- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips

Research Paradigms: Explanation and Examples

4-minute read
- 1st March 2022
Are you planning a research project? If so, you’ll need a research paradigm. But what exactly is a research paradigm, and why is it important? This blog post will cover the following:
● The definition of a research paradigm
● Why research paradigms are important
● Common examples of research paradigms
● Merging research paradigms
● Expert editing and proofreading
Read on to find out more or learn about research paradigms in the video below!
The Definition of a Research Paradigm
A research paradigm is a philosophical framework that your research is based on. It offers a pattern of beliefs and understandings from which the theories and practices of your research project operate.
A research paradigm consists of ontology, epistemology, and research methodology .
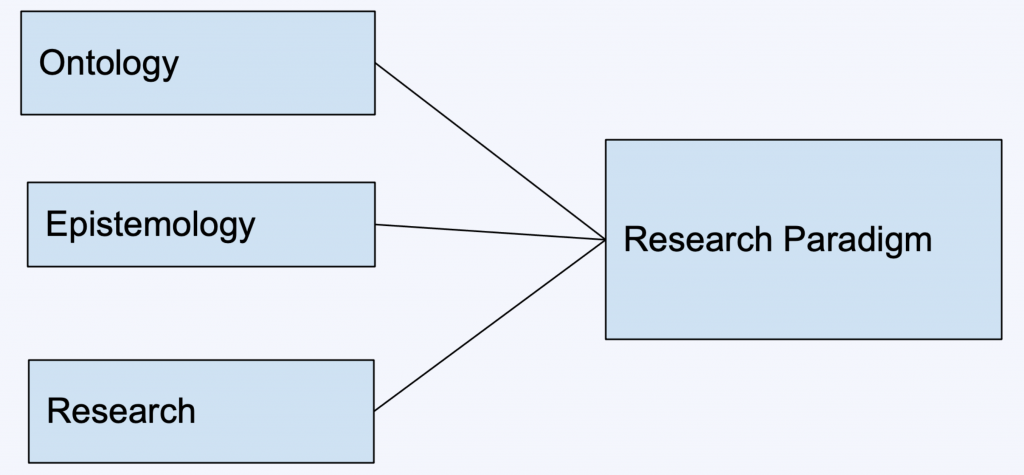
● Ontology answers the question: “What is reality?” That is, does a single reality exist within your research? An example of an ontological question would be: “Does God exist?” There are two possible realities (or ontologies) in response to this question: “Yes, God exists,” or “No, God does not exist.”
● Epistemology is the study of knowledge. It answers the question: “How is it possible to know reality?” Epistemology incorporates the validity, parameters, and methods of acquiring knowledge. An example of an epistemological question would be: “How is it possible to know whether God exists or not?”
● Research Methodology answers the question: “How do we go about discovering the answer or reality?” This includes the process of data collection and analysis. Research methodology should outline how you conduct your research and demonstrate that the findings are valid.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Together, ontology and epistemology comprise research philosophy.
Research philosophy combined with research methodology comprises a research paradigm.

Why Are Research Paradigms Important?
Research paradigms are important because they form the philosophical basis of a research project. Research paradigms influence how different schools of learning (such as the sciences versus the humanities) undertake their research. Once a research philosophy has been determined, an appropriate methodology can be chosen.
Furthermore, a knowledge of the philosophical foundation of your research will increase its quality and improve your performance in any analysis you may have to undergo!
Common Examples of Research Paradigms
1. Positivism
Positivists believe that there’s a single reality that’s possible to measure and understand. Because of this, they’re most likely to use quantitative methods in their research. Typically, positivists propose a hypothesis that can be proved or disproved using statistical data analysis. Positivism tends to investigate the existence of a relationship between two variables rather than the reason behind it.
2. Constructivism
Constructivists believe that there’s no single reality or truth, but rather multiple realities. They devote themselves to understanding and interpreting the meaning attached to an action. For this reason, constructivists tend to use qualitative research methods , such as interviews or case studies, which focus on providing different perspectives. Constructivism aims to provide the answer to “why.” For example, asking “Why do 25% of the employees of an organization regularly arrive late to work?” rather than merely establishing the relationship between two variables (e.g., time of arrival at work and availability of nearby parking).
3. Pragmatists
Pragmatists believe that reality is continually interpreted and renegotiated against the backdrop of new and unpredictable situations. Because of this, the philosophy they apply in research depends on the research question itself. Pragmatists often combine positivist and constructivist principles in the same research project, using both qualitative and quantitative methods to investigate different components of a research problem. They believe that the optimal research methods are those that most successfully answer the research question.
Merging Research Paradigms
While most social science research operates from either a positivist (experimental) or constructivist paradigm, it’s possible to combine both, as the field of psychology often does. Quantitative and qualitative methodology are frequently used together in psychology, illustrating the subject’s footing in multiple research paradigms (positivist and constructivist).

Expert Editing and Proofreading
If you’re writing a research proposal or paper , you’ll want to ensure that your writing is error-free, fluent, and precise. Although re-reading your own work is valuable, it can be very helpful to get another opinion on your writing. We offer a free trial of proofreading and editing services when you submit your first document. Find out more today!

Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
What is market research.
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
3-minute read
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....
The 7 Best Market Research Tools in 2024
Market research is the backbone of successful marketing strategies. To gain a competitive edge, businesses...
Google Patents: Tutorial and Guide
Google Patents is a valuable resource for anyone who wants to learn more about patents, whether...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Qualitative Methodologies in Organization Studies pp 1–31 Cite as
- Marta Strumińska-Kutra 4 &
- Izabela Koładkiewicz 5
- First Online: 14 December 2017
5660 Accesses
6 Citations
The main aim of the chapter is to discuss the case study method. We shall begin by confronting its definition. It is quite a challenge, as researchers representing various paradigms embark on this type of research project. These paradigms define the way we perceive the explored reality, our chances of understanding/cognizing it, and the acceptable research methods. As a consequence, not only is the case study subject to various definitions, but it is also employed to achieve manifold goals). Despite these differences, we can point out a number of characteristics that distinguish case study method; they shall be the focus of our discussion. As much as possible, we shall take into account the variety of perspectives in case study-based research, or recommend to readers the sources where they can find more detailed information on a particular issue. In this chapter, the presentation of premises and types of case studies will be followed by a manual, guiding readers in their endeavor to design their own research using the method discussed.
- Selection of cases
- Case based generalizations
- Theory and cases
- Types of case study
- Single case study
- Multiple case study
Author’s Note:
This chapter is substantially revised version of a chapter published in Jemielniak, D. ed. (2012) Badania jakościowe, PWN: Warszawa.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
The concept of strategy, as referred to by Robert Yin ( 2003a , b ), Norman Denzin and Yvonne Lincoln ( 2005 ), means research process design. Here, we shall use it interchangeably with two other terms: approach (Creswell 2007 ) and method. The latter is understood broadly as a set of directives and rules based on ontological and epistemological assumptions, indicating certain ways of conducting research. “Strategy ” and “method” are also referred to as synonyms of the case study methodology (Mills et al. 2010 ).
Even if the starting point of our research is interest in a particular case, we need to bolster our case with a theoretical framework, which will serve as a point of reference for research results.
We must remember that sampling should also involve documents, articles, posts on Internet fora, place and time of observation, and so on.
Here, “case” refers rather to a happening, an expression, or a statement that does not match the emerging pattern, and not to “case” understood as a bounded system/phenomenon.
In fact, the analysis is far less structured and multistage. It comprises abundant feedback and requires the researcher to revert to theoretical reflection; there are periods of “creative impotence” and the process is affected by the other publications read by researchers during the process.
Aaltio, I., & Heilmann, P. (2010). Case Study as a Methodological Approach. In A. J. Mills, G. Durepos, & E. Wiebe (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Case Study Research (pp. 66–76). London: Sage.
Google Scholar
Babbie, E. (2016). The Practice of Social Research (14th ed.). Belmont: Wadsworth/Cengage Learning.
Belz, F. M., & Binder, J. K. (2017). Sustainable Entrepreneurship: A Convergent Process Model. Business Strategy and the Environment, 26 (1), 1–17.
Article Google Scholar
Burawoy, M. (1998). The Extended Case Method. Sociological Theory, 16 , 4–33.
Charmaz, K. (2005). Grounded Theory in the 21st Century. Application for Advancing Social Justice Studies. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research (3rd ed., pp. 507–535). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Charmaz, K. (2006). Constructing Grounded Theory: A Practical Guide Through Qualitative Analysis . London: Sage.
Creswell, J. W. (2007). Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design. Choosing Among Five Approaches . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Davis, R. J. (2010). Case Study Database. In A. J. Mills, G. Durepos, & E. Wiebe (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Case Study Research (pp. 79–80). London: Sage.
Denis, J.-L., Lamothe, L., & Ann, L. (2001). The Dynamics of Collective Leadership and Strategic Change in Pluralistic Organizations. Academy of Management Journal, 44 , 809–837.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2005). Introduction. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research (3rd ed., pp. 1–32). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Eisenhardt, K. M. (1991). Better Stories and Better Constructs. The Case for Rigor and Comparative Logic. The Academy of Management Review, 16 , 620–627.
Eisenhardt, K. M., & Graebner, M. E. (2007). Theory Building From Cases. Opportunities and Challenges. The Academy of Management Review, 50 , 25–32.
Flyvbjerg, B. (2006). Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research. Qualitative Inquiry, 12 , 219–245.
Foucault, M. (1979). Discipline and Punish: The birth of the Prison . New York: Vintage.
Gawer, A., & Philipps, N. (2013). Institutional Work as Logics Shift: The Case of Intel’s Transformation to Platform Leader. Organization Studies, 34 , 1035–1071.
Gerring, J. (2004). What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for? American Political Science Review, 98 , 341–354.
Gerring, J. (2007). Case Study Research. Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research . Chicago: Aldine.
Hammersley, M., & Atkinson, P. (1992). Ethnography. Principles in Practice . London: Routledge.
Hassard, J., & Kelemen, M. (2010). Paradigm Plurality in Case Study Research. In A. J. Mills, G. Durepos, & E. Wiebe (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Case Study Research (pp. 147–152). London: Sage.
Haverland, M., & Yanow, D. (2012). A Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Public Administration Research Universe: Surviving Conversations on Methodologies and Methods. Public Administration Review, 72 , 401–408.
Hijmans, E., & Wester, F. (2010). Comparing Case Study with Other Methodologies. In A. J. Mills, G. Durepos, & E. Wiebe (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Case Study Research (pp. 176–179). London: Sage.
Kostera, M. (2008). Współczesne koncepcje zarządzania . Warszawa: Wydawnictwo Naukowe Wydziału Zarządzania UW.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. (1985). Naturalistic Inquiry . Beverly Hills: Sage.
Lipset, S. M., Trow, M. A., & Coleman, J. S. (1956). Union Democracy . Glencoe: Free Press.
Martin, J. A., & Eisenhardt, K. M. (2010). Rewiring: Cross-Business-Unit Collaborations in Multibusiness Organizations. Academy of Management Journal, 53 (2), 265–301.
Maxwell, J. A. (1996). Qualitative Research Design . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Michels, R. (1915). Political Parties . New York: Hearst’s International Library.
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Qualitative Data Analysis: An Expanded Sourcebook . London: Sage.
Mills, A. J., Durepos, G., & Wiebe, E. (Eds.). (2010). Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . London: Sage Publications.
Moriceau, J.-L. (2010). Generalizability. In A. J. Mills, G. Durepos, & E. Wiebe (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Case Study Research (pp. 419–422). London: Sage.
Morse, J. M., & Richards, L. (2002). Readme First for a User’s Guide to Qualitative Methods . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Rządca, R., & Strumińska-Kutra, M. (2016). Local Governance and Learning: In Search of a Conceptual Framework. Local Government Studies, 42 (6), 916–937. https://doi.org/10.1080/03003930.2016.1223632 .
Seawright, J., & Gerring, J. (2008). Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research. A Menu of Qualitative and Quantitative Options. Political Research Quarterly, 61 , 294–308.
Sharma, B. (2010). Postpositivism. In A. J. Mills, G. Durepos, & E. Wiebe (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Case Study Research (pp. 701–703). London: Sage.
Silverman, D. (2001). Interpreting Qualitative Data. Methods of Analysing Talk, Text and Interaction (2nd ed.). London: Sage.
Silverman, D. (2005). Doing Qualitative Research. A Practical Handbook (2nd ed.). London: Sage.
Stake, R. E. (2005). Qualitative Case Study. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research (3rd ed., pp. 443–466). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Stake, R. E., & Trumbull, D. J. (1982). Naturalistic Generalization. Review Journal of Philosophy and Social Science, 7 , 1–12.
Wadham, H., & Warren, R. C. (2014). Telling Organizational Tales: The Extended Case Method in Practice. Organizational Research Methods, 17 (1), 5–22.
Yin, R. K. (2003a). Case Study Research. Design and Methods . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Yin, R. K. (2003b). Applications of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Yin, R. K. (2010). Case Study Protocol. In A. J. Mills, G. Durepos, & E. Wiebe (Eds.), Encyclopaedia of Case Study Research (pp. 84–86). London: Sage.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
VID Specialized University, Oslo, Norway
Marta Strumińska-Kutra
Kozminski University, Warsaw, Poland
Izabela Koładkiewicz
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Teesside University Business School, Teesside University, Middlesbrough, United Kingdom
Malgorzata Ciesielska
Akademia Leona Koźmińskiego, Warsaw, Poland
Dariusz Jemielniak

Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Strumińska-Kutra, M., Koładkiewicz, I. (2018). Case Study. In: Ciesielska, M., Jemielniak, D. (eds) Qualitative Methodologies in Organization Studies. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65442-3_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-65442-3_1
Published : 14 December 2017
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-65441-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-65442-3
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Case study: a bridge across the paradigms
Affiliation.
- 1 School of Nursing, College of Health and Science, University of Western Sydney, New South Wales [corrected] Australia. [email protected]
- PMID: 16700753
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1800.2006.00309.x
Case study as a teaching and research tool has an extensive history in health and social sciences. Despite its suitability for many of the research questions that face nurses, nurses have not fully embraced case study as a comprehensive approach for research. The vagaries of the real-life clinical setting can confound methodologically purist researchers. Case study provides a milieu in which nurse researchers can respond to these vagaries and move towards a paradigmatic openness. In this paper, we argue that case study offers, as yet, under-explored and under-utilised potential as a bridge across the traditional research paradigms. We argue that case study has broad research application and epistemological, ontological and methodological flexibility. When used as a research approach, case study is both the process and end product of research. It provides a delineated boundary for inquiry, and a structural process within which any methods appropriate to investigating a research area can be applied.
Publication types
- Attitude of Health Personnel
- Data Collection
- Data Interpretation, Statistical
- Models, Nursing
- Nursing Records*
- Nursing Research / organization & administration*
- Nursing Theory
- Philosophy, Nursing*
- Reproducibility of Results
- Research Design / standards*
- Research Personnel / psychology
Research Paradigms and Methodologies Case Study
There are two types of research paradigms: positivism and interpretivism. While the first one is grounded in the belief that social reality is not influenced by research, the second one is quite the opposite. According to interpretivism, the investigation has a great impact on social reality (Collis & Hussey 2013). The two articles under analysis employ the interpretive paradigm since they both admit the influence made on social reality by the investigation. Saini and Budhwar (2008) analyze the issues of people management, and Şendoğdu, Kocabacak, and Güven (2013) investigate the connection between human resource management and organizational commitment.
The methodology used in Saini’s and Budhwar’s (2008) study is a case study. This method has several benefits. First of all, it allows researchers to perform a thorough investigation of the chosen issue. Also, case studies may promote new research. Finally, this method suggests new insight into the analyzed phenomena (Kin 2013). However, case studies also have some limitations. The major disadvantage of case studies is that they cannot be repeated. Thus, there is no possibility to compare results at different points. Another problem that may occur is researcher bias. Also, case studies do not present the opportunity to create a classification since their sample size is usually too small (Kin 2013).
The method employed in the article by Şendoğdu, Kocabacak, and Güven (2013) is a questionnaire. The strengths of such a method are numerous. Questionnaires are practical because they allow researchers to collect much data from many participants within a short time. Also, the questionnaires are not expensive. Another benefit is that the analysis of data gathered with the help of this method is relatively easy and inexpensive (Ang 2014). It is a good idea to use questionnaires because once the results have been analyzed, they may be compared and contrasted with the findings of other studies to assess the divergences. Finally, data obtained through questionnaires may be employed to build new theories and methods (Ang 2014). However, along with numerous advantages, questionnaires have some serious limitations. The most serious one is that such a method does not provide enough validity. Also, there is no possibility to check whether the participants are being honest while answering the questions. Another problem is that different people may understand the questions, not in the same way, which results in the inconsistency of findings. Finally, there is a danger of researchers’ bias when creating the questions since they may have some assumptions which can lead them to neglect some crucial issues (Ang 2014).
Since my research is also focused on human resource management, I could employ some of the approaches used by the authors of the analyzed articles. I think that a questionnaire is the most suitable method for my future research because it is the easiest way of finding out the opinions of many people within a short period, which will give me much information for analysis. However, I will need to be cautious regarding the ethical considerations of research (Anderson 2013). Also, I will have to think carefully about my study’s feasibility. I think that employing the questionnaire method is much easier in both organizational and financial aspects than the method of the case study. Therefore, I would rather choose a questionnaire because it has many advantages, and the limitations may be avoided if I plan the study thoroughly.
Reference List
Anderson, V 2013, Research methods in human resource management , 3rd edn, London, UK: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development.
Ang, SH 2014, Research design for business and management , Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Collis, J & Hussey, R 2013, Business research: a practical guide for undergraduate and postgraduate students , 4th edn, Palgrave-MacMillan, London.
Kin, RY 2013, Case study research: design and methods , 5th edn, Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Saini, DS & Budhwar, PS 2008, ‘Managing the human resource in Indian SMEs: the role of indigenous realities’, Journal of World Business , vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 417-434.
Şendoğdu, AA, Kocabacak, A & Güven, Ş 2013, ‘The relationship between human resource management practices and organizational commitment: a field study’, Social and Behavioral Sciences , no. 99, pp. 818-827.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, December 25). Research Paradigms and Methodologies. https://ivypanda.com/essays/research-paradigms-and-methodologies/
"Research Paradigms and Methodologies." IvyPanda , 25 Dec. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/research-paradigms-and-methodologies/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Research Paradigms and Methodologies'. 25 December.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Research Paradigms and Methodologies." December 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/research-paradigms-and-methodologies/.
1. IvyPanda . "Research Paradigms and Methodologies." December 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/research-paradigms-and-methodologies/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Research Paradigms and Methodologies." December 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/research-paradigms-and-methodologies/.
- Judaism and Taoism: Comparison and Contrast
- Positivism and Interpretivism
- Epistemology Framework of Business Research
- Research Philosophy: Importance and Types
- Social Theories in American Education System
- Organizational Culture Effect on Employee Performance
- The "Johnny Harris" YouTube Channel and Perception
- Business Research Methodology and Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science: Paradigm, Ontology, Epistemology
- "Responsible Tourism: An Inductive Approach" by Ramachandran
- E-Mail Interviewing in Research: Benefits and Limits
- Questionnaires Creation: Validity and Reliability
- Quasi-Experimental Designs: Merits and Weaknesses
- Disguised Observation: Students Food and Drink Preferences
- The Process of Designing a Questionnaire
Where is customer care in 2024?
Customer care leaders are facing their greatest challenge in decades. They must prepare their organizations for an AI-enabled future while simultaneously meeting tough commercial targets and rising customer expectations. Our latest global survey suggests that many companies are struggling on all these fronts.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Eric Buesing , Maximilian Haug, Paul Hurst, Vivian Lai, Subhrajyoti Mukhopadhyay, and Julian Raabe , representing views from McKinsey’s Operations Practice.
Major disruptions are always painful, and the transition from a care paradigm dominated by human agents to one steered by AI technologies may be the biggest disruption in the history of customer service. Can organizations find a route to hyperefficient, digitized customer care while retaining the personal contact and responsiveness that customers require?
Right now, many customer care leaders feel trapped in no-man’s-land. Technology has enabled them to evolve their operations significantly, and the traditional call center environment is rapidly becoming a thing of the past. Yet when these digitally enabled models underperform—and they often do—companies need to master entirely new approaches to performance improvement alongside their traditional tool kits.
Customer care in the spotlight
The key findings in this article are based on McKinsey’s fourth global survey of customer care executives. This survey was our largest yet, gathering the views of more than 340 leaders at the director, senior director, vice president, and C-suite levels. Respondents came from companies with annual revenues of $100 million to $10 billion-plus, representing every major industry segment.
The majority of respondents said that the companies they worked for were headquartered in North America (just over 50 percent) or Western Europe (almost 25 percent), with 10 percent headquartered in India and 4 percent in China. Most respondents said their organizations operated in multiple regions: 75 percent reported operating in North America, 58 percent in Europe, 57 percent in Asia–Pacifc, 39 percent in the Middle East and Africa, and 37 percent in Latin America. We plan to expand future research to include more organizations headquartered outside North America and Western Europe.
To make matters worse, executives say that most of the challenges highlighted in our last survey are still present today (see sidebar, “Customer care in the spotlight”). Those challenges include rising call volumes, high levels of employee attrition, and persistent talent shortages. Meanwhile, some of the largest consumer-facing technology organizations in the world have become exceptional at digitally enabled customer care, which is lifting customer expectations everywhere, piling further pressure onto customer care staff and leadership at other companies.
Our survey reveals three major themes that are top of mind for customer care leaders. First, their priorities are shifting, from an overwhelming focus on customer experience to a multidimensional approach that also emphasizes revenue goals and technology transformation. Second, they are working hard to build future-ready AI-enabled ecosystems for their operations. Finally, they are boosting their capabilities by investing in employee upskilling programs and building stronger outsourcing relationships.
Would you like to learn more about our Operations Practice ?
Reprioritizing core operations.
When we began monitoring the sentiment of customer care leaders in 2016, their priorities were clear. Customer experience came first, followed at a distance by operational improvement, technology transformation, and revenue generation—in that order.
Over the past seven years, those priorities have converged (Exhibit 1). Revenue generation, which was mentioned by about one in 20 customer care leaders in our first survey, has been rising steadily in importance ever since. It is now a priority for a third of customer care leaders. But over the past two years, technology enhancements and operational improvements have seen the fastest increases. The expectation that customer care functions can do it all and do it well has never been higher.
Leaders also understand that they need to engage with their customers to delight them. Currently, only 11 percent of respondents say reducing contact volume is important to them, a 20-percentage-point drop over 12 months. Indeed, 57 percent of leaders expect call volumes to increase by as much as one-fifth over the next one or two years.
Separate research suggests that these leaders are right to stay focused on direct personal interaction, even when many of their customers are young digital natives. In a recent McKinsey survey of 3,500 consumers, respondents of all ages said that live phone conversations were among their most preferred methods of contacting companies for help and support. That finding held true even among 18- to 28-year-old Gen Z consumers, a cohort that favors text and social messaging for interpersonal communications.
There’s also evidence that younger consumers are getting tired of the digital self-service paradigm. One financial-services company reports that its Gen Z customers are 30 to 40 percent more likely to call than millennials, and they use the phone as often as baby boomers. Premium-segment customers of all ages also prefer the phone, with many saying that live phone support is part of the premium service they are paying for.
These findings don’t point to a future of phone-only customers, however. While customers of all generations prioritize support from a real person, they also want the flexibility to use different channels according to their needs. Digital-chat services have achieved a high level of acceptance across generations, and email remains important, especially for older consumers (Exhibit 2).
The need to excel in service across multiple channels creates extra challenges for customer care leaders, especially when budgets are tight. And 37 percent of respondents in our survey say that cost is still a key priority. This tension is driving companies to look for ways to control the customer care costs that go beyond call volume reduction, with automation and outsourcing the most frequently cited levers.
Creating a future-ready AI ecosystem
The tensions in modern customer care are clearly seen in companies’ approaches to advanced digital technologies. Our survey demonstrates that digital has already become a decisive differentiator. Among respondents who report that their operations are delivering better-than-expected performance, more than half have high levels of digital integration. Banking, telecommunications, and travel and logistics are among the leading industries in this regard.
Those high performers are in the minority, however. Only 8 percent of respondents from North America report greater-than-expected satisfaction with their customer performance. In Africa, Europe, and the Middle East, the figure is 5 percent. Among organizations reporting that performance was in line with or lower than expected, more than 80 percent also say their levels of digital integration are partial or low.
Leaders agree that they need to get digital right. More than half of the respondents to our survey expect the share of inbound contacts that take place through digital channels to exceed 40 percent in the next three years.
Artificial intelligence will play a decisive role in future customer care ecosystems. Respondents to our survey are already deploying AI tools in a variety of applications, including chatbots and automated email response systems, training and support for call center agents, back-office analytics, and decision making.
Over the past 12 months, the availability of powerful generative AI (gen AI) tools, especially large language models (LLMs) that can parse and respond to unstructured text or speech, has opened new possibilities for technology in customer care. More than 80 percent of respondents are already investing in gen AI, or expect to do so in the coming months, with leaders highlighting a wide range of potential applications.
One European subsidiary of a global bank replaced its well-established rules-based customer chatbot with a new system based on gen AI technology. Seven weeks after launch, the AI chatbot was 20 percent more effective at successfully answering customer queries than the old tool. The bank has already identified a road map of improvements that could double its performance in the coming months.
Early adopters are extremely ambitious about the potential of gen AI. The executive in charge of customer care at one major global organization told us that they expect 100 percent of customer interactions to be AI-enabled in the coming years, using a combination of technologies including new virtual assistants, agent-assist tools, and AI-powered voice analytics.
For most companies, however, the gen AI customer care revolution is still in its early stages. Leaders highlight multiple issues that are making it hard for them to integrate these technologies into their existing processes and workflows. The issues include technical challenges regarding deployment and scaling; concerns about safety, security, and governance; and difficulties in defining the desired outcomes from, or business case for, gen AI investments (Exhibit 3).
Learn more about Customer Care
Rethinking skills.
Today, customer care organizations lack many of the critical skills they need to deliver excellent service and navigate the transition to a digitally mediated, AI-enabled world. In part, that’s because customer care leaders have been running to stand still. Record levels of staff attrition following the COVID-19 pandemic meant that supervisors spent much of their time interviewing and bringing new staff up to speed. They spent less time mentoring their established teams, a problem exacerbated by the introduction of hybrid and remote working arrangements. Some agents and team leaders have spent years working with little interaction or coaching from their managers.
Staff turnover has now slowed, and two in three leaders in our latest survey say upskilling and reskilling are critical priorities. Companies highlight a range of benefits that accrue from effective upskilling and reskilling programs, including improvements to employee morale, increased productivity, and faster adoption of new technologies and working methods. Meanwhile, technology is changing upskilling programs. Twenty-one percent of leaders tell us that they are already using AI-based tools to train and support their customer care staff.
AI-based agent support systems are already becoming a key tool for companies seeking to offer extremely effective personal service to demanding customers. These systems can help agents resolve complex queries the first time, simultaneously reducing care costs and boosting customer experience.
One global construction equipment company, for example, uses a gen AI system to help its call center staff navigate thousands of pages of technical-support documentation. The system selects the appropriate steps to resolve a customer’s problem in seconds, based on free text questions entered by the agent and background information such as the serial numbers of vehicles and parts. The tool has cut average call resolution times from around 125 minutes to a few seconds, and it is currently saving customers €150,000 to €300,000 per day in reduced asset downtime.
Elsewhere, companies are using AI to transform the way they manage and support their customer care agents. New AI-based tools can optimize call volume forecasting, for example. This approach helped one company improve forecast accuracy by seven percentage points, while halving the work required to manage team capacities and schedules. The change improved customer service levels by more than 10 percent, while cutting staffing and overtime costs by more than 5 percent.
Companies are also looking outside their organizations for innovative ways to fill capability gaps. Outsourcing, once viewed primarily as a way to reduce costs, is increasingly seen as an effective source of additional skilled capacity and innovation capabilities. Fifty-five percent of the companies in our survey currently outsource part of their customer care operations, and 47 percent of those organizations expect to increase their outsourcing over the next two years.
Outsourcing relationships are becoming deeper too, with respondents telling us that they are now using their business process outsourcing for a range of activities that extends far beyond traditional call and email handling. They include content management and digital-marketing services, payments handling, and the development of AI-based customer care tools. Following the blueprint established by major players in the industrial products, medical device, software, and e-commerce sectors, some companies are now working with outsourcing partners to set up global innovation hubs that will drive the development of next-generation customer care technologies.
Our survey suggests that customer care organizations are running at two different speeds. In the fast lane, top performers have seized the opportunities presented by advances in digital technologies. With ruthless prioritization, they are investing capital to drive efficiency and service excellence across the customer journey. The best have already reshaped their organizations around highly integrated digital platforms. One high-performing company with more than 5,000 service agents is on track to deliver 75 digital-experience improvements this year, for example.
Other companies are still in the slow lane, struggling to fit a patchwork of digital point solutions into legacy care ecosystems. Unsure where to put their dollars, they are trapped in a cycle of continual system adaptation with no clear destination or road map.
In 2024, both types of organizations may need to shift their positions on the road. Gen AI is raising the bar for performance, productivity, and personalization in customer care, and tomorrow’s fully AI-enabled care organizations will operate very differently from those of today. It’s time for companies to look at their care ecosystems with fresh eyes. They should formulate an independent perspective on the changing expectations of their customers and the role of advanced AI in their organization. The future of customer care is calling. Leaders should answer with a bold vision and an aggressive time line for change.
Eric Buesing is a partner in McKinsey’s Charlotte office, where Paul Hurst is an associate partner; Maximilian Haug is an associate partner in the Boston office; Vivian Lai is a consultant in the New York office; Subhrajyoti Mukhopadhyay is an expert in the Chicago office; and Julian Raabe is a partner in the Munich office.
The authors wish to thank Jorge Amar, Brian Blackader, Marcela Guaqueta, Suryansha Gupta, and Josh Wolff for their contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

The state of customer care in 2022

How AI is helping revolutionize telco service operations

How AI-driven nudges can transform an operation’s performance

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research paradigms are essential to producing rigorous research (Brown & Dueñas, 2019).They represent a researcher's beliefs and understandings of reality, knowledge, and action (Crotty, 2020; Guba & Lincoln, 1994).In qualitative research, a wide variety of paradigms exist and qualitative researchers select paradigms which are theoretically aligned with their views of how power relates to ...
The research paradigm helps you to form a research philosophy, which in turn informs your research methodology. Your research methodology is essentially the "how" of your research - how you design your study to not only accomplish your research's aims and objectives but also to ensure your results are reliable and valid.
Abstract. Case study research though increasingly popular in social sciences for positivist and intrepretivist research, a kind of confusion is prevalent when it is used ignoring its philosophical ...
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Common Examples of Research Paradigms. 1. Positivism. Positivists believe that there's a single reality that's possible to measure and understand. Because of this, they're most likely to use quantitative methods in their research. Typically, positivists propose a hypothesis that can be proved or disproved using statistical data analysis.
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
The purpose of case study research is twofold: (1) to provide descriptive information and (2) to suggest theoretical relevance. Rich description enables an in-depth or sharpened understanding of the case. It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. Case studies are inherently multimodal or mixed ...
Within a qualitative paradigm, case study research arises from the desire to understand complex social phenomena and may be utilized in numerous arenas of social science and applied disciplines, such as psychology, sociology, anthropology, environmental studies, political science, business, education, nursing, social work and economics. ...
The main aim of the chapter is to discuss the case study method. We shall begin by confronting its definition. It is quite a challenge, as researchers representing various paradigms embark on this type of research project. These paradigms define the way we perceive...
Case study provides a milieu in which nurse researchers can respond to these vagaries and move towards a paradigmatic openness. In this paper, we argue that case study offers, as yet, under-explored and under-utilised potential as a bridge across the traditional research paradigms. We argue that case study has broad research application and ...
Definitions of qualitative case study research. Case study research is an investigation and analysis of a single or collective case, intended to capture the complexity of the object of study (Stake, Citation 1995).Qualitative case study research, as described by Stake (Citation 1995), draws together "naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological, and biographic research methods ...
Research methods are the means through which data is collected and analysed in a study (Rehman and Alharthi, 2016). The set of methods that can be used in a given study depends on the paradigm in ...
Research Paradigms Interpretive Accounting Research (IAR) Case Study Research Interview Techniques Constant Comparative Method *University of Jember, Indonesia and University of South Australia Introduction Research paradigms address the philosophical dimensions of social sciences. A research paradigm is a set of fundamental assumptions
Similar research is encouraged across a greater number of case studies to validate the process of using a constructivist and critical realist paradigm to gain a more insightful understanding of ...
The research paradigm is the framework into which the theories and practices of your discipline fit to create the research plan. This foundation guides all areas of your research plan, including the aim of the study, research question, instruments or measurements used, and analysis methods. Most research paradigms are based on one of two model ...
Case study provides a milieu in which nurse researchers can respond to these vagaries and move towards a paradigmatic openness. In this paper, we argue that case study offers, as yet, under-explored and under-utilised potential as a bridge across the traditional research paradigms. We argue that case study has broad research application and ...
Research paradigms guide scientific discoveries through their assumptions and principles. Understand. ... Case Study: Lee's Experiment. In Box 3, we present a scenario in which a resident ("Lee") injects 10 times the normal medication dose. In this final section, we use this sample case to prompt an application of a positivist paradigm to ...
Answer: Qualitative research involves the collection of non-numerical data through observational methods. Studies of human behaviour along with other types of research in the social sciences often use qualitative methodologies. Unlike studies in the natural sciences, which employ a positivist research paradigm that relies on experimentation ...
Within this paradigm, case studies are designed based on natural science criteria such as controlled observations, controlled deductions, replication and generalisability (Lee, 1989). Sarker and Lee's (2002) study of 'business process redesign in ERP implementation' is a good example of positivist case study research. Several propositions ...
Case study research facilitates the in-depth, real-life exploration of complex phenomena from multiple perspectives. It is a well-established approach to deal with the complexities involved in palliative care research. Case studies are not aligned to a single epistemological paradigm but are defined by the identification of the case to be studied.
The methodology used in Saini's and Budhwar's (2008) study is a case study. This method has several benefits. First of all, it allows researchers to perform a thorough investigation of the chosen issue. Also, case studies may promote new research. Finally, this method suggests new insight into the analyzed phenomena (Kin 2013).
All Answers (17) John Steven Edwards. Aston University. Kien Nguyen-Trung. Certainly you can work from a pragmatist paradigm if it fits with the rest of your research project. Action research and ...
The study adopts an interpretive paradigm and uses a qualitative approach rooted in a case study design. Face-to-face interviews were employed as the data collection tool, and latent thematic analysis was used to analyse emergent themes. ... The interpretivist research paradigm: A subjective notion of a social context. International Journal of ...
The concepts of healthy cities and smart cities are popular in emerging research in the 21st century. This study focuses on the existing interrelations between the two notions in terms of socio-spatial quality, technology, and innovation, particularly regarding industrial sites that no longer have a role and constitute 'urban voids' with high volumetric concentrations. The fast expansion ...
This article explicates pragmatism as a relevant and useful paradigm for qualitative research on organizational processes. The article focuses on three core methodological principles that underlie a pragmatic approach to inquiry: (1) an emphasis on actionable knowledge, (2) recognition of the interconnectedness between experience, knowing and acting and (3) inquiry as an experiential process.
Our survey reveals three major themes that are top of mind for customer care leaders. First, their priorities are shifting, from an overwhelming focus on customer experience to a multidimensional approach that also emphasizes revenue goals and technology transformation. Second, they are working hard to build future-ready AI-enabled ecosystems ...