Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples

What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples
Published on January 2, 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on January 29, 2024.
A fishbone diagram is a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot possible solutions. It is also called an Ishikawa diagram, after its creator, Kaoru Ishikawa, as well as a herringbone diagram or cause-and-effect diagram.
Fishbone diagrams are often used in root cause analysis , to troubleshoot issues in quality management or product development. They are also used in the fields of nursing and healthcare, or as a brainstorming and mind-mapping technique many students find helpful.
Table of contents
How to make a fishbone diagram, fishbone diagram templates, fishbone diagram examples, advantages and disadvantages of fishbone diagrams, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about fishbone diagrams.
A fishbone diagram is easy to draw, or you can use a template for an online version.
- Your fishbone diagram starts out with an issue or problem. This is the “head” of the fish, summarized in a few words or a small phrase.
- Next, draw a long arrow, which serves as the fish’s backbone.
- From here, you’ll draw the first “bones” directly from the backbone, in the shape of small diagonal lines going right-to-left. These represent the most likely or overarching causes of your problem.
- Branching off from each of these first bones, create smaller bones containing contributing information and necessary detail.
- When finished, your fishbone diagram should give you a wide-view idea of what the root causes of the issue you’re facing could be, allowing you to rank them or choose which could be most plausible.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

There are no built-in fishbone diagram templates in Microsoft programs, but we’ve made a few free ones for you to use that you can download below. Alternatively, you can make one yourself using the following steps:
- In a fresh document, go to Insert > Shapes
- Draw a long arrow from left to right, and add a text box on the right-hand side. These serve as the backbone and the head of the fish.
- Next, add lines jutting diagonally from the backbone. These serve as the ribs, or the contributing factors to the main problem.
- Next, add horizontal lines jutting from each central line. These serve as the potential causes of the problem.
Lastly, add text boxes to label each function.
You can try your hand at filling one in yourself using the various blank fishbone diagram templates below, in the following formats:
Fishbone diagram template Excel
Download our free Excel template below!
Fishbone diagram template Word
Download our free Word template below!
Fishbone diagram template PowerPoint
Download our free PowerPoint template below!
Fishbone diagrams are used in a variety of settings, both academic and professional. They are particularly popular in healthcare settings, particularly nursing, or in group brainstorm study sessions. In the business world, they are an often-used tool for quality assurance or human resources professionals.
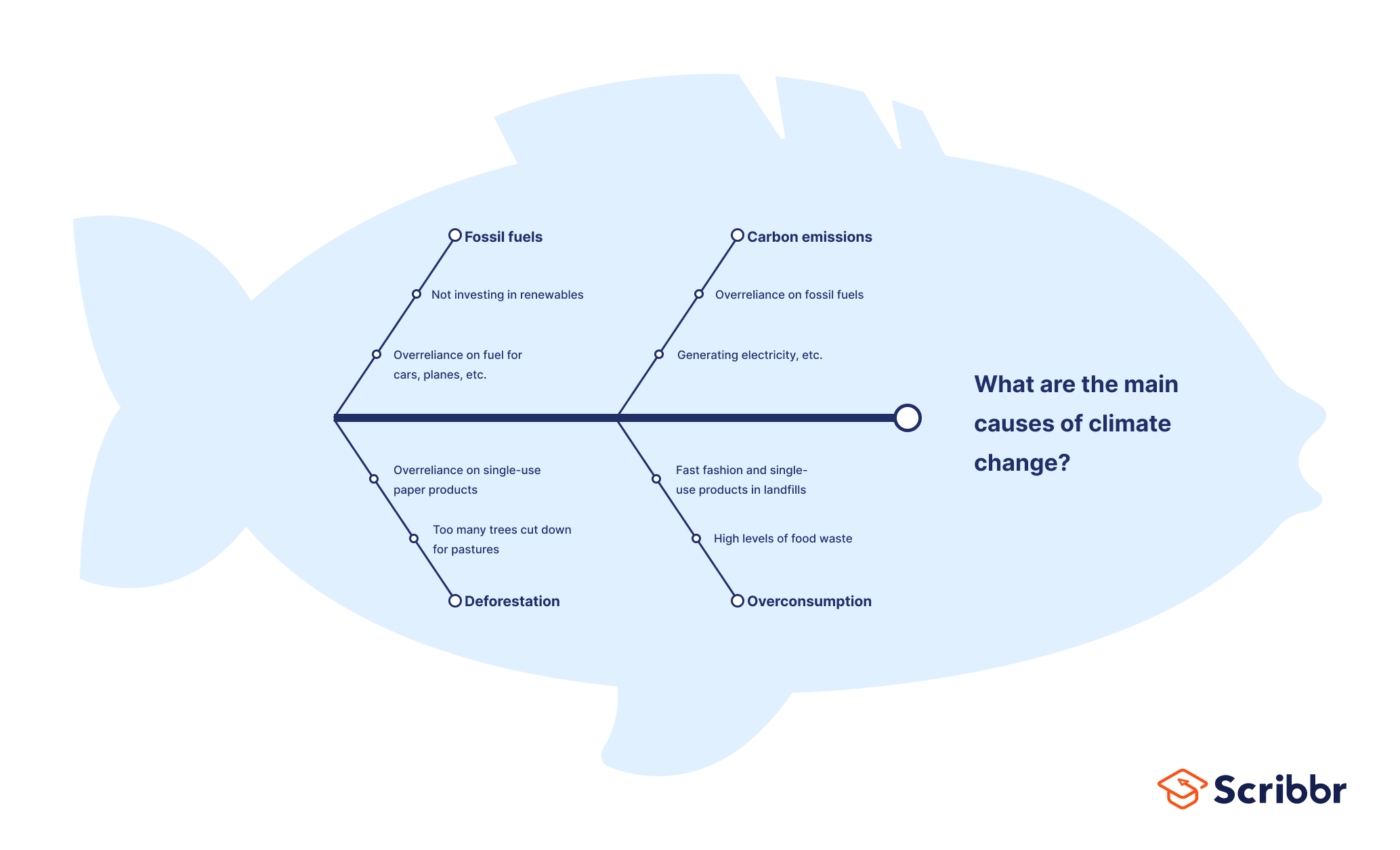
Fishbone diagram example #1: Climate change
Let’s start with an everyday example: what are the main causes of climate change?
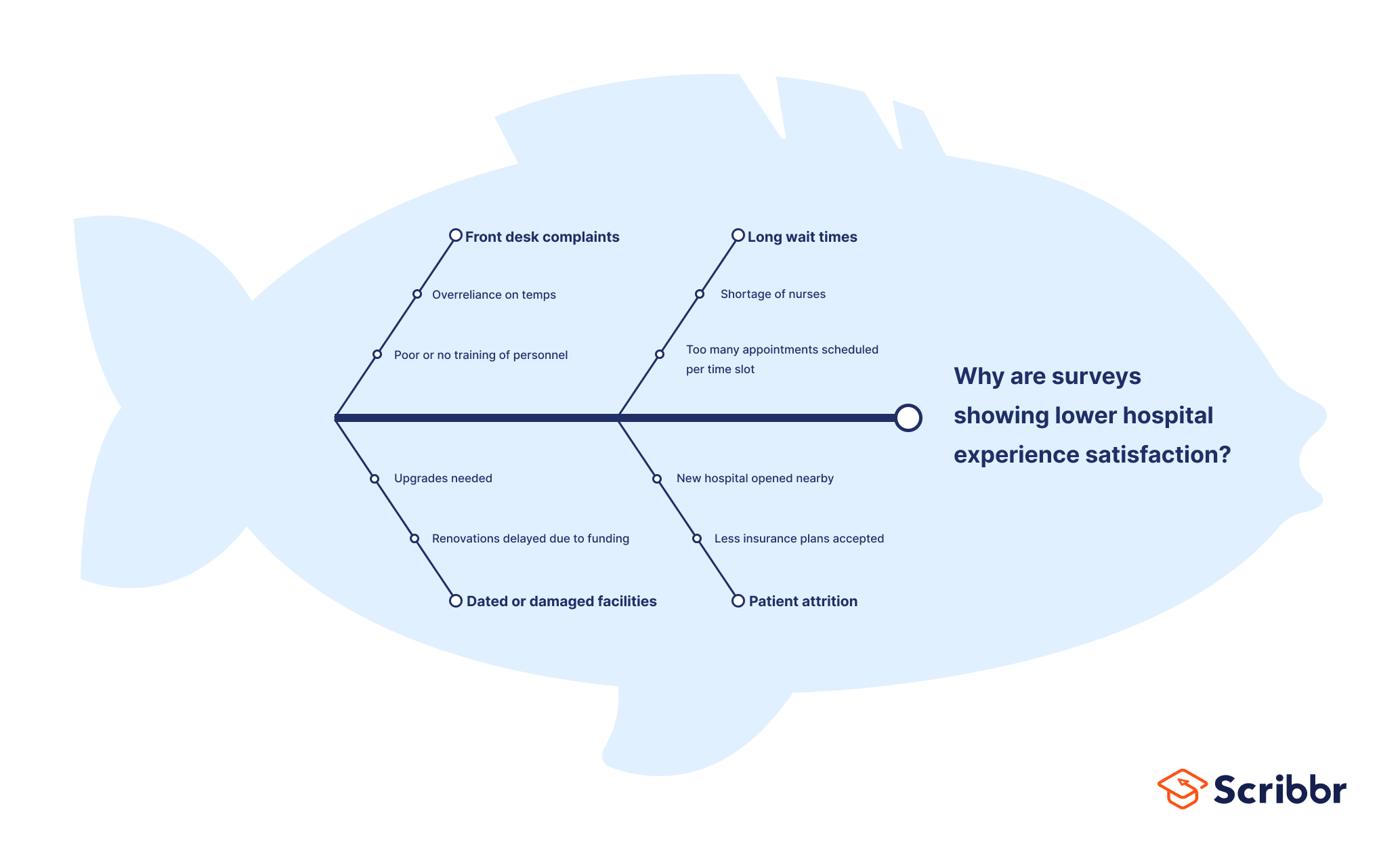
Fishbone diagram example #2: Healthcare and nursing
Fishbone diagrams are often used in nursing and healthcare to diagnose patients with unclear symptoms, or to streamline processes or fix ongoing problems. For example: why have surveys shown a decrease in patient satisfaction?
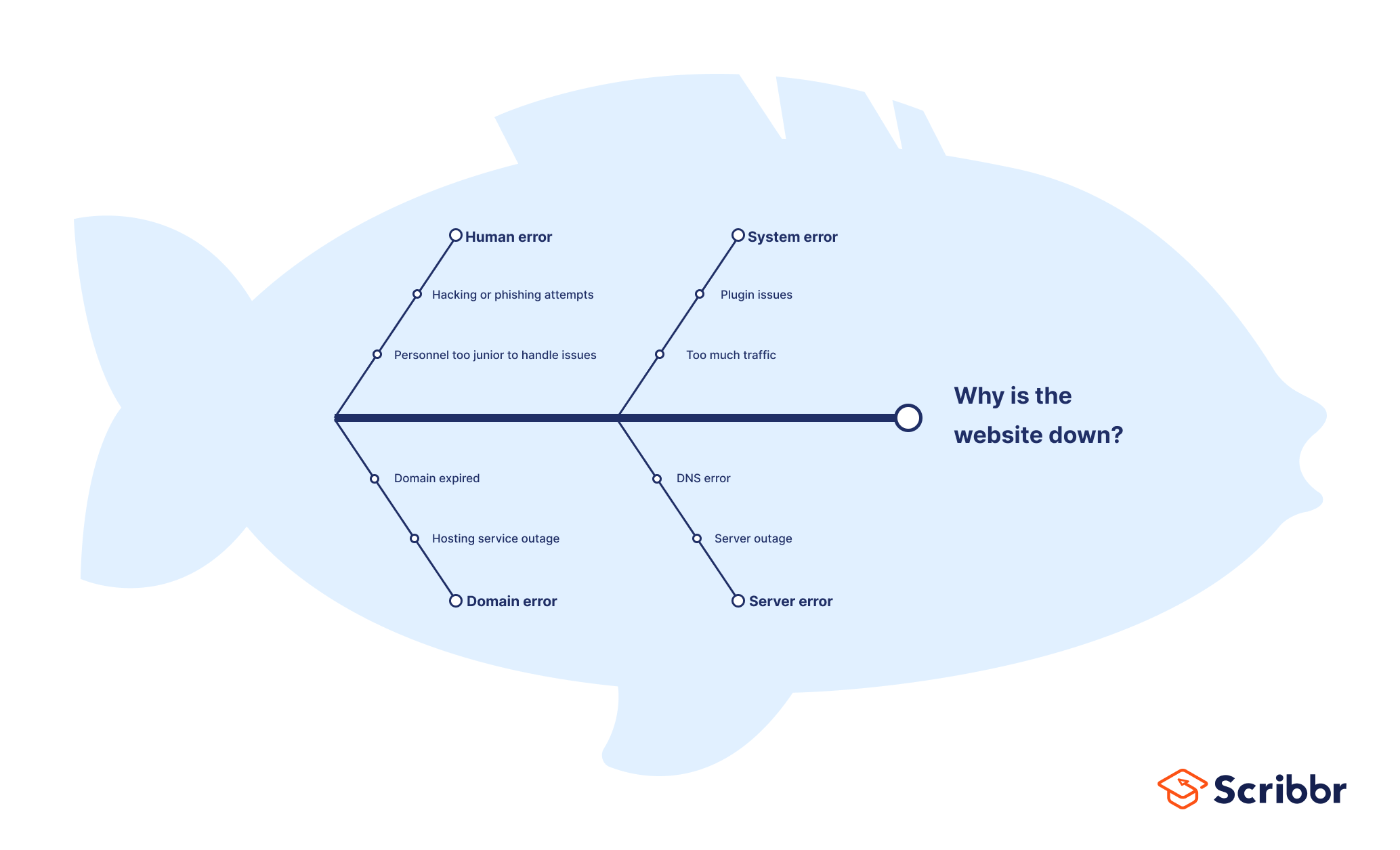
Fishbone diagram example #3: Quality assurance
QA professionals also use fishbone diagrams to troubleshoot usability issues, such as: why is the website down?
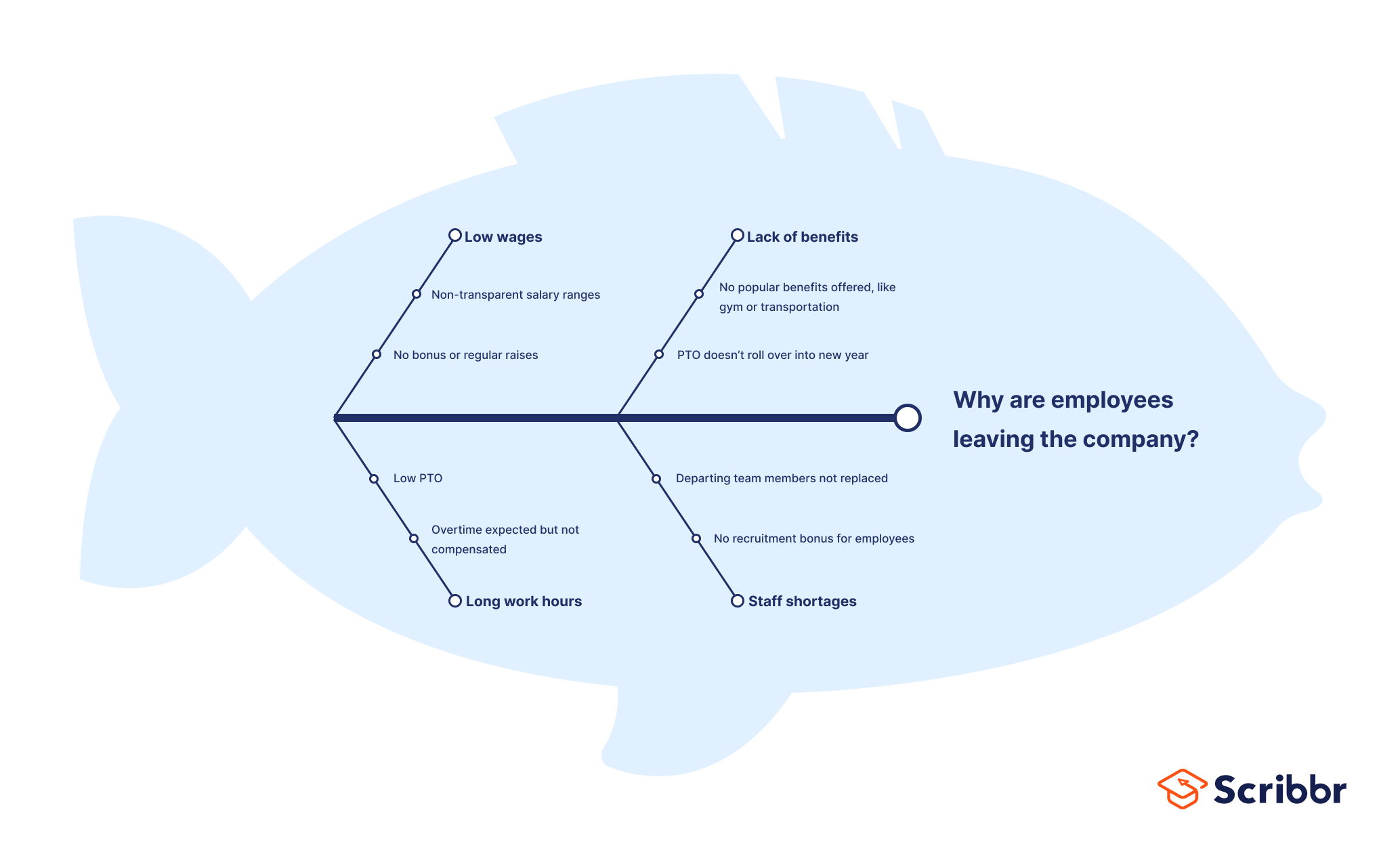
Fishbone diagram example #4: HR
Lastly, an HR example: why are employees leaving the company?
Fishbone diagrams come with advantages and disadvantages.
- Great tool for brainstorming and mind-mapping, either individually or in a group project.
- Can help identify causal relationships and clarify relationships between variables .
- Constant iteration of “why” questions really drills down to root problems and elegantly simplifies even complex issues.
Disadvantages
- Can lead to incorrect or inconsistent conclusions if the wrong assumptions are made about root causes or the wrong variables are prioritized.
- Fishbone diagrams are best suited to short phrases or simple ideas—they can get cluttered and confusing easily.
- Best used in the exploratory research phase, since they cannot provide true answers, only suggestions.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Fishbone diagrams have a few different names that are used interchangeably, including herringbone diagram, cause-and-effect diagram, and Ishikawa diagram.
These are all ways to refer to the same thing– a problem-solving approach that uses a fish-shaped diagram to model possible root causes of problems and troubleshoot solutions.
Fishbone diagrams (also called herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, and Ishikawa diagrams) are most popular in fields of quality management. They are also commonly used in nursing and healthcare, or as a brainstorming technique for students.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2024, January 29). What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/fishbone-diagram/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, data collection | definition, methods & examples, exploratory research | definition, guide, & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
What is a Fishbone diagram?
Table of Contents
Fishbone diagrams explained.
A fishbone diagram (also known as an Ishikawa fishbone diagram) is an effective problem-solving tool. Instead of focusing on a quick fix, creating a fishbone diagram helps to identify the root cause of a problem and find a long-term solution.
As a type of cause and effect diagram , the “fishbone” name comes from the diagram’s resemblance to a fish skeleton. A fishbone diagram consists of three main categories:
There’s a fish head at the head of the diagram, where you’ll outline the problem you’re trying to solve. The rest of the diagram branches out from here.
The spine stems from the head of the diagram (the problem statement), providing the outline of the fish. At the end of each spinal bone is a category that needs to be considered as part of the problem-solving process.
Branching out from each spinal bone, you’ll see a smaller rib bone. This is where the possible causes will sit to help you pinpoint the potential cause of the problem.
Benefits of fishbone diagrams
Fishbone diagrams are useful tools for improving existing processes and pinpointing causes of issues. Take a look at some benefits of performing a fishbone diagram root cause analysis:
Easily find the root cause of a problem
A fishbone diagram is a visual tool that adds structure and clarity to problem-solving. It indicates the problem and its possible causes in a single location, making it easier for teams to conduct a root cause analysis .
Prevent further problems
By finding the root cause of the problem, you fix the problem at its source and mitigate future issues. As a result, you’re far more likely to prevent the same (or similar) problems from cropping up in the future.
Collaborate with your team
A fishbone diagram is a great way to work with your team to brainstorm solutions . It’s a collaborative diagram, encouraging teams to review all the available information and discuss the best course of action.
If you’re part of a remote or hybrid team, an online platform like Miro allows you to collaborate with your team, no matter where they work. Simply share the diagram and hop on a video chat, and you can perform your root cause analysis virtually.
Example of a fishbone diagram
To see a fishbone diagram in action, look at this CEDAC Template from NEXT LEVEL Partners.
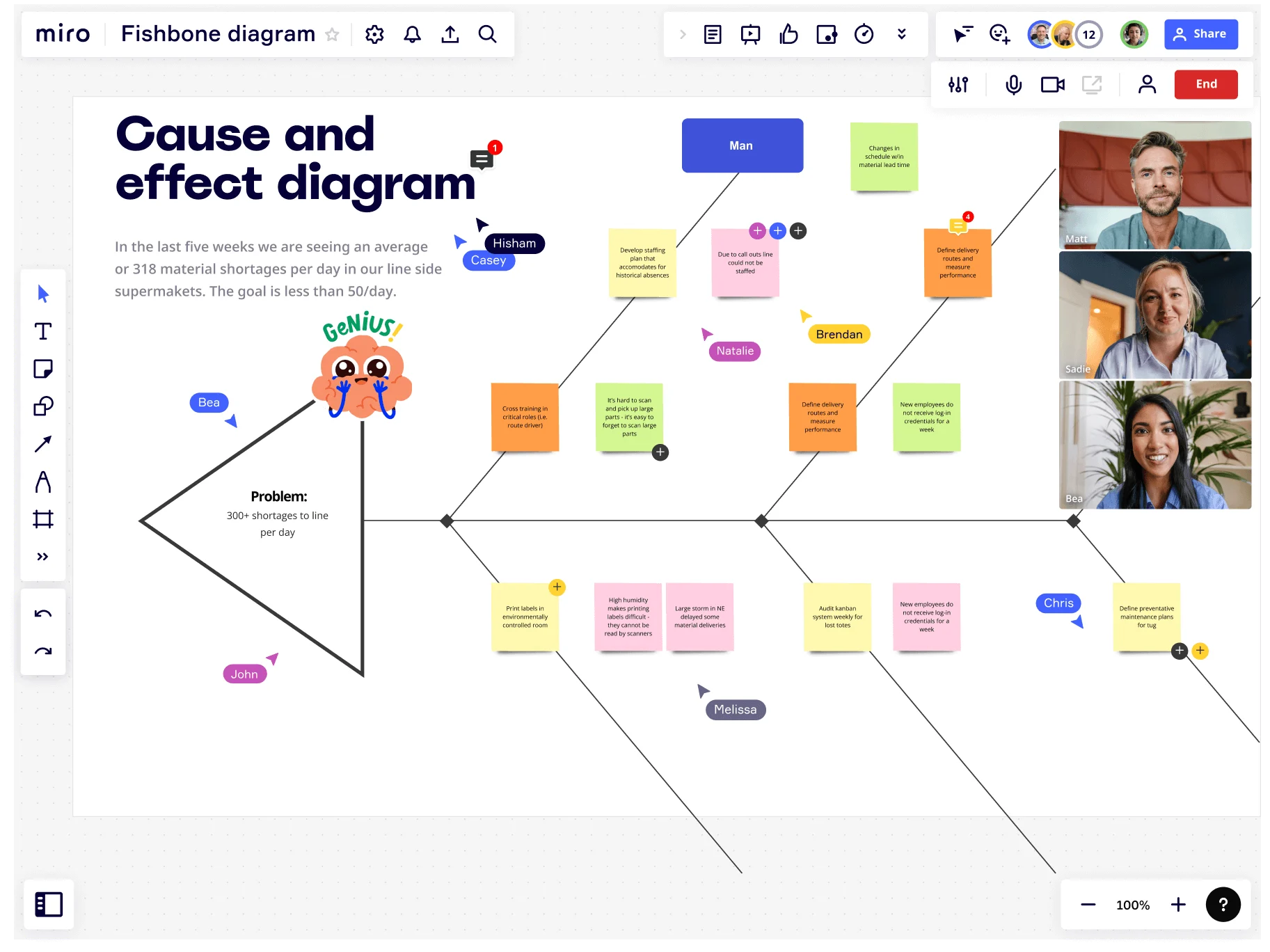
CEDAC is an acronym for Cause and Effect Diagram with the Addition of Cards. The diagram contains issues on the left-hand side of the ribs and solutions on the right-hand side.
Its inventor, Ryuji Fukuda, created CEDAC so that teams can delve deeper into their problem-solving analyses. By adding cards to the diagram, teams have a way of questioning existing information and suggesting new ideas. As a result, they’ll gain a deeper understanding of their problems and how to solve them.
Here are some of the common areas where the CEDAC model can be helpful:
Product development
Visualize issues with product development using the CEDAC diagram. Collaborate with the product team to identify the cause of the problem and use cards to identify the best possible solution.
Software features
Effectively allocate resources based on team structures and capabilities. Understand the most critical problems to solve and how they map together.
Product design
Define failures or problems with your product design, and identify effective solutions. Using the diagram’s cards, product designers can generate new and creative solutions to improve the design.
Internal processes
Pinpoint bottlenecks and figure out how to streamline and improve your business processes. Encourage team members to join in the discussion and make suggestions for improving the process going forward.
When to use a fishbone diagram
Take a look at some of the different instances when using a fishbone diagram can be useful for you and your team.
1. To analyze a problem statement
If you have a clear problem statement for your business, a fishbone diagram is a great way to analyze it in detail. You can see the problem’s culprit and decide how to fix the issue.
2. To brainstorm the causes of the problem
Also known as root cause analysis, a fishbone diagram allows you to discuss the potential causes of a problem. It’s the perfect opportunity to host a brainstorming session to identify pressing concerns and work through possible solutions.
3. To analyze a new product design
Use a fishbone diagram to map your new product design and visualize any potential hurdles before they come your way. As a result, you can put preventative measures in place before going live.
4. To improve your processes
If you’re struggling to streamline your processes and inefficiencies, a fishbone diagram can help. Use a fishbone diagram to pinpoint the troublesome areas of your process and find the cause of a problem. From there, you can determine exactly how to fix it.
5. For quality improvement
Use a fishbone diagram to visualize how and where you can improve to offer your customers a higher-quality experience. For example, you might want to improve the quality of your customer service. In this case, you can use the diagram to find areas for improvement in your existing processes.
How to make a fishbone diagram
Follow these simple steps to create an effective fishbone diagram:
1. Select the Fishbone Diagram Template
While you can always build your own diagram from scratch, you can also get a headstart by selecting this Fishbone Diagram Template . It’s free and easy to use, so you can start mapping your diagram immediately.

2. Outline your problem statement
When your diagram is ready to use, start by defining the problem. Otherwise known as a problem statement, this will sit at the head of the diagram. This must be as clear and concise as possible to find the right solution.
For example, in the diagram below, the main problem is that “40% of users cancel the subscription in the first month.” This statement clearly describes the problem and offers a solid starting point for finding a solution. Now, let’s consider how this would work if the statement were written differently — for example, “to increase customer retention.”
This statement is pretty vague, and there’s a lot of room for interpretation. Instead of focusing specifically on how to keep existing customers after the first month, teams might explore other avenues that won’t necessarily solve the actual problem.
The problem statement doesn’t have to be long and detailed. In fact, you should keep it short — ideally, no longer than a sentence. That way, it’ll be easy for your team to see the problem and won’t overcrowd the diagram. But the problem statement should always be clear and concise, leaving no room for interpretation.
If you’re new to problem statements or want a framework to guide you, look at Prime Motive’s Problem Framing Workshop Template .
3. Pinpoint your root causes
With your problem statement in place, you can now branch out and start to pinpoint the possible causes of the problem.
The specific causes will depend on what your problem statement is. For example, if your problem statement is related to product design, your root causes could include the following:
These are just a few examples. In your diagram, you might find that you have more or fewer root causes. With an intuitive platform like Miro, it’s easy to add or remove boxes based on how many you need.
When adding causes to your diagram, those with the biggest impact should be closest to the problem. The farther away a cause is from the head of the diagram, the less influence it has on the problem.
4. Identify individual causes
You can now identify the individual elements that contribute to the overall cause. These are the bones of the fish.
Let’s use an example to demonstrate how this works. Imagine that one of your root causes is “Equipment.” Here are some of the individual causes that might sit under this area:
You are using outdated and inefficient equipment
It’s expensive to replace existing equipment
There aren’t enough employees who know how to use the equipment
All of these elements could contribute to the problem you’re facing, but it’s up to you and your team to pinpoint the key elements at the root of the problem. Review all this information with your team, and you’ll be able to see which problem is most likely to have a long-term solution.
If you’re unsure how to identify the individual causes, look at the 5 Whys framework . It’s a simple brainstorming tool that helps teams explore the reasons behind a potential problem.
5. Create a plan of action
After working with your team to find the root cause of the problem, you can create an action plan for improvements. This involves mapping out the steps you need to take to solve your problem and how you’ll measure success (we suggest using the SMART Goals framework for this).
During this stage, be sure to focus on how to make lasting improvements. Don’t lose sight of the bigger picture in favor of a quick fix. The purpose of the fishbone diagram is to implement a long-lasting solution to your problem, so keep this in mind when creating your plan of action for the future.
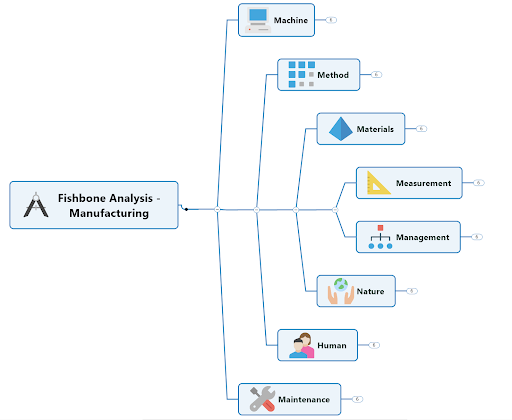
Fishbone diagram categories: the 6Ms of production
The fishbone diagram is used across various industries, but the original diagram was created to improve the manufacturing process. The six methods (6Ms) of production come from this original diagram, and engineers and designers would use this structure to cover all their bases.
The 6Ms of production are as follows:
1. Manpower
The functional activity involved in designing and delivering a product.
The production process and any other processes that contribute to the delivery of the final product.
Any systems, tools, or equipment used in manufacturing.
4. Material
The raw materials and components needed to create the end product.
5. Milieu (or Mother Nature)
Any environmental factors, such as weather, floods, or fire. Although most milieu factors can’t be controlled, there are some instances where businesses can put preventative measures in place to mitigate problems.
6. Measurement
The physical measurements (volume, distance, temperature, and so on) of a product, machine, or workspace.
The 6Ms are only relevant if you’re using the fishbone diagram to improve a manufacturing or production process. If you’re using the diagram for any other purpose, there’s no need to follow this structure.
Discover more
How to build a fishbone diagram
What is a cause and effect diagram
What is root cause analysis?
What is the 5 Whys Framework?
5 Whys: Examples, explanations, and how to find the causes of problems
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
- Corporate Courses |
- Employee Courses |
- Leadership Courses |
- Limited Time Offer

Creating A Fishbone Diagram: A Detailed Guide

In the world of problem-solving and process improvement, tools that facilitate structured analysis are essential. The Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram or Cause-and-Effect Diagram, is one such tool that can help teams identify and analyze the root causes of a problem. It’s a visual representation that aids in exploring potential causes in a systematic and organized manner.
Definition A Fishbone Diagram is a graphical technique used for identifying and categorizing the possible causes of a specific problem or effect. The diagram resembles a fish skeleton, with the “head” representing the problem and the “bones” branching out into various categories of potential causes.
Best Practices When creating a Fishbone Diagram, it’s important to adhere to some best practices to ensure its effectiveness:
- Clear Problem Statement : Begin by clearly defining the problem or effect you’re trying to address. The effectiveness of the diagram hinges on the clarity of the problem statement.
- Cross-Functional Teams : Involve individuals from different departments or functions in the analysis. Diverse perspectives can lead to a more comprehensive list of potential causes.
- Brainstorming : Encourage open and unbiased brainstorming sessions to identify possible causes. No idea should be dismissed during this phase.
- Categories : The “bones” of the fishbone represent categories that might contribute to the problem. Common categories include People, Process, Equipment, Environment, and Materials. Tailor these categories to your specific situation.
- Hierarchical Structure : Follow a hierarchical structure for the branches, with sub-causes branching from main causes. This helps in visualizing the relationships between different causes.
- Avoid Assumptions : Ensure that the identified causes are backed by data and evidence. Avoid making assumptions without proper validation.
- Use Visuals : The diagram’s strength lies in its visual representation. Use clear and concise labels, colors, and shapes to make the diagram easy to understand.
Features The key features of a Fishbone Diagram include:
- Problem Statement : Clearly defined issue placed at the “head” of the diagram.
- Categories : Major branches representing different categories of potential causes.
- Bones : Sub-branches stemming from categories, detailing specific causes.
- Cause-and-Effect Relationships : Illustrates how various causes might be linked to the problem.
Pros and Cons Pros:
- Structured Analysis : Provides a systematic approach to exploring causes.
- Visual Representation : Facilitates easy understanding and communication.
- Team Collaboration : Involves cross-functional teams, promoting diverse insights.
- Comprehensive : Helps identify both primary and secondary causes.
- Simplification : May oversimplify complex issues.
- Subjective : Relies on team’s assumptions and perceptions.
- Time-Consuming : Elaborate diagrams can be time-intensive to create.
- Limited Detail : Might not capture nuanced relationships between causes.
Benefits and Examples Benefits of using a Fishbone Diagram include:
- Root Cause Identification : Helps pinpoint the underlying reasons behind a problem.
- Problem Prevention : Enables teams to develop strategies to prevent similar issues in the future.
- Data-Driven Decision Making : Promotes evidence-based analysis over assumptions.
Example Scenario: A manufacturing company experiences frequent delays in production. Using a Fishbone Diagram, they identify causes including inadequate training (People), outdated machinery (Equipment), unclear processes (Process), and temperature fluctuations (Environment).
How to Use the Cause-and-Effect Fishbone Diagram
- Define the Problem : Clearly state the problem or effect you’re addressing.
- Identify Categories : Determine relevant categories for your situation (People, Process, Equipment, Environment, etc.).
- Brainstorm Causes : With your team, brainstorm potential causes under each category.
- Create the Diagram : Draw the main horizontal line (the “spine” of the fish) and the categories branching off from it.
- Add Sub-Causes : Extend the branches with sub-branches representing specific causes.
- Analyze Relationships : Discuss and analyze how different causes might be connected to the problem.
- Prioritize Causes : Evaluate and prioritize the causes based on their potential impact.
Tips for Creating a Cause-and-Effect Analysis Using the Fishbone Diagram
- Encourage open and unbiased brainstorming sessions.
- Use sticky notes or digital tools for a collaborative brainstorming experience.
- Involve subject matter experts to ensure accuracy.
- Use clear labels and visuals to enhance clarity.
- Update the diagram as new information becomes available.
Template Fishbone Diagram
Here’s a simplified template of a Fishbone Diagram:
Remember, the beauty of the Fishbone Diagram lies in its adaptability. Customize the categories and branches to fit your specific problem or situation.
Conclusion The Fishbone Diagram is a valuable tool for dissecting complex problems and identifying their root causes. By encouraging collaboration, fostering structured thinking, and providing a visual representation, it helps teams make informed decisions and drive process improvements.
Utilize the Fishbone Diagram to analyze problems effectively and develop strategies for continuous enhancement.
Mastering The Fishbone Analysis Technique
Practical Examples Of Cause And Effect Analysis In Action
Unlock Productivity With Mind Maps
Exciting News For All PowerPoint Enthusiasts: Discover The Top 23 Add-ins and Plug-ins
Understanding The Power Of A SIPOC Diagram

The Power Of Kanban Boards: Enhancing Workflow And Productivity

Convergent Thinking: A Guide To Problem-Solving And Decision-Making
There’s always more learning to explore..

Add to cart
Buy Quality Management Skills Workbooks
Buy Corporate Structure Skills Workbooks

Buy Issues In An Organization Workbooks

Buy Corporate Culture Skills Workbooks

Buy Negotiation Skills Workbooks

Buy Marketing Skills Workbooks

Buy Conflict Resolution Skills Workbooks

Buy Leadership Influence Skills Workbooks

Buy Delegation In Leadership Workbooks

Buy Leadership Skills Workbooks

Buy Job Design Skills Workbooks

Buy Job Analysis Skills Workbooks
Trusted by leading commercial and public sector organizations..

All-In-One Course Materials For Enterprises
Say goodbye to the ever-challenging task of developing your own training courses. Our intuitive training course material enables you to download, share, and deliver your own courses.
Saving You Time.
Give your company a faster, more flexible way of presenting training courses. Access, brand, and present training courses all from one easy-to-use download.

Want To Save More On Your Training Course Materials?
- 50+ fully tested sets of training course materials
- 17+ training guides (PDFs)
- 100% customizable content
- 90% savings on normal prices
- and more...
Frequently Asked Questions.
Oak Innovation simplifies the course creation process. Our readymade training course material will save you time. And, you'll get instant access to the training content needed to meet the needs of your audience.
You don’t need any detailed expertize to present our training course material – simply focus on your course delivery, and we’ll handle the rest. You get instant access to workbooks, guides, and resources.
Our pricing is really simple. Each set of course material costs $80.
1. Select the course you want to deliver. 2. Add the course materials to the shopping cart. 3. Securely pay using all major debit/credit cards. 4. Get instant access via a secure download page. 5. Get an email with download instructions. 6. Unzip your order and access everything in MS Office format.
Yes. You can add your logo and brand the course material as your own.
Yes, you can see a full list of our courses in our shop .
Our white-label training course materials can be used to teach all categories of employees. Senior Leadership Teams - Leadership teams play a critical role in organizations. These course materials will equip them with the skills needed to transform their companies into the future. Mid-Level Managers, Supervisors And HR Professionals - Our training course materials enable mid-level managers, supervisors and HR professionals to lead and develop their teams for success. Frontline Employees - Core to all organizations, frontline employees will benefit directly from these training course materials. Small Business Owners And Entrepreneurs - Attending courses based on these training course materials will equip all entrepreneurs and their teams with the skills, knowledge and abilities required to revolutionize their companies.
Which Training Course Materials Are Right For You?

How to Use Fishbone Diagram for Problem Solving
Fishbone diagram is a problem-solving tool, used in literal terms like a fishbone. It is also known as a cause and effect diagram. The mechanism is to specifically identify the cause and effect of any business or project problem.
A fishbone diagram can help define potential reasons for an issue. This article will dive into understanding the core principles of the fishbone diagram problem solving as a tool.
In 1943 at Tokyo University, Kaoru Ishikawa created the "Fishbone Diagram." Fishbone diagrams can also be called diagrams of "cause and effect." The fishbone diagram problem solving tool is a perfect tool to dig through an issue when we try to assess the root cause and find a solution effectively.
It offers a mechanism for explicitly identifying the "effect" and then brings you to think about the potential triggers, based on typical manufacturing problems. The fishbone diagram problem solving is a basic model that makes it easy to grasp swift and efficient root causes to implement corrective behavior.
It reflects the question or impact at the fish's head or mouth. Possible contributing factors under separate causal groups are identified on the smaller "bones." A fishbone diagram can help define potential reasons for an issue that would otherwise not be discussed by encouraging the team to look through the definitions and discuss alternate reasons.
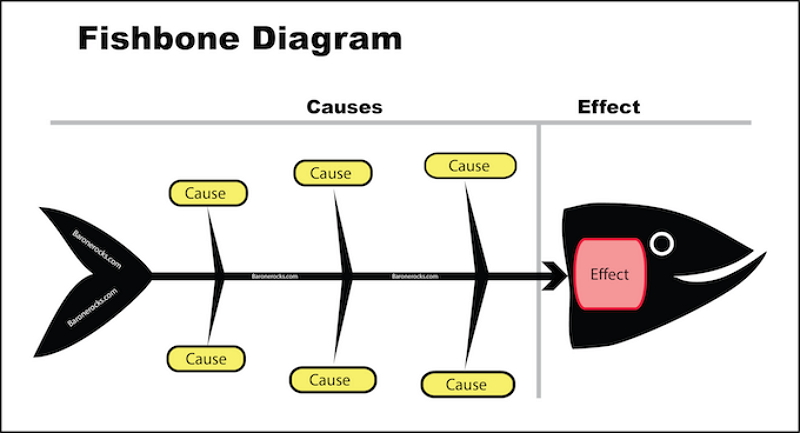
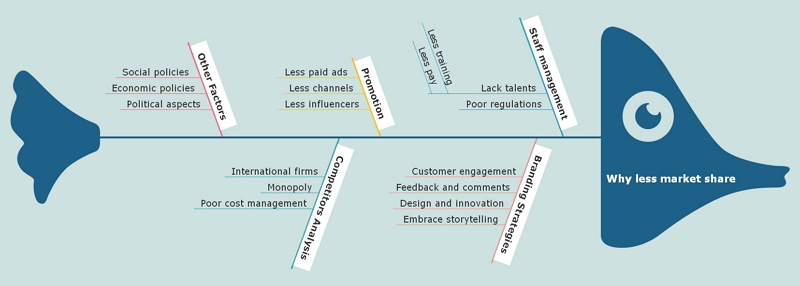
Source: EdrawMind
1.1 Why Use Fishbone Diagram for Problem Solving
The fishbone diagram makes you consider more when solving specific problems. During a brainstorming activity, various groups inspire thoughts from different areas.
The fishbone diagram brings order to the process of cause and effect . It's easy for participants to understand the main problems or issues and focus on the question across different potential triggers.
The fishbone diagram helps distinguish the causes and reasons for a problem and lets people intuitively figure out the solutions.
1.2 The Usage of Fishbone Diagram
The fishbone diagram problem solving method can be used when trying to fix problems or discover the root cause of an issue or problem, which helps you to see below the surface, and dive deeper into the real problem.
Here are several typical fishbone diagram problem solving applications:
- Manufacturing: ,nbsp;Uncover the root cause of a manufacturing problem by brainstorming and rating the likelihood and effect of all factors affecting the manufacturing cycle;
- Marketing or Product Marketing: ,nbsp;Identify the possible factors that may impede your company's popularity in the marketplace by investigating all the places that affect your product acceptance;
- Service: ,nbsp;Uncover the root cause of a business issue by brainstorming, and rate the probability and effect of all factors impacting the service delivery process.
There are 7 steps lead you to use fishbone diagram for problem solving:
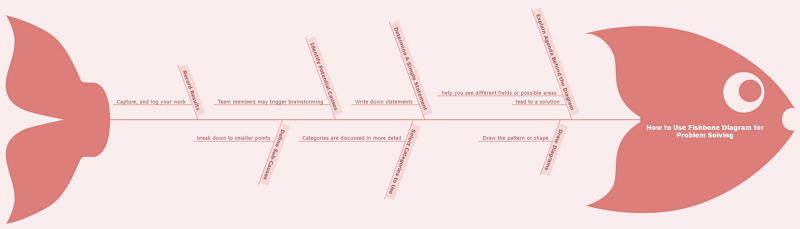
- Explain the agenda behind the diagram
Let your team members know that the diagram can help you see different fields or possible areas that might lead to a solution to your current business problem.
- Draw diagrams
Draw the pattern or shape on your whiteboard, or use a software diagramming tool to ease accessibility. If you need remote attendants to do this exercise, you can quickly build it in EdrawMind and display your computer.
- Determine a simple statement on an issue
Write down statements at the top of your page or above where you will build the diagram., which means everyone has the same idea of the issue you are concerned with.
- Select what categories to use
Categories are discussed in more detail below. For example, you can add Policies, Methods, Personnel, and Software categories.
- Identify potential causes within each category of your problem
Team members may trigger brainstorming or contribute factors that fall into this category. You can either go by category or only come up with ideas and determine which type they fit.
- Go a step deeper to define sub-causes for any cause in the category
If you decide whether something can or will break down to smaller points, build divisions from the critical point.
Team members study the diagram to determine the most relevant focus points. If you are trying to take this a step forward and fix the root cause, it helps define where you're trying to benefit your initiative. You can't solve all the root factors at once, and some can get more significant payoff than others. Check the diagram for an evaluation of where the concentration of the team is best.
- Record results
You bring the work in. Capture, and log your work. You will need to return to it later, so you don't want to miss the importance of the exercise that you got.
There are several tips that should be considered when using the fishbone diagram for solving problems:
- Using the fishbone diagram tool to keep the team focused not on signs, but the problem's causes;
- Make sure you leave ample room in the diagram between the main groups to add minor specific pointers later;
- Try making team members write every cause on sticky notes while you're brainstorming causes, moving around the community asking each person about a particular reason. Continue to go through the loops, have more pointers before all suggestions have been eliminated;
- Encourage each person to join in the brainstorming exercise and voice their own opinions;
- Remember that the strategy of "five-whys" is often used in combination with the fishbone diagram.
While it takes time to create a fishbone diagram , it will help you and your team define the real causes and encourage you to strengthen the process and make permanent improvements.
Regardless, whether you are using the graphical or indented fishbone hierarchy, this process optimization method will significantly help you understand the factors involved in a process. The root causes of the event are the underlying process and system issues, which allowed the contribution. Hence fishbone diagram , the problem-solving tool, is extremely crucial when discussing strategies to deal with problems.
EdrawMind is an easy-to-use, flexible mind mapping tool designed to help you generate modern, fresh visuals and mind maps. By combining the bullet points into a mind map on a project, EdrawMind lets you organize the thoughts or concepts and create essential strategies.

How to Motivate Yourself to Study

Meeting Management: How to Run a Meeting

How to Create a Fishbone Diagram on PowerPoint

How to Make Good Use of Mind Map for Students

Complete Beginner's Guide to Project Planning
How to Be Productive at Home: 7 Work-from-Home Tips
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

Fishbone diagrams: How to use them for problem-solving
October 5, 2023 by MindManager Blog
When something goes wrong, it’s essential to understand the root cause in order to prevent it from occurring again.
However, life and business are both complex, making it difficult to identify at times the underlying causes which created the situation you’re facing now. That’s where and when a fishbone diagram can help!
In this article, we’ll dive into everything you need to know about fishbone diagrams and how to use them for problem-solving.
What is a fishbone diagram?
Fishbone diagrams (also called Ishikawa diagrams and cause-and-effect diagrams) are visualizations used to identify and illustrate the causes for a specific event. Potential causes are often brainstormed and then categorized in order to identify a problem’s root cause.
The diagram gets its name due to the branches radiating out from the main issue in a way that resembles a side view of a fish skeleton. However, the process can be applied to most mind map layouts.
Here’s a fishbone diagram example:
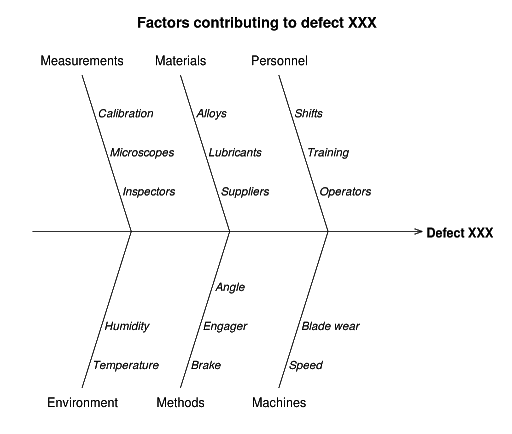
When to use fishbone diagrams
Fishbone diagrams help focus you and your team’s energy on the root cause of a problem instead of merely addressing and wasting time on the symptoms.
Here are a few common applications of Fishbone diagrams:
Manufacturing: Discover the root cause of a manufacturing issue by brainstorming and ranking the likelihood and impact of all the areas that influence the production process.
How to create a fishbone diagram in MindManager in 5 steps
Fishbone diagrams are quick to make in MindManager and the examples above are included as templates to make it even easier.
MindManager’s ease of capturing ideas during brainstorming makes it the ideal tool to capture and organize potential causes. The visual format allows you to see all the causes simultaneously, draw relationships between causes, and identify if the root cause is found multiple times within the diagram.
Here’s how to create a fishbone diagram:
- In MindManager, go to the File menu, select New and then click into the Problem-Solving folder. There you’ll find three templates for Fishbones, the manufacturing, service, and product analyses. Select a template.
- Enter the issue in the central topic.
- Next, either brainstorm potential causes and add them as floating topics initially and categorize them after the brainstorming session. Or, use each category as a guide for a mini-brainstorm session and enter the potential causes directly in the appropriate branch.
- Add more details to your causes as new subtopics or notes with the cause itself.
- Once all the potential causes have been identified, you can take the diagram a step further and rank each cause. One way to do this would be to use the Priority marker to rank the cause between 1 and 9. You can later filter the diagram and view specific priorities and hide the less important ones that will distract the focus of the team.
Key MindManager features for fishbone diagrams
There is no one single ‘right’ way to create, categorize, or rank items within a fishbone diagram.
With that said, here’s a list of ways to apply some of MindManager’s features to transform an ordinary diagram into a powerful application to visualize and empower your work.
- Use color (fonts, topic fill color) to categorize different causes.
- Change the font characteristics to emphasize different causes (e.g. bold, larger fonts, different font types, etc.).
- Use topic images to add greater context and enhance the visualizations.
- Write topic notes for more in-depth details related to each cause.
- Apply icons and tags to categorize causes.
- Hyperlink or add attachments to provide more details.
- Draw relationship lines between different connected causes throughout the diagram.
- Assign resources to any causes that you have identified. This may clarify who is responsible or accountable for that cause.
- Collapse branches for a quick overview or drill down into all the details.
- View the diagram through multiple lenses. For instance, you are not confined to the layout of the Fishbone diagram. Switch views to see the diagram as an outline, or dive in the Schedule, Icon or Tag views to see your content in groupings based on your assigned categories or due dates.
- Filter content to either show or hide topics that you have annotated with tags or icon markers. For instance, filter on all the top priority potential causes that need additional investigation.
- Share your diagram by either publishing it onto the web (and sharing a link) where anyone can open and view the Fishbone diagram interactively in their browser or export the diagram into a variety of different formats (e.g. Microsoft Word, HTML5, Microsoft Project, etc.).
Download MindManager today to get started on your fishbone diagram!
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager

The Fishbone Analysis Tool (Ishikawa Diagram): A Simple Intro
The fishbone analysis tool is a visual method used to help capture and understand various things including the root causes to a problem. Completed diagrams look like a fish skeleton. Summary by The World of Work Project
Fishbone Analysis
Fishbone analysis diagrams are also known as Ishikawa diagrams. They are a visual tool that helps individuals and teams captured and understand the root causes to a specific problem.

The problem statement that is being considered is captured in the fish’s head. The specific root-causes that contribute to the problem are captured along the fish’s fins (or rib bones). The major causes of the problem are captured at the ends of the fins.
This approach produces comprehensive visualizations of problems which help with the solution process. When designing solutions, it’s important to ensure that any proposed solution addresses the major root causes that have been identified.
Using it in Practice
Fishbone analysis is often part of a more comprehensive approach to team problem solving and is often combined with silent brainstorming .

The standard approach that we would use around a fishbone analysis forms part of a facilitated team problem solving approach, using the A3 Thinking method . This is normally completed using post-it notes initially, and is only captured in fishbone diagram at a later stage. The process is as follows:
- Firstly, have a team silently brainstorm the root causes of a chosen problem statement using the 5 whys approach to ensure depth.
- Secondly, have the team group their individual root causes into themes.
- Thirdly, have the team review the grouped thematic areas and, if happy with them, name them. These names then become the major-causes to the identified problem.
- Fourthly, review the root-causes and major causes, checking them for completeness against an appropriate list of potential major-causes.
- Finally, progress to the solution design phase.
Major-causes: 3 Common Groups
It’s important to understand the common major-causes which can affect a specific type of problem. With these in mind it’s possible to check the completeness of the root-causes you’ve identified.

For example, if you know that a common major-cause is “people capability” and you’ve identified no root-causes of this nature, you can go back and spend further time identifying appropriate root-causes to your problem.
By doing this you can ensure that you’ve identified all of the appropriate root causes, and are thus in a position to identify a better solution to your problem.
Below, we consider three groups of major-causes that you may wish to use to check your root-causes for completeness. Each group is useful in different circumstances. More groups are available, and you can always create your own group which is appropriate for your specific circumstances.
The PPPS Major-causes
PPPC stands for people, process, platform and culture. These are an excellent set of common major-causes to consider for any problem in an office or a professional-services working environment. Most problems in this environment have root causes within all four of these major-causes.

The 5 Ms Major-causes
The 5 Ms are: machine, method, material, man and measurement. These major causes are useful for consideration in the manufacturing sector where you would expect to potentially find root-causes in relation to all of them.

The 5 Ps Major-causes
The 5 Ps are: product, price, promotion, place, people. These are simply the 5 Ps of marketing (which we’ve yet to write about), converted into potential major-causes. These are appropriate major-causes to consider in relation to a product marketing problem.
Want to be a better manager?
Every year we run an open cohort of our Connected Management programme for those working in small organisations or organisations that are not able to fund personal and professional development. The 10 session programme is £1100 per person with discounts of up to 40% for self-funders and non-profits.
In 2024, we have a cohort on Wednesday 3.30pm UK time and Thursdays 9am UK time from April 17/18. It comprises 10 online live workshops with two great facilitators and access to a bank of support materials. Learn more about the programme by clicking below.
Learning More
Thinking about what we do from different perspectives and with others is very helpful for decision making. Tools like the reframing matrix process or hackathons can help us do this.
Part of the reason we’re not great at problem solving is that we all have thinking habits and cognitive biases that restrict our creativity. In particular, these decision making biases often lead us towards bad (or irrational) decisions. And sometimes we make decisions just because ISLAGIATT …
Similarly, Drilling into issues with the 5 Whys helps us understand root causes more and creating an ease/benefit matrix helps us decide what to focus on in the first place. When we are actually working on things like this in groups it’s useful to use techniques like silent brainstorming to get the best results.
To learn more about creativity, innovation and problem solving, you might enjoy the third of our three podcasts specifically on these topics. It focuses mainly on cognitive processes:
The World of Work Project View
Fishbone analysis is a helpful tool. It’s a useful way to visualize, share, track and analyze root causes to a specific problem. The approach of comparing root causes to a list of common major-causes for that kind of problem is also very helpful.
In our view though, the real magic comes from getting the right people in the room and leading an effective root-cause ideation / brainstorming activity. In many ways this is more important than how you visualize the root-causes that you capture.
Our Podcast .
Our Podcast is a great way to learn more about hundreds of fascinating topics from around the world of work.
In this instance, most of our content has come from our working experience. The original source of this model though is by Kaoru Ishikawa and you can read more in his book: “Introduction to Quality Control” .
The World of Work Project: The Fishbone Analysis Tool (Ishikawa Diagram): A Simple Intro
We’re a small organization who know we make mistakes and want to improve them. Please contact us with any feedback you have on this post. We’ll usually reply within 72 hours.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Related posts.

Predictive Analytics In The World Of Work

The Foursquare Ethical Decision Model: A Simple Summary

The ISLAGIATT Decision Making Process

The Reframing Matrix Process: A Simple Way To Improve Creativity

Bounded Rationality: A Simple Summary

Dual Process Theory: A Simple Summary
Privacy overview.

In this online seminar, we explore two key factors that shape our performance and experience at work: Trust and Social Threats. We'll explain what they are, discuss how to build trust, share the domains of social threat and share hints and tips for managing both in the workplace.
In this online seminar, we explore the thorny issue of managing the demands on our time. In many workplaces it feels like there's a potentially infinite amount of work. To succeed, we need to learn to prioritize, say no when appropriate and manage our own boundaries. This seminar will explore these challenges and share insights on how we can all improve.
In 2012 Google decided to analyse their teams to discover what makes an effective team, why some teams are so successful, and some less so. What did they discover? Amongst other things, that Psychological Safety is a key differentiator for high performing teams. In this seminar we explain what Psychological Safety is, why it matters and how to increase it in your teams.
Subscribe For Latest Updates

Nice to see you again :)
If you'd like to learn more about us and what we do, you can join thousands of members of the World of Work community around the globe in receiving our occasional newsletter, the WOW Mail. In it, we'll let you know what we're up to and share hints and tips.
After submitting this form, you'll receive an email asking you to confirm your registration. Click the button in that email to finalize your subscription. Your email provider might filter it into your junk folder, so please check there if you don't see it your main folder!
I agree to receive your newsletters and accept the data privacy statement.
We use Sendinblue as our marketing platform. By Clicking below to submit this form, you acknowledge that the information you provided will be transferred to Sendinblue for processing in accordance with their terms of use
In this online seminar, our special guest, Dr. Charlotte Rae (Sussex: Psychology, Neuroscience) shares her findings on the impact of moving to a four-day week on our performance, wellbeing and biology, and tips on how to implement a four day week well in your organization.
Part of our popular lunchtime seminar programme

- Mind Map Maker
- Concept Map Maker
- Bubble Map Maker
- Brace Map Maker
- Sunburst Chart Maker
- Online AI Note Taker
- Timeline Maker
- Tree Diagram Maker
- Fishbone Diagram Maker
- Organizational Chart Maker
- Gantt Chart Maker
- Spider Diagram Maker
- EdrawMind AI
- AI Summarize
- AI Mind map
- AI Article generation
- AI Copywriting
- AI Translation
- --> --> >--> -->