
25 Thesis Statement Examples
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
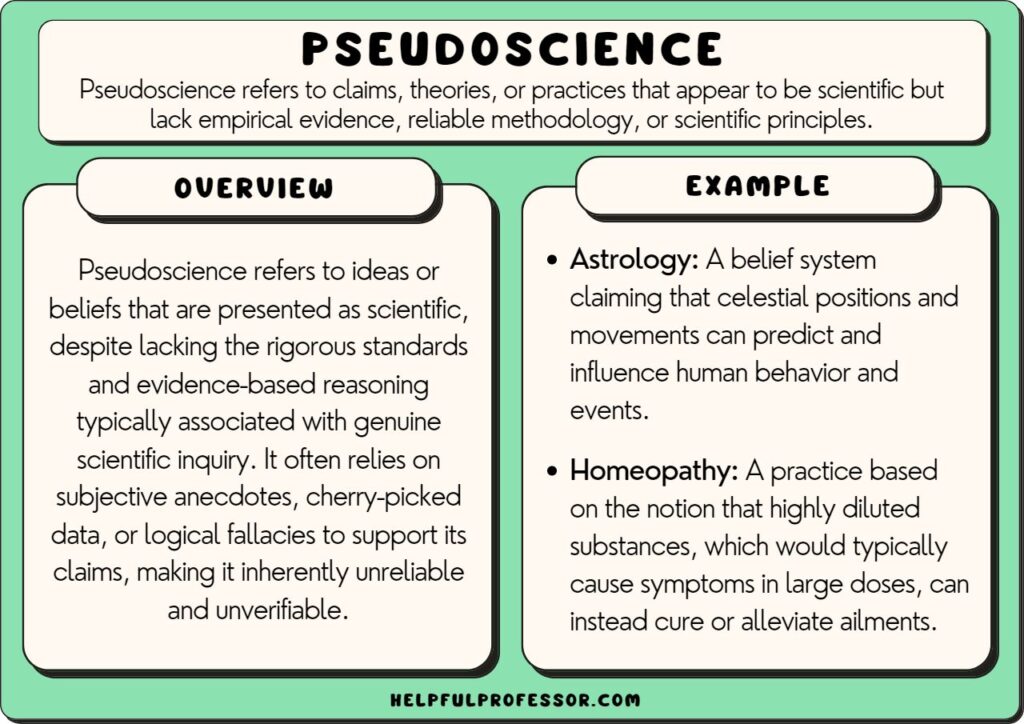
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
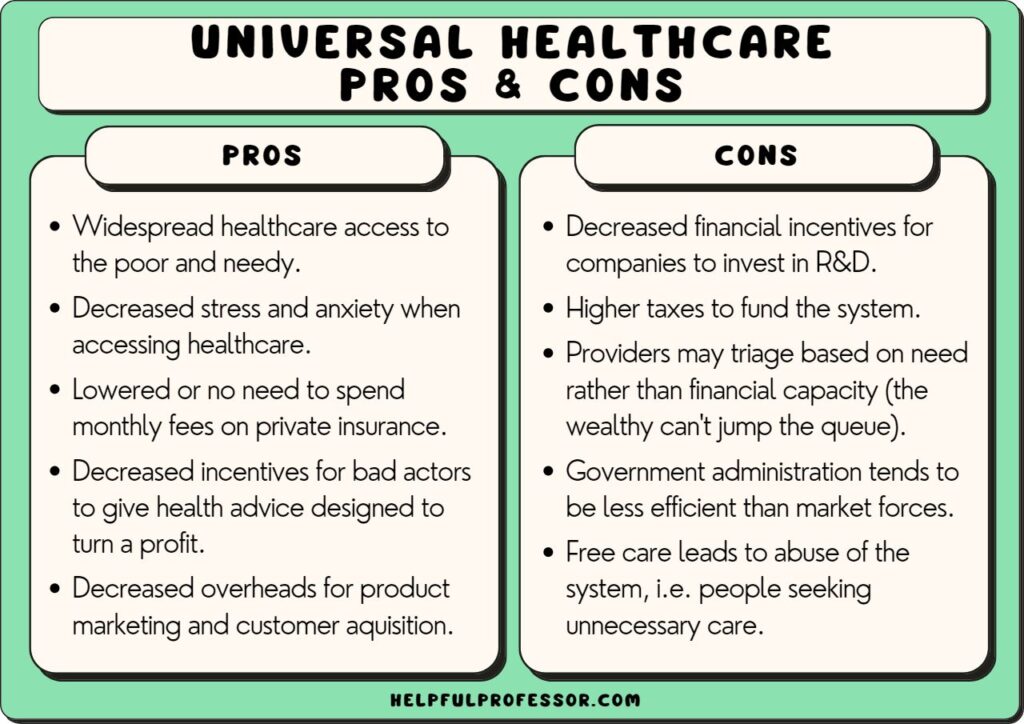
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
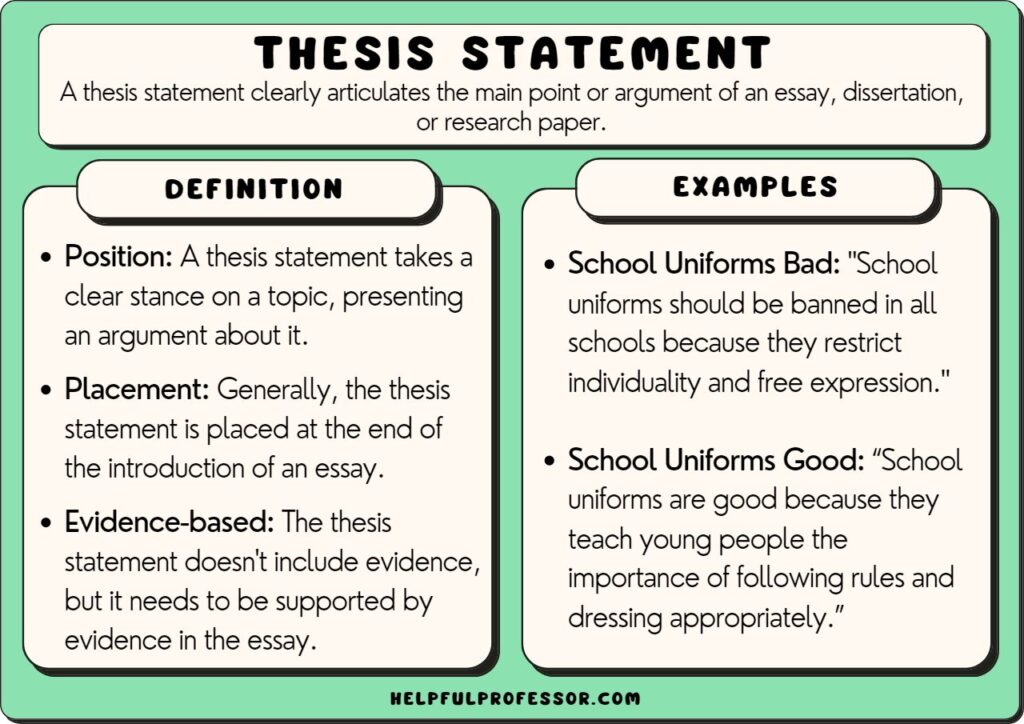
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
- What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
- Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both
Introduction How to get an essay started
Getting started can often be difficult. Even professional writers say that the hardest part of writing is the beginning. Writing an introduction to an essay can therefore seem a daunting task, though it need not be so difficult, as long as you understand the purpose and the structure of the introduction. An example essay has been given to help you understand both of these, and there is a checklist at the end which you can use for editing your introduction.
Purpose of the introduction
When writing an introduction to an academic essay, it is useful to remember the main purpose of the introduction. In general, the introduction will introduce the topic to the reader by stating what the topic is and giving some general background information. This will help the reader to understand what you are writing about, and show why the topic is important. The introduction should also give the overall plan of the essay.
In short, the main purpose of the introduction is to:
- introduce the topic of the essay;
- give a general background of the topic;
- indicate the overall plan of the essay.
This last purpose is perhaps the most important, and is the reason why many writers choose to write the introduction last , after they have written the main body , because they need to know what the essay will contain before they can give a clear plan.
Structure of the introduction
Although essays vary in length and content, most essays will have the same overall structure, including the introduction. The structure is related to the purpose mentioned above. The introduction to an essay should have the following two parts:
- general statements (to introduce the topic and give the background);
- a thesis statement (to show the structure).
General statements
The general statements will introduce the topic of the essay and give background information. The background information for a short essay will generally just be one or two sentences. The general statements should become more and more specific thesis statement , which is the most specific sentence of the introduction--> as the introduction progresses, leading the reader into the essay (some writers talk about "attracting the readers' attention", though for an academic essay, this is less important). For longer essays, the general statements could include one or more definitions , or could classify the topic, and may cover more than one paragraph.
The following is an example of background statements for a short essay ( given below ):
Although they were invented almost a hundred years ago, for decades cars were only owned by the rich. Since the 60s and 70s they have become increasingly affordable, and now most families in developed nations, and a growing number in developing countries, own a car.
These sentences introduce the topic of the essay (cars) and give some background to this topic (situation in the past, the situation now). These sentences lead nicely into the thesis statement (see below).
Thesis statement
The thesis statement is the most important part of the introduction. It gives the reader clear information about the content of the essay, which will help them to understand the essay more easily. The thesis states the specific topic, and often lists the main (controlling) ideas that will be discussed in the main body. It may also indicate how the essay will be organised, e.g. in chronological order, order of importance, advantages/disadvantages, cause/effect. It is usually at the end of the introduction, and is usually (but not always) one sentence long.
In short, the thesis statement:
- states the specific topic of the essay;
- often lists the main (controlling) ideas of the essay;
- may indicate the method of organisation of the essay;
- is usually at the end of the introduction;
- is usually one sentence.
Here is an example of a thesis statement with no subtopics mentioned:
While cars have undoubted advantages, they also have significant drawbacks.
This thesis statement tells us the specific topic of the essay (advantages and disadvantages of cars) and the method of organisation (advantages should come first, disadvantages second). It is, however, quite general, and may have been written before the writer had completed the essay.
In the following thesis statement, the subtopics are named:
While cars have undoubted advantages, of which their convenience is the most apparent, they have significant drawbacks, most notably pollution and traffic problems.
This thesis gives us more detail, telling us not just the topic (advantages and disadvantages of cars) and the method of organisation (advantages first, disadvantages second), but also tells us the main ideas in the essay (convenience, pollution, traffic problems). This essay will probably have three paragraphs in the main body.
Example essay
Below is a discussion essay which looks at the advantages and disadvantages of car ownership. This essay is used throughout the essay writing section to help you understand different aspects of essay writing. Here it focuses on the thesis statement and general statements of the introduction (mentioned on this page), topic sentences , controlling ideas, and the summary and final comment of the conclusion. Click on the different areas (in the shaded boxes to the right) to highlight the different structural aspects in this essay.
Although they were invented almost a hundred years ago, for decades cars were only owned by the rich. Since the 60s and 70s they have become increasingly affordable, and now most families in developed nations, and a growing number in developing countries, own a car. While cars have undoubted advantages, of which their convenience is the most apparent, they have significant drawbacks, most notably pollution and traffic problems . The most striking advantage of the car is its convenience. When travelling long distance, there may be only one choice of bus or train per day, which may be at an unsuitable time. The car, however, allows people to travel at any time they wish, and to almost any destination they choose. Despite this advantage, cars have many significant disadvantages, the most important of which is the pollution they cause. Almost all cars run either on petrol or diesel fuel, both of which are fossil fuels. Burning these fuels causes the car to emit serious pollutants, such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrous oxide. Not only are these gases harmful for health, causing respiratory disease and other illnesses, they also contribute to global warming, an increasing problem in the modern world. According to the Union of Concerned Scientists (2013), transportation in the US accounts for 30% of all carbon dioxide production in that country, with 60% of these emissions coming from cars and small trucks. In short, pollution is a major drawback of cars. A further disadvantage is the traffic problems that they cause in many cities and towns of the world. While car ownership is increasing in almost all countries of the world, especially in developing countries, the amount of available roadway in cities is not increasing at an equal pace. This can lead to traffic congestion, in particular during the morning and evening rush hour. In some cities, this congestion can be severe, and delays of several hours can be a common occurrence. Such congestion can also affect those people who travel out of cities at the weekend. Spending hours sitting in an idle car means that this form of transport can in fact be less convenient than trains or aeroplanes or other forms of public transport. In conclusion, while the car is advantageous for its convenience , it has some important disadvantages, in particular the pollution it causes and the rise of traffic jams . If countries can invest in the development of technology for green fuels, and if car owners can think of alternatives such as car sharing, then some of these problems can be lessened.
Union of Concerned Scientists (2013). Car Emissions and Global Warming. www.ucsusa.org/clean vehicles/why-clean-cars/global-warming/ (Access date: 8 August, 2013)

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for an essay introduction. Use it to check your own writing, or get a peer (another student) to help you.
Next section
Find out how to structure the main body of an essay in the next section.
Previous section
Go back to the previous section about essay structure .

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 26 January 2022.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
General Statement Vs. Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a succinct statement of the arguments you'll be making in a paper and is a critical component of any well-written work. A general statement, by contrast, is any declarative sentence providing supporting information or transitioning to a new topic. While both sentence structures play an important role in writing, a paper without a thesis statement can end up poorly organized with no central argument.
Role in Paper
Your thesis defines the topic and focus of your paper. Even if your paper is not an argumentative paper, you'll still need a thesis that defines your scope. For example, in a paper summarizing "Romeo and Juliet," your thesis might briefly outline three general plot themes. Your general statements should then expand upon your thesis by giving supplemental information and commentary. In some papers, the primary thesis is in the first paragraph, and then each subsequent paragraph contains a mini-thesis. For example, the "Romeo and Juliet" paper might use one paragraph to outline each plot theme, with a mini-thesis at the beginning of the paragraph providing more information about the plot theme.
Your thesis makes a central argument upon which your paper will focus. General statements either lead up to this argument by providing background information or support the argument by presenting and analyzing data. General statements are also an important part of a conclusion. You can use them to outline directions for future research or to address unsettled research debates, for example. Some students mistakenly make a general statement when they need to make a thesis statement. For example, "Poverty is a social problem" is a general statement that does not outline an argument. On the other hand, "School programs designed to counteract the effect of poverty can help undermine the long-lasting effects of low family income" is a compelling thesis statement.
Paper Structure
Both your thesis statement and general statements play roles in structuring your paper. Your thesis limits your focus to a single argument or two, and general statements support this argument. In a sociology paper, your thesis might argue that childhood poverty is the best predictor of adult poverty. General statements might then give facts about childhood poverty, statements about how to end poverty or information on the psychological ramifications of poverty. However, your general statements should not veer outside of the limited focus of your thesis. A paragraph full of general statements about how teen pregnancy contributes to poverty would likely confuse the focus of your paper.
Supporting the Thesis
The primary role of a general statement is to support your thesis. In the introductory paragraph, general statements can also build up to your thesis by providing relevant background. You might, for example, make the general statement that "Philosophers have long debated when it is ethical to kill someone," then follow up with a thesis explaining when killing is ethical or how a particular philosopher attacks this ethical dilemma.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements
- Indiana University Bloomington: How to Write a Thesis Statement
- University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign: Writing Tips -- Thesis Statements
- Louisiana Tech: Thesis Exercises -- What a Thesis Is Not
Van Thompson is an attorney and writer. A former martial arts instructor, he holds bachelor's degrees in music and computer science from Westchester University, and a juris doctor from Georgia State University. He is the recipient of numerous writing awards, including a 2009 CALI Legal Writing Award.

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on September 14, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master’s program or a capstone to a bachelor’s degree.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation , it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: choosing a relevant topic , crafting a proposal , designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement for Master’s programs, and is also sometimes required to complete a bachelor’s degree in liberal arts colleges.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
- In other countries (particularly the UK), a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: “Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807” by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: “’A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man’: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947″ by Julian Saint Reiman.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the “Insert Caption” feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialized or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetize the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyzes the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasize what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense , your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5–7% of your overall word count.
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation , you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimizing confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A thesis is typically written by students finishing up a bachelor’s or Master’s degree. Some educational institutions, particularly in the liberal arts, have mandatory theses, but they are often not mandatory to graduate from bachelor’s degrees. It is more common for a thesis to be a graduation requirement from a Master’s degree.
Even if not mandatory, you may want to consider writing a thesis if you:
- Plan to attend graduate school soon
- Have a particular topic you’d like to study more in-depth
- Are considering a career in research
- Would like a capstone experience to tie up your academic experience
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, what is your plagiarism score.
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Mission, Vision, and Inclusive Language Statement
- Locations & Hours
- Undergraduate Employment
- Graduate Employment
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Newsletter Archive
- Support WTS
- Schedule an Appointment
- Online Tutoring
- Before your Appointment
- WTS Policies
- Group Tutoring
- Students Referred by Instructors
- Paid External Editing Services
- Writing Guides
- Scholarly Write-in
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Journal Article Writing Groups
- Early Career Graduate Student Writing Workshop
- Workshops for Graduate Students
- Teaching Resources
- Syllabus Information
- Course-specific Tutoring
- Nominate a Peer Tutor
- Tutoring Feedback
- Schedule Appointment
- Campus Writing Program
Writing Tutorial Services
How to write a thesis statement, what is a thesis statement.
Almost all of us—even if we don’t do it consciously—look early in an essay for a one- or two-sentence condensation of the argument or analysis that is to follow. We refer to that condensation as a thesis statement.
Why Should Your Essay Contain a Thesis Statement?
- to test your ideas by distilling them into a sentence or two
- to better organize and develop your argument
- to provide your reader with a “guide” to your argument
In general, your thesis statement will accomplish these goals if you think of the thesis as the answer to the question your paper explores.
How Can You Write a Good Thesis Statement?
Here are some helpful hints to get you started. You can either scroll down or select a link to a specific topic.
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned
Almost all assignments, no matter how complicated, can be reduced to a single question. Your first step, then, is to distill the assignment into a specific question. For example, if your assignment is, “Write a report to the local school board explaining the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class,” turn the request into a question like, “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” After you’ve chosen the question your essay will answer, compose one or two complete sentences answering that question.
Q: “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” A: “The potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class are . . .”
A: “Using computers in a fourth-grade class promises to improve . . .”
The answer to the question is the thesis statement for the essay.
[ Back to top ]
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned
Even if your assignment doesn’t ask a specific question, your thesis statement still needs to answer a question about the issue you’d like to explore. In this situation, your job is to figure out what question you’d like to write about.
A good thesis statement will usually include the following four attributes:
- take on a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree
- deal with a subject that can be adequately treated given the nature of the assignment
- express one main idea
- assert your conclusions about a subject
Let’s see how to generate a thesis statement for a social policy paper.
Brainstorm the topic . Let’s say that your class focuses upon the problems posed by changes in the dietary habits of Americans. You find that you are interested in the amount of sugar Americans consume.
You start out with a thesis statement like this:
Sugar consumption.
This fragment isn’t a thesis statement. Instead, it simply indicates a general subject. Furthermore, your reader doesn’t know what you want to say about sugar consumption.
Narrow the topic . Your readings about the topic, however, have led you to the conclusion that elementary school children are consuming far more sugar than is healthy.
You change your thesis to look like this:
Reducing sugar consumption by elementary school children.
This fragment not only announces your subject, but it focuses on one segment of the population: elementary school children. Furthermore, it raises a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree, because while most people might agree that children consume more sugar than they used to, not everyone would agree on what should be done or who should do it. You should note that this fragment is not a thesis statement because your reader doesn’t know your conclusions on the topic.
Take a position on the topic. After reflecting on the topic a little while longer, you decide that what you really want to say about this topic is that something should be done to reduce the amount of sugar these children consume.
You revise your thesis statement to look like this:
More attention should be paid to the food and beverage choices available to elementary school children.
This statement asserts your position, but the terms more attention and food and beverage choices are vague.
Use specific language . You decide to explain what you mean about food and beverage choices , so you write:
Experts estimate that half of elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar.
This statement is specific, but it isn’t a thesis. It merely reports a statistic instead of making an assertion.
Make an assertion based on clearly stated support. You finally revise your thesis statement one more time to look like this:
Because half of all American elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar, schools should be required to replace the beverages in soda machines with healthy alternatives.
Notice how the thesis answers the question, “What should be done to reduce sugar consumption by children, and who should do it?” When you started thinking about the paper, you may not have had a specific question in mind, but as you became more involved in the topic, your ideas became more specific. Your thesis changed to reflect your new insights.
How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
1. a strong thesis statement takes some sort of stand..
Remember that your thesis needs to show your conclusions about a subject. For example, if you are writing a paper for a class on fitness, you might be asked to choose a popular weight-loss product to evaluate. Here are two thesis statements:
There are some negative and positive aspects to the Banana Herb Tea Supplement.
This is a weak thesis statement. First, it fails to take a stand. Second, the phrase negative and positive aspects is vague.
Because Banana Herb Tea Supplement promotes rapid weight loss that results in the loss of muscle and lean body mass, it poses a potential danger to customers.
This is a strong thesis because it takes a stand, and because it's specific.
2. A strong thesis statement justifies discussion.
Your thesis should indicate the point of the discussion. If your assignment is to write a paper on kinship systems, using your own family as an example, you might come up with either of these two thesis statements:
My family is an extended family.
This is a weak thesis because it merely states an observation. Your reader won’t be able to tell the point of the statement, and will probably stop reading.
While most American families would view consanguineal marriage as a threat to the nuclear family structure, many Iranian families, like my own, believe that these marriages help reinforce kinship ties in an extended family.
This is a strong thesis because it shows how your experience contradicts a widely-accepted view. A good strategy for creating a strong thesis is to show that the topic is controversial. Readers will be interested in reading the rest of the essay to see how you support your point.
3. A strong thesis statement expresses one main idea.
Readers need to be able to see that your paper has one main point. If your thesis statement expresses more than one idea, then you might confuse your readers about the subject of your paper. For example:
Companies need to exploit the marketing potential of the Internet, and Web pages can provide both advertising and customer support.
This is a weak thesis statement because the reader can’t decide whether the paper is about marketing on the Internet or Web pages. To revise the thesis, the relationship between the two ideas needs to become more clear. One way to revise the thesis would be to write:
Because the Internet is filled with tremendous marketing potential, companies should exploit this potential by using Web pages that offer both advertising and customer support.
This is a strong thesis because it shows that the two ideas are related. Hint: a great many clear and engaging thesis statements contain words like because , since , so , although , unless , and however .
4. A strong thesis statement is specific.
A thesis statement should show exactly what your paper will be about, and will help you keep your paper to a manageable topic. For example, if you're writing a seven-to-ten page paper on hunger, you might say:
World hunger has many causes and effects.
This is a weak thesis statement for two major reasons. First, world hunger can’t be discussed thoroughly in seven to ten pages. Second, many causes and effects is vague. You should be able to identify specific causes and effects. A revised thesis might look like this:
Hunger persists in Glandelinia because jobs are scarce and farming in the infertile soil is rarely profitable.
This is a strong thesis statement because it narrows the subject to a more specific and manageable topic, and it also identifies the specific causes for the existence of hunger.
Produced by Writing Tutorial Services, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN
Writing Tutorial Services social media channels
What Is a Thesis Statement?

Access thousands of exclusive scholarships for free

"Be Bold" No-Essay Scholarship
Brainstorm the Best Topic for Your Essay
How to write a good thesis statement: steps & thesis statement examples, why should your essay contain a thesis statement, what to include in a thesis statement (with example).
- How to Write Thesis Statements in Steps
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned
Develop your answer, a strong thesis statement takes some sort of stand, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
What are thesis statements, and why does it matter in academic writing? A thesis statement is a central argument or main idea that guides the reader through the author's perspective on a topic. Many students struggle to formulate and write a clear and concise thesis statement, leading to confusion, frustration, or having to backtrack or even start over their essays.
In this blog, I shed light on the complexities of crafting an effective thesis statement, offering examples and practical tips to demystify this critical aspect of writing.
Sign up on Bold.org to discover scholarship opportunities tailored to your needs and interests!

When brainstorming for the best topic for your essay, start by considering your interests and passions. If you don't have a specific topic, think about the things that intrigue you or the issues that provoke strong emotions within you. Asking questions like "What excites me?" or "What makes me angry?" can guide you in the right direction.
Additionally, engaging in activities like walking, showering, and playing with pets can spark creative and exciting ideas. Allow your mind to wander freely during these moments of relaxation, as they can be productive grounds for generating unique and compelling essay topics.
Consider the subject matter of your paper carefully from the first paragraph and write at least three diverse subjects related to the main topic being discussed.
If your subject is related to climate change, write a thesis statement by asking: What affects climate change? (Simple!).
Then, try to find something that is close to your experience and connect it to the subject of your paper: What are daily human habits affecting climate change? How does my father contribute to climate change? How do cows contribute to climate change? (by passing gas, you can look it up).
Get Matched to Thousands of Scholarships
Create your Bold.org profile to access thousands of exclusive scholarships, available only on Bold.org.
By framing your subject matter this way with a strong opinion, you allow yourself to delve deeper into its nuances and complexities. Once you have it, you can approach your topic by formulating it as a question requiring exploration and analysis.
So, for example, if you live in a building and take the elevator every day, you already can have the first step towards an exciting argument in a single sentence: "Taking the elevator every day contributes to climate change." Then you can start diving into more detail.

Phrase Your Topic as a Question and Then Answer It
When phrasing your topic as a question, make sure to write it with critical analysis that invites exploration. The thesis statement will inform, explain, and structure the rest of your essay.
For example, if you know your essay wants to explore climate change, society, and human behavior, you could mention, "How do I contribute to the global climate crisis?" This question invites an examination of personal accountability, takes a stand, and might explain the societal implications (For example, taking the elevator).
In crafting your final thesis statement paragraph, you might create a formal argument that already has some kind of answer : "Individual choices, such as reliance on fossil fuels and unsustainable consumption habits, such as taking an elevator, significantly contribute to the escalating climate crisis." This thesis statement encapsulates your position while guiding the direction of the rest of your essay.
By aligning your thesis statement with the initial question (How do I contribute to the global climate crisis?), you establish a coherent framework for your essay and can explore the topic's complexities more deeply and focus on a single topic.
Remember to be creative! This structured approach ensures that your writing remains focused and relevant, allowing you to make bold statements that are interesting and continue raising the stakes throughout your paper, but keep in mind that words matter! Use interesting language and reflect, discuss, and explore different kinds of ways to communicate your ideas.
For example, one of my professors in a Global Warming course in college used to say that taking an elevator releases the size of a closed fist of CO2 into the atmosphere. This kind of comment could effectively address the key issues surrounding climate change in your essay with interesting arguments while being relatable to the reader.
You could start a thesis argument by saying, "If you took an elevator today, you just contributed to releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) the size of a tennis ball."

Much like a map guides a traveler through unknown territory, a thesis statement directs the writer and the reader along a clear path of exploration within the essay.
It serves as a summary that convinces the reader to continue reading. It functions as a narrative-navigational tool, guaranteeing that your ideas are conveyed effectively and that the reader can easily follow the direction of your argument and sentences.
Here are some examples of key points that you might want to include as the introduction of your paper and the thesis statement that challenge the nature of an essay:
Clear Position: "Climate change poses a threat to our future."
Supporting Points: "Rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, and melting ice caps are all evidence of this phenomenon."
Scope (Aspects of the topic): "This paper will explore the impacts of climate change and the urgent need for action to mitigate its effects."
Counterargument: "While some may doubt the importance of climate change, scientific evidence overwhelmingly supports the reality of this crisis."
The thesis statement argues the significance of climate change (Clear Position) as a threat to our future. It supports this claim by presenting evidence (Supporting Points).
It also defines the scope of the paper, indicating that it will explore the impacts of climate change and advocate for mitigation efforts (Aspects). Lastly, it acknowledges potential counterarguments while emphasizing scientific consensus on the issue (Counterargument).

How to Write Thesis Statements in 3 Steps
Define Your Position : Plainly state your argument or stance on the topic. (For instance, in climate change, you could say, "Stop taking the elevator if you just take it for convenience").
Provide Supporting Points : Offer evidence or reasons that support your argument (e.g., Taking the elevator releases CO2 into the atmosphere, the health benefits of using stairs, or the amount of yearly CO2 release that can be avoided by using the stairs).
Specify the Scope : Clearly outline what your argument will focus on to define the limits of your discussion. (In the context of renewable energy policies, you can concentrate on habits as alternatives to support renewable energy policies).
Learn more about writing thesis statements now!
When generating a thesis statement for a given topic, start by simply understanding the subject and identifying key themes or issues (do research!).
Next, consider your perspective or interpretation of the topic and brainstorm potential arguments that align with your understanding.
Finally, refine your thesis statement to clearly articulate your position on the topic, guaranteeing that it provides a roadmap for your essay and effectively communicates your main point, argument, or perspective.
For instance, if the assigned topic is "The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Employment," you might explore arguments such as the potential for AI to take on jobs or the opportunity for AI to create new employment opportunities in new industries.
Finally, complete your thesis statement to make sure that it provides a blueprint for your essay and effectively communicates your main point of argument or perspective.
Wondering about formatting your essay? Check out our blog, What Is MLA Format for an Essay , to learn more!

Once you've formulated a strong argumentative thesis statement, the next step is to revise and expand the content and investigation of your paper . Begin by outlining the main points that support your thesis statement, ensuring each point directly contributes to your argument.
If your thesis statement mentions, "The advancement of artificial intelligence has implications for the future of work," you might develop your essay by discussing specific examples of AI technologies impacting current jobs such as writing. You can analyze potential challenges and opportunities and evaluate the role of possible new regulations in shaping the future of the workforce.
Additionally, complete thorough research to gather evidence, statistics, and expert opinions that support your arguments and provide credibility to your analysis.
Remember: organize your ideas logically, provide clear transitions between paragraphs, and use evidence effectively to support your claims. An excellent way to do this is to connect the last sentence of a section with the beginning of the next paragraph and consistently revise your arguments.
Finally, finish your essay by summarizing a conclusion with key points and reinforcing the significance of your thesis statement in the broader context of the topic. An effective way to do this is to leave the reader wanting more or open the topic to the discussion in the overall answer presented during your paper.
Do you love writing? Check out these writing scholarships to help you save on college costs!

A strong thesis statement asserts a clear position or argument, demonstrating the writer's perspective and opinion. It goes beyond written facts or summarizing. The topic needs to present a debate, a claim that invites discussion and analysis. It can be done in one sentence or expanded over an entire paragraph.
For example, instead of a weak thesis statement stating, "Climate change is happening," decide for a stronger thesis statement such as, "Human activities are the primary drivers of climate change, necessitating urgent action to mitigate its impacts."
By taking a decisive position, the thesis statement sets the tone for the essay. It guides the direction of the argument, prompting critical engagement and debate.
Check out how to end a college essay to learn more about college essays!

What is a thesis statement, and why does it matter in academic writing?
A thesis statement is a central argument or main idea guiding the reader through the author's perspective on a topic. Preparing an effective thesis statement is crucial as it ensures clarity and coherence in your writing, allowing readers to understand your perspective and the direction of your argument.
Why is formulating a clear and concise thesis statement essential?
Many students struggle to articulate a well-defined thesis statement, leading to confusion and frustration in their writing process. A clear and concise thesis statement is a roadmap for your essay, guiding the writer and the readers to ensure coherence throughout your entire paper.
How can I simplify the process of creating a strong thesis statement?
To simplify crafting a strong thesis statement, begin by brainstorming potential topics that resonate with your interests and passions. Consider questions like "What excites me?" or "What makes me angry?" to guide your topic selection. Activities like walking or playing with pets can also spark creative ideas. Once you've chosen a topic, frame it as a question that prompts critical analysis and exploration.
Explore Bold.org scholarships and the hundreds of articles for students , from navigating the world of financial aid to how to write scholarship essays to win free money.
Related Posts
What is the highest degree in college, how to write a thesis statement, what is a concentration in college.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide
Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Thesis Statement
Definition:
Thesis statement is a concise statement that summarizes the main point or argument of an essay, research paper, or any other written work.
It is usually located at the end of the introductory paragraph and provides a roadmap for the reader, indicating what the paper will be about and what the author’s position or argument is. The thesis statement should be clear, specific, and debatable, so that the reader knows what to expect and can evaluate the validity of the argument.
Structure of Thesis Statement
The structure of a thesis statement typically consists of two main parts: the topic and the argument or claim.
- Topic : The topic is the subject or issue that the paper will be addressing. It should be clear and specific, and should provide a context for the argument or claim that follows.
- Argument or claim: The argument or claim is the main point or position that the writer is taking on the topic. It should be clear and concise, and should be debatable or arguable, meaning that it can be supported with evidence and analysis.
For example, a thesis statement for an essay on the impact of social media on mental health could be:
“The excessive use of social media has a negative impact on individuals’ mental health as it leads to increased feelings of anxiety and depression, a distorted self-image, and a decline in face-to-face communication skills.”
In this example, the topic is the impact of social media on mental health, and the argument is that excessive social media use has negative effects on mental health, which will be supported by evidence throughout the essay.
How to Write Thesis Statement
Here are the steps to follow when writing a thesis statement:
- Identify your topic: Your thesis statement should be based on a clear understanding of your topic. Identify the key concepts, issues, and questions related to your topic.
- Research : Conduct research to gather information and evidence that supports your argument. Use reputable sources, such as academic journals, books, and websites.
- Brainstorm : Use brainstorming techniques to generate ideas and develop your argument. Consider different perspectives and opinions on your topic.
- Create a working thesis : Write a working thesis statement that expresses your argument or position on the topic. This statement should be concise and clear, and it should provide a roadmap for your paper.
- Refine your thesis : Revise your working thesis as you continue to research and develop your argument. Make sure your thesis is specific, debatable, and well-supported by evidence.
- Check for coherence : Ensure that your thesis statement is coherent with the rest of your paper. Make sure that your supporting arguments and evidence align with your thesis.
- Revisit your thesis statement : After completing your paper, revisit your thesis statement to ensure that it accurately reflects the content and scope of your work.
How to Start a Thesis Statement
Here are some steps you can follow to start a thesis statement:
- Choose your topic: Start by selecting a topic that you are interested in and that is relevant to your assignment or research question.
- Narrow your focus : Once you have your topic, narrow it down to a specific aspect or angle that you will be exploring in your paper.
- Conduct research : Conduct some research on your topic to gather information and form an understanding of the existing knowledge on the subject.
- I dentify your main argument : Based on your research, identify the main argument or point you want to make in your paper.
- Write a draft thesis statement : Using the main argument you identified, draft a preliminary thesis statement that clearly expresses your point of view.
- Refine your thesis statement : Revise and refine your thesis statement to make sure it is clear, specific, and strong. Make sure that your thesis statement is supported by evidence and relevant to your topic.
Where is the Thesis Statement Located
In academic writing, the thesis statement is usually located in the introduction paragraph of an essay or research paper. It serves as a concise summary of the main point or argument that the writer will be making in the rest of the paper. The thesis statement is typically located towards the end of the introduction and may consist of one or two sentences.
How Long Should A Thesis Statement Be
Thesis Statement Should be between 1-2 sentences and no more than 25-30 words. It should be clear, concise, and focused on the main point or argument of the paper. A good thesis statement should not be too broad or too narrow but should strike a balance between these two extremes. It should also be supported by evidence and analysis throughout the paper.
For example, if you are writing a five-paragraph essay, your thesis statement should be one sentence that summarizes the main point of the essay. If you are writing a research paper, your thesis statement may be two or three sentences long, as it may require more explanation and support.
Thesis Statement Examples
Here are a few examples of thesis statements:
- For an argumentative essay: “The use of smartphones in classrooms should be banned, as it distracts students from learning and hinders their academic performance.”
- For a literary analysis essay: “In George Orwell’s 1984, the use of propaganda and censorship is a powerful tool used by the government to maintain control over the citizens.”
- For a research paper: “The impact of social media on mental health is a growing concern, and this study aims to explore the relationship between social media use and depression in young adults.”
- For a compare and contrast essay : “Although both American and British English are forms of the English language, they differ in pronunciation, vocabulary, and spelling.”
- For an expository essay: “The importance of regular exercise for overall health and well-being cannot be overstated, as it reduces the risk of chronic diseases, improves mood and cognitive function, and enhances physical fitness.”
- For a persuasive essay: “The government should invest in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, as they are more sustainable and environmentally friendly than fossil fuels.”
- For a history research paper: “The Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s and 1960s was a pivotal moment in American history that paved the way for greater racial equality and social justice.”
- For a literary comparison essay: “In The Great Gatsby and Death of a Salesman, the theme of the American Dream is portrayed differently, with one exposing its emptiness and the other showing its destructive power.”
- For a science experiment report: “The hypothesis that increasing the amount of sunlight a plant receives will result in greater growth is supported by the results of this experiment.”
- For an analysis of a social issue : “The gender pay gap in the United States is a pervasive problem that is perpetuated by systemic discrimination and unequal access to education and opportunities.”
Good Thesis Statements Examples
Some Good Thesis Statements Examples are as follows:
- “The legalization of marijuana for medical use has proven to be a beneficial alternative to traditional pain management techniques, with numerous studies demonstrating its efficacy and safety.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and provides specific information about the benefits of medical marijuana and the evidence supporting its use.
- “The rise of social media has fundamentally changed the way we communicate and interact with each other, with both positive and negative effects on our relationships and mental health.”
This thesis statement provides a clear argument and focus for the essay, exploring the impact of social media on communication and mental health.
- “The portrayal of women in advertising perpetuates harmful stereotypes and reinforces gender inequality, contributing to a larger societal issue of sexism and misogyny.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and focus for the essay, analyzing the negative effects of advertising on women and the larger societal issue of gender inequality.
- “The implementation of renewable energy sources is crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change and transitioning to a more sustainable future.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and focus for the essay, emphasizing the importance of renewable energy sources in addressing climate change and promoting sustainability.
- “The American Dream is an illusion that perpetuates social and economic inequality, as it is based on the false notion of equal opportunity for all.”
This thesis statement presents a clear argument and focus for the essay, critiquing the concept of the American Dream and its perpetuation of inequality.
Bad Thesis Statements Examples
Some Bad Thesis Statements Examples are as follows:
- “In this essay, I will talk about my favorite hobby.”
This thesis statement is too vague and does not give any specific information about the writer’s favorite hobby or what the essay will be about.
- “This paper will explore the benefits and drawbacks of social media.”
This thesis statement is too general and does not provide a clear argument or focus for the essay.
- “The world is a beautiful place.”
This thesis statement is an opinion and does not provide any specific information or argument that can be discussed or analyzed in an essay.
- “The impact of climate change is bad.”
This thesis statement is too broad and does not provide any specific information about the impacts of climate change or the focus of the essay.
- “I am going to write about the history of the United States.”
This thesis statement is too general and does not provide a specific focus or argument for the essay.

Applications of Thesis Statement
A thesis statement has several important applications in academic writing, including:
- Guides the reader: A thesis statement serves as a roadmap for the reader, telling them what to expect from the rest of the paper and helping them to understand the main argument or focus of the essay or research paper.
- Focuses the writer: Writing a thesis statement requires the writer to identify and clarify their main argument or claim, which can help them to stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
- Organizes the paper: A thesis statement provides a framework for organizing the paper, helping the writer to develop a logical and coherent argument that supports their main claim.
- Evaluates sources: A clear thesis statement helps the writer to evaluate sources and information, determining which information is relevant and which is not.
- Helps with revision: A strong thesis statement can help the writer to revise their paper, as they can use it as a reference point to ensure that every paragraph and piece of evidence supports their main argument or claim.
Purpose of Thesis Statement
The purpose of a thesis statement is to:
- Identify the main focus or argument of the essay or research paper: A thesis statement is typically a one or two-sentence statement that identifies the main argument or claim of the paper. It should be clear, specific, and debatable, and should guide the reader on what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- Provide direction and guidance to the reader: A thesis statement helps the reader to understand the main focus of the paper and what the writer is trying to convey. It also provides a roadmap for the reader to follow, making it easier for them to understand the structure and organization of the paper.
- Focus the writer and help with organization: Writing a thesis statement requires the writer to identify and clarify their main argument or claim, which can help them to stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information. Additionally, a clear thesis statement provides a framework for organizing the paper, helping the writer to develop a logical and coherent argument that supports their main claim.
- Provide a basis for evaluation and analysis: A clear thesis statement helps the writer to evaluate sources and information, determining which information is relevant and which is not. It also provides a basis for analyzing and evaluating the evidence presented in the paper, helping the writer to determine whether or not it supports their main argument or claim.
When to Write Thesis Statement
A thesis statement should be written early in the writing process, ideally before any significant research or drafting has taken place. This is because the thesis statement serves as the foundation for the rest of the paper, providing a clear and concise summary of the paper’s main argument or claim. By identifying the main argument or claim early in the writing process, the writer can stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
However, it is important to note that the thesis statement is not necessarily set in stone and may need to be revised as the paper is developed. As the writer conducts research and develops their argument, they may find that their original thesis statement needs to be modified or refined. Therefore, it is important to revisit and revise the thesis statement throughout the writing process to ensure that it accurately reflects the main argument or claim of the paper.
Characteristics of Thesis Statement
Some of the key characteristics of a strong thesis statement include:
- Clarity : A thesis statement should be clear and easy to understand, clearly conveying the main argument or claim of the paper.
- Specificity : A thesis statement should be specific and focused, addressing a single idea or topic rather than being overly broad or general.
- Debatable : A thesis statement should be debatable, meaning that there should be room for disagreement or debate. It should not be a statement of fact or a summary of the paper, but rather a statement that can be supported with evidence and analysis.
- Coherent : A thesis statement should be coherent, meaning that it should be logical and consistent with the rest of the paper. It should not contradict other parts of the paper or be confusing or ambiguous.
- Relevant : A thesis statement should be relevant to the topic of the paper and should address the main question or problem being investigated.
- Arguable : A thesis statement should present an argument that can be supported with evidence and analysis, rather than simply stating an opinion or belief.
Advantages of Thesis Statement
There are several advantages of having a strong thesis statement in academic writing, including:
- Focuses the writer : Writing a thesis statement requires the writer to identify and clarify their main argument or claim, which can help them to stay focused and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
- Establishes credibility: A strong thesis statement establishes the writer’s credibility and expertise on the topic, as it demonstrates their understanding of the issue and their ability to make a persuasive argument.
- Engages the reader: A well-crafted thesis statement can engage the reader and encourage them to continue reading the paper, as it presents a clear and interesting argument that is worth exploring.
Limitations of Thesis Statement
While a strong thesis statement is an essential component of academic writing, there are also some limitations to consider, including:
- Can be restrictive: A thesis statement can be restrictive if it is too narrow or specific, limiting the writer’s ability to explore related topics or ideas. It is important to strike a balance between a focused thesis statement and one that allows for some flexibility and exploration.
- Can oversimplify complex topics: A thesis statement can oversimplify complex topics, presenting them as black and white issues rather than acknowledging their complexity and nuance. It is important to be aware of the limitations of a thesis statement and to acknowledge the complexities of the topic being addressed.
- Can limit creativity: A thesis statement can limit creativity and experimentation in writing, as the writer may feel constrained by the need to support their main argument or claim. It is important to balance the need for a clear and focused thesis statement with the desire for creativity and exploration in the writing process.
- May require revision: A thesis statement may require revision as the writer conducts research and develops their argument, which can be time-consuming and frustrating. It is important to be flexible and open to revising the thesis statement as needed to ensure that it accurately reflects the main argument or claim of the paper.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example...

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing Strong Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These OWL resources will help you develop and refine the arguments in your writing.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable
An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade people.
Example of a non-debatable thesis statement:
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
Example of a debatable thesis statement:
This is an example of a debatable thesis because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that this is how we should spend the nation's money. Others might feel that we should be spending more money on education. Still others could argue that corporations, not the government, should be paying to limit pollution.
Another example of a debatable thesis statement:
In this example there is also room for disagreement between rational individuals. Some citizens might think focusing on recycling programs rather than private automobiles is the most effective strategy.
The thesis needs to be narrow
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Example of a thesis that is too broad:
There are several reasons this statement is too broad to argue. First, what is included in the category "drugs"? Is the author talking about illegal drug use, recreational drug use (which might include alcohol and cigarettes), or all uses of medication in general? Second, in what ways are drugs detrimental? Is drug use causing deaths (and is the author equating deaths from overdoses and deaths from drug related violence)? Is drug use changing the moral climate or causing the economy to decline? Finally, what does the author mean by "society"? Is the author referring only to America or to the global population? Does the author make any distinction between the effects on children and adults? There are just too many questions that the claim leaves open. The author could not cover all of the topics listed above, yet the generality of the claim leaves all of these possibilities open to debate.
Example of a narrow or focused thesis:
In this example the topic of drugs has been narrowed down to illegal drugs and the detriment has been narrowed down to gang violence. This is a much more manageable topic.
We could narrow each debatable thesis from the previous examples in the following way:
Narrowed debatable thesis 1:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also how the money could actually help to control pollution.
Narrowed debatable thesis 2:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just what the focus of a national anti-pollution campaign should be but also why this is the appropriate focus.
Qualifiers such as " typically ," " generally ," " usually ," or " on average " also help to limit the scope of your claim by allowing for the almost inevitable exception to the rule.
Types of claims
Claims typically fall into one of four categories. Thinking about how you want to approach your topic, or, in other words, what type of claim you want to make, is one way to focus your thesis on one particular aspect of your broader topic.
Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or whether something is a settled fact. Example:
Claims of cause and effect: These claims argue that one person, thing, or event caused another thing or event to occur. Example:
Claims about value: These are claims made of what something is worth, whether we value it or not, how we would rate or categorize something. Example:
Claims about solutions or policies: These are claims that argue for or against a certain solution or policy approach to a problem. Example:
Which type of claim is right for your argument? Which type of thesis or claim you use for your argument will depend on your position and knowledge of the topic, your audience, and the context of your paper. You might want to think about where you imagine your audience to be on this topic and pinpoint where you think the biggest difference in viewpoints might be. Even if you start with one type of claim you probably will be using several within the paper. Regardless of the type of claim you choose to utilize it is key to identify the controversy or debate you are addressing and to define your position early on in the paper.
What is a Thesis Statement and How to Write It (with Examples)

A thesis statement is basically a sentence or two that summarizes the central theme of your research. In research papers and essays, it is typically placed at the end of the introduction section, which provides broad knowledge about the investigation/study. To put it simply, the thesis statement can be thought of as the main message of any film, which is communicated through the plot and characters. Similar to how a director has a vision, the author(s) in this case has an opinion on the subject that they wish to portray in their research report.
In this article, we will provide a thorough overview on thesis statements, addressing the most frequently asked questions, including how authors arrive at and create a thesis statement that effectively summarizes your research. To make it simpler, we’ve broken this information up into subheadings that focus on different aspects of writing the thesis statement.
Table of Contents
- What is a thesis statement?
- What should a thesis statement include (with examples)?
- How to write a thesis statement in four steps?
- How to generate a thesis statement?
- Types of thesis statements?
- Key takeaways
- Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement, in essence, is a sentence that summarizes the main concept the author(s) wishes to investigate in their research. A thesis statement is often a “question/hypothesis” the author(s) wants to address, using a certain methodology or approach to provide sufficient evidence to support their claims and findings. However, it isn’t necessarily the topic sentence (first sentence) in a research paper introduction, which could be a general statement.
Returning to our movie analogy, a thesis statement is comparable to the particular viewpoint a director wants to convey to his audience. A thesis statement tells the reader the fundamental idea of the study and the possible course it will take to support that idea. A well-structured thesis statement enables the reader to understand the study and the intended approach, so both its placement and clarity matter here. An appropriately placed thesis statement, usually at the end of an introductory paragraph, ensures the reader will not lose interest. A thesis statement plays another crucial role, it summarizes the main idea behind the study so that readers will understand the question the author is trying to answer. It gives the reader some background information and a sense of the topic’s wider context while also hinting at the work or experimental approach that will come next. To summarize, thesis statements are generally that one key phrase you skim over to rapidly understand the thesis of a study.
What should a thesis statement include (with examples)?
Now that we have understood the concept, the next step is learning how to write a good thesis statement. A strong thesis statement should let the reader understand how well-versed you are, as an author, in the subject matter of the study and your position on the topic at hand. The elements listed below should be considered while crafting a statement for your thesis or paper to increase its credibility and impact.
- The author should take a position that a sizable portion of the readership may disagree with. The subject should not be a well-known, well-defined issue with just unanimity of view. This form of thesis statement is typically viewed as weak because it implies that there is nothing substantial to investigate and demonstrate. To pique readers’ interest, the thesis statement should be debatable in some way, and the findings should advance the body of knowledge.
- A review of pertinent literature on the subject is a must in order for the author to establish an informed opinion about the questions they wish to pose and the stance they would want to take during their study, this is the basis to develop a strong thesis statement. The authors of the study should be able to support their statements with relevant research, strengthening their stance by citing literature.
- The thesis statement should highlight just one main idea, with each claim made by the authors in the paper demonstrating the accuracy of the statement. Avoid multiple themes running throughout the article as this could confuse readers and undermine the author’s perspective on the subject. It can also be a sign of the authors’ ambiguity.
- The main objective of a thesis statement is to briefly describe the study’s conclusion while posing a specific inquiry that clarifies the author’s stance or perspective on the subject. Therefore, it is crucial to clearly establish your viewpoint in the statement.
Based on the considerations above, you may wonder how to write a thesis statement for different types of academic essays. Expository and argumentative essays, the most common types of essays, both call for a statement that takes a stand on the issue and uses powerful language. These kinds of thesis statements need to be precise and contain enough background material to give a comprehensive picture of the subject. However, in persuasive essays, which typically integrate an emotive perspective and personal experiences, the opinions are presented as facts that need supporting evidence. The sole difference between argumentative and expository essays and persuasive essays is that the former require the use of strong viewpoints, while the latter does not. Last but not least, the thesis statement for a compare-and-contrast essay addresses two themes rather than just one. Authors can choose to concentrate more on examining similarities or differences depending on the nature of the study; the only caveat is that both topics must receive equal attention to prevent biases.
How to write a thesis statement in four steps?
Coming up with a research question might be challenging in situations when the research topic is not decided or it’s a new field of study. You may want to delve deeper into a widely researched subject, continue with your current research, or pursue a topic you are passionate about. If you don’t have a thesis statement yet, here are four easy stages to get you started.
- Start with a working thesis statement : Writing the statement is not so straightforward; you won’t magically write the final thesis statement at once. It is preferable to choose an initial working thesis after reviewing relevant literature on the topic. Once you have chosen a subject that interests you, attempt to think of a specific query that has not been raised or that would be fascinating to contribute to the body of literature. For example, if you are writing an article or paper about ChatGPT, you could want to look into how ChatGPT affects learning among students. You can even get more specific, like, “How does ChatGPT harm learning and education?”
- Outline your answer (your positioning on the subject): Based on your review of past research, you would form an opinion about the subject—in this example, the effect of ChatGPT on students’ learning—and then you write down your tentative answer to this question. If your initial response is that ChatGPT use has a detrimental impact on education and learning, this would serve as the foundation for your research. Your study would include research and findings to support this assertion and persuade the reader to accept your hypothesis.
- Provide evidence to support your claim : The goal of your study should be to back your hypothesis with enough evidence, relevant facts and literature, to support your claim and explain why you selected that particular response (in this case, why you believe that ChatGPT has a negative impact on learning and education). The focus should be on discussing both the benefits and drawbacks of using ChatGPT and demonstrating why the disadvantages outweigh the benefits. An argumentative thesis statement example on the same topic would be that, despite ChatGPT’s enormous potential as a virtual learning tool for students, it has a detrimental effect on their creativity and critical thinking skills and encourages problematic behaviors like cheating and plagiarism.
- Polish your thesis statement: After outlining your initial statement, improve it by keeping these three elements in mind.
- Does it make it clear what position you hold on the subject?
- Does it effectively connect the various facets of the study topic together?
- Does it summarize the key points of your narrative?
The thesis statement will also gain from your comments on the approach you will employ to validate your claim. For example, the aforementioned thesis statement may be clarified as “Although ChatGPT has enormous potential to serve as a virtual tutor for students and assistant to instructors, its disadvantages, such as plagiarism and the creation of false information, currently outweigh the advantages.” This particular illustration offers a thoughtful discussion of the subject, enabling the author to make their case more persuasively.
How to generate a thesis statement?
No matter how complicated, any thesis or paper may be explained in one or two sentences. Just identify the question your research aims to answer, then write a statement based on your anticipated response. An effective thesis statement will have the following characteristics:
- It should have a take on the subject (which is contentious/adds to existing knowledge)
- It should express a main topic (other themes should only be included if they connect to the main theme)
- It should declare your conclusion about the issue
- It should be based on an objective, broad outlook on the subject.
To understand how to write a thesis statement from scratch, let’s use an example where you may want to learn about how mental and physical health are related.
Since the subject is still broad, you should first conduct a brainstorming session to acquire further thoughts. After reading literature, you determine that you are curious to learn how yoga enhances mental health. To develop a compelling thesis statement, you must further narrow this topic by posing precise questions that you can answer through your research. You can ask, “How does yoga affect mental health. What is the possible mean”? This topic makes it plain to the reader what the study is about but it is necessary for you to adopt a position on the issue. Upon further deliberation, the premise can be rephrased as “Yoga, a low impact form of exercise, positively impacts people’s mental health by lowering stress hormones and elevating healthy brain chemicals.” This clearly states your position on the topic. Finally, you may further develop this into a clear, precise thesis statement that asks, “Does practicing yoga induce feel-good hormones and lower the stress hormone, cortisol, that positively affects people’s mental health?” to turn it into a study.
Types of thesis statements?
The three primary categories of thesis statements are analytical, expository, and argumentative. You choose one over the other depending on the subject matter of your research or essay. In argumentative thesis statements, the author takes a clear stand and strives to persuade the reader of their claims, for example, “Animal agriculture is the biggest driver of climate change.” It is specific, concise, and also contentious. On the other hand, the purpose of an expository thesis statement is to interpret, assess, and discuss various facets of a subject. Here you shortlist the key points of your interpretation, and state the conclusion based on the interpretation you drew from the study. An analytical thesis statement aims to discuss, glean information on the subject, and explain the facts of the topic. Here, the goal is to critically analyze and summarize the points you will cover in the study.
Key takeaways
- A good thesis statement summarizes the central idea of your thesis or research paper.
- It serves as a compass to show the reader what the research will contend and why.
- Before creating a thesis statement, keep in mind that the statement should be specific, coherent, and controversial.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
A thesis statement can be defined as a sentence that describes the main idea of the research or thesis to inform the reader of the argument the research will pursue and the reason the author adopts a specific stance on the subject. Essentially, it expresses the author’s judgment or opinion based on a review of the literature or personal research experience.
Any academic essay or research piece must have a thesis statement since it directs the research and attracts the reader’s attention to the main idea of the subject under discussion. In addition to confining the author to a specific subject, so they don’t veer off topic, it also enables the reader to understand the topic at hand and what to expect.
To create an impactful thesis statement, simply follow these four easy steps. Start by creating a working statement by posing the question that your research or thesis will attempt to answer. Then, outline your initial response and choose your position on the matter. Next, try to substantiate your claim with facts or other relevant information. Finally, hone your final thesis statement by crafting a cogent narrative using knowledge gained in the previous step.
Ideally the thesis statement should be placed at the end of an introduction of the paper or essay. Keep in mind that it is different from the topic sentence, which is more general.
We hope this in-depth guide has allayed your concerns and empowered you to start working craft a strong statement for your essay or paper. Good luck with drafting your next thesis statement!
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks, submission readiness and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month !
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
Academic Paraphrasing: Why Paperpal’s Rewrite Should be Your First Choice!
How to write a good humanities research paper, you may also like, quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how..., 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures, ethics in science: importance, principles & guidelines , jenni ai review: top features, pricing, and alternatives.
How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
The important sentence expresses your central assertion or argument
arabianEye / Getty Images
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
A thesis statement provides the foundation for your entire research paper or essay. This statement is the central assertion that you want to express in your essay. A successful thesis statement is one that is made up of one or two sentences clearly laying out your central idea and expressing an informed, reasoned answer to your research question.
Usually, the thesis statement will appear at the end of the first paragraph of your paper. There are a few different types, and the content of your thesis statement will depend upon the type of paper you’re writing.
Key Takeaways: Writing a Thesis Statement
- A thesis statement gives your reader a preview of your paper's content by laying out your central idea and expressing an informed, reasoned answer to your research question.
- Thesis statements will vary depending on the type of paper you are writing, such as an expository essay, argument paper, or analytical essay.
- Before creating a thesis statement, determine whether you are defending a stance, giving an overview of an event, object, or process, or analyzing your subject
Expository Essay Thesis Statement Examples
An expository essay "exposes" the reader to a new topic; it informs the reader with details, descriptions, or explanations of a subject. If you are writing an expository essay , your thesis statement should explain to the reader what she will learn in your essay. For example:
- The United States spends more money on its military budget than all the industrialized nations combined.
- Gun-related homicides and suicides are increasing after years of decline.
- Hate crimes have increased three years in a row, according to the FBI.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) increases the risk of stroke and arterial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat).
These statements provide a statement of fact about the topic (not just opinion) but leave the door open for you to elaborate with plenty of details. In an expository essay, you don't need to develop an argument or prove anything; you only need to understand your topic and present it in a logical manner. A good thesis statement in an expository essay always leaves the reader wanting more details.
Types of Thesis Statements
Before creating a thesis statement, it's important to ask a few basic questions, which will help you determine the kind of essay or paper you plan to create:
- Are you defending a stance in a controversial essay ?
- Are you simply giving an overview or describing an event, object, or process?
- Are you conducting an analysis of an event, object, or process?
In every thesis statement , you will give the reader a preview of your paper's content, but the message will differ a little depending on the essay type .
Argument Thesis Statement Examples
If you have been instructed to take a stance on one side of a controversial issue, you will need to write an argument essay . Your thesis statement should express the stance you are taking and may give the reader a preview or a hint of your evidence. The thesis of an argument essay could look something like the following:
- Self-driving cars are too dangerous and should be banned from the roadways.
- The exploration of outer space is a waste of money; instead, funds should go toward solving issues on Earth, such as poverty, hunger, global warming, and traffic congestion.
- The U.S. must crack down on illegal immigration.
- Street cameras and street-view maps have led to a total loss of privacy in the United States and elsewhere.
These thesis statements are effective because they offer opinions that can be supported by evidence. If you are writing an argument essay, you can craft your own thesis around the structure of the statements above.
Analytical Essay Thesis Statement Examples
In an analytical essay assignment, you will be expected to break down a topic, process, or object in order to observe and analyze your subject piece by piece. Examples of a thesis statement for an analytical essay include:
- The criminal justice reform bill passed by the U.S. Senate in late 2018 (" The First Step Act ") aims to reduce prison sentences that disproportionately fall on nonwhite criminal defendants.
- The rise in populism and nationalism in the U.S. and European democracies has coincided with the decline of moderate and centrist parties that have dominated since WWII.
- Later-start school days increase student success for a variety of reasons.
Because the role of the thesis statement is to state the central message of your entire paper, it is important to revisit (and maybe rewrite) your thesis statement after the paper is written. In fact, it is quite normal for your message to change as you construct your paper.
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- What Is Expository Writing?
- An Introduction to Academic Writing
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- How to Write a Response Paper
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- Understanding What an Expository Essay Is
- The Introductory Paragraph: Start Your Paper Off Right
- Tips for Writing an Art History Paper
- The Five Steps of Writing an Essay
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- Development in Composition: Building an Essay
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
- Editing Services
- Academic Editing Services
- Admissions Editing Services
- Admissions Essay Editing Services
- AI Content Editing Services
- APA Style Editing Services
- Application Essay Editing Services
- Book Editing Services
- Business Editing Services
- Capstone Paper Editing Services
- Children's Book Editing Services
- College Application Editing Services
- College Essay Editing Services
- Copy Editing Services
- Developmental Editing Services
- Dissertation Editing Services
- eBook Editing Services
- English Editing Services
- Horror Story Editing Services
- Legal Editing Services
- Line Editing Services
- Manuscript Editing Services
- MLA Style Editing Services
- Novel Editing Services
- Paper Editing Services
- Personal Statement Editing Services
- Research Paper Editing Services
- Résumé Editing Services
- Scientific Editing Services
- Short Story Editing Services
- Statement of Purpose Editing Services
- Substantive Editing Services
- Thesis Editing Services
Proofreading
- Proofreading Services
- Admissions Essay Proofreading Services
- Children's Book Proofreading Services
- Legal Proofreading Services
- Novel Proofreading Services
- Personal Statement Proofreading Services
- Research Proposal Proofreading Services
- Statement of Purpose Proofreading Services
Translation
- Translation Services
Graphic Design
- Graphic Design Services
- Dungeons & Dragons Design Services
- Sticker Design Services
- Writing Services
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
25 Thesis Statement Examples That Will Make Writing a Breeze

Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement.
Let's take a minute to first understand what makes a solid thesis statement, and what key components you need to write one of your own.

A thesis statement always goes at the beginning of the paper. It will typically be in the first couple of paragraphs of the paper so that it can introduce the body paragraphs, which are the supporting evidence for your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should clearly identify an argument. You need to have a statement that is not only easy to understand, but one that is debatable. What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute . An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic.
Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's cuteness is derived from its floppy ears, small body, and playfulness." These are three things that can be debated on. Some people might think that the cutest thing about puppies is the fact that they follow you around or that they're really soft and fuzzy.
All cuteness aside, you want to make sure that your thesis statement is not only debatable, but that it also actually thoroughly answers the research question that was posed. You always want to make sure that your evidence is supporting a claim that you made (and not the other way around). This is why it's crucial to read and research about a topic first and come to a conclusion later. If you try to get your research to fit your thesis statement, then it may not work out as neatly as you think. As you learn more, you discover more (and the outcome may not be what you originally thought).
Additionally, your thesis statement shouldn't be too big or too grand. It'll be hard to cover everything in a thesis statement like, "The federal government should act now on climate change." The topic is just too large to actually say something new and meaningful. Instead, a more effective thesis statement might be, "Local governments can combat climate change by providing citizens with larger recycling bins and offering local classes about composting and conservation." This is easier to work with because it's a smaller idea, but you can also discuss the overall topic that you might be interested in, which is climate change.
So, now that we know what makes a good, solid thesis statement, you can start to write your own. If you find that you're getting stuck or you are the type of person who needs to look at examples before you start something, then check out our list of thesis statement examples below.
Thesis statement examples
A quick note that these thesis statements have not been fully researched. These are merely examples to show you what a thesis statement might look like and how you can implement your own ideas into one that you think of independently. As such, you should not use these thesis statements for your own research paper purposes. They are meant to be used as examples only.
- Vaccinations Because many children are unable to vaccinate due to illness, we must require that all healthy and able children be vaccinated in order to have herd immunity.
- Educational Resources for Low-Income Students Schools should provide educational resources for low-income students during the summers so that they don't forget what they've learned throughout the school year.
- School Uniforms School uniforms may be an upfront cost for families, but they eradicate the visual differences in income between students and provide a more egalitarian atmosphere at school.
- Populism The rise in populism on the 2016 political stage was in reaction to increasing globalization, the decline of manufacturing jobs, and the Syrian refugee crisis.
- Public Libraries Libraries are essential resources for communities and should be funded more heavily by local municipalities.
- Cyber Bullying With more and more teens using smartphones and social media, cyber bullying is on the rise. Cyber bullying puts a lot of stress on many teens, and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Parents should limit the usage of smart phones, monitor their children's online activity, and report any cyber bullying to school officials in order to combat this problem.
- Medical Marijuana for Veterans Studies have shown that the use of medicinal marijuana has been helpful to veterans who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Medicinal marijuana prescriptions should be legal in all states and provided to these veterans. Additional medical or therapy services should also be researched and implemented in order to help them re-integrate back into civilian life.
- Work-Life Balance Corporations should provide more work from home opportunities and six-hour workdays so that office workers have a better work-life balance and are more likely to be productive when they are in the office.
- Teaching Youths about Consensual Sex Although sex education that includes a discussion of consensual sex would likely lead to less sexual assault, parents need to teach their children the meaning of consent from a young age with age appropriate lessons.
- Whether or Not to Attend University A degree from a university provides invaluable lessons on life and a future career, but not every high school student should be encouraged to attend a university directly after graduation. Some students may benefit from a trade school or a "gap year" where they can think more intensely about what it is they want to do for a career and how they can accomplish this.
- Studying Abroad Studying abroad is one of the most culturally valuable experiences you can have in college. It is the only way to get completely immersed in another language and learn how other cultures and countries are different from your own.
- Women's Body Image Magazines have done a lot in the last five years to include a more diverse group of models, but there is still a long way to go to promote a healthy woman's body image collectively as a culture.
- Cigarette Tax Heavily taxing and increasing the price of cigarettes is essentially a tax on the poorest Americans, and it doesn't deter them from purchasing. Instead, the state and federal governments should target those economically disenfranchised with early education about the dangers of smoking.
- Veganism A vegan diet, while a healthy and ethical way to consume food, indicates a position of privilege. It also limits you to other cultural food experiences if you travel around the world.
- University Athletes Should be Compensated University athletes should be compensated for their service to the university, as it is difficult for these students to procure and hold a job with busy academic and athletic schedules. Many student athletes on scholarship also come from low-income neighborhoods and it is a struggle to make ends meet when they are participating in athletics.
- Women in the Workforce Sheryl Sandberg makes a lot of interesting points in her best-selling book, Lean In , but she only addressed the very privileged working woman and failed to speak to those in lower-skilled, lower-wage jobs.
- Assisted Suicide Assisted suicide should be legal and doctors should have the ability to make sure their patients have the end-of-life care that they want to receive.
- Celebrity and Political Activism Although Taylor Swift's lyrics are indicative of a feminist perspective, she should be more politically active and vocal to use her position of power for the betterment of society.
- The Civil War The insistence from many Southerners that the South seceded from the Union for states' rights versus the fact that they seceded for the purposes of continuing slavery is a harmful myth that still affects race relations today.
- Blue Collar Workers Coal miners and other blue-collar workers whose jobs are slowly disappearing from the workforce should be re-trained in jobs in the technology sector or in renewable energy. A program to re-train these workers would not only improve local economies where jobs have been displaced, but would also lead to lower unemployment nationally.
- Diversity in the Workforce Having a diverse group of people in an office setting leads to richer ideas, more cooperation, and more empathy between people with different skin colors or backgrounds.
- Re-Imagining the Nuclear Family The nuclear family was traditionally defined as one mother, one father, and 2.5 children. This outdated depiction of family life doesn't quite fit with modern society. The definition of normal family life shouldn't be limited to two-parent households.
- Digital Literacy Skills With more information readily available than ever before, it's crucial that students are prepared to examine the material they're reading and determine whether or not it's a good source or if it has misleading information. Teaching students digital literacy and helping them to understand the difference between opinion or propaganda from legitimate, real information is integral.
- Beauty Pageants Beauty pageants are presented with the angle that they empower women. However, putting women in a swimsuit on a stage while simultaneously judging them on how well they answer an impossible question in a short period of time is cruel and purely for the amusement of men. Therefore, we should stop televising beauty pageants.
- Supporting More Women to Run for a Political Position In order to get more women into political positions, more women must run for office. There must be a grassroots effort to educate women on how to run for office, who among them should run, and support for a future candidate for getting started on a political career.
Still stuck? Need some help with your thesis statement?
If you are still uncertain about how to write a thesis statement or what a good thesis statement is, be sure to consult with your teacher or professor to make sure you're on the right track. It's always a good idea to check in and make sure that your thesis statement is making a solid argument and that it can be supported by your research.
After you're done writing, it's important to have someone take a second look at your paper so that you can ensure there are no mistakes or errors. It's difficult to spot your own mistakes, which is why it's always recommended to have someone help you with the revision process, whether that's a teacher, the writing center at school, or a professional editor such as one from ServiceScape .
Related Posts

The Best Way to Synthesize Academic Research

How to Write an Ethics Application That Gets Approved
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Everything You Need to Know About Thesis Statement

Table of Contents

Persuasion is a skill that every human leverages to achieve their goals. For example, you persuade your friends to join you on some trip, your parents to purchase you an automobile, and your committee or audience to provide you approval for your research proposal.
Likewise, every scholarly task is aimed to persuade your readers or audience for certain goals. And the end goal is to incline the readers towards your perspective (facts and evidence-based). So, the act of convincing readers of your viewpoints via research work is often termed academic argument, and it follows a predetermined pattern of guidelines-based writing. After providing a comprehensive introduction to the research topic, you are supposed to state your perspective on the topic in a sentence or two, known as Thesis Statement . It summarizes the argument you will make throughout the paper.
Also, the Thesis Statement often serves as an answer to your research question. Thus, the thesis statement is a must for every research paper and scholarly work.
What is Thesis Statement?

A Thesis Statement:
- Describes how you interpret the subject matter's cause, significance, and results.
- Is a guideline for the paper. In other words, it provides an understanding of the research topic.
- Directly answers the question you are asked. The thesis is not the question itself but an interpretation of it. For example, a thesis can be about World War II, and it should also provide a way to understand the war.
- Claims that other people might disagree with.
- Is a single sentence at the beginning of your paper or near the end of the first para (where you present your argument to the reader). The body of the essay is the rest of the paper. It gathers and organizes evidence to support your argument.
A thesis statement should be concise and easily understandable. Use it as a magnet to attract your readers to keep them reading your paper till the end.
What is the purpose or the goal of the thesis statement?
The real purpose of the thesis statement is:
- To establish a gateway through which your readers can make an entrance into your research paper.
- To bring the entire research paper together to an epicenter of various arguments provided throughout the paper.
Simply put, the goal of writing a strong thesis statement is to make your research paper appear interesting enough for the readers to understand it and prove your arguments right completely.
Additionally, the goal of the thesis statement varies from the kind of research you are presenting. If your thesis provides some claims, justifications, or study, you should present an argumentative thesis statement . However, if your thesis is based on analysis, interpretation, demonstration of cause and effect, comparisons, and contrast, you should develop a persuasive thesis statement.
What is the length of an Ideal Thesis Statement?
You should write your thesis statement in 1-2 sentences. Ideally, it should not be more than 50 words in total.
Also, you should try inserting the thesis statement at the end of the topic introduction or just before the background information.
While writing your thesis statement, be mindful that a thesis statement is never meant to be factual. Your thesis statement is one of the most important elements of your thesis that will help your audience understand what you discuss throughout your paper. So, ensure that your thesis statement must appear like an arguable statement, not a factual one.
Many early researchers or young scholars choose to write factual statements as thesis statements as they are easy to prove. However, resorting to factual statements instead of arguable ones will overshadow your analytical and critical thinking skills, which readers anticipate in your paper.
How to Start a Thesis Statement?

The thesis statement is an outline of your research topic in one sentence. Therefore, you must write it in a concise and catchy style. So, here are a few quick tips that help you understand how to start a thesis statement for a research paper:
Discover Your Research Question
Once the subject matter is finalized for writing a research paper, the next requirement is to figure out the research question. While formulating your research question, make sure that it shows the gaps in the current field of study and should serve as a primary interrogation point for your research.
Figure out the answer and develop your argument
Carry out intensive research to determine the perfect answer for your research question. Your answer should further guide you to structure your entire research paper and its content flow.
For example, if you write an argumentative paper, craft your opinion and create an argument. Then, develop your claim against the topics you want to cover and justify it through various data & facts.
Establish back-up for your Answer with Evidence
The more you research, the more you will learn about the variations in the research answer that you were trying to formulate. Similarly, with various sources and newer evidence coming up, you should be able to make an answer that should stand coherently, correctly, relevant, and justified enough. The answer should enhance the reader’s understanding of your paper from beginning to end.
How to determine if my thesis statement is strong?

Make a self-evaluation of your thesis statement and check if it stands the following interrogation:
- Does it answer the question?
Re-read to understand the question prompt to ensure that your answer or the thesis statement itself doesn't skip the focus of the question. Try rephrasing it if you feel that the question prompt is not structured or appropriately discussed.
- Does my thesis statement appear like an argument (for or against)?
Suppose you have chosen to present the facts and rationality behind it in the best way possible and assume that no one would or could ever disagree with it. It indicates that you've presented a summary instead of presenting an argument. So, always pick an opinion from the topic and justify your arguments backed with various evidence.
- Is the Thesis Statement explicit and specific?
It may lack a strong argument if you have written a very general statement or vaguely crafted a thesis statement. Your audience will figure it out instantly.
Therefore, if you have used words like “good’’ or “bad,” try to put it more specifically by answering and figuring out “Why something is good”? Or ''What makes something good or bad”?
- Does it clear the “So What” test?
After reading any research paper, the prompt question that pops up from a reader's mind is, "So What?". Now, if your thesis statement urges the reader with such questions, you need to develop a strong argument or relationship that bridges your research topic to a more significant real-world problem.
- Does it go beyond the “How” and “Why” assessments?
After going through your thesis statement, if the readers come up with questions like "How" and 'Why," it indicates that your statement failed to provide the reader with the critical insights to understand your thesis statement and is too open-ended. So, you must provide your readers with the best statement explaining the introduction's real significance and the impending need for further research.
Thesis Statement Examples
Follow through with some interesting and creative thesis statements to clarify your doubts and better understand the concept.
Example 1: Social Media affects public awareness both positively and negatively
Yeah, it does answer the question. However, the answer is pretty vague and generic as it shows the effects both positively and negatively.
Not accurately. The statement can be argued only with the people having opinions either on positive or the negative aspect. Therefore, it fails to address every section of the audience.
- Is the Thesis statement specific enough?
Not exactly. This thesis statement doesn't provide any details on positive and negative impacts.
No, not at all. The thesis statement stated above provides no clarifications over how the positive or negative impacts build up or the factors that build up such impacts.
Again, No. It fails to justify why anyone should bother about the impacts, be it positive or negative.
A stronger and alternate version for the above thesis statement can be:
Since not every piece of information provided on social media is credible and reliable enough, users have become avid consumers of critical information and, therefore, more informed.
Even though the above thesis statement is lengthy, it answers every question and provides details over cause, effect, and critical aspects that readers can easily challenge.
Example 2: Analytical Thesis Statement
- Water is extremely important for human survival, but consuming contaminated water poses many health risks.
- The hibernation period is one of the most important periods in animals for healthy well-being. Still, it renders them in a state of weakness and exposed to external and environmental threats.
Example 3: Argumentative Thesis Statement
- At the end of the nineteenth century, French women lawyers experienced misogynist attacks from male lawyers when they attempted to enter the legal profession because male lawyers wanted to keep women out of judgeships.
- High levels of alcohol consumption have detrimental effects on your health, such as weight gain, heart disease, and liver complications.
Tips for writing a Strong Thesis Statement

A strong thesis statement is the foremost requirement of academic writing, and it holds greater importance when written for research papers. However, it becomes more crucial when you want your readers to get convinced of your opinions or perspective of the subject matter.
Below are some pro-tips that can help you crack the code of how to write a strong thesis statement, especially for research papers, thesis, and dissertations:
Keep it specific
Readers often get disappointed and confused when you present a weak argument based on a generic thesis statement. To develop a strong thesis statement, focus on one key aspect and develop it further.
Keep it simple and clear
The essence of your entire research paper is dependent on your thesis statement. Also, a strong thesis statement stays hinged over the clarity it provides. Therefore, don't disrupt the meaning or clarity of your research paper by using some jargonish words or complexing it by combining different concepts.
Ingrain your opinions
Your thesis statement should explicitly display your opinion or position for the subject matter under discussion. Your reader wants to understand your position in detail and the factors you will justify with evidence and facts.
Make it unique and Original
Your audience or the readers have gone through the subject matter several times in their careers. Hence, you must present your thesis statement in a unique and completely original form. Never use generic statements; grow some risk-taking capability and surprise your readers.
Keep it Concise and Coherent
Your thesis statement can be considered good only if it is concise yet informational. Don’t make it wordy in any case, and never go beyond more than 50 words.
Additionally, your research paper will discuss many aspects of a topic. Still, in the end, every single aspect should come together to form a coherent whole, addressing, explaining, and justifying the research question.
Conclusion: How to write a Thesis Statement?
A strong thesis statement is the one of the most important elements of your research paper. The thesis statement always serves as a pillar that carries the entire load of a research paper and it’s several sections.
Whether your research paper is worthy of your audience time or not, entirely hinges upon your thesis statement. A thesis statement always depicts the plan for the research but a good thesis statement reflects your opinions, viewpoints and of course the trajectory that it sets for the entire paper.
So, always try to write a good thesis statement by carefully following its structure, about which we have already discussed.
Before you go: In view of your interest in simplifying research workflows, we suggest you take a look at SciSpace . In a single portal, you can complete all your research writing tasks, including literature searches.

SciSpace provides researchers, universities, and publishers with all the tools they need. Our comprehensive research repository features more than 200 million research papers from multiple disciplines with SEO-optimized abstracts, a publicly visible profile to highlight your expertise, a specially-built collaborative text editor, 20,000+ journal templates, and more.

Hope the article has explained everything that you needed to know about the thesis statement. In case you have any questions or doubts, join our SciSpace (Formerly Typeset) community platform and put your questions there. We will make sure that you get your answers at the earliest.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

6.1: The Topic, General Purpose, Specific Purpose, and Thesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 54935
Before any work can be done on crafting the body of your speech or presentation, you must first do some prep work—selecting a topic, formulating a general purpose, a specific purpose statement, and crafting a central idea, or thesis statement. In doing so, you lay the foundation for your speech by making important decisions about what you will speak about and for what purpose you will speak. These decisions will influence and guide the entire speechwriting process, so it is wise to think carefully and critically during these beginning stages.
Selecting a Topic
Generally, speakers focus on one or more interrelated topics—relatively broad concepts, ideas, or problems that are relevant for particular audiences. The most common way that speakers discover topics is by simply observing what is happening around them—at their school, in their local government, or around the world. Student government leaders, for example, speak or write to other students when their campus is facing tuition or fee increases, or when students have achieved something spectacular, like lobbying campus administrators for lower student fees and succeeding. In either case, it is the situation that makes their speeches appropriate and useful for their audience of students and university employees. More importantly, they speak when there is an opportunity to change a university policy or to alter the way students think or behave in relation to a particular event on campus.
But you need not run for president or student government in order to give a meaningful speech. On the contrary, opportunities abound for those interested in engaging speech as a tool for change. Perhaps the simplest way to find a topic is to ask yourself a few questions. See the textbox entitled “Questions for Selecting a Topic” for a few questions that will help you choose a topic.
Students speak about what is interesting to them and their audiences. What topics do you think are relevant today? There are other questions you might ask yourself, too, but these should lead you to at least a few topical choices. The most important work that these questions do is to locate topics within your pre-existing sphere of knowledge and interest. David Zarefsky (2010) also identifies brainstorming as a way to develop speech topics, a strategy that can be helpful if the questions listed in the textbox did not yield an appropriate or interesting topic. Starting with a topic you are already interested in will likely make writing and presenting your speech a more enjoyable and meaningful experience. It means that your entire speechwriting process will focus on something you find important and that you can present this information to people who stand to benefit from your speech.
Questions for Selecting a Topic
- What important events are occurring locally, nationally and internationally?
- What do I care about most?
- Is there someone or something I can advocate for?
- What makes me angry/happy?
- What beliefs/attitudes do I want to share?
- Is there some information the audience needs to know?
Once you have answered these questions and narrowed your responses, you are still not done selecting your topic. For instance, you might have decided that you really care about breeds of dogs. This is a very broad topic and could easily lead to a dozen different speeches. To resolve this problem, speakers must also consider the audience to whom they will speak, the scope of their presentation, and the outcome they wish to achieve.
Formulating the Purpose Statements
By honing in on a very specific topic, you begin the work of formulating your purpose statement. In short, a purpose statement clearly states what it is you would like to achieve. Purpose statements are especially helpful for guiding you as you prepare your speech. When deciding which main points, facts, and examples to include, you should simply ask yourself whether they are relevant not only to the topic you have selected, but also whether they support the goal you outlined in your purpose statement. The general purpose statement of a speech may be to inform, to persuade, to celebrate, or to entertain. Thus, it is common to frame a specific purpose statement around one of these goals. According to O’Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein, a specific purpose statement “expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in terms of the specific objectives you hope to achieve (2004). For instance, the home design enthusiast might write the following specific purpose statement: At the end of my speech, the audience will learn the pro’s and con’s of flipping houses . In short, the general purpose statement lays out the broader goal of the speech while the specific purpose statement describes precisely what the speech is intended to do. Some of your professors may ask that you include the general purpose and add the specific purpose.
Writing the Thesis Statement
The specific purpose statement is a tool that you will use as you write your talk, but it is unlikely that it will appear verbatim in your speech. Instead, you will want to convert the specific purpose statement into a central idea, or thesis statement that you will share with your audience.
Depending on your instructor’s approach, a thesis statement may be written two different ways. A thesis statement may encapsulate the main points of a speech in just a sentence or two, and be designed to give audiences a quick preview of what the entire speech will be about. The thesis statement for a speech, like the thesis of a research-based essay, should be easily identifiable and ought to very succinctly sum up the main points you will present. Some instructors prefer that your thesis, or central idea, be a single, declarative statement providing the audience with an overall statement that provides the essence of the speech, followed by a separate preview statement.
If you are a Harry Potter enthusiast, you may write a thesis statement (central idea) the following way using the above approach: J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella like story having gone from relatively humble beginnings, through personal struggles, and finally success and fame .
Writing the Preview Statement
However, some instructors prefer that you separate your thesis from your preview statement. A preview statement (or series of statements) is a guide to your speech. This is the part of the speech that literally tells the audience exactly what main points you will cover. If you were to open your Waze app, it would tell you exactly how to get there. Best of all, you would know what to look for! So, if we take our J.K Rowling example, let’s rewrite that using this approach separating out the thesis and preview:
J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella like rags to riches story. First, I will tell you about J.K. Rowling’s humble beginnings. Then, I will describe her personal struggles as a single mom. Finally, I will explain how she overcame adversity and became one of the richest women in the United Kingdom.
There is no best way to approach this. This is up to your instructor.
Writing the Body of Your Speech
Once you have finished the important work of deciding what your speech will be about, as well as formulating the purpose statement and crafting the thesis, you should turn your attention to writing the body of your speech. All of your main points are contained in the body, and normally this section is prepared well before you ever write the introduction or conclusion. The body of your speech will consume the largest amount of time to present; and it is the opportunity for you to elaborate on facts, evidence, examples, and opinions that support your thesis statement and do the work you have outlined in the specific purpose statement. Combining these various elements into a cohesive and compelling speech, however, is not without its difficulties, the first of which is deciding which elements to include and how they ought to be organized to best suit your purpose.
Good design is making something intelligible and memorable. Great design is making something memorable and meaningful.
~ Dieter Rams
Contributors and Attributions
- Template:ContribCCComm105

What is a thesis statement? I need some examples, too.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement clearly identifies the topic being discussed, includes the points discussed in the paper, and is written for a specific audience. Your thesis statement belongs at the end of your first paragraph, also known as your introduction. Use it to generate interest in your topic and encourage your audience to continue reading.
You can read chapter four of Schaum's Quick Guide to Writing Great Research Papers an eBook in our online collection, click the title to open: "How Do I Write a Thesis Statement?" .
Another option is to think of a thesis statement as one complete sentence that expresses your position .
- Narrows the topic down to a specific focus of an investigation.
- Establishes a direction for the entire paper.
- Points forward to the conclusion.
- Always stated in your introduction. (Usually at the end of the first paragraph).
- Always take a stand and justify further discussion.
A thesis statement is not a statement of fact.
Your readers—especially your instructors—want to read writing that engages them. Consequently, you must write thesis statements that are arguable, not factual. Statements of fact seem easy to write about because, well, they are easy to prove. After all, they’re facts. The problem is that you cannot write engaging papers around statements of fact. Such theses prevent you from demonstrating critical thinking and analytical skills, which you want to show your instructor. If you were to write a paper around the next two statements, your writing would probably be quite dull because you would be restating facts that the general public already knows.
Thesis Statements always take a stand and justify further discussion.
In order to make your writing interesting, you should develop a thesis statement that is arguable. Sometimes you will be writing to persuade others to see things your way and other times you will simply be giving your strong opinion and laying out your case for it.
Take a look at the following examples:
Statement of fact:
Small cars get better fuel mileage than 4x4 pickup trucks.
Arguable thesis statement:
The government should ban 4x4 pickup trucks except for work-related use.
Foul language is common in movies.
The amount of foul language in movies is disproportionate to the amount of foul language in real life.
State ment of fact:
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease.
Arguable thesis statement/opening paragraph:
Researchers think the incidence of celiac disease is increasing in the USA not only because of an increase in the ability and awareness to diagnose it, but also because of changes in the agricultural system. In particular, they are looking at the increased use of pesticides, insecticides, and genetically modified wheat as culprits. Some of these theories are more likely to be valid than others.
Links & Files
- Thesis Builder
- Reading and Writing
- Weekly Written Assignments
- Research Papers
- Last Updated Feb 27, 2024
- Views 1388197
- Answered By Kerry Louvier
FAQ Actions
- Share on Facebook
Comments (6)
- this is really helpful by rita on Nov 14, 2021
- Yes, thank you. This is really helpful. It's been YEARS since I have encountered the term "thesis statement", and I needed a refresher on what it was before beginning my final presentation for a college course. This page answered all of my questions! by Brigitte on Dec 06, 2021
- Thank You. This helped by Deborah Smith on Mar 23, 2022
- Great explanation. This will definitely help my writing, by Jack on Dec 15, 2022
- This a very helpful website for me. Thank you by Catie on Jan 09, 2023
- This is very helpful. Thank you by George Wilson on Jan 31, 2024
Hello! We're here to help! Please log in to ask your question.
Need an answer now? Search our FAQs !
How can I find my course textbook?
You can expect a prompt response, Monday through Friday, 8:00 AM-4:00 PM Central Time (by the next business day on weekends and holidays).
Questions may be answered by a Librarian, Learning Services Coordinator, Instructor, or Tutor.

- [email protected]
- Shapiro Library
- SNHU Library Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ: What is a thesis statement and how do I write one?
- 7 Academic Integrity & Plagiarism
- 60 Academic Support, Writing Help, & Presentation Help
- 27 Access/Remote Access
- 7 Accessibility
- 9 Building/Facilities
- 7 Career/Job Information
- 26 Catalog/Print Books
- 26 Circulation
- 128 Citing Sources
- 14 Copyright
- 310 Databases
- 24 Directions/Location
- 18 Faculty Resources/Needs
- 7 Hours/Contacts
- 2 Innovation Lab & Makerspace/3D Printing
- 25 Interlibrary Loan
- 43 IT/Computer/Printing Support
- 3 Library Instruction
- 37 Library Technology Help
- 6 Multimedia
- 17 Online Programs
- 19 Periodicals
- 25 Policies
- 8 RefWorks/Citation Managers
- 4 Research Guides (LibGuides)
- 217 Research Help
- 23 University Services
Last Updated: Apr 01, 2024 Views: 5
What is a thesis statement.
A thesis statement is a sentence that states the main idea of your paper. It is not just a statement of fact, but a statement of position. What argument are you making about your topic? Your thesis should answer that question.
How long should my thesis statement be?
Thesis statements are often just one sentence. Keep thesis statements concise, without extra words or information. If you are having trouble keeping your thesis statement to one sentence, consider the following:
- Is your thesis is specific enough?
- Does your thesis directly supports your paper?
- Does your thesis accurately describes your purpose or argue your claim?
Can I see some example thesis statements?
The following websites have examples of thesis statements:
- Thesis Statements This link opens in a new window (UNC)
- Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements This link opens in a new window (OWL at Purdue)
- Writing an Effective Thesis Statement This link opens in a new window (Indiana River State College)
These web resources may be helpful if you are looking for examples. However, be sure to evaluate any sources you use! The Shapiro Library cannot vouch for the accuracy of information provided on external websites.
Where can I find more information?
Video tutorials.
- The Persuasive Thesis: How to Write an Argument This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Research and Citation Playlist This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Planning a Paper series: Drafting a Thesis Statement This link opens in a new window ( Infobase Learning Cloud - SNHU Login Required)
More Information
- Build a Critical Analysis Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Build a Compare & Contrast Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Build a History Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Build a Persuasive Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
Further Help
This information is intended to be a guideline, not expert advice. Please speak to your instructor about the appropriate way to craft thesis statements for your class assignments and projects.
Campus Students
To access Academic Support, visit your Brightspace course and select “Tutoring and Mentoring” from the Academic Support pulldown menu.
Online Students
To access help with citations and more, visit the Academic Support via modules in Brightspace:
- Academic Support Overview: Getting Help with your Schoolwork This link opens in a new window
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 0 No 0
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) are a self-serve option for users to search and find answers to their questions.
Use the search box above to type your question to search for an answer or browse existing FAQs by group, topic, etc.
Tell Me More
Link to Question Form
More assistance.
Submit a Question
Related FAQs

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
Here is an example of a thesis statement with no subtopics mentioned: While cars have undoubted advantages, they also have significant drawbacks. This thesis statement tells us the specific topic of the essay (advantages and disadvantages of cars) and the method of organisation (advantages should come first, disadvantages second).
Some students mistakenly make a general statement when they need to make a thesis statement. For example, "Poverty is a social problem" is a general statement that does not outline an argument. On the other hand, "School programs designed to counteract the effect of poverty can help undermine the long-lasting effects of low family income" is a ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Using paper checkers responsibly. 2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence. 3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper. 4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your ...
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
It is a brief statement of your paper's main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile. No credit card needed. Get 30 days free. You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the ...
A thesis statement is: The statement of the author's position on a topic or subject. Clear, concise, and goes beyond fact or observation to become an idea that needs to be supported (arguable). Often a statement of tension, where the author refutes or complicates an existing assumption or claim (counterargument).
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
4. A strong thesis statement is specific. A thesis statement should show exactly what your paper will be about, and will help you keep your paper to a manageable topic. For example, if you're writing a seven-to-ten page paper on hunger, you might say: World hunger has many causes and effects. This is a weak thesis statement for two major reasons.
How to Write a Good Thesis Statement: Steps & Thesis Statement Examples. Consider the subject matter of your paper carefully from the first paragraph and write at least three diverse subjects related to the main topic being discussed. If your subject is related to climate change, write a thesis statement by asking: What affects climate change?
Write a draft thesis statement: Using the main argument you identified, draft a preliminary thesis statement that clearly expresses your point of view. Refine your thesis statement: Revise and refine your thesis statement to make sure it is clear, specific, and strong. Make sure that your thesis statement is supported by evidence and relevant ...
Using paper checkers responsibly. Pollution is bad for the environment. This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem.
A thesis statement can be defined as a sentence that describes the main idea of the research or thesis to inform the reader of the argument the research will pursue and the reason the author adopts a specific stance on the subject. Essentially, it expresses the author's judgment or opinion based on a review of the literature or personal ...
If you are writing an expository essay, your thesis statement should explain to the reader what she will learn in your essay. For example: The United States spends more money on its military budget than all the industrialized nations combined. Gun-related homicides and suicides are increasing after years of decline.
What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute. An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic. Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's ...
This statement outlines the primary effects of the internet on society and can be further developed through specific examples and analysis. This statement can be supported through studies, data, and real-life cases that demonstrate the impact of the internet on communication, information access, and privacy concerns.
A Thesis Statement: Describes how you interpret the subject matter's cause, significance, and results. Is a guideline for the paper. In other words, it provides an understanding of the research topic. Directly answers the question you are asked. The thesis is not the question itself but an interpretation of it.
The general purpose statement of a speech may be to inform, to persuade, to celebrate, or to entertain. Thus, it is common to frame a specific purpose statement around one of these goals. According to O'Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein, a specific purpose statement "expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in ...
A thesis statement clearly identifies the topic being discussed, includes the points discussed in the paper, and is written for a specific audience. Your thesis statement belongs at the end of your first paragraph, also known as your introduction. Use it to generate interest in your topic and encourage your audience to continue reading.
A thesis statement is a specific statement that tells the reader the exact purpose of the literary work. This is an example of general statements moving towards specific statements.
The following websites have examples of thesis statements: Thesis Statements This link opens in a new window (UNC) Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements This link opens in a new window (OWL at Purdue) Writing an Effective Thesis Statement This link opens in a new window (Indiana River State College)