- Precalculus
- Signup / Login


About This Course
Welcome to the Math Medic Geometry course! Here you will find a ready-to-be-taught lesson for every day of the school year, along with expert tips and questioning techniques to help the lesson be successful. Each lesson is designed to be taught in an Experience First, Formalize Later (EFFL) approach, in which students work in small groups on an engaging activity before the teacher formalizes the learning.
Our Geometry course develops reasoning, justification, and proof skills through an in-depth study of shapes and their properties, rigid transformations and congruence, and the relationship between similarity and right triangle trigonometry. Rich opportunities for problem solving culminate in the unit on surface area and volume. This course was created using the Common Core State Standards as a guide. The standards taught in each Math Medic Geometry lesson can be found here . Additionally, we've chosen to include a unit on Statistics and Probability that can be used as a stand-alone unit at any time during high school course work. The unit overviews and learning targets for the Math Medic Geometry course can be found here .
Math Medic Help
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 3: Linear relationships
Lesson 3: representing proportional relationships.
- Graphing proportional relationships: unit rate (Opens a modal)
- Graphing proportional relationships from a table (Opens a modal)
- Graphing proportional relationships from an equation (Opens a modal)
- Graphing proportional relationships Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 4: Comparing proportional relationships
- Rates & proportional relationships example (Opens a modal)
- Rates & proportional relationships: gas mileage (Opens a modal)
- Rates & proportional relationships Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
Lesson 7: Representations of linear relationships
- Linear & nonlinear functions: missing value (Opens a modal)
Lesson 8: Translating to y=mx+b
- Intro to slope-intercept form (Opens a modal)
- Graph from slope-intercept equation (Opens a modal)
Lesson 9: Slopes don't have to be positive
- Intro to intercepts (Opens a modal)
- Slope-intercept equation from slope & point (Opens a modal)
- Linear & nonlinear functions: word problem (Opens a modal)
- Intercepts from a graph Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Slope from graph Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Slope-intercept intro Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Graph from slope-intercept form Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Slope-intercept equation from graph Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 10: Calculating slope
- No videos or articles available in this lesson
- Slope from two points Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 11: Equations of all kinds of lines
- Converting to slope-intercept form (Opens a modal)
Extra practice: Slope
- Intro to slope (Opens a modal)
- Worked examples: slope-intercept intro (Opens a modal)
- Graphing slope-intercept form (Opens a modal)
- Writing slope-intercept equations (Opens a modal)
- Slope-intercept form review (Opens a modal)
- Slope-intercept from two points Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 12: Solutions to linear equations
- Solutions to 2-variable equations (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: solutions to 2-variable equations (Opens a modal)
- Solutions to 2-variable equations Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 13: More solutions to linear equations
- Completing solutions to 2-variable equations (Opens a modal)
- Complete solutions to 2-variable equations Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Extra practice: Intercepts
- x-intercept of a line (Opens a modal)
- Intercepts from an equation (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: intercepts from an equation (Opens a modal)
- Intercepts of lines review (x-intercepts and y-intercepts) (Opens a modal)
- Intercepts from an equation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!

Unit 4 Similarity and Right Triangle Trigonometry
Learning focus.
Describe the essential features of a dilation transformation.
Lesson Summary
In this lesson, we observed the key features of a dilation transformation while figuring out how a photocopy machine enlarges an image. We learned how to locate points on a dilated image by using the center and scale factor that define a specific dilation. We observed that “the same shape, different size” relationship between the pre-image and image figures are a consequence of the way dilations are defined.
Create similar figures by dilation given the scale factor.
Prove a theorem about the midlines of a triangle using dilations.
In this lesson, we extended our understanding of similar figures. Since corresponding segments of similar figures are proportional, and dilations produce similar figures, corresponding parts of an image and its pre-image after a dilation are proportional. We also learned that corresponding line segments in a dilation are parallel. These two observations provided a tool for proving a theorem about the midlines of a triangle, a segment connecting the midpoints of two sides of a triangle.
Determine criteria for triangle similarity.
In this lesson, we examined what it means to say that two figures are similar geometrically, and we examined conditions under which two triangles will be similar. We wrote and justified several theorems for triangle similarity criteria.
Prove that a line drawn parallel to one side of a triangle that intersects the other two sides divides the other two sides proportionally.
In a previous lesson, we learned that a midline of a triangle, a line that passes through the midpoints of two of the sides, is parallel to the third side and half its length. In this lesson, we extended this theorem to include other segments that cut the sides of a triangle proportionally. We also proved a non-intuitive “side-splitting” theorem about the multiple segments formed when multiple lines parallel to a side of a triangle cut the other two sides of the triangle.
Practice using geometric reasoning in computational work.
In this lesson, we drew upon a variety of theorems to support the computational work of finding missing sides and angles. To identify which theorems to use, we had to examine the available features of the diagram. For many measurements, multiple strategies could be used. We also used the diagram, along with our computed measurements, to develop and justify a conjecture for the sum of the interior angles of any polygon, similar to the theorem we proved previously about the sum of the interior angles in a triangle.
Locate the midpoint of a segment and a point that divides the segment in a given ratio.
In this lesson, we examined strategies for dividing a line segment into two parts that fit a given ratio. One common application of this concept is to find the coordinates of the midpoint of a segment, given the coordinates of the endpoints.
Prove the Pythagorean theorem algebraically.
In today’s lesson, we learned that drawing the altitude of a right triangle from the vertex at the right angle to the hypotenuse divides the right triangle into two smaller triangles that are similar to each other and to the original right triangle. We were able to prove the Pythagorean theorem using proportionality statements about the three similar triangles.
Investigate corresponding ratios of right triangles with the same acute angle.
In this lesson, we learned about some special ratios, called trigonometric ratios, that occur in right triangles. If two right triangles have a pair of corresponding acute angles that are congruent, the right triangles will be similar. Therefore, corresponding ratios of the sides of these two right triangles will be equal. This observation is so useful when working with right triangles that have the same acute angle that values of these ratios were recorded in tables for each acute angle between 0 ° and 90 ° .
Examine properties of trigonometric expressions.
In this lesson, we examined some relationships between trigonometric ratios, such as a relationship between the sine and cosine of complementary angles. We were able to use the properties of a right triangle, including the Pythagorean theorem that describes a relationship between the lengths of the sides, to justify the observations we made today.
Solve for the missing side and angle measures in a right triangle.
In this lesson, we extended our strategies for finding unknown sides and angles in a right triangle beyond using the Pythagorean theorem and the angle sum theorem for triangles, since sometimes we don’t have enough information in terms of side lengths or angle measures to use these theorems. We found that trigonometric ratios are useful in solving for unknown sides and that inverse trigonometric relationships are useful for finding unknown angles in a right triangle. Adding these tools allows us to find all of the missing sides and angles in a right triangle given two pieces of information: two sides of the triangle or one side and an angle.
Solve application problems using trigonometry.
In this lesson, we learned about the modeling process and how to use right triangle trigonometry to model many different types of applications, even applications that didn’t naturally include right triangles. A right triangle became a tool for representing a situation so we could draw upon trigonometric ratios and inverse trigonometric relationships to answer important problems in construction, aviation, transportation, and other contexts.
Geo.4 Right Triangle Trigonometry
In this unit students build an understanding of ratios in right triangles which leads to naming cosine, sine, and tangent as trigonometric ratios. Practicing without naming the ratios allows students to connect similarity, proportional reasoning, and scale factors to right triangles with a congruent acute angle before the calculator takes over some of the computation. Students encounter several contexts to both make sense of and apply right triangle measurement.
Angles and Steepness
- 1 Angles and Steepness
- 2 Half a Square
- 3 Half an Equilateral Triangle
- 4 Ratios in Right Triangles
- 5 Working with Ratios in Right Triangles
Defining Trigonometric Ratios
- 6 Working with Trigonometric Ratios
- 7 Applying Ratios in Right Triangles
- 8 Sine and Cosine in the Same Right Triangle
- 9 Using Trigonometric Ratios to Find Angles
- 10 Solving Problems with Trigonometry
- 11 Approximating Pi
- For Parents
- For Teachers
- Teaching Topics

- Kindergarten
- End of the Year
- Grade Level Goals
- Family Letters
- Student Gallery
- Understanding EM
- Algorithms/ Computation
- Student Links

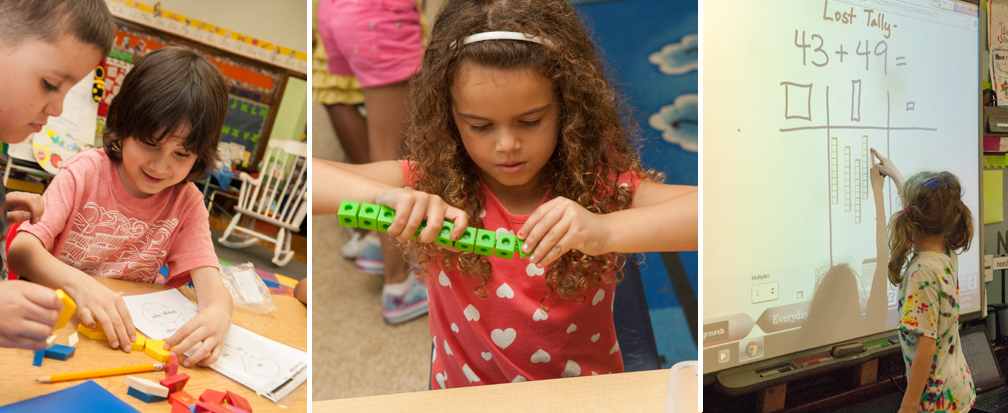
Everyday Mathematics for Parents: What You Need to Know to Help Your Child Succeed
The University of Chicago School Mathematics Project
University of Chicago Press
Learn more >>
Related Links
Help with algorithms.
Access video tutorials, practice exercises, and information on the research basis and development of various algorithms.
Everyday Mathematics Online
With a login provided by your child's teacher, access resources to help your child with homework or brush up on your math skills.
Parent Connections on Publisher's site
McGraw-Hill Education offers many resources for parents, including tips, activities, and helpful links.
Parent Resources on EverydayMath.com
EverydayMath.com features activity ideas, literature lists, and family resources for the EM curriculum.
Understanding Everyday Mathematics for Parents
Learn more about the EM curriculum and how to assist your child.

Have an account?
Suggestions for you See more

Classifying Triangles
15.1k plays, 6th - 8th , 4th - 5th , special right triangles, triangle inequality theorem.

Geometry Unit 4 Homework #3
Mathematics.
25 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
An acute triangle has __________ angles that each measure less than 90°.
An isosceles triangle has _________ equal sides.
A right triangle has one angle that measures _______ and two acute angles.
less than 90°
more than 90°
An ____________ triangle has three equal sides.
equilateral
An obtuse triangle has one angle that measures _____________ 90°.
A _________ triangle has no equal sides.
- 7. Multiple Choice Edit 5 minutes 1 pt If a triangle has all angles less than 90° and two equal sides, what type of triangle is it? Acute Isosceles Acute Scalene Obtuse Scalene Obtuse Isosceles
- 8. Multiple Choice Edit 5 minutes 1 pt If a triangle has one angle greater than 90° and no equal sides, what type of triangle is it? Acute Isosceles Acute Scalene Obtuse Scalene Obtuse Isosceles
- 9. Multiple Choice Edit 5 minutes 1 pt If a triangle has one angle exactly 90° and two equal sides, what type of triangle is it? Right Isosceles Acute Scalene Obtuse Scalene Obtuse Isosceles
- 10. Multiple Choice Edit 5 minutes 1 pt If a triangle has all three angles equivalent and all three sides equivalent, what type of triangle is it? Acute Isosceles Equilateral Obtuse Scalene Obtuse Isosceles
Find the measure of the angle indicated.
Find the value of x?
What is the value
Use the distance formula to find the measure of the sides of LMN and classify it by its sides:
L(2,7) M(-4,2) N(3,-6)
5, 6.1, 2.8: Scalene
5, 10.2, 10.2: Isosceles
7.8, 10.6, 13.0: Scalene
6.4, 9.2, 6.4: Isosceles
Use the figure to find the measure of angle P.
Solve for x in the figure
In △ QRS, if m ∠ Q is two less than six times x,
m ∠ R is sixteen less than seven times x,
and m ∠ S is three times x plus 6.
What is the value of x?
What is the measure of ∠R?
What is the measure of ∠S?
What is the measure of ∠Q?
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
which similarity statement is true. b. triangle wyz~ triangle wzx~ triangle zyx. what is the value of x. a. 2 sqrt 3. what is the value of x in the diagram below. c. x=4 sqrt 70. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like which segement of the hypotenuse is adjacent to AB, what is the geometric mean of 7 and 12, which ...
FREE Lessons, Homework Sets, and Videos. eMATHinstruction makes teaching math a whole lot easier and learning math a whole lot more fun. We provide FREE lessons, videos and homework sets for middle and high school mathematics courses. Our standards-aligned, scaffolded curricula are easy to use, and save teachers time and energy.
TIME CODES IN PINNED COMMENT. Here are all the solutions to the homework 3 geometry assignment for isosceles & equilateral triangles. All content copyright G...
Unit 1 Lines. Unit 2 Angles. Unit 3 Shapes. Unit 4 Triangles. Unit 5 Quadrilaterals. Unit 6 Coordinate plane. Unit 7 Area and perimeter. Unit 8 Volume and surface area. Unit 9 Pythagorean theorem.
This work is derived from Eureka Math ™ and licensed by Great Minds. ©2015 Great Minds. eureka-math.org -M4-TE 1.3 052 4. Lesson 2: 5Decompose and recompose shapes to compare areas. Problem Set 3Lesson 2 4 ... 3Lesson 3 Homework 4 3. Each is 1 square unit. Write the area of each rectangle. Then, draw a different rectangle with the
The unit overviews and learning targets for the Math Medic Geometry course can be found here. Units. Unit 1: Reasoning in Geometry. Unit 2: Building Blocks of Geometry. Unit 3: Congruence Transformations. Unit 4: Triangles and Proof. Unit 5: Quadrilaterals and Other Polygons. Unit 6: Similarity.
Angle and angle are both 30 degrees. and both measure 3 units. and both measure 2 units. Andre thinks thinks these triangles must be congruent. Clare says she knows they might not be congruent. Construct 2 triangles with the given measurements that aren't congruent. Explain why triangles with 3 congruent parts aren't necessarily congruent.
Unit 3: Linear relationships. 1,200 possible mastery points. Mastered. Proficient. Familiar. Attempted. Not started. ... Lesson 3: Representing proportional relationships. Learn. Graphing proportional relationships: unit rate ... Graph from slope-intercept form Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Slope-intercept equation from graph Get 3 of 4 ...
Home / For Teachers / Common Core Geometry / Unit 3 - Euclidean Triangle Proof. Unit 3 - Euclidean Triangle Proof. Lesson 1. Drawing Inferences from Givens. LESSON/HOMEWORK. LESSON VIDEO. ANSWER KEY. EDITABLE LESSON. EDITABLE KEY.
Lesson Summary. In this lesson, we learned about some special ratios, called trigonometric ratios, that occur in right triangles. If two right triangles have a pair of corresponding acute angles that are congruent, the right triangles will be similar. Therefore, corresponding ratios of the sides of these two right triangles will be equal.
The goal of this activity is to get students familiar with the two smaller right triangles formed by drawing an altitude to the hypotenuse of a right triangle. The activity previews the activities that students will do later in this lesson and the next. Listen to hear if students compare the two smaller triangles to the larger triangle, or make ...
Problem 3. In triangle ABC ( not a right triangle), altitude CD is drawn to side AB. The length of AB is c. Which of the following statements must be true? The measure of angle ACB is the same measure as angle B. b^2=c^2+a^2. Triangle ADC is similar to triangle ACB. The area of triangle ABC equals \frac {1} {2}h\boldcdot c.
3 Write each fraction or mixed number as a decimal number. ex 5 3 10 ex 12 4 100 ex 3 17 100 a 7 10 b 3 5 100 c 4 100 d 4 38 100 e 1 9 100 f 9 10 4 Use a greater than (>), less than (<), or equal sign to show the relationship between the decimal numbers below. ex 1.09 1.9 a 1.12 1.2 b 3.5 3.48 c 23.81 23.85 d 4.50 4.5 e 3.06 3.65 < hundredths ...
Table of Contents for Common Core Geometry. Unit 1 - Essential Geometric Tools and Concepts. Unit 2 - Transformations, Rigid Motions, and Congruence. Unit 3 - Euclidean Triangle Proof. Unit 4 - Constructions. Unit 5 - The Tools of Coordinate Geometry. Unit 6 - Quadrilaterals. Unit 7 - Dilations and Similarity. Unit 8 - Right Triangle Trigonometry.
Lesson 7 Reasoning About Solving Equations (Part 1) Let's see how a balanced hanger is like an equation and how moving its weights is like solving the equation. Lesson Activities. Practice Problems.
Geo.4 Right Triangle Trigonometry. In this unit students build an understanding of ratios in right triangles which leads to naming cosine, sine, and tangent as trigonometric ratios. Practicing without naming the ratios allows students to connect similarity, proportional reasoning, and scale factors to right triangles with a congruent acute ...
Unit Resources: Grade 3 Unit 4: ... Lesson. Vocabulary. Home Link Help Games. 4-1. Multiples of Equal Groups multiplication/division diagram. multiples of a number. ... With a login provided by your child's teacher, access resources to help your child with homework or brush up on your math skills.
Lesson 7. Systems of Linear Equations (Primarily 3 by 3) LESSON/HOMEWORK. LESSON VIDEO. ANSWER KEY. EDITABLE LESSON. EDITABLE KEY.
Geometry Unit 4 Homework #3 quiz for 10th grade students. Find other quizzes for Mathematics and more on Quizizz for free!
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Use the formula (x-x1)²+(y-y1)²=r² to determine the center and radius of the circle from the equation. (x-9)² + (y-8)² = 4², Use the formula (x-x1)^2+(y-y1)^2=r^2 to determine the center and radius of the circle from the equation. x² + 2x + y² + 8y + 8 = 0, Given the center and radius, write the standard equation for the ...