Lavu's Restaurant app UX Case Study

Full UX case study and UI components for restaurant app.

- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions

Making Your UX Life Easier with the MoSCoW
If you’re stuck trying to move a project forward because it seems like there are too many things to concentrate on then the MoSCoW method may help you get unstuck. It’s a prioritization technique which is easy to learn and simple to apply. It can also help you decide what’s really valuable for your UX projects before you get started on them.
There are many different prioritization techniques that can be employed on design projects but one of the simplest to use is the MoSCoW method. It’s used across all business disciplines to enable project teams to work with stakeholders to define requirements. It can also be used as a personal prioritization technique.
What Does MoSCoW Stand For?
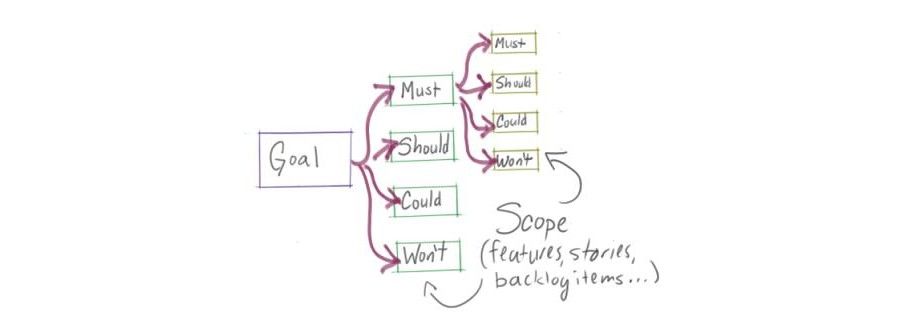
MoSCoW is an (almost) acronym designed to reflect the four categories used by the technique to determine priorities; Must have, Should have, Could have and Would like but won’t get. The lower case “o’s” are added simply to give the acronym a pronounceable form. Occasionally, you may also see the whole phrase in block capitals MOSCOW to distinguish it from the name of the city but MoSCoW is more common.
What is the MoSCoW Method?

Experts Dai Clegg and Richard Barker proposed the method in their paper “Case Method Fast-Track: A RAD Approach” and while it was initially intended to be used with the Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM) it has long since been adopted throughout many areas of business. In recent times it has become very popular in the Agile and RAD (rapid application development) communities.
The MoSCoW method is most effective when it comes to prioritizing requirements in projects with either fixed or tight deadlines. It works by understanding the idea that all project requirements can be considered important but that they should be prioritized to give the biggest benefits in the fastest possible time frame.
It breaks down the requirements into four categories:
These are the requirements without which a project will fail. They MUST be delivered within the timeframe in order for anyone involved with the project to move on. In essence they make up the MVP ( Minimum Viable Product ) though it can be argued that MUST could stand for Minimum Usable SubseT too.
Should have
Should have requirements aren’t 100% necessary for delivering the project successfully but they are the “most nice to have” out of the list. They may be less time critical than “must have” or might be better held for a future release.

Could have requirements are just “nice to have” they are desirable to provide a nice user experience or customer experience but they’re not that important to the delivery of the project. They will be delivered only if there’s enough time and resources to spare to devote to them. Otherwise, they’re likely to be tabled for future releases and re-reviewed to see if they have become higher or lower priority in the interim.
These are the requirements that everyone agrees aren’t going to happen. It might be because they cost too much to implement or provide too little ROI ( Return on Investment ) for the efforts required to implement them. These are simply left to one side until they are either removed from the requirements list or become a higher priority.
The MoSCoW method provides a simple way of clarifying the priorities involved on a project. It’s most useful in time bound situations and it can be used to prioritize your own workload (usually with the buy in from a supervisor or manager if you work for someone else) as easily as it can be used for project work.
Implementing MoSCoW – A Practical Process

The easiest way to use MoSCoW is to bring together all the relevant stakeholders to the project and then:
List the requirements (on a flip chart or on a screen)
Vote on which category each requirement falls into (bearing in mind any hierarchical issues within the company itself – the CEOs vote may count for more than the votes of everyone else in the room)
Then collate the information and ensure that each requirement is presented against the relevant category in written form so that it can be used for reference by the project team
You can repeat this exercise whenever you feel it is necessary. Priorities may change mid-project or between releases. It’s important for everyone to understand what the implications of changing priorities in the middle of a project may be in terms of costs, resources, and time.
Issues with MoSCoW
It’s important to know that the MoSCoW method isn’t without its detractors. The main flaw in the method, as identified by authors Kark Weigers and Joy Beatty in their book Software Requirements, is that the method offers no means for comparing one requirement to another. This can make it difficult for those tasked with prioritizing requirements to know which category to place them in.
The Take Away
The MoSCoW method offers a simple process for prioritizing within project delivery. It can also be used to prioritize your work load. It should be used with some caution in that it may be too simple – particularly for complex projects – but it makes for a good starting point. One of the big advantages to its simplicity is that it should be easy to get buy in from other stakeholders to put it into practice.
Check out this useful study into how the MoSCoW method is used by business analysts .
You can read about the MoSCoW method as it was originally designed in: Clegg, Dai; Barker, Richard (2004-11-09). Case Method Fast-Track: A RAD Approach. Addison-Wesley. ISBN 978-0-201-62432-8.
You can read Weigers and Beatty’s criticism and their suggestion for a more complex method in: Wiegers, Karl; Beatty, Joy (2013). Software Requirements. Washington, USA: Microsoft Press. pp. 320–321. ISBN 978-0-7356-7966-5.
Hero Image: Author/Copyright holder: Agile Connection. Copyright terms and licence: All rights reserved. Img
User Experience: The Beginner’s Guide

Get Weekly Design Insights
Topics in this article, what you should read next, apple’s product development process – inside the world’s greatest design organization.

- 1.4k shares
How to Change Your Career from Graphic Design to UX Design
What is Interaction Design?

Shneiderman’s Eight Golden Rules Will Help You Design Better Interfaces

- 1.3k shares
The Principles of Service Design Thinking - Building Better Services

A Simple Introduction to Lean UX
- 3 years ago
Dieter Rams: 10 Timeless Commandments for Good Design

The 7 Factors that Influence User Experience
- 1.2k shares
Adaptive vs. Responsive Design
The Grid System: Building a Solid Design Layout
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !

Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!
This website will offer limited functionality in this browser. We only support the recent versions of major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
New ITU case study maps the Moscow ‘smart city’ journey

Moscow reports experience with Key Performance Indicators for Smart Sustainable Cities
A new ITU case study offers an evaluation of Moscow’s progress in meeting the objectives of its ‘smart city’ strategies and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The case study , Implementing ITU-T International Standards to Shape Smart Sustainable Cities: The Case of Moscow , was undertaken using the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Smart Sustainable Cities developed by the United for Smart Sustainable Cities (U4SSC) initiativ e .
The ITU case study traces Moscow’s smart city journey from its origins in Moscow’s Information City strategy launched in 2011 to its successor the Smart Moscow 2030 strategy. It highlights the role of Moscow’s Government in coordinating the implementation of a wide array of smart city projects in the city and how these projects have substantially improved the quality of life for city residents. The report assesses Moscow’s smart city performance using U4SSC indicators that measure impact on three dimensions: the economy, environment and society & culture.
Information and communication technology (ICT) is a recognized key contributor to the Moscow economy. Building on its strengths and maintaining ICTs as a strategic lever, Moscow has adopted vibrant policies for ICT development and proliferation. These aspects are clearly reflected in the good performance by Moscow, as presented in the report, within the sub-dimensions of “ICT” and “Productivity”.
The case study also serves as a valuable reference point to other cities in Russia and Commonwealth of Independent State countries – as well as to cities around the world pursuing greater efficiency and sustainability. ITU standardization experts responsible for the refinement of the Key Performance Indicators will also find the case study to be valuable.
RELATED: Dubai reports results from implementing ITU’s Key Performance Indicators for Smart Sustainable Cities
“Home to more than 12 million people, Moscow is the largest urban area on the European continent,” said ITU Secretary-General Houlin Zhao. “Considering the size of Moscow and its population, this case study offers a unique set of lessons learned for other cities around the world developing a ‘smart city’ strategy. I commend Moscow’s leaders for their efforts to share these experiences and this knowledge with the international community, towards creating a ‘smart’ world for everyone, everywhere.”
“Moscow has made a rapid smart city journey from 2011 and we are keen on keeping up with the pace. No matter whether it is Moscow, Singapore or Barcelona – every city has the same task to make their residents’ lives enjoyable, safe and comfortable,” said Strategy and Innovations Advisor to the Chief Information Officer of Moscow, Andrey Belozerov. “We are happy to contribute to this research as it is important to develop universal metrics to access city performances all around the world.”
The findings of the case study will feed into the work of ITU’s Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) Study Group 20 , the expert group leading the development of ITU standards for the Internet of Things and smart cities. These standards assist in optimizing the application of ICTs within smart cities, in addition to supporting efficient data processing and management.
RELATED: New ITU case study shares insight into Singapore’s ‘Smart Nation’ strategy
The findings will also be taken up by the U4SSC initiative, which advocates for public policy to ensure that ICTs, and ICT standards in particular, play a definitive role in the transition to Smart Sustainable Cities. U4SSC also promotes the adoption of international standards in reaching the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and the reporting of associated experiences.
The Moscow case study follows prior smart city case studies of Dubai and Singapore. These have made valuable smart cities experiences and knowledge available to other cities around the world. This reporting also solicits feedback that helps cities to refine their smart city strategies.
U4SSC has developed a ‘Collection methodology for the Key Performance Indicators for Smart Sustainable Cities’ to guide cities in their collection of core data and information necessary to assess their progress in becoming a Smart Sustainable City. It is supported by 16 United Nations bodies, including ITU, and is open to the participation of all stakeholders interested in driving smart city innovation.
The collaboration encouraged by U4SSC has led more than 50 cities to measure their smart city strategies using the U4SSC’s KPIs for Smart Sustainable Cities, which are based on the ITU international standard, ITU Y.4903/L.1603 “Key Performance Indicators for Smart Sustainable Cities to assess the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals” .
This ITU News story was originally distributed as an ITU press release. For more ITU press releases, see the ITU Media Centre .
Related content
Competition on blockchain authentication for digital finance, national e-waste monitor: namibia 2024, connect with itu standards experts at ofc.
This information is available only to people with TIES access.
Privacy Overview

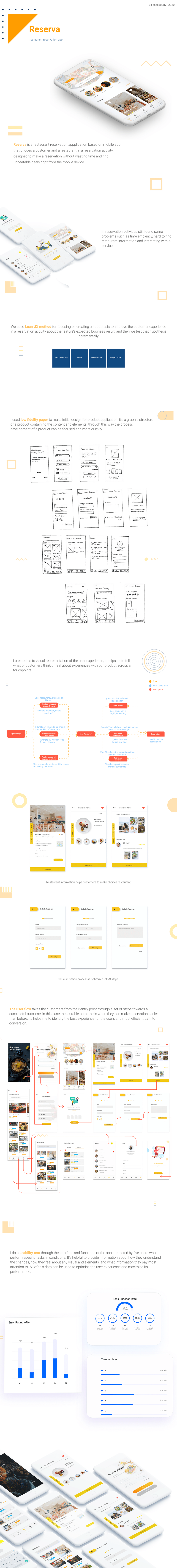
Restaurant Reservation App | UX Case Study
Creative Fields

Product Design

- interaction
- reservation
- user experience
- user interface
No use is allowed without explicit permission from owner

IMAGES
COMMENTS
UX Case Study : The case study that enhanced my portfolio My Role as a UX/UI Designer encompassed a comprehensive approach to crafting a user-centric application for professionals by combining… 4 min read · Dec 21, 2023
47. •. 2.3k users. Open in Figma. About. Comments 0. Full UX case study and UI components for restaurant app.
Hey Folks! 👋. I'm thrilled to share my latest UI/UX design case study, a culmination of my work during the Dibimbing Batch 21 UI/UX Design program. In this project, I'll be introducing ...
Overview. Cheezalicious is a concept app designed during my study at Udacity, it is designed for a conceptualized restaurant that serves all the cheesy recipes. It's a niche app that helps people order (or get delivered) the cheesy and delicious food items on the restaurant menu, without the need for a conventional paper menu or a waiter.
Case Study: Food menu app for a restaurant. Project Overview. Client: Food Point Restaurant Duration: 2 weeks Role: UX/UI Designer. Problem Statement. Food Point Restaurant currently lacks an ...
About. A client reached out to me for the design and also the development of a food delivery app for her business called Bella Foods. The MVP and everything were designed and developed in three months, including shipment real-time tracking. The product was first directly launched on the market on google play store, in order to test the traction ...
Project Vision. A self-serve dine in application for all participating restaurants in one place. Tabla aims to offer an easy and smooth self ordering experience, while at the table. The app will allow users to browse visual menus, place orders and pay digitally, while still enjoying the restaurant dine in experience.
To answer these questions, I started with looking at various menu designs of popular restaurants. Below are some of the key insights: a. good menu design uses both visual and verbal content to guide users through food ordering experience. b. menu ordering is visual. c. a short description of the food item with key ingredients help users make ...
Product Design,UI/UX,Figma,Microsoft PowerPoint,Google Docs. Restaurant reservation app UI/UX design - Case study
Problem Definition. The mobile aggregator is an application that combines various thematic platforms in order to increase their level of sales and ensure the convenience of the choice of dishes and drinks by users. A distinctive feature of the application is a single design, user-friendly interface. I decided to create competing app where to ...
The motive of this app is to provide a digitized menu which can be easily navigated by the customer and the selected items can be added to a wishlist (named as Orderlist here). This app was made as a part of an internship assessment. The brief was as follows: Design an app for a restaurant that would be able to show to the customer the menu of ...
Download on the App Store Get it on Google Play English Čeština Dansk Deutsch Español Français Italiano Nederlands Norsk Polski Português Pусский Suomi Svenska Türkçe 日本語 한국어 中文(简体) 中文(繁體)
Savora - Food Recipe App - UX Case Study. Dinesh Kumar. 320 5.5k. ... Delecious Catering Food Restaurant App Delivery UI/UX. Anas Adel. 7 201. Save. Duolingo - Case Study. Multiple Owners. 34 635. Save. Food Recipe App. Multiple Owners. 1.6k 14k. Save. Zawag Muslim App Design ( Case Study ) Yousef Ragab. 132 860.
Splitting the bill according to veg and non- veg beats the purpose as it only applies to a certain use case. Most importantly, users order beverages as well. So the solution needs to tackle it too ...
According to the LATCH method information can be organized in 5 ways — by Location, Alphabet, Time, Category and Hierarchy. In our case we can organize ingredients by Categories (Meat, Fish, Vegetables, Fruits) and Hierarchy — the most popular and widely used ingredients to go first in the list.
MoSCoW is an (almost) acronym designed to reflect the four categories used by the technique to determine priorities; Must have, Should have, Could have and Would like but won't get. The lower case "o's" are added simply to give the acronym a pronounceable form. Occasionally, you may also see the whole phrase in block capitals MOSCOW to ...
Android Presentation - Restaurant Reservation App. Ashin Rijay. 12 84.
Through experimentation and core design principles, I can define and develop a unique… · Experience: Northeastern University College of Science · Education: Northeastern University · Location ...
A new ITU case study offers an evaluation of Moscow's progress in meeting the objectives of its 'smart city' strategies and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The case study , Implementing ITU-T International Standards to Shape Smart Sustainable Cities: The Case of Moscow, was undertaken using the Key Performance ...
UI/UX,Product Design,App Design,Figma,Adobe Photoshop
Case study: housing renovation in the city of Moscow. The programme of housing renovation in the city of Moscow, initiated in February 2017, represents one of many in a sequence of policies unfolding in the broad domain of urban development in the Russian capital. To initiate the process-tracing of this case, it is crucial to appreciate ideas ...