

Literature Review Tips for the Introduction and Discussion Sections
A literature review is a summary of studies related to a particular area of research. It identifies and summarizes all the relevant research conducted on a particular topic. It is important that your literature review is focused . Therefore, you should choose a limited number of studies that are central to your topic rather than trying to collect a wide range of studies that might not be closely connected.
Literature reviews help you accomplish the following:
- Evaluate past research Collecting relevant resources will help you see what research has already been done. This will also help avoid duplication.
- Identify experts It is important to identify credible researchers who have knowledge in a given field, in order to seek their help if you get stuck with certain aspects of your research.
- Identify key questions Your ultimate aim is to bring something new to the conversation. Collecting resources will help you determine the important questions that need to be addressed.
- Determine methodologies used in past studies Knowing how others have approached a particular topic will give you the opportunity to identify problems and find new ways to research and study a topic. If the reported methodology was successful, you can use it and save time that you would otherwise be spending on optimization.
Presenting Literature Review in the Introduction and Discussion Sections
There are many benefits to presenting literature reviews in the introduction and discussion sections of your manuscripts . However, there are differences in how you can present literature reviews in each section.
What Should be Included in the Literature Review of the Introduction Section?
The literature reviewed in the introduction should:
- Introduce the topic
- Establish the significance of the study
- Provide an overview of the relevant literature
- Establish a context for the study using the literature
- Identify knowledge gaps
- Illustrate how the study will advance knowledge on the topic
As you can see, literature review plays a significant role in the introduction section. However, there are some things that you should avoid doing in this section. These include:
- Elaborating on the studies mentioned in the literature review
- Using studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research
- Directly quoting studies from the literature review
It is important to know how to integrate the literature review into the introduction in an effective way. Although you can mention other studies, they should not be the focus. Instead, focus on using the literature review to aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
What Goes in the Literature Review of the Discussion Section?
Literature reviews play an important role in the discussion section of a manuscript . In this section, your findings should be the focus, rather than those of other researchers. Therefore, you should only use the studies mentioned in the literature review as support and evidence for your study.
There are three ways in which you can use literature reviews in the discussion section:
- To Provide Context for Your Study Using studies from the literature review helps to set the foundation for how you will reveal your findings and develop your ideas.
- Compare your Findings to Other Studies You can use previous literature as a backdrop to compare your new findings. This helps describe and also advance your ideas.
- State the Contribution of Your Study In addition to developing your ideas, you can use literature reviews to explain how your study contributes to the field of study.
However, there are three common mistakes that researchers make when including literature reviews in the discussion section. First, they mention all sorts of studies, some of which are not even relevant to the topic under investigation. Second, instead of citing the original article, they cite a related article that mentions the original article. Lastly, some authors cite previous work solely based on the abstract, without even going through the entire paper.
We hope this article helps you effectively present your literature review in both the introduction as well as the discussion section of your manuscript. You can also mention any other tips that will add to this article in the comments section below.
References:
[1] http://www.math.montana.edu/jobo/phdprep/documents/phd6.pdf
[2] https://libguides.unf.edu/c.php?g=177129&p=1163732
This Is a Very Useful Information… thank you. It helped me a lot. It is explained clearfully.
YOU ARE SO NASESESSRY
it explains everything sooo goood i thought it would be hard to understand
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Beyond Spellcheck: How copyediting guarantees error-free submission
Submitting a manuscript is a complex and often an emotional experience for researchers. Whether it’s…
- Old Webinars
- Webinar Mobile App
How to Find the Right Journal and Fix Your Manuscript Before Submission
Selection of right journal Meets journal standards Plagiarism free manuscripts Rated from reviewer's POV

- Manuscripts & Grants
Research Aims and Objectives: The dynamic duo for successful research
Picture yourself on a road trip without a destination in mind — driving aimlessly, not…

How Academic Editors Can Enhance the Quality of Your Manuscript
Avoiding desk rejection Detecting language errors Conveying your ideas clearly Following technical requirements
Effective Data Presentation for Submission in Top-tier Journals
Importance of presenting research data effectively How to create tables and figures How to avoid…
How to Choose Best Research Methodology for Your Study
How to Effectively Structure an Opinion Article
Top 10 Questions for a Complete Literature Review
Impressive Academic Phrases for Writing Manuscripts

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
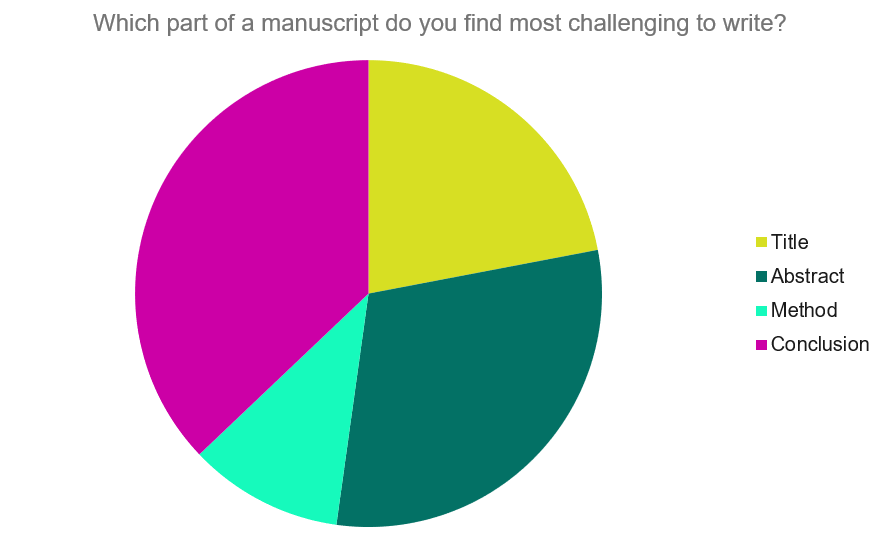
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
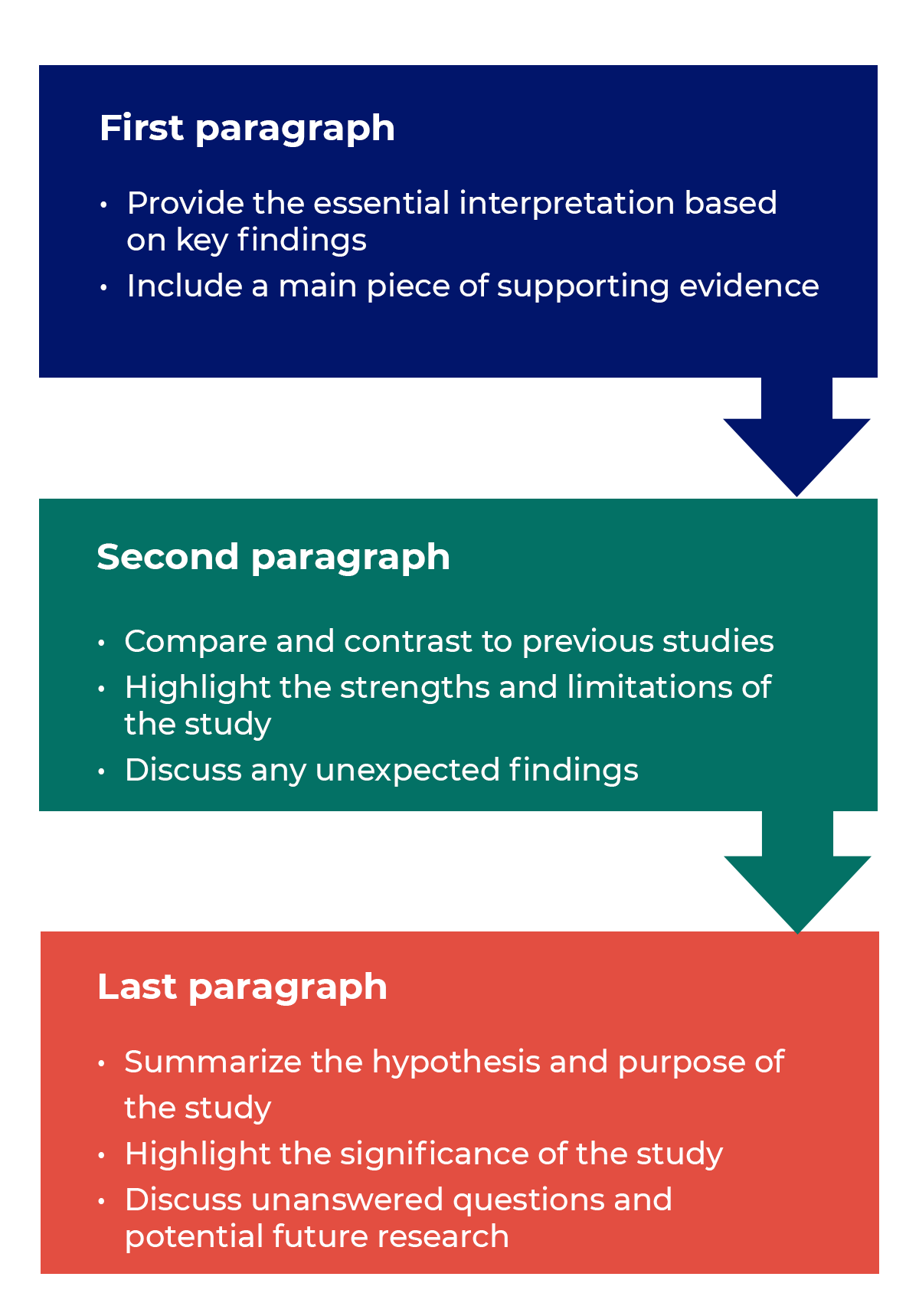
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 8. The Discussion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The purpose of the discussion section is to interpret and describe the significance of your findings in relation to what was already known about the research problem being investigated and to explain any new understanding or insights that emerged as a result of your research. The discussion will always connect to the introduction by way of the research questions or hypotheses you posed and the literature you reviewed, but the discussion does not simply repeat or rearrange the first parts of your paper; the discussion clearly explains how your study advanced the reader's understanding of the research problem from where you left them at the end of your review of prior research.
Annesley, Thomas M. “The Discussion Section: Your Closing Argument.” Clinical Chemistry 56 (November 2010): 1671-1674; Peacock, Matthew. “Communicative Moves in the Discussion Section of Research Articles.” System 30 (December 2002): 479-497.
Importance of a Good Discussion
The discussion section is often considered the most important part of your research paper because it:
- Most effectively demonstrates your ability as a researcher to think critically about an issue, to develop creative solutions to problems based upon a logical synthesis of the findings, and to formulate a deeper, more profound understanding of the research problem under investigation;
- Presents the underlying meaning of your research, notes possible implications in other areas of study, and explores possible improvements that can be made in order to further develop the concerns of your research;
- Highlights the importance of your study and how it can contribute to understanding the research problem within the field of study;
- Presents how the findings from your study revealed and helped fill gaps in the literature that had not been previously exposed or adequately described; and,
- Engages the reader in thinking critically about issues based on an evidence-based interpretation of findings; it is not governed strictly by objective reporting of information.
Annesley Thomas M. “The Discussion Section: Your Closing Argument.” Clinical Chemistry 56 (November 2010): 1671-1674; Bitchener, John and Helen Basturkmen. “Perceptions of the Difficulties of Postgraduate L2 Thesis Students Writing the Discussion Section.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 5 (January 2006): 4-18; Kretchmer, Paul. Fourteen Steps to Writing an Effective Discussion Section. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
These are the general rules you should adopt when composing your discussion of the results :
- Do not be verbose or repetitive; be concise and make your points clearly
- Avoid the use of jargon or undefined technical language
- Follow a logical stream of thought; in general, interpret and discuss the significance of your findings in the same sequence you described them in your results section [a notable exception is to begin by highlighting an unexpected result or a finding that can grab the reader's attention]
- Use the present verb tense, especially for established facts; however, refer to specific works or prior studies in the past tense
- If needed, use subheadings to help organize your discussion or to categorize your interpretations into themes
II. The Content
The content of the discussion section of your paper most often includes :
- Explanation of results : Comment on whether or not the results were expected for each set of findings; go into greater depth to explain findings that were unexpected or especially profound. If appropriate, note any unusual or unanticipated patterns or trends that emerged from your results and explain their meaning in relation to the research problem.
- References to previous research : Either compare your results with the findings from other studies or use the studies to support a claim. This can include re-visiting key sources already cited in your literature review section, or, save them to cite later in the discussion section if they are more important to compare with your results instead of being a part of the general literature review of prior research used to provide context and background information. Note that you can make this decision to highlight specific studies after you have begun writing the discussion section.
- Deduction : A claim for how the results can be applied more generally. For example, describing lessons learned, proposing recommendations that can help improve a situation, or highlighting best practices.
- Hypothesis : A more general claim or possible conclusion arising from the results [which may be proved or disproved in subsequent research]. This can be framed as new research questions that emerged as a consequence of your analysis.
III. Organization and Structure
Keep the following sequential points in mind as you organize and write the discussion section of your paper:
- Think of your discussion as an inverted pyramid. Organize the discussion from the general to the specific, linking your findings to the literature, then to theory, then to practice [if appropriate].
- Use the same key terms, narrative style, and verb tense [present] that you used when describing the research problem in your introduction.
- Begin by briefly re-stating the research problem you were investigating and answer all of the research questions underpinning the problem that you posed in the introduction.
- Describe the patterns, principles, and relationships shown by each major findings and place them in proper perspective. The sequence of this information is important; first state the answer, then the relevant results, then cite the work of others. If appropriate, refer the reader to a figure or table to help enhance the interpretation of the data [either within the text or as an appendix].
- Regardless of where it's mentioned, a good discussion section includes analysis of any unexpected findings. This part of the discussion should begin with a description of the unanticipated finding, followed by a brief interpretation as to why you believe it appeared and, if necessary, its possible significance in relation to the overall study. If more than one unexpected finding emerged during the study, describe each of them in the order they appeared as you gathered or analyzed the data. As noted, the exception to discussing findings in the same order you described them in the results section would be to begin by highlighting the implications of a particularly unexpected or significant finding that emerged from the study, followed by a discussion of the remaining findings.
- Before concluding the discussion, identify potential limitations and weaknesses if you do not plan to do so in the conclusion of the paper. Comment on their relative importance in relation to your overall interpretation of the results and, if necessary, note how they may affect the validity of your findings. Avoid using an apologetic tone; however, be honest and self-critical [e.g., in retrospect, had you included a particular question in a survey instrument, additional data could have been revealed].
- The discussion section should end with a concise summary of the principal implications of the findings regardless of their significance. Give a brief explanation about why you believe the findings and conclusions of your study are important and how they support broader knowledge or understanding of the research problem. This can be followed by any recommendations for further research. However, do not offer recommendations which could have been easily addressed within the study. This would demonstrate to the reader that you have inadequately examined and interpreted the data.
IV. Overall Objectives
The objectives of your discussion section should include the following: I. Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings
Briefly reiterate the research problem or problems you are investigating and the methods you used to investigate them, then move quickly to describe the major findings of the study. You should write a direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results, usually in one paragraph.
II. Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important
No one has thought as long and hard about your study as you have. Systematically explain the underlying meaning of your findings and state why you believe they are significant. After reading the discussion section, you want the reader to think critically about the results and why they are important. You don’t want to force the reader to go through the paper multiple times to figure out what it all means. If applicable, begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most significant or unanticipated finding first, then systematically review each finding. Otherwise, follow the general order you reported the findings presented in the results section.
III. Relate the Findings to Similar Studies
No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for your research. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps to support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your study differs from other research about the topic. Note that any significant or unanticipated finding is often because there was no prior research to indicate the finding could occur. If there is prior research to indicate this, you need to explain why it was significant or unanticipated. IV. Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings
It is important to remember that the purpose of research in the social sciences is to discover and not to prove . When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations for the study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. This is especially important when describing the discovery of significant or unanticipated findings.
V. Acknowledge the Study’s Limitations
It is far better for you to identify and acknowledge your study’s limitations than to have them pointed out by your professor! Note any unanswered questions or issues your study could not address and describe the generalizability of your results to other situations. If a limitation is applicable to the method chosen to gather information, then describe in detail the problems you encountered and why. VI. Make Suggestions for Further Research
You may choose to conclude the discussion section by making suggestions for further research [as opposed to offering suggestions in the conclusion of your paper]. Although your study can offer important insights about the research problem, this is where you can address other questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or highlight hidden issues that were revealed as a result of conducting your research. You should frame your suggestions by linking the need for further research to the limitations of your study [e.g., in future studies, the survey instrument should include more questions that ask..."] or linking to critical issues revealed from the data that were not considered initially in your research.
NOTE: Besides the literature review section, the preponderance of references to sources is usually found in the discussion section . A few historical references may be helpful for perspective, but most of the references should be relatively recent and included to aid in the interpretation of your results, to support the significance of a finding, and/or to place a finding within a particular context. If a study that you cited does not support your findings, don't ignore it--clearly explain why your research findings differ from theirs.
V. Problems to Avoid
- Do not waste time restating your results . Should you need to remind the reader of a finding to be discussed, use "bridge sentences" that relate the result to the interpretation. An example would be: “In the case of determining available housing to single women with children in rural areas of Texas, the findings suggest that access to good schools is important...," then move on to further explaining this finding and its implications.
- As noted, recommendations for further research can be included in either the discussion or conclusion of your paper, but do not repeat your recommendations in the both sections. Think about the overall narrative flow of your paper to determine where best to locate this information. However, if your findings raise a lot of new questions or issues, consider including suggestions for further research in the discussion section.
- Do not introduce new results in the discussion section. Be wary of mistaking the reiteration of a specific finding for an interpretation because it may confuse the reader. The description of findings [results section] and the interpretation of their significance [discussion section] should be distinct parts of your paper. If you choose to combine the results section and the discussion section into a single narrative, you must be clear in how you report the information discovered and your own interpretation of each finding. This approach is not recommended if you lack experience writing college-level research papers.
- Use of the first person pronoun is generally acceptable. Using first person singular pronouns can help emphasize a point or illustrate a contrasting finding. However, keep in mind that too much use of the first person can actually distract the reader from the main points [i.e., I know you're telling me this--just tell me!].
Analyzing vs. Summarizing. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University; Discussion. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Hess, Dean R. "How to Write an Effective Discussion." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004); Kretchmer, Paul. Fourteen Steps to Writing to Writing an Effective Discussion Section. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sauaia, A. et al. "The Anatomy of an Article: The Discussion Section: "How Does the Article I Read Today Change What I Will Recommend to my Patients Tomorrow?” The Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 74 (June 2013): 1599-1602; Research Limitations & Future Research . Lund Research Ltd., 2012; Summary: Using it Wisely. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Discussion. Writing in Psychology course syllabus. University of Florida; Yellin, Linda L. A Sociology Writer's Guide . Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon, 2009.
Writing Tip
Don’t Over-Interpret the Results!
Interpretation is a subjective exercise. As such, you should always approach the selection and interpretation of your findings introspectively and to think critically about the possibility of judgmental biases unintentionally entering into discussions about the significance of your work. With this in mind, be careful that you do not read more into the findings than can be supported by the evidence you have gathered. Remember that the data are the data: nothing more, nothing less.
MacCoun, Robert J. "Biases in the Interpretation and Use of Research Results." Annual Review of Psychology 49 (February 1998): 259-287; Ward, Paulet al, editors. The Oxford Handbook of Expertise . Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2018.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Write Two Results Sections!
One of the most common mistakes that you can make when discussing the results of your study is to present a superficial interpretation of the findings that more or less re-states the results section of your paper. Obviously, you must refer to your results when discussing them, but focus on the interpretation of those results and their significance in relation to the research problem, not the data itself.
Azar, Beth. "Discussing Your Findings." American Psychological Association gradPSYCH Magazine (January 2006).
Yet Another Writing Tip
Avoid Unwarranted Speculation!
The discussion section should remain focused on the findings of your study. For example, if the purpose of your research was to measure the impact of foreign aid on increasing access to education among disadvantaged children in Bangladesh, it would not be appropriate to speculate about how your findings might apply to populations in other countries without drawing from existing studies to support your claim or if analysis of other countries was not a part of your original research design. If you feel compelled to speculate, do so in the form of describing possible implications or explaining possible impacts. Be certain that you clearly identify your comments as speculation or as a suggestion for where further research is needed. Sometimes your professor will encourage you to expand your discussion of the results in this way, while others don’t care what your opinion is beyond your effort to interpret the data in relation to the research problem.
- << Previous: Using Non-Textual Elements
- Next: Limitations of the Study >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 10:40 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Turk J Urol
- v.39(Suppl 1); 2013 Sep
How to write a discussion section?
Writing manuscripts to describe study outcomes, although not easy, is the main task of an academician. The aim of the present review is to outline the main aspects of writing the discussion section of a manuscript. Additionally, we address various issues regarding manuscripts in general. It is advisable to work on a manuscript regularly to avoid losing familiarity with the article. On principle, simple, clear and effective language should be used throughout the text. In addition, a pre-peer review process is recommended to obtain feedback on the manuscript. The discussion section can be written in 3 parts: an introductory paragraph, intermediate paragraphs and a conclusion paragraph. For intermediate paragraphs, a “divide and conquer” approach, meaning a full paragraph describing each of the study endpoints, can be used. In conclusion, academic writing is similar to other skills, and practice makes perfect.
Introduction
Sharing knowledge produced during academic life is achieved through writing manuscripts. However writing manuscripts is a challenging endeavour in that we physicians have a heavy workload, and English which is common language used for the dissemination of scientific knowledge is not our mother tongue.
The objective of this review is to summarize the method of writing ‘Discussion’ section which is the most important, but probably at the same time the most unlikable part of a manuscript, and demonstrate the easy ways we applied in our practice, and finally share the frequently made relevant mistakes. During this procedure, inevitably some issues which concerns general concept of manuscript writing process are dealt with. Therefore in this review we will deal with topics related to the general aspects of manuscript writing process, and specifically issues concerning only the ‘Discussion’ section.
A) Approaches to general aspects of manuscript writing process:
1. what should be the strategy of sparing time for manuscript writing be.
Two different approaches can be formulated on this issue? One of them is to allocate at least 30 minutes a day for writing a manuscript which amounts to 3.5 hours a week. This period of time is adequate for completion of a manuscript within a few weeks which can be generally considered as a long time interval. Fundamental advantage of this approach is to gain a habit of making academic researches if one complies with the designated time schedule, and to keep the manuscript writing motivation at persistently high levels. Another approach concerning this issue is to accomplish manuscript writing process within a week. With the latter approach, the target is rapidly attained. However longer time periods spent in order to concentrate on the subject matter can be boring, and lead to loss of motivation. Daily working requirements unrelated to the manuscript writing might intervene, and prolong manuscript writing process. Alienation periods can cause loss of time because of need for recurrent literature reviews. The most optimal approach to manuscript writing process is daily writing strategy where higher levels of motivation are persistently maintained.
Especially before writing the manuscript, the most important step at the start is to construct a draft, and completion of the manuscript on a theoretical basis. Therefore, during construction of a draft, attention distracting environment should be avoided, and this step should be completed within 1–2 hours. On the other hand, manuscript writing process should begin before the completion of the study (even the during project stage). The justification of this approach is to see the missing aspects of the study and the manuscript writing methodology, and try to solve the relevant problems before completion of the study. Generally, after completion of the study, it is very difficult to solve the problems which might be discerned during the writing process. Herein, at least drafts of the ‘Introduction’, and ‘Material and Methods’ can be written, and even tables containing numerical data can be constructed. These tables can be written down in the ‘Results’ section. [ 1 ]
2. How should the manuscript be written?
The most important principle to be remembered on this issue is to obey the criteria of simplicity, clarity, and effectiveness. [ 2 ] Herein, do not forget that, the objective should be to share our findings with the readers in an easily comprehensible format. Our approach on this subject is to write all structured parts of the manuscript at the same time, and start writing the manuscript while reading the first literature. Thus newly arisen connotations, and self-brain gyms will be promptly written down. However during this process your outcomes should be revealed fully, and roughly the message of the manuscript which be delivered. Thus with this so-called ‘hunter’s approach’ the target can be achieved directly, and rapidly. Another approach is ‘collectioner’s approach. [ 3 ] In this approach, firstly, potential data, and literature studies are gathered, read, and then selected ones are used. Since this approach suits with surgical point of view, probably ‘hunter’s approach’ serves our purposes more appropriately. However, in parallel with academic development, our novice colleague ‘manuscripters’ can prefer ‘collectioner’s approach.’
On the other hand, we think that research team consisting of different age groups has some advantages. Indeed young colleagues have the enthusiasm, and energy required for the conduction of the study, while middle-aged researchers have the knowledge to manage the research, and manuscript writing. Experienced researchers make guiding contributions to the manuscript. However working together in harmony requires assignment of a chief researcher, and periodically organizing advancement meetings. Besides, talents, skills, and experiences of the researchers in different fields (ie. research methods, contact with patients, preparation of a project, fund-raising, statistical analysis etc.) will determine task sharing, and make a favourable contribution to the perfection of the manuscript. Achievement of the shared duties within a predetermined time frame will sustain the motivation of the researchers, and prevent wearing out of updated data.
According to our point of view, ‘Abstract’ section of the manuscript should be written after completion of the manuscript. The reason for this is that during writing process of the main text, the significant study outcomes might become insignificant or vice versa. However, generally, before onset of the writing process of the manuscript, its abstract might be already presented in various congresses. During writing process, this abstract might be a useful guide which prevents deviation from the main objective of the manuscript.
On the other hand references should be promptly put in place while writing the manuscript, Sorting, and placement of the references should not be left to the last moment. Indeed, it might be very difficult to remember relevant references to be placed in the ‘Discussion’ section. For the placement of references use of software programs detailed in other sections is a rational approach.
3. Which target journal should be selected?
In essence, the methodology to be followed in writing the ‘Discussion’ section is directly related to the selection of the target journal. Indeed, in compliance with the writing rules of the target journal, limitations made on the number of words after onset of the writing process, effects mostly the ‘Discussion’ section. Proper matching of the manuscript with the appropriate journal requires clear, and complete comprehension of the available data from scientific point of view. Previously, similar articles might have been published, however innovative messages, and new perspectives on the relevant subject will facilitate acceptance of the article for publication. Nowadays, articles questioning available information, rather than confirmatory ones attract attention. However during this process, classical information should not be questioned except for special circumstances. For example manuscripts which lead to the conclusions as “laparoscopic surgery is more painful than open surgery” or “laparoscopic surgery can be performed without prior training” will not be accepted or they will be returned by the editor of the target journal to the authors with the request of critical review. Besides the target journal to be selected should be ready to accept articles with similar concept. In fact editors of the journal will not reserve the limited space in their journal for articles yielding similar conclusions.
The title of the manuscript is as important as the structured sections * of the manuscript. The title can be the most striking or the newest outcome among results obtained.
Before writing down the manuscript, determination of 2–3 titles increases the motivation of the authors towards the manuscript. During writing process of the manuscript one of these can be selected based on the intensity of the discussion. However the suitability of the title to the agenda of the target journal should be investigated beforehand. For example an article bearing the title “Use of barbed sutures in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy shortens warm ischemia time” should not be sent to “Original Investigations and Seminars in Urologic Oncology” Indeed the topic of the manuscript is out of the agenda of this journal.
4. Do we have to get a pre-peer review about the written manuscript?
Before submission of the manuscript to the target journal the opinions of internal, and external referees should be taken. [ 1 ] Internal referees can be considered in 2 categories as “General internal referees” and “expert internal referees” General internal referees (ie. our colleagues from other medical disciplines) are not directly concerned with your subject matter but as mentioned above they critically review the manuscript as for simplicity, clarity, and effectiveness of its writing style. Expert internal reviewers have a profound knowledge about the subject, and they can provide guidance about the writing process of the manuscript (ie. our senior colleagues more experienced than us). External referees are our colleagues who did not contribute to data collection of our study in any way, but we can request their opinions about the subject matter of the manuscript. Since they are unrelated both to the author(s), and subject matter of the manuscript, these referees can review our manuscript more objectively. Before sending the manuscript to internal, and external referees, we should contact with them, and ask them if they have time to review our manuscript. We should also give information about our subject matter. Otherwise pre-peer review process can delay publication of the manuscript, and decrease motivation of the authors. In conclusion, whoever the preferred referee will be, these internal, and external referees should respond the following questions objectively. 1) Does the manuscript contribute to the literature?; 2) Does it persuasive? 3) Is it suitable for the publication in the selected journal? 4) Has a simple, clear, and effective language been used throughout the manuscript? In line with the opinions of the referees, the manuscript can be critically reviewed, and perfected. [ 1 ]**
Following receival of the opinions of internal, and external referees, one should concentrate priorly on indicated problems, and their solutions. Comments coming from the reviewers should be criticized, but a defensive attitude should not be assumed during this evaluation process. During this “incubation” period where the comments of the internal, and external referees are awaited, literature should be reviewed once more. Indeed during this time interval a new article which you should consider in the ‘Discussion’ section can be cited in the literature.
5. What are the common mistakes made related to the writing process of a manuscript?
Probably the most important mistakes made related to the writing process of a manuscript include lack of a clear message of the manuscript , inclusion of more than one main idea in the same text or provision of numerous unrelated results at the same time so as to reinforce the assertions of the manuscript. This approach can be termed roughly as “loss of the focus of the study” In conclusion, the author(s) should ask themselves the following question at every stage of the writing process:. “What is the objective of the study? If you always get clear-cut answers whenever you ask this question, then the study is proceeding towards the right direction. Besides application of a template which contains the intended clear-cut messages to be followed will contribute to the communication of net messages.
One of the important mistakes is refraining from critical review of the manuscript as a whole after completion of the writing process. Therefore, the authors should go over the manuscript for at least three times after finalization of the manuscript based on joint decision. The first control should concentrate on the evaluation of the appropriateness of the logic of the manuscript, and its organization, and whether desired messages have been delivered or not. Secondly, syutax, and grammar of the manuscript should be controlled. It is appropriate to review the manuscript for the third time 1 or 2 weeks after completion of its writing process. Thus, evaluation of the “cooled” manuscript will be made from a more objective perspective, and assessment process of its integrity will be facilitated.
Other erroneous issues consist of superfluousness of the manuscript with unnecessary repetitions, undue, and recurrent references to the problems adressed in the manuscript or their solution methods, overcriticizing or overpraising other studies, and use of a pompous literary language overlooking the main objective of sharing information. [ 4 ]
B) Approaches to the writing process of the ‘Discussion’ section:
1. how should the main points of ‘discussion’ section be constructed.
Generally the length of the ‘Discussion ‘ section should not exceed the sum of other sections (ıntroduction, material and methods, and results), and it should be completed within 6–7 paragraphs.. Each paragraph should not contain more than 200 words, and hence words should be counted repeteadly. The ‘Discussion’ section can be generally divided into 3 separate paragraphs as. 1) Introductory paragraph, 2) Intermediate paragraphs, 3) Concluding paragraph.
The introductory paragraph contains the main idea of performing the study in question. Without repeating ‘Introduction’ section of the manuscript, the problem to be addressed, and its updateness are analysed. The introductory paragraph starts with an undebatable sentence, and proceeds with a part addressing the following questions as 1) On what issue we have to concentrate, discuss or elaborate? 2) What solutions can be recommended to solve this problem? 3) What will be the new, different, and innovative issue? 4) How will our study contribute to the solution of this problem An introductory paragraph in this format is helpful to accomodate reader to the rest of the Discussion section. However summarizing the basic findings of the experimental studies in the first paragraph is generally recommended by the editors of the journal. [ 5 ]
In the last paragraph of the Discussion section “strong points” of the study should be mentioned using “constrained”, and “not too strongly assertive” statements. Indicating limitations of the study will reflect objectivity of the authors, and provide answers to the questions which will be directed by the reviewers of the journal. On the other hand in the last paragraph, future directions or potential clinical applications may be emphasized.
2. How should the intermediate paragraphs of the Discussion section be formulated?
The reader passes through a test of boredom while reading paragraphs of the Discussion section apart from the introductory, and the last paragraphs. Herein your findings rather than those of the other researchers are discussed. The previous studies can be an explanation or reinforcement of your findings. Each paragraph should contain opinions in favour or against the topic discussed, critical evaluations, and learning points.
Our management approach for intermediate paragraphs is “divide and conquer” tactics. Accordingly, the findings of the study are determined in order of their importance, and a paragraph is constructed for each finding ( Figure 1 ). Each paragraph begins with an “indisputable” introductory sentence about the topic to be discussed. This sentence basically can be the answer to the question “What have we found?” Then a sentence associated with the subject matter to be discussed is written. Subsequently, in the light of the current literature this finding is discussed, new ideas on this subject are revealed, and the paragraph ends with a concluding remark.

Divide and Conquer tactics
In this paragraph, main topic should be emphasized without going into much detail. Its place, and importance among other studies should be indicated. However during this procedure studies should be presented in a logical sequence (ie. from past to present, from a few to many cases), and aspects of the study contradictory to other studies should be underlined. Results without any supportive evidence or equivocal results should not be written. Besides numerical values presented in the Results section should not be repeated unless required.
Besides, asking the following questions, and searching their answers in the same paragraph will facilitate writing process of the paragraph. [ 1 ] 1) Can the discussed result be false or inadequate? 2) Why is it false? (inadequate blinding, protocol contamination, lost to follow-up, lower statistical power of the study etc.), 3) What meaning does this outcome convey?
3. What are the common mistakes made in writing the Discussion section?:
Probably the most important mistake made while writing the Discussion section is the need for mentioning all literature references. One point to remember is that we are not writing a review article, and only the results related to this paragraph should be discussed. Meanwhile, each word of the paragraphs should be counted, and placed carefully. Each word whose removal will not change the meaning should be taken out from the text.” Writing a saga with “word salads” *** is one of the reasons for prompt rejection. Indeed, if the reviewer thinks that it is difficult to correct the Discussion section, he/she use her/ his vote in the direction of rejection to save time (Uniform requirements for manuscripts: International Comittee of Medical Journal Editors [ http://www.icmje.org/urm_full.pdf ])
The other important mistake is to give too much references, and irrelevancy between the references, and the section with these cited references. [ 3 ] While referring these studies, (excl. introductory sentences linking indisputable sentences or paragraphs) original articles should be cited. Abstracts should not be referred, and review articles should not be cited unless required very much.
4. What points should be paid attention about writing rules, and grammar?
As is the case with the whole article, text of the Discussion section should be written with a simple language, as if we are talking with our colleague. [ 2 ] Each sentence should indicate a single point, and it should not exceed 25–30 words. The priorly mentioned information which linked the previous sentence should be placed at the beginning of the sentence, while the new information should be located at the end of the sentence. During construction of the sentences, avoid unnecessary words, and active voice rather than passive voice should be used.**** Since conventionally passive voice is used in the scientific manuscripts written in the Turkish language, the above statement contradicts our writing habits. However, one should not refrain from beginning the sentences with the word “we”. Indeed, editors of the journal recommend use of active voice so as to increase the intelligibility of the manuscript.
In conclusion, the major point to remember is that the manuscript should be written complying with principles of simplicity, clarity, and effectiveness. In the light of these principles, as is the case in our daily practice, all components of the manuscript (IMRAD) can be written concurrently. In the ‘Discussion’ section ‘divide and conquer’ tactics remarkably facilitates writing process of the discussion. On the other hand, relevant or irrelevant feedbacks received from our colleagues can contribute to the perfection of the manuscript. Do not forget that none of the manuscripts is perfect, and one should not refrain from writing because of language problems, and related lack of experience.
Instead of structured sections of a manuscript (IMRAD): Introduction, Material and Methods, Results, and Discussion
Instead of in the Istanbul University Faculty of Medicine posters to be submitted in congresses are time to time discussed in Wednesday meetings, and opinions of the internal referees are obtained about the weak, and strong points of the study
Instead of a writing style which uses words or sentences with a weak logical meaning that do not lead the reader to any conclusion
Instead of “white color”; “proven”; nstead of “history”; “to”. should be used instead of “white in color”, “definitely proven”, “past history”, and “in order to”, respectively ( ref. 2 )
Instead of “No instances of either postoperative death or major complications occurred during the early post-operative period” use “There were no deaths or major complications occurred during the early post-operative period.
Instead of “Measurements were performed to evaluate the levels of CEA in the serum” use “We measured serum CEA levels”
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Personalised content for
You're viewing this site as a domestic an international student
You're an international student if you are:
- intending to study on a student visa
- not a citizen of Australia or New Zealand
- not an Australian permanent resident
- not a holder of an Australian humanitarian visa.
You're a domestic student if you are:
- a citizen of Australia or New Zealand
- an Australian permanent resident
- a holder of an Australian humanitarian visa.
- Alumni & Giving
- Current students
Search Charles Darwin University
Study Skills
Writing a discussion section
In the discussion section, you will draw connections between your findings, existing theory and other research. You will have an opportunity to tell the story arising from your findings.
This page will help you to:
understand the purpose of the discussion section
follow the steps required to plan your discussion section
structure your discussion
enhance the depth of your discussion
use appropriate language to discuss your findings.
Introduction to the discussion section
When you have reached this stage, you might be thinking “All I have to do now is to sum up what I have done, and then make a few remarks about what I did” (as cited in Swales & Feak, 2012, p.263). However, writing a discussion section is not that simple. Read on to learn more.
Before you continue, reflect on your earlier writing experiences and the feedback you have received. How would you rate your ability in the following skills? Rate your ability from ‘good’ to ‘needs development’.
Reflect on your answers. Congratulations if you feel confident about your skills. You may find it helpful to review the materials on this page to confirm your knowledge and possibly learn more. Don't worry if you don't feel confident. Work through these materials to build your skills.
A discussion critically analyses and interprets the results of a scientific study, placing the results in the context of published literature and explaining how they affect the field .
In this section, you will relate the specific findings of your research to the wider scientific field. This is the opposite of the introduction section, which starts with the broader context and narrows to focus on your specific research topic.
The discussion will:
review the findings
put the findings into the context of the overall research
tell readers why the research results are important and where they fit in with the current literature
acknowledge the limitations of the study
make recommendations for future research.
Let's review your understanding of the discussion section by identifying what makes a strong discussion.
Planning for a discussion section
Planning for a discussion section starts with analysing your data. For some kinds of research, the analysis cannot be done until your data has been collected. For others, analysing data can happen early as the data already exists in literary texts, archival documents or similar.
Before starting to write the discussion section, it is important to:
analyse your data (usually reported in the Results or Findings section)
select the key issues that are the substance of your research
relate the findings to the literature and
plan for the process of going from your specific findings to the broader scientific field.
Your analysis of the results will inform the Findings or Results section of your thesis or publication. It is the stage where you organise and visualise your data, and identify trends, patterns and causal relationships in the themes.
As the section discusses the key findings without restating the results, it is important to identify the key issues. For example, you should focus on four or five issues that agree or do not agree with your hypothesis or with previously published work. It is also important to include and discuss any unexpected results.
You refer to previous research in your discussion section for explaining your results, confirming how your results support the theories and previous studies, comparing your results with similar studies, or showing how your results contradict similar studies.
Therefore, papers that you are likely to refer to in your discussion are those that led to:
your hypothesis
your experimental design
your results.
In writing the discussion section, you will start with your research and then broaden your focus to the field or scientific community. This means you will go from narrowest (your specific findings) to broadest (the wider scientific community). You do this by following the six moves:
As you can see, your discussion may follow six moves (stages) which broadens the scope of your discussion section. Watch this video to learn how to apply these moves.

Structuring your discussion
This section reviews how a discussion section can be organised.
A discussion section usually includes five parts or steps, which are illustrated in the image below.
In some disciplines, the researcher's argument determines the structure of the presentation and discussion of findings. In other disciplines, the structure follows established conventions. Therefore, it is important for you to investigate the conventions of your own discipline, by looking at theses in your discipline and articles published in your target journals. The discussion section may be:
in a combined section called Results and Discussion
in a combined section called Discussion and Conclusion
in a separate section.
Your discussion section may be an independent chapter or it might be combined with the Findings chapter. Common chapter headings include:
Discussion chapter
Findings and Discussion chapter
Discussion, Recommendations and Conclusion chapter
Discussion and Conclusion chapter
It is important to have a good understanding of the expected content of each chapter. Below is an example of a chapter in which discussion, recommendations and conclusion are combined.
Click on the hotspots to learn more.
This section focuses on useful language for writing your discussion.
Boosters and hedges should be used to demonstrate your confidence in your interpretation of the results. They help you to distinguish between clear and strong results and those that you feel less confident about or that may be open to different interpretations.
Read both sentences. Which one shows more confidence in the results?
The Dutch supervisors reported using different types of questions more frequently and deliberately than the Chinese supervisors. This difference may have its roots in the underlying educational philosophies. (Adapted from Hu, Rijst, Veen, & Verloop, 2016)
The findings clearly demonstrate that psychological capital had considerable influence on the 10 employability skills included in the study, and especially on those related to teamwork, self-knowledge and self-management (Adapted from Harper, Bregta & Rundle, 2021)
The writers of sentence two are more confident in the interpretation of their results.
Test your knowledge of hedges and boosters by doing the task below.
It is important to make it clear in your discussion:
which research has been done by you
which research has been done by other people
how they complement each other.
Image 2: Note that present perfect is also used to refer to other studies when you want to emphasise that an area of research is still current and ongoing. Take a look at the example below which uses present perfect to refer to other studies
Like other studies (e.g., Larcombe et al., 2021; Naylor, 2020) that have shown a strong connection between course experience and wellbeing, our study shows that a significant portion of international students believe that aspects of their immediate environment could be improved to better support their wellbeing.
More information on tenses in the Discussion section is presented in Language Tip 4 below.
Below are some useful discussion phrases that were adapted from Paltridge & Starfield (2020) and the APA Discussion phrases guide (7th edition).
You can download this APA discussion phrase guide here and visit the Academic Phrasebank for further phrases and examples.
Let's look at these extracts and identify the functions of the paragraphs.
Past, present and present perfect tenses are commonly used in the discussion section.
- Past tense is used to summarise the key findings and to refer to the work of previous researchers
- Present perfect is used to refer to the work of previous researchers (usually an area of research that is current and on-going rather than one single study)
- Present tense is used to interpret the results or describe the significance of the findings
- Future is used to make recommendations for further research or providing future direction
Below is an example of some paragraphs in a discussion section in which different tenses are used.

Test your knowledge of using the right tenses in the discussion section by doing the task below.
Use this template to plan your discussion.
The template is an example of a planning tool that will help you develop an overview of the key content that you are going to include in your section. You can download the draft and save it as a Word document once you have finished.
You may have more or less than 3 key findings that you would like to discuss in your section.
If you would like more support, visit the Language and Learning Advisors page.
Butler, K. (2020, 7 April). Breakdown of an ideal discussion of scientific research paper. Scientific Communications . https://butlerscicomm.com/breakdown-of-ideal-discussion-section-research-paper
Calvo, J. C. A & García, G. M. (2021). The influence of psychological capital on graduates’ perception of employability: the mediating role of employability skills. Higher Education Research & Development , 40(2), 293-308, DOI: 10.1080/07294360.2020.1738350
Cenamor, J. (2022) To teach or not to teach? Junior academics and the teaching-research relationship. Higher Education Research & Development , 41(5), 1417-1435. DOI: 10.1080/07294360.2021.1933395
Harper, R., Bretag, T & Rundle, K. (2021) Detecting contract cheating: examining the role of assessment type. Higher Education Research & Development, 40(2), 263-278, DOI: 10.1080/07294360.2020.1724899
Hu, Y., Rijst, R. M., Veen, K & N Verloop, N. (2016) The purposes and processes of master's thesis supervision: a comparison of Chinese and Dutch supervisors. Higher Education Research & Development , 35(5), 910-924, DOI: 10.1080/07294360.2016.1139550
Humphrey, P. (2015). English language proficiency in higher education: student conceptualisations and outcomes . [Doctoral dissertation, Griffith University]
Marangell, S., & Baik, C. (2022). International students’ suggestions for what universities can do to better support their mental wellbeing. Journal of International Students, 12(4), 933-954.
Merga, M., & Mason, S. (2021) Early career researchers’ perceptions of the benefits and challenges of sharing research with academic and non-academic end-users, Higher Education Research & Development , 40(7), 1482-1496, DOI: 10.1080/07294360.2020.1815662
Paltridge, B., & Starfield, S. (2019). Thesis and Dissertation Writing in a Second Language: A Handbook for Students and their Supervisors (2nd ed.). Routledge.
Rendle-Short, J. (2009). The Address Term Mate in Australian English: Is it Still a Masculine Term?. Australian Journal of Linguistics, 29(2), 245-268, DOI: 10.1080/07268600902823110
Did you know CDU Language and Learning Advisors offer a range of study support options?
https://www.cdu.edu.au/library/language-and-learning-support

Cookie compliance notice
We use cookies to improve our service. By continuing you agree to our privacy statement . EU/EA members can update your cookie settings here .
How To Structure Your Literature Review
3 options to help structure your chapter.
By: Amy Rommelspacher (PhD) | Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | November 2020 (Updated May 2023)
Writing the literature review chapter can seem pretty daunting when you’re piecing together your dissertation or thesis. As we’ve discussed before , a good literature review needs to achieve a few very important objectives – it should:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure . Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you’ll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don’t worry though – in this post, we’ll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

27 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Systematic Review Discussion Example

Automate every stage of your literature review to produce evidence-based research faster and more accurately.
What should be included in the discussion section of a systematic review.
There are a number of key elements that are included in a discussion section of a systematic review. Remember to use all these elements to ensure the quality of your review remains high, that your review is deemed useful to your peers, and that the validity of your systematic review cannot be questioned.
The first thing to do in your discussion is to summarize your most important findings. This can simply be identifying your key results. Be careful not to just repeat all the results you have outlined in your previous sections. Instead, once you have briefly mentioned them, go on to interpret them. The results from included studies are presented in a summary. The results are then compared among different studies, and the consistent themes, agreements, and contradictions among studies are identified. The consistencies are reported and reasons for contradictions are given. The themes and agreement among the studies are used to answer the research question. Your interpretations need to be backed up by evidence so that they make the intended impact. Interpretations can be based on your critical thinking. Your interpretations of study findings can be compared to the interpretation of another review on the same topic.
Another way to ensure that your review is as persuasive as possible is to discuss any strengths and weaknesses at this point, in your discussion. It is advisable to first talk about the most notable strengths and limitations of included studies. Afterward, you can show how the characteristics of individual included studies have affected the strengths and limitations of the review. Identifying weaknesses may not be immediately obvious for some writers of reviews. However, they are essential to include, especially in the discussion section, as it means you can explain them and examine why your findings are still valid, despite such weaknesses. Discussing strengths will support your view even further. By highlighting both strengths and weaknesses together, you can dismiss any negative criticism before it even begins.
Learn More About DistillerSR
(Article continues below)
How Long Should A Discussion Be In A Systematic Review?
When it comes to the length of a discussion section, there is never really a right or wrong answer. The length of the discussion section is a systematic review is usually determined by the number of included studies, the scope of the research question, and the ability of the author to analyze and synthesize data from the included studies. That being said, given the breadth and number of areas to be covered as mentioned above, it will never be just one paragraph. Examining the strengths and weaknesses of your review alone will often call for a couple of paragraphs of discussion. Then you assert your findings that will answer your research question and support your initial hypothesis. This will likely demand another paragraph or two at least.
The Importance of Systematic Review Discussion
Remember that the discussion section of your review is, arguably, the most important part of your work. It is where you can put your label on all previous studies conducted, and highlight why your research into the area has been a worthwhile process. It is an opportunity for you to set yourself apart, and have your paper be seen as evidence for the subject matter in question. Therefore, the importance of a systematic review discussion cannot be overstated. The discussion section of a review is your chance to present the results of your analysis, which takes into account all previous studies or research in the area.
3 Reasons to Connect

- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Discussion Section for a Research Paper
We’ve talked about several useful writing tips that authors should consider while drafting or editing their research papers. In particular, we’ve focused on figures and legends , as well as the Introduction , Methods , and Results . Now that we’ve addressed the more technical portions of your journal manuscript, let’s turn to the analytical segments of your research article. In this article, we’ll provide tips on how to write a strong Discussion section that best portrays the significance of your research contributions.

What is the Discussion section of a research paper?
In a nutshell, your Discussion fulfills the promise you made to readers in your Introduction . At the beginning of your paper, you tell us why we should care about your research. You then guide us through a series of intricate images and graphs that capture all the relevant data you collected during your research. We may be dazzled and impressed at first, but none of that matters if you deliver an anti-climactic conclusion in the Discussion section!
Are you feeling pressured? Don’t worry. To be honest, you will edit the Discussion section of your manuscript numerous times. After all, in as little as one to two paragraphs ( Nature ‘s suggestion based on their 3,000-word main body text limit), you have to explain how your research moves us from point A (issues you raise in the Introduction) to point B (our new understanding of these matters). You must also recommend how we might get to point C (i.e., identify what you think is the next direction for research in this field). That’s a lot to say in two paragraphs!
So, how do you do that? Let’s take a closer look.
What should I include in the Discussion section?
As we stated above, the goal of your Discussion section is to answer the questions you raise in your Introduction by using the results you collected during your research . The content you include in the Discussions segment should include the following information:
- Remind us why we should be interested in this research project.
- Describe the nature of the knowledge gap you were trying to fill using the results of your study.
- Don’t repeat your Introduction. Instead, focus on why this particular study was needed to fill the gap you noticed and why that gap needed filling in the first place.
- Mainly, you want to remind us of how your research will increase our knowledge base and inspire others to conduct further research.
- Clearly tell us what that piece of missing knowledge was.
- Answer each of the questions you asked in your Introduction and explain how your results support those conclusions.
- Make sure to factor in all results relevant to the questions (even if those results were not statistically significant).
- Focus on the significance of the most noteworthy results.
- If conflicting inferences can be drawn from your results, evaluate the merits of all of them.
- Don’t rehash what you said earlier in the Results section. Rather, discuss your findings in the context of answering your hypothesis. Instead of making statements like “[The first result] was this…,” say, “[The first result] suggests [conclusion].”
- Do your conclusions line up with existing literature?
- Discuss whether your findings agree with current knowledge and expectations.
- Keep in mind good persuasive argument skills, such as explaining the strengths of your arguments and highlighting the weaknesses of contrary opinions.
- If you discovered something unexpected, offer reasons. If your conclusions aren’t aligned with current literature, explain.
- Address any limitations of your study and how relevant they are to interpreting your results and validating your findings.
- Make sure to acknowledge any weaknesses in your conclusions and suggest room for further research concerning that aspect of your analysis.
- Make sure your suggestions aren’t ones that should have been conducted during your research! Doing so might raise questions about your initial research design and protocols.
- Similarly, maintain a critical but unapologetic tone. You want to instill confidence in your readers that you have thoroughly examined your results and have objectively assessed them in a way that would benefit the scientific community’s desire to expand our knowledge base.
- Recommend next steps.
- Your suggestions should inspire other researchers to conduct follow-up studies to build upon the knowledge you have shared with them.
- Keep the list short (no more than two).
How to Write the Discussion Section
The above list of what to include in the Discussion section gives an overall idea of what you need to focus on throughout the section. Below are some tips and general suggestions about the technical aspects of writing and organization that you might find useful as you draft or revise the contents we’ve outlined above.
Technical writing elements
- Embrace active voice because it eliminates the awkward phrasing and wordiness that accompanies passive voice.
- Use the present tense, which should also be employed in the Introduction.
- Sprinkle with first person pronouns if needed, but generally, avoid it. We want to focus on your findings.
- Maintain an objective and analytical tone.
Discussion section organization
- Keep the same flow across the Results, Methods, and Discussion sections.
- We develop a rhythm as we read and parallel structures facilitate our comprehension. When you organize information the same way in each of these related parts of your journal manuscript, we can quickly see how a certain result was interpreted and quickly verify the particular methods used to produce that result.
- Notice how using parallel structure will eliminate extra narration in the Discussion part since we can anticipate the flow of your ideas based on what we read in the Results segment. Reducing wordiness is important when you only have a few paragraphs to devote to the Discussion section!
- Within each subpart of a Discussion, the information should flow as follows: (A) conclusion first, (B) relevant results and how they relate to that conclusion and (C) relevant literature.
- End with a concise summary explaining the big-picture impact of your study on our understanding of the subject matter. At the beginning of your Discussion section, you stated why this particular study was needed to fill the gap you noticed and why that gap needed filling in the first place. Now, it is time to end with “how your research filled that gap.”
Discussion Part 1: Summarizing Key Findings
Begin the Discussion section by restating your statement of the problem and briefly summarizing the major results. Do not simply repeat your findings. Rather, try to create a concise statement of the main results that directly answer the central research question that you stated in the Introduction section . This content should not be longer than one paragraph in length.
Many researchers struggle with understanding the precise differences between a Discussion section and a Results section . The most important thing to remember here is that your Discussion section should subjectively evaluate the findings presented in the Results section, and in relatively the same order. Keep these sections distinct by making sure that you do not repeat the findings without providing an interpretation.
Phrase examples: Summarizing the results
- The findings indicate that …
- These results suggest a correlation between A and B …
- The data present here suggest that …
- An interpretation of the findings reveals a connection between…
Discussion Part 2: Interpreting the Findings
What do the results mean? It may seem obvious to you, but simply looking at the figures in the Results section will not necessarily convey to readers the importance of the findings in answering your research questions.
The exact structure of interpretations depends on the type of research being conducted. Here are some common approaches to interpreting data:
- Identifying correlations and relationships in the findings
- Explaining whether the results confirm or undermine your research hypothesis
- Giving the findings context within the history of similar research studies
- Discussing unexpected results and analyzing their significance to your study or general research
- Offering alternative explanations and arguing for your position
Organize the Discussion section around key arguments, themes, hypotheses, or research questions or problems. Again, make sure to follow the same order as you did in the Results section.
Discussion Part 3: Discussing the Implications
In addition to providing your own interpretations, show how your results fit into the wider scholarly literature you surveyed in the literature review section. This section is called the implications of the study . Show where and how these results fit into existing knowledge, what additional insights they contribute, and any possible consequences that might arise from this knowledge, both in the specific research topic and in the wider scientific domain.
Questions to ask yourself when dealing with potential implications:
- Do your findings fall in line with existing theories, or do they challenge these theories or findings? What new information do they contribute to the literature, if any? How exactly do these findings impact or conflict with existing theories or models?
- What are the practical implications on actual subjects or demographics?
- What are the methodological implications for similar studies conducted either in the past or future?
Your purpose in giving the implications is to spell out exactly what your study has contributed and why researchers and other readers should be interested.
Phrase examples: Discussing the implications of the research
- These results confirm the existing evidence in X studies…
- The results are not in line with the foregoing theory that…
- This experiment provides new insights into the connection between…
- These findings present a more nuanced understanding of…
- While previous studies have focused on X, these results demonstrate that Y.
Step 4: Acknowledging the limitations
All research has study limitations of one sort or another. Acknowledging limitations in methodology or approach helps strengthen your credibility as a researcher. Study limitations are not simply a list of mistakes made in the study. Rather, limitations help provide a more detailed picture of what can or cannot be concluded from your findings. In essence, they help temper and qualify the study implications you listed previously.
Study limitations can relate to research design, specific methodological or material choices, or unexpected issues that emerged while you conducted the research. Mention only those limitations directly relate to your research questions, and explain what impact these limitations had on how your study was conducted and the validity of any interpretations.
Possible types of study limitations:
- Insufficient sample size for statistical measurements
- Lack of previous research studies on the topic
- Methods/instruments/techniques used to collect the data
- Limited access to data
- Time constraints in properly preparing and executing the study
After discussing the study limitations, you can also stress that your results are still valid. Give some specific reasons why the limitations do not necessarily handicap your study or narrow its scope.
Phrase examples: Limitations sentence beginners
- “There may be some possible limitations in this study.”
- “The findings of this study have to be seen in light of some limitations.”
- “The first limitation is the…The second limitation concerns the…”
- “The empirical results reported herein should be considered in the light of some limitations.”
- “This research, however, is subject to several limitations.”
- “The primary limitation to the generalization of these results is…”
- “Nonetheless, these results must be interpreted with caution and a number of limitations should be borne in mind.”
Discussion Part 5: Giving Recommendations for Further Research
Based on your interpretation and discussion of the findings, your recommendations can include practical changes to the study or specific further research to be conducted to clarify the research questions. Recommendations are often listed in a separate Conclusion section , but often this is just the final paragraph of the Discussion section.
Suggestions for further research often stem directly from the limitations outlined. Rather than simply stating that “further research should be conducted,” provide concrete specifics for how future can help answer questions that your research could not.
Phrase examples: Recommendation sentence beginners
- Further research is needed to establish …
- There is abundant space for further progress in analyzing…
- A further study with more focus on X should be done to investigate…
- Further studies of X that account for these variables must be undertaken.
Consider Receiving Professional Language Editing
As you edit or draft your research manuscript, we hope that you implement these guidelines to produce a more effective Discussion section. And after completing your draft, don’t forget to submit your work to a professional proofreading and English editing service like Wordvice, including our manuscript editing service for paper editing , cover letter editing , SOP editing , and personal statement proofreading services. Language editors not only proofread and correct errors in grammar, punctuation, mechanics, and formatting but also improve terms and revise phrases so they read more naturally. Wordvice is an industry leader in providing high-quality revision for all types of academic documents.
For additional information about how to write a strong research paper, make sure to check out our full research writing series !
Wordvice Writing Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers
Additional Academic Resources
- Guide for Authors. (Elsevier)
- How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper. (Bates College)
- Structure of a Research Paper. (University of Minnesota Biomedical Library)
- How to Choose a Target Journal (Springer)
- How to Write Figures and Tables (UNC Writing Center)

Organizing Academic Research Papers: 8. The Discussion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The purpose of the discussion is to interpret and describe the significance of your findings in light of what was already known about the research problem being investigated, and to explain any new understanding or fresh insights about the problem after you've taken the findings into consideration. The discussion will always connect to the introduction by way of the research questions or hypotheses you posed and the literature you reviewed, but it does not simply repeat or rearrange the introduction; the discussion should always explain how your study has moved the reader's understanding of the research problem forward from where you left them at the end of the introduction.
Importance of a Good Discussion
This section is often considered the most important part of a research paper because it most effectively demonstrates your ability as a researcher to think critically about an issue, to develop creative solutions to problems based on the findings, and to formulate a deeper, more profound understanding of the research problem you are studying.
The discussion section is where you explore the underlying meaning of your research , its possible implications in other areas of study, and the possible improvements that can be made in order to further develop the concerns of your research.
This is the section where you need to present the importance of your study and how it may be able to contribute to and/or fill existing gaps in the field. If appropriate, the discussion section is also where you state how the findings from your study revealed new gaps in the literature that had not been previously exposed or adequately described.
This part of the paper is not strictly governed by objective reporting of information but, rather, it is where you can engage in creative thinking about issues through evidence-based interpretation of findings. This is where you infuse your results with meaning.
Kretchmer, Paul. Fourteen Steps to Writing to Writing an Effective Discussion Section . San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
These are the general rules you should adopt when composing your discussion of the results :
- Do not be verbose or repetitive.
- Be concise and make your points clearly.
- Avoid using jargon.
- Follow a logical stream of thought.
- Use the present verb tense, especially for established facts; however, refer to specific works and references in the past tense.
- If needed, use subheadings to help organize your presentation or to group your interpretations into themes.
II. The Content
The content of the discussion section of your paper most often includes :
- Explanation of results : comment on whether or not the results were expected and present explanations for the results; go into greater depth when explaining findings that were unexpected or especially profound. If appropriate, note any unusual or unanticipated patterns or trends that emerged from your results and explain their meaning.
- References to previous research : compare your results with the findings from other studies, or use the studies to support a claim. This can include re-visiting key sources already cited in your literature review section, or, save them to cite later in the discussion section if they are more important to compare with your results than being part of the general research you cited to provide context and background information.
- Deduction : a claim for how the results can be applied more generally. For example, describing lessons learned, proposing recommendations that can help improve a situation, or recommending best practices.
- Hypothesis : a more general claim or possible conclusion arising from the results [which may be proved or disproved in subsequent research].
III. Organization and Structure
Keep the following sequential points in mind as you organize and write the discussion section of your paper:
- Think of your discussion as an inverted pyramid. Organize the discussion from the general to the specific, linking your findings to the literature, then to theory, then to practice [if appropriate].
- Use the same key terms, mode of narration, and verb tense [present] that you used when when describing the research problem in the introduction.
- Begin by briefly re-stating the research problem you were investigating and answer all of the research questions underpinning the problem that you posed in the introduction.
- Describe the patterns, principles, and relationships shown by each major findings and place them in proper perspective. The sequencing of providing this information is important; first state the answer, then the relevant results, then cite the work of others. If appropriate, refer the reader to a figure or table to help enhance the interpretation of the data. The order of interpreting each major finding should be in the same order as they were described in your results section.
- A good discussion section includes analysis of any unexpected findings. This paragraph should begin with a description of the unexpected finding, followed by a brief interpretation as to why you believe it appeared and, if necessary, its possible significance in relation to the overall study. If more than one unexpected finding emerged during the study, describe each them in the order they appeared as you gathered the data.
- Before concluding the discussion, identify potential limitations and weaknesses. Comment on their relative importance in relation to your overall interpretation of the results and, if necessary, note how they may affect the validity of the findings. Avoid using an apologetic tone; however, be honest and self-critical.
- The discussion section should end with a concise summary of the principal implications of the findings regardless of statistical significance. Give a brief explanation about why you believe the findings and conclusions of your study are important and how they support broader knowledge or understanding of the research problem. This can be followed by any recommendations for further research. However, do not offer recommendations which could have been easily addressed within the study. This demonstrates to the reader you have inadequately examined and interpreted the data.
IV. Overall Objectives
The objectives of your discussion section should include the following: I. Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings
Briefly reiterate for your readers the research problem or problems you are investigating and the methods you used to investigate them, then move quickly to describe the major findings of the study. You should write a direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results.
II. Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important
No one has thought as long and hard about your study as you have. Systematically explain the meaning of the findings and why you believe they are important. After reading the discussion section, you want the reader to think about the results [“why hadn’t I thought of that?”]. You don’t want to force the reader to go through the paper multiple times to figure out what it all means. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important finding first.
III. Relate the Findings to Similar Studies
No study is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to other previously published research. The discussion section should relate your study findings to those of other studies, particularly if questions raised by previous studies served as the motivation for your study, the findings of other studies support your findings [which strengthens the importance of your study results], and/or they point out how your study differs from other similar studies. IV. Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings
It is important to remember that the purpose of research is to discover and not to prove . When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations for the study results, rather than just those that fit your prior assumptions or biases.
V. Acknowledge the Study’s Limitations
It is far better for you to identify and acknowledge your study’s limitations than to have them pointed out by your professor! Describe the generalizability of your results to other situations, if applicable to the method chosen, then describe in detail problems you encountered in the method(s) you used to gather information. Note any unanswered questions or issues your study did not address, and.... VI. Make Suggestions for Further Research
Although your study may offer important insights about the research problem, other questions related to the problem likely remain unanswered. Moreover, some unanswered questions may have become more focused because of your study. You should make suggestions for further research in the discussion section.
NOTE: Besides the literature review section, the preponderance of references to sources in your research paper are usually found in the discussion section . A few historical references may be helpful for perspective but most of the references should be relatively recent and included to aid in the interpretation of your results and/or linked to similar studies. If a study that you cited disagrees with your findings, don't ignore it--clearly explain why the study's findings differ from yours.
V. Problems to Avoid
- Do not waste entire sentences restating your results . Should you need to remind the reader of the finding to be discussed, use "bridge sentences" that relate the result to the interpretation. An example would be: “The lack of available housing to single women with children in rural areas of Texas suggests that...[then move to the interpretation of this finding].”
- Recommendations for further research can be included in either the discussion or conclusion of your paper but do not repeat your recommendations in the both sections.
- Do not introduce new results in the discussion. Be wary of mistaking the reiteration of a specific finding for an interpretation.
- Use of the first person is acceptable, but too much use of the first person may actually distract the reader from the main points.
Analyzing vs. Summarizing. Department of English Writing Guide. George Mason University; Discussion . The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Hess, Dean R. How to Write an Effective Discussion. Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004); Kretchmer, Paul. Fourteen Steps to Writing to Writing an Effective Discussion Section . San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; The Lab Report . University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Summary: Using it Wisely . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Discussion . Writing in Psychology course syllabus. University of Florida; Yellin, Linda L. A Sociology Writer's Guide. Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon, 2009.
Writing Tip
Don’t Overinterpret the Results!
Interpretation is a subjective exercise. Therefore, be careful that you do not read more into the findings than can be supported by the evidence you've gathered. Remember that the data are the data: nothing more, nothing less.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Write Two Results Sections!
One of the most common mistakes that you can make when discussing the results of your study is to present a superficial interpretation of the findings that more or less re-states the results section of your paper. Obviously, you must refer to your results when discussing them, but focus on the interpretion of those results, not just the data itself.
Azar, Beth. Discussing Your Findings. American Psychological Association gradPSYCH Magazine (January 2006)
Yet Another Writing Tip
Avoid Unwarranted Speculation!
The discussion section should remain focused on the findings of your study. For example, if you studied the impact of foreign aid on increasing levels of education among the poor in Bangladesh, it's generally not appropriate to speculate about how your findings might apply to populations in other countries without drawing from existing studies to support your claim. If you feel compelled to speculate, be certain that you clearly identify your comments as speculation or as a suggestion for where further research is needed. Sometimes your professor will encourage you to expand the discussion in this way, while others don’t care what your opinion is beyond your efforts to interpret the data.
- << Previous: Using Non-Textual Elements
- Next: Limitations of the Study >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
Foundational Research Writing, Background Discussion and Literature Review for CS, IS and CY
- First Online: 25 May 2023
Cite this chapter

- Uche M. Mbanaso 4 ,
- Lucienne Abrahams 5 &
- Kennedy Chinedu Okafor 6
307 Accesses
This chapter is dedicated to explaining the skills a researcher needs, the types of background information required to support the research enquiry and the literature review that enables the researcher to situate the research in the context of existing research, while addressing the gap in knowledge. It explains how the research problem statement, the heart of the research, is the basis for building the background discussion and literature review. It illustrates the annotated bibliography technique, as a key step in the process of translating reading into academic writing. It explains different forms of background discussion and different forms of literature reviews. It shows how the literature review forms the basis for the analytical framework that will be applied to data analysis and presents an example analytical framework diagram.
- Annotated bibliography
- Analytical diagram
- Analytical framework
- Knowledge gap
- Literature review techniques
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bibliography
Abend, G. (2008). The meaning of ‘theory’. Sociological Theory, 26 (2), 173–199. http://www.jstor.org/stable/20453103
Article Google Scholar
Adom, D., Hussein, E., & Agyem, J. (2018). Theoretical and conceptual framework: Mandatory ingredients of a quality research. International Journal of Scientific Research, 7 (1), 438–441. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322204158_THEORETICAL_AND_CONCEPTUAL_FRAMEWORK_MANDATORY_INGREDIENTS_OF_A_QUALITY_RESEARCH
Google Scholar
Babbie, E. (2016). The practice of social research (14th ed.). Cengage Learning. [Available as an e-book].
Cohen, J., Coleman, E., & Abrahams, L. (2015). Use and impacts of e-health within community health facilities in developing countries: A systematic literature review. ECIS 2015 completed research papers (Paper 33). http://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2015_cr/33
Cryer, P. (2006). The research student’s guide to success (3rd ed.). Open University Press.
Dewey, A., & Drahota, A. (2016). Introduction to systematic reviews: Online learning module. Cochrane Training . https://training.cochrane.org/interactivelearning/module-1-introduction-conducting-systematic-reviews
Imenda, S. (2014). Is there a conceptual difference between conceptual and theoretical frameworks? Journal of Social Science, 38 (2), 185–195. https://doi.org/10.1080/09718923.2015.11893249
Kitchenham, B., Brereton, O., Budgen, D., Turner, M., Bailey, J., & Linkman, S. (2009). Systematic literature reviews in software engineering – A systematic literature review. Information and Software Technology, 51 , 7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2008.09.009
Mahmud, K., & Usman, M. (2018). Trust establishment and estimation in cloud services: A systematic literature review. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 27 , 489–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-018-9475-y
Mbanaso, U., Abrahams, L., & Apene, O. (2019). Conceptual design of a cybersecurity resilience maturity measurement (CRMM) framework. The African Journal of Information and Communication, 23 , 1–26. https://doi.org/10.17159/2077-7213/2019/n23a2
Mensah, S., et al. (2019). 2021 banking sector outlook: Nigerian banks face struggles on many fronts . Standard & Poor’s Financial Services LLC. https://www.spglobal.com/_assets/documents/ratings/research/100049447.pdf
Merli, R., Preziosi, M., & Acampora, A. (2018). How do scholars approach the circular economy? A systematic literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 178 , 703–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.112
Rowe, F. (2014). What literature review is not: Diversity, boundaries and recommendations. European Journal of Information Systems, 23 , 241–255. https://doi.org/10.1057/ejis.2015.7
SABRIC. (2019). SABRIC annual crime stats 2019 . https://www.sabric.co.za/media/1265/sabric-annual-crime-stats-2019.pdf
Serianu. (2017). Nigeria cybersecurity report 2017: Demystifying Africa’s cybersecurity poverty line . https://www.serianu.com/annual-reports.html
Serianu. (2018). Africa cybersecurity report – Kenya: Cybersecurity skills gap . https://www.serianu.com/annual-reports.html
Serianu. (2019). SACCO cybersecurity report 2019: Digital transformation and cyber risk within SACCOs . https://www.serianu.com/industry-reports.html
Serianu. (2020a). Africa cybersecurity report Kenya, 2019/2020: Local perspective on data protection and privacy laws: Insights from African SMEs . https://www.serianu.com/annual-reports.html
Serianu. (2020b). Africa cybersecurity report Uganda 2019/2020: Local perspective on data protection and privacy laws: Insights from African SMEs . https://www.serianu.com/annual-reports.html
Swanson, R. (2013). Theory building in applied disciplines . Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Cybersecurity Studies, Nasarawa State University, Keffi, Nigeria
Uche M. Mbanaso
LINK Centre, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
Lucienne Abrahams
Department of Mechatronics Engineering, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria
Kennedy Chinedu Okafor
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Mbanaso, U.M., Abrahams, L., Okafor, K.C. (2023). Foundational Research Writing, Background Discussion and Literature Review for CS, IS and CY. In: Research Techniques for Computer Science, Information Systems and Cybersecurity. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30031-8_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30031-8_5
Published : 25 May 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-30030-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-30031-8
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Your Discussion Section: 4 Things to Remember
3-minute read
- 16th September 2015
When writing a master’s thesis or PhD dissertation , it’s easy to lose track of what you’ve done. This is why it’s important to plan your paper properly.
Referring back to what you’ve already done is especially vital when discussing the results of your research, as it isn’t enough to simply describe your data. You also need to relate your results back to your original hypothesis and your literature review, which will help clarify the significance of your work.
At Proofed, we’ve noticed that many overlook their literature review in the discussion section. But since this can seriously affect the clarity of your work, we’ve compiled the following list of four things to remember when discussing the results of your research.
1. Use Your Literature Review to Contextualize Your Work
The main purpose of a literature review is to contextualize your work as part of an existing debate. Don’t forget this when it comes to discussing your results, as the overall significance of your research will depend on how you have engaged with past research.
2. Compare Your Results with Existing Studies
Do your results agree or conflict with the past studies you’ve examined? If there’s a difference, why might this be?
Comparing your results with past studies is a great way to connect your research with the existing debate. It can also provide the basis for the conclusions you draw from your results.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
3. Understand the Limitations of Your Work
The discussion section of your paper should include some acknowledgement of the limitations of your study (e.g., in terms of scope or the methods used).
If you have critically analyzed similar studies in your literature review, you can compare your work against their strengths/weaknesses.
4. Don’t Be Afraid to Tweak Your Literature Review
The focus of your research may change over time when working on a long-term project. This is normal. The key thing is to adjust the focus of your literature review to reflect these changes.
When discussing your results, for example, if you notice certain themes or trends are more prominent than others, it’s often helpful to revisit your literature review to emphasize these same themes/trends there too.
If you follow this advice you should find it much easier to communicate your ideas clearly when writing up your dissertation/thesis. For more information about writing a dissertation or thesis, read our full dissertation writing guide . But to make completely sure your writing is up to scratch before submission, it’s a good idea to have one of the experts at Proofed check your work. Try sending a 500-word sample to be proofread for free today.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Your Literature Review and Discussion Sections
3-minute read
- 23rd November 2015
Many things go well together in this world, like fish and chips or the birds and the bees (figuratively speaking). However, one felicitous pairing that might not immediately jump to mind are the literature review and discussion sections of your dissertation.
This is because a dissertation is more than a set of discrete essays; rather, each part should be written in a way that contributes to your dissertation as a greater whole. Nowhere is this more important than in the discussion section, as it’s essential to refer to your literature review when interpreting your results.
Why? Let us explain via the ‘Three C-Words’ (no, not that one: we’re talking about context, comparison and contribution).
1. Context!
The main purpose of your literature review is to contextualise your research by outlining previous studies conducted in the field. Referring back to the literature review in your discussion section therefore helps set the background against which your results should be interpreted, making it easier to explain their relevance to your hypothesis.
2. Comparison!
Simply describing your results isn’t enough in the discussion section, as you also need to interpret and analyse data in terms of your research question. One way to do this is by comparing your results to those obtained in similar studies.
For example, you might want to discuss whether your results agree or disagree with those of other researchers. If there is a difference, you’ll also want to consider why this has happened and whether it’s significant.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
However, you should not introduce new research in the discussion section. Make sure that any studies you refer to in the discussion have been addressed in the literature review. And don’t be afraid to modify your literature review as your study progresses (every dissertation project will evolve as it goes on).
3. Contribution!
As well as discussing the relevance of your results, your discussion section should usually include some reference to how your research contributes to knowledge in your field of study.
This, again, requires that you refer to your literature review, where you have discussed existing research in your field. Ideally, you will also have formulated your research questions to address a gap in the current research. Your discussion section is thus where you explain how your results fill this gap.
In summary, referring to your literature review will make sure that your discussion section is always on topic. And remember the three C-words: context, comparison and contribution.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Literature reviews
- Starting your literature review
- Undertaking your literature review
- Introduction
Analysing the literature critically
Referring back from your discussion.
- Writing systematic reviews
Useful links for literature reviews
- Study Advice Helping students to achieve study success with guides, video tutorials, seminars and one-to-one advice sessions.
- Doing your literature review (video) Watch this brief video tutorial for more on the topic.
- Doing your literature review (transcript) Read along while watching the video tutorial.
- Literature searching guide A guide to finding articles, books and other materials on your subject
- Doing your literature search video - University of Reading Brief video on literature searching from our Academic Liaison Librarians.
- Royal Literary Fund: Writing a Literature Review A guide to writing literature reviews from the Royal Literary Fund
- What it means to be a critical student A brief and very useful video tutorial from the University of Leicester.
- Reading and notemaking LibGuide Expert guidance on managing your reading and making effective notes.
- Dissertations and major projects LibGuide Expert guidance on planning, researching and writing dissertations and major projects.
An important part of a literature review is being able to pull together and group what you have read in order to identify the key arguments in the previous research. This is a good foundation, but then you need to go further and analyse what others have researched. You need to offer judgements on whether the evidence shows their arguments to be convincing or less convincing and why. This analytical groundwork means you will be able to refer back to this literature economically to provide potential reasons for your own research findings: Do your results agree with, or disagree with, what others have found, and why might this be? The guidance on this page offers suggestions for developing your literature review to ensure you are critically analysing what you have read.

You can ensure you are analysing critically by testing out your own views against those you are reading about: What do you think about the topic? Then as you read each new study, does the evidence presented confirm your view, or does it provide a counter-argument that causes you to question your view?
Also think about the methods used to gather the evidence - are they reliable or do they have gaps or weaknesses?
When writing up your literature review use each of your headings or themes to compare and contrast the differing views put forward in the relevant studies and explain how they relate to your investigation.
Your literature review needs to tell an interesting "story" which leads up to how and why you are doing your investigation. If you are writing a story which reads like one thing after another, this is likely to be descriptive. However, if your story is comparing, contrasting and evaluating the previous literature, you are on the right track. See the example below:
- Writing the literature review (University of Queensland) Includes practical examples of writing for literature reviews.
Your literature review has two main purposes:
1) To place your investigation in the context of previous research and justify how you have approached your investigation.
2) To provide evidence to help explain the findings of your investigation
It is this second purpose that many people forget!
When you are writing the discussion of your findings, you need to relate these back to the background literature . Do your results confirm what was found before, or challenge it? Why might this be? For example:
When writing your discussion section, you may find that you need to redraft the focus of your literature review slightly to draw out those studies that are most important to your findings. You can always remove studies that are less relevant and add others that turned out to be more significant than you initially thought.
Some academics explain the relationship between the literature review and the discussion section like an hour-glass: Your literature review starts broad, then narrows down to explain how previous research has influenced your specific investigation. The discussion starts by analysing your results, explaining what they mean for the outcome of your study, and ends by widening out to assess how these results might contribute to your field of research as a whole.

- << Previous: Undertaking your literature review
- Next: Writing systematic reviews >>
- Last Updated: Jan 29, 2024 11:27 AM
- URL: https://libguides.reading.ac.uk/literaturereview

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results.. It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review and paper or dissertation topic, and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion.It should not be a second results section.. There are different ways to write this ...
Establish the significance of the study. Provide an overview of the relevant literature. Establish a context for the study using the literature. Identify knowledge gaps. Illustrate how the study will advance knowledge on the topic. As you can see, literature review plays a significant role in the introduction section.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
NOTE: Besides the literature review section, the preponderance of references to sources is usually found in the discussion section. A few historical references may be helpful for perspective, but most of the references should be relatively recent and included to aid in the interpretation of your results, to support the significance of a finding ...
The discussion section can be written in 3 parts: an introductory paragraph, intermediate paragraphs and a conclusion paragraph. For intermediate paragraphs, a "divide and conquer" approach, meaning a full paragraph describing each of the study endpoints, can be used. In conclusion, academic writing is similar to other skills, and practice ...
The discussion section is one of the final parts of a research paper, in which an author describes, analyzes, and interprets their findings. They explain the significance of those results and tie everything back to the research question(s). In this handout, you will find a description of what a discussion section does, explanations of how to ...
The discussion section of your research paper is where you let the reader know how your study is positioned in the literature, what to take away from your paper, and how your work helps them. It can also include your conclusions and suggestions for future studies. First, we'll define all the parts of your discussion paper, and then look into ...
The discussion section is the heart of any scientific paper. This is where new thoughts and directions are introduced and where reviewers provide context and meaning to their research findings (Hess 2004).Some suggest that the discussion is the most difficult part of a literature review to write (Aveyard 2019) and that it demands the most effort and critical thinking of reviewers (Kearney 2017).
Papers usually end with a concluding section, often called the "Discussion.". The Discussion is your opportunity to evaluate and interpret the results of your study or paper, draw inferences and conclusions from it, and communicate its contributions to science and/or society. Use the present tense when writing the Discussion section.
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
A discussion critically analyses and interprets the results of a scientific study, placing the results in the context of published literature and explaining how they affect the field.. In this section, you will relate the specific findings of your research to the wider scientific field. This is the opposite of the introduction section, which starts with the broader context and narrows to focus ...
Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic. Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these. Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one) Inform your own methodology and research design. To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure.
In this article, we will work through how to write a discussion for a systematic review - be it a living systematic review, a systematic literature review, or even if you are simply looking for some qualitative systematic review guidelines. By the end of this article, you will know what makes an effective and persuasive discussion section for ...
Again, make sure to follow the same order as you did in the Results section. Discussion Part 3: Discussing the Implications. In addition to providing your own interpretations, show how your results fit into the wider scholarly literature you surveyed in the literature review section. This section is called the implications of the study. Show ...
The discussion chapter is where you delve into the meaning, importance and relevance of your results. There are many different ways to write the discussion s...
Organization and Structure. Keep the following sequential points in mind as you organize and write the discussion section of your paper: Think of your discussion as an inverted pyramid. Organize the discussion from the general to the specific, linking your findings to the literature, then to theory, then to practice [if appropriate]. Use the ...
The following task is to write the literature review of the articles, noting their relation to each other. When preparing the literature review section, build your own argument about how the literature you use sheds light on the issue(s) raised in the problem statement. 5.2.2 Reading and Writing with Purpose
The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results.. It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review, and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion.It should not be a second results section.. There are different ways to write this section, but you can focus your ...
The discussion section of your paper should include some acknowledgement of the limitations of your study (e.g., in terms of scope or the methods used). If you have critically analyzed similar studies in your literature review, you can compare your work against their strengths/weaknesses. 4. Don't Be Afraid to Tweak Your Literature Review.
The main purpose of your literature review is to contextualise your research by outlining previous studies conducted in the field. Referring back to the literature review in your discussion section therefore helps set the background against which your results should be interpreted, making it easier to explain their relevance to your hypothesis. 2.
When writing up your literature review use each of your headings or themes to compare and contrast the differing views put forward in the relevant studies and explain how they relate to your investigation. ... Some academics explain the relationship between the literature review and the discussion section like an hour-glass: Your literature ...
If all elements of the review question and objectives have been met in the results section, the discussion section can focus on the extent of evidence available and place this evidence into context. Given the nature of scoping reviews, there are circumstances where review questions and objectives may not be addressed due to insufficient literature.