- Engineering Mathematics
- Discrete Mathematics
- Operating System
- Computer Networks
- Digital Logic and Design
- C Programming
- Data Structures
- Theory of Computation
- Compiler Design
- Computer Org and Architecture
- Computer Network Tutorial

Basics of Computer Network
- Basics of Computer Networking
- Introduction to basic Networking Terminology
- Goals of Networks
- Basic characteristics of Computer Networks
- Challenges of Computer Network
- Physical Components of Computer Network
Network Hardware and Software
- Types of Computer Networks
- LAN Full Form
- How to Set Up a LAN Network?
- MAN Full Form in Computer Networking
- MAN Full Form
- WAN Full Form
- Introduction of Internetworking
- Difference between Internet, Intranet and Extranet
- Protocol Hierarchies in Computer Network
- Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)
- Introduction of a Router
- Introduction of Gateways
- What is a network switch, and how does it work?
Network Topology
- Types of Network Topology
- Difference between Physical and Logical Topology
- What is OSI Model? - Layers of OSI Model
- Physical Layer in OSI Model
- Data Link Layer
- Session Layer in OSI model
Presentation Layer in OSI model
- Application Layer in OSI Model
- Protocol and Standard in Computer Networks
- Examples of Data Link Layer Protocols
- TCP/IP Model
- TCP/IP Ports and Its Applications
- What is Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)?
- TCP 3-Way Handshake Process
- Services and Segment structure in TCP
- TCP Connection Establishment
- TCP Connection Termination
- Fast Recovery Technique For Loss Recovery in TCP
- Difference Between OSI Model and TCP/IP Model
Medium Access Control
- MAC Full Form
- Channel Allocation Problem in Computer Network
- Multiple Access Protocols in Computer Network
- Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA)
- Collision Detection in CSMA/CD
- Controlled Access Protocols in Computer Network
SLIDING WINDOW PROTOCOLS
- Stop and Wait ARQ
- Sliding Window Protocol | Set 3 (Selective Repeat)
- Piggybacking in Computer Networks
IP Addressing
- What is IPv4?
- What is IPv6?
- Introduction of Classful IP Addressing
- Classless Addressing in IP Addressing
- Classful Vs Classless Addressing
- Classless Inter Domain Routing (CIDR)
- Supernetting in Network Layer
- Introduction To Subnetting
- Difference between Subnetting and Supernetting
- Types of Routing
- Difference between Static and Dynamic Routing
- Unicast Routing - Link State Routing
- Distance Vector Routing (DVR) Protocol
- Fixed and Flooding Routing algorithms
- Introduction of Firewall in Computer Network
Congestion Control Algorithms
- Congestion Control in Computer Networks
- Congestion Control techniques in Computer Networks
- Computer Network | Leaky bucket algorithm
- TCP Congestion Control
Network Switching
- Circuit Switching in Computer Network
- Message switching techniques
- Packet Switching and Delays in Computer Network
- Differences Between Virtual Circuits and Datagram Networks
Application Layer:DNS
- Domain Name System (DNS) in Application Layer
- Details on DNS
- Introduction to Electronic Mail
- E-Mail Format
- World Wide Web (WWW)
- HTTP Full Form
- Streaming Stored Video
- What is a Content Distribution Network and how does it work?
CN Interview Quetions
- Top 50 Networking Interview Questions (2024)
- Top 50 TCP/IP interview questions and answers
- Top 50 IP addressing interview questions and answers
- Last Minute Notes - Computer Networks
- Computer Network - Cheat Sheet
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Application Layer
Prerequisite : OSI Model
Introduction : Presentation Layer is the 6th layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. This layer is also known as Translation layer, as this layer serves as a data translator for the network. The data which this layer receives from the Application Layer is extracted and manipulated here as per the required format to transmit over the network. The main responsibility of this layer is to provide or define the data format and encryption. The presentation layer is also called as Syntax layer since it is responsible for maintaining the proper syntax of the data which it either receives or transmits to other layer(s).
Functions of Presentation Layer :
The presentation layer, being the 6th layer in the OSI model, performs several types of functions, which are described below-
- Presentation layer format and encrypts data to be sent across the network.
- This layer takes care that the data is sent in such a way that the receiver will understand the information (data) and will be able to use the data efficiently and effectively.
- This layer manages the abstract data structures and allows high-level data structures (example- banking records), which are to be defined or exchanged.
- This layer carries out the encryption at the transmitter and decryption at the receiver.
- This layer carries out data compression to reduce the bandwidth of the data to be transmitted (the primary goal of data compression is to reduce the number of bits which is to be transmitted).
- This layer is responsible for interoperability (ability of computers to exchange and make use of information) between encoding methods as different computers use different encoding methods.
- This layer basically deals with the presentation part of the data.
- Presentation layer, carries out the data compression (number of bits reduction while transmission), which in return improves the data throughput.
- This layer also deals with the issues of string representation.
- The presentation layer is also responsible for integrating all the formats into a standardized format for efficient and effective communication.
- This layer encodes the message from the user-dependent format to the common format and vice-versa for communication between dissimilar systems.
- This layer deals with the syntax and semantics of the messages.
- This layer also ensures that the messages which are to be presented to the upper as well as the lower layer should be standardized as well as in an accurate format too.
- Presentation layer is also responsible for translation, formatting, and delivery of information for processing or display.
- This layer also performs serialization (process of translating a data structure or an object into a format that can be stored or transmitted easily).
Features of Presentation Layer in the OSI model: Presentation layer, being the 6th layer in the OSI model, plays a vital role while communication is taking place between two devices in a network.
List of features which are provided by the presentation layer are:
- Presentation layer could apply certain sophisticated compression techniques, so fewer bytes of data are required to represent the information when it is sent over the network.
- If two or more devices are communicating over an encrypted connection, then this presentation layer is responsible for adding encryption on the sender’s end as well as the decoding the encryption on the receiver’s end so that it can represent the application layer with unencrypted, readable data.
- This layer formats and encrypts data to be sent over a network, providing freedom from compatibility problems.
- This presentation layer also negotiates the Transfer Syntax.
- This presentation layer is also responsible for compressing data it receives from the application layer before delivering it to the session layer (which is the 5th layer in the OSI model) and thus improves the speed as well as the efficiency of communication by minimizing the amount of the data to be transferred.
Working of Presentation Layer in the OSI model : Presentation layer in the OSI model, as a translator, converts the data sent by the application layer of the transmitting node into an acceptable and compatible data format based on the applicable network protocol and architecture. Upon arrival at the receiving computer, the presentation layer translates data into an acceptable format usable by the application layer. Basically, in other words, this layer takes care of any issues occurring when transmitted data must be viewed in a format different from the original format. Being the functional part of the OSI mode, the presentation layer performs a multitude (large number of) data conversion algorithms and character translation functions. Mainly, this layer is responsible for managing two network characteristics: protocol (set of rules) and architecture.
Presentation Layer Protocols : Presentation layer being the 6th layer, but the most important layer in the OSI model performs several types of functionalities, which makes sure that data which is being transferred or received should be accurate or clear to all the devices which are there in a closed network. Presentation Layer, for performing translations or other specified functions, needs to use certain protocols which are defined below –
- Apple Filing Protocol (AFP): Apple Filing Protocol is the proprietary network protocol (communications protocol) that offers services to macOS or the classic macOS. This is basically the network file control protocol specifically designed for Mac-based platforms.
- Lightweight Presentation Protocol (LPP): Lightweight Presentation Protocol is that protocol which is used to provide ISO presentation services on the top of TCP/IP based protocol stacks.
- NetWare Core Protocol (NCP): NetWare Core Protocol is the network protocol which is used to access file, print, directory, clock synchronization, messaging, remote command execution and other network service functions.
- Network Data Representation (NDR): Network Data Representation is basically the implementation of the presentation layer in the OSI model, which provides or defines various primitive data types, constructed data types and also several types of data representations.
- External Data Representation (XDR): External Data Representation (XDR) is the standard for the description and encoding of data. It is useful for transferring data between computer architectures and has been used to communicate data between very diverse machines. Converting from local representation to XDR is called encoding, whereas converting XDR into local representation is called decoding.
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL): The Secure Socket Layer protocol provides security to the data that is being transferred between the web browser and the server. SSL encrypts the link between a web server and a browser, which ensures that all data passed between them remains private and free from attacks.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.

- 5 Reasons to Start Using Claude 3 Instead of ChatGPT
- 6 Ways to Identify Who an Unknown Caller
- 10 Best Lavender AI Alternatives and Competitors 2024
- The 7 Best AI Tools for Programmers to Streamline Development in 2024
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Layer 6 Presentation Layer
De/Encryption, Encoding, String representation
The presentation layer (data presentation layer, data provision level) sets the system-dependent representation of the data (for example, ASCII, EBCDIC) into an independent form, enabling the syntactically correct data exchange between different systems. Also, functions such as data compression and encryption are guaranteed that data to be sent by the application layer of a system that can be read by the application layer of another system to the layer 6. The presentation layer. If necessary, the presentation layer acts as a translator between different data formats, by making an understandable for both systems data format, the ASN.1 (Abstract Syntax Notation One) used.
OSI Layer 6 - Presentation Layer
The presentation layer is responsible for the delivery and formatting of information to the application layer for further processing or display. It relieves the application layer of concern regarding syntactical differences in data representation within the end-user systems. An example of a presentation service would be the conversion of an EBCDIC-coded text computer file to an ASCII-coded file. The presentation layer is the lowest layer at which application programmers consider data structure and presentation, instead of simply sending data in the form of datagrams or packets between hosts. This layer deals with issues of string representation - whether they use the Pascal method (an integer length field followed by the specified amount of bytes) or the C/C++ method (null-terminated strings, e.g. "thisisastring\0"). The idea is that the application layer should be able to point at the data to be moved, and the presentation layer will deal with the rest. Serialization of complex data structures into flat byte-strings (using mechanisms such as TLV or XML) can be thought of as the key functionality of the presentation layer. Encryption is typically done at this level too, although it can be done on the application, session, transport, or network layers, each having its own advantages and disadvantages. Decryption is also handled at the presentation layer. For example, when logging on to bank account sites the presentation layer will decrypt the data as it is received.[1] Another example is representing structure, which is normally standardized at this level, often by using XML. As well as simple pieces of data, like strings, more complicated things are standardized in this layer. Two common examples are 'objects' in object-oriented programming, and the exact way that streaming video is transmitted. In many widely used applications and protocols, no distinction is made between the presentation and application layers. For example, HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP), generally regarded as an application-layer protocol, has presentation-layer aspects such as the ability to identify character encoding for proper conversion, which is then done in the application layer. Within the service layering semantics of the OSI network architecture, the presentation layer responds to service requests from the application layer and issues service requests to the session layer. In the OSI model: the presentation layer ensures the information that the application layer of one system sends out is readable by the application layer of another system. For example, a PC program communicates with another computer, one using extended binary coded decimal interchange code (EBCDIC) and the other using ASCII to represent the same characters. If necessary, the presentation layer might be able to translate between multiple data formats by using a common format. Wikipedia
- Data conversion
- Character code translation
- Compression
- Encryption and Decryption
The Presentation OSI Layer is usually composed of 2 sublayers that are:
CASE common application service element
Sase specific application service element, layer 7 application layer, layer 6 presentation layer, layer 5 session layer, layer 4 transport layer, layer 3 network layer, layer 2 data link layer, layer 1 physical layer.
PrepBytes Blog
ONE-STOP RESOURCE FOR EVERYTHING RELATED TO CODING
Sign in to your account
Forgot your password?
Login via OTP
We will send you an one time password on your mobile number
An OTP has been sent to your mobile number please verify it below
Register with PrepBytes
Presentation layer in osi model.
Last Updated on March 7, 2024 by Abhishek Sharma

The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework used to understand the functions of a telecommunication or computing system. It consists of seven layers, each responsible for specific tasks. The sixth layer, known as the Presentation Layer, plays a crucial role in ensuring that data exchanged between systems is readable and usable. Let’s explore the functions and importance of the Presentation Layer in the OSI model.
What is Presentation Layer in OSI Model?
The Presentation Layer, the sixth layer of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, is responsible for ensuring that data exchanged between systems is in a format that can be interpreted and used by the receiving system. It performs various functions, including data translation, encryption, compression, and formatting, to facilitate efficient and secure communication between networked devices.
Functions of the Presentation Layer
Below are some of the functions of the Presentation Layer in OSI Model:
- Data Translation: The Presentation Layer translates data from the format used by the application layer into a format that can be transmitted over the network. This includes encoding, compression, and encryption.
- Data Formatting: It ensures that data is formatted according to the specifications of the application layer. This includes converting between different character sets, such as ASCII and Unicode.
- Data Compression: The Presentation Layer compresses data to reduce the amount of bandwidth required for transmission, improving network efficiency.
- Data Encryption: It encrypts data to ensure that it remains secure during transmission, protecting it from unauthorized access.
- Data Syntax: The Presentation Layer defines the syntax for data representation, ensuring that both the sender and receiver understand the structure of the data being exchanged.
Importance of the Presentation Layer
Importance of Presentation Layer are:
- Data Integrity: By ensuring that data is formatted correctly and encrypted, the Presentation Layer helps maintain the integrity of data during transmission.
- Interoperability: The Presentation Layer enables different systems to communicate with each other by ensuring that data is translated into a common format that both systems understand.
- Efficiency: Data compression reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted, improving network efficiency and reducing bandwidth requirements.
- Security: Encryption provided by the Presentation Layer ensures that data remains secure and protected from unauthorized access.
Conclusion The Presentation Layer is a crucial component of the OSI model, responsible for ensuring that data exchanged between systems is in a format that can be understood and used. By performing functions such as data translation, formatting, compression, and encryption, the Presentation Layer plays a vital role in maintaining data integrity, facilitating interoperability, and ensuring the security of data during transmission.
FAQs related to Presentation Layer in OSI Model
Here are some of the FAQs related to Presentation Layer in OSI Model:
Q1: What is the role of the Presentation Layer in the OSI model? The Presentation Layer ensures that data exchanged between systems is in a usable format, performing functions such as data translation, encryption, compression, and formatting.
Q2: How does the Presentation Layer ensure data security? The Presentation Layer encrypts data before transmission, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties, thus ensuring data security.
Q3: Why is data compression important in the Presentation Layer? Data compression reduces the size of data packets, leading to faster transmission speeds and optimized bandwidth usage, which is crucial in high-traffic networks.
Q4: How does the Presentation Layer facilitate interoperability between systems? By translating data into a common format that both sender and receiver understand, the Presentation Layer enables different systems to communicate with each other seamlessly.
Q5: Can the Presentation Layer be bypassed in data transmission? While it is possible to bypass the Presentation Layer in some cases, doing so can lead to compatibility issues between systems and is not recommended.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Linked List
- Segment Tree
- Backtracking
- Dynamic Programming
- Greedy Algorithm
- Operating System
- Company Placement
- Interview Tips
- General Interview Questions
- Data Structure
- Other Topics
- Computational Geometry
- Game Theory
Related Post
Quantum cryptography, introduction to sniffers, multiplexing and demultiplexing in transport layer, transport layer responsibilities, tacacs+ and radius.
The OSI Model – The 7 Layers of Networking Explained in Plain English

This article explains the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model and the 7 layers of networking, in plain English.
The OSI model is a conceptual framework that is used to describe how a network functions. In plain English, the OSI model helped standardize the way computer systems send information to each other.
Learning networking is a bit like learning a language - there are lots of standards and then some exceptions. Therefore, it’s important to really understand that the OSI model is not a set of rules. It is a tool for understanding how networks function.
Once you learn the OSI model, you will be able to further understand and appreciate this glorious entity we call the Internet, as well as be able to troubleshoot networking issues with greater fluency and ease.
All hail the Internet!
Prerequisites
You don’t need any prior programming or networking experience to understand this article. However, you will need:
- Basic familiarity with common networking terms (explained below)
- A curiosity about how things work :)
Learning Objectives
Over the course of this article, you will learn:
- What the OSI model is
- The purpose of each of the 7 layers
- The problems that can happen at each of the 7 layers
- The difference between TCP/IP model and the OSI model
Common Networking Terms
Here are some common networking terms that you should be familiar with to get the most out of this article. I’ll use these terms when I talk about OSI layers next.
A node is a physical electronic device hooked up to a network, for example a computer, printer, router, and so on. If set up properly, a node is capable of sending and/or receiving information over a network.
Nodes may be set up adjacent to one other, wherein Node A can connect directly to Node B, or there may be an intermediate node, like a switch or a router, set up between Node A and Node B.
Typically, routers connect networks to the Internet and switches operate within a network to facilitate intra-network communication. Learn more about hub vs. switch vs. router.
Here's an example:
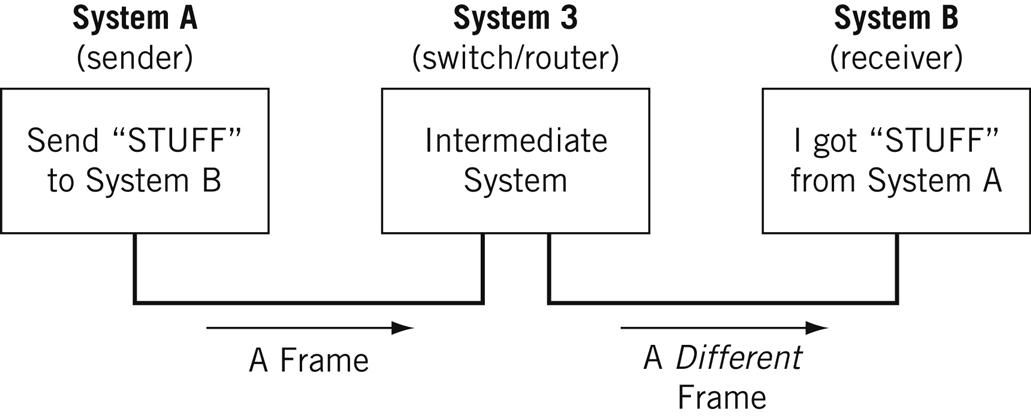
For the nitpicky among us (yep, I see you), host is another term that you will encounter in networking. I will define a host as a type of node that requires an IP address. All hosts are nodes, but not all nodes are hosts. Please Tweet angrily at me if you disagree.
Links connect nodes on a network. Links can be wired, like Ethernet, or cable-free, like WiFi.
Links to can either be point-to-point, where Node A is connected to Node B, or multipoint, where Node A is connected to Node B and Node C.
When we’re talking about information being transmitted, this may also be described as a one-to-one vs. a one-to-many relationship.
A protocol is a mutually agreed upon set of rules that allows two nodes on a network to exchange data.
“A protocol defines the rules governing the syntax (what can be communicated), semantics (how it can be communicated), and synchronization (when and at what speed it can be communicated) of the communications procedure. Protocols can be implemented on hardware, software, or a combination of both. Protocols can be created by anyone, but the most widely adopted protocols are based on standards.” - The Illustrated Network.
Both wired and cable-free links can have protocols.
While anyone can create a protocol, the most widely adopted protocols are often based on standards published by Internet organizations such as the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
A network is a general term for a group of computers, printers, or any other device that wants to share data.
Network types include LAN, HAN, CAN, MAN, WAN, BAN, or VPN. Think I’m just randomly rhyming things with the word can ? I can ’t say I am - these are all real network types. Learn more here .
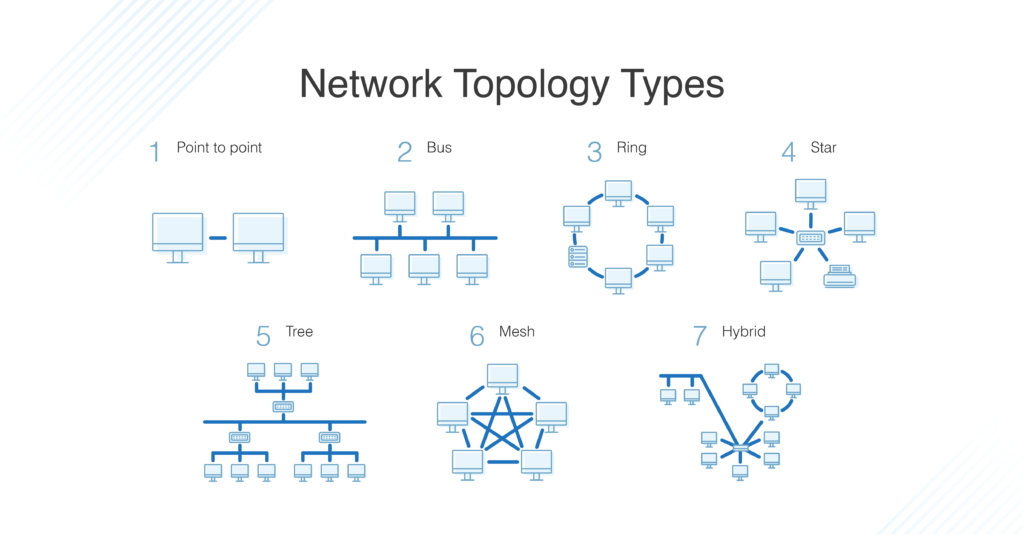
Topology describes how nodes and links fit together in a network configuration, often depicted in a diagram. Here are some common network topology types:
A network consists of nodes, links between nodes, and protocols that govern data transmission between nodes.
At whatever scale and complexity networks get to, you will understand what’s happening in all computer networks by learning the OSI model and 7 layers of networking.
What is the OSI Model?
The OSI model consists of 7 layers of networking.
First, what’s a layer?

No, a layer - not a lair . Here there are no dragons.
A layer is a way of categorizing and grouping functionality and behavior on and of a network.
In the OSI model, layers are organized from the most tangible and most physical, to less tangible and less physical but closer to the end user.
Each layer abstracts lower level functionality away until by the time you get to the highest layer. All the details and inner workings of all the other layers are hidden from the end user.
How to remember all the names of the layers? Easy.
- Please | Physical Layer
- Do | Data Link Layer
- Not | Network Layer
- Tell (the) | Transport Layer
- Secret | Session Layer
- Password (to) | Presentation Layer
- Anyone | Application Layer
Keep in mind that while certain technologies, like protocols, may logically “belong to” one layer more than another, not all technologies fit neatly into a single layer in the OSI model. For example, Ethernet, 802.11 (Wifi) and the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) procedure operate on >1 layer.
The OSI is a model and a tool, not a set of rules.
OSI Layer 1
Layer 1 is the physical layer . There’s a lot of technology in Layer 1 - everything from physical network devices, cabling, to how the cables hook up to the devices. Plus if we don’t need cables, what the signal type and transmission methods are (for example, wireless broadband).
Instead of listing every type of technology in Layer 1, I’ve created broader categories for these technologies. I encourage readers to learn more about each of these categories:
- Nodes (devices) and networking hardware components. Devices include hubs, repeaters, routers, computers, printers, and so on. Hardware components that live inside of these devices include antennas, amplifiers, Network Interface Cards (NICs), and more.
- Device interface mechanics. How and where does a cable connect to a device (cable connector and device socket)? What is the size and shape of the connector, and how many pins does it have? What dictates when a pin is active or inactive?
- Functional and procedural logic. What is the function of each pin in the connector - send or receive? What procedural logic dictates the sequence of events so a node can start to communicate with another node on Layer 2?
- Cabling protocols and specifications. Ethernet (CAT), USB, Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) , and more. Specifications include maximum cable length, modulation techniques, radio specifications, line coding, and bits synchronization (more on that below).
- Cable types. Options include shielded or unshielded twisted pair, untwisted pair, coaxial and so on. Learn more about cable types here .
- Signal type. Baseband is a single bit stream at a time, like a railway track - one-way only. Broadband consists of multiple bit streams at the same time, like a bi-directional highway.
- Signal transmission method (may be wired or cable-free). Options include electrical (Ethernet), light (optical networks, fiber optics), radio waves (802.11 WiFi, a/b/g/n/ac/ax variants or Bluetooth). If cable-free, then also consider frequency: 2.5 GHz vs. 5 GHz. If it’s cabled, consider voltage. If cabled and Ethernet, also consider networking standards like 100BASE-T and related standards.
The data unit on Layer 1 is the bit.
A bit the smallest unit of transmittable digital information. Bits are binary, so either a 0 or a 1. Bytes, consisting of 8 bits, are used to represent single characters, like a letter, numeral, or symbol.
Bits are sent to and from hardware devices in accordance with the supported data rate (transmission rate, in number of bits per second or millisecond) and are synchronized so the number of bits sent and received per unit of time remains consistent (this is called bit synchronization). The way bits are transmitted depends on the signal transmission method.
Nodes can send, receive, or send and receive bits. If they can only do one, then the node uses a simplex mode. If they can do both, then the node uses a duplex mode. If a node can send and receive at the same time, it’s full-duplex – if not, it’s just half-duplex.
The original Ethernet was half-duplex. Full-duplex Ethernet is an option now, given the right equipment.
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 1 Problems
Here are some Layer 1 problems to watch out for:
- Defunct cables, for example damaged wires or broken connectors
- Broken hardware network devices, for example damaged circuits
- Stuff being unplugged (...we’ve all been there)
If there are issues in Layer 1, anything beyond Layer 1 will not function properly.
Layer 1 contains the infrastructure that makes communication on networks possible.
It defines the electrical, mechanical, procedural, and functional specifications for activating, maintaining, and deactivating physical links between network devices. - Source
Fun fact: deep-sea communications cables transmit data around the world. This map will blow your mind: https://www.submarinecablemap.com/
And because you made it this far, here’s a koala:

OSI Layer 2
Layer 2 is the data link layer . Layer 2 defines how data is formatted for transmission, how much data can flow between nodes, for how long, and what to do when errors are detected in this flow.
In more official tech terms:
- Line discipline. Who should talk for how long? How long should nodes be able to transit information for?
- Flow control. How much data should be transmitted?
- Error control - detection and correction . All data transmission methods have potential for errors, from electrical spikes to dirty connectors. Once Layer 2 technologies tell network administrators about an issue on Layer 2 or Layer 1, the system administrator can correct for those errors on subsequent layers. Layer 2 is mostly concerned with error detection, not error correction. ( Source )
There are two distinct sublayers within Layer 2:
- Media Access Control (MAC): the MAC sublayer handles the assignment of a hardware identification number, called a MAC address, that uniquely identifies each device on a network. No two devices should have the same MAC address. The MAC address is assigned at the point of manufacturing. It is automatically recognized by most networks. MAC addresses live on Network Interface Cards (NICs). Switches keep track of all MAC addresses on a network. Learn more about MAC addresses on PC Mag and in this article . Learn more about network switches here .
- Logical Link Control (LLC): the LLC sublayer handles framing addressing and flow control. The speed depends on the link between nodes, for example Ethernet or Wifi.
The data unit on Layer 2 is a frame .
Each frame contains a frame header, body, and a frame trailer:
- Header: typically includes MAC addresses for the source and destination nodes.
- Body: consists of the bits being transmitted.
- Trailer: includes error detection information. When errors are detected, and depending on the implementation or configuration of a network or protocol, frames may be discarded or the error may be reported up to higher layers for further error correction. Examples of error detection mechanisms: Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) and Frame Check Sequence (FCS). Learn more about error detection techniques here .
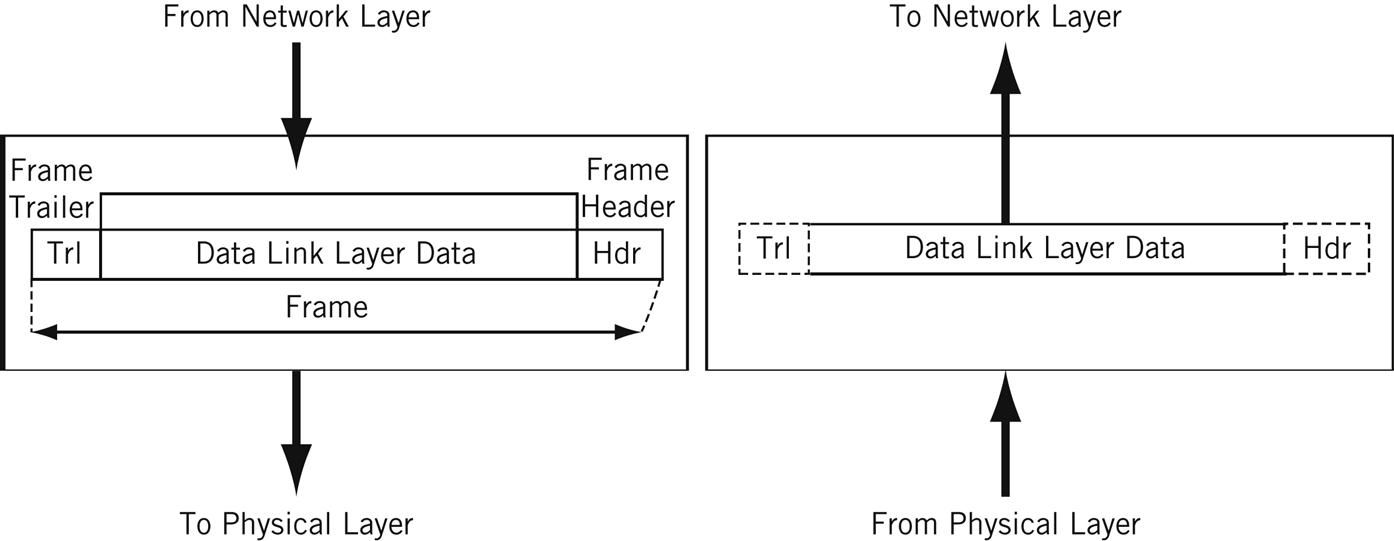
Typically there is a maximum frame size limit, called an Maximum Transmission Unit, MTU. Jumbo frames exceed the standard MTU, learn more about jumbo frames here .
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 2 Problems
Here are some Layer 2 problems to watch out for:
- All the problems that can occur on Layer 1
- Unsuccessful connections (sessions) between two nodes
- Sessions that are successfully established but intermittently fail
- Frame collisions
The Data Link Layer allows nodes to communicate with each other within a local area network. The foundations of line discipline, flow control, and error control are established in this layer.
OSI Layer 3
Layer 3 is the network layer . This is where we send information between and across networks through the use of routers. Instead of just node-to-node communication, we can now do network-to-network communication.
Routers are the workhorse of Layer 3 - we couldn’t have Layer 3 without them. They move data packets across multiple networks.
Not only do they connect to Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to provide access to the Internet, they also keep track of what’s on its network (remember that switches keep track of all MAC addresses on a network), what other networks it’s connected to, and the different paths for routing data packets across these networks.
Routers store all of this addressing and routing information in routing tables.
Here’s a simple example of a routing table:

The data unit on Layer 3 is the data packet . Typically, each data packet contains a frame plus an IP address information wrapper. In other words, frames are encapsulated by Layer 3 addressing information.
The data being transmitted in a packet is also sometimes called the payload . While each packet has everything it needs to get to its destination, whether or not it makes it there is another story.
Layer 3 transmissions are connectionless, or best effort - they don't do anything but send the traffic where it’s supposed to go. More on data transport protocols on Layer 4.
Once a node is connected to the Internet, it is assigned an Internet Protocol (IP) address, which looks either like 172.16. 254.1 (IPv4 address convention) or like 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 (IPv6 address convention). Routers use IP addresses in their routing tables.
IP addresses are associated with the physical node’s MAC address via the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which resolves MAC addresses with the node’s corresponding IP address.
ARP is conventionally considered part of Layer 2, but since IP addresses don’t exist until Layer 3, it’s also part of Layer 3.
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 3 Problems
Here are some Layer 3 problems to watch out for:
- All the problems that can crop up on previous layers :)
- Faulty or non-functional router or other node
- IP address is incorrectly configured
Many answers to Layer 3 questions will require the use of command-line tools like ping , trace , show ip route , or show ip protocols . Learn more about troubleshooting on layer 1-3 here .
The Network Layer allows nodes to connect to the Internet and send information across different networks.
OSI Layer 4
Layer 4 is the transport layer . This where we dive into the nitty gritty specifics of the connection between two nodes and how information is transmitted between them. It builds on the functions of Layer 2 - line discipline, flow control, and error control.
This layer is also responsible for data packet segmentation, or how data packets are broken up and sent over the network.
Unlike the previous layer, Layer 4 also has an understanding of the whole message, not just the contents of each individual data packet. With this understanding, Layer 4 is able to manage network congestion by not sending all the packets at once.
The data units of Layer 4 go by a few names. For TCP, the data unit is a packet. For UDP, a packet is referred to as a datagram. I’ll just use the term data packet here for the sake of simplicity.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) are two of the most well-known protocols in Layer 4.
TCP, a connection-oriented protocol, prioritizes data quality over speed.
TCP explicitly establishes a connection with the destination node and requires a handshake between the source and destination nodes when data is transmitted. The handshake confirms that data was received. If the destination node does not receive all of the data, TCP will ask for a retry.
TCP also ensures that packets are delivered or reassembled in the correct order. Learn more about TCP here .
UDP, a connectionless protocol, prioritizes speed over data quality. UDP does not require a handshake, which is why it’s called connectionless.
Because UDP doesn’t have to wait for this acknowledgement, it can send data at a faster rate, but not all of the data may be successfully transmitted and we’d never know.
If information is split up into multiple datagrams, unless those datagrams contain a sequence number, UDP does not ensure that packets are reassembled in the correct order. Learn more about UDP here .
TCP and UDP both send data to specific ports on a network device, which has an IP address. The combination of the IP address and the port number is called a socket.
Learn more about sockets here .
Learn more about the differences and similarities between these two protocols here .
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 4 Problems
Here are some Layer 4 problems to watch out for:
- Blocked ports - check your Access Control Lists (ACL) & firewalls
- Quality of Service (QoS) settings. QoS is a feature of routers/switches that can prioritize traffic, and they can really muck things up. Learn more about QoS here .
The Transport Layer provides end-to-end transmission of a message by segmenting a message into multiple data packets; the layer supports connection-oriented and connectionless communication.
OSI Layer 5
Layer 5 is the session layer . This layer establishes, maintains, and terminates sessions.
A session is a mutually agreed upon connection that is established between two network applications. Not two nodes! Nope, we’ve moved on from nodes. They were so Layer 4.
Just kidding, we still have nodes, but Layer 5 doesn’t need to retain the concept of a node because that’s been abstracted out (taken care of) by previous layers.
So a session is a connection that is established between two specific end-user applications. There are two important concepts to consider here:
- Client and server model: the application requesting the information is called the client, and the application that has the requested information is called the server.
- Request and response model: while a session is being established and during a session, there is a constant back-and-forth of requests for information and responses containing that information or “hey, I don’t have what you’re requesting.”
Sessions may be open for a very short amount of time or a long amount of time. They may fail sometimes, too.
Depending on the protocol in question, various failure resolution processes may kick in. Depending on the applications/protocols/hardware in use, sessions may support simplex, half-duplex, or full-duplex modes.
Examples of protocols on Layer 5 include Network Basic Input Output System (NetBIOS) and Remote Procedure Call Protocol (RPC), and many others.
From here on out (layer 5 and up), networks are focused on ways of making connections to end-user applications and displaying data to the user.
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 5 Problems
Here are some Layer 5 problems to watch out for:
- Servers are unavailable
- Servers are incorrectly configured, for example Apache or PHP configs
- Session failure - disconnect, timeout, and so on.
The Session Layer initiates, maintains, and terminates connections between two end-user applications. It responds to requests from the presentation layer and issues requests to the transport layer.
OSI Layer 6
Layer 6 is the presentation layer . This layer is responsible for data formatting, such as character encoding and conversions, and data encryption.
The operating system that hosts the end-user application is typically involved in Layer 6 processes. This functionality is not always implemented in a network protocol.
Layer 6 makes sure that end-user applications operating on Layer 7 can successfully consume data and, of course, eventually display it.
There are three data formatting methods to be aware of:
- American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII): this 7-bit encoding technique is the most widely used standard for character encoding. One superset is ISO-8859-1, which provides most of the characters necessary for languages spoken in Western Europe.
- Extended Binary-Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBDCIC): designed by IBM for mainframe usage. This encoding is incompatible with other character encoding methods.
- Unicode: character encodings can be done with 32-, 16-, or 8-bit characters and attempts to accommodate every known, written alphabet.
Learn more about character encoding methods in this article , and also here .
Encryption: SSL or TLS encryption protocols live on Layer 6. These encryption protocols help ensure that transmitted data is less vulnerable to malicious actors by providing authentication and data encryption for nodes operating on a network. TLS is the successor to SSL.
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 6 Problems
Here are some Layer 6 problems to watch out for:
- Non-existent or corrupted drivers
- Incorrect OS user access level
The Presentation Layer formats and encrypts data.
OSI Layer 7
Layer 7 is the application layer .
True to its name, this is the layer that is ultimately responsible for supporting services used by end-user applications. Applications include software programs that are installed on the operating system, like Internet browsers (for example, Firefox) or word processing programs (for example, Microsoft Word).
Applications can perform specialized network functions under the hood and require specialized services that fall under the umbrella of Layer 7.
Electronic mail programs, for example, are specifically created to run over a network and utilize networking functionality, such as email protocols, which fall under Layer 7.
Applications will also control end-user interaction, such as security checks (for example, MFA), identification of two participants, initiation of an exchange of information, and so on.
Protocols that operate on this level include File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Secure Shell (SSH), Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), Domain Name Service (DNS), and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
While each of these protocols serve different functions and operate differently, on a high level they all facilitate the communication of information. ( Source )
How to Troubleshoot OSI Layer 7 Problems
Here are some Layer 7 problems to watch out for:
- All issues on previous layers
- Incorrectly configured software applications
- User error (... we’ve all been there)
The Application Layer owns the services and functions that end-user applications need to work. It does not include the applications themselves.
Our Layer 1 koala is all grown up.

Learning check - can you apply makeup to a koala?
Don’t have a koala?
Well - answer these questions instead. It’s the next best thing, I promise.
- What is the OSI model?
- What are each of the layers?
- How could I use this information to troubleshoot networking issues?
Congratulations - you’ve taken one step farther to understanding the glorious entity we call the Internet.
Learning Resources
Many, very smart people have written entire books about the OSI model or entire books about specific layers. I encourage readers to check out any O’Reilly-published books about the subject or about network engineering in general.
Here are some resources I used when writing this article:
- The Illustrated Network, 2nd Edition
- Protocol Data Unit (PDU): https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-segments-packets-and-frames/
- Troubleshooting Along the OSI Model: https://www.pearsonitcertification.com/articles/article.aspx?p=1730891
- The OSI Model Demystified: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HEEnLZV2wGI
- OSI Model for Dummies: https://www.dummies.com/programming/networking/layers-in-the-osi-model-of-a-computer-network/
Chloe Tucker is an artist and computer science enthusiast based in Portland, Oregon. As a former educator, she's continuously searching for the intersection of learning and teaching, or technology and art. Reach out to her on Twitter @_chloetucker and check out her website at chloe.dev .
Read more posts .
If you read this far, thank the author to show them you care. Say Thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Presentation layer and Session layer of the OSI model
There are two popular networking models: the OSI layers model and the TCP/IP layers model. The presentation layer and session layer exist only in the OSI layers models. The TCP/IP layers model merges them into the application layer.
The Presentation Layer
The presentation layer is the sixth layer of the OSI Reference model. It defines how data and information is transmitted and presented to the user. It translates data and format code in such a way that it is correctly used by the application layer.
It identifies the syntaxes that different applications use and formats data using those syntaxes. For example, a web browser receives a web page from a web server in the HTML language. HTML language includes many tags and markup that have no meaning for the end user but they have special meaning for the web browser. the web browser uses the presentation layer's logic to read those syntaxes and format data in such a way the web server wants it to be present to the user.

On the sender device, it encapsulates and compresses data before sending it to the network to increase the speed and security of the network. On the receiver device, it de-encapsulates and decompresses data before presenting it to the user.
Examples of the presentation layer
Example standards for representing graphical information: JPEG, GIF, JPEG, and TIFF.
Example standards for representing audio information: WAV, MIDI, MP3.
Example standards for representing video information: WMV, MOV, MP4, MPEG.
Example standards for representing text information: doc, xls, txt, pdf.
Functions of the presentation layer
- It formats and presents data and information.
- It encrypts and compresses data before giving it to the session layer.
- It de-encrypts and decompresses the encrypted and compressed data it receives from the session layer.
Session layer
The session layer is the fifth layer of the OSI layers model. It is responsible for initiating, establishing, managing, and terminating sessions between the local application and the remote applications.
It defines standards for three modes of communication: full duplex, half-duplex, and simplex.

In the full duplex mode, both devices can send and receive data simultaneously. The internet connection is an example of the full duplex mode.
In the half duplex mode, only one device can send data at a time. A telephone conversation is an example of the half-duplex mode.
In the simplex mode, only one device can send data. A radio broadcast is an example of the simplex mode.
Functions of the session layer
- It is responsible for terminating sessions, creating checkpoints, and recovering data when sessions are interrupted.
- It opens and maintains logical communication channels between network applications running on the local host and network applications running on the remote host.
- If a network application uses an authentication mechanism before it opens a logical communication channel (session) with the remote host, it handles the authentication process.
Examples of the session layer
Structure Query Language (SQL), Remote Procedure Call (RPC), and Network File System (NFS) are examples of the session layer.
By ComputerNetworkingNotes Updated on 2023-10-30 05:30:01 IST
ComputerNetworkingNotes CCNA Study Guide Presentation layer and Session layer of the OSI model
We do not accept any kind of Guest Post. Except Guest post submission, for any other query (such as adverting opportunity, product advertisement, feedback, suggestion, error reporting and technical issue) or simply just say to hello mail us [email protected]

How-To Geek
The 7 osi networking layers explained.
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) networking model defines a conceptual framework for communications between computer systems.
Quick Links
- Physical Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) networking model defines a conceptual framework for communications between computer systems. The model is an ISO standard which identifies seven fundamental networking layers, from the physical hardware up to high-level software applications.
Each layer in the model handles a specific networking function. The standard helps administrators to visualize networks, isolate problems, and understand the use cases for new technologies. Many network equipment vendors advertise the OSI layer that their products are designed to slot into.
OSI was adopted as an international standard in 1984. It remains relevant today despite the changes to network implementation that have occurred since first publication. Cloud, edge, and IoT can all be accommodated within the model.
In this article, we'll explain each of the seven OSI layers in turn. We'll start from the lowest level, labelled as Layer 1.
1. Physical Layer
All networking begins with physical equipment. This layer encapsulates the hardware involved in the communications, such as switches and cables. Data is transferred as a stream of binary digits - 0 or 1 - that the hardware prepares from input it's been fed. The physical layer specifies the electrical signals that are used to encode the data over the wire, such as a 5-volt pulse to indicate a binary "1."
Errors in the physical layer tend to result in data not being transferred at all. There could be a break in the connection due to a missing plug or incorrect power supply. Problems can also arise when two components disagree on the physical encoding of data values. In the case of wireless connections, a weak signal can lead to bit loss during transmission.
2. Data Link Layer
The model's second layer concerns communication between two devices that are directly connected to each other in the same network. It's responsible for establishing a link that allows data to be exchanged using an agreed protocol. Many network switches operate at Layer 2.
The data link layer will eventually pass bits to the physical layer. As it sits above the hardware, the data link layer can perform basic error detection and correction in response to physical transfer issues. There are two sub-layers that define these responsibilities: Logical Link Control (LLC) that handles frame synchronization and error detection, and Media Access Control (MAC) which uses MAC addresses to constrain how devices acquire permission to transfer data.
3. Network Layer
The network layer is the first level to support data transfer between two separately maintained networks. It's redundant in situations where all your devices exist on the same network.
Data that comes to the network layer from higher levels is first broken up into packets suitable for transmission. Packets received from the remote network in response are reassembled into usable data.
The network layer is where several important protocols are first encountered. These include IP (for determining the path to a destination), ICMP, routing, and virtual LAN. Together these mechanisms facilitate inter-network communications with a familiar degree of usability. However operations at this level aren't necessarily reliable: messages aren't required to succeed and may not necessarily be retried.
4. Transport Layer
The transport layer provides higher-level abstractions for coordinating data transfers between devices. Transport controllers determine where data will be sent and the rate it should be transferred at.
Layer 4 is where TCP and UDP are implemented, providing the port numbers that allow devices to expose multiple communication channels. Load balancing is often situated at Layer 4 as a result, allowing traffic to be routed between ports on a target device.
Transport mechanisms are expected to guarantee successful communication. Stringent error controls are applied to recover from packet loss and retry failed transfers. Flow control is enforced so the sender doesn't overwhelm the remote device by sending data more quickly than the available bandwidth permits.
5. Session Layer
Layer 5 creates ongoing communication sessions between two devices. Sessions are used to negotiate new connections, agree on their duration, and gracefully close down the connection once the data exchange is complete. This layer ensures that sessions remain open long enough to transfer all the data that's being sent.
Checkpoint control is another responsibility that's held by Layer 5. Sessions can define checkpoints to facilitate progress updates and resumable transmissions. A new checkpoint could be set every few megabytes for a file upload, allowing the sender to continue from a particular point if the transfer gets interrupted.
Many significant protocols operate at Layer 5 including authentication and logon technologies such as LDAP and NetBIOS. These establish semi-permanent communication channels for managing an end user session on a specific device.
6. Presentation Layer
The presentation layer handles preparation of data for the application layer that comes next in the model. After data has made it up from the hardware, through the data link, and across the transport, it's almost ready to be consumed by high-level components. The presentation layer completes the process by performing any formatting tasks that may be required.
Decryption, decoding, and decompression are three common operations found at this level. The presentation layer processes received data into formats that can be eventually utilized by a client application. Similarly, outward-bound data is reformatted into compressed and encrypted structures that are suitable for network transmission.
TLS is one major technology that's part of the presentation layer. Certificate verification and data decryption is handled before requests reach the network client, allowing information to be consumed with confidence that it's authentic.
7. Application Layer
The application layer is the top of the stack. It represents the functionality that's perceived by network end users. Applications in the OSI model provide a convenient end-to-end interface to facilitate complete data transfers, without making you think about hardware, data links, sessions, and compression.
Despite its name, this layer doesn't relate to client-side software such as your web browser or email client. An application in OSI terms is a protocol that caters for the complete communication of complex data through layers 1-6.
HTTP, FTP, DHCP, DNS, and SSH all exist at the application layer. These are high-level mechanisms which permit direct transfers of user data between an origin device and a remote server. You only need minimal knowledge of the workings of the other layers.
The seven OSI layers describe the transfer of data through computer networks. Understanding the functions and responsibilities of each layer can help you identify the source of problems and assess the intended use case for new components.
OSI is an abstract model that doesn't directly map to the specific networking implementations commonly used today. As an example, the TCP/IP protocol works on its own simpler system of four layers: Network Access, Internet, Transport, and Application. These abstract and absorb the equivalent OSI layers: the application layer spans OSI L5 to L7, while L1 and L2 are combined in TCP/IP's concept of Network Access.
OSI remains applicable despite its lack of direct real-world application. It's been around so long that it's widely understood among administrators from all backgrounds. Its relatively high level of abstraction has also ensured it's remained relevant in the face of new networking paradigms, many of which have targeted Layer 3 and above. An awareness of the seven layers and their responsibilities can still help you appreciate the flow of data through a network while uncovering integration opportunities for new components.
OSI Presentation and Application Layers
Cite this chapter.

- Paul D. Bartoli 3
Part of the book series: Applications of Communications Theory ((ACTH))
251 Accesses
This chapter discusses the Application and Presentation Layers of the Reference Model of Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) [1]. The Application and Presentation Layers perform functions necessary to exchange information between application processes; the Application Layer is concerned with the semantic aspects of the information exchange, while the Presentation Layer is concerned with the syntactic aspects. The ability to manage the semantic and syntactic elements of the information to be exchanged is key to ensuring that the information can be interpreted by the communicants.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
ISO 7498, “Information processing systems—Open Systems Interconnection—Basic Reference Model,” 1984. CCITT Recommendation X.200, “Reference model of open systems interconnection for CCITT applications,” 1984 (updated expected in 1988).
Google Scholar
ISO DIS 9545, “Information processing systems—Open Systems Interconnection—Application Layer structure,” September 1988.
ISO TR 9007, “Concepts and terminology for the conceptual schema and the information base,” 1985.
ISO 8649, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Service definition for the association control service element,” 1988. ISO 8650, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Protocol specification for the association control service element,” 1988. CCITT Recommendation X.217, “Association control service definition for open systems interconnection for CCITT applications,” 1988. CCITT Recommendation X.227, “Association control protocol specification for open systems interconnection for CCITT applications,” final text December, 1987.
ISO 8571, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—File transfer, access, and management,” Parts 1–4, 1988.
ISO/DIS 9804, “Information processing systems”Open systems interconnection—Service definition for commitment, concurrency, and recovery,” 1988 (text in SC 21 N 2573, March, 1988). ISO DIS 9805, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Protocol specification for commitment, concurrency, and recovery,” 1988 (text in SC 21 N 2574, March, 1988). CCITT Recommendation X.237, “Commitment, concurrency, and recovery service definition,” Draft Text, 1988. CCITT Recommendation X.247, “Commitment, concurrency, and recovery protocol specification, Draft Text, 1988.
ISO DIS 9040, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Virtual terminal service—Basic class,” 1988 (text in SC 21 N 2615, March, 1988). ISO DIS 9041, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Virtual terminal protocol—Basic class,” 1988 (text in SC 21 N 2616, March, 1988).
ISO DIS 9066–1, “Reliable transfer service”, 1988 (text in SC 18 N 1408, March, 1988). ISO DIS 9066–2, “Reliable transfer protocol specification,” 1988 (text in SC 18 N 1409). CCITT Recommendation X.218, “Reliable transfer: Model and service definition,” 1988. CCITT Recommendation X.228, “Reliable transfer: Protocol specification,” 1988.
ISO DIS 9072–1, “Remote operations service,” 1988 (text in SC 18 N 1410, March, 1988). ISO DIS 9072–2, “Remote operations protocol specification,” 1988 (text in SC 18 N 1411, March, 1988). CCITT Recommendation X.219, “Remote operations: Model, notation, and service definition,” 1988. CCITT Recommendation X.229, “Remote operations: Protocol specification,” 1988.
ISO DIS 9594, “Information processing—Open systems interconnection—The directory,” parts 1–8, 1988 (text in SC 21 N 2751 through N 2758, April, 1988). CCITT X.500, “Series recommendations on directory,” November, 1987.
ISO DIS 10021, “Information processing—Text communication—Message oriented text interchange system,” 1988 (text in SC 18 N 1487 through N 1493, May, 1988). CCITT X.400, “Series recommendations for message handling systems,” 1988.
ISO 8613/1–8, “Office document architecture and interchange format,” 1988, awaiting publication. CCITT T.400, “Series recommendations for document architecture, transfer, and manipulation,” 1988.
ISO 8824, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Specification of abstract syntax notation one (ASN.1),” 1987; and ISO 8824/PDAD 1, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Specification for ASN.1: Proposed draft Addendum 1 on ASN.1 extensions,” 1988 (final text in SC 21 N 2341 Revised, April, 1988). CCITT Recommendation X.208, “Specification of abstract syntax notation one (ASN.1),” 1988.
ISO 8822, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Connection oriented presentation service definition,” 1988. CCITT Recommendation X.216, “Presentation service definition for open systems interconnection for CCITT applications,” 1988.
ISO 8825, “Information processing—Open systems interconnection—Specification of basic encoding rules for abstract syntax notation one (ASN.1),” 1987; and ISO 8825/ PDAD 1, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Specification of basic encoding rules for ASN.1: Proposed draft addendum 1 on ASN.1 extensions,” 1988 (text in SC 21 N 2342 Revised, April, 1988). CCITT Recommendation X.209, “Specification of basic encoding rules for abstract syntax notation one (ASN.1),” 1988.
ISO 8823, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Connection oriented presentation protocol specification,” 1988. CCITT Recommendation X.226, “Presentation protocol specification for open systems interconnection for CCITT applications,” 1988.
ISO 8326, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Basic connection oriented session service definition,” 1987; and ISO 8326/AD 2, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Basic connection oriented session service definition—Addendum 2: Incorporation of unlimited user data,” 1988. ISO 8327, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Basic connection oriented session protocol specification,” 1987; and ISO 8327/AD 2, “Information processing systems—Open systems interconnection—Basic connection oriented session protocol specification—Addendum 2: Unlimited session user data protocol specification,” 1988.
CCITT Recommendation X.215, “Session service definition for open systems interconnection for CCITT applications,” 1988. CCITT Recommendation X.225, “Session protocol specification for open systems interconnection for CCITT applications,” 1988.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
AT&T Bell Laboratories, 07733, Holmdel, New Jersey, USA
Paul D. Bartoli
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Unisys West Coast Research Center, Santa Monica, 90406, California, USA
Carl A. Sunshine
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions

Copyright information
© 1989 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Bartoli, P.D. (1989). OSI Presentation and Application Layers. In: Sunshine, C.A. (eds) Computer Network Architectures and Protocols. Applications of Communications Theory. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-0809-6_13
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-0809-6_13
Publisher Name : Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN : 978-1-4612-8093-4
Online ISBN : 978-1-4613-0809-6
eBook Packages : Springer Book Archive
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

DEV Community
Posted on Jan 22, 2021 • Originally published at educative.io
What is the OSI Model? 7 layers explained in detail
Networking is a vast topic. The OSI model helps us better understand it. In this article, we will cover the OSI model. The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a conceptual framework that describes the functions of a networking or telecommunication system in seven layers.
The OSI model describes how a network functions and standardizes the way that systems send information to one another. In this article, we will introduce you to the OSI model and discuss each layer in detail.
What is the OSI Model?
Developed in 1984, the Open Systems Interconnection or OSI model is a seven-layer model used to describe networking connections. It was initially developed by ISO, the International Organization for Standardization in 1984 and is now common practice for learning networking concepts.
The OSI models specifies how information is transmitted from a network device like a router to its destination through a physical medium and how it interacts with the application. In other words, it provides a standard for different systems to communicate with each other.

We will go through the different layers in detail below, but keep in mind that the upper layers (first 4) are about transport issues like the physical characteristics of the network and data transmission. The lower layers (last 3) are about application issues like data formatting and user interfacing.
Why should you learn this?
Some people argue that the OSI model is obsolete because it is less important than the four layers of the TCP/IP model, but this is not true. The OSI model is essential theory for understanding modern computer network technology in a connection-oriented way.
Most discussions on network communication include references to the OSI model and its conceptual framework.
The purpose of this model is to enhance interoperability and functionality between different vendors and connectors. It describes the functions of a networking system. From a design point of view, it divides larger tasks into smaller, more manageable ones.
The OSI model allows network administrators to focus on the design of particular layers. It is also useful when troubleshooting network problems by breaking them down and isolating the source.
Layer 1: Physical Layer
At the lowest layer of the OSI reference model, the physical layer is responsible for transmitting unstructured data bits across the network between the physical layers of the sending and receiving devices. In other words, it takes care of the transmission of raw bit streams.
The physical layer may include physical resources like cables, modems, network adapters, and hubs, etc.
Layer 2: Data Link Layer
The data link layer corrects any errors that may have occurred at the physical layer. It ensures that any data transfer is error-free between nodes over the physical layer. It is responsible for reliable transmission of data frames between connected nodes.
The data is packaged into frames here and transferred node-to-node. The data layer has the following sub-layers
- Media Access Control (MAC): The MAC address layer is responsible for flow control and multiplexing devices transmissions over the network.
- Logical link control (LLC): The LLC layer provides error control and flow control over the physical medium and identifies line protocols.
Layer 3: Network Layer
The network layer receives frames from the data link layer and delivers them to the intended destination based on the addresses inside the frame. It also handles packet routing. The network layer locates destinations using logical addresses like the IP. Routers are a crucial component at this layer as they route information to where it needs to go between different networks.
The main functions of the Network layer are:
- Routing: The network layer protocols determine which routes from source to destination.
- Logical Addressing: The network layer defines an addressing scheme to uniquely identify devices. The network layer places the IP addresses from the sender and receiver in the header.
Layer 4: Transport Layer
The transport layer is responsible for delivering, error checking, flow control , and sequencing data packets . It regulates the sequencing, size, and transfer of data between systems and hosts. It gets the data from the session layer and breaks it into transportable segments.
Two examples of the Transport Layer are the UDP (User Datagram Protocol) and TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) that is build on top of the Internet Protocol (IP model), which work at layer 3.
Layer 5: Session Layer
The session layer will create communication channels, called sessions , between different devices. This layer is responsible for opening those sessions and ensuring that they're functional during data transfer.
In other words, the session layer is responsible for establishing, managing, and terminating communication sessions with the lower layers with the presentation and application layer. It is also responsible for authentication and reconnections, and it can set checkpoints during a data transfer—if.
Layer 6: Presentation Layer
The presentation layer is responsible for ensuring that the data is understandable for the end system or useful for later stages. It translates or formats data based on the application's syntax or semantics. It also manages any encryption or decryption required by the application layer. It is also called the syntax layer .
Layer 7: Application Layer
The application layer is where the user directly interacts with a software application, so it is closest to the end user . When the user wants to transmit files or pictures, this layer interacts with the application communicating with the network. The application layer identifies resources, communication partners, and synchronizes communication.
Other functions of the application layer are the Network Virtual Terminal and FTAM-File transfer access, and mail/directory services. The protocol used depends on the information the user wants to send. Some common protocols include:
- POP3 or SMTP for emails
- FTP for emails
- Telnet for controlling remote devices
Examples of communications that use Layer 7 are web browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari).
Data flow example
Here is how data flows through the OSI model. Let's say you send an email to a friend. Your email passes through the application layer to the presentation layer . This layer will compress your data.
Next, the session layer initializes communication. It will then be segmented in the transportation layer, broken up into packets in the network layer, and then into frames at the data link layer. It will then be sent to the physical layer where it is converted to 0s and 1s and sent through a physical medium like cables.
When your friend gets the email through the physical medium, the data flows through the same layers but in the opposite order . The physical layer will convert the 0s and 1s to frames that will be passed to the data link layer. This will reassemble the frames into packets for the next layer.
The network layer will assemble the segments into data. The data is then passed on to the presentation layer that ends the communication session. The presentation layer will then pass the data to the application layer. The application layer feeds the human-readable data to the email software that will allow your friend to read your email.
What to learn next
Congratulations on making it to the end. I hope you now know what the OSI model is, how the OSI layers work, and why you need to know about it. These concepts are essential for understanding how networks function.
This was just the beginning, and there is a lot you can learn. You can start with:
- Access networks
- Socket programming
To get hands on with these concepts, check out Educative's course Grokking Computer Networking for Software Engineers. You will learn about networks, command-line tools, socket programming in Python, all in a hands-on environment. Any software engineer can benefit from a solid grasp on these concepts.
Happy learning!
Continue reading about networking
- Behind the Screens: What happens when you type a URL in a browser
- Computer Networking 101: Terms, Tools, and Getting Started
- Kerberos in 5 Minutes: Introducing network authentication
Top comments (3)
Templates let you quickly answer FAQs or store snippets for re-use.
- Email [email protected]
- Location MD
- Education Ramblin' wreck from Georgia Tech and 3/4 of an engineer
- Work Multifaceted Senior Engineer
- Joined Mar 26, 2019
Thanks for a great writeup. I consider myself a lot more network-knowledgeable than many developers I have worked with, but I really only ever end up dealing with Layer 4 or Layer 7 issues. Does anyone else have a different experience?
- Joined Feb 5, 2017
Layer 8 issues are the worst. ;-)
- Location Portugal
- Work Senior Software Engineer @ 25Friday
- Joined Apr 8, 2020
“All People Seem To Need Data Processing” is a good way to remember it! 🙂
Are you sure you want to hide this comment? It will become hidden in your post, but will still be visible via the comment's permalink .
Hide child comments as well
For further actions, you may consider blocking this person and/or reporting abuse

Embassy 下使用温湿度传感器
Jens - Apr 16

GoLang JWT Authentication Using Golang Gin Framework with MongoDB
codegirl - Apr 16

2nd State of Developer Wellness report
Developer Nation Survey - Apr 16

การทำนายโรคหลอดเลือดในสมองโดยใช้ XGBoost ใน python
Nattarika - Apr 16

We're a place where coders share, stay up-to-date and grow their careers.
- Network Fundamentals
- Network Cabling
- Ethernet Protocol
- TCP-UDP Protocol
- IP Protocol
- Supernetting & CIDR
- ICMP Protocol
- Domain Name System (DNS)
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- VLAN Networks
- Network Address Translation
- Cisco Routers
- Cisco Switches
- Cisco Firewalls
- Cisco Wireless
- Cisco CallManager-CCME
- Cisco Data Center (Nexus/UCS)
- Cisco Services & Technologies
- Palo Alto Networks
- F5 Networks
- SASE & SD-WAN
- Security Service Edge (SSE)
- Web Application Vulnerability Scanners
- VPN Services & Guides
- Windows Servers
- Windows Workstations (XP, 7, 8, 10, 11)
- Linux - Unix
- Virtualization & VM Backup
- OpManager - Network Monitoring & Management
- ManageEngine Firewall Analyzer
EventLog Analyzer
- Network Protocol Analyzers
- IP PBX - Unified Communications
- Security Articles
- Reviews & Interviews
- GFI Network Security
- OpenMosix - Linux Supercomputer
- More Reading
All-in-one protection

Free Download
Ransomware protection.

Download Now!

Free Download!
Get 2 vms for free.

Manage your Network!
The osi model: layer 6 - presentation layer.
The Presentation Layer gets its name from its purpose: It presents data to the Application layer. It's basically a translator and provides coding and conversion functions. A successful data transfer technique is to adapt the data into a standard format before transmission. Computers are configured to receive this generically formatted data and then convert the data back into its native format for reading. By providing translation services, the Presentation layer ensures that data transferred from the Application layer of one system can be read by the Application layer of another host.
JPEG: The Joint Photographic Experts Group brings these photo standards to us.
MIDI: The Musical Intrument Digital Interface is used for digitized music.
MPEG: The Moving Pictures Experts Group's standard for the compression and coding of motion video for CD's is very popular.
QuickTime: This is for use with Machintosh or Power PC programs, it manages audio and video applications.
The last 3 layers of the OSI model are reffered to the "Upper" layers. These layers are responsible for applications communicating between hosts. None of the upper layers know anything about networking or network addresses.
There are no protocols which work specificly at the Presentation layer, but the protocols which work at the Application layer are said to work on all 3 upper layers.
Next: The OSI Model: Layer 7 - Application Layer
Your IP address:
81.177.182.174
- All-in-one protection for Microsoft 365

FREE Hyper-V & VMware Backup

Wi-Fi Key Generator
Follow firewall.cx.
Please enable the javascript to submit this form
Network and Server Monitoring

Recommended Downloads
- Network Management - Monitor & Alert
- Free Hyper-V & VMware Backup
Bandwidth Monitor
- Patch Manager Plus
Firewall Analyzer
Cisco password crack.
Decrypt Cisco Type-7 Passwords on the fly!
Decrypt Now!

Free PatchManager

Related Articles
The osi model: layer 5 - session layer, data encapsulation & decapsulation in the osi model, the osi model: layer 3 - network layer, the osi model: layer 2 - datalink layer, the osi model: layer 1 - physical layer.
COMPUTER NETWORK BASICS
- Introduction To Computer Networks
- Uses of Computer Networks
- Line Configuration
- Types of Network Topology
- Transmission Modes
- Transmission Mediums
- Bounded/Guided Transmission Media
- UnBounded/UnGuided Transmission Media
- Types of Communication Networks
- Connection Oriented and Connectionless Services
- Network Layer
- Quality of Service(QoS)
- IGMP Protocol
- Reference Models
- Physical Layer
- Digital Transmission
- Multiplexing
- Circuit-Switched
- Message-Switched Networks
- Packet Switching
Data link layer
- Error Correction
- Data Link Control
- Flow and Error
- Simplest Protocol
- Stop-and-Wait Protocol
- Go-Back-N Automatic Repeat
- Sliding Window Protocol
- HDLC Protocol
- Point-to-Point Protocol
- Multiple Access in DL
- Channelization Protocols
- Gigabit Ethernet
- Random Access Protocol
- Controlled Access Protocols
- Carrier Sense Multiple Access
Transport layer
- Transport Layer
- Telnet vs SSH
- UDP Protocol
- TCP - Protocol
ISO/OSI REFERENCE MODEL
- Introduction to Reference Models
- OSI Model: Physical Layer
- OSI Model: Datalink Layer
- OSI Model: Network Layer
- OSI Model: Transport Layer
- OSI Model: Session Layer
- OSI Model: Presentation Layer
- OSI Model: Application Layer
TCP/IP REFERENCE MODELCOMPUTER NETWORKS
- The TCP/IP Reference Model
- Difference between OSI and TCP/IP Model
- Key Terms - Computer Network
Session layer
- Session Layer
Computer Networks
- Components of Computer Networks
- Features of Computer Network
- Protocols and Standards
- Connection Oriented and Connectionless
- OSI Vs TCP/IP
Presentation layer
- Presentation Layer
Application layer
- HTTP Protocol
- FTP Protocol
- SMTP Protocol
- POP Protocol
- SNMP Protocol
- Electronic Mail
- MIME Protocol
- World Wide Web
- DNS Protocol
The OSI Model - Features, Principles and Layers
There are n numbers of users who use computer network and are located over the world. So to ensure, national and worldwide data communication, systems must be developed which are compatible to communicate with each other ISO has developed a standard. ISO stands for International organization of Standardization . This is called a model for Open System Interconnection (OSI) and is commonly known as OSI model.
The ISO-OSI model is a seven layer architecture. It defines seven layers or levels in a complete communication system. They are:
- Application Layer
- Datalink Layer
Below we have the complete representation of the OSI model, showcasing all the layers and how they communicate with each other.
In the table below, we have specified the protocols used and the data unit exchanged by each layer of the OSI Model.
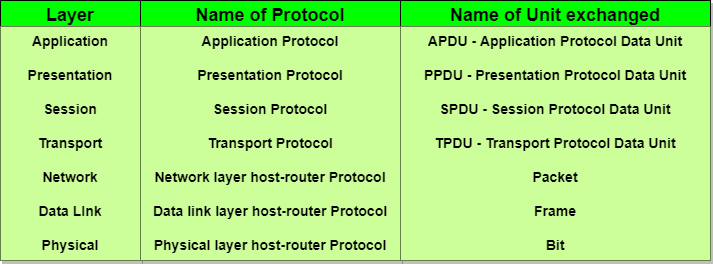
Feature of OSI Model
- Big picture of communication over network is understandable through this OSI model.
- We see how hardware and software work together.
- We can understand new technologies as they are developed.
- Troubleshooting is easier by separate networks.
- Can be used to compare basic functional relationships on different networks.
Principles of OSI Reference Model
The OSI reference model has 7 layers. The principles that were applied to arrive at the seven layers can be briefly summarized as follows:
- A layer should be created where a different abstraction is needed.
- Each layer should perform a well-defined function.
- The function of each layer should be chosen with an eye toward defining internationally standardized protocols.
- The layer boundaries should be chosen to minimize the information flow across the interfaces.
- The number of layers should be large enough that distinct functions need not be thrown together in the same layer out of necessity and small enough that architecture does not become unwieldly.
Functions of Different Layers
Following are the functions performed by each layer of the OSI model. This is just an introduction, we will cover each layer in details in the coming tutorials.
OSI Model Layer 1: The Physical Layer
- Physical Layer is the lowest layer of the OSI Model.
- It activates, maintains and deactivates the physical connection.
- It is responsible for transmission and reception of the unstructured raw data over network.
- Voltages and data rates needed for transmission is defined in the physical layer.
- It converts the digital/analog bits into electrical signal or optical signals.
- Data encoding is also done in this layer.
OSI Model Layer 2: Data Link Layer
- Data link layer synchronizes the information which is to be transmitted over the physical layer.
- The main function of this layer is to make sure data transfer is error free from one node to another, over the physical layer.
- Transmitting and receiving data frames sequentially is managed by this layer.
- This layer sends and expects acknowledgements for frames received and sent respectively. Resending of non-acknowledgement received frames is also handled by this layer.
- This layer establishes a logical layer between two nodes and also manages the Frame traffic control over the network. It signals the transmitting node to stop, when the frame buffers are full.
OSI Model Layer 3: The Network Layer
- Network Layer routes the signal through different channels from one node to other.
- It acts as a network controller. It manages the Subnet traffic.
- It decides by which route data should take.
- It divides the outgoing messages into packets and assembles the incoming packets into messages for higher levels.
OSI Model Layer 4: Transport Layer
- Transport Layer decides if data transmission should be on parallel path or single path.
- Functions such as Multiplexing, Segmenting or Splitting on the data are done by this layer
- It receives messages from the Session layer above it, convert the message into smaller units and passes it on to the Network layer.
- Transport layer can be very complex, depending upon the network requirements.
Transport layer breaks the message (data) into small units so that they are handled more efficiently by the network layer.
OSI Model Layer 5: The Session Layer
- Session Layer manages and synchronize the conversation between two different applications.
- Transfer of data from source to destination session layer streams of data are marked and are resynchronized properly, so that the ends of the messages are not cut prematurely and data loss is avoided.
OSI Model Layer 6: The Presentation Layer
- Presentation Layer takes care that the data is sent in such a way that the receiver will understand the information (data) and will be able to use the data.
- While receiving the data, presentation layer transforms the data to be ready for the application layer.
- Languages(syntax) can be different of the two communicating systems. Under this condition presentation layer plays a role of translator.
- It perfroms Data compression, Data encryption, Data conversion etc.
OSI Model Layer 7: Application Layer
- Application Layer is the topmost layer.
- Transferring of files disturbing the results to the user is also done in this layer. Mail services, directory services, network resource etc are services provided by application layer.
- This layer mainly holds application programs to act upon the received and to be sent data.
Merits of OSI reference model
- OSI model distinguishes well between the services, interfaces and protocols.
- Protocols of OSI model are very well hidden.
- Protocols can be replaced by new protocols as technology changes.
- Supports connection oriented services as well as connectionless service.
Demerits of OSI reference model
- Model was devised before the invention of protocols.
- Fitting of protocols is tedious task.
- It is just used as a reference model.
- ← Prev
- Next →
CN MCQ Tests
gate interview tests.

Computer Network
- Operating Systems
- Computer Fundamentals
- Interview Q
Physical Layer
Data link layer, network layer, routing algorithm, transport layer, application layer, application protocols, network security.
Interview Questions
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share

Learn Latest Tutorials
Transact-SQL
Reinforcement Learning
R Programming
React Native
Python Design Patterns
Python Pillow
Python Turtle
Preparation

Verbal Ability

Company Questions
Trending Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Cloud Computing
Data Science
Machine Learning
B.Tech / MCA
Data Structures
Operating System
Compiler Design
Computer Organization
Discrete Mathematics
Ethical Hacking
Computer Graphics
Software Engineering
Web Technology
Cyber Security
C Programming
Control System
Data Mining
Data Warehouse

No matching records found. Please try changing the filter settings.
- Standards catalogue
- 35.100.60 - Presentation layer

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Prerequisite : OSI Model. Introduction : Presentation Layer is the 6th layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. This layer is also known as Translation layer, as this layer serves as a data translator for the network. The data which this layer receives from the Application Layer is extracted and manipulated here as per the required ...
The presentation layer is the lowest layer at which application programmers consider data structure and presentation, instead of simply sending data in the form of datagrams or packets between hosts. This layer deals with issues of string representation - whether they use the Pascal method (an integer length field followed by the specified ...
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the presentation layer is layer 6 and serves as the data translator for the network. It is sometimes called the syntax layer. Description. Within the service layering semantics of the OSI network architecture, the presentation layer responds to service requests from the application layer and ...
The Presentation Layer is a crucial component of the OSI model, responsible for ensuring that data exchanged between systems is in a format that can be understood and used. By performing functions such as data translation, formatting, compression, and encryption, the Presentation Layer plays a vital role in maintaining data integrity ...
The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a reference model from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that "provides a common basis for the coordination of standards development for the purpose of systems interconnection." In the OSI reference model, the communications between systems are split into seven different abstraction layers: Physical, Data Link ...
Chloe Tucker. This article explains the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model and the 7 layers of networking, in plain English. The OSI model is a conceptual framework that is used to describe how a network functions. In plain English, the OSI model helped standardize the way computer systems send information to each other.
The presentation layer is the sixth layer in the OSI model. Known as a translator, the presentation layer converts data into an accurate, well-defined, standard format after it receives it from the application layer. The converted format varies, however, based on the type of data received. Some formats include:
Learn the seven layers of the OSI model and the functions of each layer in detail through examples. ... It was published in 1984 by ISO (International Organization for Standardization). ... The sixth layer of the OSI model is the Presentation layer. Applications running on the local system may or may not understand the format that is used to ...
The presentation layer is the sixth layer of the OSI Reference model. It defines how data and information is transmitted and presented to the user. It translates data and format code in such a way that it is correctly used by the application layer. It identifies the syntaxes that different applications use and formats data using those syntaxes.
Data Link Layer. Network Layer. Transport Layer. Session Layer. Presentation Layer. Application Layer. Summary. The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) networking model defines a conceptual framework for communications between computer systems. The model is an ISO standard which identifies seven fundamental networking layers, from the physical ...
The presentation layer in the OSI model has five main functions within the frame of presentation layer protocols. Character Code Translation A character code is a representation of text using a ...
Key functions of the Presentation Layer in the OSI model include: Data Encryption: It securely encrypts data to prevent unauthorized access during transmission. Data Compression: It reduces data ...
II. The Application Layer This section discusses the underlying assumptions and viewpoint that led to the development of the OSI Application Layer. The general structure of the Application Layer is presented [2]. This model describes how the Application and Presentation Layers cooperate to support the exchange of meaningful information between ...
Developed in 1984, the Open Systems Interconnection or OSI model is a seven-layer model used to describe networking connections. It was initially developed by ISO, the International Organization for Standardization in 1984 and is now common practice for learning networking concepts. The OSI models specifies how information is transmitted from a ...
Presentation Layer - OSI Model. The primary goal of this layer is to take care of the syntax and semantics of the information exchanged between two communicating systems. Presentation layer takes care that the data is sent in such a way that the receiver will understand the information (data) and will be able to use the data.
The presentation layer is the sixth layer of the OSI model. It is primarily used to convert different file formats between the sender and the receiver.The OSI model is a reference model that is used to define communication standards between two devices within a network.The development of this standard began in the 1970s and it was first published at the beginning of the following decade.
The seven Open Systems Interconnection layers are the following. Layer 7. The application layer. The application layer enables the user -- human or software -- to interact with the application or network whenever the user elects to read messages, transfer files or perform other network-related tasks.
The OSI Model: Layer 6 - Presentation Layer. Article Reads:73274. The Presentation Layer gets its name from its purpose: It presents data to the Application layer. It's basically a translator and provides coding and conversion functions. A successful data transfer technique is to adapt the data into a standard format before transmission.
OSI Model Layer 1: The Physical Layer. Physical Layer is the lowest layer of the OSI Model. It activates, maintains and deactivates the physical connection. It is responsible for transmission and reception of the unstructured raw data over network. Voltages and data rates needed for transmission is defined in the physical layer.
The presentation layer is the 6 th layer from the bottom in the OSI model. This layer presents the incoming data from the application layer of the sender machine to the receiver machine. It converts one format of data to another format of data if both sender and receiver understand different formats; hence this layer is also called the ...
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a conceptual framework that divides network communications functions into seven layers. Sending data over a network is complex because various hardware and software technologies must work cohesively across geographical and political boundaries. The OSI data model provides a universal language for ...
Information technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Presentation service definition — Amendment 1: Efficiency enhancements. 60.60. ISO/IEC JTC 1. ISO/IEC 8822:1994/Amd 2:1998. Information technology — Open Systems Interconnection — Presentation service definition — Amendment 2: Nested connections functional unit.