

REPORTED SPEECH
Sep 09, 2014
1.17k likes | 2.53k Views
REPORTED SPEECH. CONTENTS. I. DEFINITION II. BASIC RULES 1. Tense changes a. Basic tense changes b. Other tense changes 2. Time and place changes 3. Pronoun changes 4. Reporting Verbs 5. Use of 'That' in reported speech 6. Indirect Questions III. PRACTICE. I. DEFINITION.
Share Presentation
- reported speech
- direct speech
- indirect speech
- change reported speech
- reported speech doesn

Presentation Transcript
CONTENTS • I. DEFINITION • II. BASIC RULES 1. Tense changes a. Basic tense changes b. Other tense changes 2. Time and place changes 3. Pronoun changes 4. Reporting Verbs 5. Use of 'That' in reported speech 6. Indirect Questions • III. PRACTICE
I. DEFINITION • Reported speech (also known as indirect speech) refers to a sentence reporting what someone has said. It is almost always used in spoken English. • Reported speech doesn't use quotation marks to enclose what the person said and it doesn't have to be word for word. • When we use reported speech, we are usually talking about the past (because obviously the person who spoke originally spoke in the past). The verbs therefore usually have to be in the past too. "I'm going to the cinema". He said he was going to the cinema.
II. BASIC RULES When changing from quoted speech to reported speech, several changes occur. In all sentences, the quotation marks and the comma immediately before the first quotation mark are removed. Next, the word "that" is usually inserted after the reporting verb (say, ask, told, etc.) Then, the subject pronoun is changed so that the meaning of the quote is not changed. Lastly, the tense of the verb is changed, or shifted. She said, "I'm teaching English online." She said she was teaching English online.
1. Tense changes a.Basic tense changes As a rule when you report something someone has said you go back a tense (the tense on the left changes to the tense on the right):
b. modals Modal verb forms also sometimes change: Note - There is no change to; could, would, should, might and ought to.
Things are slightly more complicated with imperatives.
You can use the present tense in reported speech if you want to say that something is still true i.e. my name has always been and will always be Lynne You can also use the present tense if you are talking about a future event.
2. Time and place changes Time and place references often have to change: • If the reported sentence contains an expression of time, you must change it to fit in with the time of reporting.
Examples: • I went to the theatre last night.He said he had gone to the theatre the night before. • I'm staying here until next week. He said he was staying there until the following week. • In addition if you report something that someone said in a different place to where you heard it, you must change the place (here) to the place (there). Example:
3. Pronoun changes • In reported speech, the pronoun often changes. For example: You also need to be careful with personal pronouns.They need to be changed according to the situation. You need to know the context. For example, there is possible confusion when you try to change reported speech to direct speech: She said she'd been waiting for hours. (Is she one person or two different people?) I told them they would have to ask permission. (Are we talking about two groups of people or only one?)
4. Reporting Verbs • Said, toldand asked are the most common verbs used in indirect speech. • We use “asked”to report questions: I asked Lynne what time the lesson started. • We use “told” with an object. Lynne told me she felt tired. • We usually use “said” without an object. Lynne said she was going to teach online. If “said” is used with an object we must include “to” Lynne said to methat she'd never been to China.
There are many other verbs we can use apart from said, told and asked. These include: Using them properly can make what you say much more interesting and informative. For example: He asked me to come to the party:
5. Use of 'That' in reported speech • In reported speech, the word “that” is often used. He told me that he lived in Greenwich. • However, “that” is optional. He told me he lived in Greenwich. • Note – “That” is never used in questions, instead we often use “if”. He asked me if I would come to the party.
6. Indirect Questions • Use verbs of speech for questions (asked, wondered, enquired, wanted to know, tried to find out, etc.) • Use question words (where, when, who, why, how, etc) instead of “that” • Change verb tenses, pronouns, and time expressions (just like reported statements) • Use question word + subject + verb word order (unlike a direct question)question word + subject + verb • He asked when they would arrive. • My friend asked if I was coming
THE END KOOL!!! THANKS FOR your Attention!!
- More by User

Reported Speech
Reported Speech. John says: “I like pizza.” John says (that) he likes pizza. John said (that) he liked pizza. Reported Speech. Change the pronouns Change the references to time Change the references toplace Employ the sequence of tenses. Checklist. Tom: “ I like driving fast cars.”
482 views • 13 slides

Reported Speech. When reporting speech, the tense usually changes. The tenses of the reported clause are usually moved back. Changing verb tenses:. Examples :. Changing pronouns, personal and possessive. Pronouns change (or not) depending on the view of the reporter. Direct Speech
1.68k views • 6 slides

Reported Speech. Reported Speech we use when we want to tell another person about a conversation that took place in the past. We often use reported speech to . . . 1. Give someone a telephone message. 2. Tell someone news that we heard from someone else:.
860 views • 20 slides

REPORTED SPEECH. ¿ Qué es “reported speech”?. “Is used to relay information about what someone said, without using a direct quote.” In other words… Tim said that he liked Shelby. Morgan said that she was going to ask Shelby out. Morgan said that she would fight Tim for Shelby.
375 views • 13 slides

Reported Speech . Discurso Indireto Colégio Salesiano Dom Bosco Campo Grande-MS, 15/04/2010 Alunas: Arianne, Clesmânya, Edilene, Janaína e Mayane. Nº: 06, 11, 16, 29, 43. 2º ano A – noturno. Orientadora: Eliana. Reported Speech.
543 views • 21 slides

REPORTED SPEECH. Reported Speech. Reported speech : K alimat tidak langsung yang digunakan untuk melaporkan kembali ucapan-ucapan yang diucapkan oleh si pembicara dalam waktu yang berbeda . Reported speech disebut juga indirect speech . Example
806 views • 15 slides

REPORTED SPEECH. Direct Speech. It is one way of relating what a person has said . In direct speech we repeat the original speaker’s exact words ‘I am going to Oxford with my parents tomorrow ,’ Ben said .
621 views • 22 slides

Reported Speech. Yesterday, I saw my friend Pamela! She told me that she got a new job!. What is it? How do you use it?. ...today. ...yesterday. Reported Speech is the grammar we use when we want to tell another person about a conversation that took place in the past.
3.92k views • 12 slides

DISCURSO DIRETO E INDIRETO. REPORTED SPEECH. É um discurso (fala) indireto, relatado, reportado. É empregado para se relatar o que uma pessoa falou, sem utilizar necessariamente as palavras dessa pessoa. * Fred said , “I work on Saturdays ”.- DD
473 views • 13 slides
Reported Speech. I. Introduction 1.1. Direct Speech vs Reported Speech . 1.2. Structure . II. General Changes 2.1. Tenses backshift . 2.2. Pronouns ( subject / object / possessive ) 2.3. Adverbs (time/place)
941 views • 10 slides

Reported Speech. About me. a) I’m stupid. I live far from here. I don’t live near here. b) I’ve been a teacher for a long time. c) I went to the library. I didn’t find much information. d) I will go to the movies next Saturday. e) I can’t drive a car.
572 views • 10 slides

Reported Speech. By teacher Silvino Sieben 3ª série EM. WW: “I’ m super powerful.” WW said (that) she was super powerful. WW: “I’ m not afraid of anything.” WW told me that she wasn’t afraid of anything. Jimmy: “I’ m not riding my bike.”
723 views • 7 slides

Reported speech
Reported speech. Reported Speech. Reported Speech. Reported Speech. Reported Speech – Tense changes. DIRECT SPEECH REPORTED SPEECH PRESENT-------------------------------------------------------------PAST
15.83k views • 20 slides

Reported Speech. Statements, commands and requests. Reported statements - intro. Look at these examples: The little prince: “ I want a sheep that will live for a long time.” The little prince said (that) he wanted a sheep that would live for a long time.
667 views • 16 slides

Reported Speech. Reporting verb in the present tense: Nothing changes from direct to indirect speech except pronouns and adverbs (I he/she, our their, here there etc.) „Their cars are too small“ He says that their cars are too small. „I have been over there for one wet spring“
1.41k views • 8 slides

Reported Speech. In direct speech we repeat exactly what someone said: He said 'I don't like football' In reported speech , however, we tell what someone said without repeating his exact words. He said (that) he didn't like football. Backshift. Reported Speech.
1.9k views • 33 slides

Reported speech. Reported speech is speech in which you report what somebody else said. The most common reporting verbs are say and tell. Say and tell. He said *** (that) he was hungry. He told me (that) he was hungry. He said me (that) he was hungry.
228 views • 12 slides

Reported Speech. I am very happy today. Susanna said (that) she was very happy that day. We use reported speech to talk about what someone said. When we report a statement, we have to:. take away the quotation marks. e.g ‘Some students are talking,’ said the teacher.
322 views • 12 slides

REPORTED SPEECH. Prepared by Belma BOYACIOGLU. Direct Speech. Reported Speech. “I work hard,” he said. He said (that) he worked hard. “I am working hard,” he said. He said (that) he was working hard. “I worked hard,” he said. He said (that) he (had) worked hard.
324 views • 6 slides

REPORTED SPEECH. Four Essential Things to Remember. The use of the tenses The change of the pronouns The change of time expressions The change of demonstrative pronouns (e.g. this, those, etc.). Present Simple Present Continuous Present Perfect Past Simple Past Continuous
498 views • 9 slides
Reported speech - questions and imperatives
Katarzyna Szymańska
Created on February 2, 2021
More creations to inspire you
History of the circus.
Presentation
LETTERING PRESENTATION
Spring has sprung, biden’s cabinet, vaccines & immunity, uncovering reality, las especies animales más amenazadas.
Discover more incredible creations here
QUESTIONS AND IMPERATIVES
Reported Speech
I BUMPED INTO AN OLD FRIEND LAST SUMMER. WE USED TO BE CLASSMATES IN HIGH SCHOOL. LET ME TELL YOU WHAT I ASKED HER
lAST SUMMER....
'DO YOU HAVE MANY CUSTOMERS?''IT'S A VERY POPULAR PLACE' - she replied
'WHAT DO YOU DO?' 'I OWN A SHOP WITH ECO FOOD' - she said proudly
'WHAT ARE YOU DOING HERE?''I'M VISITING MY PARENTS' - she said
'DO YOU LIVE IN GDAŃSK?''NOT REALLY. I LIVE IN WROCŁAW NOW - she replied
I HAD SO MANY QUESTIONS TO HER.I ASKED HER:
what did i ask? What did she reply? (click on the stars to find out)
'DO YOU LIVE IN GDAŃSK?' 'NOT REALLY. I LIVE IN WROCŁAW NOW '- she replied
what are the rules of reporting questions?
Do you like me? -> I asked him if he liked me Przytaczając pytania ogólne używamy 'if' albo 'whether' (czy). Przytaczane pytanie ma szyk zdania twierdzącego. Pamiętaj też o 'cofnięciu' czasu!W pytaniach szczegółowych zachowujemy zaimek pytający:When did you break up with her? ->-> I asked him when he had broken up with her.
'WHAT DO YOU DO FOR A LIVING?' 'I OWN A SHOP WITH ECO FOOD' - she said proudly
what did i ask my friend?report and click on the icon to check :-)
Call me! - she askeddon't eat gluten ;-) - she warned me.
if you need help with reported speech
Do you think everything the mansaid was appropriate?Report it and check on the next page
I went out on a date once...it was the first date.This is what i heard from my date:
- What's your job?- What food do you like?- Are you allergic to cats?- Do you have a boyfriend?- How old are you?- Kiss me.- Could you pay for me?- Don't talk so much.- Who are you texting? Stop that!
- What's your job? - He asked me what my job was. - What food do you like? - He wanted to know what food I liked - Are you allergic to cats? - He asked me if I was allergic to cats. - Do you have a boyfriend? - He asked me if I had a boyfriend - How old are you? - He wanted to know how old I was - Kiss me. - He told me to kiss him! - Could you pay for me? - He asked if I could pay for him. - Don't talk so much. - He told me not to talk so much. (Seriously??) - Who are you texting? Stop that! - He wanted to know who(m) I was texting. He ordered me to stop.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit
https://pixabay.com/pl/
Choose a picture from the website below.With a partner write a dilogue to it, including:- 6 questions- 6 sentences- 2 imperativesPost both the picture and the dialogue on Teams
An exercise
- English Grammar
- Clause structure and verb patterns
Reported speech
Level: intermediate
Reporting and summarising
When we want to report what people say, we don't usually try to report their exact words. We usually give a summary , for example:
Direct speech (exact words) :
Mary : Oh dear. We've been walking for hours! I'm exhausted. I don't think I can go any further. I really need to stop for a rest. Peter : Don't worry. I'm not surprised you're tired. I'm tired too. I'll tell you what, let's see if we can find a place to sit down, and then we can stop and have our picnic.
Reported speech (summary) :
When Mary complained that she was tired out after walking so far, Peter said they could stop for a picnic.
Reporting verbs
When we want to report what people say, we use reporting verbs . Different reporting verbs have different patterns, for example:
Mary complained (that) she was tired . (verb + that clause) She asked if they could stop for a rest . (verb + if clause) Peter told her not to worry . (verb + to -infinitive) He suggested stopping and having a picnic . (verb + - ing form)
See reporting verbs with that , wh- and if clauses , verbs followed by the infinitive , verbs followed by the -ing form .
GapFillDragAndDrop_MTY1NTE=
GapFillTyping_MTY1NTI=
Tenses in reported speech
When reporting what people say or think in English, we need to remember that the rules for tense forms in reported speech are exactly the same as in the rest of the language.
This is a letter that Andrew wrote ten years ago:
If we wanted to report what Andrew said in his letter, we might say something like this:
Andrew said that when he was 22, he was an engineering student in his last month at university. He wanted to travel abroad after he had finished his course at the university, but he would need to earn some money while he was abroad so he wanted to learn to teach English as a foreign language. A friend had recommended a course but Andrew needed more information, so he wrote to the school and asked them when their courses started and how much they were . He also wanted to know if there was an examination at the end of the course.
We would naturally use past tense forms to talk about things which happened ten years ago. So, tenses in reports and summaries in English are the same as in the rest of the language.
Sometimes we can choose between a past tense form and a present tense form. If we're talking about the past but we mention something that's still true , we can use the present tense:
John said he'd stayed at the Shangri-la because it' s the best hotel in town. Mary said she enjoyed the film because Robert de Niro is her favourite actor. Helen said she loves visiting New York.
or the past tense:
John said he'd stayed at the Shangri-la because it was the best hotel in town. Mary said she enjoyed the film because Robert de Niro was her favourite actor. Helen said she loved visiting New York.
If we're talking about something that everybody knows is true , we normally use the present tense :
Michael said he'd always wanted to climb Everest because it' s the highest mountain in the world. Mary said she loved visiting New York because it' s such an exciting city.
Hi! I found the following paragraph from a grammar site while I was studying the reported speech. Can you help me? It says; --> We can use a perfect form with have + -ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past: He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’)
And my question is: How do we understand if it is a hypothetical event in the past or not? We normally don't change 'might' in reported speech. (e.g. ‘It might snow tonight,’ he warned. --> He warned that it might snow that night.) But why do we say 'He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters.' instead of 'He said that the noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ What's the difference between these two indirect reported speeches? Could you please explain the difference? And I also found this example which is about the same rule above: --> He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: a) ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or b) ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’) Can you also explain why we report this sentence like that. How can we both change a) and b) into the same indirect reported speech? Thank you very much!
- Log in or register to post comments
Hello Melis_06,
1. He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. 2. He said that the noise might be the postman delivering letters.
In sentence 1 it is clear that the noise has ended; it is a noise that 'he' could hear but it is not a noise that you can hear now. In sentence 2 the noise could have ended or it could be a noise that you can still hear now. For example, if the noise is one which is constant, such as a noise that comes from your car engine that you are still trying to identify, then you would use sentence 2. In other words, sentence 2 allows for a wider range of time possibilities - both past (ended) and present (still current).
Your second question is similar:
He said he would have helped us if we needed a volunteer - you no longer need a volunteer
He said he would help us if we needed a volunteer - this could still be relevant; you may still need a volunteer.
The LearnEnglish Team
Hello my friend : what are you doing now? me : I'm eating an apple now and My friend repeated his question now
my question
Can I repeat the sentence in the past ( I was eating an apple) and mean( I'm eating an apple now) ?
You can but it is unusual. If you say I was eating an apple (past continuous), it means that it was in the past. You already finished eating the apple and you are not eating it now. But if your friend asked you just a moment ago, I guess you are still eating the apple when she/he asks the second question, so I would say I'm eating an apple (because you are still doing it).
Alternatively, you can use a past tense reporting verb e.g. I said I was eating an apple (referring to the time of the first question), or I said I 'm eating an apple (to show that you are still eating it now, at the moment of speaking).
LearnEnglish team
Am I correct then? When someone wants us to repeat the sentence we have just said a moment ago we say 'I said I am doing...' if we are still doing that action. But if we are done with that action, then we say 'I said I was doing...' Did I get it right? Thanks!
Hello Meldo,
Yes, that's correct. Well done!
Hi. I wish to enquire if the verb tense used after a conjunction also changes in complex sentences as per tense transition rules, especially if it is already in simple past tense. In order to explain, could you please solve the following for me: 1. It has been quite a while since I last saw you. 2. Nevertheless, she has been quite desensitized to such perverse actions to the extent that it seldom ever seems obnoxious to her. 3. Let me keep this in my cupboard lest I misplace this. 4. I had arrived at the station before you even left your house. 5. I met my grandfather before he died.
Hi Aamna bluemoon,
The verb may or may not be backshifted, depending on whether the original speaker's point of view and the reporter's point of view are the same or not. For example:
- She said it had been quite a while since she last saw me . (it seems relatively recent, for both the original speaker and the reporter)
- She said it had been quite a while since she had last seen us . (a lot of time has passed between speaking and reporting this, or the situation has changed a lot since then e.g. they have met frequently since then)
- She said she had met her grandfather before he died . (seems quite recent)
- She said she had met her grandfather before he'd died . (a lot of time has passed between speaking and reporting this)
I hope that helps.
Hi, can you help me, please? How could I report this famous quotation: 'There's no such things as good news in America'.
Hi bri.q630,
First of all, the sentence is not grammatically correct. The phrase is 'no such thing' (singular), not 'things'.
How you report it depends. Using 'said' as the reporting verb we have two possibilities:
1. They said (that) there's no such thing as good news in America. 2. They said (that) there was no such thing as good news in America.
Sentence 2 tells that only about the time when 'they' said it. It does not tell us if it is still true or not.
Sentence 1 tells us that what 'they' said is still relevant today. In other words there was no good news (in their opinion) when they spoke, and there is still no good news now.
Thank you Peter,
All things are getting clear to me.
So, you mean, I can use both sentences depending on what I want to indicate, can't I?
then the possible indications are bellow, are those correct?
1-a I remembered the World War 2 ended in 1945. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.)
1-b I remembered the World War 2 had ended in 1945. (This would be indicated I might missunderstand.)
2-a I felt time is money. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.)
2-b I felf time was money. (This would be indicated I might not feel any more.)
3-a I knew the sun rises in the east. (This would be indicated the statement is still true.)
3-b I knew the sun rase in the east. (This would be indicated I might misunderstand or forget.)
4-a I guessed* that Darth Vader is Luke's father. (This would be indicated I still believe he is.*sorry for the typo)
4-2 I guessed that Darth Vader was Luke's father. (This would be indicated I might know he is not.)
Thank you in advance.
Hello again Nobori,
1-a I remembered the World War 2 ended in 1945. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.) 1-b I remembered the World War 2 had ended in 1945. (This would be indicated I might missunderstand.)
Both forms are possible here. The 'ending' is a moment in the past; after this there is no war. By the way, we treat 'World War 2' as a name so there is no article before it.
2-a I felt time is money. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.) 2-b I felf time was money. (This would be indicated I might not feel any more.)
That's correct. Remember that backshifting the verb does not mean something is no longer true; it simply does not tell us anything about the present. Here, it tells the reader how you felt at a given moment in time; you may
3-a I knew the sun rises in the east. (This would be indicated the statement is still true.) 3-b I knew the sun rase in the east. (This would be indicated I might misunderstand or forget.)
That's also correct. Again, remember that backshifting the verb does not mean something is no longer true; it simply does not tell us anything about the present.
4-a I guessed* that Darth Vader is Luke's father. (This would be indicated I still believe he is.*sorry for the typo) 4-2 I guessed that Darth Vader was Luke's father. (This would be indicated I might know he is not.)
Again, correct. In the second example it might still be true that he is Luke's father, or it might have turned out to be not true. The sentence does not tell us.
Hi Peter, Thank you for your thoughtful answer. Allthing is now very clear to me. Best
Hi, I am translating a fiction novel into English and need your help regarding the reporting speech as for few things I am not getting any clear understanding over the internet. As you know in fiction, we need to write in non-ordinary way to create unique impressions of the word and academic writing is different than speaking. Will be grateful if you could give your insight below, especially considering in the context of fiction/academic writing.
1) Let’s say If someone is giving a speech or presentation, I want to mix their speech, indirect-direct and past tense- present tense. Below are three examples:
-He said, their company makes excellent profit every year OR their company made excellent profit every year ( can both be correct? As the sentence)
- Roger had given his speech yesterday. He said, their company makes excellent profit every year and your company will sustain for next hundred years.(Can YOUR be used in the sentence)
- Roger said people wants to feel important OR Roger said people wanted to feel important (which will be correct as this is a trait which is true in past and present)
2) He thought why he is talking to her OR He thought why he was talking to her (are both write? As usually I see in novels the second example with WAS)
3) Gia was sitting with Jake and she told him she had met with her last year. Her mother had taken her to the dinner. Her mother had told her about her future plans. Her mother also had paid the bill for the dinner. (Do I need to use every time past perfect in this example though it doesn’t feel natural? As a rule of thumb I think past perfect needs to be used when we talk about another past event in the past )
Hello Alamgir3,
We're happy to help with a few specific grammar questions, but I'm afraid we can't help you with your translation -- I'd suggest you find an editor for that.
1) In the second clause, you can use present or past. We often use the present when it's still true now, but the past is not wrong. FYI we don't normally use a comma after 'said' in reported speech.
2) 'Why was he talking to her?' he thought.
3) This is really more of a question of style than grammar. Here I would suggest doing something like combining the four sentences into two and then leaving out 'had' in the second verb in each sentence. Even if it isn't written, it's understood to be past perfect.
All the best, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Hello teachers, I'm sorry, I could not find where to new post. Could you tell me about the back-sifting of thoughts bellow? Which forms are correct?
1-a I remembered the World War 2 ended in 1945. 1-b I remembered the World War 2 had ended in 1945.
2-a I felt time is money. 2-b I felf time was money.
3-a I knew the sun rises in the east. 3-b I knew the sun rase in the east.
4-a I guess that Darth Vader is Luke's father. 4-2 I guessed that Darth Vader was Luke's father.
Do those questions have the same conclusion as indirect speech, such as say and tell?
Hello Nobori,
The verb form remains the same when we want to make it clear that the situation described by the verb is still true, and this works in the same way as indirect speech. For example:
She said she loves me. [she loved me then and she loves me still] She said she loved me. [she loved me then; no information on how she feels now]
Other than this rule, the choice is really contextual and stylistic (up to the speaker). Sometimes a choice implies something. For example, the saying 'time is money' is a general statement, so if you choose to backshift here the listener will know it is an intentional choice and suspect that something has changed (you no longer believe it).
Hi teachers, I've read almost the section of comments below and my summarize is the present tense only can be used if the statement is still true now and past simple only tells the statement was true in the past and doesn't tell the statement is true or not now. Just to make sure, I wanna ask, If I'm not sure whether the statement is still true or not now, can I choose backshift instead (this is still apply to past tense become past perfect)? Thank you
Hello rahmanagustiansyah,
It sounds to me as if you've got the right general idea. Could you please give a couple of example sentences that illustrate your question?
Thanks in advance, Kirk The LearnEnglish Team
For example, Steve said "Anna hates you." Then I wanna tell about that to my friend, but I'm not sure whether Anna still hates me or not now. What should I choose between these two options. Answer 1:Steve said Anna hates me or Answer 2 : Steve said Anna hated me. Thank you
Hi rahmanagustiansyah,
In that case, I would choose answer 2. I might even add "... but I don't know if she still does" to the sentence to clarify, if that is the key point you want to communicate.
Jonathan The LearnEnglish Team
Hello Natasa Tanasa,
Both sentences are grammatically possible.
The first sentence is only possible if when the person asks the original question the woman is no longer there (she has already gone). The second sentence can be used in this situation too, or in a situation in which the woman was still there when the original question was asked. As the past tense is used in the original question ( Who was... ), both sentences are possible.
Hello Ahmed Imam,
When the situation is still true at the time of reporting, we can leave the verb form unchanged. For example:
1. She told me she loved me.
2. She told me she loves me.
In sentence 1 we know she loved me when she told me but we don't know whether or not she loves me now. In sentence 2, we know she loved me when she told me and we know that she loves me now.
In your example, if the supermarket is still in the same place then we can use either form. If the supermarket has been closed down or moved to another location then we need to use was .
As for which is 'safer', you'll need to make your own mind up! Keeping the verb in the same form carries more specific information and that may be appropriate or even important.
Hello eugelatina87,
I'll give you a hint: a verb is missing from the question.
Does that help you complete it?
All the best,
The first two sentences are possible and they can both mean that he is still Mary's boyfriend now. The first one makes this more clear, but the second one doesn't only refer to the past.
Hello magnuslin
Regarding your first question, the most common way of saying it is the second one. In some very specific situation, perhaps the first option would be possible.
This also answers your second question. It is not necessary to always backshift using the tenses you mention.
As for your third question, no, it is not necessary. In fact, it is probably more common to use the past simple in the reported speech as well.
All the best
Hello manu,
Both forms are possible. If you use had been then we understand that he was there earlier but not when he said it - in other words, when he said it he had already left. If you use was then he may have left at the time of speaking, or he may have still been there.
Hello _princess_
I would recommend using answer a) because this is the general pattern used in reported speech. Sometimes the verb in the reported clause can be in the present tense when we are speaking about a situation that is still true, but the reported verb in the past tense can also have the same meaning. Since here the time referred to could be either past or present, I'd recommend using the past form.
Hello mwright,
This is an example of an indirect question. An indirect question reports a question, but is not a question itself, which is why we do not use a question mark at the end. Since it is not a question, we use the normal word order without inversion or auxiliary verbs. For example:
Indicative: He lives in Rome. Interrogative: Does he live in Rome? (Where does he live?) Reported: She asked if he lives in Rome. (She asked where he lives.)
Hello ahlinthit
There are different styles of punctuating direct speech -- in other words, you might find other sources that will disagree with me -- but what I would use here is something different: "The boss is dead!" said the doctor.
Hope this helps.
Best wishes
Hello Timmosky,
The form that comes after the auxiliary verb 'do' (or 'does' or 'did') is not the plural present simple verb, but rather the bare infinitive (also known as 'base form' or 'first form') of the verb. Does that make sense?
All the best, Kirk The LearnEnglish Team
Hello sky-high,
This is very formal language. The phrase 'to the effect that' means 'with the meaning that'. In this context it can be understood to mean 'with the result that'.
Best wishes,
The difference is quite logical. If we use 'said' then we are talking about a claim by Peter in the past which he may or may not still maintain. If we use 'says' then we are talking about an opinion expressed by Peter which he still holds.
The reported information (whether or not Rooney is in good shape) can refer to only the past or to the present as well and the statement (what Peter thinks) can separately refer to only the past or the present as well. Of course, all of this is from the point of view of the person reporting Peter's opinion, and whether or not they think that Peter still thinks now what he thought then.
Both are possible. If you use the present tense then it is clear that the statement is still true (i.e. the business was not growing when Mary spoke and is still not growing now). If you use the past tense then no information is given regarding the present (i.e. the business was growing when Mary spoke and may or may not be growing now).
Hello aseel aftab,
It should be 'if they had'. This is not from this page, is it? I don't see it anywhere here, but if I've missed it please let me know.
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
THE REPORTED SPEECH.
Published by Ronan Noe Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations

Presentation on theme: "THE REPORTED SPEECH."— Presentation transcript:

PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE

STATEMENTS QUESTIONS INSTRUCTIONS

Advance with English 牛津高中英语 (模块四 ·高一下学期).

TEACHING GRAMMAR Bui Thi Thao Truong Thuy Duong.
Grammar Review 4. Reported Speech.

a cura della prof.ssa Domitilla Gerini

Reported Speech Dragana Filipović. Direct Speech Quoting someone’s actual words: “I knew the answer,” he said. “Do you take sugar?” she asked. “Let’s.

REPORTED SPEECH.

Direct and Indirect Speech

REPORTED SPEECH USE FORM VERB CHANGES OTHER CHANGES EXAMPLES

Reporting. Introduction There are two main ways of reporting people’s words, thoughts, beliefs, etc. Direct Speech Indirect Speech.

REPORTED SPEECH I speak English..

UNIT 2 GIVING DIRECTIONS.

DIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH

Reported Speech Reported speech is often also called indirect speech. When we use reported speech, we are usually talking about the past (because obviously.

Have you ever been abroad? - Yes, I have. - No, I haven’t.

Elvis said, “I don’t know anything about music. In my line, you don’t have to”
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

- Grammar & vocab
Structures of reported questions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply

Your email address will not be published.
You may use these HTML tags and attributes: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
Notify me of new posts by email.
Related Posts
- Reported speech
- Upper-intermediate grammar exercise (B2 level): word order in reported speech sentences
- Structures of reported speech
- Verb structures in English
- Upper-intermediate grammar exercise (B2 level): reported speech
- Word order in indirect questions
- Qualifiers: how to sound more polite in a business meeting
- Intermediate grammar exercise (B1 level): present perfect simple or continuous 2
- Elementary grammar exercise (A1 level): present simple questions, negatives (do, does, don’t) ex. 2
- Intermediate grammar exercise (B1 level): word order in questions and indirect questions

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Click here to read more about our learning method
3 presidents, celebrity performances and protester interruptions at Biden campaign's $26M fundraiser
President Joe Biden was joined Thursday by two of his Democratic predecessors for a star-studded fundraiser at Radio City Music Hall that his campaign said brought in more than $26 million.
Former Presidents Barack Obama and Bill Clinton participated in the event in New York with more than 5,000 supporters in attendance — including several protesters who interrupted the program when the three presidents were speaking.
Actor and comedian Mindy Kaling hosted the program, which ended at around 10 p.m., and late night host Stephen Colbert moderated a conversation with Biden, Clinton and Obama. Special guests include celebrities like Queen Latifah, Lizzo , Ben Platt, Cynthia Erivo and Lea Michele.
During the nearly hourlong moderated conversation, Colbert joked that the moment was historic because “three presidents have come to New York, and not one of them to appear in court,” taking a jab at former President Donald Trump’s criminal indictments and civil trials.
Clinton also took a swipe at Trump, the presumptive GOP nominee, arguing that he "had a good couple of years because he stole them from Barack Obama.”
But the discussion was interrupted at least five times by protesters. Colbert acknowledged one protester and asked Biden about the U.S. role in ensuring a peaceful and prosperous future for both Israelis and Palestinians.
Biden said more needed to be done to get relief into Gaza but added that Israel's very existence was at stake.
"There has to be a train for a two-state solution," Biden said. "It doesn’t have to carry today. There has to be a progression. And I think we can do that."
His response was met with a standing ovation and chants of "four more years."
Obama sternly addressed a protester when he was interrupted, saying, "You can’t just talk and not listen."
"That’s part of democracy," Obama added. "Part of democracy is not just talking. It’s listening. That’s what the other side does, and it is important for us to understand that it is possible to have moral clarity and have deeply held beliefs but still recognize that the world is complicated and it is hard to solve these problems."
The crowd erupted in applause.
Biden’s team has taken steps to minimize disruptions , including making events smaller and withholding exact locations longer than usual, after a speech in January when pro-Palestinian protesters interrupted him about a dozen times.
Outside the New York venue Thursday, more than 100 pro-Palestinian protesters chanted slogans like “Biden, Biden, you’re a liar,” and waved Palestinian flags and signs with anti-war messages.
The group Abandon Biden encouraged people to protest the president during his visit over the White House’s handling of the Israel-Hamas war.
“We cannot idly sit by as our president aides and abets genocide in Gaza,” the group’s New York co-chair Mosaab Sadia said in a statement. “The movement to Abandon Biden is only just beginning.”

Inside Radio City Music Hall, the novelty of having three presidents in the same room was not lost on attendees.
Earlier in the program, Kaling joked about having Biden, Obama and Clinton in the same room, saying that when someone shouts “Mr. President,” three people turn around.
Ticket prices started at $250, but the largest contributions shot up to half a million dollars. Some of the biggest donors were to have their pictures taken with all three presidents by photographer Annie Leibovitz.
First lady Jill Biden called the program “the fundraiser to end all fundraisers.”
House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries, D-N.Y., and Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer, D-N.Y., also delivered remarks.
For the three presidents, the fundraiser capped off a day of mobilization efforts that included sitting for an interview with the podcast "SmartLess," which the White House said would be available at a later, unspecified date.
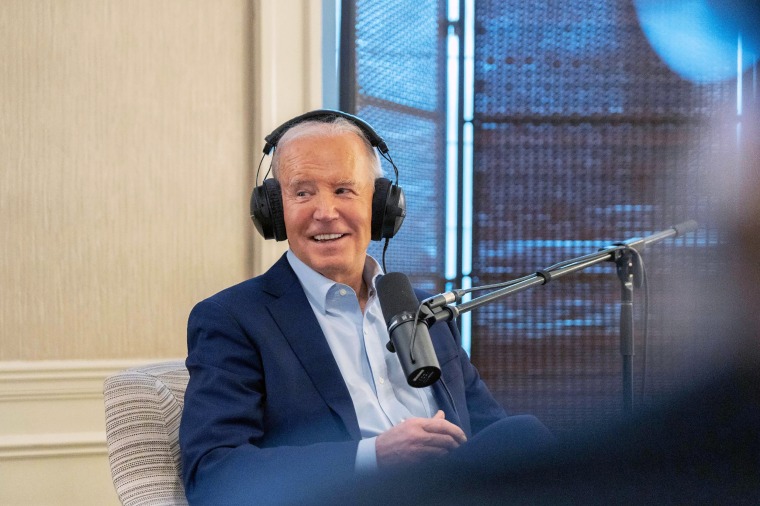

They also sat for a discussion with Biden's campaign manager, Julie Chavez Rodriguez, which was streamed to grassroots donors. The presidents talked about re-election efforts — both Clinton and Obama served two terms — as well as lighter topics, like favorite ice cream favors.
"You're all part of an incredible team we're building, and we're just getting started," Biden said in his closing message during the discussion. "So let's keep going. Let's win this November."
The trio arrived at Radio City Music Hall together in "The Beast" — the president’s car in the motorcade.
Biden also invited Obama to ride in The Beast after he landed at John F. Kennedy International Airport, where they enjoyed catching up on their personal and professional lives, an aide to Obama told NBC News.
The show of unity among Biden, Clinton and Obama stands in stark contrast to Trump, who faces opposition from members of his own administration , including former Vice President Mike Pence , as he seeks a return to the White House in November.
Former President George W. Bush — the only other Republican former president — declined to support Trump in 2020.
The Trump campaign has not held a major event since March 16. Earlier Thursday, Trump attended the wake for a New York police officer who was shot and killed in Queens on Monday.
Biden and Trump are polling neck-and-neck, with 46% of voters supporting Trump and 45% supporting Biden, according to a March poll by CNBC . That poll, however, had Trump leading Biden by 30 percentage points when respondents were asked which candidate was the best on economic issues.
During Thursday's moderated discussion, Colbert asked Clinton what he would say to voters who do not feel like the economy is strong. Clinton answered that the 2008 recession and Covid are still affecting voters and that Trump did not sustain economic growth spurred by Obama. Biden and Vice President Kamala Harris have methodically "put Humpty Dumpty back together again," Clinton said.
"We should not make 2016's mistake again," he added, referring to when Trump defeated his wife, former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton.
Mike Memoli is an NBC News correspondent.
Megan Lebowitz is a politics reporter for NBC News.
- International
March 27, 2024 - Baltimore Key Bridge collapse
By Kathleen Magramo , Antoinette Radford, Alisha Ebrahimji , Maureen Chowdhury , Elise Hammond , Tori B. Powell and Aditi Sangal , CNN
Our live coverage of the Baltimore bridge collapse has moved here .
Here's what you should know about the Key Bridge collapse
From CNN staff
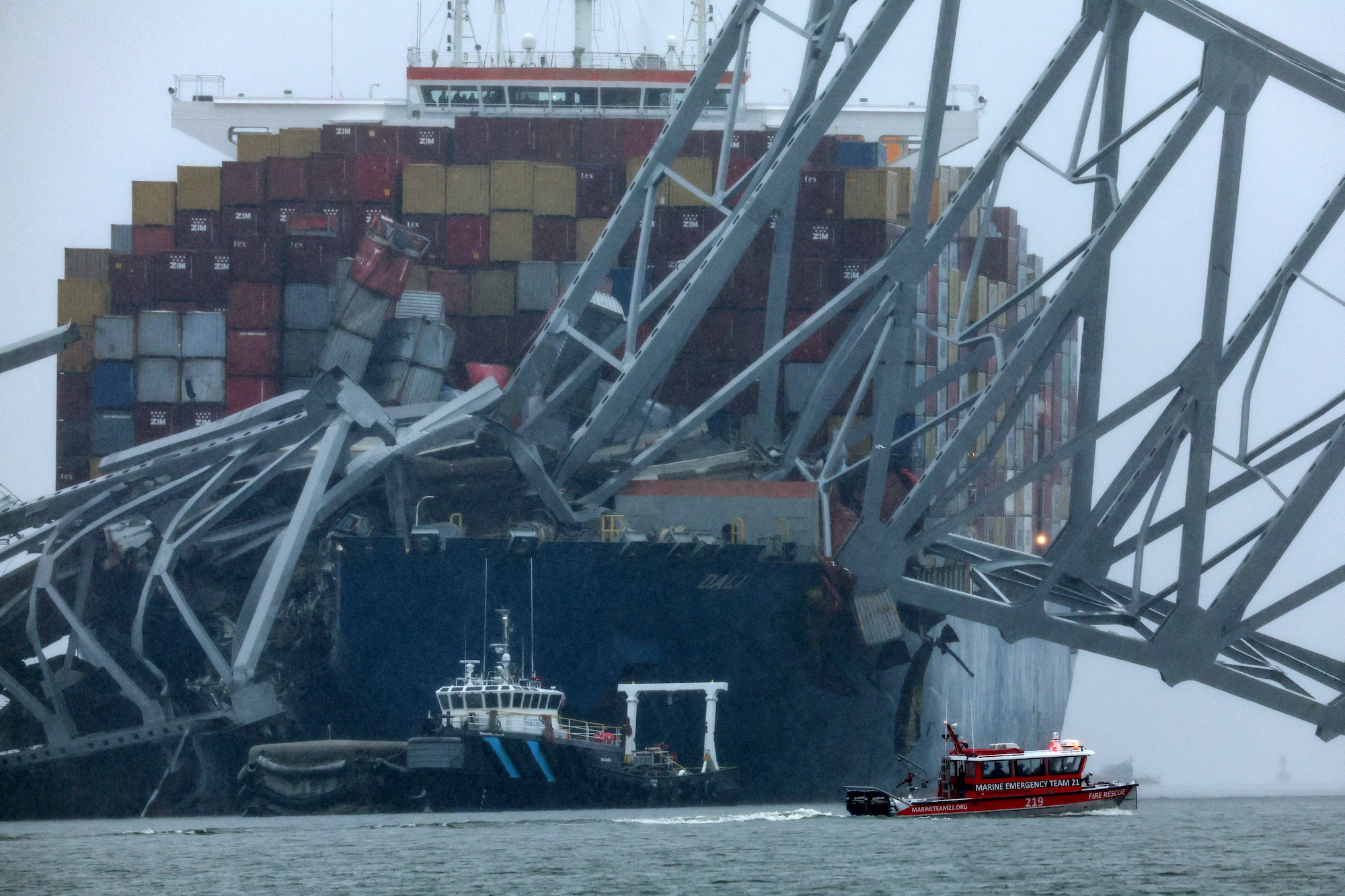

Officials recovered the bodies of two construction workers who were on Baltimore's Francis Scott Key Bridge when it collapsed early Tuesday morning after a 984-foot-long cargo ship collided into a pillar.
Maryland Gov. Wes Moore called the collapse Wednesday " a global crisis ."
"The national economy and the world's economy depends on the Port of Baltimore. The port handles more cars and more farm equipment than any other port in the country," Moore said.
Here's what you should know:
- The victims: The six people who are presumed dead were from Mexico Guatemala, El Salvador and Honduras, according to Col. Roland L. Butler Jr, the superintendent of Maryland State Police. Two bodies were recovered and have been identified as Alejandro Hernandez Fuentes from Mexico and Dorlian Ronial Castillo Cabrera from Guatemala. The two workers were filling potholes on the bridge and were later found trapped in a red pickup truck in about 25 feet of water, Butler said. The FBI is handling notifying the victims' families, Butler said.
- Recovery efforts: Authorities are pausing search efforts for the four other workers who are presumed dead, because additional vehicles are encased in concrete and other debris, making it unsafe for divers, Butler said. Once salvage operations clear the debris, divers will search for more remains, he said.
- The investigation: The National Transportation Safety Board is leading the investigation into the fatal incident, according to the agency's chair Jennifer Homendy. During a Wednesday news conference, Homendy said there were 21 crew members and two pilots on board the Dali cargo ship when it crashed into the bridge. She also said a senior NTSB hazmat investigator identified 56 containers of hazardous material, and that some containers are in the water. The agency received six hours of voyage data from the ship and the investigation could take 12 to 24 months to complete, Homendy said. She emphasized that NTSB will not analyze information collected or provide conclusions while on scene of the collapse.
- Looking forward: Department of Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg said rebuilding the bridge will not be "quick or easy" but that it will get done. He said there are four main focus points ahead: reopening the port, dealing with supply chain issues until its reopening, rebuilding the bridge and dealing with traffic issues until the bridge is rebuilt. Biden pledged the full support of the federal government in the response and recovery efforts. His administration has already conveyed a sense of urgency to open up federal funding to remove debris and ultimately rebuild the bridge. Maryland has submitted a request to the Biden administration for emergency relief funds "to assist in our work going forward," Moore said Wednesday.
It's almost impossible to place people on the bow of ship due to the unstable structure, fire official says
From CNN's Sarah Engel
Baltimore City Fire Chief James Wallace said Wednesday that the cargo ship's bridge structure and containers at the bow remain unstable.
"It's going to be very difficult, if not impossible, and very dangerous, to place people on the bow of that boat right now," Wallace told CNN's Kaitlan Collins.
"Naturally, we're still very cognizant of the fact that there are hazardous materials on board the vessel itself," Wallace said, alluding to the National Transportation Safety Board saying earlier that 56 containers were carrying hazardous materials.
Wallace said his team is relying heavily on aerial recognizance, including drones. "That's the only way we're able to see in," he said.
He added that the aerial surveillance has "been able to really assure us right now we have no [chemical] reactions on board."
"It's just utter devastation," NTSB chief says of the bridge collapse site
From CNN's Aditi Sangal
Jennifer Homendy, chair of the National Transportation Safety Board, called the site of the Key Bridge collapse "devastating."
"It's pretty devastating, certainly, seeing not just what's going on with the cargo containers, but just looking at what was a bridge span — three bridge spans that is pretty much gone. It's just utter devastation," she said at Wednesday evening's news briefing.
She added that she is thinking of families who lost loved ones and those who are waiting to reunite with their lived ones.
NTSB interviewed the Dali's captain and some other crew members today, agency chief says
The National Transportation Safety Board has interviewed the ship's captain, his mate, the chief engineer and one other engineer today, according to Chair Jennifer Homendy.
The two pilots on board the Dali at the time of collision will be interviewed tomorrow, she added.
Cargo ship's voyage data recorder is basic when compared to an airplane's, NTSB chair says
From CNN's Tori B. Powell
The voyage data recorder on the cargo ship Dali was a "newer model" but is considered basic when compared to that on an airplane, according to National Transportation Safety Board Chair Jennifer Homendy.
"But it is very basic compared to say, a flight data recorder, where we would have 1,000 parameters," she said at a news conference on Wednesday.
The NTSB chief investigator Marcel Muise added:
"It's not a ship-wide system recorder, so most of the sensors that are being recorded are from the bridge. So things like GPS, the audio, rudder feedback, rudder commands are recorded on there. But not engineering, the temperature of each cylinder, power distribution sensors."
There were no tug boats with Dali at the time of the collision. That's normal, NTSB chief says
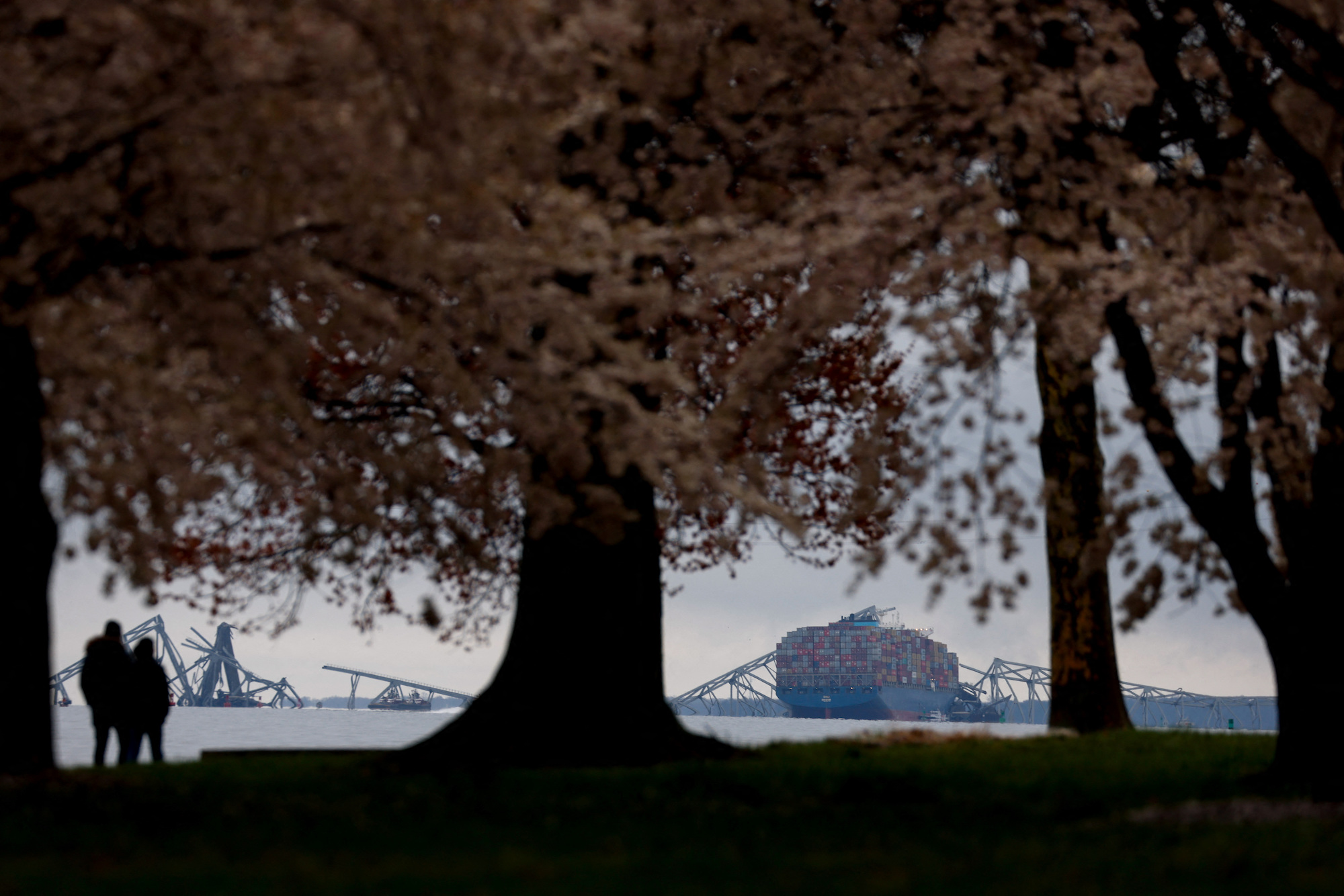

There were no tugs with Dali when the cargo vessel collided with Baltimore's Key Bridge, which is normal protocol, according to National Transportation Safety Board Chair Jennifer Homendy.
Remember: At 01:26:39 on Tuesday, Dali's pilot made a general very high frequency (VHF) radio call for tugs in the vicinity to assist, the NTSB investigator Marcel Muise had said.
"The tugs help the vessel leave the dock, leave the port and get into the main ship channel. And then they leave. Once it's on its way, it's a straight shot through the channel. So there are no tugs with the vessel at the time. So they were calling for tugs," she said.
NTSB chair says she saw some containers that were carrying hazardous materials in the water
National Transportation Safety Board Chair Jennifer Homendy said she did see some of the 56 containers that were carrying hazardous materials in the water.
When asked how many
When asked how many containers of hazardous materials were in the water, Homendy said:
"I did see some containers in the water, and some breached significantly on the vessel itself," she said. "I don't have an exact number, but it's something that we can provide in an update."
Homendy said that a preliminary report should be out in two to four weeks.
This post has been updated with more quotes from Homendy.
Bridge did not have any redundancy, unlike the preferred method for building bridges today, NTSB chair says
Baltimore's Key Bridge did not have any redundancy, which is included in the preferred method of building bridges in the present day, according to National Transportation Safety Board Chair Jennifer Homendy.
"The bridge is a fracture critical," she explained. "What that means is if a member fails that would likely cause a portion of, or the entire bridge, to collapse, there's no redundancy. The preferred method for building bridges today is that there is redundancy built in, whether that's transmitting loads to another member or some sort of structural redundancy. This bridge did not have redundancy," Homendy said.
There are 17,468 fracture critical bridges in the United States out of 615,000 bridges total, she said, citing the Federal Highway Administration.
Please enable JavaScript for a better experience.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Powerpoint with the explanation of Reported Speech, including examples and exercises. It explains how statements, questions and commands (orders, requests, invitations, warnings, suggestions, etc) are reported in English.
1/10. Let's do English ESL general grammar practice. This is a Powerpoint about Reported Speech. It is part of a set of 3, the other two being "Reported Questions" an….
Found a mistake? This is a PowerPoint presentation with sound to learn Reported Speech. A complete grammar lesson explaining the use, changes of tense, pronouns, adverbs of time and place with examples. There are also some important notes about the main rules to report statements.
reported speech (commands and requests ) We commonly use tell , command , advise , warn or order When we report commands . and ask when we report requests tell , command , advise , warn or order Commands requests ask. - The imperative changes to full infinitive or not + full infinitive • When the request is in question form , in reported ...
5. Use of 'That' in reported speech • In reported speech, the word "that" is often used. He told me that he lived in Greenwich. • However, "that" is optional. He told me he lived in Greenwich. • Note - "That" is never used in questions, instead we often use "if". He asked me if I would come to the party.
Stop that! - What's your job? - He asked me what my job was. - What food do you like? - He wanted to know what food I liked - Are you allergic to cats? - He asked me if I was allergic to cats. - Do you have a boyfriend? - He asked me if I had a boyfriend - How old are you? - He wanted to know how old I was - Kiss me.
A reported question is when we tell someone what another person asked. To do this, we can use direct speech or indirect speech. direct speech: 'Do you like working in sales?' he asked. indirect speech: He asked me if I liked working in sales. In indirect speech, we change the question structure (e.g. Do you like) to a statement structure (e.g.
Reported speech (summary): When Mary complained that she was tired out after walking so far, Peter said they could stop for a picnic. ... This is an example of an indirect question. An indirect question reports a question, but is not a question itself, which is why we do not use a question mark at the end.
Download presentation. Presentation on theme: "THE REPORTED SPEECH."—. Presentation transcript: 1 THE REPORTED SPEECH. 2 We use the Reported Speech: To report what another person has said, but not using the speaker's exact words. The structure is a little different depending on whether we want to transform a statement, question or request.
Upper-intermediate grammar exercise (B2 level): reported speech; Word order in indirect questions; Qualifiers: how to sound more polite in a business meeting; Intermediate grammar exercise (B1 level): present perfect simple or continuous 2; Elementary grammar exercise (A1 level): present simple questions, negatives (do, does, don't) ex. 2 ...
After reading and listening to the dialogues "Gossip", students are shown a few selected sentences. Their task is to notice the differences between direct and reported sentences and thus formulate the rules for reporting statements, questions, commands and requests. This presentation aims to engage students in discovering grammar.
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
Actor and comedian Mindy Kaling hosted the program, which ended at around 10 p.m., and late night host Stephen Colbert moderated a conversation with Biden, Clinton and Obama. Special guests ...
Maryland Gov. Wes Moore speaks during a press conference on the collapse of the Francis Scott Key Bridge on Wednesday, March 27. The collapse of Baltimore's Key Bridge is a global crisis ...