Learn how UpToDate can help you.
Select the option that best describes you
- Medical Professional
- Resident, Fellow, or Student
- Hospital or Institution
- Group Practice
- Patient or Caregiver
- Find in topic

RELATED TOPICS
INTRODUCTION
For patients who present in labor with a breech fetus, cesarean birth is the preferred approach in many hospitals in the United States and elsewhere. Cesarean is performed for over 90 percent of breech presentations, and this rate has increased worldwide [ 1,2 ]. However, even in institutions with a policy of routine cesarean birth for breech presentation, vaginal breech births occur because of situations such as patient preference, precipitous birth, out-of-hospital birth, and lethal fetal anomaly or fetal death. Therefore, it is essential for clinicians to maintain familiarity with the techniques required to assist in a vaginal breech birth.
In addition, some clinicians and patients consider vaginal breech birth preferable to cesarean birth. Recent trends, particularly in central Europe, support vaginal breech birth [ 3-5 ]. In selected cases, as described below and depicted in the algorithm ( algorithm 1 ), it is associated with a low risk of complications. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has opined that "Planned vaginal delivery of a term singleton breech fetus may be reasonable under hospital-specific protocol guidelines for eligibility and labor management" [ 6 ].
This topic will focus on vaginal birth of breech singletons, with a brief discussion of breech delivery at cesarean. Choosing the best route of birth for the fetus in breech presentation and delivery of the breech first or second twin are reviewed separately.
● (See "Overview of breech presentation", section on 'Approach to management at or near term' .)
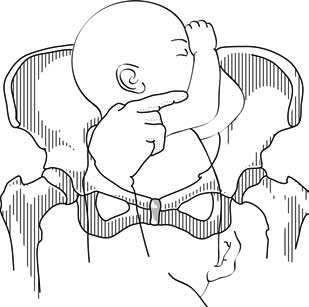
First, recognize breech presentation when the buttocks appear in the birth canal before the head does. Experienced providers can deliver some babies in frank or complete breech presentations. Have a cloth or surgical towel available as well as other instruments used for routine deliveries and prepare for what to do if vaginal delivery is unsuccessful.
This position is a frank breech.
This position is a complete breech.
And this position is an incomplete complete breech.
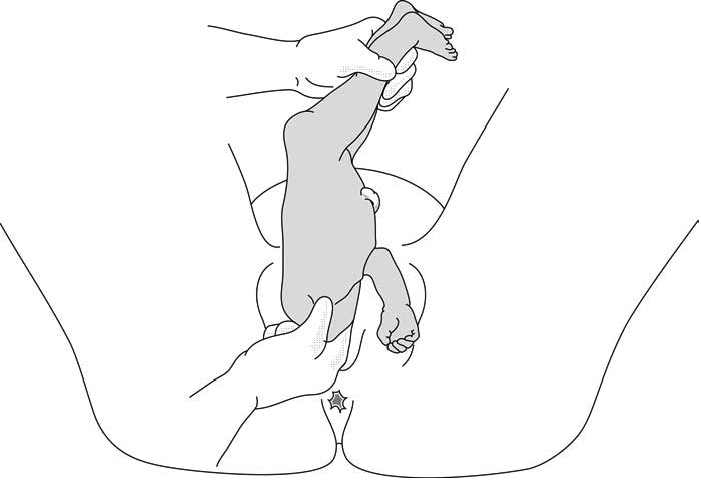
Allow delivery to the level of the umbilicus with maternal effort. If possible, do this without touching the infant. Anticipate umbilical cord compression and possibly fetal decelerations.
To deliver a leg, splint the medial thigh parallel to the femur and sweep the thigh laterally. Repeat this procedure to deliver the other leg.
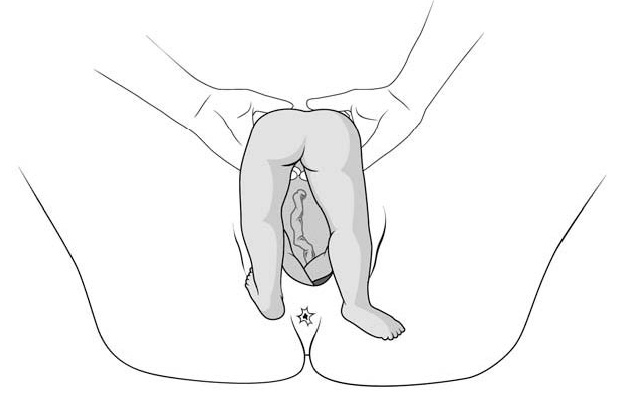
Wrap a towel around the infant, putting your fingers on the anterior superior iliac spines and your thumbs on the sacrum.
Assist the mother’s efforts during contractions by applying gentle traction to help deliver the body to the level of the scapulas.
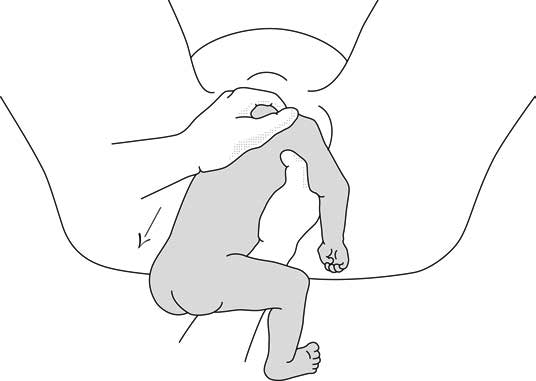
Rotate the body in either direction to make one shoulder anterior. Deliver the anterior arm by sweeping it across the chest. Rotate the infant 180 degrees in either direction. Deliver the arm that is now anterior the same way the other arm was delivered. Move the towel up to cover the arms and rotate the body to make the back anterior.
To deliver the head, place your index and middle fingers of one hand over the fetal maxilla to flex the head, while the body rests on your palm and forearm, as shown here. With your other hand, hook 2 fingers over the neck, grasp the shoulder, and apply gentle downward traction. Have an assistant apply suprapubic pressure to help maintain head flexion and deliver the head.
Procedure by Will Stone, MD, and Kate Leonard, MD, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center Residency in Obstetrics and Gynecology; and Shad Deering, COL, MD, Chair, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Uniformed Services University. Assisted by Elizabeth N. Weissbrod, MA, CMI, Eric Wilson, 2LT, and Jamie Bradshaw at the Val G. Hemming Simulation Center at the Uniformed Services University.
- Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)

- Pregnancy Classes

Breech Births
In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby’s buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3–4% of full-term births.
What are the different types of breech birth presentations?
- Complete breech: Here, the buttocks are pointing downward with the legs folded at the knees and feet near the buttocks.
- Frank breech: In this position, the baby’s buttocks are aimed at the birth canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of his or her body and the feet near the head.
- Footling breech: In this position, one or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of the body.
What causes a breech presentation?
The causes of breech presentations are not fully understood. However, the data show that breech birth is more common when:
- You have been pregnant before
- In pregnancies of multiples
- When there is a history of premature delivery
- When the uterus has too much or too little amniotic fluid
- When there is an abnormally shaped uterus or a uterus with abnormal growths, such as fibroids
- The placenta covers all or part of the opening of the uterus placenta previa
How is a breech presentation diagnosed?
A few weeks prior to the due date, the health care provider will place her hands on the mother’s lower abdomen to locate the baby’s head, back, and buttocks. If it appears that the baby might be in a breech position, they can use ultrasound or pelvic exam to confirm the position. Special x-rays can also be used to determine the baby’s position and the size of the pelvis to determine if a vaginal delivery of a breech baby can be safely attempted.
Can a breech presentation mean something is wrong?
Even though most breech babies are born healthy, there is a slightly elevated risk for certain problems. Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies and the defect might be the reason that the baby failed to move into the right position prior to delivery.
Can a breech presentation be changed?
It is preferable to try to turn a breech baby between the 32nd and 37th weeks of pregnancy . The methods of turning a baby will vary and the success rate for each method can also vary. It is best to discuss the options with the health care provider to see which method she recommends.
Medical Techniques
External Cephalic Version (EVC) is a non-surgical technique to move the baby in the uterus. In this procedure, a medication is given to help relax the uterus. There might also be the use of an ultrasound to determine the position of the baby, the location of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus.
Gentle pushing on the lower abdomen can turn the baby into the head-down position. Throughout the external version the baby’s heartbeat will be closely monitored so that if a problem develops, the health care provider will immediately stop the procedure. ECV usually is done near a delivery room so if a problem occurs, a cesarean delivery can be performed quickly. The external version has a high success rate and can be considered if you have had a previous cesarean delivery.
ECV will not be tried if:
- You are carrying more than one fetus
- There are concerns about the health of the fetus
- You have certain abnormalities of the reproductive system
- The placenta is in the wrong place
- The placenta has come away from the wall of the uterus ( placental abruption )
Complications of EVC include:
- Prelabor rupture of membranes
- Changes in the fetus’s heart rate
- Placental abruption
- Preterm labor
Vaginal delivery versus cesarean for breech birth?
Most health care providers do not believe in attempting a vaginal delivery for a breech position. However, some will delay making a final decision until the woman is in labor. The following conditions are considered necessary in order to attempt a vaginal birth:
- The baby is full-term and in the frank breech presentation
- The baby does not show signs of distress while its heart rate is closely monitored.
- The process of labor is smooth and steady with the cervix widening as the baby descends.
- The health care provider estimates that the baby is not too big or the mother’s pelvis too narrow for the baby to pass safely through the birth canal.
- Anesthesia is available and a cesarean delivery possible on short notice
What are the risks and complications of a vaginal delivery?
In a breech birth, the baby’s head is the last part of its body to emerge making it more difficult to ease it through the birth canal. Sometimes forceps are used to guide the baby’s head out of the birth canal. Another potential problem is cord prolapse . In this situation the umbilical cord is squeezed as the baby moves toward the birth canal, thus slowing the baby’s supply of oxygen and blood. In a vaginal breech delivery, electronic fetal monitoring will be used to monitor the baby’s heartbeat throughout the course of labor. Cesarean delivery may be an option if signs develop that the baby may be in distress.
When is a cesarean delivery used with a breech presentation?
Most health care providers recommend a cesarean delivery for all babies in a breech position, especially babies that are premature. Since premature babies are small and more fragile, and because the head of a premature baby is relatively larger in proportion to its body, the baby is unlikely to stretch the cervix as much as a full-term baby. This means that there might be less room for the head to emerge.
Want to Know More?
- Creating Your Birth Plan
- Labor & Birth Terms to Know
- Cesarean Birth After Care
Compiled using information from the following sources:
- ACOG: If Your Baby is Breech
- William’s Obstetrics Twenty-Second Ed. Cunningham, F. Gary, et al, Ch. 24.
- Danforth’s Obstetrics and Gynecology Ninth Ed. Scott, James R., et al, Ch. 21.
BLOG CATEGORIES
- Can I get pregnant if… ? 3
- Child Adoption 19
- Fertility 54
- Pregnancy Loss 11
- Breastfeeding 29
- Changes In Your Body 5
- Cord Blood 4
- Genetic Disorders & Birth Defects 17
- Health & Nutrition 2
- Is it Safe While Pregnant 54
- Labor and Birth 65
- Multiple Births 10
- Planning and Preparing 24
- Pregnancy Complications 68
- Pregnancy Concerns 62
- Pregnancy Health and Wellness 149
- Pregnancy Products & Tests 8
- Pregnancy Supplements & Medications 14
- The First Year 41
- Week by Week Newsletter 40
- Your Developing Baby 16
- Options for Unplanned Pregnancy 18
- Paternity Tests 2
- Pregnancy Symptoms 5
- Prenatal Testing 16
- The Bumpy Truth Blog 7
- Uncategorized 4
- Abstinence 3
- Birth Control Pills, Patches & Devices 21
- Women's Health 34
- Thank You for Your Donation
- Unplanned Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
- Healthy Pregnancy
- Privacy Policy
Share this post:
Similar post.

Episiotomy: Advantages & Complications

Retained Placenta

What is Dilation in Pregnancy?
Track your baby’s development, subscribe to our week-by-week pregnancy newsletter.
- The Bumpy Truth Blog
- Fertility Products Resource Guide
Pregnancy Tools
- Ovulation Calendar
- Baby Names Directory
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Quiz
Pregnancy Journeys
- Partner With Us
- Corporate Sponsors
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.

- Management of breech presentation
Evidence review M
NICE Guideline, No. 201
National Guideline Alliance (UK) .
- Copyright and Permissions
Review question
What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy?
Introduction
Breech presentation of the fetus in late pregnancy may result in prolonged or obstructed labour with resulting risks to both woman and fetus. Interventions to correct breech presentation (to cephalic) before labour and birth are important for the woman’s and the baby’s health. The aim of this review is to determine the most effective way of managing a breech presentation in late pregnancy.
Summary of the protocol
Please see Table 1 for a summary of the Population, Intervention, Comparison and Outcome (PICO) characteristics of this review.
Summary of the protocol (PICO table).
For further details see the review protocol in appendix A .
Methods and process
This evidence review was developed using the methods and process described in Developing NICE guidelines: the manual 2014 . Methods specific to this review question are described in the review protocol in appendix A .
Declarations of interest were recorded according to NICE’s conflicts of interest policy .
Clinical evidence
Included studies.
Thirty-six randomised controlled trials (RCTs) were identified for this review.
The included studies are summarised in Table 2 .
Three studies reported on external cephalic version (ECV) versus no intervention ( Dafallah 2004 , Hofmeyr 1983 , Rita 2011 ). One study reported on a 4-arm trial comparing acupuncture, sweeping of fetal membranes, acupuncture plus sweeping, and no intervention ( Andersen 2013 ). Two studies reported on postural management versus no intervention ( Chenia 1987 , Smith 1999 ).
Seven studies reported on ECV plus anaesthesia ( Chalifoux 2017 , Dugoff 1999 , Khaw 2015 , Mancuso 2000 , Schorr 1997 , Sullivan 2009 , Weiniger 2010 ). Of these studies, 1 study compared ECV plus anaesthesia to ECV plus other dosages of the same anaesthetic ( Chalifoux 2017 ); 4 studies compared ECV plus anaesthesia to ECV only ( Dugoff 1999 , Mancuso 2000 , Schorr 1997 , Weiniger 2010 ); and 2 studies compared ECV plus anaesthesia to ECV plus a different anaesthetic ( Khaw 2015 , Sullivan 2009 ).
Ten studies reported ECV plus a β2 receptor agonist ( Brocks 1984 , Fernandez 1997 , Hindawi 2005 , Impey 2005 , Mahomed 1991 , Marquette 1996 , Nor Azlin 2005 , Robertson 1987 , Van Dorsten 1981 , Vani 2009 ). Of these studies, 5 studies compared ECV plus a β2 receptor agonist to ECV plus placebo ( Fernandez 1997 , Impey 2005 , Marquette 1996 , Nor Azlin 2005 , Vani 2009 ); 1 study compared ECV plus a β2 receptor agonist to ECV alone ( Robertson 1987 ); and 4 studies compared ECV plus a β2 receptor agonist to no intervention ( Brocks 1984 , Hindawi 2005 , Mahomed 1991 , Van Dorsten 1981 ).
One study reported on ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker versus ECV plus placebo ( Kok 2008 ). Two studies reported on ECV plus β2 receptor agonist versus ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker ( Collaris 2009 , Mohamed Ismail 2008 ). Four studies reported on ECV plus a µ-receptor agonist ( Burgos 2016 , Liu 2016 , Munoz 2014 , Wang 2017 ), of which 3 compared against ECV plus placebo ( Liu 2016 , Munoz 2014 , Wang 2017 ) and 1 compared to ECV plus nitrous oxide ( Burgos 2016 ).
Four studies reported on ECV plus nitroglycerin ( Bujold 2003a , Bujold 2003b , El-Sayed 2004 , Hilton 2009 ), of which 2 compared it to ECV plus β2 receptor agonist ( Bujold 2003b , El-Sayed 2004 ) and compared it to ECV plus placebo ( Bujold 2003a , Hilton 2009 ). One study compared ECV plus amnioinfusion versus ECV alone ( Diguisto 2018 ) and 1 study compared ECV plus talcum powder to ECV plus gel ( Vallikkannu 2014 ).
One study was conducted in Australia ( Smith 1999 ); 4 studies in Canada ( Bujold 2003a , Bujold 2003b , Hilton 2009 , Marquette 1996 ); 2 studies in China ( Liu 2016 , Wang 2017 ); 2 studies in Denmark ( Andersen 2013 , Brocks 1984 ); 1 study in France ( Diguisto 2018 ); 1 study in Hong Kong ( Khaw 2015 ); 1 study in India ( Rita 2011 ); 1 study in Israel ( Weiniger 2010 ); 1 study in Jordan ( Hindawi 2005 ); 5 studies in Malaysia ( Collaris 2009 , Mohamed Ismail 2008 , Nor Azlin 2005 , Vallikkannu 2014 , Vani 2009 ); 1 study in South Africa ( Hofmeyr 1983 ); 2 studies in Spain ( Burgos 2016 , Munoz 2014 ); 1 study in Sudan ( Dafallah 2004 ); 1 study in The Netherlands ( Kok 2008 ); 2 studies in the UK ( Impey 2005 , Chenia 1987 ); 9 studies in US ( Chalifoux 2017 , Dugoff 1999 , El-Sayed 2004 , Fernandez 1997 , Mancuso 2000 , Robertson 1987 , Schorr 1997 , Sullivan 2009 , Van Dorsten 1981 ); and 1 study in Zimbabwe ( Mahomed 1991 ).
The majority of studies were 2-arm trials, but there was one 3-arm trial ( Khaw 2015 ) and two 4-arm trials ( Andersen 2013 , Chalifoux 2017 ). All studies were conducted in a hospital or an outpatient ward connected to a hospital.
See the literature search strategy in appendix B and study selection flow chart in appendix C .
Excluded studies
Studies not included in this review with reasons for their exclusions are provided in appendix K .
Summary of clinical studies included in the evidence review
Summaries of the studies that were included in this review are presented in Table 2 .
Summary of included studies.
See the full evidence tables in appendix D and the forest plots in appendix E .
Quality assessment of clinical outcomes included in the evidence review
See the evidence profiles in appendix F .
Economic evidence
A systematic review of the economic literature was conducted but no economic studies were identified which were applicable to this review question.
A single economic search was undertaken for all topics included in the scope of this guideline. See supplementary material 2 for details.
Economic studies not included in this review are listed, and reasons for their exclusion are provided in appendix K .
Summary of studies included in the economic evidence review
No economic studies were identified which were applicable to this review question.
Economic model
No economic modelling was undertaken for this review because the committee agreed that other topics were higher priorities for economic evaluation.
Evidence statements
Clinical evidence statements, comparison 1. complementary therapy versus control (no intervention), critical outcomes, cephalic presentation in labour.
No evidence was identified to inform this outcome.
Method of birth
Caesarean section.
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and control (no intervention) on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.74 (95% CI 0.38 to 1.43).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=200) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and control (no intervention) on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.29 (95% CI 0.73 to 2.29).
Admission to SCBU/NICU
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and control (no intervention) on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.19 (95% CI 0.02 to 1.62).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=200) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and control (no intervention) on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.40 (0.08 to 2.01).
Fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation
Infant death up to 4 weeks chronological age, important outcomes, apgar score <7 at 5 minutes.
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and control (no intervention) on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.32 (95% CI 0.01 to 7.78).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=200) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and control (no intervention) on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.33 (0.01 to 8.09).
Birth before 39 +0 weeks of gestation
Comparison 2. complementary therapy versus other treatment.
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=207) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and membrane sweeping on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.64 (95% CI 0.34 to 1.22).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and acupuncture plus membrane sweeping on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.57 (95% CI 0.30 to 1.07).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=203) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and membrane sweeping on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.13 (95% CI 0.66 to 1.94).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=207) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and membrane sweeping on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.33 (95% CI 0.03 to 3.12).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and acupuncture plus membrane sweeping on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.48 (95% CI 0.04 to 5.22).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=203) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and membrane sweeping on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.69 (95% CI 0.12 to 4.02).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=207) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and membrane sweeping on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.02 to 0.02).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=204) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture and acupuncture plus membrane sweeping on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.02 to 0.02).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=203) showed that there is no clinically important difference between acupuncture plus membrane sweeping and membrane sweeping on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.02 to 0.02).
Comparison 3. ECV versus no ECV
- Moderate quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=680) showed that there is clinically important difference favouring ECV over no ECV on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.83 (95% CI 1.53 to 2.18).
Cephalic vaginal birth
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=740) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV over no ECV on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.67 (95% CI 1.20 to 2.31).
Breech vaginal birth
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=680) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV and no ECV on breech vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.29 (95% CI 0.03 to 2.84).
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=740) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV and no ECV on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.52 (95% CI 0.23 to 1.20).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=60) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV and no ECV on admission to SCBU//NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.50 (95% CI 0.14 to 1.82).
- Very low evidence from 3 RCTs (N=740) showed that there is no statistically significant difference between ECV and no ECV on fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.29 (95% CI 0.05 to 1.73) p=0.18.
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV and no ECV on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.28 (95% CI 0.04 to 1.70).
Comparison 4. ECV + Amnioinfusion versus ECV only
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=109) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus amnioinfusion and ECV alone on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.74 (95% CI 0.74 to 4.12).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=109) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus amnioinfusion and ECV alone on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.95 (95% CI 0.75 to 1.19).
Comparison 5. ECV + Anaesthesia versus ECV only
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=210) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus anaesthesia and ECV alone on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.16 (95% CI 0.56 to 2.41).
- Very low quality evidence from 5 RCTs (N=435) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus anaesthesia and ECV alone on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.16 (95% CI 0.77 to 1.74).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=108) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus anaesthesia and ECV alone on breech vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.33 (95% CI 0.04 to 3.10).
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=263) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus anaesthesia and ECV alone on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.76 (95% CI 0.42 to 1.38).
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=69) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus anaesthesia over ECV alone on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: MD −1.80 (95% CI −2.53 to −1.07).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=126) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus anaesthesia and ECV alone on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.03).
Comparison 6. ECV + Anaesthesia versus ECV + Anaesthesia
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.13 (95% CI 0.73 to 1.74).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.81 (95% CI 0.53 to 1.23).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.96 (95% CI 0.61 to 1.50).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=95) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 0.05mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.69 (95% CI 0.37 to 1.28).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.81 (95% CI 0.53 to 1.23).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.96 (95% CI 0.61 to 1.50).
- Very low evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.19 (95% CI 0.79 to 1.79).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.92 (95% CI 0.68 to 1.24).
- Very low evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.08 (95% CI 0.78 to 1.50).
- Very low evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 2.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.94 (95% CI 0.70 to 1.28).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.17 (95% CI 0.86 to 1.61).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=120) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.03 (95% CI 0.77 to 1.37).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=119) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus 7.5mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl and ECV plus 10mg Bupivacaine plus 0.015mg Fentanyl on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.88 (95% CI 0.64 to 1.20).
Comparison 7. ECV + β2 agonist versus Control (no intervention)
- Moderate quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=256) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus β2 agonist over control (no intervention) on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 4.83 (95% CI 3.27 to 7.11).
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=265) showed that there no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and control (no intervention) on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 2.03 (95% CI 0.22 to 19.01).
- Very low quality evidence from 4 RCTs (N=513) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus β2 agonist over control (no intervention) on breech vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.38 (95% CI 0.20 to 0.69).
- Low quality evidence from 4 RCTs (N=513) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus β2 agonist over control (no intervention) on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.53 (95% CI 0.41 to 0.67).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=48) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and control (no intervention) on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.08 to 0.08).
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=208) showed that there is no statistically significant difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and control (no intervention) on fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD −0.01 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.01) p=0.66.
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=208) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and control (no intervention) on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.80 (95% CI 0.31 to 2.10).
Comparison 8. ECV + β2 agonist versus ECV only
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=172) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV only on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.32 (95% CI 0.67 to 2.62).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=58) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV only on breech vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.75 (95% CI 0.22 to 2.50).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=172) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV only on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.79 (95% CI 0.27 to 2.28).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=114) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV only on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.00 (95% CI 0.21 to 4.75).
Comparison 9. ECV + β2 agonist versus ECV + Placebo
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=146) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.54 (95% CI 0.24 to 9.76).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=125) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.27 (95% CI 0.41 to 3.89).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=227) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on breech vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.00 (95% CI 0.33 to 2.97).
- Low quality evidence from 4 RCTs (N=532) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.81 (95% CI 0.72 to 0.92)
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=146) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.78 (95% CI 0.17 to 3.63).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=124) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus placebo on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.03).
Comparison 10. ECV + Ca 2+ channel blocker versus ECV + Placebo
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.13 (95% CI 0.87 to 1.48).
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.90 (95% CI 0.73 to 1.12).
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.11 (95% CI 0.88 to 1.40).
- High quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: MD −0.20 (95% CI −0.70 to 0.30).
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no statistically significant difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.01 to 0.01) p=1.00.
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=310) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus placebo on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.52 (95% 0.05 to 5.02).
Comparison 11. ECV + Ca2+ channel blocker versus ECV + β2 agonist
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=90) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus β2 agonist over ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.62 (95% CI 0.39 to 0.98).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=126) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus β2 agonist on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.26 (95% CI 0.55 to 2.89).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=132) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus β2 agonist over ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.42 (95% CI 1.06 to 1.91).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=176) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus β2 agonist on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.53 (95% CI 0.05 to 5.22).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=176) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus Ca 2+ channel blocker and ECV plus β2 agonist on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.03).
Comparison 12. ECV + µ-receptor agonist versus ECV only
- High quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=80) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV alone on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.00 (95% CI 0.80 to 1.24).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=80) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV alone on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.00 (95% CI 0.42 to 2.40).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=126) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV alone on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.03).
Comparison 13. ECV + µ-receptor agonist versus ECV + Placebo
Cephalic vaginal birth after successful ecv.
- High quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=98) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus placebo on cephalic vaginal birth after successful ECV in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.00 (95% CI 0.86 to 1.17).
Caesarean section after successful ECV
- Low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=98) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus placebo on caesarean section after successful ECV in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.97 (95% CI 0.33 to 2.84).
Breech vaginal birth after unsuccessful ECV
- High quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=186) showed that there is a clinically important difference favouring ECV plus µ-receptor agonist over ECV plus placebo on breech vaginal birth after unsuccessful ECV in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.10 (95% CI 0.02 to 0.53).
Caesarean section after unsuccessful ECV
- Moderate quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=186) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus placebo on caesarean section after unsuccessful ECV in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.19 (95% CI 1.09 to 1.31).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=137) showed that there is no statistically significant difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus placebo on fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.03 to 0.03) p=1.00.

Comparison 14. ECV + µ-receptor agonist versus ECV + Anaesthesia
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=92) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus anaesthesia on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.04 (95% CI 0.84 to 1.29).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=212) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus anaesthesia on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.90 (95% CI 0.61 to 1.34).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=129) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus anaesthesia on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 2.30 (95% CI 0.21 to 24.74).
- Low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=255) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus µ-receptor agonist and ECV plus anaesthesia on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RD 0.00 (95% CI −0.02 to 0.02).
Comparison 15. ECV + Nitric oxide donor versus ECV + Placebo
- Very low quality evidence from 3 RCTs (N=224) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus nitric oxide donor and ECV plus placebo on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.13 (95% CI 0.59 to 2.16).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=99) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus nitric oxide donor and ECV plus placebo on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.78 (95% CI 0.49 to 1.22).
- Low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=125) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus nitric oxide donor and ECV plus placebo on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.83 (95% CI 0.68 to 1.01).
Comparison 16. ECV + Nitric oxide donor versus ECV + β2 agonist
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=74) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus β2 agonist and ECV plus nitric oxide donor on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.56 (95% CI 0.29 to 1.09).
- Very low quality evidence from 2 RCTs (N=97) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus nitric oxide donor and ECV plus β2 agonist on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.98 (95% CI 0.47 to 2.05).
- Very low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=59) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus nitric oxide donor and ECV plus β2 agonist on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.07 (95% CI 0.73 to 1.57).
Comparison 17. ECV + Talcum powder versus ECV + Gel
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=95) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus talcum powder and ECV plus gel on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.02 (95% CI 0.68 to 1.53).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=95) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus talcum powder and ECV plus gel on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.08 (95% CI 0.67 to 1.74).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=95) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus talcum powder and ECV plus gel on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.94 (95% CI 0.67 to 1.33).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=95) showed that there is no clinically important difference between ECV plus talcum powder and ECV plus gel on admission to SCBU/NICU in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.96 (95% CI 0.38 to 10.19).
Comparison 18. Postural management versus No postural management
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=76) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management and no postural management on cephalic presentation in labour in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.26 (95% CI 0.70 to 2.30).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=76) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management and no postural management on cephalic vaginal birth in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.11 (95% CI 0.59 to 2.07).
Breech vaginal delivery
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=76) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management and no postural management on breech vaginal delivery in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.15 (95% CI 0.67 to 1.99).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=76) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management and no postural management on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.69 (95% CI 0.31 to 1.52).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=76) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management and no postural management on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 0.24 (95% CI 0.03 to 2.03).
Comparison 19. Postural management + ECV versus ECV only
- Moderate quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=100) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management plus ECV and ECV only on the number of caesarean sections in pregnant women with breech presentation: RR 1.05 (95% CI 0.80 to 1.38).
- Low quality evidence from 1 RCT (N=100) showed that there is no clinically important difference between postural management plus ECV and ECV only on Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes in pregnant women with breech presentation: Peto OR 0.13 (95% CI 0.00 to 6.55).
Economic evidence statements
No economic evidence was identified which was applicable to this review question.
The committee’s discussion of the evidence
Interpreting the evidence, the outcomes that matter most.
Provision of antenatal care is important for the health and wellbeing of both mother and baby with the aim of avoiding adverse pregnancy outcomes and enhancing maternal satisfaction and wellbeing. Breech presentation in labour may be associated with adverse outcomes for the fetus, which has contributed to an increased likelihood of caesarean birth. The committee therefore agreed that cephalic presentation in labour and method of birth were critical outcomes for the woman, and admission to SCBU/NICU, fetal death after 36 +0 weeks gestation, and infant death up to 4 weeks chronological age were critical outcomes for the baby. Apgar score <7 at 5 minutes and birth before 39 +0 weeks of gestation were important outcomes for the baby.
The quality of the evidence
The quality of the evidence for interventions for managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (that is breech presentation) in late pregnancy ranged from very low to high, with most of the evidence being of a very low or low quality.
This was predominately due to serious overall risk of bias in some outcomes; imprecision around the effect estimate in some outcomes; indirect population in some outcomes; and the presence of serious heterogeneity in some outcomes, which was unresolved by subgroup analysis. The majority of included studies had a small sample size, which contributed to imprecision around the effect estimate.
No evidence was identified to inform the outcomes of infant death up to 4 weeks chronological age and birth before 39 +0 weeks of gestation.
There was no publication bias identified in the evidence. However, the committee noted the influence pharmacological developers may have in these trials as funders, and took this into account in their decision making.
Benefits and harms
The committee discussed that in the case of breech presentation, a discussion with the woman about the different options and their potential benefits, harms and implications is needed to ensure an informed decision. The committee discussed that some women may prefer a breech vaginal birth or choose an elective caesarean birth, and that her preferences should be supported, in line with shared decision making.
The committee discussed that external cephalic version is standard practice for managing breech presentation in uncomplicated singleton pregnancies at or after 36+0 weeks. The committee discussed that there could be variation in the success rates of ECV based on the experience of the healthcare professional providing the ECV. There was some evidence supporting the use of ECV for managing a breech presentation in late pregnancy. The evidence showed ECV had a clinically important benefit in terms of cephalic presentations in labour and cephalic vaginal deliveries, when compared to no intervention. The committee noted that the evidence suggested that ECV was not harmful to the baby, although the effect estimate was imprecise relating to the relative rarity of the fetal death as an outcome.
Cephalic (head-down) vaginal birth is preferred by many women and the evidence suggests that external cephalic version is an effective way to achieve this. The evidence suggested ECV increased the chance for a cephalic vaginal birth and the committee agreed that it was important to explain this to the woman during her consultation.
The committee discussed the optimum timing for ECV. Timing of ECV must take into account the likelihood of the baby turning naturally before a woman commences labour and the possibility of the baby turning back to a breech presentation after ECV if it is done too early. The committee noted that in their experience, current practice was to perform ECV at 37 gestational weeks. The majority of the evidence demonstrating a benefit of ECV in this review involved ECV performed around 37 gestational weeks, although the review did not look for studies directly comparing different timings of ECV and their relative success rates.
The evidence in this review excluded women with previous complicated pregnancies, such as those with previous caesarean section or uterine surgery. The committee discussed that a previous caesarean section indicates a complicated pregnancy and that this population of women are not the focus of this guideline, which concentrates on women with uncomplicated pregnancies.
The committee’s recommendations align with other NICE guidance and cross references to the NICE guideline on caesarean birth and the section on breech presenting in labour in the NICE guideline on intrapartum care for women with existing medical conditions or obstetric complications and their babies were made.
ECV combined with pharmacological agents
There were some small studies comparing a variety of pharmacological agents (including β2 agonists, Ca 2+ channel blockers, µ-receptor agonists and nitric oxide donors) given alongside ECV. Overall the evidence typically showed no clinically important benefit of adding any pharmacological agent to ECV except in comparisons with a control arm with no ECV where it was not possible to isolate the effect of the ECV versus the pharmacological agent. The evidence tended toward benefit most for β2 agonists and µ-receptor agonists however there was no consistent or high quality evidence of benefit even for these agents. The committee agreed that although these pharmacological agents are used in practice, there was insufficient evidence to make a recommendation supporting or refuting their use or on which pharmacological agent should be used.
The committee discussed that the evidence suggesting µ-receptor agonist, remifentanil, had a clinically important benefit in terms reducing breech vaginal births after unsuccessful ECV was biologically implausible. The committee noted that this pharmacological agent has strong sedative effects, depending on the dosage, and therefore studies comparing it to a placebo had possible design flaws as it would be obvious to all parties whether placebo or active drug had been received. The committee discussed that the risks associated with using remifentanil such as respiratory depression, likely outweigh any potential added benefit it may have on managing breech presentation.
There was some evidence comparing different anaesthetics together with ECV. Although there was little consistent evidence of benefit overall, one small study of low quality showed a combination of 2% lidocaine and epinephrine via epidural catheter (anaesthesia) with ECV showed a clinically important benefit in terms of cephalic presentations in labour and the method of birth. The committee discussed the evidence and agreed the use of anaesthesia via epidural catheter during ECV was uncommon practice in the UK and could be expensive, overall they agreed the strength of the evidence available was insufficient to support a change in practice.
Postural management
There was limited evidence on postural management as an intervention for managing breech presentation in late pregnancy, which showed no difference in effectiveness. Postural management was defined as ‘knee-chest position for 15 minutes, 3 times a day’. The committee agreed that in their experience women valued trying interventions at home first which might make postural management an attractive option for some women, however, there was no evidence that postural management was beneficial. The committee also noted that in their experience postural management can cause notable discomfort so it is not an intervention without disadvantages.
Cost effectiveness and resource use
A systematic review of the economic literature was conducted but no relevant studies were identified which were applicable to this review question.
The committee’s recommendations to offer external cephalic version reinforces current practice. The committee noted that, compared to no intervention, external cephalic version results in clinically important benefits and that there would also be overall downstream cost savings from lower adverse events. It was therefore the committee’s view that offering external cephalic version is cost effective and would not entail any resource impact.
Andersen 2013
Brocks 1984
Bujold 2003
Burgos 2016
Chalifoux 2017
Chenia 1987
Collaris 2009
Dafallah 2004
Diguisto 2018
Dugoff 1999
El-Sayed 2004
Fernandez 1997
Hindawi 2005
Hilton 2009
Hofmeyr 1983
Mahomed 1991
Mancuso 2000
Marquette 1996
Mohamed Ismail 2008
NorAzlin 2005
Robertson 1987
Schorr 1997
Sullivan 2009
VanDorsten 1981
Vallikkannu 2014
Weiniger 2010
Appendix A. Review protocols
Review protocol for review question: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 260K)
Appendix B. Literature search strategies
Literature search strategies for review question: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 281K)
Appendix C. Clinical evidence study selection
Clinical study selection for: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 113K)
Appendix D. Clinical evidence tables
Clinical evidence tables for review question: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 1.2M)
Appendix E. Forest plots
Forest plots for review question: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 678K)
Appendix F. GRADE tables
GRADE tables for review question: What is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy? (PDF, 1.0M)
Appendix G. Economic evidence study selection
Economic evidence study selection for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy, appendix h. economic evidence tables, economic evidence tables for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy, appendix i. economic evidence profiles, economic evidence profiles for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy, appendix j. economic analysis, economic evidence analysis for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy.
No economic analysis was conducted for this review question.
Appendix K. Excluded studies
Excluded clinical and economic studies for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy, clinical studies, table 24 excluded studies.
View in own window
Economic studies
No economic evidence was identified for this review.
Appendix L. Research recommendations
Research recommendations for review question: what is the most effective way of managing a longitudinal lie fetal malpresentation (breech presentation) in late pregnancy.
No research recommendations were made for this review question.
Evidence reviews underpinning recommendation 1.2.38
These evidence reviews were developed by the National Guideline Alliance, which is a part of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
Disclaimer : The recommendations in this guideline represent the view of NICE, arrived at after careful consideration of the evidence available. When exercising their judgement, professionals are expected to take this guideline fully into account, alongside the individual needs, preferences and values of their patients or service users. The recommendations in this guideline are not mandatory and the guideline does not override the responsibility of healthcare professionals to make decisions appropriate to the circumstances of the individual patient, in consultation with the patient and/or their carer or guardian.
Local commissioners and/or providers have a responsibility to enable the guideline to be applied when individual health professionals and their patients or service users wish to use it. They should do so in the context of local and national priorities for funding and developing services, and in light of their duties to have due regard to the need to eliminate unlawful discrimination, to advance equality of opportunity and to reduce health inequalities. Nothing in this guideline should be interpreted in a way that would be inconsistent with compliance with those duties.
NICE guidelines cover health and care in England. Decisions on how they apply in other UK countries are made by ministers in the Welsh Government , Scottish Government , and Northern Ireland Executive . All NICE guidance is subject to regular review and may be updated or withdrawn.
- Cite this Page National Guideline Alliance (UK). Management of breech presentation: Antenatal care: Evidence review M. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE); 2021 Aug. (NICE Guideline, No. 201.)
- PDF version of this title (2.2M)
In this Page
Other titles in this collection.
- NICE Evidence Reviews Collection
Related NICE guidance and evidence
- NICE Guideline 201: Antenatal care
Supplemental NICE documents
- Supplement 1: Methods (PDF)
- Supplement 2: Health economics (PDF)
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Review Identification of breech presentation: Antenatal care: Evidence review L [ 2021] Review Identification of breech presentation: Antenatal care: Evidence review L National Guideline Alliance (UK). 2021 Aug
- Vaginal delivery of breech presentation. [J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2009] Vaginal delivery of breech presentation. Kotaska A, Menticoglou S, Gagnon R, MATERNAL FETAL MEDICINE COMMITTEE. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2009 Jun; 31(6):557-566.
- Review Cephalic version by moxibustion for breech presentation. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005] Review Cephalic version by moxibustion for breech presentation. Coyle ME, Smith CA, Peat B. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18; (2):CD003928. Epub 2005 Apr 18.
- [Fetal expulsion: Which interventions for perineal prevention? CNGOF Perineal Prevention and Protection in Obstetrics Guidelines]. [Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2...] [Fetal expulsion: Which interventions for perineal prevention? CNGOF Perineal Prevention and Protection in Obstetrics Guidelines]. Riethmuller D, Ramanah R, Mottet N. Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2018 Dec; 46(12):937-947. Epub 2018 Oct 28.
- Foetal weight, presentaion and the progress of labour. II. Breech and occipito-posterior presentation related to the baby's weight and the length of the first stage of labour. [J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1961] Foetal weight, presentaion and the progress of labour. II. Breech and occipito-posterior presentation related to the baby's weight and the length of the first stage of labour. BAINBRIDGE MN, NIXON WC, SMYTH CN. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1961 Oct; 68:748-54.
Recent Activity
- Management of breech presentation Management of breech presentation
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
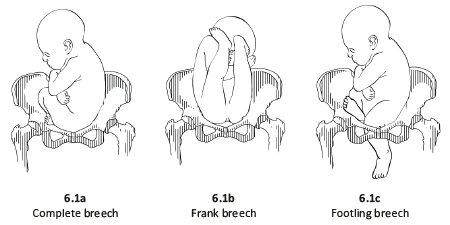
6.1 Breech presentation
Presentation of the feet or buttocks of the foetus.
6.1.1 The different breech presentations
- In a complete breech presentation, the legs are tucked, and the foetus is in a crouching position (Figure 6.1a).
- In a frank breech presentation, the legs are extended, raised in front of the torso, with the feet near the head (Figure 6.1b).
- In a footling breech presentation (rare), one or both feet present first, with the buttocks higher up and the lower limbs extended or half-bent (Figure 6.1c).
6.1.2 Diagnosis
- The cephalic pole is palpable in the uterine fundus; round, hard, and mobile; the indentation of the neck can be felt.
- The inferior pole is voluminous, irregular, less hard, and less mobile than the head.
- During labour, vaginal examination reveals a “soft mass” divided by the cleft between the buttocks, with a hard projection at end of the cleft (the coccyx and sacrum).
- After rupture of the membranes: the anus can be felt in the middle of the cleft; a foot may also be felt.
- The clinical diagnosis may be difficult: a hand may be mistaken for a foot, a face for a breech.
6.1.3 Management
Route of delivery.
Before labour, external version (Chapter 7, Section 7.7 ) may be attempted to avoid breech delivery.
If external version is contra-indicated or unsuccessful, the breech position alone – in the absence of any other anomaly – is not, strictly speaking, a dystocic presentation, and does not automatically require a caesarean section. Deliver vaginally, if possible – even if the woman is primiparous.
Breech deliveries must be done in a CEmONC facility, especially for primiparous women.
Favourable factors for vaginal delivery are:
- Frank breech presentation;
- A history of vaginal delivery (whatever the presentation);
- Normally progressing dilation during labour.
The footling breech presentation is a very unfavourable position for vaginal delivery (risk of foot or cord prolapse). In this situation, the route of delivery depends on the number of previous births, the state of the membranes and how far advanced the labour is.
During labour
- Monitor dilation every 2 to 4 hours.
- If contractions are of good quality, dilation is progressing, and the foetal heart rate is regular, an expectant approach is best. Do not rupture the membranes unless dilation stops.
- If the uterine contractions are inadequate, labour can be actively managed with oxytocin.
Note : if the dilation stales, transfer the mother to a CEmONC facility unless already done, to ensure access to surgical facility for potential caesarean section.
At delivery
- Insert an IV line before expulsion starts.
- Consider episiotomy at expulsion. Episiotomy is performed when the perineum is sufficiently distended by the foetus's buttocks.
- Presence of meconium or meconium-stained amniotic fluid is common during breech delivery and is not necessarily a sign of foetal distress.
- The infant delivers unaided , as a result of the mother's pushing, simply supported by the birth attendant who gently holds the infant by the bony parts (hips and sacrum), with no traction. Do not pull on the legs.
Once the umbilicus is out, the rest of the delivery must be completed within 3 minutes, otherwise compression of the cord will deprive the infant of oxygen. Do not touch the infant until the shoulder blades appear to avoid triggering the respiratory reflex before the head is delivered.
- Monitor the position of the infant's back; impede rotation into posterior position.
Figures 6.2 - Breech delivery
6.1.4 Breech delivery problems
Posterior orientation.
If the infant’s back is posterior during expulsion, take hold of the hips and turn into an anterior position (this is a rare occurrence).
Obstructed shoulders
The shoulders can become stuck and hold back the infant's upper chest and head. This can occur when the arms are raised as the shoulders pass through the mother's pelvis. There are 2 methods for lowering the arms so that the shoulders can descend:
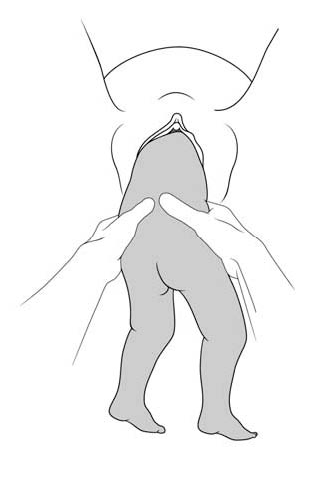
1 - Lovset's manoeuvre
- With thumbs on the infant's sacrum, take hold of the hips and pelvis with the other fingers.
- Turn the infant 90° (back to the left or to the right), to bring the anterior shoulder underneath the symphysis and engage the arm. Deliver the anterior arm.
- Then do a 180° counter-rotation (back to the right or to the left); this engages the posterior arm, which is then delivered.
Figures 6.3 - Lovset's manoeuvre
6.3c - Delivering the anterior arm and shoulder
2 - Suzor’s manoeuvre
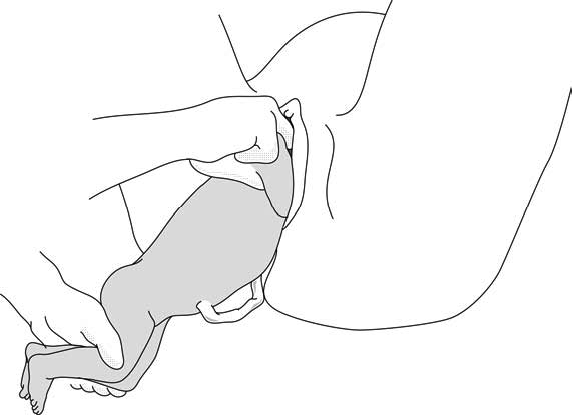
In case the previous method fails:
- Turn the infant 90° (its back to the right or to the left).
- Pull the infant downward: insert one hand along the back to look for the anterior arm. With the operator thumb in the infant armpit and middle finger along the arm, bring down the arm (Figure 6.4a).
- Lift infant upward by the feet in order to deliver the posterior shoulder (Figure 6.4b).
Figures 6.4 - Suzor's manoeuvre
6.4b - Delivering the posterior shoulder
Head entrapment
The infant's head is bulkier than the body, and can get trapped in the mother's pelvis or soft tissue.
There are various manoeuvres for delivering the head by flexing it, so that it descends properly, and then pivoting it up and around the mother's symphysis. These manoeuvres must be done without delay, since the infant must be allowed to breathe as soon as possible. All these manoeuvres must be performed smoothly, without traction on the infant.
1 - Bracht's manoeuvre
- After the arms are delivered, the infant is grasped by the hips and lifted with two hands toward the mother's stomach, without any traction, the neck pivoting around the symphysis.
- Having an assistant apply suprapubic pressure facilitates delivery of the aftercoming head.
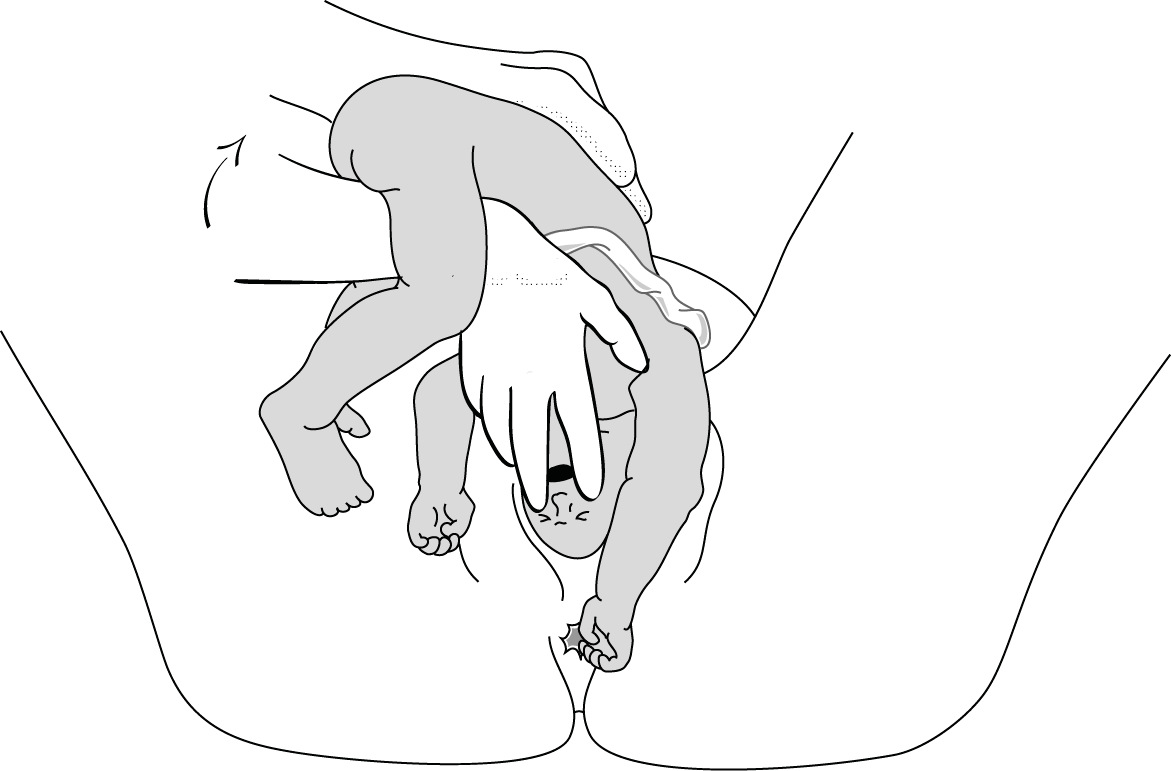
2 - Modified Mauriceau manoeuvre
- Infant's head occiput anterior.
- Kneel to get a good traction angle: 45° downward.
- Support the infant on the hand and forearm, then insert the index and middle fingers, placing them on the infant’s maxilla. Placing the index and middle fingers into the infant’s mouth is not recommended, as this can fracture the mandible.
- Place the index and middle fingers of the other hand on either side of the infant's neck and lower the infant's head to bring the sub-occiput under the symphysis (Figure 6.6a).
- Tip the infant’s head and with a sweeping motion bring the back up toward the mother's abdomen, pivoting the occiput around her symphysis pubis (Figure 6.6b).
- Suprapubic pressure on the infant's head along the pelvic axis helps delivery of the head.
- As a last resort, symphysiotomy (Chapter 5, Section 5.7 ) can be combined with this manoeuvre.
Figures 6.6 - Modified Mauriceau manoeuvre
6.6a - Step 1 Infant straddles the birth attendant's forearm; the head, occiput anterior, is lowered to bring the occiput in contact with the symphysis.
6.6b - Step 2 The infant's back is tipped up toward the mother's abdomen.
3 - Forceps on aftercoming head
This procedure can only be performed by an operator experienced in using forceps.
- Case report
- Open access
- Published: 26 April 2024
An unusual case of severe asphyxia with the fetal position unexpectedly inverted in a malformed uterus: a case report
- Jiro Abe ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3977-2679 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Takashi Nasu 1 ,
- Ayumu Noro 1 &
- Junko Tsubaki 1
Journal of Medical Case Reports volume 18 , Article number: 209 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
53 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
We present a severe neonatal consequence due to the unexpected and crucial inversion of the fetal position after sudden termination of tocolysis during early labor of a woman with congenital uterine anomaly. It has been reported that congenital uterine anomalies latently affect the fetal position. The clinical pitfalls in childbirth with uterine anomalies are discussed here on the basis of clinical evidence.
Case presentation
At a perinatal medical center in Japan, a 29-year-old Japanese mother who had a history of bicornuate uterus, received tocolysis to prolong her pregnancy for 5 days during the late preterm period after preterm-premature rupture of the membrane. She gave birth to a 2304 g male neonate of the gestational age of 35 weeks and 5 days with severe asphyxia by means of crash cesarean section for fetal sustained bradycardia after sudden termination of tocolysis. We found the fetal position to reverse from cephalic to breech position during early labor. He ended up having severe cerebral palsy after brain cooling against hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy for 3 days. The mechanism of inversion from cephalic to breech position without amnionic fluid remains unclear, although women with a known diagnosis of a uterine anomaly have higher risk of adverse outcomes such as malpresentation.
Conclusions
When considering the clinical course of this case on the basis of the medical reports, we suspected that uterine anomalies and changes in intrauterine pressure could cause fetal malpresentation and adverse neonatal outcomes.
Peer Review reports
Uterine abnormalities may be overlooked in women with successful reproductive outcomes, but one study estimated that, even in women with normal pregnancy outcomes, the incidence of congenital uterine anomalies is approximately 3%. The likelihood of fetal malpresentation at the time of delivery is notably increased by the presence of uterine anomalies [ 1 ]. A case is presented where a mother with bicornuate uterus received tocolytic treatment with β-stimulants after surpassing 35 weeks of gestation. Following the discontinuation of tocolysis associated with the onset of labor, the fetus experienced distress and malpresentation, ultimately resulting in severe cerebral palsy in the child. There are no existing case reports that show a change in fetal presentation during labor with uterine anomalies resulting in fetal asphyxia.
A 29-year-old Japanese mother who had a history of bicornuate uterus gave birth to a 2304 g male neonate of the gestational age of 35 weeks and 5 days with severe asphyxia. She was a primigravida without health issues, and her pregnancy course, including changes in maternal body mass index (BMI) and gestational weight gain, was smooth. She was admitted to our hospital to receive tocolysis treatments using ritodrine hydrochloride because of preterm premature rupture of membrane at 35 weeks’ gestation, receiving antibiotics, no antenatal corticosteroids, and no magnesium sulfate. The ultrasound examinations revealed overall fetal growth, reduced amniotic fluid, and a fetal vertex position. A total of 3 hours before the birth, the administration of the tocolytic agent, by ritodrine hydrochloride using the maximum dose of 200 µg per minute, was terminated to promote vaginal delivery, and she was transferred to a delivery room. Non-reassuring patterns repetitively emerged at 1 hour prior to the birth, which were only confirmed by cardiotocography without an ultrasound examination performed at that time (Fig. 1 A). General fetal resuscitation such as maternal oxygen administration and intravenous infusion of a liter of non-glucose crystalloid without acute tocolysis was used as part of the obstetric management of labor, while preparing for cesarean delivery for fetal distress. Quick pelvic examinations ensured the fetus’s cephalic position while observing the mother in preparation for an emergency cesarean operation, although the fetal position during delivery was not confirmed by ultrasound. Half an hour before the birth, fetal bradycardia was sustained while the pelvic examination indicated that the fetal head was unexpectedly floating (Fig. 1 A). A crash cesarean section was performed, where he was found to be in a breech presentation. We found quite little amniotic fluid without the evidence of meconium-stained amniotic fluid or cord coiling. The pathological findings of the placenta and umbilical cord proved only mild chorioamnionitis without any evidence of delivery injury or anomaly afterward.
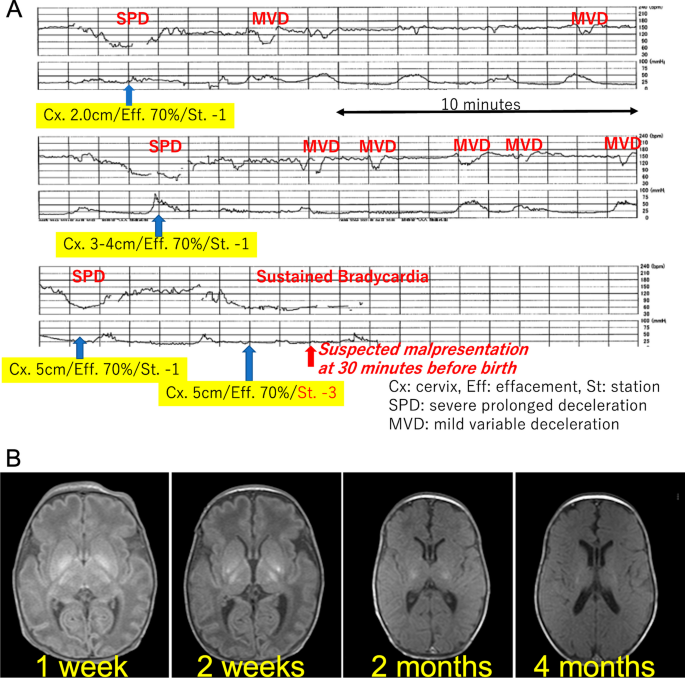
(A) Cardiotocography immediately before birth. Non-reassuring patterns repetitively emerged 1 hour prior to birth. Pelvic examinations revealed a fixed cephalic position. At half an hour, fetal bradycardia was sustained while the pelvic examination indicated that the fetal head was unexpectedly floating. (B) Sequential brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). According to sequential brain MRI findings, his lesions post hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) were mainly located in the basal ganglia and the brain stem
After delivery he presented with bradycardia and deep cyanosis without breathing, muscle movements, and reflections. Because his asphyxia turned out to be refractory to routine resuscitation, he was intubated after 1 minute. His skin color rapidly became pink, and the heart rate returned to a normal range without the recovery of muscle movements and reflex actions. He received an appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration (APGAR) score of 1 at 1 minute and 3 at 5 minutes; the arterial cord blood sample was not available, because of technical difficulty in sampling umbilical cord blood. He needed special care that included mechanical ventilation and correction of mixed acidosis (pH 6.85, pvCO2 77 mmHg, HCO 3 − 12.6 mmol/l at 15 minutes after birth), and then he was given phenobarbital. At 1.5 hours after birth, he was transferred to another tertiary care hospital where he received therapeutic hypothermia for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; the Sarnat grade was moderate, and the Thompson score was calculated as 16 points [ 2 ]. He was a late preterm and low-birth-weight newborn with no congenital anomalies or other problems that would be predictive of neonatal asphyxia through newborn screening especially focusing on the brain, heart, or metabolism. We could not find clinical and pathological evidence of his severe asphyxia in the end. Chromosomal testing was not conducted. He ended up having severe cerebral palsy after brain cooling for 3 days. His sequential brain MRI findings supported the severity of the encephalopathy that mainly affected the basal ganglia and brain stem (Fig. 1 B). He is now 9 months of age and remains in bed with special healthcare requirements that include tube feeding, while presenting with dystonia with severe mental developmental retardation.
Discussion and conclusions
The mother had some delivery risks as follows: a uterine anomaly, absent amniotic fluid after preterm-premature rupture of membrane, and threatened late-preterm labor. The placental blood flow in mothers with congenital uterine anomalies is reduced, and there is a predicted decrease in the reserve capacity for blood supply to the fetus, particularly during delivery. When a mother has congenital uterine anomalies, there is a 5-fold increased risk of preterm birth and a 20-fold increased risk of placental abruption [ 3 ]. This case is believed to be caused by circulatory insufficiency between the mother and fetus, with the influence of congenital uterine anomaly likely playing a background role. Increased intrauterine pressure might have occurred by abrupt termination of tocolysis with the lack of amniotic fluid, which would make the fetal status worse, although there was no evidence of excessively rapid uterine contractions in the tocography (Fig. 1 A).
Uterine anomalies are known to significantly elevate the chances of fetal malpresentation during delivery. According to the meta-analysis by Chan, the likelihood of fetal malpresentation was found to be higher in cases of arcuate uterus, unification defects, and canalization defects, with the odds being 2.53 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.54–4.18; p < 0.001], 3.87 (95% CI 2.42–6.18; p < 0.001), and 6.24 (95% CI 4.05–9.62; p < 0.001) times, respectively [ 4 ]. Furthermore, a retrospective study by Hua and colleagues, which encompassed all types of uterine anomalies (including uterine septum, unicornuate uterus, bicornuate uterus, and uterine didelphys), revealed that women with these anomalies were 8.6 times more likely to experience breech presentation of the fetus compared with women with standard uterine anatomy (95% CI 6.2–12.0; p < 0.01) [ 5 ]. Additionally, a comprehensive retrospective cross-sectional study, examining a total of 109,736 singleton infants (both preterm and full-term), of which 4535 were breech at birth, determined that women with any form of uterine malformation had an almost 10-fold increase in the likelihood of breech fetal presentation (odds ratio, 9.47; 95% CI 6.77–13.25) [ 6 ]. Possible causes are thought to be changes in intrauterine and external pressure, for example, the effects of uterine malformations, the sudden discontinuation of uterine contraction inhibiting drugs, and the transfer from the delivery table to the bed. The unexpected inversion of the fetal position with very little amniotic fluid during early labor would have led to the poor consequence, causing the umbilical cord to twist and consequently leading to the interruption of placental blood flow.
It may have been unavoidable, but we can suggest two preventive plans for this case. One plan would be ongoing expectant management with or without tocolysis. The issue of whether to suppress or allow progressive labor to proceed during the late-preterm period remains controversial [ 7 ]. If waiting for labor while inhibiting uterine contractions, it is necessary to carefully monitor changes in intrauterine pressure when stopping tocolytic agents. The other one would be planned earlier delivery including elective cesarean operation. Bicornuate uterus has been reported to be a risk factor for unsuccessful vaginal delivery [ 8 ]. A major meta-analysis discovered that the likelihood of undergoing a primary cesarean delivery was 2.6 times higher for women with congenital uterine anomalies (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.6; 95% CI 1.7–4.0; p < 0.01) [ 5 ]. Additionally, a retrospective cohort study over a decade at a French university hospital assessed women known to have uterine malformations, focusing on the baby’s presentation and the method of delivery. In this group, women with uterine abnormalities showed a significantly increased incidence of breech presentations (36.51% as opposed to 4.52%; p < 0.01) and cesarean deliveries (55.26% compared with 18.70%; p < 0.01), in contrast to women with normally formed uteri [ 9 ].
Women with congenital uterine anomalies face significantly higher risks of preterm birth, placental abruption, fetal malpresentation, and breech presentation. Several studies highlight the increased odds of complications such as fetal malpresentation and breech births, indicating a need for careful monitoring and possibly alternative delivery plans, including elective cesarean operations. Our report concludes with suggestions for managing such high-risk cases, emphasizing the importance of careful monitoring or possibly opting for an earlier planned delivery to mitigate risks.
Availability of data and materials
The approval from the parent allowed us to use the patient’s data and report this case with data anonymization.
Simón C, Martinez L, Pardo F, et al . Müllerian defects in women with normal reproductive outcome. Fertil Steril. 1991;56:1192–3.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chansarn P, Torgalkar R, Wilson D, Fan CPS, Widjaja E, Whyte H, Tam WYE, Lee KS. Correlation of Thompson and modified Sarnat scores in neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. J Perinatol. 2021;41:1522–3.
Vaz SA, Dotters-Katz SK, Kuller JA. Diagnosis and management of congenital uterine anomalies in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2017;72:194–201.
Chan YY, Jayaprakasan K, Tan A, et al . Reproductive outcomes in women with congenital uterine anomalies: a systematic review. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011;38:371–82.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Hua M, Odibo AO, Longman RE, et al . Congenital uterine anomalies and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011;205:558e1–5.
Article Google Scholar
Cui H, Chen Y, Li Q, et al . Cesarean rate and risk factors for singleton breech presentation in China. J Reprod Med. 2016;61:270–4.
PubMed Google Scholar
Kugelman A, Colin AA. Late preterm infants: near term but still in a critical developmental time period. Pediatrics. 2013;132:741–51.
Mastrolia SA, Baumfeld Y, Hershkovitz R, Loverro G, Naro ED, Yohai D, Schwarzman P, Weintraub AY. Bicornuate uterus is an independent risk factor for cervical OS insufficiency: a retrospective population based cohort study. Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017;30:2705–10.
Guinard E, Subtil D, Deruelle P. Congenital müllerian anomalies and delivery: analysis of 304 cases between 2000 and 2010 at the university hospital of Lille [in French]. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2014;42:471–6.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We appreciate clinical support from Asuka Takahata, Tetsuo Onda, Naho Fuseya.
We all declare no financial support or relationships that may pose a conflict of interest by disclosing any financial arrangements we have with a company whose product figures prominently in the submitted manuscript or with a company making a competing product, or any conflict relating to technology or methodology.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Pediatrics, JCHO Hokkaido Hospital, 3-18, Nakanoshima 1 Jyou 8 Tyoume, Sapporo, Japan
Jiro Abe, Takashi Nasu, Ayumu Noro & Junko Tsubaki
Department of Pediatrics, Graduate School of Medicine, Hokkaido University, Kita-15, Nishi 7, Kita-Ku, Sapporo, 060-8638, Japan
Mitochondrial Redox Biology, Medical Research Council Mitochondrial Biology Unit and Department of Medicine, University of Cambridge, The Keith Peters Building, Cambridge Biomedical Campus Hills Road, Cambridge, CB2 0XY, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Jiro Abe designed and prepared the manuscript; Takashi Nasu, Ayumu Noro, and Junko Tsubaki provided technical support and conceptual advice. All of the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jiro Abe .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
We strictly followed the rules for publication by the research ethics committee in Hokkaido University Hospital, which permitted us to participate.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
We have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Abe, J., Nasu, T., Noro, A. et al. An unusual case of severe asphyxia with the fetal position unexpectedly inverted in a malformed uterus: a case report. J Med Case Reports 18 , 209 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04524-0
Download citation
Received : 01 February 2022
Accepted : 25 March 2024
Published : 26 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04524-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Inverted fetal position
- Neonatal asphyxia
- Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Late preterm
- Uterine anomalies
Journal of Medical Case Reports
ISSN: 1752-1947
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]



IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
INTRODUCTION. Vaginal breech birth is associated with increased neonatal morbidity and mortality compared with vaginal birth of a cephalic presentation. External cephalic version of a breech fetus is an effective approach to increasing the number of patients who present in labor with cephalic presentation and is the approach that we recommend.
Rotate the body in either direction to make one shoulder anterior. Deliver the anterior arm by sweeping it across the chest. Rotate the infant 180 degrees in either direction. Deliver the arm that is now anterior the same way the other arm was delivered. Move the towel up to cover the arms and rotate the body to make the back anterior.
Overview. Breech presentation is defined as a fetus in a longitudinal lie with the buttocks or feet closest to the cervix. This occurs in 3-4% of all deliveries. The percentage of breech deliveries decreases with advancing gestational age from 22-25% of births prior to 28 weeks' gestation to 7-15% of births at 32 weeks' gestation to 3-4% of ...
Breech Births. In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby's buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3-4% of full-term births.
A breech baby, or breech birth, is when your baby's feet or buttocks are positioned to come out of your vagina first. Your baby's head is up closest to your chest and its bottom is closest to your vagina. Most babies will naturally move so their head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. Breech is common in early ...
Labour with a preterm breech should be managed as with a term breech. C. Where there is head entrapment, incisions in the cervix (vaginal birth) or vertical uterine D incision extension (caesarean section) may be used, with or without tocolysis. Evidence concerning the management of preterm labour with a breech presentation is lacking.
This guideline provides up-to-date information on methods of delivery for women with breech presentation. The aim of this guideline is to aid decision making regarding the route of delivery and choice of various techniques used during delivery. ... Breech presentation occurs in 3-4% of term deliveries and is more common in preterm deliveries ...
Breech delivery is the single most common abnormal presentation. The incidence is highly dependent on the gestational age. At 20 weeks, about one in four pregnancies are breech presentation. By full term, the incidence is about 4%. Other contributing factors include: Abnormal shape of the pelvis, uterus, or abdominal wall,
Each of the clinical guidelines were reviewed in terms of recommended methods for fetal monitoring, maternal birth positions, clinicians, available facilities, pain relief, first and second stage, labour induction or augmentation and management of women who presented with an undiagnosed breech presentation in labour (see Table 4). All but of ...
At full term, around 3%-4% of births are breech. The different types of breech presentations include: Complete: The fetus's knees are bent, and the buttocks are presenting first. Frank: The fetus's legs are stretched upward toward the head, and the buttocks are presenting first. Footling: The fetus's foot is showing first.
The committee therefore agreed that cephalic presentation in labour and method of birth were critical outcomes for the woman, ... Does advice to assume the knee-chest position reduce the incidence of breech presentation at delivery? A randomized clinical trial, Birth (Berkeley, Calif.), 14, 75-78, 1987 [PubMed: 3311064] Collaris 2009.
Breech presentation at time of delivery is associated with increased perinatal mortality and morbidity. Any factor that affects the uterine shape and tone, passenger (fetal size, maturity, structure and number) and passage (both bony pelvis and sot tissues) can predispose to breech presentation. Before allowing vaginal breech delivery it is ...
6.1.1 The different breech presentations. In a complete breech presentation, the legs are tucked, and the foetus is in a crouching position (Figure 6.1a). In a frank breech presentation, the legs are extended, raised in front of the torso, with the feet near the head (Figure 6.1b). In a footling breech presentation (rare), one or both feet ...
The mother may be offered an epidural, as vaginal breech delivery can be very painful. 6. Contraindications for vaginal delivery in a breech presentation include: Footling breech: the baby's head and trunk are more likely to be trapped if the feet pass through the dilated cervix too soon; Macrosomia: usually defined as larger than 3800g
Obstetric management of breech presentation at term is heterogeneous, and whether to recommend caesarean section or vaginal delivery is still a subject of debate. Moreover, studies on the neonatal mortality and morbidity of infants with breech presentation depending on the method of delivery have yielded inconsistent results. A major change in the clinical practice of breech presentation ...
Material and method. Single-center retrospective study of women with trials of vaginal delivery of a singleton fetus in breech presentation at of after 37 weeks of gestation. ... (Table 4), probably because in our center all obstetricians are trained to practice vaginal delivery in case of breech presentation. The non-significant increase in ...
Contemporary vaginal delivery of breech presentation began in the middle of the 20th century with Bracht who published a new method, which was named after him, with minimal interventions for delivering breeches [1]. After that, more and more research had begun in the field of minimal invasive methods in vaginal breech delivery.
Additionally, a comprehensive retrospective cross-sectional study, examining a total of 109,736 singleton infants (both preterm and full-term), of which 4535 were breech at birth, determined that women with any form of uterine malformation had an almost 10-fold increase in the likelihood of breech fetal presentation (odds ratio, 9.47; 95% CI 6. ...
Breech presentation 6 (3.7%) Hypoxic conditions 4 (2.5%) Note: Percentage is calculated using a denominator of 162. Labor and delivery events were not mutually exclusive; therefore, multiple events were coded for a single event report when appropriate. "Other event" includes a small C-section incision, cord
A prominent Soviet scientist in the field of mechanics of solids, Professor Feodos'ev was for over 40 years involved in the publication of the journal Prikladnaya Matematika i Mekhanika. He was a doctor of technical sciences, a professor, an associate member of the USSR Academy of Sciences (1977), an Honored Figure of Science and Technology ...
that delivery is not guaranteed. 2.2 Should Have Important but not vital May be painful to leave out, but the solution is still viable May need some kind of workaround, e.g. management of expectations, some inefficiency, an existing solution, paperwork, etc.
In my previous article, Prioritization Methods and Techniques - Part 1: Why Prioritize and the Kano Model, I talked about the need to prioritize and the Kano model as a prioritization method.In this second article in the series on prioritization methods and techniques, I will discuss the MoSCoW method. The MoSCoW method is a highly widespread prioritization method which was popularized by ...
Welcome to the 628DirtRooster website where you can find video links to Randy McCaffrey's (AKA DirtRooster) YouTube videos, community support and other resources for the Hobby Beekeepers and the official 628DirtRooster online store where you can find 628DirtRooster hats and shirts, local Mississippi honey and whole lot more!