- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Poetry Worksheet Bundle! Perfect for National Poetry Month.

100+ Critical Thinking Questions for Students To Ask About Anything
Critical thinkers question everything.

In an age of “fake news” claims and constant argument about pretty much any issue, critical thinking skills are key. Teach your students that it’s vital to ask questions about everything, but that it’s also important to ask the right sorts of questions. Students can use these critical thinking questions with fiction or nonfiction texts. They’re also useful when discussing important issues or trying to understand others’ motivations in general.
“Who” Critical Thinking Questions
Questions like these help students ponder who’s involved in a story and how the actions affect them. They’ll also consider who’s telling the tale and how reliable that narrator might be.
- Is the protagonist?
- Is the antagonist?
- Caused harm?
- Is harmed as a result?
- Was the most important character?
- Is responsible?
- Is most directly affected?
- Should have won?
- Will benefit?
- Would be affected by this?

- Makes the decisions?
“What” Critical Thinking Questions
Ask questions that explore issues more deeply, including those that might not be directly answered in the text.
- Background information do I know or need to know?
- Is the main message?
- Are the defining characteristics?

- Questions or concerns do I have?
- Don’t I understand?
- Evidence supports the author’s conclusion?
- Would it be like if … ?
- Could happen if … ?
- Other outcomes might have happened?
- Questions would you have asked?
- Would you ask the author about … ?
- Was the point of … ?
- Should have happened instead?
- Is that character’s motive?
- Else could have changed the whole story?

- Can you conclude?
- Would your position have been in that situation?
- Would happen if … ?
- Makes your position stronger?
- Was the turning point?
- Is the point of the question?
- Did it mean when … ?
- Is the other side of this argument?
- Was the purpose of … ?
- Does ______ mean?
- Is the problem you are trying to solve?
- Does the evidence say?
- Assumptions are you making?
- Is a better alternative?
- Are the strengths of the argument?
- Are the weaknesses of the argument?
- Is the difference between _______ and _______?
“Where” Critical Thinking Questions
Think about where the story is set and how it affects the actions. Plus, consider where and how you can learn more.
- Would this issue be a major problem?
- Are areas for improvement?
- Did the story change?
- Would you most often find this problem?

- Are there similar situations?
- Would you go to get answers to this problem?
- Can this be improved?
- Can you get more information?
- Will this idea take us?
“When” Critical Thinking Questions
Think about timing and the effect it has on the characters or people involved.
- Is this acceptable?
- Is this unacceptable?

- Does this become a problem?
- Is the best time to take action?
- Will we be able to tell if it worked?
- Is it time to reassess?
- Should we ask for help?
- Is the best time to start?
- Is it time to stop?
- Would this benefit society?

- Has this happened before?
“Why” Critical Thinking Questions
Asking “why” might be one of the most important parts of critical thinking. Exploring and understanding motivation helps develop empathy and make sense of difficult situations.
- Is _________ happening?
- Have we allowed this to happen?
- Should people care about this issue?

- Is this a problem?
- Did the character say … ?
- Did the character do … ?
- Is this relevant?
- Did the author write this?
- Did the author decide to … ?
- Is this important?
- Did that happen?
- Is it necessary?
- Do you think I (he, she, they) asked that question?
- Is that answer the best one?
- Do we need this today?
“How” Critical Thinking Questions
Use these questions to consider how things happen and whether change is possible.
- Do we know this is true?
- Does the language used affect the story?
- Would you solve … ?
- Is this different from other situations?

- Is this similar to … ?
- Would you use … ?
- Does the location affect the story?
- Could the story have ended differently?
- Does this work?
- Could this be harmful?
- Does this connect with what I already know?
- Else could this have been handled?
- Should they have responded?

- Would you feel about … ?
- Does this change the outcome?
- Did you make that decision?
- Does this benefit you/others?
- Does this hurt you/others?
- Could this problem be avoided?
More Critical Thinking Questions
Here are more questions to help probe further and deepen understanding.
- Can you give me an example?

- Do you agree with … ?
- Can you compare this with … ?
- Can you defend the actions of … ?
- Could this be interpreted differently?
- Is the narrator reliable?
- Does it seem too good to be true?

- Is ______ a fact or an opinion?
What are your favorite critical thinking questions? Come exchange ideas on the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, check out 10 tips for teaching kids to be awesome critical thinkers ., you might also like.

5 Critical Thinking Skills Every Kid Needs To Learn (And How To Teach Them)
Teach them to thoughtfully question the world around them. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
41+ Critical Thinking Examples (Definition + Practices)

Critical thinking is an essential skill in our information-overloaded world, where figuring out what is fact and fiction has become increasingly challenging.
But why is critical thinking essential? Put, critical thinking empowers us to make better decisions, challenge and validate our beliefs and assumptions, and understand and interact with the world more effectively and meaningfully.
Critical thinking is like using your brain's "superpowers" to make smart choices. Whether it's picking the right insurance, deciding what to do in a job, or discussing topics in school, thinking deeply helps a lot. In the next parts, we'll share real-life examples of when this superpower comes in handy and give you some fun exercises to practice it.
Critical Thinking Process Outline
Critical thinking means thinking clearly and fairly without letting personal feelings get in the way. It's like being a detective, trying to solve a mystery by using clues and thinking hard about them.
It isn't always easy to think critically, as it can take a pretty smart person to see some of the questions that aren't being answered in a certain situation. But, we can train our brains to think more like puzzle solvers, which can help develop our critical thinking skills.
Here's what it looks like step by step:
Spotting the Problem: It's like discovering a puzzle to solve. You see that there's something you need to figure out or decide.
Collecting Clues: Now, you need to gather information. Maybe you read about it, watch a video, talk to people, or do some research. It's like getting all the pieces to solve your puzzle.
Breaking It Down: This is where you look at all your clues and try to see how they fit together. You're asking questions like: Why did this happen? What could happen next?
Checking Your Clues: You want to make sure your information is good. This means seeing if what you found out is true and if you can trust where it came from.
Making a Guess: After looking at all your clues, you think about what they mean and come up with an answer. This answer is like your best guess based on what you know.
Explaining Your Thoughts: Now, you tell others how you solved the puzzle. You explain how you thought about it and how you answered.
Checking Your Work: This is like looking back and seeing if you missed anything. Did you make any mistakes? Did you let any personal feelings get in the way? This step helps make sure your thinking is clear and fair.
And remember, you might sometimes need to go back and redo some steps if you discover something new. If you realize you missed an important clue, you might have to go back and collect more information.
Critical Thinking Methods
Just like doing push-ups or running helps our bodies get stronger, there are special exercises that help our brains think better. These brain workouts push us to think harder, look at things closely, and ask many questions.
It's not always about finding the "right" answer. Instead, it's about the journey of thinking and asking "why" or "how." Doing these exercises often helps us become better thinkers and makes us curious to know more about the world.
Now, let's look at some brain workouts to help us think better:
1. "What If" Scenarios
Imagine crazy things happening, like, "What if there was no internet for a month? What would we do?" These games help us think of new and different ideas.
Pick a hot topic. Argue one side of it and then try arguing the opposite. This makes us see different viewpoints and think deeply about a topic.
3. Analyze Visual Data
Check out charts or pictures with lots of numbers and info but no explanations. What story are they telling? This helps us get better at understanding information just by looking at it.
4. Mind Mapping
Write an idea in the center and then draw lines to related ideas. It's like making a map of your thoughts. This helps us see how everything is connected.
There's lots of mind-mapping software , but it's also nice to do this by hand.
5. Weekly Diary
Every week, write about what happened, the choices you made, and what you learned. Writing helps us think about our actions and how we can do better.
6. Evaluating Information Sources
Collect stories or articles about one topic from newspapers or blogs. Which ones are trustworthy? Which ones might be a little biased? This teaches us to be smart about where we get our info.
There are many resources to help you determine if information sources are factual or not.
7. Socratic Questioning
This way of thinking is called the Socrates Method, named after an old-time thinker from Greece. It's about asking lots of questions to understand a topic. You can do this by yourself or chat with a friend.
Start with a Big Question:
"What does 'success' mean?"
Dive Deeper with More Questions:
"Why do you think of success that way?" "Do TV shows, friends, or family make you think that?" "Does everyone think about success the same way?"
"Can someone be a winner even if they aren't rich or famous?" "Can someone feel like they didn't succeed, even if everyone else thinks they did?"
Look for Real-life Examples:
"Who is someone you think is successful? Why?" "Was there a time you felt like a winner? What happened?"
Think About Other People's Views:
"How might a person from another country think about success?" "Does the idea of success change as we grow up or as our life changes?"
Think About What It Means:
"How does your idea of success shape what you want in life?" "Are there problems with only wanting to be rich or famous?"
Look Back and Think:
"After talking about this, did your idea of success change? How?" "Did you learn something new about what success means?"
8. Six Thinking Hats
Edward de Bono came up with a cool way to solve problems by thinking in six different ways, like wearing different colored hats. You can do this independently, but it might be more effective in a group so everyone can have a different hat color. Each color has its way of thinking:
White Hat (Facts): Just the facts! Ask, "What do we know? What do we need to find out?"
Red Hat (Feelings): Talk about feelings. Ask, "How do I feel about this?"
Black Hat (Careful Thinking): Be cautious. Ask, "What could go wrong?"
Yellow Hat (Positive Thinking): Look on the bright side. Ask, "What's good about this?"
Green Hat (Creative Thinking): Think of new ideas. Ask, "What's another way to look at this?"
Blue Hat (Planning): Organize the talk. Ask, "What should we do next?"
When using this method with a group:
- Explain all the hats.
- Decide which hat to wear first.
- Make sure everyone switches hats at the same time.
- Finish with the Blue Hat to plan the next steps.
9. SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis is like a game plan for businesses to know where they stand and where they should go. "SWOT" stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
There are a lot of SWOT templates out there for how to do this visually, but you can also think it through. It doesn't just apply to businesses but can be a good way to decide if a project you're working on is working.
Strengths: What's working well? Ask, "What are we good at?"
Weaknesses: Where can we do better? Ask, "Where can we improve?"
Opportunities: What good things might come our way? Ask, "What chances can we grab?"
Threats: What challenges might we face? Ask, "What might make things tough for us?"
Steps to do a SWOT Analysis:
- Goal: Decide what you want to find out.
- Research: Learn about your business and the world around it.
- Brainstorm: Get a group and think together. Talk about strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Pick the Most Important Points: Some things might be more urgent or important than others.
- Make a Plan: Decide what to do based on your SWOT list.
- Check Again Later: Things change, so look at your SWOT again after a while to update it.
Now that you have a few tools for thinking critically, let’s get into some specific examples.
Everyday Examples
Life is a series of decisions. From the moment we wake up, we're faced with choices – some trivial, like choosing a breakfast cereal, and some more significant, like buying a home or confronting an ethical dilemma at work. While it might seem that these decisions are disparate, they all benefit from the application of critical thinking.
10. Deciding to buy something
Imagine you want a new phone. Don't just buy it because the ad looks cool. Think about what you need in a phone. Look up different phones and see what people say about them. Choose the one that's the best deal for what you want.
11. Deciding what is true
There's a lot of news everywhere. Don't believe everything right away. Think about why someone might be telling you this. Check if what you're reading or watching is true. Make up your mind after you've looked into it.
12. Deciding when you’re wrong
Sometimes, friends can have disagreements. Don't just get mad right away. Try to see where they're coming from. Talk about what's going on. Find a way to fix the problem that's fair for everyone.
13. Deciding what to eat
There's always a new diet or exercise that's popular. Don't just follow it because it's trendy. Find out if it's good for you. Ask someone who knows, like a doctor. Make choices that make you feel good and stay healthy.
14. Deciding what to do today
Everyone is busy with school, chores, and hobbies. Make a list of things you need to do. Decide which ones are most important. Plan your day so you can get things done and still have fun.
15. Making Tough Choices
Sometimes, it's hard to know what's right. Think about how each choice will affect you and others. Talk to people you trust about it. Choose what feels right in your heart and is fair to others.
16. Planning for the Future
Big decisions, like where to go to school, can be tricky. Think about what you want in the future. Look at the good and bad of each choice. Talk to people who know about it. Pick what feels best for your dreams and goals.
Job Examples
17. solving problems.
Workers brainstorm ways to fix a machine quickly without making things worse when a machine breaks at a factory.
18. Decision Making
A store manager decides which products to order more of based on what's selling best.
19. Setting Goals
A team leader helps their team decide what tasks are most important to finish this month and which can wait.
20. Evaluating Ideas
At a team meeting, everyone shares ideas for a new project. The group discusses each idea's pros and cons before picking one.
21. Handling Conflict
Two workers disagree on how to do a job. Instead of arguing, they talk calmly, listen to each other, and find a solution they both like.
22. Improving Processes
A cashier thinks of a faster way to ring up items so customers don't have to wait as long.
23. Asking Questions
Before starting a big task, an employee asks for clear instructions and checks if they have the necessary tools.
24. Checking Facts
Before presenting a report, someone double-checks all their information to make sure there are no mistakes.
25. Planning for the Future
A business owner thinks about what might happen in the next few years, like new competitors or changes in what customers want, and makes plans based on those thoughts.
26. Understanding Perspectives
A team is designing a new toy. They think about what kids and parents would both like instead of just what they think is fun.
School Examples
27. researching a topic.
For a history project, a student looks up different sources to understand an event from multiple viewpoints.
28. Debating an Issue
In a class discussion, students pick sides on a topic, like school uniforms, and share reasons to support their views.
29. Evaluating Sources
While writing an essay, a student checks if the information from a website is trustworthy or might be biased.
30. Problem Solving in Math
When stuck on a tricky math problem, a student tries different methods to find the answer instead of giving up.
31. Analyzing Literature
In English class, students discuss why a character in a book made certain choices and what those decisions reveal about them.
32. Testing a Hypothesis
For a science experiment, students guess what will happen and then conduct tests to see if they're right or wrong.
33. Giving Peer Feedback
After reading a classmate's essay, a student offers suggestions for improving it.
34. Questioning Assumptions
In a geography lesson, students consider why certain countries are called "developed" and what that label means.
35. Designing a Study
For a psychology project, students plan an experiment to understand how people's memories work and think of ways to ensure accurate results.
36. Interpreting Data
In a science class, students look at charts and graphs from a study, then discuss what the information tells them and if there are any patterns.
Critical Thinking Puzzles
Not all scenarios will have a single correct answer that can be figured out by thinking critically. Sometimes we have to think critically about ethical choices or moral behaviors.
Here are some mind games and scenarios you can solve using critical thinking. You can see the solution(s) at the end of the post.
37. The Farmer, Fox, Chicken, and Grain Problem
A farmer is at a riverbank with a fox, a chicken, and a grain bag. He needs to get all three items across the river. However, his boat can only carry himself and one of the three items at a time.
Here's the challenge:
- If the fox is left alone with the chicken, the fox will eat the chicken.
- If the chicken is left alone with the grain, the chicken will eat the grain.
How can the farmer get all three items across the river without any item being eaten?
38. The Rope, Jar, and Pebbles Problem
You are in a room with two long ropes hanging from the ceiling. Each rope is just out of arm's reach from the other, so you can't hold onto one rope and reach the other simultaneously.
Your task is to tie the two rope ends together, but you can't move the position where they hang from the ceiling.
You are given a jar full of pebbles. How do you complete the task?
39. The Two Guards Problem
Imagine there are two doors. One door leads to certain doom, and the other leads to freedom. You don't know which is which.
In front of each door stands a guard. One guard always tells the truth. The other guard always lies. You don't know which guard is which.
You can ask only one question to one of the guards. What question should you ask to find the door that leads to freedom?
40. The Hourglass Problem
You have two hourglasses. One measures 7 minutes when turned over, and the other measures 4 minutes. Using just these hourglasses, how can you time exactly 9 minutes?
41. The Lifeboat Dilemma
Imagine you're on a ship that's sinking. You get on a lifeboat, but it's already too full and might flip over.
Nearby in the water, five people are struggling: a scientist close to finding a cure for a sickness, an old couple who've been together for a long time, a mom with three kids waiting at home, and a tired teenager who helped save others but is now in danger.
You can only save one person without making the boat flip. Who would you choose?
42. The Tech Dilemma
You work at a tech company and help make a computer program to help small businesses. You're almost ready to share it with everyone, but you find out there might be a small chance it has a problem that could show users' private info.
If you decide to fix it, you must wait two more months before sharing it. But your bosses want you to share it now. What would you do?
43. The History Mystery
Dr. Amelia is a history expert. She's studying where a group of people traveled long ago. She reads old letters and documents to learn about it. But she finds some letters that tell a different story than what most people believe.
If she says this new story is true, it could change what people learn in school and what they think about history. What should she do?
The Role of Bias in Critical Thinking
Have you ever decided you don’t like someone before you even know them? Or maybe someone shared an idea with you that you immediately loved without even knowing all the details.
This experience is called bias, which occurs when you like or dislike something or someone without a good reason or knowing why. It can also take shape in certain reactions to situations, like a habit or instinct.
Bias comes from our own experiences, what friends or family tell us, or even things we are born believing. Sometimes, bias can help us stay safe, but other times it stops us from seeing the truth.
Not all bias is bad. Bias can be a mechanism for assessing our potential safety in a new situation. If we are biased to think that anything long, thin, and curled up is a snake, we might assume the rope is something to be afraid of before we know it is just a rope.
While bias might serve us in some situations (like jumping out of the way of an actual snake before we have time to process that we need to be jumping out of the way), it often harms our ability to think critically.
How Bias Gets in the Way of Good Thinking
Selective Perception: We only notice things that match our ideas and ignore the rest.
It's like only picking red candies from a mixed bowl because you think they taste the best, but they taste the same as every other candy in the bowl. It could also be when we see all the signs that our partner is cheating on us but choose to ignore them because we are happy the way we are (or at least, we think we are).
Agreeing with Yourself: This is called “ confirmation bias ” when we only listen to ideas that match our own and seek, interpret, and remember information in a way that confirms what we already think we know or believe.
An example is when someone wants to know if it is safe to vaccinate their children but already believes that vaccines are not safe, so they only look for information supporting the idea that vaccines are bad.
Thinking We Know It All: Similar to confirmation bias, this is called “overconfidence bias.” Sometimes we think our ideas are the best and don't listen to others. This can stop us from learning.
Have you ever met someone who you consider a “know it”? Probably, they have a lot of overconfidence bias because while they may know many things accurately, they can’t know everything. Still, if they act like they do, they show overconfidence bias.
There's a weird kind of bias similar to this called the Dunning Kruger Effect, and that is when someone is bad at what they do, but they believe and act like they are the best .
Following the Crowd: This is formally called “groupthink”. It's hard to speak up with a different idea if everyone agrees. But this can lead to mistakes.
An example of this we’ve all likely seen is the cool clique in primary school. There is usually one person that is the head of the group, the “coolest kid in school”, and everyone listens to them and does what they want, even if they don’t think it’s a good idea.
How to Overcome Biases
Here are a few ways to learn to think better, free from our biases (or at least aware of them!).
Know Your Biases: Realize that everyone has biases. If we know about them, we can think better.
Listen to Different People: Talking to different kinds of people can give us new ideas.
Ask Why: Always ask yourself why you believe something. Is it true, or is it just a bias?
Understand Others: Try to think about how others feel. It helps you see things in new ways.
Keep Learning: Always be curious and open to new information.
In today's world, everything changes fast, and there's so much information everywhere. This makes critical thinking super important. It helps us distinguish between what's real and what's made up. It also helps us make good choices. But thinking this way can be tough sometimes because of biases. These are like sneaky thoughts that can trick us. The good news is we can learn to see them and think better.
There are cool tools and ways we've talked about, like the "Socratic Questioning" method and the "Six Thinking Hats." These tools help us get better at thinking. These thinking skills can also help us in school, work, and everyday life.
We’ve also looked at specific scenarios where critical thinking would be helpful, such as deciding what diet to follow and checking facts.
Thinking isn't just a skill—it's a special talent we improve over time. Working on it lets us see things more clearly and understand the world better. So, keep practicing and asking questions! It'll make you a smarter thinker and help you see the world differently.
Critical Thinking Puzzles (Solutions)
The farmer, fox, chicken, and grain problem.
- The farmer first takes the chicken across the river and leaves it on the other side.
- He returns to the original side and takes the fox across the river.
- After leaving the fox on the other side, he returns the chicken to the starting side.
- He leaves the chicken on the starting side and takes the grain bag across the river.
- He leaves the grain with the fox on the other side and returns to get the chicken.
- The farmer takes the chicken across, and now all three items -- the fox, the chicken, and the grain -- are safely on the other side of the river.
The Rope, Jar, and Pebbles Problem
- Take one rope and tie the jar of pebbles to its end.
- Swing the rope with the jar in a pendulum motion.
- While the rope is swinging, grab the other rope and wait.
- As the swinging rope comes back within reach due to its pendulum motion, grab it.
- With both ropes within reach, untie the jar and tie the rope ends together.
The Two Guards Problem
The question is, "What would the other guard say is the door to doom?" Then choose the opposite door.
The Hourglass Problem
- Start both hourglasses.
- When the 4-minute hourglass runs out, turn it over.
- When the 7-minute hourglass runs out, the 4-minute hourglass will have been running for 3 minutes. Turn the 7-minute hourglass over.
- When the 4-minute hourglass runs out for the second time (a total of 8 minutes have passed), the 7-minute hourglass will run for 1 minute. Turn the 7-minute hourglass again for 1 minute to empty the hourglass (a total of 9 minutes passed).
The Boat and Weights Problem
Take the cat over first and leave it on the other side. Then, return and take the fish across next. When you get there, take the cat back with you. Leave the cat on the starting side and take the cat food across. Lastly, return to get the cat and bring it to the other side.
The Lifeboat Dilemma
There isn’t one correct answer to this problem. Here are some elements to consider:
- Moral Principles: What values guide your decision? Is it the potential greater good for humanity (the scientist)? What is the value of long-standing love and commitment (the elderly couple)? What is the future of young children who depend on their mothers? Or the selfless bravery of the teenager?
- Future Implications: Consider the future consequences of each choice. Saving the scientist might benefit millions in the future, but what moral message does it send about the value of individual lives?
- Emotional vs. Logical Thinking: While it's essential to engage empathy, it's also crucial not to let emotions cloud judgment entirely. For instance, while the teenager's bravery is commendable, does it make him more deserving of a spot on the boat than the others?
- Acknowledging Uncertainty: The scientist claims to be close to a significant breakthrough, but there's no certainty. How does this uncertainty factor into your decision?
- Personal Bias: Recognize and challenge any personal biases, such as biases towards age, profession, or familial status.
The Tech Dilemma
Again, there isn’t one correct answer to this problem. Here are some elements to consider:
- Evaluate the Risk: How severe is the potential vulnerability? Can it be easily exploited, or would it require significant expertise? Even if the circumstances are rare, what would be the consequences if the vulnerability were exploited?
- Stakeholder Considerations: Different stakeholders will have different priorities. Upper management might prioritize financial projections, the marketing team might be concerned about the product's reputation, and customers might prioritize the security of their data. How do you balance these competing interests?
- Short-Term vs. Long-Term Implications: While launching on time could meet immediate financial goals, consider the potential long-term damage to the company's reputation if the vulnerability is exploited. Would the short-term gains be worth the potential long-term costs?
- Ethical Implications : Beyond the financial and reputational aspects, there's an ethical dimension to consider. Is it right to release a product with a known vulnerability, even if the chances of it being exploited are low?
- Seek External Input: Consulting with cybersecurity experts outside your company might be beneficial. They could provide a more objective risk assessment and potential mitigation strategies.
- Communication: How will you communicate the decision, whatever it may be, both internally to your team and upper management and externally to your customers and potential users?
The History Mystery
Dr. Amelia should take the following steps:
- Verify the Letters: Before making any claims, she should check if the letters are actual and not fake. She can do this by seeing when and where they were written and if they match with other things from that time.
- Get a Second Opinion: It's always good to have someone else look at what you've found. Dr. Amelia could show the letters to other history experts and see their thoughts.
- Research More: Maybe there are more documents or letters out there that support this new story. Dr. Amelia should keep looking to see if she can find more evidence.
- Share the Findings: If Dr. Amelia believes the letters are true after all her checks, she should tell others. This can be through books, talks, or articles.
- Stay Open to Feedback: Some people might agree with Dr. Amelia, and others might not. She should listen to everyone and be ready to learn more or change her mind if new information arises.
Ultimately, Dr. Amelia's job is to find out the truth about history and share it. It's okay if this new truth differs from what people used to believe. History is about learning from the past, no matter the story.
Related posts:
- Experimenter Bias (Definition + Examples)
- Hasty Generalization Fallacy (31 Examples + Similar Names)
- Ad Hoc Fallacy (29 Examples + Other Names)
- Confirmation Bias (Examples + Definition)
- Equivocation Fallacy (26 Examples + Description)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test

Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
What Crystal Do I Need Quiz
How to hide an electrical cord: 9 steps, 3 ways to do yo-yo tricks, 3 easy ways to set up an easel, 14 simple ways to unblock your throat chakra, 3 ways to convert mpg to liters per 100km, how to open urls on android: 7 steps, 14 easy ways to be alone after a breakup, 3 ways to build an arcade cabinet, how to update a graphics card: 12 steps, 16 critical thinking questions for students.

Introduction:
Critical thinking is an essential skill for students to develop, as it enables them to analyze information, evaluate arguments, and make informed decisions. To enhance critical thinking abilities, students can engage with thought-provoking questions that challenge assumptions and encourage deeper reflection. In this article, we present sixteen critical thinking questions that will stimulate their cognitive abilities and foster intellectual growth.
1. What evidence supports this argument?
Assessing the evidence behind an argument encourages students to analyze whether it is sufficient, credible, and logically sound. This question teaches them to question the basis of statements and seek supporting evidence.
2. How can you apply this concept in real-life situations?
Connecting abstract concepts to practical scenarios helps students understand the relevance and applicability of what they learn. This question encourages them to think beyond classroom discussions and consider real-world implications.
3. What are the underlying assumptions in this statement?
Identifying assumptions allows students to recognize hidden biases or prejudices in arguments. By questioning underlying assumptions, they can develop a more nuanced understanding of complex issues.
4. Can you think of alternative explanations?
Encouraging students to consider alternative explanations fosters their ability to think critically and challenge initial conclusions. This question helps them explore different perspectives and understand that there can be multiple plausible interpretations.
5. How might different cultural perspectives influence this situation?
Recognizing the impact of cultural perspectives on opinions and decisions develops students’ cultural sensitivity and empathy. By considering diverse viewpoints, they broaden their understanding of complex issues.
6. What are the ethical implications of this decision?
Evaluating ethical consequences encourages students to consider the wider implications of their choices. This question enables them to develop ethical reasoning and become responsible decision-makers.
7. Can you identify any logical fallacies in this argument?
Recognizing logical fallacies helps students evaluate the validity of arguments and avoid common errors in their own reasoning. This question hones their critical thinking skills by identifying flaws in reasoning.
8. How might this situation change if key variables were altered?
By altering key variables, students can explore the potential impact of different factors on a given situation. This question enhances their ability to anticipate and evaluate different scenarios.
9. What are the potential biases in this research study?
Assessing biases in research studies equips students with the skills to critically evaluate scientific literature. This question prompts them to consider possible biases and influences on research outcomes.
10. What are the counterarguments to this position?
Encouraging students to examine counterarguments encourages them to think beyond their initial beliefs and consider opposing viewpoints. This question develops their ability to engage in respectful and constructive debates.
11. How does this information relate to your prior knowledge on the subject?
Connecting new information to existing knowledge aids student comprehension and reinforces critical thinking. This question prompts them to reflect on the relevance of new knowledge in relation to what they already know.
12. What are the short-term and long-term consequences of this decision?
Considering the short-term and long-term consequences helps students make more informed decisions. This question encourages them to think beyond immediate outcomes and consider broader impacts.
13. What are the potential biases in this news article?
Examining biases in news articles helps students distinguish between objective and subjective information. This question fosters media literacy skills and enables them to critically analyze news sources.
14. Can you identify any logical inconsistencies in this theory?
Identifying logical inconsistencies enables students to evaluate the coherence and validity of theories. This question promotes critical thinking by challenging the logical structure of theories.
15. How does this information challenge or confirm your existing beliefs?
Engaging with information that challenges personal beliefs helps students develop intellectual flexibility and open-mindedness. This question encourages them to critically evaluate their own perspectives.
16. What are the implications of this historical event in today’s society?
Connecting historical events to contemporary issues fosters students’ ability to recognize patterns and understand the relevance of the past. This question prompts critical analysis of history’s impact on the present.
Conclusion:
Engaging with these sixteen critical thinking questions will empower students to become active learners, capable of analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information effectively. By consistently challenging their assumptions, seeking evidence, and considering diverse perspectives, students will develop robust critical thinking skills that will benefit them throughout their academic and professional journeys.
How to Make a Fake Rock: 13 ...
14 times star wars pretty much summed ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

Why Being a Teacher is So Difficult Right Now

Read-Aloud Strategies for Grades 4 and Up

15 Free Seesaw Activities and Resources For Every Kind of Classroom

10 Smart Ideas for Integrating Language Arts and Social Studies

16 Alternative Assessment Ideas

I am a Public School Teacher: Here’s What That Means to Me
K-12 Resources By Teachers, For Teachers Provided by the K-12 Teachers Alliance
- Teaching Strategies
- Classroom Activities
- Classroom Management
- Technology in the Classroom
- Professional Development
- Lesson Plans
- Writing Prompts
- Graduate Programs
Effective Critical-Thinking Questions to Use in Class
Jessica shaffer.
- May 17, 2021

What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking does not have just one definition, but one way to explain it is that it is “thinking about one’s thinking.” A critical thinker does not always take things at face value and will question ideas to further understand them. Critical thinkers also have the ability to see past the surface of something, and they possess important skills such as the ability to analyze, interpret, make inferences, and problem-solve. Critical thinkers also tend to be inquisitive about many issues, have a concern to remain well-informed, and embrace and even seek out critical thinking opportunities. Simply stated, critical thinkers think deep thoughts.
What is the Importance of Critical Thinking for Students?
Back in the day, school was different! Honestly, even a year ago, school was far different than it is now, but there is currently so much more emphasis on the “why” and the “how” than just knowing what the answer is. Critical thinking skills are important for students because of the curricula they are exposed to. “Right there” questions are few and far between and students have to rely on their own ability to dig deeper and read between the lines. There is a lot of emphasis placed on college and career readiness, and part of that is to prepare students to problem solve when there is no apparent answer.
Critical thinking provides students opportunities to acquire the higher-level thinking skills that will be needed for career and beyond. It is important to teach students at a young age that you cannot find the answer to everything in a book or through Google. You have to look within yourself to find many answers and, most importantly, justify why that is your answer. There are many ways teachers can incorporate these types of questions throughout the day, you just have to change your mindset a bit!
Critical Thinking Questions to Use in Class
A teacher will ask questions that usually contain one of the following components: who, what, where, when, how, or why. Using good questioning techniques is important and not always as difficult as it seems. Just changing the way that you start a question can change the way students think about an answer or solution. For example, instead of asking students “Who stole the pizza?”, ask students, “Why would that character want to steal the pizza?”
A critical thinking question should aim to make you think. It should lead students to ponder the answer and discuss possible solutions. Critical thinking questions can even lead to disagreements and arguments that can turn into an impressive teachable moment.
One way to incorporate a solid critical thinking question into a math lesson is to have the students solve a problem, and then ask students how they solved the problem. You can have the students talk it out or have each student write down a written explanation and then share it out. Either of these techniques gives various perspectives on how to solve the same problems and can help students to develop math sense.
Another way to incorporate critical thinking questions into math is to present a problem that is solved incorrectly and have students analyze the mistake. Students will have to solve for the correct answer and determine where the mistake occurred. To make this even more challenging, present a word problem or a multi-step story problem to further present critical thinking challenges.
Making inferences is generally one of the most difficult skills for students to learn. This is where students must use their critical thinking skills to understand what is not written or observed. Students must use evidence and couple it with reasoning skills to form a conclusion. A basic example would be looking at a photograph of a dog holding a leash in its mouth and coming to the conclusion that the dog would like to go for a walk.
Morning journals for students can present the perfect opportunity to enhance critical thinking skills. Instead of asking basic questions with basic answers, create questions that force students to think outside the box. For example, ask the question, “Is creativity something that can be measured? Should it be?” Instead of asking what creativity is and giving an example, this question makes a student pause and think about the answer before beginning to respond. These are the types of questions that can frustrate students “in a good way.”
A great way to encourage critical thinking in ELA is to ask students to write an alternate ending to a story. This promotes creativity and deep thinking. Then, students can explain how changing the ending of the story could have an impact on not just the novel, but the world. Encouraging students to think on a more global level also encourages a higher-level of thinking as well as a better understanding of the culture of the world, not just the small bubble they reside in.
Science is a subject perfect for inquiry! Having students think as an engineer would is a critical thinking skill at it’s finest. Students have to design a solution, test it, and then design an even better solution in order to combat weaknesses in the original design. This can be applied at any grade level.
A terrific way to incorporate critical thinking in Social Studies is similar to ELA by changing the outcome of important events in history. For example, have students discuss how our lives would be different if the Civil War had been won by the South. How would it have changed subsequent events in our history and what would life be like today? The opportunities are endless.
Ending Thoughts
All in all, teachers can create many opportunities each and every day for students to use critical thinking skills. It is as simple as starting the day off with a critical thinking question and changing certain techniques. Even if you ask the students a basic question, follow it up with something that requires more depth of thought. As the great Albert Einstein once said, “Education is not the learning of facts, but the training of the mind to think.” Force students to think about their thinking, and get them ready for the real world!
- #CriticalThinking , #TeachingStrategies
More in Teaching Strategies

Helping Students Improve Their Handwriting
Despite the widespread use of technology in the classroom, handwriting remains an essential…

Unleashing the Learning Potential of Classroom Focus Walls
Focus walls have emerged as an effective tool in today’s classrooms, and for…

Getting Older Students Excited About Science Class
As students move into middle and high school, it becomes increasingly challenging for…

AI-Powered Lesson Planning: Revolutionizing the Way Teachers Create Content
Traditional teaching methods are evolving since technology has been integrated into classrooms across…
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Don't Miss a Post! Subscribe
- Guest Posts

- Educational AI
- Edtech Tools
- Edtech Apps
- Teacher Resources
- Special Education
- Edtech for Kids
- Buying Guides for Teachers

Educators Technology
Innovative EdTech for teachers, educators, parents, and students
Examples of Critical Thinking Questions for Students
By Med Kharbach, PhD | Last Update: November 10, 2023
Critical thinking is an essential cognitive skill that entails the ability to reason, analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information. It goes beyond mere acquisition of knowledge. Instead, it involves deep, reflective thought, demanding us to question our assumptions, weigh evidence, and consider consequences. It’s about making clear, reasoned judgments. In essence, critical thinking is thinking about thinking, in a manner that allows us to improve the quality of our thinking.

In our daily lives, critical thinking helps us better understand ourselves, other people, and the world around us. It aids in problem solving, aids in the formation of beliefs and opinions, and encourages curiosity and creativity.
For example, when you’re faced with a major decision like purchasing a house, critical thinking enables you to weigh the pros and cons, assess the credibility of your sources of information, consider alternative options, and make a well-informed decision.
In professional situations, critical thinking is equally important. It helps us navigate complex work situations, make informed decisions, solve problems efficiently, and think creatively. For instance, if a company faces a decline in sales, critical thinking would help diagnose the root cause of the issue, evaluate different strategies to address the problem, and make effective decisions to rectify the situation.
The importance of critical thinking is particularly crucial for students. It provides them with the necessary skills to understand complex concepts, evaluate the credibility of sources, engage in thoughtful discussions, and develop reasoned arguments. It lays the foundation for lifelong learning and the ability to adapt to an ever-changing world.
This brings us to the concept of critical thinking questions . These are questions that are specifically designed to promote critical thinking. They go beyond factual inquiries, prompting individuals to analyze, synthesize, apply, and evaluate information. Critical thinking questions challenge the conventional wisdom and encourage individuals to think deeper, questioning the why’s and how’s.
They serve as a tool to spark intellectual engagement and stimulate thoughtful and reflective responses. As we delve further into this blog post, we will explore different types of critical thinking questions and how they can be applied in various contexts.
Related: Best TED Ed Lessons on Critical Thinking
Tips on Formulating Critical Thinking Questions
Creating good critical thinking questions involves understanding the basics of inquiry and knowing how to stimulate higher order thinking. Here are some tips and steps on formulating effective critical thinking questions:
Characteristics of Good Critical Thinking Questions:
- Open-Ended: Good critical thinking questions are typically open-ended, meaning they don’t have a single, simple answer. They invite students to think deeply and come up with their unique insights.
- Thought-Provoking: Effective questions challenge assumptions and encourage students to think creatively and critically. They provoke curiosity and exploration.
- Promote Discussion: The questions should stimulate meaningful discussions. The responses to these questions should not end the conversation, but rather, foster a deeper exploration of the topic.
- Clear and Understandable: The question should be framed in such a way that it is clear and easy to understand. Confusing questions can deter students from critical thinking.
Steps to Create Effective Critical Thinking Questions:
- Identify Your Learning Goals: Start by figuring out what you want your students to learn or achieve. Your question should align with these learning goals.
- Consider the Cognitive Level: Depending on the depth of thinking you want to stimulate, frame your questions accordingly. For instance, for higher order thinking, you might want to ask analysis, evaluation, or creation questions.
- Draft Your Question: Begin drafting your question. Remember, the best questions are open-ended and require more than a yes or no answer.
- Refine Your Question: Review your question. Is it clear? Does it promote discussion? Does it align with your learning goals? Refine as necessary.
- Test Your Question: Try out your question with a few students or colleagues to see if it stimulates the kind of discussion you’re hoping for. Be open to further refining your question based on the results.
Keep in mind that the goal of asking questions is not to ‘stump’ the students, but to promote intellectual engagement and thought. The best questions often lead to more questions, igniting a passion for learning and exploration.
Types of critical thinking questions
Critical thinking questions can be divided into the following categories:
1. Analysis Questions
Analysis questions ask the respondent to break a concept or idea into its component parts for examination. These questions can help uncover underlying structures, patterns, or meanings. They often involve words like “compare”, “contrast”, “classify”, “divide”, etc.
Example: “Compare the political ideologies of democratic socialism and laissez-faire capitalism. What are the similarities and differences between them?”
2. Evaluation Questions
Evaluation questions call for the respondent to make a judgment about the value of something, based on defined criteria. They often use terms like “critique”, “justify”, “validate”, “defend”, etc.
Example: “Evaluate the effectiveness of the government’s pandemic response measures. What were the successes and shortcomings?”
3. Inference Questions
Inference questions require the respondent to go beyond what is explicitly stated and make logical conclusions or predictions based on the information provided. Key words often include “infer”, “deduce”, “predict”, “conclude”, etc.
Example: “Given the recent surge in online shopping trends, what can you infer about the future of brick-and-mortar retail stores?”
4. Application Questions
Application questions involve applying knowledge or concepts to new situations or contexts. These questions often involve “applying”, “utilizing”, “implementing”, or “executing” learned knowledge.
Example: “How would you apply the principles of conflict resolution that we studied to resolve a disagreement in your workplace?”
5. Synthesis Questions
Synthesis questions invite the respondent to combine different pieces of information, ideas, or concepts to form a new whole or propose a solution. Words often associated with these questions are “design”, “formulate”, “propose”, “create”, etc.
Example: “Based on your understanding of climate change and renewable technologies, propose a comprehensive strategy for a city to reduce its carbon footprint.”
These types of questions, when used in the appropriate contexts, can help foster a deep level of understanding and stimulate higher-level thinking.
Examples of Critical thinking Questions
Here are some examples of critical questions that you can use to stimulate students’ critical thinking skills, encouraging them to analyze, evaluate, and create new ideas based on what they’ve learned.
- What do you think would happen if…?
- Can you explain why…?
- How would you solve this problem using different strategies?
- Can you compare and contrast these two concepts?
- How can you demonstrate your understanding of this concept in a different way?
- How would you categorize these items, and why did you choose to do it that way?
- What patterns or connections do you see in the information provided?
- How might you interpret these findings from another perspective?
- Can you design a…to…?
- How would you prove or disprove this statement?
- How can we improve…?
- What would be the consequences if…?
- Can you predict the outcome if…?
- What is the relationship between…?
- How can this be applied to other situations?
- What are the possible solutions for…?
- Why do you think that… happened?
- How can we test the validity of…?
- What alternative would you suggest for…?
- How can you illustrate this concept in a diagram?
- What would you recommend, and why?
- How is this similar to…?
- Can you make a general rule about…?
- How would you evaluate…?
- What evidence do you have for your claim?
- What are the implications of…?
- How does this contradict or confirm your understanding of…?
- Can you think of an example where…?
- How would you justify…?
- What do you think is the significance of…?
In conclusion, critical thinking questions are an indispensable tool for stimulating and nurturing the intellectual capabilities of students. They’re not just questions, but sparks that ignite the curiosity, analytical ability, and problem-solving skills in a learner. They invite students to dig deeper, challenge their preconceptions, and engage with material on a more profound level.
These questions play a pivotal role in taking learning beyond the simple absorption of facts into the realm of true understanding and application. They prepare students for the complexities of the real world, honing their ability to analyze situations, make decisions, and innovate solutions.
As educators and teachers, fostering this skill in students through the strategic use of critical thinking questions should be a top priority. So, let’s continue to question, to probe, and to encourage our students to do the same, for it’s in the exploration of these questions that true learning lies.

Join our mailing list
Never miss an EdTech beat! Subscribe now for exclusive insights and resources .

Meet Med Kharbach, PhD
Dr. Med Kharbach is an influential voice in the global educational technology landscape, with an extensive background in educational studies and a decade-long experience as a K-12 teacher. Holding a Ph.D. from Mount Saint Vincent University in Halifax, Canada, he brings a unique perspective to the educational world by integrating his profound academic knowledge with his hands-on teaching experience. Dr. Kharbach's academic pursuits encompass curriculum studies, discourse analysis, language learning/teaching, language and identity, emerging literacies, educational technology, and research methodologies. His work has been presented at numerous national and international conferences and published in various esteemed academic journals.

Join our email list for exclusive EdTech content.

150 Fun Critical Thinking Questions For Kids, Teens, & Adults
Critical thinking questions for kids get them thinking and questioning. To go beyond rote learning.
The reason they excel later in life will not be based on the information they memorized. But instead on how well they think, make decisions, communicate, and use their creativity.
These questions are designed to help them build these essential skills.

What makes a good critical thinking question?
Open ended questions are perfect for encouraging critical thinking and problem-solving. Kids (and grown-ups) have to think about their answers. Below you will find the best age-appropriate examples to use in the classroom, at home, or during your everyday routine .
In fact, there’s no question about it. Critical thinking is important for kids. And adults too!

Good Questions For Kindergarten To Think Critically
Younger kids need more concrete questions. These critical thinking questions will help them use reasoning and think deeply, even when they are small.
1. How do you know if something was a good decision?
2. How are these two things similar?
3. What are the differences between _______ and _________?
4. How would you feel if __________?
This question is great for building empathy .
5. Who was the main character? Why do you say that?
6. When is ___________ a problem?

7. What is the problem?
8. Why is this a problem?
9. What did you notice about _________?
10. Do you think he/she sees this the same way you do? Why or why not?
11. Has this happened before?
12. Do you think it will happen again? Why do you think this?
13. What is your opinion about _________? Why?
14. Is this appropriate? Why or why not?
15. What do you think would happen if __________?
16. What caused this to happen?
17. Do you think the world would be better if __________?
18. If you were in charge, what would you do differently?
19. Where can you find out more about this?
20. What does ______ mean?
21. Do you agree?
22. Can you give me an example of ________?
23. How do you know?
24. How would you solve this problem?
25. What makes something weird? What makes something normal?
Questions For Students: Elementary Through Middle School
For this age of kids, use any of the examples above and try these more abstract critical thinking questions too.

26. What do you think was the turning point?
27. Is there evidence to support your opinion (or decision)?
28. What does the evidence tell you?
29. What do you think would have been a better ending to… (book, movie, story)
30. When is the best time to start this?
31. When you think about solving a problem, where do you like to start?
32. What character/person changed the most? Why do you think this?
33. How could the author have created a thrilling twist in this story?
34. Who could help you with this? Why would they be a good fit to help?
35. Why is this important?
36. Why do you think ________ said that?
37. Why did the __________ (author, speaker) write/say this?
38. How does an idea grow? Or how does someone get from being a beginner to being an expert?
39. Do you think that what happened is what they meant to happen?
(Often, results are different than what people first think they will be.)
40. What can you use to help you decide?
41. What are the pros and cons of this?
42. Why is this happening?
43. What is the main message from this? (Or the lesson learned?)
44. What would you ask the author (speaker, etc.) if you could?
45. Do you have any questions about this?
46. Do you think it is too good to be true?
47. Can you defend these actions?
48. Compare this with this.
49. What would the world be like if ________? (kids were in charge, the sun was farther away, etc.)
50. Do you think there is a better alternative?
51. Is this person trustworthy? Why or why not?
52. At what age does someone stop being a kid? Why?

53. Can you see why someone would agree or disagree?
54. How would this ________ benefit or help others?
55. How will you know if your idea worked?
56. What is wrong with this situation?
57. What is good in this situation?
58. If someone were to argue your point, what do you think they would say?
59. Why do you think the character/person did that?
60. Is this fact or opinion? How do you know?
61. Was this change for the better? Or did it make things worse?
62. Who is most likely to _________? Why?
63. What do you think are the consequences of this decision?
64. Do you think we are asking the right question(s)? What is a different question instead?
Related Posts:
- Best Thought-Provoking Questions
- Deep Questions For Kids & Adults
- Philosophical Questions To Ponder With Kids
Critical Thinking Questions For High School & College Students
These critical thinking questions are more complex. They encourage abstract thinking, plus explore logic, ethics, and reasoning.

65. Why did you make that decision?
66. How did you get to that decision? What was your thought process?
67. What are the advantages of this?
68. What are the disadvantages of this?
69. How could we make this (project, paper, etc.) better?
70. What do you think the problem is….?
71. What do you think the best solution for this is? Why?
72. Could someone interpret this differently? How so?
73. How would you explain this to someone who doesn’t know anything about it?
74. What are a few alternative possibilities? Are any better than the others?
75. What are the short-term implications of this decision?
76. What are the long-term implications of this decision?
77. How would you achieve a big goal ?
78. (After they come up with a solution to something) Are there other possible ways to solve this problem?
79. How can you use the pros and cons to make a good decision?
80. Do you think when many people do something, it seems more “right,” even when it isn’t?
81. What are the potential risks to this decision?
82. What are the strengths of this argument?
83. What are the weaknesses of this argument?
84. Where is this lacking in evidence?
85. What can this story teach us about life?
86. Where would this solution work? Where would it not work?
87. Why do you think it is important to ask this question?
88. Why are new ideas important in our society?

89. What do you think that character’s motive is?
90. When should you reevaluate your initial thoughts/decision?
91. Do you think this is an important issue?
92. What do you think should have happened instead?
93. What is the counterargument?
94. Why is this relevant?
95. Do you think ________ will ever happen?
96. If it does, who would it affect most? Why?
97. What assumptions are being made in this situation?
98. Is it ever ok to lie?
99. Why do you think this feels like __________?
100. How is this related to your values and beliefs?
- Best Topics To Discuss With Others
- Ice Breaker Questions To Get to Know Someone
- Best Questions To Ask Teens
Critical Thinking Questions For Adults
These are great for a conversation at home or at work interviews to see how well potential candidates think on their feet.

101. Where do you see strengths?
102. Where do you think there are areas for improvement?
103. Why did these things help you in the long run?
104. What information do you need to find out before making a good decision?
105. If you could sit down and have dinner with anyone in the world, who would it be? Why?
106. What would you say to this person?
107. Should others care about this? Why?
108. When should you ask for help?
109. Who will benefit most from this decision?
110. Who will benefit least from this decision?
111. Have we considered all the options?
112. What questions do you have?
113. Are there any biases that you think are playing out here?
114. Are you making an assumption about __________?
115. When will you see your results?
116. Where do you often find this type of problem? Why?
117. In your opinion, what caused ____________ to happen?
118. Was it avoidable?

119. Does anything concern you about this?
120. When is this acceptable?
121. When is this not acceptable (or appropriate)?
122. What is one thing that would have changed everything?
123. When do you think this will benefit _________ (the company, society, etc.)?
124. When a disagreement happens at work, what do you do?
125. Is this goal achievable ?
126. How does your work experience help you fill this role?
127. Has this ever been done before? When?
128. What would need to happen for you to reconsider?
129. When will we need this?
130. What skills fit well with this position?
Related: Fun Rapid Fire Questions To Ask
Examples of Kids Critical Thinking Questions: By Word
Another way to split up your critical thinking questions is by word.

- Who is most directly affected by this decision?
- Who is the protagonist? Who is the antagonist?
- Who was the most important character?
- Who was a supporting character that was essential to the storyline?
- What is the problem you are trying to solve?
- What information is important to know about this before forming an opinion?
- What was the point of _________?
- When is it a good time to stop (or take a breather)?
- When should you know the answer?
- When will it be time for this? How do you know?
- When will this be critical?

- Where can you go to ask for help?
- Where can you find a good solution? Or information that helps you solve this problem?
- Where could this idea lead?
- Why has this issue come out into the spotlight?
- Why do you think ______ acts that way?
- Why is _______ happening, but ________ is not?
- How else could we have done that?
- How else could this be handled?
- How would you have responded in this situation?
- Fun Hobbies For Families To Do
- Best Family Challenge Ideas
More Ways To Encourage Critical Thinking In Kids
Want to go beyond questions? No problem! Here are other practical ways to build this crucial skill:

Change your questions to them.
Turn your normal yes or no questions to more open ended questions.
Example: Instead of “How was your day?” go with “What was the most interesting part of your school day today?”
Refrain from stepping in.
These days parents feel like they should be fixing their kids’ problems constantly.
Instead, hold back and force your child to problem-solve on their own. Ask questions and guide them through the problem, but let them know that they are in charge of finding their own solutions.
Play Games And Do Activities That Promote Critical Thinking
Here are a few great ones!

Two Truths & A Lie Game – The players have to decide which statements are true and which one is not. This game is great for learning to read body language too!
Good Debate Topics For Kids – Nothing builds quick critical thinking like a lively debate.
Riddles: What Am I? – These word riddles help kids think through different possibilities.
Guess The Animal Riddles for Kids – More riddles all about animals to get kids thinking.
Encourage creativity.
Provide your child with opportunities to use their imagination.
Sometimes, all this takes is getting your child off screens and outside playing with sticks!
Encourage them to build something , make up a new game, and think outside the box whenever possible.
Let them fiddle with things.
My son has a very “why” brain and loves to mess with stuff. It used to embarrass me when we were around others.
But, one day, my husband and I realized that his “working things out” isn’t bad. We just needed to teach him in what context it is appropriate. Now he fiddles with everything, and it is amazing to watch his mind work.
Let them question.
The same goes for questions. They should be challenging assumptions and questioning the world around them. Too many people take for granted the things that they hear and read. Teach your child to be different.
Promote Active Listening.
Encourage your child to ask questions to clarify understanding and develop communication skills.
Examples: “What I hear is _________.” Or, “How do you know _________?”
Try New Things.
Travel. And regularly expose your kids to new ideas and experiences. This helps them see their regular world in a new light.
Think Critically Yourself.
Finally, your child will be much more likely to think critically if they see a parent who does it. So, apply all of these strategies to yourself as well.

To Consider With Critical Thinking Questions For Kids
Teaching children to form their own opinions is how we build a generation of people that will analyze, evaluate, and make decisions for the betterment of the world.
It’s not just important. It’s critical to our future as a society.
More family-friendly posts you’ll love…
- Telephone Game Phrases & Statement Ideas
- Ice Breaker Kids & Teen Games
- Best Books List For 4 Year Olds
Creative Kids Critical Thinking Questions For Students
Jennifer is the founder and chief editor of Healthy Happy Impactful®. She believes that living, loving, and connecting deeply are the foundation for a good life. She holds a degree in education and is a mom to 3 kids.
- Our Mission
Helping Students Hone Their Critical Thinking Skills
Used consistently, these strategies can help middle and high school teachers guide students to improve much-needed skills.

Critical thinking skills are important in every discipline, at and beyond school. From managing money to choosing which candidates to vote for in elections to making difficult career choices, students need to be prepared to take in, synthesize, and act on new information in a world that is constantly changing.
While critical thinking might seem like an abstract idea that is tough to directly instruct, there are many engaging ways to help students strengthen these skills through active learning.
Make Time for Metacognitive Reflection
Create space for students to both reflect on their ideas and discuss the power of doing so. Show students how they can push back on their own thinking to analyze and question their assumptions. Students might ask themselves, “Why is this the best answer? What information supports my answer? What might someone with a counterargument say?”
Through this reflection, students and teachers (who can model reflecting on their own thinking) gain deeper understandings of their ideas and do a better job articulating their beliefs. In a world that is go-go-go, it is important to help students understand that it is OK to take a breath and think about their ideas before putting them out into the world. And taking time for reflection helps us more thoughtfully consider others’ ideas, too.
Teach Reasoning Skills
Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
One way to teach reasoning is to use problem-solving activities that require students to apply their skills to practical contexts. For example, give students a real problem to solve, and ask them to use reasoning skills to develop a solution. They can then present their solution and defend their reasoning to the class and engage in discussion about whether and how their thinking changed when listening to peers’ perspectives.
A great example I have seen involved students identifying an underutilized part of their school and creating a presentation about one way to redesign it. This project allowed students to feel a sense of connection to the problem and come up with creative solutions that could help others at school. For more examples, you might visit PBS’s Design Squad , a resource that brings to life real-world problem-solving.
Ask Open-Ended Questions
Moving beyond the repetition of facts, critical thinking requires students to take positions and explain their beliefs through research, evidence, and explanations of credibility.
When we pose open-ended questions, we create space for classroom discourse inclusive of diverse, perhaps opposing, ideas—grounds for rich exchanges that support deep thinking and analysis.
For example, “How would you approach the problem?” and “Where might you look to find resources to address this issue?” are two open-ended questions that position students to think less about the “right” answer and more about the variety of solutions that might already exist.
Journaling, whether digitally or physically in a notebook, is another great way to have students answer these open-ended prompts—giving them time to think and organize their thoughts before contributing to a conversation, which can ensure that more voices are heard.
Once students process in their journal, small group or whole class conversations help bring their ideas to life. Discovering similarities between answers helps reveal to students that they are not alone, which can encourage future participation in constructive civil discourse.

Teach Information Literacy
Education has moved far past the idea of “Be careful of what is on Wikipedia, because it might not be true.” With AI innovations making their way into classrooms, teachers know that informed readers must question everything.
Understanding what is and is not a reliable source and knowing how to vet information are important skills for students to build and utilize when making informed decisions. You might start by introducing the idea of bias: Articles, ads, memes, videos, and every other form of media can push an agenda that students may not see on the surface. Discuss credibility, subjectivity, and objectivity, and look at examples and nonexamples of trusted information to prepare students to be well-informed members of a democracy.
One of my favorite lessons is about the Pacific Northwest tree octopus . This project asks students to explore what appears to be a very real website that provides information on this supposedly endangered animal. It is a wonderful, albeit over-the-top, example of how something might look official even when untrue, revealing that we need critical thinking to break down “facts” and determine the validity of the information we consume.
A fun extension is to have students come up with their own website or newsletter about something going on in school that is untrue. Perhaps a change in dress code that requires everyone to wear their clothes inside out or a change to the lunch menu that will require students to eat brussels sprouts every day.
Giving students the ability to create their own falsified information can help them better identify it in other contexts. Understanding that information can be “too good to be true” can help them identify future falsehoods.
Provide Diverse Perspectives
Consider how to keep the classroom from becoming an echo chamber. If students come from the same community, they may have similar perspectives. And those who have differing perspectives may not feel comfortable sharing them in the face of an opposing majority.
To support varying viewpoints, bring diverse voices into the classroom as much as possible, especially when discussing current events. Use primary sources: videos from YouTube, essays and articles written by people who experienced current events firsthand, documentaries that dive deeply into topics that require some nuance, and any other resources that provide a varied look at topics.
I like to use the Smithsonian “OurStory” page , which shares a wide variety of stories from people in the United States. The page on Japanese American internment camps is very powerful because of its first-person perspectives.
Practice Makes Perfect
To make the above strategies and thinking routines a consistent part of your classroom, spread them out—and build upon them—over the course of the school year. You might challenge students with information and/or examples that require them to use their critical thinking skills; work these skills explicitly into lessons, projects, rubrics, and self-assessments; or have students practice identifying misinformation or unsupported arguments.
Critical thinking is not learned in isolation. It needs to be explored in English language arts, social studies, science, physical education, math. Every discipline requires students to take a careful look at something and find the best solution. Often, these skills are taken for granted, viewed as a by-product of a good education, but true critical thinking doesn’t just happen. It requires consistency and commitment.
In a moment when information and misinformation abound, and students must parse reams of information, it is imperative that we support and model critical thinking in the classroom to support the development of well-informed citizens.
85 Fun Critical Thinking Questions for Kids & Teens

Have you ever thought about using fun questions to practice critical thinking?
Students may need a little guidance to think their way through questions that lack straightforward answers.
But it is that process that is important!
How the Right Questions Encourage Critical Thinking
Every parent knows how natural it is for children to ask questions.
It should be encouraged. After all, asking questions helps with critical thinking.
As they grow older, however, training them to answer questions can be equally beneficial.
Posing questions that encourage kids to analyze, compare, and evaluate information can help them develop their ability to think critically about tough topics in the future.
Of course, critical thinking questions for kids need to be age-appropriate—even better if you can mix a little fun into it!
That’s what I hope to help you with today. I’ve organized the questions below into three different ages groups:
- Upper elementary
- Middle school
- High school

Get a Question-Based Critical Thinking Exercise—Free!
Introduce critical thinking gently & easily with thought-provoking exercises.
Upper Elementary
Students in upper elementary grades can be reluctant to put themselves out there, especially with answers that seem weird.
In some cases, such hesitancy is actually fear of differing from their peers (and a barrier to critical thinking ).
But that’s exactly why it’s important to practice answering ambiguous questions.
We want our children to stand firm for their beliefs—not cave to peer pressure.
Additionally, students may feel uneasy about answering serious questions, uncertain of tackling “big” problems.
However, with careful use of creative questions for kids, it’s possible to engage even the most reluctant children in this age group.
The idea is to simply get them interested in the conversation and questions asked.
If you have an especially reserved student, try starting with the funny critical thinking questions.
Humor is a natural icebreaker that can make critical thinking questions more lighthearted and enjoyable.
Of course, most younger kids just like to be silly, so playing upon that can keep them active and engaged.
With that said, here are some great questions to get you started:
1. Someone gives you a penguin. You can’t sell it or give it away. What do you do with it?
2. What would it be like if people could fly?
3. If animals could talk, what question would you ask?
4. If you were ice cream, what kind would you be and why?
5. Do you want to travel back in time? If yes, how far back would you go? If no, why not?
6. What could you invent that would help your family?
7. If you could stay up all night, what would you do?
8. What does the man on the moon do during the day?
9. What makes something weird or normal?
10. Can you describe the tastes “salty” and “sweet” without using those words?
11. What does it feel like to ride a rollercoaster?
12. What makes a joke funny?
13. What two items would you take if you knew you would be stranded on an island and why?
14. Do you have a favorite way of laughing?
15. What noise makes you cringe and cover your ears? Why?
16. If you could be the parent for the day, what would you do?
17. If you could jump into your favorite movie and change the outcome, which one would you pick and why?
18. If you could be invisible for a day, what would you do?
19. What makes a day “perfect”?
20. If you owned a store, what kind of products would you sell?
21. If your parents were your age, would you be friends with them?
22. Would you still like your favorite food if it tasted the same as always, but now had an awful smell?
23. What would you do if you forgot to put your shoes on before leaving home?
24. Who would you be if you were a cartoon character?
25. How many hot dogs do you think you could eat in one sitting?
26. If you could breathe under water, what would you explore?
27. At what age do you think you stop being a kid?
28. If you had springs in your legs, what would you be able to do?
29. Can you describe the color blue to someone if they’re blind?
Middle School
At this point, students start to acquire more complex skills and are able to form their own conclusions based on the information they’re given.
However, we can’t expect deep philosophical debates with 12 and 13 year olds.
That said, as parent-teachers, we can certainly begin using more challenging questions to help them examine and rationalize their thought processes.
Browse the fun critical thinking questions below for students in this age range.
You might be surprised to see how receptive middle school kids can be to such thought-provoking (yet still fun) questions .
30. What would happen if it really did rain cats and dogs?
31. What does it mean to be lucky?
32. If you woke up in the middle of a dream, where would you be?
33. Is it ever okay to lie? Why or why not?
34. If you were solely responsible for creating laws, what one law would you make?
35. What makes a person a good friend?
36. What do you think is the most important skill you can take into adulthood?
37. If you had to give up lunch or dinner, which would you choose? Why?
38. How much money would you need to be considered rich?
39. If you knew you wouldn’t get caught, would you cheat on a test?
40. If you could live anywhere in the world, where would that be?
41. What is your greatest strength? How is that an asset?
42. If you had an opportunity to visit the International Space Station, would you do it?
43. Is it better to keep the peace or speak your mind?
44. Imagine yourself as your favorite animal. How would you spend your day?
45. Would you be friends with someone who didn’t have the same values as you?
46. How much screen time do you think is too much?
47. Can you describe your favorite color without naming it?
48. If you suddenly became blind, would you see things differently?
49. Would you ever go skydiving?
50. Describe the time you were the happiest in your life. Why did this make you happy?
51. If you had a million dollars, what would you do?
52. If you had to move to a new city, would you change how you present yourself to others?
53. What do you need to do in order to be famous?
54. If you could rewrite the ending of your favorite book or movie, what changes would you make?
55. How would you tackle a huge goal?
56. How would you sell ice to an eskimo in Alaska successfully?
57. What makes you unique?
High School
Critical thinking takes on an entirely different role once students reach high school.
At this age, they have a greater sense of right and wrong (and what makes things so) as well as a better understanding of the world’s challenges.
Guiding teens to delve deeper and contemplate such things is an important part of developing their reasoning and critical thinking skills.

Whether it’s fun questions about hypothetical superpowers or tough critical thinking questions about life, older teens typically have what it takes to think their way to a logical conclusion .
Of course, use your discernment as you choose discussion topics, but here are some questions to help get you started:
58. How can you avoid [common problem] in the future?
59. Do you think it’s okay to take a life in order to save 5, 10, 20 or more people?
60. If you could go back and give your younger self advice, what would it be?
61. Is it better to give or receive a gift?
62. How important is it to be financially secure? Why?
63. If it was up to you, what one rule would you change in your family?
64. What would you do if a group of friends wanted to do something that you thought was a bad idea?
65. How do you know that something is a fact rather than an opinion?
66. What would it take to get you to change your mind?
67. What’s the most important thing in your life?
68. If money were of no concern, what job would you choose and why?
69. How do you know if you’re happy?
70. Do you think euthanasia is moral?
71. What is something you can do today that you weren’t able to do a year ago?
72. Is social media a good thing or not?
73. Is it right to keep animals in a zoo?
74. How does your attitude affect your abilities?
75. What would you do if you found out a friend was doing something dangerous?
76. If you could have any superpower, what would it be? Why?
77. What will life on Earth look like in 50 years?
78. Which is more important, ending world hunger or global warming?
79. Is it a good idea to lower the voting age to 16? Why or why not?
80. If the electrical power went out today, how would you cook if using wood wasn’t an option?
81. If you could magically transport yourself to any other place, where would that be and why?
82. When should teenagers be able to stay out all night?
83. Does the number zero actually exist?
84. What defines a generous person?
85. Does an influential person influence everyone?
Feel free to print out these fun critical thinking questions and incorporate them into your homeschool week!

will your children recognize truth?
About the author.
Jordan Mitchell

85 Critical Thinking Questions to Carefully Examine Any Information
There might be affiliate links on this page, which means we get a small commission of anything you buy. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Please do your own research before making any online purchase.
The ability to think critically will often determine your success in life.
Let’s face it. Every day, we are bombarded by news, social media updates, and an avalanche of information. If you take all of this at face value, it’s easy to be deceived, misled or ripped off.
That’s why it’s important to develop a mindset that focuses on critical thinking . This is a skill that needs to be developed in the classroom. But it’s also a valuable life skill.
With that in mind, the following post will share 85 critical thinking questions you can use to increase your awareness about different problems by carefully examining available information.
Let’s get started…
Table of Contents
What Are Critical Thinking Questions?
Critical thinking questions are inquiries that help you think rationally and clearly by understanding the link between different facts or ideas. These questions create a seemingly endless learning process that lets you critique, evaluate, and develop a depth of knowledge about a given subject. Moreover, you get to reinforce your viewpoints or see things in a new way.
We make decisions every day, whether at work or home. Adopting logical, rational, and practical approaches in addressing various issues requiring critical thinking is essential in decision-making. Therefore, before arriving at a decision, always ask yourself relevant questions and carefully analyze the matter’s pros and cons.
Critical Thinking Questions When in an Argument
When you make an argument using a critical thinking approach, you focus on justified claims that are valid and based on evidence. It helps one establish a strong argument.
- Do I disagree with the other person? Might the person I'm arguing with be misinformed on what they are saying?
- Would I be comfortable saying what I am telling him/her if I was in front of a group of people?
- What would happen if I lose this argument? Is engaging in this argument worth my time and energy? How will I feel if I lose?
- Is there room for ambiguity or misinterpretation? Are we arguing because I didn't make my point explicit? Should I take my time to understand his school of thought?
- Do I need some rest before saying something? Am I arguing because of other reasons other than the issues at hand? Do I need to take some time and cool down?

- Is it more important that I’m right? Am I trying to ask to prove an unnecessary point?
- Is this argument inductive, deductive, or abductive? Is it a weak or strong argument that I need to engage in? Is it compelling or sound?
- Is my opponent sincere? Given that they are wrong, are they willing to admit that they are wrong? Can they depend on available evidence, wherever it leads?
- Are my opponents only trying to shift their burden to me? What is the best way to prove them wrong without making them feel bad?
- Are the people I'm arguing with only interested in winning, or are they trying to pass some information across and help me discover the truth?
Critical Thinking Questions When Reading a Book
When you read a book, you probably ask yourself many “why” questions. Why is this a problem? Why did the character say that? Why is this important? The most challenging part of reading a book is assessing the information you are reading. These questions can help.
- If I learn only two things from this book, what will they be? How will they help me? How will I apply them in my daily life?
- What message are the authors trying to pass across? Are they making suggestions or providing evidence for their arguments?
- Given that almost every book is about solving problems, what is the most prevalent issue that the author is trying to solve?
- What is the author’s writing style? What strategy or master plan does the author employ to convey his/her main ideas throughout the book?
- Do I have background information about the book’s topic? If so, how is what the author is saying different from what I already know?
- What didn’t I understand from the book? Should I re-read the book to understand everything the writer is trying to convey?
- Which sections of the book do I love the most, and why? Generally, do I like this book? Should I look for more books that are written by the same author?
- If I had a chance to meet this book’s author, what questions would I ask him/her? What would I tell the writer about the book? Is it a great book worth recommending to your friends and family members?
- Who are the main characters of the book? If there is only one main character, what overarching goal does the character accomplish?
- In what ways did the protagonist change from the start of the book to the end? What caused the changes? Was the protagonist reckless in some ways? Which ways?
Critical Thinking Questions to Spot a Scam
Asking questions when you feel that a fraud or a scam is being presented to you is a good way to stretch your critical thinking muscles. Are you being emailed or messaged by a stranger? Or maybe there are other red flags you are unsure about. If so, ask these questions.
- Does it seem to be too good to be true? Is this stranger pushy or trying to lure me into making a poor decision?
- When trying out online dating: Is my new “friend” professing strong feelings towards me although we’ve only interacted for a few hours?
- Why is a stranger calling me to ask about my Social Security Number (SSN), personal contact information, or bank details while claiming they are from the bank or a phone company?
- When buying products online, why does the seller ask me to pay for goods using an insecure payment option like Bitcoin or money order?
- Does the email I have received have any spelling or grammatical errors? Is the language used overly formal or informal?
- If I do a quick search about the exact words of the email I received, does Google indicate it's a fraud or scam?
- Why should a stranger manipulate me using obvious questions like “Would you want to be rich or poor?” While they already know the answer?
- Is the email asking me to download an attachment? Or click a link to some insecure website?
- Is the person trying to make me feel selfish or guilty for not sending them money, whether for a donation or buying a product?
- Is the stranger portraying a sense of urgency and using pressure tactics? Are they telling me that their family member needs urgent medical attention?
Critical Thinking Questions About Your Life
It can also help to ask yourself a few critical thinking questions about your life. This way, you can gather basic information and uncover solutions to problems you might not have otherwise thought of.
- Where do I wish to be in a few years, probably two, three, or five years? What short-term and long-term goals should I set?
- What have I achieved so far from the time I set my previous goals? What should I be grateful for?
- Do I have any values that guide me in life? If so, what are these values? Am I always true to these values?
- Am I always worried about what people around me think? Can I act independently without the need to meet social expectations?
- What should people say about me at my funeral? Would they talk about how good I made them feel or how rich and flashy I was?
- If I wasn't afraid of anyone or anything, what would I have done? What if I didn't have any fear in me?
- If today was my last day, what extraordinary thing would I do? Can I do it right now?
- What should I do with the things that matter the most to me?
- What things will make the greatest difference in my future life if I take action now?
- How should I react when I feel unwanted by the people I love the most? Should I tell them?

Critical Thinking Questions for a Debate or Discussion
When you are in the middle of a debate or discussion, you need to know that what you are saying is fact, have evidence to support your claim, and position yourself as an expert in what you are saying. Here are some critical thinking questions to ask when you are in a debate or discussion.
- Is there fairness in this discussion? Is the moderator supporting one side? Do they want to make one side look stupid or wrong?
- What is the aim of this discussion? Is there a major problem that needs to be solved? If so, how can I help solve it?
- Who are the people affected by this discussion? If they were here, what would they say?
- Do my views on this discussion matter? If I raise my point, will I be redundant?
- What am I supposed to learn from this debate, and how can I use what I have learned in my daily life?
- Does the audience seem to be biased towards one side? Are they booing one side? What can I do even if it's our opponents being booed?
- Who are the discussion panel members? What views have they held about this kind of discussion or any other related discussions in the past?
- How can I make my point without being ambiguous? Before I speak, should I take down some notes to avoid any confusion during my speech?
- Am I ready to apologize if I make a mistake during the discussion? If so, what are the limits?
- What information does my team, or I need before this discussion?
Critical Thinking Questions About Lying
Admitting when you are wrong, choosing not to cheat, and sharing constructive feedback are all ways to show your honesty. Here are some critical thinking skills to ask regarding lying.
- Will the lie hurt those I am telling, or will it help them? What if being honest might cause my friend unnecessary pain?
- Should I be the one telling this person a lie, or I let someone else do it?
- Will I be the one hurt if I tell this lie? Will my friend feel I am a betrayer? Will it affect our friendship?
- Do they answer my questions in detail, or are they always trying to ignore and dodge the main problem?
- What if I ask these people the same question using different terms and wording? Will they give me the same response?
- Did the tone of my friend suddenly change after I asked him/her this question? Do they sound louder, faster, or slower compared to how they usually speak?
- Does this person have something to gain by lying to me? What is their motive?
- Does this person take a sudden pause or hesitate more than usual when responding to my question?
- When I look at these people's faces, do their facial expressions match what they say?
- Should I believe this person or not? What are my intuitions? Does it look like they are telling the truth?
- Do they blink like other days when I ask them questions? Are they always trying to avoid direct eye contact?
- Why do they seem uncomfortable when it’s just a normal conversation?
Critical Thinking Questions When Presented With a Claim
Critical thinking is much more than just evaluating whether a claim is true or not. It also means a critical thinker reflects on what follows from true claims.
- What does this claim mean, and what are its implications? What if it's a false claim?
- Which of my morals, values, or beliefs do I have to give up to accept this claim?
- Do professionals in this field agree or disagree with the claim that has been made?
- Do they have evidence to back their claim? Which is the most robust evidence to support the claim?
- What argument can I come up with to refute this claim? Or what is the best view that can support this claim?
- Who is the primary source of the claim being made? Is the basis of the claim reliable?
- Is it a claim, or it's just an opinion?
- Is the claim likely to be 100% false, true, or partially true?
- Am I allowed to refute the claim and table my evidence, or is it one-sided?
Critical Thinking Interview Questions
Critical thinking skills are valuable in any industry or field and for almost all roles. During a job interview, you will be asked questions so the potential employer can assess your skills and see how you use logic. Your critical thinking ability is just one vital part that can play into your professional development.
- Is there a time you had to convince someone to use an alternate approach to solve a problem?
- Have you ever had to make a difficult decision quickly?
- How would you handle a situation where your supervisor handled something wrong or made a mistake?
- What is one of the most difficult decisions you have ever had to make at work?
- How would you solve a disagreement between coworkers when approaching a project?
- Can you describe a time when you anticipated a problem ahead of time and took the appropriate steps to stop the problem from becoming an issue?
- If you discover a cheaper way to do something or a better solution to a problem and try to explain it to your supervisor, but they don’t understand, what do you do?
Critical Thinking Questions for Kids
We can’t leave the kids out either. Critical thinking questions for kids get them thinking and talking. It also allows a parent to get to know their child better.
- How many grains of sand do you think are on the beach?
- What would happen if it stopped raining?
- Do you think there is life on other planets?
- Should children be able to set their own bedtimes?
- How would you describe what a tree looks like without saying green or leaves?
- Can you name five different emotions?
- Can you talk for five minutes without uttering “um?”
What Are the Basic Principles of Critical Thinking?
Your critical thinking skills involve gathering complete information, understanding and defining terms, questioning the methods by which we get facts, questioning the conclusions, and looking for hidden assumptions and biases.
Additionally, we can’t expect to find all of the answers, and we need to take the time to examine the big picture of it all.
Here are the basic principles:
- Disposition: Someone with critical thinking skills is often skeptical, open-minded, and practices fair-mindedness. They can look at different viewpoints and change positions if the evidence and reason lead them to do so.
- Criteria: In order to think critically, one must also apply criteria. Certain conditions must be met before someone believes in something. The information needs to be from credible sources.
- Argument: An argument is simply a statement or proposition that is shown with supporting evidence. When you use your critical thinking skills, you identify, evaluate, and construct your argument.
- Reasoning: With critical thinking comes reasoning. You must examine logical relationships among the statements being made.
- Point of View: Critical thinkers can see things from different perspectives and different points of view.
What Are Good Analysis Questions?
Analysis is a part of critical thinking that allows you to examine something carefully. Someone with analytical skills can examine the information presented, understand what that information means, and then properly explain that information to others. Analysis in critical thinking provides more clarity on the information you process.
When analyzing, you may ask yourself, “how do I know this,” how would I solve this problem,” and “why does it matter?”
Why Is Critical Thinking an Important Skill?
Critical thinking skills allow you to express thoughts, ideas, and beliefs in a better way. It also leads to improved communication while allowing others to understand you better. Critical thinking fosters creativity and encourages out-of-the-box thinking. This is a skill that can be applied to many different areas of your life.
For example, knowing the answers to critical thinking questions for a job interview will better prepare you for the interview. Many employers, during questioning, are likely to ask you critical thinking questions to assess if you have the ability to evaluate information effectively so you can make more informed decisions.
Final Thoughts on Critical Thinking Questions
Although it's common to get torn between making two or more choices, nobody wants to make the wrong decision. The only thing you can do to avoid this is use critical thinking questions to examine your situation. The answers to these questions will help you make informed decisions and help you comprehend crucial matters in your life.
Want to learn more about critical thinking and decision-making using a real-life example? Here is how Jeff Bezos uses critical thinking to make some of the most challenging life decisions.
Finally, if you want to ask better questions, then watch this short, 20-minute course to learn how to have a great conversation with virtually anyone .

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples
What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples
Published on May 30, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment .
To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources .
Critical thinking skills help you to:
- Identify credible sources
- Evaluate and respond to arguments
- Assess alternative viewpoints
- Test hypotheses against relevant criteria
Table of contents
Why is critical thinking important, critical thinking examples, how to think critically, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about critical thinking.
Critical thinking is important for making judgments about sources of information and forming your own arguments. It emphasizes a rational, objective, and self-aware approach that can help you to identify credible sources and strengthen your conclusions.
Critical thinking is important in all disciplines and throughout all stages of the research process . The types of evidence used in the sciences and in the humanities may differ, but critical thinking skills are relevant to both.
In academic writing , critical thinking can help you to determine whether a source:
- Is free from research bias
- Provides evidence to support its research findings
- Considers alternative viewpoints
Outside of academia, critical thinking goes hand in hand with information literacy to help you form opinions rationally and engage independently and critically with popular media.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Critical thinking can help you to identify reliable sources of information that you can cite in your research paper . It can also guide your own research methods and inform your own arguments.
Outside of academia, critical thinking can help you to be aware of both your own and others’ biases and assumptions.
Academic examples
However, when you compare the findings of the study with other current research, you determine that the results seem improbable. You analyze the paper again, consulting the sources it cites.
You notice that the research was funded by the pharmaceutical company that created the treatment. Because of this, you view its results skeptically and determine that more independent research is necessary to confirm or refute them. Example: Poor critical thinking in an academic context You’re researching a paper on the impact wireless technology has had on developing countries that previously did not have large-scale communications infrastructure. You read an article that seems to confirm your hypothesis: the impact is mainly positive. Rather than evaluating the research methodology, you accept the findings uncritically.
Nonacademic examples
However, you decide to compare this review article with consumer reviews on a different site. You find that these reviews are not as positive. Some customers have had problems installing the alarm, and some have noted that it activates for no apparent reason.
You revisit the original review article. You notice that the words “sponsored content” appear in small print under the article title. Based on this, you conclude that the review is advertising and is therefore not an unbiased source. Example: Poor critical thinking in a nonacademic context You support a candidate in an upcoming election. You visit an online news site affiliated with their political party and read an article that criticizes their opponent. The article claims that the opponent is inexperienced in politics. You accept this without evidence, because it fits your preconceptions about the opponent.
There is no single way to think critically. How you engage with information will depend on the type of source you’re using and the information you need.
However, you can engage with sources in a systematic and critical way by asking certain questions when you encounter information. Like the CRAAP test , these questions focus on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
When encountering information, ask:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert in their field?
- What do they say? Is their argument clear? Can you summarize it?
- When did they say this? Is the source current?
- Where is the information published? Is it an academic article? Is it peer-reviewed ?
- Why did the author publish it? What is their motivation?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence? Does it rely on opinion, speculation, or appeals to emotion ? Do they address alternative arguments?
Critical thinking also involves being aware of your own biases, not only those of others. When you make an argument or draw your own conclusions, you can ask similar questions about your own writing:
- Am I only considering evidence that supports my preconceptions?
- Is my argument expressed clearly and backed up with credible sources?
- Would I be convinced by this argument coming from someone else?
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Critical thinking skills include the ability to:
You can assess information and arguments critically by asking certain questions about the source. You can use the CRAAP test , focusing on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
Ask questions such as:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence?
A credible source should pass the CRAAP test and follow these guidelines:
- The information should be up to date and current.
- The author and publication should be a trusted authority on the subject you are researching.
- The sources the author cited should be easy to find, clear, and unbiased.
- For a web source, the URL and layout should signify that it is trustworthy.
Information literacy refers to a broad range of skills, including the ability to find, evaluate, and use sources of information effectively.
Being information literate means that you:
- Know how to find credible sources
- Use relevant sources to inform your research
- Understand what constitutes plagiarism
- Know how to cite your sources correctly
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search, interpret, and recall information in a way that aligns with our pre-existing values, opinions, or beliefs. It refers to the ability to recollect information best when it amplifies what we already believe. Relatedly, we tend to forget information that contradicts our opinions.
Although selective recall is a component of confirmation bias, it should not be confused with recall bias.
On the other hand, recall bias refers to the differences in the ability between study participants to recall past events when self-reporting is used. This difference in accuracy or completeness of recollection is not related to beliefs or opinions. Rather, recall bias relates to other factors, such as the length of the recall period, age, and the characteristics of the disease under investigation.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/critical-thinking/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, student guide: information literacy | meaning & examples, what are credible sources & how to spot them | examples, applying the craap test & evaluating sources, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
47 Critical Thinking Questions for High School Students
Critical thinking is defined as analyzing and thinking objectively about an issue to form a judgment. Critical thinking skills are important for high school students because they encourage decision-making based on logic and reason, which will serve them well in adulthood.
In fact, it has been proven that having critical thinking skills leads to success in interpersonal, financial, and business endeavors and serves to protect against negative outcomes.
Critical thinking questions are those that encourage the development of the following skills:
- Problem-solving
- Communication
- Open-mindedness
Let’s review some of the best questions that encourage critical thinking in high school students .
If you could make your own country, what would it look like? What rules would your citizens follow?
If you could go back in time two years and give your younger self advice, what advice would you give?
If you found out you only had 24 hours left to live, what would you decide to do with your last day on earth?
If you were offered the opportunity to get on a spaceship bound for a distant planet, and you would be one of the first colonizers, would you do it?
If a train was heading down a track without brakes and you had the switch that would turn it to either one of two tracks, and there was a baby on one track and an old woman on the other, who would you choose to let live? Why?
If everyone in the world stopped using social media, would it be a good thing or a bad thing? Defend your answer.
If your best friend was doing something dangerous that could kill them or put them in jail, would you tell someone even if it meant never speaking to them again?
Should the voting age be lowered to 16? Why or why not?
Should euthanasia be legal? Why or why not?
Question 10
Is it better to take one life in order to save 5 lives? What about 10? 20?
Question 11
If you had the power to solve one major problem on earth, what problem would you solve?
Question 12
If you could transport yourself instantly anywhere in the world, what place would you choose?
Question 13
If you were stranded on a desert island, what item would you choose to bring with you, provided you would have an endless supply of food and water?
Question 14
Should the drinking age be lowered to 18? Why or why not?
Question 15
If you could spend one day with any person on earth, alive or dead, who would it be and why?
Question 16
Is it more important to have a strong military or universal healthcare? Why or why not?
Question 17
What defines adulthood? When does adulthood begin?
Question 18
Which is more important – solving climate change or solving world hunger?
Question 19
Would you rather be blind or deaf? Why?
Question 20
How would you describe a tree without using the words green, branches, or leaves?
Question 21
If you could describe the color red to a blind person, how would you describe it? What about the color blue?
Question 22
If you had the ability to transform into any animal at any time you wanted, what animal would you choose and why?
Question 23
If you could live in any historical time period, which time period would you choose and why?
Question 24
Would you rather die by falling off a skyscraper or being buried in a landslide? Why?
Question 25
How does someone become a good person? Can a bad person change into a good person? How?
Question 26
Would you rather to never have to eat or never have to sleep? Why?
Question 27
Is it better to have 1 million dollars in the bank or donate 10 million dollars to charity? Why or why not?
Question 28
How would you describe an airplane to someone who had never seen or heard of one?
Question 29
Is it better to be ignored or gossiped about? Why?
Question 30
What makes humans more important than animals?
Question 31
Is murder every justifiable? Why or why not?
Question 32
Is the death penalty immoral? Why or not?
Question 33
What characteristics make a good leader?
Question 34
If ignorance ever an excuse for breaking the law? Why or why not?
Question 35
What is more important in life: love, health, or money?
Question 36
Is it better to be feared or loved? Why?
Question 37
If you had the chance to travel through time and change one historical event, what event would you change and why? How would you change it?
Question 38
If you suddenly had a life expectancy of 500 years, would you change the way you live your life? What about if your life expectancy dropped 10 years?
Question 39
Think about the birth order with you and your siblings, if you have any. Would you rather change your birth order or remain where you are?
Question 40
If you had five minutes to defend the human race against an alien civilization who were going to destroy humanity, what would you say?
Question 41
Would you want to live forever? Why or why not?
Question 42
Is it the responsibility of wealthy countries to help impoverished countries? Why or why not?
Question 43
If you could change one rule in your family, what rule would it be and why?
Question 44
Do someone’s actions impact their value as a person, such as serial killers?
Question 45
How do you define evil?
Question 46
Is it the government’s job to ban harmful substances like drugs or alcohol, or is it the citizens’ responsibility to look after their own health?
Question 47
Should people be required to take a test before having a baby? Why or why not?
https://www.uopeople.edu/blog/why-is-critical-thinking-important/
https://www.futurelearn.com/info/courses/how-to-develop-critical-thinking-skills/0/steps/335512#:~:text=We%20develop%20specific%20techniques%20that,%2C%20independently%2C%20and%20effectively.%E2%80%9D
You may also like

Critical thinking and conflict resolution
Introduction Have you ever wondered how critical thinking can help in terms of conflict resolution? Critical thinking is a powerful tool, but […]

Best Sports for Critical Thinking: Enhancing Mental Agility through Athletics
Participating in sports is known to have numerous benefits, ranging from physical fitness to fostering social skills and teamwork. However, sports can […]

What Is Drone Mentality?
Drone mentality is a pattern of going through the motions, paying little to no attention to what’s going on around you. Think […]

Critical Reading vs. Critical Thinking
In the digital age, we are presented with information from all scopes and spectrums. In order to understand the meaning behind texts, […]
- Defining Critical Thinking
- A Brief History of the Idea of Critical Thinking
- Critical Thinking: Basic Questions & Answers
- Our Conception of Critical Thinking
- Sumner’s Definition of Critical Thinking
- Research in Critical Thinking
- Critical Societies: Thoughts from the Past
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.
Critical Thinking: Basic Questions & Answers
Before viewing our online resources, please seriously consider supporting our work with a financial contribution. As a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization, we cannot do our work without your charitable gifts. We hope you will help us continue to advance fairminded critical societies across the world.
For full copies of many other critical thinking articles, books, videos, and more, join us at the Center for Critical Thinking Community Online - the world's leading online community dedicated to critical thinking! Also featuring interactive learning activities, study groups, and even a social media component, this learning platform will change your conception of intellectual development.

40 Critical Thinking Questions for High School Students
How is electricity being produced from rainwater or do aliens exist if there are so many discoveries about them? High school students are certain to come across queries that question reality, everyday rules, general human existence, or anything out of nowhere!
Young minds are filled with an amazing potential to explore beyond their capabilities and hidden qualities. While high school students might question the existing realities of life, some students might not be aware of their imagination and thinking capacities. That is why it is important to nurture these growing minds with opportunities to question, understand, analyze, find evidence, and arrive at solutions.
In this case, critical thinking questions act as a helpful way to offer an opportunity to broaden their minds to unlimited knowledge and endless possibilities. When students are given a chance to think beyond the ordinary, they experience a sense of freedom in thinking and expressing their views.
Through critical thinking questions, they receive a wonderful chance to analyze, decode the information, and present their views without being right or wrong. Hence, the below-mentioned questions are drafted in a way to initiate abstract and informative conversations thereby boosting critical thinking.
Brain teasing critical thinking questions for high schoolers
Critical thinking skills are essential for measuring the imagination and creativity of students. High school students are likely to use the new age information and influence of others when processing their thoughts. Hence, the below-mentioned questions are a great way to channel their thoughts in a more positively empowered learning environment.
- Do you think it is okay to give up your life if you had to save someone?
- If you could go to your past, what would you change?
- What is the joy of giving for you?
- What is better – giving or receiving? Why?
- If you can change some rules of the school, which ones would you change and why?
- What if you know your future? What does it look like from your perspective?
- What if you are dragged into a situation where you disagree with others?
- What would you do if you are given a task against your willingness to complete it?
- Would you like to do – go to your past or get to know your future? Why?
- What would you choose, 1 million dollars or a lifetime free education? Why?
- What is more important to you, knowledge or money?
- How can you leverage the benefits of social media and how?
- Do you think animals should be free or kept in a zoo?
- What does life look like on the Earth 100 years from now?
- Imagine a world without mobile phones. What would you do?
- If you could choose any profession in the world, what would you choose? Why?
- Would you rather devote your life to helping others through social activities or invest in building a business?
- What is the most important matter of concern that the world needs to address?
- Do you think the voting of high school students matters in Government concerns? Why?
- Which aspect plays a major role in the success of individuals?
- If you could change any one habit of your parents, what would it be?
- If you could travel to any place in the world, where would you go? Why?
- Imagine the world is facing a major power cut issue. What would you do and how would you face the situation?
- What is more important, offering a home to the needy or offering food to the needy on an everyday basis?
- How does the number 0 change life?
- Should teenagers be allowed to make major life decisions?
- Are friendships real in today’s world?
- Does an influential person always influence others with actions and words?
- If animals could talk to you, who would you choose to talk to?
- What is the difference between happiness and achievements?
- Do you think success is the same as happiness?
- Imagine you have only 24 hours left on Earth. How would you spend it?
- What if you are given the option to reside on another planet? What would you do and how?
- Would you forgive your best friend if he/she commits a crime and is found guilty?
- If your mother and best friend are sinking in two different boats and you have the opportunity to save anyone, who would you choose? Why?
- Imagine you are stranded on an island and have access to 5 things. Which 5 things would you choose?
- Which 3 elements make a stronger nation? Why?
- What are the disadvantages of growing up? How would you tackle them?
- Would you be blind or deaf? Why?
- What if you could donate 50% of your wealth and have free food for life? What would you do?
Critical thinking in students: Why is it crucial?
High schoolers are on their way to exploring various subjects and acquiring knowledge from around the world. In such a phase, students must have the ability to think through things and make the right decision. Critical thinking empowers the brain to analyze and understand situations with complete evidence before concluding. Here’s how critical thinking shapes the life of high schoolers.
1. Develops Problem-Solving Skills
Students are sure to come across everyday problems and issues in their academic journey or personal life. While some students may develop stress, others might ignore it. However, the essence of critical thinking helps students solve these issues with intelligence. Whether it is figuring out about the project or solving an issue between friends, thinking and analyzing the possible solutions makes it easy to tackle situations.
2. Enhances Creativity
The advertisements you see every day often talk about the problem and how a product solves it. That’s exactly why you need to develop critical thinking skills. When you can identify the core issue and arrive at solutions only then can you think out of the box. Critical thinking helps students be creative with their solutions and find a way out amidst challenges.
3. Boosts Decision-Making Skills
With every project, assignment, or topic of your thesis , you need to take many decisions in the learning process. Here, critical thinking skills play a crucial role in helping you analyze, decode and disseminate information before making any decision.
4. Builds Open-mindedness
As growing individuals, it is important to be open-minded towards various problems and their suggestions. People who think critically are more likely to understand situations from different points of view. Hence, developing critical thinking skills helps you accept different perspectives and respect the opinions of others. The skill helps a long way when you need to work in a group on your projects. It is because you become capable of thinking from various perspectives.
5. Goal Setting
Success comes with proper planning and execution of tasks. However, you cannot study history if you are weak at math. Similarly, you cannot aim for a 60% growth in your academics if you have been growing at a pace of 30% in each examination. Critical thinking enables you to think practically and map your way out to reach your goals. When you think critically and practically, you can analyze your strengths and weaknesses thereby setting goals accurately.
Critical thinking indeed plays an essential role in shaping the mindset of students and exposing them to different skills simply by developing this one. As you take advantage of the critical thinking questions, know that it is important to keep questioning students to initiate conversations.
Whether it is reflective questions or would you rather-questions , these questions enable them to think beyond their imagination and dive into a world of possibilities. Apart from this, you may also involve students in interactive discussions that boost critical thinking skills.

Sananda Bhattacharya, Chief Editor of TheHighSchooler, is dedicated to enhancing operations and growth. With degrees in Literature and Asian Studies from Presidency University, Kolkata, she leverages her educational and innovative background to shape TheHighSchooler into a pivotal resource hub. Providing valuable insights, practical activities, and guidance on school life, graduation, scholarships, and more, Sananda’s leadership enriches the journey of high school students.
Explore a plethora of invaluable resources and insights tailored for high schoolers at TheHighSchooler, under the guidance of Sananda Bhattacharya’s expertise. You can follow her on Linkedin
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
17 Types of Questions for Teachers in the Classroom

Questions are the foundation of almost any class, but knowing when to ask the right ones may require some pre-planning. Educators can use different types of questions in teaching to check on a student’s understanding, spark discussion, or help others learn from their peers.
Of course, you may have the perfect list of questions to ask, but keeping students engaged and talking can become another hurdle. We’ll go over different strategies for designing effective questions and how to handle various situations, such as incorrect answers or silence. Plus, we’ll show you how tech like Poll Everywhere can help you engage your students with interactive presentations and questions .
How to design effective and engaging questions (and get students to respond)
Keeping students engaged while you ask questions designed to measure their level of understanding is an art. Here are some steps you can take to thoughtfully craft different types of questions for your classroom:
Planning what types of questions to ask
- Choose a goal for asking questions: This helps you decide which types of questions used in teaching are best for your needs.
- Decide what course material to base questions on: It’s better to choose content you feel is important to the overall learning objectives noted in your lesson plan.
- Plan critical questions ahead of time: While it’s okay to formulate questions as the class progresses, it’s important to plan questions you deem essential to gauging students’ learning or prompting critical thinking ahead of time.
- Adapt questions to students’ knowledge levels: Make sure your questions challenge your students' understanding of newly presented topics or assess their foundational knowledge—using a diagnostic assessment before and after the semester can help gauge current knowledge.
- Use a variety of question types: Using a variety of question types—even for the same concept—can help students better grasp the course material by prompting them to think about their answers in different ways. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy to develop multiple levels of questions for the same topic is helpful.
- Anticipate possible answers: This helps you ensure the phrasing of your question isn’t too vague or misleading, as well as whether the questions match your learning objectives.
Asking questions
- Phrase questions clearly: Ensure your questions are unambiguous and are phrased logically so students don’t misunderstand or end up more confused.
- Allow time to process the question: Don’t be afraid of silence—it likely means your students are contemplating the question and thinking through their responses. You should always wait a moment for students to process the question before rephrasing or assuming they don’t understand.
- Avoid including the answer in your questions: If you’re assessing students’ comprehension, including the answer in your question defeats the purpose and likely won’t encourage engagement.
- Vary the types of questions you ask: By varying the questions you use in your teaching, you can prompt students to think about the material in different ways.
Assessing student responses
- Follow student responses with reflection: A reflective statement (e.g., “It sounds like…” or “What did you mean when you said…?”) helps you show you’re listening and double-check your understanding of the response.
- Ask students to elaborate: Similar to making a reflective statement, you can outright request that a student elaborate on their response. This can help you really dig into their level of comprehension and may also help other students who are listening in by giving them insight into their peers’ thinking processes.
- Know how you’ll handle incorrect answers: Have a game plan in place in case students answer incorrectly. This not only reduces the chance of confusion but also helps you confidently guide the discussion so students can come to the correct answer and understand why their original answer was incorrect.
- Encourage other students to chime in: Turn a one-way conversation into a discussion by inviting others to offer their opinions or state if they agree or disagree (and why).
- Use positive reinforcement: Make students feel confident and glad they responded by smiling, using positive statements, nodding, and making eye contact. This positive reinforcement can help students feel safe when responding—or when asking questions.
- Keep track of who’s responded: While some students are eager to offer their two cents, others may be more reluctant. You can create a more inclusive and inviting discussion by allowing a variety of students to share. If you teach a hybrid class, be sure to include both in-person and remote students as well.
3 strategies for addressing incorrect answers or surface-level understanding
If your students don’t respond with a satisfactory answer, you can take advantage of that time to help students understand what they got wrong and what the correct answer is. Three different strategies for guiding students to a better understanding of the topic include probing, redirecting, and refocusing.
- Probing: The probing strategy encourages students to use critical thinking to analyze their answers. This may involve uncovering relationships by comparing and contrasting different concepts, or instructors can ask students to clarify their ideas by providing examples. Additionally, educators can help students pinpoint assumptions used to justify their answers.
- Redirecting: By using redirection carefully, you can invite other students to correct a peer’s incorrect answers. This strategy also encourages more students to participate in the discussion by asking if they agree with the answer or if they can provide an example to support the answer. Just be sure to lay out ground rules before opening up a discussion based on one student’s thoughts to avoid unnecessary conflict.
- Refocusing: Instructors can refocus students if their answer doesn’t quite fit with the content being discussed. For example, let’s say you ask, “What’s one way our modern food system is making people sick?” and a student responds with, “Doesn’t it encourage us to overeat?”—you might refocus the discussion to discuss how not all calories are nutritionally equal by asking, “Yes, but what if we’re talking about not just caloric intake but nutritional intake as well?”
How to use Bloom’s Taxonomy to craft engaging questions
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework intended to define different levels of learning and help teachers assess student progress. You can use this concept to develop questions that assess students’ levels of understanding. According to Bloom’s Taxonomy, there are six different levels of understanding: remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, and create.
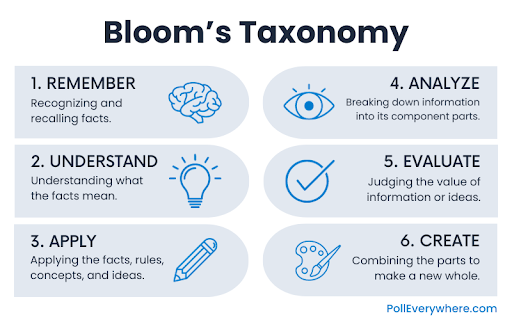
Remember, understand, and apply questions are typically used to assess learners’ comprehension to see whether anyone needs additional assistance grasping the course content. Analyze, evaluate, and create questions are more often used to encourage deeper critical thinking and problem-solving, or to spark discussions.
If you start with higher-level questions associated with the analyze, evaluate, and create levels and students aren’t sure of the answer, asking a follow-up question related to the lower levels of remember, understand, and apply can help you judge whether your learners understand the course material or not.
Here are some examples to help you craft your own questions based on Bloom’s Taxonomy:
- Can you describe ____?
- When did ____ happen?
- Which is true/false, ____ or ____?
- What does ____ mean?
- How would you show ____?
- How would you compare/contrast ____?
- What’s the main idea of ____?
- What would happen if ____?
- How would you state ____ in your own words?
- Which statements support ____?
- Do you know of another instance where ____?
- What examples can you think of to support ____?
- How would you use ____?
- How would you solve ____ using what you’ve learned?
- What questions would you ask to better understand ____?
- Why do you think ____?
- What conclusions can you draw about ____?
- Why did ____ changes occur?
- What’s the theme of ____?
- How is ____ similar to ____?
- What’s your opinion of ____ and why?
- How would you handle ____?
- Is there a better solution to ____?
- What information would you use to support the view of ____?
- Why was ____ better than ____?
- Can you see a possible solution for ____?
- What alternative can you propose for ____?
- How would you test ____?
- What would you predict is the outcome of ____?
- What new/unique uses can you come up with for ____?
What to do if students don’t respond to questions
Possibly one of the worst nightmares any instructor can have is asking a question and being met with silence. But with a few simple strategies you can turn silence into learning opportunities:
- Rephrase the question: Chances are your students don’t understand the question or aren’t sure what you’re looking for. In this case, rephrasing the question to clarify could help clear up the confusion. For example, let’s say you ask your students, “How would you define a project?” You can reword the question by asking, “In what ways are projects different from processes?”
- Prompt with information: You might be able to jog students’ memories or thinking by providing information or context. For example, if students cannot answer “How do you calculate the circumference of a circle?” you could break the question down by asking “How do you calculate the radius of a circle?”
Why is it important to use engaging questions while teaching?
At a minimum, crafting thoughtful questions can help you judge whether your class comprehends the concepts presented in the course. Additionally, strategically designing questions can improve students’ learning comprehension by helping them think critically and creatively as well as encouraging them to engage with the course content.
Questions, credibility, and feedback are all aspects of communication that can improve student engagement. A 2021 study published in the Frontiers in Psychology journal found a “strong dynamic between the aspects of academic engagement and teacher caring, credibility, feedback, and communication style.” Additionally, one study participant noted that an instructor’s credibility actually improves if they don’t always know the answers to all questions.
17 effective types of questions in teaching
Planning out your questions for each lesson also involves considering what types of questions you’ll ask. There are numerous question types and each one may elicit a different response from students. Here are some more effective types of questions to use in teaching that encourage critical thinking and creativity:
A type of rhetorical question, display questions help educators check on students’ ability to retrieve information.
- How much of the body’s oxygen consumption does the brain account for?
- Who wrote “The Faerie Queene?”
2. Referential
A referential question is used when the person asking the question doesn’t know the answer. These types of questions may be helpful to instructors when gathering student feedback about course materials and activities—or to create personal connections by checking in on how students are doing.
- Overall, do you feel this class was beneficial?
- How was your weekend?
Factual questions, also called explicit questions, call on students to answer using information pulled directly from reading assignments. Educators can use factual questions to understand whether students understand the concepts presented in the readings.
Factual questions are an essential starting point for students to expand on the information they’ve learned with critical thinking.
- Which art movement is Salvador Dali associated with?
- Who designed the Sagrada Familia in Barcelona, Spain?
4. Convergent
These types of questions ask students to pull together ideas and information from different sources and synthesize them to create a logical answer. Convergent questions are ideal for problem-solving activities.
- What was the common theme in last week’s reading?
- How would you describe this current event in one word?
5. Divergent
The opposite of convergent questions, divergent questions don’t have a single answer. These types of questions are best used to inspire creative responses and encourage students to consider different points of view, ideas, and scenarios.
- How do you think Edgar Allen Poe would have ended “The Tell-Tale Heart” if his main character didn’t confess?
- How do you think the US might be different if the assassination of John F. Kennedy never took place?
6. Evaluative
An evaluative question requires students to think of a response based on their opinion. These questions can prompt students to think critically about readings or discussions and draw connections to their own experiences or ideals.
- What do you think about Captain Ahab’s mission to find the white whale?
- Do you agree with what the author said in this paper about animal rights?
Open-ended questions are essential to prompt students to think critically about their answers. Open questions can’t be answered with a simple “Yes” or “No,” making them a powerful tool for inspiring discussion.
- What is the main purpose of the United Nations?
- What’s one major breakthrough we’ve had in science over the last 10 years?
Learn more: Marquise McGraw, Ph.D., a professional lecturer at American University, gets students involved in discussions using Poll Everywhere. Find out his personal strategies for engaging everyone —even students who are normally too shy to share—in classroom discussions.
If instructors are trying to get a student to provide more information about their answer, they can use probing questions to prompt students to clarify, justify, or elaborate on their thoughts.
- What information helped you come to that conclusion?
- Who might disagree with your answer?
9. Multiple choice
One of the most common types of questions, multiple-choice questions provide options for students to choose from when answering. Usually, multiple-choice questions have one correct answer, but alternatives include prompting students to choose the option that’s wrong out of a list of correct options or offering an “All of the above” option.
Multiple-choice questions can improve student participation by making it easier for them to respond. Tech like Poll Everywhere further enhances this accessibility by allowing students to answer using their cell phones—or answer anonymously if the instructor chooses to set up the question that way.
- Which project document includes the description, owner, source, priority, and status of product requirements? a) The project charter b) The requirements traceability matrix c) The scope management plan d) The work breakdown structure
- How are tertiary colors created? a) Mixing equal amounts of two secondary colors b) Mixing unequal amounts of two primary colors c) Mixing three primary colors d) All of the above
Focal questions encourage students to pick a side and support their position with logical reasoning. These can be helpful in inspiring students to consider alternative points of view or schools of thought.
- Do you think all US citizens should have to sign up for the draft? Why or why not?
- Do you believe it was within the right of the US Supreme Court to overturn Roe v. Wade? Why or why not?
Physicist Enrico Fermi is the namesake of the Fermi question, which requires students to estimate an answer based on limited information. You may recognize this type of question from articles covering Google’s unconventional approach to interviewing potential new employees, as Fermi questions require creative thinking and the ability to work through a problem.
- Why are manhole covers round?
- How would you explain how the internet works to a seven-year-old?
Thunk questions are intended to encourage students to pause and look at what might normally be a common, benign concept in a different light. (Fun fact: The term “thunk” is based on the irregular form of the verb “think.”)
- If your pet could talk, what would it say about you?
- What’s the difference between knowing and believing?
13. Hypothetical
Hypothetical questions use the good old “What if…” structure to prompt students to consider a scenario and how they would react or feel. Hypothetical questions inspire creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
- What if Europeans never reached North or South America, how would the world be different?
- What do you think life would be like if dinosaurs never went extinct?
14. Ethical
Educators can present students with moral dilemmas using ethical questions. These types of questions don’t have a right or wrong answer but do require students to think critically about why they believe their answer is correct. Ethical questions are excellent discussion starters.
- Do you think countries should be able to claim other planets as their own?
- Should we take care of workers whose jobs are replaced by AI?
15. Application
Instructors can use application questions to encourage students to apply newly gained knowledge related to the course. By using information they’ve learned in class and applying it to real-world situations, students can achieve a higher level of comprehension.
- What are some examples of media bias you’ve seen recently?
- How would you demonstrate Newton’s first law using objects on your desk or in the classroom?
- Using what you know about cognitive bias, how would you design a website landing page that converts leads?
16. Affective
You can encourage students to engage with course content on a more personal level by using affective questions. These types of questions ask students about their feelings toward a topic and how it relates to their values.
Poll Everywhere’s numeric rating scale allows educators to present affective questions in a friendly way. Ask students to rate how they feel about an issue using a scale from one to five, then ask if anyone wants to chime in with the reasoning behind their rating to kick the discussion off.
- How do you feel about the author’s portrayal of Lenny?
- Is the use of imagination in art important to you?
These types of questions are used to gauge your students’ understanding of a topic all at the same time. By using hinge questions, you can decide whether the day’s class should continue going over the topic or if you can move on to the next lesson.
- Which of the following examples represents an allegory?
- Which of the following is an example of soft news?
3 types of ineffective questions to avoid (or use carefully)
Along with the 17 types of effective questions above, there are three more types of questions that can become problematic if not used carefully.
- Binary: Also called a closed question, a binary question is usually answered with “Yes” or No” or variations thereof. These questions typically force students to choose a side and are more effective if there’s no right or wrong answer or if you probe for additional information.
- Leading: Leading questions are problematic because they suggest the correct or desired answer. An example of a leading question is, “How satisfied were you with the class?”
- Loaded: These types of questions include an implicit assumption about the respondent. An example of a loaded question is, “How many times did you cheat on your exams during the semester?”
Poll Everywhere makes gauging student understanding effective and engaging
Getting students to participate in discussions or even ask their own questions is challenging. Designing effective questions based on your desired outcomes or learning objectives keeps you one step ahead of in-class conversations. However, you should also be ready to guide discussions back on topic if students take off on tangents or a respectful debate becomes a heated argument.
Tech like Poll Everywhere can help you present your questions in an engaging format that invites all students to participate. With the ability to ask and share any type of question using Poll Everywhere, including multiple-choice, you can quickly and easily inspire and guide discussions that all students are excited to participate in.
Related articles
- Math Resources Links
- Math in the Real World
- Differentiated Math Unlocked
- Math in the Real World Workshop
20 Math Critical Thinking Questions to Ask in Class Tomorrow
- November 20, 2023

The level of apathy towards math is only increasing as each year passes and it’s up to us as teachers to make math class more meaningful . This list of math critical thinking questions will give you a quick starting point for getting your students to think deeper about any concept or problem.
Since artificial intelligence has basically changed schooling as we once knew it, I’ve seen a lot of districts and teachers looking for ways to lean into AI rather than run from it.
The idea of memorizing formulas and regurgitating information for a test is becoming more obsolete. We can now teach our students how to use their resources to make educated decisions and solve more complex problems.
With that in mind, teachers have more opportunities to get their students thinking about the why rather than the how.
Table of Contents
Looking for more about critical thinking skills? Check out these blog posts:
- Why You Need to Be Teaching Writing in Math Class Today
- How to Teach Problem Solving for Mathematics
- Turn the Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs into Engaging Math Activities

What skills do we actually want to teach our students?
As professionals, we talk a lot about transferable skills that can be valuable in multiple jobs, such as leadership, event planning, or effective communication. The same can be said for high school students.
It’s important to think about the skills that we want them to have before they are catapulted into the adult world.
Do you want them to be able to collaborate and communicate effectively with their peers? Maybe you would prefer that they can articulate their thoughts in a way that makes sense to someone who knows nothing about the topic.
Whatever you decide are the most essential skills your students should learn, make sure to add them into your lesson objectives.

When should I ask these math critical thinking questions?
Critical thinking doesn’t have to be complex or fill an entire lesson. There are simple ways that you can start adding these types of questions into your lessons daily!
Start small
Add specific math critical thinking questions to your warm up or exit ticket routine. This is a great way to start or end your class because your students will be able to quickly show you what they understand.
Asking deeper questions at the beginning of your class can end up leading to really great discussions and get your students talking about math.

Add critical thinking questions to word problems
Word problems and real-life applications are the perfect place to add in critical thinking questions. Real-world applications offer a more choose-your-own-adventure style assignment where your students can expand on their thought processes.
They also allow your students to get creative and think outside of the box. These problem-solving skills play a critical role in helping your students develop critical thinking abilities.

Keep reading for math critical thinking questions that can be applied to any subject or topic!
When you want your students to defend their answers.
- Explain the steps you took to solve this problem
- How do you know that your answer is correct?
- Draw a diagram to prove your solution.
- Is there a different way to solve this problem besides the one you used?
- How would you explain _______________ to a student in the grade below you?
- Why does this strategy work?
- Use evidence from the problem/data to defend your answer in complete sentences.
When you want your students to justify their opinions
- What do you think will happen when ______?
- Do you agree/disagree with _______?
- What are the similarities and differences between ________ and __________?
- What suggestions would you give to this student?
- What is the most efficient way to solve this problem?
- How did you decide on your first step for solving this problem?

When you want your students to think outside of the box
- How can ______________ be used in the real world?
- What might be a common error that a student could make when solving this problem?
- How is _____________ topic similar to _______________ (previous topic)?
- What examples can you think of that would not work with this problem solving method?
- What would happen if __________ changed?
- Create your own problem that would give a solution of ______________.
- What other math skills did you need to use to solve this problem?
Let’s Recap:
- Rather than running from AI, help your students use it as a tool to expand their thinking.
- Identify a few transferable skills that you want your students to learn and make a goal for how you can help them develop these skills.
- Add critical thinking questions to your daily warm ups or exit tickets.
- Ask your students to explain their thinking when solving a word problem.
- Get a free sample of my Algebra 1 critical thinking questions ↓

Share this:
7 thoughts on “20 math critical thinking questions to ask in class tomorrow”.
I would love to see your free math writing prompts, but there is no place for me to sign up. thank you
Ahh sorry about that! I just updated the button link!
Pingback: How to Teach Problem Solving for Mathematics -
Pingback: 5 Ways Teaching Collaboration Can Transform Your Math Classroom
Pingback: 3 Ways Math Rubrics Will Revitalize Your Summative Assessments
Pingback: How to Use Math Stations to Teach Problem Solving Skills
Pingback: How to Seamlessly Add Critical Thinking Questions to Any Math Assessment
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Critical thinking definition

Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process, which is why it's often used in education and academics.
Some even may view it as a backbone of modern thought.
However, it's a skill, and skills must be trained and encouraged to be used at its full potential.
People turn up to various approaches in improving their critical thinking, like:
- Developing technical and problem-solving skills
- Engaging in more active listening
- Actively questioning their assumptions and beliefs
- Seeking out more diversity of thought
- Opening up their curiosity in an intellectual way etc.
Is critical thinking useful in writing?
Critical thinking can help in planning your paper and making it more concise, but it's not obvious at first. We carefully pinpointed some the questions you should ask yourself when boosting critical thinking in writing:
- What information should be included?
- Which information resources should the author look to?
- What degree of technical knowledge should the report assume its audience has?
- What is the most effective way to show information?
- How should the report be organized?
- How should it be designed?
- What tone and level of language difficulty should the document have?
Usage of critical thinking comes down not only to the outline of your paper, it also begs the question: How can we use critical thinking solving problems in our writing's topic?
Let's say, you have a Powerpoint on how critical thinking can reduce poverty in the United States. You'll primarily have to define critical thinking for the viewers, as well as use a lot of critical thinking questions and synonyms to get them to be familiar with your methods and start the thinking process behind it.
Are there any services that can help me use more critical thinking?
We understand that it's difficult to learn how to use critical thinking more effectively in just one article, but our service is here to help.
We are a team specializing in writing essays and other assignments for college students and all other types of customers who need a helping hand in its making. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
- Select the topic and the deadline of your essay.
- Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the essay writing process you struggle with.
- Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
- Select your prefered payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed essay writers , online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.
- You Are At:
CBSE changes exam format for Class 11-12 from this academic year, to focus on concept application questions
The board said it is continuing with aligning of the assessments and evaluation practices with nep- 2020 for the academic session 2024-2025..

The move is expected to herald a paradigm shift in the way students approach their studies, moving away from rote memorization towards a more holistic understanding of concepts. It is envisioned to empower students to think creatively, innovate, and develop a deeper appreciation for the subjects they study.
Percentage of competency-focused questions increased
While the percentage of competency-focused questions in the form of MCQs, case-based questions, source-based integrated questions or any other type has been increased from 40 to 50 per cent, the percentage of constructed response questions including short and long answers has been reduced from 40 to 30 per cent.
What did CBSE Director (Academics) say?
"The board in accordance with National Education Policy, 2020 has taken multiple steps towards implementation of Competency-Based Education in schools, ranging from aligning assessment to competencies, development of exemplar resources for teachers and students as well as continuous capacity building of the teachers etc," said Joseph Emanuel, Director (Academics), CBSE.
"The main emphasis of the board was to create an educational ecosystem that would move away from rote memorization and towards learning that is focused on developing the creative, critical and systems thinking capacities of students to meet the challenges of the 21st century," he added.
No changes in Class 9-10 exam format
Emanuel said the board is continuing with aligning of the assessments and evaluation practices with NEP- 2020 for the academic session 2024-2025. "Consequently, in the forthcoming session, the percentage of Competency Based Questions that assess the application of concepts in real-life situations included in the question papers of the board has been altered," he said. There is no change in the exam format for Classes 9 and 10, the Director added.
(With PTI inputs)
ALSO READ: CTET July 2024: CBSE to close registration window on THIS date! check details
Read all the Breaking News Live on indiatvnews.com and Get Latest English News & Updates from Education
- Education News

ED urges for CBI probe before Jharkhand High Court into case lodged by Hemant Soren under SC/ST Act

'I obviously know about...', Ed Sheeran talks about Shah Rukh Khan with Tanmay Bhatt, Shubman Gill

SRH vs CSK: Abhishek Sharma, Aiden Markram shine in Hyderabad's dominant win over Chennai
Related Education News

NCERT to release new textbooks for classes 3 and 6 by April/May, check details

Government Exam 2024: From UPSC to JEE, list of exams scheduled to be conducted in April

KVS Admission 2024: Registration begins for Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 1, apply here from direct link

JEE Main 2024 Session 2 admit card released | Check how to download

UPSC aspirants opting for Imphal as exam centre can change it | Check full details here
Latest News

IPL 2024 points table after SRH vs CSK clash; Rajasthan Royals eye top spot in next game against RCB

Fact Check: Did AAP leader Sanjay Singh argue with police after release from jail? Here is the truth
- Aap Ki Adalat
- Aaj Ki Baat
- Kurukshetra
- Haqiqat Kya Hai
- Entertainment

Aaj Ki Baat: The Guardian publishes dubious report based on Pakistani sources, claims India is using Jihadis to kill terrorists

What is reality: Rahul's '48' pages and Narendra Modi's '48' minutes

Afjal Ansari On Mukhtar Ansari Wife: Afzal Ansari's open warning to Mukhtar Ansari's wife!

Priya Dutt Exclusive: Is Sunil Dutt's daughter a fan of PM Modi?
Keshav Prasad Maurya Exclusive: 80 in 80...Yogi's deputy explaining chemistry
- Maharashtra
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
- West Bengal
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Chhattisgarh

Lok Sabha Elections 2024: Congress releases list of 40 star campaigners for Uttarakhand | Check list

Lok Sabha Elections: Nomination of SP's Khajuraho candidate rejected | List of past cases

Priya Dutt rules out resignation from Congress, says 'have taken a back seat'

Aap Ki Adalat: Madhavi Latha to face tough questions from Rajat Sharma at 10 pm today

VIP rejoins Mahagathbandhan: When Mukesh Sahani walked out of Tejashwi's presser in Bihar | VIDEO

Congress manifesto: Sonia, Kharge and Rahul release 'Nyay Patra' for Lok Sabha Elections 2024

Lok Sabha elections 2024: 'Congress is on verge of downfall, endangered party', says Shivraj Chouhan

Hardik Pandya visits Somnath temple to offer prayers amidst crisis-hit start to IPL 2024 | WATCH

RR vs RCB Dream11 Prediction: IPL 2024 Match 19 fantasy team, captaincy picks, predicted playing XIs

RR vs RCB pitch report IPL 2024: How will surface at Sawai Mansingh Stadium in Jaipur play?

SRH vs CSK IPL 2024 Highlights: Impressive all-round performance boosts Hyderabad to easy win

"You are making ground shake": Magnitude 4.8 earthquake interrupts UN briefing on Gaza | WATCH VIDEO

US: New York, nearby areas feel tremors as earthquake at 4.7 magnitude strikes region

UNHRC adopts resolution condemning Israel’s ‘war crimes’ in Gaza; India, 12 other countries abstain

Who is Livia Voigt, the world's youngest billionaire at 19?

US: Man executed in Oklahoma for double murder, including of Indian national, in 2002
- Celebrities

Palpita to Hass Hass: Global domination of Diljit Dosanjh with THESE international collaborations

'After working...', Manjoy Bajpayee wishes to connect with the audience through exceptional stories

The Amazing Spider-Man star Andrew Garfield, Cynthia Erivo to feature in George Orwell's '1984'

'I was eleven years old...', Diljit Dosanjh speaks about his strain in relationship with parents
- Live Scores
- Other Sports

SRH v CSK: Why are Pathirana and Mustafizur not playing in Chennai's clash against Hyderabad?

RBI to allow third-party apps to use prepaid wallets for UPI payments

Google reportedly planning to charge users for its generative AI-powered search feature

Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw says India to legislate AI regulation soon

RBI announces mobile app to facilitate investment in government securities

Realme 12X goes on sale in India today: Check price, offers, availability

How did a 660-tonne steel pendulum protect Taiwan's largest skyscraper during 7.4 earthquake?

Why are Japan, Taiwan and other countries in that region prone to frequent earthquakes?

SP continues to change candidates ahead of Lok Sabha polls: Here's what led Akhilesh Yadav to do so

What is the Katchatheevu Island row all about. Know details

Centre extends AFSPA in eights districts of Nagaland for six months | Know why

Horoscope Today, April 5: Mental peace on cards for Aquarians; know about other zodiac signs

Horoscope Today, April 4: Cancerians should stop overthinking; know about other zodiac signs

Horoscope Today, April 3: Aquarius to get financial benefits; know about other zodiac signs

Horoscope Today, April 2: Leo to get support from colleagues in work; know about other zodiac signs

Horoscope Today, April 1: Aries should avoid decision making in haste; know about other zodiac signs
- Relationships

6 sun protection strategies for Indian skin: Myth vs Reality

5 delicious and nutritious ragi recipes to aid in weight loss

What is ‘Oatzempic’? Know all about the viral weight loss trend

Roasted vs Soaked Gram: Which one is good for your health?

Ramadan 2024: 5 healthy habits to sustain post Ramzan

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In an age of "fake news" claims and constant argument about pretty much any issue, critical thinking skills are key. Teach your students that it's vital to ask questions about everything, but that it's also important to ask the right sorts of questions. Students can use these critical thinking questions with fiction or nonfiction texts ...
The Ultimate Cheat Sheet For Digital Thinking by Global Digital Citizen Foundation is an excellent starting point for the 'how' behind teaching critical thinking by outlining which questions to ask. It offers 48 critical thinking questions useful for any content area or even grade level with a little re-working/re-wording. Enjoy the list!
There are many resources to help you determine if information sources are factual or not. 7. Socratic Questioning. This way of thinking is called the Socrates Method, named after an old-time thinker from Greece. It's about asking lots of questions to understand a topic.
Questions to Provoke Critical Thinking. Varying question stems can sustain engagement and promote critical thinking. The timing, sequence and clarity of questions you ask students can be as important as the type of question you ask. The table below is organized to help formulate questions provoking gradually higher levels of thinking.
Types Of Questions For Teaching. Clarifying Question: A question meant to clarify something-either a question asked by the teacher to clarify the answer a student gives or what the student thinks or a question asked by the student to the teacher to clarify something (a statement, a task, a question, etc.) Probing Questions: A probing question ...
Spread the loveIntroduction: Critical thinking is an essential skill for students to develop, as it enables them to analyze information, evaluate arguments, and make informed decisions. To enhance critical thinking abilities, students can engage with thought-provoking questions that challenge assumptions and encourage deeper reflection. In this article, we present sixteen critical thinking ...
How Questions Guide Young Students' Critical Thinking . ... Instead of reciting facts or giving a textbook answer, critical thinking skills encourage students to move beyond knowing information and get to the heart of what they really think and believe. ... Inventing an example, or pulling from experience to share a real one, is an excellent ...
Critical Thinking Questions Examples . Critical thinking questions are easy to spot. They're questions that are worded so you can take a more in-depth look at things. They're similar in nature to open-ended questions, in that it's expected the person who's being questioned will provide a substantive answer rather than a short one.
A critical thinking question should aim to make you think. It should lead students to ponder the answer and discuss possible solutions. Critical thinking questions can even lead to disagreements and arguments that can turn into an impressive teachable moment. One way to incorporate a solid critical thinking question into a math lesson is to ...
2. Evaluation Questions. Evaluation questions call for the respondent to make a judgment about the value of something, based on defined criteria. They often use terms like "critique", "justify", "validate", "defend", etc. Example: "Evaluate the effectiveness of the government's pandemic response measures.
What makes a good critical thinking question? Open ended questions are perfect for encouraging critical thinking and problem-solving. Kids (and grown-ups) have to think about their answers. Below you will find the best age-appropriate examples to use in the classroom, at home, or during your everyday routine.. In fact, there's no question about it.
Teach Reasoning Skills. Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
Incorporating critical thinking questions can help students think more analytically and prompt them to formulate their ideas. Great questions can be broken out into these different ways: Critical thinking questions start with "where." Critical thinking questions start with "what." Critical thinking questions start with "who ...
Students may need a little guidance to think their way through questions that lack straightforward answers. But it is that process that is important! How the Right Questions Encourage Critical Thinking. Every parent knows how natural it is for children to ask questions. It should be encouraged. After all, asking questions helps with critical ...
Your critical thinking skills involve gathering complete information, understanding and defining terms, questioning the methods by which we get facts, questioning the conclusions, and looking for hidden assumptions and biases. Additionally, we can't expect to find all of the answers, and we need to take the time to examine the big picture of ...
One crucial way for how to create critical thinking questions is to examine how you might feel is there were many issues and questions that don't have a black and white answer. Simple example? War. It's hell, as has often been said. But it's also as old as the first days humans lived in caves and even before.
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
Analytical. Creativity. Open-mindedness. Let's review some of the best questions that encourage critical thinking in high school students. Contents. 1 47 Critical Thinking Questions for High School Students. 1.1 Question 1. 1.2 Question 2. 1.3 Question 3.
Two things are crucial: 1) critical thinking is not just thinking, but thinking which entails self-improvement. 2) this improvement comes from skill in using standards by which one appropriately assesses thinking. To put it briefly, it is self-improvement (in thinking) through standards (that assess thinking).
Here's how critical thinking shapes the life of high schoolers. 1. Develops Problem-Solving Skills. Students are sure to come across everyday problems and issues in their academic journey or personal life. While some students may develop stress, others might ignore it. However, the essence of critical thinking helps students solve these ...
Here are some more effective types of questions to use in teaching that encourage critical thinking and creativity: 1. Display. A type of rhetorical question, display questions help educators check on students' ability to retrieve information. Examples:
Start small. Add critical thinking questions to word problems. Keep reading for math critical thinking questions that can be applied to any subject or topic! When you want your students to defend their answers. When you want your students to justify their opinions. When you want your students to think outside of the box.
Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement. Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and ...
In a significant move aimed at fostering critical thinking and practical understanding among students, the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has announced a revamp in the examination ...