

Business Plan Organization and Management: How to Write Guide .
Sep 17, 2023 | Business Consulting , Business Plan , Organization and Management , Organizational Development , Strategy

Writing the Business Plan Organization and Management Section
It provides critical information for those looking for evidence that your staff has the necessary experience, skills, and pedigree to realize the objectives detailed in the rest of your business plan.
What Is the Organization and Management Section in a Business Plan?
The organization and management section of your business plan should provide details about your business structure and team. This section typically comes after the executive summary. However, some people have it further in the document after the market analysis section.
This section generally is separated into two parts. The first concerns the organization as a whole. It gives readers an overview of the company structure, which is an excellent opportunity for the reader to lift the roof off your office and peer into its inner workings. For your legal design, you may set up as a limited liability company (LLC) or nonprofit/ charity or form a partnership. It’s crucial to include this section. However, suppose you’re starting a home business or have an already operating business where you’re the only person involved. In that case, you can skip this section or show the company registration details from either the company’s house or the awarding .gov.
The second part focuses specifically on your management team and introduces readers to each member — your chance to impress them with the many accomplishments pinned to your organization’s management team.
This section may seem less important than some of the other parts of your business plan, but the truth is that your people are your business. If they’re highly competent and accomplished, the implication is that so is your business.
Of course, if you’re a sole proprietor with no management structure or any employees, this section is unnecessary other than to talk about yourself and your achievements.

The section on organization and management should outline the hierarchy, individual roles, and corresponding responsibilities. It should also highlight each person’s strengths and qualifications for their positions.
Business Plan Organization Section
The organizational section of your business plan outlines the hierarchy of individuals involved in your business, typically in a chart format. This section identifies the President or CEO, CFO, Director of Marketing, and other roles for partnerships or multi-member LLCs. If you’re a single-person home business, this section is straightforward as you are the only person on the chart.
Although this section primarily focuses on owner members, you can include outsourced workers or virtual assistants if you plan to hire them. For example, you may have a freelance web admin, marketing assistant, or copywriter. You may even have a virtual assistant who coordinates with your other freelancers. While these individuals are not owners, they hold significant responsibilities in your business.
There are various business structures, such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, LLCs, and corporations.
Detail the Legal Structure within the Business Plan Organization and Management Section
Here is an indicative list of business structures. It would help if you talked to your accountant and legal advisors to determine which legal form is the best for your business proposition.
Sole Proprietorship
When embarking on a business venture, it’s essential to consider the various structures available. A sole proprietorship is a structure whereby the business is not regarded as separate from its owner’s finances. The owner retains complete control and responsibility for the company. However, they are unable to sell stocks or bring in new owners. The business becomes a sole proprietorship if not registered under any other structure.
Partnership
When forming a partnership, it can either be a limited partnership (LP) or a limited liability partnership (LLP). One partner assumes most liability in a limited partnership (LP). In contrast, the other partners have limited liability and control over the business. Alternatively, in a limited liability partnership (LLP), all partners have limited liability from debts and actions of other partners, and there is no general partner.
Limited Liability Company
A limited company (LTD) or limited liability company (LLC) is a mixture of business structures that mixes aspects of partnerships and corporations. It offers limited personal liability to the owner and passes profits through to their tax returns.
Corporation
There are various types of corporate structures. A C-corporation enables the issuance of stock shares, pays corporate taxes instead of personal returns, and provides the highest level of personal protection from business activities. On the other hand, nonprofit corporations are similar to C corporations. However, they do not aim to make profits and are exempt from state or federal income taxes.
More information on company legal structures is available on UK.Gov and USA.SBA websites.
Describe Your Company’s Organizational Structure
This first step illustrates the positions in your organization’s employee hierarchy and how they all relate to each other.
This is usually done graphically as a guide, using an organizational chart, or “org chart” for short. People use a Microsoft tool, i.e., PowerPoint or Excel, to help.
Organization Charts typically follow a top-down hierarchy, starting with your CEO/ Managing Director in the top box at the top of the page. Lines extend down from that person’s name to boxes containing the terms of the CEO’s direct reports.
We have included an example organizational chart below for guidelines only.
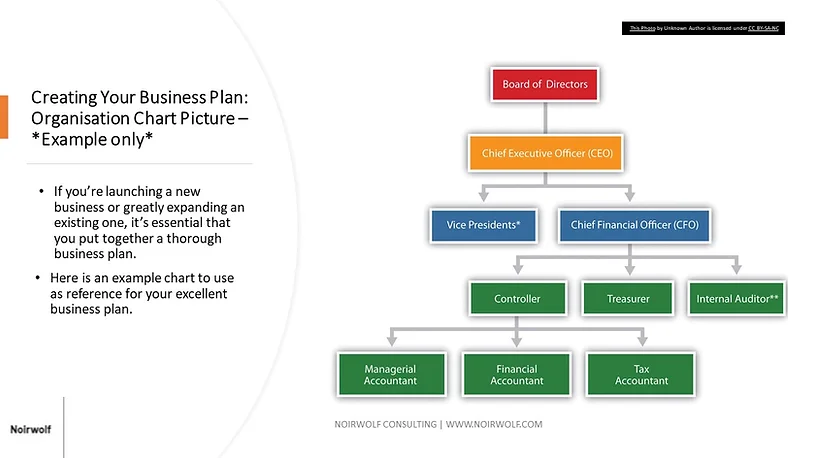
Identify your business organization structure and list your team members’ strengths and skills.
Those managers then have lines extending to those who report to them, and so on, down to your lowest staff positions.
This section will give your readers a quick understanding of your management and governance structure, the size of your organization, and your lines of control and communication.
Describe your Team in your Business Plan Organization and Management Section
In your business plan’s Organization and Management section, please provide a detailed description of your team. Y ou will discuss the company’s management team, starting with the owners.
This section highlights who is involved in the running of your business and who are the support professionals. It also includes the roles and responsibilities of managers.
Suppose the company structure is a multi-owner arrangement or some other multi-owner arrangement. In that case, you’ll want to include information for every member and their percentage of ownership and ongoing involvement in the company.
It’s important to discuss how ownership interests are split, their responsibilities, what they did before securing their current position, and how they came to be involved with the company.
Here, it would help if you talked about some of your critical team members. These people are directly responsible for large portions of your business operations.
Owner/Manager/Members
Within your business o rganization and management section, y ou should introduce the team and talk about their experience, qualifications, previous companies and achievements, role in the company, and any special skills they bring with them. Please provide the following details for each owner, manager, or member of the business within your business plan:
- Percentage of ownership (if applicable)
- Level of involvement (active or silent partner)
- Type of ownership (e.g., stock options, general partner)
- Position in the company (CEO, CFO, etc.)
- Responsibilities and Duties
- Educational background
- Relevant experience and skills
- Previous employment history
- Skills that will benefit the business
- Awards or recognition received
- Compensation structure
- How each individual’s skills and experience will complement and contribute to the business’s success
Perhaps they’re an entrepreneur, business coach, exclusive advisor, or industry specialist to help you grow.
This is an ideal opportunity for companies with an Executive Board of Directors, Governance Structure, or Advisory Board to introduce them to your readers.
Executive Board
Having a board of directors is essential for your management team. Without one, you may be missing out on crucial information. This section includes details similar to those found in the ownership and management team sub-section, such as the names, areas of expertise, positions (if applicable), and involvement with the company of each board member.
Strategic Advisors
Suppose you’re looking for funding for your business or to fill a gap in your knowledge, or you may not have the funds to hire an executive board. In that case, you must inform potential partners and investors that you have a team of professionals assisting you. This includes lawyers, accountants, and any freelancers or contractors you may be working with. When listing these individuals, include their name, title, educational background, certifications, services they provide to your business, and their relationship with you (i.e., hourly rates, projects, retainer, as-needed, regular). Additionally, highlight their skills and experience that make them an asset to your team you need
Does anything else make them stand out as quality professionals (awards, past working with credible brands)?
Spotlight on the Wider Team Structure
Now, you’ve showcased the management team in its entirety. You can provide brief bios for hiring team needs or secondary members and talk at length about how the team’s combined skills complement each other and how they amplify the team’s effectiveness.
It’s also important to point out any gaps in the knowledge your team is currently suffering. Your readers will likely be savvy enough to pick up on existing holes.
Therefore, you’ll want to get ahead of these criticisms and demonstrate that you’re already aware of the positions and complementary skill sets your management team still requires and how you plan to address the knowledge gaps with future hires.
Do you need help writing your business plan o rganization and management section ?
Every successful business plan should include the organization and management section, helping you communicate your legal structure and team.
Writing a business plan can seem overwhelming, especially when starting a small, one-person business. However, it can be a reasonably simple task. This section of the plan should be updated if there are any changes to the organization structure or team members, such as additional training, awards, or other resume changes that benefit the business.
Creating your comprehensive business plan takes planning, research, time, and a herculean effort. If, at any point, the work becomes too much to handle, we can step in to assist.
Do you want an expert “second opinion” before creating your business plan or financial forecasts? Let’s talk !
Get in Touch
Are you looking to grow your business but unsure where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We’ll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free 30-minute consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let’s get started!
Contact Noirwolf Consulting today using the website contact form or by emailing [email protected] or call us at +44 113 328 0868.
Recent posts .

What is Program Management?
Apr 2, 2024
Program management is a vital component of organizational success, as it enables the coordinated execution of interdependent projects that yield benefits beyond the scope of individual project management. It involves the judicious application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet specific program requirements. Our experience has demonstrated that organizations with well-developed program management and program management offices (PMOs) consistently outperform those that lack such structures. Therefore, it is imperative that organizations prioritize the establishment of robust program management frameworks to achieve their strategic objectives.

Business Transformation Strategy: A 10-Step Strategy Guide
Mar 4, 2024
Business transformation strategy is a complex and dynamic process that fundamentally restructures an organization’s strategy, processes, and systems. Though each business transformation is unique, several critical steps remain foundational to a successful change management plan. A comprehensive business transformation framework ensures a smooth and practical transformation. This framework should encompass various elements, such as defining the vision and aims of the transformation, assessing the current state of the business, identifying gaps and areas of improvement, developing a roadmap and action plan, implementing the changes, monitoring and measuring progress, and continuously refining the transformation approach as needed.

What is the Change Management Process?
Feb 2, 2024
Change is the only constant in today’s fast-paced world, and organizations must adapt to stay ahead. Fortunately, change management provides a structured and coordinated approach that enables businesses to move from their current state to a future desirable state. To deliver business value, organizations introduce change through projects, programs, and portfolios. However, introducing change is just the beginning! The real challenge is to embed the change and make it a new normal state for the organization. This calls for implementing the main principles of change management, which we will discuss in this article. Get ready to transform your organization and achieve your desired outcomes by mastering the art of change management!
Happy clients .
Trevor mcomber, us.
I recently worked with Zoe@Noirwolf, who provided me with an outstanding 5-year business plan. The expertise in financial planning, market research, SWOT analysis, and consulting was exceptional. Zoe provided me with a comprehensive and well-researched plan tailored to my business. The entire process was professional, timely, and communicative.
Bill Walton, Leeds
Zoe provided first-rate work and is an excellent business consultant. I was trying to figure out my cash flow forecast for my startup. Zoe gave me an interactive consultation session over MS teams, which was valuable and saved me a lot of time. She is super quick in excel and knowledgeable about what to include in your estimates. She was able to offer me ideas & choices that I hadn't considered. Highly recommended.
Jeendanie Lorthe, US
Warren kim, us, oscar sinclair, london, get in touch ..
Looking to grow your business but feeling unsure about where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We'll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free one-hour consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let's get started!
Business Plan Section 3: Organization and Management
This section explains how your business runs and who’s on your team. Learn how to present the information in this section of your business plan.

This section of your business plan, Organization and Management, is where you’ll explain exactly how you’re set up to make your ideas happen, plus you’ll introduce the players on your team.
As always, remember your audience. If this is a plan for your internal use, you can be a little more general than if you’ll be presenting it to a potential lender or investor. No matter what its purpose, you’ll want to break the organization and management section into two segments: one describing the way you’ve set up the company to run (its organizational structure), and the other introducing the people involved (its management).
Business Organization
Having a solid plan for how your business will run is a key component of its smooth and successful operation. Of course, you need to surround yourself with good people, but you have to set things up to enable them to work well with each other and on their own.
It’s important to define the positions in the company, which job is responsible for what, and to whom everyone will report. Over time, the structure may grow and change and you can certainly keep tweaking it as you go along, but you need to have an initial plan.
If you’re applying for funding to start a business or expand one, you may not even have employees to fit all the roles in the organization. However, you can still list them in your plan for how the company will ideally operate once you have the ability to do so.
Obviously, for small businesses, the organization will be far more streamlined and less complicated than it is for larger ones, but your business plan still needs to demonstrate an understanding of how you’ll handle the workflow. At the very least, you’ll need to touch on sales and marketing, administration, and the production and distribution of your product or the execution of your service.
For larger companies, an organizational plan with well-thought-out procedures is even more important. This is the best way to make sure you’re not wasting time duplicating efforts or dealing with internal confusion about responsibilities. A smooth-running operation runs far more efficiently and cost-effectively than one flying by the seat of its pants, and this section of your business plan will be another indication that you know what you’re doing. A large company is also likely to need additional operational categories such as human resources and possibly research and development.
One way to explain your organizational structure in the business plan is graphically. A simple diagram or flowchart can easily demonstrate levels of management and the positions within them, clearly illustrating who reports to whom, and how different divisions of the company (such as sales and marketing) relate to each other.
Here is where you can also talk about the other levels of employees in your company. Your lower-level staff will carry out the day-to-day work, so it’s important to recognize the types of people you’ll need, how many, what their qualifications should be, where you’ll find them, and what they’ll cost.
If the business will use outside consultants, freelancers, or independent contractors, mention it here as well. And talk about positions you’d want to add in the future if you’re successful enough to expand.
Business Management
Now that we understand the structure of your business, we need to meet the people who’ll be running it. Who does what, and why are they onboard? This section is important even for a single practitioner or sole proprietorship, as it will introduce you and your qualifications to the readers of your plan.
Start at the top with the legal structure and ownership of the business. If you are incorporated, say so, and detail whether you are a C or S corporation. If you haven’t yet incorporated, make sure to discuss this with your attorney and tax advisor to figure out which way to go. Whether you’re in a partnership or are a sole owner, this is where to mention it.
List the names of the owners of the business, what percent of the company each of them owns, the form of ownership (common or preferred stock, general or limited partner), and what kind of involvement they’ll have with day-to-day operations; for example, if they’re an active or silent partner.
Here’s where you’ll list the names and profiles of your management team, along with what their responsibilities are. Especially if you’re looking for funding, make sure to highlight the proven track record of these key employees. Lenders and investors will be keenly interested in their previous successes, particularly in how they relate to this current venture.
Include each person’s name and position, along with a short description of what the individual’s main duties will be. Detail his or her education, and any unique skills or experience, especially if they’re relevant to the job at hand. Mention previous employment and any industry awards or recognition related to it, along with involvement with charities or other non-profit organizations.
Think of this section as a resume-in-a-nutshell, recapping the highlights and achievements of the people you’ve chosen to surround yourself with. Actual detailed resumes for you and your management team should go in the plan’s appendix, and you can cross-reference them here. You want your readers to feel like your top staff complements you and supplements your own particular skill set. You also want readers to understand why these people are so qualified to help make your business a success.
This section will spell out the compensation for management team members, such as salary, benefits, and any profit-sharing you might be offering. If any of the team will be under contract or bound by non-compete agreements, you would mention that here, as well.
If your company will have a Board of Directors, its members also need to be listed in the business plan. Introduce each person by name and the position they’ll hold on the board. Talk about how each might be involved with the business (in addition to board meetings.
Similar to what you did for your management team, give each member’s background information, including education, experience, special skills, etc., along with any contributions they may already have had to the success of the business. Include the full resumes for your board members in the appendix.
Alternately, if you don’t have a Board of Directors, include information about an Advisory Board you’ve put together, or a panel of experts you’ve convened to help you along the way. Having either of these, by the way, is something your company might want to consider whether or not you’re putting together the organization and management section or your business plan.
NEXT ARTICLE > Business Plan Section 4: Products and Services
Apply for a loan, get started.
Loans from $5,000 - $100,000 with transparent terms and no prepayment penalty. Tell us a little about yourself, your business and receive your quote in minutes without impacting your credit score.
Thanks for applying!
Loans are originated and funded through our lending arm, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development. By clicking “Continue to Application,” you consent to, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development’s Terms of Use and Privacy Policy ; and to receive emails, calls and texts , potentially for marketing purposes, including autodialed or pre-recorded calls. You may opt out of receiving certain communications as provided in our Privacy Policy .
If you still have questions or prefer to get help directly from an agent, please submit a request. We’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
Please fill out the contact form below and we will reply as soon as possible.
- Business Management & Operations
- Strategy, Entrepreneurship, & Innovation
Business Plan - Management and Organization
Management and Organization Section of a Business Plan
Written by Jason Gordon
Updated at April 21st, 2024
- Marketing, Advertising, Sales & PR Principles of Marketing Sales Advertising Public Relations SEO, Social Media, Direct Marketing
- Accounting, Taxation, and Reporting Managerial & Financial Accounting & Reporting Business Taxation
- Professionalism & Career Development
- Law, Transactions, & Risk Management Government, Legal System, Administrative Law, & Constitutional Law Legal Disputes - Civil & Criminal Law Agency Law HR, Employment, Labor, & Discrimination Business Entities, Corporate Governance & Ownership Business Transactions, Antitrust, & Securities Law Real Estate, Personal, & Intellectual Property Commercial Law: Contract, Payments, Security Interests, & Bankruptcy Consumer Protection Insurance & Risk Management Immigration Law Environmental Protection Law Inheritance, Estates, and Trusts
- Business Management & Operations Operations, Project, & Supply Chain Management Strategy, Entrepreneurship, & Innovation Business Ethics & Social Responsibility Global Business, International Law & Relations Business Communications & Negotiation Management, Leadership, & Organizational Behavior
- Economics, Finance, & Analytics Economic Analysis & Monetary Policy Research, Quantitative Analysis, & Decision Science Investments, Trading, and Financial Markets Banking, Lending, and Credit Industry Business Finance, Personal Finance, and Valuation Principles
What is the Management and Organization Section of the Business Plan?
Outline your organizational structure and then tell about your primaries. How your business will be managed and who will be involved is an important consideration in your choice of business entity. For example, in a partnership, it is assumed that partners have equal control in managing the business. In an LLC you make the choice of whether it will be managed by members of the LLC or by hired managers.
In a corporation, the owners/shareholders may or may not be a part of the management team. In any of the above situations, you will want to develop a plan for the roles of individual members. While individual member roles and responsibilities often change rapidly, you want to have a formalized chain of authority within the business. Remember, too many decision-makers and no single person with authority can be a major challenge to the success of a business.
Business Management
This section should include the names, positions, and general biography of the key business personnel. This section will be incredibly important to outsider investors (angels or venture capitalists) who are assessing your business. Within the Business Management section you should include answers to the following questions:
- Name : Who are the key individuals involved in the management of your business?
- Title : What will be that person's title?
- Responsibilities : What primary responsibilities does that position entail?
- Qualifications : What is their background and qualifications for carrying out their intended responsibilities? (This will include work experience, educational degrees, and prior experience in startup ventures.)
Organizational Chart
I recommend that you create a formalized flow-chart demonstrating the hierarchy of authority within the business. This organizational chart should be cross-laid with the key core operational responsibilities of the business. For example, you may split the business responsibilities into: Operations, Sales & Marketing, and Administration & Governance. Outlining the business in this fashion will give individuals a clear sense of their responsibilities. Further, it will establish formal chains of authority that will become increasingly important as the business grows. As you add new employees you will want to integrate them within the organizational chart.Make clear the chain of authority and reporting. Outline both the responsibilities of each individual and their authority to represent the interests of the business. As the business grows you will gradually become more and more specific about the roles and responsibilities of individual members.You may also consider developing a plan for cross-training individuals for specific tasks? You don't want your business to hinge or become dependent solely on the presence of a single individual. This chart will also serve as credentials for business when approaching outside investors. These investors will want to see that the business is stable and that there is ample talent to perform all of the functions necessary to carry out the business's functions and grow goals.
Professional and Advisory Support
When forming your business you will begin to forge relationships with outside parties who can provide advice and services to your business. Depending on your business organization, you may have professional advisors, such as a board of directors or you may have a less formal advisory board. Below are a list and explanation of some of the more common professional and advisory support for a startup business.
- Accountant - An accountant can be extremely valuable in 3 areas: Entity formation, business compliance, and tax strategy. An accountant will be able to help you understand the tax considerations that go into choosing an entity type. They can also help you understand the rules for business compliance state and federal income tax, tax deductions, tax credits, sales & use, transfer, deductions, capital gain loss, employee withholding, estimated tax payments, financial statements, auditing, etc.
- Small Business Attorney - A small business attorney is useful in a number of important areas. Entity selection and formation, contracts, intellectual property, employment law, securities regulation, business compliance & governance, collection efforts, etc.
- Insurance Agent - Depending on the nature of the business, you may require various types of insurance coverage. Common types of insurance includes casualty & damage on property, personal injury protection, professional liability, life insurance, health insurance in employee benefit plans, etc.
- Banker - I cannot express the importance of having a relationship with your bank representative. Many small businesses make the mistake of banking with large financial institutions, rather than choosing smaller, more intimate, local banks. When you are seeking loans to operate your business you will have a much easier time working with a banker who knows you personally and understands your business.
- Mentors - Find someone who you know and respect to serve as your mentor. Preferably, this is someone who has experience with startup ventures. Starting a venture can be nerve-racking. It helps to have someone close who has gone through this process before. This person will provide moral support more than expertise in a particular industry.
- Board of Advisors - A board of advisors is like a semi-formal group of mentors. Rather than providing moral support, these individuals help to guide you through the process of starting, managing and growing your business. You should try to assemble a diverse group with a variety of professional experiences. Preferably, these individuals will be a mix of knowledgeable entrepreneurs and industry experts.
- Board of Directors - If you choose the corporate form to do business, you will have a board of directors. Many closely held corporations don't have outside members on the board of directors; rather, the board consists of the owners and key members. As the business begins to grow, you may have directors who are either equity investors or experts who you compensate with equity ownership. In either case, you should seek investors and experts who can provide the greatest degree of guidance and support to your business.
You will want to detail the names, experience, and qualifications of these individuals within the business plan. The primary purpose is to demonstrate to outside investors that you have adequate support to handle your operations and intended growth path.
Related Topics
- Business Plan, Part 1 (Outline Overview)
- Business Plan, Part 2 (The Executive Summary)
- What is a Mission Statement?
- What is a Values Statement?
- Setting Company Goals
- Business Plan, Part 4 (Market Analysis)
- Business Plan, Part 5 (Competitive Analysis)
- Business Plan, Part 6 (Marketing Plan)
- Business Plan, Part 7 (Operations)
- Business Plan, Part 8 (Management and Organization)
- Business Plan, Part 9 (Financial Projections)
- Business Plan, Part 10 (Appendices)
- Business Plan , (Final Modifications)
Related Articles
- Loss Leader Strategy - Explained
- Investor Pitch - Slide 2: The Business Team
- Industry Lifecycle Analysis - Explained
- Click and Mortar (Business Model) - Explained
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write the Management Summary
Overview of the Management Summary Section of a Business Plan
Alyssa Gregory is an entrepreneur, writer, and marketer with 20 years of experience in the business world. She is the founder of the Small Business Bonfire, a community for entrepreneurs, and has authored more than 2,500 articles for The Balance and other popular small business websites.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/alyssa-headshot-2018-5b73ee0046e0fb002531cb50.png)
The management summary section of your business plan describes how your business is structured, introduces who is involved, outlines external resources and explains how the business is managed.
This section backs up all of the data you've included elsewhere in the business plan by demonstrating the expertise of the team and resources behind your company.
Example of a Management Summary Section of a Business Plan
For an example of a management summary section, see the Coffee Kiosk Business Plan .
What Does a Management Summary Section of a Business Plan Include?
The management summary section covers all of the relevant information about personnel, anticipated growth and how the company is organized. This section can be broken down into the following parts:
- Business Structure: What business structure will your company take, a sole proprietorship , an LLC, a partnership or a corporation? This determination will form the basis for the rest of the areas in this section.
- Management Team: Who will oversee the company? If you're forming a corporation, who will make up the Board of Directors ? An organizational chart can be a good visual to use to illustrate this element.
- Management Team Gaps: What are your anticipated personnel needs? How will each role, once filled, contribute to the success of your company?
- Other Personnel: Aside from your Board and employees, what external support will help the business function? This could include attorneys, accountants, public relations professionals, administrative support and even an external advisory board.
- Personnel Growth Plan: What are the salaries of each person to be involved with the company for the next three years? This should provide a bottom line cost for personnel expenditures.
Tips for Writing the Management Summary Section of a Business Plan
The management summary helps the reader understand who is behind the company and what personnel resources may be needed in the future. Here are a few tips for ensuring that the management summary gives the reader the information they need to accurately analyze your company's potential.
Explain the Intricacies
Very rarely does a team function exactly as outlined in an organizational chart. Describe how key personnel will interact and how roles may cross to provide a well-rounded picture of the overall management.
Relate Personnel to Business Activities
Your goal should be to directly attach personnel to an individual role and the overall success of the company. You can accomplish this by relating the specific experience of each person to the role they will play in the business.
Don't Include the Kitchen Sink
In the management summary section, focus only on the most relevant biographical information that is most important to your business plan. Put the full bios in your appendix.
Let the Team Review
When you have drafted the summary, give your key personnel a chance to review it. This will give you a chance to confirm that you've accurately described the roles and responsibilities as understood by the team.
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated April 25, 2024
If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
Related Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
The best way to start is by reviewing examples and downloading a business plan template. These resources will provide you with guidance and inspiration to help you write a plan.
We recommend starting with a simple one-page plan ; it streamlines the planning process and helps you organize your ideas. However, if one page doesn’t fit your needs, there are plenty of other great templates available that will put you well on your way to writing a useful business plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
Don't Make These 4 Mistakes in Your Executive Summary

How Long Should a Business Plan Be?
8 Min. Read
How to Write a Home Health Care Business Plan

9 Min. Read
How to Create a Sales Plan for Your Business
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Management Plan in a Business Plan
What is a management plan in a business plan? As a small business owner, you know you face an uphill battle. 4 min read updated on February 01, 2023
What is a management plan in a business plan? As a small business owner, you know you face an uphill battle. About 80 percent of new ventures fail within their first five years. Why? Most of the time it's due to flawed operating procedures or a less-than-optimal management structure.
What Is a Management Plan?
The management plan is all about employees and operations.
- Employees are one of the most important parts of any new venture. Good employees can make your life much easier, while bad employees can distract you and be a detriment to your success.
- Operational structure can be the difference between a successful venture and a failure.
When you're putting together a business plan , the operations and management section will describe how your business will operate on a day-to-day basis. It will cover all the essentials:
- Your company's physical location
- Other important processes
This section is an easy way to answer basic questions about your business without overwhelming readers.
Carefully crafting a professional and thorough business plan is an important step in forming a new venture. It will keep you on track and clearly define strategy and goals. However, business plans are only as good as the people behind them.
A venture's biggest asset is the entrepreneur. Investors won't make a move until they know they have complete confidence in an entrepreneur. Does he or she have the right experience? Is he or she willing to put in the work? These are just two of the questions Investors will have to answer before working with a new entrepreneur .
The management section of your business plan is an excellent space to highlight the members of your management team . Tell your readers and potential investors who will be managing your company, where they come from, how they will help your venture, and anything else that will signal your venture's future success. Be sure to cast the best light on your management team. Your investors need to know that this team is capable of anything.
There are usually three parts to a good Management and Staffing portion of a business plan:
- Management team details
- Key supporters and alliances, such as an advisory board
- Staffing and employment requirements
A few things to remember as you work on this section of your business plan:
- Your readers are usually potential investors. They need to know you and your management team are trustworthy and deserving of their investment.
- Investors need to know that you and your team can do the job; they need to get a feel for your attitudes and your abilities.
- Showing your team has a wide variety of skills and experiences will give you an advantage when presenting your business plan.
- It's all about the people. Business plans are great for answering key questions about the new venture, but at the end of the day, investors are looking to partner with hard-working, trustworthy people.
Now let's talk about operations. The operations section of the business plan describes several key characteristics of your business. For example, if your business has a physical, "brick and mortar" location, take time in this portion of the business plan to describe the area around your business. Tell your investors why your location is optimal for your business.
Make a note of your standard operating hours. Answer questions like,
- When will you open every day?
- When will you close?
- Will you be open during holidays?
- If so, which ones?
This is also a great section to list out your daily operation details, the different products or services you will provide, your standard operating procedures, customer service, and so on.
Take time in the Inventory section of your operations plan to list out potential suppliers, vendors, or contractors with whom you have agreements. Your partners, even the third-party ones, reflect upon you, so make sure to sing their praises. Put some thought into an inventory plan. Remember, too much inventory means you're likely wasting valuable resources that could be deployed elsewhere. On the other hand, too little inventory means you could be losing out on potential customers.
Once again, your management team plays a crucial role in your operations plan. Tell your investors exactly who they are, how they are uniquely qualified, and how their responsibilities will be divided with operations.
The management and operations sections of your business plan will demonstrate to your investors that you have the right team and the right strategy to be successful in a competitive industry.
If you need help with a management plan in a business plan, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Business Plan Management Structure: What You Need to Know
- Service Business Plan
- Purpose of Business Plan Sample: Everything You Need To Know
- Creating a Business Plan
- Business Description Outline
- Do I Need a Business Plan
- Nature of a Business Plan
- LLC Business Plan Template
- How to Write Up a Business Plan for Investors
- Business Plan for Existing Company

How to Write the Management Team Section of a Business Plan + Examples
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Over the last 20+ years, we’ve written business plans for over 4,000 companies and hundreds of thousands of others have used the best business plan template and our other business planning materials.
From this vast experience, we’ve gained valuable insights on how to write a business plan effectively , specifically in the management section.
What is a Management Team Business Plan?
A management team business plan is a section in a comprehensive business plan that introduces and highlights the key members of the company’s management team. This part provides essential details about the individuals responsible for leading and running the business, including their backgrounds, skills, and experience.
It’s crucial for potential investors and stakeholders to evaluate the management team’s competence and qualifications, as a strong team can instill confidence in the company’s ability to succeed.
Why is the Management Team Section of a Business Plan Important?
Your management team plan has 3 goals:
- To prove to you that you have the right team to execute on the opportunity you have defined, and if not, to identify who you must hire to round out your current team
- To convince lenders and investors (e.g., angel investors, venture capitalists) to fund your company (if needed)
- To document how your Board (if applicable) can best help your team succeed
What to Include in Your Management Team Section
There are two key elements to include in your management team business plan as follows:
Management Team Members
For each key member of your team, document their name, title, and background.
Their backgrounds are most important in telling you and investors they are qualified to execute. Describe what positions each member has held in the past and what they accomplished in those positions. For example, if your VP of Sales was formerly the VP of Sales for another company in which they grew sales from zero to $10 million, that would be an important and compelling accomplishment to document.
Importantly, try to relate your team members’ past job experience with what you need them to accomplish at your company. For example, if a former high school principal was on your team, you could state that their vast experience working with both teenagers and their parents will help them succeed in their current position (particularly if the current position required them to work with both customer segments).
This is true for a management team for a small business, a medium-sized or large business.
Management Team Gaps
In this section, detail if your management team currently has any gaps or missing individuals. Not having a complete team at the time you develop your business plan. But, you must show your plan to complete your team.
As such, describe what positions are missing and who will fill the positions. For example, if you know you need to hire a VP of Marketing, state this. Further, state the job description of this person. For example, you might say that this hire will have 10 years of experience managing a marketing team, establishing new accounts, working with social media marketing, have startup experience, etc.
To give you a “checklist” of the employees you might want to include in your Management Team Members and/or Gaps sections, below are the most common management titles at a growing startup (note that many are specific to tech startups):
- Founder, CEO, and/or President
- Chief Operating Officer
- Chief Financial Officer
- VP of Sales
- VP of Marketing
- VP of Web Development and/or Engineering
- UX Designer/Manager
- Product Manager
- Digital Marketing Manager
- Business Development Manager
- Account Management/Customer Service Manager
- Sales Managers/Sales Staff
- Board Members
If you have a Board of Directors or Board of Advisors, you would include the bios of the members of your board in this section.
A Board of Directors is a paid group of individuals who help guide your company. Typically startups do not have such a board until they raise VC funding.
If your company is not at this stage, consider forming a Board of Advisors. Such a board is ideal particularly if your team is missing expertise and/or experience in certain areas. An advisory board includes 2 to 8 individuals who act as mentors to your business. Usually, you meet with them monthly or quarterly and they help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. You typically do not pay advisory board members with cash, but offering them options in your company is a best practice as it allows you to attract better board members and better motivate them.
Management Team Business Plan Example
Below are examples of how to include your management section in your business plan.
Key Team Members
Jim Smith, Founder & CEO
Jim has 15 years of experience in online software development, having co-founded two previous successful online businesses. His first company specialized in developing workflow automation software for government agencies and was sold to a public company in 2003. Jim’s second company developed a mobile app for parents to manage their children’s activities, which was sold to a large public company in 2014. Jim has a B.S. in computer science from MIT and an M.B.A from the University of Chicago
Bill Jones, COO
Bill has 20 years of sales and business development experience from working with several startups that he helped grow into large businesses. He has a B.S. in mechanical engineering from M.I.T., where he also played Division I lacrosse for four years.
We currently have no gaps in our management team, but we plan to expand our team by hiring a Vice President of Marketing to be responsible for all digital marketing efforts.
Vance Williamson, Founder & CEO
Prior to founding GoDoIt, Vance was the CIO of a major corporation with more than 100 retail locations. He oversaw all IT initiatives including software development, sales technology, mobile apps for customers and employees, security systems, customer databases/CRM platforms, etc. He has a B.S in computer science and an MBA in operations management from UCLA.
We currently have two gaps in our Management Team:
A VP of Sales with 10 years of experience managing sales teams, overseeing sales processes, working with manufacturers, establishing new accounts, working with digital marketing/advertising agencies to build brand awareness, etc.
In addition, we need to hire a VP of Marketing with experience creating online marketing campaigns that attract new customers to our site.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Resources for Writing Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Executive Summary
- How to Expertly Write the Company Description in Your Business Plan
- How to Write the Market Analysis Section of a Business Plan
- The Customer Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
- Completing the Competitive Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
- Financial Assumptions and Your Business Plan
- How to Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan
- Everything You Need to Know about the Business Plan Appendix
- Business Plan Conclusion: Summary & Recap
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for April 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This is the ultimate guide to creating a comprehensive and effective plan to start a business . In today’s dynamic business landscape, having a well-crafted business plan is an important first step to securing funding, attracting partners, and navigating the challenges of entrepreneurship.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Embarking on the journey of creating a successful business requires a solid foundation, and a well-crafted business plan is the cornerstone. Here is the process of writing a comprehensive business plan and the main parts of a winning business plan . From setting objectives to conducting market research, this guide will have everything you need.
Executive Summary

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Think of it as an elevator pitch in written form: it should be compelling enough to engage potential investors or stakeholders and provide them with a clear understanding of what your business is about, its goals, and why it’s a promising investment.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives

In the Overview and Business Objectives section, outline your business’s core goals and the strategic approaches you plan to use to achieve them. This section should set forth clear, specific objectives that are attainable and time-bound, providing a roadmap for your business’s growth and success.
It’s important to detail how these objectives align with your company’s overall mission and vision. Discuss the milestones you aim to achieve and the timeframe you’ve set for these accomplishments.
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
- Introducing three new products within the first two years of operation.
- Achieving annual revenue growth of 30%.
- Expanding our customer base to over 10,000 clients by the end of the third year.
Company Description

The Company Description section is your opportunity to delve into the details of your business. Provide a comprehensive overview that includes your company’s history, its mission statement, and its vision for the future.
Highlight your unique selling proposition (USP) – what makes your business stand out in the market. Explain the problems your company solves and how it benefits your customers.
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market

Defining Your Target Market is critical for tailoring your business strategy effectively. This section should describe your ideal customer base in detail, including demographic information (such as age, gender, income level, and location) and psychographic data (like interests, values, and lifestyle).
Elucidate on the specific needs or pain points of your target audience and how your product or service addresses these. This information will help you know your target market and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis

The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
This analysis will enable you to spot market opportunities and anticipate potential challenges. Include data and statistics to back up your claims, and use graphs or charts to illustrate market trends.
This section should demonstrate that you have a deep understanding of the market in which you operate and that your business is well-positioned to capitalize on its opportunities.
Example: The market for eco-friendly technology products has experienced significant growth in recent years, with an estimated annual growth rate of 10%. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable solutions continues to rise.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis

A SWOT analysis in your business plan offers a comprehensive examination of your company’s internal and external factors. By assessing Strengths, you showcase what your business does best and where your capabilities lie.
Weaknesses involve an honest introspection of areas where your business may be lacking or could improve. Opportunities can be external factors that your business could capitalize on, such as market gaps or emerging trends.
Threats include external challenges your business may face, like competition or market changes. This analysis is crucial for strategic planning, as it helps in recognizing and leveraging your strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and preparing for potential threats.
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
- Innovative and eco-friendly product offerings.
- Strong commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Skilled and experienced team with expertise in technology and sustainability.
Weaknesses:
- Limited brand recognition compared to established competitors.
- Reliance on third-party manufacturers for product development.
Opportunities:
- Growing consumer interest in sustainable products.
- Partnerships with environmentally-focused organizations and influencers.
- Expansion into international markets.
- Intense competition from established technology companies.
- Regulatory changes could impact the sustainable technology market.
Competitive Analysis

In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
By conducting a thorough competitive analysis, you can gain insights into your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to develop strategies to differentiate your business and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Example: Key competitors include:
GreenTech: A well-known brand offering eco-friendly technology products, but with a narrower focus on energy-saving devices.
EarthSolutions: A direct competitor specializing in sustainable technology, but with a limited product range and higher prices.
By offering a diverse product portfolio, competitive pricing, and continuous innovation, we believe we can capture a significant share of the growing sustainable technology market.
Organization and Management Team

Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Showcasing your team’s background, skills, and accomplishments instills confidence in investors and other stakeholders, proving that your business has the leadership and talent necessary to achieve its objectives and manage growth effectively.
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered

Describe the products or services your business offers, focusing on their unique features and benefits. Explain how your offerings solve customer pain points and why they will choose your products or services over the competition.
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Example: EcoTech offers a range of eco-friendly technology products, including energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers, and smart home devices that optimize energy usage. Our products are designed to help customers reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Marketing and Sales Strategy

In this section, articulate your comprehensive strategy for reaching your target market and driving sales. Detail the specific marketing channels you plan to use, such as social media, email marketing, SEO, or traditional advertising.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
This section is critical to convey to investors and stakeholders that you have a well-thought-out approach to market your business effectively and drive sales growth.
Example: Our marketing strategy includes digital advertising, content marketing, social media promotion, and influencer partnerships. We will also attend trade shows and conferences to showcase our products and connect with potential clients. Our sales strategy involves both direct sales and partnerships with retail stores, as well as online sales through our website and e-commerce platforms.
Logistics and Operations Plan

The Logistics and Operations Plan is a critical component that outlines the inner workings of your business. It encompasses the management of your supply chain, detailing how you acquire raw materials and manage vendor relationships.
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Quality control measures are essential to maintain product standards and customer satisfaction. This plan assures investors and stakeholders of your operational competency and readiness to meet business demands.
Highlighting your commitment to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction underlines your business’s capability to maintain smooth, effective operations even as it scales.
Example: EcoTech partners with reliable third-party manufacturers to produce our eco-friendly technology products. Our operations involve maintaining strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring quality control, and managing inventory.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan

In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Ground these projections in solid assumptions based on your market analysis, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth scenarios. Break down revenue streams and include an analysis of the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and potential investments.
This section should also discuss your break-even analysis, cash flow projections, and any assumptions about external funding requirements.
By presenting a thorough and data-backed financial forecast, you instill confidence in potential investors and lenders, showcasing your business’s potential for profitability and financial stability.
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Example: Over the next three years, we expect to see significant growth in revenue, driven by new product launches and market expansion. Our financial projections include:
- Year 1: $1.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $200,000.
- Year 2: $3 million in revenue, with a net profit of $500,000.
- Year 3: $4.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $1 million.
These projections are based on realistic market analysis, growth rates, and product pricing.
Income Statement

The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing your income statement allows you to monitor the health of your business, evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize profitability and growth.
Example: The income statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
- Revenue: $1,500,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $800,000
- Gross Profit: $700,000
- Operating Expenses: $450,000
- Net Income: $250,000
This statement highlights our company’s profitability and overall financial health during the first year of operation.
Cash Flow Statement

A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
By including a cash flow statement in your business plan, you demonstrate your ability to manage your company’s finances effectively.
Example: The cash flow statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
Operating Activities:
- Depreciation: $10,000
- Changes in Working Capital: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Operating Activities: $210,000
Investing Activities:
- Capital Expenditures: -$100,000
- Net Cash from Investing Activities: -$100,000
Financing Activities:
- Proceeds from Loans: $150,000
- Loan Repayments: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Financing Activities: $100,000
- Net Increase in Cash: $210,000
This statement demonstrates EcoTech’s ability to generate positive cash flow from operations, maintain sufficient liquidity, and invest in growth opportunities.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan

1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively.
2. Conduct thorough research: Before writing your business plan, gather as much information as possible about your industry, competitors, and target market. Use reliable sources and industry reports to inform your analysis and make data-driven decisions.
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
5. Be flexible and adaptable: A business plan is a living document that should evolve as your business grows and changes. Be prepared to update and revise your plan as you gather new information and learn from your experiences.
6. Use visuals to enhance understanding: Include charts, graphs, and other visuals to help convey complex data and ideas. Visuals can make your business plan more engaging and easier to digest, especially for those who prefer visual learning.
7. Seek feedback from trusted sources: Share your business plan with mentors, industry experts, or colleagues and ask for their feedback. Their insights can help you identify areas for improvement and strengthen your plan before presenting it to potential investors or partners.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
The template is divided into the following sections:
- Mission statement
- Business Overview
- Key products or services
- Target market
- Financial highlights
- Company goals
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Measurable, time-bound objectives
- Company History
- Mission and vision
- Unique selling proposition
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Pain points
- Industry trends
- Customer needs
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Competitor products and services
- Market positioning
- Pricing strategies
- Organizational structure
- Key roles and responsibilities
- Management team backgrounds
- Product or service features
- Competitive advantages
- Marketing channels
- Advertising campaigns
- Promotional activities
- Sales strategies
- Supply chain management
- Inventory control
- Production processes
- Quality control measures
- Projected revenue
- Assumptions
- Cash inflows
- Cash outflows
- Net cash flow
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s goals, objectives, and the steps required to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap as you start a business , guiding the company’s direction and growth while identifying potential obstacles and opportunities.
Typically, a business plan covers areas such as market analysis, financial projections, marketing strategies, and organizational structure. It not only helps in securing funding from investors and lenders but also provides clarity and focus to the management team.
A well-crafted business plan is a very important part of your business startup checklist because it fosters informed decision-making and long-term success.

Why You Should Write a Business Plan
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
- Attract Investors and Secure Funding : A well-written business plan demonstrates your venture’s potential and profitability, making it easier to attract investors and secure the necessary funding for growth and development. It provides a detailed overview of your business model, target market, financial projections, and growth strategies, instilling confidence in potential investors and lenders that your company is a worthy investment.
- Clarify Business Objectives and Strategies : Crafting a business plan forces you to think critically about your goals and the strategies you’ll employ to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for success. This process helps you refine your vision and prioritize the most critical objectives, ensuring that your efforts are focused on achieving the desired results.
- Identify Potential Risks and Opportunities : Analyzing the market, competition, and industry trends within your business plan helps identify potential risks and uncover untapped opportunities for growth and expansion. This insight enables you to develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, positioning your business for long-term success.
- Improve Decision-Making : A business plan serves as a reference point so you can make informed decisions that align with your company’s overall objectives and long-term vision. By consistently referring to your plan and adjusting it as needed, you can ensure that your business remains on track and adapts to changes in the market, industry, or internal operations.
- Foster Team Alignment and Communication : A shared business plan helps ensure that all team members are on the same page, promoting clear communication, collaboration, and a unified approach to achieving the company’s goals. By involving your team in the planning process and regularly reviewing the plan together, you can foster a sense of ownership, commitment, and accountability that drives success.
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
- Startup Business Plan: Tailored for new ventures, a startup business plan outlines the company’s mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. It helps entrepreneurs clarify their vision, secure funding from investors, and create a roadmap for their business’s future. Additionally, this plan identifies potential challenges and opportunities, which are crucial for making informed decisions and adapting to changing market conditions.
- Internal Business Plan: This type of plan is intended for internal use, focusing on strategies, milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation. It serves as a management tool for guiding the company’s growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. The internal business plan also helps identify areas of improvement, fosters collaboration among team members, and provides a reference point for measuring performance.
- Strategic Business Plan: A strategic business plan outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for the company’s direction. It typically includes a SWOT analysis, market research, and competitive analysis. This plan allows businesses to align their resources with their objectives, anticipate changes in the market, and develop contingency plans. By focusing on the big picture, a strategic business plan fosters long-term success and stability.
- Feasibility Business Plan: This plan is designed to assess the viability of a business idea, examining factors such as market demand, competition, and financial projections. It is often used to decide whether or not to pursue a particular venture. By conducting a thorough feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs can avoid investing time and resources into an unviable business concept. This plan also helps refine the business idea, identify potential obstacles, and determine the necessary resources for success.
- Growth Business Plan: Also known as an expansion plan, a growth business plan focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. It includes market analysis, new product or service offerings, and financial projections to support expansion plans. This type of plan is essential for businesses looking to enter new markets, increase their customer base, or launch new products or services. By outlining clear growth strategies, the plan helps ensure that expansion efforts are well-coordinated and sustainable.
- Operational Business Plan: This type of plan outlines the company’s day-to-day operations, detailing the processes, procedures, and organizational structure. It is an essential tool for managing resources, streamlining workflows, and ensuring smooth operations. The operational business plan also helps identify inefficiencies, implement best practices, and establish a strong foundation for future growth. By providing a clear understanding of daily operations, this plan enables businesses to optimize their resources and enhance productivity.
- Lean Business Plan: A lean business plan is a simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements such as value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structure. It is perfect for startups looking for a flexible, adaptable planning approach. The lean business plan allows for rapid iteration and continuous improvement, enabling businesses to pivot and adapt to changing market conditions. This streamlined approach is particularly beneficial for businesses in fast-paced or uncertain industries.
- One-Page Business Plan: As the name suggests, a one-page business plan is a concise summary of your company’s key objectives, strategies, and milestones. It serves as a quick reference guide and is ideal for pitching to potential investors or partners. This plan helps keep teams focused on essential goals and priorities, fosters clear communication, and provides a snapshot of the company’s progress. While not as comprehensive as other plans, a one-page business plan is an effective tool for maintaining clarity and direction.
- Nonprofit Business Plan: Specifically designed for nonprofit organizations, this plan outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation. It helps secure grants and donations while ensuring the organization stays on track with its objectives. The nonprofit business plan also helps attract volunteers, board members, and community support. By demonstrating the organization’s impact and plans for the future, this plan is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability within the nonprofit sector.
- Franchise Business Plan: For entrepreneurs seeking to open a franchise, this type of plan focuses on the franchisor’s requirements, as well as the franchisee’s goals, strategies, and financial projections. It is crucial for securing a franchise agreement and ensuring the business’s success within the franchise system. This plan outlines the franchisee’s commitment to brand standards, marketing efforts, and operational procedures, while also addressing local market conditions and opportunities. By creating a solid franchise business plan, entrepreneurs can demonstrate their ability to effectively manage and grow their franchise, increasing the likelihood of a successful partnership with the franchisor.
Using Business Plan Software

Creating a comprehensive business plan can be intimidating, but business plan software can streamline the process and help you produce a professional document. These tools offer a number of benefits, including guided step-by-step instructions, financial projections, and industry-specific templates. Here are the top 5 business plan software options available to help you craft a great business plan.
1. LivePlan
LivePlan is a popular choice for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features. It offers over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, and the ability to track your progress against key performance indicators. With LivePlan, you can create visually appealing, professional business plans that will impress investors and stakeholders.
2. Upmetrics
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
Bizplan is designed to simplify the business planning process with a drag-and-drop builder and modular sections. It offers financial forecasting tools, progress tracking, and a visually appealing interface. With Bizplan, you can create a business plan that is both easy to understand and visually engaging.
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
5. Tarkenton GoSmallBiz
Developed by NFL Hall of Famer Fran Tarkenton, GoSmallBiz is tailored for small businesses and startups. It features a guided business plan builder, customizable templates, and financial projection tools. GoSmallBiz also offers additional resources, such as CRM tools and legal document templates, to support your business beyond the planning stage.
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are to guide the company’s strategy, attract investment, and evaluate performance against objectives. Here’s a closer look at each of these:
- It outlines the company’s purpose and core values to ensure that all activities align with its mission and vision.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of the market, including trends, customer needs, and competition, helping the company tailor its products and services to meet market demands.
- It defines the company’s marketing and sales strategies, guiding how the company will attract and retain customers.
- It describes the company’s organizational structure and management team, outlining roles and responsibilities to ensure effective operation and leadership.
- It sets measurable, time-bound objectives, allowing the company to plan its activities effectively and make strategic decisions to achieve these goals.
- It provides a comprehensive overview of the company and its business model, demonstrating its uniqueness and potential for success.
- It presents the company’s financial projections, showing its potential for profitability and return on investment.
- It demonstrates the company’s understanding of the market, including its target customers and competition, convincing investors that the company is capable of gaining a significant market share.
- It showcases the management team’s expertise and experience, instilling confidence in investors that the team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
- It establishes clear, measurable objectives that serve as performance benchmarks.
- It provides a basis for regular performance reviews, allowing the company to monitor its progress and identify areas for improvement.
- It enables the company to assess the effectiveness of its strategies and make adjustments as needed to achieve its objectives.
- It helps the company identify potential risks and challenges, enabling it to develop contingency plans and manage risks effectively.
- It provides a mechanism for evaluating the company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow.
Can I write a business plan by myself?
Yes, you can write a business plan by yourself, but it can be helpful to consult with mentors, colleagues, or industry experts to gather feedback and insights. There are also many creative business plan templates and business plan examples available online, including those above.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
A typical business plan ranges from 20 to 50 pages, but the length may vary depending on the complexity and needs of the business.
What is a business plan outline?
A business plan outline is a structured framework that organizes the content of a business plan into sections, such as the executive summary, company description, market analysis, and financial projections.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
The five most common business plan mistakes include inadequate research, unrealistic financial projections, lack of focus on the unique selling proposition, poor organization and structure, and failure to update the plan as circumstances change.
What questions should be asked in a business plan?
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan focuses on the overall vision, goals, and tactics of a company, while a strategic plan outlines the specific strategies, action steps, and performance measures necessary to achieve the company’s objectives.
How is business planning for a nonprofit different?
Nonprofit business planning focuses on the organization’s mission, social impact, and resource management, rather than profit generation. The financial section typically includes funding sources, expenses, and projected budgets for programs and operations.
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.

12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![what is management and organization in business plan How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![what is management and organization in business plan 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![what is management and organization in business plan The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

“What Is Organization and Management in the Business Plan?”

How do you write the organization and management section of your business plan?
- Remember that the purpose of a business plan is to sell people on your potential for success!
- Determine the legal structure of your business
- Develop a rough organizational flowchart. Keep in mind that owners/shareholders, directors, and third parties can also be included
- For every individual in your organizational flowchart – specify their name and responsibilities. Most importantly – highlight their qualifications for the role!
- Include official resumes and critical procedures in the appendix
- Circle back and make adjustments to the previous steps as you progress in the writing of your business plan
The organization and management part of your business plan focuses less on the business itself and more on the people behind it. A business is only as good as the people making decisions. Until (if ever), artificial intelligence can run businesses, it’s going to be people pulling the strings behind the curtain. For better or worse.
Also, keep in mind that banks lend money to people, not ideas. Venture capitalists invest in people, not mindless assets. Your business plan might be great. But, it will require one or more humans to execute that plan.
Whoever might be investing in your company will want to know the chain of command. A formal declaration of who employees report to and who the final decision maker is. If these sorts of things aren’t clarified, it can lead to catastrophe.
There are, essentially, two main parts to the organization and management section of the business plan. You’ve probably guessed what they are.
In one part you’ll discuss the business’ organizational structure. For example who will report to who, and what the chain of command looks like.
In the other part, you’ll describe the individuals who will populate those positions. Plus, their qualifications for doing so.
The organization of your business
The reader of your business plan will want to know what the organizational structure is when you are starting your business. They need to know who the key people are in the organization and what their roles will be.
Businesses need smooth running chains of command in order to be successful. And, while your business can consist of one person – there’s a good chance that at some point you’ll need quality people to help you out.
Who’s responsible for what?
Obviously, this will change over time, as your business evolves. The reader of your business plan will want to know the lay of the land when the business launches, however.
Particularly, if you’re asking for money to add additional roles in the future, you’ll want to be crystal clear about who those individuals will report to, what their responsibilities will be, and most importantly, how they’ll add value to the organization.
Generally speaking, small businesses are simpler organizations than larger ones. But, there still needs to be clarity in terms of the flow of work. Some of the critical departments to think about are sales/marketing, manufacturing/distribution, and accounting/administration. Depending on the nature of your business, research and development might be critical too. Who will be responsible for these important tasks?
Don’t be afraid to use graphics here. An illustration of the hierarchy of your business and/or the process flow can help clarify everything you’ve written about. This organizational chart can and should be used in the future – for clarification’s sake, as the business grows.
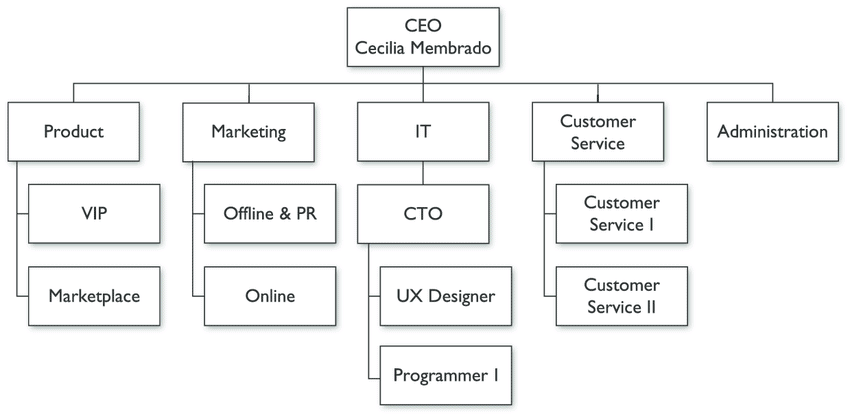
A free tool like draw.io can be used to make a good looking flowchart.
Procedures?
Beyond the organizational structure and the workflow, you might consider adding some procedures for the routine duties that these roles will handle. In fact, as you write the organization and management section of the business plan, it might dawn on you that you’ve given precious little thought to how day-to-day business will be conducted! This is the perfect opportunity to conceptualize exactly how you’ll take inputs and turn them into outputs.
Procedures demonstrate to the reader that you’ve given thought to the most efficient way to handle these tasks. They also show that you won’t be planning on wasting money on excess manpower. A business without proper procedures is one that’s going to run into trouble with inefficiency and poor customer service.
Since written procedures are detailed documents, it might best to include them in the appendix.
Third parties?
Include any roles that might be filled by third parties. Independent contractors or freelancers, for instance. Even if you anticipate relying upon consultants – that should be addressed in this section as well. Where will these people fit in the organizational chart?
If your business is going to depend on these types of individuals, the reader of your business plan wants to know about it.
More about the third parties you might consider, below.
Legal structure
Finally, the organizational section of your business plan should address the legal structure of the business. Anybody investing in your business is going to want to know whether you’re incorporated as a C or an S corporation. Or, conversely, organized as a general or limited partnership. Maybe the best legal structure for you is something as simple as in LLC or a sole proprietorship. Whatever the case may be, it’s important to convey this information.
In a corporation, the shareholders may or may not be part of the Board of Directors or the management team.
In a partnership, the assumption is that the partners will all have equal control in managing the new business.
With an LLC it can be a situation where the business is managed by the members. Or, it could be that outside managers are hired.
You can see how these sorts of things must be clarified for the reader of your business plan.
The management of your business
If you are the owner of a business, then you will list yourself. If any owners are going to be on the Board of Directors, involved with the business heavily, or on the management team you need to include a “Resume” of their skills and qualifications.
The previous section outlined the roles necessary for your startup to succeed. Now, you want to discuss the people that will fill those roles.
Whatever your role may be, the reader of your business plan will probably understand why you hired yourself. That’s one of the privileges of being a founder.
However, that doesn’t mean that you don’t have to justify why you gave yourself a particular position.
What qualifies you for this role? Hopefully, the fact that your business plan is well-polished helps to convey your qualifications. But, just because you’re a founder doesn’t mean that you can do anything. For instance, if your company will rely heavily on scientific or engineering know-how, then you had better be well-qualified if you wish to fill one of those roles.
Formalized resumes for yourself and the rest of your team can be included in the appendix. However, some of the things that you want to highlight here are:
- Their title
- What decision will they be making?
- Previous positions that they’ve held
- Leadership experience
- Industry experience
- Sales and marketing expertise
- Anything else that will inspire confidence in your company!
Here’s an idea of the individual parties you need to name/address:
Ownership/Shareholders
The number of individuals and depth of information included here will depend, in part, on the legal structure of your business.
If it’s a corporation, you’ll list the shareholders along with the type of stock they’ll own (common or preferred).
If the business is a partnership, your list the partners along with the type of partner they are (general or limited).
For an LLC, you’ll list the members.
And, as you might expect, if your business as a sole proprietorship you will list yourself.
Additionally, if any of the owners are going to be on the Board of Directors, involved with the business heavily, or on the management team you need to include a “resume” of the skills and qualifications they bring to the table.
Board of directors
Not every small business will have a Board of Directors. If your legal structure will be an S or C corporation though, it will be required. Make sure you’re familiar with the laws of the state you live in and the state in which you incorporate in.
If you have a Board of Directors then you want to specify each of the individuals that will comprise the board. As with everyone else you would summarize the skills and qualifications that they’ll bring to the table. Resumes can, again, go in the appendix.
Furthermore, you might detail any other involvement they’ll have with your startup. That is, beyond, attending board meetings.
If your business legal structure is a partnership, LLC, or sole proprietorship you will not have a Board of Directors. It may be, however, that you have a group of trusted advisors who have expressed their willingness to help your startup succeed. If that’s the case, consider naming them here. Or, you can include them with the other third parties below. It’s up to you.
Again, these sorts of things help to sell the potential for the success of your burgeoning business.
I’m sure you know the routine by now. List the names, skills, and qualifications of the upper management team.
Since these are the people that will be making the day-to-day operational decisions in your business, you want to make their accomplishments a focal point. Lenders and investors will be especially interested in how these people can earn them a healthy ROI.
Another thing to consider is that since you’ll likely be the top dog at your start up (and rightfully so) you want to emphasize how the rest of the management staff will compliment you as a manager. Particularly, how their strengths will compensate for your shortcomings. And, how your strengths will compensate for their shortcomings.
Admitting your shortcomings is not always an easy pill to swallow for an entrepreneur. We like to think that we can do it all. Again, keep in mind this is a sales document. Put your ego aside and write a management and organization section of your business plan that will get funding.
Lastly, it is here that you will specify the details of compensation for yourself and the rest of the management team. Compensation includes, of course, things such as salary, benefits, and profit-sharing.
Additionally, if any individuals will be bound by contracts or non-compete agreements, this is the place to itemize those particulars.
Other support roles
- Insurance agent
In addition to the key ownership, directors, and management, you should consider outlining key third-party professionals who will serve in advisory roles. Remember, the whole point of the organization and management section of your business plan is to highlight the individuals who have your back and how they can help your business succeed. Not every key individual is going to be inside the company either.
Your accountant
Accounting is not most people’s strong suit. If that’s the case with you, then a competent professional accountant will be an extremely valuable asset. This individual will help you with business compliance, taxes, and financial operations. Also with financial statement preparation, auditing, and payroll.
All critical tasks.
Your attorney
An attorney is also a crucial part of your advisory team. They can help you choose the appropriate legal structure for your business (with help from your accountant). They provide valuable support with any contracts, intellectual property, regulation, compliance, and governance.
The law is complex and “winging it” in these areas could stop your business in its tracks.
An insurance agent or risk management advisor
Some businesses will rely more upon this than others. However, keep in mind that many of the risks your business will run into what is called “unknown unknowns” (circumstances that you could not foresee).
Having someone in your corner that understands how to identify and mitigate these risks will put investors at ease.
Your banker
Having a good relationship with a local banker who understands your industry will help you achieve your goals.
A small bank may be preferable to a larger bank. Small banks can offer a more intimate relationship which, in turn, would facilitate a more beneficial long-term relationship.
If you have someone in your life who can provide sage advice you may consider adding them to your list of trusted advisors. Maybe you even have more than one?
If this person (these people) is particularly well versed in your industry or in entrepreneurship, then all the better! Knowing that you have someone in your corner who has been in your shoes before will inspire confidence.
An organization and management example
As with all of the other posts written on the topic of business plans, I like to include an example from my own hypothetical startup. It gives me the opportunity to follow along with the subject at hand and to “do” rather than just “say.”
The hypothetical startup is a would-be manufacturer and distributor of an all-natural, topical hair regrowth supplement for men and women.
As I alluded to above, it might dawn on you at this stage that you have some serious thinking to do as far as the operations of your business go. So much time thus far has been spent on market analysis (and rightfully so) that the day-to-day comings and goings have slipped through the cracks. Well, these things can’t get put off forever, so this is a good time to at least get rough drafts created.
With that in mind, here’s my first pass at an organizational flowchart for this hypothetical business:
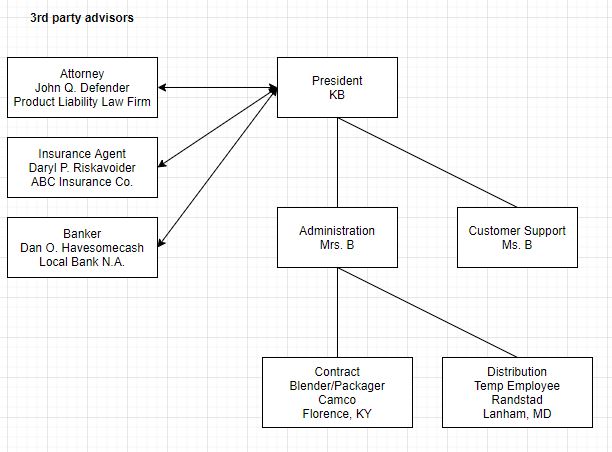
Below, are some “resumes” for full-time employees and third-party advisors. These are loosely based on real people. But, for the sake of anonymity, facts are obscured.
These “resumes” are, admittedly, a little generic. While I did want to go through the exercise of creating a management and organization section for my hypothetical business plan – I did not necessarily want to commit too much time to the careful crafting of resumes for fictional people. The same goes for the creation of procedures.
Of course, if this were the real deal, I would include more formal resumes (as appropriate) in the appendix.
Management/employees
KB, President
Responsibilities – Providing strong leadership. Establishing short and long-term goals, plans, and strategies. Presiding over the entire workforce (internal and external). Managing finances. Ensuring resources are allocated properly.
Qualifications – Researched and studied the factors critical to business success in his blogs, SpreadsheetsForBusiness.com , and InvestSomeMoney.com . Performed in the capacity as a Financial Analyst and Cost Accountant for a chemical manufacuturer nearly 15 years. Assisted small businesses in problem solving as a SCORE volunteer.
Mrs. B, Administration
Responsibilities – Assist in the day-to-day management of the value chain. Implementing processes and practices across the organization. Improving performance, procuring material/resources, and securing compliance.
Qualifications – 20 years of multitasking and personality management in the education industry. Experience keeping executives and business owners organized and prioritized. Practices an intuitive approach to assistance that rests on empathy, efficiency, and astute problem-solving.
Ms. B, Customer Support
Responsibilities – Leading the charge to reach sales targets. Setting quotas. Evaluating and adjusting performance. Developing processes that drive sales. Managing social media presence.
Qualifications – Major in marketing. 4 years’ experience in a customer-facing role. Experience in setting and meeting sales goals. Proficient in CRM software.
Third-party partners
For third parties, it wouldn’t necessarily be appropriate for me to ask for a formal resume. Most of these professionals will have qualifications made public on their websites or social media – for the purpose of marketing themselves.
John Q. Defender, Attorney
Mr. Defender focuses on commercial litigation. He helps his clients with insurance coverage and claims, including general liability. He serves in both an advisory capacity and represents clients before and after litigation. Additionally, he has experience litigating cases to a verdict, including claims regarding product liability and insurance coverage.
Daryl P. Riskavoider, Insurance Advisory
A 15-year agent with Countrywide Insurance. Mr. Riskavoider has helped dozens of other startup manufacturers identify risks and protect their downside with Countrywide’s diverse array of insurance products. Countrywide Insurance has been in business for 90 years. They focus on small business needs and are one of the largest insurers in the world.
Dan O. Havesomecash, Banker
An experienced loan professional with WeTrust Bank. Mr. Havesomecash has underwritten over $50 million in financing for similar startup manufacturers. WeTrust Bank is a premier local bank with a 100-year history. They provide competitive and flexible financing solutions for regional SMBs and are committed to contributing to the growth of local business.
Other notable partners
I’ll also include a brief synopsis of my contract blender/packager and the temp service I would use to man the distribution facility. Again, the purpose of the business plan generally, (and the organization and management section specifically) is to sell the success of your business. I think that including these partners will help to do that and potentially quell any concerns that readers might have.
In these instances, however, I’m just going to copy + paste info from their respective websites. No need in trying to improve on what they’ve already put a lot of time and effort into.
Camco Chemicals, Contract Blending & Packaging
Camco’s contract blending services are both extensive and broad. With 21 liquid and 5 powder mixers, Camco can produce an impressive 1.25 million pounds of product per eight hour shift. Importantly, Camco possesses unused capacity that can serve your project’s current and future needs while assuring you of the ongoing manufacturing flexibility necessary to deliver the response time that you need to meet your customers’ demands for delivery. https://www.camco-chem.com/contract-blending
Camco is a family owned business that was founded in 1960 and continues to operate under private ownership with several second and third generation family members active in the business’ daily operation. Camco employs approximately 175 associates and operates a thirty-two acre campus situated in an industrial park setting in three adjacent buildings collectively comprising 587,000 square feet of manufacturing, packaging and distribution services. As a contract chemical manufacturer and contract packaging contractor, Camco operates on a five day week schedule with three shifts and blends a broad variety of chemical products that are sold by Camco’s customers in the consumer, industrial, agricultural, transportation, water treatment and food industries, to name just a few. Importantly, Camco does not market any products, so that its customers can be assured that their proprietary and confidential information will remain so. Camco’s overall manufacturing capacity totals nearly 300 million pounds of packaged goods with potentially several hundred million additional pounds for bulk shipments and transloads. The level of available capacity is such that virtually any project can be accommodated. https://www.camco-chem.com/about-camco
Randstad Staffing, Temporary Agency
Companies partner with us to hire better talent faster, save on HR costs and get workforce solutions that make sense for them. If you’re looking to do the same, then there are a lot of reasons to work together. We’re able to reach into our talent network and get the ball rolling for you fast thanks to the relationships we’ve built with professionals in your area. We match candidate skills, personality and working style to your company because when you place candidates in environments where they can thrive, you’re much less likely to make a bad hire. Why do people work with us? It’s because of the ways their business changes with our partnership. When we work together, you won’t have to worry about missing out on the market’s most sought-after candidates because our streamlined process will help you hire faster — but the benefits don’t stop once your new talent has been onboarded. Employee engagement and retention rates will improve with quality talent that fits your workplace — not just the job description, and your business will be set up for long-term success because our experts will provide you with tailored workforce strategies. https://rlc.randstadusa.com/for-business/randstad-learning-center/working-with-us/why-people-work-with-us
Create an organization plan: types, steps, and examples

If you want to start or grow your business – or make it more profitable – you need an organization plan. It’s no secret that the most successful companies have the best organizational goals and the right strategies for attracting top talent to achieve their objectives.
Planning plays a vital role in any business organization. As such, the right organizational plan will help make your business a titan in its industry, whereas a poor one will allow your competitors to pull ahead of your company.
Read on to discover creative ways an organizational plan will bring value to your business and can improve your revenue.
Table of contents
What is an organizational plan, why is an organizational plan important , what are the 4 types of organizational planning, what are some examples of organizational planning, 5 steps to develop an effective organizational plan, strengthen your recruitment process with testgorilla.
An organizational plan is how businesses prepare their affairs to achieve success in their industry. It may include daily business operations, organizational goals, and potential expenses.
An organizational plan usually begins with big, long-term objectives but is then broken down into smaller, attainable goals. This makes it easier for your organization to define success, plan ahead, and achieve its goals.
Organizational plans are crucial for businesses because they enable you to create an effective, realizable method to achieve your business goals.
A solid organizational plan will therefore improve your company’s performance. Research shows that businesses with good plans are 16% more likely to succeed .
Organizational plans may also clarify the roles, expectations, and responsibilities of employees in your organization. And they are a great way to highlight the areas in which your business has shortcomings or issues.
Effective planning relies on a firm understanding of the four types of organizational planning. Knowing which organizational plan to apply to your business is crucial to steer your company toward a profitable and prosperous future.

1. Strategic planning
A strategic plan involves the creation of broad, long-term goals for your company. Senior management will usually oversee these kinds of plans; however, smaller companies tend to involve other employees.
Typically, strategic planning considers controllable and non-controllable variables and how to adjust them. The objectives must align with your company’s general mission, vision, and values.
2. Tactical planning
These shorter-term goals show how your company plans to achieve its longer-term strategic plan. Tactical plans typically take a year to complete, with middle managers establishing these goals and overseeing the actions.
3. Operational planning
Operational plans include department-specific objectives and targets and are focused on executing the tactical plan. Thus, for example, your company should have a working plan for the finance, marketing, and IT departments.
4. Contingency planning
Usually, contingency planning is associated with risk management, because a good contingency plan will address both known and unknown risks. Such planning enables your company to prepare for unforeseen circumstances that could harm your business.
Below are examples of organizational planning to help you understand the various forms a plan can take. With this knowledge, you can decide which kind of organizational plan suits your company.
1. Workforce development planning
Industry-leading companies do not become successful by chance. Instead, they earn their success through years of practical workforce training. Workforce development planning entails training your employees to increase their productivity and output.
By investing in your employees, you’ll create a loyal, diverse, and satisfied workforce focused on achieving your business’s ambitious goals.
2. Product and services planning
Product and service planning aims to make your organization’s products or services more appealing to its target market. This involves strategically creating schemes that set your business apart from competitors.
Being in a highly competitive industry can be difficult. That’s why the operations, finance, and marketing departments are tasked with developing innovative ways to keep your business ahead in its industry.
3. Expansion plans
A good business is always focused on growth. Hence, expansion plans identify growth opportunities and roadblocks your organization might face in its industry, helping you develop strategies to take advantage of those opportunities and overcome the obstacles.
4. Financial planning
Making plans to manage debt and utilize profits is one of the best ways to ensure your business is sustainable. Financial analysts are in charge of this, so they will analyze financial performance and give recommendations to help your business make better decisions.
Financial planning ensures you optimize every fund flow in and out of your business. You’ll also require employees with the right budget-management skills to draft the perfect plan.

1. Come up with a strategic plan
Identifying your company’s objectives will help you create more concrete strategic plans. But to identify these goals, you’ll need adequate data about your company.
Good data will guide you in making strategic decisions based on previous performance and other indicators, ensuring you can pave a clear path toward your goals.
2. Transform the strategic plan into practical steps
Establishing practical steps for achieving your strategic goals is the focus at this stage. A good example is requesting quarterly reports to ensure that the IT department is hitting its quota.
It also involves implementing every action that contributes to hitting your targets, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing the final product.
3. Plan day-to-day operations
This stage focuses on individual employee performance. Managers set goals and targets to ensure employees convert their work hours into profit for your business and more effective functioning of your teams. HR, for example, can be tasked with ensuring that unconscious bias does not exist in the workplace.
Similarly, the quality assurance team can create schedules to inspect raw materials before manufacturing begins.
4. Execute daily operations
At this stage, you should execute the theoretical strategies you set for daily operations. This requires applying all the planning from the previous steps to enable your organization to reach its strategic goals.
You can check these daily targets on your vision board as you progress, gradually allowing your longer-term objectives to materialize.
5. Monitor results and adjust plans
A plan is more likely to fail if you don’t monitor any progressive performance. To verify that your plan is complete, you should make provisions for adjusting and monitoring results to ensure they align with the goals you set.
Doing this will help your organization identify areas where your company didn’t meet its goals and inform you of any necessary changes. By extension, you should have the information required for performance management .
Although organizational planning might be a long and complex process, it is vital for your company’s success. Why? The right strategy will ensure your employees are clear on your organization’s vision and the actions required to achieve these goals.
A well-defined organizational plan will positively impact your workforce, since all employees will understand their day-to-day tasks and why they are needed. They’ll have explicit objectives to ensure they remain productive and focused.
TestGorilla facilitates your recruitment of skilled professionals who can help you develop a stellar organizational plan. Moreover, it helps you minimize any chance of unconscious bias creeping into your recruitment, helping you employ the best.
Create a free account with TestGorilla today to begin hiring.
Related posts

65 Apache Kafka interview questions to hire top talent (+ 25 sample answers)

Employee referrals: A powerful tool for finding – and keeping – top talent

How to hire a squarespace designer (And mistakes to avoid)
Hire the best candidates with TestGorilla
Create pre-employment assessments in minutes to screen candidates, save time, and hire the best talent.

Latest posts

The best advice in pre-employment testing, in your inbox.
No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
Hire the best. No bias. No stress.
Our screening tests identify the best candidates and make your hiring decisions faster, easier, and bias-free.
Free resources

This checklist covers key features you should look for when choosing a skills testing platform

This resource will help you develop an onboarding checklist for new hires.

How to assess your candidates' attention to detail.

Learn how to get human resources certified through HRCI or SHRM.

Learn how you can improve the level of talent at your company.

Learn how CapitalT reduced hiring bias with online skills assessments.

Learn how to make the resume process more efficient and more effective.

Improve your hiring strategy with these 7 critical recruitment metrics.

Learn how Sukhi decreased time spent reviewing resumes by 83%!

Hire more efficiently with these hacks that 99% of recruiters aren't using.

Make a business case for diversity and inclusion initiatives with this data.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Business Skills
- Business Writing
How to Write a Management Plan
Last Updated: September 18, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Madison Boehm . Madison Boehm is a Business Advisor and the Co-Founder of Jaxson Maximus, a men’s salon and custom clothiers based in southern Florida. She specializes in business development, operations, and finance. Additionally, she has experience in the salon, clothing, and retail sectors. Madison holds a BBA in Entrepreneurship and Marketing from The University of Houston. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 237,201 times.
A management plan describes how an organization or business is run. Writing a management plan allows you to formalize your management structure and operations. It also ensures that everyone is on the same page and that your goals will be accomplished. You can easily write your own management plan with a few simple steps.
Management Plan Outline and Example

Starting Your Management Plan

- Defining roles also creates accountability by making it clear who's fault it was that something did or did not happen. [3] X Trustworthy Source Kansas University Center for Community Health and Development Community-based research center focused on supporting public health development and education Go to source

- A section detailing management members and their responsibilities and authorities.
- A chart of section detailing interactions between and responsibilities of each level of the organization.
- A section explaining different aspects of your organization being managed and the policies and procedures of that management.
- A schedule for updating, enhancing, and growing management and the management plan. [6] X Research source

Describing Ownership and Management

- Include a copy of board policies, including election policies, term length, responsibility, authority, and conflict resolution. This information should already be stated in your operating agreement or other founding documents.

- List past positions and duties of each member that apply to their current management obligations. Explain how these obligations highlight applicable skills and strengthen the management positions.
- Highlight all relevant educational backgrounds for each of the managers. Explain how their training will benefit the company. Only include the education that is relevant to the positions that they currently hold.
- If you are the only employee in your business, be sure to include your own experience and strengths.

- Accountants.
- Insurance brokers.
- Consultants.

- For example, “Our team, with its diverse array of skills, have a combined forty years of experience in this field. With our coordinated democratic structure, they can work together effectively to produce results. With this team, we are confident that our business will become profitable in two years.”

Writing Out Policies and Procedures

- For example, a policy might be using and selling only green materials and products. The procedures to support that policy might be shopping from approved green vendors or checking the environmental impact of each material or product used.

Revising Your Plan

- When they approve, have all owners sign the plan before you submit it to your investors, bank, or fundraising bodies.

- Make sure there is a way for all management and employees to submit their feedback regarding the plan.
- Then, create a method by which changes to the plan can be approved and instituted. [20] X Trustworthy Source Kansas University Center for Community Health and Development Community-based research center focused on supporting public health development and education Go to source
Expert Q&A

- Many investors will read the management section of your business plan before any other section, including marketing and finances, so you want to make sure that you have the best proposal possible. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Do not neglect your management plan in favor of your financial plans. Both are equally important to a business plan. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ Madison Boehm. Business Advisor, Jaxson Maximus. Expert Interview. 24 August 2021.
- ↑ http://ctb.ku.edu/en/table-of-contents/leadership/effective-manager/management-plan/main
- ↑ https://www.brown.edu/research/conducting-research-brown/preparing-proposal/proposal-development-services/writing-management-plan
- ↑ https://www.thebalance.com/how-to-write-the-management-summary-2951561
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/humanresourcemanagement/chapter/4-1-the-recruitment-process/
- ↑ https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/241072
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ http://www.businessnewsdaily.com/4533-business-plan-outline.html
About This Article

The best way to write a management report is to describe the company’s management structure in 10 to 20 pages. Name the board members and explain the company’s ownership policies. Introduce all management members and present the strengths of each team member. Then, write out workplace policies and procedures. Send the management report to the company’s bank, investors, or fundraising bodies. For more tips from our Financial Reviewer, like how to outline, format, and revise your plan, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Moshakge Molokwane
Apr 12, 2017
Did this article help you?
Mar 14, 2019
Jamie Willacy
Feb 1, 2023

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

Career Tips , Choosing a Job , Getting a Job
What is Strategic Management? How Does it Ensure Business Success?
Updated: April 22, 2024
Published: April 19, 2024

To get ahead, corporations are emphasizing strategic management skills as they hire for leadership positions. Whether you are focused on finance, marketing, research and development, or operations, chances are good that you will be called upon to strategically manage projects or processes.
In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at strategic management, including the steps in the process, the benefits and pitfalls, and how you can become a strategy manager.

What is Strategic Management?
Strategic management is a comprehensive process that aligns a company’s strategic direction with its operational activities, ensuring it can navigate competitive markets successfully and achieve long-term success.
The main purpose of strategic management is to guide an organization in meeting its goals and objectives through the efficient use of resources. The process includes the continuous planning, monitoring, analysis, and assessment of an organization’s resources and capabilities. As changes or challenges arise – both internally and externally – a strategic manager will implement solutions to effectively adapt business activities. More simply put, strategic management ensures that all employees within a company are focused on the same goals.
Strategic management theory is the process an organization uses to accomplish strategic management and typically involves five steps: goal setting, analysis, strategy formation, strategy implementation, and strategy monitoring.
Goal Setting
It involves establishing clear objectives for the organization, including defining its vision, mission, and overall strategic goals.
It involves gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data about the organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities and threats. This phase often results in a SWOT analysis.
Strategy Formation
It involves developing strategic options based on the results of the analysis phase, and then selecting the most appropriate strategies to pursue.
Strategy Implementation
It involves executing the chosen strategies by allocating resources, developing programs, and making necessary adjustments.
Strategy Monitoring
It involves continuously evaluating and controlling the strategic process to ensure the organization remains on track toward its goals, adjusting as needed based on performance and environmental changes.
Applying Strategic Management
Although strategic management should always be used to guide operations, it can be particularly useful during key moments, including periods of significant growth, market change, and future planning. By keeping long-range success in the foreground, strategic management can ensure employees focus on areas most likely to achieve management’s desired outcomes.
The benefits of strategic management are numerous and can significantly impact an organization’s success. They include:
Improved Decision Making
Strategic management provides a framework for making informed decisions by evaluating the internal and external environments of the organization.
Increased Efficiency
By aligning resources with strategic objectives, organizations can operate more efficiently.
Better Coordination Between Departments
Strategic management ensures that all departments work towards common goals, enhancing coordination and reducing conflict.
Financial Benefits
Strategic management leads to improved financial health via liquidity monitoring, revenue generation, profitability management, and solvency planning.
Setting a Clear Direction
By setting a clear direction for the future, strategic management ensures that employees and management are aligned toward achieving the organization’s goals.
Competitive Advantage
Strategic management is crucial for maintaining and achieving a competitive advantage in the market.
As you can see, strategic management is not just about planning; it’s also about adapting to changes, making informed decisions, and ensuring that an organization remains relevant and competitive in a rapidly changing environment.
What Skills are Important for Strategic Management?
Strategic management is a multifaceted discipline that requires a range of skills from leaders and managers. Central is the ability to negotiate, find common ground, and achieve buy-in across diverse stakeholder groups. These skills are essential for unifying different viewpoints and agendas to move the company forward.
Effective delegation is also a cornerstone of strategic management, allowing for the efficient distribution of tasks. In addition, communication skills play a pivotal role. Leaders should be able to impart information clearly and use active listening skills, both key traits of emotional intelligence . The goal is to inspire confidence within your team and among stakeholders.
Finally, strategic management is underpinned by the ability to think strategically. Leaders with critical thinking and problem-solving skills are better able to anticipate future trends, recognize potential issues and opportunities, and craft appropriate solutions.
Together, these skills facilitate the development and implementation of strategic goals, ensuring organizations are well-positioned to navigate complex environments and achieve sustainable success.

How to Become a Strategic Manager?
To become a strategic manager, a solid educational background is typically required. Typically, strategic management roles require at least a bachelor’s degree in a field of study like business administration, finance, economics, or a similar discipline.
Moreover, some positions may look for candidates with more advanced degrees, like a Master’s in Business Administration (MBA) or related areas. This advanced education can provide deeper insights into business strategies, leadership, and organizational management.
UoPeople offers a variety of educational options for aspiring strategic leaders. Both the Associate and Bachelor degrees in business administration focus on the core competencies of leadership, while our Master’s of Business Administration is well-known to help advance your career .
UoPeople’s tuition-free model allows us to offer students an affordable solution to earning a quality business degree. In addition, our classes are all taught online and are asynchronous, making us perfect for adult students balancing career and family lives along with academic goals. UoPeople courses can be completed on your own schedule and in a matter of months.
If you don’t want to undertake a degree program, UoPeople also offers convenient certificate programs that are perfect for adult workers looking to upskill. In particular, our Certificate in Strategy gives students a solid foundation in strategic business methods, business management, accounting, marketing, and economic theory in as little as four months.
Furthermore, combining a bachelor’s or master’s degree with several years of practical experience in business or strategy roles can significantly enhance a candidate’s qualifications for becoming a strategy manager.
Also useful are less formal leadership training programs, workshops, seminars, and conferences that focus on key competencies like strategic thinking, communication, and change management. Additionally, finding a mentor within your company can also be beneficial, especially for someone working in a strategic management role. By working closely with your mentor, you can learn what techniques are the most successful within your business environment.
Strategic management is critical to the operation and profitability of any organization. Because it is so integral to long-term financial success, many corporations are now prioritizing strategic management skills when they are making hiring decisions. For this reason, upskilling in strategic management is currently one of the most popular paths to career advancement.
To deliver on their goals, companies use strategic management continuously. Therefore, there will always be opportunities for strategic managers in the workforce. By keeping a keen eye on how a company’s operations are aligned with its goals, strategic managers can guide their companies to success.
Related Articles
.webp)
How to Calculate Your Sample Size Using a Sample Size Formula

Maria Noesi
November 25, 2021
7 Organizational Change Management Frameworks That Stick
Let’s rephrase: In any business environment, change should happen. It shows you're committed to the kind of growth and evolution it takes to stay modern, relevant, and competitive.

Emily Smith
March 22, 2024
Employee Research
Change in business is inevitable.
Countless factors make change in business inevitable. Think of technological advancements, globalization, cultural shifts, and shifting economies. And since nobody's corporate goals include falling behind or growing stale, embracing change is a must.
But what kind of change are we talking about here? Change can include things like:
- Introducing new software or updating marketing practices
- Updated business processes
- A full-on restructuring
- Leadership changes
- Updated thinking
- New project management tools
- Budget constraints
- Shifts in strategy
These all fall under the umbrella of organizational change. If you’re already on board with shaking things up, you’re ahead of the game. And you're not alone.
According to Gartner, 99% of all organizations have undergone a major organizational change in the last three years. But big or small, change in business doesn't happen naturally. Therefore, effective change requires a clear action plan .
What is Organizational Change Management?
Simply put, it's is a game plan. It’s a methodology that helps businesses adapt to adjustments of all kinds. It helps employees, stakeholders, and project teams prepare and set expectations for coming change. It helps businesses roll out and acclimate to change.
To say this concept is broad and open-ended is an understatement. This is by design. The idea exists to support whatever potential problems your organization comes up against that don’t involve business as usual.
Read: How PMI Worldwide Manages Teams Through Change
Organizational change management techniques .
There are countless OCM methods out there. Each involves a basic series of steps or practices that could be linear or cyclical in approach. Some of the most popular methods include:
- Kotter 8-Step Process for Leading Change: Create → Build → Form → Enlist → Enable → Generate → Sustain → Institute
- McKinsey & Company’s 7-S Framework: Style, Skills, Systems, Structure, Staff, and Strategies = Shared Values & Goals
- Kurt Lewin’s Change Model: Unfreeze → Change → Refreeze
- ADKAR Model: Awareness → Desire → Knowledge → Ability → Reinforcement
- The Kübler-Ross Model: Shock → Anger → Bargaining → Depression → Acceptance
- Satir Change Management Model: Late Status Quo → Resistance → Chaos → Integration → New Status Quo
- William Bridges’ Transition Model: Ending → Neutral Zone → New Beginnings
However, there is no right or wrong in terms of which method to choose. Any method can facilitate smooth transitions and positive change in business. The best method depends on the organization and stakeholder needs and preferences. Methods are generally seen as interchangeable.
The Standard
Regardless of the method being applied, let’s get an overarching sense of how organizational change management happens. One of the most popular and widely accepted guiding approaches out there is The Association of Professional Change Management (ACMP) Standard for Change Management.
The ACMP Standard includes a definition of practices, processes, tasks, and activities for change management. It also includes guidance for any type of change and generally accepted practices and processes across industries, organizations, and roles.
Here’s how the association breaks down organizational change management across companies and industries:
Step 1 Evaluate Change Impact & Readiness
Examine the proposed change, how it will impact the organization, and whether the organization is ready.
Step 2 Formulate Your Strategy Develop an approach for taking the organization from point A to point B while achieving specific outcomes. Step 3 Develop Change Management Plans Document scope, actions, timelines, and resources necessary for the success of your plan.
Executing Change Management Plans
Address implementation by monitoring, measuring, and controlling delivery against baseline plans.
Step 5 Closing the Change Management Effort Documents the actions and resources needed to close the change.
Moreover, breaking the process into doable parts makes it more manageable. It also provides a framework and a clear vision for everyone on board. It’s key to make sure you’re all working toward the same goal.
Organizational Change Management Challenges
Business transitions require support because change is hard. It’s unfamiliar. It’s disruptive and can feel threatening. It has the ability to cause confusion amongst your team members, delays in timelines , frustrated employees, lower productivity, and beyond.
Organizational change management helps stakeholders get buy-in for their business case. It helps foresee, prepare, and handle change-related issues. It’s about recognizing all of the ways that change impacts things. From there, change management makes the process as painless as possible for everyone involved.
It’s important to look at employee involvement during this process.
Let’s be real. Organizations can’t run successful change management without people's power. That’s why companies should involve employees in the organization's change management process from start to finish, whether through something as involved as an online focus group or simply as a survey. Without employee buy-in, change management can fail.
Extract from: Driving Organizational Change with Business Insider (Webinar)
But uninvested stakeholders aren’t the only reason organizational change management fails. It also takes a knowledgeable, prepared leadership, and an HR team that is equipped for the process. The top three reasons that change management fails are:
- Poorly planned integration approaches and communication plan
- Incorrect target or goal identification
- Delayed implementation
These issues lie with the change management planners. They are tasked with identifying a change process that will work for their business. From there, they must keep the project on time and on target to ensure project success.
Watch: Driving Organizational Change with Business Insider (Webinar)
Making changes that stick.
Some 70% of all organizational change transformations fail, according to McKinsey. Gartner begs to differ, with research that shows 50% of organizational change efforts are considered a clear failure. But that’s still pretty darn dismal!

Change has to happen. But if nearly half of all organizational changes are considered failures, how can leaders and stakeholders ensure transitional success? There are a number of ways to make the change smoother.
Get your employees on board
Clear and effective communication is key.
Keep employees in the loop on vision and strategy. Share the key messages and your reasoning behind change-making decisions. Allow them to feel heard, and ensure they know the important role they’re expected to play.
One of the easiest ways to ensure this is by conducting an employee engagement survey or focus group, like the one below. Establish a number of open-ended questions to gauge interest in organizational change, or try a focus group for more detailed qualitative responses.
If you make sure employees are part of the process, they will feel invested. And, they will be more inclined to champion the cause.
Read: 100 Open-Ended Employee Engagement Questions
Plan for the worst.
Another way that OCM success happens is by planning for the worst. Know how you’ll handle things that don’t go according to plan! Expecting setbacks and overcoming hurdles has to be baked into your strategy. It’s the only path to success.
You can’t know when issues will arise. But you can mitigate risk by taking inventory on a regular basis and employing a resistance management plan.
Milestones and timelines may need renegotiating, expectations may need to be reset, and project leads and liaisons could be reevaluated. But, if you expect these things as part of the journey, you won’t be flustered when they happen along the way.
Empower, don’t mandate
The most successful outcomes occur by empowering your people and planning for pitfalls. Remember that a successful transformation is about real change. It’s not just about meeting goals.
Why is Organizational Change Management Important?
Change is inevitable. As the world around us evolves, so must we. And it’s not just one change, just one time.
Organizational change management matters because how people feel about it have a tremendous impact on your entire business. This includes the change itself, but also the entire process, as well as their involvement. Change is meaningless unless the people it impacts on a day-to-day basis are behind it.
We live in a rapidly changing world that shows no signs of slowing down. But, process-driven dilemmas around change implementation are possible, thanks to organizational change management .
Choose a method or framework that jives with your company and vision. Check-in often. Communicate at every stage. Apply proper project management.
Then, enjoy the results that come from a well-planned, well-implemented institutional change! And the sound knowledge that your employees are behind a big decision.
Want to empower your employees while change is happening in the workplace? Check our ebook on the state of employee engagement ! {{cta('4abf9265-99f0-44cd-85ce-80d0e374681d')}}

Remesh Evolution: AI-Powered Insights Platform Unveils Major Updates to Satisfy Market Demand for High-Quality, Human-Centric Research

Whole Self at Work
What's New at Remesh!
Stay up-to date..
Stay ahead of the curve. Get it all. Or get what suits you. Our 101 material is great if you’re used to working with an agency. Are you a seasoned pro? Sign up to receive just our advanced materials.

Get insights in your inbox . Sign up to stay up to date on the latest research tactics and breakthroughs.

©All Rights Reserved 2024. Read our Privacy policy
No data capture tricks. No bull SEO content for ranking. Just good, solid, honest, research ed.
By entering your email address, you agree to receive marketing communications in accordance with our privacy policy.

Request a demo
Dive Deeper

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Create A Strong Business Plan for Any Industry Without the Wait, For Less Cost. Create a Strong Business Plan in 1/2 The Time w/ Twice The Impact. 50% Off Now!
This document can clarify these roles for yourself, as well as investors and employees. The organization and management section should explain the chain of command, roles, and responsibilities. It should also explain a bit about what makes each person particularly well-suited to take charge of their area of the business.
The management section of a business plan helps show how your management team and company are structured. The first section shows the ownership structure, which might be a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation. The internal management section shows the department heads, including sales, marketing, administration, and production.
What Is the Organization and Management Section in a Business Plan? The organization and management section of your business plan should provide details about your business structure and team. This section typically comes after the executive summary. However, some people have it further in the document after the market analysis section.
The following important ownership information should be incorporated into your business plan: Names of owners. Percentage ownership. Extent of involvement with the company. Forms of ownership (i.e., common stock, preferred stock, general partner, limited partner) Outstanding equity equivalents (i.e., options, warrants, convertible debt) Common ...
This section of your business plan, Organization and Management, is where you'll explain exactly how you're set up to make your ideas happen, plus you'll introduce the players on your team. As always, remember your audience. If this is a plan for your internal use, you can be a little more general than if you'll be presenting it to a ...
Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections. Executive summary. Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company's leadership team, employees, and location.
What is the Management and Organization Section of the Business Plan? Outline your organizational structure and then tell about your primaries. How your business will be managed and who will be involved is an important consideration in your choice of business entity. For example, in a partnership, it is assumed that partners have equal control ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Photo: Hero Images / Getty Images. The management summary section of your business plan describes how your business is structured, introduces who is involved, outlines external resources and explains how the business is managed. This section backs up all of the data you've included elsewhere in the business plan by demonstrating the expertise ...
Growth plan: An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up. Internal plan: A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders - ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts. Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business and details how its objectives will be achieved. ... Section 5: Management Plan. Describe the organizational structure of the company. List the owners of the company and their ownership percentages. List the key executives, their roles, and remuneration
The management team is responsible for identifying and analyzing the objectives and goals of the company. After completing these tasks, experienced management professionals can implement and enforce strategies that will lead to success. In your business plan, this team should include the managers, owners, and board of directors (if applicable ...
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are ...
The management plan is all about employees and operations. Employees are one of the most important parts of any new venture. Good employees can make your life much easier, while bad employees can distract you and be a detriment to your success. Operational structure can be the difference between a successful venture and a failure.
A management team business plan is a section in a comprehensive business plan that introduces and highlights the key members of the company's management team. This part provides essential details about the individuals responsible for leading and running the business, including their backgrounds, skills, and experience. ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Organization and Management Team. Provide an overview of your company's organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. ... Internal Business Plan: Serves as a management tool for guiding the company's growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
The organizational planning process includes five phases that, ideally, form a cycle. Strategic, tactical, operational, and contingency planning fall within these five stages. 1. Develop the strategic plan. Steps in this initial stage include: Review your mission, vision, and values.
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you'll write, it's the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company's mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals. 3.
Circle back and make adjustments to the previous steps as you progress in the writing of your business plan; The organization and management part of your business plan focuses less on the business itself and more on the people behind it. A business is only as good as the people making decisions. Until (if ever), artificial intelligence can run ...
Knowing which organizational plan to apply to your business is crucial to steer your company toward a profitable and prosperous future. 1. Strategic planning. A strategic plan involves the creation of broad, long-term goals for your company. Senior management will usually oversee these kinds of plans; however, smaller companies tend to involve ...
1. Helps formulate better strategies using a logical, systematic approach. This is often the most important benefit. Some studies show that the strategic planning process itself makes a significant contribution to improving a company's overall performance, regardless of the success of a specific strategy. 2.
A management plan describes how an organization or business is run. Writing a management plan allows you to formalize your management structure and operations. It also ensures that everyone is on the same page and that your goals will be accomplished. You can easily write your own management plan with a few simple steps.
More simply put, strategic management ensures that all employees within a company are focused on the same goals. Strategic management theory is the process an organization uses to accomplish strategic management and typically involves five steps: goal setting, analysis, strategy formation, strategy implementation, and strategy monitoring.
An operational plan is the "how" to any organization's long-term vision. It lays out how a department will accomplish a specific project that is part of a larger effort in the company's vision ...
For a company to grow, it must embrace change. Yet change management is one of the most challenging business concepts to grasp. Organizations underestimate its importance; transforming staff ...
Organizational Change Management Challenges. Business transitions require support because change is hard. It's unfamiliar. It's disruptive and can feel threatening. It has the ability to cause confusion amongst your team members, delays in timelines, frustrated employees, lower productivity, and beyond.
Financial management: While a finance background is not always necessary for success, you must have some knowledge of budgeting and financial forecasting. Business managers are often responsible for managing expenses and financial prudence. Leadership: Though the title is "business manager" there is a difference between management and ...
An action plan differs from a project management plan in that it's often used for small, simple projects, whereas complex or long-term projects with an extensive list of stakeholders and ...