EdDPrograms.org

What is an Ed.D. Dissertation? Complete Guide & Support Resources
Wondering how to tackle the biggest doctoral challenge of all? Use our guide to the Ed.D. dissertation to get started! Learn about the purpose of a Doctor of Education dissertation and typical topics for education students. Read through step-by-step descriptions of the dissertation process and the 5-chapter format. Get answers to Ed.D. dissertation FAQs . Or skip to the chase and find real-world examples of Doctor of Education dissertations and websites & resources for Ed.D. dissertation research.
What is an Ed.D. Dissertation?
Definition of an ed.d. dissertation.
An Ed.D. dissertation is a 5-chapter scholarly document that brings together years of original research to address a problem of practice in education. To complete a dissertation, you will need to go through a number of scholarly steps , including a final defense to justify your findings.
Purpose of an Ed.D. Dissertation
In a Doctor of Education dissertation, you will be challenged to apply high-level research & creative problem-solving to real-world educational challenges. You may be asked to:
- Take a critical look at current educational & administrative practices
- Address urgent issues in the modern education system
- Propose original & practical solutions for improvements
- Expand the knowledge base for educational practitioners
Topics of Ed.D. Dissertations
An Ed.D. dissertation is “customizable.” You’re allowed to chose a topic that relates to your choice of specialty (e.g. elementary education), field of interest (e.g. curriculum development), and environment (e.g. urban schools).
Think about current problems of practice that need to be addressed in your field. You’ll notice that Ed.D. dissertation topics often address one of the following:
- Academic performance
- Teaching methods
- Access to resources
- Social challenges
- Legislative impacts
- System effectiveness
Wondering how others have done it? Browse through Examples of Ed.D. Dissertations and read the titles & abstracts. You’ll see how current educators are addressing their own problems of practice.
Ed.D. Dissertation Process
1. propose a dissertation topic.
Near the beginning of a Doctor of Education program, you’ll be expected to identify a dissertation topic that will require substantial research. This topic should revolve around a unique issue in education.
Universities will often ask you to provide an idea for your topic when you’re applying to the doctoral program. You don’t necessarily need to stick to this idea, but you should be prepared to explain why it interests you. If you need inspiration, see our section on Examples of Ed.D. Dissertations .
You’ll be expected to solidify your dissertation topic in the first few semesters. Talking to faculty and fellow Ed.D. students can help in this process. Better yet, your educational peers will often be able to provide unique perspectives on the topic (e.g. cultural differences in teaching methods).
2. Meet Your Dissertation Chair & Committee
You won’t be going through the Ed.D. dissertation process alone! Universities will help you to select a number of experienced mentors. These include:
- Dissertation Chair/Faculty Advisor: The Chair of the Dissertation Committee acts as your primary advisor. You’ll often see them referred to as the Supervising Professor, Faculty Advisor, or the like. You’ll rely on this “Obi Wan” for their knowledge of the field, research advice & guidance, editorial input on drafts, and more. They can also assist with shaping & refining your dissertation topic.
- Dissertation Committee: The Dissertation Committee is made up of ~3 faculty members, instructors and/or adjuncts with advanced expertise in your field of study. The Committee will offer advice, provide feedback on your research progress, and review your work & progress reports. When you defend your proposal and give your final defense , you’ll be addressing the Dissertation Committee.
3. Study for Ed.D. Courses
Doctor of Education coursework is designed to help you: a) learn how to conduct original research; and b) give you a broader perspective on your field of interest. If you take a look at the curriculum in any Ed.D. program, you’ll see that students have to complete credits in:
- Practical Research Methods (e.g. Quantitative Design & Analysis for Educational Leaders)
- Real-World Educational Issues (e.g. Educational Policy, Law & Practice)
When you’re evaluating possible Ed.D. programs, pay attention to the coursework in real-world educational issues. You’ll want to pick an education doctorate with courses that complement your dissertation topic.
4. Complete a Literature Review
A literature review is an evaluation of existing materials & research work that relate to your dissertation topic. It’s a written synthesis that:
- Grounds your project within the field
- Explains how your work relates to previous research & theoretical frameworks
- Helps to identify gaps in the existing research
Have a look at Literature Review Guides if you’d like to know more about the process. Our section on Resources for Ed.D. Dissertation Research also has useful links to journals & databases.
5. Craft a Dissertation Proposal
During the first two years of your Doctor of Education, you’ll use the knowledge you’ve learned from your coursework & discussions to write the opening chapters of your dissertation, including an:
- Introduction that defines your chosen topic
- Literature Review of existing research in the field
- Proposed Research Methodology for finding the answer to your problem
When you’re putting together these elements, think about the practicals. Is the topic too big to address in one dissertation? How much time will your research take and how will you conduct it? Will your dissertation be relevant to your current job? If in doubt, ask your faculty advisor.
6. Defend Your Dissertation Proposal
About midway through the Ed.D. program, you will need to present your proposal to your Dissertation Committee. They will review your work and offer feedback. For example, the Committee will want to see that:
- Your research topic is significant.
- Your research methodology & timeline make sense.
- Relevant works are included in the literature review.
After the Committee approves your proposal, you can get stuck into conducting original research and writing up your findings. These two important tasks will take up the final years of your doctorate.
7. Conduct Original Research into Your Topic
As a Doctor of Education student, you will be expected to conduct your own research. Ed.D. students often use a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods (quantitative/qualitative) approach in this process.
- Quantitative Research: Collection & analysis of numerical data to identify characteristics, discover correlations, and/or test hypotheses.
- Qualitative Research: Collection & analysis of non-numerical data to understand & explain phenomena (e.g. questionnaires, in-depth interviews, focus groups, video artifacts, etc.).
Your Ed.D. coursework will ground you in research methods & tools, so you’ll be prepared to design your own project and seek IRB approval for any work involving human subjects.
Note: Occasionally, universities can get creative. For example, the Ed.D. program at San Jose State University asks students to produce a documentary film instead of conducting traditional research.
8. Write the Rest of Your Dissertation
Once you have written up the first few chapters of your dissertation (Intro, Literature Review & Proposed Methodology) and completed your research work, you’ll be able to complete the final chapters of your dissertation.
- Chapter 4 will detail your research findings.
- Chapter 5 is a conclusion that summarizes solutions to your problem of practice/topic.
This is where you and your faculty advisor will often have a lot of interaction! For example, you may need to rework the first few chapters of your dissertation after you’ve drafted the final chapters. Faculty advisors are extremely busy people, so be sure to budget in ample time for revisions and final edits.
9. Defend Your Dissertation
The final defense/candidacy exam is a formal presentation of your work to the Dissertation Committee. In many cases, the defense is an oral presentation with visual aides. You’ll be able to explain your research findings, go through your conclusions, and highlight new ideas & solutions.
At any time, the Committee can challenge you with questions, so you should be prepared to defend your conclusions. But this process is not as frightening as it sounds!
- If you’ve been in close contact with the Committee throughout the dissertation, they will be aware of your work.
- Your faculty advisor will help you decide when you’re ready for the final defense.
- You can also attend the defenses of other Ed.D. students to learn what questions may be asked.
Be aware that the Committee has the option to ask for changes before they approve your dissertation. After you have incorporated any notes from the Committee and addressed their concerns, you will finalize the draft, submit your dissertation for a formal review, and graduate.
Ed.D. Dissertation Format: 5 Chapters
Chapter 1: introduction.
Your Doctor of Education dissertation will begin with an introduction. In it, you’ll be expected to:
- Provide an overview of your educational landscape
- Explain important definitions & key concepts
- Define a real-world topic/problem of practice
- Outline the need for new studies on this topic
Chapter 2: Literature Review
The literature review is a summary of existing research in the field. However, it is not an annotated bibliography. Instead, it’s a critical analysis of current research (e.g. trends, themes, debates & current practices). While you’re evaluating the literature, you’re also looking for the gaps where you can conduct original research.
Sources for a literature review can include books, articles, reports, websites, dissertations, and more. Our section on Resources for Ed.D. Dissertation Research has plenty of places to start.
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
In the research methodology, you’ll be expected to explain:
- The purpose of your research
- What tools & methods you plan to use to research your topic/problem of practice
- The design of the study
- Your timeline for gathering quantitative & qualitative data
- How you plan to analyze that data
- Any limitations you foresee
Chapter 4: Results & Analysis
Chapter 4 is the place where you can share the results of your original research and present key findings from the data. In your analysis, you may also be highlighting new patterns, relationships, and themes that other scholars have failed to discover. Have a look at real-life Examples of Ed.D. Dissertations to see how this section is structured.
Chapter 5: Discussions & Conclusions
The final chapter of your Ed.D. dissertation brings all of your work together in a detailed summary. You’ll be expected to:
- Reiterate the objectives of your dissertation
- Explain the significance of your research findings
- Outline the implications of your ideas on existing practices
- Propose solutions for a problem of practice
- Make suggestions & recommendations for future improvements
Ed.D. Dissertation FAQs
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis.
- Dissertation: A dissertation is a 5-chapter written work that must be completed in order to earn a doctoral degree (e.g. Ph.D., Ed.D., etc.). It’s often focused on original research.
- Thesis: A thesis is a written work that must be completed in order to earn a master’s degree. It’s typically shorter than a dissertation and based on existing research.
How Long is a Ed.D. Dissertation?
It depends. Most Ed.D. dissertations end up being between 80-200 pages. The length will depend on a number of factors, including the depth of your literature review, the way you collect & present your research data, and any appendices you might need to include.
How Long Does it Take to Finish an Ed.D. Dissertation?
It depends. If you’re in an accelerated program , you may be able to finish your dissertation in 2-3 years. If you’re in a part-time program and need to conduct a lot of complex research work, your timeline will be much longer.
What’s a Strong Ed.D. Dissertation Topic?
Experts always say that Doctor of Education students should be passionate about their dissertation topic and eager to explore uncharted territory. When you’re crafting your Ed.D. dissertation topic , find one that will be:
- Significant
See the section on Examples of Ed.D. Dissertations for inspiration.
Do I Have to Complete a Traditional Dissertation for an Ed.D.?
No. If you’re struggling with the idea of a traditional dissertation, check out this guide to Online Ed.D. Programs with No Dissertation . Some Schools of Education give Ed.D. students the opportunity to complete a Capstone Project or Dissertation in Practice (DiP) instead of a 5-chapter written work.
These alternatives aren’t easy! You’ll still be challenged at the same level as you would be for a dissertation. However, Capstone Projects & DiPs often involve more group work and an emphasis on applied theory & research.
What’s the Difference Between a Ph.D. Dissertation and Ed.D. Dissertation?
Have a look at our Ed.D. vs. Ph.D. Guide to get a sense of the differences between the two degrees. In a nutshell:
- Ed.D. dissertations tend to focus on addressing current & real-world topics/problems of practice in the workplace.
- Ph.D. dissertations usually put more emphasis on creating new theories & concepts and even completely rethinking educational practices.
How Can I Learn More About Ed.D. Dissertations?
Start with the section on Examples of Ed.D. Dissertations . You can browse through titles, abstracts, and even complete dissertations from a large number of universities.
If you have a few Doctor of Education programs on your shortlist, we also recommend that you skim through the program’s Dissertation Handbook . It can usually be found on the School of Education’s website. You’ll be able to see how the School likes to structure the dissertation process from start to finish.
Ed.D. Dissertation Support
University & campus resources, dissertation chair & committee.
The first port of call for any questions about the Ed.D. dissertation is your Dissertation Chair. If you get stuck with a terrible faculty advisor, talk to members of the Dissertation Committee. They are there to support your journey.
University Library
An Ed.D. dissertation is a massive research project. So before you choose a Doctor of Education program, ask the School of Education about its libraries & library resources (e.g. free online access to subscription-based journals).
Writing Center
Many universities have a Writing Center. If you’re struggling with any elements of your dissertation (e.g. editing), you can ask the staff about:
- Individual tutoring
- Editorial assistance
- Outside resources
Mental Health Support
It’s well-known that doctoral students often face a lot of stress & isolation during their studies. Ask your faculty advisor about mental health services at the university. Staff in the School of Education and the Graduate School will also have information about on-campus counselors, free or discounted therapy sessions, and more.
Independent Dissertation Services
Dissertation editing services: potentially helpful.
There are scores of independent providers who offer dissertation editing services. But they can be expensive. And many of these editors have zero expertise in educational fields.
If you need help with editing & proofreading, proceed with caution:
- Start by asking your Dissertation Chair about what’s permitted for third party involvement (e.g. you may need to note any editor’s contribution in your dissertation acknowledgments) and whether they have any suggestions.
- The Graduate School is another useful resource. For example, Cornell’s Graduate School maintains a list of Editing, Typing, and Proofreading Services for graduate students.
Dissertation Coaches: Not Worth It
Dissertation coaches are defined as people who offer academic & mental support, guidance, and editorial input.
- That means the person who should be your coach is your Dissertation Chair/Faculty Advisor. Remember that faculty members on the Dissertation Committee can also provide assistance.
- If you’re looking for extra support, you might consider consulting a mentor in your line of work and collaborating with fellow Ed.D. students.
But hiring an independent Ed.D. dissertation coach is going to be an absolute waste of money.
Dissertation Writing Services: Just Don’t!
Universities take the dissertation process very seriously . An Ed.D. dissertation is supposed to be the culmination of years of original thought and research. You’re going to be responsible for the final product. You’re going to be defending your written work in front of a phalanx of experienced faculty members. You’re going to be putting this credential on your résumé for everyone to see.
If you cheat the process by having someone else write up your work, you will get caught.
Ed.D. Dissertation Resources
Examples of ed.d. dissertations, dissertation databases.
- Open Access Theses and Dissertations
- ProQuest Dissertations & Theses
- EBSCO Open Dissertations
Ed.D. Dissertations
- USF Scholarship Repository: Ed.D. Dissertations
- George Fox University: Doctor of Education
- UW Tacoma: Ed.D. Dissertations in Practice
- Liberty University: School of Education Doctoral Dissertations
- University of Mary Hardin-Baylor: Dissertation Collection
Ed.D. Dissertation Abstracts
- Michigan State University: Ed.D. Dissertation Abstracts
Ed.D. Dissertation Guides & Tools
General ed.d. guides.
- SNHU: Educational Leadership Ed.D./Ph.D. Guide
Dissertation Style Manuals
- Chicago Manual of Style
Style manuals are designed to ensure that every Ed.D. student follows the same set of writing guidelines for their dissertation (e.g. grammatical rules, footnote & quotation formats, abbreviation conventions, etc.). Check with the School of Education to learn which style manual they use.
Examples of Ed.D. Dissertation Templates
- Purdue University: Dissertation Template
- Walden University: Ed.D. Dissertation Template
Each School of Education has a standard dissertation template. We’ve highlighted a couple of examples so you can see how they’re formatted, but you will need to acquire the template from your own university.
Literature Review Guides
- UNC Chapel Hill: Writing Guide for Literature Reviews
- University of Alabama: How to Conduct a Literature Review
Resources for Ed.D. Dissertation Research
Journal articles.
- EBSCO Education Research Databases
- Education Resources Information Center (ERIC)
- Emerald Education eJournal Collection
- Gale OneFile: Educator’s Reference Complete
- Google Scholar
- NCES Bibliography Search Tool
- ProQuest Education Database
- SAGE Journals: Education
Useful Websites
- Harvard Gutman Library: Websites for Educators
- EduRef: Lesson Plans
Educational Data & Statistics
- Digest of Education Statistics
- Education Policy Data Center (EPDC)
- ICPSR Data Archive
- National Assessment of Educational Progress
- National Center for Education Statistics (NCES)
- UNESCO Institute for Statistics

Capstone Form and Style
Programs: edd dissertation/project study, edd dissertation/project study resources.
- EdD Project Study Template (APA 7)
- EdD Dissertation Template (APA 7)
- Instructions for Using the EdD Capstone Templates (APA 7)
Information on the Prospectus is located on the EdD page of the Office of Research and Doctoral Services website.
To prepare for the form and style review, use the following checklist, which is the same checklist we use when we review capstone manuscripts and the checklist we return to the student and committee along with their completed review.
- Form and Style Review Checklist (APA 7)
About the EdD Dissertation/Project Study
A dissertation or project study is a formal manuscript written to address a gap in educational practice, thus resolving a local problem. Walden dissertations consist of five chapters (Chapter 1: Introduction to the Study, Chapter 2: Literature Review, Chapter 3: Research Method, Chapter 4: Reflections and Conclusions, Chapter 5: Discussion, Conclusions, and Recommendations). Walden project studies consist of four sections (Section 1: The Problem, Section 2: The Methodology, Section 3: The Project, Section 4: Reflections and Conclusions).
Access samples of published dissertations through the Walden library website under Databases. You can also access the Office of Research and Doctoral Services's Doctoral Capstone and Project Resources for additional information on the dissertation and project study process, including the rubrics and the EdD Project Guide. If you have writing or APA questions about the proposal or final doctoral study, contact [email protected] .
Doctoral Capstone Template Guidance
To accompany the doctoral capstone template document, here is some information to note when first beginning to use the template.
- The document may contain various front matter elements (i.e., two title pages, the abstract, a Dedication page, and an Acknowledgements page), a Table of Contents (TOC), Lists of Tables and Figures, the document body text, a References list, and Appendices.
- Students should ensure that the text in brackets [ ] on the two title pages is changed to reflect their own information and then remove the brackets. This includes the title, name, degrees earned, degree program, and date of anticipated completion.
- Begin using the template by copying and pasting the text from a working document into the appropriate headings of the template and references to the reference list.
How to tag headings (so that headings show up in the TOC):
- Most headings are already placed into the document. Headings students add (i.e., primarily for the literature review and results chapters and sections) should be added by creating a new heading and tagging it so that it appears in the TOC when updated.
- Add a heading by first ensuring that the pilcrow [ ¶ ] is turned on—this allows the writer to see hidden formatting in the document that should not be deleted (e.g., page breaks and section breaks).
- Add the heading by placing the cursor where the heading should be inserted and creating a hard return.
- Then type the text for the heading and highlight it with the cursor, ensuring that you do NOT highlight the pilcrow.
- Once the text is highlighted, choose the appropriate APA Style heading from the Styles box on the Home tab. This is called tagging a heading. HINT: The Styles tab may need to be expanded by clicking on the small box with the arrow at the bottom of the Styles section.
How to update the TOC (to bring in new headings and update page numbers):
- Once new headings have been added or text created or inserted such that the page numbers have shifted, the TOC should be updated.
- Update the TOC by clicking on it with the cursor so that the section becomes grey.
- Then, right click (or control click on a Mac) and choose “Update field.”
- Depending on whether headings or just text has been added, choose “Update entire table” or “Update page numbers only.”
Template and Formatting Resources:
- Form and Style Document Formatting Expectations , including information on APA, margins, pagination, etc.
- SMRTguide on Fixing Errors in the TOC
- Academic Skills Center (ASC) Capstone Template Formatting Videos
- For questions regarding layout formatting in the doctoral capstone, contact [email protected]
- Previous Page: DSW Capstone Project
- Next Page: PhD Dissertation
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- News & Insights
- All News & Insights
PhD vs. EdD in Education: Nine expert tips to help you choose [with infographic]

If you want to elevate your career in education, an advanced degree can open the door to more job opportunities. Many schools offer graduate programs in education, but before you go down a rabbit hole of research, first decide if you want to get a PhD or EdD degree.
A PhD and EdD in education are both doctoral degrees. The one you choose will have a significant impact on your graduate school experience, and your career as well. (Already know what you want? Visit our Admission and Deadlines and Requirements pages for more information.)
For a quick overview of differences between the two degrees, view the infographic below or download it here .

Before we explore tips to guide your decision, let’s review important context for each degree.
What is a PhD in Education?
A PhD is a doctorate in philosophy. Historically, it was the first degree offered to students in the field of education and is perhaps more well-known than the EdD.
The PhD in Education is ideal for students who are excited by a career in research. Programs train you to interpret existing theory on a subject, identify opportunities for exploration, and advance theory through critical analysis. It is not necessarily a degree that prepares you for an administrative or leadership role.
With a PhD in Education, you will become an authority on a particular topic or range of topics, and make recommendations on how practitioners should approach or implement them. Examples of research topics might include teaching practices, the effect of learning environments on student outcomes, and inequity in education.
What is an EdD in Education?
An EdD is a doctorate in education, and prepares you for a career in educational leadership. Like the PhD degree, you will learn to interpret research. However, EdD programs train you to apply the research in real-world settings.
While pursuing your EdD degree, you will study critical theory and determine how you can implement it to drive change in K–12 classrooms, universities, community colleges and other organizations. You will also reflect on your role as a leader. Top EdD programs encourage you to analyze your relationship to your research topics and work environments. The goal is to ensure that your leadership is fair and equitable for all people.
PhD vs. EdD: What are the main differences?
The table below summarizes the key differences between a PhD and EdD in education:
Find your program
PhD vs. EdD: How to choose
To help you figure out which doctorate in education is right for you, check out these nine helpful tips:
1. Follow your passion
Rather than focusing on the title of the degree, think about what motivates you. Why did you get into education in the first place? Do you want to have a direct impact on classrooms or pursue big-picture change behind the scenes? You may assume that one degree is more prestigious than another, but it’s important to choose a path that will bring you personal satisfaction that is consistent with your career goals.
2. Picture your day-to-day
PhD and EdD programs are a significant time investment. If you’re struggling to decide because both degrees sound rewarding, try picturing what your daily life might look like in each program.
A PhD in Education is decidedly more research-heavy. A majority of your study will include—but is not limited to—investigating theory and research methodologies. By contrast, EdD programs include the application of your research. Much of your time will be spent using your knowledge to solve professional challenges.
3. Explore career options with a PhD in Education
Earning your PhD in education will make you a more desirable candidate for a range of research-oriented positions. Your ability to evaluate research and make recommendations will be a valuable skill to many organizations.
Many people with PhD in education degrees secure jobs as:
- University professor
- Research scholar
- Education director
- Policy researcher
Want specific examples? For a list of positions held by recent graduates from USC Rossier’s PhD in Urban Education program (PhD), check out our Benefits and Career Paths page.
4. Explore career options with an EdD in Education
EdD programs prepare you for different kinds of senior positions. You will be eligible for leadership roles primarily in education administration, however your high-level skill-set will be desirable to certain nonprofits and businesses as well.
Position titles for professionals with an EdD degree may include:
- Superintendent
- University or college president
- Director of a research center
- Development manager
- Curriculum developer
5. Compare PhD vs. EdD coursework
Doctor in education programs are rigorous and challenging, and while both are rooted in research, their paths diverge. Coursework in PhD programs highlights qualitative and quantitative research methods, and gives you the tools needed to perform your own research. You will also work on your dissertation, and be required to take oral and written exams.
Additionally, PhD students typically have the chance to work one-on-one with a research faculty member on their research. As you narrow your search for a graduate school, remember to review faculty and consider opportunities for collaboration.
EdD courses in educational leadership train you to view common problems in education from multiple perspectives. Courses early in the program urge you to use research as a tool that can provide practical solutions that promote equity. As you progress, you will then take actionable steps to address a problem of practice.
6. Review PhD vs. EdD specializations at different schools
You want to choose a university that aligns with your personal interests. Start by reviewing schools’ mission statements. Do they seem principle-driven or focused on ushering you through the program? You also want to check out the concentrations offered by each program. Select a program that is going to let you explore issues and challenges that matter to you.
Concentrations vary by university. For example, some concentrations may include educational leadership in K–12 schools, educational psychology or higher education. Expect universities located in or near cities to offer concentrations exploring urban education settings as well.
7. Consider PhD and EdD online programs
If you’re a working professional and don’t want to commute to a physical campus while you earn a degree, an online doctor of education program may be right for you. Online programs cover the same information as their in-person counterparts, but offer a little more flexibility for students.
However, classes such as those included in USC Rossier’s Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership online program are held live, meaning you are required to attend the online class at a specific day and time.Note: It may be easier to find online options for EdD than PhD programs.
8. Research PhD vs. EdD dissertation requirements
A traditional part of a PhD in education is the dissertation. Dissertation requirements vary by program and school, but generally include thorough investigation of a topic from multiple angles, copious research, and an exam to defend your written work once it’s completed.
By contrast, some EdD programs require you to complete a dissertation in practice. Using research methods learned in the program, you will attempt to resolve a problem in education dealing with equity and access. You may also have the chance to work alongside a group of students and an advisor to tackle the problem. In addition to the different requirements of PhD and EdD dissertations, individual schools may want you to explore issues that fall within their philosophical focus.
9. Estimate your time commitment
Before committing to a doctorate in education program, make sure you understand how much time it will take. A PhD in Education typically requires four to six years to complete, while EdD programs take three years, and may be completed while you work.
Additionally, some PhD programs are full-time commitments. Because of the workload, you can’t work a full-time schedule. However, your tuition is covered by a graduate assistantship. A Master’s degree may also not be necessary for acceptance into a PhD program.
USC Rossier resources
If you’re still unsure about which doctorate in education is right for you, we’re happy to provide personalized guidance .
You can also use USC Rossier’s simple career survey tool.
Curious about the requirements for our doctoral programs ? Check out the list of program comparisons. As a school that has offered doctoral degrees for 100 years, USC Rossier is uniquely positioned to provide insight and expertise on doctoral programs in education
Article Type
Article topics.
- Higher education
Related News & Insights
March 20, 2024

Higher education DEI myths demystified
In a rebuke to a congressional hearing attacking DEI efforts on university campuses, 12 scholars debunk the politicized misinformation with evidence-based responses.
Featured Faculty
- Shaun Harper
March 13, 2024

Preparing future teachers for the AI era
USC Rossier faculty aim to instill curiosity and inquiry in students as they grapple with and integrate artificial intelligence in their classrooms.
- Nooshan Ashtari
- Jenifer Crawford
- Corinne Hyde
- Anthony B. Maddox
March 11, 2024
“The arrows of influence are as crucial as what’s in the boxes themselves”
Center for Enrollment Research, Policy and Practice Conference 2024: Defending Equity created spaces for reflection and sharing strategies to address pressing issues in enrollment.
- Julie R. Posselt
How Long Does It Take to Write an Education Dissertation? Guide to Sharing Research Findings

Writing a dissertation is the culmination of a doctoral education program . It is an exacting task, calling for dedication and perseverance, especially when you experience time constraints due to work or family obligations. Gaining a clear understanding of how long it takes to write an education dissertation and carefully planning your dissertation process—from carving out time in your busy daily schedule to setting achievement milestones to keep a steady pace—are crucial steps to earning a doctoral degree.
It takes longer than a year for most PhD students to complete a first draft of a dissertation. Students typically spend one to two years conducting research and reviewing literature while they complete doctoral courses before tackling a dissertation draft. The writing process typically takes a year or two beyond that. It can take five or more years for PhD students who get stuck in research phases, experience writer’s block, or have a high level of distractions or time constraints. The average time for students to complete all requirements for a doctorate in the US is nearly six years, according to U.S. News & World Report .
The Education Dissertation Timeline
About how long will the dissertation process take? Many factors can influence the dissertation timeline length, such as:
- Job status : Doctoral students working in full- or part-time positions will need to be diligent about dedicating time to their dissertation work.
- Academic support : PhD students with strong support from faculty members, mentors, and peers are likely to find greater success in keeping the dissertation process on track.
- Topic selection : An initial dissertation topic’s success can keep a timeline on track. When doctoral students change a dissertation’s focus midstream, it typically adds extra research time.
- Time management : Writing a dissertation takes careful planning and scheduling. When students stick to their schedules and work efficiently, they’re more likely to complete their dissertations sooner.
The Dissertation Process
Before doctoral students can submit a dissertation proposal, they must complete all of their doctorate-level coursework and pass their comprehensive exams. This designates them as doctoral candidates. However, just because a student hasn’t achieved candidate status does not mean they can’t or shouldn’t start the dissertation process. On the contrary, students are expected to identify their dissertation topic and start preparing for the proposal while they are engaged in graduate coursework.
Many of the classes offered in a Doctorate of Education (EdD) program will help students explore potential topics and research techniques. For example, American University’s online EdD program includes three weekend residency sessions during which students connect with faculty and participate in workshops to help them develop their dissertations. The program also includes two course sessions on applied research methods to familiarize students with qualitative and quantitative research methods.
The dissertation process includes the following steps:
1. Draft and Defend a Proposal
The dissertation proposal may include the first few chapters of the dissertation. Students must be prepared to defend the proposal to the dissertation committee, which will evaluate the topic itself and approve, deny, or request revisions to the proposal. Many education dissertation topics relate to leadership strategies, literacy, or future learning trends.
2. Conduct Research
This stage can include conducting surveys and interviews on the chosen education topic. Students look for evidence to support their hypotheses, take notes, and conduct interviews along the way.
3. Conduct Literature Review
Students need to gather a broad range of articles and books that are pertinent to their dissertation topic. Resources cited in the dissertation are included in a bibliography.
4. Create an Outline
Structuring research and data in an outline helps students stay focused and organized during the dissertation writing stages.
5. Write the Dissertation
The elements of a dissertation paper can include abstract, introduction, background, hypothesis, literature review, methodology, conclusion, and bibliography sections. Universities often provide templates and style guides to help students format their dissertations correctly.

Tips for Writing a Dissertation
Your dissertation strategy should take into account your unique strengths and weaknesses. If you know that you are most productive in the morning, for instance, schedule your research and writing time for early in the day. To successfully navigate the dissertation process, you should:
Get familiar with the dissertation process before you begin writing. Look at dissertation samples and guideline documents to get a firm grasp on formatting and style. Keep yourself on track by setting milestone deadlines.
Write Often
Don’t put off the writing process. It’s easy to find excuses not to write, such as having a busy schedule or feeling that your argument isn’t fully formed. But sitting down to write every day, for at least two hours (with at least one break), can help you find your voice and establish your structure through experimentation.
Don’t Get Discouraged
Writing a dissertation can be a trial-and-error process. You will have to be self-reliant in many of the independent learning stages, including finding quality research sources and conducting your own studies. Don’t give in to self-doubt when you hit a roadblock and remember not to sacrifice your health and well-being by overstressing about your progress.
Find a Good Mentor
Students should feel comfortable checking in with a supervisor or committee member when they need support, advice, or encouragement. Making sure that you have an engaged and enthusiastic mentor can make a big difference in the dissertation process. Some mentors encourage regular meetings to keep in touch. Connecting with a group of peers who are also drafting dissertations can give you feedback as well. In addition, university libraries often support dissertation work through research and writing labs.
Sharing Your Research Findings
Once you’ve determined how long it will take you to write your education dissertation, consider how actively you’ll pursue publication. Students often want to share their work with a greater audience so that others can benefit from their insights.
Typically, a university will require students to publish their dissertation in an electronic database. For instance, American University requires students to submit dissertations to the ProQuest Dissertations and Theses (PQDT) database and the American University Digital Research Archive (AUDRA).
Publication is also a plus on any academic CV. Some students reformat their dissertation into an article (or articles) for submission to a professional journal, or even as a book for publication. Others present their findings at educational conferences. Regardless of the arena, sharing a dissertation with a wider audience is a rewarding capstone achievement.
Advance Your Career as an Education Leader
Individuals who are passionate about improving the education system through cutting-edge learning strategies should consider pursuing an advanced degree program. American University’s School of Education Online provides a number of high-quality degree programs, including a Doctorate of Education (EdD) in Education Policy and Leadership . The university’s EdD program provides a flexible, part-time learning environment that helps education professionals gain the skills to effect positive change across all school levels and community settings.
What’s the Difference Between Educational Equity and Equality?
The Role of Educational Leadership in Forming a School and Community Partnership
EdD vs. PhD in Education: Requirements, Career Outlook, and Salary
American University, Submitting Your Thesis and Dissertation Files Electronically
Inside Higher Ed, “Give It a Rest”
Inside Higher Ed, “How to Draft a Dissertation in a Year”
Studies in Graduate and Postdoctoral Education , “Preparing for Dissertation Writing: Doctoral Education Students’ Perceptions”
U.S. News & World Report , “How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?”
Request Information
- Apply Apply (link opens in new window)
- Request Info
- Applied Nutrition
- Healthcare Administration
- Health Informatics
- Public Health
- Social Work
- Science Prerequisites
- UNE's Awards & Recognition
- Application Tips
- Resources for Students
- Faculty Development
- Resources, Links & News
- Alumni Spotlights
- Ambassador Spotlights
- Faculty Spotlights
- Student Spotlights
- Team Spotlights
What Can You Do With an EdD?

A Diverse Student and Faculty Body Provides Opportunity
The EdD student body is the most diverse audience served by our graduate programs in education. In addition to K-12 education professionals, students in the EdD come from clinical backgrounds in healthcare settings, community colleges, and non-profit community groups and service agencies. Likewise, in addition to holding terminal degrees themselves, our EdD instructors are drawn from a wide variety of professional leadership roles such as K-12, higher education and healthcare administration from across the country. The diversity of our faculty aligns with the diverse professions of our students who are themselves mid-career professionals. This synergy creates opportunities for networking and mentorship beyond the program.
How Long Does it Take to Get an EdD?
The EdD program can be completed in as little as three years, including the dissertation. In fact, approximately 72% our EdD students complete the program in three and a half years. This is in comparison to a national completion average of only 56.6% over a 10 year period for students in doctoral programs (Sowell, Zhang, Redd, & King, 2008) .
Furthermore, over 70% of recent EdD graduates report increased leadership or authority as a result of completing their degree, and 57% of graduates reported using their research in a professional context since completing the program.
Our graduates’ successes speak to the commitment of staff and faculty to the success of our students by overcoming the barriers that derail so many in the pursuit of a doctorate.
See What You Can Do With an EdD in our Student Profiles

Kylie Bragdon, UNE Online EdD Student
Recently, we profiled two of our EdD students in an effort to illustrate the varied career paths both have chosen, and to show how their EdD has helped them to become distinct leaders in their fields.
Kylie Bragdon is a student in the EdD program and currently serves as the Assistant Director of Education for an organization called KidsPeace in Ellsworth, Maine. Kylie’s dissertation research is focused on understanding how to create non-traditional education pathways that make sense for the lobstermen in her community. On top of being a principal, an EdD student, and conducting research for her dissertation, Kylie is also running for the Maine State House of Representatives in November. You can watch Kylie’s video profile here .

Dan Mickool graduated from the College of Graduate and Professional Studies in 2017 with his EdD. Dan is currently a faculty member for the University of New England College of Pharmacy, as well as a registered pharmacist. Dan’s dissertation research focused on interprofessional education and teaching. You can view Dan’s video profile here .

Dan and Kylie are just two of our many amazing EdD students and graduates and their journeys illustrate just a fraction of the many pathways, as well as leadership and research opportunities, that come along with earning your EdD at UNE Online.
Now that you’ve seen where the EdD can bring you, get your unique path to transformational leadership started today by downloading our EdD program brochure:

EdD vs PhD: Which Education Degree Should You Get?
Teachers that are looking to use their leadership skills to create change in policy, curriculum, and research can use a doctorate degree to get roles in research, postsecondary schools, and K-12 education. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), postsecondary education jobs are projected to grow 12% between 2020-2030.
However, teachers wanting to earn a high-level degree must choose between a doctor of education (EdD) or a doctor of philosophy in education (PhD) degree. While both are excellent options, the two degrees lead to very different coursework, requirements, and career outcomes.
What Are EdD and PhD In Education Degrees For?
A doctorate degree in education gives people a variety of career paths. The different programs can lead to private and public sector jobs including:
- Administrator
- Superintendent
- Policy maker
- Postsecondary teacher
- College president
- Education director
The EdD and PhD are both terminal degrees that make teachers and educators experts in their fields. A good job outlook and growth projections make a doctorate degree worth the time and money.
Picking Between an EdD or PhD In Education Program
The curriculum and job prospects of an EdD and PhD program are different. You should consider your interests and career goals when deciding which type of degree to obtain.
- A PhD program is rooted in research and theory and students learn to interpret research.
- And EdD program is rooted in leadership and application and students are taught how to apply the research to a real-world setting.
The EdD degree is available to professionals who already hold a master’s degree and want to advance their career and receive a boost in income.
The EdD program prepares students to apply research to real-world settings and to find work in educational leadership. This degree rewards students with the skill set and ability to create change in their professional environment by:
- Develop the tools to become a better administrator
- Résumé credibility and expanded career search
- Learn the latest technology in instructional design
- Qualify for senior educational leadership positions
The overall goal of getting an EdD degree is to become a good leader and transfer knowledge to an education environment to create positive change.
Coursework includes a focus on professional leadership, solutions, and solving problems in practice.
Teachers and administrators are best suited for an EdD. Many programs are geared towards the working professional and are offered online or in a hybrid model.
Those who complete an EdD degree often choose to work in a K-12 setting or in college administration.
On average, an EdD degree takes three years to complete including a dissertation. This timeframe can be dependent on:
- Previous education
- Online vs. in-person programs
- Part-time vs. full-time study
Since obtaining an EdD degree is both time-consuming and a financial commitment, finding a program that meets a person’s career goals, work-life balance, and interests is critical.
EdD Career Outcomes And Salaries
Careers in education are growing and the job outlook for this profession is positive. Someone with an EdD degree can expect an increase in income and responsibility.
A few examples of careers available to people with an EdD degree are highlighted below.
- Median Salary: $80,560
- Career Outlook: +912% (2020-2030)
Postsecondary teachers instruct students beyond high school. They are typically referred to as faculty or professors and may write books, conduct research, and publish papers.
- Median Salary: $97,500
- Career Outlook: +8% (2020-2030)
A postsecondary education administrator works in the college setting usually in student services, student affairs, admission, registrar’s office, or oversees faculty, research, and academics.
- Median Salary: $107,680
Top executives are usually in charge of the organization’s big picture. They create strategies and policies to meet goals.
- Median Salary: $98,490
School principals oversee all aspects of the school setting including managing staff, curriculum, and the health and safety of the students.
A PhD in education prepares people to critically analyze and interpret research.
Those that hold a PhD become experts in a given field of education such as teaching practices, inequity in education, and how learning environments shape student outcomes.
Coursework includes a focus on education, quantitative and qualitative research, and a close collaboration with faculty.
A PhD dissertation focuses on creating new research in a particular field whereas a dissertation in an EdD program focuses on solving a particular problem found in a school setting.
People who have a passion for new research and advanced theory along with the desire to become an expert in a particular education field are best suited for a PhD in education.
Career options for those that hold a PhD in education include:
- University professor
- Research scholar
- Policy researcher
PhD of education students will enjoy using their skill set to shape new research and create best practices that will affect teaching and learning for years to come.
On average, a PhD in education degree takes 4-6 years to complete including an original research dissertation.
Unlike the EdD degree, the PhD program is a full-time commitment and not well suited for the working professional. Not many schools offer an online PhD in Education program.
Program timeline may be dependent on:
- Student funding
- Dissertation complexity
Since obtaining a PhD degree is both time-consuming and a financial commitment, finding a program that meets a person’s career goals, work-life balance, and interests is critical.
PhD In Education Career Outcomes And Salaries
As with EdD careers, careers for PhD graduates are projected to see significant job growth. Someone with a PhD degree can expect an increase in income and responsibility.
While EdD professionals seek to obtain roles as superintendents, deans, principals, and other education administrative positions, PhD professionals seek roles as professors, scholars, and researchers.
- Career Outlook: +12% (2020-2030)
Postsecondary professors instruct students beyond high school. They may also be referred to as faculty. Professors often write books, conduct research, and publish papers.
Postsecondary education administrators who hold a PhD may oversee faculty research, or work in student affairs, attendance, and academics.
- Median Salary: $59,870
- Career Outlook: +4% (2020-2030)
Survey researchers conduct qualitative research and analyze the data for trends that can influence education policy and help shape education decisions and plans.
Doctor Of Education (EdD) vs Educational Specialist (EdS)
Another option for career advancement in education is the educational specialist (EdS). An EdS is a postgraduate degree for those that already have a master’s degree, but don’t want to pursue a doctorate. This program is designed for the working professional who wants to add to their skill set but in half the time it takes to complete an EdD program.
The EdS is a graduate certificate that does not require a dissertation or capstone project to complete and is geared towards those that work in the K-12 setting. However, this option is not designed for people who want to work in higher education or organizational leadership.
What To Look For In Educational Doctoral Degree Programs
When comparing different EdD and PhD programs, you should also consider factors outside of career outcomes such as online flexibility and accreditation.
Online vs. On-Campus Learning
While most PhD programs are full-time and conducted in person, online EdD programs are becoming more abundant, and many schools offer the option to complete the degree on a part-time or full-time basis to accommodate busy schedules and the working professional. The biggest benefits of online learning include:
- Flexibility and self-paced learning
- Better time management
- Improved virtual and communication and collaboration
- Faster graduation times
- Ability to work from anywhere
Accreditation
Accreditation is critical for any educational institute. It certifies that the school and its curriculum meet the appropriate standards and qualifications outlined by the U.S. Department of Education and/or the Council for Higher Education accreditation.
Choosing a school that is accredited is extremely important and it gives degrees credibility and validity and will be valued by employers.
Many programs and departments within a school may have a separate accreditation called programmatic accreditation. This accreditation elevates the credibility of the program and shows that the department has designed a program that meets a standard of excellence.
Programmatic accreditation also ensures that students will receive the appropriate training and knowledge to be successful in their given fields.
Applying To Education Doctoral Programs
Admissions requirements for education doctoral programs depend on the type of school, degree, and program modality desired. A master’s degree, letters of recommendation, GRE score, work experience, and prior grades are a few examples of typical education doctoral application requirements.
Admission Requirements For EdD and PhD Programs
Admission requirements for an EdD program typically include:
- A minimum grade point average of 3.0 in the last 60 units of upper-division courses taken
- Passing GRE score
- Three academic or professional letters of recommendation
- A statement of purpose
- Essay on an assigned topic
- Master’s or specialist degree in education
- Three years practical experience
- Currently employed as a full-time educator
- Application fee
Admission requirements for a PhD program typically include:
- Statement of purpose
- Three letters of recommendation
- College and university transcripts
EdD vs PhD in Education FAQ
- One degree is not considered “better” than the other. Both the PhD and EdD pathways end in a terminal doctorate degree and both programs are designed for different career goals and interests.
- An EdD is a terminal doctorate degree that is designed for the working educational professional (teacher or administrator) who wants to advance their career and apply research in a real-life setting.
- An EdD program is typically three years in length, while a PhD program typically takes four to six years to complete.
- The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that doctoral degrees in education are a growing profession that offers both rewarding and healthy salaries for those who pursue them.
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/education-training-and-library/postsecondary-teachers.htm
- https://rossier.usc.edu/phd-vs-edd-in-education-nine-expert-tips-to-help-you-choose-with-infographic/
- https://www.franklin.edu/blog/is-a-doctorate-in-education-worth-it
- https://www.eddprograms.org/resources/is-an-edd-worth-it/
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/management/postsecondary-education-administrators.htm
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/management/top-executives.htm
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/management/elementary-middle-and-high-school-principals.htm
- https://www.waldenu.edu/programs/education/resource/how-to-tell-if-i-want-an-edd-or-a-phd-in-education
- https://www.bls.gov/ooh/life-physical-and-social-science/survey-researchers.htm
- https://www.onlineeddprograms.com/faqs/edd-vs-eds-degree
- https://education.ufl.edu/curriculum-teaching/edd/admissions-requirements/
- https://ed.stanford.edu/admissions/application-reqs/phd
Your browser is unsupported
We recommend using the latest version of IE11, Edge, Chrome, Firefox or Safari.
College of Education
Edd urban education leadership.
Ranked #16 in Education Administration by US News and World Report
The EdD in Urban Education Leadership is a nationally-recognized program designed to prepare and develop principals who are able to lead the improvement of teaching and learning in urban schools. The program faculty and staff are comprised of equity-minded educators committed to developing aspiring leaders who have the drive to disrupt inequities and advance learning opportunities within diverse student populations. The EdD program partners with The Center for Urban Education Leadership ( CUEL ) to conduct research, development, dissemination, policy advocacy to enhance the capacities of school leaders and improve the educational outcomes and life opportunities of PK-12 urban school students. Our program creates rigorous learning experiences that intensify leaders’ capacity as change agents who enlist the talents and energies of teachers, families, community members, and students to improve school culture, climate, and learning outcomes.
This an intensive, highly-selective cohort program combining coursework with supervised practicum experiences at the school level. It leads to the Illinois Principal Endorsement after successful completion of the first 18 months of coursework and residency, and to the Ed.D. degree upon three more years of successful leadership and study. We seek applicants who are preeminent teachers and leaders seeking to develop as equity-minded school principals. Applicants also include principals seeking to take their schools and their leadership skills to the next level. The EdD Urban Education Leadership Program looks for candidates with a strong understanding of effective instruction, the willingness to self-critique and improve through intensive coaching, a history of working effectively with adults, and a clear commitment to challenging inequity in schools.
Program Accolades
- Identified as a “model program” by the Illinois Board of Higher Education Commission on School Leader Preparation.
- Ranked #16 in Education Administration by US News and World Report.
- Awarded as Exemplary Educational Leadership Preparation Program by University Council for Education Administration.
- Awarded the Dr. Shirley S. Schwartz Urban Education Impact Award from the Council of Great City Schools, honoring an outstanding partnership between a university and an urban school district that has had a positive and significant impact on student learning.
- First higher education leadership preparation program in the US to receive Exemplary Affiliate Status (highest designation) by the George W. Bush Institute’s Alliance to Reform Education Leaders, which seeks to improve the way America’s principals are prepared and supported.
- With the Center for Urban Education Leadership, first higher education institution to receive Carnegie Foundation for Advancement of Teaching Spotlight Award for Continuous Improvement.
Degree Requirements Heading link Copy link
- Book icon Summary of Program Curriculum
- Book icon UIC Graduate Catalog
Summary: 88 credit hours to obtain the EdD or 112 hours to obtain the EdD with Superintendent Endorsement.
Faculty and Leadership Coaches Heading link Copy link
Frequently asked questions heading link copy link, what is the difference between the phd in urban education and the edd in urban education leadership.
Typically, the PhD in Urban Education leads to positions such as research faculty at a university, administration at the university level, or research in a local/state agency or other policy organization. The EdD in Urban Education Leadership is focused on educational leadership practice and leads to positions in school/district level leadership in K to 12 schools.
What are the minimum qualifications for admission into the EdD program in Urban Education Leadership?
The minimum qualifications include an earned master’s degree, four years of teaching experience, a Professional Educator License, experience as a teacher-leader or school/district leader, and a demonstrated commitment to leading the improvement of high needs urban schools. The admissions process is highly selective.
How do I apply to the program?
Please visit our application process page.
How are students selected for the EdD program in Urban Education Leadership?
After you have submitted all required materials to the Graduate College, you may qualify for an interview with the program faculty. Doctoral candidates must hold a master’s degree, have demonstrated exceptional classroom instruction as well as leadership as teachers or administrators, have evidence of parent and community involvement and demonstrate clear commitment to transforming schools where the leadership need is most evident. Decisions for admission are made by the program faculty and are ultimately based on the content of the submitted documents and a successful interview. The admissions process is highly selective.
How long does it take to complete the EdD program in Urban Education Leadership and is a dissertation required?
On average, students complete EdD program requirements in four years.
Can I transfer in credit hours I have already earned elsewhere?
If the hours have not been applied toward another degree and the course content matches the curriculum in the EdD program, then most likely you will be able to transfer in some course credit. There is no guarantee that hours will automatically transfer. The final decision is made by the program faculty once you have been admitted to the program.
Do I have to leave my current position in order to be in the EdD program in Urban Education Leadership?
The EdD program requires that you are in a school-wide or system-level leadership position by the third semester of the program.
What days and times are courses typically offered for the EdD program in Urban Education Leadership?
In the first year, courses are typically offered in the evenings and Saturdays to minimize conflicts between coursework and practice. In the second and third years, other weeknights are used for courses. Students are encouraged to enroll in summer course work to ensure progress toward the degree. The course work is co-designed and co-taught by UIC academic faculty together with transformative principals and system level leaders who have themselves transformed urban schools.
Can I get an Illinois PreK-Age22 Principal Endorsement through the EdD program in Urban Education Leadership?
Principal Certificate. Students will earn an Illinois PreK-Age22 Principal Endorsement at the end of the first eighteen (18) months of the Ed.D. program after meeting program and state requirements.
Will the EdD program in Urban Education Leadership directly assist in job placement when I am finished?
The EdD program provides an abundance of networking opportunities and job application support but does not guarantee job placement after completion of degree. We seek to prepare candidates to be successful in a highly competitive job market.
Where are classes/courses held?
Most classes/courses in the EdD program are held on the east side of campus in ETMSW.
Is financial aid available for the EdD program?
In recent years, fellowships have been made available to a limited number of advanced students.
Ready to Apply? Heading link Copy link
- Check icon Learn about applying
- Book icon Learn more about the curriculum
Do you have questions about the EdD Urban Education Leadership program, or want to speak with someone? Reach out! Heading link Copy link
- Name First Last
- Do you have questions about the EdD Urban Education Leadership program?
Additional Information Heading link Copy link
- People Icon Leaders & positions
- Newsletter icon Newsletters
- Calendar icon Info Sessions
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
How long is a dissertation, published by steve tippins on april 9, 2019 april 9, 2019.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 05:03 am
How long is a dissertation? This is a question that almost every doctoral student asks at some point. It is not a new question–in fact, it’s been asked every time a paper of some sort is assigned in any class.
The simple answer (for any paper) is, “long enough to answer the question.” Not a really helpful answer, but satisfying from a professor’s perspective.
The truth is, there is no one answer to how long a dissertation is. I can’t say 146 pages is what’s needed, as you may write to page 146 and stop without fully exploring your topic. 90 pages could adequately address your research question, or you could write 200 pages and still not fully answer what you set out to. Every topic is unique, as is each person’s writing style.
Some websites even give specific answers that are simply inaccurate. In my experience, dissertations vary too much to be pinned down like that.
However, there are some practical suggestions I can make about how long your dissertation should be, how to adequately address the requirements of each section, as well as how to expand or reduce the length of specific chapters according to your needs. I’ll explore these below.
But first, let’s try and at least give the beginning of an answer to the question “how long is a dissertation?”
Marcus Beck Sets Out to Answer “How Long Is A Dissertation?”
Any discussion of dissertation length must include the work done by Marcus Beck . As a way to distract himself from his own dissertation writing, Beck calculated the average length of dissertations in the University of Minnesota database.
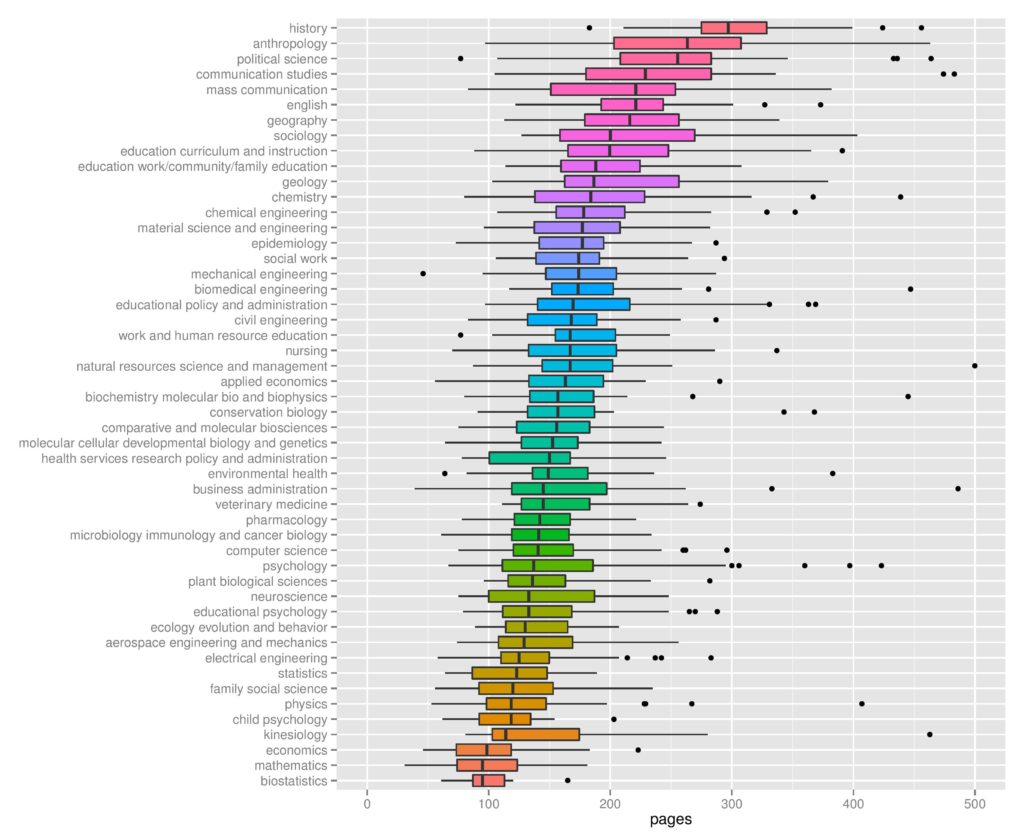
You can see from looking at his data that average length varies by discipline. So the first answer to how long a dissertation is, is that it depends upon what area you are writing your dissertation. It appears that a dissertation in History will be much longer, on average, than one in Chemistry. He also calculated the average across all disciplines.
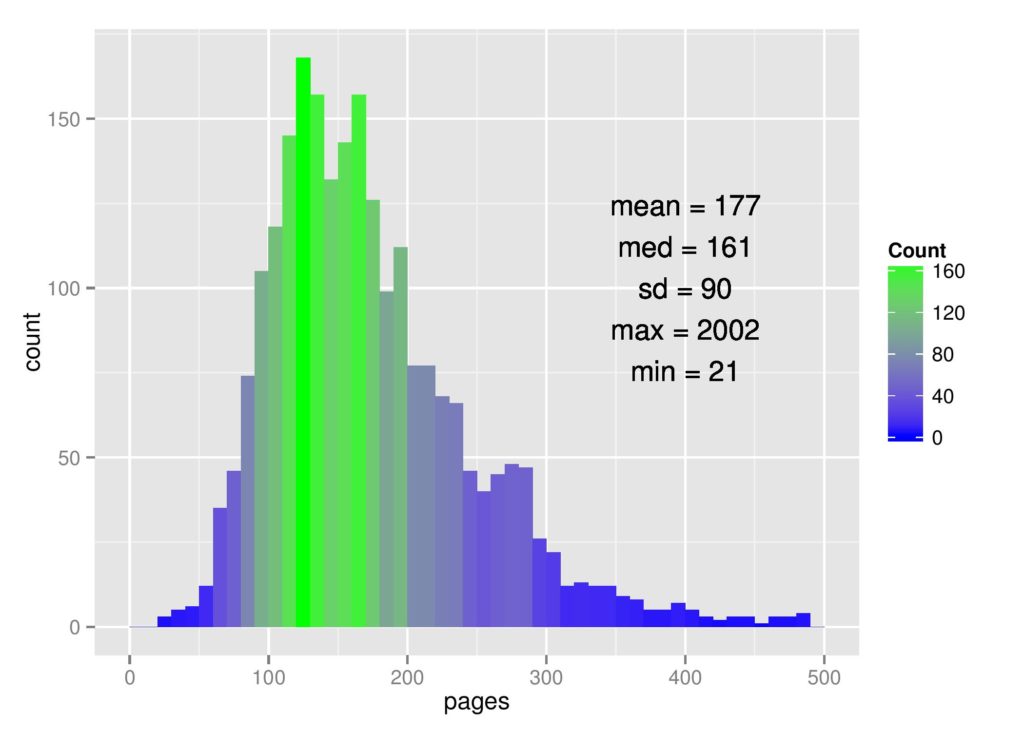
Don’t be intimidated by how long the average dissertation is.
Many people look at the average length of a dissertation and get intimidated by the high page count. But, as Marcus Beck says in his blog post, “The actual written portion may only account for less than 50% of the page length.”
I’ve found this to be true. References, appendixes, tables and figures, page breaks, and white space all contribute to the high page count. The actual number of words you need to write is likely considerably less than the page count initially implies.
How Long Should My Dissertation Be?
Even though there’s no single answer about how long a dissertation should be, there probably is an ideal range which your dissertation falls into. This depends on your topic of research, but also on other factors. I’ll discuss some of these below.
Institutional Guidelines
I know of schools that have policies such as “Chapter 2 must be at least 40 pages long and no more than 60 pages.” Why this type of requirement? In my mind, there are two reasons.
First, they want to give some sort of guideline for students that is helpful but does not overburden faculty (a 230-page lit review is daunting to read).
Second, credibility is important. An 8-page lit review does not reflect well upon the student or the institution.
Most schools now have a dissertation template with the headings that are needed for most sections. If you take the time to completely fill in the headings with all of the relevant information, you should come up with an adequate number of pages. Remember, in academic writing, we don’t leave much to chance, we tell the reader everything.
Committee Preferences
It is likely that you will get a committee member who will give you priceless advice such as, “more is needed here.” When you get this type of comment it can be frustrating as specific feedback can be much more helpful.
Usually, what a committee member means by comments like this is that you haven’t really convinced the reader that you have fully explored the area or demonstrated a strong understanding of the material. So, expand what you are saying. Don’t imply anything, state it directly. This lets your committee know that you really do get it.
Sometimes you will get committee members giving contradictory advice. One member may want more information and another may want less. My first piece of advice is to negotiate these types of requests through your Chairperson.
This is where your Chair’s experience and guidance can be very helpful. Second, if a member really wants material included but others do not think it is very helpful, then adding the material in an appendix may make everyone happy.
Practical Suggestions For Dissertation Length, Chapter-By-Chapter

If you adequately and succinctly address each required section, you should end up with the right length for each chapter (and therefore, a dissertation of the right length). I’ll also give some rough guidelines on average page length where appropriate.
This is the introduction to your study. It is important to lay out the agenda for your research. Be sure that your problem statement, title, and research questions are in alignment (all referring to the same idea).
Chapter 1 tends to average in the 15-25 page range. If you get beyond 25 pages, you are usually including material that is better presented elsewhere in the dissertation.
Chapter 2 should thoroughly explore the existing research on your topic. However, it shouldn’t go on and on.
- If you are looking to beef up Chapter 2, it is always helpful to add research that supports the methodology that you are planning to use.
- If the chapter is too long, try to reduce the references you cite to those that are the most relevant and recent.
Make sure that you tell the reader what you did and how you did it. What type of analysis did you use and why? How many respondents were involved and how did you find them? The idea is to make sure that readers understand what you did and could replicate it if they want to.
As this is a plan for your research, it seems to naturally fall in the 15 to 20 page range.
The results of your study are presented here. Include all material that will help the reader understand what you found. There is a tendency to inundate the reader with tables, charts, and graphs. If they don’t directly relate to what you found or are redundant they can be included in an appendix. You don’t want to lose your reader in an avalanche of tables and numbers.
In most dissertations, it is Chapter 5 where you get to explain what the results of your research mean and the implications. This is the only chapter where you have some freedom to really express your opinions. Go ahead and do so.
I am always surprised when someone has spent 15 months of their life working on a research topic and they submit a Chapter 5 that is 8 pages long. Spread your wings and really explore what your results mean.

How Long is a Dissertation? Summary
The is no doubt about it, a dissertation is a long document. It is, however, not written in one sitting. You work on it for many months, crafting paragraphs and coming to conclusions. Many people find that because the document can be written in pieces that when it’s all put together, it is longer than expected. Keep writing and adding your thoughts and you will make it.
Many students find it helps to have a supportive guide who’s both been through the dissertation writing process before and is experienced in helping students. If that would be useful to you, feel free to reach out to me about my dissertation coaching or dissertation editing services.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
What makes a good research question.
Creating a good research question is vital to successfully completing your dissertation. Here are some tips that will help you formulate a good research question. What Makes a Good Research Question? These are the three Read more…

Dissertation Structure
When it comes to writing a dissertation, one of the most fraught questions asked by graduate students is about dissertation structure. A dissertation is the lengthiest writing project that many graduate students ever undertake, and Read more…

Choosing a Dissertation Chair
Choosing your dissertation chair is one of the most important decisions that you’ll make in graduate school. Your dissertation chair will in many ways shape your experience as you undergo the most rigorous intellectual challenge Read more…
Make This Your Last Round of Dissertation Revision.
Learn How to Get Your Dissertation Accepted .
Discover the 5-Step Process in this Free Webinar .
Almost there!
Please verify your email address by clicking the link in the email message we just sent to your address.
If you don't see the message within the next five minutes, be sure to check your spam folder :).
Hack Your Dissertation
5-Day Mini Course: How to Finish Faster With Less Stress
Interested in more helpful tips about improving your dissertation experience? Join our 5-day mini course by email!

Question: Are there any online EdS to EdD degree programs?
Answer: Yes – there are schools that offer online programs specifically for students who already possess an Educational Specialist degree and want to earn a Doctor of Education. Online EdS to EdD programs are currently available at three institutions: Northwest Nazarene University, University of Arkansas, and William Carey University. In addition to these programs, which explicitly require an EdS for admission, there are many other traditional EdD programs offered online that allow students to transfer credits from an EdS toward completion of their doctorate. This typically satisfies a significant portion of the EdD requirements, making it possible to graduate in less time than those entering with only a master’s degree.
The EdS and EdD are both post-master’s degrees in the field of education. However, they differ quite a bit when it comes to their overall focus and requirements. An EdS requires around half as many post-masters credits as a doctorate (typically around 30, instead of the 60 or so needed for an EdD) and is intended primarily for those looking to gain specific job skills related to career advancement. For example, many professionals pursue an EdS to gain the qualifications necessary for a certain position, certification, or licensure, such as those needed to become a principal or superintendent. While the EdD is also a practitioner’s degree, focused on preparing educators for advanced roles in academic leadership, it involves additional coursework in theory and research, as well as a substantial dissertation project. (For more about the differences between these two credentials, check out our FAQ on EdD vs. EdS degree programs .)
The majority of online EdD programs only require a master’s degree for admission (or in some rare cases, accept a bachelor’s degree along with sufficient graduate credits or professional experience). There are, however, some programs designed specifically for students who have completed an Educational Specialist degree and are now looking to earn the additional doctoral credits necessary to get an EdD. These EdS to EdD pathways generally require less credits than full EdD programs, as students will have already completed certain post-master’s requirements as part of their EdS. However, a major component that EdS holders will need to complete in order to earn their doctorate is a dissertation (or applied research project, for programs that have that option), which can take a considerable amount of time depending on the scope and focus of their research.
To learn more about online EdS to EdD programs available from schools in the U.S., as well as other options for students who possess an EdS and want to pursue their doctorate, continue reading below.
Schools with Online EdS to EdD Programs
As mentioned above, only three schools in the United States offer dedicated EdS to EdD programs online at this time.
Northwest Nazarene University in Idaho offers a Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership online designed for EdS graduates. This program has a curricular emphasis on K-12 Education, with courses that train students in doctoral level qualitative and quantitative research, effective leadership and change management, and education policy. This EdS to EdD program requires a total of 36 doctoral credits, and can be completed in just 26 months with a two-week on-campus residency session.
The University of Arkansas offers an online EdS to EdD program in Educational Leadership, which consists of 42 credit hours and takes around three years to finish. While the majority of coursework is delivered online, students must attend three intensive doctoral seminars on the U of A campus over the course of their studies. These in-person sessions give students the opportunity to meet and collaborate with classmates and faculty face to face, as well as receive help with their dissertation and attend lectures given by scholars and practitioners in the field.
William Carey University in Mississippi offers a Doctor of Education in P-12 Educational Leadership through entirely online study. The EdD requires 33 credit hours of doctoral coursework and research, along with 30 hours transferred from an accredited EdS program. Students must complete a 15-credit Advanced Leadership Core, comprised of courses in Data Analysis for Instructional and Performance Improvement Using Technology Tools, Professional Educational Development for Adult Learners, Developing the Culture of Learning, Developing Advocacy for the School and Community, and Using Conflict Resolution and Mediation. The curriculum also includes two required research courses (Descriptive Statistics and Survey Design, and Advanced Applied Research), as well as 12 credits dedicated to applied research in educational administration.
Online EdD Programs that Accept EdS Transfer Credits
Along with the dedicated EdS to EdD pathways discussed above, many schools offer online program options that allow students who have earned an Educational Specialist or equivalent degree to apply some of their post-master’s credits toward completion of an EdD. For example, Central Michigan University has a Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership students can pursue in one of four concentrations: K-12 Leadership, K-12 Curriculum, Higher Education Leadership, or Educational Technology. While the EdD requires a total of 63 credit hours, those with an EdS from an approved institution may be able to transfer up to 27 credits toward their doctorate. Students entering the online EdD programs at Appalachian State University, Belhaven University, or Regent University with an EdS can similarly waive a portion of the total credit requirements, depending on faculty approval.
Some schools even offer clearly defined EdS to EdD bridge options as part of their more traditional online Doctor of Education programs. At the University of Bridgeport in Connecticut, students can pursue a doctorate online in Education Leadership with a specialization in International Education. While the full program requires a total of 62 credits, there is a 42-credit option for those who have completed a post-master’s Sixth-Year certificate program or Educational Specialist degree. Murray State University in Kentucky offers a similar pathway for EdS graduates, allowing them to waive up to half of the credit hours needed to earn their online Doctor of Education in P-20 and Community Leadership.
Note : These are only some of the options for students with an EdS looking to complete their doctorate online. Those interested in an online EdD program not mentioned on this page can always reach out to an admissions representative to inquire about their policies regarding transfer credits. It is possible that other programs may allow students to apply some or most of their EdS credits toward an EdD degree.
Online EdD Program FAQs
- Are there any fully online EdD programs?
- FAQ: Are there any online EdD programs in kinesiology?
- FAQ: Are there any online EdD programs in TESOL and English Language Learning?
- Are there any online EdD programs that can be completed in 2 years?
- Are there any online EdD programs that do not require a dissertation?
- Are there any online EdD programs that do not require a master’s degree for admission?
- Are there any online EdD programs that do not require the GRE for admission?
- Are there any schools that offer faith-based EdD programs online?
- Are there online EdD programs with an ABD option?
- How long does it take to complete an online EdD program?
- What is an embedded dissertation in EdD programs?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Dissertation: A dissertation is a 5-chapter written work that must be completed in order to earn a doctoral degree (e.g. Ph.D., Ed.D., etc.). It's often focused on original research. Thesis: A thesis is a written work that must be completed in order to earn a master's degree.
The Doctor of Education (EdD) dissertation is considered a central component of EdD programs. The EdD dissertation is a five-chapter document that investigates an issue in education, reviews the existing literature on this issue, adds additional insight through a qualitative and/or quantitative research study, and proposes one or more solutions ...
Next, as students begin preparing to write, they should review the materials related to the EdD Doctoral Study document and process, provided on the Office of Research and Doctoral Services website. The EdD Prospectus Guide is also helpful in getting started. This page contains resources for writing the prospectus, proposal, and final study.
EDD 690 Dissertation Supervision II (4) EDD 642 Student Development Theory (4) EDD 641 Higher Education Administration (4) Concentration course (4) Concentration course (4) EDD 700 Dissertation Supervision III (4) v.1 8/17/15 5. 6 . AN INTRODUCTION TO THE THREE ARTICLE DISSERTATION .
EdD Dissertation Manual ... long quoted passages, and lists of tables and figures, which are single-spaced). Font: Any non-italic font 10-12 points in size should be used. Headings may be larger. For enhanced screen readability, use Arial (10pt), Courier New (10pt), Georgia (11pt), Times
A dissertation or project study is a formal manuscript written to address a gap in educational practice, thus resolving a local problem. Walden dissertations consist of five chapters (Chapter 1: Introduction to the Study, Chapter 2: Literature Review, Chapter 3: Research Method, Chapter 4: Reflections and Conclusions, Chapter 5: Discussion, Conclusions, and Recommendations).
Ed.D. DISSERTATION MANUAL . 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1: ... EDD DISSERTATION TEMPLATE. 6 ORGANIZATION OF THE MANUSCRIPT Preliminary Pages, in the following order: ... The text of the dissertation must be double-spaced (except for footnotes, long quoted passages, and lists of tables and figures, which are single-spaced).
Here is a breakdown of what your dissertation will include: Chapter 1: Introducing the problem of practice you have chosen to study. Chapter 2: Literature review (remember, you have done some of this in quarter two!) Chapter 3: The methodology you used to research the problem. Chapter 4: What you learned from your data and how it relates to ...
You should have submitted your Dissertation Proposal Approval form by 1/14. Your Defense Announcement should be submitted by 1/14. It would be best if you defended by 2/23. You are required to submit your content-complete dissertation by 3/15. You are required to be enrolled for the Spring semester.
8. Research PhD vs. EdD dissertation requirements. A traditional part of a PhD in education is the dissertation. Dissertation requirements vary by program and school, but generally include thorough investigation of a topic from multiple angles, copious research, and an exam to defend your written work once it's completed.
An EdD or Doctor of Education is a terminal degree awarded after completing a dissertation on educational theory and practice. This degree may be right for you if you're passionate about education and learning theory or have goals to be a school administrator or education policy change maker at the local or national level. ... EdD programs tend ...
The dissertation process includes the following steps: 1. Draft and Defend a Proposal. The dissertation proposal may include the first few chapters of the dissertation. Students must be prepared to defend the proposal to the dissertation committee, which will evaluate the topic itself and approve, deny, or request revisions to the proposal.
Drexel University School of Education's doctoral programs are designed with flexibility in mind. The EdD program is a part-time program available 100% online or as a hybrid program where students take courses online and meet face-to-face with faculty and their fellow students 3 weekends per term. The EdD can be taken as a 3-year or 5-year ...
The EdD program can be completed in as little as three years, including the dissertation. In fact, approximately 72% our EdD students complete the program in three and a half years. This is in comparison to a national completion average of only 56.6% over a 10 year period for students in doctoral programs (Sowell, Zhang, Redd, & King, 2008) .
Publication of the dissertation is a University requirement for the PhD and EdD degrees and a bound copy of your dissertation will be shelved in the University library. A digital copy is in. cluded in the ProQuest/UMI database, accessible online to subscribers and libraries. As of fall 2015, Penn requires open access publication of dissertations.
How Long Does A PhD In Education Take? On average, a PhD in education degree takes 4-6 years to complete including an original research dissertation. Unlike the EdD degree, the PhD program is a full-time commitment and not well suited for the working professional. Not many schools offer an online PhD in Education program.
In addition to earning enough credits, a PhD also requires completing a dissertation. All of this can be done both online and on-campus. Pursuing Your Career in Education. At its core, the EdD vs PhD difference really comes down to what you want from your degree and long-term career goals.
Most Ed.D. programs require three years for full-time students. Part-time learners generally spend four or more years earning their degree. Some universities offer accelerated Ed.D. programs that take as little as two years to complete. Educators can also earn an Ed.D. online.
Updated: February 1, 2024. Answer: The time it takes to complete an EdD online will vary by program, as well as if students enroll on a full- or part-time basis. Most full-time EdD programs are designed to be completed in around three years. However, that number can change based on whether or not a student has transfer credits, and students are ...
Ranked #16 in Education Administration by US News and World Report. The EdD in Urban Education Leadership is a nationally-recognized program designed to prepare and develop principals who are able to lead the improvement of teaching and learning in urban schools. The program faculty and staff are comprised of equity-minded educators committed ...
When you submit. Your dissertation must be converted to a PDF file and then submitted online at Rutgers Electronic Theses and Dissertations Submission system ( https://etd.libraries.rutgers.edu ). You must submit the signed title page to Dean Matt Winkler, who can be reached at 848-932-3232 or [email protected].
The truth is, there is no one answer to how long a dissertation is. I can't say 146 pages is what's needed, as you may write to page 146 and stop without fully exploring your topic. 90 pages could adequately address your research question, or you could write 200 pages and still not fully answer what you set out to.
This EdS to EdD program requires a total of 36 doctoral credits, and can be completed in just 26 months with a two-week on-campus residency session. The University of Arkansas offers an online EdS to EdD program in Educational Leadership, which consists of 42 credit hours and takes around three years to finish.