What is a Marketing Plan & How to Write One [+Examples]
Published: December 27, 2023
For a while now, you've been spearheading your organization's content marketing efforts, and your team's performance has convinced management to adopt the content marketing strategies you’ve suggested.

Now, your boss wants you to write and present a content marketing plan, but you‘ve never done something like that before. You don't even know where to start.
![business plan marketing aspects Download Now: Free Marketing Plan Template [Get Your Copy]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/aacfe6c7-71e6-4f49-979f-76099062afa0.png)
Fortunately, we've curated the best content marketing plans to help you write a concrete plan that's rooted in data and produces results. But first, we'll discuss what a marketing plan is and how some of the best marketing plans include strategies that serve their respective businesses.

What is a marketing plan?
A marketing plan is a strategic roadmap that businesses use to organize, execute, and track their marketing strategy over a given period. Marketing plans can include different marketing strategies for various marketing teams across the company, all working toward the same business goals.
The purpose of a marketing plan is to write down strategies in an organized manner. This will help keep you on track and measure the success of your campaigns.
Writing a marketing plan will help you think of each campaign‘s mission, buyer personas, budget, tactics, and deliverables. With all this information in one place, you’ll have an easier time staying on track with a campaign. You'll also discover what works and what doesn't. Thus, measuring the success of your strategy.
Featured Resource: Free Marketing Plan Template

Looking to develop a marketing plan for your business? Click here to download HubSpot's free Marketing Plan Template to get started .
To learn more about how to create your marketing plan, keep reading or jump to the section you’re looking for:
How to Write a Marketing Plan
Types of marketing plans, marketing plan examples, marketing plan faqs, sample marketing plan.

If you're pressed for time or resources, you might not be thinking about a marketing plan. However, a marketing plan is an important part of your business plan.
Marketing Plan vs. Business Plan
A marketing plan is a strategic document that outlines marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics.
A business plan is also a strategic document. But this plan covers all aspects of a company's operations, including finance, operations, and more. It can also help your business decide how to distribute resources and make decisions as your business grows.
I like to think of a marketing plan as a subset of a business plan; it shows how marketing strategies and objectives can support overall business goals.
Keep in mind that there's a difference between a marketing plan and a marketing strategy.

Free Marketing Plan Template
Outline your company's marketing strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
- Pre-Sectioned Template
- Completely Customizable
- Example Prompts
- Professionally Designed
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Marketing Strategy vs. Marketing Plan
A marketing strategy describes how a business will accomplish a particular goal or mission. This includes which campaigns, content, channels, and marketing software they'll use to execute that mission and track its success.
For example, while a greater plan or department might handle social media marketing, you might consider your work on Facebook as an individual marketing strategy.
A marketing plan contains one or more marketing strategies. It's the framework from which all of your marketing strategies are created and helps you connect each strategy back to a larger marketing operation and business goal.
For example, suppose your company is launching a new software product, and it wants customers to sign up. The marketing department needs to develop a marketing plan that'll help introduce this product to the industry and drive the desired signups.
The department decides to launch a blog dedicated to this industry, a new YouTube video series to establish expertise, and an account on Twitter to join the conversation around this subject. All this serves to attract an audience and convert this audience into software users.
To summarize, the business's marketing plan is dedicated to introducing a new software product to the marketplace and driving signups for that product. The business will execute that plan with three marketing strategies : a new industry blog, a YouTube video series, and a Twitter account.
Of course, the business might consider these three things as one giant marketing strategy, each with its specific content strategies. How granular you want your marketing plan to get is up to you. Nonetheless, every marketing plan goes through a particular set of steps in its creation.
Learn what they are below.
- State your business's mission.
- Determine the KPIs for this mission.
- Identify your buyer personas.
- Describe your content initiatives and strategies.
- Clearly define your plan's omissions.
- Define your marketing budget.
- Identify your competition.
- Outline your plan's contributors and their responsibilities.
1. State your business's mission.
Your first step in writing a marketing plan is to state your mission. Although this mission is specific to your marketing department, it should serve your business‘s main mission statement.
From my experience, you want to be specific, but not too specific. You have plenty of space left in this marketing plan to elaborate on how you'll acquire new customers and accomplish this mission.

Need help building your mission statement? Download this guide for examples and templates and write the ideal mission statement.
2. Determine the KPIs for this mission.
Every good marketing plan describes how the department will track its mission‘s progress. To do so, you need to decide on your key performance indicators (KPIs) .
KPIs are individual metrics that measure the various elements of a marketing campaign. These units help you establish short-term goals within your mission and communicate your progress to business leaders.
Let's take our example of a marketing mission from the above step. If part of our mission is “to attract an audience of travelers,” we might track website visits using organic page views. In this case, “organic page views” is one KPI, and we can see our number of page views grow over time.
These KPIs will come into the conversation again in step 4.
3. Identify your buyer personas.
A buyer persona is a description of who you want to attract. This can include age, sex, location, family size, and job title. Each buyer persona should directly reflect your business's current and potential customers. So, all business leaders must agree on your buyer personas.

Create your buyer personas with this free guide and set of buyer persona templates.
4. Describe your content initiatives and strategies.
Here's where you'll include the main points of your marketing and content strategy. Because there's a laundry list of content types and channels available to you today, you must choose wisely and explain how you'll use your content and channels in this section of your marketing plan.
When I write this section , I like to stipulate:
- Which types of content I'll create. These might include blog posts, YouTube videos, infographics, and ebooks.
- How much of it I'll create. I typically describe content volume in daily, weekly, monthly, or even quarterly intervals. It all depends on my workflow and the short-term goals for my content.
- The goals (and KPIs) I'll use to track each type. KPIs can include organic traffic, social media traffic, email traffic, and referral traffic. Your goals should also include which pages you want to drive that traffic to, such as product pages, blog pages, or landing pages.
- The channels on which I'll distribute my content. Popular channels include Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube, Pinterest, and Instagram.
- Any paid advertising that will take place on these channels.
Build out your marketing plan with this free template.
Fill out this form to access the template., 5. clearly define your plan's omissions..
A marketing plan explains the marketing team's focus. It also explains what the marketing team will not focus on.
If there are other aspects of your business that you aren't serving in this particular plan, include them in this section. These omissions help to justify your mission, buyer personas, KPIs, and content. You can’t please everyone in a single marketing campaign, and if your team isn't on the hook for something, you need to make it known.
In my experience, this section is particularly important for stakeholders to help them understand why certain decisions were made.
6. Define your marketing budget.
Whether it's freelance fees, sponsorships, or a new full-time marketing hire, use these costs to develop a marketing budget and outline each expense in this section of your marketing plan.
You can establish your marketing budget with this kit of 8 free marketing budget templates .
7. Identify your competition.
Part of marketing is knowing whom you're marketing against. Research the key players in your industry and consider profiling each one.
Keep in mind not every competitor will pose the same challenges to your business. For example, while one competitor might be ranking highly on search engines for keywords you want your website to rank for, another competitor might have a heavy footprint on a social network where you plan to launch an account.
Easily track and analyze your competitors with t his collection of ten free competitive analysis templates .
8. Outline your plan's contributors and their responsibilities.
With your marketing plan fully fleshed out, it's time to explain who’s doing what. I don't like to delve too deeply into my employees’ day-to-day projects, but I know which teams and team leaders are in charge of specific content types, channels, KPIs, and more.
Now that you know why you need to build an effective marketing plan, it’s time to get to work. Starting a plan from scratch can be overwhelming if you haven't done it before. That’s why there are many helpful resources that can support your first steps. We’ll share some of the best guides and templates that can help you build effective results-driven plans for your marketing strategies.
Ready to make your own marketing plan? Get started using this free template.
Depending on the company you work with, you might want to create various marketing plans. We compiled different samples to suit your needs:
1. Quarterly or Annual Marketing Plans
These plans highlight the strategies or campaigns you'll take on in a certain period.
Forbes published a marketing plan template that has amassed almost 4 million views. To help you sculpt a marketing roadmap with true vision, their template will teach you how to fill out the 15 key sections of a marketing plan, which are:
- Executive Summary
- Target Customers
- Unique Selling Proposition
- Pricing & Positioning Strategy
- Distribution Plan
- Your Offers
- Marketing Materials
- Promotions Strategy
- Online Marketing Strategy
- Conversion Strategy
- Joint Ventures & Partnerships
- Referral Strategy
- Strategy for Increasing Transaction Prices
- Retention Strategy
- Financial Projections
If you're truly lost on where to start with a marketing plan, I highly recommend using this guide to help you define your target audience, figure out how to reach them, and ensure that audience becomes loyal customers.
2. Social Media Marketing Plan
This type of plan highlights the channels, tactics, and campaigns you intend to accomplish specifically on social media. A specific subtype is a paid marketing plan, which highlights paid strategies, such as native advertising, PPC, or paid social media promotions.
Shane Snow's Marketing Plan for His Book Dream Team is a great example of a social media marketing plan:
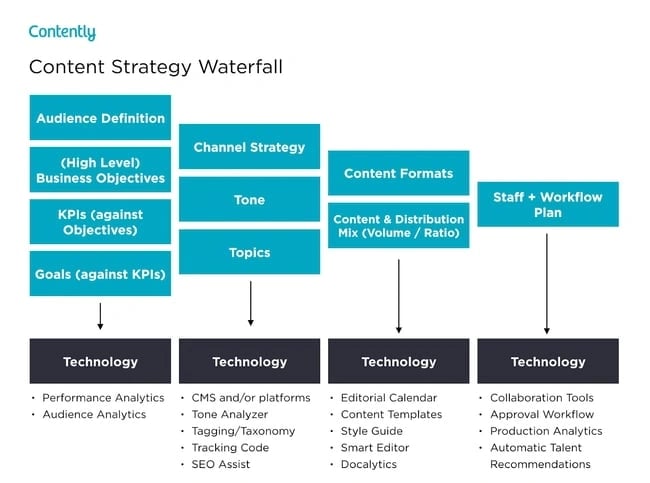
When Shane Snow started promoting his new book, "Dream Team," he knew he had to leverage a data-driven content strategy framework. So, he chose his favorite one: the content strategy waterfall. The content strategy waterfall is defined by Economic Times as a model used to create a system with a linear and sequential approach.
Snow wrote a blog post about how the waterfall‘s content strategy helped him launch his new book successfully. After reading it, you can use his tactics to inform your own marketing plan. More specifically, you’ll learn how he:
- Applied his business objectives to decide which marketing metrics to track.
- Used his ultimate business goal of earning $200,000 in sales or 10,000 purchases to estimate the conversion rate of each stage of his funnel.
- Created buyer personas to figure out which channels his audience would prefer to consume his content.
- Used his average post view on each of his marketing channels to estimate how much content he had to create and how often he had to post on social media.
- Calculated how much earned and paid media could cut down the amount of content he had to create and post.
- Designed his process and workflow, built his team, and assigned members to tasks.
- Analyzed content performance metrics to refine his overall content strategy.
I use Snow's marketing plan to think more creatively about my content promotion and distribution plan. I like that it's linear and builds on the step before it, creating an air-tight strategy that doesn't leave any details out.
![business plan marketing aspects → Free Download: Social Media Calendar Template [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/3e56e15d-47bd-46c9-a256-99fde52abfe7.png)
3. Content Marketing Plan
This plan could highlight different strategies, tactics, and campaigns in which you'll use content to promote your business or product.
HubSpot's Comprehensive Guide for Content Marketing Strategy is a strong example of a content marketing plan:

At HubSpot, we‘ve built our marketing team from two business school graduates working from a coffee table to a powerhouse of hundreds of employees. Along the way, we’ve learned countless lessons that shaped our current content marketing strategy. So, we decided to illustrate our insights in a blog post to teach marketers how to develop a successful content marketing strategy, regardless of their team's size.

In this comprehensive guide for modern marketers, you'll learn:
- What exactly content marketing is.
- Why your business needs a content marketing strategy.
- Who should lead your content marketing efforts?
- How to structure your content marketing team based on your company's size.
- How to hire the right people for each role on your team.
- What marketing tools and technology you'll need to succeed.
- What type of content your team should create, and which employees should be responsible for creating them.
- The importance of distributing your content through search engines, social media, email, and paid ads.
- And finally, the recommended metrics each of your teams should measure and report to optimize your content marketing program.
This is a fantastic resource for content teams of any size — whether you're a team of one or 100. It includes how to hire and structure a content marketing team, what marketing tools you'll need, what type of content you should create, and even recommends what metrics to track for analyzing campaigns. If you're aiming to establish or boost your online presence, leveraging tools like HubSpot's drag-and-drop website builder can be extremely beneficial. It helps you create a captivating digital footprint that sets the foundation for your content marketing endeavors.
4. New Product Launch Marketing Plan
This will be a roadmap for the strategies and tactics you‘ll implement to promote a new product. And if you’re searching for an example, look no further than Chief Outsiders' Go-To-Market Plan for a New Product :

After reading this plan, you'll learn how to:
- Validate a product
- Write strategic objectives
- Identify your market
- Compile a competitive landscape
- Create a value proposition for a new product
- Consider sales and service in your marketing plan
If you're looking for a marketing plan for a new product, the Chief Outsiders template is a great place to start. Marketing plans for a new product will be more specific because they target one product versus its entire marketing strategy.
5. Growth Marketing Plan
Growth marketing plans use experimentation and data to drive results, like we see in Venture Harbour’s Growth Marketing Plan Template :
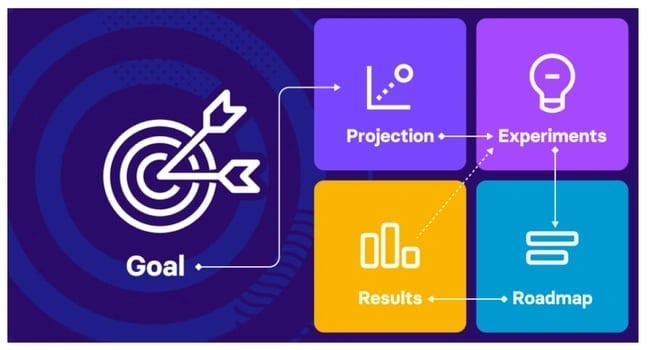
Venture Harbour's growth marketing plan is a data-driven and experiment-led alternative to the more traditional marketing plan. Their template has five steps intended for refinement with every test-measure-learn cycle. The five steps are:
- Experiments

I recommend this plan if you want to experiment with different platforms and campaigns. Experimentation always feels risky and unfamiliar, but this plan creates a framework for accountability and strategy.
- Louisville Tourism
- University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
- Visit Oxnard
- Safe Haven Family Shelter
- Wright County Economic Development
- The Cultural Council of Palm Beach County
- Cabarrus County Convention and Visitors Bureau
- Visit Billings
1. Louisville Tourism

It also divides its target market into growth and seed categories to allow for more focused strategies. For example, the plan recognizes Millennials in Chicago, Atlanta, and Nashville as the core of it's growth market, whereas people in Boston, Austin, and New York represent seed markets where potential growth opportunities exist. Then, the plan outlines objectives and tactics for reaching each market.
Why This Marketing Plan Works
- The plan starts with a letter from the President & CEO of the company, who sets the stage for the plan by providing a high-level preview of the incoming developments for Louisville's tourism industry
- The focus on Louisville as "Bourbon City" effectively leverages its unique cultural and culinary attributes to present a strong brand
- Incorporates a variety of data points from Google Analytics, Arrivalist, and visitor profiles to to define their target audience with a data-informed approach
2. University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign

For example, students who become prospects as freshman and sophomore will receive emails that focus on getting the most out of high school and college prep classes. Once these students become juniors and seniors — thus entering the consideration stage — the emails will focus more on the college application process and other exploratory content.
- The plan incorporates competitive analysis, evaluation surveys, and other research to determine the makeup of its target audience
- The plan lists each marketing program (e.g., direct mail, social media, email etc.) and supplements it with examples on the next page
- Each marketing program has its own objectives, tactics, and KPIs for measuring success
3. Visit Oxnard
This marketing plan by Visit Oxnard, a convention and visitors bureau, is packed with all the information one needs in a marketing plan: target markets, key performance indicators, selling points, personas, marketing tactics by channel, and much more.
It also articulates the organization’s strategic plans for the upcoming fiscal year, especially as it grapples with the aftereffects of the pandemic. Lastly, it has impeccable visual appeal, with color-coded sections and strong branding elements.
- States clear and actionable goals for the coming year
- Includes data and other research that shows how their team made their decisions
- Outlines how the team will measure the success of their plan
4. Safe Haven Family Shelter

This marketing plan by a nonprofit organization is an excellent example to follow if your plan will be presented to internal stakeholders at all levels of your organization. It includes SMART marketing goals , deadlines, action steps, long-term objectives, target audiences, core marketing messages , and metrics.
The plan is detailed, yet scannable. By the end of it, one can walk away with a strong understanding of the organization’s strategic direction for its upcoming marketing efforts.
- Confirms ongoing marketing strategies and objectives while introducing new initiatives
- Uses colors, fonts, and formatting to emphasize key parts of the plan
- Closes with long-term goals, key themes, and other overarching topics to set the stage for the future
5. Wright County Economic Development

Wright County Economic Development’s plan drew our attention because of its simplicity, making it good inspiration for those who’d like to outline their plan in broad strokes without frills or filler.
It includes key information such as marketing partners, goals, initiatives, and costs. The sections are easy to scan and contain plenty of information for those who’d like to dig into the details. Most important, it includes a detailed breakdown of projected costs per marketing initiative — which is critical information to include for upper-level managers and other stakeholders.
- Begins with a quick paragraph stating why the recommended changes are important
- Uses clear graphics and bullet points to emphasize key points
- Includes specific budget data to support decision-making
6. The Cultural Council of Palm Beach County
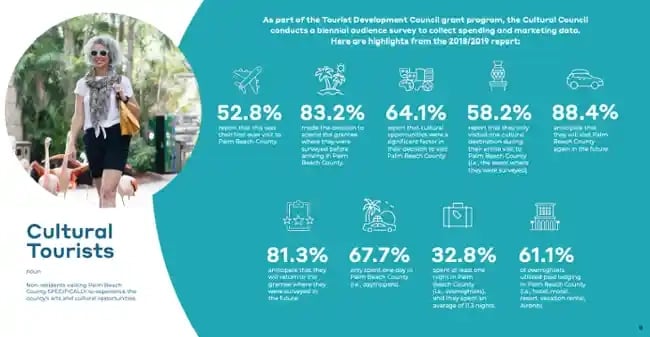
This marketing plan presentation by a cultural council is a great example of how to effectively use data in your plan, address audiences who are new to the industry, and offer extensive detail into specific marketing strategies.
For instance, an entire slide is dedicated to the county’s cultural tourism trends, and at the beginning of the presentation, the organization explains what an arts and culture agency is in the first place.
That’s a critical piece of information to include for those who might not know. If you’re addressing audiences outside your industry, consider defining terms at the beginning, like this organization did.
- Uses quality design and images to support the goals and priorities in the text
- Separate pages for each big idea or new strategy
- Includes sections for awards and accomplishments to show how the marketing plan supports wider business goals
- Defines strategies and tactics for each channel for easy skimming
7. Cabarrus County Convention & Visitors Bureau
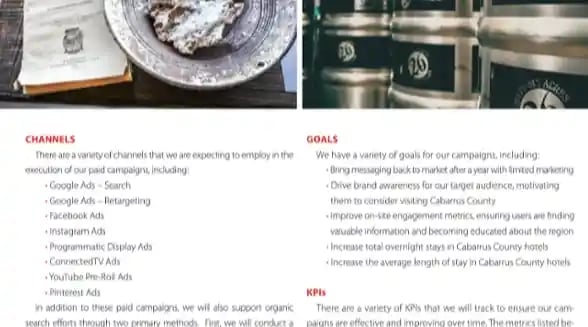
Cabarrus County’s convention and visitors bureau takes a slightly different approach with its marketing plan, formatting it like a magazine for stakeholders to flip through. It offers information on the county’s target audience, channels, goals, KPIs, and public relations strategies and initiatives.
We especially love that the plan includes contact information for the bureau’s staff members, so that it’s easy for stakeholders to contact the appropriate person for a specific query.
- Uses infographics to expand on specific concepts, like how visitors benefit a community
- Highlights the team members responsible for each initiative with a photo to emphasize accountability and community
- Closes with an event calendar for transparency into key dates for events
8. Visit Billings

Visit Billing’s comprehensive marketing plan is like Cabarrus County’s in that it follows a magazine format. With sections for each planned strategy, it offers a wealth of information and depth for internal stakeholders and potential investors.
We especially love its content strategy section, where it details the organization’s prior efforts and current objectives for each content platform.
At the end, it includes strategic goals and budgets — a good move to imitate if your primary audience would not need this information highlighted at the forefront.
- Includes a section on the buyer journey, which offers clarity on the reasoning for marketing plan decisions
- Design includes call-outs for special topics that could impact the marketing audience, such as safety concerns or "staycations"
- Clear headings make it easy to scan this comprehensive report and make note of sections a reader may want to return to for more detail
What is a typical marketing plan?
In my experience, most marketing plans outline the following aspects of a business's marketing:
- Target audience
Each marketing plan should include one or more goals, the path your team will take to meet those goals, and how you plan to measure success.
For example, if I were a tech startup that's launching a new mobile app, my marketing plan would include:
- Target audience or buyer personas for the app
- Outline of how app features meet audience needs
- Competitive analysis
- Goals for conversion funnel and user acquisition
- Marketing strategies and tactics for user acquisition
Featured resource : Free Marketing Plan Template
What should a good marketing plan include?
A good marketing plan will create a clear roadmap for your unique marketing team. This means that the best marketing plan for your business will be distinct to your team and business needs.
That said, most marketing plans will include sections for one or more of the following:
- Clear analysis of the target market
- A detailed description of the product or service
- Strategic marketing mix details (such as product, price, place, promotion)
- Measurable goals with defined timelines
This can help you build the best marketing plan for your business.
A good marketing plan should also include a product or service's unique value proposition, a comprehensive marketing strategy including online and offline channels, and a defined budget.
Featured resource : Value Proposition Templates
What are the most important parts of a marketing plan?
When you‘re planning a road trip, you need a map to help define your route, step-by-step directions, and an estimate of the time it will take to get to your destination. It’s literally how you get there that matters.
Like a road map, a marketing plan is only useful if it helps you get to where you want to go. So, no one part is more than the other.
That said, you can use the list below to make sure that you've added or at least considered each of the following in your marketing plan:
- Marketing goals
- Executive summary
- Target market analysis
- Marketing strategies
What questions should I ask when making a marketing plan?
Questions are a useful tool for when you‘re stuck or want to make sure you’ve included important details.
Try using one or more of these questions as a starting point when you create your marketing plan:
- Who is my target audience?
- What are their needs, motivations, and pain points?
- How does our product or service solve their problems?
- How will I reach and engage them?
- Who are my competitors? Are they direct or indirect competitors?
- What are the unique selling points of my product or service?
- What marketing channels are best for the brand?
- What is our budget and timeline?
- How will I measure the success of marketing efforts?
How much does a marketing plan cost?
Creating a marketing plan is mostly free. But the cost of executing a marketing plan will depend on your specific plan.
Marketing plan costs vary by business, industry, and plan scope. Whether your team handles marketing in-house or hires external consultants can also make a difference. Total costs can range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands. This is why most marketing plans will include a budget.
Featured resource : Free Marketing Budget Templates
What is a marketing plan template?
A marketing plan template is a pre-designed structure or framework that helps you outline your marketing plan.
It offers a starting point that you can customize for your specific business needs and goals. For example, our template includes easy-to-edit sections for:
- Business summary
- Business initiatives
- Target market
- Market strategy
- Marketing channels
- Marketing technology
Let’s create a sample plan together, step by step.
Follow along with HubSpot's free Marketing Plan Template .

1. Create an overview or primary objective.
Our business mission is to provide [service, product, solution] to help [audience] reach their [financial, educational, business related] goals without compromising their [your audience’s valuable asset: free time, mental health, budget, etc.]. We want to improve our social media presence while nurturing our relationships with collaborators and clients.
For example, if I wanted to focus on social media growth, my KPIs might look like this:
We want to achieve a minimum of [followers] with an engagement rate of [X] on [social media platform].
The goal is to achieve an increase of [Y] on recurring clients and new meaningful connections outside the platform by the end of the year.
Use the following categories to create a target audience for your campaign.
- Profession:
- Background:
- Pain points:
- Social media platforms that they use:
- Streaming platforms that they prefer:
For more useful strategies, consider creating a buyer persona in our Make My Persona tool .
Our content pillars will be: [X, Y, Z].
Content pillars should be based on topics your audience needs to know. If your ideal clients are female entrepreneurs, then your content pillars can be: marketing, being a woman in business, remote working, and productivity hacks for entrepreneurs.
Then, determine any omissions.
This marketing plan won’t be focusing on the following areas of improvement: [A, B, C].
5. Define your marketing budget.
Our marketing strategy will use a total of [Y] monthly. This will include anything from freelance collaborations to advertising.
6. Identify your competitors.
I like to work through the following questions to clearly indicate who my competitors are:
- Which platforms do they use the most?
- How does their branding differentiate?
- How do they talk to their audiences?
- What valuable assets do customers talk about? And if they are receiving any negative feedback, what is it about?
7. Outline your plan's contributors and their responsibilities.
Create responsible parties for each portion of the plan.
Marketing will manage the content plan, implementation, and community interaction to reach the KPIs.
- Social media manager: [hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations]
- Content strategist: [hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations]
- Community manager: [hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations]
Sales will follow the line of the marketing work while creating and implementing an outreach strategy.
- Sales strategists: [hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations]
- Sales executives: [hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations]
Customer Service will nurture clients’ relationships to ensure that they have what they want. [Hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations].
Project Managers will track the progress and team communication during the project. [Hours per week dedicated to the project, responsibilities, team communication requirements, expectations].
Get started on your marketing plan.
These marketing plans serve as initial resources to get your content marketing plan started. But, to truly deliver what your audience wants and needs, you'll likely need to test some different ideas out, measure their success, and then refine your goals as you go.
Editor's Note: This post was originally published in April 2019, but was updated for comprehensiveness. This article was written by a human, but our team uses AI in our editorial process. Check out our full disclosure t o learn more about how we use AI.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

9 Pivotal Marketing Trends to Watch in 2024, According to Experts

The Ultimate Guide to Marketing Strategies & How to Improve Your Digital Presence

Diving Deep Into Marketing in Construction (My Takeaways)
![business plan marketing aspects 11 Recommendations for Marketers in 2024 [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Marketing%20Recommendations.png)
11 Recommendations for Marketers in 2024 [New Data]
![business plan marketing aspects The Top 5 B2C Marketing Trends of 2024 [New HubSpot Blog Data + Expert Insights]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/top%20b2c%20marketing%20trends.png)
The Top 5 B2C Marketing Trends of 2024 [New HubSpot Blog Data + Expert Insights]
![business plan marketing aspects 5 Marketing Trends That Might Not Survive in 2024 [HubSpot Research + Expert Insights]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketing%20trends%20that%20might%20not%20survive%202024.png)
5 Marketing Trends That Might Not Survive in 2024 [HubSpot Research + Expert Insights]
Everything You Need to Know About Webinar Marketing

7 Marketing Questions Teams are Asking in 2024 (+Data & Insights)

50 Small Business Marketing Ideas for 2024

How Luxury Brands Market and What You Can Learn
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5th, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Marketing |
- How to create a winning marketing plan, ...
How to create a winning marketing plan, with 3 examples from world-class teams

A marketing plan helps leaders clearly visualize marketing strategies across channels, so they can ensure every campaign drives pipeline and revenue. In this article you’ll learn eight steps to create a winning marketing plan that brings business-critical goals to life, with examples from word-class teams.
To be successful as a marketer, you have to deliver the pipeline and the revenue.”
In other words—they need a well-crafted marketing plan.
Level up your marketing plan to drive revenue in 2024
Learn how to create the right marketing plan to hit your revenue targets in 2024. Hear best practices from marketing experts, including how to confidently set and hit business goals, socialize marketing plans, and move faster with clearer resourcing.

7 steps to build a comprehensive marketing plan
How do you build the right marketing plan to hit your revenue goals? Follow these eight steps for success:
1. Define your plan
First you need to define each specific component of your plan to ensure stakeholders are aligned on goals, deliverables, resources, and more. Ironing out these details early on ensures your plan supports the right business objectives, and that you have sufficient resources and time to get the job done.
Get started by asking yourself the following questions:
What resources do I need?
What is the vision?
What is the value?
What is the goal?
Who is my audience?
What are my channels?
What is the timeline?
For example, imagine you’re creating an annual marketing plan to improve customer adoption and retention in the next fiscal year. Here’s how you could go through the questions above to ensure you’re ready to move forward with your plan:
I will need support from the content team, web team, and email team to create targeted content for existing customers. One person on each team will need to be dedicated full-time to this initiative. To achieve this, the marketing team will need an additional $100K in budget and one new headcount.
What is the vision?
To create a positive experience for existing customers, address new customer needs, and encourage them to upgrade. We’ll do this by serving them how-to content, new feature updates, information about deals and pricing, and troubleshooting guides.
According to the Sales Benchmark Index (SBI) , CEOs and go-to-market leaders report that more than 60% of their net-new revenue will come from existing customers in 2023. By retaining and building on the customers we have, we can maintain revenue growth over time.
To decrease the customer churn rate from 30% to 10%, and increase upgrades from 20% to 30% in the next fiscal year.
All existing customers.
The main channel will be email. Supporting marketing channels include the website, blog, YouTube, and social media.
The first half of the next fiscal year.
One of the most important things to do as you create your marketing strategy is to identify your target audience . As with all marketing, you need to know who you’re marketing to. If you’re having a hard time determining who exactly your target audience is, try the bullseye targeting framework . The bullseye makes it easy for you to determine who your target audience is by industry, geography, company size, psychographics, demographics, and more.
2. Identify key metrics for success
Now it’s time to define what key marketing metrics you’ll use to measure success. Your key metrics will help you measure and track the performance of your marketing activities. They’ll also help you understand how your efforts tie back to larger business goals.
Once you establish key metrics, use a goal-setting framework—like objectives and key results (OKRs) or SMART goals —to fully flush out your marketing objectives. This ensures your targets are as specific as possible, with no ambiguity about what should be accomplished by when.
Example: If a goal of your marketing plan is to increase email subscriptions and you follow the SMART goal framework (ensuring your objective is specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound) your goal might look like this: Increase email subscription rate from 10% to 20% in H1 .
3. Research your competition
It’s easy to get caught up in your company’s world, but there’s a lot of value in understanding your competitors . Knowing how they market themselves will help you find opportunities to make your company stand out and capture more market share.
Make sure you’re not duplicating your competitors’ efforts. If you discover a competitor has already executed your idea, then it might be time to go back to the drawing board and brainstorm new ways to differentiate yourself. By looking at your competitors, you might be surprised at the type of inspiration and opportunities you’ll find.
To stay ahead of market trends, conduct a SWOT analysis for your marketing plan. A SWOT analysis helps you improve your plan by identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Example: If your competitor launches a social media campaign identical to what you had planned, go back to the drawing board and see how you can build off their campaign. Ask yourself: How can we differentiate our campaign while still getting our message across? What are the weaknesses of their campaign that we can capitalize on? What angles did they not approach?
4. Integrate your marketing efforts
Here’s where the fun comes in. Let’s dive into the different components that go into building a successful marketing plan. You’ll want to make sure your marketing plan includes multiple supporting activities that all add up into a powerful marketing machine. Some marketing plan components include:
Lead generation
Social media
Product marketing
Public relations
Analyst relations
Customer marketing
Search engine optimization (SEO)
Conversational marketing
Knowing where your consumer base spends the most time is significant for nailing this step. You need to have a solid understanding of your target audience before integrating your marketing efforts.
Example: If your target audience is executives that spend a lot of time on LinkedIn, focus your social media strategy around placing branded content on LinkedIn.
5. Differentiate with creative content
Forty-nine percent of marketers say visual images are hugely important to their content strategy. In other words, a clear brand and creative strategy is an essential component to every marketing plan. As you craft your own creative strategy, here are some tips to keep in mind:
Speak to your audience: When defining your creative strategy, think about your audience—what you want them to feel, think, and do when they see your marketing. Will your audience find your creative work relevant? If your audience can’t relate to your creative work, they won’t feel connected to the story you’re trying to tell.
Think outside the box: Find innovative ways to engage your audience, whether through video, animations, or interactive graphics. Know what screens your creative work will live on, whether desktop, mobile, or tablet, and make sure they display beautifully and load quickly across every type of device.
Tie everything back to CTAs: It’s easy to get caught up in the creative process, so it’s important to never lose sight of your ultimate goal: Get your audience to take action. Always find the best way to display strong Calls to Action (CTAs) in your creative work. We live in a visual world—make sure your creative content counts.
Streamline creative production: Once you’ve established a strong creative strategy, the next step is to bring your strategy to life in the production stage. It’s vital to set up a strong framework for your creative production process to eliminate any unnecessary back and forth and potential bottlenecks. Consider establishing creative request forms , streamlining feedback and approval processes, and taking advantage of integrations that might make your designers’ lives easier.
Example: If your brand is fun and approachable, make sure that shows in your creative efforts. Create designs and CTAs that spark joy, offer entertainment, and alleviate the pressure in choosing a partner.
6. Operationalize your marketing plan
Turn your plan into action by making goals, deliverables, and timelines clear for every stakeholder—so teams stay accountable for getting work done. The best way to do this is by centralizing all the details of your marketing plan in one platform , so teams can access the information they need and connect campaign work back to company goals.
With the right work management tool , you can:
Set goals for every marketing activity, and connect campaign work to overarching marketing and business objectives so teams focus on revenue-driving projects.
Centralize deliverables for your entire marketing plan in one project or portfolio .
Mark major milestones and visualize your plan as a timeline, Gantt chart, calendar, list, or Kanban board—without doing any extra work.
Quickly loop in stakeholders with status updates so they’re always up to date on progress. This is extremely important if you have a global team to ensure efforts aren’t being duplicated.
Use automations to seamlessly hand off work between teams, streamlining processes like content creation and reviews.
Create dashboards to report on work and make sure projects are properly staffed , so campaigns stay on track.
With everything housed in one spot, you can easily visualize the status of your entire marketing plan and keep work on track. Building an effective marketing plan is one thing, but how you operationalize it can be your secret to standout marketing.
Example: If your strategy focuses on increasing page views, connect all campaign work to an overarching OKR—like “we will double page views as measured by the amount of organic traffic on our blog.” By making that goal visible to all stakeholders, you help teams prioritize the right work.
See marketing planning in action
With Asana, marketing teams can connect work, standardize processes, and automate workflows—all in one place.

7. Measure performance
Nearly three in four CMOs use revenue growth to measure success, so it’s no surprise that measuring performance is necessary. You established your key metrics in step two, and now it’s time to track and report on them in step eight.
Periodically measure your marketing efforts to find areas of improvement so you can optimize in real-time. There are always lessons to be learned when looking at data. You can discover trends, detect which marketing initiatives performed well, and course-correct what isn’t performing well. And when your plan is complete, you can apply these learnings to your next initiative for improved results.
Example: Say you discover that long-form content is consistently bringing in 400% more page views than short-form content. As a result, you’ll want to focus on producing more long-form content in your next marketing plan.
Marketing plan examples from world-class teams
The best brands in the world bring their marketing plans to life every day. If you’re looking for inspiration, check out these examples from successful marketing teams.
Autodesk grows site traffic 30% three years in a row
When the Autodesk team launched Redshift, it was initially a small business blog. The editorial team executed a successful marketing plan to expand it into a premier owned-media site, making it a destination for stories and videos about the future of making.
The team scaled content production to support seven additional languages. By standardizing their content production workflow and centralizing all content conversations in one place, the editorial team now publishes 2X more content monthly. Read the case study to learn more about how Autodesk runs a well-oiled content machine.
Sony Music boosts creative production capacity by 4X
In recent years the music industry has gone through a pivotal transition—shifting from album sales to a streaming business model. For marketing and creative teams at Sony Music, that meant adopting an “always on” campaign plan.
The team successfully executed this campaign plan by centralizing creative production and approvals in one project. By standardizing processes, the team reduced campaign production time by 75%. Read the case study to learn more about how Sony Music successfully scaled their creative production process.
Trinny London perfects new customer acquisition
In consumer industries, social media is crucial for building a community of people who feel an affinity with the brand—and Trinny London is no exception. As such, it was imperative that Trinny London’s ad spend was targeted to the correct audience. Using a work management tool, Trinny London was able to nail the process of creating, testing, and implementing ads on multiple social channels.
With the help of a centralized tool, Trinny London improved its ad spend and drove more likes and subscriptions on its YouTube page. Read the case study to learn more about how Trinny London capitalized on paid advertising and social media.
Turn your marketing plan into marketing success
A great marketing plan promotes clarity and accountability across teams—so every stakeholder knows what they’re responsible for, by when. Reading this article is the first step to achieving better team alignment, so you can ensure every marketing campaign contributes to your company’s bottom line.
Use a free marketing plan template to get started
Once you’ve created your marketing strategy and are ready to operationalize your marketing plan, get started with one of our marketing templates .
Our marketing templates can help you manage and track every aspect of your marketing plan, from creative requests to approval workflows. Centralize your entire marketing plan in one place, customize the roadmap, assign tasks, and build a timeline or calendar.
Once you’ve operationalized your entire marketing plan with one of our templates, share it with your stakeholders so everyone can work together in the same tool. Your entire team will feel connected to the marketing plan, know what to prioritize, and see how their work contributes to your project objectives . Choose the best marketing template for your team:
Marketing project plan template
Marketing campaign plan template
Product marketing launch template
Editorial calendar template
Agency collaboration template
Creative requests template
Event planning template
GTM strategy template
Still have questions? We have answers.
What is a marketing plan.
A marketing plan is a detailed roadmap that outlines the different strategies your team will use to achieve organizational objectives. Rather than focusing solely on the end goal, a marketing plan maps every step you need to reach your destination—whether that’s driving pipeline for sales, nurturing your existing customer base, or something in-between.
As a marketing leader, you know there’s never a shortage of great campaign and project ideas. A marketing plan gives you a framework to effectively prioritize work that aligns to overarching business goals—and then get that work done. Some elements of marketing plans include:
Current business plan
Mission statement
Business goals
Target customers
Competitive analysis
Current marketing mix
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Marketing budget
What is the purpose of a marketing plan?
The purpose of a marketing plan is to grow your company’s consumer base and strengthen your brand, while aligning with your organization’s mission and vision . The plan should analyze the competitive landscape and industry trends, offer actionable insights to help you gain a competitive advantage, and document each step of your strategy—so you can see how your campaigns work together to drive overarching business goals.
What is the difference between a marketing plan and a marketing strategy?
A marketing plan contains many marketing strategies across different channels. In that way, marketing strategies contribute to your overall marketing plan, working together to reach your company’s overarching business goals.
For example, imagine you’re about to launch a new software product and the goal of your marketing plan is to drive downloads. Your marketing plan could include marketing strategies like creating top-of-funnel blog content and launching a social media campaign.
What are different types of marketing plans?
Depending on what you’re trying to accomplish, what your timeline is, or which facet of marketing you’re driving, you’ll need to create a different type of marketing plan. Some different types of marketing plans include, but aren’t limited to:
General marketing plan: A general marketing plan is typically an annual or quarterly marketing plan that details the overarching marketing strategies for the period. This type of marketing plan outlines marketing goals, the company’s mission, buyer personas, unique selling propositions, and more. A general marketing plan lays the foundation for other, more specific marketing plans that an organization may employ.
Product launch marketing plan: A product launch marketing plan is a step-by-step plan for marketing a new product or expanding into a new market. It helps you build awareness and interest by targeting the right audience, with the right messaging, in the right timeframe—so potential customers are ready to buy your new offering right away. Nailing your product launch marketing plan can reinforce your overall brand and fast-track sales. For a step-by-step framework to organize all the moving pieces of a launch, check out our product marketing launch template .
Paid marketing plan: This plan includes all the paid strategies in your marketing plan, like pay-per-click, paid social media advertising, native advertising, and display advertising. It’s especially important to do audience research prior to launching your paid marketing plan to ensure you’re maximizing ROI. Consult with content strategists to ensure your ads align with your buyer personas so you know you’re showing ads to the right people.
Content marketing plan: A content marketing plan outlines the different content strategies and campaigns you’ll use to promote your product or service. When putting together a content marketing plan, start by identifying your audience. Then use market research tools to get the best insights into what topics your target audience is most interested in.
SEO marketing plan: Your SEO marketing plan should work directly alongside your content marketing plan as you chart content that’s designed to rank in search results. While your content marketing plan should include all types of content, your SEO marketing plan will cover the top-of-funnel content that drives new users to your site. Planning search engine-friendly content is only one step in your SEO marketing plan. You’ll also need to include link-building and technical aspects in order to ensure your site and content are as optimized as possible.
Social media marketing plan: This plan will highlight the marketing strategies you plan to accomplish on social media. Like in any general or digital marketing plan , your social media strategy should identify your ideal customer base and determine how they engage on different social media platforms. From there, you can cater your social media content to your target audience.
Related resources
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production

Build a marketing operations strategy in 4 steps
How Asana uses work management for more impactful campaigns
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
The Marketing Plan Section of the Business Plan
Writing The Business Plan: Section 5
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
- Products, Services, and Your USP
Pricing and Positioning Strategy
Sales and distribution plan, advertising and promotion plan.
The marketing plan section of the business plan explains how you're going to get your customers to buy your products or services. The marketing plan, then, will include sections detailing your:
- Products and services and your unique selling proposition (USP)
- Pricing strategy
- Sales and distribution plan
- Advertising and promotions plan
The easiest way to develop your marketing plan is to work through each of these sections, referring to the market research you completed when you were writing the previous sections of the business plan . (Note that if you are developing a marketing plan on its own, rather than as part of a business plan, you will also need to include a target market and a competitors' analysis section.)
Let's look at each of these four sections in detail.
Products, Services, and Your Unique Selling Proposition
Focus on the uniqueness of your product or service and how the customer will benefit from what you're offering. Use these questions to write a paragraph summarizing these aspects for your marketing plan:
- What are the features of your product or service?
- Describe the physical attributes of your product or service and any other relevant features such as what it does or how it differs from competitors' offerings.
- How will your product or service benefit the customer?
- Remember that benefits can be intangible as well as tangible; for instance, if you're selling a cleaning product, your customers will benefit by having a cleaner house, but they may also benefit by enjoying better health. Brainstorm as many benefits as possible to begin with, then choose to emphasize the benefits that your targeted customers will most appreciate in your marketing plan.
- What is it that sets your product or service apart from all the rest? In other words, what is your USP, the message you want your customers to receive about your product or service? This will be at the heart of your marketing plan.
Examples of Unique Selling Propositions
Unique selling propositions should be short (no more than a sentence) and concise. Here are a few great examples:
- Domino's Pizza : "We deliver hot, fresh pizza in 30 minutes or less, or it's free."
- FedEx Corporation : "When it absolutely, positively has to be there overnight."
- M&Ms : "The milk chocolate melts in your mouth, not in your hand ."
- Dollar Shave Club: “Everything you need in the bathroom—from razor blades to grooming products—automatically delivered to your door. It doesn’t get any simpler than that.”
The pricing strategy portion of the marketing plan involves determining how you will price your product or service. The price you charge has to be competitive but still allow you to make a reasonable profit.
Being reasonable is key—you can charge any price you want to, but for every product or service there's a limit to how much the consumer is willing to pay. Your pricing strategy needs to take this consumer threshold into account.
The most common question small business people have about the pricing strategy section of the marketing plan is, "How do you know what price to charge?" Basically, you set your pricing through a process of calculating your costs, estimating the benefits to consumers, and comparing your products, services, and prices to others that are similar.
Set your pricing by examining how much it cost you to produce the product or service and adding a fair price for the benefits that the customer will enjoy. You may find it useful to conduct a breakeven analysis to determine your minimum threshold. Competitor pricing will also help guide you toward the fair market value and help you determine how high you can reasonably go.
The pricing strategy you outline in your marketing plan will answer the following questions:
- What is the cost of your product or service? Make sure you include all your fixed and variable costs when you're calculating this. The costs of labor and materials are obvious, but you may also need to include freight costs, administrative costs, and selling costs, for example.
- How does the pricing of your product or service compare to the market price of similar products or services?
- Explain how the pricing of your product or service is competitive. For instance, if the price you plan to charge is lower, why are you able to do this? If it's higher, why would your customers be willing to pay more? This is where the strategy aspect comes into play; will your business be more competitive if you charge more, less, or the same as your competitors, and why?
- What kind of return on investment (ROI) are you expecting with this pricing strategy, and within what time frame?
Remember, the primary goal of the marketing plan is to get people to buy your products or services. Here's where you detail how this is going to happen.
There are usually three parts to the sales and distribution section, although all three parts may not apply to your business.
Distribution Methods
- How is your product or service going to get to the customer? Will you distribute your product or service through a website, through the mail, through sales representatives, home delivery, or through retail?
- What distribution channel is going to be used? In a direct distribution channel, the product or service goes directly from the manufacturer to the consumer. In a one-stage distribution channel, it goes from manufacturer to retailer to consumer. The traditional distribution channel is from manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer. Outline all the different companies, people and technologies that will be involved in the process of getting your product or service to your customer.
- What are the costs associated with distribution?
- What are the delivery terms?
- How will the distribution methods affect production time frames or delivery? How long will it take to get your product or service to your customer?
If your business involves selling a product, you should also include information about inventory levels and packaging in this part of your marketing plan. For instance:
- How are your products to be packaged for shipping and for display?
- Does the packaging meet all regulatory requirements (such as labeling)?
- Is the packaging appropriately coded, priced, and complementary to the product?
- What minimum inventory levels must be maintained to ensure that there is no loss of sales due to problems such as late shipments and backorders?
Transaction Process
- What system will be used for processing orders, shipping, and billing?
- What methods of payment will customers be able to use?
- What credit terms will customers be offered? If you will offer discounts for early payment or impose penalties for late payment, they should be mentioned in this part of your marketing plan.
- What is your return policy?
- What warranties will the customer be offered? Describe these or any other service guarantees.
- What after-sale support will you offer customers and what will you charge (if anything) for this support?
- Is there a system for customer feedback so customer satisfaction (or the lack of it) can be tracked and addressed?
Sales Strategy
- What types of salespeople will be involved (commissioned salespeople, product demonstrators, telephone solicitors, etc.)?
- Describe your expectations of these salespeople and how sales effectiveness will be measured.
- Will a sales training program be offered? If so, describe it in this section of the marketing plan.
- Describe the incentives salespeople will be offered to encourage their achievements (such as getting new accounts, the most orders, etc.).
Essentially the advertising and promotion section of the marketing plan describes how you're going to deliver your USP to your prospective customers. While there are literally thousands of different promotion avenues available to you, what distinguishes a successful plan from an unsuccessful one is the focus—and that's what your USP provides.
So think first of the message that you want to send to your target audience. Then look at these promotion possibilities and decide which to emphasize in your marketing plan:
Advertising
The best approach to advertising is to think of it in terms of media—specifically, which media will be most effective in reaching your target market. Then you can make decisions about how much of your annual advertising budget you're going to spend on each medium.
What percentage of your annual advertising budget will you invest in applicable methods of advertising, such as:
- The internet (including business website, email, social media campaigns, etc.)
- Direct mail
- Door-to-door flyer delivery
- Cooperative advertising with wholesalers, retailers, or other businesses
- Directories
- Bench/bus/subway ads
Include not only the cost of the advertising but your projections about how much business the advertising will bring in.
Sales Promotion
If it's appropriate to your business, you may want to incorporate sales promotional activities into your advertising and promotion plan, such as:
- Offering free samples
- Point of purchase displays
- Product demonstrations
Marketing Materials
Every business will include some of these in its promotion plans. The most common marketing material is the business card, but brochures, pamphlets, and service sheets are also popular.
This is another avenue of promotion that every business should use. Describe how you plan to generate publicity. While press releases spring to mind, that's only one way to get people spreading the word about your business. Consider:
- Product launches
- Social media
- Special events, including community involvement
- Writing articles
- Getting and using testimonials
Your Business's Website
If your business has or will have a website and a business Facebook page, describe how these fit into your advertising and promotion plan.
Trade Shows
Trade shows can be incredibly effective promotion and sales opportunities if you pick the right ones and go equipped to put your promotion plan into action.
Other Promotion Activities
Your promotion activities are limited only by your imagination. But whether you plan to teach a course, sponsor a community event, or conduct an email campaign, you'll want to include it in your advertising and promotion plan. Sporadic, disconnected attempts to promote your product or service are bound to fail. Your goal is to plan and carry out a sequence of focused promotion activities that will communicate the message you want to send about your products or services.
No business is too small to have a marketing plan. After all, no business is too small for customers or clients. And if you have these, you need to communicate with them about what you have to offer.
Harvard Business Review. " How to Find Out What Customers Will Pay ." Accessed Jan. 16, 2020.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated April 17, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Laundromat Business Plan + Example Templates

13 Min. Read
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan

6 Min. Read
How to Do a SWOT Analysis for Better Strategic Planning

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Starting a Business
Our Top Picks
- Best Small Business Loans
- Best Business Internet Service
- Best Online Payroll Service
- Best Business Phone Systems
Our In-Depth Reviews
- OnPay Payroll Review
- ADP Payroll Review
- Ooma Office Review
- RingCentral Review
Explore More
- Business Solutions
- Entrepreneurship
- Franchising
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Merchant Services Providers
- Best Credit Card Processors
- Best Mobile Credit Card Processors
- Clover Review
- Merchant One Review
- QuickBooks Online Review
- Xero Accounting Review
- Financial Solutions
Human Resources
- Best Human Resources Outsourcing Services
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- Best PEO Services
- Best Business Employee Retirement Plans
- Bambee Review
- Rippling HR Software Review
- TriNet Review
- Gusto Payroll Review
- HR Solutions
Marketing and Sales
- Best Text Message Marketing Services
- Best CRM Software
- Best Email Marketing Services
- Best Website Builders
- Textedly Review
- Salesforce Review
- EZ Texting Review
- Textline Review
- Business Intelligence
- Marketing Solutions
- Marketing Strategy
- Public Relations
- Social Media
- Best GPS Fleet Management Software
- Best POS Systems
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Document Management Software
- Verizon Connect Fleet GPS Review
- Zoom Review
- Samsara Review
- Zoho CRM Review
- Technology Solutions
Business Basics
- 4 Simple Steps to Valuing Your Small Business
- How to Write a Business Growth Plan
- 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
- How to Start a One-Person Business
- FreshBooks vs. QuickBooks Comparison
- Salesforce CRM vs. Zoho CRM
- RingCentral vs. Zoom Comparison
- 10 Ways to Generate More Sales Leads
Your Guide to Creating a Small Business Marketing Plan


Table of Contents
To have a successful business, you need a well-thought-out marketing plan to promote your products or services. Although making a few social media posts or blasting a few promotional emails may seem simple enough, disjointed marketing efforts not only confuse your target audience, but can ultimately harm your business.
What is a marketing plan?
A marketing plan is a strategic road map for how you communicate (online and offline) with your target audience to successfully promote your products or services. Depending on your goal, marketing plans can be extremely basic or highly detailed.
According to Molly Maple Bryant, vice president of marketing at Vibrent Health, a marketing plan is not simply a list of things you want to accomplish. Instead, it should list the outcomes you seek — measurable and contextual, like the pipeline you’re developing, or leads you’re generating — and it should explain the high-level strategies you will use to achieve those outcomes. Developing strategies can be complicated, but they make a major difference in keeping you on track and avoiding diversions, also called scope creep .
“Once you have an agreed-upon plan, you are able to compare any incoming requests against your strategies to determine ‘Yes, this adheres to my strategy so we can add it,’ or ‘No, this sounds good in theory, but it doesn’t adhere to our agreed-upon strategy, so we won’t adjust resources,'” Bryant told us.
Download a copy of our free marketing plan template .
Types of marketing plans
There are several different types of marketing plans you can use based on certain strategies that make sense for your organization. Your business will likely need a combination of the following marketing plans to create an effective, comprehensive marketing strategy:
- Advertising plan
- Branding plan
- Content marketing plan
- Customer acquisition plan
- Direct marketing plan
- Email marketing plan
- Public relation plan
- Print marketing plan
- Reputation management plan
- Retention plan
- Search engine optimization plan
- Social media marketing plan
Depending on your product positioning, niche marketing plans like influencer marketing or video marketing can be incredibly effective.
Why is it important to have a marketing plan for your business?
A marketing plan is a crucial resource for any small business because it helps you identify the market needs your product or service meets, how your product is different from competitors, and who your product or service is for. Marketing plans also serve as a road map for your sales strategy, branding direction and building your overall business. This is important for successfully conveying your brand messaging to your target audience .
Another significant benefit of a marketing plan for your company is that rather than simply guessing metrics, it forces you to sit down and do the math about your business goals and how to realistically fulfill them. When you look at your growth outcomes, you can delve further to determine what it will take to get to those numbers.
Bryant offered the following example: “Need $100,000 in revenue? How many sales is that? If 10, what’s your close rate? Let’s say 10 percent from lead to closed deal. Now you have a metric to start with — to get to 10 sales, we need 100 leads. Where will they come from, and what strategies will you use? The plan helps you put it all on paper so you can map out resources and tactics later with a lot of preparation and realism,” said Bryant.
When analyzing outcomes and resources, you can save time and avoid scope creep by focusing only on strategies that are relevant to your marketing plan. A marketing plan helps you think realistically about your strategies, gets your stakeholders on the same page, and holds your marketing team accountable for their decisions.
“When everyone’s tasks and goals are laid out for the stakeholders and company partners to see, it is much easier for the entire team to feel at ease about reaching sales goals and allowing the marketing team the space and freedom needed to execute work without constant supervision,” said Cassady Dill, digital marketing consultant and owner of Ethos Agency.
Additionally, Dill said a marketing plan should be easily understood by your entire team, executives and outside departments. Your plan should also serve as an easy guide for future marketing managers and team members to understand and implement.
What are the key elements of an effective business marketing plan?
A marketing plan should be customized to fit your business; however, Dill said, all marketing plans contain five essential functions:
- Your business goals
- Key metrics (how you quantify and measure success)
- Strategies (an overview of implementation and how that will achieve goals)
- A plan (the details of execution and the human resources, departments and software that will be involved)
- Reporting (what reports of progress will include and/or look like)
We broke down those five functions into 10 actionable categories to help you create a marketing plan that is unique and effective for your business.
1. Executive summary
The executive summary is a great place to give the reader of your plan an overview of your business’s mission or goals, as well as the marketing strategy you’re looking to employ. An executive summary is often written after you’ve completed the rest of the marketing plan, to ensure it covers all the important elements of your plan. If the executive summary is the only part of your marketing plan that someone reads (which is highly possible), you want to be sure they understand the most crucial details.
2. Mission statement
The mission statement , not to be confused with a vision statement, is a statement that encompasses your company’s values and how they relate to your overall goals as an organization. Here are some good questions to get you thinking:
- What does your company do today?
- What’s important to your company?
- What would your company like to do in the future?
- What is your brand identity?
- What’s your culture like ?
- How does your company benefit customers, employees and stakeholders?
3. Target markets
Identifying your target market is one of the most important parts of your marketing plan. Without a defined target audience, your marketing expenses will be wasted. Think of it like this: Some people need your service or product but don’t know it exists yet. Who are those people?
Here are some other questions to help you brainstorm your target market :
- What is the demographic of your customers (gender, age, income, education, etc.)?
- What are their needs and interests?
- What’s their psychographic profile (attitudes, philosophies, values, lifestyle, etc.)?
- How do they behave?
- What are some existing products they use?
4. Products and services
In this section, don’t just list what your product or service is. Think critically about what you have to offer your customers and what that value proposition means to them.
- What do you make or provide for customers?
- What are your customers’ needs?
- How does your product or service fulfill customers’ needs?
- What value do you add to your customers’ lives?
- What type of product or service are you offering?
5. Distribution channels
At this point in your report, you should transition your thinking into actual marketing theory and practices. Distribution channels are the avenues you’ll use to reach a prospective customer or business . Think of all current and potential sales channels on which your specific target audience is active. One distribution channel that works great for one organization may be useless to another. For example, one company may host their website for free on a site like HubSpot and solely rely on that as their sales channel, while another company may have a whole team of people using Pinterest to drive sales. [Learn how CRM systems can help track your marketing leads based on various distribution channels.]
Examples of sales channels include the following:
- Mobile text message marketing
- Social media
- Print (newspapers, magazines, brochures, catalogs, direct mail)
- Broadcast (TV, radio)
- Press releases
- Trade shows, product demonstrations, event marketing
6. Competitive profile
One of the major aspects of your marketing plan is developing your unique selling proposition (USP). A USP is a feature or stance that separates your product or service from competitors. Finding your USP is all about differentiation and distinguishing your company as a sole proprietor of one type of good or service. Conduct a competitive analysis to identify your competitive profile and how you stack up against the competition. It is important to remain unbiased when conducting this analysis.
Here are some ideas to consider:
- What’s your USP?
- Who are your competitors? What do they offer?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of your competition?
- What needs of the market (or customer) are not being served? What can you do to meet those needs?
If you are creating your USP for the first time, here are seven surefire strategies to help you stand out from the competition .
7. A pricing strategy
Consider pricing when drafting your marketing plan. Developing the right pricing strategy helps you better market your product. Think about your current and projected finances when developing a long-term marketing strategy that is realistic and beneficial for your business. Here are some key questions to ask yourself about your pricing:
- What are reasonable margins to make a profit and cover production costs?
- Is there a market for products or services at your projected price point?
- Are you willing to sacrifice profit margins in return for a greater market share?
- What are your marketing and distribution costs?
8. Objectives
Consider your objectives when developing a marketing plan. This aspect of your plan should involve specific goals related to market penetration and revenue targets. Be sure to keep your marketing objectives on-brand with your business. Here are some things to consider:
- Sales quotas
- Number of new customers gained
- Customer retention percentages
- Revenue targets
- Market penetration
- Brand awareness
- Website traffic
9. Action plans
With all of the above items outlined, determine what steps need to be taken to enact your marketing plan. This includes determining the proper steps, setting goals, breaking down responsibilities, and establishing an overall timeline.
It’s also important to brainstorm potential roadblocks your business could face and some solutions to overcome them. Your research is useless if you don’t have an actionable plan that can be realistically implemented to carry out your ideas.
10. Financial projections
This last step allows you to establish a realistic marketing budget and better understand your marketing plan from a cost perspective. In addition to setting a budget, consider the overall return on investment as well. Here are some other financial projections to consider:
- Cost of implementation
- Cost to produce product or service
- Existing and projected cash flow
- Projected sales
- Desired profit margin on projected sales
What is a template for creating a successful marketing plan?
The internet is full of useful tools, including paid and free marketing plan templates, to help you build a successful marketing plan .
Whether you are looking for a free template generator to build a new marketing plan or a benchmarking tool to evaluate your current strategies, several great resources are available. Keep in mind that the best marketing plan for your business will be a customized one.
“Ultimately, you should design a marketing plan that best serves the needs of your team as you see fit,” said Dill. “Don’t force yourself into a plan that doesn’t fit your team. Use templates to shorten the workload time, but then adjust it for a more custom plan.”
Here are some tools and templates to get you started:
- Free marketing plan template : business.com has developed a free template that is fully customizable based on the needs of your business. Each section provides in-depth explanations, examples and resources to help you create an impressive marketing plan.
- Smart Insights: In addition to offering marketing plan templates, some companies, like Smart Insights, offer marketing benchmarking templates to help you evaluate your strategy performance. These are accessible with a free Smart Insights membership.
- GERU: Similarly, GERU offers a funnel-planning, profit-prediction and simulation tool to help you assess mock business ideas and simulations. This can help you identify weak points in your marketing strategy that need improvement. Although GERU requires users to sign up for a paid account, you can access a free trial to test it out.
What mistakes should you avoid when creating your marketing plan?
When creating an effective marketing plan, you need to avoid falling for common missteps and mistakes. For starters, failing to identify any of the 10 actionable categories above is an obvious mistake.
Here are some other key mistakes to avoid:
- Setting unrealistic budgets: Underestimating the costs of marketing activities or setting an unrealistic budget can limit your ability to execute your plan effectively. Marketing can be expensive, so it’s important to fully understand the estimated cost and budget before building a marketing strategy that you can’t afford.
- Focusing on quantity over quality: “More” doesn’t always mean “better” if you are posting on irrelevant marketing channels or your efforts are bringing in unqualified leads. Prioritizing the quantity of marketing activities over their quality can lead to superficial engagement and a lack of meaningful results.
- Not testing campaigns: Launching large campaigns without testing can lead to wasted resources if the messaging or tactics don’t resonate as expected. Test out your new campaigns to ensure they achieve your intended goal.
- Ignoring customer feedback: You may be tempted to ignore negative feedback, but disregarding customer comments and failing to address their concerns can lead to negative perceptions of your brand. Instead, use customer feedback to your advantage to improve your product and marketing efforts.
- Overpromising and underdelivering: Setting unrealistic expectations in your marketing messages that your products or services can’t fulfill can damage your brand’s reputation.
- Ignoring seasonality and trends: Failing to account for seasonal trends and market changes can result in missed opportunities for timely marketing efforts.
- Not reviewing and updating your plan: A rigid marketing plan that doesn’t allow for adjustments in response to market feedback and changing conditions can hinder your success. A marketing plan should be a living document that is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the market and your business’s goals.
Avoiding these mistakes and missteps can help you create a more effective and successful marketing plan that drives results for your business.
How can you take action with your new marketing plan?
Before you dive into marketing plan templates, it’s important to understand how to think about a marketing plan.
A good marketing plan targets who your buyers are, establishes the service or product you are offering, and determines your unique selling proposition. From here, you will tackle the marketing planning process and develop the best way to get your product in front of buyers who want your product or service.
Dill created a simple four-step process for how small businesses can take action with creating a marketing plan.
- The first step is to hold a marketing meeting with all the marketing team and executives or stakeholders. This gives them time to offer questions, concerns and criticisms you haven’t thought of so you can go back to the board room and revise your strategy or plan.
- Next, add a timeline to all your tasks and assign team members and all the help you’ll need to execute that plan.
- Once your plan is in action, hold weekly check-ins in person or by email to keep everyone on track.
- Share a weekly progress report with all parties involved and execs to ensure you are moving in the right direction.
In addition to drafting your own plan, you can work with a digital marketing agency or use internet marketing and pay-per-click management services to leverage your online presence.
Once you’ve established a general road map, update it annually. Developing an evolving marketing plan sets your business up for continued success because it allows you to prepare for the unexpected and establish a connection between your brand and your audience.
Matt D’Angelo contributed to this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.

Get Weekly 5-Minute Business Advice
B. newsletter is your digest of bite-sized news, thought & brand leadership, and entertainment. All in one email.
Our mission is to help you take your team, your business and your career to the next level. Whether you're here for product recommendations, research or career advice, we're happy you're here!
.png)
Building a Robust Marketing Plan: Techniques and Insights

A marketing plan serves as the roadmap for achieving business objectives and successfully reaching a targeted audience. It provides detailed strategies for identifying the market, the competition, and the core tactics that will be used to accomplish marketing goals.
This guide offers a deep dive into crafting a marketing plan, providing specific techniques and insights essential for success. Whether refining an existing strategy or charting new territory, you will find valuable guidance to navigate the complexities of marketing planning.
What is a Marketing Plan?
A marketing plan is a strategic document that outlines a company's marketing objectives and the tactics it will employ to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap, guiding businesses in promoting their products or services, reaching their target audience, and ultimately, achieving desired sales and brand recognition.
At its core, a marketing plan is anchored in research. It begins with an understanding of the market environment, including competitor analysis, target audience demographics, and emerging industry trends. This foundational knowledge ensures that strategies are not only innovative but also relevant and timely.
Beyond mere promotion, a marketing plan encompasses the entire customer journey. It details how a business will attract potential customers, nurture them through the sales funnel, and foster post-purchase loyalty. This holistic approach ensures consistent brand messaging and a seamless experience for the consumer.
Marketing Plan vs. Business Plan
While a marketing plan focuses on strategies and actions related to marketing activities, a business plan covers the overall operation of the organization. A business plan includes financial forecasts, management structure, and operational plans, whereas the marketing plan concentrates on how to reach the target audience and how to position the product or service in the market.
Marketing Strategy vs. Marketing Plan
Marketing strategy is a long-term approach that outlines the overall marketing direction and goals, while a marketing plan is a detailed roadmap on how to achieve those goals. Understanding how to write a marketing strategy is essential to crafting a compelling marketing plan.
The 7 P's of a Marketing Plan
Understanding the 7 P's of a marketing plan isn't just about knowing what they are, but also how they work together to create a successful and well-rounded strategy. Let's take a closer look at these essential elements:
- Product: The product or service must meet the needs and wants of the target audience. Consider aspects like design, features, quality, and how it stands out from the competition. If the product or service doesn't fit the market needs, other parts of the plan may not work effectively.
- Price: The pricing strategy is more than just determining a cost. It's about understanding what the market is willing to pay, what competitors charge, and what price will provide a reasonable profit margin. It also considers discounts, payment plans, and other financial factors that might appeal to customers.
- Place: Place refers to where and how the product or service will be sold. It includes choosing the right distribution channels, such as online stores, retail outlets, direct sales, or wholesale. Deciding the best place to sell ensures that the product reaches the right audience at the right time.
- Promotion: Promotion involves spreading the word about the product or service. This includes advertising, sales promotions, public relations, and more. Effective promotion ensures that the target audience knows about the product, understands its benefits, and feels motivated to buy it.
- People: This includes not only the target audience but also the team responsible for creating and delivering the product or service. Understanding what motivates the audience and training the team to meet those needs can make a significant difference in success.
- Process: The process is all about how the product or service is delivered to the customer. It includes everything from ordering, manufacturing, shipping, and service after the sale. A smooth and efficient process enhances customer satisfaction and encourages repeat business.
- Physical Evidence: Physical evidence refers to the tangible aspects that customers can see, touch, or experience, such as packaging, a retail environment, or online user experience. It provides visible proof of quality and helps build trust and confidence in the product or service.
How to Create a Comprehensive Marketing Plan
Creating a comprehensive marketing plan is like putting together a puzzle where all the pieces must fit perfectly. Each step in the process is vital to the whole, and knowing how to write a marketing plan with precision and care can lead to tremendous success..
Conduct a Situation Analysis for the Marketing Plan
A situation analysis is like taking a snapshot of where the business currently stands. This includes understanding the market conditions, competitors, strengths and weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (often referred to as a SWOT analysis). By knowing the landscape, a business can make informed decisions that align with current realities.
Determine the Target Market
Identifying the target market means understanding who the ideal customers are. What do they want? What do they need? What problems are they trying to solve? By answering these questions, a business can create a marketing plan that speaks directly to the people most likely to buy the product or service.
Define Marketing Goals and Objectives
Goals and objectives set the course for the marketing plan. Goals are broad and overarching, while objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). They guide what the business wants to achieve through its marketing efforts.
Develop Marketing Strategies and Tactics
This step involves deciding how to reach the marketing goals and objectives. Strategies are the broad approaches, while tactics are the specific actions that will be taken. For example, a strategy might be to increase brand awareness, while a tactic might be to run a social media advertising campaign.
Determine the Budget and Resources Needed
Without the right budget and resources, even the best-laid plans can fall flat. This step involves figuring out what will be needed in terms of money, time, personnel, and other resources. It ensures that the plan is realistic and achievable.
Implement the Plan
Once everything is in place, it's time to put the plan into action. This means launching the marketing efforts and working diligently to ensure that everything goes as planned. It requires careful coordination, attention to detail, and a willingness to adapt as needed.
Monitor, Review, and Update the Plan as Needed
A marketing plan isn't a "set it and forget it" thing. It requires ongoing attention to ensure that it's working as intended. This includes monitoring results, reviewing progress, and making updates as needed. It ensures that the plan stays relevant and continues to drive towards the goals and objectives.
Types of Marketing Plans
Understanding the various types of marketing plans is essential for tailoring strategies to specific business needs.
Content Marketing Plan
A content marketing plan focuses on creating, publishing, and promoting engaging content that appeals to the target audience. This plan requires identifying the types of content that resonate with the audience, like blog posts, videos, or infographics, and then organizing them into a consistent schedule.
Related: Read our guide highlighting the key steps of building a content marketing dashboard, including the essential metrics to track and the best tools to use.
New Product Launch Marketing Plan
A new product launch marketing plan ensures that all the marketing elements involved in product promotion are aligned and ready to make a big splash. This includes everything from product positioning to advertising campaigns to in-store promotions.
Growth Marketing Plan
When a business is looking to expand, a growth marketing plan can guide the way. This plan focuses on strategies and tactics that will increase market share, enter new markets, or grow the customer base. It's about big picture thinking and long-term success.
Email Marketing Plan
An email marketing plan can be a powerful tool. This plan focuses on building and nurturing relationships through email . It requires understanding what the audience wants to hear about and delivering it directly to their inboxes.
Social Media Marketing Plan
Social media marketing plans are all about connecting with people where they hang out online. This includes platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and more. This plan requires understanding the nuances of each platform and creating content that engages and delights the audience.
Related: Learn how to build an effective social media analytics dashboard and the best practices to know when using third-party solutions.
Next Steps in Your Marketing Journey
It's evident that the journey doesn't end with a well-drafted document. The true test lies in its execution and adaptability. As market dynamics shift and new challenges arise, it's essential to revisit and refine the plan, ensuring it remains aligned with evolving business objectives and market realities.
The insights and techniques shared in this guide serve as foundational blocks. However, the world of marketing is vast, and there's always more to learn, explore, and implement. Consider this guide a starting point. The next steps involve diving deeper into specific tactics, measuring the effectiveness of your strategies, and continuously optimizing for better results.
Frequently Asked Questions
A marketing plan is a vital strategic guide that outlines a company's marketing efforts over a set time frame. It includes an in-depth analysis of the market, goals, strategies, and tactics necessary to align all marketing activities with business objectives.
What's the Difference Between a Marketing Plan and a Business Plan?
A marketing plan focuses exclusively on marketing strategies and activities, while a business plan covers the entire operation of the organization, including financial forecasts, management structure, and operational plans.
How Do Marketing Strategy and Marketing Plan Differ?
A marketing strategy is a long-term blueprint that outlines the overall marketing direction and goals. In contrast, a marketing plan is a detailed guide on how to achieve those goals through specific steps and actions.
What Are the 7 P's of a Marketing Plan?
The 7 P's of a marketing plan refer to Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence. These elements work together to form a comprehensive strategy that addresses various aspects of marketing, from product design to promotion to delivery.
How Do You Create a Comprehensive Marketing Plan?
Creating a comprehensive marketing plan involves several vital steps, such as conducting a situation analysis, determining the target market, defining goals and objectives, developing strategies and tactics, deciding on the budget, implementing the plan, and monitoring and updating as needed.
What Types of Marketing Plans Are There?
There are various types of marketing plans to cater to different business needs, such as Content Marketing Plan, New Product Launch Marketing Plan, Time-Based Marketing Plan, Growth Marketing Plan, Email Marketing Plan, and Social Media Marketing Plan. Each type has its unique focus and requires a specific approach.
Why Is Understanding the Target Market Important in Writing a Marketing Plan?
Understanding the target market is crucial in crafting a marketing plan as it allows the business to create strategies that speak directly to the people most likely to buy the product or service. It involves knowing what the target audience wants, needs, and the problems they are trying to solve.
How Do You Determine the Budget and Resources Needed for a Marketing Plan?
Determining the budget and resources involves analyzing what will be needed in terms of money, time, personnel, and other resources to execute the marketing plan successfully. This step ensures that the plan is realistic and can be carried out as intended.

500+ data sources under one roof to drive business growth. 👇
With Improvado, every plan step is data-backed and optimized

Unshackling Marketing Insights With Advanced UTM Practices
Improvado Labs: experience the latest marketing analytics technology
%20(1).png)
Im provado - AI-powered marketing analytics & intelligence
From data to insights, automate and activate your marketing reporting with Al.

From the blog

San Diego | Headquarters
3919 30th St, San Diego, CA 92104
San Francisco
2800 Leavenworth St, Suite 250, San Francisco, CA 94133

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

- Frequently Asked Questions
- Business Credit Cards
- Talk to Us 1-800-496-1056

How to Write the Marketing Plan in Business Plan?
A marketing plan in business plan is one of the very important sections of a business plan. Marketing is done to spread awareness about your business and its product/service.
What is a marketing plan?
Marketing plan vs marketing strategy, how to write a marketing plan for a business plan.
An effective marketing strategy helps you achieve early success.
Use this article to write an effective marketing plan section in a business plan.
A marketing section of a business plan gives you a roadmap to organize, execute and track the progress of your marketing efforts.
Your marketing plan helps you align your marketing efforts with your business goals. It gives your marketing effort a direction and you can evaluate your efforts at any point.
Types of marketing plan
A perfect type of marketing plan in business plan will depend on your business, your goals, and how soon you want to achieve them.
We have outlined some marketing plans that most businesses need to use. Since this is the age of the internet, we have also included online marketing plans and digital marketing plans.
Want to write a business plan?
Hire our professional business plan writers to prepare your business plan!
Quarterly or Annual Marketing Plans
These are your business marketing plans with a timeline. Every business has its quarterly, bi-yearly, and yearly goals. You will use these goals to monitor the effectiveness of your marketing efforts over time.
Paid Marketing Plans
Paid marketing plans include online advertising, buying billboards, or marketing on vehicles. Pay Per Click marketing and social media marketing for your small business.
Social Media Marketing Plan
Social media marketing plan for business plan can be done in two ways. You can hire a team and raise awareness about your business by sharing regular updates.
You can also do paid marketing on social media. You will need to invest in buying ads on that social media platform and pay for a team of social media marketers.
You can also leverage these effective digital marketing channels for your business.
Content Marketing Plan
A content marketing plan is about attracting potential customers to your website with the help of SEO. You create value for your potential customer first and then by extension, market your business. It can be offline in the form of free workshops etc or online in the form of guides and resources.
Product Launch Marketing Plan
A product lunch sales and marketing plan in business plan will help you decide on the marketing tools, tactics, and tracking you will do when launching a new product or service.
You can also hire WiseBusinessPlans Digital Marketing Services to run successful marketing campaigns for your business.
The difference between a marketing plan and a marketing strategy is simple; a marketing plan is what methods, tools, and tactics you will use for marketing, and a market strategy in business plan is how you will implement your plan.
Learn how to develop an effective marketing strategy with this detailed guide.
Access our free business plan examples now!

Follow these simple steps to write a marketing plan in business plan.
Business Mission
Write your business mission statement and translate it into the efforts the marketing department will make.
For example, your business mission is to help people with home gardening. Your marketing department version will be to attract people who want to do home gardening.
These are performance indicators. These metrics will help you evaluate performance and progress. An example of KPIs for marketing is customer visits to your website, social media page, or brick-and-mortar store.
Create Buyer Personas
A buyer persona is a short description of your average customer. When you have no data, a buyer persona will describe the customer you want to attract.
Decide on Marketing Strategies and Content
Go through the marketing strategies you can use and select the one that will produce the best return on investment for your business.
Similarly, think about the content type that is attractive to your target audience . For example, video format may attract your audience or you may need to share more about your business on social media to grab their attention.
Define Marketing Plan Scope
Define the scope and limits of your marketing plan. Clearly mention what your marketing team will do and will not do.
This will help you save time, cost, and effort in wasted resources.
Set Marketing Budget
You can only spend a set amount on marketing. Set your marketing budget and be creative in that budget to produce the best return.
Your budget is directly related to your marketing goals. Set your marketing budget in a way that does not hamper marketing efforts.
Know your Competition
Knowing and profiling your customer helps you market better. See what are strong spots of competitors’ marketing plans, are and how they are attracting audiences to make a plan to compete effectively.
Appoint your Team & their Responsibilities
Decide on job roles for your team. Set their KPIs, marketing channels they will manage, what content they will create, etc.
Bonus Tip: Here is a step by step guide on how to write a marketing plan executive summary with example and template.
Example of Marketing Plan in Business Plan PDF
See this example of a marketing plan in a business plan to understand how it is done. You can create your marketing plan in the same way.
In the marketing plan section, include details about your target market, competition analysis, marketing strategies, pricing, promotion, and distribution channels. It should outline your approach to reaching and engaging your target audience.
Conduct market research by analyzing your target audience, understanding their needs and preferences, studying your competitors, and identifying market trends. Use surveys, interviews, and industry reports to gather relevant data for your marketing plan.
Consider including a mix of marketing strategies such as digital marketing, social media marketing, content marketing, email marketing, advertising, public relations, and networking. Choose strategies that align with your target audience and business goals.
Determine pricing by considering factors such as production costs, competitor pricing, market demand, and perceived value. Conduct a pricing analysis to ensure your prices are competitive and profitable for your business.
It is recommended to review and update your marketing plan regularly, at least annually or whenever there are significant changes in your business or market conditions. This allows you to adapt your strategies, stay relevant, and capitalize on new opportunities.
WiseBusinessPlans is the company that writes business plans
One comment.
It is a very useful guide. I was wondering If your site offers marketing plan writers for businesses. If any, kindly reply.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

Plan Projections
ideas to numbers .. simple financial projections
Home > Business Plan > Marketing Strategy in a Business Plan

Marketing Strategy in a Business Plan
… we will get this market share by …
- Product USP : Why buy our product? What characteristics does the product have to meet customer needs?
- Promotion : What marketing activities will be undertaken? What means of communication will the business use to persuade customers of the benefits of the product? Will it use above the line promotion or below the line promotion?
- Place : What are the distribution channels? How is the business going to reach customers with its product?
- Price : What price will the business charge for the product, and what goal is it pursuing with the pricing strategy? Will the business use premium, penetration, economy or skimming pricing strategies.
Marketing Strategy Presentation
The marketing strategy section of the business plan can be presented in four sections relating to each of the four P’s product, promotion, place, and price as shown in the example layout below.
The marketing strategy is a key section of the business plan, at this stage you are not trying to present a complete marketing plan, but simply trying to show the investor that each major section of the marketing strategy has been thought about and that you have a good marketing mix.
All of the four sections should be consistent with and support each other, for example, if you are planning to adopt a high price strategy, then the product would be aimed at an upmarket target customer, distributed at high end stores, and make use of one to one personal selling.
This is part of the financial projections and Contents of a Business Plan Guide , a series of posts on what each section of a simple business plan should include. The next post in this series sets out the business model which the business intends to use to generate revenue.
About the Author
Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Plan Projections. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
You May Also Like
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for April 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

- Managed WordPress Website Hosting
- Marketing Strategy
MARKETING STRATEGY

9 Elements of an Effective Marketing Plan
There is no short-cutting the most critical part of any marketing campaign — the plan. That’s why this article goes into detail about the nine ingredients every effective marketing plan should have. You’ll gain clarity about each component’s purpose, along with specific examples to crystallize your thinking.
What you’ll gain from this article:
- How to develop the right marketing goals
- How to identify your plan’s truest key performance indicators
- The insights you may be lacking about your target audience(s)
- The difference and relationship between marketing strategy and tactics
- The greatest pitfall when it comes to the marketing budget
Estimated read time = 12 mins
It’s very easy to get distracted and jump right into the weeds. By “weeds,” we mean marketing tactics. Marketers have experienced this far too often. We get a group of colleagues together to develop an annual marketing plan or an upcoming campaign, and folks start blurting out specific ways to go to market. Email marketing. Facebook ads. Publicity. A TV spot. Google ads. Etc.
Please avoid this temptation with all your might. This type of planning is no longer sustainable, especially with today’s marketers being asked to do more than ever. Often with less budget and less staff. We need to be more thoughtful and more measurable with our actions, and a sound marketing plan should be that blueprint. So let’s cover each of these elements in detail:
- Business goals
- Marketing goals
- Target audiences
BUSINESS / ORGANIZATIONAL GOALS
Every organization — for-profit or non-profit, large or small — has goals. Goals give businesses purpose and must have a direct impact on their existence. They come in many forms, including:
- increases in sales revenue
- increases in average order value
- increases in customer lifetime value
- increases in applications and enrollments (colleges and universities)
- increases in fundraising revenue (non-profits)
- increases in the total number of people helped or served (non-profits)
And the list could go on. There are many forms of business goals, and we as marketers have little to no control over how they get created. That said, there’s one key thing we need to remember when creating our marketing plan: Good marketing goals must concretely support business goals . So what should our marketing goals be and how must they support business goals? Read on …
MARKETING GOALS
First, good marketing goals must consist of five key attributes. Many of us have heard about SMART goals , which are:
- Time-related
We set ourselves up for failure if even one of these criterion is lacking. SMART goals give us a foundation for holding ourselves accountable, and knowing when we’ve succeeded (or failed). Here are some SMART examples (let’s assume they’re assignable and realistic, too):
- To increase consumer phone calls (leads) by 10% year-over-year between now and June 30
- To increase in-store foot traffic by 5% during Q4 for the NYC store location
- To increase consumer unaided awareness of our brand by 10% within 1 year
- To increase average donation amounts by 10% during November
Next, we fuse our SMART marketing goals with business goals through an activity called Performance Modeling. (Hubspot also refers to this as Smarketing , FYI for you inbound lovers.) A performance model essentially maps the entire consumer journey in a linear progression from the start of campaign promotion to the resulting consumer activity (i.e. leads), and then to actual sales and profitability. Think of the performance model as another way to express the traditional marketing funnel , but with two, key exceptions :
- It gives volume and conversion details for each “micro” conversion of the journey, and
- It reflects sales conversion rates and business goals
Here’s a performance model example for one of our clients offering a high-end kitchen design and installation service:
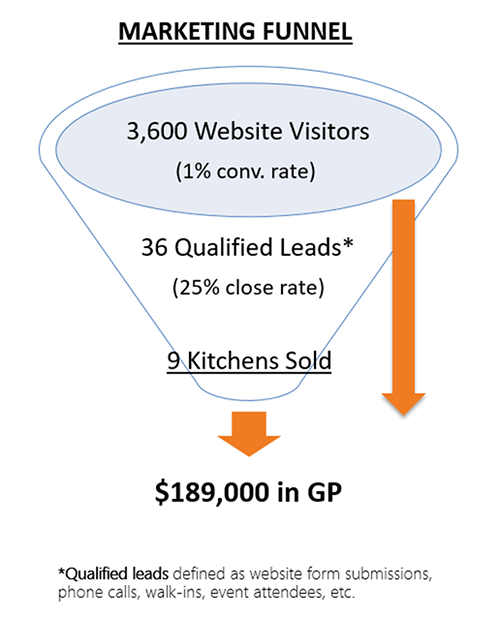
Performance modeling also offers a framework for future marketing reports at the management/CMO level. It provides crystal clear understanding of which metrics need to be tracked and reported as a campaign progresses. These become our Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). The model essentially becomes a real-time barometer of the campaign’s health and likelihood of reaching its goals. More importantly, it “sounds the alarm” when things are under-performing and prompts much needed campaign adjustments with budget and time still remaining.
And finally, performance modeling gets everyone on board — leadership, marketing and sales . It provides a direct “line of sight” from promotions to profitability, and is easily understood by anyone (not just marketers).
TARGET AUDIENCE(S)
For this blog article, we’ll assume you already know the basics of your target audience. This is usually demographic information such as:
- Male/female (or skew toward one of them)
- Countries, regions, and cities and towns in which they live and work
- Annual household income
- Race or ethnicity
That’s a great start, but many marketers overlook the behavioral and psychographic attributes of their target audiences. Some of these are:
- “Mindset” – How do they think about your product or service?
- economic factors (recession that decreases household spending)
- competitors (with better price points, benefits/features, etc.)
- consumer trends (new ways of thinking that have permanently changed spending habits … think “gluten free”)
- political landscape (new gov’t regulations or election year influences)
- “Habits” – What do they do at each stage of the consumer decision-making process , and what can we do to get in front of them?
The answers to these questions may involve both qualitative (focus groups, interviews, etc.) and quantitative (polls/surveys) research, while some insights could be gained from secondary research (i.e., paying providers like GfK MRI or Nielsen-Scarborough for the data). Either way, the time and investment for these insights will produce a more effective strategy and tactics in the long run.
Surprisingly, this is an area we see far too many clients lacking in. This is especially painful for sales teams, which are responsible for closing. How can we expect them to convert customers if we don’t equip them with the necessary tools?
Key considerations:
- Establishing the brand position
- Developing a messaging platform to support the brand position (tagline/slogan, elevator pitch, support points/key benefits, competitive differentiation, etc.)
- Understanding how the messaging translates into multiple marketing formats
Bottom line : If we can’t explain the value of what we’re promoting, how can we expect to meet our marketing goals?
It’s very easy to confuse marketing strategy and marketing tactics, so we’ll address these two elements together:
- A strategy is the approach for achieving marketing (and business) goals,
- Tactics are the specific things that execute on the strategy
It’s easiest to think of strategy as “what we need to do” and tactics as “how we’ll get it done”.
Example #1: Old Spice
Business goal: To increase U.S. sales of men’s deodorant by 10% in 12 months Marketing goal: To increase consumer unaided awareness (by 50%) and favorability (by 20%) of Old Spice deodorant over other brands Strategy: Target women (wives/girlfriends) because they do the household shopping One Tactic: Air national TV spots showing an attractive man talking directly to these women … like this …
Example #2: Fictional e-commerce business
Let’s say you sell products through your website. The goal is to increase sales revenue by 15% in 6 months with only a very modest budget.
After much research, you decide that the strategic elements of your marketing plan should be to:
- Increase return visitors to the website
- Increase repeat purchases with current/loyal customers
- Increase the average order value of each checkout
Corresponding tactics for those strategic elements could be:
- Show Google re-marketing ads to customers who viewed specific products, but left without making a purchase
- Email free shipping offers to current customers
- Optimize the checkout process by suggesting complementary products (“you may also like …”) with each item added to the online shopping cart
It is critically important to have a firm and realistic marketing budget. This is a decision that only management — not your marketing department and certainly not your consultant! — can make given how much the organization wishes to invest in future marketing efforts in order to meet its goals.
Businesses too often come to us and say, “Why don’t you tell us how much we should spend?” Or, “We have a zero-based budget … what would you recommend based on our business goals?” The truth is that no marketer or consultant knows how to objectively answer this question. The only way would be an unbelievably perfect scenario of a business knowing their conversion rates for every marketing tactic and how they generated sales for every product or service . (That would be a performance modeling dream, but it is just that.)
The pitfall of this question is the internal marketing team and/or consultant(s) must then needlessly spin their wheels to develop multiple marketing plans for multiple budget scenarios. It’s valuable time and resources wasted. Urge management to give you a firm budget from which to plan. It doesn’t help anyone to develop elaborate marketing plans when there’s only enough money to pay for Google advertising at the end of the day.
The marketing plan or campaign’s timing should be influenced by the following:
- The organization’s budget cycle (fiscal year or calendar year)
- Seasonality (holiday shopping season, the Super Bowl, etc.)
- Organizational events (date of a new product launch, store opening, sales promotion, etc.)
A good campaign reflects a timeline to accommodate these circumstances. But a great marketing plan takes it a step further, and projects how it will support sales revenue milestones each month in order to provide cash flow. Here’s an example going back to our kitchen design and installation client. A simple spreadsheet of the performance model is more than sufficient:
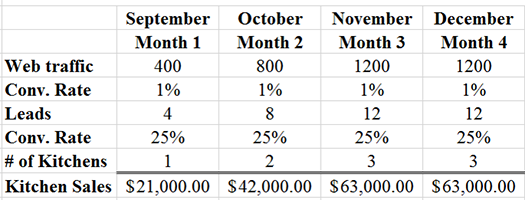
And finally, no marketing plan will ever meet its goals unless there’s a proper team in place, with each member having clearly defined roles and responsibilities.The best plan in the world is nothing more than ideas unless it can be executed. And it takes the right person or people to do that. There are also great (and cheap) project management tools, like Basecamp or Trello , to keep everyone organized and accountable.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Related posts.

- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
Business Plan Section 6: Sales and Marketing
Learn about the points to address in the sales and marketing section of your business plan, plus key aspects for a successful sales strategy.

Remember all that research and hard work you put into the Market Analysis section of your business plan? You learned all about your company, your customers, and your competition. This is where it will all pay off: sales and marketing!
In this section of the plan, you’re actually going to spell out how you’ll market your idea, along with the specifics of how you’ll get business. Sales and marketing are what will grow your business and help you achieve success.
As always, keep your audience in mind. If your business plan is meant for your eyes only, or as an internal document for your staff, you won’t have to be as detailed or specific as you should if it’s intended for a lender or potential investors. In the latter case, you’ll want to demonstrate a very well-planned strategy that will give them confidence in your proposal and make them more likely to want to fund your business.
Sales and marketing strategies will vary by industry, and your strategy will be individually tailored to your company, but there are general guidelines that cover most businesses. Because your marketing plan will lead to sales, let’s start there.
4 Things Your Marketing Plan Must Cover
Many marketing textbooks refer to the “four Ps” of marketing, which is an easy way to remember what’s involved in a solid plan.
Explain in detail the product(s) or service(s) you’re offering, particularly how they are different from or better than what’s already available. What benefits do they provide to your potential customers? What ways is your product or service unique? What makes doing business with you preferable to dealing with someone else? All of these things will help make up your marketing message.
Talk about how you’ll portray the company and what kind of image you’ll present, especially how it will help connect you to your potential customers. Include a picture of your logo and anything that might carry your image, such as vans, trucks, or uniforms. Show screenshots of your website, photos of your store, pictures of your packaging, and anything else that conveys your company’s brand.
Once you’ve gotten the customers in the door (or online), you have to deliver on what you’ve sold them. Marketing isn’t just about promising, it’s also following through and delivering what you said you would.
You may find it helpful to outline exactly how a transaction with your business would take place. Also touch on return policies and customer service. You may not immediately think of these as “marketing” issues, but think back to the last time you had difficulty with a company and told five friends you’d never do business with them again, or you saw someone complain about a company on Facebook or Twitter. Cover your bases before you get caught short in a situation you hadn’t planned for.
It’s important to talk about where you’ll be located and how you’ll get your products and services to your customers. If you’re planning an online business, will you also have a brick and mortar store? What percentage of sales do you project will come from each?
If your business involves manufacturing or distribution of a product, discuss shipping and labeling requirements, and how you’ll meet them. What are your delivery terms and costs? Are you using distributors, and will you charge separately for shipping or build that into the product price?
How you decide to price your product or service is key to how much you’ll sell and how much profit you can make. Again, the Market Analysis work you did will come in very handy in helping you to price your product competitively while still turning a worthwhile profit.
By now, you should have a solid understanding of what your expenses will be, so you know how much you need to make to break even. Of course, if you have startup expenses (and who doesn’t?), you will need to factor those in, as well, understanding that your profit margin will grow when they’re paid off.
Discuss how you’ve arrived at the prices you have, where they fit in with what the competition is doing, and what kind of volume you’ll need to do to be profitable.
You can have the best idea in the world, but if no one knows about it, it won’t sell. So, how are you going to reach your target audience and turn them into customers? Will you advertise? Which media? How often? And how will you split up the budget?
Keep in mind that some forms of traditional and digital advertising cost money, such as buying radio or print ads, or advertising through Google. Some, such as social media or public relations can be handled in-house by a staff member (or outsourced for a fee). And others can be quite variable in cost, such as printing brochures, flyers, catalogs, etc.
How much business do you think you’ll get from each campaign? Will you give coupons, discounts, or offer other incentives to get people to try you out?
Describe how you’ll know whether or not your marketing strategy is effective, such as how many coupons are redeemed or how much of an increase in web or store traffic you expect. You’ll need to project what kind of a return on your advertising investment you anticipate to figure out how much you should be spending.
The Fifth P: People
Some marketing experts think a fifth “P” should be added to the four we’ve already discussed: people. We touched on it under customer service, but a big part of marketing is the level of service you’re able to offer to your customers, and your people are the ones responsible for that.
Your restaurant might serve the best food in town, but your servers can have an even greater impact on the dining experience. You can discuss it here or in the next section, sales, but do make sure to talk about the people who will deal with your customers and handle your customer service, what kind of training they’ll get, and how you’ll measure their effectiveness.
Now that you have your marketing plan together, you need to close the sale and make it pay off. Marketing will help you get customers in the door, to your website, or on the phone, but the best marketing in the world doesn’t matter if you don’t make the sale. That brings us to the next step of the plan, your sales strategy.
What to include in your sales plan:
How much product will you sell or how many contracts will you close over the first month, six months, and year? Be specific, understanding what your cash flow needs to be to keep the lights on and your employees paid. Keep the numbers realistic, however, even though you may want to impress potential funders.
How will you make the sale, and who will do it? Are you selling a product directly to users through a website? Will you bring your merchandise to retailers for them to sell? Are you doing the selling yourself or will you have a sales force? If you have salespeople, will they be paid a straight salary or commission? If you have a service business, where will you get your leads, and how will you follow up? Perhaps you’ll offer an incentive program to current customers for referrals. Describe the sales effort in your plan.
If you offer different product lines or services, you may need a separate strategy for each. Similarly, if you’re selling to different segments of the market, you shouldn’t rely on the same approach to sell everyone. Selling at a craft fair is quite different than setting up a website or offering your product through ebay.com or etsy.com.
Detail whichever approaches you’ve decided on and spell out how you’ll proceed, including any sales quotas you may have established.
Get specific about the numbers you’re looking to achieve over a specific time period. Not only will investors want to see that, it’s an important way for you to know if you’re meeting your targets so you can make any necessary adjustments along the way.
Once you’ve established yourself, how will you continue to expand? This covers both your internal growth as a company, such as how you’ll increase your staff, and how you’ll grow beyond your current boundaries, such as buying another business or setting up franchises, if that’s applicable. Will you grow by offering a wider range of products and services? Perhaps you’ll expand by offering your current goods to a wider audience.
Perhaps more than any other section of your business plan, the Sales and Marketing section will act as your playbook for the actual running of your company , so think it through very carefully and use it!
Next Article: Business Plan Section 7 – Financial Information
Apply for a loan, get started.
Loans from $5,000 - $100,000 with transparent terms and no prepayment penalty. Tell us a little about yourself, your business and receive your quote in minutes without impacting your credit score.
Thanks for applying!
Loans are originated and funded through our lending arm, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development. By clicking “Continue to Application,” you consent to, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development’s Terms of Use and Privacy Policy ; and to receive emails, calls and texts , potentially for marketing purposes, including autodialed or pre-recorded calls. You may opt out of receiving certain communications as provided in our Privacy Policy .
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Marketing Plan Report Outline
Popular searches
Exxonmobil unveils thailand 2024 business plan.
- Catering to diverse needs with Mobil 1 ™ and Mobil Super ™
- Celebrate Mobil 1 ™ 50th Anniversary – The living proof of trust from consumers and motorsports partners worldwide
selected item
4/4 From left to right: Manoch Munjitjuntra, director of ExxonMobil Marketing (Thailand) Limited and lubricant sales manager, Suda Ninvoraskul, managing director, Dr. Taweesak Bunluesin, public and government affairs manager, ExxonMobil Limited.
April 24th, 2024, Bangkok – ExxonMobil Marketing (Thailand) Limited revealed its 2024 business plan for Thailand under the theme, “ Unrivaled quality, Journey with confidence, ” levering on the strength of “Quality Wins with Mobil™ lubricants, while offering Mobil Super™ to fulfill diverse consumer needs. This year, the company targeted 10% growth for its flagship product, Mobil 1™.
Today, there are more than 20 million personal vehicles on the roads of Thailand,1 ranging from personal cars for daily commutes to pickup trucks for heavy loads. Engine oil is a key element that enables the cars’ engines to function consistently. Therefore, good engine oil must effectively protect the engines, enhance their performance, extend lifespan, and improve fuel economy to enable all vehicles to function as intended in transporting goods and people.
Quality Wins – Mobil ™ ’s Vision and DNA
Manoch Munjitjuntra, director of ExxonMobil Marketing (Thailand) Limited and lubricant sales manager , said, “Mobil™ has been in Thailand for over 90 years. The word ‘quality’ is not just a standard but our way of work. Our commitment to ‘ Quality Wins ’ shows in every product we deliver. This year, under the theme, “ Unrivaled quality, Journey with confidence, ” we want to be the top-of-mind brand regarding quality and innovation. Customers can trust our products, which have proven successful.”
Driving Ultimate Performance with Mobil 1™ and Extending Proven Protection with Mobil Super™ 2
“With our commitment to quality and innovation, we applied the technology used in Mobil 1™ to the production of Mobil Super™ as well. While Mobil 1™ serves the drivers of high-performance cars, Mobil Super™ serves those who want to protect their engines from heavy usage, such as pickup trucks and SUVs. As part of our customer base expansion plan in 2024, we plan to utilize our products’ highlights to capture more customers.”
“We are targeting 10% growth for our flagship products, Mobil 1™, and expanding Mobil Super™ customer base through the network of more than 700 auto part shops and 1,400 car maintenance workshops and lubes centers, including Mobil 1 Center, B-Quik, and Auto1 network. We planned to add 30-50 service locations this year to become more accessible to our customers,” said Manoch
50 Years of Mobil 1 ™ Success is Proof of World-Class Innovation and Quality.
Mobil 1™ is the first full synthetic engine oil introduced in 1974. From then on, it continues to be widely recognized as the leader in the engine oil industry. Various leading racing teams, including Oracle Red Bull Racing, Porsche Racing, Red Bull KTM Factory Racing, and high-performance carmaker partners like Porsche, have trusted this flagship product.
Mobil™ is committed to developing future products to support modern engine technologies, electric vehicles, and the automotive industry.
“For 50 years, we have believed that ‘Quality Wins’ and ‘Quality’ are the driving forces that propel us to develop the best possible oil for our customers. We continue to maintain our quality standard and innovate for the future,” said Manoch
For special promotions, additional information, or inquiries, please visit http://www.mobil.co.th
For more information, please contact Public and Government Affairs Email : [email protected]
- From the transportation statistics report, fiscal year 2019-2023 https://web.dlt.go.th/statistics/plugins/UploadiFive/uploads/6f6897ce35cd1d6a488eab4c29a548a0b5d0973421176078322eff0d7d61b5a5.pdf
- Based on Sequence IVB (Iron Wear) test results compared to API SP standards for Mobil Super All-in-one Protection 0W-20 and 5W-30 only.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Marketing strategy. The marketing strategy portion of your business plan presents the approach you plan to take to provide products or services to your customers. It explains, at a high level, what you are going to do to get your customers to buy in the desired quantities. Someone who reads your market strategy should come away with a "big ...
Marketing Plan vs. Business Plan. A marketing plan is a strategic document that outlines marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics. A business plan is also a strategic document. But this plan covers all aspects of a company's operations, including finance, operations, and more. It can also help your business decide how to distribute ...
You need to have a solid understanding of your target audience before integrating your marketing efforts. Example: If your target audience is executives that spend a lot of time on LinkedIn, focus your social media strategy around placing branded content on LinkedIn. 5. Differentiate with creative content.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Sales and distribution plan. Advertising and promotions plan. The easiest way to develop your marketing plan is to work through each of these sections, referring to the market research you completed when you were writing the previous sections of the business plan. (Note that if you are developing a marketing plan on its own, rather than as part ...
A marketing plan is a core component of a business plan. It relates specifically to the marketing of a particular product or service and it describes: An overall marketing objective. A broad marketing strategy. The tactical detail related to specific marketing activities. The various costs associated with these activities.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
A marketing plan is a document that a business uses to execute a marketing strategy. It is tactical in nature, and, as later sections of this article explore, it typically includes campaign objectives, buyer personas, competitive analysis, key performance indicators, an action plan, and a method for analyzing campaign results.
Your business will likely need a combination of the following marketing plans to create an effective, comprehensive marketing strategy: Advertising plan. Branding plan. Content marketing plan. Customer acquisition plan. Direct marketing plan. Email marketing plan. Public relation plan. Print marketing plan.
1. Describe your product/service and target market. The idea is to paint a picture of your product or service as valuable to the customers in your target market. This component details what you ...
Marketing Plan: A marketing plan is a business's operational document for advertising campaigns designed to reach its target market . A marketing plan pulls together all the campaigns that will be ...
Aspect Marketing Plan Business Plan; Purpose: Focuses on strategies to promote products/services, aiming to reach the target audience and achieve specific marketing objectives. Provides a holistic view of the company's mission, objectives, and strategies for overall growth and operations. Often used to secure funding or guide the company's ...
Strategies to consider: Networking - Go where your market is. Direct marketing - sales letters, brochures, and flyers. Advertising - print media and directories. Training programs - to increase awareness. Write articles, give advice, become known as an expert. Direct/personal selling.
The purpose of a marketing plan includes the following: To clearly define the marketing objectives of the business that align with the corporate mission and vision of the organization. The marketing objectives indicate where the organization wishes to be at any specific period in the future. The marketing plan usually assists in the growth of ...
5. Develop Your Timeline and Budget. Establish a timeline and budget for your marketing strategy that reaches your audience throughout the year. It should include all scheduled promotions for the ...
Appoint your Team & their Responsibilities. Decide on job roles for your team. Set their KPIs, marketing channels they will manage, what content they will create, etc. Bonus Tip: Here is a step by step guide on how to write a marketing plan executive summary with example and template.
The marketing strategy section of the business plan can be presented in four sections relating to each of the four P's product, promotion, place, and price as shown in the example layout below. The marketing strategy is a key section of the business plan, at this stage you are not trying to present a complete marketing plan, but simply trying ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
We need to be more thoughtful and more measurable with our actions, and a sound marketing plan should be that blueprint. So let's cover each of these elements in detail: Business goals. Marketing goals. Target audiences. Messaging. Strategy. Tactics. Budget.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
This is where it will all pay off: sales and marketing! In this section of the plan, you're actually going to spell out how you'll market your idea, along with the specifics of how you'll get business. Sales and marketing are what will grow your business and help you achieve success. As always, keep your audience in mind.
Business document from Saint Leo University, 1 page, Marketing Plan Report (KA) The specific instructions and requirements for the Final Written Report include (refer to Writing Guide): • Collegiate level writing is expected • Incorporate all corrections suggested by your instructor • Well organized and pro ... Aspects of the SWOT ...
ExxonMobil Marketing (Thailand) Limited revealed its 2024 business plan for Thailand under the theme, "Unrivaled quality, Journey with confidence," levering on the strength of "Quality Wins with Mobil™ lubricants, while offering Mobil Super™ to fulfill diverse consumer needs. This year, the company targeted 10% growth for its flagship product, Mobil 1™.