- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board

Gender Confirmation Surgery (GCS)
What is Gender Confirmation Surgery?
- Transfeminine Tr
Transmasculine Transition
- Traveling Abroad
Choosing a Surgeon
Gender confirmation surgery (GCS), known clinically as genitoplasty, are procedures that surgically confirm a person's gender by altering the genitalia and other physical features to align with their desired physical characteristics. Gender confirmation surgeries are also called gender affirmation procedures. These are both respectful terms.
Gender dysphoria , an experience of misalignment between gender and sex, is becoming more widely diagnosed. People diagnosed with gender dysphoria are often referred to as "transgender," though one does not necessarily need to experience gender dysphoria to be a member of the transgender community. It is important to note there is controversy around the gender dysphoria diagnosis. Many disapprove of it, noting that the diagnosis suggests that being transgender is an illness.
Ellen Lindner / Verywell
Transfeminine Transition
Transfeminine is a term inclusive of trans women and non-binary trans people assigned male at birth.
Gender confirmation procedures that a transfeminine person may undergo include:
- Penectomy is the surgical removal of external male genitalia.
- Orchiectomy is the surgical removal of the testes.
- Vaginoplasty is the surgical creation of a vagina.
- Feminizing genitoplasty creates internal female genitalia.
- Breast implants create breasts.
- Gluteoplasty increases buttock volume.
- Chondrolaryngoplasty is a procedure on the throat that can minimize the appearance of Adam's apple .
Feminizing hormones are commonly used for at least 12 months prior to breast augmentation to maximize breast growth and achieve a better surgical outcome. They are also often used for approximately 12 months prior to feminizing genital surgeries.
Facial feminization surgery (FFS) is often done to soften the lines of the face. FFS can include softening the brow line, rhinoplasty (nose job), smoothing the jaw and forehead, and altering the cheekbones. Each person is unique and the procedures that are done are based on the individual's need and budget,
Transmasculine is a term inclusive of trans men and non-binary trans people assigned female at birth.
Gender confirmation procedures that a transmasculine person may undergo include:
- Masculinizing genitoplasty is the surgical creation of external genitalia. This procedure uses the tissue of the labia to create a penis.
- Phalloplasty is the surgical construction of a penis using a skin graft from the forearm, thigh, or upper back.
- Metoidioplasty is the creation of a penis from the hormonally enlarged clitoris.
- Scrotoplasty is the creation of a scrotum.
Procedures that change the genitalia are performed with other procedures, which may be extensive.
The change to a masculine appearance may also include hormone therapy with testosterone, a mastectomy (surgical removal of the breasts), hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus), and perhaps additional cosmetic procedures intended to masculinize the appearance.
Paying For Gender Confirmation Surgery
Medicare and some health insurance providers in the United States may cover a portion of the cost of gender confirmation surgery.
It is unlawful to discriminate or withhold healthcare based on sex or gender. However, many plans do have exclusions.
For most transgender individuals, the burden of financing the procedure(s) is the main difficulty in obtaining treatment. The cost of transitioning can often exceed $100,000 in the United States, depending upon the procedures needed.
A typical genitoplasty alone averages about $18,000. Rhinoplasty, or a nose job, averaged $5,409 in 2019.
Traveling Abroad for GCS
Some patients seek gender confirmation surgery overseas, as the procedures can be less expensive in some other countries. It is important to remember that traveling to a foreign country for surgery, also known as surgery tourism, can be very risky.
Regardless of where the surgery will be performed, it is essential that your surgeon is skilled in the procedure being performed and that your surgery will be performed in a reputable facility that offers high-quality care.
When choosing a surgeon , it is important to do your research, whether the surgery is performed in the U.S. or elsewhere. Talk to people who have already had the procedure and ask about their experience and their surgeon.
Before and after photos don't tell the whole story, and can easily be altered, so consider asking for a patient reference with whom you can speak.
It is important to remember that surgeons have specialties and to stick with your surgeon's specialty. For example, you may choose to have one surgeon perform a genitoplasty, but another to perform facial surgeries. This may result in more expenses, but it can result in a better outcome.
A Word From Verywell
Gender confirmation surgery is very complex, and the procedures that one person needs to achieve their desired result can be very different from what another person wants.
Each individual's goals for their appearance will be different. For example, one individual may feel strongly that breast implants are essential to having a desirable and feminine appearance, while a different person may not feel that breast size is a concern. A personalized approach is essential to satisfaction because personal appearance is so highly individualized.
Davy Z, Toze M. What is gender dysphoria? A critical systematic narrative review . Transgend Health . 2018;3(1):159-169. doi:10.1089/trgh.2018.0014
Morrison SD, Vyas KS, Motakef S, et al. Facial Feminization: Systematic Review of the Literature . Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;137(6):1759-70. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000002171
Hadj-moussa M, Agarwal S, Ohl DA, Kuzon WM. Masculinizing Genital Gender Confirmation Surgery . Sex Med Rev . 2019;7(1):141-155. doi:10.1016/j.sxmr.2018.06.004
Dowshen NL, Christensen J, Gruschow SM. Health Insurance Coverage of Recommended Gender-Affirming Health Care Services for Transgender Youth: Shopping Online for Coverage Information . Transgend Health . 2019;4(1):131-135. doi:10.1089/trgh.2018.0055
American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Rhinoplasty nose surgery .
Rights Group: More U.S. Companies Covering Cost of Gender Reassignment Surgery. CNS News. http://cnsnews.com/news/article/rights-group-more-us-companies-covering-cost-gender-reassignment-surgery
The Sex Change Capital of the US. CBS News. http://www.cbsnews.com/2100-3445_162-4423154.html
By Jennifer Whitlock, RN, MSN, FN Jennifer Whitlock, RN, MSN, FNP-C, is a board-certified family nurse practitioner. She has experience in primary care and hospital medicine.
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, male-to-female gender-affirming surgery: 20-year review of technique and surgical results.

- 1 Serviço de Urologia, Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, Brazil
- 2 Serviço de Psiquiatria, Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, Brazil
- 3 Serviço de Psiquiatria, Pontifical Catholic University of Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil
Purpose: Gender dysphoria (GD) is an incompatibility between biological sex and personal gender identity; individuals harbor an unalterable conviction that they were born in the wrong body, which causes personal suffering. In this context, surgery is imperative to achieve a successful gender transition and plays a key role in alleviating the associated psychological discomfort. In the current study, a retrospective cohort, we report the 20-years outcomes of the gender-affirming surgery performed at a single Brazilian university center, examining demographic data, intra and postoperative complications. During this period, 214 patients underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty.
Results: Results demonstrate that the average age at the time of surgery was 32.2 years (range, 18–61 years); the average of operative time was 3.3 h (range 2–5 h); the average duration of hormone therapy before surgery was 12 years (range 1–39). The most commons minor postoperative complications were granulation tissue (20.5 percent) and introital stricture of the neovagina (15.4 percent) and the major complications included urethral meatus stenosis (20.5 percent) and hematoma/excessive bleeding (8.9 percent). A total of 36 patients (16.8 percent) underwent some form of reoperation. One hundred eighty-one (85 percent) patients in our series were able to have regular sexual intercourse, and no individual regretted having undergone GAS.
Conclusions: Findings confirm that it is a safety procedure, with a low incidence of serious complications. Otherwise, in our series, there were a high level of functionality of the neovagina, as well as subjective personal satisfaction.
Introduction
Transsexualism (ICD-10) or Gender Dysphoria (GD) (DSM-5) is characterized by intense and persistent cross-gender identification which influences several aspects of behavior ( 1 ). The terms describe a situation where an individual's gender identity differs from external sexual anatomy at birth ( 1 ). Gender identity-affirming care, for those who desire, can include hormone therapy and affirming surgeries, as well as other procedures such as hair removal or speech therapy ( 1 ).
Since 1998, the Gender Identity Program (PROTIG) of the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA), Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil has provided public assistance to transsexual people, is the first one in Brazil and one of the pioneers in South America. Our program offers psychosocial support, health care, and guidance to families, and refers individuals for gender-affirming surgery (GAS) when indicated. To be eligible for this surgery, transsexual individuals must have been adherent to multidisciplinary follow-up for at least 2 years, have a minimum age of 21 years (required for surgical procedures of this nature), have a positive psychiatric or psychological report, and have a diagnosis of GD.
Gender-affirming surgery (GAS) is increasingly recognized as a therapeutic intervention and a medical necessity, with growing societal acceptance ( 2 ). At our institution, we perform the classic penile inversion vaginoplasty (PIV), with an inverted penis skin flap used as the lining for the neovagina. Studies have demonstrated that GAS for the management of GD can promote improvements in mental health and social relationships for these patients ( 2 – 5 ). It is therefore imperative to understand and establish best practice techniques for this patient population ( 2 ). Although there are several studies reporting the safety and efficacy of gender-affirming surgery by penile inversion vaginoplasty, we present the largest South-American cohort to date, examining demographic data, intra and postoperative complications.
Patients and Methods
Subjects and study setup.
This is a retrospective cohort study of Brazilian transgender women who underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty between January of 2000 and March of 2020 at the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, Brazil. The study was approved by our institutional medical and research ethics committee.
At our institution, gender-affirming surgery is indicated for transgender women who are under assistance by our program for transsexual individuals. All transsexual women included in this study had at least 2 years of experience as a woman and met WPATH standards for GAS ( 1 ). Patients were submitted to biweekly group meetings and monthly individual therapy.
Between January of 2000 and March of 2020, a total of 214 patients underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty. The surgical procedures were performed by two separate staff members, mostly assisted by residents. A retrospective chart review was conducted recording patient demographics, intraoperative and postoperative complications, reoperations, and secondary surgical procedures. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Hormonal Therapy
The goal of feminizing hormone therapy is the development of female secondary sex characteristics, and suppression/minimization of male secondary sex characteristics.
Our general therapy approach is to combine an estrogen with an androgen blocker. The usual estrogen is the oral preparation of estradiol (17-beta estradiol), starting at a dose of 2 mg/day until the maximum dosage of 8 mg/day. The preferred androgen blocker is spironolactone at a dose of 200 mg twice a day.
Operative Technique
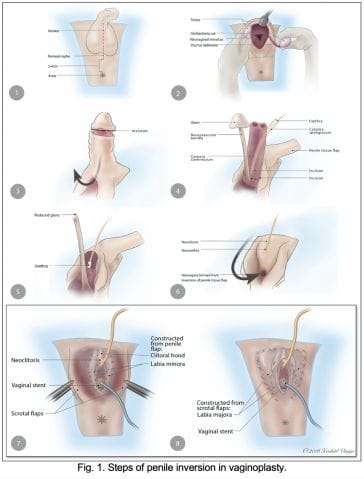
At our institution, we perform the classic penile inversion vaginoplasty, with an inverted penis skin flap used as the lining for the neovagina. For more details, we have previously published our technique with a step-by-step procedure video ( 6 ). All individuals underwent intestinal cleansing the evening before the surgery. A first-generation cephalosporin was used as preoperative prophylaxis. The procedure was performed with the patient in a dorsal lithotomy position. A Foley catheter was placed for bladder catheterization. A inverted-V incision was made 4 cm above the anus and a flap was created. A neovaginal cavity was created between the prostate and the rectum with blunt dissection, in the Denonvilliers space, until the peritoneal fold, usually measuring 12 cm in extension and 6 cm in width. The incision was then extended vertically to expose the testicles and the spermatic cords, which were removed at the level of the external inguinal rings. A circumferential subcoronal incision was made ( Figure 1 ), the penis was de-gloved and a skin flap was created, with the de-gloved penis being passed through the scrotal opening ( Figure 2 ). The dorsal part of the glans and its neurovascular bundle were bluntly dissected away from the penile shaft ( Figure 3 ) as well as the urethra, which included a portion of the bulbospongious muscle ( Figure 4 ). The corpora cavernosa was excised up to their attachments at the symphysis pubis and ligated. The neoclitoris was shaped and positioned in the midline at the level of the symphysis pubis and sutured using interrupted 5-0 absorbable suture. The corpus spongiosum was reduced and the urethra was shortened, spatulated, and placed 1 cm below the neoclitoris in the midline and sutured using interrupted 4-0 absorbable suture. The penile skin flap was inverted and pulled into the neovaginal cavity to become its walls ( Figure 5 ). The excess of skin was then removed, and the subcutaneous tissue and the skin were closed using continuous 3-0 non-absorbable suture ( Figure 6 ). A neo mons pubis was created using a 0 absorbable suture between the skin and the pubic bone. The skin flap was fixed to the pubic bone using a 0 absorbable suture. A gauze impregnated with Vaseline and antibiotic ointment was left inside the neovagina, and a customized compressive bandage was applied ( Figure 7 —shows the final appearance after the completion of the procedures).
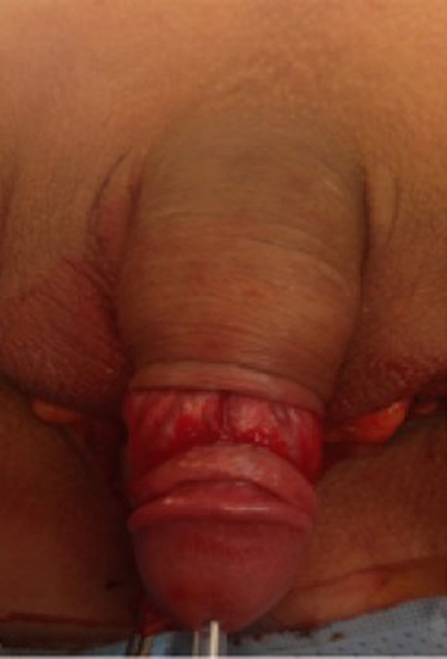
Figure 1 . The initial circumferential subcoronal incision.
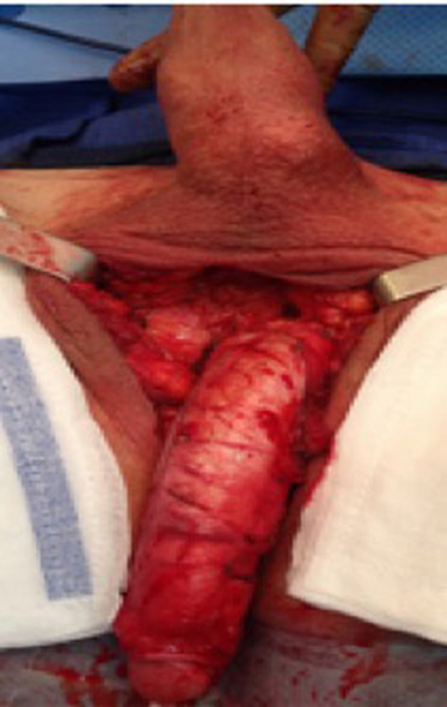
Figure 2 . The de-gloved penis being passed through the scrotal opening.
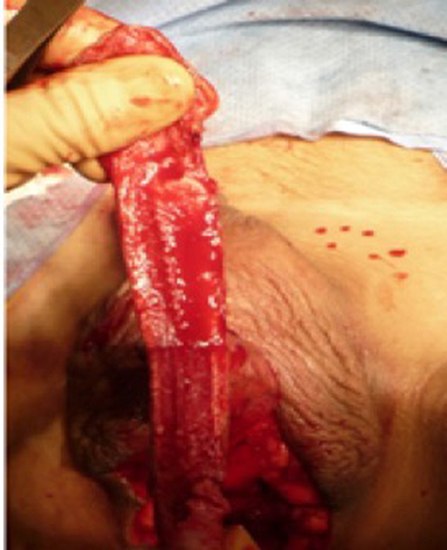
Figure 3 . The dorsal part of the glans and its neurovascular bundle dissected away from the penile shaft.
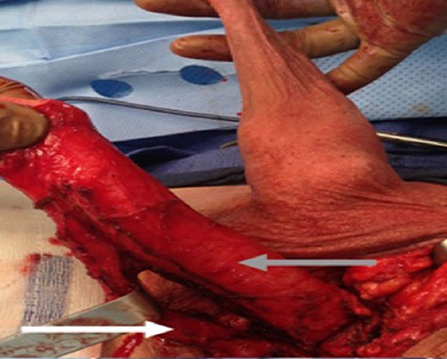
Figure 4 . The urethra dissected including a portion of the bulbospongious muscle. The grey arrow shows the penile shaft and the white arrow shows the dissected urethra.
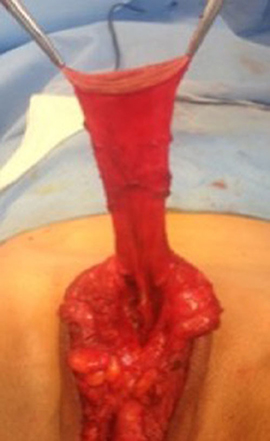
Figure 5 . The inverted penile skin flap.
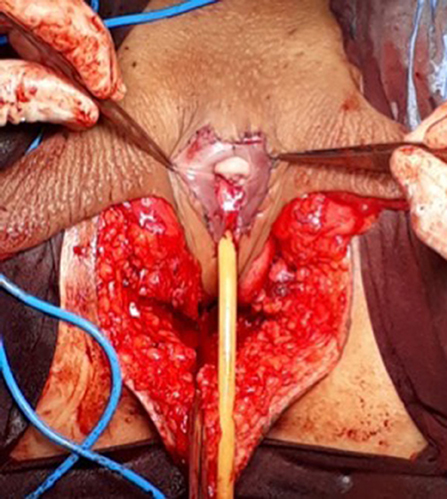
Figure 6 . The neoclitoris and the urethra sutured in the midline and the neovaginal cavity.
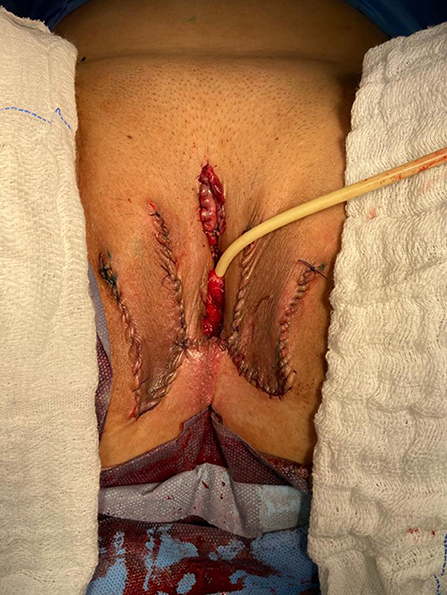
Figure 7 . The final appearance after the completion of the procedures.
Postoperative Care and Follow-Up
The patients were usually discharged within 2 days after surgery with the Foley catheter and vaginal gauze packing in place, which were removed after 7 days in an ambulatorial attendance.
Our vaginal dilation protocol starts seven days after surgery: a kit of 6 silicone dilators with progressive diameter (1.1–4 cm) and length (6.5–14.5 cm) is used; dilation is done progressively from the smallest dilator; each size should be kept in place for 5 min until the largest possible size, which is kept for 3 h during the day and during the night (sleep), if possible. The process is performed daily for the first 3 months and continued until the patient has regular sexual intercourse.
The follow-up visits were performed 7 days, 1, 2, 3, 6, and 12 months after surgery ( Figure 8 ), and included physical examination and a quality-of-life questionnaire.
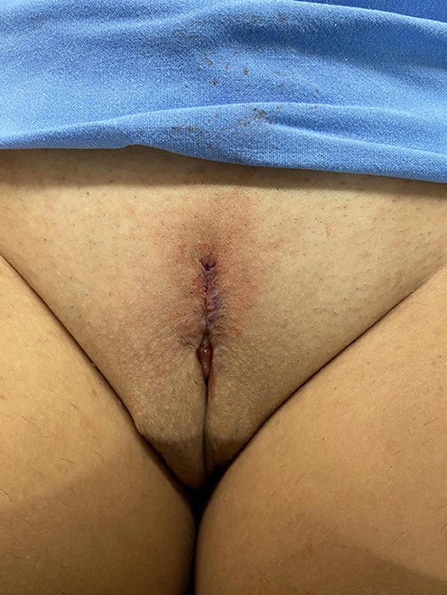
Figure 8 . Appearance after 1 month of the procedure.
Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was conducted using Statistical Product and Service Solutions Version 18.0 (SPSS). Outcome measures were intra-operative and postoperative complications, re-operations. Descriptive statistics were used to evaluate the study outcomes. Mean values and standard deviations or median values and ranges are presented as continuous variables. Frequencies and percentages are reported for dichotomous and ordinal variables.
Patient Demographics
During the period of the study, 214 patients underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty, performed by two staff surgeons, mostly assisted by residents ( Table 1 ). The average age at the time of surgery was 32.2 years (range 18–61 years). There was no significant increase or decrease in the ages of patients who underwent SRS over the study period (Fisher's exact test: P = 0.065; chi-square test: X 2 = 5.15; GL = 6; P = 0.525). The average of operative time was 3.3 h (range 2–5 h). The average duration of hormone therapy before surgery was 12 years (range 1–39). The majority of patients were white (88.3 percent). The most prevalent patient comorbidities were history of tobacco use (15 percent), human immunodeficiency virus infection (13 percent) and hypertension (10.7 percent). Other comorbidities are listed in Table 1 .
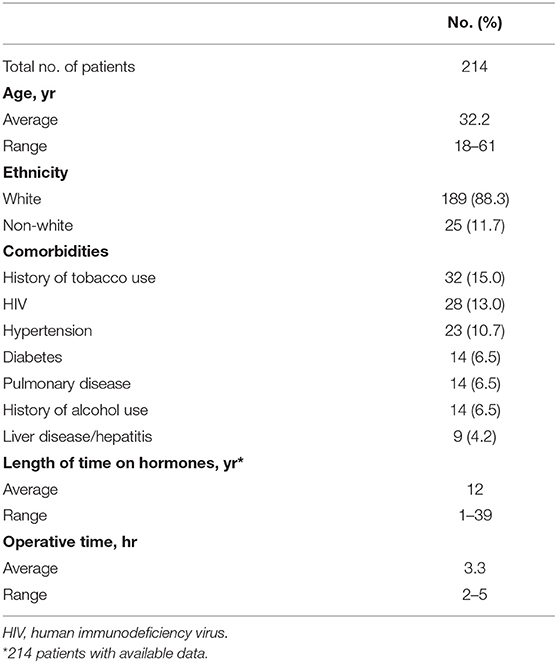
Table 1 . Patient demographics.
Multidisciplinary follow-up was comprised of 93.45% of patients following up with a urologist and 59.06% of patients continuing psychiatric follow-up, median follow-up time of 16 and 9.3 months after surgery, respectively.
Postoperative Results
The complications were classified according to the Clavien-Dindo score ( Table 2 ). The most common minor postoperative complications (Grade I) were granulation tissue (20.5 percent), introital stricture of the neovagina (15.4 percent) and wound dehiscence (12.6 percent). The major complications (Grade III-IV) included urethral stenosis (20.5 percent), urethral fistula (1.9 percent), intraoperative rectal injury (1.9 percent), necrosis (primarily along the wound edges) (1.4 percent), and rectovaginal fistula (0.9 percent). A total of 17 patients required blood transfusion (7.9 percent).
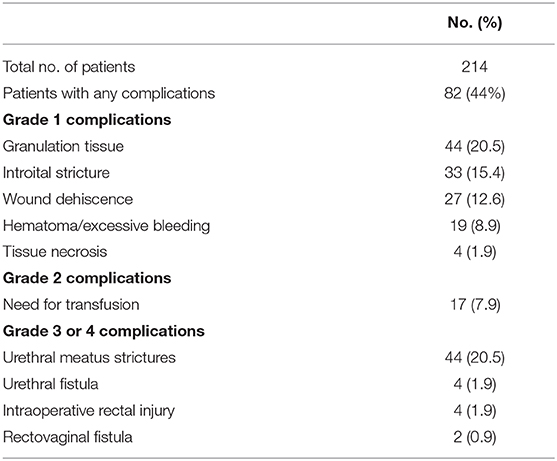
Table 2 . Complications after penile inversion vaginoplasty.
A total of 36 patients (16.8 percent) underwent some form of reoperation.
One hundred eighty-one (85 percent) patients in our series were able to have regular sexual vaginal intercourse, and no individual regretted having undergone GAS.
Penile inversion vaginoplasty is the gold-standard in gender-affirming surgery. It has good functional outcomes, and studies have demonstrated adequate vaginal depths ( 3 ). It is recognized not only as a cosmetic procedure, but as a therapeutic intervention and a medical necessity ( 2 ). We present the largest South-American cohort to date, examining demographic data, intra and postoperative complications.
The mean age of transsexual women who underwent GAS in our study was 32.2 years (range 18–61 years), which is lower than the mean age of patients in studies found in the literature. Two studies indicated that the mean ages of patients at time of GAS were 36.7 years and 41 years, respectively ( 4 , 5 ). Another study reported a mean age at time of GAS of 36 years and found there was a significant decrease in age at the time of GAS from 41 years in 1994 to 35 years in 2015 ( 7 ). According to the authors, this decrease in age is associated with greater tolerance and societal approval regarding individuals with GD ( 7 ).
There was no grade IV or grade V complications. Excessive bleeding noticed postoperatively occurred in 19 patients (8.9 percent) and blood transfusion was required in 17 cases (7.9 percent); all patients who required blood transfusions were operated until July 2011, and the reason for this rate of blood transfusion was not identified.
The most common intraoperative complication was rectal injury, occurring in 4 patients (1.9 percent); in all patients the lesion was promptly identified and corrected in 2 layers absorbable sutures. In 2 of these patients, a rectovaginal fistula became evident, requiring fistulectomy and colonic transit deviation. This is consistent with current literature, in which rectal injury is reported in 0.4–4.5 percent of patients ( 4 , 5 , 8 – 13 ). Goddard et al. suggested carefully checking for enterotomy after prostate and bladder mobilization by digital rectal examination ( 4 ). Gaither et al. ( 14 ) commented that careful dissection that closely follows the urethra along its track from the central tendon of the perineum up through the lower pole of the prostate is critical and only blunt dissection is encouraged after Denonvilliers' fascia is reached. Alternatively, a robotic-assisted approach to penile inversion vaginoplasty may aid in minimizing these complications. The proposed advantages of a robotic-assisted vaginoplasty include safer dissection to minimize the risk of rectal injury and better proximal vaginal fixation. Dy et al. ( 15 ) has had no rectal injuries or fistulae to date in his series of 15 patients, with a mean follow-up of 12 months.
In our series, we observed 44 cases (20.5 percent) of urethral meatus strictures. We credit this complication to the technique used in the initial 5 years of our experience, in which the urethra was shortened and sutured in a circular fashion without spatulation. All cases were treated with meatal dilatation and 11 patients required surgical correction, being performed a Y-V plastic reconstruction of the urethral meatus. In the literature, meatal strictures are relatively rare in male-to-female (MtF) GAS due to the spatulation of the urethra and a simple anastomosis to the external genitalia. Recent systematic reviews show an incidence of five percent in this complication ( 16 , 17 ). Other studies report a wide incidence of meatal stenosis ranging from 1.1 to 39.8 percent ( 4 , 8 , 11 ).
Neovagina introital stricture was observed in 33 patients (15.4 percent) in our study and impedes the possibility of neovaginal penetration and/or adversely affects sexual life quality. In the literature, the reported incidence of introital stenosis range from 6.7 to 14.5 percent ( 4 , 5 , 8 , 9 , 11 – 13 ). According to Hadj-Moussa et al. ( 18 ) a regimen of postoperative prophylactic dilation is crucial to minimize the development of this outcome. At our institution, our protocol for vaginal dilation started seven days after surgery and was performed three to four times a day during the first 3 months and was continued until the individual had regular sexual intercourse. We treated stenosis initially with dilation. In case of no response, we propose a surgical revision with diamond-shaped introitoplasty with relaxing incisions. In recalcitrant cases, we proposed to the patient a secondary vaginoplasty using a full-thickness skin graft of the lower abdomen.
One hundred eighty-one (85 percent) patients were classified as having a “functional vagina,” characterized as the capacity to maintain satisfactory sexual vaginal intercourse, since the mean neovaginal depth was not measured. In a review article, the mean neovaginal depth ranged from 10 to 13.5 cm, with the shallowest neovagina depth at 2.5 cm and the deepest at 18 cm ( 17 ). According to Salim et al. ( 19 ), in terms of postoperative functional outcomes after penile inversion vaginoplasty, a mean percentage of 75 percent (range from 33 to 87 percent) patients were having vaginal intercourse. Hess et al. found that 91.4% of patients who responded to a questionnaire were very satisfied (34.4%), satisfied (37.6%), or mostly satisfied (19.4%) with their sexual function after penile inversion vaginoplasty ( 20 ).
Poor cosmetic appearance of the vulva is common. Amend et al. reported that the most common reason for reoperation was cosmetic correction in the form of mons pubis and mucosa reduction in 50% of patients ( 16 ). We had no patient regrets about performing GAS, although 36 patients (16.8 percent) were reoperated due to cosmetic issues. Gaither et al. propose in order to minimize scarring to use a one-stage surgical approach and the lateralization of surgical scars to the groin ( 14 ). Frequently, cosmetic issues outcomes are often patient driven and preoperative patient education is necessary ( 14 ).
Analyzing the quality of life, in 2016, our health care group (PROTIG) published a study assessing quality of life before and after gender-affirming surgery in 47 patients using the diagnostic tool 100-item WHO Quality of Life Assessment (WHOQOL-100) ( 21 ). The authors found that GAS promotes the improvement of psychological aspects and social relations. However, even 1 year after GAS, MtF persons continue to report problems in physical and difficulty in recovering their independence. In a systematic review and meta-analysis of QOL and psychosocial outcomes in transsexual people, researchers verified that sex reassignment with hormonal interventions more likely corrects gender dysphoria, psychological functioning and comorbidities, sexual function, and overall QOL compared with sex reassignment without hormonal interventions, although there is a low level of evidence for this ( 22 ). Recently, Castellano et al. assessed QOL in 60 Italian transsexuals (46 transwomen and 14 transmen) at least 2 years after SRS using the WHOQOL-100 (general QOL score and quality of sexual life and quality of body image scores) to focus on the effects of hormonal therapy. Overall satisfaction improved after SRS, and QOL was similar to the controls ( 23 ). Bartolucci et al. evaluated the perception of quality of sexual life using four questions evaluating the sexual facet in individuals with gender dysphoria before SRS and the possible factors associated with this perception. The study showed that approximately half the subjects with gender dysphoria perceived their sexual life as “poor/dissatisfied” or “very poor/very dissatisfied” before SRS ( 24 ).
Our study has some limitations. The total number of operated patients is restricted within the long follow-up period. This is due to a limitation in our health system, which allows only 1 sexual reassignment surgery to be performed per month at our institution. Neovagin depth measurement was not performed routinely in the follow-up of operated patients.
Conclusions
The definitive treatment for patients with gender dysphoria is gender-affirming surgery. Our series demonstrates that GAS is a feasible surgery with low rates of serious complications. We emphasize the high level of functionality of the vagina after the procedure, as well as subjective personal satisfaction. Complications, especially minor ones, are probably underestimated due to the nature of the study, and since this is a surgical population, the results may not be generalizable for all transgender MTF individuals.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
GM: conception and design, data acquisition, data analysis, interpretation, drafting the manuscript, review of the literature, critical revision of the manuscript and factual content, and statistical analysis. ML and TR: conception and design, data interpretation, drafting the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript and factual content, and statistical analysis. DS, KS, AF, AC, PT, AG, and RC: conception and design, data acquisition and data analysis, interpretation, drafting the manuscript, and review of the literature. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This study was supported by the Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa e Eventos (FIPE - Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa e Eventos) of Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
1. Coleman E, Bockting W, Botzer M, Cohen-Kettenis P, DeCuypere G, Feldman J, et al. Standards of care for the health of transsexual, transgender, and gender-non-conforming people, version 7. Int J Transgend. (2012) 13:165–232. doi: 10.1080/15532739.2011.700873
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Massie JP, Morrison SD, Maasdam JV, Satterwhite T. Predictors of patient satisfaction and postoperative complications in penile inversion vaginoplasty. Plast Reconstruct Surg. (2018) 141:911–921. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000004427
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
3. Pan S, Honig SC. Gender-affirming surgery: current concepts. Curr Urol Rep . (2018) 19:62. doi: 10.1007/s11934-018-0809-9
4. Goddard JC, Vickery RM, Qureshi A, Summerton DJ, Khoosal D, Terry TR. Feminizing genitoplasty in adult transsexuals: early and long-term surgical results. BJU Int . (2007) 100:607–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07017.x
5. Rossi NR, Hintz F, Krege S, Rübben H, Vom DF, Hess J. Gender reassignment surgery – a 13 year review of surgical outcomes. Eur Urol Suppl . (2013) 12:e559. doi: 10.1016/S1569-9056(13)61042-8
6. Silva RUM, Abreu FJS, Silva GMV, Santos JVQV, Batezini NSS, Silva Neto B, et al. Step by step male to female transsexual surgery. Int Braz J Urol. (2018) 44:407–8. doi: 10.1590/s1677-5538.ibju.2017.0044
7. Aydin D, Buk LJ, Partoft S, Bonde C, Thomsen MV, Tos T. Transgender surgery in Denmark from 1994 to 2015: 20-year follow-up study. J Sex Med. (2016) 13:720–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2016.01.012
8. Perovic SV, Stanojevic DS, Djordjevic MLJ. Vaginoplasty in male transsexuals using penile skin and a urethral flap. BJU Int. (2001) 86:843–50. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2000.00934.x
9. Krege S, Bex A, Lümmen G, Rübben H. Male-to-female transsexualism: a technique, results and long-term follow-up in 66 patients. BJU Int. (2001) 88:396–402. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410X.2001.02323.x
10. Wagner S, Greco F, Hoda MR, Inferrera A, Lupo A, Hamza A, et al. Male-to-female transsexualism: technique, results and 3-year follow-up in 50 patients. Urol International. (2010) 84:330–3. doi: 10.1159/000288238
11. Reed H. Aesthetic and functional male to female genital and perineal surgery: feminizing vaginoplasty. Semin PlasticSurg. (2011) 25:163–74. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1281486
12. Raigosa M, Avvedimento S, Yoon TS, Cruz-Gimeno J, Rodriguez G, Fontdevila J. Male-to-female genital reassignment surgery: a retrospective review of surgical technique and complications in 60 patients. J Sex Med. (2015) 12:1837–45. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12936
13. Sigurjonsson H, Rinder J, Möllermark C, Farnebo F, Lundgren TK. Male to female gender reassignment surgery: surgical outcomes of consecutive patients during 14 years. JPRAS Open. (2015) 6:69–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2015.09.003
14. Gaither TW, Awad MA, Osterberg EC, Murphy GP, Romero A, Bowers ML, et al. Postoperative complications following primary penile inversion vaginoplasty among 330 male-to-female transgender patients. J Urol. (2018) 199:760–5. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.10.013
15. Dy GW, Sun J, Granieri MA, Zhao LC. Reconstructive management pearls for the transgender patient. Curr. Urol. Rep. (2018) 19:36. doi: 10.1007/s11934-018-0795-y
16. Amend B, Seibold J, Toomey P, Stenzl A, Sievert KD. Surgical reconstruction for male-to-female sex reassignment. Eur Urol. (2013) 64:141–9. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.12.030
17. Horbach SER, Bouman MB, Smit JM, Özer M, Buncamper ME, Mullender MG. Outcome of vaginoplasty in male-to-female transgenders: a systematic review of surgical techniques. J Sex Med . (2015) 12:1499–512. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12868
18. Hadj-Moussa M, Ohl DA, Kuzon WM. Feminizing genital gender-confirmation surgery. Sex Med Rev. (2018) 6:457–68.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.11.005
19. Salim A, Poh M. Gender-affirming penile inversion vaginoplasty. Clin Plast Surg. (2018) 45:343–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cps.2018.04.001
20. Hess J, Rossi NR, Panic L, Rubben H, Senf W. Satisfaction with male-to-female gender reassignment surgery. DtschArztebl Int. (2014) 111:795–801. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2014.0795
21. Silva DC, Schwarz K, Fontanari AMV, Costa AB, Massuda R, Henriques AA, et al. WHOQOL-100 before and after sex reassignment surgery in brazilian male-to-female transsexual individuals. J Sex Med. (2016) 13:988–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2016.03.370
22. Murad MH, Elamin MB, Garcia MZ, Mullan RJ, Murad A, Erwin PJ, et al. Hormonal therapy and sex reassignment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of quality of life and psychosocial outcomes. Clin Endocrinol . (2010) 72:214–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2009.03625.x
23. Castellano E, Crespi C, Dell'Aquila C, Rosato R, Catalano C, Mineccia V, et al. Quality of life and hormones after sex reassignment surgery. J Endocrinol Invest . (2015) 38:1373–81. doi: 10.1007/s40618-015-0398-0
24. Bartolucci C, Gómez-Gil E, Salamero M, Esteva I, Guillamón A, Zubiaurre L, et al. Sexual quality of life in gender-dysphoric adults before genital sex reassignment surgery. J Sex Med . (2015) 12:180–8. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12758
Keywords: transsexualism, gender dysphoria, gender-affirming genital surgery, penile inversion vaginoplasty, surgical outcome
Citation: Moisés da Silva GV, Lobato MIR, Silva DC, Schwarz K, Fontanari AMV, Costa AB, Tavares PM, Gorgen ARH, Cabral RD and Rosito TE (2021) Male-to-Female Gender-Affirming Surgery: 20-Year Review of Technique and Surgical Results. Front. Surg. 8:639430. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.639430
Received: 17 December 2020; Accepted: 22 March 2021; Published: 05 May 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Moisés da Silva, Lobato, Silva, Schwarz, Fontanari, Costa, Tavares, Gorgen, Cabral and Rosito. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gabriel Veber Moisés da Silva, veber.gabriel@gmail.com
This article is part of the Research Topic
Gender Dysphoria: Diagnostic Issues, Clinical Aspects and Health Promotion
- Patient Care & Health Information
- Tests & Procedures
- Feminizing surgery
Mayo Clinic's approach
The Transgender and Intersex Specialty Care Clinic (TISCC) provides integrated medical, psychosocial and surgical intervention to individuals with gender dysphoria or incongruence and to those with differences of sexual development, also called intersex. The team includes providers from various specialties including endocrinology, pediatric endocrinology, social work, psychiatry, psychology, voice therapy, gynecology, urology and plastic surgery.
Treatments offered include:
- Behavioral health assessment and management
- Gender-affirming hormone therapy
- Assistance with social and legal issues and referrals to community resources
- Fertility preservation
- Referrals for sexually transmitted infection screening and preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP)
- Gender-affirming voice therapy
- Electrolysis and laser hair removal
- Hair transplant
- Gynecological care for trans men
- Chaplain services
- Preoperative and postoperative pelvic floor physical therapy
- Breast augmentation
- Facial feminization
- Tracheal shave
- Body-contouring procedures
- Orchiectomy
- Vaginoplasty and labioplasty
- Robot-assisted peritoneal flap vaginoplasty
- Mastectomy with chest masculinization
- Hysterectomy and oophorectomy
- Metoidioplasty
Before you start treatment, you meet with at least one member of the TISCC medical team — a physician, a physician assistant or a nurse practitioner — and a member of the TISCC mental health team, such as a social worker, psychologist or psychiatrist. You have a complete medical evaluation to make sure that your treatment risks are identified and addressed. Before a surgical procedure, you are seen by the appropriate TISCC surgical team. Evaluation of your mental health ensures that any mood or mental health concerns are reasonably well managed before you start treatment.
Each person is different. Your providers look at your specific case in order to come up with the best recommendations for you. Your health care team works with you during your treatment and makes sure your expectations are realistic. Your team wants to make sure your goals are being met, any risks are managed and your questions are answered.
Advanced technology
Mayo Clinic specialists are committed to providing the latest, most comprehensive treatment options for gender dysphoria. Your Mayo Clinic specialist's advice about the best treatment for you is based on expert knowledge of and experience with all treatment options.
Expertise and rankings
At Mayo Clinic, endocrinologists, psychiatrists, psychologists, nurse practitioners, social workers and surgeons work together to provide the care you need.
Having all of this expertise in a single place, focused on you, means that you're not just getting one opinion. Your care is discussed among the team, your test results are available quickly and your appointments are scheduled in coordination. Highly specialized experts are all working together to help determine what's best for you.
Locations, travel and lodging
Mayo Clinic has major campuses in Phoenix and Scottsdale, Arizona; Jacksonville, Florida; and Rochester, Minnesota. The Mayo Clinic Health System has dozens of locations in several states.
For more information on visiting Mayo Clinic, choose your location below:

Mayo Clinic's campus in Arizona

Mayo Clinic's campus in Florida

Mayo Clinic's campus in Minnesota

Mayo Clinic Health System

Mayo Clinic Healthcare, located in London
Costs and insurance.
Mayo Clinic works with hundreds of insurance companies and is an in-network provider for millions of people.
In most cases, Mayo Clinic doesn't require a physician referral. Some insurers require referrals or may have additional requirements for certain medical care. All appointments are prioritized on the basis of medical need.
Learn more about appointments at Mayo Clinic .
Please contact your insurance company to verify medical coverage and to obtain any needed authorization prior to your visit. Often, your insurer's customer service number is printed on the back of your insurance card.
More information about billing and insurance:
Mayo Clinic in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies of tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.
- Tangpricha V, et al. Transgender women: Evaluation and management. https://www.uptodate.com/ contents/search. Accessed Aug. 16, 2022.
- Erickson-Schroth L, ed. Surgical transition. In: Trans Bodies, Trans Selves: A Resource by and for Transgender Communities. 2nd ed. Kindle edition. Oxford University Press; 2022. Accessed Aug. 17, 2022.
- Coleman E, et al. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, version 8. International Journal of Transgender Health. 2022; doi:10.1080/26895269.2022.2100644.
- AskMayoExpert. Gender-affirming procedures (adult). Mayo Clinic; 2022.
- Nahabedian, M. Implant-based breast reconstruction and augmentation. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Aug. 17, 2022.
- Erickson-Schroth L, ed. Medical transition. In: Trans Bodies, Trans Selves: A Resource by and for Transgender Communities. 2nd ed. Kindle edition. Oxford University Press; 2022. Accessed Aug. 17, 2022.
- Ferrando C, et al. Gender-affirming surgery: Male to female. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Aug. 17, 2022.
- Anatomy before and after bowel flap procedure
- Anatomy before and after penile inversion
- Breast augmentation incisions
- Gender dysphoria
- Placement of breast implants or tissue expanders
Products & Services
- A Book: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th Edition
- Available Sexual Health Solutions at Mayo Clinic Store
- Newsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital Edition
- Doctors & Departments
- Care at Mayo Clinic
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.

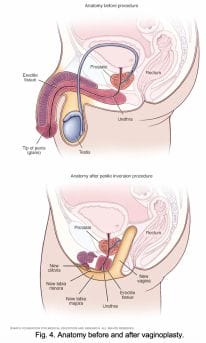
Vaginoplasty (MTF)
Vaginoplasty , gender confirmation surgery.
Medically reviewed by Tuan A. Tran, M.D., M.B.A., F.A.C.S. | Written by Nhuhao Do on May 27 th , 2021
Overview
Transgender and intersex people follow different paths to express their gender identity. Some may choose to pursue gender confirmation surgery (GCS), also known as sex reassignment surgery (SRS) or bottom surgery to better identify with their gender expression. This article will focus on bottom surgery for assigned male at birth (AMAB). Male-to-female, or male to non-binary people may elect to undergo vaginoplasty to obtain female genital. They may also decide to pursue other procedures as part of gender confirmation surgery including, chest reconstruction and facial feminization surgery .
Before the surgery
A good candidate for vaginoplasty is a healthy adult with realistic expectations of what the procedure can help them achieve along with the understanding of potential risks. Before proceeding with your surgery, your surgeon will go over an informed consent with you; you will be asked to provide a psychiatric evaluation; and other medical screening including, blood tests and electrocardiogram (EKG).
Leading up to your surgery, you will be required to stop hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for two weeks before surgery, and refrain for another two weeks after surgery. Most people will also need to go through hair removal via electrolysis. In vaginoplasty, hair will be removed on the skin that will eventually comprise the lining of the neovagina. Be sure to discuss in detail with Dr. Tran about the any medications that you take regularly and any recreational drugs you may use. He will advise whether or not you will need to stop taking any of those medications before your surgery.
Procedure in Detail
There are three main methods of vaginoplasty performed today:
Penile inversion
- Rectosigmoid or colon graft
- Non-penile inversion vaginoplasty
In all three surgical methods, the clitoris is sculpted from the head of the penis. Dr. Tran will discuss with you to determine the best technique for body to achieve your desired results.
Penile inversion involves using the penile skin to form the neovagina. The labia major and minora are primarily made from scrotal tissue. This results in a sensate vagina and labia.
One main drawback is the lack of self-lubrication by the vaginal wall. Common variations include using the remaining scrotal tissue as a graft for additional vaginal depth, and using the intact mucosal urethra recovered from the penis to line part of the vagina, creating some self-lubrication.
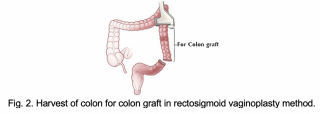
Rectosigmoid vaginoplasty
Rectosigmoid vaginoplasty involves the use of intestinal tissue to form the vaginal wall. This technique is sometimes used in conjunction with penile inversion. Intestinal tissue helps when penile and scrotal tissue is scarce.
This method is an option for transgender women who began hormone therapy at puberty and were never exposed to testosterone.
Intestinal tissue offers the benefit of being mucosal, and therefore self-lubricating. This technique is also used to reconstruct vaginas for cisgender women who developed atypically short vaginal canals.
Non-penile inversion
Non-penile inversion is also known as the Suporn technique or the Chonburi Flap. This method uses perforated scrotal tissue graft for the vaginal lining, and intact scrotal tissue for the labia majora similar to the penile inversion technique. The penile tissue is used for the labia minora and clitoral hood. This technique reported greater vaginal depth, more sensate inner labia, and improved cosmetic appearance.
After your surgery, you will stay hospitalized for 3-6 days. During that time, you will have a catheter until you can purge the bulk of your urine through your urethra on your own. You will follow-up with Dr. Tran 7 days after your surgery for a post-operative appointment.
Risks and side effects
Pain and swelling are expected after your surgery. Some may experience minor urinary incontinence , similar to that after giving birth and should subsides overtime. Although rare, there are other side effects after vaginoplasty to be considered:
- Loss of sensation in part or all of the neoclitoris due to nerve damage
- Rectovaginal fistula
- Vaginal prolapse
Cost and Consultation
Many major medical insurances in California, including CalOptima, cover for vaginoplasty as part of gender confirmation surgery. If you have more questions or would like to schedule a free consultation with Dr. Tran, please contact us via our website , Tran Plastic mobile app or call us today at 714-839-8000.
References
Bizic M., Kojovic, V., Duisin, D., Stanojecvic, D., Vujovic, S., Milosevic, A., Korac, G., & Djordjevic, M. (2014, May 26). An overview of neovaginal reconstruction options in male to female transsexuals . Hindawi The Scientific World Journal. DOI: dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/638919
Cavanaugh, T., Hopwood, R., & Lambert, C. (2016, November 18). Informed consent in the medical care of transgender and gender-nonconforming patients . AMA Journal of Ethics | Illuminating the Art of Medicine. Retreived from journalofethics.ama-assn.org/2016/11/sect1-1611.html
Mayo Clinic Staff. Anatomy before and after penile inversion. Mayo Clinic . Mayo Clinic. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/feminizing-surgery/multimedia/img-20358606
Watanyusakul, S. (2002, July 27). A new method for sensated clitoris and labia minora reconstruction in male-to-female sex reassignment surgery . Aikchol Hospital, Chonburi. Retrieved from https://supornclinic.com/paper/
Weyers, S., Verstraelen, H., Gerris, J., Monstrey, S., Santiago, G., Saerens, B., Backer, E., Claeys, G., Vaneechoutte, M., & Verhelst, R. (2009, May 20). Microflora of the penile skin-lined neovagina in
Privacy Overview
MTFsurgery .net
- Orchiectomy
- Penile Inversion Vaginoplasty
- Peritoneal Vaginoplasty
- Rectosigmoid Vaginoplasty
- Vulvoplasty
- Non-Binary Bottom Surgery
- Facial Feminization Surgery
- Breast Augmentation
- Breast Augmentation w/ Fat Transfer
- Body Feminization
- What Is Board Certification?
- Getting Surgery In Thailand
- Vaginoplasty Hair Removal
- Follicular Cautery vs. Hair Removal
- Vaginal Stenosis After Vaginoplasty
- Importance of Dilation
- Breast Aug & Surgeon Experience
- Browse All Surgeons
- Orchiectomy Surgeons
Vaginoplasty Surgeons
- FFS Surgeons
- Breast Augmentation Surgeons
- Body Feminization Surgeons
- MTF Breast Augmentation
- MTF Vaginoplasty
MTF Surgery » Surgeons
Surgeons Who Perform Gender-Affirming Surgery
Trans feminine Gender Affirming Surgery is becoming more and more common, but it can still be tough to find the right surgeon. The surgeons listed below are highly qualified plastic, reconstructive, urological and cosmetic surgeons who regularly perform gender-affirming procedures for those on the trans feminine spectrum. When choosing a surgeon, look for board certification, experience with transgender surgery, and a someone you feel confident and comfortable with.
Also see: Vaginoplasty Surgeons , Orchiectomy Surgeons
Featured Surgeons
Dr. Kathy Rumer
Dr. Kathy Rumer is an expert in transgender surgery, performing 200-250 MTF gender reassignment surgeries per year. Dr. Rumer also directs a 1-year gender surgery fellowship program. She offers the full range of male to female surgery procedures, including Vaginoplasty, Facial Feminization Surgery and Breast Augmentation. Read more »
Dr. Scott Mosser
Dr. Scott W. Mosser is a board certified and award-winning surgeon based in San Francisco who specializes in MTF/N Breast Augmentation and Body Feminization. He has worked with the transgender community for more than 10 years. Dr. Mosser is co-founder of the American Society of Gender Surgeons (ASGS), and Medical Director of the Gender Institute at Saint Francis Memorial Hospital. Read more »
Dr. Gabriel Del Corral
Dr. Del Corral is a double board-certified plastic and reconstructive surgeon who offers Vaginoplasty and other gender-affirming procedures at the Medstar Center for Gender Affirmation in Washington D.C. and Baltimore, Maryland. Fellowship trained in microsurgery, Dr. Del Corral also has expertise in reconstructive surgery, maxillofacial surgery and cosmetic surgery. He specializes in Gender Affirmation Surgery and has a particular interest in Vaginoplasty and Facial Feminization. More »
Dr. Scott W. Mosser is a board certified and award-winning surgeon based in San Francisco who specializes in MTF/N Breast Augmentation and Body Feminization. He has worked with the transgender community for more than 10 years. Dr. Mosser is co-founder of the American Society of Gender Surgeons (ASGS), and Medical Director of the Gender Institute at Saint Francis Memorial Hospital. More »
Dr. Danny Hanna
Dr. Hanna is a fellowship-trained Gender Surgeon based in Dallas, Texas. At the Hanna Gender Center, Dr. Hanna works exclusively with transgender and non-binary patients, offering gender-affirming genital surgeries as well as Breast Augmentation, Body Sculpting and Hair Grafting. More »
Newly Added Surgeons
Dr. Kenan Celtik
Dr. Celtik is a Reconstructive Urologist who specializes in gender-affirming Vaginoplasty. He is fellowship-trained in Gender Surgery and has completed 15 years of advanced medical education, including rigorous training in female pelvic reconstruction, robotic surgery and neurourology. Dr. Celtik's deep expertise and commitment to providing exceptional care and surgical outcomes make him a great choice of Vaginoplasty surgeon. He joined the Crane Center for Transgender Surgery in 2023 and is based in the San Francisco area. More »
Dr. Drew Marano
Dr. Marano is a fellowship-trained plastic and reconstructive surgeon in New York City who has deep expertise in Gender Affirmation Surgery. Dr. Marano is fellowship-trained in the full spectrum of gender-affirming procedures and is particularly passionate about Robotic Vaginoplasty and Facial Feminization Surgery. Dr. Marano's extensive training and dedication to provide the highest level of care make him a sound choice of surgeon in the New York metropolitan area. More »
Dr. Aneesh Gupta
Dr. Gupta is a triple board-certified cosmetic surgeon in Philadelphia who offers Breast Augmentation and Body Feminization surgery. Dr. Gupta's experience with gender-affirming care has informed how Jazzi Cosmetic Surgery has created a welcoming environment for all patients. Throughout your surgical journey, you can expect everyone you interact with at Jazzi to be friendly and professional. More »
Facial Feminization Experts
Dr. Joel Beck
Dr. Beck is a board certified plastic and reconstructive surgeon who has been offering gender-affirming facial surgery since 2003. Based in Charlotte, North Carolina, Dr. Beck is one of only a few FFS Surgeons in the Southeast. He also offers Breast Augmentation, Body Sculpting and Hair Grafting. More »
Dr. Gerhard Mundinger
Dr. Mundinger is a board-certified plastic surgeon with broad training and expertise in craniofacial and gender-affirming surgery. Dr. Mundinger joined the Austin branch of the Crane Center for Transgender Surgery in 2021, where he offers Facial Feminization Surgery, Vaginoplasty and Breast Augmentation. More »
Dr. Thomas Satterwhite
Dr. Satterwhite is a Plastic Surgeon in San Francisco works exclusively with transgender and non-binary patients. Dr. Satterwhite performs Facial Feminization Surgery, Vaginoplasty, Breast and Buttock Augmentation, and Body Sculpting. More »
Dr. Josef Hadeed
Dr. Hadeed is a board certified, Duke University-trained surgeon who offers gender-affirming feminizing surgery in Beverly Hills, California and Miami, Florida. Dr. Hadeed's surgical offerings include Orchiectomy, Facial Feminization, Breast Augmentation and Body Sculpting. More »
Dr. Alexander Facque
Dr. Facque is a board-certified plastic surgeon in San Francisco, California who joined the Gender Confirmation Center's team in September 2020 as a full-time Associate Surgeon with deep expertise in Facial Gender Confirmation Surgery, Breast Augmentation and Body Sculpting. Dr. Facque was introduced to gender-affirming care in 2012 and now works exclusively with transgender and non-binary patients. More »
Dr. Drew Schnitt
Dr. Schnitt is a board certified cosmetic, plastic, reconstructive and craniofacial surgeon. In practice since 2002, Dr. Schnitt's extensive experience in cosmetic and craniofacial surgery make him a great choice for Facial Feminization Surgery in Florida, as well as Breast Augmentation, and Body Sculpting. More »
Dr. Toby Meltzer
Dr. Meltzer is a plastic and reconstructive surgeon who is widely recognized as one of the leading surgeons in the field of Gender Reassignment Surgery. Dr. Meltzer has been performing MTF Surgery since 1993 and has completed over 4000 gender affirming surgeries. He performs about 200 gender reassignment surgery cases per year in Scottsdale, Arizona. More »
Dr. Christopher Salgado
Dr. Salgado is a board-certified plastic surgeon in Florida who has deep expertise in Gender Affirming Surgery. In practice for more than 20 years, Dr. Salgado performs all aspects of male-to-female surgery, from Facial Feminization and Breast Augmentation to Vaginoplasty, giving patients the opportunity to experience a continuity of care throughout their surgical transition. After many years in academic practice, Dr. Salgado opened his private practice in Miami in 2019. More »
Dr. Eric Bensimon
Dr. Bensimon has dedicated his career to helping trans women seeking FFS. With over 15 years experience in FFS, Dr. Eric Bensimon is one of the world's most experienced surgeons practicing Facial Feminization Surgery. Dr. Bensimon is based in Montreal, Canada. More »
Dr. Praful Ramineni
Dr. Ramineni is a highly experienced, board-certified plastic and reconstructive surgeon who specializes in gender-affirming top and bottom surgeries. Dr. Ramineni has more than 15 years of experience as a surgeon and performs at least 600 procedures a year. He's known for not just his exceptional surgical skills and natural-looking results, but also for his caring bedside manner and great communication style. More »
Dr. Daniel J. Freet
Dr. Freet is a board certified Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon who offers the full spectrum of MTF Surgery procedures at the University of Texas in Houston. Leading a multidisciplinary gender surgery team, Dr. Freet performs Gender Reassignment Surgery (Vaginoplasty), as well as Facial Feminization and Breast Augmentation. More »
Dr. Angela Rodriguez
Dr. Rodriguez is a board-certified plastic surgeon in San Francisco who is dedicated full time to providing surgical care for transgender patients. She is highly proficient in gender-affirming Vaginoplasty and has a special interest in Facial Feminization. Her commitment to transforming lives and passion for social justice drove her pursuance to master transgender surgery, but it's Dr. Rodriguez's surgical skills, bedside manner and results that patients love. More »
Dr. Curtis Crane
Dr. Crane is a board-certified plastic surgeon in Austin, Texas who has deep experience with the full spectrum of male-to-female Gender Reassignment Surgery procedures. Dr. Crane and his team perform approximately 130 Vaginoplasty surgeries every year, as well as Vulvoplasty, Facial Feminization and Breast Augmentation. More »
Dr. Richard Santucci
Dr. Santucci, who spent 18 years as one of the nation's most distinguished academic Reconstructive Urologists, hasn't looked back since turning his focus to Gender Affirming Surgery. Before joining the Crane Center for Transgender Surgery, Dr. Santucci served as the Director of the Center for Urologic Reconstruction and the Specialist-in-Chief for Urology at the Detroit Medical Center. Dr. Santucci's years of experience with complex genitourinary surgery uniquely qualifies him to excel at gender-affirming genital reconstruction. More »
Dr. Ashley DeLeon
Dr. DeLeon is a board-certified surgeon who specializes exclusively in Gender Affirmation Surgery. Dr. DeLeon was fellowship trained in gender-affirming procedures by Dr. Curtis Crane. Dr. DeLeon practices in Austin, Texas at the Crane Center for Transgender Surgery, one of the busiest gender surgery practices in the world. Dr. DeLeon's special focus is on male-to-female bottom surgery procedures: Orchiectomy, Vulvoplasty and Vaginoplasty. More »
Dr. Dev Gurjala
Dr. Gurjala is a board-certified plastic surgeon in San Francisco who offers the full array of male-to-female surgery. Prior to joining Align Surgical Associates in 2019, Dr. Gurjala performed gender surgery, microsurgery, and general reconstructive and aesthetic surgery for five years in the Kaiser Permanente system in California. More »
Dr. Michael Safir
Dr. Safir is a board-certified urologist in Los Angeles who specializes exclusively in gender-affirming bottom surgery procedures. With sub-specialty certification in Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery (FPM-RS), Dr. Safir is one of a handful of urologists in the world with individual fellowship training and experience in both male and female genital reconstruction. He gained signicant experience performing gender-affirming genital procedures for five years at one of the highest volume gender surgery centers in the world. More »
Dr. John Henry Pang
Dr. Pang is a double board-certified plastic and reconstructive surgeon who has also completed fellowship training in Gender Affirming Surgery. Before joining Align Surgical Associates in San Francisco, Dr. Pang completed the Transgender Surgery training program at Mount Sinai in New York City. His practice is dedicated to providing the highest level of care for his transgender and non-binary patients. More »
Dr. Heidi Wittenberg
Dr. Wittenberg is an experienced Urogynecologist in San Francisco who works exclusively with trans and non-binary patients. Dr. Wittenberg is the director of MoZaic Care, which specializes in gender affirming genital and pelvic surgeries, and a Founder Surgeon and Co-Director for the first SRC accredited Center of Excellence in Gender Confirmation Surgery, at Greenbrae Surgery Center. More »
Dr. Adam Bonnington
Dr. Bonnington is a Gender Surgeon in San Francisco who has focused his career on working with underrepresented patient populations. He joined Dr. Heidi Wittenberg at MoZaic Care as a Surgical Associate in 2020 where he works exclusively with transgender and non-binary individuals. Dr. Bonnington performs Orchiectomy and Vaginoplasty. More »
Dr. Loren Schechter
Dr. Schechter is one of the country's foremost experts on gender-affirming surgery. He is the Medical Director of the Gender Affirmation Surgery Program at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago. Dr. Schechter's outstanding surgical skills and more than 20 years experience with transgender surgery have made him an in-demand surgeon. He offers the full spectrum MTF Gender Confirmation procedures, including Breast Augmentation, single-stage Vaginoplasty, and FFS. More »
Dr. Ellie Zara Ley
Dr. Ley is a board-certified plastic surgeon who had over 15 years of training and experience in plastic surgery, craniofacial surgery and microsurgery before completing Gender Surgery training. Now based in San Francisco, Dr. Ley provides superb surgical care for those seeking Vaginoplasty, Facial Feminization and other feminizing surgeries. More »
Dr. Kathy Rumer is an expert in transgender surgery, performing 200-250 MTF gender reassignment surgeries per year. Dr. Rumer also directs a 1-year gender surgery fellowship program. She offers the full range of male to female surgery procedures, including Vaginoplasty, Facial Feminization Surgery and Breast Augmentation. More »
Dr. John Whitehead
Dr. Whitehead offers gender affirming male-to-female surgery in Florida. Dr. Whitehead was trained in the art of gender reassignment surgery by Dr. Harold Reed, the now-retired urologist who practiced at The Reed Center for decades. Dr. Whitehead offers Orchiectomy, Vaginoplasty and Vulvoplasty. More »
Dr. Dmitriy Nikolavsky
Dr. Nikolavsky is a highly regarded Reconstructive Urologist and Gender Surgeon at SUNY Upstate Medical University in Syracuse NY. In addition to offering primary Vaginoplasty surgery, Dr. Nikolavsky is also an expert at treating post-operative urinary complications and provides long term follow-up care for patients who have had Vaginoplasty. Read more »
Dr. Jonathan Keith
Dr. Keith is a fellowship-trained Plastic Surgeon in New Jersey with expertise in Gender Reassignment Surgery. In 2018, Dr. Keith co-founded the first multidisciplinary clinical program for transgender patients in New Jersey. He is the first surgeon in New Jersey to offer the full range of gender-affirming procedures, including Facial Surgery, Vaginoplasty and Breast Augmentation. More »
Dr. Nick Esmonde
Dr. Esmonde is a Gender Surgeon in Portland, Oregon who has impeccable training in Gender Affirmation Surgery and whose practice is almost exclusively focused on helping transgender and non-binary patients. Dr. Esmonde offers the full spectrum of feminizing surgeries, from Facial Feminization to Vaginoplasty. More »
Dr. Christopher McClung
Dr. McClung is a board-certified urologist in Columbus, Ohio who specializes in gender-affirming Vaginoplasty. Dr. McClung's deep experience with complex urological reconstructions provided an ideal background for becoming a Gender Surgeon. He has now performed over 200 feminizing bottom surgeries and his practice is fully dedicated to providing gender-affirming surgical care. In addition to his urology and reconstructive expertise, Dr. McClung's patients also appreciate his gentle bedside manner. More »
Dr. Min Jun
Dr. Min Jun is an exceptionally trained Reconstructive Urologist and Gender Surgeon in San Francisco who specializes in Robotic Peritoneal Flap Vaginoplasty. Dr. Jun has completed fellowship training in both Reconstructive Urology and Gender Affirming Surgery. He worked with the Crane Center for Transgender Surgery in 2020-2023 and now has his own practice in San Francisco. More »
Surgeons in Thailand
Dr. Pichet Rodchareon
Dr. Pichet Rodchareon is a board-certified plastic surgeon in Bangkok who has extensive experience performing male-to-female Gender Reassignment Surgery. Dr. Pichet is considered one of top SRS surgeons in Thailand. His training includes plastic surgery, hand surgery, craniofacial and maxillofacial surgery. More »
Dr. Kamol Pansritum
Dr. Kamol Pansritum is recognized as one of the most experienced GRS Surgeons in the world, having completed over 5,000 gender reassignment surgeries, and more than 10,000 related surgical procedures for trans women since 1997. Dr. Kamol currently performs more than 200 MTF reassignment surgeries a year at his private hospital in Bangkok, Thailand. More »
More MTF Surgeons
Dr. E. Antonio Mangubat
Dr. E. Antonio Mangubat is the Pacific Northwest's most sought-after surgeon for transgender surgery, with more than 20 years of experience performing procedures for trans women, including Facial Feminization, MTF Breast Augmentation, Body Sculpting and Hair Restoration. More »
Dr. Alvina Won
Dr. Won is a board-certified Cosmetic Surgeon who is committed to providing the highest level of compassionate care in a welcoming environment for all patients. Dr. Won gained significant experience with gender-affirming surgery during a year-long cosmetic surgery fellowship with Dr. Tony Mangubat, a 20+ year veteran of transgender surgery. Based in the Seattle area, just north of Seattle, Dr. Won now devotes part of her practice to performing MTF Breast Augmentation, Buttock Augmentation and Body Sculpting. More »
Dr. Laurel Chandler
Dr. Chandler is a Harvard fellowship-trained plastic surgeon who has received specialty training in gender-affirming breast surgery. During both her residency and fellowship training, Dr. Chandler worked with established gender surgeons to learn the aesthetic nuances of transgender Breast Augmentation. Dr. Chandler provides individualized care for a diverse range of patients, up to 90% of whom are transgender and non-binary. More »
Dr. Russell Sassani
Dr. Russell Sassani is a board certified plastic and reconstructive surgeon who has quickly become one of the most popular surgeons in the Southeastern United States for trans women. He performs Breast Augmentation, Facial Feminization and Body Sculpting in the Mami/Fort Lauderdale area. More »
Dr. Mark Youssef
Dr. Mark Youssef, Director of the Transgender Surgery Institute of Southern California, is a Cosmetic Surgeon in Santa Monica who helps clients on the trans feminine spectrum with Breast Augmentation, Body Feminization and Facial Feminization surgeries. He operates at his private surgery center, Younique Surgery Center in Santa Monica. More »
Dr. Hope Sherie
Dr. Hope Sherie is a board-certified cosmetic surgeon who has extensive training in MTF surgery procedures. Dr. Sherie offers trans women the highest level of surgical care at her practice in Charlotte, North Carolina. Procedures available include Orchiectomy and Breast Augmentation. More »
Dr. Javad Sajan
Voted #1 Best Surgeon in Seattle in 2016 and 2017, Dr. Sajan is an internationally recognized Cosmetic & Reconstructive Plastic Surgeon whose specializations include Facial Feminization and Breast Augmentation. Dr. Sajan enjoys providing gender-affirming surgical care and is honored to play a role in his patients' transitions. More »
Dr. Daniel Jacobs
Dr. Jacobs is a board-certified plastic surgeon in San Francisco, California who joined the Gender Confirmation Center in July 2022. With more than 30 years of plastic experience and a practice that's dedicated to gender-affirming care, Dr. Jacobs is a sound choice for transfeminine and non-binary individuals seeking Breast Augmentation surgery. More »
Dr. Daniel Crane
Dr. Crane is a plastic surgeon in the Miami area who has expertise in breast, body and facial surgeries. He was one of only 30 residents selected from across the country to participate in a highly specialized aesthetic fellowship training program. In 2022, Dr. Crane joined Dr. Drew Schnitt's Inspire Aesthetics.. His unique training in plastic and aesthetic surgery provides him with the knowledge and experience to help you achieve your surgery goals. More »
Dr. Charles Lee
Dr. Charles Lee is a board-certified plastic and reconstructive surgeon who has deep expertise in microsurgery and breast surgery. In practice since 2003, Dr. Lee offers MTF Top Surgery at Crane Center for Transgender Surgery in San Francisco. More »
Dr. Alan Dulin
Dr. Alan Dulin is a board-certified surgeon who has many years of experience performing Male-to-Female Surgery in the Dallas area. Dr. Dulin offers transgender women Breast Augmentation & Body Contouring, Facial Feminization Surgery and Orchiectomy. More »
Dr. Scott Harris
Dr. Scott Harris is a board-certified Surgeon with years of experience performing Male to Female Surgery in Texas. Known for his meticulous attention to detail, Dr. Harris offers a number of feminizing surgeries for trans women, including Facial Feminization Surgery, Breast Augmentation and Body Sculpting procedures. More »
Dr. Cassie Nghiem
Dr. Nghiem is an Ivy League-educated, fellowship-trained plastic surgeon in Washington, D.C. who specializes in Gender-Affirming Surgery, including Breast Augmentation and Facial Feminization. She works closely with her patients to deliver the best quality care that is aligned with their goals. Known for her advanced surgical skills, Dr. Nghiem's patients also love her friendly personality and kind demeanor. More »
Dr. Manish Champaneria
Dr. Manish Champaneria is a board-certified surgeon with extensive training and experience in plastic surgery and a special focus on reconstructive breast procedures and Facial Feminization. Dr. Champaneria practices in San Diego, California. More »
Dr. Walter Lin
Dr. Walter Lin is a fellowship-trained Plastic Surgeon in San Francisco who performs Breast Augmentation for transfeminine individuals. Dr. Lin's expertise in the areas of microsurgical reconstruction of the extremities, breast, and lymphatic systems has greatly contributed to his skill with gender-affirming Breast Augmentation. Dr. Lin joined the staff of Buncke Clinic and the San Francisco Transgender Institute in 2017. More »
Dr. Michelle Lee
Dr. Lee is a board-certified and fellowship-trained plastic surgeon with high proficiency in aesthetic and reconstructive procedures for the breast and face. Widely regarded as being one of the finest plastic surgeons in the Los Angeles area, Dr. Lee possesses the perfect combination of skill, artistry, experience and compassion, which makes her ideally suited to performing gender-affirming surgery. More »
Dr. Dustin Reid
Dr. Dustin Reid is a double board-certified plastic surgeon in Austin who offers Breast Augmentation, Body Feminization and Hair Restoration. Dr. Reid is committed to providing expert surgical care and guidance throughout your surgery experience. More »
Dr. Daniel Medalie
Dr. Daniel Medalie is a board certified plastic and reconstructive surgeon who has been performing gender-affirming surgeries since 1996. Based in the Cleveland area, he offers Breast Augmentation and Tracheal Shave procedures for transfeminine individuals. More »

Dr. Jeffrey Marvel
Dr. Marvel is a board-certified cosmetic surgeon who has developed a great reputation in Nashville and Central Tennessee for his technical skills, attention to detail and natural-looking results. Since 1997, Dr. Marvel and Marvel Cosmetic Surgery's dedicated staff have offered top-notch hospitality and care for patients seeking a wide range of cosmetic procedures, including Facial Feminization, Breast Augmentation and Hair Grafting. More »
Dr. Eric Emerson
Dr. Eric Emerson is a Board-Certified Plastic Surgeon with over 20 years experience specializing in breast surgery, body contouring and facial surgery. Dr. Emerson is a sound choice for trans women seeking breast augmentation and body and facial feminization surgery in the Carolinas and eastern United States. More »
Dr. Gregory Swank
Dr. Gregory Swank a board-certified, Duke University-trained surgeon who offers male-to-female surgery in North Carolina. Dr. Swank's surgical offerings for trans women include Breast Augmentation, and Body and Facial Feminization. More »
Dr. Michael Beckenstein
Dr. Michael Beckenstein is a double-board-certified Plastic Surgeon in Birmingham who is pleased to offer his expertise and skills in cosmetic and reconstructive surgery to the MTF community in Alabama and throughout the Southeast. Dr. Beckenstein specializes in Breast Augmentation as well as Hair Restoration. More »
Dr. Helena Guarda
Dr. Helena Guarda is a board-certified Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon who is committed to offering Breast Augmentation and Feminization Surgeries as part of her LGBT-friendly practice in Suffolk, Virginia. Dr. Guarda is excited to work with patients from all parts of Virginia, as well as those coming from nearby states such as North Carolina, Maryland, West Virginia, Tennessee, and Kentucky. More »
Dr. Elliot Jacobs
Dr. Jacobs is a nationally-recognized, board-certified plastic surgeon in Boca Raton, Florida with more than 30 years of experience in breast and facial surgeries. Dr. Jacobs offers MTF Surgery procedures at his private, modern and fully accredited surgical suite. More »
Dr. Rex Moulton-Barrett
Dr. Rex Moulton-Barrett is a double board certified cosmetic, plastic and reconstructive surgeon in the San Francisco Bay Area who has been performing MTF Breast Augmentation surgery since 2010. Read more »
Dr. Vartan Mardirossian
Dr. Vartan Mardirossian is a surgeon in South Florida who specializes in Facial Feminization Surgery. Dr. Mardirossian has extensive training and experience performing Facial Feminization procedures, including 7 years of training under renowned FFS surgeon Dr. Jeffrey Spiegel . Read more »
Last updated: 04/03/24

- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Asthma & Allergies
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Breast Cancer
- Cardiovascular Health
- Environment & Sustainability
- Exercise & Fitness
- Headache & Migraine
- Health Equity
- HIV & AIDS
- Human Biology
- Men's Health
- Mental Health
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Parkinson's Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Sexual Health
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Women's Health
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Vitamins & Supplements
- At-Home Testing
- Men’s Health
- Women’s Health
- Latest News
- Medical Myths
- Honest Nutrition
- Through My Eyes
- New Normal Health
- 2023 in medicine
- Why exercise is key to living a long and healthy life
- What do we know about the gut microbiome in IBD?
- My podcast changed me
- Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health?
- Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut
- Health Hubs
- Find a Doctor
- BMI Calculators and Charts
- Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide
- Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide
- Sleep Calculator
- RA Myths vs Facts
- Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar
- Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction
- Our Editorial Process
- Content Integrity
- Conscious Language
- Health Conditions
- Health Products
Sex and sexual health tips for transgender women after gender-affirming surgery

Lower gender-affirming surgery for trans women will mean they need to wait until the surgical site heals before having sex. Using lubricant and taking additional steps to protect against contracting sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can also help during the healing process.
Three options for lower gender-affirming surgery for transgender women include:
- Orchidectomy : This involves the removal of the testes. It can be a stand-alone procedure or occur during a vaginoplasty.
- Vaginoplasty: This involves removing the penis, testicles, and scrotum and creating a vaginal canal and labia. The surgeon will also create a clitoris using a portion of the glans penis.
- Vulvoplasty: This creates a vulva, including the mons pubis, labia, clitoris, and urethral opening. People may opt for this surgery if they are uninterested in receptive vaginal sex or do not wish to maintain the dilation and aftercare regime necessary after vaginoplasty. People may also refer to this option as a minimal depth vaginoplasty.
This article discusses how long recovery can take and when people can have sex after gender-affirming surgery.
It also looks at what to expect during sex after surgery and tips for hygiene, contraception , and protection from infections.
When can a person have sex after surgery?

According to Johns Hopkins Medicine , people can have receptive intercourse or take part in any sexual activity 12 weeks after a vaginoplasty. Sexual activity before this may lead to delayed wound healing and complications.
After an orchidectomy, it may take 1–2 days for people to become fully mobile again. They may be able to return to work a few days to a week after surgery.
Full recovery from an orchidectomy may take 2–8 weeks . For a few weeks following surgery, people will not be able to carry out certain activities such as driving or heavy lifting. The area of surgery will need to fully heal before people can have sex.
A healthcare professional can advise people when it is safe for them to have sex after gender-affirming surgery.
Will it be possible to achieve orgasm?
Following surgery, it can take time for people to recover and start to experience orgasms.
When people undergo a vulvoplasty, the surgeon forms a clitoris from the head of the penis. This means most people will still be able to experience orgasms through clitoral stimulation.
Johns Hopkins Medicine states that people may experience clitoral sensation after a vaginoplasty, although it can vary for each individual. Nerve regeneration may begin around 3 weeks following surgery, but in some cases, it may take a year or more to regain sensation.
People may experience a shooting or tingling sensation as the nerves regenerate, which should decrease over time.
In a 2017 study , 84 participants had rectosigmoid vaginoplasty. A post-surgery interview found that 79 of the participants had had sexual intercourse, and 72 had experienced orgasm.
Some reported infrequent symptoms, such as pain after sex and vaginal spotting , but these improved within 6 months.
A 2016 study of 22 people who had undergone a vaginoplasty and clitoroplasty found that 86% of participants could experience orgasm after surgery.
In addition, research from 2017 involving 28 transgender women found that pressure and vibration provided the best results for genital sensitivity after gender-affirming surgery.
How will it affect libido?
Transgender women may experience a decrease in sex drive after gender-affirming surgery.
According to a 2020 article , people can stop taking anti- testosterone medication and may experience a decreased sex drive following an orchidectomy.
Hormone replacement therapy may help maintain a regular sex drive.
Vaginal depth and lubrication
Vaginal depth after a vaginoplasty can vary for each person and depend on the amount of skin in the genital area before surgery.
An average vaginal depth after a vaginoplasty is 4–6 inches . For comparison, the average depth of a cisgender female’s vagina measures from 3.5 to 5 inches .
In people who have a rectosigmoid vaginoplasty or colovaginoplasty, the vagina may have more depth.
The University of California, San Francisco Medical Centre notes that the most common vaginoplasty technique uses the penile inversion procedure. This does not create a vaginal mucosa. As a result, the vagina will not self-lubricate, and a person will need to use lubricants to undergo dilation or have penetrative sex.
Another vaginoplasty technique uses the colon or small bowel to line the vagina, which will result in a self-lubricating vagina. However, it is a far less common procedure that may lead to serious and possibly life threatening complications.
When using lubrication, people should use a water or silicone-based lube with latex condoms, as oil-based lubricants can damage latex.
Aftercare and dilation
After a vaginoplasty, people need to use a vaginal dilator to stretch the vaginal canal and keep it open. Following surgery, people may need to dilate twice each day for a minimum of 15 minutes. This helps prevent loss of vaginal depth and width.
A healthcare professional will provide instructions on how to safely and correctly use a dilator. Although people may experience some discomfort when they begin dilating, they should not experience any severe pain.
If people experience pain when dilating, they will need to stop and readjust the dilator and body position. People will also need to use lubrication during dilation.
An orchidectomy can cause testosterone levels to drop. A sudden drop in testosterone may lead to mood swings or low energy following surgery.
To help prevent this, people may want to discuss mild testosterone replacement options with a healthcare professional to allow a more gradual reduction in testosterone.
People may need to use plenty of lubricant to make sex feel more comfortable and prevent any tears. They may also find the rest of the genital area, including the anus, is more tender following surgery.
Contraception and STIs
According to the Terrence Higgins Trust , surgery can increase the risk of contracting STIs , as any unhealed skin can allow infections to pass more easily into the body.
If people have had a vaginoplasty that uses part of the colon, a mucus membrane will line the vagina, making it easier for STIs to pass through.
If people have had a vaginoplasty that uses penile and scrotal skin, the vagina is less susceptible to STIs, but any unhealed skin can still be a risk factor.
Dilation of the vagina can also cause bleeding, so it is important to use a condom for any sex following dilation.
Using a condom during sex can help protect from STIs. People can use an external condom over a penis or sex toy and an internal condom inside a vagina. An internal condom may not suit everyone, as using an internal condom will depend on vaginal depth.
People can also use a dental dam during oral-vaginal sex. Regular testing can help to prevent passing on or contracting STIs from a sexual partner.
If people have not had an orchidectomy or vasectomy, they will need to use contraception for any penetrative sex with a partner who is able to get pregnant and is not using contraception.
If people are taking estrogen or other hormone therapy, these will not provide enough contraceptive protection, so they will need to use other contraceptive methods.
Learn more about sexual health for transgender women here.
Hygiene tips
After a vaginoplasty, it is important to keep the genital area clean and free of infection .
People will need to keep the outside of the vagina dry. It may be useful to place an absorbent pad between the labia to soak up any excess moisture.
Once the genital area is allowed to get wet, people should use soap and water to gently wash the area. It is important to avoid scrubbing or allowing shower spray to reach the surgical site.
Johns Hopkins Medicine states that people will need to douche using a non-fragranced vaginal douche , beginning 8 days after surgery. Depending on how much vaginal discharge people have, douching may be required 1–2 times each week. More frequent douching may be necessary if there is a large amount of discharge.
Following an orchidectomy, people may experience some mild discomfort, bruising, and swelling around the area of surgery. Some bleeding may occur, although this is rare . People may need to apply topical antibiotics to prevent infection.
People will need to speak with a healthcare professional to check when they can bathe the area of surgery following an orchidectomy.
It can take time to heal, recover, and adjust to sex and intimacy after gender-affirming surgery.
If people are experiencing any physical or emotional issues regarding surgery, they can speak with a doctor, a mental health professional, or a sex therapist.
Last medically reviewed on October 27, 2021
- Sexual Health / STDs
How we reviewed this article:
- Can transgender women have orgasms after gender-reassignment surgery? (n.d.). https://issm.info/sexual-health-qa/can-transgender-women-have-orgasms-after-gender-reassignment-surgery
- FAQ: Vaginoplasty. (n.d.). https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/center-transgender-health/services-appointments/faq/vaginoplasty
- Kim, S-K., et al . (2017). Is rectosigmoid vaginoplasty still useful? https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5300923/
- LeBreton, M., et al. (2016). Genital sensory detection thresholds and patient satisfaction with vaginoplasty in male-to-female transgender women. https://www.jsm.jsexmed.org/article/S1743-6095(16)30859-1/fulltext
- Meltzer, T. (2016). Vaginoplasty procedures, complications and aftercare. https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines/vaginoplasty
- Orchiectomy. (n.d.). https://transcare.ucsf.edu/orchiectomy
- Orchiectomy. (n.d.). https://www.transhub.org.au/orchiectomy
- Orchiectomy. (n.d.). http://www.phsa.ca/transcarebc/surgery/gen-affirming/lower-body-surgeries/orchiectomy#Post--surgery
- Safer sex and sexual health for trans feminine people. (n.d.). https://www.tht.org.uk/hiv-and-sexual-health/sexual-health/trans-people/trans-feminine/safer-sex
- Sigurjónsson, H., et al. (2017). Long-term sensitivity and patient-reported functionality of the neoclitoris after gender reassignment surgery. https://www.jsm.jsexmed.org/article/S1743-6095(16)30857-8/fulltext
- Vaginoplasty / vulvoplasty. (n.d.). https://healthcare.utah.edu/transgender-health/gender-affirmation-surgery/vaginoplasty.php
- van der Sluis, W. B., et al . (2020). Orchiectomy in transgender individuals: A motivation analysis and report of surgical outcomes. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/26895269.2020.1749921
Share this article
Latest news
- A 'balanced' diet is better than a vegetarian one in supporting brain health
- Ozempic-like drug may help slow the progression of Parkinson's symptoms
- Can we leverage immunotherapy against Alzheimer’s disease?
- A certain type of gut bacteria may help lower heart disease risk
- Blended antioxidant supplement may help boost memory and cognition
Related Coverage
There is no age limit on when a person can transition. Learn more about how to do so here.
Transgender is a term to refer to those who have a different gender identity than the one assigned to them at birth. Learn more here.
Estrogen hormone therapy can cause physical, sexual, reproductive, and emotional changes. Learn more about how it affects the body here.
The Go-To Guide to Gender Surgeons
Find a qualified surgeon for gender-affirming care.
Start Your Search
Find a Surgeon
Search by U.S. State, Procedure and Insurance Search by Country and Procedure Browse the Global Surgeon Maps
The Go-To Guide To Gender Surgeons

- Search Close Search submit
Accommodation bookings for the World Congress 2024 are offered only through direct bookings on our website. Beware of scams!
Procedure: Male to Female Gender Reassignment Surgery (MTF GRS)
Male-to-female gender reassignment surgery (MTF GRS) is a complex and irreversible genital surgery for male transsexual who is diagnosed with gender identity disorder and has a strong desire to live as female. The procedure is to remove all male genital organs including the penis and testes with the construction of female genitalia composed of labia major/minor, clitoris and neovagina simultaneously.
The patient who is fit for this surgery must strictly follow the standard of care set by the World Professional Association of Transgender Healthcare (WPATH) or equivalent criteria; Express desire or live in another gender role (Male gender) long enough, under hormonal replacement therapy, evaluated and approved by a psychiatrist or other qualified professional gender therapist.
Apart from genital surgery, the patient would seek other procedures to allow them to live as female smoothly such as breast aesthetic surgery, facial feminization surgery, body contouring, hair removal, voice change surgery, etc.
Interested in having this procedure?
Useful Information
Ensure you consider all aspects of a procedure. You can speak to your surgeon about these areas of the surgery in more detail during a consultation.
The surgery is quite complicated and only a handful of surgeons are able to perform this procedure. It can be completed in one stage or more stages depending on techniques and surgeons. The average surgical time ranges between 5-8 hours. There are several options of neovaginal construction depending on the type of tissue, single or in combination, such as penile skin, scrotal skin, large intestine, small intestine, or peritoneum.
The procedure is done under general anesthesia and might be combined with spinal anesthesia for faster recovery by reducing the usage of anesthetic gas.
Inpatient/Outpatient
The patient will be hospitalized as an in-patient for between 5-14 days depending on the technique and surgeon. The patient will have a urinary catheter at all times in the hospital.
Additional Information
What is the recovery process.
During hospitalization, the patient must be restricted in bed continuously or intermittently for several days between 3-5 days. After release from the hospital, the patient can return to their normal lives but not have to do physical exercise during the first 2 months after surgery. The patient has to do vaginal dilation continuously for 6 months to maintain the neovagina canal until completely healed and is ready for sexual intimacy.
What are the results?
With the good surgical technique, the result is very satisfying with an improved quality of life. The patient is able to live in a female role completely and happily either on their own or with their male or female partners.
What are the risks?
The most frequent complication of MTF GRS is bleeding, wound infection, skin flap or graft necrosis, urinary stenosis, neovaginal contracture, unsightly scar or deformed genitalia, vaginal fistula, etc. The revision procedures to improve external appearance are composed of secondary labiaplasty/ urethroplasty/ perineoplasty/ and vulvaplasty. The other revision procedure is secondary vaginoplasty to help the patient able to have sexual intimacy with the partner.
- Patient Information
- Global Statistics
- Media Centre
- World Congress
- Global Sponsors
- Privacy Policy
19 Mantua Road, Mount Royal, NJ 08061 United States
Registration number: 0330131
US Office: +1-603-643-2325
UK Office: +44 20 7038 7812
© 2022 International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. All Rights Reserved.
- Create an account
Log into My ISAPS
Forgot your password? Reset it here
Join the ISAPS Community
All members will continue to receive information relevant to their membership and ISAPS events.
I confirm by clicking below I would like to receive information about:
Welcome to the ISAPS community
By creating an account, you can:.
- Register for events
- Update your personal details
- Gain access to ISAPS publications and video library
- Become a member (explore our memberships here)
ISAPS Members can also:
- Access your member benefits
- Secure discounted member rates for events
- Read the Aesthetic Plastic Surgery Journal
- Gain full access to the video library
- View the Members Directory
- Update your 'Find a Surgeon' profile details
- Renew/Upgrade your Membership
The first step to becoming a part of the community is creating an account, so join us!
Keelee MacPhee, M.D.
Transgender Surgery & Plastic Surgery
TRANSGENDER SURGERY COSMETIC PLASTIC SURGERY BOARD CERTIFIED
MTF Vaginoplasty
In male-to-female sex reassignment, the trans woman may choose to undergo vaginoplasty – the inversion of the penis to create a vagina – as part of her physical transition. This procedure can result in a fully sensate neovagina.
Dr. MacPhee performs this reconstructive procedure by disassembling the penis and utilizing the inverted penile and scrotal skin flap and urethral flap to construct a new vulva, clitoris and vagina. The blood and nerve supplies are preserved to provide sensation, and the urethra is used to create the mucosal part of the vagina that provides additional sensitivity and wetting. The remaining penile and scrotal tissue are used to form the clitoral hood and labia.
The depth and diameter of the neovagina may be limited due the narrowness of the male pelvis. At the time of surgery, a stent is put in place to form vaginal dimensions, and the patient will need to dilate the vagina following surgery, frequently at first and tapering over time. A typical post-op protocol will involve dilating three times a day for 50 minutes each time for the first year. After that, maintenance dilation will be necessary for life. View MTF genital reconstruction results in our Photo Gallery.
Dr. MacPhee also performs orchiectomy, scrotal skin removal and limit-depth vaginoplasty procedures as alternatives to full MTF genital reconstruction .
PHOTO GALLERY

We are grateful for our many patients who are willing to share their experiences and results. Click … Read More >
MEET DR. MACPHEE

A highly skilled Plastic & Reconstructive surgeon in practice for more than 17 years, Dr. Keelee … Read More >
TRANSGENDER SURGERY

Dr. Keelee MacPhee has been performing gender affirming surgery since 2005 and is grateful for the … Read More >
READ OUR BLOG

Tune into our blog for recent news about GRS and the latest trends in cosmetic surgery procedures … Read More >
- About Dr. MacPhee
- Office Environment
- Surgery Hospitals
- Blog / News
- Photo Gallery
- Patient Forms
- Price Transparency
- Referring Therapists
- Referring Physicians

Graphic Medical Content
Content May be Inappropriate for Younger Audiences
Are you over 18 years of age?
- FIND A PROVIDER
I'm a Candidate
I'm a Provider
Log In / Sign Up
I'm a candidate
Provider login
I'm a provider
List your practice
MTF Gender Confirmation: Genital Construction
The specifics, the takeaway.
Download the app
As part of a transgender individual’s transition, genital reassignment surgery alters male genitalia into female genitalia.
Written By: Erin Storm, PA-C
Published: October 07, 2021
Last updated: February 18, 2022
- Procedure Overview
- Ideal Candidate
- Side Effects
- Average Cost
thumbs-up Pros
- Can Help Complete A Gender Affirmation Journey
thumbs-down Cons
- Potentially Cost Prohibitive
Invasiveness Score
Invasiveness is graded based on factors such as anesthesia practices, incisions, and recovery notes common to this procedure.
Average Recovery
Application.
Surgical Procedure
$ 7000 - $ 24000
What is a male to female (MTF) gender reassignment surgery?
Male to female (MTF) gender reassignment surgery is also known as sex reassignment surgery (SRS), genital construction, and generally as Gender Confirmation Surgery. These procedures are used to remove and alter male genitalia into traditional female genitalia. Plastic surgeons will remove the scrotum, perform a penile inversion to create the neovagina, remove and alter penile erectile tissue to form the clitoral tissue of the clitoris, and construct labia usually from scrotal tissue. The prostate gland is left intact. These procedures create fully functional female genitalia in transgender patients.
Typically gender reassignment surgery is performed as a last step in a transgender individuals transition journey. Guidelines from The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) state candidates must have letters of recommendation from their mental health provider and physician, have been living full time as a woman for one year, and have completed one year of hormonal therapy to be eligible.
Information on facial feminization surgeries, top surgeries (like a breast construction), and other male to female gender affirming surgeries as part of a gender transition for transwomen can be found in our comprehensive guide to MTF gender affirmation solutions .
What concerns does a MTF gender reassignment surgery treat?
- Transfeminine Bottom Surgery & Genital Construction : Male to female gender reassignment surgery creates female genitalia that are aesthetically authentic and functional. A vaginoplasty, penectomy, orchiectomy (testicle removal), clitoroplasty, and labiaplasty are typically performed.
Who is the ideal candidate for a MTF gender reassignment surgery?
The ideal candidate for MTF gender reassignment surgery is a transgender women seeking to complete her physical embodiment of her gender identity. This reconstructive genital surgery creates functioning female genitalia.
MTF gender reassignment surgery is not recommended for those who have not been on hormone therapy for one year, have not been living full time as a woman for one year, do not have letters of recommendation from their mental health provider and physician, children under the age of 18, and those with certain chronic medical conditions.
What is the average recovery associated with a MTF gender reassignment surgery?
Most patients experience four to six weeks of recovery time following a MTF gender reassignment surgery. Patients can expect bruising, swelling, and tenderness following the procedure. A urinary catheter is placed for one week and vaginal packing as well which may cause a sensation of fullness. Vaginal dilation is a component of the procedure and the patient will be advised on how to complete this progressive dilation at home over the course of a few weeks.
What are the potential side effects of a MTF gender reassignment surgery?
Possible side effects following a MTF gender reassignment surgery include bleeding, swelling, bruising, site infection, altered sensation, difficulty urinating, difficulty with sexual function, prolonged edema, and complications from anesthesia or the procedure.
What can someone expect from the results of a MTF gender reassignment surgery?
The results of MTF gender reassignment surgery are permanent. This procedure creates functional female genitalia and removes all male genitalia. The prostate gland is left intact which is important for transgender individuals ongoing healthcare and preventative screenings.
What is the average cost of a MTF gender reassignment surgery?
What to expect.
A MTF Gender Reassignment Surgery creates female genitalia. Here is a quick guide for what to expect before, during, and after a MTF Gender Reassignment Surgery:
Before Surgery
- Prophylactic antibiotics or antivirals may be prescribed
- Stop taking blood thinning medications two weeks prior to surgery. Blood thinners may include, Advil, Tylenol, Aspirin, and prescription anticoagulants
- Stop smoking four weeks prior to the procedure and continue cessation for four weeks post op
- No alcohol two days prior to the procedure
- Do not eat or drink six hours before
During Surgery
- General anesthesia
- A penile inversion is performed to create the vaginal canal
- The scrotum is removed
- Skin grafts are used to create the labia and vulva
- Erectile tissue is removed from the new vaginal walls, and erectile tissue from the head of the penis is used to create the clitoris
- The urethra is shortened
Immediately After Treatment
- Swelling, bruising, and tenderness
1 - 30 After Treatment & Beyond
- Resume most activities after a few days
- Swelling typically resolves within a few weeks
- Avoid strenuous activity for two to four weeks
- Remove urinary catheter and vaginal packing after one week
- Continue progressive vaginal dilation
Result Notes
- Results are permanent
- Proper aftercare will ensure optimal results
Gender confirmation surgeries for transgender individuals are an important component of transgender health and in creating an embodied gender identity. Gender reassignment surgery allows transgender women who feel it is a part of their transition to more fully embrace their gender identity.
To learn more about our content creation practices, visit our Editorial Process page .
Source List
AEDIT uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons Gender Confirmation Surgeries plasticsurgery.org
- Karel E Y Claes Chest Surgery for Transgender and Gender Nonconforming Individuals PubMed.gov ; 2018-07-02
Related Procedures

MTF Gender Confirmation Solutions

MTF Gender Confirmation: Facial Feminization

Adam’s Apple Reduction

MTF Gender Confirmation: Transfeminine Top & Bottom Surgeries
View all procedures
Learn More About MTF Gender Confirmation: Genital Construction in The AEDITION

Gender Transitioning And Skincare: Taking Care Of Your Changing Face
Side effects of hormone therapy often show up on the skin in the form of acne, pigmentation, and uneven skin texture. Here’s what you need to know about the most common skin concerns and treatment options.

A Guide To Non-Surgical Facial Feminization
Facial feminization procedures have been gaining popularity among men hoping to look more approachable or transition to female as well as among women hoping to have a more feminine appearance.

Finding The Right Plastic Surgeon, Dermatologist, Or Cosmetic Dentist
When considering a cosmetic procedure, it is so important to find the right doctor for you.
Discover more articles

‘Try on’ aesthetic procedures and instantly visualize possible results with AEDIT and our patented 3D aesthetic simulator.
Find Top Aesthetic Providers Near You
Providers by locations.
- Alpharetta, GA Providers
- Cockeysville, MD Providers
- Fall River, MA Providers
- Glenview, IL Providers
- Lone Tree, CO Providers
- Metairie, LA Providers
- Minneapolis, MN Providers
- More Locations
- New Haven, CT Providers
- Pasadena, CA Providers
- Scottsdale, AZ Providers
- Southfield, MI Providers
- Springdale, AR Providers
- Tampa, FL Providers
- Washington, DC Providers
Providers by Specialties
- Cosmetic Dentistry Providers
- Cosmetic Dermatology Providers
- Cosmetic Surgery Providers
- Dermatologic Surgery Providers
- Dermatology Providers
- Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Providers
- General Surgery Providers
- Hair Restoration Surgery Providers
- Head and Neck Surgery Providers
- Medspa Providers
- More Procedures
- Oculoplastic Surgery Providers
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Providers
- Vaginal Rejuvenation Providers
Providers by Procedures
- Acne Scar Treatment Providers
- Acne Treatment Providers
- Birthmark Removal Providers
- Blepharoplasty Providers
- Botox Providers
- Brow Lift Providers
- Buccal Fat Removal (Cheek Reduction) Providers
- Cheek Augmentation (Cheek Implants) Providers
- Cheek Surgery Providers
- Chemical Peels Providers
- Chin Surgery (Mentoplasty) Providers
- Dental Treatments Providers
- Dermabrasion Treatment Providers
- Dermal Fillers & Injectables Providers
- More Specialties

A Pioneering Approach to Gender Affirming Surgery From a World Leader in the Field
Miroslav Djordjevic, MD, PhD, an internationally renowned surgeon and a leading authority on surgery for transgender individuals, is developing a procedure to match two patients undergoing transgender surgery—one male-to-female, the other female-to-male—and transfer the genitalia between these live donors in a one-stage procedure instead of discarding them as is done now.
For years, the main challenge associated with sex reassignment surgery (SRS) has been the ability to provide patients with genitalia that is not only fully functional but also aesthetically acceptable. Miroslav Djordjevic, MD, PhD , an internationally renowned surgeon and a leading authority on surgery for transgender individuals, believes he has the answer.
His idea is matching two patients undergoing transgender surgery—one male-to-female, the other female-to-male—and transferring the genitalia between these live donors in a one-stage procedure instead of discarding them as is done now.
“This will result in a huge improvement over what we currently offer patients,” says Dr. Djordjevic, who joined Mount Sinai Health System in June 2019 as a Professor of Urology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and a urogenital reconstructive surgeon at the Mount Sinai Center for Transgender Medicine and Surgery . “We are striving to find a way to use all genital organs that are planned for removal in transition surgery to improve the lives of others who request this surgery and enable them to lead a normal life.”
Dr. Djordjevic says he is ready to proceed with transplantation now that he has developed the necessary special surgical techniques.
His confidence in this new approach is the result of nearly three decades of expertise and innovation in SRS and urogenital reconstructive surgery, which includes 600 male-to-female vaginoplasties, 900 female-to-male metoidioplasties, 300 female-to-male phalloplasties, and the co-development of a penile disassembly technique for epispadias repair. He also performed his first uterus transplant in 2017 and the second-ever testicular transplant in December 2019 at the Belgrade Center for Genital Reconstructive Surgery. Dr. Djordjevic is also a Professor of Urology and Surgery at the School of Medicine at the University of Belgrade in Serbia.
“Through the procedures I have done, I have demonstrated to the world that it is possible to successfully perform uterine and penile transplantation,” says Dr. Djordjevic, who joined Mount Sinai from the Belgrade Center for Genital Reconstructive Surgery in Serbia, where he was one of the few urologists in the world whose scope of expertise encompassed treatment of all anomalies of the genital system regardless of sex or age.
Dr. Djordjevic joined Mount Sinai to develop his procedures, which would include finding the right pairing of donor and candidate and leading surgeons in performing concurrent transplant surgeries.
Although there have been five successful penile transplantations performed since the introduction of the procedure in 2006, Dr. Djordjevic notes that these cases involved trauma or removal of the penis due to oncological reasons. In all cases, patients had retained the corpora cavernosa and some degree of tissue, which facilitated transplantation.
His approach is novel in that it will not only involve transplantation of the entire penis with the corpora cavernosa and their crura but also determining the best position for fixation. He also expects to transplant a penis from a male to a female body.
“We are striving to find a way to use all genital organs that are planned for removal in transition surgery to improve the lives of others who request this surgery and enable them to lead a normal life.” -Miroslav Djordjevic, MD, PhD
“This is a far more complex procedure,” he explains. “I am continuing to refine my technique through cadaveric and micrometric study, and I plan to publish papers that detail the approach so that other surgeons can offer it to their patients.” For example, he plans to publish a cadaveric study in 2021 on penile transplantation.
If his technique proves successful, Dr. Djordjevic believes it will offer considerable advantages over existing modalities for creating male genitals, such as metoidioplasty or a full phalloplasty involving musculocutaneous latissimus dorsi (MLD). For one, penile transplantation with the corpora cavernosa would result in improved sexual function and sensation, and it would reduce the 50 percent risk of complications among patients who have undergone creation of the urethra from oral mucosa or surrounding material.
“Current surgical treatments do not enable us to provide a urethra with surrounding spongiosa as is present in normal penile anatomy,” Dr. Djordjevic says. “A penile transplant would enable the usage of existing urethra and corpora cavernosa, which promises an almost ideal solution for patients looking for male genitalia because there is a good channel for voiding and good erectile tissue for normal sexual function.”
Dr. Djordjevic says advances in therapeutics could address the risks involved in transplantation of reproductive organs, specifically the effects of postoperative immunosuppressant therapy among patients. But he has also developed strategies for mitigating risk in the meantime.
For example, he notes that the first successful organ transplantation was made possible by the fact that the patients involved were monozygotic twins. The testicular transplant he performed also involved monozygotic twins, and no immunosuppressive therapy was required.
Three decades of experience
male-to-female vaginoplasties performed
female-to-male metoidioplasties performed
female-to-male phalloplasties performed
“What I will be looking for is a possible genetic match between two candidates that would minimize the need to administer immunosuppressants, or a candidate who has undergone transplant surgery and is doing well on immunosuppressant therapy because the risk of rejection will be much lower,” he says.
To facilitate identification of candidates who match these criteria, Dr. Djordjevic envisions a worldwide network or registry of patients seeking SRS. In the meantime, he continues to develop his technique, optimistic that transplantation of genitalia will eventually become standard of care in the same way that hand and face transplants are becoming routine.
“Ultimately, I would like to see us reach the point where a patient is able to conceive and deliver a baby after transplantation of a uterus and ovaries, or has a functioning, anatomically acceptable penis with normal erection and voiding,” he says. “By pioneering these procedures, we are one step closer to enabling people to live the lives they want to live.”

Miroslav Djordjevic, MD, PhD
Professor of Urology and a urogenital reconstructive surgeon at the Mount Sinai Center for Transgender Medicine and Surgery
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
Male-to-Female Gender-Affirming Surgery: 20-Year Review of Technique and Surgical Results
Gabriel veber moisés da silva.
1 Serviço de Urologia, Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, Brazil
Maria Inês Rodrigues Lobato
2 Serviço de Psiquiatria, Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, Brazil
Dhiordan Cardoso Silva
Karine schwarz, anna martha vaitses fontanari, angelo brandelli costa.
3 Serviço de Psiquiatria, Pontifical Catholic University of Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil
Patric Machado Tavares
Antonio rebello horta gorgen, renan desimon cabral, tiago elias rosito, associated data.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Purpose: Gender dysphoria (GD) is an incompatibility between biological sex and personal gender identity; individuals harbor an unalterable conviction that they were born in the wrong body, which causes personal suffering. In this context, surgery is imperative to achieve a successful gender transition and plays a key role in alleviating the associated psychological discomfort. In the current study, a retrospective cohort, we report the 20-years outcomes of the gender-affirming surgery performed at a single Brazilian university center, examining demographic data, intra and postoperative complications. During this period, 214 patients underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty.
Results: Results demonstrate that the average age at the time of surgery was 32.2 years (range, 18–61 years); the average of operative time was 3.3 h (range 2–5 h); the average duration of hormone therapy before surgery was 12 years (range 1–39). The most commons minor postoperative complications were granulation tissue (20.5 percent) and introital stricture of the neovagina (15.4 percent) and the major complications included urethral meatus stenosis (20.5 percent) and hematoma/excessive bleeding (8.9 percent). A total of 36 patients (16.8 percent) underwent some form of reoperation. One hundred eighty-one (85 percent) patients in our series were able to have regular sexual intercourse, and no individual regretted having undergone GAS.
Conclusions: Findings confirm that it is a safety procedure, with a low incidence of serious complications. Otherwise, in our series, there were a high level of functionality of the neovagina, as well as subjective personal satisfaction.
Introduction
Transsexualism (ICD-10) or Gender Dysphoria (GD) (DSM-5) is characterized by intense and persistent cross-gender identification which influences several aspects of behavior ( 1 ). The terms describe a situation where an individual's gender identity differs from external sexual anatomy at birth ( 1 ). Gender identity-affirming care, for those who desire, can include hormone therapy and affirming surgeries, as well as other procedures such as hair removal or speech therapy ( 1 ).
Since 1998, the Gender Identity Program (PROTIG) of the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA), Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil has provided public assistance to transsexual people, is the first one in Brazil and one of the pioneers in South America. Our program offers psychosocial support, health care, and guidance to families, and refers individuals for gender-affirming surgery (GAS) when indicated. To be eligible for this surgery, transsexual individuals must have been adherent to multidisciplinary follow-up for at least 2 years, have a minimum age of 21 years (required for surgical procedures of this nature), have a positive psychiatric or psychological report, and have a diagnosis of GD.
Gender-affirming surgery (GAS) is increasingly recognized as a therapeutic intervention and a medical necessity, with growing societal acceptance ( 2 ). At our institution, we perform the classic penile inversion vaginoplasty (PIV), with an inverted penis skin flap used as the lining for the neovagina. Studies have demonstrated that GAS for the management of GD can promote improvements in mental health and social relationships for these patients ( 2 – 5 ). It is therefore imperative to understand and establish best practice techniques for this patient population ( 2 ). Although there are several studies reporting the safety and efficacy of gender-affirming surgery by penile inversion vaginoplasty, we present the largest South-American cohort to date, examining demographic data, intra and postoperative complications.
Patients and Methods
Subjects and study setup.
This is a retrospective cohort study of Brazilian transgender women who underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty between January of 2000 and March of 2020 at the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, Brazil. The study was approved by our institutional medical and research ethics committee.
At our institution, gender-affirming surgery is indicated for transgender women who are under assistance by our program for transsexual individuals. All transsexual women included in this study had at least 2 years of experience as a woman and met WPATH standards for GAS ( 1 ). Patients were submitted to biweekly group meetings and monthly individual therapy.
Between January of 2000 and March of 2020, a total of 214 patients underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty. The surgical procedures were performed by two separate staff members, mostly assisted by residents. A retrospective chart review was conducted recording patient demographics, intraoperative and postoperative complications, reoperations, and secondary surgical procedures. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Hormonal Therapy
The goal of feminizing hormone therapy is the development of female secondary sex characteristics, and suppression/minimization of male secondary sex characteristics.
Our general therapy approach is to combine an estrogen with an androgen blocker. The usual estrogen is the oral preparation of estradiol (17-beta estradiol), starting at a dose of 2 mg/day until the maximum dosage of 8 mg/day. The preferred androgen blocker is spironolactone at a dose of 200 mg twice a day.
Operative Technique
At our institution, we perform the classic penile inversion vaginoplasty, with an inverted penis skin flap used as the lining for the neovagina. For more details, we have previously published our technique with a step-by-step procedure video ( 6 ). All individuals underwent intestinal cleansing the evening before the surgery. A first-generation cephalosporin was used as preoperative prophylaxis. The procedure was performed with the patient in a dorsal lithotomy position. A Foley catheter was placed for bladder catheterization. A inverted-V incision was made 4 cm above the anus and a flap was created. A neovaginal cavity was created between the prostate and the rectum with blunt dissection, in the Denonvilliers space, until the peritoneal fold, usually measuring 12 cm in extension and 6 cm in width. The incision was then extended vertically to expose the testicles and the spermatic cords, which were removed at the level of the external inguinal rings. A circumferential subcoronal incision was made ( Figure 1 ), the penis was de-gloved and a skin flap was created, with the de-gloved penis being passed through the scrotal opening ( Figure 2 ). The dorsal part of the glans and its neurovascular bundle were bluntly dissected away from the penile shaft ( Figure 3 ) as well as the urethra, which included a portion of the bulbospongious muscle ( Figure 4 ). The corpora cavernosa was excised up to their attachments at the symphysis pubis and ligated. The neoclitoris was shaped and positioned in the midline at the level of the symphysis pubis and sutured using interrupted 5-0 absorbable suture. The corpus spongiosum was reduced and the urethra was shortened, spatulated, and placed 1 cm below the neoclitoris in the midline and sutured using interrupted 4-0 absorbable suture. The penile skin flap was inverted and pulled into the neovaginal cavity to become its walls ( Figure 5 ). The excess of skin was then removed, and the subcutaneous tissue and the skin were closed using continuous 3-0 non-absorbable suture ( Figure 6 ). A neo mons pubis was created using a 0 absorbable suture between the skin and the pubic bone. The skin flap was fixed to the pubic bone using a 0 absorbable suture. A gauze impregnated with Vaseline and antibiotic ointment was left inside the neovagina, and a customized compressive bandage was applied ( Figure 7 —shows the final appearance after the completion of the procedures).

The initial circumferential subcoronal incision.

The de-gloved penis being passed through the scrotal opening.

The dorsal part of the glans and its neurovascular bundle dissected away from the penile shaft.

The urethra dissected including a portion of the bulbospongious muscle. The grey arrow shows the penile shaft and the white arrow shows the dissected urethra.

The inverted penile skin flap.

The neoclitoris and the urethra sutured in the midline and the neovaginal cavity.

The final appearance after the completion of the procedures.
Postoperative Care and Follow-Up
The patients were usually discharged within 2 days after surgery with the Foley catheter and vaginal gauze packing in place, which were removed after 7 days in an ambulatorial attendance.
Our vaginal dilation protocol starts seven days after surgery: a kit of 6 silicone dilators with progressive diameter (1.1–4 cm) and length (6.5–14.5 cm) is used; dilation is done progressively from the smallest dilator; each size should be kept in place for 5 min until the largest possible size, which is kept for 3 h during the day and during the night (sleep), if possible. The process is performed daily for the first 3 months and continued until the patient has regular sexual intercourse.
The follow-up visits were performed 7 days, 1, 2, 3, 6, and 12 months after surgery ( Figure 8 ), and included physical examination and a quality-of-life questionnaire.

Appearance after 1 month of the procedure.
Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was conducted using Statistical Product and Service Solutions Version 18.0 (SPSS). Outcome measures were intra-operative and postoperative complications, re-operations. Descriptive statistics were used to evaluate the study outcomes. Mean values and standard deviations or median values and ranges are presented as continuous variables. Frequencies and percentages are reported for dichotomous and ordinal variables.
Patient Demographics
During the period of the study, 214 patients underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty, performed by two staff surgeons, mostly assisted by residents ( Table 1 ). The average age at the time of surgery was 32.2 years (range 18–61 years). There was no significant increase or decrease in the ages of patients who underwent SRS over the study period (Fisher's exact test: P = 0.065; chi-square test: X 2 = 5.15; GL = 6; P = 0.525). The average of operative time was 3.3 h (range 2–5 h). The average duration of hormone therapy before surgery was 12 years (range 1–39). The majority of patients were white (88.3 percent). The most prevalent patient comorbidities were history of tobacco use (15 percent), human immunodeficiency virus infection (13 percent) and hypertension (10.7 percent). Other comorbidities are listed in Table 1 .
Patient demographics.
HIV, human immunodeficiency virus .
Multidisciplinary follow-up was comprised of 93.45% of patients following up with a urologist and 59.06% of patients continuing psychiatric follow-up, median follow-up time of 16 and 9.3 months after surgery, respectively.
Postoperative Results
The complications were classified according to the Clavien-Dindo score ( Table 2 ). The most common minor postoperative complications (Grade I) were granulation tissue (20.5 percent), introital stricture of the neovagina (15.4 percent) and wound dehiscence (12.6 percent). The major complications (Grade III-IV) included urethral stenosis (20.5 percent), urethral fistula (1.9 percent), intraoperative rectal injury (1.9 percent), necrosis (primarily along the wound edges) (1.4 percent), and rectovaginal fistula (0.9 percent). A total of 17 patients required blood transfusion (7.9 percent).
Complications after penile inversion vaginoplasty.
A total of 36 patients (16.8 percent) underwent some form of reoperation.
One hundred eighty-one (85 percent) patients in our series were able to have regular sexual vaginal intercourse, and no individual regretted having undergone GAS.
Penile inversion vaginoplasty is the gold-standard in gender-affirming surgery. It has good functional outcomes, and studies have demonstrated adequate vaginal depths ( 3 ). It is recognized not only as a cosmetic procedure, but as a therapeutic intervention and a medical necessity ( 2 ). We present the largest South-American cohort to date, examining demographic data, intra and postoperative complications.
The mean age of transsexual women who underwent GAS in our study was 32.2 years (range 18–61 years), which is lower than the mean age of patients in studies found in the literature. Two studies indicated that the mean ages of patients at time of GAS were 36.7 years and 41 years, respectively ( 4 , 5 ). Another study reported a mean age at time of GAS of 36 years and found there was a significant decrease in age at the time of GAS from 41 years in 1994 to 35 years in 2015 ( 7 ). According to the authors, this decrease in age is associated with greater tolerance and societal approval regarding individuals with GD ( 7 ).
There was no grade IV or grade V complications. Excessive bleeding noticed postoperatively occurred in 19 patients (8.9 percent) and blood transfusion was required in 17 cases (7.9 percent); all patients who required blood transfusions were operated until July 2011, and the reason for this rate of blood transfusion was not identified.
The most common intraoperative complication was rectal injury, occurring in 4 patients (1.9 percent); in all patients the lesion was promptly identified and corrected in 2 layers absorbable sutures. In 2 of these patients, a rectovaginal fistula became evident, requiring fistulectomy and colonic transit deviation. This is consistent with current literature, in which rectal injury is reported in 0.4–4.5 percent of patients ( 4 , 5 , 8 – 13 ). Goddard et al. suggested carefully checking for enterotomy after prostate and bladder mobilization by digital rectal examination ( 4 ). Gaither et al. ( 14 ) commented that careful dissection that closely follows the urethra along its track from the central tendon of the perineum up through the lower pole of the prostate is critical and only blunt dissection is encouraged after Denonvilliers' fascia is reached. Alternatively, a robotic-assisted approach to penile inversion vaginoplasty may aid in minimizing these complications. The proposed advantages of a robotic-assisted vaginoplasty include safer dissection to minimize the risk of rectal injury and better proximal vaginal fixation. Dy et al. ( 15 ) has had no rectal injuries or fistulae to date in his series of 15 patients, with a mean follow-up of 12 months.
In our series, we observed 44 cases (20.5 percent) of urethral meatus strictures. We credit this complication to the technique used in the initial 5 years of our experience, in which the urethra was shortened and sutured in a circular fashion without spatulation. All cases were treated with meatal dilatation and 11 patients required surgical correction, being performed a Y-V plastic reconstruction of the urethral meatus. In the literature, meatal strictures are relatively rare in male-to-female (MtF) GAS due to the spatulation of the urethra and a simple anastomosis to the external genitalia. Recent systematic reviews show an incidence of five percent in this complication ( 16 , 17 ). Other studies report a wide incidence of meatal stenosis ranging from 1.1 to 39.8 percent ( 4 , 8 , 11 ).
Neovagina introital stricture was observed in 33 patients (15.4 percent) in our study and impedes the possibility of neovaginal penetration and/or adversely affects sexual life quality. In the literature, the reported incidence of introital stenosis range from 6.7 to 14.5 percent ( 4 , 5 , 8 , 9 , 11 – 13 ). According to Hadj-Moussa et al. ( 18 ) a regimen of postoperative prophylactic dilation is crucial to minimize the development of this outcome. At our institution, our protocol for vaginal dilation started seven days after surgery and was performed three to four times a day during the first 3 months and was continued until the individual had regular sexual intercourse. We treated stenosis initially with dilation. In case of no response, we propose a surgical revision with diamond-shaped introitoplasty with relaxing incisions. In recalcitrant cases, we proposed to the patient a secondary vaginoplasty using a full-thickness skin graft of the lower abdomen.
One hundred eighty-one (85 percent) patients were classified as having a “functional vagina,” characterized as the capacity to maintain satisfactory sexual vaginal intercourse, since the mean neovaginal depth was not measured. In a review article, the mean neovaginal depth ranged from 10 to 13.5 cm, with the shallowest neovagina depth at 2.5 cm and the deepest at 18 cm ( 17 ). According to Salim et al. ( 19 ), in terms of postoperative functional outcomes after penile inversion vaginoplasty, a mean percentage of 75 percent (range from 33 to 87 percent) patients were having vaginal intercourse. Hess et al. found that 91.4% of patients who responded to a questionnaire were very satisfied (34.4%), satisfied (37.6%), or mostly satisfied (19.4%) with their sexual function after penile inversion vaginoplasty ( 20 ).
Poor cosmetic appearance of the vulva is common. Amend et al. reported that the most common reason for reoperation was cosmetic correction in the form of mons pubis and mucosa reduction in 50% of patients ( 16 ). We had no patient regrets about performing GAS, although 36 patients (16.8 percent) were reoperated due to cosmetic issues. Gaither et al. propose in order to minimize scarring to use a one-stage surgical approach and the lateralization of surgical scars to the groin ( 14 ). Frequently, cosmetic issues outcomes are often patient driven and preoperative patient education is necessary ( 14 ).
Analyzing the quality of life, in 2016, our health care group (PROTIG) published a study assessing quality of life before and after gender-affirming surgery in 47 patients using the diagnostic tool 100-item WHO Quality of Life Assessment (WHOQOL-100) ( 21 ). The authors found that GAS promotes the improvement of psychological aspects and social relations. However, even 1 year after GAS, MtF persons continue to report problems in physical and difficulty in recovering their independence. In a systematic review and meta-analysis of QOL and psychosocial outcomes in transsexual people, researchers verified that sex reassignment with hormonal interventions more likely corrects gender dysphoria, psychological functioning and comorbidities, sexual function, and overall QOL compared with sex reassignment without hormonal interventions, although there is a low level of evidence for this ( 22 ). Recently, Castellano et al. assessed QOL in 60 Italian transsexuals (46 transwomen and 14 transmen) at least 2 years after SRS using the WHOQOL-100 (general QOL score and quality of sexual life and quality of body image scores) to focus on the effects of hormonal therapy. Overall satisfaction improved after SRS, and QOL was similar to the controls ( 23 ). Bartolucci et al. evaluated the perception of quality of sexual life using four questions evaluating the sexual facet in individuals with gender dysphoria before SRS and the possible factors associated with this perception. The study showed that approximately half the subjects with gender dysphoria perceived their sexual life as “poor/dissatisfied” or “very poor/very dissatisfied” before SRS ( 24 ).
Our study has some limitations. The total number of operated patients is restricted within the long follow-up period. This is due to a limitation in our health system, which allows only 1 sexual reassignment surgery to be performed per month at our institution. Neovagin depth measurement was not performed routinely in the follow-up of operated patients.
Conclusions
The definitive treatment for patients with gender dysphoria is gender-affirming surgery. Our series demonstrates that GAS is a feasible surgery with low rates of serious complications. We emphasize the high level of functionality of the vagina after the procedure, as well as subjective personal satisfaction. Complications, especially minor ones, are probably underestimated due to the nature of the study, and since this is a surgical population, the results may not be generalizable for all transgender MTF individuals.
Data Availability Statement
Ethics statement.
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
GM: conception and design, data acquisition, data analysis, interpretation, drafting the manuscript, review of the literature, critical revision of the manuscript and factual content, and statistical analysis. ML and TR: conception and design, data interpretation, drafting the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript and factual content, and statistical analysis. DS, KS, AF, AC, PT, AG, and RC: conception and design, data acquisition and data analysis, interpretation, drafting the manuscript, and review of the literature. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Funding. This study was supported by the Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa e Eventos (FIPE - Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa e Eventos) of Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre.
How Gender Reassignment Surgery Works (Infographic)
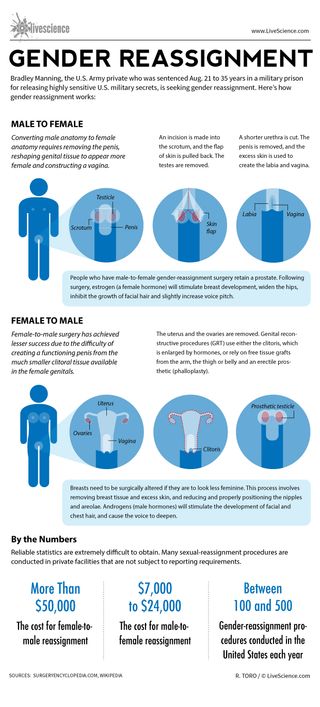
Bradley Manning, the U.S. Army private who was sentenced Aug. 21 to 35 years in a military prison for releasing highly sensitive U.S. military secrets, is seeking gender reassignment. Here’s how gender reassignment works:
Converting male anatomy to female anatomy requires removing the penis, reshaping genital tissue to appear more female and constructing a vagina.
An incision is made into the scrotum, and the flap of skin is pulled back. The testes are removed.
A shorter urethra is cut. The penis is removed, and the excess skin is used to create the labia and vagina.
People who have male-to-female gender-reassignment surgery retain a prostate. Following surgery, estrogen (a female hormone) will stimulate breast development, widen the hips, inhibit the growth of facial hair and slightly increase voice pitch.
Female-to-male surgery has achieved lesser success due to the difficulty of creating a functioning penis from the much smaller clitoral tissue available in the female genitals.
The uterus and the ovaries are removed. Genital reconstructive procedures (GRT) use either the clitoris, which is enlarged by hormones, or rely on free tissue grafts from the arm, the thigh or belly and an erectile prosthetic (phalloplasty).
Breasts need to be surgically altered if they are to look less feminine. This process involves removing breast tissue and excess skin, and reducing and properly positioning the nipples and areolae. Androgens (male hormones) will stimulate the development of facial and chest hair, and cause the voice to deepen.
Reliable statistics are extremely difficult to obtain. Many sexual-reassignment procedures are conducted in private facilities that are not subject to reporting requirements.
The cost for female-to-male reassignment can be more than $50,000. The cost for male-to-female reassignment can be $7,000 to $24,000.
Between 100 to 500 gender-reassignment procedures are conducted in the United States each year.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Man's years of premature ejaculation had a rare cause
Viagra alternatives? Study of mouse erections hints at new ways to treat erectile dysfunction
Pet fox with 'deep relationship with the hunter-gatherer society' buried 1,500 years ago in Argentina
Most Popular
By Anna Gora December 27, 2023
By Anna Gora December 26, 2023
By Anna Gora December 25, 2023
By Emily Cooke December 23, 2023
By Victoria Atkinson December 22, 2023
By Anna Gora December 16, 2023
By Anna Gora December 15, 2023
By Anna Gora November 09, 2023
By Donavyn Coffey November 06, 2023
By Anna Gora October 31, 2023
By Anna Gora October 26, 2023
- 2 How and where to watch the April 8 solar eclipse online for free
- 3 NASA engineers discover why Voyager 1 is sending a stream of gibberish from outside our solar system
- 4 Giant coyote killed in southern Michigan turns out to be a gray wolf — despite the species vanishing from region 100 years ago
- 5 When is the next total solar eclipse after 2024 in North America?
- 2 Giant 'toe biter' water bugs discovered in Cyprus for the 1st time
- 3 Watch live! The total solar eclipse has begun over North America.
- 4 8,200-year-old campsite of 'Paleo-Archaic' peoples discovered on US Air Force base in New Mexico
+44 204 513 2244
[email protected]

About MtF Gender Confirmation Surgery
Home » About Gender Reassignment Surgery
MtF Gender Reassignment Surgery FAQ’s
How much does mtf gender reassignment surgery cost, what happens at the consultation for mtf gender reassignment surgery, how do i prepare for my surgery, what happens on the day of surgery, what aftercare will be provided for me, what happens if there is a complication.
- The patient ignored the post-operative instructions.
- The patient failed to attend for the agreed postoperative examinations.
- The patient sustained physical injury out of our control.
- FFS – Facial Feminisation Surgery
- Hairline Lowering Foreheadplasty
- Brow Contouring
- Rhinoplasty
- Cheek Augmentation
- Chin Reduction / Shaping surgery
- Jaw Contouring Surgery
- Upper Lip Lift
- Lip Enhancement / Augmentation
- Thyroid cartilage reduction / Tracheal Shave
- Breast Augmentation
- Buttock Enhancement
- Body – Silhouette Shaping
- Revision genital surgery
- Revision neovaginal surgery
- Scar revision surgery
- Hormone Therapy
- Speech and communication therapy
- Psychological assessment, counselling, psychotherapy

Shane’s Top Surgery Testimonial
Do I really need Facial Feminisation Surgery?

Diary Meets… Gaynor Mary Warren-Wright

LGBTQ+ History Month 2022: Defining History

How does dilation work after Gender Confirmation Surgery?

Finding Gaynor: an uplifting story of embracing one’s true self

@londontransclinic
Londontransclinic.

Wednesday, April 10, 2024
Military doctor: transgender surgery uptick paid for with us tax dollars.
- by: Tracy Beanz

Read our latest news on any of these social networks!
Get the latest news delivered daily!
We will send you breaking news right to your inbox
Recent Articles
Hong Kong Amends Its Surgery Requirements to Change Gender Markers on IDs

H ong Kong no longer requires transgender people to undergo full gender-affirming surgery to change their legal gender markers in their IDs, more than a year after the Chinese enclave’s top court called the requirement unconstitutional.
The government announced the change on Wednesday, “having prudently considered the objective of the policy, relevant legal and medical advice, as well as drawing reference from the relevant practices overseas.”
Under the new rules, Hong Kong residents who have not undergone full sex reassignment surgery [SRS] who want to have their gender marker on their ID changed still must have completed select surgical treatment to modify their sexual characteristics—removal of the breasts for transgender men, removal of the penis and testes for transgender women—along with medical documentation. Previous guidelines required the removal of the uterus and ovaries or the construction of a penis or “some form” of it for female-to-male transition, and the removal of the penis and testes and the construction of a vagina for male-to-female transition.
“We are still concerned about the heavy emphasis on sex reassignment surgeries being a requirement,” Wong Hiu-chong, the lawyer for transgender activist Henry Tse , whose case led to the policy change, told TIME. “SRS can be life threatening.”
Those who wish to change their gender markers must also statutorily declare that they have gender dysphoria—the medical term for the psychological distress a person feels when their gender identity does not match with their assigned sex at birth—and have lived as the opposite sex for at least two years before their application. They must also show proof of receiving hormonal treatment throughout the previous two years, and will be subjected to random blood tests to check their hormonal profile.
“Our clients have waited a very long time for such an unconstitutional policy to be revised, and for them, the wait has been painful,” Wong said in a statement. She also questioned the need for blood tests, calling this requirement, among others that remain for gender marker changes, “potentially discriminatory” as it does not apply to other Hong Kong ID card holders.
A government spokesperson clarified in the announcement that the gender marker change will only apply to the Hong Kong Identity Card and that “the sex entry on a Hong Kong identity card does not represent the holder’s sex as a matter of law. It does not affect any other policies of the Government or the handling of any other gender-related matters under the law in Hong Kong or relevant legal procedures.”
The policy change comes years after Tse filed a case in 2017 to question the full gender-affirming surgery requirement. Despite the city’s Court of Final Appeal issuing a ruling deeming the requirement unconstitutional in February 2023, implementation of the ruling was long-delayed, which Tse also challenged . The ruling said “such surgical procedures are at the most invasive end of the treatment spectrum” and that “full SRS is not medically required by many transgender persons whose gender dysphoria has been effectively treated.”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- Exclusive: Google Workers Revolt Over $1.2 Billion Contract With Israel
- Stop Looking for Your Forever Home
- Jane Fonda Champions Climate Action for Every Generation
- Hormonal Birth Control Doesn’t Deserve Its Bad Reputation
- The Sympathizer Counters 50 Years of Hollywood Vietnam War Narratives
- Essay: The Relentless Cost of Chronic Diseases
- The Best TV Shows to Watch on Peacock
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
You May Also Like
Court to decide if Ontario must pay for surgery to make vagina if patient also wants to keep penis
A non-binary Ontario resident is locked in a legal battle over public funding for surgery to create a vagina while leaving the penis intact
You can save this article by registering for free here . Or sign-in if you have an account.
Article content
In a lengthy legal battle that could lead to more requests for individually customized and unorthodox gender-affirming surgeries, an Ontario resident is seeking publicly funded surgery to construct a vagina while preserving the penis.
The case, now before the courts, reflects a small but growing demand for niche surgeries for people who identify as non-binary, meaning neither exclusively female nor exclusively male.
Enjoy the latest local, national and international news.
- Exclusive articles by Conrad Black, Barbara Kay, Rex Murphy and others. Plus, special edition NP Platformed and First Reading newsletters and virtual events.
- Unlimited online access to National Post and 15 news sites with one account.
- National Post ePaper, an electronic replica of the print edition to view on any device, share and comment on.
- Daily puzzles including the New York Times Crossword.
- Support local journalism.
Create an account or sign in to continue with your reading experience.
- Access articles from across Canada with one account.
- Share your thoughts and join the conversation in the comments.
- Enjoy additional articles per month.
- Get email updates from your favourite authors.
Don't have an account? Create Account
To critics, the procedures are risky experiments that illustrate “how far off the rails” gender-affirming medicine has gone and the excesses of “consumer-driven gender embodiment.”
“Our public health-care system is at the breaking point and really needs to focus on procedures that are medically necessary,” Pamela Buffone, founder of the parents’ group Canadian Gender Report, said in an email to the National Post.
“Is this type of surgery health care? The patient will not be physically healthier because of the operation, which is likely to result in complications and the need for corrective surgeries and further demands on the health system.”
LGBTQ rights groups say such surgeries can profoundly improve a person’s quality of life and reduce the distress and deep sense of unease from gender dysphoria. Health-care providers shouldn’t make assumptions about what care may be medically necessary, Egale Canada argued in a written submission to the court.
“Ultimately OHIP’s interpretation (of a vaginoplasty) is exclusionary and discriminates against nonbinary people on the basis of their gender identity,” Egale said. If there is any ambiguity in what should be publicly covered, it should be resolved in favour of the claimant, they said.
As National Post columnist Jamie Sarkonak first reported in September , the case involves 33-year-old K.S., as she is identified in court documents, who was born male but who identifies as female dominant and uses a feminine name.
Ontario’s Health Insurance Plan (OHIP) originally denied K.S.’s request in 2022 for funding for a penile sparing vaginoplasty, a procedure that isn’t available in Canada. The surgery was to be performed at the Crane Center for Transgender Surgery in Austin, Texas.
Is this type of surgery health care?
According to legal documents, K.S. argued that “to ignore ‘the other third’ of her and how she presents would be invalidating; she is ‘both,’ not exclusively one or the other but literally a mix.”
OHIP argued that, while it may be of medical benefit to K.S., a vaginoplasty without penectomy (removal of the penis) is considered an experimental procedure and isn’t listed as an insured service under its schedule of benefits.
K.S. complained to Ontario’s Health Services Appeal and Review Board, which overturned OHIP’s decision, ruling that a vaginoplasty is among the 11 external genital surgeries listed for public coverage, and that it shouldn’t inherently include a penectomy.
Get a dash of perspective along with the trending news of the day in a very readable format.
- There was an error, please provide a valid email address.
By signing up you consent to receive the above newsletter from Postmedia Network Inc.
A welcome email is on its way. If you don't see it, please check your junk folder.
The next issue of NP Posted will soon be in your inbox.
We encountered an issue signing you up. Please try again
OHIP, in turn, appealed the review board’s decision to Ontario’s Superior Court of Justice. The case was heard in late February. “We do not yet have a decision — it could still be months,” K.S.’s lawyer, John McIntyre, said in an email.
K.S., who has experienced gender dysphoria since a teen, doesn’t completely align with either the male or female genders, the appeal board heard. Her doctor, an Ottawa endocrinologist, supported K.S.’s request for a specific type of bottom surgery.
“It is very important for (K.S.) to have a vagina for her personal interpretation of her gender expression but she also wishes to maintain her penis,” the doctor wrote in a letter to OHIP supporting the request for prior funding approval. “(K.S.) is transfeminine but not completely on the ‘feminine” end of the spectrum (and) for this reason it’s important for her to have a vagina while maintaining a penis.”
K.S. argued that forcing a non-binary person to undergo binary surgery — male to female, or female to male — would only exacerbate her gender dysphoria and would be akin to an act of conversion therapy, which has been banned in Canada since 2022.
She also wishes to preserve her penis for sexual health reasons and out of concern the “urological rerouting” could create urinary incontinence problems, a recognized complication.
In its decision, the health services appeal tribunal referenced standards of care as set out by the influential World Professional Association for Transgender Health, or WPATH, which considers a penile sparing vaginoplasty a valid treatment option for non-binary people. The board said it adopted the trans care group’s logic that “gender diverse presentations may lead to individually customized surgical requests some may consider ‘non-standard.'”
The Ontario health ministry said it doesn’t comment on matters still before the courts.
K.S. declined to comment when contacted through her lawyer.
In a similar case reported last year by the Globe and Mail, OHIP initially denied coverage to a 41-year-old Ottawa public servant who identifies as transmasculine non-binary and who was seeking the surgical construction of a penis without the removal of the vagina and uterus.
Nathaniel Le May and his lawyers argued that phalloplasty, on its own, is listed as an insured service, and that OHIP was wrong in interpreting that it was only insured if also accompanied by a vaginectomy. The additional procedures, they also argued, amounted to coerced sterilization.
Two days before the case was set to be heard by the appeal board, OHIP reversed its decision and agreed to fund the surgery.
“My outcome is the same as K.S. We will both have a penis and a vagina,” Le May said in an email to the National Post.
“Why is it considered experimental in her case to have a vagina and a penis, but not in my case? Why did OHIP concede that it is an insured service for me but continue to fight that hers is not? OHIP is being inconsistent,” Le May said.
The Crane Center in Texas offers several non-binary surgical options. “We offer everything you could think of,” Dr. Curtis Crane, a plastic surgeon and reconstructive urologist with fellowship training in transgender surgery, said during a Facebook live Q&A session for patients three years ago. “I can’t think of a time that a patient has come up with a surgical request that I haven’t been able to fulfill.”
Hundreds of messages recently leaked from WPATH’s internal forum included discussions about an anticipated “wave” of requests for non-binary affirming surgeries such as mastectomies without nipples, “nullification” (removal of all external genitalia, just smooth skin) and phallus-preserving vaginoplasty — “non-standard” procedures resulting in bodies that one therapist said “either don’t exist in nature or represent the first of their kind and therefore probably have few examples of best practices.”
Crane argues that vaginoplasty without penectomy surgery is not experimental. “I probably do 10 or so a year; it’s not uncommon,” he said in an interview with National Post. Bodies with mixed genitalia “absolutely do exist in nature,” he added. “There are disorders of differentiation of sexual genitalia that will leave both parts.”
Techniques vary, but with the standard male-to-female vaginoplasty — penile inversion vaginoplasty — a vaginal canal is created and lined using penile tissue. “Next you would move on to surgically dissecting out the phallus, shortening the urethra and making a clitoris,” Crane said.
With penile preservation vaginoplasty, the vagina can be created using scrotal tissue or tissue from other parts of the body, like the abdomen or colon.
Crane said some patients seeking vaginoplasty get sexual gratification from their phallus and don’t want to have to sit to urinate.
“There are all kinds of reasons. I don’t say one reason is not a good enough reason. It’s the patient’s body,” he said. During the Facebook session, Crane said, “It’s kind of assault to make a patient remove an organ that they’re enjoying.”
But Dr. Yonah Krakowsky, a staff urologist at Women’s College Hospital in Toronto and medical lead of the hospital’s transition-related surgeries program, told the review board that phallus-sparing vaginoplasties are considered experimental by most surgeons, published reports on the “functional or psychological outcomes” are lacking and that the surgical technique used in the process is poorly understood.
Crane said he couldn’t recall, “off the top of my head,” the cost of a penile preserving vaginoplasty. When Sarkonak, the Post’s columnist, called the Texas clinic, she was told gender-affirming surgeries can range from US$10,000 to US$70,000, depending on what’s done.
“If someone just has an agenda to say, ‘no,’ (to public funding), you can never compete with that,” Crane said. “And unfortunately, that’s what it is the majority of the time: ‘I’m just gonna say no, because I don’t like this.’”
Others said it’s hard to justify the public coverage when Canadians across the country are facing lengthy wait lists for standard surgeries, and standard diagnostic tests.
“It’s hard to call this actual health care,” said Dr. Roy Eappen, a Montreal endocrinologist and senior fellow at Do No Harm, a medical and policy advocacy group. “There is no evidence that it improves anything physically, and the evidence that it helps mental health is not there either.”
“I can’t see the justification for paying. This is not something that really exists in nature and there is a very high complication rate for these kinds of surgeries,” Eappen said.
“WPATH wants to separate this all from any psychiatric diagnosis and call this ‘consumer driven.’ If that’s the case, then you can pay for it.”
While more people are identifying as non-binary, Crane said there are “plenty” of non-binary people who don’t want any surgery.
Eappen agreed. “I don’t know how many of them will want this kind of surgery. But I think this (case) would encourage them to ask. And I’m not sure we’re actually doing anyone a favour.”
National Post
Postmedia is committed to maintaining a lively but civil forum for discussion. Please keep comments relevant and respectful. Comments may take up to an hour to appear on the site. You will receive an email if there is a reply to your comment, an update to a thread you follow or if a user you follow comments. Visit our Community Guidelines for more information.
Telford testifies PMO saw errors in foreign interference intelligence; unaware of some allegations
Gen. rick hillier: ideology masking as leadership killed the canadian dream, pm's six-day indo-pacific trip cost $2m, including $200k in catering.

Air Canada Boeing 737 makes emergency landing in Idaho after warning light goes on
Montreal suburb passes non-confidence measure on federal liberals' israel stance, how to get rid of ants from your home, without hiring someone.
Cinnamon, ant traps and diatomaceous earth to the rescue
ANINE BING and Reebok just released a collab — and it's too good to miss
Iconic sport and activewear brand Reebok has teamed up with Los Angeles-based 'cool-girl' clothing company ANINE BING to create a retro-inspired collection that's 100 per cent covetable.
Advertisement 2 Story continues below This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Editor favourites: Our top finds this month
Products we couldn’t get enough of this March
Trying Puzzmo puzzles as a dedicated NYT Games user
Puzzmo is refining the newspaper game experience
Ride or relax in style with our favourite bike shorts
From functional fitness to mainstream fashion, add this multi-faceted garment to your collection
This website uses cookies to personalize your content (including ads), and allows us to analyze our traffic. Read more about cookies here . By continuing to use our site, you agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy .
You've reached the 20 article limit.
You can manage saved articles in your account.
and save up to 100 articles!
Looks like you've reached your saved article limit!
You can manage your saved articles in your account and clicking the X located at the bottom right of the article.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Gender-affirming surgery for male-to-female transgender women or transfeminine non-binary people describes a variety of surgical procedures that alter the body to provide physical traits more comfortable and affirming to an individual's gender identity and overall functioning.. Often used to refer to vaginoplasty, sex reassignment surgery can also more broadly refer to other gender-affirming ...
Breast augmentation is often performed as an outpatient procedure but some patients may require one night stay in the hospital. 1 of 7. See before and after photos of patients who have undergone gender-affirming surgeries at Cleveland Clinic, including breast augmentations, facial feminizations, mastectomies and vaginoplasty.
Breast Augmentation 101. MTF Breast Augmentation is a surgery procedure that transforms a masculine-looking chest into breasts that have a feminine shape and size. Using breast implants, MTF Breast Augmentation can provide a female breast contour when hormone replacement therapy alone has proved insufficient for breast development.
Overview. Feminizing surgery, also called gender-affirming surgery or gender-confirmation surgery, involves procedures that help better align the body with a person's gender identity. Feminizing surgery includes several options, such as top surgery to increase the size of the breasts. That procedure also is called breast augmentation.
Research consistently shows that people who choose gender affirmation surgery experience reduced gender incongruence and improved quality of life. Depending on the procedure, 94% to 100% of people report satisfaction with their surgery results. Gender-affirming surgery provides long-term mental health benefits, too.
Gender affirming surgery can be used to create a vulva and vagina. It involves removing the penis, testicles and scrotum. During a vaginoplasty procedure, tissue in the genital area is rearranged to create a vaginal canal (or opening) and vulva (external genitalia), including the labia. A version of vaginoplasty called vulvoplasty can create a ...
The cost of transitioning can often exceed $100,000 in the United States, depending upon the procedures needed. A typical genitoplasty alone averages about $18,000. Rhinoplasty, or a nose job, averaged $5,409 in 2019. Insurance Coverage for Sex Reassignment Surgery.
Purpose: Gender dysphoria (GD) is an incompatibility between biological sex and personal gender identity; individuals harbor an unalterable conviction that they were born in the wrong body, which causes personal suffering. In this context, surgery is imperative to achieve a successful gender transition and plays a key role in alleviating the associated psychological discomfort. In the current ...
Teamwork. The Transgender and Intersex Specialty Care Clinic (TISCC) provides integrated medical, psychosocial and surgical intervention to individuals with gender dysphoria or incongruence and to those with differences of sexual development, also called intersex. The team includes providers from various specialties including endocrinology ...
It is also known as sex reassignment surgery, gender confirmation surgery, and several other names. ... Dora Richter is the first known trans woman to undergo complete male-to-female genital surgery. She was one of several transgender people in the care of sexologist Magnus Hirschfeld at Berlin's Institute for Sexual Research. In 1922, Richter ...
Many major medical insurances in California, including CalOptima, cover for vaginoplasty as part of gender confirmation surgery. If you have more questions or would like to schedule a free consultation with Dr. Tran, please contact us via our website, Tran Plastic mobile app or call us today at 714-839-8000. References.
Dr. Toby Meltzer. Dr. Meltzer is a plastic and reconstructive surgeon who is widely recognized as one of the leading surgeons in the field of Gender Reassignment Surgery. Dr. Meltzer has been performing MTF Surgery since 1993 and has completed over 4000 gender affirming surgeries.
Sex and sexual health tips for transgender women after gender-affirming surgery. Sex after surgery. Achieving orgasm. Libido. Vaginal depth and lubrication. Aftercare. Contraceptions and STIs ...
The Gender Confirmation Center is pleased to announce the addition of Dr. Daniel Jacobs to the practice. The expansion is the result of a thorough search for an exceptional plastic surgeon to join the practice and improve access to Top Surgery by decreasing wait times. Crane Center Launches Texas Hormone Clinic.
Male-to-female gender reassignment surgery (MTF GRS) is a complex and irreversible genital surgery for male transsexual who is diagnosed with gender identity disorder and has a strong desire to live as female. The procedure is to remove all male genital organs including the penis and testes with the construction of female genitalia composed of ...
MTF Vaginoplasty. In male-to-female sex reassignment, the trans woman may choose to undergo vaginoplasty - the inversion of the penis to create a vagina - as part of her physical transition. This procedure can result in a fully sensate neovagina. Dr. MacPhee performs this reconstructive procedure by disassembling the penis and utilizing the ...
Male to female (MTF) gender reassignment surgery is also known as sex reassignment surgery (SRS), genital construction, and generally as Gender Confirmation Surgery. These procedures are used to remove and alter male genitalia into traditional female genitalia. Plastic surgeons will remove the scrotum, perform a penile inversion to create the ...
Miroslav Djordjevic, MD, PhD, an internationally renowned surgeon and a leading authority on surgery for transgender individuals, is developing a procedure to match two patients undergoing transgender surgery—one male-to-female, the other female-to-male—and transfer the genitalia between these live donors in a one-stage procedure instead of discarding them as is done now.
Abstract. Male-to-Female (MtF) gender affirmation surgery (GAS) comprises the creation of a functional and aesthetic perineogenital complex. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of GAS on sexuality. We retrospectively surveyed all 254 MtF transsexual patients who had undergone GAS with penile inversion vaginoplasty at the Department of ...
During this period, 214 patients underwent penile inversion vaginoplasty. Results: Results demonstrate that the average age at the time of surgery was 32.2 years (range, 18-61 years); the average of operative time was 3.3 h (range 2-5 h); the average duration of hormone therapy before surgery was 12 years (range 1-39).
The cost for male-to-female reassignment can be $7,000 to $24,000. Between 100 to 500 gender-reassignment procedures are conducted in the United States each year. Sign up for the Live Science ...
Male to Female Sex change surgery, more appropriately known as MtF gender confirmation surgery (GCS), MtF gender reassignment surgery (GRS) is the final stage in the physical transitioning of a transgendered male-to-female. MtF GCS is a surgical procedure that entails removing the external genitalia, followed by reconstruction of female genital ...
However, understand this: with increasing frequency, the US Military is performing gender reassignment surgery—up to and including the removal of genitals and the ... Transgender Active Duty Service Member DHA: Defense Health Agency MTF: Military Medical Treatment Facility So, without further delay, let's take a gander through the policy, how ...
Hong Kong's top court ruled last year that a full sex reassignment surgery requirement was unconstitutional, following an appeal from transgender activist Henry Tse.
K.S. argued that forcing a non-binary person to undergo binary surgery — male to female, or female to male — would only exacerbate her gender dysphoria and would be akin to an act of ...