
- Entrepreneurship
- Starting a Business
- My #1 Online Biz
- Business Planning
- Advertising
- Content Marketing
- Digital Marketing
- Public Relations
- Business Model
- Financial Forecasting
- Market Research
- Risk Management
- Business Plan
- Conferences
- Online Communities
- Professional Associations
- Social Media
- Human Resource
- Productivity
- Legal Requirements
- Business Structure
- Mission Statement
- Financial Plan
- Market Analysis
- Operational Plan
- SWOT Analysis
- Target Market
- Competitor Analysis
- Customer Profiling
- Market Trends
- Pricing Strategies
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership
- Cooperative
- Corporation
- Limited Liability

The Importance Of Business Planning: A Beginner’s Guide
by Mike Vestil
Business planning is the process of determining the goals and objectives of a business and developing a roadmap to achieve them.
It involves the analysis of current and future market conditions, operational capabilities, financial resources, and other factors that impact business success.
Effective business planning helps entrepreneurs and organizations navigate the complexities of the market and make strategic decisions that increase profitability and longevity.
Whether you are starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a well-crafted business plan is critical to your success.
In this article, we will explore the key components of business planning and provide insights on how to create a plan that meets your specific needs.
Introduction To Business Planning
What is business planning.
A business plan can be described as a document that outlines and describes the goals of a business and the strategies that will be employed to achieve these goals.
It typically includes detailed information about the company, such as the products, services, and customers that it intends to target, as well as an analysis of the market and the competition.
A business plan also describes the financial projections and resources needed to achieve these goals, such as the amount of money that will be invested, the sales projections, and the operational costs.
The purpose of a business plan is to provide a roadmap for the business owner and all stakeholders, including investors, employees, and management teams.
The importance of a business plan cannot be overstated as it serves as a guide to identify and address potential challenges that a business owner may encounter along the way.
Starting and running a business can be a daunting task, but having a well-crafted business plan can help alleviate some of the stress associated with the unknowns of business ownership.
A business plan helps to define and communicate the vision of the business, which can be invaluable to gaining traction with potential investors or partners who can assist in the growth and development of the company.
It also serves as a tool for measuring success as it provides specific goals and objectives that can be compared to actual results.
In conclusion, a well-written business plan is essential to the overall success of a business.
It provides a clear road map of what the business hopes to achieve and how it intends to do so. It serves as a guide for all stakeholders and helps to communicate the vision of the business to potential investors, employees, and partners.
Ultimately, a business plan helps to mitigate potential risks and set the business up for success.
Importance Of Business Planning
Business planning is an essential activity that every organization must engage in irrespective of its nature or size. It helps organizations in setting goals, staying focused, and measuring progress.
There are several reasons why business planning is of great importance, such as guiding decision-making, allocating resources, and identifying potential risks and opportunities.
First and foremost, business planning helps organizations in setting realistic goals and determining the best strategies to achieve them. It provides a roadmap for the future that enables executives and managers to make informed decisions based on available data and market trends.
Additionally, business planning is a critical tool for allocating resources and ensuring that they are used efficiently.
By analyzing financial data and identifying areas of potential wastage, organizations can reduce costs and increase profitability.
Furthermore, business planning is an effective means of identifying potential risks and opportunities that an organization may face.
By conducting a thorough analysis of internal and external factors that may impact the business, organizations can develop contingency plans to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
Another essential aspect of business planning is that it enables organizations to monitor and measure their progress.
Through the use of key performance indicators (KPIs), organizations can track their performance against set objectives and make adjustments where necessary.
This helps to ensure that the organization is on track towards achieving its goals and that everyone within the organization is working towards the same objectives.
Moreover, business planning is a critical tool for securing external funding. Investors and lenders are more likely to invest in organizations that have a well-defined strategy and a clear understanding of their market and industry.
In conclusion, business planning is a critical activity for any organization that wants to thrive in a competitive marketplace.
It provides a framework for decision-making, resource allocation, risk management, and measuring progress. Without a solid business plan, organizations are likely to struggle to achieve their goals, make efficient use of their resources, and identify potential risks and opportunities.
Therefore, it is crucial for organizations to invest time and resources into developing a comprehensive and realistic business plan that reflects their unique strengths, weaknesses, and objectives.
Purpose Of Business Planning
Business planning is a critical aspect of establishing a successful business. The purpose of business planning is to outline the objectives, strategies, and steps necessary to achieve those objectives.
This process involves creating a roadmap for the future of the business, identifying potential obstacles and opportunities, and developing tactics to overcome or leverage them.
Business planning is essential for potential investors, as it provides an overview of the company’s goals and how they plan to achieve them. It also allows for more effective decision-making, as it provides a framework for assessing whether or not certain decisions align with the company’s overall goals.
Similarly, business planning is critical for internal stakeholders, as it helps to establish a shared vision and objective for the company, as well as the roadmap for achieving it.
Ultimately, business planning is a vital tool for any business owner or entrepreneur looking to establish a thriving enterprise in today’s complex and competitive market.
Key Elements Of Business Planning
Executive summary.
The executive summary is a critical component of any business plan, providing a concise yet comprehensive summary of the key elements of the plan.
It should provide a clear and compelling overview of the business, highlighting its unique value proposition, target market, competitive advantages, and key strategies for success.
Key financial projections should also be included, providing investors and other stakeholders with a clear understanding of the anticipated risks and rewards associated with the venture.
The executive summary should be written in a clear and concise manner, using language that is both easy to understand and engaging to the reader.
It should be designed to capture the attention of potential investors, lenders, or other stakeholders, providing them with a clear understanding of the business and its potential for success.
Market Analysis Of Business Planning
The Market Analysis section of a business plan is a crucial component that provides a thorough analysis of the target market, industry trends, competition, and customer base.
This subsection should focus on the target market’s size, demographics, and psychographics, including their purchasing habits, preferences, and behaviors.
The assessment of industry trends involves investigating the direction of the market, identifying opportunities, and assessing the impact of external factors such as economic conditions and government regulations.
The section on competition analysis must provide a detailed analysis of direct and indirect competitors, including their strengths, weaknesses, and market share.
This information can be obtained through the use of surveys, online research, and networking. The subsection should also assess the customer base, including market segmentation, potential growth, and loyalty.
Moreover, the subsection should include a SWOT analysis that examines the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the company.
The analysis should focus on the potential challenges faced by the company as well as the opportunities that can be leveraged to achieve success.
This analysis provides an insight into the company’s competitive position and helps identify areas where the company can improve.
Overall, the Market Analysis section is critical for any business plan as it provides a well-rounded understanding of the target market, industry trends, and competitive landscape.
The information provided in this section can be used to develop a sound business strategy and make informed decisions that drive the company’s success.
Company Description Of A Business Plan
The Company Description subsection of a business plan provides an overview of the company and its history, current status, and future prospects.
It should detail what the company does, what sets it apart from competitors, and how it intends to achieve success. A well-crafted company description should also communicate the company’s core values, mission statement, and vision for the future.
It is important to include any relevant company history and milestones as well as any notable achievements, partnerships, or industry awards.
Additionally, a clear explanation of the management team’s experience and qualifications, including their education, certifications, and industry experience, is essential to demonstrate the company’s capacity to succeed.
Furthermore, the products or services offered by the company and how they meet the needs and desires of customers should also be emphasized.
Overall, a concise and compelling company description sets the foundation for the rest of the business plan and conveys a sense of confidence and expertise to potential investors and stakeholders.
Organization And Management
The Organization and Management subsection is crucial in any business plan as it highlights the structure, roles, and responsibilities of the key personnel who will be at the helm of the organization.
The success of any business is largely dependent on the capabilities of the people managing it.
Therefore, it is essential to outline the experience and expertise of each member of the management team. This subsection should also provide clear information on the ownership structure of the organization, including the distribution of shares or ownership percentages.
It is important to highlight any legal or regulatory requirements that the management needs to fulfill to operate the business effectively.
Additionally, the subsection should explain the key operational and administrative functions, as well as any external professional services that will be necessary to ensure the smooth running of the business.
Service Or Product Line
Service or Product Line is a crucial section of a business plan that outlines the products or services a company intends to offer.
This section must describe the key attributes of the product or service, including its unique features, the target market, and what sets it apart from competitors.
Additionally, this section must touch on the production process and costs, as well as the pricing strategy the company will use to ensure that the product or service is profitable.
A successful business plan must ensure that its offerings add value to the target market and adapt accordingly by conducting market research, understanding the competition, and leveraging innovation to create new and improved products.
Marketing And Sales Of A Business Plan
The Marketing and Sales subsection of a business planning document is designed to outline the strategies that will be used to promote and sell a company’s product or service.
This section should include a market analysis and an explanation of how the company plans to differentiate itself from competitors. The marketing plan should identify target customers, their needs, and the benefits that the product or service will provide.
The sales plan should identify the distribution channels that will be used, as well as the pricing model and the sales team structure.
Additionally, this section should identify any marketing and sales metrics that will be used to measure success, such as conversion rates and lead generation.
It is crucial for companies to have a comprehensive marketing and sales plan in place to ensure that they are able to effectively reach their target audience and drive revenue growth.
Funding Request Of A Business Plan
The Funding Request subsection of a business plan is where the entrepreneur explains their financial needs to potential investors or lenders. This section starts with the amount of money required and how it will be utilized, such as for inventory, facilities, or equipment.
The business owner must provide an accurate estimate of the total costs involved, including monthly expenses and projected revenues.
It is also essential to explain how the funding request will affect the company’s financial position and how it will help achieve the specified goals.
Sometimes, entrepreneurs may need to explain their willingness to give up a portion of their company’s ownership to secure financing.
The funding request should be provided with detailed financial statements and projections to support the proposal.
Moreover, entrepreneurs should also specify the repayment schedule and interest rates if they are looking for loans.
The objective is to persuade potential investors or lenders that the proposed investment is feasible, and the revenue from the company is likely to provide a satisfactory return on investment within an acceptable time frame.
A well-written and researched funding request inspires confidence in potential investors or lenders and increases the entrepreneur’s chance of securing the necessary funds.
Importance Of Financial Projections In Business Plan
The subsection Financial Projections is a crucial aspect of any business plan. It entails forecasting the financial outcomes of the proposed business operations.
Financial projections encompass several critical elements, including income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets.
Accurately projecting financial outcomes is vital for securing funding from investors and financial institutions.
Furthermore, it is a critical tool for managing resources, making critical financial decisions, and monitoring day-to-day financial activities.
When preparing financial projections, it is essential to consider various factors that might influence the outcomes, such as market trends, competition, industry regulations, and other economic indicators.
One critical element that should not be overlooked is setting realistic goals and timelines for achieving the forecasted outcomes.
Additionally, it is essential to prepare alternative scenarios to gauge the impact of unforeseen events on the business’s financial health.
Overall, the Financial Projection subsection provides insights into the potential financial performance of the business and enables entrepreneurs to develop a well-informed roadmap for success.
Appendix Section In A Business Plan
The Appendix section is an optional section that can be included in a business plan. This section provides space to include any additional information that investors or lenders may find useful in evaluating the business plan.
The Appendix can be used to include resumes of key personnel, product or service brochures, legal documents, and any other relevant information that supports the business plan.
It is important to remember that the Appendix should not be used to include information that should be in other sections, but rather to include supplementary information that adds value to the overall plan.
Steps In Business Planning
Step 1: research and analysis.
A crucial step in creating a successful business plan is conducting thorough research and analysis. This step involves collecting and analyzing relevant data from various sources, such as industry reports, customer surveys, and competitor analysis.
The purpose of this research is to gain a deep understanding of the market, identify potential customers, and evaluate market trends and changes.
Analyzing the data collected enables entrepreneurs to identify opportunities and potential threats that their business may face.
Additionally, this step involves evaluating the resources required to establish and run the business, including understanding the costs associated with acquiring and retaining customers, product development, and distribution.
One of the essential factors to consider during the research and analysis stage is the target market. It is important to identify the audience who would be interested in the product or service offered by the business.
Identifying the target market helps entrepreneurs to evaluate the size of the market, the preferences of their potential customers, and the most effective marketing strategies.
Moreover, research provides entrepreneurs with an understanding of customer spending habits and the overall demand for the product.
This knowledge enables entrepreneurs to tailor their business plan to meet the needs of the target market and increase the likelihood of success.
Another critical aspect of the research and analysis stage is evaluating the competition. An analysis of the existing businesses in the industry helps entrepreneurs identify potential rivals.
It also provides insights into the strengths and weaknesses of competitors, their marketing strategies, and the types of products or services they offer.
This information empowers entrepreneurs to develop unique value propositions and competitive advantages that will differentiate their business from others in the market.In summary, research and analysis are the foundation of a successful business plan.
It provides entrepreneurs with a clear understanding of the market, target audience, and competition.
This information enables entrepreneurs to create a comprehensive plan that outlines the steps required to establish and run a profitable business.
Conducting thorough research and analysis is essential to increase the chances of success and minimize the risks associated with starting a new business.
Step 2: Develop A Strategic Plan
The second step in the business planning process is to develop a strategic plan. This is a critical step that involves identifying goals and objectives for the company, as well as the strategies and tactics that will be used to achieve them.
A strategic plan should include a detailed analysis of the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This information can be obtained through market research, customer surveys, and other methods.
Once this analysis is complete, the company can begin to develop a plan for achieving its goals. This should include a detailed description of the company’s products or services, its target market, and its competitors.
It should also include a plan for marketing and sales, as well as financial projections for the next few years.
An important component of the strategic plan is the identification of key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure the success of the plan.
These KPIs should be specific and measurable, and should be reviewed regularly to ensure that the plan is on track.
The strategic plan should also consider the company’s resources, including its human capital, financial resources, and technological infrastructure. It should identify any gaps in these resources and make recommendations for how they can be filled.
Ultimately, the strategic plan should be a living document that is reviewed and updated regularly. As the company grows and changes, the plan should be adjusted accordingly to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
Step 3: Create A Business Plan
Step 4: implement the plan.
The actual implementation of a business plan involves executing each step of the strategy. The effectiveness of the plan heavily relies on the satisfaction of the plan’s objectives, the use of realistic timelines, and the deployment of adequate resources.
The business’ management will need to generate functional plans to ensure that resources are allocated optimally. Timelines must also be established for every step of the process to monitor progress and adjust the plan if necessary.
Good communication with all stakeholders is essential to successful implementation. The plan must be communicated to all employees, contractors, and vendors.
The resources, including personnel and funding, must be aligned with the plan. Efficient coordination is necessary to ensure that everyone is working towards the same end goal.
Performance measurement is crucial, as adjustment to the plan may be necessary to achieve the intended outcomes.
Technology and software may also be necessary in executing specific strategies, which should be included in the plan.
Addressing challenges and roadblocks along the way may also require flexible thinking and adapting the plan accordingly.
Therefore, the process of implementing a business plan involves evaluating the plan’s success and adaption of the plan to current business operations.
By successfully implementing the plan, the business can achieve its desired outcome and ultimately achieve its end goal.
Step 5: Monitor And Review
After implementing a business plan, monitoring and reviewing are crucial steps to ensure success. This stage is vital because it allows a business owner to determine if their strategies are working effectively or if changes need to be made.
It is an opportunity to observe the strengths and weaknesses of a business, discover any financial or operational problems, and measure progress toward established goals.
Monitoring includes tracking financial performance, sales figures, production levels, and customer satisfaction rates.
Reviewing involves analyzing the data gathered from monitoring activities and implementing changes to improve the business.
Monitoring and reviewing also help with business planning, providing entrepreneurs with a basis for decision-making.
Ongoing tracking and analysis can identify potential areas of growth, new opportunities, and potential risks.
Keeping current with industry trends, competitive analysis, and customer feedback can be included in the monitoring and review process.
By identifying and addressing challenges, a business can stay ahead of the competition and improve operations, products, and services.
Regular reviews act as a preventative measure for changes in the market or industry. Real-time optimization can be applied to marketing campaigns, cost structures, sales techniques, and more.
By consistently monitoring and reviewing, a business owner can take immediate corrective action instead of waiting until it’s too late.
Additionally, reviewing allows for continual improvement by providing insight into potential opportunities for growth and increased profitability.
A monitoring and review system should be established as part of the overall plan. This should include setting benchmarks and metrics, as well as scheduling regular reviews of progress toward established goals.
Once the system is in place, the focus should shift towards utilizing data gathered from monitoring and review activities.
This data should be analyzed, identifying areas that require changes and taking action to implement those changes.
In conclusion, monitoring and reviewing are important elements to ensure the continued success of a business.
Through monitoring and reviewing activities, entrepreneurs can gain a better understanding of their business operations and optimize accordingly.
By utilizing data and implementing changes, businesses can ensure long-term profitability and sustainable growth.
Types Of Business Plans
Startup business plan.
A startup business plan is an essential document that outlines the road map for a new business venture.
It is a comprehensive document that typically includes an executive summary, market analysis, company description, product or service offerings, marketing and sales strategies, financials, and a timeline.
The purpose of the business plan is to help entrepreneurs map out their goals and objectives, identify potential roadblocks, and develop strategies to overcome them.
By creating a startup business plan, entrepreneurs can gain a better understanding of their customers, competitors, and market trends.
In addition, they can use the plan to secure funding from investors or financial institutions, to communicate their vision to potential employees, and to develop a clear and concise strategy for scaling the business.
A well-crafted startup business plan is a crucial component of launching a successful new business venture.
Internal Business Plan
The Internal Business Plan is a critical component of the overall business plan. It outlines the internal strategies and tactics that a company will use to achieve its objectives.
This plan is developed by the management team and guides the day-to-day operations of the company. The Internal Business Plan addresses the company’s marketing, operations, financial, and human resources objectives.
A key part of the plan is developing a clear understanding of the company’s competitive advantage and how it will use this advantage to successfully compete within the marketplace.
The Internal Business Plan is also used to assess the company’s progress toward its goals and to make adjustments to the plan as needed.
This plan is different from the Strategic Business Plan which addresses the direction and overall vision of the company, while the Internal Business Plan is focused on the day-to-day operations.
A successful Internal Business Plan is critical to any start-up business as it provides a roadmap for the company to follow and helps create a culture of accountability and focus on achieving the company’s objectives.
Strategic Business Plan
A strategic business plan is a vital component of any successful business. It outlines a company’s overall direction, goals, and objectives over the long term.
A strategic business plan is not just a document, but rather a roadmap that guides a company’s decision-making processes.
It involves conducting a thorough analysis of a company’s market, competition, resources, and capabilities to create a unique value proposition.
The strategic business plan enables a company to position itself in the market and differentiate itself from competitors. The plan should also outline specific actions that need to be taken to achieve the desired objectives.
The strategic business plan typically includes the mission statement, which defines the company’s purpose, values, and culture.
It should also identify the target market and customer segments, as well as the channels and strategies used to reach them.
The plan should also analyze the competitive landscape, identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) to the business.
One of the critical components of a strategic business plan is setting clear and measurable goals and objectives over the long term.
These should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). The goals and objectives should align with the company’s mission statement and vision, and support the overall strategy.
The strategic plan should also outline the tactics and actions that will be taken to achieve these goals, as well as the timeline and resources required.
Another important element of a strategic business plan is the financial plan. This should include a detailed budget, sales forecast, cost of goods sold, cash flow projection, and profit and loss statement.
The financial plan should also consider contingencies and risk management strategies.
A well-executed strategic business plan can significantly benefit a company’s growth and success.
It provides a clear roadmap for decision-making, enabling a company to make informed and strategic choices.
It also helps to align all stakeholders around a common vision and direction, which can improve employee engagement and motivation.
Finally, a strategic business plan enhances a company’s credibility and reputation, which can attract investors, customers, and partners.
Operations Business Plan
The Operations Business Plan is a crucial component of any business plan, as it details the necessary steps to achieve operational efficiency and success.
This subsection focuses on the day-to-day running of the business, outlining the processes and procedures that will be followed, including production, logistics, inventory management, customer service, and more.
A well-crafted Operations Business Plan should provide clear guidance on how the company will meet its goals, reduce costs, and optimize processes.
One of the key elements of an Operations Business Plan is the production plan, which outlines the processes and resources needed to manufacture products or deliver services to customers.
This plan should include production schedules, quality control measures, and contingency plans in case of unexpected delays or problems.
Additionally, inventory management is crucial to ensure that the business has the appropriate amount of goods on hand, minimizing waste and avoiding shortages.
Another important aspect of an Operations Business Plan is logistics, covering the transport of goods and services from the company to the customers.
Logistics might include shipping, delivery, or other transportation-related activities that can affect the efficiency and effectiveness of the business.
Customer service is also a critical component, ensuring that customers feel valued and satisfied with their interactions with the company.
Efficient operation requires effective management, and an Operations Business Plan should outline the organizational structure of the company, including roles and responsibilities of staff members.
Clear communication and collaboration among team members are essential to ensuring that the business runs smoothly and effectively.
Overall, a well-conceived Operations Business Plan is a fundamental component of an effective business plan.
By addressing the day-to-day operations and processes needed for a business to function, this plan helps ensure that the company can operate effectively, minimize waste, and achieve its goals.
Feasibility Business Plan
One of the most critical components of a successful business launch is creating a feasibility business plan.
This type of plan focuses on determining whether a business idea is practical and worth pursuing.
At its core, a feasibility plan looks at the market demand for a product or service, analyzes the competition, examines potential revenue streams, and evaluates the resources required to bring the idea to fruition.
The plan should also outline the risks and challenges associated with the business, as well as any legal and regulatory considerations that may impact its viability.
During the feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs should identify their target audience and understand their behavior and needs.
This analysis is crucial in determining the market demand for the product or service. At the same time, businesses must determine how they will differentiate themselves from the competition.
It’s important to analyze your competition’s strengths and weaknesses, identify opportunities, and determine how to leverage them to create a competitive advantage.
Another critical aspect of the feasibility analysis is identifying potential revenue streams. Businesses need to consider the various ways they can generate income and determine which ones are the most viable.
They should also consider potential expenses, such as marketing and advertising, rent, utilities, and employee salaries.
Once revenue and expenses have been identified, businesses can create financial projections to determine their profitability and whether their business idea is economically sound.
Resource allocation is another essential consideration in a feasibility business plan. Entrepreneurs need to determine what resources they will require to launch and sustain their business.
This includes financial resources, such as startup capital and ongoing funding, as well as human resources, such as employees and contractors.
Businesses must also consider the resources required for production, such as equipment, raw materials, and supplies.
Finally, it’s essential to identify and understand the risks and challenges associated with launching and running a business.
This includes legal and regulatory concerns, such as permits and licenses, as well as other challenges, such as technological advancements or changes in the market.
By identifying and evaluating these risks, businesses can create contingency plans and ensure they have the resources and expertise needed to overcome potential obstacles.
In conclusion, creating a feasibility business plan is an essential first step in launching a successful business.
It provides a comprehensive overview of the business idea, evaluating its potential and risks, and determines whether it is a sound investment.
By conducting a thorough analysis of the market demand, competition, potential revenue streams, resource allocation, and risk and challenges, entrepreneurs can make an informed decision and pursue their business idea with a greater level of confidence and success.
Growth Business Plan
Growth Business Plan is a vital component for businesses that have survived their initial stages and are looking to scale up their operations.
This type of plan focuses on strategies that can be implemented to facilitate growth and increased profitability.
One of the primary concerns of a Growth Business Plan is identifying new areas for expansion, such as new products, markets, or services.
It also involves assessing current operations to determine how they can be optimized and scaled efficiently.
The first step to creating a Growth Business Plan is conducting a market analysis to gain a comprehensive understanding of industry trends, consumer demands, and emerging opportunities.
This involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources such as industry reports, competitor analysis, and consumer feedback.
The goal is to identify untapped markets, potential partnerships, and new revenue streams that can be leveraged to facilitate growth.
The second step is to assess the existing organizational structure to determine if changes need to be made to support growth.
This includes hiring additional staff, expanding the physical infrastructure, or investing in new technology.
A comprehensive growth strategy must also address potential risks and challenges that may arise during the scaling process, such as changes in consumer behavior, supply chain disruptions, or regulatory changes.
Another critical aspect of a Growth Business Plan is financial planning. This involves conducting a financial analysis of the company’s operations to identify areas where cost savings can be realized and new revenue streams can be generated.
The plan must also include a detailed financial forecast that outlines revenue projections, cash flow forecasts, and budgets for capital expenditures.
Ultimately, a successful Growth Business Plan must articulate a clear and comprehensive strategy that establishes a roadmap for scaling up operations while maintaining profitability.
The plan must be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the market, consumer behavior, or the regulatory environment while also being prudent in managing risks associated with growth.
Clear communication of the plan to all the stakeholders of the business is necessary for flawless execution of the expansion efforts.
Exit Business Plan
One important aspect of business planning that is often overlooked is the Exit Business Plan. This subsection of a business plan outlines the steps that the company will take in the event that it needs to close down or be sold.
This can be an important consideration for investors and stakeholders, as it can help them understand the potential risks and rewards associated with their investment.
The Exit Business Plan should include a thorough analysis of the company’s financials, including any outstanding debts or liabilities, as well as projections for future revenue and expenses.
It should also outline the company’s strategy for selling its assets or winding down its operations, including any legal or regulatory considerations that may come into play.
Another important aspect of the Exit Business Plan is succession planning. This involves identifying key personnel who will be responsible for ensuring a smooth transition in the event of an exit, and outlining their roles and responsibilities.
It may also involve identifying potential buyers or partners who could take over the company, and developing a strategy for negotiating a sale or merger.
Ultimately, the purpose of the Exit Business Plan is to minimize risk and maximize value for all stakeholders involved.
By planning for the possibility of an exit from the outset, companies can be better prepared to handle unforeseen circumstances and minimize the potential impact on their investors and employees.
Summary Of Business Planning
Business planning is an essential component of any successful enterprise. It serves as a roadmap for achieving business objectives, providing a framework for decision-making, and establishing accountability.
Through the process of business planning, a company can identify its strengths and weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate risks.
When developing a business plan, it is essential to consider a variety of factors, such as market trends, competitive analysis, financial projections, and growth strategies.
Although it can be challenging to predict the future, a comprehensive business plan can help a company navigate the uncertainties of the marketplace, establish credibility with stakeholders, and secure funding.
The process of creating a business plan can also reveal gaps in knowledge or resources, providing an opportunity for further research or collaboration.
As businesses continue to evolve and adapt to changing market conditions, a robust business plan can serve as a foundation for future growth and success.
Future Outlook Of Business Planning
The future of business planning is promising and exciting. As technology continues to advance, businesses are able to gather more data and better understand their customers, which can inform their strategic planning.
With the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning, businesses can gather insights faster and with greater accuracy. This allows for more precise forecasting and strategic decision-making.
Another relevant trend is the growing popularity of sustainability-focused business planning. Many companies are recognizing the importance of sustainability, given the impact of climate change and the increasing demand for sustainable products and services.
This approach to planning involves looking beyond short-term profits and considering the long-term impact of a business’s actions on the environment and society.
Moreover, the trend toward remote work and decentralized teams is changing how businesses approach planning. Virtual collaboration tools, such as video conferencing and online project management platforms, have made it easier for teams to work effectively from anywhere in the world.
This allows businesses to tap into talent pools globally, which can lead to more diverse and innovative ideas.
Finally, the future of business planning involves adapting to the changing needs of customers, who are increasingly looking for personalized and convenient experiences. Businesses that can offer this are likely to thrive, while those that fail to adapt may fall behind.
This means incorporating customer feedback into planning and investing in technologies, such as chatbots and personalization engines, that can help businesses provide more targeted and relevant experiences to their customers.
Implementing Recommendations
After conducting a thorough examination of Business Planning, it is clear that several recommendations must be made to ensure successful implementation of a business plan.
Firstly, businesses must ensure that every employee is included in the planning process. All departments within the company must have clear communication channels, as collaboration is essential to the success of the plan.
Secondly, businesses should regularly collect and analyze data relevant to their operations. This data can be used to improve and adjust plans as necessary.
Thirdly, businesses must regularly review their business plans and make necessary alterations to keep their plan relevant and up-to-date.
Finally, businesses should always have contingency plans in place. This will help them prepare for unexpected circumstances and better navigate potential risks.
In conclusion, businesses must remain flexible and adaptable in their planning to achieve success, and implementation of the above recommendations will enable them to do so.
Business Planning: FAQs
1. what is business planning.
Business Planning is the process of creating a roadmap for a business’s future. It comprises various steps, including identifying company objectives, conducting a market analysis, determining financial projections, and outlining strategies to achieve goals.
2. Who Needs A Business Plan?
Business planning is essential for any business, irrespective of its size, stage of operations, or industry. Entrepreneurs, startups, and established businesses that want to scale their operations and increase their profitability require a comprehensive and well-structured business plan.
3. Why Is Business Planning Important?
It ensures that a business has a clear direction and vision, helps identify potential opportunities, mitigates challenges, and reduces risks. Furthermore, it plays a crucial role in securing financing, attracting investors, and keeping the organization focused and accountable for its actions.
4. What Should My Business Plan Include?
A comprehensive business plan should include an executive summary, company overview, market analysis, products and services description, marketing and sales strategy, financial projections, organization structure, and operational plan.
5. How Often Should I Update My Business Plan?
Business plans aren’t static documents and should be updated regularly to reflect changes in the market, business evolution, and goals. A business plan should be reviewed annually and updated as needed to ensure that it remains effective and relevant.
6. Can I Write My Own Business Plan?
Yes, although it may be challenging to develop a comprehensive and effective business plan without prior experience. However, there are several resources and tools available, including templates, guides, software, or seeking the services of a business consultant.

Learn how to make passive income online
I've put together a free training on *How We Used The Brand New "Silver Lining Method" To Make $3k-$10k/mo (profit) With Just A Smart Phone In As Little As 8 Weeks …
About the author
Mike Vestil
Mike Vestil is an author, investor, and speaker known for building a business from zero to $1.5 million in 12 months while traveling the world.
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
Table of Contents
What is a business plan, the advantages of having a business plan, the types of business plans, the key elements of a business plan, best business plan software, common challenges of writing a business plan, become an expert business planner, business planning: it’s importance, types and key elements.

Every year, thousands of new businesses see the light of the day. One look at the World Bank's Entrepreneurship Survey and database shows the mind-boggling rate of new business registrations. However, sadly, only a tiny percentage of them have a chance of survival.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, about 20% of small businesses fail in their first year, about 50% in their fifth year.
Research from the University of Tennessee found that 44% of businesses fail within the first three years. Among those that operate within specific sectors, like information (which includes most tech firms), 63% shut shop within three years.
Several other statistics expose the abysmal rates of business failure. But why are so many businesses bound to fail? Most studies mention "lack of business planning" as one of the reasons.
This isn’t surprising at all.
Running a business without a plan is like riding a motorcycle up a craggy cliff blindfolded. Yet, way too many firms ( a whopping 67%) don't have a formal business plan in place.
It doesn't matter if you're a startup with a great idea or a business with an excellent product. You can only go so far without a roadmap — a business plan. Only, a business plan is so much more than just a roadmap. A solid plan allows a business to weather market challenges and pivot quickly in the face of crisis, like the one global businesses are struggling with right now, in the post-pandemic world.
But before you can go ahead and develop a great business plan, you need to know the basics. In this article, we'll discuss the fundamentals of business planning to help you plan effectively for 2021.
Now before we begin with the details of business planning, let us understand what it is.
No two businesses have an identical business plan, even if they operate within the same industry. So one business plan can look entirely different from another one. Still, for the sake of simplicity, a business plan can be defined as a guide for a company to operate and achieve its goals.
More specifically, it's a document in writing that outlines the goals, objectives, and purpose of a business while laying out the blueprint for its day-to-day operations and key functions such as marketing, finance, and expansion.
A good business plan can be a game-changer for startups that are looking to raise funds to grow and scale. It convinces prospective investors that the venture will be profitable and provides a realistic outlook on how much profit is on the cards and by when it will be attained.
However, it's not only new businesses that greatly benefit from a business plan. Well-established companies and large conglomerates also need to tweak their business plans to adapt to new business environments and unpredictable market changes.
Before getting into learning more about business planning, let us learn the advantages of having one.
Since a detailed business plan offers a birds-eye view of the entire framework of an establishment, it has several benefits that make it an important part of any organization. Here are few ways a business plan can offer significant competitive edge.
- Sets objectives and benchmarks: Proper planning helps a business set realistic objectives and assign stipulated time for those goals to be met. This results in long-term profitability. It also lets a company set benchmarks and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) necessary to reach its goals.
- Maximizes resource allocation: A good business plan helps to effectively organize and allocate the company’s resources. It provides an understanding of the result of actions, such as, opening new offices, recruiting fresh staff, change in production, and so on. It also helps the business estimate the financial impact of such actions.
- Enhances viability: A plan greatly contributes towards turning concepts into reality. Though business plans vary from company to company, the blueprints of successful companies often serve as an excellent guide for nascent-stage start-ups and new entrepreneurs. It also helps existing firms to market, advertise, and promote new products and services into the market.
- Aids in decision making: Running a business involves a lot of decision making: where to pitch, where to locate, what to sell, what to charge — the list goes on. A well thought-out business plan provides an organization the ability to anticipate the curveballs that the future could throw at them. It allows them to come up with answers and solutions to these issues well in advance.
- Fix past mistakes: When businesses create plans keeping in mind the flaws and failures of the past and what worked for them and what didn’t, it can help them save time, money, and resources. Such plans that reflects the lessons learnt from the past offers businesses an opportunity to avoid future pitfalls.
- Attracts investors: A business plan gives investors an in-depth idea about the objectives, structure, and validity of a firm. It helps to secure their confidence and encourages them to invest.
Now let's look at the various types involved in business planning.
Become a Business and Leadership Professional
- Top 10 skills in demand Business Analysis As A Skill In 2020
- 14% Growth in Jobs Of Business Analysis Profile By 2028
Business Analyst
- Industry-recognized certifications from IBM and Simplilearn
- Masterclasses from IBM experts
Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis
- Certificate from Simplilearn in collaboration with Purdue University
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Assistant Consultant at Tata Consultancy Services , Tata Consultancy Services
My experience with Simplilearn has been great till now. They have good materials to start with, and a wide range of courses. I have signed up for two courses with Simplilearn over the past 6 months, Data Scientist and Agile and Scrum. My experience with both is good. One unique feature I liked about Simplilearn is that they give pre-requisites that you should complete, before a live class, so that you go there fully prepared. Secondly, there support staff is superb. I believe there are two teams, to cater to the Indian and US time zones. Simplilearn gives you the most methodical and easy way to up-skill yourself. Also, when you compare the data analytics courses across the market that offer web-based tutorials, Simplilearn, scores over the rest in my opinion. Great job, Simplilearn!
I was keenly looking for a change in my domain from business consultancy to IT(Business Analytics). This Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis course helped me achieve the same. I am proficient in business analysis now and am looking for job profiles that suit my skill set.
Business plans are formulated according to the needs of a business. It can be a simple one-page document or an elaborate 40-page affair, or anything in between. While there’s no rule set in stone as to what exactly a business plan can or can’t contain, there are a few common types of business plan that nearly all businesses in existence use.
Here’s an overview of a few fundamental types of business plans.
- Start-up plan: As the name suggests, this is a documentation of the plans, structure, and objections of a new business establishments. It describes the products and services that are to be produced by the firm, the staff management, and market analysis of their production. Often, a detailed finance spreadsheet is also attached to this document for investors to determine the viability of the new business set-up.
- Feasibility plan: A feasibility plan evaluates the prospective customers of the products or services that are to be produced by a company. It also estimates the possibility of a profit or a loss of a venture. It helps to forecast how well a product will sell at the market, the duration it will require to yield results, and the profit margin that it will secure on investments.
- Expansion Plan: This kind of plan is primarily framed when a company decided to expand in terms of production or structure. It lays down the fundamental steps and guidelines with regards to internal or external growth. It helps the firm to analyze the activities like resource allocation for increased production, financial investments, employment of extra staff, and much more.
- Operations Plan: An operational plan is also called an annual plan. This details the day-to-day activities and strategies that a business needs to follow in order to materialize its targets. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of the managing body, the various departments, and the company’s employees for the holistic success of the firm.
- Strategic Plan: This document caters to the internal strategies of the company and is a part of the foundational grounds of the establishments. It can be accurately drafted with the help of a SWOT analysis through which the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats can be categorized and evaluated so that to develop means for optimizing profits.
There is some preliminary work that’s required before you actually sit down to write a plan for your business. Knowing what goes into a business plan is one of them.
Here are the key elements of a good business plan:
- Executive Summary: An executive summary gives a clear picture of the strategies and goals of your business right at the outset. Though its value is often understated, it can be extremely helpful in creating the readers’ first impression of your business. As such, it could define the opinions of customers and investors from the get-go.
- Business Description: A thorough business description removes room for any ambiguity from your processes. An excellent business description will explain the size and structure of the firm as well as its position in the market. It also describes the kind of products and services that the company offers. It even states as to whether the company is old and established or new and aspiring. Most importantly, it highlights the USP of the products or services as compared to your competitors in the market.
- Market Analysis: A systematic market analysis helps to determine the current position of a business and analyzes its scope for future expansions. This can help in evaluating investments, promotions, marketing, and distribution of products. In-depth market understanding also helps a business combat competition and make plans for long-term success.
- Operations and Management: Much like a statement of purpose, this allows an enterprise to explain its uniqueness to its readers and customers. It showcases the ways in which the firm can deliver greater and superior products at cheaper rates and in relatively less time.
- Financial Plan: This is the most important element of a business plan and is primarily addressed to investors and sponsors. It requires a firm to reveal its financial policies and market analysis. At times, a 5-year financial report is also required to be included to show past performances and profits. The financial plan draws out the current business strategies, future projections, and the total estimated worth of the firm.
The importance of business planning is it simplifies the planning of your company's finances to present this information to a bank or investors. Here are the best business plan software providers available right now:
- Business Sorter
The importance of business planning cannot be emphasized enough, but it can be challenging to write a business plan. Here are a few issues to consider before you start your business planning:
- Create a business plan to determine your company's direction, obtain financing, and attract investors.
- Identifying financial, demographic, and achievable goals is a common challenge when writing a business plan.
- Some entrepreneurs struggle to write a business plan that is concise, interesting, and informative enough to demonstrate the viability of their business idea.
- You can streamline your business planning process by conducting research, speaking with experts and peers, and working with a business consultant.
Whether you’re running your own business or in-charge of ensuring strategic performance and growth for your employer or clients, knowing the ins and outs of business planning can set you up for success.
Be it the launch of a new and exciting product or an expansion of operations, business planning is the necessity of all large and small companies. Which is why the need for professionals with superior business planning skills will never die out. In fact, their demand is on the rise with global firms putting emphasis on business analysis and planning to cope with cut-throat competition and market uncertainties.
While some are natural-born planners, most people have to work to develop this important skill. Plus, business planning requires you to understand the fundamentals of business management and be familiar with business analysis techniques . It also requires you to have a working knowledge of data visualization, project management, and monitoring tools commonly used by businesses today.
Simpliearn’s Executive Certificate Program in General Management will help you develop and hone the required skills to become an extraordinary business planner. This comprehensive general management program by IIM Indore can serve as a career catalyst, equipping professionals with a competitive edge in the ever-evolving business environment.
What Is Meant by Business Planning?
Business planning is developing a company's mission or goals and defining the strategies you will use to achieve those goals or tasks. The process can be extensive, encompassing all aspects of the operation, or it can be concrete, focusing on specific functions within the overall corporate structure.
What Are the 4 Types of Business Plans?
The following are the four types of business plans:
Operational Planning
This type of planning typically describes the company's day-to-day operations. Single-use plans are developed for events and activities that occur only once (such as a single marketing campaign). Ongoing plans include problem-solving policies, rules for specific regulations, and procedures for a step-by-step process for achieving particular goals.
Strategic Planning
Strategic plans are all about why things must occur. A high-level overview of the entire business is included in strategic planning. It is the organization's foundation and will dictate long-term decisions.
Tactical Planning
Tactical plans are about what will happen. Strategic planning is aided by tactical planning. It outlines the tactics the organization intends to employ to achieve the goals outlined in the strategic plan.
Contingency Planning
When something unexpected occurs or something needs to be changed, contingency plans are created. In situations where a change is required, contingency planning can be beneficial.
What Are the 7 Steps of a Business Plan?
The following are the seven steps required for a business plan:
Conduct Research
If your company is to run a viable business plan and attract investors, your information must be of the highest quality.
Have a Goal
The goal must be unambiguous. You will waste your time if you don't know why you're writing a business plan. Knowing also implies having a target audience for when the plan is expected to get completed.
Create a Company Profile
Some refer to it as a company profile, while others refer to it as a snapshot. It's designed to be mentally quick and digestible because it needs to stick in the reader's mind quickly since more information is provided later in the plan.
Describe the Company in Detail
Explain the company's current situation, both good and bad. Details should also include patents, licenses, copyrights, and unique strengths that no one else has.
Create a marketing plan ahead of time.
A strategic marketing plan is required because it outlines how your product or service will be communicated, delivered, and sold to customers.
Be Willing to Change Your Plan for the Sake of Your Audience
Another standard error is that people only write one business plan. Startups have several versions, just as candidates have numerous resumes for various potential employers.
Incorporate Your Motivation
Your motivation must be a compelling reason for people to believe your company will succeed in all circumstances. A mission should drive a business, not just selling, to make money. That mission is defined by your motivation as specified in your business plan.
What Are the Basic Steps in Business Planning?
These are the basic steps in business planning:
Summary and Objectives
Briefly describe your company, its objectives, and your plan to keep it running.
Services and Products
Add specifics to your detailed description of the product or service you intend to offer. Where, why, and how much you plan to sell your product or service and any special offers.
Conduct research on your industry and the ideal customers to whom you want to sell. Identify the issues you want to solve for your customers.
Operations are the process of running your business, including the people, skills, and experience required to make it successful.
How are you going to reach your target audience? How you intend to sell to them may include positioning, pricing, promotion, and distribution.
Consider funding costs, operating expenses, and projected income. Include your financial objectives and a breakdown of what it takes to make your company profitable. With proper business planning through the help of support, system, and mentorship, it is easy to start a business.
Our Business And Leadership Courses Duration And Fees
Business And Leadership Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Business and Leadership
Business Analysis Basics
Data Science & Business Analytics
Business Intelligence Fundamentals
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
From Concept to Market - How to Excel at Product Management in 2024 with SP Jain Program
Ascend the Product Management Career Ladder in 2024 with UC San Diego
Career Information Session: Find Out How to Become a Business Analyst with IIT Roorkee
Recommended Reads
Business Intelligence Career Guide: Your Complete Guide to Becoming a Business Analyst
Corporate Succession Planning: How to Create Leaders According to the Business Need
Top Business Analyst Skills
Business Analytics Basics: A Beginner’s Guide
Financial Planning for Businesses Across the Globe
How to Become a Business Analyst
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
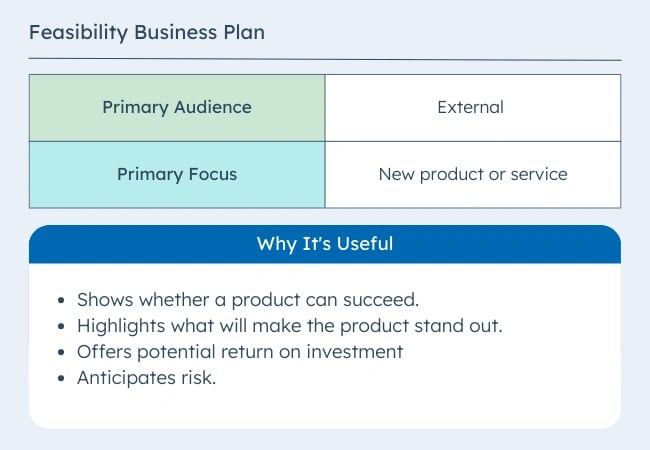
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![discuss the importance of business planning in entrepreneurship How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![discuss the importance of business planning in entrepreneurship 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![discuss the importance of business planning in entrepreneurship The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
What is a Business Plan? Definition and Resources

9 min. read
Updated April 19, 2024
If you’ve ever jotted down a business idea on a napkin with a few tasks you need to accomplish, you’ve written a business plan — or at least the very basic components of one.
The origin of formal business plans is murky. But they certainly go back centuries. And when you consider that 20% of new businesses fail in year 1 , and half fail within 5 years, the importance of thorough planning and research should be clear.
But just what is a business plan? And what’s required to move from a series of ideas to a formal plan? Here we’ll answer that question and explain why you need one to be a successful business owner.
- What is a business plan?

A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business.
Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research , analyze their competitors , validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition .
The business plan captures that opportunity you see for your company: it describes your product or service and business model , and the target market you’ll serve.
It also includes details on how you’ll execute your plan: how you’ll price and market your solution and your financial projections .
Reasons for writing a business plan
If you’re asking yourself, ‘Do I really need to write a business plan?’ consider this fact:
Companies that commit to planning grow 30% faster than those that don’t.
Creating a business plan is crucial for businesses of any size or stage.
If you plan to raise funds for your business through a traditional bank loan or SBA loan , none of them will want to move forward without seeing your business plan. Venture capital firms may or may not ask for one, but you’ll still need to do thorough planning to create a pitch that makes them want to invest.
But it’s more than just a means of getting your business funded . The plan is also your roadmap to identify and address potential risks.
It’s not a one-time document. Your business plan is a living guide to ensure your business stays on course.
Related: 14 of the top reasons why you need a business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
What research shows about business plans
Numerous studies have established that planning improves business performance:
- 71% of fast-growing companies have business plans that include budgets, sales goals, and marketing and sales strategies.
- Companies that clearly define their value proposition are more successful than those that can’t.
- Companies or startups with a business plan are more likely to get funding than those without one.
- Starting the business planning process before investing in marketing reduces the likelihood of business failure.
The planning process significantly impacts business growth for existing companies and startups alike.
Read More: Research-backed reasons why writing a business plan matters
When should you write a business plan?
No two business plans are alike.
Yet there are similar questions for anyone considering writing a plan to answer. One basic but important question is when to start writing it.
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business.
But the reality can be more nuanced – it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written.
Ideal times to write a business plan include:
- When you have an idea for a business
- When you’re starting a business
- When you’re preparing to buy (or sell)
- When you’re trying to get funding
- When business conditions change
- When you’re growing or scaling your business
Read More: The best times to write or update your business plan
How often should you update your business plan?
As is often the case, how often a business plan should be updated depends on your circumstances.
A business plan isn’t a homework assignment to complete and forget about. At the same time, no one wants to get so bogged down in the details that they lose sight of day-to-day goals.
But it should cover new opportunities and threats that a business owner surfaces, and incorporate feedback they get from customers. So it can’t be a static document.
Related Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
For an entrepreneur at the ideation stage, writing and checking back on their business plan will help them determine if they can turn that idea into a profitable business .
And for owners of up-and-running businesses, updating the plan (or rewriting it) will help them respond to market shifts they wouldn’t be prepared for otherwise.
It also lets them compare their forecasts and budgets to actual financial results. This invaluable process surfaces where a business might be out-performing expectations and where weak performance may require a prompt strategy change.
The planning process is what uncovers those insights.
Related Reading: 10 prompts to help you write a business plan with AI
- How long should your business plan be?
Thinking about a business plan strictly in terms of page length can risk overlooking more important factors, like the level of detail or clarity in the plan.
Not all of the plan consists of writing – there are also financial tables, graphs, and product illustrations to include.
But there are a few general rules to consider about a plan’s length:
- Your business plan shouldn’t take more than 15 minutes to skim.
- Business plans for internal use (not for a bank loan or outside investment) can be as short as 5 to 10 pages.
A good practice is to write your business plan to match the expectations of your audience.
If you’re walking into a bank looking for a loan, your plan should match the formal, professional style that a loan officer would expect . But if you’re writing it for stakeholders on your own team—shorter and less formal (even just a few pages) could be the better way to go.
The length of your plan may also depend on the stage your business is in.
For instance, a startup plan won’t have nearly as much financial information to include as a plan written for an established company will.
Read More: How long should your business plan be?
What information is included in a business plan?
The contents of a plan business plan will vary depending on the industry the business is in.
After all, someone opening a new restaurant will have different customers, inventory needs, and marketing tactics to consider than someone bringing a new medical device to the market.
But there are some common elements that most business plans include:
- Executive summary: An overview of the business operation, strategy, and goals. The executive summary should be written last, despite being the first thing anyone will read.
- Products and services: A description of the solution that a business is bringing to the market, emphasizing how it solves the problem customers are facing.
- Market analysis: An examination of the demographic and psychographic attributes of likely customers, resulting in the profile of an ideal customer for the business.
- Competitive analysis: Documenting the competitors a business will face in the market, and their strengths and weaknesses relative to those competitors.
- Marketing and sales plan: Summarizing a business’s tactics to position their product or service favorably in the market, attract customers, and generate revenue.
- Operational plan: Detailing the requirements to run the business day-to-day, including staffing, equipment, inventory, and facility needs.
- Organization and management structure: A listing of the departments and position breakdown of the business, as well as descriptions of the backgrounds and qualifications of the leadership team.
- Key milestones: Laying out the key dates that a business is projected to reach certain milestones , such as revenue, break-even, or customer acquisition goals.
- Financial plan: Balance sheets, cash flow forecast , and sales and expense forecasts with forward-looking financial projections, listing assumptions and potential risks that could affect the accuracy of the plan.
- Appendix: All of the supporting information that doesn’t fit into specific sections of the business plan, such as data and charts.
Read More: Use this business plan outline to organize your plan
- Different types of business plans
A business plan isn’t a one-size-fits-all document. There are numerous ways to create an effective business plan that fits entrepreneurs’ or established business owners’ needs.
Here are a few of the most common types of business plans for small businesses:
- One-page plan : Outlining all of the most important information about a business into an adaptable one-page plan.
- Growth plan : An ongoing business management plan that ensures business tactics and strategies are aligned as a business scales up.
- Internal plan : A shorter version of a full business plan to be shared with internal stakeholders – ideal for established companies considering strategic shifts.
Business plan vs. operational plan vs. strategic plan
- What questions are you trying to answer?
- Are you trying to lay out a plan for the actual running of your business?
- Is your focus on how you will meet short or long-term goals?
Since your objective will ultimately inform your plan, you need to know what you’re trying to accomplish before you start writing.
While a business plan provides the foundation for a business, other types of plans support this guiding document.
An operational plan sets short-term goals for the business by laying out where it plans to focus energy and investments and when it plans to hit key milestones.
Then there is the strategic plan , which examines longer-range opportunities for the business, and how to meet those larger goals over time.
Read More: How to use a business plan for strategic development and operations
- Business plan vs. business model
If a business plan describes the tactics an entrepreneur will use to succeed in the market, then the business model represents how they will make money.
The difference may seem subtle, but it’s important.
Think of a business plan as the roadmap for how to exploit market opportunities and reach a state of sustainable growth. By contrast, the business model lays out how a business will operate and what it will look like once it has reached that growth phase.
Learn More: The differences between a business model and business plan
- Moving from idea to business plan
Now that you understand what a business plan is, the next step is to start writing your business plan .
The best way to start is by reviewing examples and downloading a business plan template. These resources will provide you with guidance and inspiration to help you write a plan.
We recommend starting with a simple one-page plan ; it streamlines the planning process and helps you organize your ideas. However, if one page doesn’t fit your needs, there are plenty of other great templates available that will put you well on your way to writing a useful business plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Reasons to write a business plan
- Business planning research
- When to write a business plan
- When to update a business plan
- Information to include
- Business vs. operational vs. strategic plans
Related Articles

8 Min. Read
What Type of Business Plan Do You Need?

1 Min. Read
Free Clothing Retail Sample Business Plan

15 Min. Read
How to Write a Cannabis Business Plan + Free Sample Plan

10 Min. Read
How to Set and Use Milestones in Your Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Why Is Planning an Important Step in Starting a Business?
- Small Business
- Setting Up a New Business
- Steps for Starting a Business
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
What Are the Main Purposes of a Business Plan?
What are the six elements of a business plan, how to develop a one-year business plan.
- The Importance of Business Plans
- What Are the 4 Important Parts of a Business Plan?
There are two primary reasons for writing a business plan. The first is to organize yourself, set priorities and identify the steps needed to achieve them. Secondly, a business plan is a principal means of showcasing your business to investors. However, not all companies need to develop a formal plan.
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a means of ensuring systematic planning in entrepreneurship. It is an important tool for starting a business and planning expansions of well-established businesses.
The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) considers a business plan to be the foundation of a small business startup. As the SBA describes them, business plans generally are written documents that can either be lengthy and highly detailed or shorter "lean" plans that act more as bullet-point style summaries of the business-to-be.
Business plans are usually written documents, but in the electronic age, they also take the form of Powerpoint slides or other styles of graphical presentation. Whatever the form, business plans typically cover several major areas:
- Executive summary: A quick overview of the business and the detailed information to follow in the plan
- Business description: What the new business will do, how it will make money, and why it will be successful against its competitors
- Market analysis: Typically, a quantitative presentation of the market for a company's goods or services and the competition in the marketplace
- Structure and management: The principal executives of the company and how the firm will be organized
- Marketing: The strategies the company will use to reach out to prospective customers and build up sales
- Finances: Money the company has on hand and anticipated near-term and long-term income and expenses
A business plan may include an explicit funding request that specifies how much it needs from lenders or financiers to take the steps envisioned in the overall plan.

Planning as an Organizational Tool
The importance of a business plan to an entrepreneur is hard to overstate, especially for entrepreneurs who are planning a sizable operation.
The preparation of a business plan forces a company's founders to confront the realities of building a successful business. Covering each of the planning topics requires you to articulate who will do what in the new company and identify the strengths and weaknesses of your ideas.
For example, preparing a market analysis requires you to research the competition in your field, identify realistic pricing for your products, and get a handle on what realistic sales numbers might look like in your initial years of operation.
Importance of a Business Plan to Investors
Whether you approach a bank for a business loan, angel investors for startup funding, or your friends and family for some financial help, would-be financiers want to have a good understanding of your business strategy, who will be involved in building the business, and your overall prospects of success.
These areas are all communicated, at least in part, through your business plan. In addition, business people are often asked to make in-person presentations, much as you might see on Shark Tank , and your business plan can provide the basis for the information you present in person.
Does Every Business Need a Formal Plan?
Almost all sizable businesses benefit from going through the process of creating a business plan.
However, most businesses in the U.S. are very small, one-person businesses known as sole proprietorships. Many of these are part-time enterprises that are expansions of existing hobbies such as dog-walking or photography. While businesses this small may not need a formal plan, it certainly doesn't hurt to think through the content of a typical plan to take away any lessons that may apply to your small business.
- U.S. Small Business Administration: Write Your Business Plan
- Shark Tank: Homepage
David Sarokin is a well-known Internet specialist with publications in a wide variety of business topics, from the best uses of information technology to the steps for incorporating your business. He is the author of The Corporation, Its History and Future (Cambridge Scholars, 2020) on the role of big business in the modern world, and Missed Information (MIT Press, 2016), detailing how our social systems like health care, finance and government can be improved with better quality information.
Related Articles
What are the key elements of a business plan, the importance of a business plan, importance of following a business plan, what is the overall purpose of a business plan, 6 types of business plans, why is an effective business plan introduction important, business plan vs. business strategy, what are the components of a good business plan, what are the benefits of a business plan, most popular.
- 1 What Are the Key Elements of a Business Plan?
- 2 The Importance of a Business Plan
- 3 Importance of Following a Business Plan
- 4 What Is the Overall Purpose of a Business Plan?
- > Master in Management (MiM)
- > Master in Research in Management (MRM)
- > PhD in Management
- > Executive MBA
- > Global Executive MBA
- Programs for Individuals
- Programs for Organizations
- > Artificial Intelligence for Executives
- > Foundations of Scaling
- > Sustainability & ESG
- CHOOSE YOUR MBA
- IESE PORTFOLIO
- PROGRAM FINDER
- > Faculty Directory
- > Academic Departments
- > Initiatives
- > Competitive Projects
- > Academic Events
- > Behavioral Lab
- > Limitless Learning
- > Learning Methodologies
- > The Case Method
- > IESE Insight: Research-Based Ideas
- > IESE Business School Insight Magazine
- > StandOut: Career Inspiration
- > Professors' Blogs
- > Alumni Learning Program
- > IESE Publishing
- SEARCH PUBLICATIONS
- IESE NEWSLETTERS
- > Our Mission, Vision and Values
- > Our History
- > Our Governance
- > Our Alliances
- > Our Impact
- > Diversity at IESE
- > Sustainability at IESE
- > Accreditations
- > Annual Report
- > Roadmap for 2023-25
- > Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- > Barcelona
- > São Paulo
- > Security & Campus Access
- > Loans and Scholarships
- > Chaplaincy
- > IESE Shop
- > Jobs @IESE
- > Compliance Channel
- > Contact Us
- GIVING TO IESE
- WORK WITH US

IESE Insight
The power of planning for entrepreneurs

Don't underestimate the importance of planning. Beyond keeping banks happy, IESE's Govert Vroom finds planning can transform the entrepreneur's approach.
"A goal without a plan is just a wish," the adage goes. Entrepreneurs looking to launch a new business should take heed.
The planning phase of a start-up isn't just providing a song and dance to please banks or investors. It plays a vital role in building the entrepreneur's self-belief and helps gauge the chances of success with greater accuracy. That is according to a 2015 study by Brian McCann and Govert Vroom published in the International Small Business Journal .
Analyzing data from a major U.S. survey of entrepreneurs over time, McCann and Vroom find that entrepreneurs who take more actions during the planning stage of a business help reduce the uncertainty surrounding it and realize their plans.
An opportunity, not an imposition
Many entrepreneurs regard business plans and financial projections as obligations imposed on them by banks or investors. Notably, Guy Kawasaki, a serial entrepreneur and venture capitalist, told IESE MBA students in November 2014 that he believes "it is no longer necessary to write a business plan. You can't foresee the future five years from now."
And while that may be patently true, the very exercise of trying to foresee the future five years from now is helpful, McCann and Vroom's study finds, and it is a helpful reminder in the power of processes to help entrepreneurs learn and profit from their knowledge.
Their study says entrepreneurs should take a wider view of planning, which may include actions such as defining potential markets and drawing up business plans with projections. These actions do not only help by possibly bringing in funding and other external resources, they also help develop the entrepreneurs themselves . Planning actions can indeed change the way entrepreneurs view their prospective business and their own competence to run it.
"Overall, our work provides unique evidence from a large-scale, representative sample of nascent entrepreneurs working to set up real businesses that nascency involves 'a critical, albeit often underestimated, learning process,'" they write, quoting from peers D. Ravasi and C. Turati who study entrepreneurial learning.
Survey says...
For this research, the authors work with the Panel Study of Entrepreneurial Dynamics (PSED), a large-scale survey of entrepreneurs in the process of starting businesses in the United States tracked over multiple waves of data collection.
Starting with over 1,000 survey respondents, McCann and Vroom first weeded out respondents who didn't meet their study's interest in individuals working to launch new ventures, such as those involved with restarting existing corporations or operating franchises. They then focused on the responses over time that addressed three key issues:
- Uncertainty . How much uncertainty did respondents perceive in their business environment in terms of how markets would develop, the competition and how key stakeholders would react to the start-up?
- Self-efficacy . How confident did they feel about their abilities to effectively run their businesses?
- Expectations of financial performance . How well did they feel their business would perform in financial terms? Did expectations grow or fall over time?
The authors found that engaging in planning activities over a period of 12 months led to significant changes in perceptions in each of these three areas — increasing certainty, self-efficacy and sales projections. Even experienced entrepreneurs seemed to learn and change their beliefs through planning activities. In fact, serial entrepreneurs' beliefs changed to a similar extent as novice entrepreneurs'.
In terms of reducing uncertainty, the data suggests planning actions are most helpful for understanding financial and competitive factors — namely, attracting funding, attracting customers, competing with other firms, complying with regulations, and keeping up with technological advances. Meanwhile, operational uncertainty — specifically, how to obtain raw materials, attract employees and deal with distributors — was reduced a bit, but not enough to be statistically significant.
On a side note, there was also evidence to suggest that entrepreneurs who were part of larger teams saw more positive results, perhaps (and commonsensically) due to their pooled knowledge and experiences.
Previous studies on nascent entrepreneurs have tended to concentrate on how the planning process helps them gain legitimacy or gather external resources. But McCann and Vroom's study looks at how entrepreneurs make ongoing assessments of their fledgling businesses — transforming their internal views in the process.
"Focusing on the legitimation aspects of planning might lead nascents to see it largely as an obligation imposed by external parties," they write. "Our research indicates that planning also serves an important complementary role of generating information and driving changes in beliefs, which will ultimately foster development of the opportunity."
Planning may not make perfect, but budding entrepreneurs should ignore it at their peril.
- entrepreneurship
Sign up for our newsletter for product updates, new blog posts, and the chance to be featured in our Small Business Spotlight!

The importance of a business plan
Business plans are like road maps: it’s possible to travel without one, but that will only increase the odds of getting lost along the way.
Owners with a business plan see growth 30% faster than those without one, and 71% of the fast-growing companies have business plans . Before we get into the thick of it, let’s define and go over what a business plan actually is.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a 15-20 page document that outlines how you will achieve your business objectives and includes information about your product, marketing strategies, and finances. You should create one when you’re starting a new business and keep updating it as your business grows.
Rather than putting yourself in a position where you may have to stop and ask for directions or even circle back and start over, small business owners often use business plans to help guide them. That’s because they help them see the bigger picture, plan ahead, make important decisions, and improve the overall likelihood of success.
Why is a business plan important?
A well-written business plan is an important tool because it gives entrepreneurs and small business owners, as well as their employees, the ability to lay out their goals and track their progress as their business begins to grow. Business planning should be the first thing done when starting a new business. Business plans are also important for attracting investors so they can determine if your business is on the right path and worth putting money into.
Business plans typically include detailed information that can help improve your business’s chances of success, like:
- A market analysis : gathering information about factors and conditions that affect your industry
- Competitive analysis : evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors
- Customer segmentation : divide your customers into different groups based on specific characteristics to improve your marketing
- Marketing: using your research to advertise your business
- Logistics and operations plans : planning and executing the most efficient production process
- Cash flow projection : being prepared for how much money is going into and out of your business
- An overall path to long-term growth
10 reasons why you need a business plan
I know what you’re thinking: “Do I really need a business plan? It sounds like a lot of work, plus I heard they’re outdated and I like figuring things out as I go...”.
The answer is: yes, you really do need a business plan! As entrepreneur Kevin J. Donaldson said, “Going into business without a business plan is like going on a mountain trek without a map or GPS support—you’ll eventually get lost and starve! Though it may sound tedious and time-consuming, business plans are critical to starting your business and setting yourself up for success.
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business.
1. To help you with critical decisions
The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and crisis management. Sitting down and considering all the ramifications of any given decision is a luxury that small businesses can’t always afford. That’s where a business plan comes in.
Building a business plan allows you to determine the answer to some of the most critical business decisions ahead of time.
Creating a robust business plan is a forcing function—you have to sit down and think about major components of your business before you get started, like your marketing strategy and what products you’ll sell. You answer many tough questions before they arise. And thinking deeply about your core strategies can also help you understand how those decisions will impact your broader strategy.
*While subscribed to Wave’s Pro Plan, get 2.9% + $0 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0 (Amex) per transaction for unlimited transactions during the offer period. After the offer ends: over 10 transactions per month at 2.9% + $0.60 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0.60 (Amex) per transaction. Discover processing is only available to US customers. See full terms and conditions.
See Terms of Service for more information.
Send invoices, get paid, track expenses, pay your team, and balance your books with our financial management software.
2. To iron out the kinks
Putting together a business plan requires entrepreneurs to ask themselves a lot of hard questions and take the time to come up with well-researched and insightful answers. Even if the document itself were to disappear as soon as it’s completed, the practice of writing it helps to articulate your vision in realistic terms and better determine if there are any gaps in your strategy.
3. To avoid the big mistakes
Only about half of small businesses are still around to celebrate their fifth birthday . While there are many reasons why small businesses fail, many of the most common are purposefully addressed in business plans.
According to data from CB Insights , some of the most common reasons businesses fail include:
- No market need : No one wants what you’re selling.
- Lack of capital : Cash flow issues or businesses simply run out of money.
- Inadequate team : This underscores the importance of hiring the right people to help you run your business.
- Stiff competition : It’s tough to generate a steady profit when you have a lot of competitors in your space.
- Pricing : Some entrepreneurs price their products or services too high or too low—both scenarios can be a recipe for disaster.
The exercise of creating a business plan can help you avoid these major mistakes. Whether it’s cash flow forecasts or a product-market fit analysis , every piece of a business plan can help spot some of those potentially critical mistakes before they arise. For example, don’t be afraid to scrap an idea you really loved if it turns out there’s no market need. Be honest with yourself!
Get a jumpstart on your business plan by creating your own cash flow projection .
4. To prove the viability of the business
Many businesses are created out of passion, and while passion can be a great motivator, it’s not a great proof point.
Planning out exactly how you’re going to turn that vision into a successful business is perhaps the most important step between concept and reality. Business plans can help you confirm that your grand idea makes sound business sense.

A critical component of your business plan is the market research section. Market research can offer deep insight into your customers, your competitors, and your chosen industry. Not only can it enlighten entrepreneurs who are starting up a new business, but it can also better inform existing businesses on activities like marketing, advertising, and releasing new products or services.
Want to prove there’s a market gap? Here’s how you can get started with market research.
5. To set better objectives and benchmarks
Without a business plan, objectives often become arbitrary, without much rhyme or reason behind them. Having a business plan can help make those benchmarks more intentional and consequential. They can also help keep you accountable to your long-term vision and strategy, and gain insights into how your strategy is (or isn’t) coming together over time.
6. To communicate objectives and benchmarks
Whether you’re managing a team of 100 or a team of two, you can’t always be there to make every decision yourself. Think of the business plan like a substitute teacher, ready to answer questions any time there’s an absence. Let your staff know that when in doubt, they can always consult the business plan to understand the next steps in the event that they can’t get an answer from you directly.
Sharing your business plan with team members also helps ensure that all members are aligned with what you’re doing, why, and share the same understanding of long-term objectives.
7. To provide a guide for service providers
Small businesses typically employ contractors , freelancers, and other professionals to help them with tasks like accounting , marketing, legal assistance, and as consultants. Having a business plan in place allows you to easily share relevant sections with those you rely on to support the organization, while ensuring everyone is on the same page.
8. To secure financing
Did you know you’re 2.5x more likely to get funded if you have a business plan?If you’re planning on pitching to venture capitalists, borrowing from a bank, or are considering selling your company in the future, you’re likely going to need a business plan. After all, anyone that’s interested in putting money into your company is going to want to know it’s in good hands and that it’s viable in the long run. Business plans are the most effective ways of proving that and are typically a requirement for anyone seeking outside financing.
Learn what you need to get a small business loan.
9. To better understand the broader landscape
No business is an island, and while you might have a strong handle on everything happening under your own roof, it’s equally important to understand the market terrain as well. Writing a business plan can go a long way in helping you better understand your competition and the market you’re operating in more broadly, illuminate consumer trends and preferences, potential disruptions and other insights that aren’t always plainly visible.
10. To reduce risk
Entrepreneurship is a risky business, but that risk becomes significantly more manageable once tested against a well-crafted business plan. Drawing up revenue and expense projections, devising logistics and operational plans, and understanding the market and competitive landscape can all help reduce the risk factor from an inherently precarious way to make a living. Having a business plan allows you to leave less up to chance, make better decisions, and enjoy the clearest possible view of the future of your company.
Understanding the importance of a business plan
Now that you have a solid grasp on the “why” behind business plans, you can confidently move forward with creating your own.
Remember that a business plan will grow and evolve along with your business, so it’s an important part of your whole journey—not just the beginning.
Related Posts
Now that you’ve read up on the purpose of a business plan, check out our guide to help you get started.

The information and tips shared on this blog are meant to be used as learning and personal development tools as you launch, run and grow your business. While a good place to start, these articles should not take the place of personalized advice from professionals. As our lawyers would say: “All content on Wave’s blog is intended for informational purposes only. It should not be considered legal or financial advice.” Additionally, Wave is the legal copyright holder of all materials on the blog, and others cannot re-use or publish it without our written consent.

Business planning is originally a whole process in itself. This planning process has its own components, features, types, etc. The soul of the business planning process itself resides in the process of decision-making. So, let’s get ready to learn about all these important aspects in detail!
- Importance, Features, and Limitations of Planning
- Types of Plans
- Planning Components
- Planning Process
- Concept of Forecasting
- Principles in Decision Making
- Steps in Decision Making
- Decision Making in Groups
Customize your course in 30 seconds
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Knowledge and Science Bulletin Board System
Exploring the World of Knowledge and Understanding
The importance of business planning for successful entrepreneurship
By knbbs-sharer.

Starting a business can be exciting, challenging, and rewarding, but it’s crucial to ensure that you have a solid plan in place. Business planning is essential for entrepreneurs looking to start or grow a business that will thrive in today’s competitive economy. In this article, we will discuss the importance of business planning and provide insights into how to create a practical, actionable business plan that will help you succeed.
What is business planning?
Business planning involves setting objectives, defining strategies, and identifying the resources required to achieve success. It helps entrepreneurs understand their business, customers, competitors, and market environment better. A well-researched business plan provides a roadmap that helps entrepreneurs navigate around obstacles, take advantage of opportunities, and achieve their goals successfully.
Why is business planning important?
Business planning is essential for entrepreneurs for several reasons:
1. Clarifying the business idea:
A business plan helps entrepreneurs articulate their vision, mission, and values. They can identify their business’s unique value proposition and how it will differentiate itself from its competitors.
2. Devising a strategy:
A business plan helps entrepreneurs devise a strategy that outlines how the business will achieve its objectives. Strategies can focus on product development, marketing, distribution, pricing, and customer service.
3. Assessing feasibility:
A business plan helps entrepreneurs assess the feasibility of their business idea. They can identify the resources required, estimate costs, and forecast revenues. This information helps entrepreneurs determine if their business idea is viable.
4. Attracting investors:
A well-researched business plan can attract investors, lenders, and partners. Investors look for businesses with clear objectives, strategies, and compelling market analysis. A business plan can provide this information and demonstrate the business’s potential for growth and profitability.
How to create a successful business plan?
Creating a successful business plan requires time, research, and attention to detail. Here are some tips to help you create a practical, actionable business plan:
1. Conduct thorough market research:
Market research helps entrepreneurs understand their target audience, competitors, and industry trends. It helps them identify opportunities, gaps, and potential challenges.
2. Define your business objectives:
Business objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Entrepreneurs should set realistic targets for revenue, market share, and customer acquisition.
3. Outline your strategies:
Strategies should be aligned with business objectives. Entrepreneurs should define strategies for product development, marketing, sales, customer service, and operations.
4. Identify the resources required:
Entrepreneurs should identify the resources required to achieve their business objectives. These resources may include funding, personnel, equipment, and technology.
5. Forecast financial projections:
Entrepreneurs should forecast financial projections, including revenues, expenses, profits, and cash flow. They should use realistic assumptions and be conservative in their estimates.
6. Monitor and evaluate:
A business plan is a living document that requires continuous monitoring and evaluation. Entrepreneurs should track their progress against their objectives and adjust their strategies as needed.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, business planning is crucial for entrepreneurs looking to start or grow a successful business. It helps them clarify their business idea, develop strategies, assess feasibility, attract investors, and achieve their objectives. A well-researched and well-executed business plan can make the difference between success and failure. By following the tips outlined in this article, entrepreneurs can create practical, actionable business plans that will help them succeed in the competitive world of entrepreneurship.
(Note: Do you have knowledge or insights to share? Unlock new opportunities and expand your reach by joining our authors team. Click Registration to join us and share your expertise with our readers.)
Share this:
Discovery new post:.
- Why Every Entrepreneur Needs to Know What a Business Plan Is
- 5 Tips for Starting a Successful Small Business
- Why Every Business Needs a Plan: Understanding the Basics of a Business Plan
- The Benefits of Strategic Business Planning for Entrepreneurs
Hi, I'm Happy Sharer and I love sharing interesting and useful knowledge with others. I have a passion for learning and enjoy explaining complex concepts in a simple way.
Related Post
2023 food business trends: from sustainability to automation, future of the fashion business: top 5 trends to watch out for in 2023, the top food business trends that are taking the industry by storm, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Explore the Colors and Traditions of Global Cultural Festivals
5 simple strategies for learning english faster and more effectively, 5 common great dane health issues you need to know about.
Just in Time for Spring 🌻 50% Off for 3 Months. BUY NOW & SAVE
50% Off for 3 Months Buy Now & Save
Wow clients with professional invoices that take seconds to create
Quick and easy online, recurring, and invoice-free payment options
Automated, to accurately track time and easily log billable hours
Reports and tools to track money in and out, so you know where you stand
Easily log expenses and receipts to ensure your books are always tax-time ready
Tax time and business health reports keep you informed and tax-time ready
Automatically track your mileage and never miss a mileage deduction again
Time-saving all-in-one bookkeeping that your business can count on
Track project status and collaborate with clients and team members
Organized and professional, helping you stand out and win new clients
Set clear expectations with clients and organize your plans for each project
Client management made easy, with client info all in one place
Pay your employees and keep accurate books with Payroll software integrations
- Team Management
FreshBooks integrates with over 100 partners to help you simplify your workflows
Send invoices, track time, manage payments, and more…from anywhere.
- Freelancers
- Self-Employed Professionals
- Businesses With Employees
- Businesses With Contractors
- Marketing & Agencies
- Construction & Trades
- IT & Technology
- Business & Prof. Services
- Accounting Partner Program
- Collaborative Accounting™
- Accountant Hub
- Reports Library
- FreshBooks vs QuickBooks
- FreshBooks vs HoneyBook
- FreshBooks vs Harvest
- FreshBooks vs Wave
- FreshBooks vs Xero
- Free Invoice Generator
- Invoice Templates
- Accounting Templates
- Business Name Generator
- Estimate Templates
- Help Center
- Business Loan Calculator
- Mark Up Calculator
Call Toll Free: 1.866.303.6061
1-888-674-3175
- All Articles
- Productivity
- Project Management
- Bookkeeping
Resources for Your Growing Business
The importance of business plan: 5 key reasons.
A key part of any business is its business plan. They can help define the goals of your business and help it reach success. A good business plan can also help you develop an adequate marketing strategy. There are a number of reasons all business owners need business plans, keep reading to learn more!
Here’s What We’ll Cover:
What Is a Business Plan?
5 reasons you need a well-written business plan, how do i make a business plan, key takeaways.
A business plan contains detailed information that can help determine its success. Some of this information can include the following:
- Market analysis
- Cash flow projection
- Competitive analysis
- Financial statements and financial projections
- An operating plan
A solid business plan is a good way to attract potential investors. It can also help you display to business partners that you have a successful business growing. In a competitive landscape, a formal business plan is your key to success.

Check out all of the biggest reasons you need a good business plan below.
1. To Secure Funding
Whether you’re seeking funding from a venture capitalist or a bank, you’ll need a business plan. Business plans are the foundation of a business. They tell the parties that you’re seeking funding from whether or not you’re worth investing in. If you need any sort of outside financing, you’ll need a good business plan to secure it.
2. Set and Communicate Goals
A business plan gives you a tangible way of reviewing your business goals. Business plans revolve around the present and the future. When you establish your goals and put them in writing, you’re more likely to reach them. A strong business plan includes these goals, and allows you to communicate them to investors and employees alike.
3. Prove Viability in the Market
While many businesses are born from passion, not many will last without an effective business plan. While a business concept may seem sound, things may change once the specifics are written down. Often, people who attempt to start a business without a plan will fail. This is because they don’t take into account all of the planning and funds needed to get a business off of the ground.
Market research is a large part of the business planning process. It lets you review your potential customers, as well as the competition, in your field. By understanding both you can set price points for products or services. Sometimes, it may not make sense to start a business based on the existing competition. Other times, market research can guide you to effective marketing strategies that others lack. To have a successful business, it has to be viable. A business plan will help you determine that.
4. They Help Owners Avoid Failure
Far too often, small businesses fail. Many times, this is due to the lack of a strong business plan. There are many reasons that small businesses fail, most of which can be avoided by developing a business plan. Some of them are listed below, which can be avoided by having a business plan:
- The market doesn’t need the business’s product or service
- The business didn’t take into account the amount of capital needed
- The market is oversaturated
- The prices set by the business are too high, pushing potential customers away
Any good business plan includes information to help business owners avoid these issues.

5. Business Plans Reduce Risk
Related to the last reason, business plans help reduce risk. A well-thought-out business plan helps reduce risky decisions. They help business owners make informed decisions based on the research they conduct. Any business owner can tell you that the most important part of their job is making critical decisions. A business plan that factors in all possible situations helps make those decisions.
Luckily, there are plenty of tools available to help you create a business plan. A simple search can lead you to helpful tools, like a business plan template . These are helpful, as they let you fill in the information as you go. Many of them provide basic instructions on how to create the business plan, as well.
If you plan on starting a business, you’ll need a business plan. They’re good for a vast number of things. Business plans help owners make informed decisions, as well as set goals and secure funding. Don’t put off putting together your business plan!
If you’re in the planning stages of your business, be sure to check out our resource hub . We have plenty of valuable resources and articles for you when you’re just getting started. Check it out today!
RELATED ARTICLES

Save Time Billing and Get Paid 2x Faster With FreshBooks
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
Get more great content in your Inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive communications from FreshBooks and acknowledge and agree to FreshBook’s Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time by contacting us at [email protected].
👋 Welcome to FreshBooks
To see our product designed specifically for your country, please visit the United States site.

- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Master’s Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Nursing Degrees
- Cybersecurity
- Human Services
- Science & Mathematics
- Communication
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Computer Science
- Admissions Overview
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Incoming Freshman and Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Military Students
- International Students
- Early Access Program
- About Maryville
- Our Faculty
- Our Approach
- Our History
- Accreditation
- Tales of the Brave
- Student Support Overview
- Online Learning Tools
- Infographics
Home / Blog
Importance of Entrepreneurship: Types, Benefits, and Styles
February 12, 2021

Economies are powered by innovation. Much of that innovation derives from forward-thinking individuals who possess the drive, skills, and background to turn a business vision into reality. The importance of entrepreneurs extends beyond the effect those individuals have on their own companies, however. They impact their broader communities, and, in some cases, even the world.
Entrepreneurs have played a pivotal role in the growth of the U.S. economy since the 19th century. They spur industry transformations, create entirely new markets, and help to build resilient communities. Investopedia describes four ways entrepreneurs benefit society:
- Economic growth : The success of the products and services created and sold by entrepreneurs cascades to other businesses and markets.
- Wealth generation : Entrepreneurs frequently target new markets and tap audiences outside the focus of established firms. This creates new sources of revenue and profits.
- Social change : The innovative goods and services entrepreneurs offer reduce dependence on outdated processes and technologies. One example is the way smartphones have affected how businesses communicate with customers, employees, and partners.
- Community development : Entrepreneurs foster a sense of community among people with common goals and interests, whether in a single neighborhood or across continents. Their products and services contribute to the communities’ social and economic well-being.

The companies that entrepreneurs found tend to mirror their founders’ personalities. Entrepreneurs come from every economic and social background. To prepare for the challenges of translating innovation into rewarding business ventures, entrepreneurs rely on the training and experience they receive from programs such as the Master of Arts in Management and Leadership degree.
Successful entrepreneurs make their dreams and the dreams of others come true. They are able to match their personality, skills, and creativity with customer needs and market opportunities. This guide explains the importance of entrepreneurship, presents the various types and styles of entrepreneurship, and describes the skills that are most essential for reaching your entrepreneurial goals.
Types of Entrepreneurship
Most people think of an entrepreneur as someone with dreams of becoming a titan of industry. While many would-be entrepreneurs have lofty goals, most hope only to create a successful business, whether that success spans the globe or reaches no farther than their local community. Types of entrepreneurship range from hometown storefront businesses to technological innovations that can change the world.
These snapshot profiles of various entrepreneur types demonstrate the range of opportunities available to people who dream of starting their own business.
Small-Business Entrepreneurs
The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) reports that small businesses generate 44% of all business activity in the country. Small-business entrepreneurs differ from other small-business owners in their company’s legal status: Entrepreneurs generally incorporate their businesses, while owners operate as sole proprietors, partnerships, or other nonincorporated entities.
Small-business entrepreneurs take greater risks than the typical small-business owner, and they tend to rely on a broader set of skills that encompass high-level thinking, analytical reasoning, and complex interpersonal communication.
Investor Entrepreneurs
The roles of investors and entrepreneurs are typically seen as complementary but distinct: Entrepreneurs seek investors to bankroll their new companies. However, some entrepreneurs focus solely on providing financial backing to new business entities. Investor entrepreneurs may start their careers in one of the two roles and segue into a hybrid of both to tap the strengths of each.
For example, entrepreneurs may feel the need to continually tweak their operations, which can prevent business processes from being firmly established. By taking an investor role and purchasing an ownership share in a business, entrepreneurs are likely to address business opportunities more strategically to capitalize on short-term performance as well as long-term goals.
Technology Entrepreneurs
As new technologies permeate industries of all types, it could be said that all entrepreneurs are technology entrepreneurs in some regard. However, over the past 40 years the image of technology entrepreneurs has been dominated by billionaires such as Bill Gates, Jeff Bezos, and Mark Zuckerberg. What distinguishes this type of entrepreneur is their practical application of scientific innovations to solve business problems.
Technology entrepreneurs are characterized by their passion and unshakeable belief in the inherent value of the products or services they create. Becoming a tech entrepreneur typically entails working long hours and making financial sacrifices in the short term for the prospects of long-term gain. Tech entrepreneurs must also possess the ability to sell their ideas, persevere through hard times, and make others feel as enthusiastic about their ideas as they do.
Internal Entrepreneurs
Internal entrepreneurs, or “intrapreneurs,” apply the principles of entrepreneurship to projects within an existing company or organization. One important distinction between entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs is the latter’s lack of personal investment, which reduces the impact of potential failure on any individual.
Intrapreneurs tend to be self-motivated, proactive, and innovative employees who create an entrepreneurial spirit within their team. When companies give employees the freedom to experiment and grow within an organization, they can benefit from the success of their employees’ internal projects. However, firms that fail to personally recognize the work of intrapreneurs risk seeing them leave to become true independent entrepreneurs.
Online Entrepreneurs
Internet-based businesses offer many advantages to entrepreneurs, including low startup costs and the ability to establish an online presence quickly to take advantage of the fast pace of changing markets. However, the low barrier to entry can be a dangerous illusion for online entrepreneurs who fail to realize the hard work and perseverance required to achieve their business goals.
Online enterprises require the same time and effort commitment as other forms of entrepreneurship, and they are subject to their own challenges, many related to technology. For example, an online business will likely rely on partnerships with many different service providers, an outage at any of which could knock the business offline.
Entrepreneurship Styles
Just as no two companies are identical, each entrepreneurial endeavor is as unique as the person behind it. Entrepreneurship styles are as varied as the ideas that spur entrepreneurs to action. One key for entrepreneurial success is to create a company whose strengths match the prominent characteristics of its founder.
Matching Entrepreneurship Approach to Personality
An entrepreneur’s personality, background, and experience influence their approach to starting a business. These are among the most common entrepreneurship styles:
- Innovators have the potential to transform entire industries with novel ideas. Inventor Thomas Edison was the prototype for the modern innovative entrepreneur. These entrepreneurs possess extensive knowledge of their industry, including its customers’ needs. They also know how to develop and market their innovative products.
- Managers are often considered the antithesis of entrepreneurs, but management skills are paramount in bringing a great idea to fruition as a commercial product or service. Manager entrepreneurs understand the importance of choosing and nurturing a good team of workers, and ensuring that they have the tools and resources to succeed.
- Opportunists identify an important business or technical problem, devise a winning solution to the problem, and plot a course to bring that solution to market in the form of a commercial product. Opportunity entrepreneurs tend to have a business background rather than a technical one, so they may focus too much on short-term goals and lose sight of the larger picture.
- Revolutionaries are in many ways the antithesis of manager and opportunity entrepreneurs because they typically have technical backgrounds and may show disdain for established business practices. While revolutionary entrepreneurs such as Apple founder Steve Jobs leave a legacy that is both broad and deep, they often need the help of nontechnical business people to realize their world-changing vision.
Entrepreneurs Whose Businesses Match Their Personalities
Just as Steve Jobs’ larger-than-life personality was the perfect fit for his dream of making computers “for the rest of us,” as Apple’s marketing slogan proclaimed, other important entrepreneurs succeed by applying their unique, inimitable style to the task of devising brand-new solutions to real-world problems.
- John D. Rockefeller was “the richest man in history,” according to Investopedia, after founding Standard Oil in the late 19th century. Rockefeller’s fortune was due in large part to his focus on running the company as efficiently as possible by creating vertical and horizontal integrations for its operations. However, Rockefeller’s ruthless quest for efficiency bordered on unethical business practices. The social backlash to the Standard Oil monopoly ultimately led to the company’s breakup.
- Walt Disney is famous as a pioneering animator and entertainment mogul, but his greatest innovation may have been in recognizing the potential of merchandising his creations in the form of toys, clothing, and other items. The Disney Company remains one of the largest and most successful entertainment enterprises in the world.
- Jeff Bezos founded Amazon out of a garage in Seattle in the 1990s. Less than 25 years later, the company is one of the most valuable in the world, and Bezos is a billionaire many times over. Since his school days, Bezos has had a vision that extends beyond our planet, but he also has a practical side that realized the potential of the internet long before the rest of the world did. As Amazon achieved record-breaking growth early this century, Bezos simultaneously invested in a variety of endeavors outside online retail, including the commercial space project Blue Origin.
Entrepreneurs Arise from Diverse Backgrounds
Any field can serve as a springboard for a successful new business enterprise. Entrepreneurs arise from a range of educational, technical, and business experiences that include management, technology, sales and marketing, and scientific research. In addition to an abiding passion to see their innovations realized, entrepreneurs share certain characteristics:
- They are independent thinkers.
- They are optimistic and confident about their chances for success.
- They are creative problem solvers.
- They are tenacious, visionary, and focused.
- They are more likely to act than to wait, and they attack challenges rather than avoid them.
Entrepreneurship Skills
Growing a business requires a diverse set of skills, but the one trait that ties them all together is leadership. Entrepreneurs transform an idea into a product or service that has value to customers. Each step in the process from creating the business plan to achieving profitability calls for a range of organizational and interpersonal skills, all of which depend on leadership.
Important entrepreneurship skills run the gamut from understanding the risks versus rewards of the business venture, to having a plan in place for responding as circumstances change. These are the capabilities that entrepreneurs need to make their businesses thrive:
- Leadership : Entrepreneurs demonstrate their zeal for the enterprise in all of their interactions with investors, employees, and outside parties. They are confident in themselves and in the business, and they are decisive yet adaptable. They listen to and respect the opinions of others, and are always taking advantage of opportunities to study and learn.
- Interpersonal communication : Entrepreneurs understand that the lines of communication in an organization must run both ways. Communication is particularly important to entrepreneurs because it makes all their other skills more effective. Communication skills are used to close sales, boost employee morale, resolve conflicts, and negotiate contracts.
- Organizational behavior : Technology is a vital part of any new business venture, but the ability to manage people will ultimately determine a company’s success. People management takes many forms, but the key is to match the organizational approach with the characteristics of the business and its employees.
- Business strategy : The importance of having a clear business focus and being optimistic and driven to achieve the company’s goals is balanced by the need to be adaptable and acknowledge when industries, markets, and customer preferences change. Entrepreneurs are decisive and passionate, but they are also ready and willing to make changes when necessary to keep the company on a path forward.
- Collaboration and project management : Entrepreneurs understand the importance of being a good team member as well as serving as a team leader. They establish relationships with managers, investors, partners, and stakeholders as peers who all have important roles to play rather than as a hierarchy.
Benefits of Entrepreneurship
The benefits of entrepreneurship extend beyond the businesses they establish. Entrepreneurs improve the lives of individuals and communities, as well as the overall economy. Entrepreneurs have been instrumental in spurring social change and improving the way people live and work. They help raise the standard of living for everyone by creating jobs and making products safer, less expensive, and more functional.
- Entrepreneurs ’ rewards for taking on the risks entailed in transforming an idea into a business include the earnings their investment generates, as well as the ability to set their own schedule. However, entrepreneurs also gain the satisfaction of seeing their idea transformed into a thriving enterprise, and of knowing their skills and leadership helped to make it happen.
- Communities reap the benefit of entrepreneurship because businesses help to foster innovation, promote economic development, and create jobs. A successful company is likely to expand, which generates taxes, jobs, and other benefits for the area. Thriving businesses tend to attract other ventures in the same or related fields, and they often invest in community projects and support local charities.
- Entrepreneurs play an important role in growing and sustaining the U.S. economy . The technologies pioneered by entrepreneurs have created entire industries, including smartphones, wireless products, online retail, social media, and streaming entertainment.
Despite the many benefits of entrepreneurship, it has inherent risks. Lack of appropriate government oversight can result in unfair labor practices, corruption, and criminal activity. Also, new business ventures have a high rate of failure: According to data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) cited by Fundera, 20% of small businesses fail in the first year, 50% fail within five years, and 70% fail within 10 years of opening. The benefits of entrepreneurship are realized only after much preparation, planning, and hard work.
An Education Geared to the Needs of Entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs need the right foundation in business and management. A program such as Maryville University’s online Master of Arts in Management and Leadership can offer the crucial training and skills innovators need to succeed. Courses such as Interpersonal Management Skills, Enterprise Planning and Control, Leadership, and Organizational Behavior and Development prepare tomorrow’s important entrepreneurs for the challenges they will face as they pursue their career goals.
Discover more about how the Master of Arts in Management and Leadership program helps people planning a career in business gain the entrepreneurial skills they’ll need.
Recommended Reading
Exploring Entrepreneurship: Starting and Operating a Small Business
Four Ways a Business Degree Can Prepare Entrepreneurs for Economic Volatility
Ethical Leadership in Business: Why It Matters
The Balance Careers, “Important Skills Entrepreneurs Need with Examples”
The Balance Small Business, “9 Essential Qualities of Entrepreneurial Leadership ”
The Balance Small Business, “What Is an Entrepreneur?”
Business News Daily, “Entrepreneur or Small Business Owner: Which One Are You?”
Entrepreneur, “The Hard Truth You Need to Know Before Becoming an Online Entrepreneur”
Entrepreneur, “This Tool-cum-Skill Is a Must if You Are Turning Entrepreneur This Year”
Entrepreneur, “The True Failure Rate of Small Businesses”
Entrepreneur, “Why Entrepreneurs Need to Be Good Managers and Great Leaders”
Fundera, “What Percentage of Small Businesses Fail (and Other Need-to-Know Stats)”
Influencive, “How to Transition from an Entrepreneur to an Investor, According to Jeremy Harbour”
Investopedia, “How Jeff Bezos Became the World’s Richest Man”
Investopedia, “The 10 Greatest Entrepreneurs”
Investopedia, “What Is Intrapreneurship?”
Investopedia, “Why Entrepreneurship Is Important to the Economy”
U.S. Small Business Administration, “Small Businesses Generate 44 Percent of U.S. Economic Activity”
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.
Take Your Next Brave Step
Receive information about the benefits of our programs, the courses you'll take, and what you need to apply.
The Importance of Strategy for Entrepreneurial Success
- September 20, 2023
- Business Strategy & Innovation

In the fast-paced world of entrepreneurship, success often hinges on the ability to navigate strategic challenges with finesse. But what exactly does it mean to have a winning strategy? And how can entrepreneurs harness its power to drive innovation and achieve their goals?
This article delves into the importance of strategy for entrepreneurial success, offering key insights and actionable advice. By exploring the fundamental principles and asking the right questions, aspiring innovators can unlock the potential of strategy and pave their way to triumph in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Strategy is often overlooked by entrepreneurs, but it is crucial for success.
- Familiarizing oneself with the basic tenets of strategy is important.
- The operating model defines how the business carries out its operations.
- Identifying and leveraging sources of uniqueness is crucial for long-term success.
The Role of Strategy in Entrepreneurial Success
Strategy plays a crucial role in entrepreneurial success. It allows entrepreneurs to make choices and trade-offs that create value and establish a competitive advantage. The role of planning and strategic decision-making cannot be underestimated in the pursuit of innovation.
By developing a clear strategy, entrepreneurs can identify their target customers, define their value proposition, and differentiate themselves from competitors. This strategic approach enables entrepreneurs to design their operating model, making deliberate choices and trade-offs that align with their overall business objectives.
Through strategic decision-making, entrepreneurs can identify and leverage their sources of uniqueness. This could be unique and valuable assets or inputs, which can help establish a competitive advantage that is difficult for competitors to replicate.
Strategy empowers entrepreneurs to navigate the dynamic and ever-changing business landscape. It enables them to adapt and thrive in an environment that desires innovation.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Strategy
Understanding the fundamentals of strategy involves gaining insight into how a business operates and creates value for customers. Strategic thinking is essential for entrepreneurs who desire innovation and long-term success. Here are five key points to consider when delving into strategy fundamentals:
- Strategy goes beyond product development and scaling, and should not be overlooked.
- Timeless rules of strategy still apply, despite modern trends.
- Strategy requires an integrated view of the business and its value creation.
- Identifying and leveraging sources of uniqueness is crucial for a competitive advantage.
- Designing an effective operating model is essential for creating value.
Key Questions to Guide Your Strategic Approach
Identifying the target customers and clarifying the value intended to be created are key questions that guide an entrepreneur’s strategic approach.
In order to develop a successful differentiation strategy, entrepreneurs must first understand who their target customers are and what they value. By identifying the specific attributes that define their customers, entrepreneurs can tailor their value proposition to meet their needs and differentiate themselves from competitors.
This requires a deep understanding of the market and the ability to identify unique and valuable assets or inputs that give the business a competitive advantage. By leveraging these sources of uniqueness, entrepreneurs can create a value proposition that is hard to imitate and establish a long-term competitive advantage.
This strategic approach is essential for entrepreneurs who desire innovation and want to stand out in the market.
Defining and Designing Your Operating Model
Defining and designing the operating model involves making choices and trade-offs to create value for customers while considering the entire enterprise and its activities. It requires evaluating activities to identify key practices that contribute to value creation.
To grab the attention of the audience, here are five key aspects to consider when defining and designing your operating model:
- Purposeful choices: Every decision should align with the overall strategy and goals of the business.
- Efficient resource allocation: Optimize the use of resources to maximize value generation.
- Streamlined processes: Identify and eliminate unnecessary steps or bottlenecks to enhance efficiency.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Foster collaboration across different departments to improve coordination and effectiveness.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly evaluate and refine your operating model to adapt to changing market conditions and customer needs.
Unleashing Competitive Advantage for Long-Term Success
To achieve long-term success, entrepreneurs must unleash their competitive advantage through the strategic leveraging of unique and valuable assets or inputs.
The key to this lies in identifying competitive advantages and leveraging sources of uniqueness. Competitive advantage is the driving force behind sustained profitability and growth.
It comes from possessing assets or inputs that are valuable, rare, hard to imitate, durable, and specific to the business. Identifying these advantages requires a deep understanding of the market, customers, and industry dynamics.
Once identified, entrepreneurs must strategically leverage these sources of uniqueness to establish a strong position in the market. This involves aligning the business’s value proposition, operating model, and key activities to maximize the value created for customers.
Taking the First Steps: Getting Started With Strategy
In order to unleash competitive advantage and achieve long-term success, entrepreneurs must develop a strategic mindset and align their strategy with their business goals. Taking the first steps towards this strategic approach is crucial for entrepreneurial success. Here are five key actions to get started with strategy:
Clarify the value: Clearly define the value you intend to create and for whom, identifying your target customers.
Differentiate from competitors: Craft a unique value proposition and clearly articulate how it differentiates from competitors.
Design the operating model: Make choices and trade-offs that create value, considering the entire enterprise and its activities.
Identify uniqueness: Identify and leverage your sources of uniqueness to establish a competitive advantage that is valuable, rare, and hard to imitate.
Align strategy with goals: Ensure that your strategy aligns with your business goals, creating a roadmap for success.
The Link Between Strategy and Entrepreneurial Success
Crafting a clear and differentiated value proposition is essential for entrepreneurs looking to achieve long-term success by aligning their strategy with their business goals.
Strategy implementation and strategic decision making play a crucial role in the link between strategy and entrepreneurial success. Entrepreneurs must not only develop a compelling product, but also devise a strategy that sets them apart from competitors and creates a sustainable competitive advantage.
By making strategic decisions that align with their value proposition, entrepreneurs can effectively implement their strategy and drive their business towards success. This requires a deep understanding of the market, customers, and the business’s unique strengths and capabilities.
Through strategic decision making, entrepreneurs can navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and position their business for growth and innovation in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Strategy: A Critical Ingredient for Entrepreneurial Achievement
Entrepreneurs who neglect to prioritize the development of a well-defined strategic approach often struggle to achieve their desired levels of achievement. The role of strategic planning cannot be overstated in the pursuit of entrepreneurial success. Strategic decision making has a significant impact on the direction and outcomes of a business venture.
To grab the attention of the audience, consider the following key points:
- Strategy is the foundation for entrepreneurial achievement.
- It provides a roadmap for navigating challenges and seizing opportunities.
- Strategic planning enables entrepreneurs to align their actions with their long-term goals.
- Effective strategic decision making helps entrepreneurs anticipate market trends and stay ahead of the competition.
- A well-defined strategy allows entrepreneurs to make informed choices and allocate resources wisely.
In today’s dynamic business landscape, innovation is paramount. Entrepreneurs who prioritize strategic planning and decision making position themselves for success in an ever-evolving market.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can entrepreneurs effectively balance product development and strategy.
Entrepreneurs can effectively balance product development and strategy by ensuring they have a strong product-market fit through market analysis. This allows them to understand customer needs, differentiate from competitors, and make strategic decisions that drive business growth and success.
What Are Some Common Pitfalls Entrepreneurs Face When It Comes to Strategy?
Common mistakes entrepreneurs face when it comes to strategy include neglecting to define a clear value proposition, failing to identify and leverage sources of uniqueness, and overlooking the importance of a well-designed operating model. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for entrepreneurial success.
How Can Entrepreneurs Identify and Evaluate Key Practices and Activities Within Their Operating Model?
Entrepreneurs can identify key practices and activities in their operating model by first identifying opportunities for value creation and then evaluating the risks associated with each practice or activity. This analytical approach allows for strategic decision-making and innovation.
What Are Some Examples of Valuable and Rare Assets or Inputs That Can Contribute to a Competitive Advantage?
Valuable assets such as proprietary technology, unique intellectual property, strong brand reputation, and exclusive partnerships can contribute to a competitive advantage for entrepreneurs. These assets are rare, difficult to imitate, and provide long-term benefits in the market.
What Are Some Practical Steps Entrepreneurs Can Take to Leverage Their Sources of Uniqueness and Establish a Competitive Advantage?
Entrepreneurs can leverage their sources of uniqueness and establish a competitive advantage by identifying their value proposition and differentiating it from competitors, designing an effective operating model, and consistently leveraging their valuable and rare assets.

Financial Planning in Entrepreneurship: Process, Importance, Tools, Sources
- Post author: Anuj Kumar
- Post published: 6 September 2023
- Post category: Entrepreneurship
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Financial planning is a critical aspect of entrepreneurship . It involves creating a comprehensive strategy for managing your business’s finances to ensure its long-term success and sustainability. Effective financial planning helps entrepreneurs make informed decisions, allocate resources efficiently, secure funding, and navigate potential challenges.
Table of Contents
- 1.1 Budgeting
- 1.2 Cash Flow Management
- 1.3 Revenue Projections
- 1.4 Expense Control
- 1.5 Financial Forecasting
- 1.6 Risk Assessment
- 1.7 Funding Options
- 1.8 Financial Records
- 1.9 Debt Management
- 1.10 Profitability Analysis
- 1.11 Tax Planning
- 1.12 Contingency Planning
- 1.13 Long-Term Goals
- 1.14 Review and Adapt
- 1.15 Professional Help
- 2 Financial Analysis of Entrepreneurial Venture
- 3.1 Determine Feasibility
- 3.2 Variance Analysis
- 3.3 Forecasting Financial Requirements
- 3.4 Obtaining Fund
- 3.5 Cash Flow Shortages
- 4.1 Comparative Statements
- 4.2 Comparative Income Statement
- 4.3 Comparative Balance Sheet
- 4.4 Common Size Statements
- 4.5 Trend Analysis
- 4.6 Average Analysis
- 4.7 Statement of Changes in Working Capital
- 4.8 Fund Flow Analysis
- 4.9 Cash Flow Analysis
- 4.10 Ratio Analysis
- 4.11 Cost Volume Profit Analysis
- 5.1 Personal Savings
- 5.2 Patient Capital
- 5.3 Angel Investing
- 5.4 Venture Capital
- 5.5 Incubators
- 5.6 Bank Loans
- 5.7 Government Grants
- 5.8 Bartering Exchanging Goods or Services
- 5.9 Partnership
- 5.10 Peer-to-Peer Lenders
- 5.11 Major Customer Commitment
- 5.12 Crowd-Funding Campaign
- 6.1 What is the process of financial planning in entrepreneurship?
Process of Financial Planning in Entrepreneurship
Here are some key steps and considerations for financial planning in entrepreneurship :
Cash Flow Management
Revenue projections, expense control, financial forecasting, risk assessment, funding options, financial records, debt management, profitability analysis, tax planning, contingency planning, long-term goals, review and adapt, professional help.

Start by creating a detailed budget that outlines your expected revenues and expenses. Be as accurate as possible in estimating costs such as rent, utilities, salaries, marketing, and materials. Regularly review and adjust your budget as your business grows and evolves.
Managing cash flow is crucial. Monitor your cash inflows and outflows to ensure you have enough liquidity to cover operational expenses. Analyze your cash flow statement to identify trends and potential issues.
Develop realistic revenue projections based on market research and historical data. Understand your sales cycle and seasonality to anticipate fluctuations in income.
Keep a close eye on your expenses. Look for cost-saving opportunities without sacrificing quality. Consider negotiating with suppliers for better terms or finding more affordable alternatives.
Create financial forecasts that extend into the future (e.g., monthly, quarterly, and annually). These forecasts can help you plan for growth, set targets, and identify potential financial gaps.
Identify and assess potential financial risks your business may face. Develop strategies to mitigate these risks, such as building an emergency fund or securing insurance coverage.
Determine your capital needs and explore various funding options , including personal savings, loans, investors, grants, or crowdfunding. Each source of capital comes with its advantages and trade-offs.
Maintain accurate financial records. Use accounting software or hire a professional accountant to track income, expenses, and taxes. Well-organized financial records are essential for tax compliance and decision-making.
If you have loans or lines of credit, manage them carefully. Make timely payments and consider refinancing options if they can reduce your interest costs.
Regularly assess your business’s profitability by calculating key financial ratios, such as gross margin, net profit margin, and return on investment (ROI). This analysis can help you make informed pricing and investment decisions.
Work with a tax professional to optimize your tax strategy. Explore tax incentives or deductions available to small businesses.
Prepare for unexpected events or downturns by building a contingency plan. This may involve setting aside reserves, diversifying revenue streams, or having a crisis management strategy in place.
Align your financial planning with your long-term business goals. Consider factors like expansion, product development, and exit strategies (e.g., selling the business or passing it on to a successor).
Regularly review your financial plan and adjust it as needed. Market conditions, competition, and internal factors may necessitate changes in your financial strategy.
Don’t hesitate to seek advice from financial professionals, such as accountants, financial advisors, or consultants. They can provide valuable insights and guidance.
Financial Analysis of Entrepreneurial Venture
Financial analysis is used to evaluate economic trends, set financial policy, build long-term plans for business activity, and identify projects or companies for investment. A financial analyst will thoroughly examine a company’s financial statements the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
Any entrepreneurial activity before execution requires financial planning to be done. It is included in the Business Plan that is presented for approval. The plan includes a projected profit-and-loss statement for the next three to five years and a cash flow statement.
A balance sheet is sometimes included as well as a break-even analysis. The financial plan in entrepreneurship is important because it establishes the financial goals of the company.
Importance of Financial Planning in Entrepreneurship
The following are the importance of financial planning in entrepreneurship :
Determine Feasibility
Variance analysis, forecasting financial requirements, obtaining fund, cash flow shortages.

Any business idea that is presented for approval needs to have a feasibility evaluation done and once the feasibility report is attached only the business idea gets approval. Financial analysis is an effective way of determining the feasibility of any business venture.
Financial analysis helps in finding out the variance in any venture, by comparing actual performance with expected performance. Thereby enabling to take corrective measures in time.
One of the biggest points of importance for entrepreneurial finance is monitoring the actual results against the line-item budget in the financial plan to give you the opportunity to take whatever steps are necessary to get back on track. For example, if you’re not reaching the projected revenue, either the projections are wrong or the marketing program is not as effective as you thought.
Financial Analysis enables the entrepreneur to have an estimated financial requirement that is required in the future. As a result of which entrepreneurs can do perfect planning with respect to future activity and maintain financial health.
Investors and lenders request to see the entrepreneur’s business plan, including the financial plan with projections and assumptions behind the forecast.
If the financial plan is unrealistic, a common mistake with entrepreneurs, the loan or investment will not be forthcoming. Hence financial analysis will be taken into consideration before granting any amount of financial support.
Financial analysis also helps an entrepreneur to overcome any kind of cash flow shortage. Any venture despite accurate forecasts suffers from this problem of shortages, as the environmental conditions are constantly evolving and bear a direct impact on any business.
The significance of financial analysis of entrepreneurial venture can also be summed up, as:
- Assessing the operational efficiency and managerial effectiveness of the venture.
- Analyzing the financial strengths and weaknesses and creditworthiness of the venture.
- Analyzing the current position of financial analysis,
- Assessing the types of assets owned by a business enterprise and the liabilities that are due to the venture.
- Providing information about the cash position the company is holding and how much debt the company has in relation to equity
Tools of Financial Analysis in Entrepreneurship
Financial analysis involves the process of evaluating a company’s financial performance and health by examining its financial statements, ratios, and other relevant data.
Various tools and techniques are used in financial analysis to assess a company’s profitability, liquidity, solvency, and overall financial stability. Here are some essential methods and tools of financial analysis in entrepreneurship :
Comparative Statements
Comparative income statement, comparative balance sheet, common size statements, trend analysis, average analysis, statement of changes in working capital, fund flow analysis, cash flow analysis, ratio analysis, cost volume profit analysis.

Comparative statements deal with the comparison of different items of the Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheets of two or more periods. Separate comparative statements are prepared for the Profit and Loss Account as Comparative Income Statements and for Balance Sheets.
Any financial statement can be presented in the form of a comparative statement such as a comparative balance sheet, comparative profit and loss account, comparative cost of production statement, comparative statement of working capital , and the like.
Comparative Income Statements are Gross Profit, Operating Profit, and Net Profit. The changes or the improvement in the profitability of the business concern is found out over a period of time. If the changes or improvement is not satisfactory, the management can find out the reasons for it and some corrective action can be taken.
The financial condition of the business concern can be found out by preparing a comparative balance sheet. The various items of the Balance sheet for two different periods are used.
The assets are classified as current assets and fixed assets for comparison & the liabilities are classified as current liabilities, long-term liabilities, and shareholder’s net worth. The term shareholder’s net worth includes Equity Share Capital, Preference Share Capital, Reserves and Surplus, and the like.
A vertical presentation of financial information is followed for preparing common-size statements. The total assets or total liabilities or sales is taken as 100 and the balance items are compared to the total assets, total liabilities, or sales in terms of percentage.
Thus, a common size statement shows the relation of each component to the whole. A separate common size statement is prepared for the profit and loss account as a Common Size Income Statement and for the balance sheet as a Common Size Balance Sheet.
The ratios of different items for various periods are found and then compared under this analysis. The analysis of the ratios over a period of years gives an idea of whether the business concern is trending upward or downward.
The trend ratios are calculated for a business concern, such ratios are compared with the industry average. These trends can be presented on graph paper in the shape of curves. This presentation of facts in the shape of pictures makes the analysis and comparison more comprehensive and impressive.
The extent of the increase or decrease of working capital is identified by preparing the statement of changes in working capital. The amount of net working capital is calculated by subtracting the sum of current liabilities from the sum of current assets. It does not detail the reasons for changes in working capital.
Fund flow analysis deals with detailed sources and application of funds of the business concern for a specific period. It indicates where funds come from and how they are used during the period under review. It highlights the changes in the financial structure of the company.
Cash flow analysis is based on the movement of cash and bank balances. In other words, the movement of cash instead of the movement of working capital would be considered in the cash flow analysis. There are two types of cash flows. They are actual cash flows and notional cash flows.
Ratio analysis is an attempt to develop a meaningful relationship between individual items (or groups of items) in the balance sheet or profit and loss account.
Ratio analysis is not only useful to internal parties of business concern but also useful to external parties. Ratio analysis highlights the liquidity, solvency, profitability, and capital gearing.
This analysis discloses the prevailing relationship between sales, cost, and profit. The cost is divided into two. They are fixed costs and variable costs. There is a constant relationship between sales and variable costs. Cost analysis enables the management to better profit planning .
Sources of Development Finance
Any entrepreneurial venture that starts needs to have good financial planning. The major issue for these ventures are arrangement or sources of funds.
Without capital, an entrepreneur won’t be able to buy inventory, cover payroll, or the many other expenses associated with launching a business’s operations. The various sources of funds for entrepreneurial ventures can be arranged through:
Personal Savings
Patient capital, angel investing, venture capital, government grants, bartering exchanging goods or services, partnership, peer-to-peer lenders, major customer commitment, crowd-funding campaign.

Personal savings are the safest mode of source available for entrepreneurs, this is also referred to as Bootstrapping. This is the single most common source of capital for entrepreneurs. Personal savings, however, isn’t always enough for any venture, hence entrepreneur needs to depend on other sources.
Patient capital is money loaned by the help of family or friends. The money will be repaid later as the business starts growing. When borrowing patient capital, entrepreneurs should be aware that family and friends rarely have much capital. However, this is again a limited way of funds.
Angel investing has become a popular method of funding among entrepreneurs. With angel investing, an angel provides large sums of money to an entrepreneur so that he or she can start their own business.
The angel may provide this funding in exchange for stock shares of the entrepreneur’s business, or they may require the entrepreneur to pay back the funding with interest.
Venture capital is another common way in which entrepreneurs fund their business. In many ways, venture capital is the same as angel investing. They both involve funding from a private investor or investment firm. The difference, however, is that angels typically invest more money than venture capitalists, and angels invest in early-stage businesses.
Business incubators or accelerators generally focus on the high-tech sector by providing support for new businesses in various stages of development. However, there are also local economic development incubators, which are focused on areas such as job creation, revitalization, and hosting and sharing services.
Bank loans remain a time-tested funding option for entrepreneurs. If an entrepreneur has good credit, they may be eligible for a small business loan.
Many government agencies such as SIDBI, IDBI, NABAD, etc. in the form of grants and subsidies that may be available to a start-up business. Often governmental websites provide a comprehensive listing of various government programs at the federal and state levels.
This form of sourcing as a substitute for cash can be a great way to run on a little wallet. An example would be negotiating free office space by agreeing to support the `computer systems for all the other office tenants. Another common example is exchanging equity for legal and accounting support.
A more established company may have a strategic interest in helping to develop a product – and be willing to advance funding to make it happen. Several companies develop customized social networks for large enterprises, with the expectation of using that funding and experience to compete in the consumer market someday.
This is another safe way of sourcing any venture that allows people to seek financing from other individuals.
This is not a popular mode of funding, yet some customers would be willing to cover development costs in order to be able to buy a product before the rest of the world can.
Their advantage is the control over the production process and the promise of dedicated support. Even large companies look to their best customers to fund new projects – this is the essence of good business development.
Crowd-funding is still a viable funding option used by entrepreneurs. It is a way by which funds can be arranged through the help of approaching the public via the Internet. It’s called crowdfunding because the investments come from a large “crowd” of people.
In comparison, angel investments come from a single investor or investment firm. Crowdfunding is a great platform for innovative products that could have mass appeal.
FAQs Section About the Financial Planning in Entrepreneurship
What is the process of financial planning in entrepreneurship.
These are the following steps in the process of financial planning in entrepreneurship: 1. Budgeting 2. Cash Flow Management 3. Revenue Projections 4. Expense Control 5. Financial Forecasting 6. Risk Assessment 7. Funding Options 8. Financial Records 9. Debt Management 10. Profitability Analysis.
Related posts:
- Entrepreneurship: Concept, Definition, 11 Nature, Types, Role
- 17 Main Characteristics of Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneur: Definitions, Characteristics, Types, Advantages and Disadvantages
- 10 Main Factors Affecting Entrepreneurial Growth
- Essential Traits: 14 Characteristics of Entrepreneur
- 5 Important Functions of an Entrepreneur
21 Major Types of Entrepreneurs
- 16 Important Keys of Traits of Entrepreneurs
5 Stages of Process of Entrepreneurship
- Entrepreneurial Culture: Meaning, Elements, Steps to Change
- 3 Major Theories of Entrepreneurship | Explained
- Entrepreneurial Venture
- Entrepreneurial Environment: Characteristics, 8 Importance
- 10 Problems of Entrepreneurship in Modern Business
- Social Entrepreneurship: Characteristics, Importance, Advantages, Disadvantages
You Might Also Like
5 major functions of modern office, cooperative society: 8 features, advantages and disadvantages, ethical issues in business | in setting a new business, 5 important entrepreneurial skills for any entrepreneur, 9 characteristics of small scale business, entrepreneurial competencies: 3 components, developing method, 4 tax benefits to small-scale industries, importance of entrepreneurship development programme, objectives of a project | explained, 6 keys to managing pitfalls of entrepreneurship, small scale industrial: definitions, features, objectives, advantages and disadvantages of company | explained, 9 major role of entrepreneurs, district industry centre: objectives, 15 functions, schemes, entrepreneurship development.

5 Responsibilities of Office Management
Entrepreneurial behavior: definition, features, models, importance, and difference, economic environment in business and factors.
- Entrepreneurship
- Organizational Behavior
- Financial Management
- Communication
- Human Resource Management
- Sales Management
- Marketing Management
Explore Greyhound Nation
- Loyola Today
The growing importance of sustainability in business

As Loyola University Maryland celebrates Earth Month, two professors at Loyola’s Sellinger School of Business define and discuss sustainability and its growing importance to organizations, different business disciplines, and the planet. Stacy Chavez, Ph.D., assistant professor of accounting, and Astrid Schmidt-King, J.D., teaching assistant professor of management and organizations, specialize in sustainability management, corporate social responsibility, sustainability measurement and reporting, and international business.
What is sustainability? Why is it important?
Chavez: Sustainability can be defined in many ways depending on the context. Business sustainability refers to the ability of an organization to survive and prosper into the future. More commonly, and especially important during Earth Month, sustainability refers to the longevity and ability for the people and the planet to survive, to use only what we need to preserve the future.
It is not possible for one person alone to act in a way that will sustain our world for future generations. The more we know about how to be a better global citizen, be it recycling and reducing waste or simply seeking knowledge about how our actions have a domino impact on the world, the more of a positive force we can be.
Why must organizations work toward sustainability?
Schmidt-King: Sustainability exists at many levels: individual, organizational, societal, and global. Not only are organizations, firms and businesses positioned to be agents and engines of innovation and impact, but a sustainable future is a prerequisite for their own survival. Given the scope, reach and operations of businesses, they can create and adopt sustainable business practices that serve and support their business and stakeholders, including the well-being of the ecosystem. Organizations are realizing that doing well and doing good are not mutually exclusive terms. Businesses can find the balance to do both and, in doing so, can be leaders in sustainability.
What are the different kinds of sustainability?
Schmidt-King: Sustainability is a broad term, which can be a challenge and opportunity. In 2015, the United Nations created 17 Sustainable Development Goals focusing on the dimensions of sustainability including people, planet, prosperity, peace, and partnerships. For businesses and organizations, this has translated into terms like the triple bottom line – PPP for people, planet, and profit and ESG for environmental, social, and governance – and calls upon businesses to see their role and responsibility in advancing sustainable strategies and sustainable development. Our sustainability management major at the Sellinger School of Business views sustainability as “how corporations deliver value to people, planet, and profit while creating and sustaining a competitive advantage.”
How do different business disciplines support sustainability?
Chavez: All business disciplines have a role to play in supporting sustainability. Examples include considering green companies or initiatives in financing and investing decisions, proper messaging and handling of sustainability initiatives to prevent greenwashing or misleading claims, and accounting to help with measurement, assurance of information, and presentation of data.
Schmidt-King: McCormick & Co. and Pompeian Olive Oil visited Loyola to speak to our students about their organizations’ integration of sustainability into their business practices and strategies. From management, to marketing, to collecting and assessing data, to reporting, to understanding global trends in areas such as climate and geopolitics, sustainability requires collaboration not only across disciplines, but also across organizational divisions.
How do organizations measure and report on sustainability?
Chavez: The world of sustainability reporting is like the Wild West. Companies may feel pressure from their stakeholders – investors, customers, employees, etc. – to report on certain activities, or they may report based on their mission or ethics. Unlike financial reporting, sustainability reporting is not yet universally mandated or prescribed, so companies have some autonomy as to what topics they choose to report on, how often they report, which published guidelines they use to measure their impact, and the format of their reporting. We are beginning to see mandated emissions (GHG) disclosure proposals, which is the first step in moving towards more uniform reporting on sustainability.
How does sustainability follow the Jesuit commitment of “caring for our common home”?
Schmidt-King: Laudato Si’ is the name of Pope Francis’ encyclical on caring for our common home, planet earth. It calls to action “every person living on this planet” and calls for an integral ecology that sees the interconnectedness of environmental, economic, political, social, cultural, and ethical issues. In 2021, Loyola University Maryland joined the first cohort of Laudato Si’ universities, committing to responding to the cry of the earth and the cry of the poor through fostering ecological economics, adopting sustainable lifestyles, fostering ecological education, fostering ecological spirituality, and building community resilience and empowerment.
Why should students study sustainability?
Chavez: Students should study sustainability because it is quickly becoming ingrained in the corporate world. Having knowledge of the vocabulary, reporting frameworks, specific industry impacts, etc., will help students succeed and contribute to their chosen path. For instance, the accounting industry expects that Loyola’s current freshmen in the Class of 2027 will be involved in auditing sustainability information in their first year of employment. The focus on sustainability is growing in all facets, so it is imperative that our students know the issues.
Schmidt-King: Not that long ago, sustainability was something extra a business would consider. Now it is integral and ingrained in an organization’s strategy and operations. I am proud that Loyola University Maryland was the first institution in Maryland to create a sustainability management major. It is a path that allows students to do well by doing good, and it provides a career path that highlights the critical role of businesses in effectuating meaningful change.
Loyola’s Sellinger School of Business introduced the Bachelor of Business Administration in sustainability management in 2020. On the graduate level, Emerging Leaders MBA students participate in a sustainability colloquium that addresses the question, “How do competent, credible, confident emerging leaders contribute to sustainable value creation for all stakeholders?” Colloquium participants earn a certification in ESG reporting.
Media Relations Contact
If you are a member of the media and have questions about this story, please contact Rita Buettner at [email protected] .
Additional Links
- University Profile
- Media Resources
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Social Media Directory
- Loyola Magazine

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business plan is essential as an entrepreneur. It helps you set clear goals and guidelines for how you will manage your business. A business plan may also be needed to set employee goals, obtain funding or even to sell your business one day. In this article, we discuss the importance of a business plan for entrepreneurs, as well as a few main ...
There are several reasons why business planning is of great importance, such as guiding decision-making, allocating resources, and identifying potential risks and opportunities. First and foremost, business planning helps organizations in setting realistic goals and determining the best strategies to achieve them.
A business plan is of significant importance when it comes to guiding entrepreneurs in succession planning, which involves preparing for the future transition of leadership and ownership within a business. To effectively use a business plan for succession planning, assess current leadership and ownership, identify potential successors, define ...
Here are the key elements of a good business plan: Executive Summary: An executive summary gives a clear picture of the strategies and goals of your business right at the outset. Though its value is often understated, it can be extremely helpful in creating the readers' first impression of your business.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing. As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly ...
The Importance Of Planning In Entrepreneurship Benjamin Franklin once said, "If you fail to plan, you plan to fail." Planning is an important part of many aspects of our lives, and is especially true in business. Success often doesn't simply happen by chance, but requires a willingness to plan and put in
The business planning process in entrepreneurship helps an entrepreneur identify exactly what needs to be accomplished to build the venture, and what human and financial resources are required to ...
A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business. Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research, analyze their competitors, validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition.
A business plan is a means of ensuring systematic planning in entrepreneurship. It is an important tool for starting a business and planning expansions of well-established businesses.
Beyond keeping banks happy, IESE's Govert Vroom finds planning can transform the entrepreneur's approach. "A goal without a plan is just a wish," the adage goes. Entrepreneurs looking to launch a new business should take heed. The planning phase of a start-up isn't just providing a song and dance to please banks or investors.
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business. 1. To help you with critical decisions. The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and ...
Business planning is originally a whole process in itself. This planning process has its own components, features, types, etc. The soul of the business planning process itself resides in the process of decision-making. So, let's get ready to learn about all these important aspects in detail! Importance, Features, and Limitations of Planning.
Published Aug 14, 2023. A business plan is essential as an entrepreneur. It helps you set clear goals and guidelines for how you will manage your business. A business plan may also be needed to ...
The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs. Purposes of a Business Plan. A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external.
Importance of a Business Plan. The importance of a business plan cannot be overstated. It is a crucial tool for entrepreneurs and small business owners, helping them define their goals and monitor their progress as their company evolves. A well-thought-out business strategy should be the top priority when starting a new business.
Taking Action. Planning may include actions such as defining potential markets and drawing up business plans with projections. Entrepreneurs who take more actions during the planning stage of a ...
Business planning is essential for entrepreneurs looking to start or grow a business that will thrive in today's competitive economy. In this article, we will discuss the importance of business planning and provide insights into how to create a practical, actionable business plan that will help you succeed. What is business planning? Business ...
A business plan gives you a tangible way of reviewing your business goals. Business plans revolve around the present and the future. When you establish your goals and put them in writing, you're more likely to reach them. A strong business plan includes these goals, and allows you to communicate them to investors and employees alike. 3.
Provide projections for two to four years in the future, including: 1. Forecasted income (monthly for first two years, then by quarter or year thereafter), 2. Forecasted cash flows by month (monthly for first two years, then by quarter or year thereafter), 3. Forecasted balance sheet for all years (year-end), and. 4.
Investopedia describes four ways entrepreneurs benefit society: Economic growth: The success of the products and services created and sold by entrepreneurs cascades to other businesses and markets. Wealth generation: Entrepreneurs frequently target new markets and tap audiences outside the focus of established firms.
The role of strategic planning cannot be overstated in the pursuit of entrepreneurial success. Strategic decision making has a significant impact on the direction and outcomes of a business venture. To grab the attention of the audience, consider the following key points: Strategy is the foundation for entrepreneurial achievement.
Importance of Financial Planning in Entrepreneurship. The following are the importance of financial planning in entrepreneurship: Determine Feasibility. Variance Analysis. Forecasting Financial Requirements. Obtaining Fund. Cash Flow Shortages. Importance of Financial Planning in Entrepreneurship.
To understand the importance of entrepreneurship, recognising what an entrepreneur does is necessary. The term itself comes from the French 'entreprendre', which means 'to undertake.' An entrepreneur is someone who undertakes or plans for all the risks and responsibilities that come with the formation of a new business to earn profits.
Individuals dive into entrepreneurship for various reasons, including autonomy. Over 50% of entrepreneurs start a business for financial reasons, and 22% favor job flexibility.
As Loyola University Maryland celebrates Earth Month, two professors at Loyola's Sellinger School of Business define and discuss sustainability and its growing importance to organizations, different business disciplines, and the planet. Stacy Chavez, Ph.D., assistant professor of accounting, and Astrid Schmidt-King, J.D., teaching assistant professor of management and organizations ...