- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Additional menu
Khan Academy Blog
Free Math Worksheets — Over 100k free practice problems on Khan Academy
Looking for free math worksheets.
You’ve found something even better!
That’s because Khan Academy has over 100,000 free practice questions. And they’re even better than traditional math worksheets – more instantaneous, more interactive, and more fun!
Just choose your grade level or topic to get access to 100% free practice questions:
Kindergarten, basic geometry, pre-algebra, algebra basics, high school geometry.
- Trigonometry
Statistics and probability
High school statistics, ap®︎/college statistics, precalculus, differential calculus, integral calculus, ap®︎/college calculus ab, ap®︎/college calculus bc, multivariable calculus, differential equations, linear algebra.
- Addition and subtraction
- Place value (tens and hundreds)
- Addition and subtraction within 20
- Addition and subtraction within 100
- Addition and subtraction within 1000
- Measurement and data
- Counting and place value
- Measurement and geometry
- Place value
- Measurement, data, and geometry
- Add and subtract within 20
- Add and subtract within 100
- Add and subtract within 1,000
- Money and time
- Measurement
- Intro to multiplication
- 1-digit multiplication
- Addition, subtraction, and estimation
- Intro to division
- Understand fractions
- Equivalent fractions and comparing fractions
- More with multiplication and division
- Arithmetic patterns and problem solving
- Quadrilaterals
- Represent and interpret data
- Multiply by 1-digit numbers
- Multiply by 2-digit numbers
- Factors, multiples and patterns
- Add and subtract fractions
- Multiply fractions
- Understand decimals
- Plane figures
- Measuring angles
- Area and perimeter
- Units of measurement
- Decimal place value
- Add decimals
- Subtract decimals
- Multi-digit multiplication and division
- Divide fractions
- Multiply decimals
- Divide decimals
- Powers of ten
- Coordinate plane
- Algebraic thinking
- Converting units of measure
- Properties of shapes
- Ratios, rates, & percentages
- Arithmetic operations
- Negative numbers
- Properties of numbers
- Variables & expressions
- Equations & inequalities introduction
- Data and statistics
- Negative numbers: addition and subtraction
- Negative numbers: multiplication and division
- Fractions, decimals, & percentages
- Rates & proportional relationships
- Expressions, equations, & inequalities
- Numbers and operations
- Solving equations with one unknown
- Linear equations and functions
- Systems of equations
- Geometric transformations
- Data and modeling
- Volume and surface area
- Pythagorean theorem
- Transformations, congruence, and similarity
- Arithmetic properties
- Factors and multiples
- Reading and interpreting data
- Negative numbers and coordinate plane
- Ratios, rates, proportions
- Equations, expressions, and inequalities
- Exponents, radicals, and scientific notation
- Foundations
- Algebraic expressions
- Linear equations and inequalities
- Graphing lines and slope
- Expressions with exponents
- Quadratics and polynomials
- Equations and geometry
- Algebra foundations
- Solving equations & inequalities
- Working with units
- Linear equations & graphs
- Forms of linear equations
- Inequalities (systems & graphs)
- Absolute value & piecewise functions
- Exponents & radicals
- Exponential growth & decay
- Quadratics: Multiplying & factoring
- Quadratic functions & equations
- Irrational numbers
- Performing transformations
- Transformation properties and proofs
- Right triangles & trigonometry
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry (Advanced)
- Analytic geometry
- Conic sections
- Solid geometry
- Polynomial arithmetic
- Complex numbers
- Polynomial factorization
- Polynomial division
- Polynomial graphs
- Rational exponents and radicals
- Exponential models
- Transformations of functions
- Rational functions
- Trigonometric functions
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry
- Trigonometric equations and identities
- Analyzing categorical data
- Displaying and comparing quantitative data
- Summarizing quantitative data
- Modeling data distributions
- Exploring bivariate numerical data
- Study design
- Probability
- Counting, permutations, and combinations
- Random variables
- Sampling distributions
- Confidence intervals
- Significance tests (hypothesis testing)
- Two-sample inference for the difference between groups
- Inference for categorical data (chi-square tests)
- Advanced regression (inference and transforming)
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Scatterplots
- Data distributions
- Two-way tables
- Binomial probability
- Normal distributions
- Displaying and describing quantitative data
- Inference comparing two groups or populations
- Chi-square tests for categorical data
- More on regression
- Prepare for the 2020 AP®︎ Statistics Exam
- AP®︎ Statistics Standards mappings
- Polynomials
- Composite functions
- Probability and combinatorics
- Limits and continuity
- Derivatives: definition and basic rules
- Derivatives: chain rule and other advanced topics
- Applications of derivatives
- Analyzing functions
- Parametric equations, polar coordinates, and vector-valued functions
- Applications of integrals
- Differentiation: definition and basic derivative rules
- Differentiation: composite, implicit, and inverse functions
- Contextual applications of differentiation
- Applying derivatives to analyze functions
- Integration and accumulation of change
- Applications of integration
- AP Calculus AB solved free response questions from past exams
- AP®︎ Calculus AB Standards mappings
- Infinite sequences and series
- AP Calculus BC solved exams
- AP®︎ Calculus BC Standards mappings
- Integrals review
- Integration techniques
- Thinking about multivariable functions
- Derivatives of multivariable functions
- Applications of multivariable derivatives
- Integrating multivariable functions
- Green’s, Stokes’, and the divergence theorems
- First order differential equations
- Second order linear equations
- Laplace transform
- Vectors and spaces
- Matrix transformations
- Alternate coordinate systems (bases)
Frequently Asked Questions about Khan Academy and Math Worksheets
Why is khan academy even better than traditional math worksheets.
Khan Academy’s 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don’t need to be graded, and don’t require a printer.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets look like?
Here’s an example:
What are teachers saying about Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets?
“My students love Khan Academy because they can immediately learn from their mistakes, unlike traditional worksheets.”
Is Khan Academy free?
Khan Academy’s practice questions are 100% free—with no ads or subscriptions.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets cover?
Our 100,000+ practice questions cover every math topic from arithmetic to calculus, as well as ELA, Science, Social Studies, and more.
Is Khan Academy a company?
Khan Academy is a nonprofit with a mission to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere.
Want to get even more out of Khan Academy?
Then be sure to check out our teacher tools . They’ll help you assign the perfect practice for each student from our full math curriculum and track your students’ progress across the year. Plus, they’re also 100% free — with no subscriptions and no ads.
Get Khanmigo
The best way to learn and teach with AI is here. Ace the school year with our AI-powered guide, Khanmigo.
For learners For teachers For parents
- Prodigy Math
- Prodigy English
- Is a Premium Membership Worth It?
- Promote a Growth Mindset
- Help Your Child Who's Struggling with Math
- Parent's Guide to Prodigy
- Assessments
- Math Curriculum Coverage
- English Curriculum Coverage
- Game Portal
120 Math Word Problems To Challenge Students Grades 1 to 8

Written by Marcus Guido
Hey teachers! 👋
Use Prodigy to spark a love for math in your students – including when solving word problems!
- Teaching Tools
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Mixed operations
- Ordering and number sense
- Comparing and sequencing
- Physical measurement
- Ratios and percentages
- Probability and data relationships
You sit at your desk, ready to put a math quiz, test or activity together. The questions flow onto the document until you hit a section for word problems.
A jolt of creativity would help. But it doesn’t come.
Whether you’re a 3rd grade teacher or an 8th grade teacher preparing students for high school, translating math concepts into real world examples can certainly be a challenge.
This resource is your jolt of creativity. It provides examples and templates of math word problems for 1st to 8th grade classes.
There are 120 examples in total.
The list of examples is supplemented by tips to create engaging and challenging math word problems.
120 Math word problems, categorized by skill
Addition word problems.

Best for: 1st grade, 2nd grade
1. Adding to 10: Ariel was playing basketball. 1 of her shots went in the hoop. 2 of her shots did not go in the hoop. How many shots were there in total?
2. Adding to 20: Adrianna has 10 pieces of gum to share with her friends. There wasn’t enough gum for all her friends, so she went to the store to get 3 more pieces of gum. How many pieces of gum does Adrianna have now?
3. Adding to 100: Adrianna has 10 pieces of gum to share with her friends. There wasn’t enough gum for all her friends, so she went to the store and got 70 pieces of strawberry gum and 10 pieces of bubble gum. How many pieces of gum does Adrianna have now?
4. Adding Slightly over 100: The restaurant has 175 normal chairs and 20 chairs for babies. How many chairs does the restaurant have in total?
5. Adding to 1,000: How many cookies did you sell if you sold 320 chocolate cookies and 270 vanilla cookies?
6. Adding to and over 10,000: The hobby store normally sells 10,576 trading cards per month. In June, the hobby store sold 15,498 more trading cards than normal. In total, how many trading cards did the hobby store sell in June?
7. Adding 3 Numbers: Billy had 2 books at home. He went to the library to take out 2 more books. He then bought 1 book. How many books does Billy have now?
8. Adding 3 Numbers to and over 100: Ashley bought a big bag of candy. The bag had 102 blue candies, 100 red candies and 94 green candies. How many candies were there in total?
Subtraction word problems
Best for: 1st grade, second grade
9. Subtracting to 10: There were 3 pizzas in total at the pizza shop. A customer bought 1 pizza. How many pizzas are left?
10. Subtracting to 20: Your friend said she had 11 stickers. When you helped her clean her desk, she only had a total of 10 stickers. How many stickers are missing?
11. Subtracting to 100: Adrianna has 100 pieces of gum to share with her friends. When she went to the park, she shared 10 pieces of strawberry gum. When she left the park, Adrianna shared another 10 pieces of bubble gum. How many pieces of gum does Adrianna have now?

Practice math word problems with Prodigy Math
Join millions of teachers using Prodigy to make learning fun and differentiate instruction as they answer in-game questions, including math word problems from 1st to 8th grade!
12. Subtracting Slightly over 100: Your team scored a total of 123 points. 67 points were scored in the first half. How many were scored in the second half?
13. Subtracting to 1,000: Nathan has a big ant farm. He decided to sell some of his ants. He started with 965 ants. He sold 213. How many ants does he have now?
14. Subtracting to and over 10,000: The hobby store normally sells 10,576 trading cards per month. In July, the hobby store sold a total of 20,777 trading cards. How many more trading cards did the hobby store sell in July compared with a normal month?
15. Subtracting 3 Numbers: Charlene had a pack of 35 pencil crayons. She gave 6 to her friend Theresa. She gave 3 to her friend Mandy. How many pencil crayons does Charlene have left?
16. Subtracting 3 Numbers to and over 100: Ashley bought a big bag of candy to share with her friends. In total, there were 296 candies. She gave 105 candies to Marissa. She also gave 86 candies to Kayla. How many candies were left?
Multiplication word problems

Best for: 2nd grade, 3rd grade
17. Multiplying 1-Digit Integers: Adrianna needs to cut a pan of brownies into pieces. She cuts 6 even columns and 3 even rows into the pan. How many brownies does she have?
18. Multiplying 2-Digit Integers: A movie theatre has 25 rows of seats with 20 seats in each row. How many seats are there in total?
19. Multiplying Integers Ending with 0: A clothing company has 4 different kinds of sweatshirts. Each year, the company makes 60,000 of each kind of sweatshirt. How many sweatshirts does the company make each year?
20. Multiplying 3 Integers: A bricklayer stacks bricks in 2 rows, with 10 bricks in each row. On top of each row, there is a stack of 6 bricks. How many bricks are there in total?
21. Multiplying 4 Integers: Cayley earns $5 an hour by delivering newspapers. She delivers newspapers 3 days each week, for 4 hours at a time. After delivering newspapers for 8 weeks, how much money will Cayley earn?
Division word problems
Best for: 3rd grade, 4th grade, 5th grade
22. Dividing 1-Digit Integers: If you have 4 pieces of candy split evenly into 2 bags, how many pieces of candy are in each bag?
23. Dividing 2-Digit Integers: If you have 80 tickets for the fair and each ride costs 5 tickets, how many rides can you go on?
24. Dividing Numbers Ending with 0: The school has $20,000 to buy new computer equipment. If each piece of equipment costs $50, how many pieces can the school buy in total?
25. Dividing 3 Integers: Melissa buys 2 packs of tennis balls for $12 in total. All together, there are 6 tennis balls. How much does 1 pack of tennis balls cost? How much does 1 tennis ball cost?
26. Interpreting Remainders: An Italian restaurant receives a shipment of 86 veal cutlets. If it takes 3 cutlets to make a dish, how many cutlets will the restaurant have left over after making as many dishes as possible?
Mixed operations word problems
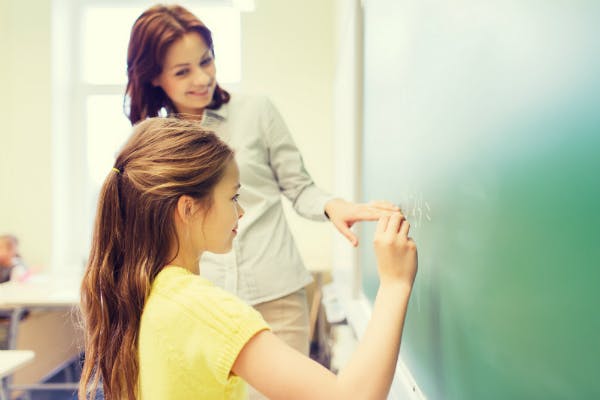

27. Mixing Addition and Subtraction: There are 235 books in a library. On Monday, 123 books are taken out. On Tuesday, 56 books are brought back. How many books are there now?
28. Mixing Multiplication and Division: There is a group of 10 people who are ordering pizza. If each person gets 2 slices and each pizza has 4 slices, how many pizzas should they order?
29. Mixing Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction: Lana has 2 bags with 2 marbles in each bag. Markus has 2 bags with 3 marbles in each bag. How many more marbles does Markus have?
30. Mixing Division, Addition and Subtraction: Lana has 3 bags with the same amount of marbles in them, totaling 12 marbles. Markus has 3 bags with the same amount of marbles in them, totaling 18 marbles. How many more marbles does Markus have in each bag?
Ordering and number sense word problems
31. Counting to Preview Multiplication: There are 2 chalkboards in your classroom. If each chalkboard needs 2 pieces of chalk, how many pieces do you need in total?
32. Counting to Preview Division: There are 3 chalkboards in your classroom. Each chalkboard has 2 pieces of chalk. This means there are 6 pieces of chalk in total. If you take 1 piece of chalk away from each chalkboard, how many will there be in total?
33. Composing Numbers: What number is 6 tens and 10 ones?
34. Guessing Numbers: I have a 7 in the tens place. I have an even number in the ones place. I am lower than 74. What number am I?
35. Finding the Order: In the hockey game, Mitchell scored more points than William but fewer points than Auston. Who scored the most points? Who scored the fewest points?
Fractions word problems

Best for: 3rd grade, 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade
36. Finding Fractions of a Group: Julia went to 10 houses on her street for Halloween. 5 of the houses gave her a chocolate bar. What fraction of houses on Julia’s street gave her a chocolate bar?
37. Finding Unit Fractions: Heather is painting a portrait of her best friend, Lisa. To make it easier, she divides the portrait into 6 equal parts. What fraction represents each part of the portrait?
38. Adding Fractions with Like Denominators: Noah walks ⅓ of a kilometre to school each day. He also walks ⅓ of a kilometre to get home after school. How many kilometres does he walk in total?
39. Subtracting Fractions with Like Denominators: Last week, Whitney counted the number of juice boxes she had for school lunches. She had ⅗ of a case. This week, it’s down to ⅕ of a case. How much of the case did Whitney drink?
40. Adding Whole Numbers and Fractions with Like Denominators: At lunchtime, an ice cream parlor served 6 ¼ scoops of chocolate ice cream, 5 ¾ scoops of vanilla and 2 ¾ scoops of strawberry. How many scoops of ice cream did the parlor serve in total?
41. Subtracting Whole Numbers and Fractions with Like Denominators: For a party, Jaime had 5 ⅓ bottles of cola for her friends to drink. She drank ⅓ of a bottle herself. Her friends drank 3 ⅓. How many bottles of cola does Jaime have left?
42. Adding Fractions with Unlike Denominators: Kevin completed ½ of an assignment at school. When he was home that evening, he completed ⅚ of another assignment. How many assignments did Kevin complete?
43. Subtracting Fractions with Unlike Denominators: Packing school lunches for her kids, Patty used ⅞ of a package of ham. She also used ½ of a package of turkey. How much more ham than turkey did Patty use?
44. Multiplying Fractions: During gym class on Wednesday, the students ran for ¼ of a kilometre. On Thursday, they ran ½ as many kilometres as on Wednesday. How many kilometres did the students run on Thursday? Write your answer as a fraction.
45. Dividing Fractions: A clothing manufacturer uses ⅕ of a bottle of colour dye to make one pair of pants. The manufacturer used ⅘ of a bottle yesterday. How many pairs of pants did the manufacturer make?
46. Multiplying Fractions with Whole Numbers: Mark drank ⅚ of a carton of milk this week. Frank drank 7 times more milk than Mark. How many cartons of milk did Frank drink? Write your answer as a fraction, or as a whole or mixed number.
Decimals word problems
Best for: 4th grade, 5th grade
47. Adding Decimals: You have 2.6 grams of yogurt in your bowl and you add another spoonful of 1.3 grams. How much yogurt do you have in total?
48. Subtracting Decimals: Gemma had 25.75 grams of frosting to make a cake. She decided to use only 15.5 grams of the frosting. How much frosting does Gemma have left?
49. Multiplying Decimals with Whole Numbers: Marshall walks a total of 0.9 kilometres to and from school each day. After 4 days, how many kilometres will he have walked?
50. Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers: To make the Leaning Tower of Pisa from spaghetti, Mrs. Robinson bought 2.5 kilograms of spaghetti. Her students were able to make 10 leaning towers in total. How many kilograms of spaghetti does it take to make 1 leaning tower?
51. Mixing Addition and Subtraction of Decimals: Rocco has 1.5 litres of orange soda and 2.25 litres of grape soda in his fridge. Antonio has 1.15 litres of orange soda and 0.62 litres of grape soda. How much more soda does Rocco have than Angelo?
52. Mixing Multiplication and Division of Decimals: 4 days a week, Laura practices martial arts for 1.5 hours. Considering a week is 7 days, what is her average practice time per day each week?
Comparing and sequencing word problems

Best for: Kindergarten, 1st grade, 2nd grade
53. Comparing 1-Digit Integers: You have 3 apples and your friend has 5 apples. Who has more?
54. Comparing 2-Digit Integers: You have 50 candies and your friend has 75 candies. Who has more?
55. Comparing Different Variables: There are 5 basketballs on the playground. There are 7 footballs on the playground. Are there more basketballs or footballs?
56. Sequencing 1-Digit Integers: Erik has 0 stickers. Every day he gets 1 more sticker. How many days until he gets 3 stickers?
57. Skip-Counting by Odd Numbers: Natalie began at 5. She skip-counted by fives. Could she have said the number 20?
58. Skip-Counting by Even Numbers: Natasha began at 0. She skip-counted by eights. Could she have said the number 36?
59. Sequencing 2-Digit Numbers: Each month, Jeremy adds the same number of cards to his baseball card collection. In January, he had 36. 48 in February. 60 in March. How many baseball cards will Jeremy have in April?
Time word problems
66. Converting Hours into Minutes: Jeremy helped his mom for 1 hour. For how many minutes was he helping her?
69. Adding Time: If you wake up at 7:00 a.m. and it takes you 1 hour and 30 minutes to get ready and walk to school, at what time will you get to school?
70. Subtracting Time: If a train departs at 2:00 p.m. and arrives at 4:00 p.m., how long were passengers on the train for?
71. Finding Start and End Times: Rebecca left her dad’s store to go home at twenty to seven in the evening. Forty minutes later, she was home. What time was it when she arrived home?
Money word problems
Best for: 1st grade, 2nd grade, 3rd grade, 4th grade, 5th grade
60. Adding Money: Thomas and Matthew are saving up money to buy a video game together. Thomas has saved $30. Matthew has saved $35. How much money have they saved up together in total?
61. Subtracting Money: Thomas has $80 saved up. He uses his money to buy a video game. The video game costs $67. How much money does he have left?
62. Multiplying Money: Tim gets $5 for delivering the paper. How much money will he have after delivering the paper 3 times?
63. Dividing Money: Robert spent $184.59 to buy 3 hockey sticks. If each hockey stick was the same price, how much did 1 cost?
64. Adding Money with Decimals: You went to the store and bought gum for $1.25 and a sucker for $0.50. How much was your total?
65. Subtracting Money with Decimals: You went to the store with $5.50. You bought gum for $1.25, a chocolate bar for $1.15 and a sucker for $0.50. How much money do you have left?
67. Applying Proportional Relationships to Money: Jakob wants to invite 20 friends to his birthday, which will cost his parents $250. If he decides to invite 15 friends instead, how much money will it cost his parents? Assume the relationship is directly proportional.
68. Applying Percentages to Money: Retta put $100.00 in a bank account that gains 20% interest annually. How much interest will be accumulated in 1 year? And if she makes no withdrawals, how much money will be in the account after 1 year?
Physical measurement word problems

Best for: 1st grade, 2nd grade, 3rd grade, 4th grade
72. Comparing Measurements: Cassandra’s ruler is 22 centimetres long. April’s ruler is 30 centimetres long. How many centimetres longer is April’s ruler?
73. Contextualizing Measurements: Picture a school bus. Which unit of measurement would best describe the length of the bus? Centimetres, metres or kilometres?
74. Adding Measurements: Micha’s dad wants to try to save money on gas, so he has been tracking how much he uses. Last year, Micha’s dad used 100 litres of gas. This year, her dad used 90 litres of gas. How much gas did he use in total for the two years?
75. Subtracting Measurements: Micha’s dad wants to try to save money on gas, so he has been tracking how much he uses. Over the past two years, Micha’s dad used 200 litres of gas. This year, he used 100 litres of gas. How much gas did he use last year?
76. Multiplying Volume and Mass: Kiera wants to make sure she has strong bones, so she drinks 2 litres of milk every week. After 3 weeks, how many litres of milk will Kiera drink?
77. Dividing Volume and Mass: Lillian is doing some gardening, so she bought 1 kilogram of soil. She wants to spread the soil evenly between her 2 plants. How much will each plant get?
78. Converting Mass: Inger goes to the grocery store and buys 3 squashes that each weigh 500 grams. How many kilograms of squash did Inger buy?
79. Converting Volume: Shad has a lemonade stand and sold 20 cups of lemonade. Each cup was 500 millilitres. How many litres did Shad sell in total?
80. Converting Length: Stacy and Milda are comparing their heights. Stacy is 1.5 meters tall. Milda is 10 centimetres taller than Stacy. What is Milda’s height in centimetres?
81. Understanding Distance and Direction: A bus leaves the school to take students on a field trip. The bus travels 10 kilometres south, 10 kilometres west, another 5 kilometres south and 15 kilometres north. To return to the school, in which direction does the bus have to travel? How many kilometres must it travel in that direction?
Ratios and percentages word problems
Best for: 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade
82. Finding a Missing Number: The ratio of Jenny’s trophies to Meredith’s trophies is 7:4. Jenny has 28 trophies. How many does Meredith have?
83. Finding Missing Numbers: The ratio of Jenny’s trophies to Meredith’s trophies is 7:4. The difference between the numbers is 12. What are the numbers?
84. Comparing Ratios: The school’s junior band has 10 saxophone players and 20 trumpet players. The school’s senior band has 18 saxophone players and 29 trumpet players. Which band has the higher ratio of trumpet to saxophone players?
85. Determining Percentages: Mary surveyed students in her school to find out what their favourite sports were. Out of 1,200 students, 455 said hockey was their favourite sport. What percentage of students said hockey was their favourite sport?
86. Determining Percent of Change: A decade ago, Oakville’s population was 67,624 people. Now, it is 190% larger. What is Oakville’s current population?
87. Determining Percents of Numbers: At the ice skate rental stand, 60% of 120 skates are for boys. If the rest of the skates are for girls, how many are there?
88. Calculating Averages: For 4 weeks, William volunteered as a helper for swimming classes. The first week, he volunteered for 8 hours. He volunteered for 12 hours in the second week, and another 12 hours in the third week. The fourth week, he volunteered for 9 hours. For how many hours did he volunteer per week, on average?
Probability and data relationships word problems

Best for: 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, 7th grade
89. Understanding the Premise of Probability: John wants to know his class’s favourite TV show, so he surveys all of the boys. Will the sample be representative or biased?
90. Understanding Tangible Probability: The faces on a fair number die are labelled 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. You roll the die 12 times. How many times should you expect to roll a 1?
91. Exploring Complementary Events: The numbers 1 to 50 are in a hat. If the probability of drawing an even number is 25/50, what is the probability of NOT drawing an even number? Express this probability as a fraction.
92. Exploring Experimental Probability: A pizza shop has recently sold 15 pizzas. 5 of those pizzas were pepperoni. Answering with a fraction, what is the experimental probability that he next pizza will be pepperoni?
93. Introducing Data Relationships: Maurita and Felice each take 4 tests. Here are the results of Maurita’s 4 tests: 4, 4, 4, 4. Here are the results for 3 of Felice’s 4 tests: 3, 3, 3. If Maurita’s mean for the 4 tests is 1 point higher than Felice’s, what’s the score of Felice’s 4th test?
94. Introducing Proportional Relationships: Store A is selling 7 pounds of bananas for $7.00. Store B is selling 3 pounds of bananas for $6.00. Which store has the better deal?
95. Writing Equations for Proportional Relationships: Lionel loves soccer, but has trouble motivating himself to practice. So, he incentivizes himself through video games. There is a proportional relationship between the amount of drills Lionel completes, in x , and for how many hours he plays video games, in y . When Lionel completes 10 drills, he plays video games for 30 minutes. Write the equation for the relationship between x and y .
Geometry word problems
Best for: 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, 7th grade, 8th grade
96. Introducing Perimeter: The theatre has 4 chairs in a row. There are 5 rows. Using rows as your unit of measurement, what is the perimeter?
97. Introducing Area: The theatre has 4 chairs in a row. There are 5 rows. How many chairs are there in total?
98. Introducing Volume: Aaron wants to know how much candy his container can hold. The container is 20 centimetres tall, 10 centimetres long and 10 centimetres wide. What is the container’s volume?
99. Understanding 2D Shapes: Kevin draws a shape with 4 equal sides. What shape did he draw?
100. Finding the Perimeter of 2D Shapes: Mitchell wrote his homework questions on a piece of square paper. Each side of the paper is 8 centimetres. What is the perimeter?
101. Determining the Area of 2D Shapes: A single trading card is 9 centimetres long by 6 centimetres wide. What is its area?
102. Understanding 3D Shapes: Martha draws a shape that has 6 square faces. What shape did she draw?
103. Determining the Surface Area of 3D Shapes: What is the surface area of a cube that has a width of 2cm, height of 2 cm and length of 2 cm?
104. Determining the Volume of 3D Shapes: Aaron’s candy container is 20 centimetres tall, 10 centimetres long and 10 centimetres wide. Bruce’s container is 25 centimetres tall, 9 centimetres long and 9 centimetres wide. Find the volume of each container. Based on volume, whose container can hold more candy?
105. Identifying Right-Angled Triangles: A triangle has the following side lengths: 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm. Is this triangle a right-angled triangle?
106. Identifying Equilateral Triangles: A triangle has the following side lengths: 4 cm, 4 cm and 4 cm. What kind of triangle is it?
107. Identifying Isosceles Triangles: A triangle has the following side lengths: 4 cm, 5 cm and 5 cm. What kind of triangle is it?
108. Identifying Scalene Triangles: A triangle has the following side lengths: 4 cm, 5 cm and 6 cm. What kind of triangle is it?
109. Finding the Perimeter of Triangles: Luigi built a tent in the shape of an equilateral triangle. The perimeter is 21 metres. What is the length of each of the tent’s sides?
110. Determining the Area of Triangles: What is the area of a triangle with a base of 2 units and a height of 3 units?
111. Applying Pythagorean Theorem: A right triangle has one non-hypotenuse side length of 3 inches and the hypotenuse measures 5 inches. What is the length of the other non-hypotenuse side?
112. Finding a Circle’s Diameter: Jasmin bought a new round backpack. Its area is 370 square centimetres. What is the round backpack’s diameter?
113. Finding a Circle's Area: Captain America’s circular shield has a diameter of 76.2 centimetres. What is the area of his shield?
114. Finding a Circle’s Radius: Skylar lives on a farm, where his dad keeps a circular corn maze. The corn maze has a diameter of 2 kilometres. What is the maze’s radius?
Variables word problems

Best for: 6th grade, 7th grade, 8th grade
115. Identifying Independent and Dependent Variables: Victoria is baking muffins for her class. The number of muffins she makes is based on how many classmates she has. For this equation, m is the number of muffins and c is the number of classmates. Which variable is independent and which variable is dependent?
116. Writing Variable Expressions for Addition: Last soccer season, Trish scored g goals. Alexa scored 4 more goals than Trish. Write an expression that shows how many goals Alexa scored.
117. Writing Variable Expressions for Subtraction: Elizabeth eats a healthy, balanced breakfast b times a week. Madison sometimes skips breakfast. In total, Madison eats 3 fewer breakfasts a week than Elizabeth. Write an expression that shows how many times a week Madison eats breakfast.
118. Writing Variable Expressions for Multiplication: Last hockey season, Jack scored g goals. Patrik scored twice as many goals than Jack. Write an expression that shows how many goals Patrik scored.
119. Writing Variable Expressions for Division: Amanda has c chocolate bars. She wants to distribute the chocolate bars evenly among 3 friends. Write an expression that shows how many chocolate bars 1 of her friends will receive.
120. Solving Two-Variable Equations: This equation shows how the amount Lucas earns from his after-school job depends on how many hours he works: e = 12h . The variable h represents how many hours he works. The variable e represents how much money he earns. How much money will Lucas earn after working for 6 hours?
How to easily make your own math word problems & word problems worksheets

Armed with 120 examples to spark ideas, making your own math word problems can engage your students and ensure alignment with lessons. Do:
- Link to Student Interests: By framing your word problems with student interests, you’ll likely grab attention. For example, if most of your class loves American football, a measurement problem could involve the throwing distance of a famous quarterback.
- Make Questions Topical: Writing a word problem that reflects current events or issues can engage students by giving them a clear, tangible way to apply their knowledge.
- Include Student Names: Naming a question’s characters after your students is an easy way make subject matter relatable, helping them work through the problem.
- Be Explicit: Repeating keywords distills the question, helping students focus on the core problem.
- Test Reading Comprehension: Flowery word choice and long sentences can hide a question’s key elements. Instead, use concise phrasing and grade-level vocabulary.
- Focus on Similar Interests: Framing too many questions with related interests -- such as football and basketball -- can alienate or disengage some students.
- Feature Red Herrings: Including unnecessary information introduces another problem-solving element, overwhelming many elementary students.
A key to differentiated instruction , word problems that students can relate to and contextualize will capture interest more than generic and abstract ones.
Final thoughts about math word problems
You’ll likely get the most out of this resource by using the problems as templates, slightly modifying them by applying the above tips. In doing so, they’ll be more relevant to -- and engaging for -- your students.
Regardless, having 120 curriculum-aligned math word problems at your fingertips should help you deliver skill-building challenges and thought-provoking assessments.
The result?
A greater understanding of how your students process content and demonstrate understanding, informing your ongoing teaching approach.
- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities
What can QuickMath do?
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students.
- The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and cancelling common factors within a fraction.
- The equations section lets you solve an equation or system of equations. You can usually find the exact answer or, if necessary, a numerical answer to almost any accuracy you require.
- The inequalities section lets you solve an inequality or a system of inequalities for a single variable. You can also plot inequalities in two variables.
- The calculus section will carry out differentiation as well as definite and indefinite integration.
- The matrices section contains commands for the arithmetic manipulation of matrices.
- The graphs section contains commands for plotting equations and inequalities.
- The numbers section has a percentages command for explaining the most common types of percentage problems and a section for dealing with scientific notation.
Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions

- Mathematicians
- Math Lessons
- Square Roots
- Math Calculators
Simple Algebra Problems – Easy Exercises with Solutions for Beginners
JUMP TO TOPIC
Understanding Algebraic Expressions
Breaking down algebra problems, solving algebraic equations, tackling algebra word problems, types of algebraic equations, algebra for different grades.
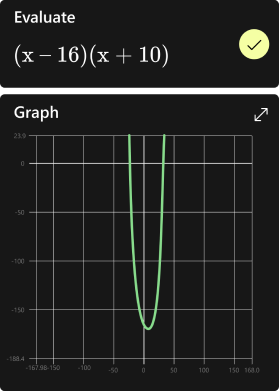
For instance, solving the equation (3x = 7) for (x) helps us understand how to isolate the variable to find its value.

I always find it fascinating how algebra serves as the foundation for more advanced topics in mathematics and science. Starting with basic problems such as ( $(x-1)^2 = [4\sqrt{(x-4)}]^2$ ) allows us to grasp key concepts and build the skills necessary for tackling more complex challenges.
So whether you’re refreshing your algebra skills or just beginning to explore this mathematical language, let’s dive into some examples and solutions to demystify the subject. Trust me, with a bit of practice, you’ll see algebra not just as a series of problems, but as a powerful tool that helps us solve everyday puzzles.
Simple Algebra Problems and Strategies
When I approach simple algebra problems, one of the first things I do is identify the variable.
The variable is like a placeholder for a number that I’m trying to find—a mystery I’m keen to solve. Typically represented by letters like ( x ) or ( y ), variables allow me to translate real-world situations into algebraic expressions and equations.
An algebraic expression is a mathematical phrase that can contain ordinary numbers, variables (like ( x ) or ( y )), and operators (like add, subtract, multiply, and divide). For example, ( 4x + 7 ) is an algebraic expression where ( x ) is the variable and the numbers ( 4 ) and ( 7 ) are terms. It’s important to manipulate these properly to maintain the equation’s balance.
Solving algebra problems often starts with simplifying expressions. Here’s a simple method to follow:
- Combine like terms : Terms that have the same variable can be combined. For instance, ( 3x + 4x = 7x ).
- Isolate the variable : Move the variable to one side of the equation. If the equation is ( 2x + 5 = 13 ), my job is to get ( x ) by itself by subtracting ( 5 ) from both sides, giving me ( 2x = 8 ).
With algebraic equations, the goal is to solve for the variable by performing the same operation on both sides. Here’s a table with an example:
Algebra word problems require translating sentences into equations. If a word problem says “I have six less than twice the number of apples than Bob,” and Bob has ( b ) apples, then I’d write the expression as ( 2b – 6 ).
Understanding these strategies helps me tackle basic algebra problems efficiently. Remember, practice makes perfect, and each problem is an opportunity to improve.
In algebra, we encounter a variety of equation types and each serves a unique role in problem-solving. Here, I’ll brief you about some typical forms.
Linear Equations : These are the simplest form, where the highest power of the variable is one. They take the general form ( ax + b = 0 ), where ( a ) and ( b ) are constants, and ( x ) is the variable. For example, ( 2x + 3 = 0 ) is a linear equation.
Polynomial Equations : Unlike for linear equations, polynomial equations can have variables raised to higher powers. The general form of a polynomial equation is ( $a_nx^n + a_{n-1}x^{n-1} + … + a_2x^2 + a_1x + a_0 = 0$ ). In this equation, ( n ) is the highest power, and ( $a_n$ ), ( $a_{n-1} $), …, ( $a_0$ ) represent the coefficients which can be any real number.
- Binomial Equations : They are a specific type of polynomial where there are exactly two terms. Like ($ x^2 – 4 $), which is also the difference of squares, a common format encountered in factoring.
To understand how equations can be solved by factoring, consider the quadratic equation ( $x^2$ – 5x + 6 = 0 ). I can factor this into ( (x-2)(x-3) = 0 ), which allows me to find the roots of the equation.
Here’s how some equations look when classified by degree:
Remember, identification and proper handling of these equations are essential in algebra as they form the basis for complex problem-solving.
In my experience with algebra, I’ve found that the journey begins as early as the 6th grade, where students get their first taste of this fascinating subject with the introduction of variables representing an unknown quantity.
I’ve created worksheets and activities aimed specifically at making this early transition engaging and educational.
6th Grade :
Moving forward, the complexity of algebraic problems increases:
7th and 8th Grades :
- Mastery of negative numbers: students practice operations like ( -3 – 4 ) or ( -5 $\times$ 2 ).
- Exploring the rules of basic arithmetic operations with negative numbers.
- Worksheets often contain numeric and literal expressions that help solidify their concepts.
Advanced topics like linear algebra are typically reserved for higher education. However, the solid foundation set in these early grades is crucial. I’ve developed materials to encourage students to understand and enjoy algebra’s logic and structure.
Remember, algebra is a tool that helps us quantify and solve problems, both numerical and abstract. My goal is to make learning these concepts, from numbers to numeric operations, as accessible as possible, while always maintaining a friendly approach to education.
I’ve walked through various simple algebra problems to help establish a foundational understanding of algebraic concepts. Through practice, you’ll find that these problems become more intuitive, allowing you to tackle more complex equations with confidence.
Remember, the key steps in solving any algebra problem include:
- Identifying variables and what they represent.
- Setting up the equation that reflects the problem statement.
- Applying algebraic rules such as the distributive property ($a(b + c) = ab + ac$), combining like terms, and inverse operations.
- Checking your solutions by substituting them back into the original equations to ensure they work.
As you continue to engage with algebra, consistently revisiting these steps will deepen your understanding and increase your proficiency. Don’t get discouraged by mistakes; they’re an important part of the learning process.
I hope that the straightforward problems I’ve presented have made algebra feel more manageable and a little less daunting. Happy solving!
- Pre Calculus
- Probability
- Sets & Set Theory
- Trigonometry
MathPapa Practice
MathPapa Practice has practice problems to help you learn algebra.
Basic Arithmetic
Subtraction, multiplication, basic arithmetic review, multi-digit arithmetic, addition (2-digit), subtraction (2-digit), multiplication (2-digit by 1-digit), division (2-digit answer), multiplication (2-digit by 2-digit), multi-digit division, negative numbers, addition: negative numbers, subtraction: negative numbers, multiplication: negative numbers, division: negative numbers, order of operations, order of operations 1, basic equations, equations: fill in the blank 1, equations: fill in the blank 2, equations: fill in the blank 3 (order of operations), fractions of measurements, fractions of measurements 2, adding fractions, subtracting fractions, adding fractions: fill in the blank, multiplication: fractions 1, multiplication: fractions 2, division: fractions 1, division: fractions 2, division: fractions 3, addition (decimals), subtraction (decimals), multiplication 2 (example problem: 3.5*8), multiplication 3 (example problem: 0.3*80), division (decimals), division (decimals 2), percentages, percentages 1, percentages 2, chain reaction, balance arithmetic, number balance, basic balance 1, basic balance 2, basic balance 3, basic balance 4, basic balance 5, basic algebra, basic algebra 1, basic algebra 2, basic algebra 3, basic algebra 4, basic algebra 5, algebra: basic fractions 1, algebra: basic fractions 2, algebra: basic fractions 3, algebra: basic fractions 4, algebra: basic fractions 5.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&

Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems

Try Math Solver

Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Early math review
Kindergarten, basic geometry and measurement, pre-algebra, algebra basics, high school geometry, trigonometry, statistics and probability, high school statistics, ap®︎/college statistics, college algebra, precalculus, differential calculus, integral calculus, ap®︎/college calculus ab, ap®︎/college calculus bc, multivariable calculus, differential equations, linear algebra, 6th grade (illustrative mathematics), 7th grade (illustrative mathematics), 8th grade (illustrative mathematics), algebra 1 (illustrative mathematics), 3rd grade (eureka math/engageny), 4th grade (eureka math/engageny), 5th grade (eureka math/engageny), 6th grade (eureka math/engageny), 7th grade (eureka math/engageny), 8th grade (eureka math/engageny), algebra 1 (eureka math/engageny), geometry (eureka math/engageny), algebra 2 (eureka math/engageny), precalculus (eureka math/engageny), 3rd grade foundations (eureka math/engageny), 4th grade foundations (eureka math/engageny), 5th grade foundations (eureka math/engageny), 6th grade foundations (eureka math/engageny), 7th grade foundations (eureka math/engageny), 8th grade foundations (eureka math/engageny), integrated math 1, integrated math 2, integrated math 3, arithmetic (all content), algebra (all content), geometry (all content), get ready for 3rd grade, get ready for 4th grade, get ready for 5th grade, get ready for 6th grade, get ready for 7th grade, get ready for 8th grade, get ready for algebra 1, get ready for geometry, get ready for algebra 2, get ready for precalculus, map recommended practice, get ready for ap® calculus, get ready for ap® statistics, grade 6 math (fl b.e.s.t.), grade 7 math (fl b.e.s.t.), grade 8 math (fl b.e.s.t.), algebra 1 (fl b.e.s.t.), geometry (fl b.e.s.t.), algebra 2 (fl b.e.s.t.), grade 6 (virginia), grade 7 (virginia), grade 8 (virginia), grade 3 (fl b.e.s.t.), grade 4 math (fl b.e.s.t.), grade 5 math (fl b.e.s.t.), class 9 (od), class 10 (od).
High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
Free ready-to-use math resources
Hundreds of free math resources created by experienced math teachers to save time, build engagement and accelerate growth
20 Effective Math Strategies To Approach Problem-Solving
Katie Keeton
Math strategies for problem-solving help students use a range of approaches to solve many different types of problems. It involves identifying the problem and carrying out a plan of action to find the answer to mathematical problems.
Problem-solving skills are essential to math in the general classroom and real-life. They require logical reasoning and critical thinking skills. students must be equipped with strategies to help them find solutions to problems.
This article explores mathematical problem solving strategies, logical reasoning and critical thinking skills to help learners with solving math word problems independently in real-life situations.
What are problem-solving strategies?
Problem-solving strategies in math are methods students can use to figure out solutions to math problems. Some problem-solving strategies:
- Draw a model
- Use different approaches
- Check the inverse to make sure the answer is correct
Students need to have a toolkit of math problem-solving strategies at their disposal to provide different ways to approach math problems. This makes it easier to find solutions and understand math better.
Strategies can help guide students to the solution when it is difficult ot know when to start.

The ultimate guide to problem solving techniques
Download these ready-to-go problem solving techniques that every student should know. Includes printable tasks for students including challenges, short explanations for teachers with questioning prompts.
20 Math Strategies For Problem-Solving
Different problem-solving math strategies are required for different parts of the problem. It is unlikely that students will use the same strategy to understand and solve the problem.
Here are 20 strategies to help students develop their problem-solving skills.
Strategies to understand the problem
Strategies that help students understand the problem before solving it helps ensure they understand:
- The context
- What the key information is
- How to form a plan to solve it
Following these steps leads students to the correct solution and makes the math word problem easier .
Here are five strategies to help students understand the content of the problem and identify key information.
1. Read the problem aloud
Read a word problem aloud to help understand it. Hearing the words engages auditory processing. This can make it easier to process and comprehend the context of the situation.
2. Highlight keywords
When keywords are highlighted in a word problem, it helps the student focus on the essential information needed to solve it. Some important keywords help determine which operation is needed. For example, if the word problem asks how many are left, the problem likely requires subtraction. Ensure students highlight the keywords carefully and do not highlight every number or keyword. There is likely irrelevant information in the word problem.
3. Summarize the information
Read the problem aloud, highlight the key information and then summarize the information. Students can do this in their heads or write down a quick summary. Summaries should include only the important information and be in simple terms that help contextualize the problem.
4. Determine the unknown
A common problem that students have when solving a word problem is misunderstanding what they are solving. Determine what the unknown information is before finding the answer. Often, a word problem contains a question where you can find the unknown information you need to solve. For example, in the question ‘How many apples are left?’ students need to find the number of apples left over.
5. Make a plan
Once students understand the context of the word problem, have dentified the important information and determined the unknown, they can make a plan to solve it. The plan will depend on the type of problem. Some problems involve more than one step to solve them as some require more than one answer. Encourage students to make a list of each step they need to take to solve the problem before getting started.
Strategies for solving the problem
1. draw a model or diagram.
Students may find it useful to draw a model, picture, diagram, or other visual aid to help with the problem solving process. It can help to visualize the problem to understand the relationships between the numbers in the problem. In turn, this helps students see the solution.
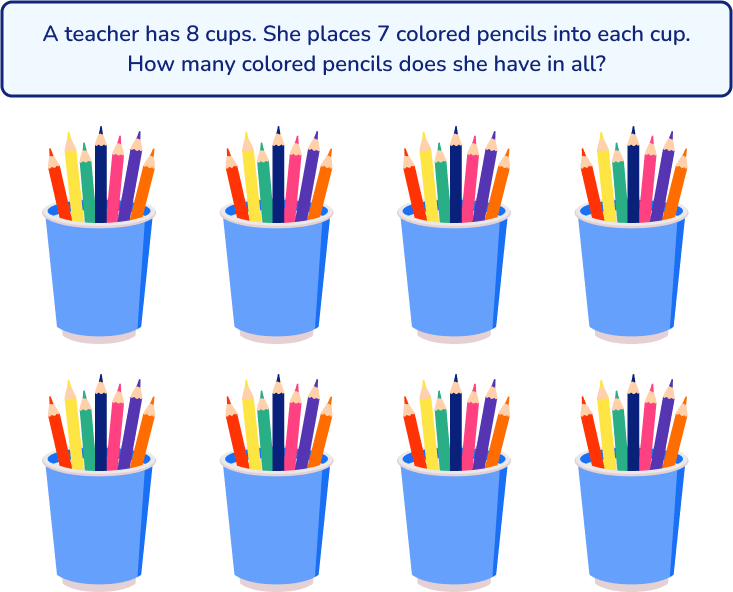
Similarly, you could draw a model to represent the objects in the problem:
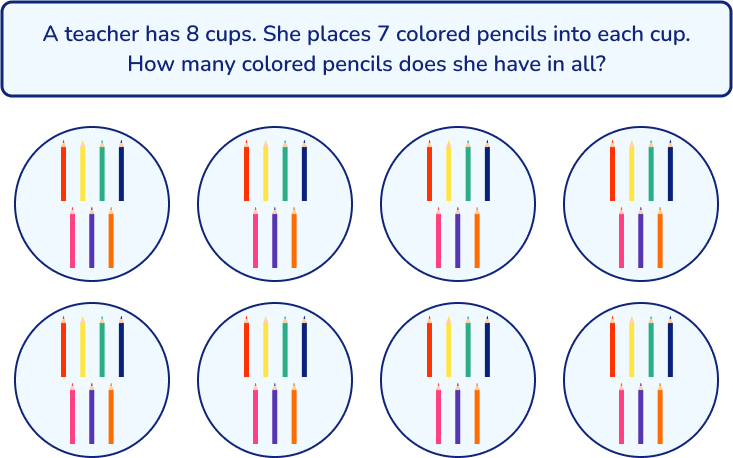
2. Act it out
This particular strategy is applicable at any grade level but is especially helpful in math investigation in elementary school . It involves a physical demonstration or students acting out the problem using movements, concrete resources and math manipulatives . When students act out a problem, they can visualize and contectualize the word problem in another way and secure an understanding of the math concepts. The examples below show how 1st-grade students could “act out” an addition and subtraction problem:
3. Work backwards
Working backwards is a popular problem-solving strategy. It involves starting with a possible solution and deciding what steps to take to arrive at that solution. This strategy can be particularly helpful when students solve math word problems involving multiple steps. They can start at the end and think carefully about each step taken as opposed to jumping to the end of the problem and missing steps in between.
For example,

To solve this problem working backwards, start with the final condition, which is Sam’s grandmother’s age (71) and work backwards to find Sam’s age. Subtract 20 from the grandmother’s age, which is 71. Then, divide the result by 3 to get Sam’s age. 71 – 20 = 51 51 ÷ 3 = 17 Sam is 17 years old.

4. Write a number sentence
When faced with a word problem, encourage students to write a number sentence based on the information. This helps translate the information in the word problem into a math equation or expression, which is more easily solved. It is important to fully understand the context of the word problem and what students need to solve before writing an equation to represent it.
5. Use a formula
Specific formulas help solve many math problems. For example, if a problem asks students to find the area of a rug, they would use the area formula (area = length × width) to solve. Make sure students know the important mathematical formulas they will need in tests and real-life. It can help to display these around the classroom or, for those who need more support, on students’ desks.
Strategies for checking the solution
Once the problem is solved using an appropriate strategy, it is equally important to check the solution to ensure it is correct and makes sense.
There are many strategies to check the solution. The strategy for a specific problem is dependent on the problem type and math content involved.
Here are five strategies to help students check their solutions.
1. Use the Inverse Operation
For simpler problems, a quick and easy problem solving strategy is to use the inverse operation. For example, if the operation to solve a word problem is 56 ÷ 8 = 7 students can check the answer is correct by multiplying 8 × 7. As good practice, encourage students to use the inverse operation routinely to check their work.
2. Estimate to check for reasonableness
Once students reach an answer, they can use estimation or rounding to see if the answer is reasonable. Round each number in the equation to a number that’s close and easy to work with, usually a multiple of ten. For example, if the question was 216 ÷ 18 and the quotient was 12, students might round 216 to 200 and round 18 to 20. Then use mental math to solve 200 ÷ 20, which is 10. When the estimate is clear the two numbers are close. This means your answer is reasonable.
3. Plug-In Method
This method is particularly useful for algebraic equations. Specifically when working with variables. To use the plug-in method, students solve the problem as asked and arrive at an answer. They can then plug the answer into the original equation to see if it works. If it does, the answer is correct.

If students use the equation 20m+80=300 to solve this problem and find that m = 11, they can plug that value back into the equation to see if it is correct. 20m + 80 = 300 20 (11) + 80 = 300 220 + 80 = 300 300 = 300 ✓
4. Peer Review
Peer review is a great tool to use at any grade level as it promotes critical thinking and collaboration between students. The reviewers can look at the problem from a different view as they check to see if the problem was solved correctly. Problem solvers receive immediate feedback and the opportunity to discuss their thinking with their peers. This strategy is effective with mixed-ability partners or similar-ability partners. In mixed-ability groups, the partner with stronger skills provides guidance and support to the partner with weaker skills, while reinforcing their own understanding of the content and communication skills. If partners have comparable ability levels and problem-solving skills, they may find that they approach problems differently or have unique insights to offer each other about the problem-solving process.
5. Use a Calculator
A calculator can be introduced at any grade level but may be best for older students who already have a foundational understanding of basic math operations. Provide students with a calculator to allow them to check their solutions independently, accurately, and quickly. Since calculators are so readily available on smartphones and tablets, they allow students to develop practical skills that apply to real-world situations.
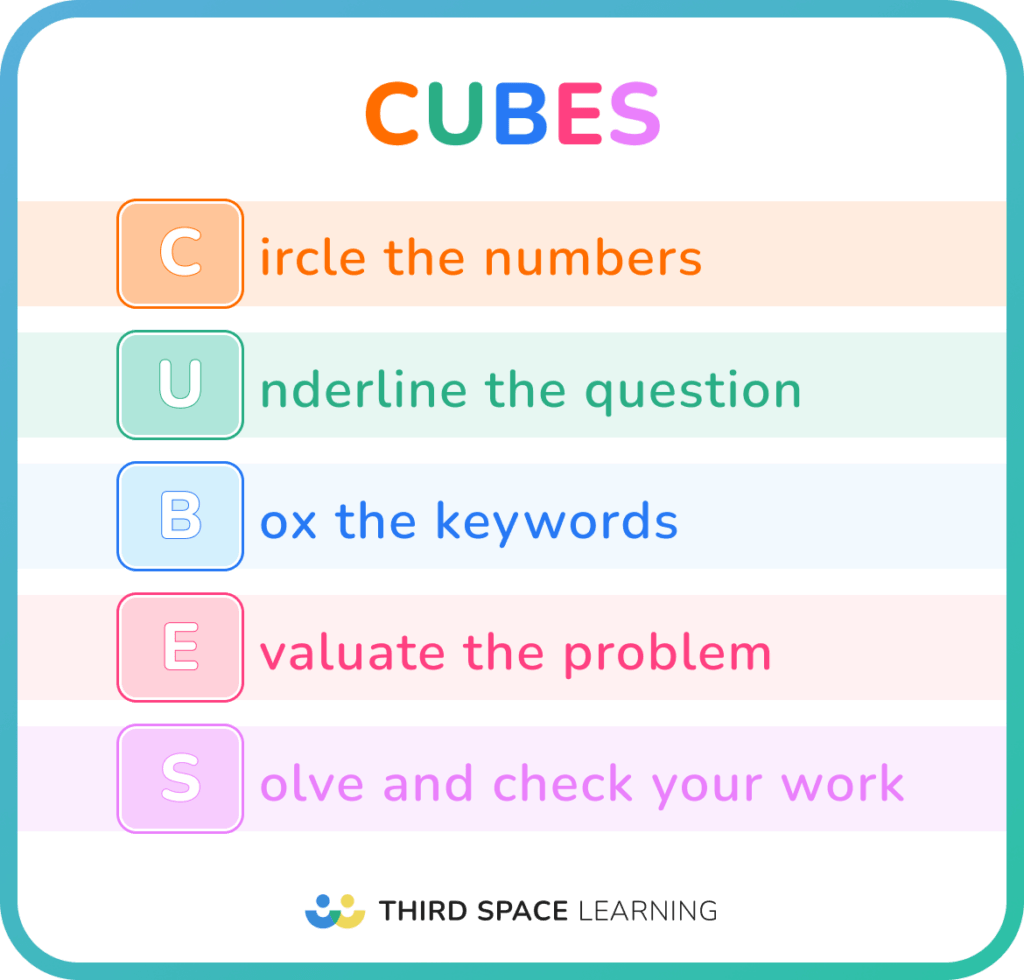
Step-by-step problem-solving processes for your classroom
In his book, How to Solve It , published in 1945, mathematician George Polya introduced a 4-step process to solve problems.
Polya’s 4 steps include:
- Understand the problem
- Devise a plan
- Carry out the plan
Today, in the style of George Polya, many problem-solving strategies use various acronyms and steps to help students recall.
Many teachers create posters and anchor charts of their chosen process to display in their classrooms. They can be implemented in any elementary, middle school or high school classroom.
Here are 5 problem-solving strategies to introduce to students and use in the classroom.
How Third Space Learning improves problem-solving
Resources .
Third Space Learning offers a free resource library is filled with hundreds of high-quality resources. A team of experienced math experts carefully created each resource to develop students mental arithmetic, problem solving and critical thinking.
Explore the range of problem solving resources for 2nd to 8th grade students.
One-on-one tutoring
Third Space Learning offers one-on-one math tutoring to help students improve their math skills. Highly qualified tutors deliver high-quality lessons aligned to state standards.
Former teachers and math experts write all of Third Space Learning’s tutoring lessons. Expertly designed lessons follow a “my turn, follow me, your turn” pedagogy to help students move from guided instruction and problem-solving to independent practice.
Throughout each lesson, tutors ask higher-level thinking questions to promote critical thinking and ensure students are developing a deep understanding of the content and problem-solving skills.
Problem-solving
Educators can use many different strategies to teach problem-solving and help students develop and carry out a plan when solving math problems. Incorporate these math strategies into any math program and use them with a variety of math concepts, from whole numbers and fractions to algebra.
Teaching students how to choose and implement problem-solving strategies helps them develop mathematical reasoning skills and critical thinking they can apply to real-life problem-solving.
READ MORE : 8 Common Core math examples
There are many different strategies for problem-solving; Here are 5 problem-solving strategies: • draw a model • act it out • work backwards • write a number sentence • use a formula
Here are 10 strategies of problem-solving: • Read the problem aloud • Highlight keywords • Summarize the information • Determine the unknown • Make a plan • Draw a model • Act it out • Work backwards • Write a number sentence • Use a formula
1. Understand the problem 2. Devise a plan 3. Carry out the plan 4. Look back
Some strategies you can use to solve challenging math problems are: breaking the problem into smaller parts, using diagrams or models, applying logical reasoning, and trying different approaches.
Related articles

Why Student Centered Learning Is Important: A Guide For Educators

13 Effective Learning Strategies: A Guide to Using them in your Math Classroom

Differentiated Instruction: 9 Differentiated Curriculum And Instruction Strategies For Teachers

5 Math Mastery Strategies To Incorporate Into Your 4th and 5th Grade Classrooms
Ultimate Guide to Metacognition [FREE]
Looking for a summary on metacognition in relation to math teaching and learning?
Check out this guide featuring practical examples, tips and strategies to successfully embed metacognition across your school to accelerate math growth.
Privacy Overview
30 Fun Maths Questions with Answers
Table of Contents
Introduction
Mathematics can be fun if you treat it the right way. Maths is nothing less than a game, a game that polishes your intelligence and boosts your concentration. Compared to older times, people have a better and friendly approach to mathematics which makes it more appealing. The golden rule is to know that maths is a mindful activity rather than a task.
There is nothing like hard math problems or tricky maths questions, it’s just that you haven’t explored mathematics well enough to comprehend its easiness and relatability. Maths tricky questions and answers can be transformed into fun math problems if you look at it as if it is a brainstorming session. With the right attitude and friends and teachers, doing math can be most entertaining and delightful.

Math is interesting because a few equations and diagrams can communicate volumes of information. Treat math as a language, while moving to rigorous proof and using logical reason for performing a particular step in a proof or derivation.
Treating maths as a language totally eradicates the concept of hard math problems or tricky maths questions from your mind. Introducing children to fun maths questions can create a strong love and appreciation for maths at an early age. This way you are setting up the child’s successful future. Fun math problems will urge your child to choose to solve it over playing bingo or baking.
Apparently, there are innumerable methods to make easy maths tricky questions and answers. This includes the inception of the ideology that maths is simpler than their fear. This can be done by connecting maths with everyday life. Practising maths with the aid of dice, cards, puzzles and tables reassures that your child effectively approaches Maths.
If you wish to add some fun and excitement into educational activities, also check out
- Check out some mind-blowing Math Magic Tricks!
- Mental Maths: How to Improve it?
Cuemath is one of the world's leading math learning platforms that offers LIVE 1-to-1 online math classes for grades K-12 . Our mission is to transform the way children learn math, to help them excel in school and competitive exams. Our expert tutors conduct 2 or more live classes per week, at a pace that matches the child's learning needs.
Fun Maths Questions with answers - PDF
Here is the Downloadable PDF that consists of Fun Math questions. Click the Download button to view them.
Here are some fun, tricky and hard to solve maths problems that will challenge your thinking ability.
Answer: is 3, because ‘six’ has three letters
What is the number of parking space covered by the car?

This tricky math problem went viral a few years back after it appeared on an entrance exam in Hong Kong… for six-year-olds. Supposedly the students had just 20 seconds to solve the problem!
Believe it or not, this “math” question actually requires no math whatsoever. If you flip the image upside down, you’ll see that what you’re dealing with is a simple number sequence.
Replace the question mark in the above problem with the appropriate number.

Which number is equivalent to 3^(4)÷3^(2)
This problem comes straight from a standardized test given in New York in 2014.
There are 49 dogs signed up for a dog show. There are 36 more small dogs than large dogs. How many small dogs have signed up to compete?
This question comes directly from a second grader's math homework.
To figure out how many small dogs are competing, you have to subtract 36 from 49 and then divide that answer, 13 by 2, to get 6.5 dogs, or the number of big dogs competing. But you’re not done yet! You then have to add 6.5 to 36 to get the number of small dogs competing, which is 42.5. Of course, it’s not actually possible for half a dog to compete in a dog show, but for the sake of this math problem let’s assume that it is.
Add 8.563 and 4.8292.
Adding two decimals together is easier than it looks. Don’t let the fact that 8.563 has fewer numbers than 4.8292 trip you up. All you have to do is add a 0 to the end of 8.563 and then add like you normally would.
I am an odd number. Take away one letter and I become even. What number am I?
Answer: Seven (take away the ‘s’ and it becomes ‘even’).
Using only an addition, how do you add eight 8’s and get the number 1000?
Answer:
888 + 88 + 8 + 8 + 8 = 1000
Sally is 54 years old and her mother is 80, how many years ago was Sally’s mother times her age?
41 years ago, when Sally was 13 and her mother was 39.
Which 3 numbers have the same answer whether they’re added or multiplied together?
There is a basket containing 5 apples, how do you divide the apples among 5 children so that each child has 1 apple while 1 apple remains in the basket?
4 children get 1 apple each while the fifth child gets the basket with the remaining apple still in it.
There is a three-digit number. The second digit is four times as big as the third digit, while the first digit is three less than the second digit. What is the number?
Fill in the question mark

Two girls were born to the same mother, at the same time, on the same day, in the same month and the same year and yet somehow they’re not twins. Why not?
Because there was a third girl, which makes them triplets!
A ship anchored in a port has a ladder which hangs over the side. The length of the ladder is 200cm, the distance between each rung in 20cm and the bottom rung touches the water. The tide rises at a rate of 10cm an hour. When will the water reach the fifth rung?
The tide raises both the water and the boat so the water will never reach the fifth rung.
The day before yesterday I was 25. The next year I will be 28. This is true only one day in a year. What day is my Birthday?
You have a 3-litre bottle and a 5-litre bottle. How can you measure 4 litres of water by using 3L and 5L bottles?
Solution 1 :
First, fill 3Lt bottle and pour 3 litres into 5Lt bottle.
Again fill the 3Lt bottle. Now pour 2 litres into the 5Lt bottle until it becomes full.
Now empty 5Lt bottle.
Pour remaining 1 litre in 3Lt bottle into 5Lt bottle.
Now again fill 3Lt bottle and pour 3 litres into 5Lt bottle.
Now you have 4 litres in the 5Lt bottle. That’s it.
Solution 2 :
First, fill the 5Lt bottle and pour 3 litres into 3Lt bottle.
Empty 3Lt bottle.
Pour remaining 2 litres in 5Lt bottle into 3Lt bottle.
Again fill the 5Lt bottle and pour 1 litre into 3 Lt bottle until it becomes full.
3 Friends went to a shop and purchased 3 toys. Each person paid Rs.10 which is the cost of one toy. So, they paid Rs.30 i.e. total amount. The shop owner gave a discount of Rs.5 on the total purchase of 3 toys for Rs.30. Then, among Rs.5, Each person has taken Rs.1 and remaining Rs.2 given to the beggar beside the shop. Now, the effective amount paid by each person is Rs.9 and the amount given to the beggar is Rs.2. So, the total effective amount paid is 9*3 = 27 and the amount given to beggar is Rs.2, thus the total is Rs.29. Where has the other Rs.1 gone from the original Rs.30?
The logic is payments should be equal to receipts. We cannot add the amount paid by persons and the amount given to the beggar and compare it to Rs.30.The total amount paid is ₹27. So, from ₹27, the shop owner received 25 rupees and beggar received ₹ 2. Thus, payments are equal to receipts.
How to get a number 100 by using four sevens (7’s) and a one (1)?
Answer 1: 177 – 77 = 100 ;
Answer 2: (7+7) * (7 + (1/7)) = 100
Move any four matches to get 3 equilateral triangles only (don’t remove matches)

Find the area of the red triangle.

To solve this fun maths question, you need to understand how the area of a parallelogram works. If you already know how the area of a parallelogram and the area of a triangle are related, then adding 79 and 10 and subsequently subtracting 72 and 8 to get 9 should make sense.
How many feet are in a mile?
Solve - 15+ (-5x) =0
What is 1.92÷3
A man is climbing up a mountain which is inclined. He has to travel 100 km to reach the top of the mountain. Every day He climbs up 2 km forward in the day time. Exhausted, he then takes rest there at night time. At night, while he is asleep, he slips down 1 km backwards because the mountain is inclined. Then how many days does it take him to reach the mountain top?
If 72 x 96 = 6927, 58 x 87 = 7885, then 79 x 86 = ?
Answer:
Look at this series: 36, 34, 30, 28, 24, … What number should come next?
Look at this series: 22, 21, 23, 22, 24, 23, … What number should come next?
If 13 x 12 = 651 & 41 x 23 = 448, then, 24 x 22 =?
Look at this series: 53, 53, 40, 40, 27, 27, … What number should come next?
The ultimate goals of mathematics instruction are students understanding the material presented, applying the skills, and recalling the concepts in the future. There's little benefit in students recalling a formula or procedure to prepare for an assessment tomorrow only to forget the core concept by next week.
Teachers must focus on making sure that the students understand the material and not just memorize the procedures. After you learn the answers to a fun maths question, you begin to ask yourself how you could have missed something so easy. The truth is, most trick questions are designed to trick your mind, which is why the answers to fun maths questions are logical and easy.
How to Solve Math Problems
Last Updated: April 15, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Daron Cam . Daron Cam is an Academic Tutor and the Founder of Bay Area Tutors, Inc., a San Francisco Bay Area-based tutoring service that provides tutoring in mathematics, science, and overall academic confidence building. Daron has over eight years of teaching math in classrooms and over nine years of one-on-one tutoring experience. He teaches all levels of math including calculus, pre-algebra, algebra I, geometry, and SAT/ACT math prep. Daron holds a BA from the University of California, Berkeley and a math teaching credential from St. Mary's College. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 590,381 times.
Although math problems may be solved in different ways, there is a general method of visualizing, approaching and solving math problems that may help you to solve even the most difficult problem. Using these strategies can also help you to improve your math skills overall. Keep reading to learn about some of these math problem solving strategies.
Understanding the Problem

- Draw a Venn diagram. A Venn diagram shows the relationships among the numbers in your problem. Venn diagrams can be especially helpful with word problems.
- Draw a graph or chart.
- Arrange the components of the problem on a line.
- Draw simple shapes to represent more complex features of the problem.

Developing a Plan

Solving the Problem

Joseph Meyer
When doing practice problems, promptly check to see if your answers are correct. Use worksheets that provide answer keys for instant feedback. Discuss answers with a classmate or find explanations online. Immediate feedback will help you correct your mistakes, avoid bad habits, and advance your learning more quickly.
Expert Q&A

- Seek help from your teacher or a math tutor if you get stuck or if you have tried multiple strategies without success. Your teacher or a math tutor may be able to easily identify what is wrong and help you to understand how to correct it. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Keep practicing sums and diagrams. Go through the concept your class notes regularly. Write down your understanding of the methods and utilize it. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ Daron Cam. Math Tutor. Expert Interview. 29 May 2020.
- ↑ http://www.interventioncentral.org/academic-interventions/math/math-problem-solving-combining-cognitive-metacognitive-strategies
- ↑ http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu/Extras/StudyMath/ProblemSolving.aspx
- ↑ https://math.berkeley.edu/~gmelvin/polya.pdf
About This Article

To solve a math problem, try rewriting the problem in your own words so it's easier to solve. You can also make a drawing of the problem to help you figure out what it's asking you to do. If you're still completely stuck, try solving a different problem that's similar but easier and then use the same steps to solve the harder problem. Even if you can't figure out how to solve it, try to make an educated guess instead of leaving the question blank. To learn how to come up with a solid plan to use to help you solve a math problem, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Thakgalo Mokalapa
Feb 16, 2018
Did this article help you?
Offor Chukwuemeka
May 17, 2018
Jan 21, 2017
May 3, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Solving Equations
What is an equation.
An equation says that two things are equal. It will have an equals sign "=" like this:
That equations says:
what is on the left (x − 2) equals what is on the right (4)
So an equation is like a statement " this equals that "
What is a Solution?
A Solution is a value we can put in place of a variable (such as x ) that makes the equation true .
Example: x − 2 = 4
When we put 6 in place of x we get:
which is true
So x = 6 is a solution.
How about other values for x ?
- For x=5 we get "5−2=4" which is not true , so x=5 is not a solution .
- For x=9 we get "9−2=4" which is not true , so x=9 is not a solution .
In this case x = 6 is the only solution.
You might like to practice solving some animated equations .
More Than One Solution
There can be more than one solution.
Example: (x−3)(x−2) = 0
When x is 3 we get:
(3−3)(3−2) = 0 × 1 = 0
And when x is 2 we get:
(2−3)(2−2) = (−1) × 0 = 0
which is also true
So the solutions are:
x = 3 , or x = 2
When we gather all solutions together it is called a Solution Set
The above solution set is: {2, 3}
Solutions Everywhere!
Some equations are true for all allowed values and are then called Identities
Example: sin(−θ) = −sin(θ) is one of the Trigonometric Identities
Let's try θ = 30°:
sin(−30°) = −0.5 and
−sin(30°) = −0.5
So it is true for θ = 30°
Let's try θ = 90°:
sin(−90°) = −1 and
−sin(90°) = −1
So it is also true for θ = 90°
Is it true for all values of θ ? Try some values for yourself!
How to Solve an Equation
There is no "one perfect way" to solve all equations.
A Useful Goal
But we often get success when our goal is to end up with:
x = something
In other words, we want to move everything except "x" (or whatever name the variable has) over to the right hand side.
Example: Solve 3x−6 = 9
Now we have x = something ,
and a short calculation reveals that x = 5
Like a Puzzle
In fact, solving an equation is just like solving a puzzle. And like puzzles, there are things we can (and cannot) do.
Here are some things we can do:
- Add or Subtract the same value from both sides
- Clear out any fractions by Multiplying every term by the bottom parts
- Divide every term by the same nonzero value
- Combine Like Terms
- Expanding (the opposite of factoring) may also help
- Recognizing a pattern, such as the difference of squares
- Sometimes we can apply a function to both sides (e.g. square both sides)
Example: Solve √(x/2) = 3
And the more "tricks" and techniques you learn the better you will get.
Special Equations
There are special ways of solving some types of equations. Learn how to ...
- solve Quadratic Equations
- solve Radical Equations
- solve Equations with Sine, Cosine and Tangent
Check Your Solutions
You should always check that your "solution" really is a solution.
How To Check
Take the solution(s) and put them in the original equation to see if they really work.
Example: solve for x:
2x x − 3 + 3 = 6 x − 3 (x≠3)
We have said x≠3 to avoid a division by zero.
Let's multiply through by (x − 3) :
2x + 3(x−3) = 6
Bring the 6 to the left:
2x + 3(x−3) − 6 = 0
Expand and solve:
2x + 3x − 9 − 6 = 0
5x − 15 = 0
5(x − 3) = 0
Which can be solved by having x=3
Let us check x=3 using the original question:
2 × 3 3 − 3 + 3 = 6 3 − 3
Hang On: 3 − 3 = 0 That means dividing by Zero!
And anyway, we said at the top that x≠3 , so ...
x = 3 does not actually work, and so:
There is No Solution!
That was interesting ... we thought we had found a solution, but when we looked back at the question we found it wasn't allowed!
This gives us a moral lesson:
"Solving" only gives us possible solutions, they need to be checked!
- Note down where an expression is not defined (due to a division by zero, the square root of a negative number, or some other reason)
- Show all the steps , so it can be checked later (by you or someone else)
- Math Article
Maths Quiz Questions
We are providing here maths quiz questions for children to help them increase their knowledge of the subject. These questions are prepared based on fundamental mathematical concepts. The problems here are provided with four multiple answers and students have to choose the right answer. The questions here could be solved by students of all the classes from 6 to 10, as they are based on basic arithmetic operations and geometrical concepts. Thus, on solving them they can also participate in quiz competitions conducted in schools.
Solving these quizzes will help students to gain more knowledge and boost their problem-solving skills. These questions are very easy to solve and will not take much time. Hence, it is recommended to all the children to solve each one of them and test their abilities.
Maths Quiz Questions with Answers (MCQs)
Let us answer here some of the quizzes which are based on simple arithmetic concepts. These problems are based on fundamental concepts, which students can easily answer without picking up a pen and paper.
Q.1. What is the sum of 130+125+191?
Q.2: If we minus 712 from 1500, how much do we get?
Q.3: 50 times of 8 is equal to:
Q.4: 110 divided by 10 is:
D. None of these
Q.5: 20+(90÷2) is equal to:
Q.6: The product of 82 and 5 is:
Q.7: Find the missing terms in multiple of 3: 3, 6, 9, __, 15
Q.8: Solve 24÷8+2.
Q.9: Solve: 300 – (150×2)
Q.10: The product of 121 x 0 x 200 x 25 is
Q.11: What is the next prime number after 5?
Also, read:
- Class 8 Maths MCQs
- Class 9 Maths MCQs
- Class 10 Maths MCQs
Maths Quizzes and Answers
Here are some quiz questions which children should be able to answer quickly.
Q.12: The circumference of the circle is also sometimes called:
Answer: Perimeter of a circle
Q.13: 90 – 35 is equal to:
Q.14: 72 divided by 8 is equal to:
Q.15: How many sides does a decagon have?
Answer: Ten
Q.16: Is -5 an integer? Yes or No.
Answer: Yes
Q.17: The value of pi is equal to:
Answer: 22/7 or 3.14
Q.18: 9 x 7 is equal to:
Q.19: Is triangle a two-dimensional or three-dimensional shape?
Answer: A two-dimensional shape
Q.20: An equilateral triangle has two of its sides equal. True or false?
Answer: False
All the sides of the equilateral triangle are equal.
Q.21: 10 is a natural number. True or false?
Answer: True
Q.22: -10 is a whole number. True or false?
Q.23: 8 raised to the power 0 is equal to:
Q.24: The largest 4 digit number is:
Answer: 9999
Q.25: The smallest 4-digit number is:
Answer: 1000
Q.26: The square of 8 is equal to:
8 2 = 8 x 8 = 64
Q.27: The square root of 5 is:
Answer: 2.23
Q.28: 3 is a perfect square. True or False?
Answer: False.
Q.29: Cube of 5 is equal to:
Answer: 125
5 3 = 5 x 5 x 5 = 125
Q.30: Cube root of 1331 is:
1331 = 11 x 11 x 11 = 11 3
Q.31: 27 is a perfect cube. True or False?
27 = 3 x 3 x 3= 3 3
Q.32: A square has all its angles equal to:
Answer: 90 degrees
Q.33: The area of rectangle is equal to:
Answer: Length x Breadth
Q.34: If a is the side of cube, then the volume of the cube is:
Answer: a 3
Q.35: A regular polygon has all its sides:
Answer: Equal
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Great thank you
I am a student
Great work keep it up
thanks byjus because tommorow is my mental maths exam and this quiz increase my confidence to solve the mental maths exam [thanks a lot] .
Best of studying
It was a very nice quiz. I enjoyed answering.
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


Home / Blog / Math / Hardest Math Questions That Are Surprisingly Easy To Solve!

Hardest Math Questions That Are Surprisingly Easy To Solve!

Have you ever struggled enough with a math problem only to realize that it was too easy to solve? Many students will definitely vouch for it—a math question looked quite simple when they sat with it, but within minutes they understood that they had no idea how to solve it!
Sometimes you come across some of the most difficult math questions that are both challenging and brain teasers. Even if you are well-prepared for your exam, you will encounter difficult math questions. But here’s the thing: They can be solved in a flash, regardless of how ridiculously difficult they appear.
Yes, you heard that right! If you understand basic math skills and concepts, all you need are some math tricks and practice to solve the problems in a jiffy.
Check out These 10 Hardest Math Questions That will Test Your Logic and Problem-solving Skills
Interestingly, these hard math problems can be solved easily with basic math operators. Ready to test your math skills?
- A bat and a ball cost one dollar and ten cents in total. The bat costs a dollar more than the ball. How much does the ball cost?
Answer: The ball costs 5 cents. How did that happen? If you were thinking of some other answers to this problem, then this explanation might help you. Well, to simplify the question, the difference between $1 and 10 cents is 90 cents, not $1. The only way for the bat to cost a dollar more than the ball while still having the total cost equal to $1.10 is for the baseball bat to cost $1.05 and the ball to cost 5 cents.
- The classic PEMDAS problem: 6 ÷ 2(1+2) = ?
Answer: 9 Every PEMDAS problem leads to a huge disruption of opinions, splitting the masses into various answers while everyone believes that they have the correct answer. So, how was this solved and how did they arrive at “9” as the solution? If you remember the order of operations of PEMDAS from grade school, one generally works through the problem by solving parentheses, then the exponents, multiplication, and division, followed by addition and subtraction. Sometimes, some people interpret PEMDAS differently, and that is when the disagreement begins. According to the PEMDAS rule, one should solve anything inside parentheses, then exponents, and then all multiplication and division, starting from the left to the right, as per the operations.
- Replace the question mark in the above diagram with an appropriate number.
Answer: 6 If you enjoy playing Sudoku, then this hard math problem would have been quite a breeze for you! The rows and columns all add up to 15, and that is how the answer turned out to be 6.
- Solve the unfinished equation:
Answer: 4 = 256 Have a close look at the equation again, and find out the common thing among the equations. There is a formula that has been used for these equations. 4^x = Y. So, 4^1 = 4, 4^2 = 16, 4^3 = 64, and 4^4 = 256.
- The Lily Pad problem: A lake has a patch of lily pads. Every day, the patch doubles in size. If it takes 48 days for the patch to cover the entire lake, how long will it take for the patch to cover half of the lake?
Answer: It will take 47 days for the patch to cover half of the lake. If you assumed that half of the lake would be covered in half of the time, then your assumption could be incorrect. Here, in the math problem, it says that the patch “doubles” in size, which means, given any day, the lily pad was half the size the day before. So if the patch covers up the entire lake on the 48th day, it means the lily pad was half the size of the lake on day 47.
- When you add five to nine, you get two. The answer is correct, but how?
Answer: Well, here’s the trick. When it is 9 a.m., you add five hours to it. Voila, you get 2 p.m. as your answer! Getting smarter every minute, aren’t we?
- A group of students was standing in the sun facing due west on a march past event. The captain shouted at them: Right turn! About turn! Left turn! At the end of these commands, which direction are the students facing now?
Answer: East. Well, this one might seem tricky, but the answer is quite simple. The students will first turn 90 degrees in a right turn and then 180 degrees in an about-turn. The students will finally turn 90 degrees in a left turn. Therefore, the students are now facing east.
- Guess how many triangles are there in the above picture?
Answer: 18 This is another tricky math question where different people have come up with different answers. While some forget to count the hidden triangles, others forget to count the giant triangle. Why don’t you concentrate on the triangle again and find all the triangles?
- How to make the following equation precise using three of these four mathematical symbols: + – × ÷ without following any order as such?
Equation: 21 _ 3 _ 18 _ 6 = 6
Answer: 21 – 3 + 18 ÷ 6 = 6 This is more of a symbol math problem than a PEMDAS problem. You can keep testing with the math operators until you find the correct answer.
- John was asked to paint numbers outside 100 apartments. This means he will have to paint numbers one through 100. How many times will he have to paint the number eight?
Answer: 20 times If you carefully read the question, the answer is within the question itself. It’s a tricky one, but this is how it goes: John paints on apartment 8, then he paints on apartment 18 (where the 8 digit comes up again) and, similarly, 28th, 38th, 48th, 58th, 68th, 78th, 80th, 81st, 82nd, 83rd, 84th, 85th, 86th, 87th, 88th, 89th, and 98th apartments.
These were some of the hardest math questions, which probably left your mind boggled. You can always keep improving your logical and math skills with these kinds of math problems that might seem difficult but are easier than you had thought. So, keep testing yourself with more tricky math problems and get your logical juices flowing.
To read more about versatile and new online techniques to improve your math concepts and boost your confidence in solving difficult problems, visit Byju’s FutureSchool blog.
References:
- Jamie Spafford on Twitter: “Here’s a riddle for you: If a baseball bat and a baseball together cost $1.10 and the bat costs a dollar more than the ball, how much does the ball cost? (H/T @ScottMonty for including it in his really great article: https://t.co/foD6RdOUgy)” / Twitter . (n.d.). Retrieved April 22, 2022, from https://twitter.com/jamiespafford/status/1290641293891317770
- 20 Tricky But Fun Grade-School Math Questions – Hard Math Problems . (n.d.). Retrieved April 22, 2022, from https://bestlifeonline.com/tricky-math-questions/
- 34 Hard Math Riddles and Word Problems for Future Geniuses | Fatherly . (n.d.). Retrieved April 22, 2022, from https://www.fatherly.com/play/hard-math-riddles-for-kids-with-answers/
- Southern Math Riddles Jeopardy . (n.d.). Retrieved April 22, 2022, from https://jeopardylabs.com/print/math-riddles-jeopardy
About the Author
Byju's futureschool.
Share Article:
You might also like
What are some applications of math in the real world, teaching math through your child’s passions, parents: why your child needs math to be good at computer science, the importance of visual learning in math.
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.
Are ‘Forever Chemicals’ a Forever Problem?
The environmental protection agency says “forever chemicals” must be removed from tap water. but they lurk in much more of what we eat, drink and use..
This transcript was created using speech recognition software. While it has been reviewed by human transcribers, it may contain errors. Please review the episode audio before quoting from this transcript and email [email protected] with any questions.
From “The New York Times,” I’m Sabrina Tavernise. And this is “The Daily.”
[THEME MUSIC]
This month for the first time, the Environmental Protection Agency began to regulate a class of synthetic chemicals, known as forever chemicals, in America’s drinking water. But the chemicals, which have been linked to liver disease and other serious health problems, are in far more than just our water supply. Today, my colleague Kim Tingley explains.
It’s Wednesday, April 17.
So Kim, any time the EPA announces a regulation, I think we all sort of take notice because implicit in it is this idea that we have been exposed to something — something bad, potentially, lead or asbestos. And recently, the EPA is regulating a type of chemical known as PFAS So for those who don’t know, what are PFAS chemicals
Yeah, so PFAS stands for per and polyfluoroalkyl substances. They’re often called forever chemicals just because they persist so long in the environment and they don’t easily break down. And for that reason, we also use them in a ton of consumer products. They’re in makeup. They’re in carpet. They’re in nonstick cookware. They’re in food packaging, all sorts of things.
Yeah, I feel like I’ve been hearing about these chemicals actually for a very long time. I mean, nonstick pans, Teflon — that’s the thing that’s in my mind when I think PFAS.
Absolutely. Yeah, this class of chemicals has been around for decades. And what’s really important about this is that the EPA has decided, for the first time, to regulate them in drinking water. And that’s a ruling that stands to affect tens of millions of people.
So, help me understand where these things came from and how it’s taken so long to get to the point where we’re actually regulating them.
So, they really actually came about a long time ago. In 1938, DuPont, the people who eventually got us to Teflon, they were actually looking for a more stable kind of refrigerant. And they came upon this kind of chemical, PFAS. The thing that all PFAS chemicals have is a really strong bond between carbon atoms and fluorine atoms. This particular pairing is super strong and super durable.
They have water repellent properties. They’re stain resistant. They’re grease resistant. And they found a lot of uses for them initially in World War II. They were using them as part of their uranium enrichment process to do all these kinds of things. And then —
Well, good thing it’s Teflon.
In the 1950s is when they really started to come out as commercial products.
Even burned food won’t stick to Teflon. So it’s always easy to clean.
So, DuPont started using it in Teflon pans.
Cookware never needs scouring if it has DuPont Teflon.
And then another company, 3M also started using a kind of PFAS —
Scotchgard fabric protector. It keeps ordinary spills from becoming extraordinary stains.
— in one of their big products, Scotchgard. So you probably remember spraying that on your shoes if you want to make your shoes waterproof.
Use Scotchgard fabric protector and let your cup runneth over.
Right — miracle product, Scotchgard, Teflon. But of course, we’re talking about these chemicals because they’ve been found to pose health threats. When does that risk start to surface?
Yeah, so it’s pretty early on that DuPont and 3M start finding effects in animals in studies that they’re running in house.
Around the mid ‘60s, they start seeing that PFAS has an effect on rats. It’s increasing the liver and kidney weights of the rats. And so that seems problematic. And they keep running tests over the next decade and a half. And they try different things with different animals.
In one study, they gave monkeys really, really high levels of PFAS. And those monkeys died. And so they have a pretty strong sense that these chemicals could be dangerous. And then in 1979, they start to see that the workers that are in the plants manufacturing, working with these chemicals, that they’re starting to have higher rates of abnormal liver function. And in a Teflon plant, they had some pregnant workers that were working with these chemicals. And one of those workers in 1981 gave birth to a child who had some pretty severe birth defects.
And then by the mid 1980s, DuPont figures out that it’s not just their workers who are being exposed to these chemicals, but communities that are living in areas surrounding their Teflon plant, particularly the one in Parkersburg, West Virginia, that those communities have PFAS in their tap water.
Wow, so based on its own studies, DuPont knows its chemicals are making animals sick. They seem to be making workers sick. And now they found out that the chemicals have made their way into the water supply. What do they do with that information?
As far as we know, they didn’t do much. They certainly didn’t tell the residents of Parkersburg who were drinking that water that there was anything that they needed to be worried about.
How is that possible? I mean, setting aside the fact that DuPont is the one actually studying the health effects of its own chemicals, presumably to make sure they’re safe, we’ve seen these big, regulating agencies like the EPA and the FDA that exist in order to watch out for something exactly like this, a company that is producing something that may be harming Americans. Why weren’t they keeping a closer watch?
Yeah, so it goes kind of back to the way that we regulate chemicals in the US. It goes through an act called the Toxic Substances Control Act that’s administered by the EPA. And basically, it gives companies a lot of room to regulate themselves, in a sense. Under this act they have a responsibility to report to the EPA if they find these kinds of potential issues with a chemical. They have a responsibility to do their due diligence when they’re putting a chemical out into the environment.
But there’s really not a ton of oversight. The enforcement mechanism is that the EPA can find them. But this kind of thing can happen pretty easily where DuPont keeps going with something that they think might really be a problem and then the fine, by the time it plays out, is just a tiny fraction of what DuPont has earned from producing these chemicals. And so really, the incentive is for them to take the punishment at the end, rather than pull it out early.
So it seems like it’s just self-reporting, which is basically self-regulation in a way.
Yeah, I think that is the way a lot of advocacy groups and experts have characterized it to me, is that chemical companies are essentially regulating themselves.
So how did this danger eventually come to light? I mean, if this is in some kind of DuPont vault, what happened?
Well, there’s a couple different things that started to happen in the late ‘90s.
The community around Parkersburg, West Virginia, people had reported seeing really strange symptoms in their animals. Cows were losing their hair. They had lesions. They were behaving strangely. Some of their calves were dying. And a lot of people in the community felt like they were having health problems that just didn’t really have a good answer, mysterious sicknesses, and some cases of cancers.
And so they initiate a class action lawsuit against DuPont. As part of that class action lawsuit, DuPont, at a certain point, is forced to turn over all of their internal documentation. And so what was in the files was all of that research that we mentioned all of the studies about — animals, and workers, the birth defects. It was really the first time that the public saw what DuPont and 3M had already seen, which is the potential health harms of these chemicals.
So that seems pretty damning. I mean, what happened to the company?
So, DuPont and 3M are still able to say these were just a few workers. And they were working with high levels of the chemicals, more than a person would get drinking it in the water. And so there’s still an opportunity for this to be kind of correlation, but not causation. There’s not really a way to use that data to prove for sure that it was PFAS that caused these health problems.
In other words, the company is arguing, look, yes, these two things exist at the same time. But it doesn’t mean that one caused the other.
Exactly. And so one of the things that this class action lawsuit demands in the settlement that they eventually reach with DuPont is they want DuPont to fund a formal independent health study of the communities that are affected by this PFAS in their drinking water. And so they want DuPont to pay to figure out for sure, using the best available science, how many of these health problems are potentially related to their chemicals.
And so they ask them to pay for it. And they get together an independent group of researchers to undertake this study. And it ends up being the first — and it still might be the biggest — epidemiological study of PFAS in a community. They’ve got about 69,000 participants in this study.
Wow, that’s big.
It’s big, yeah. And what they ended up deciding was that they could confidently say that there was what they ended up calling a probable link. And so they were really confident that the chemical exposure that the study participants had experienced was linked to high cholesterol, ulcerative colitis, thyroid disease, testicular cancer, kidney cancer, and pregnancy induced hypertension.
And so those were the conditions that they were able to say, with a good degree of certainty, were related to their chemical exposure. There were others that they just didn’t have the evidence to reach a strong conclusion.
So overall, pretty substantial health effects, and kind of vindicates the communities in West Virginia that were claiming that these chemicals were really affecting their health.
Absolutely. And as the years have gone on, that was sort of just the beginning of researchers starting to understand all the different kinds of health problems that these chemicals could potentially be causing. And so since the big DuPont class action study, there’s really just been like this building and building and building of different researchers coming out with these different pieces of evidence that have accumulated to a pretty alarming picture of what some of the potential health outcomes could be.
OK, so that really kind of brings us to the present moment, when, at last, it seems the EPA is saying enough is enough. We need to regulate these things.
Yeah, it seems like the EPA has been watching this preponderance of evidence accumulate. And they’re sort of deciding that it’s a real health problem, potentially, that they need to regulate.
So the EPA has identified six of these PFAS chemicals that it’s going to regulate. But the concern that I think a lot of experts have is that this particular regulation is not going to keep PFAS out of our bodies.
We’ll be right back.
So, Kim, you just said that these regulations probably won’t keep PFAS chemicals out of our bodies. What did you mean?
Well, the EPA is talking about regulating these six kinds of PFAS. But there are actually more than 10,000 different kinds of PFAS that are already being produced and out there in the environment.
And why those six, exactly? I mean, is it because those are the ones responsible for most of the harm?
Those are the ones that the EPA has seen enough evidence about that they are confident that they are probably causing harm. But it doesn’t mean that the other ones are not also doing something similar. It’s just sort of impossible for researchers to be able to test each individual chemical compound and try to link it to a health outcome.
I talked to a lot of researchers who were involved in this area and they said that they haven’t really seen a PFAS that doesn’t have a harm, but they just don’t have information on the vast majority of these compounds.
So in other words, we just haven’t studied the rest of them enough yet to even know how harmful they actually are, which is kind of alarming.
Yeah, that’s right. And there’s just new ones coming out all the time.
Right. OK, so of the six that the EPA is actually intending to regulate, though, are those new regulations strict enough to keep these chemicals out of our bodies?
So the regulations for those six chemicals really only cover getting them out of the drinking water. And drinking water only really accounts for about 20 percent of a person’s overall PFAS exposure.
So only a fifth of the total exposure.
Yeah. There are lots of other ways that you can come into contact with PFAS. We eat PFAS, we inhale PFAS. We rub it on our skin. It’s in so many different products. And sometimes those products are not ones that you would necessarily think of. They’re in carpets. They’re in furniture. They’re in dental floss, raincoats, vinyl flooring, artificial turf. All kinds of products that you want to be either waterproof or stain resistant or both have these chemicals in them.
So, the cities and towns are going to have to figure out how to test for and monitor for these six kinds of PFAS. And then they’re also going to have to figure out how to filter them out of the water supply. I think a lot of people are concerned that this is going to be just a really expensive endeavor, and it’s also not really going to take care of the entire problem.
Right. And if you step back and really look at the bigger problem, the companies are still making these things, right? I mean, we’re running around trying to regulate this stuff at the end stage. But these things are still being dumped into the environment.
Yeah. I think it’s a huge criticism of our regulatory policy. There’s a lot of onus put on the EPA to prove that a harm has happened once the chemicals are already out there and then to regulate the chemicals. And I think that there’s a criticism that we should do things the other way around, so tougher regulations on the front end before it goes out into the environment.
And that’s what the European Union has been doing. The European Chemicals Agency puts more of the burden on companies to prove that their products and their chemicals are safe. And the European Chemicals Agency is also, right now, considering just a ban on all PFAS products.
So is that a kind of model, perhaps, of what a tough regulation could look like in the US?
There’s two sides to that question. And the first side is that a lot of people feel like it would be better if these chemical companies had to meet a higher standard of proof in terms of demonstrating that their products or their chemicals are going to be safe once they’ve been put out in the environment.
The other side is that doing that kind of upfront research can be really expensive and could potentially limit companies who are trying to innovate in that space. In terms of PFAS, specifically, this is a really important chemical for us. And a lot of the things that we use it in, there’s not necessarily a great placement at the ready that we can just swap in. And so it’s used in all sorts of really important medical devices or renewable energy industries or firefighting foam.
And in some cases, there are alternatives that might be safer that companies can use. But in other cases, they just don’t have that yet. And so PFAS is still really important to our daily lives.
Right. And that kind of leaves us in a pickle because we know these things might be harming us. Yet, we’re kind of stuck with them, at least for now. So, let me just ask you this question, Kim, which I’ve been wanting to ask you since the beginning of this episode, which is, if you’re a person who is concerned about your exposure to PFAS, what do you do?
Yeah. So this is really tricky and I asked everybody this question who I talked to. And everybody has a little bit of a different answer based on their circumstance. For me what I ended up doing was getting rid of the things that I could sort of spot and get rid of. And so I got rid of some carpeting and I checked, when I was buying my son a raincoat, that it was made by a company that didn’t use PFAS.
It’s also expensive. And so if you can afford to get a raincoat from a place that doesn’t manufacture PFAS, it’s going to cost more than if you buy the budget raincoat. And so it’s kind of unfair to put the onus on consumers in that way. And it’s also just not necessarily clear where exactly your exposure is coming from.
So I talk to people who said, well, it’s in dust, so I vacuum a lot. Or it’s in my cleaning products, so I use natural cleaning products. And so I think it’s really sort of a scattershot approach that consumers can take. But I don’t think that there is a magic approach that gets you a PFAS-free life.
So Kim, this is pretty dark, I have to say. And I think what’s frustrating is that it feels like we have these government agencies that are supposed to be protecting our health. But when you drill down here, the guidance is really more like you’re on your own. I mean, it’s hard not to just throw up your hands and say, I give up.
Yeah. I think it’s really tricky to try to know what you do with all of this information as an individual. As much as you can, you can try to limit your individual exposure. But it seems to me as though it’s at a regulatory level that meaningful change would happen, and not so much throwing out your pots and pans and getting new ones.
One thing about PFAS is just that we’re in this stage still of trying to understand exactly what it’s doing inside of us. And so there’s a certain amount of research that has to happen in order to both convince people that there’s a real problem that needs to be solved, and clean up what we’ve put out there. And so I think that we’re sort of in the middle of that arc. And I think that that’s the point at which people start looking for solutions.
Kim, thank you.
Here’s what else you should know today. On Tuesday, in day two of jury selection for the historic hush money case against Donald Trump, lawyers succeeded in selecting 7 jurors out of the 12 that are required for the criminal trial after failing to pick a single juror on Monday.
Lawyers for Trump repeatedly sought to remove potential jurors whom they argued were biased against the president. Among the reasons they cited were social media posts expressing negative views of the former President and, in one case, a video posted by a potential juror of New Yorkers celebrating Trump’s loss in the 2020 election. Once a full jury is seated, which could come as early as Friday, the criminal trial is expected to last about six weeks.
Today’s episode was produced by Clare Toeniskoetter, Shannon Lin, Summer Thomad, Stella Tan, and Jessica Cheung, with help from Sydney Harper. It was edited by Devon Taylor, fact checked by Susan Lee, contains original music by Dan Powell, Elisheba Ittoop, and Marion Lozano, and was engineered by Chris Wood.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly.
That’s it for The Daily. I’m Sabrina Tavernise. See you tomorrow.

- April 26, 2024 • 21:50 Harvey Weinstein Conviction Thrown Out
- April 25, 2024 • 40:33 The Crackdown on Student Protesters
- April 24, 2024 • 32:18 Is $60 Billion Enough to Save Ukraine?
- April 23, 2024 • 30:30 A Salacious Conspiracy or Just 34 Pieces of Paper?
- April 22, 2024 • 24:30 The Evolving Danger of the New Bird Flu
- April 19, 2024 • 30:42 The Supreme Court Takes Up Homelessness
- April 18, 2024 • 30:07 The Opening Days of Trump’s First Criminal Trial
- April 17, 2024 • 24:52 Are ‘Forever Chemicals’ a Forever Problem?
- April 16, 2024 • 29:29 A.I.’s Original Sin
- April 15, 2024 • 24:07 Iran’s Unprecedented Attack on Israel
- April 14, 2024 • 46:17 The Sunday Read: ‘What I Saw Working at The National Enquirer During Donald Trump’s Rise’
- April 12, 2024 • 34:23 How One Family Lost $900,000 in a Timeshare Scam
Hosted by Sabrina Tavernise
Featuring Kim Tingley
Produced by Clare Toeniskoetter , Shannon M. Lin , Summer Thomad , Stella Tan and Jessica Cheung
With Sydney Harper
Edited by Devon Taylor
Original music by Dan Powell , Elisheba Ittoop and Marion Lozano
Engineered by Chris Wood
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music
The Environmental Protection Agency has begun for the first time to regulate a class of synthetic chemicals known as “forever chemicals” in America’s drinking water.
Kim Tingley, a contributing writer for The New York Times Magazine, explains how these chemicals, which have been linked to liver disease and other serious health problems, came to be in the water supply — and in many more places.
On today’s episode
Kim Tingley , a contributing writer for The New York Times Magazine.

Background reading
“Forever chemicals” are everywhere. What are they doing to us?
The E.P.A. issued its rule about “forever chemicals” last week.
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
Fact-checking by Susan Lee .
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Khan Academy's 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don't need to be graded, and don't require a printer. Math Worksheets. Khan Academy. Math worksheets take forever to hunt down across the internet. Khan Academy is your one-stop-shop for practice from arithmetic to calculus. Math worksheets can vary in quality from ...
Make Questions Topical: Writing a word problem that reflects current events or issues can engage students by giving them a clear, tangible way to apply their knowledge. Include Student Names: Naming a question's characters after your students is an easy way make subject matter relatable, helping them work through the problem.
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students. The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and ...
Solving algebra problems often starts with simplifying expressions. Here's a simple method to follow: Combine like terms: Terms that have the same variable can be combined. For instance, ( 3x + 4x = 7x ). Isolate the variable: Move the variable to one side of the equation. If the equation is ( 2x + 5 = 13 ), my job is to get ( x ) by itself ...
MathPapa Practice has practice problems to help you learn algebra. Basic Arithmetic Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division Basic Arithmetic Review Multi-Digit Arithmetic Addition (2-digit) Subtraction (2-digit) Multiplication (2-digit by 1-digit) ...
Teachers could make use of these math problem solving questions in a number of ways. They can: incorporate the questions into a relevant math lesson. ... Math word problems 1. Home on time - easy . Type: Elapsed time, Number, Addition. A movie theater screening starts at 2:35 pm. The movie lasts for 2 hours, 32 minutes after 23 minutes of ...
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store. get Go. Algebra.
Get math help in your language. Works in Spanish, Hindi, German, and more. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
Even simple math problems become easier to solve when broken down into steps. From basic additions to calculus, the process of problem solving usually takes a lot of practice before answers could come easily. As problems become more complex, it becomes even more important to understand the step-by-step process by which we solve them.
AP Calculus AB solved free response questions from past exams: AP®︎/College Calculus AB. ... They were created by Khan Academy math experts and reviewed for curriculum alignment by experts at both Illustrative Mathematics and Khan Academy. ... Problem solving with the coordinate plane: 5th grade (Eureka Math/EngageNY) 6th grade (Eureka Math ...
To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem.
Problem-solving strategies in math are methods students can use to figure out solutions to math problems. Some problem-solving strategies: Draw a model; Use different approaches; Check the inverse to make sure the answer is correct; Students need to have a toolkit of math problem-solving strategies at their disposal to provide different ways to ...
This way you are setting up the child's successful future. Fun math problems will urge your child to choose to solve it over playing bingo or baking. Apparently, there are innumerable methods to make easy maths tricky questions and answers. This includes the inception of the ideology that maths is simpler than their fear.
Use w for width of rectangle: w = 12m. Use h for height of rectangle: h = 5m. Formula for Area of a Rectangle: A = w × h. We are being asked for the Area. Solve: A = w × h = 12 × 5 = 60 m2. The area is 60 square meters. Now let's try the example from the top of the page: Example: Sam and Alex play Tennis.
Popular Calculators. Fractions Radical Equation Factoring Inverse Quadratic Simplify Slope Domain Antiderivatives Polynomial Equation Log Equation Cross Product Partial Derivative Implicit Derivative Tangent Complex Numbers. Symbolab: equation search and math solver - solves algebra, trigonometry and calculus problems step by step.
3. Work on an easier problem. If there is an easier problem available that is similar to the one you are trying to solve, work on the easier problem first. Solving an easier problem that requires some of the same steps and formulas will help you to tackle the more difficult problem. [8] [9] 4.
Math and Logic Puzzles. ... then this is the page for you ! Whosoever shall solve these puzzles shall Rule The Universe!... or at least they should ... Starter Puzzles. Puzzle Games. Measuring Puzzles. Symmetry Jigsaw Puzzles. Logic Puzzles. Sam Loyd Puzzles. Shape Puzzles. Einstein Puzzles.
In fact, solving an equation is just like solving a puzzle. And like puzzles, there are things we can (and cannot) do. Here are some things we can do: ... Let us check x=3 using the original question: 2 × 3 3 − 3 + 3 = 6 3 − 3. Hang On: 3 − 3 = 0 That means dividing by Zero!
9. Logic Puzzle: There are three people (Alex, Ben and Cody), one of whom is a knight, one a knave, and one a spy. The knight always tells the truth, the knave always lies, and the spy can either ...
Answer: 1. Start by solving the division part of the equation. In order to do that, in case you forgot, you have to flip the fraction and switch from division to multiplication, thus getting 3 x 3 = 9. Now you have 9 - 9 + 1, and from there you can simply work from left to right and get your final answer: 1. 11.
Hence, it is recommended to all the children to solve each one of them and test their abilities. Maths Quiz Questions with Answers (MCQs) Let us answer here some of the quizzes which are based on simple arithmetic concepts. These problems are based on fundamental concepts, which students can easily answer without picking up a pen and paper. Q.1.
Replace the question mark in the above diagram with an appropriate number. Answer: 6. If you enjoy playing Sudoku, then this hard math problem would have been quite a breeze for you! The rows and columns all add up to 15, and that is how the answer turned out to be 6. Solve the unfinished equation: 1 = 4. 2 = 16.
Even burned food won't stick to Teflon. So it's always easy to clean. kim tingley. So, DuPont started using it in Teflon pans. archived recording 2. Cookware never needs scouring if it has ...