- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers


Everything You Need to Know About Thesis Statement

Table of Contents

Persuasion is a skill that every human leverages to achieve their goals. For example, you persuade your friends to join you on some trip, your parents to purchase you an automobile, and your committee or audience to provide you approval for your research proposal.
Likewise, every scholarly task is aimed to persuade your readers or audience for certain goals. And the end goal is to incline the readers towards your perspective (facts and evidence-based). So, the act of convincing readers of your viewpoints via research work is often termed academic argument, and it follows a predetermined pattern of guidelines-based writing. After providing a comprehensive introduction to the research topic, you are supposed to state your perspective on the topic in a sentence or two, known as Thesis Statement . It summarizes the argument you will make throughout the paper.
Also, the Thesis Statement often serves as an answer to your research question. Thus, the thesis statement is a must for every research paper and scholarly work.
What is Thesis Statement?

A Thesis Statement:
- Describes how you interpret the subject matter's cause, significance, and results.
- Is a guideline for the paper. In other words, it provides an understanding of the research topic.
- Directly answers the question you are asked. The thesis is not the question itself but an interpretation of it. For example, a thesis can be about World War II, and it should also provide a way to understand the war.
- Claims that other people might disagree with.
- Is a single sentence at the beginning of your paper or near the end of the first para (where you present your argument to the reader). The body of the essay is the rest of the paper. It gathers and organizes evidence to support your argument.
A thesis statement should be concise and easily understandable. Use it as a magnet to attract your readers to keep them reading your paper till the end.
What is the purpose or the goal of the thesis statement?
The real purpose of the thesis statement is:
- To establish a gateway through which your readers can make an entrance into your research paper.
- To bring the entire research paper together to an epicenter of various arguments provided throughout the paper.
Simply put, the goal of writing a strong thesis statement is to make your research paper appear interesting enough for the readers to understand it and prove your arguments right completely.
Additionally, the goal of the thesis statement varies from the kind of research you are presenting. If your thesis provides some claims, justifications, or study, you should present an argumentative thesis statement . However, if your thesis is based on analysis, interpretation, demonstration of cause and effect, comparisons, and contrast, you should develop a persuasive thesis statement.
What is the length of an Ideal Thesis Statement?
You should write your thesis statement in 1-2 sentences. Ideally, it should not be more than 50 words in total.
Also, you should try inserting the thesis statement at the end of the topic introduction or just before the background information.
While writing your thesis statement, be mindful that a thesis statement is never meant to be factual. Your thesis statement is one of the most important elements of your thesis that will help your audience understand what you discuss throughout your paper. So, ensure that your thesis statement must appear like an arguable statement, not a factual one.
Many early researchers or young scholars choose to write factual statements as thesis statements as they are easy to prove. However, resorting to factual statements instead of arguable ones will overshadow your analytical and critical thinking skills, which readers anticipate in your paper.
How to Start a Thesis Statement?

The thesis statement is an outline of your research topic in one sentence. Therefore, you must write it in a concise and catchy style. So, here are a few quick tips that help you understand how to start a thesis statement for a research paper:
Discover Your Research Question
Once the subject matter is finalized for writing a research paper, the next requirement is to figure out the research question. While formulating your research question, make sure that it shows the gaps in the current field of study and should serve as a primary interrogation point for your research.
Figure out the answer and develop your argument
Carry out intensive research to determine the perfect answer for your research question. Your answer should further guide you to structure your entire research paper and its content flow.
For example, if you write an argumentative paper, craft your opinion and create an argument. Then, develop your claim against the topics you want to cover and justify it through various data & facts.
Establish back-up for your Answer with Evidence
The more you research, the more you will learn about the variations in the research answer that you were trying to formulate. Similarly, with various sources and newer evidence coming up, you should be able to make an answer that should stand coherently, correctly, relevant, and justified enough. The answer should enhance the reader’s understanding of your paper from beginning to end.
How to determine if my thesis statement is strong?

Make a self-evaluation of your thesis statement and check if it stands the following interrogation:
- Does it answer the question?
Re-read to understand the question prompt to ensure that your answer or the thesis statement itself doesn't skip the focus of the question. Try rephrasing it if you feel that the question prompt is not structured or appropriately discussed.
- Does my thesis statement appear like an argument (for or against)?
Suppose you have chosen to present the facts and rationality behind it in the best way possible and assume that no one would or could ever disagree with it. It indicates that you've presented a summary instead of presenting an argument. So, always pick an opinion from the topic and justify your arguments backed with various evidence.
- Is the Thesis Statement explicit and specific?
It may lack a strong argument if you have written a very general statement or vaguely crafted a thesis statement. Your audience will figure it out instantly.
Therefore, if you have used words like “good’’ or “bad,” try to put it more specifically by answering and figuring out “Why something is good”? Or ''What makes something good or bad”?
- Does it clear the “So What” test?
After reading any research paper, the prompt question that pops up from a reader's mind is, "So What?". Now, if your thesis statement urges the reader with such questions, you need to develop a strong argument or relationship that bridges your research topic to a more significant real-world problem.
- Does it go beyond the “How” and “Why” assessments?
After going through your thesis statement, if the readers come up with questions like "How" and 'Why," it indicates that your statement failed to provide the reader with the critical insights to understand your thesis statement and is too open-ended. So, you must provide your readers with the best statement explaining the introduction's real significance and the impending need for further research.
Thesis Statement Examples
Follow through with some interesting and creative thesis statements to clarify your doubts and better understand the concept.
Example 1: Social Media affects public awareness both positively and negatively
Yeah, it does answer the question. However, the answer is pretty vague and generic as it shows the effects both positively and negatively.
Not accurately. The statement can be argued only with the people having opinions either on positive or the negative aspect. Therefore, it fails to address every section of the audience.
- Is the Thesis statement specific enough?
Not exactly. This thesis statement doesn't provide any details on positive and negative impacts.
No, not at all. The thesis statement stated above provides no clarifications over how the positive or negative impacts build up or the factors that build up such impacts.
Again, No. It fails to justify why anyone should bother about the impacts, be it positive or negative.
A stronger and alternate version for the above thesis statement can be:
Since not every piece of information provided on social media is credible and reliable enough, users have become avid consumers of critical information and, therefore, more informed.
Even though the above thesis statement is lengthy, it answers every question and provides details over cause, effect, and critical aspects that readers can easily challenge.
Example 2: Analytical Thesis Statement
- Water is extremely important for human survival, but consuming contaminated water poses many health risks.
- The hibernation period is one of the most important periods in animals for healthy well-being. Still, it renders them in a state of weakness and exposed to external and environmental threats.
Example 3: Argumentative Thesis Statement
- At the end of the nineteenth century, French women lawyers experienced misogynist attacks from male lawyers when they attempted to enter the legal profession because male lawyers wanted to keep women out of judgeships.
- High levels of alcohol consumption have detrimental effects on your health, such as weight gain, heart disease, and liver complications.
Tips for writing a Strong Thesis Statement

A strong thesis statement is the foremost requirement of academic writing, and it holds greater importance when written for research papers. However, it becomes more crucial when you want your readers to get convinced of your opinions or perspective of the subject matter.
Below are some pro-tips that can help you crack the code of how to write a strong thesis statement, especially for research papers, thesis, and dissertations:
Keep it specific
Readers often get disappointed and confused when you present a weak argument based on a generic thesis statement. To develop a strong thesis statement, focus on one key aspect and develop it further.
Keep it simple and clear
The essence of your entire research paper is dependent on your thesis statement. Also, a strong thesis statement stays hinged over the clarity it provides. Therefore, don't disrupt the meaning or clarity of your research paper by using some jargonish words or complexing it by combining different concepts.
Ingrain your opinions
Your thesis statement should explicitly display your opinion or position for the subject matter under discussion. Your reader wants to understand your position in detail and the factors you will justify with evidence and facts.
Make it unique and Original
Your audience or the readers have gone through the subject matter several times in their careers. Hence, you must present your thesis statement in a unique and completely original form. Never use generic statements; grow some risk-taking capability and surprise your readers.
Keep it Concise and Coherent
Your thesis statement can be considered good only if it is concise yet informational. Don’t make it wordy in any case, and never go beyond more than 50 words.
Additionally, your research paper will discuss many aspects of a topic. Still, in the end, every single aspect should come together to form a coherent whole, addressing, explaining, and justifying the research question.
Conclusion: How to write a Thesis Statement?
A strong thesis statement is the one of the most important elements of your research paper. The thesis statement always serves as a pillar that carries the entire load of a research paper and it’s several sections.
Whether your research paper is worthy of your audience time or not, entirely hinges upon your thesis statement. A thesis statement always depicts the plan for the research but a good thesis statement reflects your opinions, viewpoints and of course the trajectory that it sets for the entire paper.
So, always try to write a good thesis statement by carefully following its structure, about which we have already discussed.
Before you go: In view of your interest in simplifying research workflows, we suggest you take a look at SciSpace . In a single portal, you can complete all your research writing tasks, including literature searches.

SciSpace provides researchers, universities, and publishers with all the tools they need. Our comprehensive research repository features more than 200 million research papers from multiple disciplines with SEO-optimized abstracts, a publicly visible profile to highlight your expertise, a specially-built collaborative text editor, 20,000+ journal templates, and more.

Hope the article has explained everything that you needed to know about the thesis statement. In case you have any questions or doubts, join our SciSpace (Formerly Typeset) community platform and put your questions there. We will make sure that you get your answers at the earliest.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on September 14, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master’s program or a capstone to a bachelor’s degree.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation , it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: choosing a relevant topic , crafting a proposal , designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement for Master’s programs, and is also sometimes required to complete a bachelor’s degree in liberal arts colleges.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
- In other countries (particularly the UK), a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: “Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807” by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: “’A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man’: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947″ by Julian Saint Reiman.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the “Insert Caption” feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialized or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetize the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyzes the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasize what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense , your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5–7% of your overall word count.
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation , you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimizing confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A thesis is typically written by students finishing up a bachelor’s or Master’s degree. Some educational institutions, particularly in the liberal arts, have mandatory theses, but they are often not mandatory to graduate from bachelor’s degrees. It is more common for a thesis to be a graduation requirement from a Master’s degree.
Even if not mandatory, you may want to consider writing a thesis if you:
- Plan to attend graduate school soon
- Have a particular topic you’d like to study more in-depth
- Are considering a career in research
- Would like a capstone experience to tie up your academic experience
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 20, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Locating and Evaluating Thesis Statements
The following video offers a definition of thesis statements, and guidance for finding thesis statements as you read.
Pay attention to the difference between explicit thesis statements and implicit (or implied ) thesis statements .
(This video was made for a specific class, so it will make references to assignments that won’t apply to you. You can also stop watching at 6:00, since the video then proceeds to writing thesis statements, which is not our focus at the moment.)
- Video: Locating and Evaluating Thesis Statements. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Locating, Evaluating, & Writing Thesis Statements. Authored by : H Ortiz. Located at : https://youtu.be/8a0T_ySxda8 . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- Table of Contents
Instructor Resources (available upon sign-in)
- Overview of Instructor Resources
- Quiz Survey
Reading: Types of Reading Material
- Introduction to Reading
- Outcome: Types of Reading Material
- Characteristics of Texts, Part 1
- Characteristics of Texts, Part 2
- Characteristics of Texts, Part 3
- Characteristics of Texts, Conclusion
- Self Check: Types of Writing
Reading: Reading Strategies
- Outcome: Reading Strategies
- The Rhetorical Situation
- Academic Reading Strategies
- Self Check: Reading Strategies
Reading: Specialized Reading Strategies
- Outcome: Specialized Reading Strategies
- Online Reading Comprehension
- How to Read Effectively in Math
- How to Read Effectively in the Social Sciences
- How to Read Effectively in the Sciences
- 5 Step Approach for Reading Charts and Graphs
- Self Check: Specialized Reading Strategies
Reading: Vocabulary
- Outcome: Vocabulary
- Strategies to Improve Your Vocabulary
- Using Context Clues
- The Relationship Between Reading and Vocabulary
- Self Check: Vocabulary
Reading: Thesis
- Outcome: Thesis
- The Organizational Statement
- Self Check: Thesis
Reading: Supporting Claims
- Outcome: Supporting Claims
- Types of Support
- Supporting Claims
- Self Check: Supporting Claims
Reading: Logic and Structure
- Outcome: Logic and Structure
- Rhetorical Modes
- Inductive and Deductive Reasoning
- Diagramming and Evaluating Arguments
- Logical Fallacies
- Evaluating Appeals to Ethos, Logos, and Pathos
- Self Check: Logic and Structure
Reading: Summary Skills
- Outcome: Summary Skills
- How to Annotate
- Paraphrasing
- Quote Bombs
- Summary Writing
- Self Check: Summary Skills
- Conclusion to Reading
Writing Process: Topic Selection
- Introduction to Writing Process
- Outcome: Topic Selection
- Starting a Paper
- Choosing and Developing Topics
- Back to the Future of Topics
- Developing Your Topic
- Self Check: Topic Selection

Writing Process: Prewriting
- Outcome: Prewriting
- Prewriting Strategies for Diverse Learners
- Rhetorical Context
- Working Thesis Statements
- Self Check: Prewriting
Writing Process: Finding Evidence
- Outcome: Finding Evidence
- Using Personal Examples
- Performing Background Research
- Listening to Sources, Talking to Sources
- Self Check: Finding Evidence
Writing Process: Organizing
- Outcome: Organizing
- Moving Beyond the Five-Paragraph Theme
- Introduction to Argument
- The Three-Story Thesis
- Organically Structured Arguments
- Logic and Structure
- The Perfect Paragraph
- Introductions and Conclusions
- Self Check: Organizing
Writing Process: Drafting
- Outcome: Drafting
- From Outlining to Drafting
- Flash Drafts
- Self Check: Drafting
Writing Process: Revising
- Outcome: Revising
- Seeking Input from Others
- Responding to Input from Others
- The Art of Re-Seeing
- Higher Order Concerns
- Self Check: Revising
Writing Process: Proofreading
- Outcome: Proofreading
- Lower Order Concerns
- Proofreading Advice
- "Correctness" in Writing
- The Importance of Spelling
- Punctuation Concerns
- Self Check: Proofreading
- Conclusion to Writing Process
Research Process: Finding Sources
- Introduction to Research Process
- Outcome: Finding Sources
- The Research Process
- Finding Sources
- What are Scholarly Articles?
- Finding Scholarly Articles and Using Databases
- Database Searching
- Advanced Search Strategies
- Preliminary Research Strategies
- Reading and Using Scholarly Sources
- Self Check: Finding Sources
Research Process: Source Analysis
- Outcome: Source Analysis
- Evaluating Sources
- CRAAP Analysis
- Evaluating Websites
- Synthesizing Sources
- Self Check: Source Analysis
Research Process: Writing Ethically
- Outcome: Writing Ethically
- Academic Integrity
- Defining Plagiarism
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Using Sources in Your Writing
- Self Check: Writing Ethically
Research Process: MLA Documentation
- Introduction to MLA Documentation
- Outcome: MLA Documentation
- MLA Document Formatting
- MLA Works Cited
- Creating MLA Citations
- MLA In-Text Citations
- Self Check: MLA Documentation
- Conclusion to Research Process
Grammar: Nouns and Pronouns
- Introduction to Grammar
- Outcome: Nouns and Pronouns
- Pronoun Cases and Types
- Pronoun Antecedents
- Try It: Nouns and Pronouns
- Self Check: Nouns and Pronouns
Grammar: Verbs
- Outcome: Verbs
- Verb Tenses and Agreement
- Non-Finite Verbs
- Complex Verb Tenses
- Try It: Verbs
- Self Check: Verbs
Grammar: Other Parts of Speech
- Outcome: Other Parts of Speech
- Comparing Adjectives and Adverbs
- Adjectives and Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- Prepositions
- Try It: Other Parts of Speech
- Self Check: Other Parts of Speech
Grammar: Punctuation
- Outcome: Punctuation
- End Punctuation
- Hyphens and Dashes
- Apostrophes and Quotation Marks
- Brackets, Parentheses, and Ellipses
- Semicolons and Colons
- Try It: Punctuation
- Self Check: Punctuation
Grammar: Sentence Structure
- Outcome: Sentence Structure
- Parts of a Sentence
- Common Sentence Structures
- Run-on Sentences
- Sentence Fragments
- Parallel Structure
- Try It: Sentence Structure
- Self Check: Sentence Structure
Grammar: Voice
- Outcome: Voice
- Active and Passive Voice
- Using the Passive Voice
- Conclusion to Grammar
- Try It: Voice
- Self Check: Voice
Success Skills
- Introduction to Success Skills
- Habits for Success
- Critical Thinking
- Time Management
- Writing in College
- Computer-Based Writing
- Conclusion to Success Skills
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing Strong Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These OWL resources will help you develop and refine the arguments in your writing.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable
An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade people.
Example of a non-debatable thesis statement:
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
Example of a debatable thesis statement:
This is an example of a debatable thesis because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that this is how we should spend the nation's money. Others might feel that we should be spending more money on education. Still others could argue that corporations, not the government, should be paying to limit pollution.
Another example of a debatable thesis statement:
In this example there is also room for disagreement between rational individuals. Some citizens might think focusing on recycling programs rather than private automobiles is the most effective strategy.
The thesis needs to be narrow
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Example of a thesis that is too broad:
There are several reasons this statement is too broad to argue. First, what is included in the category "drugs"? Is the author talking about illegal drug use, recreational drug use (which might include alcohol and cigarettes), or all uses of medication in general? Second, in what ways are drugs detrimental? Is drug use causing deaths (and is the author equating deaths from overdoses and deaths from drug related violence)? Is drug use changing the moral climate or causing the economy to decline? Finally, what does the author mean by "society"? Is the author referring only to America or to the global population? Does the author make any distinction between the effects on children and adults? There are just too many questions that the claim leaves open. The author could not cover all of the topics listed above, yet the generality of the claim leaves all of these possibilities open to debate.
Example of a narrow or focused thesis:
In this example the topic of drugs has been narrowed down to illegal drugs and the detriment has been narrowed down to gang violence. This is a much more manageable topic.
We could narrow each debatable thesis from the previous examples in the following way:
Narrowed debatable thesis 1:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also how the money could actually help to control pollution.
Narrowed debatable thesis 2:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just what the focus of a national anti-pollution campaign should be but also why this is the appropriate focus.
Qualifiers such as " typically ," " generally ," " usually ," or " on average " also help to limit the scope of your claim by allowing for the almost inevitable exception to the rule.
Types of claims
Claims typically fall into one of four categories. Thinking about how you want to approach your topic, or, in other words, what type of claim you want to make, is one way to focus your thesis on one particular aspect of your broader topic.
Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or whether something is a settled fact. Example:
Claims of cause and effect: These claims argue that one person, thing, or event caused another thing or event to occur. Example:
Claims about value: These are claims made of what something is worth, whether we value it or not, how we would rate or categorize something. Example:
Claims about solutions or policies: These are claims that argue for or against a certain solution or policy approach to a problem. Example:
Which type of claim is right for your argument? Which type of thesis or claim you use for your argument will depend on your position and knowledge of the topic, your audience, and the context of your paper. You might want to think about where you imagine your audience to be on this topic and pinpoint where you think the biggest difference in viewpoints might be. Even if you start with one type of claim you probably will be using several within the paper. Regardless of the type of claim you choose to utilize it is key to identify the controversy or debate you are addressing and to define your position early on in the paper.

Implicit vs. Explicit: What’s the Difference?
Home » Implicit vs. Explicit: What’s the Difference?
There are many words in English that despite having very similar sounds have completely different meanings. This can lead to confusion and usage problems for native and non-native speakers alike, and the words implicit vs. explicit are no exception to this.
These two words have almost opposite meanings but are regularly confused because of their similar sound. Since they do have such different meanings, you want to be sure you’re using the right one. In this post, I want to go over the definitions of these words, explain their differences, and have you take a quiz on their meanings.
After reading this post, you won’t ever again ask yourself the question, “Is it explicit or implicit?”
When to Use Implicit

- There is a morality implicit in his writings.
- She implicitly said she likes white shoes by saying she likes all colors but tan.
In the first example, the writer may not have clearly or directly laid out a moral vision, but it is understood through the characters, their actions, and their experiences.
In the second example, the woman states that she likes all shoe colors but tan. While she doesn’t directly say she likes white shoes, she implicitly does because white is not tan.
When to Use Explicit
The definition of explicit is, “to fully and clearly express something, leaving nothing implied.” Something is explicit when it is cleared stated and spelled out and there is no room for confusion, as in the writing of a contract or statute. For example,
- The law was explicit in whose tax rates were to be raised.
- He said explicitly, you will not attend that concert.
In both of these examples, the word explicit is used to demonstrate something that has been clearly and unambiguously expressed or stated. There is no room for doubt because everything is clearly and directly communicated.
This is what separates these two words. Something is implicit when it is implied but not directly stated. Something is explicit when it is directly stated and leaves no room for uncertainty.
Quiz and Sentence Examples
- The speaker’s intentions were not made ______.
- The students found an ______ political statement in their teacher’s remarks.
- Let me be ______, I do not support this.
- We have not finalized the decision, but have an ______ agreement.
Display the answers below .
Tricks to Remember
Here is a handy trick to remember the difference between these words. Remember this and you won’t ever fall short when thinking, “Is it implicit or explicit?”
A good way to keep explicit vs implicit apart is to remember that I mplicit is an I mplied or I ndirect statement. Both of these start with the letter “I.”
E xplicit starts with an “E” and is Sp e ll e d Out, so there is no confusion.
Implicit and explicit have near opposite meanings, so it’s important to remember their difference.
Implicit is indirectly stated or implied.
Explicit is directly stated and spelled out. If you have any other questions about commonly misused English words, feel free to check out our other posts on affect/effect , principal/principle , and countless others.
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This IP Address is Blocked
Critical Reading
Identifying thesis statements, introduction, learning objectives.
- identify explicit thesis statements in texts
- identify implicit thesis statements in texts
- identify strategies for using thesis statements to predict content of texts
Being able to identify the purpose and thesis of a text, as you’re reading it, takes practice. This section will offer you that practice.
One fun strategy for developing a deeper understanding the material you’re reading is to make a visual “map” of the ideas. Mind maps, whether hand-drawn or done through computer programs, can be fun to make, and help put all the ideas of an essay you’re reading in one easy-to-read format.
Your understanding of what the “central” element of the mind map is might change as you read and re-read. Developing the central idea of your mind map is a great way to help you determine the reading’s thesis.

Hand-drawn Mind Map
Locating Explicit and Implicit Thesis Statements
In academic writing, the thesis is often explicit : it is included as a sentence as part of the text. It might be near the beginning of the work, but not always–some types of academic writing leave the thesis until the conclusion.
Journalism and reporting also rely on explicit thesis statements that appear very early in the piece–the first paragraph or even the first sentence.
Works of literature, on the other hand, usually do not contain a specific sentence that sums up the core concept of the writing. However, readers should finish the piece with a good understanding of what the work was trying to convey. This is what’s called an implicit thesis statement: the primary point of the reading is conveyed indirectly, in multiple locations throughout the work. (In literature, this is also referred to as the theme of the work.)
Academic writing sometimes relies on implicit thesis statements, as well.
This video offers excellent guidance in identifying the thesis statement of a work, no matter if it’s explicit or implicit.
Topic Sentences
We’ve learned that a thesis statement conveys the primary message of an entire piece of text. Now, let’s look at the next level of important sentences in a piece of text: topic sentences in each paragraph.
A useful metaphor would be to think of the thesis statement of a text as a general: it controls all the major decisions of the writing. There is only one thesis statement in a text. Topic sentences, in this relationship, serve as captains: they organize and sub-divide the overall goals of a writing into individual components. Each paragraph will have a topic sentence.
It might be helpful to think of a topic sentence as working in two directions simultaneously. It relates the paragraph to the essay’s thesis, and thereby acts as a signpost for the argument of the paper as a whole, but it also defines the scope of the paragraph itself. For example, consider the following topic sentence:
Many characters in Lorraine Hansberry’s play A Raisin in the Sun have one particular dream in which they are following, though the character Walter pursues his most aggressively.
If this sentence controls the paragraph that follows, then all sentences in the paragraph must relate in some way to Walter and the pursuit of his dream.
Topic sentences often act like tiny thesis statements. Like a thesis statement, a topic sentence makes a claim of some sort. As the thesis statement is the unifying force in the essay, so the topic sentence must be the unifying force in the paragraph. Further, as is the case with the thesis statement, when the topic sentence makes a claim, the paragraph which follows must expand, describe, or prove it in some way. Topic sentences make a point and give reasons or examples to support it.
The topic sentence is often, though not always, the first sentence of a paragraph.
- Outcome: Thesis. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Revision and Adaptation of Topic Sentences. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of hand-drawn mind map. Authored by : Aranya. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Guru_Mindmap.jpg . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Topic Sentences. Authored by : Ms. Beardslee. Located at : http://msbeardslee.wikispaces.com/Topic+Sentences?showComments=1 . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
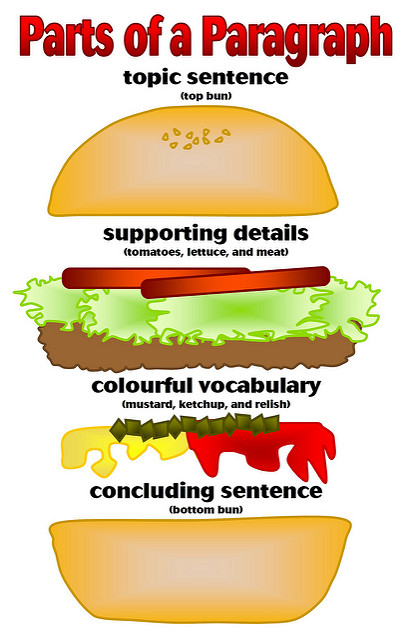
- Image of Parts of a Paragraph. Authored by : Enokson. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/ak9H3v . License : CC BY: Attribution
- How to Identify the Thesis Statement. Authored by : Martha Ann Kennedy. Located at : https://youtu.be/di1cQgc1akg . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

3.8: Main Ideas and Supporting Details
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 31307

- Athena Kashyap & Erika Dyquisto
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
Analyze Thesis or Main Ideas of Texts
Being able to identify the purpose and thesis of a text, while you’re reading it, takes practice. Questioning the text you’re reading is a good place to start. When trying to isolate the thesis, or main idea, of your reading material, consider these questions:
- What is the primary subject of this text?
- Is the author trying to inform me, or persuade me?
- What does the author think I need to know about this subject?
- Why does the author think I need to know about this subject?
Sometimes the answer to these questions will be very clearly stated in the text itself. Sometimes it is less obvious, and in those cases, the techniques on the following page will be useful.
Implicit vs. Explicit Main Idea/ Thesis Statements
According to author Pavel Zemliansky,
Arguments then, can be explicit and implicit, or implied. Explicit arguments contain noticeable and definable thesis statements and lots of specific proofs. Implicit arguments, on the other hand, work by weaving together facts and narratives, logic and emotion, personal experiences and statistics. Unlike explicit arguments, implicit ones do not have a one-sentence thesis statement. Instead, authors of implicit arguments use evidence of many different kinds in effective and creative ways to build and convey their point of view to their audience. Research is essential for creative effective arguments of both kinds.
Even if what you’re reading is an informative text, rather than an argumentative one, it might still rely on an implicit thesis statement. It might ask you to piece together the overall purpose of the text based on a series of content along the way.
The following video defines the key terms explicit and implicit, as they relate to thesis statements and other ideas present in what you read. It also introduces the excellent idea of the reading voice and the thinking voice that strong readers use as they work through a text.
To help keep you on your toes, the author of this video challenges you to find her spelling mistake in one of her cards along the way!
Explicit v. implicit . Authored by: Michele Armentrout. All Rights Reserved. License Terms: Standard YouTube license.
Take the quiz about implicit and explicit thesis statements to see how well you have understood the information.
Thesis and Topic Sentences
You’ll remember that the first step of the reading process, previewing, allows you to get a big-picture view of the document you’re reading. This way, you can begin to understand the structure of the overall text. A later step in the reading process, summarizing , allows you to encapsulate what a paragraph, section, or the whole document is about. When summarizing individual paragraphs, it’s likely that your summary ends up looking like a paraphrase of that paragraph’s topic sentence .
A paragraph is composed of multiple sentences focused on a single, clearly-defined topic. There should be exactly one main idea per paragraph, so whenever an author moves on to a new idea, he or she will start a new paragraph. For example, this paragraph defines what a paragraph is, and now we will start a new paragraph to deal with a new idea: how a paragraph is structured.
Paragraphs are actually organized much like persuasive papers are. Just like a paper has a thesis statement followed by a body of supportive evidence, paragraphs have a topic sentence followed by several sentences of support or explanation. If you look at this paragraph, for example, you will see that it starts with a clear topic sentence letting you know that paragraphs follow a structure similar to that of papers. The next sentence explains how a paragraph is like a paper, and then two more sentences show how this paragraph follows that structure. All of these sentences are clearly connected to the main idea.
The topic sentence of a paragraph serves two purposes: first, it lets readers know what the paragraph is going to be about; second, it highlights the connection between the present paragraph and the one that came before. The topic sentence of this paragraph explains to a reader what a topic sentence does, fulfilling the first function. It also tells you that this paragraph is going to talk about one particular aspect of the previous paragraph’s main idea: we are now moving from the general structure of the paragraph to the particular role of the topic sentence.
After the topic sentence introduces the main idea, the remainder of the sentences in a paragraph should support or explain this topic. These additional sentences might detail the author’s position on the topic. They might also provide examples, statistics, or other evidence to support that position. At the end of the paragraph, the author may include some sort of conclusion or a transition that sets up the next idea he or she will be discussing (for example, you can see this clearly in the last sentence of the third paragraph).
The Three Parts of a Paragraph
The topic is the subject of the paragraph. It can be:
- A few words long
- These words (or words related to the topic) are typically repeated throughout the paragraph
- Answers the question: What is this paragraph about?
2) Main Idea
This is the writer’s overall point. It can be:
- If stated in the paragraph, it’s called a “topic sentence”
- If unstated in the paragraph, the reader must figure it out (infer it) from details
- General enough to cover the more specific supporting details
- Usually (but not always!) near the beginning of the paragraph
- Answers the question: What is the overall point being made about the topic?”
3) Supporting Details
These are the details in the paragraph that support the main idea. They can be either major or minor supporting details.
Tips for Identifying Main Ideas
Although you are learning to put the main idea first in your own paragraphs, professional writers often don’t. Sometimes the first sentence of a paragraph provides background information, poses a question, or serves as a bridge from a previous paragraph. Don’t assume it is the main idea. Use these tips instead:
- Look for a general statement that appears to “cover” the other information.
- Figure out the general topic of the paragraph first. Then ask yourself, “What point is the writer trying to make about this topic?”
- Look for clue words. Main ideas sometimes have words such as “some” or plural nouns like “ways” or “differences” that signal a list of details to come.
- Is this statement supported by most of the other information?
- If I turn this statement into a question, does the other information answer it?
SPECIAL NOTE: Sometimes a main idea covers more than one paragraph. This may happen in newspaper articles or when the writer has a lot to say about one topic.
Difference Between the Topic and Main Idea
To understand the difference between a main idea and the topic, imagine that you are listening to your friends talk about their pets. The TV is on, so all you can make out are the name of their pets. If someone asked you what the topic was, you would say “pets.” But because you couldn’t hear the whole thing, you didn’t understand the “main idea” was whose pet was the best. The topic is very broad – the main idea is more specific. The sentences that follow in the paragraph exercise offer examples or descriptions to illustrate or explain the main idea. Note the reading-writing connection--while we are finding the main idea as readers, we will be using the main ideas to write topic sentences in paragraphs.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Read the following paragraph and then decide what the main idea is.
One myth about exercise is that if a woman lifts weights, she will develop muscles as large as a man’s. Without male hormones, however, a woman cannot increase her muscle bulk as much as a man’s. Another misconception about exercise is that it increases the appetite. Actually, regular exercise stabilizes the blood-sugar level and prevents hunger pangs. Some people also think that a few minutes of exercise a day or one session a week is enough, but at least three solid workouts a week are needed for muscular and cardiovascular fitness.
Choose the Main Idea:
a) Women who lift weights cannot become as muscular as men.
b) There are several myths about exercise.
c) Exercise is beneficial to everyone.
d) People use many different excuses to avoid exercising.
Explain why you did or did not choose each possible answer above.
a) ________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
b) ________________________________________________________________________
c) ________________________________________________________________________
d) ________________________________________________________________________
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
“To Sherlock Holmes she is always THE woman. I have seldom heard him mention her under any other name. In his eyes she eclipses and predominates the whole of her sex. It was not that he felt any emotion akin to love for Irene Adler. All emotions, and that one particularly, were abhorrent to his cold, precise but admirably balanced mind. He was, I take it, the most perfect reasoning and observing machine that the world has seen, but as a lover he would have placed himself in a false position. He never spoke of the softer passions, save with a gibe and a sneer. They were admirable things for the observer--excellent for drawing the veil from men's motives and actions. But for the trained reasoner to admit such intrusions into his own delicate and finely adjusted temperament was to introduce a distracting factor which might throw a doubt upon all his mental results.“
The main idea of this paragraph is the first sentence. The first sentence identifies the two characters that the rest of the paragraph is going to describe, and suggests at their relationship. Each sentence that follows either describes the woman, Sherlock Holmes, or how he felt about her or her effect on him.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Here is another example from the same story, see if you can find the main idea:
One night--it was on the twentieth of March, 1888--I was returning from a journey to a patient (for I had now returned to civil practice), when my way led me through Baker Street. As I passed the well-remembered door, which must always be associated in my mind with my wooing, and with the dark incidents of the Study in Scarlet, I was seized with a keen desire to see Holmes again, and to know how he was employing his extraordinary powers. His rooms were brilliantly lit, and, even as I looked up, I saw his tall, spare figure pass twice in a dark silhouette against the blind. He was pacing the room swiftly, eagerly, with his head sunk upon his chest and his hands clasped behind him. To me, who knew his every mood and habit, his attitude and manner told their own story. He was at work again.
a. One night--it was on the twentieth of March, 1888--I was returning from a journey to a patient (for I had now returned to civil practice), when my way led me through Baker Street.
b. As I passed the well-remembered door, which must always be associated in my mind with my wooing, and with the dark incidents of the Study in Scarlet, I was seized with a keen desire to see Holmes again, and to know how he was employing his extraordinary powers
c. His rooms were brilliantly lit, and, even as I looked up, I saw his tall, spare figure pass twice in a dark silhouette against the blind.
d. He was pacing the room swiftly, eagerly, with his head sunk upon his chest and his hands clasped behind him.
The correct answer is a. The first sentence gives you the point-of-view, or who is the person explaining what is happening, and it lets you know that this person is going into a particular place. Each of the other sentences describes the place where he, Dr. Watson, entered, what it looked like, and who was in there.
B is not as strong a choice as a, because it refers to Study in Scarlet and Holmes’ powers, which are not described in the rest of the paragraph. Choice B is too specific to be the main idea of this paragraph. Choices c and d are not correct because they are describing Holmes’ actions, and his walking is not what the whole paragraph is about.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Let’s try one more. Read the following and select which one is the main idea from the list below:
“At three o'clock precisely I was at Baker Street, but Holmes had not yet returned. The landlady informed me that he had left the house shortly after eight o'clock in the morning. I sat down beside the fire, however, with the intention of awaiting him, however long he might be. I was already deeply interested in his inquiry, for, though it was surrounded by none of the grim and strange features which were associated with the two crimes which I have already recorded, still, the nature of the case and the exalted station of his client gave it a character of its own. Indeed, apart from the nature of the investigation which my friend had on hand, there was something in his masterly grasp of a situation, and his keen, incisive reasoning, which made it a pleasure to me to study his system of work, and to follow the quick, subtle methods by which he disentangled the most inextricable mysteries. So accustomed was I to his invariable success that the very possibility of his failing had ceased to enter into my head.”
a. At three o'clock precisely I was at Baker Street, but Holmes had not yet returned.
b. The landlady informed me that he had left the house shortly after eight o'clock in the morning.
c. I sat down beside the fire, however, with the intention of awaiting him, however long he might be
d. I was already deeply interested in his inquiry, for, though it was surrounded by none of the grim and strange features which were associated with the two crimes which I have already recorded, still, the nature of the case and the exalted station of his client gave it a character of its own.
The way to figure out that the answer, this time, is d, is to look at each sentence that follows and ask, does this refer back to the location, Baker Street? Do they refer back to the landlady? Do they refer back to Dr. Watson’s waiting? Or, do they refer back to the case? They both refer back to the current investigation, by talking about Holmes’ way of untangling mysteries, and that Watson’s belief that the investigation would be a success.
The introduction to this paragraph may have thrown you off so be careful to read through the entire paragraph each time, and look at each sentence and its role within the paragraph. Mostly the main idea comes right up front – but not always!
Reading-Writing Connection: Thesis Statements
Exercise \(\PageIndex{5}\)
I. Develop a paragraph. Your paragraph must include the following:
- Between 7-9 sentences
- A main idea sentence
- Each sentence must be developed, and checked for correct spelling and grammar
- Have at least three of the four different types of sentences (simple, complex, compound, compound-complex)
- Attach your pre-writing practice after the paragraph, to identify which sentences are major and minor detail sentence
Supporting Details
Earlier we covered what a main idea sentence was: a sentence that names the topic, and allows the reader to understand the focus of the paragraph to follow. It is logical then that the rest of the sentences in the paragraph support the main idea sentence. Support means that they either explain something about the topic, or they offer an example.
We’ve examined the relationship between a text’s thesis statement and its overall organization through the idea of topic sentences in body paragraphs. But of course body paragraphs have a lot more “stuff” in them than just topic sentences. This section will examine in more detail what that “stuff” is made of.
First, watch this video that details the relationship between a topic sentence and supporting details, using the metaphor of a house. The video establishes the difference between major and minor details, which will be useful to apply in coming discussions. (The video has instrumental guitar for audio, but no spoken words, so it can be watched without sound if desired.)
Video: Supporting Details . Authored by: Mastering the Fundamentals of College Reading and Writing. All Rights Reserved. License Terms: Standard YouTube license.
The following image shows the visual relationship between the overall thesis, topic sentences, and supporting ideas:
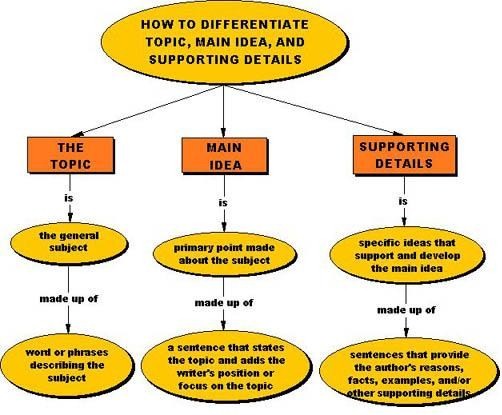
This next image shows where a topic sentence might reside in the paragraph, in relation to the rest of the supporting details:
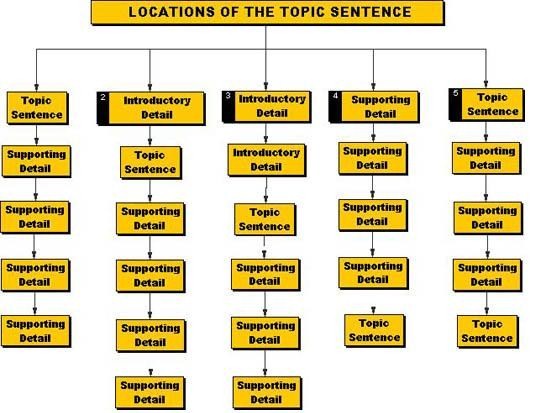
In #5 of the sequence above, the topic sentence is rephrased between the opening and closing of the paragraph, to reinforce the concept more strongly.
Point, Illustration, Explanation (P.I.E.)
Many authors use the PIE format to structure their essays. PIE = point, illustration, explanation to structure their body paragraph and support their thesis. The point furthers a thesis or claim and is the same as the main idea, the illustration provides support for the point, and the explanation tells the audience why the evidence provided furthers the point and/or the thesis.

For example, in his argument against the +/- grading system at Radford, student-writer Tareq Hajj makes the Point that “Without the A+, students with high grades in the class would be less motivated to work even harder in order to increase their grades.”
He Illustrates with a quote from a professor who argues, “‘(students) have less incentive to try’” (Fesheraki, 2013).
Hajj then Explains that “not providing [the most motivated students] with additional motivation of a higher grade … is inequitable.”
Through his explanation, Hajj links back to his claim that “A plus-minus grading scale … should not be used at Radford University” because, as he explains, it is “inequitable.” The PIE structure of his paragraph has served to support his thesis.
All Claims Need Evidence
Ever heard the phrase “everyone is entitled to his opinion”? It is indeed true that people are free to believe whatever they wish. However, the mere fact that a person believes something is not an argument in support of a position. If a text’s goal is to communicate effectively, it must provide valid explanations and sufficient and relevant evidence to convince its audience to accept that position. In other words, “every author is entitled to his opinion, but no author is entitled to have his opinion go unchallenged.”
What are the types of evidence?
Any text should provide illustrations for each of its points, but it is especially important to provide reliable evidence in an academic argument. This evidence can be based on primary source material or data (the author’s own experience and/or interviews, surveys, polls, experiments, that she may have created and administered). Evidence can also stem from secondary source material or data (books, journals, newspapers, magazines, websites or surveys, experiments, statistics, polls, and other data collected by others).
Let’s say, for example, that you are reading an argument that college instructors should let students use cell phones in class. Primary source material might include a survey the author administered that asks students if policies forbidding cell phone usage actually stop them from using their phones in class. Secondary sources might include articles about the issue from Faculty Focus or The Chronicle of Higher Education .
Logos, Ethos, Pathos
Writers are generally most successful with their audiences when they can skillfully and appropriately balance the three core types of appeals. These appeals are referred to by their Greek names: logos (the appeal to logic), pathos (the appeal to emotion), and ethos (the appeal to authority). All of these are used in one way or another in your body paragraphs, particularly as it relates to the support or information in the paragraph.
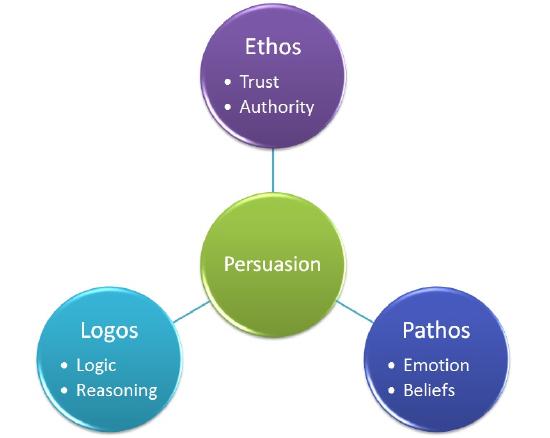
Logical Appeals
Authors using logic to support their claims will include a combination of different types of evidence. These include the following:
- established facts
- case studies
- experiments
- analogies and logical reasoning
- citation of recognized experts on the issue
Authoritative Appeals
Authors using authority to support their claims can also draw from a variety of techniques. These include the following:
- personal anecdotes
- illustration of deep knowledge on the issue
- testimony of those involved first-hand on the issue
Emotional Appeals
Authors using emotion to support their claims again have a deep well of options to do so. These include the following:
- impact studies
As you can see, there is some overlap on these lists. One technique might work simultaneously on multiple levels.
Most texts rely on one of the three as the primary method of support, but may also draw upon one or two others at the same time.
Check your understanding of supporting details by doing this quiz.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{6}\)
Read the paragraph below and find the main idea and supporting details.
My parents were very strict when I was growing up. My mother in particular was always correcting my behavior. One day when I forgot to look both ways when I was crossing the street, my mother made me go back home; she said that I could not go out at all if I could not be safe. My father was more concerned with my grades. Every night he would make me go to my room before I could watch television.
Let’s examine the pattern for this paragraph. The first sentence (1) presents the main idea, that my parents were strict. The second sentence (2) explains what I mean by “strict,” by saying that my mother was strict in correcting my behavior. The third sentence (3) offers an example of how she would correct my behavior. The fourth sentence (4) explains further, that my father was strict when it came to schoolwork, and then the fifth sentence (5) offers an example of how he was strict.
If we were going to diagram the paragraph above, it would look like this:
EXPLAIN (2)-___________________EXPLAIN (4)
EXAMPLE (3) EXAMPLE (5)
Major and Minor Supporting Details
One way to talk about whether a sentence directly supports the main idea (the second level), or indirectly supports the main idea (the third level) is to call them MAJOR detail sentences or MINOR detail sentences. Major details directly explain something about the topic, while minor details offer examples for the Major detail that came right before.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7}\)
Read the paragraphs, and then identify each sentence as either a main idea, a major detail, or a minor detail sentence.
Single parents have to overcome many obstacles to return to school. If the child is very young, finding quality babysitting can be difficult. Many babysitters are unreliable and that can mean that the parent has to miss many classes, which can hurt their grades. It is also hard to find enough time to study. Children require a lot of attention and are also noisy, and that can interfere with a parent's ability to complete their homework. Finally, raising children is expensive. Many single parents discover that they can’t meet the costs of both raising children and paying for tuition, books, and fees.
Sentence #1: Sentence #2: Sentence #3: Sentence #4: Sentence #5: Sentence #6: Sentence #7:
My grandmother turned 70 last year and celebrated by going skydiving. She said she always wanted to try and figured it was now or never. Many people think that when you get older you can no longer do fun things, but this is not true. The senior center in town offers dance lessons and also takes groups to the art museum. The classes are always full because so many people want to try new things. Towns are even developing senior living communities around activities such as golf and tennis. Those communities are very popular because people like to live with others who share their interests.
Sentence #1: Sentence #2: Sentence #3: Sentence #4: Sentence #5: Sentence #6: Sentence #7
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8}\)
Below you will find several main idea sentences. Provide appropriate supporting sentences following the pattern of Major-Minor-Major- Minor.
1. It is not a good idea to watch a lot of television. Major: Minor: Major: Minor:
2. Coaches have good reasons to be firm with the players on their team. Major: Minor: Major: Minor:
3. Many people believe it is a bad idea to spank children. Major: Minor: Major: Minor:
4. There are several steps I can take to be successful in college.
Major: Minor: Major: Minor:
Reading-Writing Connection: Supporting Details
Exercise \(\PageIndex{9}\)
Return to the Thesis exercise you did previously. As part of that exercise, you identified two topic sentences from your selected reading. Now, look more closely at the paragraphs where those two topic sentences came from.
- Write a paragraph that identifies the type of support that each paragraph from the reading uses to reinforce each of those two topic sentences. Are they narrative or personal examples? Are they facts or statistics? Are they quotes or paraphrases from research materials?
- Write another paragraph that compares the effectiveness of the supporting claims of one of the selected paragraphs against the other one. Which seems more successful in its goal? Why do you feel that way?
Contributors
- Adapted from English 9Y Pre-College English . Provided by: Open Course Library. CC BY 3.0
- Adapted from Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences . Provided by: Lumen Learning. CC-BY-NC-SA
- Adapted from Methods of Discovery: A Guide to Research Writing . Authored by: Pavel Zemliansky. Provided by: Libretexts. CC BY: Attribution
This page last updated June 6, 2020.
Research Writing Process (Book)
Find the following links to be useful in learning about the research writing process., writing a thesis statement, open thesis vs. closed thesis.
Open Thesis vs. Closed Thesis
Implicit Thesis vs. Explicit Thesis
The thesis is a declarative sentence. It is a clear, specific statement, which states the main point of a the paper, thereby limiting the topic and indicating the researcher’s approach to the topic. For this research paper we will be discussing the difference between the open (implicit) thesis approach, and the closed (explicit) thesis. Open (implicit) thesis: Let’s say you are writing a paper on the relationship between the United States criminal court system and the media. You have read on article related to this topic, but you have not yet begun your research. Still, it is possible for you to arrive at a very basic and general opinion without going into detail, secondary topics, or supporting reasons for your assertion. Broad Topic: The United States criminal court system and the media. Example of an open (implicit) thesis statement: The media plays too influential a role in criminal court trials. To assist you in formulating your preliminary thesis, ask basic “W” questions that are related to your topic: who, what, when, where, and why? This will help you determine your particular interests and a possible starting point for your research. Based on the topic above, the following list demonstrates the different kinds of questions that can be generated. *Why is the media involved in court cases? *When did the media start reporting court cases? *What is the media’s role in criminal court cases? *What aspects of the media am I going to write about? *What kind of criminal case is it? *When did the case take place? *Where did the case take place? *Who were the people involved in the case? If you are writing a research paper and you have come up with a long list of random questions, select three or four questions that hold the most interest for you. These questions will narrow your focus and help you to plan your research strategy.
Closed (Explicit) Thesis: If you make an assertion and include the reason or reasons which support your assertion, and it is broad enough in scope, yet specific enough to be unified and to perform as a substantial generalization of your essay, you have written a closed thesis statement. The evidence can take many forms: facts, opinions, anecdotes, statistics, analogies, etc., but the essential relationship between the thesis and the major points of support is one of conclusion to reason: This is believed to be true because… (reasons). Broad Topic: The United States criminal court system and the media. Example of a closed (explicit) thesis: The media plays a very influential role in criminal court trials because of their access to the people, their bias, and because of the special privileges. Based on the topic that YOU have chosen, ask yourself basic “W” questions that are related to YOUR topic to help you plan your research strategy and form a thesis. (Written by Lisa Tolhurst for the Hunter College Reading/Writing Center, 1998) WHY – WHEN – WHAT – WHERE – WHO – HOW – KEEP GOING!.....

COMMENTS
5.2: Explicit Versus Implicit Thesis Statements. Page ID. The following video defines the key terms explicit and implicit, as they relate to thesis statements and other ideas present in what you read. It also introduces the excellent idea of the reading voice and the thinking voice that strong readers use as they work through a text.
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
Arguments then, can be explicit and implicit, or implied. Explicit arguments contain noticeable and definable thesis statements and lots of specific proofs. Implicit arguments, on the other hand, work by weaving together facts and narratives, logic and emotion, personal experiences and statistics. Unlike explicit arguments, implicit ones do not ...
A Thesis Statement: Describes how you interpret the subject matter's cause, significance, and results. Is a guideline for the paper. In other words, it provides an understanding of the research topic. Directly answers the question you are asked. The thesis is not the question itself but an interpretation of it.
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write! In this article, we explain how to write a thesis ...
An analytical thesis statement is a clear and specific statement of what you plan to analyze in your paper and what your findings are. Also, a thesis statement can be explicit or implicit : An explicit thesis statement states the main argument or claim of your essay explicitly with a lot of facts and proof.
Locating and Evaluating Thesis Statements. The following video offers a definition of thesis statements, and guidance for finding thesis statements as you read. Pay attention to the difference between explicit thesis statements and implicit (or implied) thesis statements. (This video was made for a specific class, so it will make references to ...
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement. 1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing: An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.; An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.; An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies ...
The thesis is the author's reason for writing. The word thesis is a Greek word meaning position. The thesis statement is the controlling idea. It is the point the writer wants to make. It is not necessarily in the beginning of an essay. It is not even necessarily physically present. It might be implied.
Each paragraph will have a topic sentence. Figure 2.5.2 2.5. 2. It might be helpful to think of a topic sentence as working in two directions simultaneously. It relates the paragraph to the essay's thesis, and thereby acts as a signpost for the argument of the paper as a whole, but it also defines the scope of the paragraph itself.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable. An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. ... Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or ...
Like a thesis statement, a topic sentence makes a claim of some sort. As the thesis statement is the unifying force in the essay, so the topic sentence must be the unifying force in the paragraph. Further, as is the case with the thesis statement, when the topic sentence makes a claim, the paragraph which follows must expand, describe, or prove ...
A good way to keep explicit vs implicit apart is to remember that Implicit is an Implied or Indirect statement. Both of these start with the letter "I." Explicit starts with an "E" and is Spelled Out, so there is no confusion. Summary. Implicit and explicit have near opposite meanings, so it's important to remember their difference.
Locating and Evaluating Thesis Statements. The following video offers a definition of thesis statements, and guidance for finding thesis statements as you read. Pay attention to the difference between explicit thesis statements and implicit (or implied) thesis statements. (This video was made for a specific class, so it will make references to ...
A thesis statement is a declaration of one or two sentences that gives the topic and purpose of an essay or speech. More specifically, it provides information to the audience about what the author/speaker intends to prove or declare, with specific discussion points. The thesis statement is usually placed toward the end of the introductory ...
• The thesis may be implied or explicitly stated, but it should always be evident to the reader. • The thesis may differ in form depending on the type of writing (argumentative, persuasive, informative, narrative, etc.). • The thesis should be restated in a new and interesting way in the conclusion. Explicit vs. Implied • An explicit thesis
In academic writing, the thesis is often explicit: it is included as a sentence as part of the text. It might be near the beginning of the work, but not always-some types of academic writing leave the thesis until the conclusion. Journalism and reporting also rely on explicit thesis statements that appear very early in the piece-the first ...
Explicit arguments contain noticeable and definable thesis statements and lots of specific proofs. Implicit arguments, on the other hand, work by weaving together facts and narratives, logic and emotion, personal experiences and statistics. Unlike explicit arguments, implicit ones do not have a one-sentence thesis statement.
Explicit arguments contain noticeable and definable thesis statements and lots of specific proofs. Implicit arguments, on the other hand, work by weaving together facts and narratives, logic and emotion, personal experiences and statistics. Unlike explicit arguments, implicit ones do not have a one-sentence thesis statement.
According to author Pavel Zemliansky, Arguments then, can be explicit and implicit, or implied. Explicit arguments contain noticeable and definable thesis statements and lots of specific proofs. Implicit arguments, on the other hand, work by weaving together facts and narratives, logic and emotion, personal experiences and statistics.
The thesis is a declarative sentence. It is a clear, specific statement, which states the main point of a the paper, thereby limiting the topic and indicating the researcher's approach to the topic. For this research paper we will be discussing the difference between the open (implicit) thesis approach, and the closed (explicit) thesis. Open ...