

Yale Computer Science Acceptance Rate: An In-Depth Look
Getting accepted into Yale University’s prestigious computer science program is a dream for many prospective students. With an average acceptance rate of just 6%, gaining admission is highly competitive.
If you’re considering applying to Yale’s computer science program, you’ll want all the details on what it takes to get accepted.
If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer to your question: Yale University’s computer science program acceptance rate is around 6-8% on average . This makes it one of the most selective computer science programs in the country.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take an in-depth look at Yale’s computer science acceptance rates over the years. You’ll learn key factors that influence admission chances like average test scores, GPA, demographics, and extracurriculars.
We’ll also provide expert tips to strengthen your application.
Yale Computer Science Acceptance Rates by Year
Overall acceptance rate.
Getting accepted into one of the prestigious Ivy League universities is a dream for many aspiring students. Yale University, known for its excellent academic programs, is no exception. For those interested in the field of computer science, the acceptance rate at Yale can greatly impact their chances of being admitted.
Over the years, Yale’s overall acceptance rate has fluctuated, reflecting the competitiveness of the admissions process. It is important to keep in mind that acceptance rates can vary depending on the year and the pool of applicants.
For example, in the past decade, Yale’s overall acceptance rate has ranged from around 6% to 7%, making it one of the most selective universities in the United States. This means that out of every 100 applicants, only a small number are admitted to the university.
To increase your chances of acceptance, it is crucial to not only have strong academic credentials but also showcase your unique qualities and experiences that set you apart from other applicants. Additionally, demonstrating a genuine passion for computer science through your essays and extracurricular activities can make a significant difference in the admissions process.
Computer Science Acceptance Rate
While Yale’s overall acceptance rate provides a general understanding of the university’s selectivity, it is also essential to examine the acceptance rate specifically for the field of computer science.
Unfortunately, Yale does not publicly release acceptance rate data for individual majors or departments, including computer science. However, it is widely known that computer science is a highly competitive field with rapidly growing demand.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the employment of computer and information technology occupations is projected to grow much faster than the average for all occupations. This increasing demand for computer science professionals may contribute to the competitiveness of computer science programs at top universities like Yale.
While we cannot provide specific acceptance rate data for Yale’s computer science program, it is safe to assume that the acceptance rate for this field is highly competitive and similar to or even lower than Yale’s overall acceptance rate.
Therefore, it is crucial for prospective computer science students to present a strong application that highlights their skills, achievements, and passion for the field.
For more information on Yale’s computer science program and admissions process, you can visit the official Yale University website at https://www.yale.edu/ .
Factors That Influence Admission Chances
When it comes to the Yale Computer Science program, several factors play a significant role in determining admission chances. Admissions officers carefully evaluate each applicant’s academics, test scores, extracurriculars, essays, and recommendations.
Let’s take a closer look at how these factors can influence your chances of getting accepted into this prestigious program.
Academics are undoubtedly a crucial aspect of the application process. Yale Computer Science looks for students who have excelled in their high school coursework, particularly in subjects related to computer science and mathematics.
A strong foundation in these areas demonstrates your ability to handle the rigorous coursework at Yale.
It’s important to note that while academic performance is crucial, it’s not the only determining factor for admission. Yale also values applicants who showcase a well-rounded profile with a diverse range of skills and experiences.
Test Scores
Standardized test scores, such as the SAT or ACT, are another essential consideration. While there is no specific cutoff for these scores, higher scores generally improve your chances of admission. It’s worth noting that Yale Computer Science takes a holistic approach to admissions, meaning they consider your test scores in conjunction with other application components.
It’s vital to prepare thoroughly for these tests and aim for scores that are competitive with previous admitted students. Consider taking advantage of resources such as prep courses or practice exams to maximize your chances of success.
Extracurriculars
Yale Computer Science recognizes the importance of extracurricular activities in shaping a well-rounded applicant. Engaging in activities outside of the classroom showcases your ability to manage time effectively, work collaboratively, and pursue your passions.
Participating in computer science-related clubs, competitions, or internships can demonstrate your dedication and interest in the field. However, it’s crucial to emphasize quality over quantity. Admissions officers are more interested in seeing meaningful involvement and leadership roles rather than a long list of activities.
Essays offer applicants the opportunity to showcase their unique personality, experiences, and motivations. This is your chance to differentiate yourself from other candidates and provide insights into why you are a strong fit for the Yale Computer Science program.
When crafting your essay, be authentic and genuine. Share personal anecdotes or stories that highlight your passion for computer science and demonstrate your ability to overcome challenges. Remember to proofread and seek feedback from trusted individuals to ensure your essay is polished and impactful.
Recommendations
Letters of recommendation offer valuable insights into your character, work ethic, and potential for success. It’s essential to choose recommenders who know you well and can speak to your strengths and abilities.
Consider asking teachers, mentors, or supervisors who can provide specific examples of your academic achievements, leadership skills, or dedication to computer science. Ensure you give your recommenders ample time to write their letters and provide them with any necessary information or context.
How to Improve Your Odds of Acceptance
Take challenging coursework.
One way to improve your odds of acceptance into Yale’s computer science program is by taking challenging coursework during high school. Admissions officers at top universities like Yale are looking for students who have demonstrated a strong academic foundation in computer science and related fields.
Taking advanced courses such as AP Computer Science or honors math and science courses can showcase your dedication and interest in the subject.
According to a study conducted by the College Board , students who take challenging coursework in high school are more likely to succeed in college. So, not only will taking challenging courses improve your chances of acceptance, but it will also better prepare you for the rigorous curriculum at Yale.
Aim for High Standardized Test Scores
In addition to challenging coursework, high standardized test scores can significantly improve your odds of acceptance. For Yale’s computer science program, it’s essential to aim for high scores on the SAT or ACT, as well as any subject tests that may be required.
According to the most recent data from Yale University, the average SAT score for admitted students is between 1470 and 1570 out of 1600. Similarly, the average ACT score is between 33 and 35 out of 36.
These scores are highly competitive, so it’s crucial to dedicate time and effort to preparing for these exams.
Participate in CS Extracurriculars
Getting involved in computer science extracurricular activities can demonstrate your passion and commitment to the field, which can improve your chances of acceptance into Yale’s computer science program.
Consider joining a coding club, participating in programming competitions, or contributing to open-source projects.
Not only will these extracurriculars enhance your technical skills, but they will also showcase your ability to work collaboratively and think critically. Admissions officers at Yale value well-rounded applicants who have a genuine interest in computer science beyond just the classroom.
Craft a Strong Personal Narrative
One often overlooked aspect of college applications is the personal narrative or statement of purpose. This is your opportunity to showcase your unique experiences, goals, and aspirations in computer science.
When crafting your personal narrative, be sure to highlight any significant projects, internships, or research opportunities you’ve had in the field. Additionally, connect your personal experiences or challenges to your passion for computer science.
Admissions officers are interested in understanding your motivations and how you will contribute to the Yale community.
Connect with Current Students
One way to gain insight into the computer science program at Yale is by connecting with current students. Reach out to current computer science majors or join online forums to ask questions and learn more about the program.
By connecting with current students, you can gain valuable insights into the coursework, professors, and research opportunities available at Yale. Additionally, this can help you tailor your application to align with the values and strengths of the program.
Remember, acceptance into Yale’s computer science program is highly competitive. However, by taking challenging coursework, aiming for high standardized test scores, participating in CS extracurriculars, crafting a strong personal narrative, and connecting with current students, you can improve your odds of acceptance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How competitive is yale computer science.
The computer science program at Yale is extremely competitive, with only a 7% acceptance rate in 2022. On average, Yale computer science receives over 1,500 applications each year for around 110 spots.
Applicants need outstanding academics, test scores, extracurriculars, and recommendations to get in. Yale computer science is comparable to top programs like MIT, Stanford, and Carnegie Mellon in terms of competitiveness.
What GPA do you need for Yale computer science?
Yale does not publish specific GPA requirements, but successful applicants typically have a GPA of 4.0 or very close to it . However, Yale takes a holistic approach – they look at the rigor of high school courses, upwards GPA trend, and any extenuating circumstances.
Applicants should aim for mostly A’s throughout high school, especially in math, science, and technology courses.
Does Yale University have a good computer science program?
Yes, Yale’s computer science program is one of the best in the world. It is ranked #15 globally by U.S. News . The department has pioneering faculty doing cutting-edge research in areas like robotics, cryptography, and quantum computing.
Students benefit from small class sizes, close faculty mentorship, and access to excellent facilities like the Center for Engineering Innovation and Design .
How many apply to Yale computer science each year?
According to Yale’s 2022 admissions data , the university received 1,578 applications for computer science and accepted 110 students. The number of applications has risen over the past few years as interest in computer science grows.
Yale has maintained an acceptance rate around 7% as the program continues to be highly selective.
What SAT score is needed for Yale computer science?
Yale does not publish specific SAT score cutoffs, but successful applicants tend to score in the top 1% nationally , usually 1500+ out of 1600 . However, SAT is just one part of the application – strong grades in challenging courses, glowing recommendations, and impressive extracurriculars are also vital.
The SAT score needed varies based on the overall strength of an applicant’s profile.
The road to getting accepted into Yale’s prestigious computer science program is undoubtedly challenging. By understanding the highly competitive acceptance rates and factors that influence admission decisions, you can tailor your application to stand out.
With outstanding academics, test scores, extracurriculars, and essays, your chances of receiving the coveted acceptance letter will be that much higher. Stay focused on presenting your best self, and you’ll be on your way to joining the ranks of elite Yale computer scientists.
Similar Posts

Examining Iowa State’S National Rankings In Computer Science
As one of the top computing colleges in the Midwest, Iowa State University has a reputation for excellence in computer science education. But how does ISU’s program compare on a national scale? If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer to Iowa State’s rankings: Iowa State’s computer science program is consistently ranked among the…

Is Ap Human Geography A Social Science? An In-Depth Look
For high school students looking to get a head start on college credits, Advanced Placement (AP) courses offer an attractive opportunity. AP Human Geography is a popular AP course choice, covering the study of human populations and how they relate to their physical environments. But is AP Human Geography considered a social science? Let’s take…

Demystifying The Uic Computer Science Acceptance Rate
With strong programs and an urban location, the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC) is an attractive option for computer science applicants. But you may be wondering, just how competitive is it to get into UIC computer science? Understanding the department’s historical acceptance rates and admissions factors can help demystify your chances. If you’re short…

Getting A Computer Science Job Without A Degree – Challenges, Alternative Pathways, And Tips
While a computer science degree has long been considered the standard path into the field, is it still possible to break into a CS career without one? In this comprehensive guide, we dive deep on the challenges of getting a computer science job sans degree, evaluate alternative pathways like bootcamps and self-teaching, and provide tips…

What Science Courses Are Taught In 12Th Grade? An In-Depth Look
As a high school senior, you’re so close to graduation! This final year is crucial for cementing your science knowledge and skills before college. Choosing the right science curriculum can also boost your applications if you plan to major in a science field. If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer: Most 12th graders…

Michigan Math And Science Scholars Program: A Guide For Aspiring Stem Students
For top STEM students in Michigan looking to challenge themselves and access specialized guidance, the Michigan Math and Science Scholars program offers an engaging pathway to develop skills and connections. This accelerated learning opportunity allows students to tackle college-level coursework in math and science while still in high school. If you’re short on time, here’s…
Computer Science
Graduate program.
Director of Graduate Studies - Lin Zhong
The following programs are available to study at Yale University Computer Science.
- The Master of Science - The Master of Science (MS) program is intended for students planning to pursue a professional career directly after finishing the MS program, rather than continuing on in a PhD program. The MS program is also suitable for students interested in undertaking a research project but who are not sure yet whether they want to make the multi-year commitment to a PhD program.
- The Doctor of Philosophy - The Department offers a Doctoral Program leading to a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) degree. It typically takes four to six years to get a Ph.D. The Ph.D. program is focused on research. There are course requirements in the first three terms, but starting in the third term the main focus is on research, guided by an advisor and supervisory committee.
- Yale Computer Science Graduate Handbook - Information about the department and more.
- Yale Computer Science Admissions FAQ - Frequently Asked Questions for those who are interested in enrolling in the Yale Computer Science programs.
You seem to be using an unsupported browser
To get the best user experience please use a supported browser. Here are a few we recommend:

- Department of Computer Science
New Haven, CT
Department of Computer Science / Department of Computer Science is located in New Haven, CT, in an urban setting.
Degrees & Awards
Degrees offered, degrees awarded, earning your degree, degree requirements, acceptance rate, application deadlines, entrance requirements, tuition & fees, financial support, student body, race/ethnicity, location & contact.
- Grad Schools
- Search Results
- Yale University
- Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
- PhD/Master's Application Process
Who is Eligible to Apply?
If you have completed your undergraduate degree (bachelor's or equivalent) or will have completed it prior to your intended matriculation date at Yale, you may apply to the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences (GSAS).
A Master's degree is not required to apply for a PhD at Yale, although some programs give preference to applicants with post-baccalaureate training. Consult your program of interest directly for information on how it evaluates applications.
We value diversity of all kinds at the Graduate School, and we encourage students from all backgrounds to apply if Yale is a good fit for your intellectual and professional goals. All are welcome to apply, without regard to citizenship or immigration status, socioeconomic level, race, religion, gender identification, sexual orientation, disability, etc.
Requirements for All PhD and Master's Degree Applicants
You will need to provide the following with your application for admission:
- A statement of academic purpose. You will find the prompt for the statement of purpose in our Application Question FAQs .
- A list of all the prior colleges or universities you have attended, accompanied by unofficial transcripts from each school. Unofficial transcripts should be uploaded with your application. Official or paper transcripts are not needed at this time.
- Three letters of recommendation. Enter the names of your recommenders directly in the application and they will receive a link to upload a letter on your behalf.
- $105 application fee or fee waiver.
- Standardized tests . GRE requirements vary by program. TOEFL or IELTS are necessary for most non-native English speakers.
- Resume/CV .
- Some programs have additional requirements, such as a writing sample . You can find information about any specific requirements on the program's website.
Where Do I Begin?
Decide whether you will apply for a PhD or a terminal Master’s (MA, MS) in one of the programs available at the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences . (Note that you will earn one or more Master's degrees en route to a PhD.) Learn about the program: its faculty, course offerings, and resources. Read the faculty's research publications. If you can identify and articulate why the program is a good fit for you and show how your preparation and interests align well with it, you will have a strong application.
A note to students applying to one of Yale’s professional schools or programs:
- If you are applying for a PhD in Architecture, Environment, Investigative Medicine, Law, Management, Music, Nursing, or Public Health; for an MS in Public Health; or for an MA in Music, be sure to use the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences PhD/Master's application.
- If you are applying for any other degree at one of the University’s professional schools (Art, Architecture, Divinity, Drama, Environment, Global Affairs, Law, Management, Medicine, Music, Nursing, and Public Health), visit that school’s website for further instructions. Those programs have separate admissions policies and processes that are administered by the professional schools, not GSAS.
Application deadlines vary by program, so please see Dates & Deadlines for information about your program of interest.
All new students matriculate in the fall. The admissions process begins nearly a year in advance of matriculation.
Some PhD and Master’s degree programs require Graduate Record Examination (GRE) scores. Check your program's standardized testing requirement before you apply.
In addition, applicants whose native language is not English may need to take an English Language test (TOEFL or IELTS).
The application for Fall 2024 entry is closed. The application for Fall 2025 entry will be available starting in mid-August 2024.
Be sure to complete and submit the application before your program's application deadline.
Your application fee or an approved fee waiver is due upon submission of your application.
Your letters of recommendation do not need to be received before you will be able to submit your application. However, since programs begin reviewing applications shortly after the respective application deadline, please be sure that your letters of recommendation are submitted promptly.
What Happens After I Submit My Application?
The faculty admissions committee in each department and program begins reviewing applications shortly after their application deadline. Led by the director of graduate studies (DGS) or director of graduate admissions (DGA), the committee will recommend students for admission to the Graduate School. Once confirmed by the deans of the Graduate School, the admissions office will release final decisions to applicants.
Unlike undergraduate admissions, the admissions office and staff of the Graduate School maintain the application, the application process, and other administrative transactions, but the admissions staff does not review applications or make admissions decisions. That responsibility is handled by the faculty of each department or program.
Most admissions decisions are provided between February and early March. You will receive an email notification when your admissions decision is available.
If you are accepted for admission, you will need to decide if you wish to accept our offer by April 15. We abide by Council of Graduate School's April 15 Resolution , regarding graduate financial support.
Ready to apply? Begin your application today.

PhD/Master's Applicants
- Why Choose Yale Graduate School?
- Dates and Deadlines
- Standardized Testing Requirements

Non-Degree Program Applicants
Looking for non-degree programs? In some cases, it is possible to enroll at the Graduate School as a non-degree student. Non-degree students receive a transcript and many of the benefits of being a Yale student, but do not earn a degree upon completion of their enrollment. We offer three types of non-degree programs.
- Non-Degree Programs
Testimonials
Free Resources
PrepScholar GRE Prep
Gre prep online guides and tips, graduate school acceptance rates: can you get in.
Even the most qualified and confident applicants worry about getting into grad school. But don’t panic! Graduate school acceptance rates, which give the percentage of applicants that were admitted to a particular school or program in an academic year, can help you determine how likely you are to get into a given program. But where can you find grad school admissions statistics?
In this article, we’ll first investigate the trends and factors associated with graduate school acceptance rates. Then, we’ll take a look at some of the current acceptance rates and give you expert tips on how to find acceptance rates for your programs. Finally, we’ll show you how to determine your odds of getting into grad school.
Graduate School Acceptance Rates: Factors and Trends
Grad school acceptance rates are the same as any other acceptance rate: the lower the acceptance rate, the more selective the school or program is. Similarly, the higher the acceptance rate, the less selective the school or program is. As with undergrad acceptance rates, grad school acceptance rates vary widely, from extraordinarily selective (less than 5 percent) to incredibly lenient (nearly 100 percent).
Unlike undergrad rates, though, grad school acceptance rates are usually calculated for specific programs or departments and not for entire universities. This is because with grad school, you are essentially applying to an individual program rather than an overall institution (as you did for undergrad).
Now that we’ve covered all of the basics, let’s look at a few key trends. Our research indicates there are three major factors that help determine grad school acceptance rates:
- School or program prestige
- Degree type
- Amount of funding
Let’s look at how each of these factors influences grad school acceptance rates.
Quick side note: we've created the world's leading online GRE prep program that adapts to you and your strengths and weaknesses. Not sure what to study? Confused by how to improve your score? We give you minute by minute guide.
You don't NEED a prep program to get a great GRE score. But we believe PrepScholar is the best GRE prep program available right now , especially if you find it hard to organize your study schedule and don't know what to study .
Click here to learn how you can improve your GRE score by 7 points, guaranteed .
#1: School or Program Prestige
How prestigious a particular grad school or program is can affect its overall competitiveness and selectivity. In general, the more prestigious a program is, the more competitive it’ll be and thus the lower acceptance rate it’ll have.
An easy way to determine school or program prestige is to consult official rankings, such as those listed on U.S. News . (Grad schools are typically ranked by field or program and not by overall institution.)
For example, a 2017 U.S. News list of the best political science grad programs ranked Duke’s political science program at #7 and Northwestern’s at #23. Because both of the programs have fairly high rankings, it’s safe to assume they’re probably quite selective.
And this is true: in 2016, Duke reported a mere 10 percent acceptance rate to its political science doctoral program, while Northwestern reported a 12 percent acceptance rate.

#2: Degree Type
Another major factor is degree type. Generally, doctoral programs tend to be more selective than master’s programs (though this isn’t always the case as I’ll explain in a moment). This trend is likely due to the fact that doctoral programs often look for higher-quality applicants with proven academic track records and more relevant experience in their fields.
For example, in 2016 University of Michigan’s math doctoral program had a 17.2 percent acceptance rate, whereas its master’s program had a much higher 31.8 percent rate. In this case, the doctoral program is clearly tougher to get into than the master’s program.
Still, master’s programs can have lower acceptance rates than doctoral programs. If we were to take the University of Michigan’s grad programs in computer science and engineering, we’d find that the doctoral program has a 15 percent acceptance rate and the master’s an even lower 8 percent acceptance rate .
Additionally, M.F.A. programs are particularly cutthroat. In 2015, the creative writing M.F.A. program at UT Austin’s James A. Michener Center for Writers only admitted 12 out of 678 applicants — that’s a mere 1.8 percent acceptance rate !
#3: Amount of Funding
Funding, too, plays a big role in how selective a grad program is.
Well-funded programs typically receive more applications than those offering little to no aid, thereby raising their selectivity. Competition is especially fierce for fully funded programs — possibly because fewer people are willing to go into debt for grad school.
Compared to fully funded doctoral programs, fully funded master’s programs are somewhat rare and thus pretty competitive. UT Austin’s Creative Writing M.F.A. program, for instance, is not only a prestigious program but also one of the most well-funded Creative Writing M.F.A. programs in the country: it offers full tuition remission and a $27,500 stipend per academic year . It’s no wonder, then, that its acceptance rate is below 2 percent!

What Are the Current Graduate School Acceptance Rates?
For this section, we’ve scoured the internet to bring you a robust assortment of acceptance rates for popular U.S. grad schools.
Before we dive in, note that not all institutions calculate grad school acceptance rates using the same methodologies. Some offer only a single acceptance rate for all of their grad schools put together, while others offer individual rates by school, field, or program.
Now, let’s see how selective these schools really are!
*Statistics for NYU are based on the number of enrolled students and not the number of admitted students. Therefore, expect actual acceptance rates to be slightly higher.

How to Find Graduate School Acceptance Rates: 4 Methods
Unfortunately, grad school admissions statistics tend to be more difficult to find than undergrad acceptance rates. But there are ways to search for them — you just have to do a lot of digging and possibly a little reaching out.
Below are our top four methods for finding grad school acceptance rates for the programs you’re applying to.
#1: Consult School Websites
By far the most reliable resources for grad school admissions statistics are school websites.
Start your search by consulting program and departmental pages, particularly admissions and FAQ pages. Look out for any statistics-related keywords or phrases, such as “admission(s) rates,” “acceptance rates,” “enrollment,” “facts and figures,” etc. Use ctrl+F to move swiftly through large chunks of text.
Not all schools publish grad admissions information online, and those that do don’t always report it in the same way as others. For example, Princeton offers a handy PDF containing acceptance rates for all academic fields of study. On the other hand, Notre Dame gives separate admissions charts for each of its grad programs (which you can access by selecting a program and then clicking “Admissions Statistics”).
Additionally, many schools release admissions statistics without explicitly publishing acceptance rates. In this case, it’s your job to take the statistics provided and use them to calculate an acceptance rate. To find the acceptance rate of a school or program, you’ll need the following information:
- The total number of applicants in a year
- The total number of applicants granted admission that year
The acceptance rate equals the total number of applicants offered admission divided by the total number of applicants and then multiplied by 100, or:
$$\acceptance \rate = {\number \of \applicants \offered \admission}/{\total \number \of \applicants}100$$
Be sure to avoid conflating the number of students who were offered admission with the number of students who accepted their offers of admission. These two concepts sound alike but are actually different. What you’re looking for is the first statistic — that is, the number of admitted students (regardless of whether they decided to enroll).
If you’re having trouble finding admissions statistics by browsing school websites, search on Google for “[Your School] graduate acceptance rate” and see if any relevant school pages appear. While searching for acceptance rates to use in the table above, I consistently swapped “acceptance rate” with similar phrases, such as “admission(s) rate,” “facts and figures,” “student statistics,” “admittance rates,” and “admission(s) statistics.”
Want to improve your GRE score by 7 points? We have the industry's leading GRE prep program. Built by world-class instructors with 99th percentile GRE scores , the program learns your strengths and weaknesses through machine learning data science, then customizes your prep program to you so you get the most effective prep possible.
Try our 5-day full access trial for free:
Don’t be afraid to get creative! You can also use phrases like “Ph.D. admissions statistics” or “master’s admissions statistics” to narrow your search even further. Try to think outside the box as you do your research. What are other ways people talk about acceptance rates?
#2: Check U.S. News
If your school or program doesn’t offer any admissions statistics on its website, go to U.S. News . This website offers official rankings of grad programs as well as lists of the most (and least) selective programs in various fields.
For example, I found a 2016 list of the most competitive online M.B.A. programs and a 2015 list of the most competitive online graduate engineering programs .
If U.S. News doesn’t offer any relevant lists for you to use, try skimming the current grad school rankings to gauge how competitive your program is compared with others in the same field.

#3: Search Other Websites
One less reliable method for looking up grad school admissions statistics is to look for (unofficial) websites discussing acceptance rates for your school or program.
The Grad Cafe’s admissions results section is a solid place to start. Here, applicants post whether they’ve been accepted, rejected, or waitlisted for grad programs.
Search for your program to get a rough feel for how many acceptances and rejections go out each year. You might notice that certain types of applicants are more active than others. Creative Writing M.F.A. applicants, for example, are prolific posters in winter and spring (during admissions season).
Occasionally, Google itself will provide you with grad school acceptance rates, but this only appears to work consistently for well-known law schools, medical schools, and business schools.
Additionally, while using Google, don’t assume that any acceptance rates that pop up are directly connected to your search terms. For example, when I searched “stanford graduate acceptance rate,” Google gave me this result:
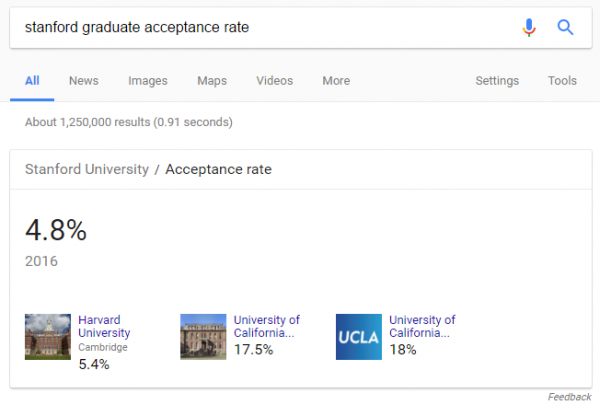
This 4.8 percent acceptance rate is not the acceptance rate for Stanford’s grad programs (what I searched for) but rather the acceptance rate for undergrads. So always cross-check any statistics Google gives you.
You can also consult grad school data websites such as Peterson’s and StartClass . Take their grad school acceptance rates with a grain of salt, though — their data isn’t always verifiable online. If possible, try to compare any data you find on these types of websites with the school websites themselves or U.S. News .

#4: Contact Schools
If the internet isn’t giving you the help you need, call or email your schools. Be polite but upfront: ask whether the school calculates acceptance rates for grad programs and where you can find this information online (if available).
If a school refuses to divulge admissions statistics or simply doesn’t report acceptance rates, see if they can give you estimates for how many applications they receive each year, or for how many acceptances they usually extend to applicants in your program.

Graduate School Acceptance: What Are Your Odds?
By this point, you might be wondering how likely it is you’ll actually get into the grad program you wish to attend. After all, acceptance rates are pretty broad — they tell you what everyone’s odds are but not your odds specifically.
Below are three easy steps for determining your odds of getting into grad school, including advice on when it’s better to go for it or choose another program.
Step 1: Check Program Requirements
First, go to your program’s website and pinpoint the admissions requirements page. Now, ask yourself: do you meet all of the program’s basic requirements? If not, you’ll likely wind up with a rejection (and might not even be able to apply).
However, if you’re still interested in applying, contact the program and ask if they’ll make an exception for you. Your chance of getting accepted is still low, but you’ll at least have your application considered.
If your program strongly recommends qualities you lack, don’t interpret this as an automatic rejection. Sometimes, applicants can make up for deficiencies in other ways. For example, if your undergrad GPA is 3.1 and your program recommends applicants have a minimum 3.2, don’t write off the program — you might still have a shot at getting in as long as the rest of your application is solid.
On the other hand, even if you meet all of a program’s requirements, you’re not necessarily a shoo-in. Remember, all other applicants have met these requirements, too, so you’ll need to find a unique way to make your application stand out.

Step 2: Find Average GRE Scores and GPAs
Your next step is to look up your program’s average GRE scores and GPA to see how your own scores and GPA compare with those of previously admitted applicants.
You can usually find GRE score information on admissions requirements or FAQ pages. You can also search on Google for “[Your School] [Your Program] average GRE scores.” For step-by-step instructions on how to find average GRE scores, check out my article on average GRE scores by school .
For GPAs, you can use the same basic methodology. Check admissions requirements and FAQ pages and use ctrl+F to search for “GPA.” If GPA information is available, you’ll most likely come across minimum GPAs or average GPAs (or both). For more tips on how to find GPA information for your grad schools, read our guide .
Now, compare your own GRE scores and GPA with the averages you’ve found. Below are all possible scenarios and what they mean for you and your odds of getting into the program:
Want to improve your GRE score by 7+ points?
Check out our best-in-class online GRE prep program . We guarantee your money back if you don't improve your GRE score by 7 points or more.
PrepScholar GRE is entirely online, and it customizes your prep program to your strengths and weaknesses . We also feature 2,000 practice questions , official practice tests, 150 hours of interactive lessons, and 1-on-1 scoring and feedback on your AWA essays.
Check out our 5-day free trial now:
- Your GRE scores and GPA are both higher than your program’s averages: Congratulations! You have an excellent chance of getting accepted, especially if the rest of your application is equally impressive. Keep up the great work!
- Your GRE scores and GPA are both about the same as your program’s averages: You’re doing pretty well! You are just the type of applicant your program is looking for. The only drawback is that you probably won’t stand out as much from other applicants who have similar GRE scores and GPAs. So take time to make your application sparkle (I’m looking at you, statement of purpose).
- Your GRE scores and GPA are both lower than your program’s averages (or just one of the two is lower): It ain’t over ’til it’s over! You can still make up for your deficiencies in other ways. While you can’t change your GPA, you can retake the GRE . If your GPA is low, a great strategy for combating this is to discuss it in your statement of purpose, taking care to highlight any external factors that contributed to the low GPA as well as any attributes of yours that prove you’re indeed ready for grad school.
Step 3: Decide Whether to Apply
Now, we get to the final question: do you apply to the program or not? This is a vague question that’s difficult to answer as is. The real questions you should be asking yourself are as follows:
- Do I meet all of the program’s basic requirements?
- Do I meet most or all of the program’s expectations of applicants (in terms of GRE scores, GPA, etc.)?
- Is the program’s acceptance rate extremely low?
- Do I really like this program?
Although acceptance rates and GRE/GPA comparisons are helpful, don’t base your decision to apply solely on how difficult the program is to get into. We can’t know for sure what kind of applicant a grad program is looking for or who they’re willing to make an exception for.
Take a moment to think deeply about how interested you are in this particular program. Be realistic about your chances of getting in — but don’t cross the line into pessimism. If you don’t meet most or all of a program’s expectations and you’re not super invested in it, consider applying elsewhere.
But if you meet some, most, or all of a program’s expectations and you’re extremely interested in enrolling, give the application a go. Remember, it’s totally normal (and even encouraged) to have a few reach schools. Plus, you’ll never get in if you don’t apply!

Key Takeaways: Graduate School Acceptance Rates
Grad school acceptance rates quantify for us the selectivity of grad schools and programs. More specifically, acceptance rates tell us what percentage of applicants were offered admission to a particular grad school or program.
With grad school, acceptance rates are often reported for individual schools or programs, not entire universities. Acceptance rates can vary widely depending on program prestige, the type of degree you’re seeking, and how much (or how little) funding a program offers.
Unlike undergrad acceptance rates, grad school acceptance rates are somewhat difficult to locate online. You can look for them using any of the following four methods:
- Peruse school websites
- Check grad school facts and lists on U.S. News
- Browse other websites and forums such as The Grad Cafe
- Call or email your schools
When trying to determine your odds of getting into a program, look at your program’s requirements as well as the average GPA and GRE scores of previously admitted applicants to your program. If your GRE scores and GPA are comparable to those of your program, you have a decent shot at getting accepted. If one or both are lower than your program’s averages, however, you can always try to raise your GRE score with a retake or address your GPA in your statement of purpose.
At the end of the day, what ultimately matters isn’t that you get accepted to a highly competitive grad program but that you make the right decision for you and you alone!
What’s Next?
Need help with your grad school application? Learn about the most common grad school requirements and get tips on how to write a grad school CV or resume !
Is your GPA good enough for grad school ? Read our in-depth guide to learn how you can make up for a less-than-stellar GPA and ultimately raise your chances of getting into the school of your dreams.
Do you have to take the GRE for grad school ? When are grad school deadlines ? Check out our guides for answers to these questions and more.
Ready to improve your GRE score by 7 points?
Author: Hannah Muniz
Hannah graduated summa cum laude from the University of Southern California with a bachelor’s degree in English and East Asian languages and cultures. After graduation, she taught English in Japan for two years via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel. View all posts by Hannah Muniz

Search form
Computing and the arts, you are here, phd program.
C2 doctoral education is carried on within the Computer Science department. C2 faculty advise doctoral research in a variety of topics within computing and the arts. We seek students with strong computer science preparation and interest in the arts. Students may or may not be artists themselves. Our purpose of the program is not to train students who want careers in the arts, but computer scientists for whom the arts play an important role in their lives as a whole.
Our education and training strategy builds on a successful existing core curriculum in place for first and second year computer science students, with a set of courses tailored for the students in computing and the arts. The existing pattern of projects that transition students to full time research will also be followed, with projects and mentoring focused on the arts. In addition to course work, students will receive training as teaching assistants in courses aimed at computing and the arts associated students and as interns in industry, government laboratories or at academic institutions outside of the US.
The Computer Science core PhD curriculum is flexible in the general plan, with 8 non-project courses required distributed across theory, systems and applications. Specific arts related courses will be included in C2 students’ program of study. Course work will further be enriched by events such as the C2 Distinguished speaker series. In addition to the 8 non-project courses, the existing program in computer science is designed to transition students from advanced coursework to full-time research by working on a one-year research project designated CPSC 690/691. For C2 students these will all be arts-motivated projects. Students will identify the fundamental computer science issues revealed in their projects, which will form the basis for formulating their dissertation prospectus in their third year. For each fundamental issue, the students will also identify arts-related applications that would use their research results.
Students will serve as teaching fellows and will potentially complete internships. Students will primarily be assigned as teaching fellows for the courses for non-technical majors to increase their interaction with the broader C2 community. Doctoral students will also be encouraged to spend at least one summer at an internship in industry or at an institution outside of the US.
Internally, student progress would be evaluated by project critiques by computing and the arts faculty. In their third and fourth years, the students would be required to give oral presentations of their work to the computer science faculty as a whole, as well as computing and the arts faculty, for evaluation and feedback. We will obtain both formal and informal feedback on student performance from their mentors in their internships. Assessment of teaching fellow performance will be obtained in part by student mid-year and end-of-year evaluations as well as faculty feedback.
Examples of research topics that may be pursued are described here . The general requirements of the Yale PhD in Computer Science are listed here .
Yale University
Ranked in 9 program s and 10+ specialt ies
Yale University Graduate Programs
Yale University is one of more than 800 institutions with graduate schools surveyed by U.S. News on an annual basis. Yale University confers degrees through various schools, such as: the School of Management, the Law School, the Yale School of Medicine, the School of Engineering and Applied Science, and the School of Nursing.
More from This School
- Graduate Schools
- Global Universities
School of Management
- Best Business Schools
- Executive MBA
- International
- Best Law Schools
- Business/Corporate Law
- Clinical Training
- Constitutional Law
- Contracts/Commercial Law
- Criminal Law
- Dispute Resolution
- Environmental Law
- Health Care Law
- Intellectual Property Law
- International Law
- Legal Writing
- Trial Advocacy
Yale School of Medicine
UNLOCK WITH COMPASS
- Anesthesiology
- Best Medical Schools: Primary Care
- Best Medical Schools: Research
- Internal Medicine
- Most Diverse Medical Schools
- Most Graduates Practicing in Medically Underserved Areas
- Most Graduates Practicing in Primary Care Fields
- Most Graduates Practicing in Rural Areas
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
School of Engineering and Applied Science
- Best Engineering Schools
- Biomedical Engineering / Bioengineering
- Chemical Engineering
- Computer Engineering
- Electrical / Electronic / Communications Engineering
- Environmental / Environmental Health Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
School of Nursing
- Best Nursing Schools: Doctor of Nursing Practice
- Best Nursing Schools: Master's
- Master's Nurse Practitioner: Adult / Gerontology, Primary Care
- Master's Nurse Practitioner: Family
- Master's Nurse Practitioner: Psychiatric / Mental Health, Across the Lifespan
- Master's Nursing Practitioner: Pediatric Primary Care
- Best Fine Arts Programs
- Graphic Design
- Painting / Drawing
- Photography
- Clinical Psychology
- Nursing-Midwifery
- Physician Assistant
- Public Health
- Biological Sciences
- Biostatistics
- Computer Science
- Earth Sciences
- Mathematics
Social Sciences and Humanities
- Political Science
Do you work at Yale University ?
Manage your school's public image and connection with students using U.S. News Student Connect.
U.S. News Grad Compass
See expanded profiles of nearly 1,800 schools. Unlock entering class stats including MCAT, GMAT and GRE scores.
Unlock U.S. News Grad Compass
Access all of the Business, Law, Medicine, Engineering and Nursing School data for Yale University.
Graduate School Advice
Applying to Grad School

Paying for Grad School

About the GRE

Studying at a U.S. Grad School

You May Also Like
College majors and mba admissions.
Anthony Todd Carlisle March 20, 2024

Tips While Awaiting Med School Decision
Zach Grimmett March 19, 2024

2024 Best Grad Schools Rankings Coming
Robert Morse and Eric Brooks March 19, 2024

Tips for Aspiring Lawyers in High School
Gabriel Kuris March 18, 2024

4 Surprising MBA Application Mistakes
Andrew Warner March 18, 2024

Types of Doctors Premeds Can Become
Jarek Rutz March 14, 2024

Applying to Law School as a Minority
Sammy Allen March 14, 2024

Law School Websites: What to Look for
Gabriel Kuris March 12, 2024

Are You Too Old for Medical School?
Kathleen Franco, M.D., M.S. March 12, 2024

How to Get a Great MBA Recommendation
Cole Claybourn March 8, 2024

You can compare up to 25 schools at a time. Please remove a school before adding another.

Department of Statistics and Data Science
Ph.d. admissions.
The Ph.D. program admits only a small number of new students each year. We received about 300 applications for the Fall 2023 cohort; in general, we hope to make 12-14 offers and obtain an entering class of about six students.
All applications for this program should be submitted directly to the Yale Graduate School Office of Admissions through the online application page.
Application requirements and guidelines
Scores from the GRE General Test are now optional. A GRE Subject Test is also optional, although the Mathematics Subject Test is not recommended for students whose undergraduate major was not Mathematics.
All applicants should have a strong mathematical background, including advanced calculus, linear algebra, elementary probability theory, and at least one course providing an introduction to mathematical statistics. An undergraduate major may be in statistics, mathematics, computer science, or in a subject in which significant statistical problems may arise.
For those whose native language is not English, the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) scores are required. A strong command of English is essential for success at Yale. This requirement is waived only for applicants who, prior to matriculation at Yale, will have received a baccalaureate degree or its international equivalent with three years of residency from a college or university where English is the primary language of instruction.
The offer of admission typically includes full tuition ($48,300 in 2023-24) and a generous stipend (roughly $40,300 for 2023-24) for five years. Consult the Graduate School’s financial assistance page (UPDATE NEEDED) for additional detail on living costs and funding.
For incoming students whose TOEFL scores fall below the level required to satisfy the Graduate School’s Oral English Proficiency Standard, the Graduate School provides a stipend for support during a three week Immersive English Program , held late in summer on the Yale campus.
Tuition and Living Costs (UPDATE NEEDED)
- Skip to Content
- Catalog Home
- Institution Home
Yale College Programs of Study 2023–2024
- Yale University Publications /
- Yale College Programs of Study /
- Subjects of Instruction /
Computer Science
Current edition: ycps archive . click to change..
- Certificate
Directors of undergraduate studies: Y. Richard Yang , 432-6400, AKW 208A; cpsc.yale.edu
The Department of Computer Science offers both B.S. and B.A. degree programs, as well as four combined major programs in cooperation with other departments: Electrical Engineering and Computer Science , Computer Science and Economics , Computer Science and Mathematics , and Computer Science and Psychology . Each program not only provides a solid technical education but also allows students either to take a broad range of courses in other disciplines or to complete the requirements of a second major.
The Computer Science and combined major programs share a common core of five computer science courses. The first is CPSC 201 , a survey that demonstrates the breadth and depth of the field to students who have taken the equivalent of an introductory programming course. The remaining core courses cover discrete mathematics ( CPSC 202 or MATH 244 ), data structures ( CPSC 223 ), systems programming and computer architecture ( CPSC 323 ), and algorithm analysis and design CPSC 365 , 366 or 368 . Only one of CPSC 365 , 366 , and 368 may be taken for major credit. Together these courses include the material that every major should know.
The core courses are supplemented by electives (and, for a combined major, core courses in the other discipline) that offer great flexibility in tailoring a program to each student's interests. The capstone is the senior project ( CPSC 490 ), through which students experience the challenges and rewards of original research under the guidance of a faculty adviser.
Prospective majors are encouraged to discuss their programs with the director of undergraduate studies (DUS) as early as possible.
Introductory Courses
The department offers a broad range of introductory courses to meet the needs of students with varying backgrounds and interests. Except for CPSC 200 and CPSC 201 , none assumes previous knowledge of computers.
- CPSC 100 is taught jointly with Harvard University and teaches students majoring in any subject area how to program a computer and solve problems. No prior programming experience is required. Students with previous programming experience should consider taking CPSC 201 instead. This course satisfies the Quantitative Reasoning distributional requirement.
- CPSC 110 teaches programming for humanities and social sciences using the Python programming language. No prior programming experience is required. This course satisfies the Quantitative Reasoning distributional requirement.
- CPSC 112 teaches students majoring in any subject area how to program a computer and solve problems using the Java programming language. No prior programming experience is required. Students with previous programming experience should consider taking CPSC 201 instead. This course satisfies the Quantitative Reasoning distributional requirement.
- CPSC 134 provides an introduction to computer music, including musical representations for computing, automated music analysis and composition, interactive systems, and virtual instrument design.
- CPSC 150 explores how some of the key ideas in computer science have affected philosophy of mind, cognitivism, connectionism, and related areas. This humanities-style course requires a significant amount of reading and writing a paper, and satisfies the Writing and the Humanities and Arts distributional requirements.
- CPSC 151 studies the history of the graphical user interface in an attempt to guess its future. This course satisfies the Writing distributional requirement.
- CPSC 183 explores the myriad ways that law and technology intersect, with a special focus on the role of cyberspace. This course satisfies the Social Sciences distributional requirement.
- CPSC 184 focuses on the evolving and oftentimes vexing intellectual property regime of the new digital age. This course satisfies the Social Sciences and the Humanities and Arts distributional requirements.
- CPSC 185 covers the evolution of various legal doctrines with and around technological development. This course satisfies the Social Sciences and the Writing distributional requirements.
- CPSC 200 , intended as a survey course for non-majors, focuses on practical applications of computing technology while examining topics including computer hardware, computer software, and related issues such as security and software engineering. This course satisfies the Quantitative Reasoning distributional requirement.
- CPSC 201 teaches the basic concepts, techniques, and applications of computer science, including systems (computers and their languages) and theory (complexity and computability). Students with sufficient programming experience may elect CPSC 201 without taking CPSC 112 . (These courses meet at the same time so that students are easily able to change levels if necessary.) This course satisfies the Quantitative Reasoning distributional requirement.
- CPSC 202 presents the formal methods of reasoning and the concepts of discrete mathematics and linear algebra used in computer science and related disciplines. This course satisfies the Quantitative Reasoning distributional requirement.
- CPSC 210 examines the political challenges wrought by massive increases in the power of computational and communication technologies and the potential for citizens and governments to harness those technologies to solve problems. This course satisfies the Social Sciences distributional requirement.
Requirements of the Major
The B.S. and the B.A. degree programs have the same required five core courses: CPSC 201 ; CPSC 202 or MATH 244 ; CPSC 223 ; CPSC 323 ; and CPSC 365 or 366 or 368 .
B.S. degree program The B.S. degree program requires a total of twelve term courses: the five core courses, six intermediate or advanced courses in Computer Science, and the senior requirement.
B.A. degree program The B.A. degree program requires a total of ten term courses: the five core courses, four intermediate or advanced courses in Computer Science, and the senior requirement.
Combined B.S./M.S. degree Exceptionally able and well-prepared students may complete a course of study leading to the simultaneous award of the B.S. and M.S. degrees after eight terms of enrollment. General eligibility requirements are described in the Academic Regulations, section L, Special Academic Arrangements , “Simultaneous Award of the Bachelor's and Master's Degrees.” Specific requirements for the combined degree in Computer Science are as follows:
- Candidates must satisfy the Yale College requirements for the B.S. degree in Computer Science.
- At the end of their fifth term of enrollment candidates must have earned at least nine of their Computer Science required course credits, which together with three additional Computer Science required course credits, satisfy the requirements for the B.S. in Computer Science. Candidates must also have achieved A grades in at least three quarters of these courses.
- Candidates must also complete eight graduate courses from the approved list, up to two of which may, with the permission of the DUS and the director of graduate studies, also be applied toward completion of the B.S. degree. At most, one of these eight courses may be CPSC 690 , 691 , or 692 . All eight graduate courses must be completed in the final four terms of enrollment, and at least six of them must be completed in the final three terms of enrollment.
Credit/D/Fail Courses taken Credit/D/Fail may not be counted toward the major. All courses in the major must be taken for a letter grade.
Senior Requirement
In the senior year, students must take CPSC 490 , an independent project course, in which a student selects an adviser to conduct original research with substantial work in a subfield of computer science. With permission of the DUS, students may enroll in 490 more than once or before their senior year.
All Computer Science majors in the sophomore, junior, and senior years should review their programs with their class advisers and the DUS. Students majoring in Computer Science are advised to complete CPSC 201 and 223 by the end of their sophomore year.
Electives The field of computer science has broadened substantially in the last few decades and the Computer Science department advises its majors to choose intermediate and advanced electives covering the breadth of computer science, including theoretical computer science; computer systems and languages (e.g., database, networking, operating systems, programming languages, and systems security); and computer applications (e.g., artificial intelligence, computer graphics, computer vision, human-computer interactions, machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics).
The Computer Science department encourages interdisciplinary study in which computer science plays a major role. Advanced courses in other departments that involve concepts from computer science and are relevant to an individual program may, with permission of the DUS, be counted toward the requirements, but no more than two such courses may be counted toward the B.S., and no more than one toward the B.A.
Students interested in using computers to solve scientific and engineering problems are advised to take CPSC 440 as well as computational courses offered in Applied Mathematics and in Engineering and Applied Science .
The core mathematical background necessary to complete the Computer Science major is provided in CPSC 202 . However, many advanced courses in graphics, computer vision, neural networks, and numerical analysis assume additional knowledge of linear algebra and calculus. Students who plan to take such courses as electives and who are unsure whether they have the appropriate mathematical background are encouraged to take MATH 222 or 225 , MATH 226 , and MATH 120 .
Typical programs For students who already know how to program, typical B.S. programs starting in the first and sophomore years are indicated below. For typical B.A. programs, two of the electives would be omitted.
SUMMARY OF MAJOR REQUIREMENTS
Prerequisites None
Number of courses B.S. —12 term courses taken for letter grades (incl senior project); B.A. —10 term courses taken for letter grades (incl senior project)
Specific courses required B.S. and B.A. — CPSC 201 ; CPSC 202 or MATH 244 ; CPSC 223 ; CPSC 323 ; and CPSC 365 or 366 or 368
Distribution of courses B.S. —6 addtl intermediate or advanced Comp Sci courses; B.A. —4 addtl intermediate or advanced Comp Sci courses
Substitution permitted Advanced courses in other depts, with DUS permission
Senior requirement Senior project ( CPSC 490 )
The Computer Science department offers two degree programs, B.S. and B.A., and combined majors with Economics, Electrical Engineering, Mathematics, and Psychology. Each program provides a solid technical education yet allows students to take the broad range of courses in other disciplines that is an essential part of a liberal education.
The programs share a common core of five computer science courses, including CPSC 201 and courses in discrete mathematics, data structures, systems programming and computer architecture, and algorithm analysis and design. This core is supplemented by electives and, for the combined majors, core courses in the other discipline. The capstone of the major is the senior project, in which students conduct original research under the guidance of a faculty mentor.
Prospective majors are encouraged to discuss their program with the director of undergraduate studies (DUS) as early as possible.
The department offers a broad range of introductory courses for first-year students with varying backgrounds and interests. Except for CPSC 200 and CPSC 201 , none assumes previous knowledge of computers.
- CPSC 100 is taught jointly with Harvard University, and teaches students majoring in any subject area how to program a computer and solve problems. No prior programming experience is required. Students with previous programming experience should consider taking CPSC 201 instead. This course satisfies the Quantitative Reasoning distributional requirement.
- CPSC 110 teaches programming for humanities and social sciences using the Python programming language. No prior programming experience is required. This course satisfies the Quantitative Reasoning distributional requirement.
- CPSC 112 teaches students majoring in any subject area how to program a computer and solve problems using the Java programming language. No prior programming experience is required. Students with previous programming experience should consider taking CPSC 201 instead. This course satisfies the Quantitative Reasoning distributional requirement.
- CPSC 150 explores how some of the key ideas in computer science have affected philosophy of mind, cognitivism, connectionism, and related areas. This humanities-style course requires a significant amount of reading and writing a paper, and satisfies the Writing and the Humanities and Arts distributional requirements.
- CPSC 151 studies the history of the graphical user interface in an attempt to guess its future. This course satisfies the Writing distributional requirement.
- CPSC 183 explores the myriad ways that law and technology intersect, with a special focus on the role of cyberspace. This course satisfies the Social Sciences distributional requirement.
- CPSC 184 focuses on the evolving and oftentimes vexing intellectual property regime of the new digital age. This course satisfies the Social Sciences and the Humanities and Arts distributional requirements.
- CPSC 185 covers the evolution of various legal doctrines with and around technological development. This course satisfies the Social Sciences and the Writing distributional requirements.
- CPSC 201 teaches the basic concepts, techniques, and applications of computer science, including systems (computers and their languages) and theory (complexity and computability). Students with sufficient programming experience may elect CPSC 201 without taking CPSC 112 . (These courses meet at the same time so that students are easily able to change levels if necessary.) This course satisfies the Quantitative Reasoning distributional requirement.
- CPSC 202 presents the formal methods of reasoning and the concepts of discrete mathematics and linear algebra used in computer science and related disciplines. This course satisfies the Quantitative Reasoning distributional requirement.
- CPSC 210 examines the political challenges wrought by massive increases in the power of computational and communication technologies and the potential for citizens and governments to harness those technologies to solve problems. This course satisfies the Social Science distributional requirement.
Certificate in Programming
Certificate in programming advisor: T heodore Kim , AKW 412; cpsc.yale.edu
The Certificate in Programming prepares students to program computers in support of work in any area of study. While the certificate does not provide the grounding in theory and systems that the computer science majors do, it does provide a short path to programming literacy that can be completed in a span of four terms. Majors in Computer Science, and in the joint programs with Economics, Electrical Engineering, Mathematics, and Psychology, or in Computing and the Arts may not pursue the Certificate.
Refer to the C omputer Science website for more information.
Prerequisite
The prerequisite for the Certificate is an introductory programming course, CPSC 100 , 110 , 112 , S115 or successful completion of an AP Computer Science course.
Requirements of the Certificate
Students may not use any of the five required courses, indicated below, to satisfy the requirements of any major or other certificate. If such a course is required for another program, the student must substitute another course from the same category or a more advanced one for the Programming Certificate. No course taken Credit/D/Fail may be used to satisfy any of the requirements; no course may be used to satisfy more than one of them.
Programming One from CPSC 201 or CPSC 200
Data structures CPSC 223
Advanced programming One from CPSC 327 or CPSC 323
A programming elective A CPSC course with CPSC 223 as a listed or implied prerequisite and a primary focus on programming (such as CPSC 424 , 437 , 439 , 446 , or 478 ) or a second course that satisfies the advanced programming requirement
An applications or algorithms elective Either a programming in context course that requires significant programming (such as CPSC 334 , 335 , 376 , 431 , 432 , 474 , 477 , or LING 380 ) or a course in algorithms (such as CPSC 365 or 366 or 368 )
Theodore Kim from the Department of Computer Science is the Certificate Coordinator. He advises students pursuing the Certificate. Exceptions to the requirements, other than the substitution of a more advanced course for a required one, are limited.
Summary of Requirements
Prerequisite CPSC 100 , 110 , 112 , S115 or AP Computer Science course
Number of courses 5 term courses
Specific courses required CPSC 201 or 200 ; CPSC 223 ; CPSC 327 or 323
Distribution of courses 2 electives, as specified
FACULTY OF THE DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE
Professors Dana Angluin ( Emeritus ), James Aspnes, *Dirk Bergemann, Julie Dorsey, Joan Feigenbaum, Michael Fischer, David Gelernter, *Mark Gerstein, Dragomir Radev, †Vladimir Rokhlin, Holly Rushmeier, Brian Scassellati, Martin Schultz ( Emeritus ), Zhong Shao ( Chair ), Avi Silberschatz, †Daniel Spielman, Nisheeth Vishnoi, Y. Richard Yang ( DUS ), Lin Zhong, †Steven Zucker
Associate Professors Abhishek Bhattacharjee, Yang Cai, Theodore Kim, Smita Krishnaswamy, Charalampos Papamanthou, Ruzica Piskac, Robert Soulé
Assistant Professors *Kim Blenman, Arman Cohan, Yongshan Ding, Benjamin Fisch, Tesca Fitzgerald, Anurag Khandelwal, Daniel Rakita, Marynel Vázquez, Andre Wibisono, Rex Ying
Senior Research Scientists Robert Bjornson, Andrew Sherman
Senior Lecturers James Glenn, Stephen Slade
Lecturers Timothy Barron, Andrew Bridy, Ozan Erat, Jay Lim, Dylan McKay, Cody Murphey, Sohee Park, Scott Petersen, Brad Rosen, Inyoung Shin, Alan Weide, Cecillia Xie
*A secondary appointment with primary affiliation in another department or school.
†A joint appointment with primary affiliation in another department or school.
For a complete list of Computer Science Department personnel, visit the department website.
See visual roadmap of the requirements.
Print Options
Send Page to Printer
Print this page.
Download Page (PDF)
The PDF will include all information unique to this page.
Download Overview (PDF)
The PDF will include content on the Overview tab only.
Download 2023-24 YCPS PDF
All pages in YCPS Catalog.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The deadline for admission in the fall term, 2024, is January 2, 2024 for master's student applicants. The deadline for applicants to the doctoral program is December 15, 2023. There is no way to apply during a spring term, although once admitted a student may delay admission for a year or possibly less, with final permission from the Dean of ...
Admissions; Yale GSAS: Facts & Figures The Graduate School of Arts and Sciences offers MA, MS, and PhD degrees, as well as non-degree programs, in more than 70 fields of study. GSAS Students by the Numbers ~3,500. Graduate Students. 3,200+ PhD Students ~350. Master's Students ...
The acceptance rate also varies, but has been at about 15%. 8.) What do students in the program do after receiving the degree? Most students go on to work in industry, some at large companies (i.e. Microsoft, Google, Facebook, etc.) and some at small companies (including start-ups.) A few choose to go on to a PhD program.
Relative to its peers (Ivy), its not that good at CS. The CS powerhouses in the ivy league would first be Cornell and then Princeton, with Yale honestly kind of far behind. If you want to do CS, and have the stats competitive for Yale, you should apply MIT, Stanford, CMU, Cornell and Georgia tech. Yale is not particularly known for CS.
By Jamie Foster November 5, 2023. Getting accepted into Yale University's prestigious computer science program is a dream for many prospective students. With an average acceptance rate of just 6%, gaining admission is highly competitive. If you're considering applying to Yale's computer science program, you'll want all the details on ...
the requirements for graduate degrees in Computer Science at Yale. The Yale Graduate School sets general requirements for all graduate programs underDegree Requirements1. The specific requirements for Computer Science are also published by the Graduate School underComputer Science Program2. The information in this
The Department offers a Doctoral Program leading to a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) degree. It typically takes four to six years to get a Ph.D. The Ph.D. program is focused on research. There are course requirements in the first three terms, but starting in the third term the main focus is on research, guided by an advisor and supervisory committee.
https://registration.yale.edu/ Students must register every term in which they are enrolled in the Graduate School. Registration for a given term takes place the semester prior, and so it's important to stay on top of your academic plan. The University Registrar's Office oversees the systems that students use to register.
Director of Graduate Studies - Lin Zhong The following programs are available to study at Yale University Computer Science. The Master of Science- The Master of Science (MS) program is intended for students planning to pursue a professional career directly after finishing the MS program, rather than continuing on in a PhD program. The MS program is also suitable for students interested in ...
Department of Computer Science at Yale University provides on-going educational opportunities to those students seeking advanced degrees. ... Acceptance Rate. 259 Applied 33 ... Total Graduate Students 60% International Breakout (representing other countries) ...
The Doctoral Program of graduate study leads to the Ph.D. degree and is normally completed in 4-5 years. The M.S. and the M.Phil. degrees are granted to qualified students in the Ph.D. program who wish intermediate degrees. (See Master's Degrees en Route to the Ph.D .) A Brief Overview of the Doctoral Program. Requirements.
Apply Now. 2) Verify the application deadline for your program. 4) Complete your application. Decide whether you will apply for a PhD or a terminal Master's (MA, MS) in one of the programs available at the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences. (Note that you will earn one or more Master's degrees en route to a PhD.)
Worried about graduate school acceptance rates? We explain how to find grad school admissions statistics and what they mean for you. ... If we were to take the University of Michigan's grad programs in computer science and engineering, ... Arts: 17% Humanities: 20.4% Sciences: 18.6% Social sciences: 22.8%: Yale: School of Engineering ...
The work of Yale University is carried on in the following schools: Undergraduate Majors: Yale College (Est. 1701) Courses in humanities, social sciences, natural sciences, mathematical and computer sciences, and engineering. Bachelor of Arts (B.A.) and Bachelor of Science (B.S.). Yale Graduate School of Arts and Sciences (Est. 1847)
Graduate Programs. The Department offers two graduate programs: a Doctoral Program leading to a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) degree, and a terminal Master's Program leading to a Master of Science (M.S.) degree. The Doctoral Program is intended for students preparing for a career in teaching and/or research.
The Computer Science core PhD curriculum is flexible in the general plan, with 8 non-project courses required distributed across theory, systems and applications. Specific arts related courses will be included in C2 students' program of study. Course work will further be enriched by events such as the C2 Distinguished speaker series.
225 Prospect Street , New Haven, CT 06520-8107 (203) 432-3915. [email protected] . Website
Yale University is one of more than 800 institutions with graduate schools surveyed by U.S. News on an annual basis. Yale University confers degrees through various schools, such as: the School of ...
Ph.D. Admissions. The Ph.D. program admits only a small number of new students each year. We received about 300 applications for the Fall 2023 cohort; in general, we hope to make 12-14 offers and obtain an entering class of about six students. All applications for this program should be submitted directly to the Yale Graduate School Office of ...
The PhD program in Yale Computer Science is a rigorous and research-intensive course of study designed to prepare students for careers in advanced research and academia. The program typically takes five to six years to complete, with the first two years primarily devoted to coursework. Students are required to take a variety of courses ...
Computer Science. Directors of undergraduate studies: Y. Richard Yang , 432-6400, AKW 208A; cpsc.yale.edu. The Department of Computer Science offers both B.S. and B.A. degree programs, as well as four combined major programs in cooperation with other departments: Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Computer Science and Economics ...
Yale University Computer Science Acceptance Rate. All of these programs are built around a common core of five computer science courses. The first, CPSC 201 Introduction to Computer Science, is a survey that illustrates the breadth and depth of the field to students who have already completed a one-term introductory course in programming.