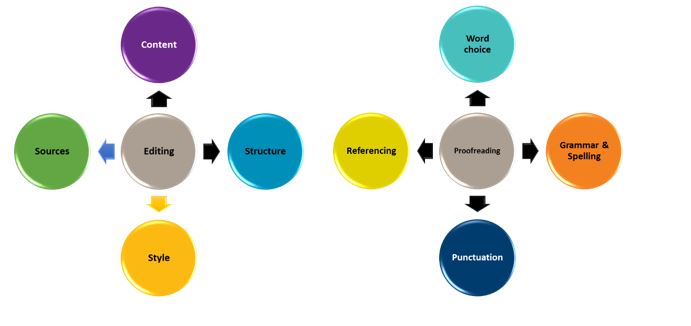
As can be seen in the figure above there are four main areas that you should review during the editing phase of the revision process. The main things to consider when editing include content, structure, style, and sources. It is important to check that all the content relates to the assignment task, the structure is appropriate for the purposes of the assignment, the writing is academic in style, and that sources have been adequately acknowledged. Use the checklist below when editing your work.
Editing checklist
- Have I answered the question accurately?
- Do I have enough credible, scholarly supporting evidence?
- Is my writing tone objective and formal enough or have I used emotive and informal language?
- Have I written in the third person not the first person?
- Do I have appropriate in-text citations for all my information?
- Have I included the full details for all my in-text citations in my reference list?
There are also several key things to look out for during the proofreading phase of the revision process. In this stage it is important to check your work for word choice, grammar and spelling, punctuation and referencing errors. It can be easy to mis-type words like ‘from’ and ‘form’ or mix up words like ‘trail’ and ‘trial’ when writing about research, apply American rather than Australian spelling, include unnecessary commas or incorrectly format your references list. The checklist below is a useful guide that you can use when proofreading your work.
Proofreading checklist
- Is my spelling and grammar accurate?
- Are they complete?
- Do they all make sense?
- Do they only contain only one idea?
- Do the different elements (subject, verb, nouns, pronouns) within my sentences agree?
- Are my sentences too long and complicated?
- Do they contain only one idea per sentence?
- Is my writing concise? Take out words that do not add meaning to your sentences.
- Have I used appropriate discipline specific language but avoided words I don’t know or understand that could possibly be out of context?
- Have I avoided discriminatory language and colloquial expressions (slang)?
- Is my referencing formatted correctly according to my assignment guidelines? (for more information on referencing refer to the Managing Assessment feedback section).
This chapter has examined the experience of writing assignments. It began by focusing on how to read and break down an assignment question, then highlighted the key components of essays. Next, it examined some techniques for paraphrasing and summarising, and how to build an argument. It concluded with a discussion on planning and structuring your assignment and giving it that essential polish with editing and proof-reading. Combining these skills and practising them, can greatly improve your success with this very common form of assessment.
- Academic writing requires clear and logical structure, critical thinking and the use of credible scholarly sources.
- A thesis statement is important as it tells the reader the position or argument you have adopted in your assignment. Not all assignments will require a thesis statement.
- Spending time analysing your task and planning your structure before you start to write your assignment is time well spent.
- Information you use in your assignment should come from credible scholarly sources such as textbooks and peer reviewed journals. This information needs to be paraphrased and referenced appropriately.
- Paraphrasing means putting something into your own words and synthesising means to bring together several ideas from sources.
- Creating an argument is a four step process and can be applied to all types of academic writing.
- Editing and proofreading are two separate processes.
Academic Skills Centre. (2013). Writing an introduction and conclusion . University of Canberra, accessed 13 August, 2013, http://www.canberra.edu.au/studyskills/writing/conclusions
Balkis, M., & Duru, E. (2016). Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 31 (3), 439-459.
Custer, N. (2018). Test anxiety and academic procrastination among prelicensure nursing students. Nursing education perspectives, 39 (3), 162-163.
Yerdelen, S., McCaffrey, A., & Klassen, R. M. (2016). Longitudinal examination of procrastination and anxiety, and their relation to self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: Latent growth curve modeling. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 16 (1).
Writing Assignments Copyright © 2021 by Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

In-Class Writing Exercises
If you find yourself wishing your students would write more thoughtful papers or think more deeply about the issues in your course, this handout may help you. At the Writing Center, we work one-on-one with thousands of student writers and find that giving them targeted writing tasks or exercises encourages them to problem-solve, generate, and communicate more fully on the page. You’ll find targeted exercises here and ways to adapt them for use in your course or with particular students.
Writing requires making choices. We can help students most by teaching them how to see and make choices when working with ideas. We can introduce students to a process of generating and sorting ideas by teaching them how to use exercises to build ideas. With an understanding of how to discover and arrange ideas, they will have more success in getting their ideas onto the page in clear prose.
Through critical thinking exercises, students move from a vague or felt sense about course material to a place where they can make explicit the choices about how words represent their ideas and how they might best arrange them. While some students may not recognize some of these activities as “writing,” they may see that doing this work will help them do the thinking that leads to easier, stronger papers.
Brainstorming
In order to write a paper for a class, students need ways to move from the received knowledge of the course material to some separate, more synthesized or analyzed understanding of the course material. For some students this begins to happen internally or through what we call “thinking,” unvoiced mulling, sorting, comparing, speculating, applying, etc. that leads them to new perspectives, understanding, questions, reactions about the course material. This thinking is often furthered through class discussion and some students automatically, internally move from these initial sortings of ideas into complex, logical interpretations of material at this point. But, for more students, their thinking will remain an unorganized, vague set of ideas referring to the subject. Many will have trouble moving beyond this vague sense or simple reaction toward ideas that are more processed, complex, or what we often call “deep.” We can foster that move to a deeper understanding by providing opportunities to externalize and fix their ideas on paper so that they may both see their ideas and then begin to see the relationships between them. The following activities will help students both generate and clarify initial responses to course material:
- Free-writing. Find a clock, watch, or timer to help you keep track of time. Choose a topic, idea, question you would like to consider. It can be a specific detail or a broad concept-whatever you are interested in exploring at the moment. Write (on paper or on a computer) for 7-10 minutes non-stop on that topic. If you get stuck and don’t know what to say next, write “I’m stuck and don’t know what to say next…” or try asking yourself “what else?” until another idea comes to you. Do not concern yourself with spelling, grammar, or punctuation. Your goal is to generate as much as you can about the topic in a short period of time and to get used to the feeling of articulating ideas on the page. It’s ok if it’s messy or makes sense only to you. You can repeat this exercise several times, using the same or a variety of topics connecting to your subject. Read what you have written to see if you have discovered anything about your subject or found a line of questioning you’d like to pursue.
- Clustering/Webbing. Find a clock, watch, or timer to help you keep track of time. Put a word you’d like to explore in the center of a piece of paper and put a circle around it. As fast as you can, free-associate or jot down anywhere on the page as many words as you can think of associated with your center word. If you get stuck, go back to the center word and launch again. Speed is important and quantity is your goal. Don’t discount any word or phrase that comes to you, just put it down on the page. Jot words for between 5-10 minutes. When you are finished you will have a page filled with seemingly random words. Read around on the page and see if you have discovered anything or can see connections between any ideas.
- Listing. On a piece of paper list all the ideas you can think of connected to subjects you are considering exploring. Consider any idea or observation as valid and worthy of listing. List quickly and then set your list aside for a few minutes. Come back and read your list and do the exercise again.
- Cubing. This technique helps you look at your subject from six different points of view (imagine the 6 sides of a cube and you get the idea). Take your topic or idea and 1) describe it, 2) compare it, 3) associate it with something else you know, 4) analyze it (meaning break it into parts), 5) apply it to a situation you are familiar with, 6) argue for or against it. Write at a paragraph, page, or more about each of the six points of view on your subject.
- Journalistic questions. Write these questions down the left hand margin of a piece of paper: Who? What? Where? When? How? And Why? Think about your topic in terms of each question.
- What? So What? Now what? To begin to explore an idea first ask yourself, “What do I want to explore?” and write about that topic for a page or more. Then read what you have written and ask “So what?” of the ideas expressed so far. Again, write for a page or more. Finally ask yourself, “Now what?” to begin to think about what else you might consider or where you might go next with an idea.
- Defining terms. Although this suggestion is simple and may seem obvious, it is often overlooked. Write definitions for key terms or concepts in your own words. Find others’ articulations of the terms in your course readings, the dictionary, or in conversations, and compare these definitions to your own. Seek input from your instructor if you can’t get a working definition of a term for yourself.
- Summarizing positions. Sometimes it’s helpful to simply describe what you know as a way to solidify your own understanding of something before you try to analyze or synthesize new ideas. You can summarize readings by individual articles or you can combine what you think are like perspectives into a summary of a position. Try to be brief in your description of the readings. Write a paragraph or up to a page describing a reading or a position.
- Metaphor writing. Metaphors or similes are comparisons sometimes using the words “like” or “as.” For example, “writing is like swimming” or the “sky is as blue as map water” or “the keyboard wrinkled with ideas.” When you create a metaphor, you put one idea in terms of another and thereby create a new vision of the original idea. Sometimes it may be easier to create a metaphor or simile may help you understand your view of an idea before you can put it fully into sentences or paragraphs. Write a metaphor or simile and then explain to someone why your metaphor works or what it means to you.
- Applying ideas to personal circumstance or known situations. Sometimes ideas come clearest when you can put them in a frame that is meaningful to you. Take a concept from your reading assignments and apply it so a situation in your own life or to a current event with which you are familiar. You may not end up using this application in your final draft, but applying it to something you know will help you to understand it better and prepare you to analyze the idea as your instructor directs.
Once students have something on the page to work with, they can begin the decision-making process crucial to developing a coherent idea or argument. At this point, students will choose which ideas most appeal to them, which ideas seem to fit together, which ideas need to be set aside, and which ideas need further exploration. The following activities will help students make decisions as they shape ideas:
- Drawing diagrams. Sometimes it helps to look for the shape your ideas seem to be taking as you develop them. Jot down your main ideas on the page and then see if you can connect them in some way. Do they form a square? A circle? An umbrella with spokes coming down? A pyramid? Does one idea seem to sit on a shelf above another idea? Would equal signs, greater or less signs help you express the relationships you see between your idea? Can you make a flow chart depicting the relationships between your ideas?
- Making charts or piles. Try sorting your ideas into separate piles. You can do this literally by putting ideas on note cards or scraps of paper and physically moving them into different piles. You can do this on the page by cutting and pasting ideas into a variety of groups on the computer screen. You can also make charts that illustrate the relationships between ideas. Common charts include timelines, authors sitting around a dinner table, and comparison/contrast charts.
- Scrap pile. Be prepared to keep a scrap pile of ideas somewhere as you work. Some people keep this pile as a separate document as they work; others keep notes at the bottom of a page where they store scrap sentences or thoughts for potential use later on. Remember that it is sometimes important to throw out ideas as a way to clarify and improve the ones you are trying to develop along the way.
- Shifting viewpoints (role-playing). When you begin to feel you have some understanding of your idea, it sometimes helps to look at it from another person’s point of view. You can do this by role-playing someone who disagrees with your conclusions or who has a different set of assumptions about your subject. Make a list or write a dialogue to begin to reveal the other perspective.
- Applying an idea to a new situation. If you have developed a working thesis, test it out by applying it to another event or situation. If you idea is clear, it will probably work again or you will find other supporting instances of your theory.
- Problem/Solution writing. Sometimes it helps to look at your ideas through a problem-solving lens. To do so, first briefly outline the problem as you see it or define it. Make sure you are through in listing all the elements that contribute to the creation of the problem. Next, make a list of potential solutions. Remember there is likely to be more than one solution.
- Theory/application writing. If your assignment asks you to develop a theory or an argument, abstract it from the situation at hand. Does your theory hold through the text? Would it apply to a new situation or can you think of a similar situation that works in the same way? Explain your ideas to a friend.
- Defining critical questions. You may have lots of evidence or information and still feel uncertain what you should do with it or how you should write about it. Look at your evidence and see if you can find repeated information or a repeated missing piece. See if you can write a question or a series of questions that summarize the most important ideas in your paper. Once you have the critical questions, you can begin to organize your ideas around potential answers to the question.
- Explaining/teaching idea to someone else. Sometimes the most efficient way to clarify your ideas is to explain them to someone else. The other person need not be knowledgeable about your subject-in fact it sometimes helps if they aren’t familiar with your topic-but should be willing to listen and interrupt you when he or she doesn’t follow you. As you teach your ideas to someone else, you may begin to have more confidence in the shape of your ideas or you may be able to identify the holes in your argument and be more able to fix them.
- Lining up evidence. If you think you have a good idea of how something works, find evidence in your course material, through research in the library or on the web that supports your thinking. If your ideas are strong, you should find supporting evidence to corroborate your ideas.
- Rewriting idea. Sometimes what helps most is rewriting an idea over the course of several days. Take the central idea and briefly explain it in a paragraph or two. The next day, without looking at the previous day’s writing, write a new paragraph explaining your ideas. Try it again the next day. Over the course of three days, you may find your ideas clarifying, complicating, or developing holes. In all cases, you will have a better idea of what you need to do next in writing your draft.
As students have been working with their ideas, they have been making a series of choices about their ideas that will lead them to feel “ready” to put them in a more complete, coherent form; they will feel “ready to write” their ideas in something closer to the assignment or paper form. But for most, the tough moments of really “writing” begin at this point. They may still feel that they “have ideas” but have trouble “getting them on the page.” Some will suddenly be thrust into “writing a paper” mode and be both constrained and guided by their assumptions about what an assignment asks them to do, what academic writing is, and what prior experience has taught them about writing for teachers. These exercises may ease their entry into shaping their ideas for an assignment:
- Clarify all questions about the assignment. Before you begin writing a draft, make sure you have a thorough understanding of what the assignment requires. You can do this by summarizing your understanding of the assignment and emailing your summary to your TA or instructor. If you have questions about points to emphasize, the amount of evidence needed, etc. get clarification early. You might try writing something like, “I’ve summarized what I think I’m supposed to do in this paper, am I on the right track?
- Write a letter describing what the paper is going to be about. One of the simplest, most efficient exercises you can do to sort through ideas is to write a letter to yourself about what you are planning to write in your paper. You might start out, “My paper is going to be about….” And go on to articulate what evidence you have to back up your ideas, what parts still feel rough to you about your ideas. In about 20 minutes, you can easily have a good sense of what you are ready to write and the problems you still need to solve in your paper.
- Write a full draft. Sometimes you don’t know what you think until you see what you’ve said. Writing a full draft, even if you think the draft has problems, is sometimes important. You may find your thesis appears in your conclusion paragraph.
- Turn your ideas into a five-minute speech. Pretend you have to give a 5 minute speech to your classmates. How would you begin the speech? What’s your main point? What key information would you include? How much detail do you need to give the listener? What evidence will be most convincing or compelling for your audience?
- Make a sketch of the paper. Sometimes it helps to literally line up or order you evidence before you write. You can do so quickly by making a numbered list of your points. Your goal is something like a sketch outline—first I am going to say this; next I need to include this point; third I need to mention this idea. The ideas should flow logically from one point to the next. If they don’t-meaning if you have to backtrack, go on a tangent, or otherwise make the reader wait to see the relationship between ideas, then you need to continue tinkering with the list.
- Make an outline. If you have successfully used formal outlines in the past, use one to structure your paper. If you haven’t successfully used outlines, don’t worry. Try some of the other techniques listed here to get your ideas on the page
- Start with the easiest part. If you have trouble getting started on a draft, write what feels to you like the easiest part first. There’s nothing magic about starting at the beginning-unless that’s the easiest part for you. Write what you know for sure and a beginning will probably emerge as you write.
- Write the body of the paper first. Sometimes it’s helpful NOT to write the beginning or introductory paragraph first. See what you have to say in the bulk of your draft and then go back to craft a suitable beginning.
- Write about feelings about writing. Sometimes it’s helpful to begin a writing session by spending 5-10 minutes writing to yourself about your feelings about the assignment. Doing so can help you set aside uncertainty and frustration and help you get motivated to write your draft.
- Write with the screen turned off. If you are really stuck getting starting or in the middle of a draft, turn the monitor off and type your ideas. Doing so will prevent you from editing and critiquing your writing as you first produce it. You may be amazed at the quantity and quality of ideas you can produce in a short time. You’ll have to do some cleanup on the typos, but it may be well worth it if it allows you to bang out a draft.
- Write in alternatives (postpone decision-making). You may need to test out more than one idea before you settle into a particular direction for a paper. It’s actually more efficient to spend time writing in several directions i.e. trying out one idea for awhile, then trying out another idea, than it is to try to fit all of your ideas into one less coherent draft. Your writing may take the form of brief overviews that begin, “If I were going to write about XYZ idea, I would…” until you are able to see which option suits the assignment and your needs.
- Write with a timer. Sometimes what you need most is to get all of your ideas out on paper in a single sitting. To do so, pretend you are taking an essay exam. Set a timer for an appropriate amount of time (1 hour? 3 hours?) depending on the length of your draft. Assume that it will take you approximately 1 hour per page of text you produce. Set a goal for the portion of your draft you must complete during the allotted time and don’t get up from your seat until the timer goes off.
As students use language to shape ideas, they begin to feel the need to test their ideas or move beyond their own perspectives. Sometimes we have ideas that make good sense to us, but seem to lose or confuse readers as we voice them in conversation or on the page. Once students have a complete draft of a paper, they need ways to share their ideas to learn points where their ideas need further development. With feedback from an audience, students are better able to see the final decisions they still need to make in order for their ideas to reach someone. These decisions may be ones of word choice, organization, logic, evidence, and tone. Keep in mind that this juncture can be unsettling for some students. Having made lots of major decisions in getting their ideas down on the page, they may be reluctant to tackle another round of decision-making required for revising or clarifying ideas or sentences. Remind students that ideas don’t exist apart from words, but in the words themselves. They will need to be able to sell their ideas through the words and arrangement of words on the page for a specific audience.
- Talk your paper. Tell a friend what your paper is about. Pay attention to your explanation. Are all of the ideas you describe actually in the paper? Where did you start explaining your ideas? Does your paper match your description? Can the listener easily find all of the ideas you mention in your description?
- Ask someone to read your paper out loud to you. Ask a friend to read your draft out loud to you. What do you hear? Where does your reader stumble? Sound confused? Have questions? Did your reader ever get lost in your text? Did ideas flow in the order the reader expected them to? Was anything missing for the reader? Did the reader need more information at any point?
- Share your draft with your instructor. If you give them enough notice, most instructors will be willing to read a draft of a paper. It sometimes helps to include your own assessment of the draft when you share it with a teacher. Give them your assessment of the strengths and weaknesses of the draft, as you see it, to begin a conversation.
- Share your draft with a classmate. Arrange to exchange papers with a classmate several days before the due date. You can do so via email and make comments for revision using Word’s comment function.
- Look at your sentences. Often you will need to analyze your draft of the sentence level. To do so, break your paper into a series of discrete sentences by putting a return after each period or end punctuation. Once you have your paper as a list of sentences, you can more easily see and solve sentence level problems. Try reading the sentences starting with the last sentence of the draft and moving up. Doing so will take them out of context and force you to see them as individual bits of communication rather than familiar points.
- Discuss key terms in your paper with someone else. After you have completed a draft, it’s sometimes helpful to look back at the key terms you are using to convey your ideas. It’s easy, in the midst of thinking about an idea, to write in loaded language or code in which certain key words come to have special meaning for you that isn’t necessarily shared by a reader. If you suspect this is the case, talk about your key terms with a friend, and ask them to read your draft to see if the idea is adequately explained for the reader.
- Outline your draft. After you have a complete draft, go back and outline what you have said. Next to each paragraph write a word or phrase that summarizes the content of that paragraph. You might also look to see if you have topic sentences that convey the ideas of individual paragraphs. If you can’t summarize the content of a paragraph, you probably have multiple ideas in play in that paragraph that may need revising. Once you have summarized each paragraph, turn your summary words into a list. How does the list flow? Is it clear how one idea connects to the next?
- Underline your main point. Highlight the main point of your paper. It should probably be (although it will depend on the assignment) in one sentence somewhere on the first page. If it’s not, the reader will likely be lost and wondering what you paper is about as he or she reads through it. Your draft should not read like a mystery novel in which the reader has to wait until the end to have all the pieces fit together.
- Ask someone without knowledge of the course to read your paper. You can tell if your draft works by sharing it with someone outside of the context. If they can follow your ideas, someone inside the class will be able to as well.
- Ask a reader to judge specific elements of your paper. Share your draft with someone and ask them to read for something specific i.e. organization, punctuation, transitions. A reader will give more specific feedback to you if you give them some specific direction.
Implementing exercises
Many of these exercises can be used in short in-class writing assignments, as part of group work, or as incremental steps in producing a paper. If you’ve assigned an end-of-semester term paper, you may want to assign one or two activities from each of the four stages-brainstorming, organizing, drafting, editing-at strategic points throughout the semester. You could also give the students the list of exercises for each stage and ask them to choose one or two activities to complete at each point as they produce a draft.
If you’d like to discuss how these exercises might work in your course, talk about other aspects of student writing, contact Kimberly Abels [email protected] at the Writing Center.

- Sign Up for Mailing List
- Search Search
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Resources for Teachers: Creating Writing Assignments
This page contains four specific areas:
Creating Effective Assignments
Checking the assignment, sequencing writing assignments, selecting an effective writing assignment format.
Research has shown that the more detailed a writing assignment is, the better the student papers are in response to that assignment. Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an “assignment sheet” tend to produce the best results. These instructions might make explicit the process or steps necessary to complete the assignment. Assignment sheets should detail:
- the kind of writing expected
- the scope of acceptable subject matter
- the length requirements
- formatting requirements
- documentation format
- the amount and type of research expected (if any)
- the writer’s role
- deadlines for the first draft and its revision
Providing questions or needed data in the assignment helps students get started. For instance, some questions can suggest a mode of organization to the students. Other questions might suggest a procedure to follow. The questions posed should require that students assert a thesis.
The following areas should help you create effective writing assignments.
Examining your goals for the assignment
- How exactly does this assignment fit with the objectives of your course?
- Should this assignment relate only to the class and the texts for the class, or should it also relate to the world beyond the classroom?
- What do you want the students to learn or experience from this writing assignment?
- Should this assignment be an individual or a collaborative effort?
- What do you want students to show you in this assignment? To demonstrate mastery of concepts or texts? To demonstrate logical and critical thinking? To develop an original idea? To learn and demonstrate the procedures, practices, and tools of your field of study?
Defining the writing task
- Is the assignment sequenced so that students: (1) write a draft, (2) receive feedback (from you, fellow students, or staff members at the Writing and Communication Center), and (3) then revise it? Such a procedure has been proven to accomplish at least two goals: it improves the student’s writing and it discourages plagiarism.
- Does the assignment include so many sub-questions that students will be confused about the major issue they should examine? Can you give more guidance about what the paper’s main focus should be? Can you reduce the number of sub-questions?
- What is the purpose of the assignment (e.g., review knowledge already learned, find additional information, synthesize research, examine a new hypothesis)? Making the purpose(s) of the assignment explicit helps students write the kind of paper you want.
- What is the required form (e.g., expository essay, lab report, memo, business report)?
- What mode is required for the assignment (e.g., description, narration, analysis, persuasion, a combination of two or more of these)?
Defining the audience for the paper
- Can you define a hypothetical audience to help students determine which concepts to define and explain? When students write only to the instructor, they may assume that little, if anything, requires explanation. Defining the whole class as the intended audience will clarify this issue for students.
- What is the probable attitude of the intended readers toward the topic itself? Toward the student writer’s thesis? Toward the student writer?
- What is the probable educational and economic background of the intended readers?
Defining the writer’s role
- Can you make explicit what persona you wish the students to assume? For example, a very effective role for student writers is that of a “professional in training” who uses the assumptions, the perspective, and the conceptual tools of the discipline.
Defining your evaluative criteria
1. If possible, explain the relative weight in grading assigned to the quality of writing and the assignment’s content:
- depth of coverage
- organization
- critical thinking
- original thinking
- use of research
- logical demonstration
- appropriate mode of structure and analysis (e.g., comparison, argument)
- correct use of sources
- grammar and mechanics
- professional tone
- correct use of course-specific concepts and terms.
Here’s a checklist for writing assignments:
- Have you used explicit command words in your instructions (e.g., “compare and contrast” and “explain” are more explicit than “explore” or “consider”)? The more explicit the command words, the better chance the students will write the type of paper you wish.
- Does the assignment suggest a topic, thesis, and format? Should it?
- Have you told students the kind of audience they are addressing — the level of knowledge they can assume the readers have and your particular preferences (e.g., “avoid slang, use the first-person sparingly”)?
- If the assignment has several stages of completion, have you made the various deadlines clear? Is your policy on due dates clear?
- Have you presented the assignment in a manageable form? For instance, a 5-page assignment sheet for a 1-page paper may overwhelm students. Similarly, a 1-sentence assignment for a 25-page paper may offer insufficient guidance.
There are several benefits of sequencing writing assignments:
- Sequencing provides a sense of coherence for the course.
- This approach helps students see progress and purpose in their work rather than seeing the writing assignments as separate exercises.
- It encourages complexity through sustained attention, revision, and consideration of multiple perspectives.
- If you have only one large paper due near the end of the course, you might create a sequence of smaller assignments leading up to and providing a foundation for that larger paper (e.g., proposal of the topic, an annotated bibliography, a progress report, a summary of the paper’s key argument, a first draft of the paper itself). This approach allows you to give students guidance and also discourages plagiarism.
- It mirrors the approach to written work in many professions.
The concept of sequencing writing assignments also allows for a wide range of options in creating the assignment. It is often beneficial to have students submit the components suggested below to your course’s STELLAR web site.
Use the writing process itself. In its simplest form, “sequencing an assignment” can mean establishing some sort of “official” check of the prewriting and drafting steps in the writing process. This step guarantees that students will not write the whole paper in one sitting and also gives students more time to let their ideas develop. This check might be something as informal as having students work on their prewriting or draft for a few minutes at the end of class. Or it might be something more formal such as collecting the prewriting and giving a few suggestions and comments.
Have students submit drafts. You might ask students to submit a first draft in order to receive your quick responses to its content, or have them submit written questions about the content and scope of their projects after they have completed their first draft.
Establish small groups. Set up small writing groups of three-five students from the class. Allow them to meet for a few minutes in class or have them arrange a meeting outside of class to comment constructively on each other’s drafts. The students do not need to be writing on the same topic.
Require consultations. Have students consult with someone in the Writing and Communication Center about their prewriting and/or drafts. The Center has yellow forms that we can give to students to inform you that such a visit was made.
Explore a subject in increasingly complex ways. A series of reading and writing assignments may be linked by the same subject matter or topic. Students encounter new perspectives and competing ideas with each new reading, and thus must evaluate and balance various views and adopt a position that considers the various points of view.
Change modes of discourse. In this approach, students’ assignments move from less complex to more complex modes of discourse (e.g., from expressive to analytic to argumentative; or from lab report to position paper to research article).
Change audiences. In this approach, students create drafts for different audiences, moving from personal to public (e.g., from self-reflection to an audience of peers to an audience of specialists). Each change would require different tasks and more extensive knowledge.
Change perspective through time. In this approach, students might write a statement of their understanding of a subject or issue at the beginning of a course and then return at the end of the semester to write an analysis of that original stance in the light of the experiences and knowledge gained in the course.
Use a natural sequence. A different approach to sequencing is to create a series of assignments culminating in a final writing project. In scientific and technical writing, for example, students could write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic. The next assignment might be a progress report (or a series of progress reports), and the final assignment could be the report or document itself. For humanities and social science courses, students might write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic, then hand in an annotated bibliography, and then a draft, and then the final version of the paper.
Have students submit sections. A variation of the previous approach is to have students submit various sections of their final document throughout the semester (e.g., their bibliography, review of the literature, methods section).
In addition to the standard essay and report formats, several other formats exist that might give students a different slant on the course material or allow them to use slightly different writing skills. Here are some suggestions:
Journals. Journals have become a popular format in recent years for courses that require some writing. In-class journal entries can spark discussions and reveal gaps in students’ understanding of the material. Having students write an in-class entry summarizing the material covered that day can aid the learning process and also reveal concepts that require more elaboration. Out-of-class entries involve short summaries or analyses of texts, or are a testing ground for ideas for student papers and reports. Although journals may seem to add a huge burden for instructors to correct, in fact many instructors either spot-check journals (looking at a few particular key entries) or grade them based on the number of entries completed. Journals are usually not graded for their prose style. STELLAR forums work well for out-of-class entries.
Letters. Students can define and defend a position on an issue in a letter written to someone in authority. They can also explain a concept or a process to someone in need of that particular information. They can write a letter to a friend explaining their concerns about an upcoming paper assignment or explaining their ideas for an upcoming paper assignment. If you wish to add a creative element to the writing assignment, you might have students adopt the persona of an important person discussed in your course (e.g., an historical figure) and write a letter explaining his/her actions, process, or theory to an interested person (e.g., “pretend that you are John Wilkes Booth and write a letter to the Congress justifying your assassination of Abraham Lincoln,” or “pretend you are Henry VIII writing to Thomas More explaining your break from the Catholic Church”).
Editorials . Students can define and defend a position on a controversial issue in the format of an editorial for the campus or local newspaper or for a national journal.
Cases . Students might create a case study particular to the course’s subject matter.
Position Papers . Students can define and defend a position, perhaps as a preliminary step in the creation of a formal research paper or essay.
Imitation of a Text . Students can create a new document “in the style of” a particular writer (e.g., “Create a government document the way Woody Allen might write it” or “Write your own ‘Modest Proposal’ about a modern issue”).
Instruction Manuals . Students write a step-by-step explanation of a process.
Dialogues . Students create a dialogue between two major figures studied in which they not only reveal those people’s theories or thoughts but also explore areas of possible disagreement (e.g., “Write a dialogue between Claude Monet and Jackson Pollock about the nature and uses of art”).
Collaborative projects . Students work together to create such works as reports, questions, and critiques.
- Make a Gift
- Directories
Search form
You are here.
- Autumn 2024
ENGL 108 B: Writing Ready: Preparing for College Writing
- Newsletter
In-Class Writing
From john bean’s engaging ideas: the professor’s guide to integrating writing, critical thinking, and active learning in the classroom (san francisco: jossey bass, 2011), 131-133.
Perhaps the easiest way to use exploratory writing is to set aside five minutes or so during a class period for silent, uninterrupted writing in response to a thinking or learning task. Students can write at their desks while the teacher writes at the chalkboard, on an overhead transparency, or in a notebook. (Teachers who are willing to write with their students are powerful role models.) Here are four suggestions for using in-class writing.
- Writing at the Beginning of Class to Probe a Subject
Give students a question that reviews previous material or stimulates interest in what’s coming. Review tasks can be open-ended and exploratory (“What questions do you want to ask about last night’s readings?”) or precise and specific (“What does it mean when we say that a certain market is ‘efficient’?”). Or use a question to prime the pump for the day’s discussion (“How does Plato’s allegory of the cave make you look at knowledge in a new way?”). In-class writing gives students a chance to gather and focus their thoughts and, when shared, gives the teacher an opportunity to see students’ thinking processes. Teachers can ask one or two students to read their responses, or they can collect a random sampling of responses to read after class. Since students are always eager to hear what the teacher has written, you might occasionally share your own in-class writing.
- Writing During Class to Refocus a Lagging Discussion or Cool Off a Heated One
When students run out of things to say or when the discussion gets so heated that everyone wants to talk at once, suspend the discussion and ask for several minutes of writing.
- Writing During Class to Ask Questions or Express Confusion
When lecturing on tough material, stop for a few minutes and ask students to respond to a writing prompt like this: “If you have understood my lecture so far, summarize my main points in your own words. If you are currently confused about something, please explain to me what is puzzling you; ask me the questions you need answered.” You will find it an illuminating check on your teaching to collect a representative sample of responses to see how well students are understanding your presentations.
- Writing at the End of Class to Sum Up a Lecture or Discussion
Give students several minutes at the end of class to sum up the day’s lecture or discussion and to prepare questions to ask at the beginning of the next class period. (Some teachers take roll by having students write out a question during the last two minutes of class and submit it on a signed slip of paper.) A popular version of this strategy is the “minute paper” as reported by Angelo and Cross ( Classroom Assessment Techniques: A Handbook for College Teachers , 1993, pp. 148-153). At the end of class, the professor asks two questions: (1) “What is the most significant thing you learned today?” and (2) “What question is uppermost in your mind at the conclusion of this class session?” In another variation, the professor asks, “What is the muddiest point in the material I have just covered?” (Tobias, “Writing to Learn Science and Mathematics” in Connolly and Vilardi [eds.] Writing to Learn Mathematics and Science , 1989, pp. 53-54).
Free tools to make your students better writers and readers .
Quill.org, a non-profit, provides free literacy activities that build reading comprehension, writing, and language skills for elementary, middle, and high school students.
Writing Across the Curriculum: Quill's nonprofit mission is to now build both reading and writing skills through free, OER content across the curriculum. Over the coming years, we will be building a library of free ELA, social studies, and science activities that engage students in deeper thinking through writing prompts that provide immediate feedback.
9 million students have written 2 billion sentences on Quill.
Quill Reading for Evidence
Provide your students with nonfiction texts paired with AI-powered writing prompts, instead of multiple-choice questions, to enable deeper thinking.
Students read a nonfiction text and build their comprehension through writing prompts, supporting a series of claims with evidence sourced from the text. Quill challenges students to write responses that are precise, logical, and based on textual evidence, with Quill coaching the student through custom, targeted feedback on each revision so that students strengthen their reading comprehension and hone their writing skills.
Video not supported
Culture & Society Topics

"Should Schools Have Grade Requirements for Student Athletes?"
Science Topics

"How Does Eating Meat Impact Global Warming?"
Social Studies Topics

U.S. History
World History
Under Development, Coming 2023
Quill Connect
Help your students advance from fragmented and run-on sentences to complex and well structured ones.
Using the evidence-based strategy of sentence combining, students combine multiple ideas into a single sentence. They then receive instant feedback designed to help them improve their clarity and precision.

Quill Lessons
The Quill Lessons tool enables teachers to lead whole-class and small-group writing instruction.
Teachers control interactive slides that contain writing prompts, and the entire class responds to each prompt. Each Quill Lessons activity provides a lesson plan, writing prompts, discussion topics, and a follow up independent practice activity.
Quill Diagnostic
Quickly determine which skills your students need to work on with our diagnostics.
The diagnostics cover vital sentence construction skills and generate personalized learning plans based on the student’s performance.

Quill Proofreader
Proofreader teaches your students editing skills by having them proofread passages.
Students edit passages and receive personalized exercises based on their results. With over 100 expository passages, Proofreader gives students the practice they need to spot common grammatical errors.
Quill Grammar
Students practice basic grammar skills, from comma placement to parallel structure.
Quill Grammar has over 150 sentence writing activities to help your students. Our activities are designed to be completed in 10 minutes so you have the freedom to use them in the way that works best for your classroom.
How Quill Works
Set up your classroom, without it.
You can quickly and easily set up your classroom in Quill by inputting student names or providing students with a unique code. If you use Google Classroom or Clever, you can automatically set up your classroom with one click.
Choose activities
Decide if you want your students to proofread passages, combine sentences, or complete a diagnostic. Use our ten minute activities as building blocks during your classroom instruction.
Use easy-to-consume reporting
Use our reporting to spot trends and identify growth opportunities. Monitor comprehension on specific writing standards.
Get immediate feedback for your students
Save time grading and watch your students correct their mistakes instantly.
Intervene where students struggle
See exactly where your students need intervention with our comprehensive reports.
Differentiate learning to meet the needs of all students
Assign specific activities for ELLs and students with learning differences.
Engage students with adaptive activities
Challenge students with questions that automatically adapt based on their previous responses.
Align with the Common Core Standards
Easily meet Common Core language standards with our aligned activities.
Easily sign up with Google Classroom
With one click all of your students and classes will be imported.
Over 100 concepts totaling 50 hours of quality curriculum.
Teacher stories
Quill in the classroom.
ROXANNA BUTKUS, RANGEVIEW ELEMENTARY
SARA ANGEL, KIPP LA
COLETTE KANG, EAST BAY INNOVATION ACADEMY
DANIEL SCIBIENSKI, PRINCETON PUBLIC SCHOOLS
3rd Grade ELA
5th Grade ELA
6th Grade ELA
8th Grade ELA & ELL
Join over 2,000 schools using Quill to advance student writing.
Quill Premium
Quill Premium's advanced reporting features are the best way to support teachers at the school or district level.

- The Student Experience
- Financial Aid
- Degree Finder
- Undergraduate Arts & Sciences
- Departments and Programs
- Research, Scholarship & Creativity
- Centers & Institutes
- Geisel School of Medicine
- Guarini School of Graduate & Advanced Studies
- Thayer School of Engineering
- Tuck School of Business
Campus Life
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Athletics & Recreation
- Student Groups & Activities
- Residential Life
Writing Program
- [email protected] Contact & Department Info Mail
- Writing Instruction
- Writing Support
- Past Prize Winners
- Writing 2-3 Teaching Assistantships
- Apply to Tutor
- Writing Requirement & Scheduling
- Differences Among First-Year Writing Courses
- Writing 2-3
- Humanities 1-2
- First-Year Seminars
- Directed Self-Placement
- Writing 2-3 Registration
- Writing 5 Registration
- First-year Seminar Registration
- Registration FAQ
- Teaching Writing in the First Year
- Expectations for Teaching Writing 2-3
- Expectations for Teaching Writing 5
- Expectations for Teaching First-Year Seminar
- Active Learning
Syllabus and Assignment Design
- Teaching Writing as Process
- Integrating Reading and Writing
- Diagnosing and Responding
- Conducting Writing Workshops
- Collaborative Learning
- Teaching Argument
- Teaching Research
- Addressing Grammar
- Useful Links
- Academic Integrity
- Processes & Practices of a Scholarly Community
- Quality of Sources
- The Writing Center
- Multilingual Support
- News & Events
Search form
- Teaching Guidelines
- Gocsik's Twelve-step Research Assignment
Designing your Syllabus: Backward Design
When you design a syllabus for any course, you begin with the outcomes that you intend for your students to achieve, and you work backwards from these to particular readings and writing assignments. This method, formalized, is called the method of backward design. Backward design is a useful method for any professor in that it ensures that all assignments, readings, and activities will connect students with the outcomes that the professor deems essential to the course.
At the first stage of backward design, writing instructors should consider two issues: what they want their students to know/experience in their courses, and what they want them to be able to do, in these courses and afterwards. Put another way, instructors need to think both about their focusing questions and their course outcomes.
You'll note that the first issue—what instructors want their students to know/experience—distinguishes between knowledge and experience. Indeed, this distinction is significant in a writing class, where course content (while important) does not drive the course. The best writing classes consider the students' experiential learning in their course design. To accomplish the aims of experiential learning, it's important to come up with a course question that can bring together the many smaller questions of the course and that can engage students intellectually and experientially. For instance: What is happiness? What are the roots of violence? What is the nature of the self? Technology: friend or foe?
These are the kinds of questions that can focus course readings and class discussions. They are also the kinds of questions that students can engage with outside of the context of the writing classroom. Finally, they are the kinds of questions around which professors can build a course that is intellectually coherent.
Even more important the the course questions, however, are the course outcomes — in other words, what students should be able to do when the course comes to an end. In the first-year writing classes, an instructor's set of outcomes will be informed by the course outcomes (see the outcomes for Writing 2-3 , Writing 5 , or the First-Year Seminar ) . Take some time to review these outcomes, and to consider how every assignment and classroom activity might work to help students achieve them.
Designing Your Assignment
As you design your assignments, you'll want first to determine the outcomes that each assignment will work to accomplish. If your aim is to ensure, for instance, that students learn how to shape good academic questions, you might ask them to compose, share, and then revise their questions. If you want them to develop their research capabilities, have them take these questions to the library databases in order to look for appropriate sources. If you want to ensure that students learn how to work with sources, ask them to compose a summary and synthesis document, in which they nutshell their sources and show how these sources are in conversation with one another. Finally, if you want to ensure that they learn how to compose and revise, assign drafts and give them feedback. Have their peers offer feedback as well. Whatever you decide to assign, use the outcomes to guide you.
Second, you'll want to scaffold your assignments, so that students can build on their capabilities. You'll see in the examples cited in the paragraph above that each assignment builds on the one before. Students work on one step in the process and get feedback on it (from the instructor or their peers) before moving on to the next challenge. By scaffolding, instructors can be sure that students know how to successfully complete the final assignment. Students can also track the evolution and transfer of their skills.
Third, writing instructors frequently comment that Dartmouth's ten-week term is very short. Assignments must therefore be designed to achieve multiple outcomes. Consider the first step of the assignment sequence outlined above: "Ask students to compose, share, and then revise their questions." Several outcomes are achieved here: students are composing, they are collaborating, and they are revising. If you design your assignments to achieve multiple outcomes, you'll be surprised at how much your students can accomplish.
Whatever assignments you design, do understand that simply making an assignment does not ensure that students will acquire the desired skills. For an assignment to succeed it should be transparent and progressive—that is, your students should understand your goals for the assignment, and they should be able to chart their own development in relation to these goals. The better students understand your assignments and your vision for your course, the better they'll be able to meet the course aims.
Spacing Your Assignments
When designing your syllabus, you will want to consider carefully the spacing of your writing assignments. It's important that students are given enough time to write and to revise their papers. Professors who use a writing assistant will also want to be sure that they provide the writing assistant enough time to read and respond to students' papers.
Here are some things to consider:
- Give students time to move through the writing process. If you are teaching a first-year course whose purpose is to make students able writers, you will have to give them time to move through the various inventions, composing, and revision processes. One way of making room for these various steps in the writing process is by assigning a paper in three parts: the pre-draft (which could consist of crafting questions, writing a discovery draft, creating an outline, and so on), the first draft, and the revised final draft.
- Give students time to revise. If we want our students to revise their papers substantively, we must give them adequate time. This means that we need to get their papers back on time, particularly the first drafts. Consider whether you'll need two days, four days, or a full week to return an assignment. Also consider whether or not you expect the student to see a writing assistant or to meet with you between drafts.
- Try not to make a reading assignment on the day a major paper is due. Let your students focus their attention fully on their writing. Schedule writing workshops the day that a paper is due instead.
- Long assignments (particularly those that involve research) work better if you break them up into smaller assignments. Ask students to bring in an annotated bibliography, a working thesis, an outline, etc. Scheduling these shorter assignments ensures that students remain engaged in the writing process. It also prevents them from writing the paper at the last minute.
- Consider what's best for you. Many students and instructors like Monday due dates: students get the weekend to work on their papers, and professors keep their weekends free. Other instructors prefer for papers to come in on Thursday or Friday, so that they can use the weekends to respond. Think of your own rhythms as you plan.
Crafting Your Assignments
Professors often wonder, when creating writing assignments, how detailed the assignments should be. Some professors don't use prompts, requiring students to come up with the topics and questions themselves. Others create detailed writing assignments, arguing that this allows students to save energy for writing their papers (as opposed to generating topics and questions). Still others craft writing prompts that offer students ideas for writing but that leave plenty of room for students to come up with ideas of their own. We'll consider the options of prompting and not prompting here.
The Open Writing Assignment
Professors who don't use writing prompts believe that an important part of scholarship is learning to raise questions that will yield a good academic argument. Instead of creating a writing prompt, these professors craft an assignment process that supports students as they work through the various challenges of scholarly inquiry. In a sense, these professors are asking students to craft their own prompts, and to write the paper that will answer the questions that they outline there. The obvious pedagogical advantage of the open assignment is that it allows students to learn to develop topics on their own. In the open assignment, students are not only permitted to pursue intellectual questions that are of interest to them, they also gain some experience in framing a topic that is neither too narrow nor too broad.
If you elect not to use prompts, you should intend to devote class and conference time to assisting students in this process. For instance, you might ask students to come up with three good academic questions about the course's reading materials. Students can post these questions on the Canvas discussion board. You can then workshop these questions, using class time to talk about which questions will (or won't) yield a good academic argument, and why. You should also comment thoroughly on the questions submitted, raising further questions for the student to consider. You might also invite students to comment on one another's questions on the Canvas site. Students can then revise their questions and resubmit them for another round of feedback before they write.
Some professors find it useful to offer students models of good academic questions. Other professors give explicit instruction regarding what the paper shouldn't do and leave it to the students to determine what they want to do within these parameters. All professors ask students to submit their prompts in advance of drafting so that they can determine, before the students proceed too far, whether or not these topics are appropriate and promising.
Whatever you decide, do note that a prompt-less writing assignment needs a good infrastructure in order to succeed. Indeed, Karen Gocsik's research assignment for Writing 2-3 has twelve steps, indicating the many moments of support and feedback that first-year students require as they work through the process of writing a research paper Your assignment need not have twelve steps to be effective; it may have four steps, for instance, or five. Craft your assignment steps according to the aims of your assignment.
Crafting a Good Prompt
Writing a good prompt for a writing assignment is a difficult task. Too often, professors write prompts for writing assignments knowing exactly what sorts of essays they want their students to produce, only to get papers that miss the mark. How can you produce writing assignments that clearly convey the tasks and questions you want your students to undertake?
Before writing your prompts, you will want to consider a few matters.
- Consider what you want the assignment to require the students to do, in relation to the course outcomes. What outcomes are most important at this point in your course? How can the assignment move students closer to achieving these outcomes?
- Consider what you want the assignment to do, in terms of the larger questions of your course. What questions, in particular, do you want your students to consider? Are these questions related closely or peripherally to topics you've been discussing in class?
- Consider what kinds of thinking you want students to do. Do you want your students to define, illustrate, compare, analyze, or evaluate? You will want to come up with prompts that clearly direct students as to the kind of thinking they will have to do.
- Consider your students' writing processes. Are you focusing on teaching students to place their arguments within a larger conversation or context? If so, your prompt should address the importance of context and suggest things that you want students to consider as they write. Are you hoping to get your students to understand the mechanics of the paragraph? Your prompt might ask students to write paragraphs that summarize, then analyze, then synthesize, so that they can see how different tasks require different paragraph development.
- If the paper involves research, consider outlining your research requirements in a way that educates students about the research process. You may want to require students to use a variety of sources, or to use certain sources that you've either put on reserve or listed in the course syllabus. Understand that students may need help with finding sources, evaluating them, and incorporating them successfully into their arguments. Craft your prompt accordingly.
Once you've determined the outcomes for your writing assignment, you're ready to craft the prompt. Here are some things to consider:
- Break the assignment down into specific tasks. If, for example, you want students to compare the effectiveness of two political movements, you might first ask students to define the goals of each movement; then to consider the history of each movement; then to discuss how the history of the movement affected the creation of its goals; and finally, to consider how history influenced the movement's ultimate success (or failure).
- Break the assignment down into specific questions. For example, if you want students to discuss the formal elements of a particular painting, you might, as Art Historian Joy Kenseth does, ask the students: What is the focus of the painting? How does the artist treat such things as light and shadow, line, space, and composition? How does this treatment communicate the painting's ideas? If you don't want students to answer all of the questions you put to them, but want them simply to consider these questions before writing their responses, make that clear.
- Provide context. A writing prompt that asks students to discuss whether or not the films of Leni Riefenstahl are propagandistic does not point students to the interesting controversy surrounding Riefenstahl's work. Nor does it indicate whether they should limit themselves to discussing the formal elements of Riefenstahl's films, or whether they should include biographical detail. The more contextual information you give your students, the more precise their responses will be.
- Craft each sentence carefully. You will want to be sure that there is no room for misunderstanding the assignment. If you ask students to analyze how a myth informed paintings and sculptors during the first century of the Renaissance, do you want students to examine the works themselves or the artists that produced them? Sometimes a slip in word choice or the careless placement of a modifier can leave students confused as to what, precisely, you are asking them to do.
- Be clear about what you don't want. If you don't want students to discuss Virginia Woolf's personal experiences as they relate to A Room of One's Own , then be sure to instruct them not to include biographical references. In addition, explaining why such information should be excluded will help students to understand better the questions and the desired response.
- Be clear about the paper requirements. Have you indicated the paper's due date? How many pages you require? How many sources you require? What special criteria (if any) you will use when grading this paper? If your requirements are rigid, say so. If you're flexible, let the students know. This may be the aspect of the prompt that students are most anxious about, so offer as much detail as you think is necessary.
- Try to write (or at least to outline) the assignment yourself. If you have trouble outlining a paper based on this prompt, your students will, too. You will want to think about ways of revising the assignment to make it clearer and more manageable.
- Discuss the assignment with the class. When you distribute the assignment to the class, take time to go over it. Ask for their questions. Make notes as to where their understanding of the assignment differs from yours so that you can improve the prompt the next time you use it.

16 Meaningful Writing Activities that Engage Students
Looking for writing assignments middle and high school students actually enjoy? Yes! You’re in the right place for exploring relevant, integrated, and visually engaging writing activities.

When most teachers announce a new writing activity, students typically reply with moans, groans, or a sudden onset of stomach flu that requires a pass to the nurse's office right now . Which is your favorite response when you announce your middle or high school students will have the privilege to do some writing in your class? No teacher wants to bore or overwhelm students. Of course, we want to engage them, but writing is….well…an essential skill.
“Maybe essays are an antiquated practice,” someone recently commented in an online community. As I continued to read, I felt my brows furrow, my heart squeeze.
Effective communication in formal settings is extremely important. Students need to be prepared to identify their opinions, support them with solid evidence, identify counterclaims, synthesize ideas, and do it all in both formal and informal contexts.
While it would certainly be the easy thing to do, we can’t just throw essays out like bell bottom pants. Sometimes, students need to develop some grit. Essays? They help them to develop confidence, to think deeply, to take charge of their learning.
Literary analysis responses and argumentative essays are pillars of the secondary ELA curriculum.
Yet, part of the trick to helping students learn to enjoy writing is to build their confidence and stamina with smaller writing assignments that allow for more flexibility. After all, writing should also be a creative buzz that tugs at students’ emotions and provides them with an authentic audience.
Teachers should never feel like they have to sacrifice helping to cultivate a love for writing because of the demanding nature of more formal, academic writing. We really can live in the best of both worlds.
So, what types of writing activities do most middle and high school students actually enjoy? I’ll share my top 5 categories ( and 16 specific activities! ) of writing lessons that make students smile.

1. REAL-WORLD WRITING
Make writing relevant by connecting it to the real world.
WHY DID YOU GIVE ME A ZERO? I TURNED IN MY PAPER TODAY. PUT IN A GRADE PLEASE. MY PARENTS ARE GROUNDING ME. ALSO, WHAT IS THE EXTRA CREDIT?
Totally over rude, unaddressed student emails? I used to be offended, and then it dawned on me: They just don’t know. Students generally aren’t aware of their tone, let alone how to fix it.
So, I made a fun email etiquette unit to help give students a taste of real-world writing. Here’s what Sarah had to say about this lesson:
“Engaging, but more importantly: this resulted in much better emails from my students.”

2. RELEVANT WRITING
Picture this. Energetic lyrics fill the air as students listen, think critically, and analyze them. Or, students snap a photo of a page from an independent reading book, grinning as they annotate it with gifs, text, emojis, and more.
Spotify and Snapchat are extremely popular apps for students. So, let them channel those passions by creating booksnaps to make connections with a text or or playlists to capture the overarching theme of their year .
Moncada validates the power of tapping into social media for engagement with her review:
“Just what I was looking for to get my students fully engaged. In this era of instagram and snapchat, this tool is going to be a great addition to my lessons! Thanks!”

3. GRAMMAR THAT TRANSFERS TO WRITING
Students: When are we ever going to use this?!
You: Now, we are going to use this now. Because…grammar transfers to writing. That’s why we study it!
Grammar is most meaningful when students can both see and apply grammar lessons in their daily writing. A few of my favorite grammar lessons to teach (because they are interactive and provide multiple, scaffolded learning angles) are commas , prepositional phrases , and sentence types .
And, if you want students to go back and apply grammar to writing they’ve already completed, this free grammar in writing game is perfect for revision sessions!
There’s just something rewarding about working your patootie off, knowing you have learned a challenging skill, and then observing the growth as you apply the skill to something that matters.

4. POETRY Visuals
Reading poetry with students allows us to address several standards. For example, we can analyze complex texts, determine theme, evaluate mood and tone, and assess figurative language.
Unfortunately, the fact that we can address standards doesn’t impress students. So, what can we do to help them enjoy writing poetry or writing in response to it?
One way we can lure them in is by incorporating music and color. Think about tone and mood as being symbolic. What if we put them through a musical equalizer? I use a graphic organizer to help them visualize the mood and tone at different points throughout the text. Because of the color and the visual nature of the organizer, students can see how mood and tone change. Next? They write in response. What causes these fluctuations? How do the literary elements work together and influence one another?
Students DO enjoy poetry-related writing assignments. Try texting couplets (great for practicing rhythm and rhyme!), picture-inspired poetry (visuals are the best), and nonfiction-inspired poetry (because bringing a little creativity to informational texts changes everything).

5. VOCABULARY IN WRITING
The source said the health effects are good. [Sigh]
Tired of reading trite sentences? Helping students to bring life to their word choice in writing is inspiring for all. When I teach word choice lessons using class vocabulary, students experience one of the main reasons we study language. Plus, developing an appreciation for words results in a more curious life that connects to reading and writing.
One of my favorite word choice mini lessons involves bell ringers, word walls, and replacing cliches and colloquialisms with more formal, academic vocabulary.
Plus, you can have students use their vocabulary words in a variety of short creative and informative writing assignments that are not overwhelming for students or teachers but that allow for integration of vocabulary study with writing.
I can 100% relate to what this teacher shared after using these vocabulary in writing activities:
“I love how these activities get the students writing, and isn't that the whole purpose of teaching vocabulary…to ultimately get the students to use the words in their writing? Great activities and my students are enjoying using them.”
Out with the moans, groans, frustration, and suddenly urgent trips to the moon or anywhere outside of the classroom. Meaningful and engaging writing assignments include a dash of real-world, relevant writing opportunities, a pinch of skill transfer, and a sprinkling of creative freedom.
Let’s elevate students’ writing experiences while meeting standards. But, don’t forget to balance tough, academic-style writing with some more flexible options that will engage students and keep them thinking outside the box.
RELATED ARTICLES:
20 ways to engage middle and high school students, 3 high-interest writing assignments, 9 writing activities to use with any shakespeare play , spotlight resource:.
Teach students how to integrate all four sentence structures purposefully in writing with these engaging grammar and writing lessons . Perfect for scaffolding!

ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Melissa is the author of Reading and Writing Haven and a collaborative blogger on Teachwriting.org .
A middle and high school English teacher for over a decade now turned instructional coach, Melissa is an avid reader and writer, and she loves sharing ideas and collaborating with fellow educators. Melissa use her degrees in English, Curriculum & Instruction, and Reading as well as her Reading Specialist certification to ponder today’s educational issues while developing resources to help teachers, students, and parents make learning more relevant, meaningful, and engaging.
Visit Melissa on Instagram , Facebook , or Twitter for English teacher camaraderie and practical, engaging teaching ideas.

- Writing Activities
105 Creative Writing Exercises To Get You Writing Again
You know that feeling when you just don’t feel like writing? Sometimes you can’t even get a word down on paper. It’s the most frustrating thing ever to a writer, especially when you’re working towards a deadline. The good news is that we have a list of 105 creative writing exercises to help you get motivated and start writing again!
What are creative writing exercises?
Creative writing exercises are short writing activities (normally around 10 minutes) designed to get you writing. The goal of these exercises is to give you the motivation to put words onto a blank paper. These words don’t need to be logical or meaningful, neither do they need to be grammatically correct or spelt correctly. The whole idea is to just get you writing something, anything. The end result of these quick creative writing exercises is normally a series of notes, bullet points or ramblings that you can, later on, use as inspiration for a bigger piece of writing such as a story or a poem.
Good creative writing exercises are short, quick and easy to complete. You shouldn’t need to think too much about your style of writing or how imaginative your notes are. Just write anything that comes to mind, and you’ll be on the road to improving your creative writing skills and beating writer’s block .
Use the generator below to get a random creative writing exercise idea:
List of 105+ Creative Writing Exercises
Here are over 105 creative writing exercises to give your brain a workout and help those creative juices flow again:
- Set a timer for 60 seconds. Now write down as many words or phrases that come to mind at that moment.
- Pick any colour you like. Now start your sentence with this colour. For example, Orange, the colour of my favourite top.
- Open a book or dictionary on a random page. Pick a random word. You can close your eyes and slowly move your finger across the page. Now, write a paragraph with this random word in it. You can even use an online dictionary to get random words:
- Create your own alphabet picture book or list. It can be A to Z of animals, food, monsters or anything else you like!
- Using only the sense of smell, describe where you are right now.
- Take a snack break. While eating your snack write down the exact taste of that food. The goal of this creative writing exercise is to make your readers savour this food as well.
- Pick a random object in your room and write a short paragraph from its point of view. For example, how does your pencil feel? What if your lamp had feelings?
- Describe your dream house. Where would you live one day? Is it huge or tiny?
- Pick two different TV shows, movies or books that you like. Now swap the main character. What if Supergirl was in Twilight? What if SpongeBob SquarePants was in The Flash? Write a short scene using this character swap as inspiration.
- What’s your favourite video game? Write at least 10 tips for playing this game.
- Pick your favourite hobby or sport. Now pretend an alien has just landed on Earth and you need to teach it this hobby or sport. Write at least ten tips on how you would teach this alien.
- Use a random image generator and write a paragraph about the first picture you see.
- Write a letter to your favourite celebrity or character. What inspires you most about them? Can you think of a memorable moment where this person’s life affected yours? We have this helpful guide on writing a letter to your best friend for extra inspiration.
- Write down at least 10 benefits of writing. This can help motivate you and beat writer’s block.
- Complete this sentence in 10 different ways: Patrick waited for the school bus and…
- Pick up a random book from your bookshelf and go to page 9. Find the ninth sentence on that page. Use this sentence as a story starter.
- Create a character profile based on all the traits that you hate. It might help to list down all the traits first and then work on describing the character.
- What is the scariest or most dangerous situation you have ever been in? Why was this situation scary? How did you cope at that moment?
- Pretend that you’re a chat show host and you’re interviewing your favourite celebrity. Write down the script for this conversation.
- Using extreme detail, write down what you have been doing for the past one hour today. Think about your thoughts, feelings and actions during this time.
- Make a list of potential character names for your next story. You can use a fantasy name generator to help you.
- Describe a futuristic setting. What do you think the world would look like in 100 years time?
- Think about a recent argument you had with someone. Would you change anything about it? How would you resolve an argument in the future?
- Describe a fantasy world. What kind of creatures live in this world? What is the climate like? What everyday challenges would a typical citizen of this world face? You can use this fantasy world name generator for inspiration.
- At the flip of a switch, you turn into a dragon. What kind of dragon would you be? Describe your appearance, special abilities, likes and dislikes. You can use a dragon name generator to give yourself a cool dragon name.
- Pick your favourite book or a famous story. Now change the point of view. For example, you could rewrite the fairytale , Cinderella. This time around, Prince Charming could be the main character. What do you think Prince Charming was doing, while Cinderella was cleaning the floors and getting ready for the ball?
- Pick a random writing prompt and use it to write a short story. Check out this collection of over 300 writing prompts for kids to inspire you.
- Write a shopping list for a famous character in history. Imagine if you were Albert Einstein’s assistant, what kind of things would he shop for on a weekly basis?
- Create a fake advertisement poster for a random object that is near you right now. Your goal is to convince the reader to buy this object from you.
- What is the worst (or most annoying) sound that you can imagine? Describe this sound in great detail, so your reader can understand the pain you feel when hearing this sound.
- What is your favourite song at the moment? Pick one line from this song and describe a moment in your life that relates to this line.
- You’re hosting an imaginary dinner party at your house. Create a list of people you would invite, and some party invites. Think about the theme of the dinner party, the food you will serve and entertainment for the evening.
- You are waiting to see your dentist in the waiting room. Write down every thought you are having at this moment in time.
- Make a list of your greatest fears. Try to think of at least three fears. Now write a short story about a character who is forced to confront one of these fears.
- Create a ‘Wanted’ poster for a famous villain of your choice. Think about the crimes they have committed, and the reward you will give for having them caught.
- Imagine you are a journalist for the ‘Imagine Forest Times’ newspaper. Your task is to get an exclusive interview with the most famous villain of all time. Pick a villain of your choice and interview them for your newspaper article. What questions would you ask them, and what would their responses be?
- In a school playground, you see the school bully hurting a new kid. Write three short stories, one from each perspective in this scenario (The bully, the witness and the kid getting bullied).
- You just won $10 million dollars. What would you spend this money on?
- Pick a random animal, and research at least five interesting facts about this animal. Write a short story centred around one of these interesting facts.
- Pick a global issue that you are passionate about. This could be climate change, black lives matters, women’s rights etc. Now create a campaign poster for this global issue.
- Write an acrostic poem about an object near you right now (or even your own name). You could use a poetry idea generator to inspire you.
- Imagine you are the head chef of a 5-star restaurant. Recently the business has slowed down. Your task is to come up with a brand-new menu to excite customers. Watch this video prompt on YouTube to inspire you.
- What is your favourite food of all time? Imagine if this piece of food was alive, what would it say to you?
- If life was one big musical, what would you be singing about right now? Write the lyrics of your song.
- Create and describe the most ultimate villain of all time. What would their traits be? What would their past look like? Will they have any positive traits?
- Complete this sentence in at least 10 different ways: Every time I look out of the window, I…
- You have just made it into the local newspaper, but what for? Write down at least five potential newspaper headlines . Here’s an example, Local Boy Survives a Deadly Illness.
- If you were a witch or a wizard, what would your specialist area be and why? You might want to use a Harry Potter name generator or a witch name generator for inspiration.
- What is your favourite thing to do on a Saturday night? Write a short story centred around this activity.
- Your main character has just received the following items: A highlighter, a red cap, a teddy bear and a fork. What would your character do with these items? Can you write a story using these items?
- Create a timeline of your own life, from birth to this current moment. Think about the key events in your life, such as birthdays, graduations, weddings and so on. After you have done this, you can pick one key event from your life to write a story about.
- Think of a famous book or movie you like. Rewrite a scene from this book or movie, where the main character is an outsider. They watch the key events play out, but have no role in the story. What would their actions be? How would they react?
- Three very different characters have just won the lottery. Write a script for each character, as they reveal the big news to their best friend.
- Write a day in the life story of three different characters. How does each character start their day? What do they do throughout the day? And how does their day end?
- Write about the worst experience in your life so far. Think about a time when you were most upset or angry and describe it.
- Imagine you’ve found a time machine in your house. What year would you travel to and why?
- Describe your own superhero. Think about their appearance, special abilities and their superhero name. Will they have a secret identity? Who is their number one enemy?
- What is your favourite country in the world? Research five fun facts about this country and use one to write a short story.
- Set yourself at least three writing goals. This could be a good way to motivate yourself to write every day. For example, one goal might be to write at least 150 words a day.
- Create a character description based on the one fact, three fiction rule. Think about one fact or truth about yourself. And then add in three fictional or fantasy elements. For example, your character could be the same age as you in real life, this is your one fact. And the three fictional elements could be they have the ability to fly, talk in over 100 different languages and have green skin.
- Describe the perfect person. What traits would they have? Think about their appearance, their interests and their dislikes.
- Keep a daily journal or diary. This is a great way to keep writing every day. There are lots of things you can write about in your journal, such as you can write about the ‘highs’ and ‘lows’ of your day. Think about anything that inspired you or anything that upset you, or just write anything that comes to mind at the moment.
- Write a book review or a movie review. If you’re lost for inspiration, just watch a random movie or read any book that you can find. Then write a critical review on it. Think about the best parts of the book/movie and the worst parts. How would you improve the book or movie?
- Write down a conversation between yourself. You can imagine talking to your younger self or future self (i.e. in 10 years’ time). What would you tell them? Are there any lessons you learned or warnings you need to give? Maybe you could talk about what your life is like now and compare it to their life?
- Try writing some quick flash fiction stories . Flash fiction is normally around 500 words long, so try to stay within this limit.
- Write a six-word story about something that happened to you today or yesterday. A six-word story is basically an entire story told in just six words. Take for example: “Another football game ruined by me.” or “A dog’s painting sold for millions.” – Six-word stories are similar to writing newspaper headlines. The goal is to summarise your story in just six words.
- The most common monsters or creatures used in stories include vampires, werewolves , dragons, the bigfoot, sirens and the loch-ness monster. In a battle of intelligence, who do you think will win and why?
- Think about an important event in your life that has happened so far, such as a birthday or the birth of a new sibling. Now using the 5 W’s and 1 H technique describe this event in great detail. The 5 W’s include: What, Who, Where, Why, When and the 1 H is: How. Ask yourself questions about the event, such as what exactly happened on that day? Who was there? Why was this event important? When and where did it happen? And finally, how did it make you feel?
- Pretend to be someone else. Think about someone important in your life. Now put yourself into their shoes, and write a day in the life story about being them. What do you think they do on a daily basis? What situations would they encounter? How would they feel?
- Complete this sentence in at least 10 different ways: I remember…
- Write about your dream holiday. Where would you go? Who would you go with? And what kind of activities would you do?
- Which one item in your house do you use the most? Is it the television, computer, mobile phone, the sofa or the microwave? Now write a story of how this item was invented. You might want to do some research online and use these ideas to build up your story.
- In exactly 100 words, describe your bedroom. Try not to go over or under this word limit.
- Make a top ten list of your favourite animals. Based on this list create your own animal fact file, where you provide fun facts about each animal in your list.
- What is your favourite scene from a book or a movie? Write down this scene. Now rewrite the scene in a different genre, such as horror, comedy, drama etc.
- Change the main character of a story you recently read into a villain. For example, you could take a popular fairytale such as Jack and the Beanstalk, but this time re-write the story to make Jack the villain of the tale.
- Complete the following sentence in at least 10 different ways: Do you ever wonder…
- What does your name mean? Research the meaning of your own name, or a name that interests you. Then use this as inspiration for your next story. For example, the name ‘Marty’ means “Servant Of Mars, God Of War”. This could make a good concept for a sci-fi story.
- Make a list of three different types of heroes (or main characters) for potential future stories.
- If someone gave you $10 dollars, what would you spend it on and why?
- Describe the world’s most boring character in at least 100 words.
- What is the biggest problem in the world today, and how can you help fix this issue?
- Create your own travel brochure for your hometown. Think about why tourists might want to visit your hometown. What is your town’s history? What kind of activities can you do? You could even research some interesting facts.
- Make a list of all your favourite moments or memories in your life. Now pick one to write a short story about.
- Describe the scariest and ugliest monster you can imagine. You could even draw a picture of this monster with your description.
- Write seven haikus, one for each colour of the rainbow. That’s red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.
- Imagine you are at the supermarket. Write down at least three funny scenarios that could happen to you at the supermarket. Use one for your next short story.
- Imagine your main character is at home staring at a photograph. Write the saddest scene possible. Your goal is to make your reader cry when reading this scene.
- What is happiness? In at least 150 words describe the feeling of happiness. You could use examples from your own life of when you felt happy.
- Think of a recent nightmare you had and write down everything you can remember. Use this nightmare as inspiration for your next story.
- Keep a dream journal. Every time you wake up in the middle of the night or early in the morning you can quickly jot down things that you remember from your dreams. These notes can then be used as inspiration for a short story.
- Your main character is having a really bad day. Describe this bad day and the series of events they experience. What’s the worst thing that could happen to your character?
- You find a box on your doorstep. You open this box and see the most amazing thing ever. Describe this amazing thing to your readers.
- Make a list of at least five possible settings or locations for future stories. Remember to describe each setting in detail.
- Think of something new you recently learned. Write this down. Now write a short story where your main character also learns the same thing.
- Describe the most beautiful thing you’ve ever seen in your whole life. Your goal is to amaze your readers with its beauty.
- Make a list of things that make you happy or cheer you up. Try to think of at least five ideas. Now imagine living in a world where all these things were banned or against the law. Use this as inspiration for your next story.
- Would you rather be rich and alone or poor and very popular? Write a story based on the lives of these two characters.
- Imagine your main character is a Librarian. Write down at least three dark secrets they might have. Remember, the best secrets are always unexpected.
- There’s a history behind everything. Describe the history of your house. How and when was your house built? Think about the land it was built on and the people that may have lived here long before you.
- Imagine that you are the king or queen of a beautiful kingdom. Describe your kingdom in great detail. What kind of rules would you have? Would you be a kind ruler or an evil ruler of the kingdom?
- Make a wish list of at least three objects you wish you owned right now. Now use these three items in your next story. At least one of them must be the main prop in the story.
- Using nothing but the sense of taste, describe a nice Sunday afternoon at your house. Remember you can’t use your other senses (i.e see, hear, smell or touch) in this description.
- What’s the worst pain you felt in your life? Describe this pain in great detail, so your readers can also feel it.
- If you were lost on a deserted island in the middle of nowhere, what three must-have things would you pack and why?
- Particpate in online writing challenges or contests. Here at Imagine Forest, we offer daily writing challenges with a new prompt added every day to inspire you. Check out our challenges section in the menu.
Do you have any more fun creative writing exercises to share? Let us know in the comments below!

Marty the wizard is the master of Imagine Forest. When he's not reading a ton of books or writing some of his own tales, he loves to be surrounded by the magical creatures that live in Imagine Forest. While living in his tree house he has devoted his time to helping children around the world with their writing skills and creativity.
Related Posts

Comments loading...
The Portfolio – Culminating Activity (Your Final)
Portfolio assignment.
EN 111 Final Portfolio
The portfolio is a selection of work that demonstrates your writing abilities and knowledge about writing and critical thinking at the close of EN 111. For the purposes of this class, this assignment will be considered the final.
What goes in the Portfolio?
- Title page (title + optional picture and/or quote)
- Reflective Essay (~2 pages)
- A final (2nd) draft copy of all essays completed during the semester (Experience, Compare/Contrast, Issues) and the prior drafts for all essays.
- Selected Artifacts (2-3)
You should title the portfolio in a way that captures your sense of yourself as a writer and critical thinker at this point in your educational journey. You can include a picture and/or quote on the title page as well. A quote can come from anywhere (any text, movie, lyrics, etc.) but should illustrate your perspective about writing and/or critical thinking. You will discuss the significance of your title (picture and quote too if you included them) in your Reflective Essay.
Reflective Essay for Portfolio
The Reflective Essay is a self-assessment that examines the entire body of your work (all of your writing up to this point) rather than a single subject and/or inquiry thread. Your task is to examine, or reflect on , your own writing and situate your observations and interpretations within the context of our discussions about writing and critical thinking skills. The portfolio, in essence, is a presentation—a somewhat persuasive demonstration illustrating how you approached writing and critical thinking before EN 111, and how you see yourself, as a writer and thinker, now, in relation to these same abilities/skills at the close of the course.
What goes in the Reflective Essay?
This essay should be a fairly polished and focused piece of writing that supports its claims and reflections with specific evidence (i.e. cite yourself). It will run ~2 pages in length. All reflective essays should take into account the following, but not necessarily in the order presented here:
- The significance of your title (and picture and quote, if included).
- What you now understand about effective writing and how it is achieved and what the portfolio reveals about your writing and your abilities to think on paper. (Refer to your included essays and selected artifacts).
- What you now understand about writing and critical inquiry that this portfolio might not reveal. (You may understand more than your portfolio reveals).
- What the portfolio reveals about you as a writer and critical thinker at this point in your educational journey (Refer to your included essays and selected artifacts).
- What challenges you continue to face as writer and critical thinker. (What is hard for you? In what areas have you gotten stronger and more confident? What immediate goals have you set for yourself as you continue to develop as a writer and critical thinker?)
- (Optional) Discuss, document, and evaluate the extent to which you were actively engaged in this class (i.e. determine how much time/effort you put into this course and whether your writing reflects that same time/effort).
You are to include final (2nd) draft copies (at minimum) of all the essays you have written in this course. In including your essays, you will be expected to discuss why you have included them in your Reflective Essay, and explain specifically what they illustrate about you as a writer and critical thinker. As such, I recommend that you discuss how the essays reveal your analytical skills at work—your abilities to develop, examine, and communicate an informed perspective.
Selected Artifacts
I am asking you to include 2-3 artifacts from the course (or outside of EN 111) that are significant to, and reflective of, you in terms of yourself as a writer and critical thinker. You may select anything from your Informal Writing Collection (freewrites, peer exchanges, etc.), your formal writing (part of your essay(s), or parts of them as a sequence from the first draft to the final draft stage) or other texts (a particular paper or assignment from another class you found pertinent to your overall growth).
How Do I Submit It?
You should submit the portfolio, in the dropbox on the preceding page, as a Word document or a PDF so that I may open it in Microsoft Word or Adobe Acrobat Reader.
- Portfolio Assignment. Authored by : Jason Brown. Provided by : Herkimer College. Project : AtD OER Course. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more.
Assignments are typically designed to be completed outside of class time and may require independent research, critical thinking, and analysis. They are often graded and used as a significant component of a student’s overall course grade. The instructions for an assignment usually specify the goals, requirements, and deadlines for completion, and students are expected to meet these criteria to earn a good grade.
History of Assignment
The use of assignments as a tool for teaching and learning has been a part of education for centuries. Following is a brief history of the Assignment.
- Ancient Times: Assignments such as writing exercises, recitations, and memorization tasks were used to reinforce learning.
- Medieval Period : Universities began to develop the concept of the assignment, with students completing essays, commentaries, and translations to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of the subject matter.
- 19th Century : With the growth of schools and universities, assignments became more widespread and were used to assess student progress and achievement.
- 20th Century: The rise of distance education and online learning led to the further development of assignments as an integral part of the educational process.
- Present Day: Assignments continue to be used in a variety of educational settings and are seen as an effective way to promote student learning and assess student achievement. The nature and format of assignments continue to evolve in response to changing educational needs and technological innovations.
Types of Assignment
Here are some of the most common types of assignments:
An essay is a piece of writing that presents an argument, analysis, or interpretation of a topic or question. It usually consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Essay structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and thesis statement
- Body paragraphs : each paragraph presents a different argument or idea, with evidence and analysis to support it
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and reiterates the thesis statement
Research paper
A research paper involves gathering and analyzing information on a particular topic, and presenting the findings in a well-structured, documented paper. It usually involves conducting original research, collecting data, and presenting it in a clear, organized manner.
Research paper structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the paper, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the paper’s main points and conclusions
- Introduction : provides background information on the topic and research question
- Literature review: summarizes previous research on the topic
- Methodology : explains how the research was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the research
- Discussion : interprets the results and draws conclusions
- Conclusion : summarizes the key findings and implications
A case study involves analyzing a real-life situation, problem or issue, and presenting a solution or recommendations based on the analysis. It often involves extensive research, data analysis, and critical thinking.
Case study structure:
- Introduction : introduces the case study and its purpose
- Background : provides context and background information on the case
- Analysis : examines the key issues and problems in the case
- Solution/recommendations: proposes solutions or recommendations based on the analysis
- Conclusion: Summarize the key points and implications
A lab report is a scientific document that summarizes the results of a laboratory experiment or research project. It typically includes an introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Lab report structure:
- Title page : includes the title of the experiment, author’s name, date, and institution
- Abstract : summarizes the purpose, methodology, and results of the experiment
- Methods : explains how the experiment was conducted
- Results : presents the findings of the experiment
Presentation
A presentation involves delivering information, data or findings to an audience, often with the use of visual aids such as slides, charts, or diagrams. It requires clear communication skills, good organization, and effective use of technology.
Presentation structure:
- Introduction : introduces the topic and purpose of the presentation
- Body : presents the main points, findings, or data, with the help of visual aids
- Conclusion : summarizes the key points and provides a closing statement
Creative Project
A creative project is an assignment that requires students to produce something original, such as a painting, sculpture, video, or creative writing piece. It allows students to demonstrate their creativity and artistic skills.
Creative project structure:
- Introduction : introduces the project and its purpose
- Body : presents the creative work, with explanations or descriptions as needed
- Conclusion : summarizes the key elements and reflects on the creative process.
Examples of Assignments
Following are Examples of Assignment templates samples:
Essay template:
I. Introduction
- Hook: Grab the reader’s attention with a catchy opening sentence.
- Background: Provide some context or background information on the topic.
- Thesis statement: State the main argument or point of your essay.
II. Body paragraphs
- Topic sentence: Introduce the main idea or argument of the paragraph.
- Evidence: Provide evidence or examples to support your point.
- Analysis: Explain how the evidence supports your argument.
- Transition: Use a transition sentence to lead into the next paragraph.
III. Conclusion
- Restate thesis: Summarize your main argument or point.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your essay.
- Concluding thoughts: End with a final thought or call to action.
Research paper template:
I. Title page
- Title: Give your paper a descriptive title.
- Author: Include your name and institutional affiliation.
- Date: Provide the date the paper was submitted.
II. Abstract
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of your research.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct your research.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of your research.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions of your research.
III. Introduction
- Background: Provide some background information on the topic.
- Research question: State your research question or hypothesis.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your research.
IV. Literature review
- Background: Summarize previous research on the topic.
- Gaps in research: Identify gaps or areas that need further research.
V. Methodology
- Participants: Describe the participants in your study.
- Procedure: Explain the procedure you used to conduct your research.
- Measures: Describe the measures you used to collect data.
VI. Results
- Quantitative results: Summarize the quantitative data you collected.
- Qualitative results: Summarize the qualitative data you collected.
VII. Discussion
- Interpretation: Interpret the results and explain what they mean.
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your research.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of your research.
VIII. Conclusion
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your paper.
Case study template:
- Background: Provide background information on the case.
- Research question: State the research question or problem you are examining.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the case study.
II. Analysis
- Problem: Identify the main problem or issue in the case.
- Factors: Describe the factors that contributed to the problem.
- Alternative solutions: Describe potential solutions to the problem.
III. Solution/recommendations
- Proposed solution: Describe the solution you are proposing.
- Rationale: Explain why this solution is the best one.
- Implementation: Describe how the solution can be implemented.
IV. Conclusion
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your case study.
Lab report template:
- Title: Give your report a descriptive title.
- Date: Provide the date the report was submitted.
- Background: Summarize the background and purpose of the experiment.
- Methodology: Describe the methods you used to conduct the experiment.
- Results: Summarize the main findings of the experiment.
- Conclusion: Provide a brief summary of the implications and conclusions
- Background: Provide some background information on the experiment.
- Hypothesis: State your hypothesis or research question.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of the experiment.
IV. Materials and methods
- Materials: List the materials and equipment used in the experiment.
- Procedure: Describe the procedure you followed to conduct the experiment.
- Data: Present the data you collected in tables or graphs.
- Analysis: Analyze the data and describe the patterns or trends you observed.
VI. Discussion
- Implications: Discuss the implications of your findings.
- Limitations: Identify any limitations or weaknesses of the experiment.
VII. Conclusion
- Restate hypothesis: Summarize your hypothesis or research question.
- Review key points: Summarize the main points you made in your report.
Presentation template:
- Attention grabber: Grab the audience’s attention with a catchy opening.
- Purpose: Explain the purpose of your presentation.
- Overview: Provide an overview of what you will cover in your presentation.
II. Main points
- Main point 1: Present the first main point of your presentation.
- Supporting details: Provide supporting details or evidence to support your point.
- Main point 2: Present the second main point of your presentation.
- Main point 3: Present the third main point of your presentation.
- Summary: Summarize the main points of your presentation.
- Call to action: End with a final thought or call to action.
Creative writing template:
- Setting: Describe the setting of your story.
- Characters: Introduce the main characters of your story.
- Rising action: Introduce the conflict or problem in your story.
- Climax: Present the most intense moment of the story.
- Falling action: Resolve the conflict or problem in your story.
- Resolution: Describe how the conflict or problem was resolved.
- Final thoughts: End with a final thought or reflection on the story.
How to Write Assignment
Here is a general guide on how to write an assignment:
- Understand the assignment prompt: Before you begin writing, make sure you understand what the assignment requires. Read the prompt carefully and make note of any specific requirements or guidelines.
- Research and gather information: Depending on the type of assignment, you may need to do research to gather information to support your argument or points. Use credible sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
- Organize your ideas : Once you have gathered all the necessary information, organize your ideas into a clear and logical structure. Consider creating an outline or diagram to help you visualize your ideas.
- Write a draft: Begin writing your assignment using your organized ideas and research. Don’t worry too much about grammar or sentence structure at this point; the goal is to get your thoughts down on paper.
- Revise and edit: After you have written a draft, revise and edit your work. Make sure your ideas are presented in a clear and concise manner, and that your sentences and paragraphs flow smoothly.
- Proofread: Finally, proofread your work for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. It’s a good idea to have someone else read over your assignment as well to catch any mistakes you may have missed.
- Submit your assignment : Once you are satisfied with your work, submit your assignment according to the instructions provided by your instructor or professor.
Applications of Assignment
Assignments have many applications across different fields and industries. Here are a few examples:
- Education : Assignments are a common tool used in education to help students learn and demonstrate their knowledge. They can be used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic, to develop critical thinking skills, and to improve writing and research abilities.
- Business : Assignments can be used in the business world to assess employee skills, to evaluate job performance, and to provide training opportunities. They can also be used to develop business plans, marketing strategies, and financial projections.
- Journalism : Assignments are often used in journalism to produce news articles, features, and investigative reports. Journalists may be assigned to cover a particular event or topic, or to research and write a story on a specific subject.
- Research : Assignments can be used in research to collect and analyze data, to conduct experiments, and to present findings in written or oral form. Researchers may be assigned to conduct research on a specific topic, to write a research paper, or to present their findings at a conference or seminar.
- Government : Assignments can be used in government to develop policy proposals, to conduct research, and to analyze data. Government officials may be assigned to work on a specific project or to conduct research on a particular topic.
- Non-profit organizations: Assignments can be used in non-profit organizations to develop fundraising strategies, to plan events, and to conduct research. Volunteers may be assigned to work on a specific project or to help with a particular task.
Purpose of Assignment
The purpose of an assignment varies depending on the context in which it is given. However, some common purposes of assignments include:
- Assessing learning: Assignments are often used to assess a student’s understanding of a particular topic or concept. This allows educators to determine if a student has mastered the material or if they need additional support.
- Developing skills: Assignments can be used to develop a wide range of skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, research, and communication. Assignments that require students to analyze and synthesize information can help to build these skills.
- Encouraging creativity: Assignments can be designed to encourage students to be creative and think outside the box. This can help to foster innovation and original thinking.
- Providing feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for teachers to provide feedback to students on their progress and performance. Feedback can help students to understand where they need to improve and to develop a growth mindset.
- Meeting learning objectives : Assignments can be designed to help students meet specific learning objectives or outcomes. For example, a writing assignment may be designed to help students improve their writing skills, while a research assignment may be designed to help students develop their research skills.
When to write Assignment
Assignments are typically given by instructors or professors as part of a course or academic program. The timing of when to write an assignment will depend on the specific requirements of the course or program, but in general, assignments should be completed within the timeframe specified by the instructor or program guidelines.
It is important to begin working on assignments as soon as possible to ensure enough time for research, writing, and revisions. Waiting until the last minute can result in rushed work and lower quality output.
It is also important to prioritize assignments based on their due dates and the amount of work required. This will help to manage time effectively and ensure that all assignments are completed on time.
In addition to assignments given by instructors or professors, there may be other situations where writing an assignment is necessary. For example, in the workplace, assignments may be given to complete a specific project or task. In these situations, it is important to establish clear deadlines and expectations to ensure that the assignment is completed on time and to a high standard.
Characteristics of Assignment
Here are some common characteristics of assignments:
- Purpose : Assignments have a specific purpose, such as assessing knowledge or developing skills. They are designed to help students learn and achieve specific learning objectives.
- Requirements: Assignments have specific requirements that must be met, such as a word count, format, or specific content. These requirements are usually provided by the instructor or professor.
- Deadline: Assignments have a specific deadline for completion, which is usually set by the instructor or professor. It is important to meet the deadline to avoid penalties or lower grades.
- Individual or group work: Assignments can be completed individually or as part of a group. Group assignments may require collaboration and communication with other group members.
- Feedback : Assignments provide an opportunity for feedback from the instructor or professor. This feedback can help students to identify areas of improvement and to develop their skills.
- Academic integrity: Assignments require academic integrity, which means that students must submit original work and avoid plagiarism. This includes citing sources properly and following ethical guidelines.
- Learning outcomes : Assignments are designed to help students achieve specific learning outcomes. These outcomes are usually related to the course objectives and may include developing critical thinking skills, writing abilities, or subject-specific knowledge.
Advantages of Assignment
There are several advantages of assignment, including:
- Helps in learning: Assignments help students to reinforce their learning and understanding of a particular topic. By completing assignments, students get to apply the concepts learned in class, which helps them to better understand and retain the information.
- Develops critical thinking skills: Assignments often require students to think critically and analyze information in order to come up with a solution or answer. This helps to develop their critical thinking skills, which are important for success in many areas of life.
- Encourages creativity: Assignments that require students to create something, such as a piece of writing or a project, can encourage creativity and innovation. This can help students to develop new ideas and perspectives, which can be beneficial in many areas of life.
- Builds time-management skills: Assignments often come with deadlines, which can help students to develop time-management skills. Learning how to manage time effectively is an important skill that can help students to succeed in many areas of life.
- Provides feedback: Assignments provide an opportunity for students to receive feedback on their work. This feedback can help students to identify areas where they need to improve and can help them to grow and develop.
Limitations of Assignment
There are also some limitations of assignments that should be considered, including:
- Limited scope: Assignments are often limited in scope, and may not provide a comprehensive understanding of a particular topic. They may only cover a specific aspect of a topic, and may not provide a full picture of the subject matter.
- Lack of engagement: Some assignments may not engage students in the learning process, particularly if they are repetitive or not challenging enough. This can lead to a lack of motivation and interest in the subject matter.
- Time-consuming: Assignments can be time-consuming, particularly if they require a lot of research or writing. This can be a disadvantage for students who have other commitments, such as work or extracurricular activities.
- Unreliable assessment: The assessment of assignments can be subjective and may not always accurately reflect a student’s understanding or abilities. The grading may be influenced by factors such as the instructor’s personal biases or the student’s writing style.
- Lack of feedback : Although assignments can provide feedback, this feedback may not always be detailed or useful. Instructors may not have the time or resources to provide detailed feedback on every assignment, which can limit the value of the feedback that students receive.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

8 Ways to Create AI-Proof Writing Prompts
C reating 100 percent AI-proof writing prompts can often be impossible but that doesn’t mean there aren’t strategies that can limit the efficacy of AI work. These techniques can also help ensure more of the writing submitted in your classroom is human-generated.
I started seeing a big uptick in AI-generated work submitted in my classes over the last year and that has continued. As a result, I’ve gotten much better at recognizing AI work , but I’ve also gotten better at creating writing prompts that are less AI-friendly.
Essentially, I like to use the public health Swiss cheese analogy when thinking about AI prevention: All these strategies on their own have holes but when you layer the cheese together, you create a barrier that’s hard to get through.
The eight strategies here may not prevent students from submitting AI work, but I find these can incentivize human writing and make sure that any work submitted via AI will not really meet the requirements of the assignment.
1. Writing AI-Proof Prompts: Put Your Prompt Into Popular AI tools such as ChatGPT, Copilot, and Bard
Putting your writing prompt into an AI tools will give you an immediate idea of how most AI tools will handle your prompt. If the various AI chatbots do a good, or at least adequate, job immediately, it might be wise to tweak the prompt.
One of my classes asks students to write about a prized possession. When you put this prompt into an AI chatbot, it frequently returns an essay about a family member's finely crafted watch. Obviously, I now watch out for any essays about watches.
2. Forbid Cliché Use
Probably the quickest and easiest way to cut back on some AI use is to come down hard on cliché use in writing assignments. AI tools are essentially cliché machines, so banning these can prevent a lot of AI use.
Equally as important, this practice will help your students become better writers. As any good writer knows, clichés should be avoided like the plague.
3. Incorporate Recent Events
The free version of ChatGPT only has access to events up to 2022. While there are plugins to allow it to search the internet and other internet-capable AI tools, some students won’t get further than ChatGPT.
More importantly, in my experience, all AI tools struggle to incorporate recent events as effectively as historic ones. So connecting class material and assignments to events such as a recent State of Union speech or the Academy Awards will make any AI writing use less effective.
4. Require Quotes
AI tools can incorporate direct quotations but most are not very good at doing so. The quotes used tend to be very short and not as well-placed within essays.
Asking an AI tool for recent quotes also can be particularly problematic for today’s robot writers. For instance, I asked Microsoft's Copilot to summarize the recent Academy Awards using quotes, and specifically asked it to quote from Oppenheimer's director Christopher Nolan’s acceptance speech. It quoted something Nolan had previously said instead. Copilot also quoted from Wes Anderson’s acceptance speech, an obvious error since Anderson wasn’t at the awards .
5. Make Assignments Personal
Having students reflect on material in their own lives can be a good way to prevent AI writing. In-person teachers can get to know their students well enough to know when these types of personal details are fabricated.
I teach online but still find it easier to tell when a more personalized prompt was written by AI. For example, one student submitted a paper about how much she loved skateboarding that was so non-specific it screamed AI written. Another submitted a post about a pair of sneakers that was also clearly written by a "sole-less" AI (I could tell because of the clichés and other reasons).
6. Make Primary or Scholarly Sources Mandatory
Requiring sources that are not easily accessible on the internet can stop AI writing in its tracks. I like to have students find historic newspapers for certain assignments. The AI tools I am familiar with can’t incorporate these.
For instance, I asked Copilot to compare coverage of the first Academy Awards in the media to the most recent awards show and to include quotes from historic newspaper coverage. The comparison was not well done and there were no quotes from historical newspaper coverage.
AI tools also struggle to incorporate journal articles. Encouraging your students to include these types of sources ensures the work they produce is deeper than something that can be revealed by a quick Google search, which not only makes it harder for AI to write but also can raise the overall quality.
7. Require Interviews, Field Trips, Etc.
Building on primary and scholarly sources, you can have your students conduct interviews or go on field trips to historic sites, museums, etc.
AI is still, thankfully, incapable of engaging in these types of behavior. This requires too much work for every assignment but it is the most effective way to truly ensure your work is human- not computer-written.
If you’re still worried about AI use, you can even go a step further by asking your students to include photos of them with their interview subjects or from the field trips. Yes, AI art generators are getting better as well, but remember the Swiss cheese analogy? Every layer of prevention can help.
8. Have Students Write During Class
As I said to start, none of the methods discussed are foolproof. Many ways around these safeguards already exist and there will be more ways to bypass these in the future. So if you’re really, really worried about AI use you may want to choose what I call the “nuclear option.” If you teach in person you can require students to write essays in person.
This approach definitely works for preventing AI and is okay for short pieces, but for longer pieces, it has a lot of downsides. I would have trouble writing a long piece in this setting and imagine many students will as well. Additionally, this requirement could create an accusatory class atmosphere that is more focused on preventing AI use than actually teaching. It’s also not practical for online teaching.
That all being said, given how common AI writing has become in education, I understand why some teachers will turn to this method. Hopefully, suggestions 1-7 will work but if AI-generated papers are still out of hand in your classroom, this is a blunt-force method that can work temporarily.
Good luck and may your assignments be free of AI writing!
- 7 Ways To Detect AI Writing Without Technology
- Best Free AI Detection Sites
- My Student Was Submitting AI Papers. Here's What I Did

You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Professional learning
Teach. Learn. Grow.
Teach. learn. grow. the education blog.

Anchor your writing instruction in big ideas students can remember

Years later, when one of my journalism students won a Los Angeles Times award for news writing, I thought more deeply about the instructional changes I had made. I also thought about the social and emotional factors that likely enabled this once-timid reporter to tackle tough issues and blossom into an adept writer. What I realized from this exercise is that many of my instructional shifts had more to do with “leaning in” and getting to know my student as a writer, along with “letting go” of some outdated notions about what good writing is.
These are the three most important lessons I learned that I’d like to pass along.
Lesson #1: Writing instruction begins with a shared language for talking about writing and a shared understanding of the purposes for writing
Anchoring your instruction in a few big ideas that students can remember helps simplify the experience for everyone—and writing is always an experience.
As a new English language arts teacher, I often made writing more complicated than it needed to be. In my journalism classes, things were simple: we focused on the 5Ws and H (who? What? When? Where? Why? How?). It was easy for every student to remember and internalize these guiding questions.
If only there were a similar list of questions I could apply to other writing tasks! Over time, I found that there was. And at NWEA, I’ve had the opportunity to collaborate with current and former teachers to hone that list of essential questions down to the following five.
If anchoring your instruction in big ideas students can remember resonates with you, like it did for me, I encourage you to try incorporating these five essential questions into your writing curriculum.
We’ve even compiled these big ideas for growing writers into a free resource aimed at building a shared language for talking about writing with students. To that end, we’ve created a student version , too.
1. Why am I writing?
This question encourages students to ponder their purpose for writing. Often, their immediate response to this question is, “I’m writing because my teacher assigned me this essay/report/research paper.”
If we can get students to push past the idea of writing as an assignment and toward writing as a form of communication, we may see a dramatic increase in their motivation and writing quality. “What do you want to accomplish with this piece of writing?” becomes the question, not “What kind of writing does your teacher want from you?”
Writing is always the intellectual product of the writer, and the more we can encourage students to see themselves as writers and to take ownership of their writing, the better the results. Before students write, it’s critical they know and understand their purpose for writing, as this purpose informs so many other choices they will make.
2. Who are my readers?
This question forces students to consider their audience . When writers can anticipate the needs of their audience, they increase the effectiveness of their communication.
If the only audience a student ever has for their writing is a teacher, they lose the opportunity to make writerly decisions based on different audiences, such as considering their unique feelings and opinions about a topic, their different vocabularies (e.g., familiarity with code switching, idioms, or jargon), and their varying degrees of background knowledge. This is why giving students authentic writing tasks is so important . Authentic writing engages students in the same cognitive processes they use to write for real-world situations, such as applying for a job, taking civic action, or even communicating with family and friends.
3. What am I writing?
This question gets students to think more deeply about the task , genre , and form for their writing. While some of this information is likely included in the writing assignment, it’s still important for students to work through the task details on their own.
Students will make more informed writing decisions when they are able to clearly articulate the expectations and success criteria for a writing task . The writing genre provides another framework for students to think about their purpose for writing. Each genre’s unique features have developed over time through socially agreed-upon conventions, and experienced writers understand how to use these features to communicate more clearly with their audiences. Finally, form —or format—describes the type of text to be produced, and today’s writers have more forms to choose from—both analog and digital—than ever before.
When students put time and thought into their purpose, audience, and task, they have a greater command over their writing and what they want it to accomplish. And that’s when we get to see students’ communication skills and creativity truly shine through.
4. How am I presenting ideas in my writing?
This question addresses the myriad of choices a writer must make when they embark on a task, including decisions about writing development , organization , style , and conventions . Too often, this is where we ask students to start, and it can be overwhelming to make all these decisions before a student has wrapped their head around what they plan to write and why. In addition, while these writerly decisions are important, we may place too great an emphasis on a student’s final written product when a focus on their writing process may have more instructional utility.
My advice to students is, “Don’t sweat the small stuff when it comes to presenting ideas in your writing.” The ideas themselves are what’s most important. They’ll have numerous opportunities to practice and hone their writing development, organization, style, and conventions with every piece they write and over an entire lifetime.
5. How am I using the writing process?
This question reminds students that writing is both a product and a process . And the writing process is where much of the learning and critical thinking takes place.
Though writing is often taught as a sequence of forward-moving steps, the writing process is recursive and iterative, not linear . For example, writers go back and forth between planning, drafting, translating, reviewing, and revising to meet their writing goals, and writing goals can be self-generated or revised at any time during the writing process.
Writing itself is a work in progress that includes collaboration, self-regulation, and self-evaluation in addition to the other steps students typically learn. The more frequently students engage in and reflect on their own writing process, the more likely they are to develop productive and efficient writing habits, as well as growth mindsets that can help them overcome writing challenges in their school, career, and personal lives.
Lesson #2: Writing instruction is most impactful when it extends through professional learning communities (PLC) that offer students school-wide support for writing
As students move from grade to grade, a strong and coordinated PLC can help them build on what they already know about writing and focus on becoming even more expressive and effective writers.
In my first year of teaching, a colleague and I had an opportunity to attend a professional learning summit on writing. One session led by Harry Noden taught us how his Image Grammar could help students expand, vary, and improve their sentence structures. The majority of our student population was multilingual learners, and we rightly suspected that focused practice on writing, even at the sentence level, could increase language development in English . In part, this is because writing has a slower pace, provides a permanent record, and calls for greater precision in word choice.
We accurately assumed that sentence writing would benefit all our students , too. And once we were satisfied with the results, we leveraged our PLC to encourage a school-wide adoption of teaching grammar with Noden’s “brushstrokes.” We saw students quickly embrace the concept of “brushstrokes” because it positioned them as “artists” painting with words. This artistry was reinforced by the quality of their sentence writing. Often shared aloud, these sentences could be chill inducing they were so beautiful. For many students, this was their first proof they could be excellent writers, once they learned how.
Lesson #3: Writing outcomes can be improved through the use of common assessments and common rubrics at the school, district, or even state level
Common assessments and common rubrics help educators develop a shared understanding of how to evaluate writing. This includes providing students with meaningful feedback and grading writing more consistently across a school, district, or even state.
Coordination among teachers can help establish a school-wide writing community that all students can tap into for peer review. It can also lead to greater consistency in writing instruction and evaluation. Such consistency builds trust between students and teachers, which in turn can strengthen students’ view of themselves as learners and increase their motivation to learn .
When students don’t have to figure out individual teacher preferences for writing—and they feel confident every teacher will grade their writing for substance not style—they can focus their mental energy on becoming better writers. This includes developing their own sense of how to use language(s) effectively for personal, academic, and civic purposes.
One way to foster student-teacher collaboration is to encourage students to enter writing contests . Student writing contests can range from local to national, and it’s worth some extra effort to find ones that are a good fit for your students. Once my journalism students began entering (and winning!) writing contests, these events became an annual tradition. My students also became more willing to work on their digital portfolios throughout the year.
At the district level, common assessments and common rubrics can help leaders identify schools that need more support, such as more professional learning for educators or more high-dosage tutoring for students . They can also identify schools that have model instruction and can serve as resources for others. If you’re looking for a place to start in your district, the Literacy Design Collaborative offers common analytic rubrics for several writing genres , and the New York Performance Standards Consortium provides a robust set of performance-based assessments and rubrics .
Districts that use state rubrics in their common writing assessments help ensure all educators have similar expectations of student writing. If your state assesses writing, check the state department of education website for newly released writing assessments and their accompanying rubrics. And if your state doesn’t assess writing, they may still offer writing materials for teachers to use.
Finally, NWEA is often asked about the connection between MAP® Growth™ and writing. MAP Growth does not include writing prompts, so it can’t take the place of high-quality formative assessment in the classroom ; it simply wasn’t designed to assess students’ writing. But MAP Growth can provide insights into students’ strengths and opportunities for growth, and these insights are especially helpful when educators use an integrated approach to reading and writing instruction.
The MAP Growth instructional areas for reading, for example, offer some information about how well students understand literary text, informational text, and vocabulary. Students who are performing below grade-level for vocabulary would likely benefit from more explicit vocabulary instruction, including more strategic exposure to roots and affixes. This expanded vocabulary knowledge can later be applied to students’ writing. One approach is to have students “speak in synonyms,” a kind of oral rehearsal that can be done with peers or small groups and then integrated into a piece of student writing. Meanwhile, students who struggle to comprehend informational text might benefit from a self-regulated strategy development (SRSD) approach to writing . This method teaches students to recognize, internalize, and utilize important genre features in writing. And since reading and writing are related, SRSD can help improve students’ comprehension of informational texts, too.
A recap of lessons learned
Writing is hard, and teaching writing may be harder still. As educators, we continually learn new lessons about how to help our students (and ourselves) become better writers. I hope the three lessons I’ve shared here are helpful to you and bring you closer to having every student see themselves as a capable writer or, better yet, an artist painting with words.
Recommended for you

The science of teaching reading comprehension

6 strategies for teaching multisyllabic word reading

The science of reading explained

Helping students grow
Students continue to rebound from pandemic school closures. NWEA® and Learning Heroes experts talk about how best to support them here on our blog, Teach. Learn. Grow.
See the post

Put the science of reading into action
The science of reading is not a buzzword. It’s the converging evidence of what matters and what works in literacy instruction. We can help you make it part of your practice.
Get the guide

Support teachers with PL
High-quality professional learning can help teachers feel invested—and supported—in their work.
Read the article
STAY CURRENT by subscribing to our newsletter
You are now signed up to receive our newsletter containing the latest news, blogs, and resources from nwea..

Spotlight: Peter the Anteater’s Communication Assignment

The Communication Spotlight features innovative instructors who teach written, oral, digital/technological, kinetic, and visual communication modes.
Peter the Anteater is an instructor in the Department of Anthill Analysis and has been known to eat upwards of 100 termites a minute with his candle.
What is the assignment?
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur. Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident, sunt in culpa qui officia deserunt mollit anim id est laborum.
How does it work?
What do students say, student artifact: .

Why does this work?
You may also like....

Spotlight: Assigning a Creative Short Story in a Gender & Sexuality Studies Course
Dr. Mahaliah A. Little is a proud alumna of Spelman College and the UNCF Mellon Mays Undergraduate Fellowship. In addition to her research interests, she is passionate about feminist pedagogy, media literacy, and the teaching of writing. Check out some of her work...

Spotlight: Engaging Public Audiences with Multimedia
Christofer A. Rodelo is an assistant professor of Chicano/Latino Studies at the University of California, Irvine. A proud first-generation college student and queer Latinx scholar, he hails from the Inland Empire region of Southern California. He earned his Ph.D. in...
latest in US News

Texas boy, 10, confesses to killing a man in 2022, but he can't...

Rep. Ilhan Omar's first remarks since 21-year-old daughter...

Planes nearly collide on runway at Reagan National Airport...

Columbia anti-Israel protest arrests include Letitia James...

Hochul, Adams take victory lap on smoke shops crackdown — but...

FBI found it ‘alarming’ that Fauci-funded virus research at...

Susan Sarandon, ex-NYC prof who pulled machete on Post reporter...

NY farm that supplies Michelin-starred restaurant in hot water...
Outrage as high school student is suspended just for using the term ‘illegal alien’ in class discussion.
- View Author Archive
- Email the Author
- Follow on Twitter
- Get author RSS feed
Contact The Author
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
A 16-year-old North Carolina high school student says he was suspended just for saying “illegal alien” while discussing word meaning in English class — possibly ruining his chances of landing a college sports scholarship.
Christian McGhee, a student at Central Davidson High School in Lexington, received a three-day suspension last week after he used the term in English class, the Carolina Journal reported .
His mother, Leah McGhee, said his teacher had given an assignment that used the word “alien,” and Christian asked: “Like space aliens or illegal aliens without green cards?”
Another student reportedly took offense and threatened to fight Christian, so the teacher took the matter to the assistant principal, according to the Carolina Journal.

Eventually, his words were determined to be offensive and disrespectful to Hispanic classmates, so he was suspended.
“I didn’t make a statement directed towards anyone — I asked a question,” Christian told the outlet.
“I wasn’t speaking of Hispanics because everyone from other countries needs green cards, and the term ‘illegal alien’ is an actual term that I hear on the news and can find in the dictionary,” he added.
The suspension may also affect the student-athlete’s prospects of securing a college sports scholarship, the Journal noted.

“Because of his question, our son was disciplined and given THREE days OUT of school suspension for ‘racism,’” Leah wrote in an email describing the incident.
“He is devastated and concerned that the racism label on his school record will harm his future goal of receiving a track scholarship. We are concerned that he will fall behind in his classes due to being absent for three consecutive days,” she added in the message, which was shared with the outlet.
The irate mom said the assistant principal has refused to remove the suspension from the boy’s record, so the family has hired an attorney.

On Tuesday, Leah appeared on “The Pete Kaliner Show,” which airs on radio station WBT, and said her family had once lived in England, and Christian mentioned how Britons also need green cards to live in the US, Newsweek reported . She said she and her husband told the assistant principal that “illegal alien” is a term their son can look up in a dictionary. “It is a term used as federal code, and it is a term that is heard frequently on many news broadcasts,” Leah said on the show. “I feel that if this was handled properly in the classroom, it could have easily been used as a teachable moment for everyone.”
Republican state Sen. Steve Jarvis said he has contacted the school district superintendent about the matter — but he has not yet taken a stance on what should be done.
“I do not see that that would be an offensive statement, just in getting clarification,” Jarvis told the Journal. “But there again, I don’t know. I don’t know the situation of this particular incident.”
Keep up with today's most important news
Stay up on the very latest with Evening Update.
Thanks for signing up!
Please provide a valid email address.
By clicking above you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Never miss a story.
The popular X account Libs of TikTok also weighed in by saying Christian’s record could be “damaged” by the brouhaha over political correctness.
“Please support this based student by helping to raise awareness to his story!” the conservative account wrote in the post, which has received more than 4 million views.
Among those to respond was X owner Elon Musk, who wrote: “This is absurd.”
Conservative personality Ian Miles Chong called it “insane.”

“How does one get suspended for using the term illegal alien?” he asked.
Libs of TikTok added: “Hopefully North Carolina officials can step in and ensure his record isn’t tarnished in any way because he’s trying to secure an athletic scholarship for college.
“He should not be persecuted for using the correct term just because the left is trying to change our entire language,” the account added.
A staffer at Central Davidson High School told Newsweek that they could not comment about a specific student due to federal protections.
“Please know that Davidson County Schools administrators take all discipline incidents seriously and investigate each one thoroughly,” the rep told the mag. “Any violation of the code of conduct is handled appropriately by administrators.”
The student handbook says that “schools may place restrictions on a student’s right to free speech when the speech is obscene, abusive, promoting illegal drug use, or is reasonably expected to cause a substantial disruption to the school day,” the Carolina Journal reported.
Share this article:

Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this course, you'll learn all about academic essay writing and, specifically, how to write three types of essays: compare/contrast, cause/effect, and argument. To pass this course, you need to pass all four quizzes and pass all three writing assignments. When you finish one activity, you can continue to the next one.
Common Writing Assignments. These OWL resources will help you understand and complete specific types of writing assignments, such as annotated bibliographies, book reports, and research papers. This section also includes resources on writing academic proposals for conference presentations, journal articles, and books.
Course description. Writing reports and assignments can be a daunting prospect. Learn how to interpret questions and how to plan, structure and write your assignment or report. This free course, Essay and report writing skills, is designed to help you develop the skills you need to write effectively for academic purposes.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
This course on Writing in the Disciplines offers a modular curriculum that explores the meaning of genre, why and how to develop genre-based writing assignments, and effective techniques for using writing to enhance learning. Academic Writing in English for ESL Learners University College London via FutureLearn
Designing Effective Writing Assignments. One of the best ways for students to determine what they know, think, and believe about a given subject is to write about it. To support students in their writing, it is important to provide them with a meaningful writing task, one that has an authentic purpose, clear guidelines, and engages students in ...
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You'll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you'll be expected to write your essays, research papers, and dissertation in academic style. Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but ...
This resource describes some steps you can take to better understand the requirements of your writing assignments. This resource works for either in-class, teacher-led discussion or for personal use. ... as we discussed in class, or a printout of an Open Mind project. It must be a minimum of 1 page typed information, plus 1 page outline. This ...
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount: 1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it. However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you're inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit ...
Crafting Assignment Sequences. A well-designed writing assignment can give students the chance to engage course material in a deep, sustained, and individual way, and to learn essential aspects of writing in a particular discipline. A well-designed assignment can also prepare students for the ultimate challenge—writing on a topic of their own ...
Writing Assignments Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine. Figure 19.1 Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Image by Kampus Production used under CC0 licence. Introduction. Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research.
Many of these exercises can be used in short in-class writing assignments, as part of group work, or as incremental steps in producing a paper. If you've assigned an end-of-semester term paper, you may want to assign one or two activities from each of the four stages-brainstorming, organizing, drafting, editing-at strategic points throughout ...
Additional tips for writing an Assignment Prompt. ... This may include application of course concepts, addressing the multiple parts of the prompt, use of sources, writing skills/errors, etc. Include the percentage or points possible for each category. Leave room in this area to input the student's score, or create a separate column for this.
Establish small groups. Set up small writing groups of three-five students from the class. Allow them to meet for a few minutes in class or have them arrange a meeting outside of class to comment constructively on each other's drafts. The students do not need to be writing on the same topic. Require consultations.
Writing in college is usually a response to class materials—an assigned reading, a discussion in class, an experiment in a lab. Generally speaking, these writing tasks can be divided into three broad categories: summary assignments, defined-topic assignments, and undefined-topic assignments.
Builds writing confidence through frequent informal writing, and introductions to key learning strategies. Includes user-friendly orientation to library and research documents, revision skills, and peer review work central to 100- and 200-level college writing assignments. Offered: A.
In-class writing gives students a chance to gather and focus their thoughts and, when shared, gives the teacher an opportunity to see students' thinking processes. Teachers can ask one or two students to read their responses, or they can collect a random sampling of responses to read after class. Since students are always eager to hear what ...
The Quill Lessons tool enables teachers to lead whole-class and small-group writing instruction. Teachers control interactive slides that contain writing prompts, and the entire class responds to each prompt. Each Quill Lessons activity provides a lesson plan, writing prompts, discussion topics, and a follow up independent practice activity.
In the first-year writing classes, an instructor's set of outcomes will be informed by the course outcomes (see the outcomes for Writing 2-3, Writing 5, or the First-Year Seminar). Take some time to review these outcomes, and to consider how every assignment and classroom activity might work to help students achieve them.
2. RELEVANT WRITING. Picture this. Energetic lyrics fill the air as students listen, think critically, and analyze them. Or, students snap a photo of a page from an independent reading book, grinning as they annotate it with gifs, text, emojis, and more. Spotify and Snapchat are extremely popular apps for students.
Here are over 105 creative writing exercises to give your brain a workout and help those creative juices flow again: Set a timer for 60 seconds. Now write down as many words or phrases that come to mind at that moment. Pick any colour you like. Now start your sentence with this colour.
The portfolio is a selection of work that demonstrates your writing abilities and knowledge about writing and critical thinking at the close of EN 111. For the purposes of this class, this assignment will be considered the final. What goes in the Portfolio? Title page (title + optional picture and/or quote) Reflective Essay (~2 pages) A final ...
Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more. Assignments are typically designed to be completed outside of class ...
5. Make Assignments Personal. Having students reflect on material in their own lives can be a good way to prevent AI writing. In-person teachers can get to know their students well enough to know ...
5. How am I using the writing process? This question reminds students that writing is both a product and a process. And the writing process is where much of the learning and critical thinking takes place. Though writing is often taught as a sequence of forward-moving steps, the writing process is recursive and iterative, not linear. For example ...
Spotlight: Assigning a Creative Short Story in a Gender & Sexuality Studies Course Dr. Mahaliah A. Little is a proud alumna of Spelman College and the UNCF Mellon Mays Undergraduate Fellowship. In addition to her research interests, she is passionate about feminist pedagogy, media literacy, and the teaching of writing.
A 16-year-old North Carolina high school student says he was suspended just for saying "illegal alien" while discussing word meaning in English class -- possibly ruining his chances of landing a ...