

How to structure an essay
It is important to present your ideas in the correct essay structure which consists of: Essay topic (or title or question), introduction, body, conclusion, references.
- Basic structure of an academic essay (PDF)
- Example of an essay outline (PDF) “Discuss the effects of the unemployment benefit system on the New Zealand economy.”
- Essay title
- Introduction
- Body paragraphs
A good introduction paragraph:
- Provides background or scope context to your essay.
- Introduces the essay topic.
- States the main point of your essay in a thesis statement in one or two sentences.
- Shows in the last one or two sentences what you plan to cover in the body paragraphs.
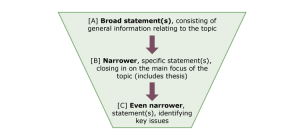
A – Broad statement(s) consisting of general information relating to the topic. B – Narrower, specific statement(s), closing in on the main focus of the topic (includes thesis). C – Even narrower, statement(s), identifying key issues.
Learn more about writing essay introductions in the Essay writing resource website. The body paragraphs address each of the main points (or sub-topics) of your essay in the same order they were mentioned in your essay introduction. Each paragraph will be related to your essay’s central focus and thesis.
- Before you start to write, draw a map of your ideas for the different paragraphs which support the thesis statement.
- After you have made your map, write each body paragraph with a clear structure to describe, discuss and develop your topic.
Learn more about writing good essay body paragraphs from the Essay writing resource website. The conclusion paragraph is your last chance to impress your reader. You can either:
- Start your conclusion with a phrase such as “In conclusion” or “To sum up” as this will indicate to your reader that you are finishing your essay.
- Immediately begin with a summary of the main points, and then write an end statement. In this statement you can restate the thesis, make final comments that could be evaluative, or refer to the larger issues related to the larger context or background.
Learn more about writing good essay conclusions from the Essay writing resource website. You will need to provide a full list of references at the end of your essay. These will demonstrate that the opinions you expressed in your essay were informed from your reading. Make sure you acknowledge your sources using the correct referencing style.
What are common essay types?
At university you have to demonstrate the ability to write different types of essays. While all academic essays have the same basic structure (introduction, body paragraphs, conclusion), the purpose, style of delivery, and organisation of the ideas may vary.
Examples of common essay types
“A discussion essay discusses a range of evidence, views, theories, findings or approaches on a topic to develop a position through the essay. The conclusion usually states this position” Academic Writing at Auckland (AWA) .
See the discussion essay examples on the AWA site.
“An Analysis Essay critically analyses an object of study (a book extract, artwork, film, article, cultural artefact, event, example, situation…) through the lens of broader concepts (theories, themes, values, systems, processes…). It builds and supports a position and argument through this critical analysis and demonstrates understanding of both the object and the broader concepts” Academic Writing at Auckland (AWA) .
See the analysis essay examples on the AWA site.
Additional resources
The following resources provide you further information about essay writing and examples of essays in different disciplines:
- write@uni: Examples of student writing
- Academic Writing at Auckland

Related topics
- Critical thinking
- Finding information
- Understanding assessments
- Note-taking
- Time management
- Paraphrasing and quoting
- Referencing and avoiding plagiarism
See all available workshops .
Short on time? Watch a video on:
- Essay writing – 6:28
- Paraphrasing and quoting – 22:22
- Using active and passive voice – 9:58
- Editing your work – 5:12
Have any questions?
This is the footer
Forms of writing
Essay writing.
- Report writing
- Reflective writing
- Writing for business contexts
- Writing a memorandum
- Email etiquette
- Producing Word documents and GoogleDocs
Essays are often used to demonstrate in-depth understanding of a particular topic. There are two main types of essays:
- Descriptive – when you give a thorough description of a particular topic
- Persuasive – when you present an argument and demonstrate that you have at least looked at both sides
1. Plan your essay
Deconstruct the question
A crucial first step is to understand exactly what the question requires of you. View the deconstructing a question resources .
Brainstorm an essay map
You will be asked to write an essay based on content you have learnt in class. Once you know exactly what the question is asking of you, do a quick brainstorm to map what you already know about the topic and what you need to find out.
Find and review information sources
Your lecturer will likely ask you to include course readings and to refer to additional readings. A good place to start is to refer to your course readings, revise these and see who the authors refer to in their reference list. You will also need to conduct a focused search for further information. View resources on finding quality sources of information .
Start writing
2. Write your essay
The Introduction
The Introduction sets the scene for the essay and gives the reader a clear idea of what they can expect. A good introduction briefly introduces the topic and gives signposts to the main points that the essay will address.
The Body consists of paragraphs that address your essay topic. Paragraphs should focus on one theme and they should be structured in a logical manner. View resources on writing paragraphs .
The Conclusion
The Conclusion summarises key points of the essay. A good conclusion doesn’t simply regurgitate content, rather it gives the reader a concise summary of the key points and a clear idea of your stance on the topic. The conclusion should not contain any new information.
3. Revise, edit and refine your essay
- Check the essay question – does your essay address the question?
- Check the marking criteria in the assignment rubric – if the lecturer wants you to address specific points, make sure you do so
- Read it out loud – by reading your work out loud, you get a better sense of how the reader will interpret your work
- Give it to someone to check for flow and to proof-read. If you’ve written a good essay it will make sense to someone who has no previous knowledge of the topic. This shows that your essay is clear and is structured in a way that develops understanding for the reader
- Proof-read your work – make sure you proof-read your work to identify spelling and grammar errors
- Check your referencing – make sure your work adheres to APA referencing standards
Further information
- Massey University’s assignment planner will map a timeline to complete key essay writing steps
- Use this list of linking words to help you link paragraphs and/or sentences within paragraphs
- Refer to examples of essays on AWA .
- Our resources on paraphrasing will help you incorporate evidence into your writing
- Our resources on grammar will help you edit and refine your essay
Learning Hub

Learning Hub team Workshops Drop in booth Learning leaders Pass Leaders Business library guides
Life on campus Careers centre Student support He Tuākana AskAuckland student centre

Writing and Presentations
Introduction.
- Academic Style
- E-portfolios
- Grammar and Punctuation
- Paraphrasing
- Presentations
- Proofreading and Editing
- Referencing and Plagiarism
- Reflective Writing
- Academic Writing Guide - Logic and Flow Improve your paragraphs with the words and phrases (discourse markers) in this guide
- Academic Writing Guide - Passive Voice Learn the difference between active and passive voice and when you might use passive structures in academic writing
- APA Style Guide - Italics, Bold, Headings Use this guide for examples of when to use italic and bold styles for text, and how to format headings in APA style
- APA Style Guide - Formatting Use this guide as a reference for font size, line spacing, margins, page numbers, and more in APA style
- APA Style Guide - Abbreviations Use this guide for examples of how to correctly shorten words, terms, and more.
- APA Style Guide - Numbers and Units Use this guide for examples of how to correctly express numbers and units in APA style
An academic essay is a form of writing that often contains an answer to a question and usually contains an argument. Making an argument means taking a position on a topic and critically analysing information and ideas that are relevant to that topic. An essay should both inform the reader about the topic and convince the reader that the writer's argument is valid. Writing essays helps develop critical thinking skills as the writer organises ideas into paragraphs and an orderly sequence of points.
Essay Structure
To be convincing and to make sense, an essay needs to be presented as a well-structured piece of writing. The general framework of an academic essay consists of the following:
Example structure of an essay:
- Introduction (10% of total essay length)
- Paragraph 1: First supporting statement, Definition, Explanation, Evidence
- Paragraph 2: Second Supporting Statement, Definition, Explanation, Evidence
- Paragraph 3: Third Supporting Statement, Definition, Explanation, Evidence
- Conclusion (10% of total essay length)
Example for a 2,000-word essay:
- 200-word introduction
- 1600-word body
- 200-word conclusion
The introduction opens your essay and introduces the reader to the main argument and points which you will discuss and develop in your essay. An introduction can be broken into three parts:
- General statement(s)
- Indication of essay structure
- Thesis statement
The body is the place to fully develop the argument that you outlined in the introduction. Each paragraph within the body discusses one major point in the development of the overall argument. Each main point needs to be clearly stated in the form of a topic sentence, which is then supported with evidence.
There are four types of paragraphs:
- Narrative – Tells a story
- Persuasive – Convinces the reader
- Descriptive – Describes something
- Explanatory – Gives information/explains something
Each paragraph should explain one major point and can be laid out in the following format:
- Define – Describe the main idea of the paragraph
- Explain – Clearly outline the main idea of the argument and link to research
- Evidence – Use research and examples to support your main idea
The conclusion is where you wrap up the essay. You should restate the main argument or thesis and reinforce the most important evidence supporting the argument.
You can break up a conclusion into three parts:
- Restate your thesis statement
- Summarise key points in your essay
Since the conclusion is the last opportunity to convince the reader to accept your argument, ensure you end on a strong note.
Check out the Academic Style section of our Study Toolbox for information on the type of style used in academic essays (e.g. formal language, avoiding cliches). Also, see the writing guides in the Guides box on this page for helpful information relevant to essay writing and formatting.
Transitions and Links
Paragraphs focus on one main point, but all individual paragraphs should link together as a whole. There are plenty of words and phrases that can be useful to help link together paragraphs. These transitions can also be used to link ideas within paragraphs. Below are some examples:
Adding to a point or introducing a new point:
Also; further; in addition; following this; subsequently; in regards to.
To reinforce a point:
With this in mind; in other words; that is to say.
Identifying a stage in process:
First; second; third; in addition; consequently; next; following this.
Explaining or introducing an example:
For example; such as; for instance; namely.
Showing cause and effect:
As a result; it is evident; hence; for this reason; this suggests that.
Showing concession:
After all; granted; however; in any case; admittedly.
Showing conditions:
In these circumstances; provided that; even if; unless; although; despite.
Compare/Contrast:
In comparison; on the one hand; on the other hand; on the contrary; alternatively; otherwise.
Adding emphasis:
Evidently; conceivably; conclusively; undoubtedly; unfortunately.
Summing up/concluding:
To sum up; in conclusion; to summarise; therefore; to sum up.
Essay checklist
- Have you proofread your essay for spelling and grammatical errors?
- Does your essay answer the essay question?
- Have you gone in-depth and backed up evidence with research?
- Are your discussion points relevant to the essay question?
- Is your introduction clear and concise, giving the reader a preview of what your essay is about?
- Do your paragraphs link to each other? Are they concise and clear?
- Does your conclusion sum up the key points in your essay?
- Have you adhered to the word count limit?
- Do you have a reference list and have you checked your citations?
- Have you used the correct referencing style?
- << Previous: E-portfolios
- Next: Grammar and Punctuation >>
- Last Updated: Feb 1, 2024 11:14 AM
- URL: https://library.manukau.ac.nz/Writing
Understanding essay types
Introduction.
- Sample essays 1
- Sample essays 2
At university, you have to demonstrate the ability to write different types of essays. The aim of this unit is to study the style features of three main types of essays: expository, discussion and argumentative.
Although all university writing is essentially argumentative, most essays have elements of exposition, discussion and argument. A critical review or literature review , for example, may begin with a brief outline or summary of what the article or book is about and its relation to a particular field and the author's viewpoint, before discussing the weaknesses and strengths of the article.
At university, you do not just write your own opinion; your opinion is often an informed opinion , formed from reading and synthesising other people's opinions. You will then support your opinion or claims with evidence and relevant theory. At university, you do not just describe; you analyse, examine, explain, interpret, discuss, assess and evaluate.
In this unit, we will look at:
- some definitions of each essay type (expository, discussion, and argumentative)
- their characteristic features
- some sample essays
Definitions
While all academic essays have the same basic structure – they all begin with typical introductions, develop ideas in body paragraphs, and end with typical conclusions – there are variations in the style of delivery and organisation of the ideas to fit the purpose of the essay. You may find these broad dictionary meanings useful:

Sample discussion essays
The two sample discussion essays presented here represent varying degrees of discursive style. The first combines exposition with discussion; the second combines discussion with argument. Both essays demonstrate some basic principles of essay structure, including the construction of effective introductions, body paragraphs, and conclusions using the models explained in this unit.
Essay sample 1
Sample essay: Impact of iPods on the music retail industry and music consumption
The writing style has elements of exposition and argumentation. The tone is less assertive; the style is exploratory, but the discussion is built around a clear thesis or point of view stated in the introduction.
Answer the following questions:
Essay Sample 2: Language and Gender
This commentary on a literature review attempts to show how the writer of the review combines discussion with exposition, critical analysis and argumentative style (ie, concession and refutation). However, the annotations are not very easy to read; it might be useful to print out a hard copy to study it properly. At the end of the article, you can click on the original document without the comments.
Argumentative essays
Argumentative essays are about issues. They are written to support or refute (argue against) an opinion or claim in order to reach a decision. In terms of writing style, they are more forceful than a discursive essay, because they attempt to effect a change of opinion through reasoned discussion.
Some function words used in questions requiring argument include: Do you agree or disagree with ...? Should ...? Develop an argument for or againts this statement. Discuss the claim that .... To what extent do you agree or disagree with ...?
The language of argument
Academic arguments are characterised more by logical appeal than emotional appeal. If emotional appeal or language were used the writing would read more like a public speech or an oral debate than an academic argument. Avoid the following:
- subjective comments (eg, I believe ...)
- sweeping generalisations, absolute statements or exaggeration without solid evidence (eg, Everyone buys furniture from Trade Me .)
- rhetorical questions: These are not reallly questions. They make the writing style unnecessarily wordy and dramatic, and therefore inapporpriate in academic arguments. (eg, What factors contribute to such a phenomenon? Is this the kind of attitude to be encouraged in young people today?)
- emotionally charged language ( The idea is utterly impractical and doomed to fail. )
- exclamation marks ( Robots will never supersede humans!)
Click here to view a language summary .
Basic features of argumentative essays
The following presentation discusses some of the features of an argumentative essay.

Sample argumentative essays
In this section you can review some of the basic principles of argumentative essays. The sample essays are shorter than most stage 1 essays, but they demonstrate the conventions of academic essay structure and argmentative style, especially the use of concession and refutation. Some essays have notes in the margins to alert you to the distinctive style features of argumentation. Other essays are followed by some short questions.
Read the introduction and the first body paragraph of this essay. The purpose of the extract is to help you understand the style and structure of argumentative essays from what you have learnt about them so far. Use the questions to work through the extract.
Essay Question: Should state or local governments have the power to use surveillance cameras in their communities?
Sample essay: Federal government should regulate the use of surveillance cameras in all states to protect citizens’ rights
Essay sample 2
Essay question: “Separating girls from boys in middle school (years 8 and 9) yields positive results.” How far do you agree or disagree with the statement.
Sample essay: Separating the sexes
Essay sample 3
Question: “The TV effect is a myth”. To what extent do you agree or disagree with this claim?
Sample essay: The TV effect is a myth

Critical reviews
Critical reviews and literature reviews both provide appraisals, but whereas literature reviews usually avoid giving judgement on the positions or ideas of the works under review, critical reviews take a more argumentative approach. They provide a critique of the work.
A critique is a piece of writing produced by“careful, thoughtful examination and judgement of a situation or of a person's work or ideas” (Collins Cobuild English Language Dicitonary, 1987). Typically, it involves “consideration of the strengths and weaknesses of a piece (or pieces) of work in relation to its intended purpose, the evaluation of the contributions that it makes to a field of knowledge, and a comparison with other relevant work that may shed light on its value” (Manalo & Trafford, 2004, p. 45).
Manalo, E., & Trafford, J. (2004). Thinking to thesis. Auckland: Pearson Longman.
- Select text to style.
- Paste youtube/vimeo url to add embeded video.
- Click + sign or type / at the beginning of line to show plugins selection.
- Use image plugin to upload or copy/paste image searched from internet or paste in snip/sketched image from snap tool
Skip to Content
Massey University
- Search OWLL
- Handouts (Printable)
- Pre-reading Service
- StudyUp Recordings
- StudyUp Postgraduate
- Academic writing
- Intro to academic writing
- What is academic writing?
- Writing objectively
- Writing concisely
- 1st vs. 3rd person
- Inclusive language
- Te Reo Māori
- Assignment planning
- Assignment planning calculator
- Interpreting the assignment question
- Command words
- Organising points
- Researching
- Identifying academic sources
- Evaluating source quality
- Editing & proofreading
- Apostrophes
- Other punctuation
- Active voice
- American vs. British spelling
- Conditionals
- Prepositions
- Pronoun Reference
- Sentence fragments
- Sentence Structure
- Subject-verb agreement
- Formatting and layout
- Word limits and assignment length
- Commonly confused words
- How assignments are marked
- Marking guides
- Getting an A
- Levels of assessment
- Using feedback
- Professional emails
- Forum posts
- Forum netiquette guidelines
- Sharing personal information
- Writing about personal experiences
- Assignment types
- What is an essay?
- Essay planning and structure
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Body paragraphs
- Essay revision
- Essay writing resources
- What is a report?
- Report structure
- Analysing issues for a report
- Business report
- What is a business report?
- Business report structure
- Inductive vs. deductive reports
- Other kinds of business communication
- Business report format and layout
- What is a lab report?
- Lab report structure
- Science lab report writing resources
- Psychology lab report writing resources
- Lab report body paragraphs
- Literature review
- What is a literature review?
- Writing a literature review
- Literature review structure
- Literature review writing resources
- Research proposal
- Writing a research proposal
- Research proposal structure
- Other types
- Article critique
- Book review
- Annotated bibliography
- Reflective writing
- Oral presentation
- Thesis / dissertation
- Article / conference paper
- Shorter responses
- Computer skills
- Microsoft Word
- Basic formatting
- Images, tables, & figures
- Long documents
- Microsoft Excel
- Basic spreadsheets
- Navigating & printing spreadsheets
- Charts / graphs & formulas
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Basic skills
- Advanced skills
- Distance study
- Getting started
- How to study
- Online study techniques
- Distance support
- Reading & writing
- Reading strategies
- Writing strategies
- Grammar resources
- Listening & speaking
- Listening strategies
- Speaking strategies
- Maths & statistics
- Trigonometry
- Finance formulas
- Postgraduate study
- Intro to postgrad study
- Planning postgrad study
- Postgrad resources
- Postgrad assignment types
- Referencing
- Intro to referencing
- What is referencing?
- Why reference?
- Common knowledge
- Referencing styles
- What type of source is this?
- Reference list vs. bibliography
- Referencing software
- Quoting & paraphrasing
- Paraphrasing & summarising
- Paraphrasing techniques
- APA Interactive
- In-text citation
- Reference list
- Online material
- Other material
- Headings in APA
- Tables and Figures
- Referencing elements
- 5th vs. 6th edition
- 6th vs. 7th edition
- Chicago style
- Chicago Interactive
- About notes system
- Notes referencing elements
- Quoting and paraphrasing
- Author-date system
- MLA Interactive
- Abbreviations
- List of works cited
- Captions for images
- 8th vs 9th edition
- Oxford style
- Other styles
- Harvard style
- Vancouver style
- Legal citations
- Visual material
- Sample assignments
- Sample essay 1
- Sample essay 2
- Sample annotated bibliography
- Sample book review
- Study skills
- Time management
- Intro to time management
- Procrastination & perfectionism
- Goals & motivation
- Time management for internal students
- Time management for distance students
- Memory skills
- Principles of good memory
- Memory strategies
- Note-taking
- Note-taking methods
- Note-taking in lectures
- Note-taking while reading
- Digital note-taking
- Reading styles
- In-depth reading
- Reading comprehension
- Reading academic material
- Reading a journal article
- Reading an academic book
- Critical thinking
- What is critical thinking?
- Constructing an argument
- Critical reading
- Logical fallacies
- Tests & exams
- Exam & test study
- Planning exam study
- Gathering & sorting information
- Reviewing past exams
- Phases of revision
- Last-minute study strategies
- Question types
- Short answer
- Multi-choice
- Problem / computational
- Case-study / scenario
- Open book exam
- Open web exam or test
- Take home test
- In the exam
- Online exam
- Physical exam
Essay introduction
The introduction to an essay has three primary objectives:
- Explain the context of the essay
- Give the answer : the response to the question or the overall focus of the essay (the thesis statement)
- Describe the structure and organisation of the essay
These aims can be given more or less emphasis depending on the length and type of essay. In a very short essay (less than 1000 words), for example, there is not much room to give a full and detailed context or structure. A longer essay has room for greater detail.
Essays are usually written for an intelligent but uninformed audience, so begin with some context: the background of the topic, the topic scope, and any essential definitions.
- Introductions often begin with a broad opening statement that establishes the subject matter and background. Don't make it too broad (“Since time began…”), but identify the relevant topic and sub-topic (e.g. human resource management, early childhood development, animal behaviour…).
- To establish the scope, answer basic questions: Who? What? When? Where? How? Why? Is the essay limited to a particular time period, a particular group of people, a particular country?
- Definitions are often established after the introduction, so only include them here if they are absolutely essential.
Answer / focus
The most important part of the introduction is the response to the question: the thesis statement. Thesis statements are discussed in detail here: thesis statements .
An introduction often ends on the thesis statement. It begins with a broad statement and gradually narrows down until it directly addresses the question:
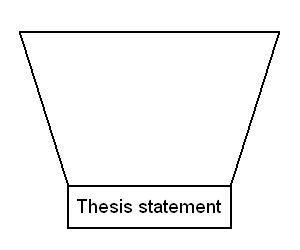
This order of introduction elements is not set in stone, however. Sometimes the thesis statement is followed by a breakdown of the essay's structure and organisation. Ultimately, you must adapt the order to suit the needs of each particular essay.
Strong introductions tell the reader how the upcoming body paragraphs will be organised.
This can be as easy as outlining the major points that your essay will make on the way to the conclusion. You don't need to go into much detail in the introduction: just signal the major ‘landmarks.’
It can help to identify how all of the paragraphs are organised:
- Do the paragraphs deal with the issue from earliest to most recent (chronological)?
- Are the paragraphs grouped by broader themes (thematic)?
- Does the essay answer several related questions one after the other (sequential)?
- Do the paragraphs describe two elements and them compare them (contrasting)?
The essay will be much more readable once the reader knows what to expect from the body paragraphs.
Introduction examples
See sample essay 1 and sample essay 2 for model introductions.
Page authorised by Director - Centre for Learner Success Last updated on 25 October, 2012
- Academic Q+A
Have a study or assignment writing question? Ask an expert at Academic Q+A
Live online workshops
- StudyUp (undergraduate)
- Campus workshops
- Albany (undergraduate)
- Albany (postgraduate)
- Albany (distance)
- Manawatu (undergraduate)
- Manawatu (postgraduate)
Upcoming events
- All upcoming events
- Academic writing and learning support
- 0800 MASSEY | (+64 6 350 5701)
- [email protected]
- Online form


School & Study
Beyond school, just for fun, wholesome half-hour, study advice, walkthrough guides + more, past papers, resource answers, ncea level 1, ncea level 2, ncea level 3, account details.

6 Step Guide to Writing a Killer Essay
Written by studytimenz
At high school, particularly here in new zealand, ideas are always assessed in the form of essays..
With so many rules surrounding ‘proper’ essay form, it’s easy for ideas to get lost to the format, or for you to lose sight of what they’re arguing for in the first place.
Sadly, this means that students often can’t get their thoughts across effectively, and are marked down for things that have no bearing on their ideas or intelligence.
However frustrating they might be, research has shown that learning how to compile an argument in written form is a skill that does great things for your grades, employability and general life-confidence.
As a soon-to-be graduate of high school – whatever you choose to do – the importance of strong communication skills cannot be understated.
If you choose to head straight into the workforce, you’ll be expected to demonstrate this skill in your cover letters and CV’s during job applications, and at University, essays are pretty much the stock standard assignment in most courses (otherwise there are always reports, reviews and reflections).
Writing skills will even get you further in your travels: Visas can involve lengthy letters and application processes, and administrators are always impressed by a well-written application.
Considering all the evidence, it’s a smart move to get a good feel for essay writing now – the seeds you plant now will help you out big-time in the long run.
How can I write a good essay then?
Contrary to popular opinion, anyone can write a good essay. It’s a skill, not a trait, and like any other skill, it only improves with practice. The tricky thing is getting your head around all the niggly bits, like structure, and themes, and ideas, and topic sentences, and punctuation, and clarity, blah blah blah, etc. That’s what we’re here for.
This guide will help you to break through the sludge of essay writing and help you to get to the heart of their purpose: communicating an idea. We’ll decipher the intimidating jargon and wordy standards for you, and give you solid, smooth steps to follow so you can smash an essay for every topic, any time. The guide will cover:
Deciding on an “idea”
Planning your argument
Essay structure
Introduction
Body paragraphs
Proofreading
THE BIG “IDEA” AND WHY IT MATTERS
The term ‘idea’ in the context of essay-writing causes a lot of confusion – and rightly so – it’s unfairly vague!
Simply put, an idea is the argument you’re making in your essay. While definitions may vary across standards and subjects (“hypothesis”; “argument”; “thesis statement”; “theme” etc.) your idea is your overarching claim that the rest of your essay will prove or justify .
An idea could be anything from “ Romeo and Juliet’s relationship demonstrates the difficulty of defying familial expectations ” to “ The use of guerilla warfare helped the Viet Cong to defeat America in the in the Vietnam war .”
Ideas can be universal, personal, fundamental, controversial or challenging. They don’t necessarily have to be ‘good’ or ‘moral.’ Writing an essay isn’t about agreeing with the message of the text, or the topic you’ve been asked to engage with. Teachers are more concerned with your ability to look at a topic or text critically, interpret it, and relate that interpretation to the outside world in one way or another.
The idea is the spine of your essay. The rest of it will work towards demonstrating how and why you’re arguing for this claim. So before you start writing an essay, it’s smart to get a firm grip on your idea first.
Brainstorming is a good start. On a piece of paper, jot down all the observations you’ve made about your essay topic. You’ll usually have a question or a demand in the guidelines to narrow things down. If you can’t think of any ideas, do some extra revision!
Once you’ve done this, try to think of one connection to bind your ideas about the text/topic/event together. Then make it into a statement – e.g: “ In Bend it Like Beckham , Jesminder’s character explores the tension between cultural expectations and social belonging .” Make sure you’ve got a good amount of supporting points to bolster whatever your claim says.
Pro tips: Don’t overcomplicate it! Fancy wording doesn’t matter. It’s more about the insight of your claim, and showing that you can develop a perceptive opinion on something.
Don’t fall into the trap of the one-word-idea. “Love” is not an idea. Instead, your idea should take the form of a firm statement about love.
If your essay is given to you in the form of a question, think of the idea as an answer to that question.
Example question: “ Should the Hunger Games be considered a feminist text ?”
Idea/claim/argument/thesis: “ Despite The Hunger Games having a female protagonist, the character of Katniss reinforces masculine notions of strength, therefore it should not be considered a feminist text.
Your idea should show some critical thinking. For example: “ The Hunger Games should not be considered a feminist text ” is not a strong enough observation – you need some substance behind it.
If you’re too vague or short with your idea, your supporting evidence will lose structure, and could go on forever. Think about your idea as if you were explaining the main point of your essay to another person.
If you read your idea aloud – ask yourself: Does it make sense? Does it answer the question or fulfill the demand? Does it summarise most of your essay’s argument?
If the answer is no to any of these three questions, refine and try again.
2. GET PLANNING
Essays almost always follow the same linear structure:
- Introduction.
- Body Paragraphs
- Conclusion.
We’ll break down the anatomy behind each element later on – but for now – it’s useful to know how they work together to make an essay. The introduction is the clincher: its job is to contextualise your argument, interest the reader, briefly explain your argument and of course, introduce the idea . The body paragraphs are the supporting points to hold up your main idea, with evidence from the text . The conclusion brings together everything you’ve argued in a neat summary , reinforcing the idea one more time.
Whether you’re writing under time pressure or doing a take-home assignment, it’s important to know (at least in part) where your argument is going to go. Planning is a sure way to do this – and it doesn’t have to be boring. While ‘fluking it’ might work for some people, having no plan makes it easy to get lost in your own train of thought and go off on long tangents. There are loads of different ways to plan, and you should give yourself enough flexibility so that you have the freedom to incorporate new points or ideas as you’re writing.
A great, easy and flexible way to plan is the Box Plan. This plan can be adapted for a range of subjects; it’s a neat and easy visualisation of your essay’s skeleton and key points; and also serves as a great resource for revision – because who wants to spend hours rewriting the same essay over and over?
See the table below for an easy template of the Box Plan. Feel free to print it out, and if you’re feeling extra-motivated for revision, spend some time making it colour co-ordinated or adding some visual doodles to help memorise the content and make things fun.
DIY BOX PLAN
Introduction :
Clearly state your main IDEA .
What are the THREE MAIN POINTS that you will use to support this idea?
Body Paragraph One :
Clearly state the main POINT you will discuss in this paragraph.
Record all of the EVIDENCE you will use to prove this point.
Connect this evidence back to the MAIN IDEA or the OUTSIDE world.
Body Paragraph Two :
Body Paragraph Three :
Conclusion :
Clearly state the main ARGUMENT you have made or IDEA you have explored.
Review how all of your points have supported this IDEA .
3. ANATOMY OF AN INTRO
There’s lots of advice out there that tells you an introduction is the least important part of an essay, something you can rush over to get to the ‘good stuff’. They’re wrong.
Writing a killer introduction is the magic ticket to an excellent essay. A great intro lays out your ideas concisely and persuasively, and can provide focus and momentum for the rest of the essay. Plus having something concrete to come back to can be really helpful when you’re feeling stuck or lost – and remind you of your overarching argument or idea. Our best advice for nailing the intro is to start broad and then narrow down.
Here’s a quick formula to follow for writing an introduction that’ll blow your teacher out of the water.
Pro tip: Get a hook, start broad and narrow down. Finish on by going SUPER broad (society/the world/the universe) to be extra fancy.
- Hook (rhetoric question/quotation/exclamation to engage the reader)
- Context (the boring but important contextual bits like the author/director/poet/setting/title/characters/etc.)
- Idea (see our first chapter for a definition)
- Brief explanation of how you’ll prove this idea (whatever points/evidence you’re putting in your body paragraphs)
- For extra points, round up your intro by making a connection to the outside world (some profound and relevant moral lesson about society usually works)
Here’s an example of a great introduction for a basic English text analysis essay. Each colour in the paragraph corresponds with the formula above (Hook = purple; Context = red; and so on).
Why do bad things happen to good people? The majority of society believes that there are no logical answers to this question. Terrible things can happen to the best of us, for no particular reason. However, in William Shakespeare’s “King Lear”, the main character, King Lear, who claims to be “a man more sinned against than sinning”, is fully responsible for his own downfall. In fact, the sins committed against King Lear are a result of his personal faults of rashness, blindness, and foolishness. Though a good king, Lear’s actions cause his family and kingdom to fall apart. Furthermore, he is personally punished for disrupting the natural order, with his poor decision-making. King Lear’s downfall demonstrates how good people can still make terrible decisions – inviting the reader to consider the complex nature of humans, and emphasising the importance of taking responsibility for your own actions.
4. BREAKING DOWN THE BODY PARAGRAPH
The body paragraph makes up the “flesh” of the essay “skeleton” you have at the moment. Three body paragraphs is enough for a strong essay, however you can add as many more as you need to strengthen or fully unpack your overall argument (provided you’re not ranting). It’s important that each body paragraph is sharp and clean, and backed up by some relevant evidence. The point of a paragraph is to indicate a break – so make sure that each paragraph has only ONE predominant focus. If you find yourself going off topic from your original focus, consider making a new self-contained paragraph to explore that idea in full depth.
WHAT’S THE POINT?
Your main point should be introduced at the beginning of your body paragraph, and take form in what the experts call a “topic sentence”. This is similar to your big idea, but it’s a bit more specific. Similarly, it should make some sort of definitive claim about the text or topic, and help to support your main idea. If your main idea is the spine of your essay, your topic sentence is the spine of your body paragraph.
Let’s have a look at F. Scott Fitzgerald’s novel The Great Gatsby for some ideas:
Main Essay Idea:
“ Through the use of motifs and symbolism, The Great Gatsby explores the disintegration of the American dream in 1920’s America. ”
Point of Body Paragraph 1:
“Geography is used as a motif to illustrate the different classes of the decaying nation, and their clashing social values.”
Point of Body Paragraph 2:
“The distant Green Light is used to symbolise the ideal of the American Dream – relentlessly pursued but never realised up close.”
Focus of Body Paragraph 3:
“The Valley of the Ashes symbolises the moral and social decay of the nation, figured literally by its desolation and pollution, but also by the poor citizens who live there.”
SHOW ME THE EVIDENCE
It’s all very well and good to be able to make big claims – but you have to be able to back them up, otherwise for all we know, you’re just peddling conspiracies.
The evidence is all the stuff you need to show your reader that your argument has some validity to it. The evidence can be a quote, technique, event, plot point, character, excerpt, symbol, motif, etc. – so long as it’s relevant to the point you’re making and taken directly from whatever your essay is about.
Remember that it has to be factually correct too, don’t ever think you can get away with making up a quote! Your marker knows more than you think, and chances are they’ll sense something fishy and look it up.
ROUND IT UP
To finish your body paragraph in style, throw in one or two sentences that link back to the main idea of your essay. Better yet, reflect on something bigger to show your ability engage critically with the world around you. This final element is your chance to give an opinion on something, it can be as abstract or far-fetched as you like, provided your body paragraph is strong enough to support the claim.
Connecting your essay to wider forces in the world shows that you’re thinking about what you’re writing, rather than simply regurgitating content you’ve learned in class.
Markers love this part – especially in NCEA – and it often makes the difference between a Merit and an Excellence essay.
Here’s a quick table showing the anatomy of a body paragraph:
Focus of Body Paragraph One:
“Geography is used as a motif to illustrate the different classes of the decaying nation, and their clashing social values”
“ I lived at West Egg, the – well, the least fashionable of the two, though this is a most superficial tag to express the bizarre and not a little sinister contrast between them[…]Across the courtesy bay the white palaces of fashionable East Egg glittered along the water, and the history of the summer really begins on the evening I drove over there to have dinner with the Tom Buchanans .” (1.14)
Explanation :
This quote from Nick demonstrates how he envisions class distinctions geographically – drawing a literal and figurative contrast between the two sides of the lake and economic status.
Reflection :
The geographic illustration of class in The Great Gatsby mirrors the growing disparity between rich and poor that was taking place in America in the 1920’s.
5. CONCLUSIONS – MAKING A LASTING IMPRESSION
By the time you’ve made it here, you’re probably sick to death of your topic.
At this point, it’s tempting to just spurt out whatever your mind can muster, and hope that the rest of your essay holds you afloat when it comes to marking.
Avoid thinking like this! Your conclusion is the your final chance to leave an impression on your reader.
If anything, it’s a golden opportunity to boost the quality of your essay by tying it all together with a sparkly bow.
This doesn’t mean the conclusion has to be a difficult or particularly long process. All the work is pretty much done for you, now it’s a matter of selecting the most important points to drive home.
At bare minimum, your conclusion must accomplish three things:
- Restate the main idea of your essay.
- Summarize the three points in your body paragraphs.
- Leave the reader with an interesting final thought or impression.
Excellent conclusions will convey a sense of closure while also providing scope for other trains of thought – like an appetizer of a main dish at a different restaurant.
This is a tricky balance to strike, but it makes a world of difference.
6. PROOFREADING – YOUR FINAL SAFETY NET
At this point, after so much energy has been spent dutifully perfecting your work, it’s probably likely that the sentences in your essay are looking less and less like words and more like meaningless drivel on a page.
You might be itching to hand it in so that you can treat yourself to a well-deserved Big Mac Combo and never ever look at The Great Gatsby again in your life.
This is why proofreading is so crucial. When you’ve spent a while writing something, it’s really difficult to pick up on the mistakes you may have made during the process.
You may feel attached to certain parts that took you ages to spit out, when really, they’re unnecessary waffling.
Your mind may have convinced itself that some sentences are elegant masterpieces, but when you get your marks back, you realise they made no sense at all.
We all know too well the shameful feeling of getting an essay back and realising all the obvious errors you failed to pick up on in your frenzied state.
BUT, a great essay riddled with linguistic and grammatical errors will instantly make your ideas seem less valid than they are.
That’s why it’s really important to allow yourself time for proofreading, and even better, for reading it over with fresh eyes.
If you’re writing from home – take a break! Go for a walk, get some food, try a guided meditation, watch an episode of GoT, whatever – but come back to the essay later.
It’s amazing what a short break can do for your detection of mistakes. Even if you’re really strapped for time and you’re pulling an all nighter, go to sleep now and wake-up a bit earlier to proofread.
If you’re writing under pressure in an exam environment, make sure to plan for 5-10 minutes of proofreading. When you’ve finished the writing, go to another question or take a very short breather to clear your mind.
One great way to ensure your essay is pristine for hand-in is to run through this mental checklist for each individual sentence of your essay:
- Read the sentence aloud (or at least in your head). Does it make full sense when you hear it?
- Can it stand in isolation and still hold up as a sentence?
- Does it support the point that you’re making, or is it waffling to fill up space?
- Could it be articulated in a clearer way?
- Do the commas, full-stops and speech-marks “flow” properly when read aloud?
- Does it repeat a point that you’ve already made?
- Does it go on for too long? Could it be split into two separate sentences?
- Does it begin with a capital letter? Does it end with correct punctuation?
Next time you’re assigned an essay for an internal or exam, don’t put it off until the night before and put yourself through a half-hearted, exhausting, unproductive all nighter.
Bookmark this page, breathe, and walk through the guide step-by-step. You might even enjoy the process.
The Study Method You’re Forgetting: Retrieval Methods
How to analyse ncea film in 6 steps, writing in the real world, how to bounce back from mock exams, a procrastinator’s guide to planning, 3 ways to study for your drama exam, how to juggle the internal rush, what to do in high school to prepare for university, has your motivation hit a wall here’s how to push through, navigating life after high school, the never-ending capacity of the brain, moving onwards and upwards after exams, how to catch up on your studies, how to effectively study with a past paper, what to do when your goals aren’t going to plan, 8 solutions to your study problems, types of learners don’t exist, why failure is okay.
Failure’s often seen as a bad thing, but sometimes it can actually be good. We share how you can turn failure into success.
Planning your University Studies
The science of habit-building, dealing with multiple assessments, how to study with past exams, timetabling options for the busy student, understanding university degrees, comments 0 comments, submit a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Are You Ready for Life After School? | WHH Season 2 #25
Biggest fears for 2020 | whh season 2 #29, last minute tips for ncea level 2 biology, approaching the big decisions: how to think about life after school | whh season 3 #11, how to actually study, how do you take your notes, merry christmas from studytime: 2017 blooper reel, we’re back for 2019 | whh season 2 #1, ncea horror stories part 2 | whh season 2 #26, last minute tips for ncea level 1 science, dealing with exam anxiety, how to analyse ncea poetry in 6 steps, how to prepare for exams, a crash course for good research, how to plan an internal, 7 things to remember before results are out, maintaining new habits.
AWA: Academic Writing at Auckland
An Essay requires independent thinking and the development of an argument supported by clear and logical ideas (Nesi and Gardner, 2012, p. 91). The essay can be developed in different ways, including analysis, evaluation and synthesis of perspectives, theories and research, application of definitions, theories and frameworks to examples and vice versa, arguing against opposing views, explaining cause and effect, comparing and contrasting, classifying, and other ways of building and supporting a position. 3 types of essay are found in AWA: Analysis Essay , Argument Essay and Discussion Essay .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates
Published on September 18, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction , a body , and a conclusion . But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
The basics of essay structure, chronological structure, compare-and-contrast structure, problems-methods-solutions structure, signposting to clarify your structure, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about essay structure.
There are two main things to keep in mind when working on your essay structure: making sure to include the right information in each part, and deciding how you’ll organize the information within the body.
Parts of an essay
The three parts that make up all essays are described in the table below.
Order of information
You’ll also have to consider how to present information within the body. There are a few general principles that can guide you here.
The first is that your argument should move from the simplest claim to the most complex . The body of a good argumentative essay often begins with simple and widely accepted claims, and then moves towards more complex and contentious ones.
For example, you might begin by describing a generally accepted philosophical concept, and then apply it to a new topic. The grounding in the general concept will allow the reader to understand your unique application of it.
The second principle is that background information should appear towards the beginning of your essay . General background is presented in the introduction. If you have additional background to present, this information will usually come at the start of the body.
The third principle is that everything in your essay should be relevant to the thesis . Ask yourself whether each piece of information advances your argument or provides necessary background. And make sure that the text clearly expresses each piece of information’s relevance.
The sections below present several organizational templates for essays: the chronological approach, the compare-and-contrast approach, and the problems-methods-solutions approach.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The chronological approach (sometimes called the cause-and-effect approach) is probably the simplest way to structure an essay. It just means discussing events in the order in which they occurred, discussing how they are related (i.e. the cause and effect involved) as you go.
A chronological approach can be useful when your essay is about a series of events. Don’t rule out other approaches, though—even when the chronological approach is the obvious one, you might be able to bring out more with a different structure.
Explore the tabs below to see a general template and a specific example outline from an essay on the invention of the printing press.
- Thesis statement
- Discussion of event/period
- Consequences
- Importance of topic
- Strong closing statement
- Claim that the printing press marks the end of the Middle Ages
- Background on the low levels of literacy before the printing press
- Thesis statement: The invention of the printing press increased circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation
- High levels of illiteracy in medieval Europe
- Literacy and thus knowledge and education were mainly the domain of religious and political elites
- Consequence: this discouraged political and religious change
- Invention of the printing press in 1440 by Johannes Gutenberg
- Implications of the new technology for book production
- Consequence: Rapid spread of the technology and the printing of the Gutenberg Bible
- Trend for translating the Bible into vernacular languages during the years following the printing press’s invention
- Luther’s own translation of the Bible during the Reformation
- Consequence: The large-scale effects the Reformation would have on religion and politics
- Summarize the history described
- Stress the significance of the printing press to the events of this period
Essays with two or more main subjects are often structured around comparing and contrasting . For example, a literary analysis essay might compare two different texts, and an argumentative essay might compare the strengths of different arguments.
There are two main ways of structuring a compare-and-contrast essay: the alternating method, and the block method.
Alternating
In the alternating method, each paragraph compares your subjects in terms of a specific point of comparison. These points of comparison are therefore what defines each paragraph.
The tabs below show a general template for this structure, and a specific example for an essay comparing and contrasting distance learning with traditional classroom learning.
- Synthesis of arguments
- Topical relevance of distance learning in lockdown
- Increasing prevalence of distance learning over the last decade
- Thesis statement: While distance learning has certain advantages, it introduces multiple new accessibility issues that must be addressed for it to be as effective as classroom learning
- Classroom learning: Ease of identifying difficulties and privately discussing them
- Distance learning: Difficulty of noticing and unobtrusively helping
- Classroom learning: Difficulties accessing the classroom (disability, distance travelled from home)
- Distance learning: Difficulties with online work (lack of tech literacy, unreliable connection, distractions)
- Classroom learning: Tends to encourage personal engagement among students and with teacher, more relaxed social environment
- Distance learning: Greater ability to reach out to teacher privately
- Sum up, emphasize that distance learning introduces more difficulties than it solves
- Stress the importance of addressing issues with distance learning as it becomes increasingly common
- Distance learning may prove to be the future, but it still has a long way to go
In the block method, each subject is covered all in one go, potentially across multiple paragraphs. For example, you might write two paragraphs about your first subject and then two about your second subject, making comparisons back to the first.
The tabs again show a general template, followed by another essay on distance learning, this time with the body structured in blocks.
- Point 1 (compare)
- Point 2 (compare)
- Point 3 (compare)
- Point 4 (compare)
- Advantages: Flexibility, accessibility
- Disadvantages: Discomfort, challenges for those with poor internet or tech literacy
- Advantages: Potential for teacher to discuss issues with a student in a separate private call
- Disadvantages: Difficulty of identifying struggling students and aiding them unobtrusively, lack of personal interaction among students
- Advantages: More accessible to those with low tech literacy, equality of all sharing one learning environment
- Disadvantages: Students must live close enough to attend, commutes may vary, classrooms not always accessible for disabled students
- Advantages: Ease of picking up on signs a student is struggling, more personal interaction among students
- Disadvantages: May be harder for students to approach teacher privately in person to raise issues
An essay that concerns a specific problem (practical or theoretical) may be structured according to the problems-methods-solutions approach.
This is just what it sounds like: You define the problem, characterize a method or theory that may solve it, and finally analyze the problem, using this method or theory to arrive at a solution. If the problem is theoretical, the solution might be the analysis you present in the essay itself; otherwise, you might just present a proposed solution.
The tabs below show a template for this structure and an example outline for an essay about the problem of fake news.
- Introduce the problem
- Provide background
- Describe your approach to solving it
- Define the problem precisely
- Describe why it’s important
- Indicate previous approaches to the problem
- Present your new approach, and why it’s better
- Apply the new method or theory to the problem
- Indicate the solution you arrive at by doing so
- Assess (potential or actual) effectiveness of solution
- Describe the implications
- Problem: The growth of “fake news” online
- Prevalence of polarized/conspiracy-focused news sources online
- Thesis statement: Rather than attempting to stamp out online fake news through social media moderation, an effective approach to combating it must work with educational institutions to improve media literacy
- Definition: Deliberate disinformation designed to spread virally online
- Popularization of the term, growth of the phenomenon
- Previous approaches: Labeling and moderation on social media platforms
- Critique: This approach feeds conspiracies; the real solution is to improve media literacy so users can better identify fake news
- Greater emphasis should be placed on media literacy education in schools
- This allows people to assess news sources independently, rather than just being told which ones to trust
- This is a long-term solution but could be highly effective
- It would require significant organization and investment, but would equip people to judge news sources more effectively
- Rather than trying to contain the spread of fake news, we must teach the next generation not to fall for it
Signposting means guiding the reader through your essay with language that describes or hints at the structure of what follows. It can help you clarify your structure for yourself as well as helping your reader follow your ideas.
The essay overview
In longer essays whose body is split into multiple named sections, the introduction often ends with an overview of the rest of the essay. This gives a brief description of the main idea or argument of each section.
The overview allows the reader to immediately understand what will be covered in the essay and in what order. Though it describes what comes later in the text, it is generally written in the present tense . The following example is from a literary analysis essay on Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
Transitions
Transition words and phrases are used throughout all good essays to link together different ideas. They help guide the reader through your text, and an essay that uses them effectively will be much easier to follow.
Various different relationships can be expressed by transition words, as shown in this example.
Because Hitler failed to respond to the British ultimatum, France and the UK declared war on Germany. Although it was an outcome the Allies had hoped to avoid, they were prepared to back up their ultimatum in order to combat the existential threat posed by the Third Reich.
Transition sentences may be included to transition between different paragraphs or sections of an essay. A good transition sentence moves the reader on to the next topic while indicating how it relates to the previous one.
… Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
However , considering the issue of personal interaction among students presents a different picture.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarized in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-structure/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, how to write the body of an essay | drafting & redrafting, transition sentences | tips & examples for clear writing, what is your plagiarism score.
Welcome to Student Learning Te Taiako
Essay structure.
After researching and further developing your ideas, you can begin to transfer these into an essay structure. Thinking about the brainstorming activity earlier, the arguments against a global language outweighed the arguments for a global language. Therefore, it would be logical that the ideas in the essay emphasise the arguments against. This doesn't mean that you can't write an assignment that makes the case for a global language. However, if you would like to do this, then you would need to go back to the brainstorming stage and find other ideas to support your argument.
Read the sentences on the right. Drag and drop each into the correct area in the Essay Structure. Sometimes it is easier to first identify which one is the thesis statement for the introduction, and which one summarises the ideas for the conclusion.
Well-planned online essay writing assistance by PenMyPaper
Writing my essays has long been a part and parcel of our lives but as we grow older, we enter the stage of drawing critical analysis of the subjects in the writings. This requires a lot of hard work, which includes extensive research to be done before you start drafting. But most of the students, nowadays, are already overburdened with academics and some of them also work part-time jobs. In such a scenario, it becomes impossible to write all the drafts on your own. The writing service by the experts of PenMyPaper can be your rescuer amidst such a situation. We will write my essay for me with ease. You need not face the trouble to write alone, rather leave it to the experts and they will do all that is required to write your essays. You will just have to sit back and relax. We are offering you unmatched service for drafting various kinds for my essays, everything on an online basis to write with. You will not even have to visit anywhere to order. Just a click and you can get the best writing service from us.
Finished Papers

Finished Papers
How will you prove that the drafts are original and unique?
Why is writing essays so hard?
Patterns and boring topics imposed by schools and universities are not very conducive to creativity and human development. Such essays are very difficult to write, because many are not interested in this and do not see the meaning of the text. There are a number of criteria that make it impossible to write essays:
- Boring and incomprehensible topics. Many topics could be more interesting, but teachers formulate them in a way that makes you want to yawn.
- Templates. 90% do not know how to make an essay interesting, how to turn this detailed answer to a question into a living story.
- Fear of not living up to expectations. It seems to many that the essay is stupid and that they simply did not understand the question. There is a fear of getting a bad mark and disappointing the professor, parents and classmates. There is a fear of looking stupid and embarrassing in front of the team.
- Lack of experience. People don't know what and how to write about. In order to make a good essay, you need to have a perfect understanding of the topic and have the skills of a writer.
That is why the company EssaysWriting provides its services. We remove the responsibility for the result from the clients and do everything to ensure that the scientific work is recognized.
Customer Reviews
Our team of writers is native English speakers from countries such as the US with higher education degrees and go through precise testing and trial period. When working with EssayService you can be sure that our professional writers will adhere to your requirements and overcome your expectations. Pay your hard-earned money only for educational writers.
Terms of Use
Privacy Policy

Customer Reviews
Will I get caught if I buy an essay?
The most popular question from clients and people on the forums is how not to get caught up in the fact that you bought an essay, and did not write it yourself. Students are very afraid that they will be exposed and expelled from the university or they will simply lose their money, because they will have to redo the work themselves.
If you've chosen a good online research and essay writing service, then you don't have to worry. The writers from the firm conduct their own exploratory research, add scientific facts and back it up with the personal knowledge. None of them copy information from the Internet or steal ready-made articles. Even if this is not enough for the client, he can personally go to the anti-plagiarism website and check the finished document. Of course, the staff of the sites themselves carry out such checks, but no one can forbid you to make sure of the uniqueness of the article for yourself.
Thanks to the privacy policy on web platforms, no one will disclose your personal data and transfer to third parties. You are completely safe from start to finish.

Constant customer Assistance


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay structure. Having a structure to your essay makes sure that each main idea is presented logically and cohesively. ... [email protected]; Faculties; Contacts and directories; Campuses; Study; Students; Staff; Careers; Alumni; 0800 04 04 04 +64 4 472 1000; [email protected];
It is important to present your ideas in the correct essay structure which consists of: Essay topic (or title or question), introduction, body, conclusion, references. Basic structure of an academic essay (PDF) Example of an essay outline (PDF) "Discuss the effects of the unemployment benefit system on the New Zealand economy."
Essay structure. All essays share the same basic structure, although they may differ in content and style. The essence of an essay is an opinion, expressed as a thesis statement or proposition, and a logical sequence of arguments and information organised in support of the proposition.
Essays are often used to demonstrate in-depth understanding of a particular topic. There are two main types of essays: The way an essay question is presented will give you an indication of the type of essay you will need to produce. Regardless, there are similar processes you should follow to plan for and write your essay. 1. Plan your essay. 2.
(03) 364 2314 • www.learningskills.canterbury.ac.nz 150-200 words 10% of word count Introduction Body Conclusion Defining terms Sometimes, if there are many key words and ... The structure of a 1000-3000 word essay . Personal vs. academic essays Essays are pieces of writing that creatively and engagingly discuss a given topic ...
The general framework of an academic essay consists of the following: Introduction. Body. Conclusion. Example structure of an essay: Introduction (10% of total essay length) Body Paragraphs (80% of total essay length) Paragraph 1: First supporting statement, Definition, Explanation, Evidence. Paragraph 2: Second Supporting Statement, Definition ...
Essay Writing 1307 Learning Skills Centre (03) 364 2314 University of Canterbury www.learningskills.canterbury.ac.nz Glossary Academic essay: The aim of an academic essay is to present an argument in order to persuade the reader. An academic essay must include an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. It is written in formal language.
Writing for success: A practical guide for New Zealand students. Auckland: Addison Wesley Longman. pp. 107-122. Essay sample 3: Japan and the United States: ... The sample essays are shorter than most stage 1 essays, but they demonstrate the conventions of academic essay structure and argmentative style, especially the use of concession and ...
Video source: Smrt English. This video includes: Introduction (with hook, background, thesis) Body (develops the thesis, with citations) Conclusion (with summary, thesis restatement, final comment) We agree with much of what Shaun suggests here. As you look at the excerpts provided by students in this collection, we invite you to decide how ...
A general statement that establishes the focus of the essay. Outline the main ideas of the essay and the order in which they will be discussed. Each paragraph in the body should have: A topic sentence that states the main point of the paragraph. An explanation and/or expansion of the main point. Evidence to support the main point. Conclusion:
Essay Writing . Expository. background, and • according to . Essay . Structure • Allow 10% of the word count for the introduction • Introduce the topic and gain the readers' attention • Provide background/contextual information • Introduce the reader to the main points covered in the essay and how these are addressed
The introduction to an essay has three primary objectives: Explain the context of the essay. Give the answer: the response to the question or the overall focus of the essay (the thesis statement) Describe the structure and organisation of the essay. These aims can be given more or less emphasis depending on the length and type of essay.
4. BREAKING DOWN THE BODY PARAGRAPH. The body paragraph makes up the "flesh" of the essay "skeleton" you have at the moment. Three body paragraphs is enough for a strong essay, however you can add as many more as you need to strengthen or fully unpack your overall argument (provided you're not ranting).
AWA: Academic Writing at Auckland. An Essay requires independent thinking and the development of an argument supported by clear and logical ideas (Nesi and Gardner, 2012, p. 91). The essay can be developed in different ways, including analysis, evaluation and synthesis of perspectives, theories and research, application of definitions, theories and frameworks to examples and vice versa ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Essay structure. After researching and further developing your ideas, you can begin to transfer these into an essay structure. Thinking about the brainstorming activity earlier, the arguments against a global language outweighed the arguments for a global language. Therefore, it would be logical that the ideas in the essay emphasise the arguments against.
Professional authors can write an essay in 3 hours, if there is a certain volume, but it must be borne in mind that with such a service the price will be the highest. The cheapest estimate is the work that needs to be done in 14 days. Then 275 words will cost you $ 10, while 3 hours will cost you $ 50. Please, take into consideration that VAT ...
Essay Structure Nz, 6 Traits Writing Printables For Secondary Classrooms, Business Plan Examples Products And Services, Gauger Cobbs Homework Line, Sample Resume For Mba Lecturer Post, Objective Statement For Administrative Assistant Resume, What Are Good Topics To Write About For A Research Paper
Essay Structure Nz: $ 12.99. REVIEWS HIRE. 4.8/5. Didn't receive the email yet? Resend the email. Nursing Management Business and Economics Economics +96. ID 4817. If you can't write your essay, then the best solution is to hire an essay helper. Since you need a 100% original paper to hand in without a hitch, then a copy-pasted stuff from the ...
Our cheap essay writer service is a lot helpful in making such a write-up a brilliant one. View Sample. News. 90 % Daftar pencarian. ... Essay Structure Nz, Business Communication Issues Case Study, I Need A Business Plan Because, Science Thesis Topics For High School, Cover Letter For Receptionist At Dental Office, Glass Castle Homework ...
Ying Tsai. #3 in Global Rating. Toll free 1 (888)499-5521 1 (888)814-4206. 100% Success rate. 377. Essay Structure Nz -.