

Civil Rights Movement, 1954-90 A-Level History Teaching Resources & Student Activities
Civil rights movement, 1954-90 a-level teaching resources (16-18 years). can be used across examination board specifications. perfect for classroom teaching or the homeschool environment., teach any civil rights movement, 1954-90 topic, no prep needed.
Do you want to save dozens of hours in time? Get your evenings and weekends back? Be fully prepared to teach any Civil Rights Movement, 1954-90 A Level topic?
Every Civil Rights Movement, 1954-90 topic is covered, and each module comes complete with:
Lesson Presentation
Revision notes, student activities.
Download free samples →
A Level Civil Rights Movement, 1954-90 Resources
At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
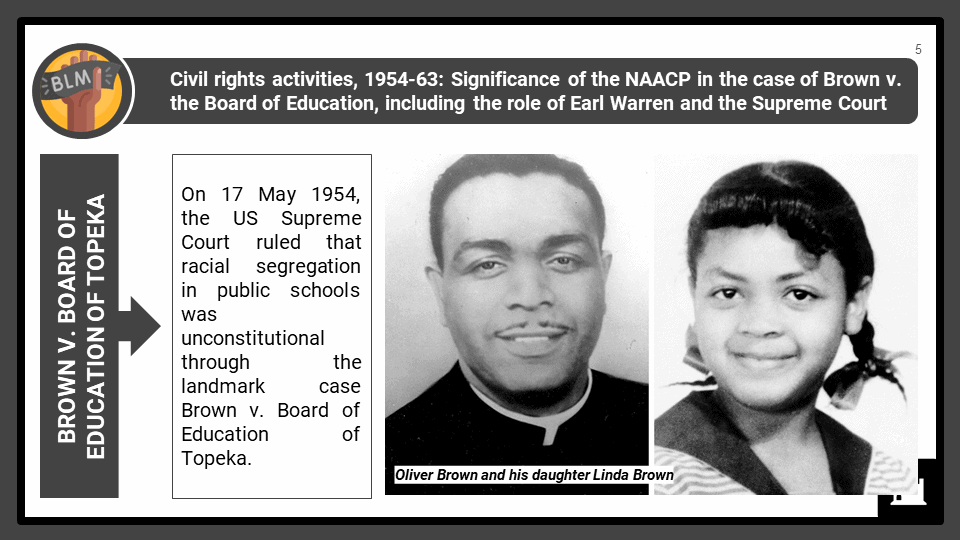
- Analyse the impact of landmark case Brown v. Board of Education in the desegregation of schools in the US
- Assess the roles of Martin Luther King, Jr., Rosa Parks, and Malcolm X in achieving black equality in the US
- Explain the importance of the Civil Rights legislatures
- Justify how media played a role towards black equality during the Civil Rights Era
- Describe the significance and impact of the Civil Rights Movement towards the African-American experience in modern USA
Resource Examples
Lesson presentation:.
Student Assessment:

- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

AQA A Level History Civil Rights
Subject: History
Age range: 16+
Resource type: Other
Last updated
7 February 2022
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

AQA A Level History Civil Rights Movement
Includes handouts and presentations to inspire lessons.
- Ella Fitzgerald handout exploring impact on the Civil Rights Movement
- Ella Fitzgerald presentation
- Harriet Beecher Stowe handout exploring her role in the Civil Rights Movement
- Harriet Beecher Stowe presentation
- Civil Rights Act 1964 PPT, exploring its legislative and symbolic significance
- List of influential female figures in the Civil Rights Movement to research
- Sheet discussing how to explore and measure the influence of historical figures
Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have downloaded this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

A Level History Coursework Edexcel – A Guide
- Post author By admin
- Post date November 16, 2023
- No Comments on A Level History Coursework Edexcel – A Guide
This guide shows you how to plan, research and write A Level History coursework for Edexcel using ideas, resources, examples and structure. This coursework is weighted towards Assessment Objective Three (AO3) 15% and Assessment Objective One (AO1) 5%. This makes it substantially different from coursework assessed under AQA or OCR. For Edexcel coursework, the focus is on differing interpretations of the past and analysis of them, alongside your own view of the events.
A Level History Coursework Edexcel – Ideas, Examples and Resources
Question Format – The question that you decide to answer for the Edexcel Coursework will always use the following template.
- Historians have disagreed about [ the chosen question, problem or issue ].
- What is your view about [ the chosen question, problem or issue ]?
Thus, we can see that there are two parts to this coursework:
- Part 1 – dealing with the historian’s viewpoints which is (AO3) and worth 15%
- Part 2 – your own viewpoint which is (A01) and worth 5%
Question Ideas, Example and Selection
There are two key points to consider when selecting a question, problem or issue for your coursework.
- Is there enough debate around this question? – There needs to be a scholarly debate around the question or issue. This means differing views on the question from different historians. This makes it easier to select appropriate works to analyse and compare.
- Can you access the appropriate resources? – You must use a minimum of three different key works as well as two supplementary works. Your three key works should hold opposing views about the question or issue. Let’s look at an example question to make this clear:
Historians have disagreed about the extent to which by 1924 the Russian people had exchanged one authoritarian regime for another. What is your view about the extent to which by 1924 the Russian people had exchanged one authoritarian regime for another?
- View 1 – Tsarist Rule was more authoritarian. (C. Hill argues this)
- View 2 – Bolshevik rule was more authoritarian. (R. Service argues this)
- View 3 – The regimes were equally authoritarian. (R. Pipes argues this)
This is the ideal example of having three viewpoints that would be spread across the historiographical spectrum. This helps us to engage with the historical debate and hit the following criteria for the coursework:
- analyse ways in which interpretations of the question or issue differ.
- explain the differences you have identified.
- evaluate the arguments, indicating which you found most persuasive and why.
You would then add to this a minimum of two supplementary works, (more is better) that would assist in helping you form your view and add weight to your analysis and arguments. Critically, you must be able to access all these resources to use them effectively in completing the coursework.
Coursework Resources
- Library – school, local, college, university – you should be able to borrow appropriate works.
- Teacher – your teacher should be able to provide you with copies of appropriate resources to use.
- JSTOR – www.jstor.org – contains a large collection of journal articles from historical publications covering numerous topics. These will often engage in the historical debate by replying to opposing views.
- Purchase Books – many second-hand books are available to purchase at very cheap prices through Amazon or similar sites.

A Level History Coursework Edexcel – How to Research and Write

Researching the Coursework – When researching our coursework we use the resource record form, which acts as a bibliography to the books, articles and online resources we are using. As we go through these resources we want to make notes that help us to identify the overall argument of the historian. Key quotes or passages should be noted down, alongside a reference. If we then use this material in our write up, we can add the appropriate footnote.
Writing the Coursework – When writing our coursework we need to be aware of the total word count as well as making sure that we hit all the assessment criteria. This means dividing up the 4000 words (maximum word count) effectively between the assessment criteria. An example structure to implement this is shown in the next section.

A Level History Coursework Edexcel – Structure and Planning
First section – introduction to the overall question and key works (c. 1000 words).
Introduction to the overall topic. You need to put the question into context by providing relevant information regarding what was happening at the time. You then need to define any key terms in the question.
Example from our question above – authoritarian regime would be defined as ‘a regime in which power is highly centralised and maintained regardless of popular support, with the use of repression and violence’.
Finally, you need to set out valid criteria by which the question can be judged.
Example from our question and definition above – we need to compare the Tsarist regime to the Bolshevik regime in terms of:
- Centralisation of power .
- Power maintained despite lacking popular support.
- Power maintained through repression and violence.
You should now have a complete introduction to the topic (1 paragraph)
Introduction to the debate by placing each of the key works in the historiographical debate. You can also place your supplementary works on the historiographical line here. (1 paragraph)
Set out the arguments in extended detail from the three key works. What are the historians’ views on this question? (1 paragraph)
Show how the arguments from each of the key works differ or are like one another. (1 paragraph)
Summary of the views of the key works. (1 paragraph)
Second Section – Explaining why the key works differ from one another (c. 1000 words)
Introduction – You need to set out three valid criteria to explain why the key works differ. Why is it that the historians’ arguments differ? There are several different potential criteria that could be used here: When was the work written? What sources and evidence did they use? Have they defined the key terms of the question differently? Have they defined the criteria to answer the question differently? Do they have different scopes of enquiry? What is the purpose of the work? What is the historians background and view?
Example from our question – The historians have defined the key term to answer the question differently – C. Hill has focused on authoritarian being defined as lacking popular support. R. Service is more focused on authoritarian being defined through repression. R. Pipes is mostly focused on authoritarian being defined as a centralisation of power.
The historians have defined the key term ‘authoritarian’ differently. (1 paragraph)
Paragraphs – This is where you use the criteria set out from the introduction to this section. You want one paragraph per item of criteria that we are judging the key works on.
Example from our question – one paragraph regarding how the historians have defined the key term ‘authoritarian’ differently.
Then you need to consider the three works in terms of the criteria set out for that paragraph. Show why there are differences in the key works regarding that criteria and how that leads the historian to arrive at their interpretation. Use evidence to support your points. (3 paragraphs – 1 for each criterion)
Conclusion – Brief conclusion that offers a summary of why the key works are different. (1 paragraph)
Third Section – Your own viewpoint on the question (c. 1000 words)
Brief introduction of your own viewpoint and line of argument that will be taken, remembering to re-instate the criteria by which the question can be judged . (1 paragraph)
Paragraphs that set out your own view on the question. This is where you should be using the criteria set out in your introductions. You want one paragraph per item of criteria.
Example from our question – one paragraph regarding ‘centralisation of power’.
Then you need to bring evidence and analysis to assess the criteria being judged. You can also use the key works and the supplementary works in this section to help you. (3 paragraphs – 1 for each criterion)
Conclusion that reaches a judgement on the question and follows your line of argument that has flowed throughout. (1 paragraph)
Fourth Section – Evaluation and Judgement of the key works and of the question (c. 1000 words)
Go through each of the key works and make a judgement on how convincing and valid the arguments from the historians are compared to the criteria. (3 paragraphs – 1 for each key work)
Form an overall judgement on the question and an overall judgement on which of the key works is most convincing. These should broadly align together. (1 paragraph)
How To Improve Further at A Level History
Pass A Level History – is our sister site, which shows you step by step, how to most effectively answer any A Level History extract, source or essay question. Please click the following link to visit the site and get access to your free preview lesson. www.passalevelhistory.co.uk
Previous and Next Blog Posts
Previous – A Level History Essay Structure – A Guide passhistoryexams.co.uk/a-level-history-essay-structure/
Next – A Level History Coursework AQA – A Guide passhistoryexams.co.uk/a-level-history-coursework-aqa/
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This website works best with JavaScript switched on. Please enable JavaScript
- Centre Services
- Associate Extranet
- All About Maths
AS and A-level History
- Specification
- Planning resources
- Teaching resources
- Assessment resources
- Introduction
Specification at a glance
- 1A The Age of the Crusades, c1071–1204
- 1B Spain in the Age of Discovery, 1469–1598 (A-level only)
- 1C The Tudors: England, 1485–1603
- 1D Stuart Britain and the Crisis of Monarchy, 1603–1702
- 1E Russia in the Age of Absolutism and Enlightenment, 1682–1796 (A-level only)
- 1F Industrialisation and the people: Britain, c1783–1885
- 1G Challenge and transformation: Britain, c1851–1964
- 1H Tsarist and Communist Russia, 1855–1964
- 1J The British Empire, c1857–1967
- 1K The making of a Superpower: USA, 1865–1975
- 1L The quest for political stability: Germany, 1871–1991
- 2A Royal Authority and the Angevin Kings, 1154–1216
- 2B The Wars of the Roses, 1450–1499
- 2C The Reformation in Europe, c1500–1564 (A-level only)
- 2D Religious conflict and the Church in England, c1529–c1570
- 2E The English Revolution, 1625–1660
- 2F The Sun King: Louis XIV, France and Europe, 1643–1715 (A-level only)
- 2G The Birth of the USA, 1760–1801
- 2H France in Revolution, 1774–1815 (A-level only)
- 2J America: A Nation Divided, c1845–1877
- 2K International Relations and Global Conflict, c1890–1941 (A-level only)
- 2L Italy and Fascism, c1900–1945
- 2M Wars and Welfare: Britain in Transition, 1906–1957
- 2N Revolution and dictatorship: Russia, 1917–1953
- 2O Democracy and Nazism: Germany, 1918–1945
- 2P The Transformation of China, 1936–1997
- 2Q The American Dream: reality and illusion, 1945–1980
- 2R The Cold War, c1945–1991
- 2S The Making of Modern Britain, 1951–2007
- 2T The Crisis of Communism: The USSR and the Soviet Empire, 1953–2000 (A-level only)
- Component 3: Historical investigation (non-exam assessment) (A-level only)
- Scheme of assessment
- Non-exam assessment administration
- General administration

Subject content
- Component 1: Breadth study
1A The Age of the Crusades, c1071–1204
1B Spain in the Age of Discovery, 1469–1598
1C The Tudors: England, 1485–1603
1D Stuart Britain and the Crisis of Monarchy, 1603–1702
1E Russia in the Age of Absolutism and Enlightenment, 1682–1796
1F Industrialisation and the people: Britain, c1783–1885
1G Challenge and transformation: Britain, c1851–1964
1H Tsarist and Communist Russia, 1855–1964
1J The British Empire, c1857–1967
1K The making of a Superpower: USA, 1865–1975
1L The quest for political stability: Germany, 1871–1991
- Component 2: Depth study
2A Royal Authority and the Angevin Kings, 1154–1216
2B The Wars of the Roses, 1450–1499
2C The Reformation in Europe, c1500–1564
2D Religious conflict and the Church in England, c1529–c1570
2E The English Revolution, 1625–1660
2F The Sun King: Louis XIV, France and Europe, 1643–1715
2G The Birth of the USA, 1760–1801
2H France in Revolution, 1774–1815
2J America: A Nation Divided, c1845–1877
2K International Relations and Global Conflict, c1890–1941
2L Italy and Fascism, c1900–1945
2M Wars and Welfare: Britain in Transition, 1906–1957
2N Revolution and dictatorship: Russia, 1917–1953
2O Democracy and Nazism: Germany, 1918–1945
2P The Transformation of China, 1936–1997
2Q The American Dream: reality and illusion, 1945–1980
2R The Cold War, c1945–1991
2S The Making of Modern Britain, 1951–2007
2T The Crisis of Communism: The USSR and the Soviet Empire, 1953–2000
Component 3: Historical Investigation
AS students must take assessments in both of the following components, in the same series.
Students must:
- study the history of more than one country
- study a British history option for Component 1 or 2
- study a non-British history option for Component 1 or 2
Assessments

Prohibited Combinations
Students must study a British history option for either Component 1 or Component 2. If a British history option is chosen for Component 1, it must be combined with a non-British option for Component 2. If a British history option is chosen for Component 2, it must be combined with a non-British option for Component 1. Any British option may be combined with any non-British option.
The following are designated British history options :
Component 1
1C The Tudors: England, 1485–1547
1D Stuart Britain and the Crisis of Monarchy, 1603–1649
1F Industrialisation and the People: Britain, c1783–1832
1G Challenge and Transformation: Britain, c1851–1914
1J The British Empire, c1857–1914
Component 2
2A Royal Authority and the Angevin Kings, 1154–1189
2B The Wars of the Roses, 1450–1471
2D Religious Conflict and the Church in England, c1529–c1547
2E The English Revolution, 1625–1642
2M Wars and Welfare: Britain in Transition, 1906–1929
2S The Making of Modern Britain, 1951–1979
A-level students must take assessments in all three of the following components in the same series:
- Component 3: Historical investigation (Personal study)
- study topics from a chronological range of at least 200 years
- Through the topics studied in Components 1, 2 and 3 (Historical investigation), A-level students must cover a chronological range of at least 200 years.
Students must study a British history option for either Component 1 or Component 2. If a British history option is chosen for Component 1, it must be combined with a non-British option for Component 2. If a British history option is chosen for Component 2, it must be combined with a non-British option for Component 1. Any British option may be combined with any non-British option, other than the following:
- 1C The Tudors may not be combined with 2C The Reformation in Europe
- 1D Stuart Britain and the Crisis of Monarchy may not be combined with 2F The Sun King: Louis XIV, France and Europe
This is because there is a strong conceptual emphasis which runs across both breadth and depth options which would result in a narrowing of the student’s experience.
The following are designated British history options:
1F Industrialisation and the People: Britain, c1783–1885
1G Challenge and Transformation: Britain, c1851–1964
2D Religious Conflict and the Church in England, c1529–c1570

COMMENTS
Civil Rights Coursework on the impact of presidents on furthering the civil rights movement compared to other factors charlie gibbs word count: 4097 how far ... he built on the NAACP's work and challenged anti-civil rights legislation. An example being through the MIA, eventually leading to a ruling in 1956 that stated segregation laws ...
Specimen Answer 1 (Martin Luther King) Within the context of the years 1865 to 1968, how important was Martin Luther King in the pursuit of black civil rights in America? 'If King had never lived, the black struggle would have followed a course of development similar to the one it did.'1. Verney states that there is no 'mono-causal ...
Level 2: 3-4 Shows some understanding of the differing historical interpretations raised by the question. They may refer to the time, context and/or limitations placed on the historians in an unconvincing way. Level 1: 1-2 Shows limited understanding of the differing historical interpretations raised by the question. Comment on historical ...
AQA A-Level History - Component 3: Historical Investigation (non-exam assessment) Black Civil Rights Movement (1865-1975) Key Opposing Historiographical Arguments About the author: This Teacher CPD resource was created by Professor George Lewis, Professor of American History in the School of History, Politics and International Relations at the
It is crucial that the question is one to which a substantiated answer can be arrived at within a reasonable amount of work. Schools are urged to fully utilise the services of their NEA Advisor. The contextual element of the question must be historically valid, and the full date range set in the question should be addressed.
A-level . HISTORY . Non-exam assessment (NEA) ... Published: July 2019 . AQA Education (AQA) is a registered charity (number 1073334) and a company limited by guarantee registered in England and Wales (number 3644723). Our registered address is AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX. ... of 'improvement in black civil rights'. Students
REPORT ON THE EXAMINATION - A-LEVEL HISTORY - 7042/C - JUNE 2022. Whilst it was clear that many students had worked exceptionally hard to research material relevant to their question, these same students were often keen to include as much factual material as they could within the word limit. Just as in the examined units, it is important ...
Our registered address is AQA, Devas Street, Manchester M15 6EX. 1 of 5 . NEA: specification requirements . and management. First published: July 2019 . This resource provides guidance on the non-exam assessment (NEA) requirements for A-level History, and should be read in conjunction with the NEA requirements set out in the specification. It
Marks awarded. AO1: the mark awarded is a low Level 4. It is placed in Level 4 because the Investigation is generally analytical, it offers judgements and shows good awareness of change and continuity. It is well written with sound understanding of some of the concepts that are relevant to the issue of the question. There are, however, a number ...
Assessment resources. Answers and commentary (A-level): Component 1E Russia in the Age of Absolutism and Englightenment, 1682-1796 - Sample set 1 New. Answers and commentary (A-level): Component 2D Religious conflict and the Church in England, c1529-1570 - Sample set 1 New. Answers and commentary (A-level): Component 1L The quest for political ...
The School of History, Politics and International Relations University of Leicester University Road, Leicester, LE1 7RH T +44(0)116 252 2587 E [email protected] AQA A-Level History - Component 3: Historical Investigation (non-exam assessment) Women's Rights in Britain (1897-1997) Key Opposing Historiographical Arguments About the author:
A Level History Coursework AQA - Ideas, Examples and Resources. Choosing an Issue and Question - You are required to identify an issue or topic that you wish to study and develop a question from this. This gives a broad scope for potential questions. There are however two specific requirements of the question.
File previews. docx, 183.63 KB. Question: To what extent were key individuals responsible for the gains made by African-Americans in their struggle for equality between 1863 and 1965? Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Response A. Green argues that Henry VII's reign was achieved by his frugal nature. They argue that Henry's shrewdness with money was the product of his own insensitivity and greed. Green focuses in Henry's financial aims in his suppression of the nobility.
A Level Civil Rights Movement, 1954-90 Resources. Analyse the impact of landmark case Brown v. Board of Education in the desegregation of schools in the US. Assess the roles of Martin Luther King, Jr., Rosa Parks, and Malcolm X in achieving black equality in the US. Justify how media played a role towards black equality during the Civil Rights Era.
pptx, 1010.44 KB. docx, 12.24 KB. docx, 13.22 KB. AQA A Level History Civil Rights Movement. Includes handouts and presentations to inspire lessons. Ella Fitzgerald handout exploring impact on the Civil Rights Movement. Ella Fitzgerald presentation. Harriet Beecher Stowe handout exploring her role in the Civil Rights Movement.
A-level. At A-level, there are three assessment components. Component 1 assesses students' understanding of breadth and of historical interpretations. Component 2 assesses understanding of depth and of the value of primary sources. Component 3 is a Historical Investigation (non-exam assessment).
The resource record can be found in Appendix 5 on page 153 of the Edexcel A level History Specification. Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced GCE in History Centre name: Candidate name: Resources used. The three works chosen for the assignment must be asterisked. Page/web reference. Student comments Student date(s) when accessed
Guide to source questions - A-level History 7042. 2. Introduction. This Guide has been produced to show how the mark scheme for the Component 2 source question (Question 1), will be applied and to illustrate approaches to assessment to assist teachers in preparing students for the examination.
The non-exam assessment (NEA) for the A-level specification only is a Historical Investigation. Visit aqa.org.uk/7042 for detailed information about all aspects of NEA administration. The head of the school or college is responsible for making sure that NEA is conducted in line with our instructions and Joint Council for Qualifications (JCQ ...
This guide shows you how to plan, research and write A Level History coursework for Edexcel using ideas, resources, examples and structure. This coursework is weighted towards Assessment Objective Three (AO3) 15% and Assessment Objective One (AO1) 5%. This makes it substantially different from coursework assessed under AQA or OCR. For Edexcel ...
A-level students must take assessments in all three of the following components in the same series: Component 1: Breadth study. Component 2: Depth study. Component 3: Historical investigation (Personal study) Students must: study the history of more than one country. study a British history option for Component 1 or 2.