

How to Write a PhD Research Proposal
- Applying to a PhD
- A research proposal summarises your intended research.
- Your research proposal is used to confirm you understand the topic, and that the university has the expertise to support your study.
- The length of a research proposal varies. It is usually specified by either the programme requirements or the supervisor upon request. 1500 to 3500 words is common.
- The typical research proposal structure consists of: Title, Abstract, Background and Rationale, Research Aims and Objectives, Research Design and Methodology, Timetable, and a Bibliography.
What is a Research Proposal?
A research proposal is a supporting document that may be required when applying to a research degree. It summarises your intended research by outlining what your research questions are, why they’re important to your field and what knowledge gaps surround your topic. It also outlines your research in terms of your aims, methods and proposed timetable .
What Is It Used for and Why Is It Important?
A research proposal will be used to:
- Confirm whether you understand the topic and can communicate complex ideas.
- Confirm whether the university has adequate expertise to support you in your research topic.
- Apply for funding or research grants to external bodies.
How Long Should a PhD Research Proposal Be?
Some universities will specify a word count all students will need to adhere to. You will typically find these in the description of the PhD listing. If they haven’t stated a word count limit, you should contact the potential supervisor to clarify whether there are any requirements. If not, aim for 1500 to 3500 words (3 to 7 pages).
Your title should indicate clearly what your research question is. It needs to be simple and to the point; if the reader needs to read further into your proposal to understand your question, your working title isn’t clear enough.
Directly below your title, state the topic your research question relates to. Whether you include this information at the top of your proposal or insert a dedicated title page is your choice and will come down to personal preference.
2. Abstract
If your research proposal is over 2000 words, consider providing an abstract. Your abstract should summarise your question, why it’s important to your field and how you intend to answer it; in other words, explain your research context.
Only include crucial information in this section – 250 words should be sufficient to get across your main points.
3. Background & Rationale
First, specify which subject area your research problem falls in. This will help set the context of your study and will help the reader anticipate the direction of your proposed research.
Following this, include a literature review . A literature review summarises the existing knowledge which surrounds your research topic. This should include a discussion of the theories, models and bodies of text which directly relate to your research problem. As well as discussing the information available, discuss those which aren’t. In other words, identify what the current gaps in knowledge are and discuss how this will influence your research. Your aim here is to convince the potential supervisor and funding providers of why your intended research is worth investing time and money into.
Last, discuss the key debates and developments currently at the centre of your research area.
4. Research Aims & Objectives
Identify the aims and objectives of your research. The aims are the problems your project intends to solve; the objectives are the measurable steps and outcomes required to achieve the aim.
In outlining your aims and objectives, you will need to explain why your proposed research is worth exploring. Consider these aspects:
- Will your research solve a problem?
- Will your research address a current gap in knowledge?
- Will your research have any social or practical benefits?
If you fail to address the above questions, it’s unlikely they will accept your proposal – all PhD research projects must show originality and value to be considered.
5. Research Design and Methodology
The following structure is recommended when discussing your research design:
- Sample/Population – Discuss your sample size, target populations, specimen types etc.
- Methods – What research methods have you considered, how did you evaluate them and how did you decide on your chosen one?
- Data Collection – How are you going to collect and validate your data? Are there any limitations?
- Data Analysis – How are you going to interpret your results and obtain a meaningful conclusion from them?
- Ethical Considerations – Are there any potential implications associated with your research approach? This could either be to research participants or to your field as a whole on the outcome of your findings (i.e. if you’re researching a particularly controversial area). How are you going to monitor for these implications and what types of preventive steps will you need to put into place?
6. Timetable
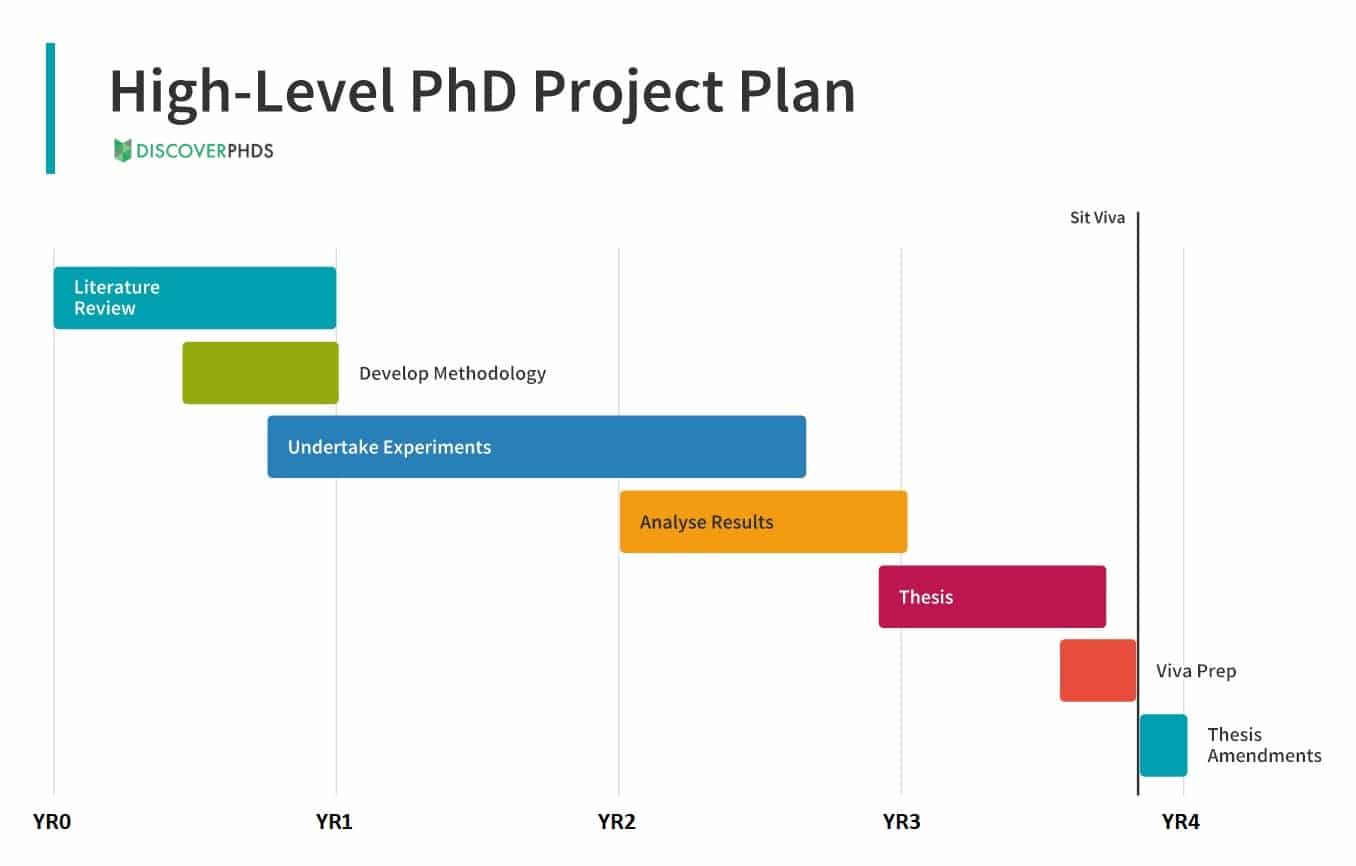
We’ve outlined the various stages of a PhD and the approximate duration of a PhD programme which you can refer to when designing your own research study.
7. Bibliography
Plagiarism is taken seriously across all academic levels, but even more so for doctorates. Therefore, ensure you reference the existing literature you have used in writing your PhD proposal. Besides this, try to adopt the same referencing style as the University you’re applying to uses. You can easily find this information in the PhD Thesis formatting guidelines published on the University’s website.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Questions & Answers
Here are answers to some of the most common questions we’re asked about the Research Proposal:
Can You Change a Research Proposal?
Yes, your PhD research proposal outlines the start of your project only. It’s well accepted that the direction of your research will develop with time, therefore, you can revise it at later dates.
Can the Potential Supervisor Review My Draft Proposal?
Whether the potential supervisor will review your draft will depend on the individual. However, it is highly advisable that you at least attempt to discuss your draft with them. Even if they can’t review it, they may provide you with useful information regarding their department’s expertise which could help shape your PhD proposal. For example, you may amend your methodology should you come to learn that their laboratory is better equipped for an alternative method.
How Should I Structure and Format My Proposal?
Ensure you follow the same order as the headings given above. This is the most logical structure and will be the order your proposed supervisor will expect.
Most universities don’t provide formatting requirements for research proposals on the basis that they are a supporting document only, however, we recommend that you follow the same format they require for their PhD thesis submissions. This will give your reader familiarity and their guidelines should be readily available on their website.
Last, try to have someone within the same academic field or discipline area to review your proposal. The key is to confirm that they understand the importance of your work and how you intend to execute it. If they don’t, it’s likely a sign you need to rewrite some of your sections to be more coherent.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
You're viewing this site as a domestic an international student
You're a domestic student if you are:
- a citizen of Australia or New Zealand,
- an Australian permanent resident, or
- a holder of an Australian permanent humanitarian visa.
You're an international student if you are:
- intending to study on a student visa,
- not a citizen of Australia or New Zealand,
- not an Australian permanent resident, or
- a temporary resident (visa status) of Australia.

How to write a good PhD proposal
Study tips Published 3 Mar, 2022 · 5-minute read
Want to make sure your research degree starts smoothly? We spoke with 2 PhD candidates about overcoming this initial hurdle. Here’s their advice for how to write a good PhD proposal.
Writing your research proposal is an integral part of commencing a PhD with many schools and institutes, so it can feel rather intimidating. After all, how you come up with your PhD proposal could be the difference between your supervisor getting on board or giving your project a miss.
Let’s explore how to make a PhD research proposal with UQ candidates Chelsea Janke and Sarah Kendall.
Look at PhD proposal examples

Look at other PhD proposals that have been successful. Ask current students if you can look at theirs.
Nobody’s asking you to reinvent the wheel when it comes to writing your PhD proposal – leave that for your actual thesis. For now, while you’re just working out how to write a PhD proposal, examples are a great starting point.
Chelsea knows this step is easier if you’ve got a friend who is already doing a PhD, but there are other ways to find a good example or template.
“Look at other PhD proposals that have been successful,” she says.
“Ask current students if you can look at theirs.”
“If you don’t know anyone doing their PhD, look online to get an idea of how they should be structured.”
What makes this tricky is that proposals can vary greatly by field and disciplinary norms, so you should check with your proposed supervisor to see if they have a specific format or list of criteria to follow. Part of writing a good PhD proposal is submitting it in a style that's familiar to the people who will read and (hopefully) become excited by it and want to bring you into their research area.
Here are some of the key factors to consider when structuring your proposal:
- meeting the expected word count (this can range from a 1-page maximum to a 3,000-word minimum depending on your supervisor and research area)
- making your bibliography as detailed as necessary
- outlining the research questions you’ll be trying to solve/answer
- discussing the impact your research could have on your field
- conducting preliminary analysis of existing research on the topic
- documenting details of the methods and data sources you’ll use in your research
- introducing your supervisor(s) and how their experience relates to your project.
Please note this isn't a universal list of things you need in your PhD research proposal. Depending on your supervisor's requirements, some of these items may be unnecessary or there may be other inclusions not listed here.
Ask your planned supervisor for advice
Alright, here’s the thing. If sending your research proposal is your first point of contact with your prospective supervisor, you’ve jumped the gun a little.
You should have at least one researcher partially on board with your project before delving too deep into your proposal. This ensures you’re not potentially spending time and effort on an idea that no one has any appetite for. Plus, it unlocks a helpful guide who can assist with your proposal.
PhD research isn’t like Shark Tank – you’re allowed to confer with academics and secure their support before you pitch your thesis to them. Discover how to choose the right PhD supervisor for you.
For a time-efficient strategy, Chelsea recommends you approach your potential supervisor(s) and find out if:
- they have time to supervise you
- they have any funds to help pay for your research (even with a stipend scholarship , your research activities may require extra money)
- their research interests align with yours (you’ll ideally discover a mutual ground where you both benefit from the project).
“The best way to approach would be to send an email briefly outlining who you are, your background, and what your research interests are,” says Chelsea.
“Once you’ve spoken to a potential supervisor, then you can start drafting a proposal and you can even ask for their input.”
Chelsea's approach here works well with some academics, but keep in mind that other supervisors will want to see a research proposal straight away. If you're not sure of your proposed supervisor's preferences, you may like to cover both bases with an introductory email that has a draft of your research proposal attached.
Sarah agrees that your prospective supervisor is your most valuable resource for understanding how to write a research proposal for a PhD application.
“My biggest tip for writing a research proposal is to ask your proposed supervisor for help,” says Sarah.
“Or if this isn’t possible, ask another academic who has had experience writing research proposals.”
“They’ll be able to tell you what to include or what you need to improve on.”
Find the 'why' and focus on it

One of the key aspects of your research proposal is emphasising why your project is important and should be funded.
Your PhD proposal should include your major question, your planned methods, the sources you’ll cite, and plenty of other nitty gritty details. But perhaps the most important element of your proposal is its purpose – the reason you want to do this research and why the results will be meaningful.
In Sarah’s opinion, highlighting the 'why' of your project is vital for your research proposal.
“From my perspective, one of the key aspects of your research proposal is emphasising why your project is important and should be funded,” she says.
“Not only does this impact whether your application is likely to be successful, but it could also impact your likelihood of getting a scholarship .”
Imagine you only had 60 seconds to explain your planned research to someone. Would you prefer they remember how your project could change the world, or the statistical models you’ll be using to do it? (Of course, you’ve got 2,000 words rather than 60 seconds, so do make sure to include those little details as well – just put the why stuff first.)
Proofread your proposal, then proof it again
As a PhD candidate, your attention to detail is going to be integral to your success. Start practising it now by making sure your research proposal is perfect.
Chelsea and Sarah both acknowledge that clarity and writing quality should never be overlooked in a PhD proposal. This starts with double-checking that the questions of your thesis are obvious and unambiguous, followed by revising the rest of your proposal.
“Make sure your research questions are really clear,” says Sarah.
“Ensure all the writing is clear and grammatically correct,” adds Chelsea.
“A supervisor is not going to be overly keen on a prospective student if their writing is poor.”
It might sound harsh, but it’s fair. So, proofread your proposal multiple times – including after you get it back from your supervisor with any feedback and notes. When you think you’ve got the final, FINAL draft saved, sleep on it and read it one more time the next morning.
Still feeling a little overwhelmed by your research proposal? Stay motivated with these reasons why a PhD is worth the effort .
Want to learn more from Chelsea and Sarah? Easy:
- Read about Chelsea’s award-winning PhD thesis on keeping crops healthy.
- Read Sarah’s series on becoming a law academic .
Share this Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Email
Related stories

How to get a PhD
4-minute read

How to find a PhD supervisor
5-minute read

How long does a PhD take?
3-minute read

Tips for PhD students from Samantha and Glenn
7-minute read
- Log in
- Site search
How to write a successful research proposal
As the competition for PhD places is incredibly fierce, your research proposal can have a strong bearing on the success of your application - so discover how to make the best impression
What is a research proposal?
Research proposals are used to persuade potential supervisors and funders that your work is worthy of their support. These documents setting out your proposed research that will result in a Doctoral thesis are typically between 1,500 and 3,000 words in length.
Your PhD research proposal must passionately articulate what you want to research and why, convey your understanding of existing literature, and clearly define at least one research question that could lead to new or original knowledge and how you propose to answer it.
Professor Leigh Wilson, director of the graduate school at the University of Westminster, explains that while the research proposal is about work that hasn't been done yet, what prospective supervisors and funders are focusing on just as strongly is evidence of what you've done - how well you know existing literature in the area, including very recent publications and debates, and how clearly you've seen what's missing from this and so what your research can do that's new. Giving a strong sense of this background or frame for the proposed work is crucial.
'Although it's tempting to make large claims and propose research that sweeps across time and space, narrower, more focused research is much more convincing,' she adds. 'To be thorough and rigorous in the way that academic work needs to be, even something as long as a PhD thesis can only cover a fairly narrow topic. Depth not breadth is called for.'
The structure of your research proposal is therefore important to achieving this goal, yet it should still retain sufficient flexibility to comfortably accommodate any changes you need to make as your PhD progresses.
Layout and formats vary, so it's advisable to consult your potential PhD supervisor before you begin. Here's what to bear in mind when writing a research proposal.
Your provisional title should be around ten words in length, and clearly and accurately indicate your area of study and/or proposed approach. It should be catchy, informative and interesting.
The title page should also include personal information, such as your name, academic title, date of birth, nationality and contact details.
Aims and objectives
This is a short summary of your project. Your aims should be two or three broad statements that emphasise what you ultimately want to achieve, complemented by several focused, feasible and measurable objectives - the steps that you'll take to answer each of your research questions. This involves clearly and briefly outlining:
- how your research addresses a gap in, or builds upon, existing knowledge
- how your research links to the department that you're applying to
- the academic, cultural, political and/or social significance of your research questions.
Literature review
This section of your PhD proposal discusses the most important theories, models and texts that surround and influence your research questions, conveying your understanding and awareness of the key issues and debates.
It should focus on the theoretical and practical knowledge gaps that your work aims to address, as this ultimately justifies and provides the motivation for your project.
Methodology
Here, you're expected to outline how you'll answer each of your research questions. A strong, well-written methodology is crucial, but especially so if your project involves extensive collection and significant analysis of primary data.
In disciplines such as humanities the research proposal methodology identifies the data collection and analytical techniques available to you, before justifying the ones you'll use in greater detail. You'll also define the population that you're intending to examine.
You should also show that you're aware of the limitations of your research, qualifying the parameters that you plan to introduce. Remember, it's more impressive to do a fantastic job of exploring a narrower topic than a decent job of exploring a wider one.
Concluding or following on from your methodology, your timetable should identify how long you'll need to complete each step - perhaps using bi-weekly or monthly timeslots. This helps the reader to evaluate the feasibility of your project and shows that you've considered how you'll go about putting the PhD proposal into practice.
Bibliography
Finally, you'll provide a list of the most significant texts, plus any attachments such as your academic CV . Demonstrate your skills in critical reflection by selecting only those resources that are most appropriate.
Final checks
Before submitting this document along with your PhD application, you'll need to ensure that you've adhered to the research proposal format. This means that:
- every page is numbered
- it's professional, interesting and informative
- the research proposal has been proofread by both an experienced academic (to confirm that it conforms to academic standards) and a layman (to correct any grammatical or spelling errors)
- it has a contents page
- you've used a clear and easy-to-read structure, with appropriate headings.
Research proposal examples
To get a better idea of how your PhD proposal may look, some universities have provided examples of research proposals for specific subjects:
- The Open University - Social Policy and Criminology
- University of Sheffield - Sociological Studies
- University of Sussex
- University of York - Politics
Find out more
- Explore PhD studentships .
- For tips on writing a thesis, see 7 steps to writing a dissertation .
- Read more about PhD study .
How would you rate this page?
On a scale where 1 is dislike and 5 is like
- Dislike 1 unhappy-very
- Like 5 happy-very
Thank you for rating the page
We use cookies on reading.ac.uk to improve your experience, monitor site performance and tailor content to you
Read our cookie policy to find out how to manage your cookie settings
This site may not work correctly on Internet Explorer. We recommend switching to a different browser for a better experience.
Writing your research proposal
When applying to study for a PhD or MPhil in the School of Psychology and Clinical Language Sciences, you will typically need to send us an initial 500-word research proposal.
The content and structure of your research proposal will be influenced by the nature of the project you wish to pursue. The guidance and suggested headings provided here should help you to structure and present your ideas clearly.
Your initial research proposal
When writing your initial research proposal, you can either address it to the School generally, or to a specific supervisor if you have one in mind.
Potential supervisors in the School will review your initial research proposal, and get in touch with you to discuss it. Your proposal may change following this conversation. Depending on the supervisor and the outcome of this discussion, you may be asked to produce a longer research proposal of between 2,000 and 4,000 words.
Tips on writing a research proposal
Before you write your research proposal, we strongly recommend that you check our research page and individual supervisor profiles to view our areas of expertise.
- You should avoid the use of overly long sentences and technical jargon.
- It is important that the proposed research is realistic and feasible so that the outcomes can be achieved within the scale of a typical research degree programme. This is usually three years full-time for a PhD (or two years for an MPhil).
- A strong research proposal can and should make a positive first impression about your potential to become a good researcher. It should demonstrate that your ideas are focused, interesting and realistic.
Although you should write your proposal yourself, it is best if you discuss its contents with your proposed supervisor before you submit it. If this is not possible, then try to get someone else (such as an academic at your current or previous institution) to read and comment on it to ensure that it is sufficiently clear.
Your proposal needs a clear working title that gives an indication of what you want to study. You are not committed to continuing with the same title once you begin your studies.
Research question
For many projects, you'll usually address one main question, which can sometimes be broken down into several sub-questions. However, it's OK to have two or three research questions where appropriate.
In your research proposal, you'll need to state your main research question(s), explain its significance, and locate it within the relevant literature, in order to set out the context into which your research will fit. You should only refer to research that is directly relevant to your proposal.
Questions to address in your research proposal
You will need to address questions such as:
- What is the general area in which you will be working, and the specific aspect(s) of that area that will be your focus of inquiry?
- What is the problem, shortcoming, or gap in this area that you would like to address?
- What is the main research question or aim that you want to address?
- What are the specific objectives for the proposed research that follow from this?
- Why is the proposed research significant, why does it matter (either theoretically or practically), and why does it excite you?
- How does your work relate to other relevant research in the department?
Methodology
You will need to explain how you will go about answering your question (or achieving your aim), and why you will use your intended approach to address the question/aim.
Questions you might need to address include:
- What steps will you take and what methods will you use to address your question? For instance, do you plan to use quantitative or qualitative methods?
- How will your proposed method provide a reliable answer to your question?
- What sources or data will you use?
- If your project involves an experimental approach, what specific hypothesis or hypotheses will you address?
- What specific techniques will you use to test the hypothesis? For example, laboratory procedures, interviews, questionnaires, modelling, simulation, text analysis, use of secondary data sources.
- What practical considerations are there? For example, what equipment, facilities, and other resources will be required?
- What relevant skills and experience do you have with the proposed methods?
- Will you need to collaborate with other researchers and organisations?
- Are there particular ethical issues that will need to be considered (for example, all projects using human participants require ethical approval)?
- Are there any potential problems or difficulties that you foresee (for example, delays in gaining access to special populations or materials) that might affect your rate of progress?
You will need to provide a rough timeline for the completion of your research to show that the project is achievable (given the facilities and resources required) in no more than three years of full-time study (or part-time equivalent) for a PhD, and two years for an MPhil.
Expected outcomes
You need to say something about what the expected outcomes of your project would be.
How, for example, does it make a contribution to knowledge? How does it advance theoretical understanding? How might it contribute to policy or practice?
If you are aiming to study for a PhD, then you need to say how your proposed research will make an original contribution to knowledge. This is not essential if you are aiming to study for an MPhil, although you will still need to show originality in the application of knowledge.
List of references
You will need to provide a list of any key articles or texts that you have referred to in your proposal.
References should be listed in the appropriate style for your subject area (e.g. Harvard). You should only reference texts that you think are central to your proposed work, rather than a bibliography listing everything written on the subject.
Format and proofreading
Make sure that your proposal is well structured and clearly written. It is important that you carefully check your proposal for typographical and spelling errors, consistency of style, and accuracy of references, before submitting it.
The proposal should be aesthetically well presented, and look professional (e.g. no font inconsistencies, headings clearly identifiable). If you include figures, then they should be accompanied by captions underneath).
How to apply for a PhD

PhD opportunities
Our research


Take the next step
- How to apply
- Get a prospectus
- Ask us a question
- Learn about the Doctoral and Researcher College
Writing a good PhD research proposal
The purpose of your proposal is to show that you have a relevant theme, a viable project and the competence to carry it out. The information is vital when we evaluate your proposed study and decide if we have the right staff expertise to supervise you.
The format and length of the proposal is likely to vary according to the type of project. Typically a proposal is no less than 1500 words (3-4 pages) long and will cover the following points.
- Provisional title (max 50 words ): the title should indicate the central focus of the research and should contain the key words associated with proposed work.
- Central question/hypothesis for investigation (max 15-50 words): State the central question/hypothesis of your proposed research. Eg. 'This thesis asks…' or 'This thesis examines the hypothesis that….'.
- Key aims of the research (max 200 words): Set out a number of specific aims (3-5) of the research which indicate the intended contribution and impact of the PhD. They should answer the question: 'what will the PhD achieve'?
- Literature review (max 700-1,000 words): This section should situate your chosen topic in the existing research and should show that you are familiar with the key works in the area. Explain how the current literature addresses the issue you have identified, give a summary of recent debates in the area and explain the current shortcomings in the existing scholarship.
- Description of your topic (max 300-700 words): Explain how your research will address the gap or shortcomings in knowledge, why it is original and why further research in the area is important.
- Methodology (max 300 words) Explain how you will obtain the information necessary to write your thesis. Include an explanation of the approach(es) will you be taking to the research (library-based? empirical?) and any relevant quantitative/qualitative methods (interviews, questionnaires, survey and to whom etc). Outline any ethical concerns (eg interviewing children/prisoners/refugees etc).
- Resources and ethical clearance: Will your research comply with the agreed international standards for good practise in social research? Using published ethical guidelines show that you are aware of the specific documents and clearances you will need.
- Project management: You should map out a schedule for your project, from the start date onwards, showing when you expect to conduct periods of fieldwork (if applicable) and the time required for data analysis and writing up your results.
- References: You should include a list of the references cited in your proposal, using Harvard notation. This will be useful for potential supervisors to evaluate your knowledge of the research topic.
It looks like you’re visiting from outside the UK, would you like to be redirected to the international page?

Guidelines to Writing a Research Proposal
All Doctor of Philosophy (DPhil) students must write an acceptable research proposal.
This has a clear and explicit purpose:
- it makes certain that you have a worthwhile research project - you have a good grasp of the relevant literature and the major issues, and that your methodology is sound;
- it will show that you have the competence and work-plan to complete the research;
- it includes sufficient information for us to evaluate the proposed study; and
- we can be certain we have the right staff expertise to supervise you.
All research proposals must address the question of what you plan to accomplish and why you want to and how you are going to do it.
A research proposal is usually around 2,500 words long although there is no upper or lower limit to this.
In preparing a research proposal, the first thing that you have to do is to decide what it really is that you want to know more about. The questions that you want to research have to viable as a research project and lead to the creation of new knowledge and understanding.
Your research proposal should include a section on each of the following areas:
Ethical considerations
You will need to give consideration to issues of power and confidentiality. You should read any appropriate ethical guidelines and ask yourself how/whether you project follows these. [All research students at Oxford University are required (before they commence fieldwork) to complete the Central University Research Ethics Committee (CUREC) checklist and obtain permission to undertake any fieldwork].
Time scales
It is important that you map out a reasonable schedule of your work so that you can monitor your own progress and manage your project effectively. Start with your intended finishing date and do not underestimate the amount of time that it takes to finalise your drafts into a finished product.
Dissemination
A key indicator of the work of much research is whether it is of publishable quality. You might like to give some consideration at this stage as to what sorts of things might be publishable and where you would like them to appear. This is especially important if you wish to pursue a career as an academic in a UK university.
When you have completed all of this then get other people, your peers as well as those more experienced than you, to read it and comment. This will help you to revise the proposal before you submit it. You can also make contact with departmental staff whose research interests are in a similar area to those you intend to undertake. They would be happy to give you advice and to discuss possible supervision.

- Skip to content
- Skip to footer
- Accessibility options

- Business and employers
- Alumni and supporters
- For students

- Postgraduate research degrees
- Our postgraduate research disciplines
- Apply for a PhD
- Funding and studentships
- International
- Support and training
- Research Masters
- Postgraduate info session
- Writing a research proposal for a PhD application
How to write a research proposal for a PhD application
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal gives details of the direction of your future research, usually based on a research question and a chapter-by-chapter approach to answering it.
For PhD applications, this proposal will be assessed to see:
- whether the project is likely to be completed within three years of full-time research
- whether it can be effectively supervised at the university
- whether you are competent and keen enough to complete it.
There may be other factors affecting whether you get a place at the University of Brighton:
- whether the project fits a growing or established research priority of the university
- how the proposal fits with a current cohort and the research environment
A successful proposal will leave the panel in no doubt on these, and you should prepare to show the strength of your idea and demonstrate your suitability.
Within the proposal, you should take the opportunity to clearly outline your research idea; your research methodology and critical approaches; your experience in this field of research where you can; and how your work will be offering an original contribution to knowledge, theories and/or practice.
Find more details about a PhD in your discipline at the University of Brighton
How to get a prospective supervisor's help with your proposal
The strongest proposals are often ones that have been written jointly between a prospective student and prospective supervisor.
As Professor Pollen states in our film, supervisors have an understanding of the language used in proposals and the skillsets that asessors will want to see -- whether for a university position or a funding application.
To develop a strong proposal, we recommend you work with a possible supervisor at the University of Brighton who can help shape your project for feasibility and suitability within our institution. This person may then become your lead supervisor.
Please enable targeting cookies in order to view this video content on our website, or you can watch the video on YouTube .
What journey leads to a PhD application? This film was made by the University of Brighton for UKRI and features University of Brighton students and academics as well as those from other partner universities.
Finding a PhD theme and understanding the university research environment
You may be responding to an advertised call for a particular project that has already achieved funding. Alternatively, you may want to propose a personally developed project.
If you are responding to a call then the advertisement will have clear guidance as to what research experience and interest a candidate will need. This should help you structure your PhD research proposal.
If you are proposing a personally developed project then it should be carefully written to show the viability within the university's current research environment and a specific supervisory possibility at the university.
Some applicants have found our repository of theses helpful for the development and refinement of their research idea. You can find over 1000 theses completed at the University of Brighton over the past 40 years at our repository of successful PhD student theses .
Our research database has useful leads to potential supervisory staff and a strong idea of the university's current research priorities online:
- Explore our PhD disciplinary programme search tools including free search and A-Z
- Explore our research centres (COREs) or our research groups (REGs)
- Visit our research database of staff, projects and organisational units.
Once you have identified a potential lead researcher of a research project most aligned to yours, do not hesitate to email them.
Explain who you are, your motivation to do a PhD in their field of study and with them. They will let you know if they are interested in your project and would be interested in potentially supervising your PhD. If they cannot commit, they may be able to help you identify another researcher who could be available and interested.
By liaising with a suitable supervisor, your proposal will benefit from expert help and be channelled towards the appropriate disciplinary environment.
If you are in doubt about whether we can offer the appropriate supervision, please contact the Doctoral College .
Find out more about your opportunities for a PHD on our FAQ page
What should a research proposal contain?
A research proposal should include the following:
1. Indicative title of the topic area
This should accurately reflect what it is that you want to study and the central issues that you are going to address.
It may be useful to present this in the format of a statement (perhaps a quote) and a question, separated by a colon. For example: '"The tantalising future of research": how are research proposals developed and assessed?'
2. Context / rationale / why is this study important? (300 – 500 words)
Introduce your specific area of study. You should identify the theoretical context within which your research will be developed by discussing the discipline(s) and or field/s of study relevant to your research.
This means outlining the key theoretical area(s) you will draw upon to enable you to find out what it is that you want to know (for example, how it is underpinned from methods in the social sciences; arts and humanities; life, health and physical sciences).
What we are looking for here is an indication that you understand and have done some research into the wider theoretical context.
Developing the context is just one part of this section; you are building a case / rationale for the study area. Why is this study important, which theoretical areas support this? Can you identify any gaps in current understanding that help you build the case for this research study?
For example, this section might take the form of: a series of statements on the current landmark areas of thought; a recognition of what has not yet been done thoroughly enough or where there is territory for research between these landmark studies; and where your study will fill the gaps you have identified.
3. Literature review (approximately 700 – 900 words)
Here you are demonstrating that you are aware of what has been and what is currently being written about your topic.
It will certainly include the up-to-date and relevant past landmark academic literature. It may also include other evidence of current thought and attitude, for example, government documents or media coverage. Practice-led PhD studies may make reference to innovation and trends in industry or professional practice.
We are looking for you to make links between this body of literature and your proposed area of study. This will support the ways you have identified gaps in the current global knowledge-base. A PhD thesis arises from original research leading to new knowledge or a significant contribution to existing knowledge. If, at this stage, you have some thoughts on how your research is likely to contribute to knowledge then include details in your proposal.
This section should include citations which are compiled into a reference list at the end of the document (see point 7).
4. The research questions or hypotheses (approximately 200 words)
Having told us what you want to study and why, and then illustrated these ideas with reference to a body of literature, the next task is to distil your ideas into a tentative set of research questions, hypotheses, aims and objectives (as per the underpinning discipline requires) that are manageable and achievable within a normal PhD timeframe (see 6 below). There are typically between three and ten questions/aims of this kind.
5. Research approach/ methodologies / methods (approximately 400 words)
There will be many research approaches open to you. In your proposal, suggest the methodological approach that you might take and make a reasoned case as to why the research questions you have posed are best addressed by this approach.
You might also suggest what methods you would use to generate data that can help you address your research questions.
6. Timescale/research planning (approximately 200 words)
A full-time PhD should take three years to complete, although you may require more time to acquire the relevant skills prior to commencing your research. Part-time study will take longer (up to five - six years). Within this timeframe, you will need to demonstrate your awareness of time management and planning, for example the length of time for primary research/ fieldwork.
7. Reference list
You should include a reference list of all the sources that you referred to in the text using a recognised referencing style appropriate to your discipline (for example Harvard or Vancouver for Sciences).
Evidence of thorough background reading might include between ten and twenty citations at this point. They should demonstrate to an expert that you are knowledgeable of the landmark work in your field.
There are a number of books widely available that may help in preparing your research proposal (as well as in completing your research degree), here are a couple to point you in the right direction:
Bell, J (2010, 5th edn) Doing Your Research Project: A Guide for First-time Researchers in Education & Social Science , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Baxter, L, Hughes, C and Tight, M (2007, 3rd edn) How to Research , Buckingham: Open University Press.

Research proposals in practice-led and professionally-based disciplines
The University of Brighton prides itself on the quality of its research in areas that intersect with professional practices and direct impact through in-the-field relationships with co-producers.
We are very supportive of doctoral projects that bring positive results from these methodolgies and practices.
Some of the subject areas that have supported personal practice as research include: design, art, architecture, media production and creative writing, with successful approaches including autoethnographic methods and public participation or site-specific interventions.
Some of the areas that have benefited from significant professional practice and industry relationship-focused research have included: engineering, nursing, business administration and teaching.
The research proposal will still need to demonstrate your capability as a researcher with a project that is workable and fits with the university's interests and capacities.
You should, however, adapt your proposal to demonstrate the value that your practice can bring to the research. This should be in tandem with a clear understanding of the relationship between practice and research.
A clear competence in practice should be evidenced, but do be aware that your proposal will be judged on its research and the new knowledge that is developed and shared, rather than the quality of practice in and of itself.
Personal practices, experiences and data gained through professional relationships may form part of a standard PhD thesis and proposal as description of work and resulting data. You will only be appyling for a practice-led component to be taken into account if this will form a significant part of the representation and examination of the knowledge-base. In such cases, the thesis is signficantly shorter.
Some pitfalls in the applications for practice-led or practice-focused research include:
- An imbalance between the practical and theoretical elements
- Too arbitrary a divide between the practice and theory
- Using practice to simply provide personal illustrations of established theories or concepts
- Insufficient sense of how the research knowledge will be held and disseminated
- Insufficiently contained scope for a three-year project – for example, where the practice is described as a life-long investigation – with no clarity on an end-point
- A project that could be better or similarly tackled through a standard PhD in terms of efficient response to the research questions. For example where the practice element might be represented as data or results instead of examined practice.
Your potential supervisor will be able to advise where a proposal will include significant elements beyond the traditional thesis. For further information, please contact the Doctoral College .

A set of designed objects submitted as part of a practice-led PhD project in medical therapeutic design, by Dr Tom Ainsworth, who went on to become a teacher, researcher and supervisor at the University of Brighton.
How to write a research proposal
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal should present your idea or question and expected outcomes with clarity and definition – the what.
It should also make a case for why your question is significant and what value it will bring to your discipline – the why.
What it shouldn't do is answer the question – that's what your research will do.
Why is it important?
Research proposals are significant because Another reason why it formally outlines your intended research. Which means you need to provide details on how you will go about your research, including:
- your approach and methodology
- timeline and feasibility
- all other considerations needed to progress your research, such as resources.
Think of it as a tool that will help you clarify your idea and make conducting your research easier.
How long should it be?
Usually no more than 2000 words, but check the requirements of your degree, and your supervisor or research coordinator.
Presenting your idea clearly and concisely demonstrates that you can write this way – an attribute of a potential research candidate that is valued by assessors.
What should it include?
Project title.
Your title should clearly indicate what your proposed research is about.
Research supervisor
State the name, department and faculty or school of the academic who has agreed to supervise you. Rest assured, your research supervisor will work with you to refine your research proposal ahead of submission to ensure it meets the needs of your discipline.
Proposed mode of research
Describe your proposed mode of research. Which may be closely linked to your discipline, and is where you will describe the style or format of your research, e.g. data, field research, composition, written work, social performance and mixed media etc.
This is not required for research in the sciences, but your research supervisor will be able to guide you on discipline-specific requirements.
Aims and objectives
What are you trying to achieve with your research? What is the purpose? This section should reference why you're applying for a research degree. Are you addressing a gap in the current research? Do you want to look at a theory more closely and test it out? Is there something you're trying to prove or disprove? To help you clarify this, think about the potential outcome of your research if you were successful – that is your aim. Make sure that this is a focused statement.
Your objectives will be your aim broken down – the steps to achieving the intended outcome. They are the smaller proof points that will underpin your research's purpose. Be logical in the order of how you present these so that each succeeds the previous, i.e. if you need to achieve 'a' before 'b' before 'c', then make sure you order your objectives a, b, c.
A concise summary of what your research is about. It outlines the key aspects of what you will investigate as well as the expected outcomes. It briefly covers the what, why and how of your research.
A good way to evaluate if you have written a strong synopsis, is to get somebody to read it without reading the rest of your research proposal. Would they know what your research is about?
Now that you have your question clarified, it is time to explain the why. Here, you need to demonstrate an understanding of the current research climate in your area of interest.
Providing context around your research topic through a literature review will show the assessor that you understand current dialogue around your research, and what is published.
Demonstrate you have a strong understanding of the key topics, significant studies and notable researchers in your area of research and how these have contributed to the current landscape.
Expected research contribution
In this section, you should consider the following:
- Why is your research question or hypothesis worth asking?
- How is the current research lacking or falling short?
- What impact will your research have on the discipline?
- Will you be extending an area of knowledge, applying it to new contexts, solving a problem, testing a theory, or challenging an existing one?
- Establish why your research is important by convincing your audience there is a gap.
- What will be the outcome of your research contribution?
- Demonstrate both your current level of knowledge and how the pursuit of your question or hypothesis will create a new understanding and generate new information.
- Show how your research is innovative and original.
Draw links between your research and the faculty or school you are applying at, and explain why you have chosen your supervisor, and what research have they or their school done to reinforce and support your own work. Cite these reasons to demonstrate how your research will benefit and contribute to the current body of knowledge.
Proposed methodology
Provide an overview of the methodology and techniques you will use to conduct your research. Cover what materials and equipment you will use, what theoretical frameworks will you draw on, and how will you collect data.
Highlight why you have chosen this particular methodology, but also why others may not have been as suitable. You need to demonstrate that you have put thought into your approach and why it's the most appropriate way to carry out your research.
It should also highlight potential limitations you anticipate, feasibility within time and other constraints, ethical considerations and how you will address these, as well as general resources.
A work plan is a critical component of your research proposal because it indicates the feasibility of completion within the timeframe and supports you in achieving your objectives throughout your degree.
Consider the milestones you aim to achieve at each stage of your research. A PhD or master's degree by research can take two to four years of full-time study to complete. It might be helpful to offer year one in detail and the following years in broader terms. Ultimately you have to show that your research is likely to be both original and finished – and that you understand the time involved.
Provide details of the resources you will need to carry out your research project. Consider equipment, fieldwork expenses, travel and a proposed budget, to indicate how realistic your research proposal is in terms of financial requirements and whether any adjustments are needed.
Bibliography
Provide a list of references that you've made throughout your research proposal.
Apply for postgraduate study
New hdr curriculum, find a supervisor.
Search by keyword, topic, location, or supervisor name
- 1800 SYD UNI ( 1800 793 864 )
- or +61 2 8627 1444
- Open 9am to 5pm, Monday to Friday
- Student Centre Level 3 Jane Foss Russell Building Darlington Campus
Scholarships
Find the right scholarship for you
Research areas
Our research covers the spectrum – from linguistics to nanoscience
Our breadth of expertise across our faculties and schools is supported by deep disciplinary knowledge. We have significant capability in more than 20 major areas of research.
Research facilities
High-impact research through state-of-the-art infrastructure
School of Sociology, Politics and International Studies
How to write a phd research proposal.
In order to help you with your application, the information below aims to give some guidance on how a typical research proposal might look.
Your research proposal is a concise statement (up to 3,000 words) of the rationale for your research proposal, the research questions to be answered and how you propose to address them. We know that during the early stages of your PhD you are likely to refine your thinking and methodology in discussion with your supervisors.
However, we want to see that you can construct a fairly rigorous, high quality research proposal.
We use your research proposal to help us decide whether you would be a suitable candidate to study at PhD level. We therefore assess your proposal on its quality, originality, and coherence. It also helps us to decide if your research interests match those of academics in the School of Sociology, Politics and International Studies (SPAIS) and whether they would be able to provide suitably qualified supervision for your proposed research.
Format of the research proposal
Your proposal should include the following:
Title. A short, indicative title is best.
Abstract. This is a succinct summary of your research proposal (approximately 200-300 words) that will present a condensed outline, enabling the reader to get a very quick overview of your proposed project, lines of inquiry and possible outcomes. An abstract is often written last, after you have written the proposal and are able to summarise it effectively.
Rationale for the research project. This might include a description of the question/debate/phenomenon of interest; an explanation of why the topic is of interest to you; and an outline of the reasons why the topic should be of interest to research and/ or practice (the 'so what?' question).
Aims and initial research question. What are the aims and objectives of the research? State clearly the puzzle you are addressing, and the research question that you intend to pursue. It is acceptable to have multiple research questions, but it is a good idea to clarify which is the main research question. If you have hypotheses, discuss them here. A research proposal can and should make a positive and persuasive first impression and demonstrate your potential to become a good researcher. In particular, you need to demonstrate that you can think critically and analytically as well as communicate your ideas clearly.
Research context for your proposed project. Provide a short introduction to your area of interest with a succinct, selective and critical review of the relevant literature. Demonstrate that you understand the theoretical underpinnings and main debates and issues in your research area and how your proposed research will make an original and necessary contribution to this. You need to demonstrate how your proposed research will fill a gap in existing knowledge.
Intended methodology. Outline how you plan to conduct the research and the data sources that you will use. We do not expect you to have planned a very detailed methodology at this stage, but you need to provide an overview of how you will conduct your research (qualitative and/or quantitative methods) and why this methodology is suited for your proposed study. You need to be convincing about the appropriateness and feasibility of the approaches you are suggesting, and reflective about problems you might encounter (including ethical and data protection issues) in collecting and analysing your data.
Expected outcomes and impact. How do you think the research might add to existing knowledge; what might it enable organisations or interested parties to do differently? Increasingly in academia (and this is particularly so for ESRC-funded studentships), PhD students are being asked to consider how their research might contribute to both academic impact and/or economic and societal impact. (This is well explained on the ESRC website if you would like to find out more.) Please consider broader collaborations and partnerships (academic and non-academic) that will support your research. Collaborative activity can lead to a better understanding of the ways in which academic research can translate into practice and it can help to inform and improve the quality of your research and its impact.
Timetable. What is your initial estimation of the timetable of the dissertation? When will each of the key stages start and finish (refining proposal; literature review; developing research methods; fieldwork; analysis; writing the draft; final submission). There are likely to overlaps between the stages.
Why Bristol? Why – specifically – do you want to study for your PhD at Bristol ? How would you fit into the School's research themes and research culture . You do not need to identify supervisors at the application stage although it can be helpful if you do.
Bibliography. Do make sure that you cite what you see as the key readings in the field. This does not have to be comprehensive but you are illustrating the range of sources you might use in your research.
We expect your research proposal to be clear, concise and grammatically correct. Prior to submitting your research proposal, please make sure that you have addressed the following issues:
- Have you included a clear summary of what the proposed research is about and why it is significant?
- Have you clearly identified what your proposed research will add to our understanding of theory, knowledge or research design?
- Does it state what contributions it will make to policy and/or practice?
- Does the proposal clearly explain how you will do the research?
- Is the language clear and easy to understand by someone who is not an expert in the field?
- Is the grammar and spelling correct?

Tips for writing a PhD dissertation: FAQs answered
From how to choose a topic to writing the abstract and managing work-life balance through the years it takes to complete a doctorate, here we collect expert advice to get you through the PhD writing process
Campus team
Additional links.

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
A diy guide to starting your own journal, universities, ai and the common good, artificial intelligence and academic integrity: striking a balance, create an onboarding programme for neurodivergent students.
Embarking on a PhD is “probably the most challenging task that a young scholar attempts to do”, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith in their practical guide to dissertation and thesis writing. After years of reading and research to answer a specific question or proposition, the candidate will submit about 80,000 words that explain their methods and results and demonstrate their unique contribution to knowledge. Here are the answers to frequently asked questions about writing a doctoral thesis or dissertation.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
Whatever the genre of the doctorate, a PhD must offer an original contribution to knowledge. The terms “dissertation” and “thesis” both refer to the long-form piece of work produced at the end of a research project and are often used interchangeably. Which one is used might depend on the country, discipline or university. In the UK, “thesis” is generally used for the work done for a PhD, while a “dissertation” is written for a master’s degree. The US did the same until the 1960s, says Oxbridge Essays, when the convention switched, and references appeared to a “master’s thesis” and “doctoral dissertation”. To complicate matters further, undergraduate long essays are also sometimes referred to as a thesis or dissertation.
The Oxford English Dictionary defines “thesis” as “a dissertation, especially by a candidate for a degree” and “dissertation” as “a detailed discourse on a subject, especially one submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of a degree or diploma”.
- Ten platinum rules for PhD supervisors
- Fostering freedom in PhD students: how supervisors can shape accessible paths for doctoral research
- Lessons from students on effective research supervision
The title “doctor of philosophy”, incidentally, comes from the degree’s origins, write Dr Felix, an associate professor at Mahidol University in Thailand, and Dr Smith, retired associate professor of education at the University of Sydney , whose co-authored guide focuses on the social sciences. The PhD was first awarded in the 19th century by the philosophy departments of German universities, which at that time taught science, social science and liberal arts.
How long should a PhD thesis be?
A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words ( 100 to 300 pages in length ) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) – from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion.
The structure of a dissertation will vary depending on discipline (humanities, social sciences and STEM all have their own conventions), location and institution. Examples and guides to structure proliferate online. The University of Salford , for example, lists: title page, declaration, acknowledgements, abstract, table of contents, lists of figures, tables and abbreviations (where needed), chapters, appendices and references.
A scientific-style thesis will likely need: introduction, literature review, materials and methods, results, discussion, bibliography and references.
As well as checking the overall criteria and expectations of your institution for your research, consult your school handbook for the required length and format (font, layout conventions and so on) for your dissertation.
A PhD takes three to four years to complete; this might extend to six to eight years for a part-time doctorate.
What are the steps for completing a PhD?
Before you get started in earnest , you’ll likely have found a potential supervisor, who will guide your PhD journey, and done a research proposal (which outlines what you plan to research and how) as part of your application, as well as a literature review of existing scholarship in the field, which may form part of your final submission.
In the UK, PhD candidates undertake original research and write the results in a thesis or dissertation, says author and vlogger Simon Clark , who posted videos to YouTube throughout his own PhD journey . Then they submit the thesis in hard copy and attend the viva voce (which is Latin for “living voice” and is also called an oral defence or doctoral defence) to convince the examiners that their work is original, understood and all their own. Afterwards, if necessary, they make changes and resubmit. If the changes are approved, the degree is awarded.
The steps are similar in Australia , although candidates are mostly assessed on their thesis only; some universities may include taught courses, and some use a viva voce. A PhD in Australia usually takes three years full time.
In the US, the PhD process begins with taught classes (similar to a taught master’s) and a comprehensive exam (called a “field exam” or “dissertation qualifying exam”) before the candidate embarks on their original research. The whole journey takes four to six years.
A PhD candidate will need three skills and attitudes to get through their doctoral studies, says Tara Brabazon , professor of cultural studies at Flinders University in Australia who has written extensively about the PhD journey :
- master the academic foundational skills (research, writing, ability to navigate different modalities)
- time-management skills and the ability to focus on reading and writing
- determined motivation to do a PhD.

How do I choose the topic for my PhD dissertation or thesis?
It’s important to find a topic that will sustain your interest for the years it will take to complete a PhD. “Finding a sustainable topic is the most important thing you [as a PhD student] would do,” says Dr Brabazon in a video for Times Higher Education . “Write down on a big piece of paper all the topics, all the ideas, all the questions that really interest you, and start to cross out all the ones that might just be a passing interest.” Also, she says, impose the “Who cares? Who gives a damn?” question to decide if the topic will be useful in a future academic career.
The availability of funding and scholarships is also often an important factor in this decision, says veteran PhD supervisor Richard Godwin, from Harper Adams University .
Define a gap in knowledge – and one that can be questioned, explored, researched and written about in the time available to you, says Gina Wisker, head of the Centre for Learning and Teaching at the University of Brighton. “Set some boundaries,” she advises. “Don’t try to ask everything related to your topic in every way.”
James Hartley, research professor in psychology at Keele University, says it can also be useful to think about topics that spark general interest. If you do pick something that taps into the zeitgeist, your findings are more likely to be noticed.
You also need to find someone else who is interested in it, too. For STEM candidates , this will probably be a case of joining a team of people working in a similar area where, ideally, scholarship funding is available. A centre for doctoral training (CDT) or doctoral training partnership (DTP) will advertise research projects. For those in the liberal arts and social sciences, it will be a matter of identifying a suitable supervisor .
Avoid topics that are too broad (hunger across a whole country, for example) or too narrow (hunger in a single street) to yield useful solutions of academic significance, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith. And ensure that you’re not repeating previous research or trying to solve a problem that has already been answered. A PhD thesis must be original.
What is a thesis proposal?
After you have read widely to refine your topic and ensure that it and your research methods are original, and discussed your project with a (potential) supervisor, you’re ready to write a thesis proposal , a document of 1,500 to 3,000 words that sets out the proposed direction of your research. In the UK, a research proposal is usually part of the application process for admission to a research degree. As with the final dissertation itself, format varies among disciplines, institutions and countries but will usually contain title page, aims, literature review, methodology, timetable and bibliography. Examples of research proposals are available online.
How to write an abstract for a dissertation or thesis
The abstract presents your thesis to the wider world – and as such may be its most important element , says the NUI Galway writing guide. It outlines the why, how, what and so what of the thesis . Unlike the introduction, which provides background but not research findings, the abstract summarises all sections of the dissertation in a concise, thorough, focused way and demonstrates how well the writer understands their material. Check word-length limits with your university – and stick to them. About 300 to 500 words is a rough guide – but it can be up to 1,000 words.
The abstract is also important for selection and indexing of your thesis, according to the University of Melbourne guide , so be sure to include searchable keywords.
It is the first thing to be read but the last element you should write. However, Pat Thomson , professor of education at the University of Nottingham , advises that it is not something to be tackled at the last minute.
How to write a stellar conclusion
As well as chapter conclusions, a thesis often has an overall conclusion to draw together the key points covered and to reflect on the unique contribution to knowledge. It can comment on future implications of the research and open up new ideas emanating from the work. It is shorter and more general than the discussion chapter , says online editing site Scribbr, and reiterates how the work answers the main question posed at the beginning of the thesis. The conclusion chapter also often discusses the limitations of the research (time, scope, word limit, access) in a constructive manner.
It can be useful to keep a collection of ideas as you go – in the online forum DoctoralWriting SIG , academic developer Claire Aitchison, of the University of South Australia , suggests using a “conclusions bank” for themes and inspirations, and using free-writing to keep this final section fresh. (Just when you feel you’ve run out of steam.) Avoid aggrandising or exaggerating the impact of your work. It should remind the reader what has been done, and why it matters.
How to format a bibliography (or where to find a reliable model)
Most universities use a preferred style of references , writes THE associate editor Ingrid Curl. Make sure you know what this is and follow it. “One of the most common errors in academic writing is to cite papers in the text that do not then appear in the bibliography. All references in your thesis need to be cross-checked with the bibliography before submission. Using a database during your research can save a great deal of time in the writing-up process.”
A bibliography contains not only works cited explicitly but also those that have informed or contributed to the research – and as such illustrates its scope; works are not limited to written publications but include sources such as film or visual art.
Examiners can start marking from the back of the script, writes Dr Brabazon. “Just as cooks are judged by their ingredients and implements, we judge doctoral students by the calibre of their sources,” she advises. She also says that candidates should be prepared to speak in an oral examination of the PhD about any texts included in their bibliography, especially if there is a disconnect between the thesis and the texts listed.
Can I use informal language in my PhD?
Don’t write like a stereotypical academic , say Kevin Haggerty, professor of sociology at the University of Alberta , and Aaron Doyle, associate professor in sociology at Carleton University , in their tongue-in-cheek guide to the PhD journey. “If you cannot write clearly and persuasively, everything about PhD study becomes harder.” Avoid jargon, exotic words, passive voice and long, convoluted sentences – and work on it consistently. “Writing is like playing guitar; it can improve only through consistent, concerted effort.”
Be deliberate and take care with your writing . “Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense,” advises THE ’s Ms Curl. “Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency. If you are too involved with the text to be able to take a step back and do this, then ask a friend or colleague to read it with a critical eye. Remember Hemingway’s advice: ‘Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.’ Clarity is key.”
How often should a PhD candidate meet with their supervisor?
Since the PhD supervisor provides a range of support and advice – including on research techniques, planning and submission – regular formal supervisions are essential, as is establishing a line of contact such as email if the candidate needs help or advice outside arranged times. The frequency varies according to university, discipline and individual scholars.
Once a week is ideal, says Dr Brabazon. She also advocates a two-hour initial meeting to establish the foundations of the candidate-supervisor relationship .
The University of Edinburgh guide to writing a thesis suggests that creating a timetable of supervisor meetings right at the beginning of the research process will allow candidates to ensure that their work stays on track throughout. The meetings are also the place to get regular feedback on draft chapters.
“A clear structure and a solid framework are vital for research,” writes Dr Godwin on THE Campus . Use your supervisor to establish this and provide a realistic view of what can be achieved. “It is vital to help students identify the true scientific merit, the practical significance of their work and its value to society.”
How to proofread your dissertation (what to look for)
Proofreading is the final step before printing and submission. Give yourself time to ensure that your work is the best it can be . Don’t leave proofreading to the last minute; ideally, break it up into a few close-reading sessions. Find a quiet place without distractions. A checklist can help ensure that all aspects are covered.
Proofing is often helped by a change of format – so it can be easier to read a printout rather than working off the screen – or by reading sections out of order. Fresh eyes are better at spotting typographical errors and inconsistencies, so leave time between writing and proofreading. Check with your university’s policies before asking another person to proofread your thesis for you.
As well as close details such as spelling and grammar, check that all sections are complete, all required elements are included , and nothing is repeated or redundant. Don’t forget to check headings and subheadings. Does the text flow from one section to another? Is the structure clear? Is the work a coherent whole with a clear line throughout?
Ensure consistency in, for example, UK v US spellings, capitalisation, format, numbers (digits or words, commas, units of measurement), contractions, italics and hyphenation. Spellchecks and online plagiarism checkers are also your friend.

How do you manage your time to complete a PhD dissertation?
Treat your PhD like a full-time job, that is, with an eight-hour working day. Within that, you’ll need to plan your time in a way that gives a sense of progress . Setbacks and periods where it feels as if you are treading water are all but inevitable, so keeping track of small wins is important, writes A Happy PhD blogger Luis P. Prieto.
Be specific with your goals – use the SMART acronym (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and timely).
And it’s never too soon to start writing – even if early drafts are overwritten and discarded.
“ Write little and write often . Many of us make the mistake of taking to writing as one would take to a sprint, in other words, with relatively short bursts of intense activity. Whilst this can prove productive, generally speaking it is not sustainable…In addition to sustaining your activity, writing little bits on a frequent basis ensures that you progress with your thinking. The comfort of remaining in abstract thought is common; writing forces us to concretise our thinking,” says Christian Gilliam, AHSS researcher developer at the University of Cambridge ’s Centre for Teaching and Learning.
Make time to write. “If you are more alert early in the day, find times that suit you in the morning; if you are a ‘night person’, block out some writing sessions in the evenings,” advises NUI Galway’s Dermot Burns, a lecturer in English and creative arts. Set targets, keep daily notes of experiment details that you will need in your thesis, don’t confuse writing with editing or revising – and always back up your work.
What work-life balance tips should I follow to complete my dissertation?
During your PhD programme, you may have opportunities to take part in professional development activities, such as teaching, attending academic conferences and publishing your work. Your research may include residencies, field trips or archive visits. This will require time-management skills as well as prioritising where you devote your energy and factoring in rest and relaxation. Organise your routine to suit your needs , and plan for steady and regular progress.
How to deal with setbacks while writing a thesis or dissertation
Have a contingency plan for delays or roadblocks such as unexpected results.
Accept that writing is messy, first drafts are imperfect, and writer’s block is inevitable, says Dr Burns. His tips for breaking it include relaxation to free your mind from clutter, writing a plan and drawing a mind map of key points for clarity. He also advises feedback, reflection and revision: “Progressing from a rough version of your thoughts to a superior and workable text takes time, effort, different perspectives and some expertise.”
“Academia can be a relentlessly brutal merry-go-round of rejection, rebuttal and failure,” writes Lorraine Hope , professor of applied cognitive psychology at the University of Portsmouth, on THE Campus. Resilience is important. Ensure that you and your supervisor have a relationship that supports open, frank, judgement-free communication.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
Authoring a PhD Thesis: How to Plan, Draft, Write and Finish a Doctoral Dissertation (2003), by Patrick Dunleavy
Writing Your Dissertation in Fifteen Minutes a Day: A Guide to Starting, Revising, and Finishing Your Doctoral Thesis (1998), by Joan Balker
Challenges in Writing Your Dissertation: Coping with the Emotional, Interpersonal, and Spiritual Struggles (2015), by Noelle Sterne
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
Global perspectives: navigating challenges in higher education across borders, how to help young women see themselves as coders, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, authentic assessment in higher education and the role of digital creative technologies, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
- Staff & students
Writing a research proposal
Primary page content, what is a research proposal.
If you’re thinking of applying to do an MPhil and/or PhD, you will need to write a research proposal.
The proposal is your chance to demonstrate that you are capable of PhD study and persuade academics that you have the knowledge, skills and stamina to work through your ideas to a satisfactory conclusion.
It needs to:
- signal the importance of what you want to do
- communicate the intellectual content in relation to existing research and its topicality
- demonstrate that your research strategy is feasible and that you can take the project from proposal to thesis stage
- demonstrate how it relates to the department you want to study in (make sure you research the community and make contact with your prospective supervisor prior to writing and submitting your proposal)
- be original
- show the contribution your research would make to its field
- stay within the length stipulated
- be persuasive, with a clearly defined problem or issue
- be interesting and imaginative
- provide intellectual excitement
Writing your proposal
Although there is no prescribed format, most research proposals have similar structures.
You should formulate your problem or identified ‘gap’ as a question and make sure to set aims and objectives. The aims are the principal directions and themes of your work. The objectives are the specific, reliable outcomes you will achieve.
Throughout the proposal you need to demonstrate an awareness of the academic literature around the project itself and the question you have set; this means defining the intellectual landscape that you want to work and intervene within.
You also need to show that you’ve given some thought about how you’ll use the time period for your studies. Define the stages of your research, showing how you will organise your work and the achievement of your key objectives. For full-time research this will be 3-4 years and for part-time 7-8 years.
If relevant, you should also outline the kind of materials you will work with, what you are going to make and/or create, and how they connect.
One of the most important things to do is to make sure you put forward your case in clear and accessible terms. Steer clear of disciplinary jargon or academic shorthand unless it is absolutely necessary to effectively communicate your thinking.

COMMENTS
The best place to look for a PhD proposal sample is your university. Consider asking your supervisor if they can share a good proposal from a previous student in your subject - or put you in touch with a current student you can ask. #3 Confuse the proposal with the PhD. We've covered this on the blog, but it's simple enough to include here too.
Therefore, in a good research proposal you will need to demonstrate two main things: 1. that you are capable of independent critical thinking and analysis. 2. that you are capable of communicating your ideas clearly. Applying for a PhD is like applying for a job, you are not applying for a taught programme.
1. Title. Your title should indicate clearly what your research question is. It needs to be simple and to the point; if the reader needs to read further into your proposal to understand your question, your working title isn't clear enough. Directly below your title, state the topic your research question relates to.
Guidance for PhD applicants Faculty of Education, University of Cambridge. The 1,500 word research proposal is an important element of your application to doctoral study, whether full-time or part-time. It offers you the opportunity to outline the research you intend to conduct, including how you plan to go about it, and how your research might ...
When writing your PhD proposal you need to show that your PhD is worth it, achievable, and that you have the ability to do it at your chosen university. With all of that in mind, let's take a closer look at each section of a standard PhD research proposal and the overall structure. 1. Front matter.
Research proposal length. The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor's or master's thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
Guidance on Writing a Research Proposal A crucial part of the PhD application is the research proposal. It is one of the key criteria that the University of Salford uses to differentiate between different applicants and to make decisions on whether to make offers of acceptance onto the doctoral programme. This page provides guidance
References: Do not forget to specify all the references at the end of the proposal. An obvious but very important point is the format of your research proposal. Make sure that the formatting of the document is consistent throughout and that the structure is clear. If possible, it can be a good idea to give the document to your academic tutor or ...
This starts with double-checking that the questions of your thesis are obvious and unambiguous, followed by revising the rest of your proposal. "Make sure your research questions are really clear," says Sarah. "Ensure all the writing is clear and grammatically correct," adds Chelsea. "A supervisor is not going to be overly keen on a ...
Research proposals are used to persuade potential supervisors and funders that your work is worthy of their support. These documents setting out your proposed research that will result in a Doctoral thesis are typically between 1,500 and 3,000 words in length. Your PhD research proposal must passionately articulate what you want to research and ...
Writing your research proposal. When applying to study for a PhD or MPhil in the School of Psychology and Clinical Language Sciences, you will typically need to send us an initial 500-word research proposal. The content and structure of your research proposal will be influenced by the nature of the project you wish to pursue. The guidance and ...
Typically a proposal is no less than 1500 words (3-4 pages) long and will cover the following points. Provisional title (max 50 words ): the title should indicate the central focus of the research and should contain the key words associated with proposed work. Central question/hypothesis for investigation (max 15-50 words): State the central ...
The point of the PhD proposal is to demonstrate that you can come up with a coherent and in te re stin g question that is answerable in 80 100,000 words and three four years of serious research. W here do PhD topics come from? MA or BA essays of course, but also from problems and
A research proposal is usually around 2,500 words long although there is no upper or lower limit to this. In preparing a research proposal, the first thing that you have to do is to decide what it really is that you want to know more about. The questions that you want to research have to viable as a research project and lead to the creation of ...
1. Indicative title of the topic area. This should accurately reflect what it is that you want to study and the central issues that you are going to address. It may be useful to present this in the format of a statement (perhaps a quote) and a question, separated by a colon.
Your proposal should be typed double-spaced, if possible, and be between 1,000 and 2,000 words. Your PhD proposal can be added under the 'Supporting Documents' section of the Postgraduate Applications Online System. Your proposal should contain at least the following elements: A provisional title. A key question, hypothesis or the broad topic ...
A research proposal should present your idea or question and expected outcomes with clarity and definition - the what. It should also make a case for why your question is significant and what value it will bring to your discipline - the why. What it shouldn't do is answer the question - that's what your research will do.
Here are a few aspects to include and remember when writing your PhD proposal: 1. Include a title page. The working title is usually around ten words long and indicates what you plan to study. Try to choose an interesting and thought-provoking title that attracts the reader's attention.
Your research proposal is a concise statement (up to 3,000 words) of the rationale for your research proposal, the research questions to be answered and how you propose to address them. We know that during the early stages of your PhD you are likely to refine your thinking and methodology in discussion with your supervisors.
Most dissertations are 100 to 300 pages in length. All dissertations should be divided into appropriate sections, and long dissertations may need chapters, main divisions, and even subdivisions. Students should keep in mind that GSAS and many departments deplore overlong and wordy dissertations.
A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words ( 100 to 300 pages in length) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) - from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion. The structure of a dissertation will vary depending on discipline (humanities, social ...
Make sure you develop a good system that works for you and use it. 3. Don't write a laundry list of papers A literature review should be a synthesis of the papers you have read to tell a meaningful story about the literature, not a simple list of paraphrases of what each paper said. 4.
Writing your proposal. Although there is no prescribed format, most research proposals have similar structures. You should formulate your problem or identified 'gap' as a question and make sure to set aims and objectives. The aims are the principal directions and themes of your work. The objectives are the specific, reliable outcomes you ...
On April 19, 2024, the U.S. Department of Education released its final rule to fully effectuate Title IX's promise that no person experiences sex discrimination in federally funded education. Before issuing the proposed regulations, the Department received feedback on its Title IX regulations, as amended in 2020, from a wide variety of ...