My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics

How to Write an Outline for a Persuasive Speech, with Examples

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

Persuasive speeches are one of the three most used speeches in our daily lives. Persuasive speech is used when presenters decide to convince their presentation or ideas to their listeners. A compelling speech aims to persuade the listener to believe in a particular point of view. One of the most iconic examples is Martin Luther King’s ‘I had a dream’ speech on the 28th of August 1963.
In this article:
What is Persuasive Speech?
Here are some steps to follow:, persuasive speech outline, final thoughts.

Persuasive speech is a written and delivered essay to convince people of the speaker’s viewpoint or ideas. Persuasive speaking is the type of speaking people engage in the most. This type of speech has a broad spectrum, from arguing about politics to talking about what to have for dinner. Persuasive speaking is highly connected to the audience, as in a sense, the speaker has to meet the audience halfway.
Persuasive Speech Preparation
Persuasive speech preparation doesn’t have to be difficult, as long as you select your topic wisely and prepare thoroughly.
1. Select a Topic and Angle
Come up with a controversial topic that will spark a heated debate, regardless of your position. This could be about anything. Choose a topic that you are passionate about. Select a particular angle to focus on to ensure that your topic isn’t too broad. Research the topic thoroughly, focussing on key facts, arguments for and against your angle, and background.
2. Define Your Persuasive Goal
Once you have chosen your topic, it’s time to decide what your goal is to persuade the audience. Are you trying to persuade them in favor of a certain position or issue? Are you hoping that they change their behavior or an opinion due to your speech? Do you want them to decide to purchase something or donate money to a cause? Knowing your goal will help you make wise decisions about approaching writing and presenting your speech.
3. Analyze the Audience
Understanding your audience’s perspective is critical anytime that you are writing a speech. This is even more important when it comes to a persuasive speech because not only are you wanting to get the audience to listen to you, but you are also hoping for them to take a particular action in response to your speech. First, consider who is in the audience. Consider how the audience members are likely to perceive the topic you are speaking on to better relate to them on the subject. Grasp the obstacles audience members face or have regarding the topic so you can build appropriate persuasive arguments to overcome these obstacles.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
4. Build an Effective Persuasive Argument
Once you have a clear goal, you are knowledgeable about the topic and, have insights regarding your audience, you will be ready to build an effective persuasive argument to deliver in the form of a persuasive speech.
Start by deciding what persuasive techniques are likely to help you persuade your audience. Would an emotional and psychological appeal to your audience help persuade them? Is there a good way to sway the audience with logic and reason? Is it possible that a bandwagon appeal might be effective?
5. Outline Your Speech
Once you know which persuasive strategies are most likely to be effective, your next step is to create a keyword outline to organize your main points and structure your persuasive speech for maximum impact on the audience.
Start strong, letting your audience know what your topic is, why it matters and, what you hope to achieve at the end of your speech. List your main points, thoroughly covering each point, being sure to build the argument for your position and overcome opposing perspectives. Conclude your speech by appealing to your audience to act in a way that will prove that you persuaded them successfully. Motivation is a big part of persuasion.
6. Deliver a Winning Speech
Select appropriate visual aids to share with your audiences, such as graphs, photos, or illustrations. Practice until you can deliver your speech confidently. Maintain eye contact, project your voice and, avoid using filler words or any form of vocal interference. Let your passion for the subject shine through. Your enthusiasm may be what sways the audience.

Topic: What topic are you trying to persuade your audience on?
Specific Purpose:
Central idea:
- Attention grabber – This is potentially the most crucial line. If the audience doesn’t like the opening line, they might be less inclined to listen to the rest of your speech.
- Thesis – This statement is used to inform the audience of the speaker’s mindset and try to get the audience to see the issue their way.
- Qualifications – Tell the audience why you are qualified to speak about the topic to persuade them.
After the introductory portion of the speech is over, the speaker starts presenting reasons to the audience to provide support for the statement. After each reason, the speaker will list examples to provide a factual argument to sway listeners’ opinions.
- Example 1 – Support for the reason given above.
- Example 2 – Support for the reason given above.
The most important part of a persuasive speech is the conclusion, second to the introduction and thesis statement. This is where the speaker must sum up and tie all of their arguments into an organized and solid point.
- Summary: Briefly remind the listeners why they should agree with your position.
- Memorable ending/ Audience challenge: End your speech with a powerful closing thought or recommend a course of action.
- Thank the audience for listening.
Persuasive Speech Outline Examples

Topic: Walking frequently can improve both your mental and physical health.
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to start walking to improve their health.
Central idea: Regular walking can improve your mental and physical health.
Life has become all about convenience and ease lately. We have dishwashers, so we don’t have to wash dishes by hand with electric scooters, so we don’t have to paddle while riding. I mean, isn’t it ridiculous?
Today’s luxuries have been welcomed by the masses. They have also been accused of turning us into passive, lethargic sloths. As a reformed sloth, I know how easy it can be to slip into the convenience of things and not want to move off the couch. I want to persuade you to start walking.
Americans lead a passive lifestyle at the expense of their own health.
- This means that we spend approximately 40% of our leisure time in front of the TV.
- Ironically, it is also reported that Americans don’t like many of the shows that they watch.
- Today’s studies indicate that people were experiencing higher bouts of depression than in the 18th and 19th centuries, when work and life were considered problematic.
- The article reports that 12.6% of Americans suffer from anxiety, and 9.5% suffer from severe depression.
- Present the opposition’s claim and refute an argument.
- Nutritionist Phyllis Hall stated that we tend to eat foods high in fat, which produces high levels of cholesterol in our blood, which leads to plaque build-up in our arteries.
- While modifying our diet can help us decrease our risk for heart disease, studies have indicated that people who don’t exercise are at an even greater risk.
In closing, I urge you to start walking more. Walking is a simple, easy activity. Park further away from stores and walk. Walk instead of driving to your nearest convenience store. Take 20 minutes and enjoy a walk around your neighborhood. Hide the TV remote, move off the couch and, walk. Do it for your heart.
Thank you for listening!
Topic: Less screen time can improve your sleep.
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to stop using their screens two hours before bed.
Central idea: Ceasing electronics before bed will help you achieve better sleep.
Who doesn’t love to sleep? I don’t think I have ever met anyone who doesn’t like getting a good night’s sleep. Sleep is essential for our bodies to rest and repair themselves.
I love sleeping and, there is no way that I would be able to miss out on a good night’s sleep.
As someone who has had trouble sleeping due to taking my phone into bed with me and laying in bed while entertaining myself on my phone till I fall asleep, I can say that it’s not the healthiest habit, and we should do whatever we can to change it.
- Our natural blue light source is the sun.
- Bluelight is designed to keep us awake.
- Bluelight makes our brain waves more active.
- We find it harder to sleep when our brain waves are more active.
- Having a good night’s rest will improve your mood.
- Being fully rested will increase your productivity.
Using electronics before bed will stimulate your brainwaves and make it more difficult for you to sleep. Bluelight tricks our brains into a false sense of daytime and, in turn, makes it more difficult for us to sleep. So, put down those screens if you love your sleep!
Thank the audience for listening
A persuasive speech is used to convince the audience of the speaker standing on a certain subject. To have a successful persuasive speech, doing the proper planning and executing your speech with confidence will help persuade the audience of your standing on the topic you chose. Persuasive speeches are used every day in the world around us, from planning what’s for dinner to arguing about politics. It is one of the most widely used forms of speech and, with proper planning and execution, you can sway any audience.
How to Write the Most Informative Essay
How to Craft a Masterful Outline of Speech
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples
March 17, 2021 - Gini Beqiri
A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything – voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on.
A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing you come across as trustworthy and knowledgeable about the topic you’re discussing.
So, how do you start convincing a group of strangers to share your opinion? And how do you connect with them enough to earn their trust?
Topics for your persuasive speech
We’ve made a list of persuasive speech topics you could use next time you’re asked to give one. The topics are thought-provoking and things which many people have an opinion on.
When using any of our persuasive speech ideas, make sure you have a solid knowledge about the topic you’re speaking about – and make sure you discuss counter arguments too.
Here are a few ideas to get you started:
- All school children should wear a uniform
- Facebook is making people more socially anxious
- It should be illegal to drive over the age of 80
- Lying isn’t always wrong
- The case for organ donation
Read our full list of 75 persuasive speech topics and ideas .

Preparation: Consider your audience
As with any speech, preparation is crucial. Before you put pen to paper, think about what you want to achieve with your speech. This will help organise your thoughts as you realistically can only cover 2-4 main points before your audience get bored .
It’s also useful to think about who your audience are at this point. If they are unlikely to know much about your topic then you’ll need to factor in context of your topic when planning the structure and length of your speech. You should also consider their:
- Cultural or religious backgrounds
- Shared concerns, attitudes and problems
- Shared interests, beliefs and hopes
- Baseline attitude – are they hostile, neutral, or open to change?
The factors above will all determine the approach you take to writing your speech. For example, if your topic is about childhood obesity, you could begin with a story about your own children or a shared concern every parent has. This would suit an audience who are more likely to be parents than young professionals who have only just left college.
Remember the 3 main approaches to persuade others
There are three main approaches used to persuade others:
The ethos approach appeals to the audience’s ethics and morals, such as what is the ‘right thing’ to do for humanity, saving the environment, etc.
Pathos persuasion is when you appeal to the audience’s emotions, such as when you tell a story that makes them the main character in a difficult situation.
The logos approach to giving a persuasive speech is when you appeal to the audience’s logic – ie. your speech is essentially more driven by facts and logic. The benefit of this technique is that your point of view becomes virtually indisputable because you make the audience feel that only your view is the logical one.
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos: 3 Pillars of Public Speaking and Persuasion
Ideas for your persuasive speech outline
1. structure of your persuasive speech.
The opening and closing of speech are the most important. Consider these carefully when thinking about your persuasive speech outline. A strong opening ensures you have the audience’s attention from the start and gives them a positive first impression of you.
You’ll want to start with a strong opening such as an attention grabbing statement, statistic of fact. These are usually dramatic or shocking, such as:
Sadly, in the next 18 minutes when I do our chat, four Americans that are alive will be dead from the food that they eat – Jamie Oliver
Another good way of starting a persuasive speech is to include your audience in the picture you’re trying to paint. By making them part of the story, you’re embedding an emotional connection between them and your speech.
You could do this in a more toned-down way by talking about something you know that your audience has in common with you. It’s also helpful at this point to include your credentials in a persuasive speech to gain your audience’s trust.

Obama would spend hours with his team working on the opening and closing statements of his speech.
2. Stating your argument
You should pick between 2 and 4 themes to discuss during your speech so that you have enough time to explain your viewpoint and convince your audience to the same way of thinking.
It’s important that each of your points transitions seamlessly into the next one so that your speech has a logical flow. Work on your connecting sentences between each of your themes so that your speech is easy to listen to.
Your argument should be backed up by objective research and not purely your subjective opinion. Use examples, analogies, and stories so that the audience can relate more easily to your topic, and therefore are more likely to be persuaded to your point of view.
3. Addressing counter-arguments
Any balanced theory or thought addresses and disputes counter-arguments made against it. By addressing these, you’ll strengthen your persuasive speech by refuting your audience’s objections and you’ll show that you are knowledgeable to other thoughts on the topic.
When describing an opposing point of view, don’t explain it in a bias way – explain it in the same way someone who holds that view would describe it. That way, you won’t irritate members of your audience who disagree with you and you’ll show that you’ve reached your point of view through reasoned judgement. Simply identify any counter-argument and pose explanations against them.
- Complete Guide to Debating
4. Closing your speech
Your closing line of your speech is your last chance to convince your audience about what you’re saying. It’s also most likely to be the sentence they remember most about your entire speech so make sure it’s a good one!
The most effective persuasive speeches end with a call to action . For example, if you’ve been speaking about organ donation, your call to action might be asking the audience to register as donors.
Practice answering AI questions on your speech and get feedback on your performance .
If audience members ask you questions, make sure you listen carefully and respectfully to the full question. Don’t interject in the middle of a question or become defensive.
You should show that you have carefully considered their viewpoint and refute it in an objective way (if you have opposing opinions). Ensure you remain patient, friendly and polite at all times.
Example 1: Persuasive speech outline
This example is from the Kentucky Community and Technical College.
Specific purpose
To persuade my audience to start walking in order to improve their health.
Central idea
Regular walking can improve both your mental and physical health.
Introduction
Let’s be honest, we lead an easy life: automatic dishwashers, riding lawnmowers, T.V. remote controls, automatic garage door openers, power screwdrivers, bread machines, electric pencil sharpeners, etc., etc. etc. We live in a time-saving, energy-saving, convenient society. It’s a wonderful life. Or is it?
Continue reading
Example 2: Persuasive speech
Tips for delivering your persuasive speech
- Practice, practice, and practice some more . Record yourself speaking and listen for any nervous habits you have such as a nervous laugh, excessive use of filler words, or speaking too quickly.
- Show confident body language . Stand with your legs hip width apart with your shoulders centrally aligned. Ground your feet to the floor and place your hands beside your body so that hand gestures come freely. Your audience won’t be convinced about your argument if you don’t sound confident in it. Find out more about confident body language here .
- Don’t memorise your speech word-for-word or read off a script. If you memorise your persuasive speech, you’ll sound less authentic and panic if you lose your place. Similarly, if you read off a script you won’t sound genuine and you won’t be able to connect with the audience by making eye contact . In turn, you’ll come across as less trustworthy and knowledgeable. You could simply remember your key points instead, or learn your opening and closing sentences.
- Remember to use facial expressions when storytelling – they make you more relatable. By sharing a personal story you’ll more likely be speaking your truth which will help you build a connection with the audience too. Facial expressions help bring your story to life and transport the audience into your situation.
- Keep your speech as concise as possible . When practicing the delivery, see if you can edit it to have the same meaning but in a more succinct way. This will keep the audience engaged.
The best persuasive speech ideas are those that spark a level of controversy. However, a public speech is not the time to express an opinion that is considered outside the norm. If in doubt, play it safe and stick to topics that divide opinions about 50-50.
Bear in mind who your audience are and plan your persuasive speech outline accordingly, with researched evidence to support your argument. It’s important to consider counter-arguments to show that you are knowledgeable about the topic as a whole and not bias towards your own line of thought.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
50 Fun Earth Day Crafts and Activities 🌎!
40 Strong Persuasive Writing Examples (Essays, Speeches, Ads, and More)
Learn from the experts.

The more we read, the better writers we become. Teaching students to write strong persuasive essays should always start with reading some top-notch models. This round-up of persuasive writing examples includes famous speeches, influential ad campaigns, contemporary reviews of famous books, and more. Use them to inspire your students to write their own essays. (Need persuasive essay topics? Check out our list of interesting persuasive essay ideas here! )
- Persuasive Essays
- Persuasive Speeches
- Advertising Campaigns
Persuasive Essay Writing Examples

From the earliest days of print, authors have used persuasive essays to try to sway others to their own point of view. Check out these top persuasive essay writing examples.
Professions for Women by Virginia Woolf
Sample lines: “Outwardly, what is simpler than to write books? Outwardly, what obstacles are there for a woman rather than for a man? Inwardly, I think, the case is very different; she has still many ghosts to fight, many prejudices to overcome. Indeed it will be a long time still, I think, before a woman can sit down to write a book without finding a phantom to be slain, a rock to be dashed against. And if this is so in literature, the freest of all professions for women, how is it in the new professions which you are now for the first time entering?”
The Crisis by Thomas Paine
Sample lines: “These are the times that try men’s souls. The summer soldier and the sunshine patriot will, in this crisis, shrink from the service of their country; but he that stands by it now, deserves the love and thanks of man and woman. Tyranny, like hell, is not easily conquered; yet we have this consolation with us, that the harder the conflict, the more glorious the triumph. What we obtain too cheap, we esteem too lightly: it is dearness only that gives every thing its value.”
Politics and the English Language by George Orwell
Sample lines: “As I have tried to show, modern writing at its worst does not consist in picking out words for the sake of their meaning and inventing images in order to make the meaning clearer. It consists in gumming together long strips of words which have already been set in order by someone else, and making the results presentable by sheer humbug.”
Letter From a Birmingham Jail by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
Sample lines: “We know through painful experience that freedom is never voluntarily given by the oppressor; it must be demanded by the oppressed. Frankly, I have yet to engage in a direct action campaign that was ‘well timed’ in the view of those who have not suffered unduly from the disease of segregation. For years now I have heard the word ‘Wait!’ It rings in the ear of every Negro with piercing familiarity. This ‘Wait’ has almost always meant ‘Never.’ We must come to see, with one of our distinguished jurists, that ‘justice too long delayed is justice denied.'”
Civil Disobedience by Henry David Thoreau
Sample lines: “Even voting for the right is doing nothing for it. It is only expressing to men feebly your desire that it should prevail. A wise man will not leave the right to the mercy of chance, nor wish it to prevail through the power of the majority. There is but little virtue in the action of masses of men.”
Go Gentle Into That Good Night by Roger Ebert
Sample lines: “‘Kindness’ covers all of my political beliefs. No need to spell them out. I believe that if, at the end of it all, according to our abilities, we have done something to make others a little happier, and something to make ourselves a little happier, that is about the best we can do. To make others less happy is a crime.”
The Way to Wealth by Benjamin Franklin
Sample lines: “Methinks I hear some of you say, must a man afford himself no leisure? I will tell thee, my friend, what Poor Richard says, employ thy time well if thou meanest to gain leisure; and, since thou art not sure of a minute, throw not away an hour. Leisure is time for doing something useful; this leisure the diligent man will obtain, but the lazy man never; so that, as Poor Richard says, a life of leisure and a life of laziness are two things.”
The Crack-Up by F. Scott Fitzgerald
Sample lines: “Of course all life is a process of breaking down, but the blows that do the dramatic side of the work—the big sudden blows that come, or seem to come, from outside—the ones you remember and blame things on and, in moments of weakness, tell your friends about, don’t show their effect all at once.”
Open Letter to the Kansas School Board by Bobby Henderson
Sample lines: “I am writing you with much concern after having read of your hearing to decide whether the alternative theory of Intelligent Design should be taught along with the theory of Evolution. … Let us remember that there are multiple theories of Intelligent Design. I and many others around the world are of the strong belief that the universe was created by a Flying Spaghetti Monster. … We feel strongly that the overwhelming scientific evidence pointing towards evolutionary processes is nothing but a coincidence, put in place by Him. It is for this reason that I’m writing you today, to formally request that this alternative theory be taught in your schools, along with the other two theories.”
Open Letter to the United Nations by Niels Bohr
Sample lines: “Humanity will, therefore, be confronted with dangers of unprecedented character unless, in due time, measures can be taken to forestall a disastrous competition in such formidable armaments and to establish an international control of the manufacture and use of the powerful materials.”
Persuasive Speech Writing Examples
Many persuasive speeches are political in nature, often addressing subjects like human rights. Here are some of history’s most well-known persuasive writing examples in the form of speeches.
I Have a Dream by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
Sample lines: “And so even though we face the difficulties of today and tomorrow, I still have a dream. It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream. I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.”
Woodrow Wilson’s War Message to Congress, 1917
Sample lines: “There are, it may be, many months of fiery trial and sacrifice ahead of us. It is a fearful thing to lead this great peaceful people into war, into the most terrible and disastrous of all wars, civilization itself seeming to be in the balance. But the right is more precious than peace, and we shall fight for the things which we have always carried nearest our hearts—for democracy, for the right of those who submit to authority to have a voice in their own governments, for the rights and liberties of small nations, for a universal dominion of right by such a concert of free peoples as shall bring peace and safety to all nations and make the world itself at last free.”
Chief Seattle’s 1854 Oration
Sample lines: “I here and now make this condition that we will not be denied the privilege without molestation of visiting at any time the tombs of our ancestors, friends, and children. Every part of this soil is sacred in the estimation of my people. Every hillside, every valley, every plain and grove, has been hallowed by some sad or happy event in days long vanished. Even the rocks, which seem to be dumb and dead as they swelter in the sun along the silent shore, thrill with memories of stirring events connected with the lives of my people, and the very dust upon which you now stand responds more lovingly to their footsteps than yours, because it is rich with the blood of our ancestors, and our bare feet are conscious of the sympathetic touch.”
Women’s Rights Are Human Rights, Hillary Rodham Clinton
Sample lines: “What we are learning around the world is that if women are healthy and educated, their families will flourish. If women are free from violence, their families will flourish. If women have a chance to work and earn as full and equal partners in society, their families will flourish. And when families flourish, communities and nations do as well. … If there is one message that echoes forth from this conference, let it be that human rights are women’s rights and women’s rights are human rights once and for all.”
I Am Prepared to Die, Nelson Mandela
Sample lines: “Above all, My Lord, we want equal political rights, because without them our disabilities will be permanent. I know this sounds revolutionary to the whites in this country, because the majority of voters will be Africans. This makes the white man fear democracy. But this fear cannot be allowed to stand in the way of the only solution which will guarantee racial harmony and freedom for all. It is not true that the enfranchisement of all will result in racial domination. Political division, based on color, is entirely artificial and, when it disappears, so will the domination of one color group by another. … This then is what the ANC is fighting. Our struggle is a truly national one. It is a struggle of the African people, inspired by our own suffering and our own experience. It is a struggle for the right to live.”
The Struggle for Human Rights by Eleanor Roosevelt
Sample lines: “It is my belief, and I am sure it is also yours, that the struggle for democracy and freedom is a critical struggle, for their preservation is essential to the great objective of the United Nations to maintain international peace and security. Among free men the end cannot justify the means. We know the patterns of totalitarianism—the single political party, the control of schools, press, radio, the arts, the sciences, and the church to support autocratic authority; these are the age-old patterns against which men have struggled for 3,000 years. These are the signs of reaction, retreat, and retrogression. The United Nations must hold fast to the heritage of freedom won by the struggle of its people; it must help us to pass it on to generations to come.”
Freedom From Fear by Aung San Suu Kyi
Sample lines: “Saints, it has been said, are the sinners who go on trying. So free men are the oppressed who go on trying and who in the process make themselves fit to bear the responsibilities and to uphold the disciplines which will maintain a free society. Among the basic freedoms to which men aspire that their lives might be full and uncramped, freedom from fear stands out as both a means and an end. A people who would build a nation in which strong, democratic institutions are firmly established as a guarantee against state-induced power must first learn to liberate their own minds from apathy and fear.”
Harvey Milk’s “The Hope” Speech
Sample lines: “Some people are satisfied. And some people are not. You see there is a major difference—and it remains a vital difference—between a friend and a gay person, a friend in office and a gay person in office. Gay people have been slandered nationwide. We’ve been tarred and we’ve been brushed with the picture of pornography. In Dade County, we were accused of child molestation. It is not enough anymore just to have friends represent us, no matter how good that friend may be.”
The Union and the Strike, Cesar Chavez
Sample lines: “We are showing our unity in our strike. Our strike is stopping the work in the fields; our strike is stopping ships that would carry grapes; our strike is stopping the trucks that would carry the grapes. Our strike will stop every way the grower makes money until we have a union contract that guarantees us a fair share of the money he makes from our work! We are a union and we are strong and we are striking to force the growers to respect our strength!”
Nobel Lecture by Malala Yousafzai
Sample lines: “The world can no longer accept that basic education is enough. Why do leaders accept that for children in developing countries, only basic literacy is sufficient, when their own children do homework in algebra, mathematics, science, and physics? Leaders must seize this opportunity to guarantee a free, quality, primary and secondary education for every child. Some will say this is impractical, or too expensive, or too hard. Or maybe even impossible. But it is time the world thinks bigger.”
Persuasive Writing Examples in Advertising Campaigns
Ads are prime persuasive writing examples. You can flip open any magazine or watch TV for an hour or two to see sample after sample of persuasive language. Here are some of the most popular ad campaigns of all time, with links to articles explaining why they were so successful.
Nike: Just Do It

The iconic swoosh with the simple tagline has persuaded millions to buy their kicks from Nike and Nike alone. Teamed with pro sports-star endorsements, this campaign is one for the ages. Blinkist offers an opinion on what made it work.
Dove: Real Beauty
Beauty brand Dove changed the game by choosing “real” women to tell their stories instead of models. They used relatable images and language to make connections, and inspired other brands to try the same concept. Learn why Global Brands considers this one a true success story.
Wendy’s: Where’s the Beef?
Today’s kids are too young to remember the cranky old woman demanding to know where the beef was on her fast-food hamburger. But in the 1980s, it was a catchphrase that sold millions of Wendy’s burgers. Learn from Better Marketing how this ad campaign even found its way into the 1984 presidential debate.
De Beers: A Diamond Is Forever

A diamond engagement ring has become a standard these days, but the tradition isn’t as old as you might think. In fact, it was De Beers jewelry company’s 1948 campaign that created the modern engagement ring trend. The Drum has the whole story of this sparkling campaign.
Volkswagen: Think Small
Americans have always loved big cars. So in the 1960s, when Volkswagen wanted to introduce their small cars to a bigger market, they had a problem. The clever “Think Small” campaign gave buyers clever reasons to consider these models, like “If you run out of gas, it’s easy to push.” Learn how advertisers interested American buyers in little cars at Visual Rhetoric.
American Express: Don’t Leave Home Without It
AmEx was once better known for traveler’s checks than credit cards, and the original slogan was “Don’t leave home without them.” A simple word change convinced travelers that American Express was the credit card they needed when they headed out on adventures. Discover more about this persuasive campaign from Medium.
Skittles: Taste the Rainbow

These candy ads are weird and intriguing and probably not for everyone. But they definitely get you thinking, and that often leads to buying. Learn more about why these wacky ads are successful from The Drum.
Maybelline: Maybe She’s Born With It
Smart wordplay made this ad campaign slogan an instant hit. The ads teased, “Maybe she’s born with it. Maybe it’s Maybelline.” (So many literary devices all in one phrase!) Fashionista has more on this beauty campaign.
Coca-Cola: Share a Coke
Seeing their own name on a bottle made teens more likely to want to buy a Coke. What can that teach us about persuasive writing in general? It’s an interesting question to consider. Learn more about the “Share a Coke” campaign from Digital Vidya.
Always: #LikeaGirl

Talk about the power of words! This Always campaign turned the derogatory phrase “like a girl” on its head, and the world embraced it. Storytelling is an important part of persuasive writing, and these ads really do it well. Medium has more on this stereotype-bashing campaign.
Editorial Persuasive Writing Examples

Newspaper editors or publishers use editorials to share their personal opinions. Noted politicians, experts, or pundits may also offer their opinions on behalf of the editors or publishers. Here are a couple of older well-known editorials, along with a selection from current newspapers.
Yes, Virginia, There Is a Santa Claus (1897)
Sample lines: “Yes, Virginia, there is a Santa Claus. He exists as certainly as love and generosity and devotion exist, and you know that they abound and give to your life its highest beauty and joy. Alas! How dreary would be the world if there were no Santa Claus. It would be as dreary as if there were no Virginias.”
What’s the Matter With Kansas? (1896)
Sample lines: “Oh, this IS a state to be proud of! We are a people who can hold up our heads! What we need is not more money, but less capital, fewer white shirts and brains, fewer men with business judgment, and more of those fellows who boast that they are ‘just ordinary clodhoppers, but they know more in a minute about finance than John Sherman,’ we need more men … who hate prosperity, and who think, because a man believes in national honor, he is a tool of Wall Street.”
America Can Have Democracy or Political Violence. Not Both. (The New York Times)
Sample lines: “The nation is not powerless to stop a slide toward deadly chaos. If institutions and individuals do more to make it unacceptable in American public life, organized violence in the service of political objectives can still be pushed to the fringes. When a faction of one of the country’s two main political parties embraces extremism, that makes thwarting it both more difficult and more necessary. A well-functioning democracy demands it.”
The Booster Isn’t Perfect, But Still Can Help Against COVID (The Washington Post)
Sample lines: “The booster shots are still free, readily available and work better than the previous boosters even as the virus evolves. Much still needs to be done to build better vaccines that protect longer and against more variants, including those that might emerge in the future. But it is worth grabbing the booster that exists today, the jab being a small price for any measure that can help keep COVID at bay.”
If We Want Wildlife To Thrive in L.A., We Have To Share Our Neighborhoods With Them (Los Angeles Times)
Sample lines: “If there are no corridors for wildlife movement and if excessive excavation of dirt to build bigger, taller houses erodes the slope of a hillside, then we are slowly destroying wildlife habitat. For those people fretting about what this will do to their property values—isn’t open space, trees, and wildlife an amenity in these communities?”
Persuasive Review Writing Examples

Book or movie reviews are more great persuasive writing examples. Look for those written by professionals for the strongest arguments and writing styles. Here are reviews of some popular books and movies by well-known critics to use as samples.
The Great Gatsby (The Chicago Tribune, 1925)
Sample lines: “What ails it, fundamentally, is the plain fact that it is simply a story—that Fitzgerald seems to be far more interested in maintaining its suspense than in getting under the skins of its people. It is not that they are false: It is that they are taken too much for granted. Only Gatsby himself genuinely lives and breathes. The rest are mere marionettes—often astonishingly lifelike, but nevertheless not quite alive.”
Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone (The Washington Post, 1999)
Sample lines: “Obviously, Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone should make any modern 11-year-old a very happy reader. The novel moves quickly, packs in everything from a boa constrictor that winks to a melancholy Zen-spouting centaur to an owl postal system, and ends with a scary surprise. Yet it is, essentially, a light-hearted thriller, interrupted by occasional seriousness (the implications of Harry’s miserable childhood, a moral about the power of love).”
Twilight (The Telegraph, 2009)
Sample lines: “No secret, of course, at whom this book is aimed, and no doubt, either, that it has hit its mark. The four Twilight novels are not so much enjoyed, as devoured, by legions of young female fans worldwide. That’s not to say boys can’t enjoy these books; it’s just that the pages of heart-searching dialogue between Edward and Bella may prove too long on chat and too short on action for the average male reader.”
To Kill a Mockingbird (Time, 1960)
Sample lines: “Author Lee, 34, an Alabaman, has written her first novel with all of the tactile brilliance and none of the preciosity generally supposed to be standard swamp-warfare issue for Southern writers. The novel is an account of an awakening to good and evil, and a faint catechistic flavor may have been inevitable. But it is faint indeed; novelist Lee’s prose has an edge that cuts through cant, and she teaches the reader an astonishing number of useful truths about little girls and about Southern life.”
The Diary of Anne Frank (The New York Times, 1952)
Sample lines: “And this quality brings it home to any family in the world today. Just as the Franks lived in momentary fear of the Gestapo’s knock on their hidden door, so every family today lives in fear of the knock of war. Anne’s diary is a great affirmative answer to the life-question of today, for she shows how ordinary people, within this ordeal, consistently hold to the greater human values.”
What are your favorite persuasive writing examples to use with students? Come share your ideas in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, the big list of essay topics for high school (120+ ideas) ..

You Might Also Like

101 Interesting Persuasive Essay Topics for Kids and Teens
Use your words to sway the reader. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Engaging Strategies for Teaching Persuasion, Argument, and Debate
Year after year, I love teaching persuasion. I love persuading my students that persuasion is a life skill worth learning. (Because isn’t all teaching just persuading kids to listen and learn?!) Luckily, with the right mix of ethos, pathos, and logos, this is usually an easy sell to my audience of adolescents.
After all, teens love to argue…with their peers, their parents, and *gasp* their teachers. They have plenty of practice with real-life persuasion, whether it’s convincing their parents to stay out past their curfew or proposing just one extra day to work on that project. And they’re always dying to debate: which sports team is superior, why they deserve more freedom, and what’s wrong with school, society, and this world! If you’ve ever taught teenagers, you know that they have no shortage of opinions. So suffice it to say: your students are already arguers.
The challenge, of course, is helping students channel their opinions and energy into structured, academic argumentation. To do this, you’ll need high-engagement activities that match your students’ energy… not the ancient 5-paragraph persuasive essay over a subject on that random list of 100 debatable topics you found online. If we want to move students to a more sophisticated level of debate, we need to offer them student-centered, authentic, and relevant tasks to practice their persuasion.
Ready to ditch the 5-paragraph persuasive essay and engage your students in meaningful persuasion? Here are dozen different strategies for your ELA classroom.
MOCK TRIALS
Want to teach students how important it is to support your argument with evidence (and what happens when you don’t)? Ready to watch your class eagerly annotate a text and cite said evidence *without* complaints?

I wasn’t sure my students would ever see citing evidence as more than a chore until I dressed up as “Judge G,” borrowed a gavel, and facilitated my first mock trial!
A mock trial is the perfect way to practice persuasion and argumentation because it’s student-centered, inherently engaging, and 100% authentic. You’ll watch students become intrigued, take ownership, and get competitive real quick! Because students know they’ll be arguing in front of a jury of their peers, the standards become strategy. Citing textual evidence is no longer a chore, but a competition! The stakes are higher than a grade from the teacher because the real prize is bragging rights.
To structure a mock trial in your ELA classroom, you’ll need a murder, crime, ethical dilemma, or essential question. In other words: literature! From there, you’ll want to divide students into teams of prosecution, defense, and jury. After that, students will get to work within their groups. In my classroom, this is what it looks like:
The prosecution and defense teams prepare evidence-based claims and rebuttals. Each student is responsible for a section, whether that’s the opening, a claim, a rebuttal, or the closing. Meanwhile, the jury works together to create a rubric and anticipate the arguments they may hear during the trial.
You can read more about mock trials HERE or find everything you need to facilitate a virtual or in-person trial HERE.
RHETORICAL BAR GRAPHS
Bar graphs in ELA? Oh yes you can! Getting a gold star from her math cohorts, Ashley Bible at Building Book Love has her students create rhetorical bar graphs to analyze persuasion.

This digital or tactile strategy is simple yet highly effective! All you do is assign each appeal a color before taking students on a color-coded text hunt. (In her rhetoric lesson plan , Ashley uses: Pink Pathos, Light Blue Logos, and Emerald Green Ethos).
Once students have each appeal coded, they arrange the rhetorical devices into a bar graph and analyze which appeal the speaker relies most heavily on and how they could make their argument stronger. This visualization technique always generates important insights about the topic at hand!
From analyzing speeches in Julius Caesar , to recognizing propaganda in Animal Farm , to tackling social justice in Dolly Parton’s America , this strategy is a gift that keeps on giving! Tag her @BuildingBookLove if you give it a try!
ANALYZING COMMERCIALS & ADVERTISEMENTS
To help students identify persuasive appeals and techniques in action, Shana Ramin from Hello, Teacher Lady suggests deconstructing commercials and advertisements.

When teaching in person, Shana enjoys facilitating this type of analysis with the tried-and-true “chalk talk” approach. After gathering a series of printed advertisements, Shana glues each one in the center of large chart paper and places them at various points around the room. Students rotate through each station with a small group, annotating each ad silently with an eye for purpose, audience, tone, etc. At the end of the activity, students return to their original stations and share out their final observations with the class.
To mimic this activity in a hybrid or digital environment, Shana recommends using Jamboard, an easy-to-use, digital whiteboard app by Google. The setup process is pretty much the same, but replace the printed ads with image screenshots and the white chart paper with a digital Jamboard slide. Students can then use the sticky note and marker features on Jamboard to annotate the images in breakout rooms.
Click here to learn more about the collaborative features of Google Jamboard .
ARGUMENT OLYMPICS
The Argument Olympics are Emily Aierstok’s favorite way to teach middle and high school students evidence based writing. Emily, from Read it. Write it. Learn it. , uses an Olympic theme to deconstruct arguments, write outlines, and compete in the “strongest evidence” game complete with gold medals! Kids LOVE it and quickly understand the qualities of strong evidence in their writing.
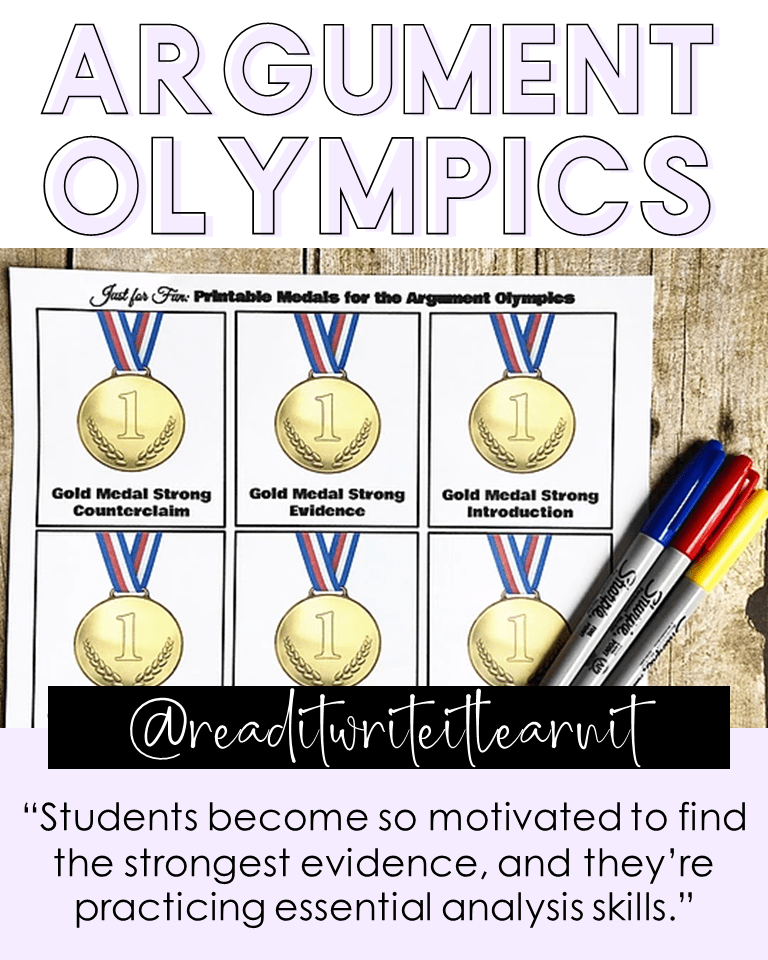
To really create an Olympic games feel, Emily creates a very simple (and free!) classroom transformation. She strings red, yellow, and blue streamers around the room, plays the Olympic theme song from YouTube, and prints gold medals to hand out for gold-medal-level deconstructed essays, strongest outlines, and strongest evidence.
Next, Emily introduces the “Olympic events.” For example, the first Olympic Event she introduces to students is The Strongest Evidence Competition. Students are given two sides of an argument topic and asked to find three pieces of evidence to support each argument. After finding their evidence, students are tasked with identifying the evidence that’s the strongest. Students become so motivated to find the strongest evidence, and they’re practicing essential analysis skills. The quality of evidence students find is amazing.
You can read more about implementing the Argument Olympics in your classroom here .
SILENT DISCUSSIONS
Jenna, @DrJennaCopper , loves using silent discussions for students to debate the impact of articles and artifacts. The rules are simple: students are only allowed to write. This type of stipulation helps students really think about their responses since they can’t talk.

Here’s how it works:
- Choose an artifact or article.
- Get a big piece of poster board or a big paper and paste the article or artifact in the center.
- Tell students to read the article and then, discuss with the stipulation that they are only allowed to write. No talking! It helps if students color-code their writing.
- As students “discuss,” walk around the room and comment (in writing, of course!) to generate more debate.
- When the discussion is over, place the posters on the walls and give students a chance to walk around and view.
- Facilitate a talking classroom discussion to discuss insights and observations.
That’s it! Not only will your students be highly engaged, but you’ll also enjoy the few short minutes of precious silence!
As a bonus, this activity works great for a remote lesson as well. Just paste your article or artifact in a Google Doc and share it so they all have editing access. They can complete their silent discussions right in the document.
STUDYING FAMOUS SPEECHES
Lauralee from the Language Arts Classroom frequently uses famous speeches and commercials to teach persuasion. By bringing in authentic examples to the classroom, this strategy offers history and media lessons, too.

When students realize that they see strategies every day in social media, on their phones, and within stores, they engage and are excited to apply those concepts to their public speaking endeavors.
For instance, students can study the techniques in a Susan B. Anthony speech and then apply those techniques to their own speeches. Teachers can even pair her speech with a narrative speech assignment. Students can then employ sentence structure, tone, and logos into their speeches. Although ELA teachers often use persuasive techniques during public speaking lessons, many of the same activities work well with argumentative writing.
NAILED IT! & SHARK TANK
Staci Lamb from The Engaging Station loves switching up her creative lessons on ethos, logos, and pathos every year. She has had students watch Shark Tank and sell their own products, but last year, she was inspired to try something new by making a connection to the Netflix show Nailed It .

Right before winter break, she went to Walmart to buy graham crackers, icing, candies, and more. Dollar Tree also had a great selection of inexpensive candy. Students had to create a gingerbread masterpiece and then use ethos, logos, and pathos to justify why their house was the best. The kids had a lot of fun, and it was an engaging activity to end the calendar year.
You can see this idea and more with free resources on her blog post Creative Ways to Teach Persuasive Appeals .
REAL WORLD TOPICS + CHOICE
Today, students have access to more information than ever at their fingertips. Tanesha from Tanesha B. Forman leverages real world topics – that students want to debate in the classroom – with argu mentative writing lessons. Choice is the bedrock of Tanesha’s approach to lit eracy and she offers students a choice on a topic (e.g. should college athletes be paid?), and tells them the format (e.g. speech, letter).

Next, students research their topic. Tanesha always warns students to think about their position, but be open to changing based on what the research from credible sources reveals. Students spend a day or two gathering information for their writing assignment. For students who need support with this, Tanesha has 3-4 sources readily available. Once students have their evidence, they enter the writing process that Tanesha creates mini-lessons aligned to their needs and they present their work. Throughout the year, Tanesha encourages students to share topics they want to “argue” and she repeats the cycle.
THE ELEVATOR PITCH
No matter what you’re reading or learning about, adding a persuasive pitch to “sell” an idea, is a great way to include elements of persuasion beyond a persuasive unit.

For example, if students are creating something to aid a character , rather than just explain it, challenge your students to create a short elevator pitch! It can even be used with literary analysis by asking a question such as: Which character is the most (insert character trait here)? Staci from Donut Lovin’ Teacher finds that when students have to pitch their ideas, they really begin to reflect on their work and what makes it great, and also where it can grow.
Staci likes starting with a graphic organizer to get students thinking and then begins layering in mini-lessons that consider the audience, point of view, tone, and rhetorical appeals, depending on how much time you have. Students can then begin crafting their pitch on a guided template and practice saying it aloud. If you’re able to incorporate this multiple times throughout the year, your students will really grow confidence in their speaking skills, too!
MUSICAL DEBATES
Middle and high school students can at times feel intimidated by debate and persuasion. That’s why Melissa from Reading and Writing Haven recommends a mini debate activity that engages all students and makes debate relaxed and approachable.

Musical debates amplify the energy, creativity, and social interaction in the physical classroom and online. By adding a simple twist of music, it lightens the mood and provides natural brain breaks so students have time to collect their thoughts.
Here are Melissa’s simple steps for using this debate-style discussion strategy in your classroom:
- Give students a thought-provoking or humorous prompt.
- Play music as students think, research, jot notes, and (if possible) walk around the room.
- Stop the music and have students get into groups of two or three.
- Students quickly choose roles. Two of the students need to take one of the sides (pro / con or for / against). The third person is a neutral judge who can build on what the speakers say, offer a different perspective, or make connections between ideas.
- After a set amount of time, follow up with a question that digs deeper into the topic or provides another angle. Play music, and allow students to brainstorm again, or take some notes.
- Students then pair up again with different peers.
- After as many rounds as you would like to run, bring the whole class together and use a Jamboard, Mentimeter, or Padlet as a common visual location to share ideas as a whole group.
To make this strategy work online, you can use breakout rooms to group students together randomly.
Of course, you can run the same type of mini debates without the music. And, that’s fun, too! But, for students, the music adds energy and connectedness. Plus, it reduces the anxiety for students who are more reluctant to engage in debates.
Musical debates create a warm, relaxed environment conducive to critical thinking and dialogue. And, students have multiple short opportunities to hone their skills and hear a variety of perspectives. Melissa wrote about engaging variations, prompts for musical discussions, and how to prepare students on her blog. Click here to read the post .
PSA PASSION PROJECTS
One way that Christina, The Daring English Teacher , likes to incorporate persuasion, argument, and debate into the classroom is by assigning a PSA Passion Project to students.

After learning about rhetorical appeals and argument writing , Christina assigns her students a PSA Passion Project. Her students select an important social issue and create a public service announcement campaign to raise awareness for their chosen issue.
The public service campaign usually includes a variety of items. To place students in charge of their learning, they choose several products to produce from a list of items: a speech, a persuasive letter, a graphic essay , a poster, an infographic, an informational video, a narrative video, a social media campaign, and more. It is important to make sure that students choose at least two items, and that their combination includes a writing component and a media literacy component.
To make the class project more fun, no two students can choose the same topic. To share their projects with the class, Christina likes to use Padlet.
ANALYZING MUSIC
Amanda from Mud and Ink Teaching likes to head the Disney direction when it comes to learning the ins and outs of argumentation.

So many great Disney songs offer an argumentative core, and their popularity and familiarity help build engagement with students. Take “Under the Sea” for example: Sebastian has quite the task in front of him. Somehow, he must convince an uninterested Ariel to curb her curiosity about the human world and appreciate her home under ‘de water. Reversely, Moana sings of the importance of heeding the call to the ocean in “How Far I’ll Go” as she debates within herself how far she is actually willing to go. Each of these speakers has an important message to impart, and these are things that students are comfortable wrestling with.
Amanda’s favorite song to teach, however, is the well-loved classic “Be Our Guest” from Beauty and the Beast . In this lesson that she outlines in her blog post and provides a free Google Slide lesson download , Amanda teaches students the importance of understanding the rhetorical situation (the rhetorical triangle) as well as the devices and techniques that the speaker uses to communicate his message. Through practice and discussion with familiar texts and characters, students begin to embrace the fundamental ideas of argumentation.
I hope this post helps you make persuasion more engaging, authentic, and student-centered! What are your other favorite activities to teach persuasion? Let me know in the comments!
If you like any of these ideas, don’t forget to pin them! 🙂
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
You may also enjoy:
10 activities for any dystopian novel, how to use the “what do you …, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Check out my most popular posts!
August 5, 2018: why i don’t review the syllabus on the first day …, december 16, 2018: 10 ideas for planning engaging novel units, december 11, 2017: comfort in the classroom with flexible seating, july 21, 2018: teaching american literature: my units & favorite lessons.
Key Takeaways:
- For middle school students, acquiring the critical-thinking and communication skills they need to evaluate both sides of a debate and write persuasive essays isn’t always easy.
- With Junior Scholastic ’s free Social Studies Debate Kit, learning how to debate and craft an effective argument essay will be an exciting and inspiring experience for your students.
- Featuring teacher-approved stories, middle school teaching resources, and engaging activities, Junior Scholastic makes teaching your students the essential skills they need for success not only fun, but easy too!
Looking for a fun, yet effective, way to teach your students the art of debating and how to craft the perfect argument essay? With this free Social Studies Debate Kit from Junior Scholastic , you’ll help your students acquire the essential critical-thinking and communication skills they need to ensure their success inside and outside the classroom. Featuring teacher-approved articles, free middle school teaching resources, and engaging activities, Junior Scholastic is the perfect teaching tool for helping middle school students evaluate both sides of a debate and write a powerful and persuasive essay.
Try print and digital resources from Junior Scholastic , the social studies magazine for grades 6–8, for free in your classroom!
A Reheated Argument
The argument surrounding the food dished out to your students has certainly been heated over the years. In our story, “ Food Fight! ,” your teens will learn how the debate has been reheated after the government recently changed school lunch requirements. With engaging infographics, informative photos showing school lunches from around the world, and a “Pick a Side” persuasive writing activity, this lesson is the perfect way to kick off debate season in your classroom.
Tossing a Ball vs. Saving Lives
“Someone who tosses a ball shouldn’t earn 700 times as much as someone who saves lives.”
In this lesson, we present students two compelling arguments related to how much professional athletes earn . Of course, after reading the article your students will have to choose a side and back up their own arguments on why or why not they believe pro athletes are overpaid. Follow our step-by-step lesson plan, including close-reading questions and differentiation tips. Then extend the lesson with our “What’s Your Opinion?” writing activity.
In our story, “ Should We Try to Send Humans to Mars? ,” your students will have to decide whether sending humans to Mars will help us learn more about Earth or if it’s just a waste of time and money. With compelling arguments on both sides, an informative video, an “Analyzing Authors’ Claims” activity, and more, your students will have all the supporting evidence they need to craft a persuasive and informed response that could alter the future of space exploration.
Staying on Track
Privacy is always a hot topic for debate. With this engaging story and lesson , your students will take on tracking apps that allow parents to follow their teens’ movements in real time. Is it a matter of safety? Or are kids unwillingly giving up their right to privacy? Follow our step-by-step lesson plan and accompanying teaching resources to help your students decide where to draw the line when it comes to privacy.
Try Junior Scholastic for Free
Once your students master the art of debating and writing argument essays, you’ll know why so many teachers use Junior Scholastic in their middle school classrooms. With each issue, we help create learning excitement about curricular topics from history to civics, geography, science, social-emotional learning, and more. Plus, every issue comes with flexible, timesaving print and digital teaching tools to help you meet your instructional goals. Try Junior Scholastic in your classroom and make history relevant to today’s teens. Start a FREE 30-Day Trial !
877-542-5504 877-542-5504
/ Lessons Plans / Language Arts Lesson Plans / Delivering a Persuasive Speech Lesson Plan
Delivering a Persuasive Speech Lesson Plan
Want to help fellow teachers.
Please help us grow this free resource by submitting your favorite lesson plans.
Lesson Plan #: AELP-SPH0200 Submitted by: Douglas Parker Email: [email protected] School/University/Affiliation: Albany Academy, Albany, NY Date: May 30, 2001
Grade Level: 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12
Subject(s):
- Language Arts/Speech
Duration: Two 50-minute sessions
Description: Students need to understand that how they say something and how they physically present themselves are just as important as what they say. By understanding the dynamics involved in effective persuasive speaking, students will improve their overall confidence in communicating.
Goals: The goal of this lesson is to improve students’ speaking skills by understanding persuasion proficiencies.
Objectives: Students will be able to:
- Demonstrate the appropriate classroom public speaking and listening skills (e.g., body language, articulation, listening to be able to identify specific examples of the speaker’s coordination of talking and action) that would be necessary to influence or change someone’s mind or way of thinking about a topic.
- Define the elements of persuasion.
- Recognize the elements of personal credibility.
- Develop methods to analyze other students’ speeches.
- Understand outlining main ideas.
- Create a persuasive speech.
- teacher-prepared topics for persuasive speeches
- sample rubric (available in .pdf format)
- Sample Rubric
Procedure: During class discussion, define and explain how people make decisions based on what they see and hear. Explain that sometimes we have to use skills to convince others about our positions. Have the students recall and list their own experiences trying to convince their friends about something, and then ask them to share these with the class. Have the students pick a proposition that not everyone would agree with such as: nuclear power plants are superior energy sources. Have them write a 6-8 minute speech in outline form to persuade the class. Each student will then deliver this speech in front of the class while the rest of the students take notes and prepare to give the speaker feedback on the speech.
The voice and the body are the best tools — every student is a natural persuader! They have done it all their lives. Every time someone enters a conversation, he or she engages in elementary persuasion techniques. It is true that any time students make a statement of fact, they are asserting its validity and assuming that their listener agrees. This speech goes further than a normal conversational assertion: now students have to assume that not everyone will agree with them from the start, and it is their job to make them see things their way. The goal of this speech is to change someone’s mind or way of thinking about a topic. This is not a speech to sell, as students do not ask that the listener do anything except to agree with them or to begin to listen to their way of thinking. Their message is, of course, very important in this speech, but their voice and body language are even more important. Here they will learn how their delivery can help. There are several important aspects of presentation to keep in mind; the academic elements of persuasion are:
- Body Language – Make sure that they have a proper posture. If their shoulders are sagging and their legs are crossed, they will not appear as being sincere, and people just will not accept their message.
- Articulation – Articulation means how their total vocal process works. There are several steps to this entire process. Students need to understand the process. First, they need air from the lungs, their vocal cords in their larynx must be working, their mouth and tongue must be in sync, and they have to make sure that they have got some saliva in their mouths to keep things oiled. They should be aware of their physical makeup to be able to understand how they speak.
- Pronunciation – Students need to pronounce each word. They must avoid slang, except to make a point, and not slur the words. They must avoid saying, you know.
- Pitch – Pitch refers to the highs and lows of the voice. Whatever they do, they must avoid a monotone!
- Speed – The speed, or pace, is an important variable to control. Between 140-160 words per minute is the normal pace for a persuasive speech. Any faster and they may appear to be glib; any slower and they sound like they are lecturing. If they are not sure about their speed, tape them for one minute and then replay it and count the number of words they used in the minute! The human ear and brain can compile and decode over 400 spoken words per minute, so if they are going too slow their listeners’ minds are going to start to wander as the brains finds other ways to keep themselves occupied.
- Pauses – The pause, or caesura, is a critical persuasive tool. When they want to emphasize a certain word, have them just pause for one second before; this highlights the word. If they really want to punch it, tell them to pause before and after the word!
- Volume – Volume is another good tool for a persuasive speech, but they should use it with caution. If they scream all the way through their speech, people will become accustomed to it and it will lose its effectiveness. On the other hand, a few well-timed shouts can liven up the speech! They must try to project or throw their voice out over the entire class – or speak to the last row.
- Quality – Quality of voice is gauged by the overall impact that their voice has on their listeners. Quality of voice is the net caliber of their voice, its character and attributes. They must try to keep the vocal quality high; it is what separates their voices from everyone else’s.
- Variance – Variance of vocal elements is the most important consideration of all! One of the most persuasive speakers in modern history was Winston Churchill. One of his most remarkable qualities was his ability to vary the elements of his voice. He would start with a slow, laconic voice and then switch gears to a more rapid pace. People were light-headed after listening to him! Even if they have no desire to run for political office, students can still use the tools of variance. Have them try to change their pitch, volume, and speed at least once every 30 seconds, if only for just one word. Never let them go more than one paragraph without a vocal variance. This keeps the class locked into the speech, if for no other reason than it sounds interesting! Let the students’ words speak for themselves; reflect their nature through their voices. If they use the word strangle, have them say it with a hint of menace in their voices. If they say the word heave, let the class feel the onomatopoeic force behind it. If they say the word bulldozer, make it sound like a titan earthmover, not like a baby with a shovel.
The Strategy: Appear Rational When students are trying to convince someone of something, they must first establish their credibility, or in other words, they must sell themselves before they sell their message. If people feel that they are not being reasonable or rational, they do not stand a chance. They must be committed to the ideals and goals of their speech and what they are saying. They should not use words such as maybe or might- the should use positive words such as will and must. Students must portray themselves as the authority figures in this speech, so they had better supply enough information to prove their points so that they can seem knowledgeable, and they had better know their material cold. People can usually spot someone who is trying to wing a speech. They should also appear to be truthful – even when they are really stretching a point. If they do not appear to be earnest, even if their message is the 100% truth, people will doubt their word and tune out their speech. Lastly, they must not be afraid to show a little emotion – this is not a sterile or static speech. Students’ bodies and voices must match the tone of their words. If their language is strong, they must present a physical force to go along with their deliveries.
The Class Reaction The class has two major criteria to consider after each member’s speech. First, the delivery. Were the speaker’s body, words, and actions in synchronization and harmony? Did one support the other or was there tension between the body and the voice? Secondly, were the students persuaded? Why or why not? Discuss what makes a persuasive speech work and how the intangibles effect a positive outcome. Assessment: The class will assess each speaker’s performance in terms of voice and body coordination and in terms of persuasiveness. Each class can develop performance assessments such as rubrics to facilitate this process (see sample rubric in Materials ).
Useful Internet Resource: * Basic Public Speaking, 2nd edition (written by the lesson plan author) http://www.capital.net/~bps2

Table of Contents
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
KidsKonnect
Reading Comprehension Cause and Effect Context Clues Compare and Contrast
Noun Worksheets Writing Prompts Compound Words Figurative Language
The Wizard of Oz Hans Christian Andersen Types of Writing Text Structure
Literary Devices
Alliteration Hyperbole Metaphor Irony
Subject Verb Agreement Poetry Climax Rhyme
View all reading worksheets
Action Verbs Tragedy Transition Words Phonics
View all writing worksheets
Dramatic Irony Cacophony Anaphora Setting
View all literature worksheets
Abbreviations Transition Words Conclusion Situational Irony
View all literary device worksheets
Women’s History
Inspirational Women Women's History Month First Lady of the US Women's Equality Day International Women's Day
View all Women's History worksheets
American Revolution
American Revolution Patriots & Loyalists Patrick Henry Sons of Liberty
View all American Revolution worksheets
US Constitution US Independence Trail of Tears The Pilgrims
View all US History worksheets
Ancient History
Ancient China Ancient Mayan Ancient Rome Ancient Aztec
View all Ancient History worksheets
World History
Roaring Twenties Industrial Revolution Middle Ages The Renaissance
View all World History worksheets
Famous Wars
World War 1 World War 2 Vietnam War American Civil War
View all Famous War worksheets
Anne Frank Sally Ride Neil Armstrong Christopher Columbus
View all famous figure worksheets
Joe Biden Donald Trump Abraham Lincoln George Washington
View all President worksheets
Roald Dahl Dr Seuss JK Rowling Michael Morpurgo
View all author worksheets
Civil Rights
Rosa Parks Sojourner Truth Medger Evers Martin Luther King
Elvis Presley Johann Sebastian Bach Ella Fitzgerald Wolfgang Mozart
View all musician worksheets
Thomas Edison Albert Einstein Henry Ford Wright Brothers
View all inventor worksheets
Muhammad Ali Michael Jordan Jackie Robinson Jesse Owens
View all athlete worksheets
Nat Turner Ruby Bridges Harriet Tubman Booker T Washington Malcolm X
View all civil rights worksheets
Natural Wonders
River Nile Mount Everest Sahara Desert Mount Etna Ancient Pyramids Amazon River
Landmarks/Sights
Mount Rushmore Statue Of Liberty White House Stonehenge Great Wall of China Santa Fe Trail
New York Texas South Carolina Alaska Nevada Ohio
Australia United Kingdom China Canada Argentina Brazil
Mount Fuji Mississippi River Rocky Mountains Volcano Glacier The Great Barrier Reef
View all natural wonders worksheets
Hoover Dam Bermuda Triangle Leaning Tower Of Pisa Arc De Triomphe Golden Gate Bridge Colosseum
View all landmark worksheets
California Colorado Indiana Florida Washington Georgia
View all US state worksheets
Poland Greece Philippines Japan France India
View all country worksheets
April Topics
April Fools’ Day World Autism Awareness Day International Children’s Book Day Passover Eid Al-Fitr Ramadan Patriots’ Day Rama Navami Earth Day World Book Day
View all Seasonal worksheets
Social Emotional Learning
Morals and Values Self Management Ethics Depression Relationship Skills Self-Awareneess Self-Esteem Emotions and Feelings Goal-Setting Interpersonal Skills
View all Social-Emotional Learning worksheets
Celebrations
Easter Saint Patrick’s Day Valentines Day Chinese New Year Rosh Hashanah Thanksgiving Flag Day Cinco de Mayo Beginning Of Lent Yom Kippur View all Celebrations worksheets
Remembrance
Pearl Harbor Day Veterans’ Day Memorial Day Battle Of The Somme D-Day 9/11 Anzac Day Martin Luther King Jr. Day International Women’s Day Victoria Day View all Remembrance worksheets
Camels Fox Bears Penguin Wolf Beavers Mountain Lion Red Panda Snow Leopard White Tigers Silverback Gorilla Okapi
View all mammal worksheets
Marine Life
Crabs Starfish Fish Octopus Great White Shark Dolphin Walrus Narwhal Megalodon Shark Killer Whale Beluga Whale Lionfish
View all marine life worksheets
Insects/Invertebrates/Reptiles
Millipede Praying Mantis Ladybug Ants Spider Iguana Chameleon Komodo Dragon Lizard Bearded Dragon Gila Monster Snakes
View all insect worksheets
Eagle Peregrine Falcon Snowy Owl Emu Woodpecker Albatross Swan Quail Bald Eagle Hummingbird Peacock
View all Bird worksheets
Natural World
Avalanche Flood Tsunami Natural Disasters Fossils Ice Age
View all natural world worksheets
Earth Sciences
Water Cycle Global Warming Deciduous Forests Hurricane Sandy Hurricane Katrina Global Warming
View all earth science worksheets
Food Chain Fossils Photosynthesis Cells Ecosystem Plants
View all biology worksheets
Solar System Black Holes Eclipse Stars and Constellations The Moon Comets
View all space worksheets
Chemistry/Physics
Magnetism Graduated Cylinders Solid, Liquid, Gas Gravity Light Sound
View all science worksheets
Kangaroo Horse Bear Lion Lizard Octopus
View all animal worksheets
Addition Sentences Single Digital Addition Two-Digit Addition Three Digit Addition Repeated Addition
View all Addition Worksheets
Ordinal Numbers Cardinal Numbers Rounding Numbers Odd & Even Numbers Comparing Numbers
View all Numbers Worksheets
Counting Money Subtracting Money Change Money Coin Name & Value Calculate Change (Money)
View all Money Worksheets
Number Line Single Digit Subtraction Place Value Subtraction Sentences Input & Output Tables
View all Math Worksheets
Persuasive Speech Topic Examples & Worksheets
Search for worksheets, download the persuasive speech topic examples & worksheets.
Click the button below to get instant access to these worksheets for use in the classroom or at a home.
Download This Worksheet
This download is exclusively for KidsKonnect Premium members! To download this worksheet, click the button below to signup (it only takes a minute) and you'll be brought right back to this page to start the download! Sign Me Up
Edit This Worksheet
Editing resources is available exclusively for KidsKonnect Premium members. To edit this worksheet, click the button below to signup (it only takes a minute) and you'll be brought right back to this page to start editing! Sign Up
This worksheet can be edited by Premium members using the free Google Slides online software. Click the Edit button above to get started.
Download This Sample
This sample is exclusively for KidsKonnect members! To download this worksheet, click the button below to signup for free (it only takes a minute) and you'll be brought right back to this page to start the download! Sign Me Up
Table of Contents
Persuasive speech is used to argue ‘for’ or ‘against’ a specific point. The aim is to start with a statement (which you either do or don’t agree with) and then use persuasive language to get other people to agree with your point of view. Persuasive speech could be used for a speech read by one person to a crowd, or for a group of people in a debate about a topic.
Of course it’s much easier to use persuasive speech if you pick a statement that you strongly agree or disagree with, but if you’re struggling for ideas then take a look at the following ideas.
100 Examples of Persuasive Speech Topics
1: The death penalty should be removed in all states. 2. The modern world is causing global warming to speed up. 3. The fast food industry is responsible for obesity. 4. People consume too much meat. 5. Violence in video games turns children into violent adults. 6. Plastic surgery should be free for everyone. 7. It should be mandatory for students to walk to school. 8. The legal drinking age needs to be raised. 9. Schools should teach children about body image. 10. Women are better leaders than men. 11. Our grandparents had a healthier diet than we do. 12. The President should step down. 13. All sports stars should be drug tested before every game. 14. University should be mandatory. 15. All children should be given vitamin supplements. 16. The voting age needs to be lowered. 17. Cars should carry a higher tax. 18. Not wearing a seat-belt needs to be made illegal. 19. Marijuana should be legalized in all states. 20. Children should be allowed to move out whenever they want. 21. Male and female players should be allowed on the same sports teams. 22. The world would be better without cars. 23. The USA could solve world hunger. 24. School should start later and finish earlier. 25. Abortion should be considered illegal. 26. It’s OK to use curse words on TV. 27. Suicide needs stricter legislation. 28. Fast food should be taxed. 29. Vitamins added to foods are essential for the future. 30. R-Rated films should be made available for younger viewers. 31. The UK is a better place to live than the US. 32. People in the USA are the happiest in the world. 33. Humans are responsible for the melting ice caps. 34. It should be illegal to leave school before 18. 35. The internet needs to be censored. 36. Speed limits need to be lowered in all towns. 37. Immigration should be limited. 38. Supermarkets should only sell organic fruit and vegetables. 39. People need to drink more water. 40. Women are equal to men in the workplace. 41. Homosexual men should not join the military. 42. We should all get at least 9 hours’ sleep each night. 43. There are aliens outside of our solar system. 44. We should take responsibility for homeless people. 45. Hallowe’en should be a national holiday. 46. Pets help to lower stress levels. 47. Everyone should get the day off on his or her birthday. 48. The world would be better if war was illegal. 49. Condoms should be given out for free in schools. 50. The US should become a dictatorship. 51. Teachers should wear uniforms. 52. Fast food should be banned in schools. 53. Health care should be free for everyone. 54. School holidays need to be twice as long. 55. Wi-fi should be available everywhere. 56. We all have the right to free speech. 57. Cycling is healthier than walking. 58. Sex education should be taught at a lower age. 59. The cost of alcohol needs to be reduced. 60. Gambling should be illegal. 61. Children should be required to read 100 books before leaving school. 62. The government should subsidize healthy restaurants. 63. All criminals should be sentenced to death. 64. Miracles are real. 65. Adoption should be encouraged. 66. Language should never be allowed to change. 67. Everyone in the world needs to speak English. 68. Religion has no place in schools. 69. Unmarried women should not have children. 70. Positive thinking can cure illness. 71. High heel shoes should carry an age rating. 72. The retirement age should be increased. 73. There is life after death. 74. Cats speak in different languages. 75. Going on a diet has no health benefits. 76. Donating blood should be mandatory. 77. All credit card debt should be written off. 78. The moon landing was faked. 79. Animals should be equal to humans. 80. Prostitution should be legalized. 81. Obama is the greatest President of all time. 82. A 3-day weekend should be introduced. 83. Guns should be made illegal. 84. Magazines should ban size zero models. 85. All teenagers should carry out community service. 86. All religion can be disproved by science. 87. The money spent on space exploration is a waste. 88. Private colleges are better than state colleges. 89. Social media will soon go out of fashion. 90. Silent letters in words should be removed. 91. Anyone can become a millionaire. 92. Dangerous animals should be killed. 93. Famous people set a bad example for children. 94. Athletes should never be allowed to move teams. 95. Teenagers should take parenting classes in school. 96. All students should have a year studying abroad. 97. Families don’t spend enough time together. 98. Internet access should be free. 99. Cigarettes should be more expensive. 100. Music videos promote an unhealthy lifestyle.
Persuasive Speech Worksheets
This bundle contains 5 ready-to-use worksheets that are perfect to test student knowledge and understanding of Persuasive speech which is used to argue ‘for’ or ‘against’ a specific point. The aim is to start with a statement (which you either do or don’t agree with) and then use persuasive language to get other people to agree with your point of view.
Link/cite this page
If you reference any of the content on this page on your own website, please use the code below to cite this page as the original source.
Link will appear as Persuasive Speech Topic Examples & Worksheets: https://kidskonnect.com - KidsKonnect, November 8, 2017
Use With Any Curriculum
These worksheets have been specifically designed for use with any international curriculum. You can use these worksheets as-is, or edit them using Google Slides to make them more specific to your own student ability levels and curriculum standards.
Related Resources
KidsKonnect is a growing library of high-quality, printable worksheets for teachers and homeschoolers.
Home Facts Privacy About Blog Contact Terms
Safe & Secure
We pride ourselves on being a safe website for both teachers and students. KidsKonnect uses a secure SSL connection to encrypt your data and we only work with trusted payment processors Stripe and PayPal.

How to Teach Argument Writing Step-By-Step

No doubt, teaching argument writing to middle school students can be tricky. Even the word “argumentative” is off-putting, bringing to mind pointless bickering. But once I came up with argument writing lessons that were both fun and effective, I quickly saw the value in it. And so did my students.
You see, we teachers have an ace up our sleeve. It’s a known fact that from ages 11-14, kids love nothing more than to fire up a good ole battle royale with just about anybody within spitting distance.
Yup. So we’re going to use their powers of contradiction to OUR advantage by showing them how to use our argument writing lessons to power up their real-life persuasion skills. Your students will be knocking each other over in the hall to get to the room first!
I usually plan on taking about three weeks on the entire argument writing workshop. However, there are years when I’ve had to cut it down to two, and that works fine too.
Here are the step-by-step lessons I use to teach argument writing. It might be helpful to teachers who are new to teaching the argument, or to teachers who want to get back to the basics. If it seems formulaic, that’s because it is. In my experience, that’s the best way to get middle school students started.
Prior to Starting the Writer’s Workshop
A couple of weeks prior to starting your unit, assign some quick-write journal topics. I pick one current event topic a day, and I ask students to express their opinion about the topic.
Quick-writes get the kids thinking about what is going on in the world and makes choosing a topic easier later on.
Define Argumentative Writing
I’ll never forget the feeling of panic I had in 7th grade when my teacher told us to start writing an expository essay on snowstorms. How could I write an expository essay if I don’t even know what expository MEANS, I whined to my middle school self.
We can’t assume our students know or remember what argumentative writing is, even if we think they should know. So we have to tell them. Also, define claim and issue while you’re at it.
Establish Purpose
I always tell my students that learning to write an effective argument is key to learning critical thinking skills and is an important part of school AND real-life writing.
We start with a fictional scenario every kid in the history of kids can relate to.
ISSUE : a kid wants to stay up late to go to a party vs. AUDIENCE : the strict mom who likes to say no.
The “party” kid writes his mom a letter that starts with a thesis and a claim: I should be permitted to stay out late to attend the part for several reasons.
By going through this totally relatable scenario using a modified argumentative framework, I’m able to demonstrate the difference between persuasion and argument, the importance of data and factual evidence, and the value of a counterclaim and rebuttal.
Students love to debate whether or not strict mom should allow party kid to attend the party. More importantly, it’s a great way to introduce the art of the argument, because kids can see how they can use the skills to their personal advantage.
Persuasive Writing Differs From Argument Writing
At the middle school level, students need to understand persuasive and argument writing in a concrete way. Therefore, I keep it simple by explaining that both types of writing involve a claim. However, in persuasive writing, the supporting details are based on opinions, feelings, and emotions, while in argument writing the supporting details are based on researching factual evidence.
I give kids a few examples to see if they can tell the difference between argumentation and persuasion before we move on.
Argumentative Essay Terminology
In order to write a complete argumentative essay, students need to be familiar with some key terminology . Some teachers name the parts differently, so I try to give them more than one word if necessary:
- thesis statement
- bridge/warrant
- counterclaim/counterargument*
- turn-back/refutation
*If you follow Common Core Standards, the counterargument is not required for 6th-grade argument writing. All of the teachers in my school teach it anyway, and I’m thankful for that when the kids get to 7th grade.
Organizing the Argumentative Essay
I teach students how to write a step-by-step 5 paragraph argumentative essay consisting of the following:
- Introduction : Includes a lead/hook, background information about the topic, and a thesis statement that includes the claim.
- Body Paragraph #1 : Introduces the first reason that the claim is valid. Supports that reason with facts, examples, and/or data.
- Body Paragraph #2 : The second reason the claim is valid. Supporting evidence as above.
- Counterargument (Body Paragraph #3): Introduction of an opposing claim, then includes a turn-back to take the reader back to the original claim.
- Conclusion : Restates the thesis statement, summarizes the main idea, and contains a strong concluding statement that might be a call to action.
Mentor Texts
If we want students to write a certain way, we should provide high-quality mentor texts that are exact models of what we expect them to write.
I know a lot of teachers will use picture books or editorials that present arguments for this, and I can get behind that. But only if specific exemplary essays are also used, and this is why.
If I want to learn Italian cooking, I’m not going to just watch the Romanos enjoy a holiday feast on Everybody Loves Raymond . I need to slow it down and follow every little step my girl Lidia Bastianich makes.
The same goes for teaching argument writing. If we want students to write 5 paragraph essays, that’s what we should show them.
In fact, don’t just display those mentor texts like a museum piece. Dissect the heck out of those essays. Pull them apart like a Thanksgiving turkey. Disassemble the essay sentence by sentence and have the kids label the parts and reassemble them. This is how they will learn how to structure their own writing.
Also, encourage your detectives to evaluate the evidence. Ask students to make note of how the authors use anecdotes, statistics, and facts. Have them evaluate the evidence and whether or not the writer fully analyzes it and connects it to the claim.
This is absolutely the best way for kids to understand the purpose of each part of the essay.
Research Time
Most of my students are not very experienced with performing research when we do this unit, so I ease them into it. (Our “big” research unit comes later in the year with our feature article unit .)
I start them off by showing this short video on how to find reliable sources. We use data collection sheets and our school library’s database for research. There are also some awesome, kid-friendly research sites listed on the Ask a Tech Teacher Blog .
Step-By-Step Drafting
The bedrock of drafting is to start with a solid graphic organizer. I have to differentiate for my writers, and I’ve found they have the most success when I offer three types of graphic organizers.
1- Least Support: This is your standard graphic organizer. It labels each paragraph and has a dedicated section for each part of the paragraph.
2- Moderate Support: This one has labels and sections, but also includes sentence stems for each sentence in the paragraph.
3- Most Support: This one has labels and sections and also includes fill-in-the-blank sentence frames . It’s perfect for my emerging writers, and as I’ve mentioned previously, students do NOT need the frames for long and soon become competent and independent writers.
Writing the Introduction
The introduction has three parts and purposes.
First, it has a hook or lead. While it should be about the topic, it shouldn’t state the writer’s position on the topic. I encourage students to start with a quote by a famous person, an unusual detail, a statistic, or a fact.
Kids will often try to start with a question, but I discourage that unless their question also includes one of the other strategies. Otherwise, I end up with 100 essays that start with, “Do you like sharks?” Lol
Next, it’s time to introduce the issue. This is the background information that readers need in order to understand the controversy.
Last, students should state the claim in the thesis statement. I call it a promise to the reader that the essay will deliver by proving that the claim is valid.
Writing the Supporting Body Paragraphs
Each supporting body paragraph should start with a topic sentence that introduces the idea and states the reason why the claim is valid. The following sentences in the paragraph should support that reason with facts, examples, data, or expert opinions. The bridge is the sentence that connects that piece of evidence to the argument’s claim. The concluding sentence should restate the reason.
Writing the Counterclaim Paragraph
The counterclaim paragraph is a very important aspect of argument writing. It’s where we introduce an opposing argument and then confidently take the reader back to the original argument. I tell students that it’s necessary to “get in the head” of the person who might not agree with their claim, by predicting their objections.
It can be tough for kids to “flip the switch” on their own argument, so I like to practice this a bit. I give them several pairs of transitions that go together to form a counterclaim and rebuttal. I also switch up what I call this part so that they use the terminology interchangeably.
- It might seem that [ counterargument . ]However, [ turn-back .]
- Opponents may argue that [ counterargument .] Nevertheless, [ turn back .]
- A common argument against this position is [ counterargument .] Yet, [ turn-back .]
A great way for kids to practice this is to have them work with partners to write a few counterarguments together. I let them practice by giving them easy role-playing topics.
- Your cousins want to jump into a poison ivy grove for a TikTok challenge. Choose your position on this and write a counterargument and turn-back.
- Your friend wants to get a full-face tattoo of their boyfriend’s name. Choose your position on this and write a counterargument and turn-back.
This kind of practice makes the counterargument much more clear.
The concluding paragraph should remind the reader of what was argued in the essay and why it matters. It might also suggest solutions or further research that could be done on the topic. Or students can write a call to action that asks the reader to perform an action in regard to the information they’ve just learned.
My students write about local issues and then turn the essays into letters to our superintendent, school board, or state senators. It’s an amazing way to empower kids and to show them that their opinion matters. I’ve written about that here and I’ve included the sentence frames for the letters in my argumentative writing unit.
I hope this gives you a good overview of teaching argument writing. Please leave any questions below. Please also share your ideas, because we all need all the help we can give each other!
And one more thing. Don’t be surprised if parents start asking you to tone down the unit because it’s become harder to tell their kids why they can’t stay up late for parties. 🙂
Stay delicious!

Narrative Writing Workshop for Middle School ELA

Fiction & Nonfiction Reading -Teach, Practice, Test BUNDLE – Middle School ELA

RACES Writing Introduction to Paragraph Frames DIGITAL & EDITABLE

Middle School Speech

Making a speech is never meant to be easy. It is perhaps one of the most daunting tasks that you could ever ask a middle school student to do.
- Speech Examples in Doc
- How to Start a Speech
New Graduation Speech Example

Size: 58 KB
Middle School Graduation Speech Example

Size: 98 KB
High School President Speech Example

Size: 172 KB
It is not only in terms of the topic, but also about the content and how the speech is going to be structured. But worry not, this article may be of some help to you as it will help you go through the step-by-step procedure in drafting a said speech. You may also see some examples of speech templates for further reference.
The Basics of Speech Writing
1. choose your topic well.
Take a moment and a breather to think this through. What might be a suitable topic for middle school students? For one thing, it has to be inspirational to the point that students are willing to do better not only in their academic work but also with their private life as well. An example of a good topic would be about the value of hard work in finishing your studies, which does not involve cheating. Middle school students are able to relate to this topic as they are still studying. You may also see examples of writing a welcome speech for further insight.
2. Find Purpose or Thesis
Why are you giving a speech on this topic? Otherwise, there would be no point in delivering it the first place. They say that everything has a purpose and that there is no such thing as an accident. What is the end goal that your speech is trying to achieve? A good speech is made for a good reason: to inspire, to instruct, to rally support, to lead to action, etc. These are noble purposes — and not merely to sound off; feed the speaker’s ego; or to flatter, intimidate, or shame anyone. You may also check the 8 steps needed in speech composition should you need further assistance.
3. Get Organized
Speaking a disorganized speech would only make things worse. Start small. Make a point. Eventually, you will get there. Start with the introduction. Make it catchy and make it snappy because the attention span of today’s students is rather short. One of the best and famous ways that people start their professional speech is with a joke. Once you’ve got their attention, go on with the body and end strong with the conclusion.
- The body of the speech. State at least three points to support your argument. If they build on each other, good. Make a list and pick out the strongest arguments later when writing the first draft. You may also check out wedding speech examples if you happen to be selected as the best an or maid-of-honor.
4. Get Persuasive
There are two kinds of speeches: persuasive and informative. So with the topic you’ve chosen to deliver to the whole student body, look back and think as to whether the content of your speech is to inform or persuade the students. And how will you do that? Even if you have written a damn fine speech, but lack the emotional capability to deliver it, then all that effort and time would have been for nothing. You may also discover on writing examples of a dedication speech .
School Campaign Speech Example

Size: 138 KB
School Award Speech Example

Size: 81 KB
School Demonstration Speech Outline Example

Size: 92 KB
Making it Effective
1. choose words wisely.
Remember that your audience is middle-schoolers; not elderly gentlemen or young adults or parents or teachers. Speakers must exercise the precaution on carefully selecting what terminology they decide to use with the audience. Because if they are not so careful, the speaker might end up insulting or hurt the feelings of their audience without them realizing it. Should you wish to thank someone for the things they have done, you may research on how to write a good thank-you speech .
2. Grab their Attention
There are many ways to get the students attention other than a joke or a story. To the more creative ones, you can come up with a role play or let the students themselves participate in whatever game or activity you are planning. Just as long as you grab their attention, I am sure that they will be able to keep themselves fixed on you throughout the rest of the day. Yes, even making an introduction speech also needs to be practiced and worked on. Making an after-dinner speech also helps out in lightening the mood.
3. Focus on Your Message
Don’t forget that you are there to deliver your speech. That’s why it is important to focus mainly on the message at hand and not get sidetracked. Although it is perfectly understandable for a person to get lost along the way but you should know how to bounce back in any situation. The audience is not there to hear your ramblings and whatnot, they are there to hear your topic. If it really cannot be avoided, then make an outline as to help you keep track of where you are heading in the speech. You may also see on how to make a leadership speech if you’re into that sort of thing.
4. Illustrate
Show and don’t tell. You have to make them visualize the scene and not just tell them about it. When visualizing the given scene, it is important to try and add life to the scene with the use of adjectives, adverbs, and figures of speech.
5. Think in Pauses
Pausing is not all bad. There are 2 advantages that can be thought off when adding pauses in the said speech: First, it gives you time to collect your thoughts. Let’s admit it: there are one too many times that people forget what they’re supposed to say. By adding pauses to some of the words or lines in your general speech helps correct that issue.
But the main reason why people add pauses in their speeches is to give emphasis on that certain phrase or word that the public should know about. Once you start a pause right after a specific word, the whole crowd becomes silent to reflect and ponder about the certain situation, meaning that you have control of the entire room.
- Speeches need to be natural – not read off of a paper. And when you talk, you have pauses. This is not slowing you down or showing your weakness, it shows that you have this down so well, you’re talking about it like an old pro.
Forming Your Speech
1. start off with a strong introduction.
Introductions are perhaps the most important part of your speech as it is often perceived as the most crucial factor to whether the audience will get bored of your speech or pay attention to you all throughout. There are many ways to begin your introduction So just try to find out what you can about the audience and wing it from there. You may also see tribute speech examples & samples .
- Opening with important remarks or quotes will immediately establish credibility.
2. Use Inclusive Terms for Individuals
Point to “our” things — our team, our city/state/country, or our school, our class-year, our work, people, and product/candidate, etc. Your audience will feel more included and a sense of belonging. If “we” feel that way, they’ll feel the pressure to feel that way, too. You may also like appreciation speech examples & samples .
- In a speech by Nelson Mandela, he started off with, “Today we celebrate not the victory of a party, but a victory for all the people of South Africa.”Now that’s a man whose oratorical prowess cannot be questioned.
3. Build the Body of the Speech
This part should contain the main points of the issue and support for each one. That list you made earlier? Narrow it down to about three. Which ones are the most convincing?
- Start off with your strongest point. You want the audience to start off seeing zero holes through your argument. Get them on your side before they get the chance to nitpick what you have to say. You may also check out presentation speech examples & samples .
- Put your weakest argument in the middle. You’re sandwiching it here to make it the most forgettable. And, indeed, it will be.
- End with your second strongest argument. You want to vamp it up a notch towards the end. Reel them back in, rounding out your argument with your last piece of evidence.
4. Be Aware of Your Transitions.
Transitions should not only go in between points in the body, but also after the introduction and into the conclusion. Again, your speech is one cohesive work, not a series of points that work independently. Show your audience that by transitioning clearly. You might be interested in how do you write a speech?
5. End with a firm conclusion.
Conclude with a powerful nail-down, summarizing what you came here to say. Leave them with a question or thoughts of implications; leave them with something — what do you want that something to be?
- Repeat key ideas. Make the audience recall and get on the mainline. Be sure they leave with the ideas you don’t want them to forget. You may also see orientation speech examples & samples .
- Give your audience a sense of completion in what you write. Bring them back to the beginning, but with a louder spirit — after all, they have all the knowledge necessary to be passionate now, too. This can be done by starting the last paragraph with a strong, declarative sentence that re-makes your point. You may also like acceptance speech examples .
School Demonstration Speech Example

Size: 99 KB
School Valedictory Speech Example

Size: 110 KB
Making a speech if you’re a middle school student is certainly not easy. So we’ve compiled some sample speech templates and examples for you to use. Good luck with your speech writing!
Middle School Speech Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a middle school speech for a new student orientation
2. Help me write a middle school speech for our annual sports day
Learning Goals
- Use this rubric to self-assess your persuasive speech as you work on it.
Persuasive Speech Rubric
No Alignments yet.
Cite this work
- Varsity Tutors
- K-5 Subjects
- Study Skills
- All AP Subjects
- AP Calculus
- AP Chemistry
- AP Computer Science
- AP Human Geography
- AP Macroeconomics
- AP Microeconomics
- AP Statistics
- AP US History
- AP World History
- All Business
- Business Calculus
- Microsoft Excel
- Supply Chain Management
- All Humanities
- Essay Editing
- All Languages
- Mandarin Chinese
- Portuguese Chinese
- Sign Language
- All Learning Differences
- Learning Disabilities
- Special Education
- College Math
- Common Core Math
- Elementary School Math
- High School Math
- Middle School Math
- Pre-Calculus
- Trigonometry
- All Science
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- All Engineering
- Chemical Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science
- Electrical Engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Materials Science & Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Thermodynamics
- Biostatistics
- College Essays
- High School
- College & Adult
- 1-on-1 Private Tutoring
- Online Tutoring
- Instant Tutoring
- Pricing Info
- All AP Exams
- ACT Tutoring
- ACT Reading
- ACT Science
- ACT Writing
- SAT Tutoring
- SAT Reading
- SAT Writing
- GRE Tutoring
- NCLEX Tutoring
- Real Estate License
- And more...
- StarCourses
- Beginners Coding
- Early Childhood
- For Schools Overview
- High-Dosage Tutoring
- Free 24/7 Tutoring & Classes
- Live Learning Platform
- Learning Outcomes
- About The Tutors
- Talk with Our Team
- Reviews & Testimonials
- Press & Media Coverage
- Tutor/Instructor Jobs
- Corporate Solutions
- About Nerdy
- Become a Tutor

- Book Reports
- Children’s Literature
- Interdisciplinary
- Just for Fun
- Literature (Prose)
- Professional Resources
- Reading/Literacy
- Shakespeare
- Study Guides
- Technology Integration
- Young Adult Literature
Middle School Persuasive Writing
| Elementary Persuasive Writing | | Middle School Persuasive Writing | | High School Persuasive Writing |
Can't Complain? Writing About Pet Peeves How can students express their complaints in articulate and constructive ways? In this lesson, students read the New York Times "Complaint Box" series and use descriptive and persuasive writing strategies to communicate their own pet peeves succinctly and productively.
Decoding text types: One of these things is not like the others This blog explains the difference between opinion writing, persuasive writing, and argument.
Developing Persuasive Writing Strategies This strategy guide describes the techniques used in effective persuasive writing and shares activities you can use to help students understand and use persuasion in their writing and critical thinking.
Don't Throw Away that Junk Mail! Students use old junk mail to identify persuasive techniques used to attract and hold the reader's attention.
Logical fallacies Definitions and examples of faulty thinking.
Making an Argument: Effective use of Transition Words Students explore and understand the use of transition words in context and write their own persuasive essay using transition words. Includes printable handout. This lesson is designed for grades 5-8.
Movie Trailers As Persuasive Texts This page is a resource for teachers who wish to consider using trailers to teach students about persuasive texts and techniques.
Persuade Me Students analyze the persuasive techniques found in junk mail. Designed for grades 6-8.
Persuasive Writing: Beyond the Three Reasons Nine learning activities to develop persuasive writing skills. Designed for middle school.
Persuasive Writing Prompts 100 prompts for a range from middle to high school.
Pictures and Slogans Persuade an Audience! Designed for 6-9, this unit asks students to examine persuasive techniques in advertising.
Techniques of Persuasive Presentations — Ebony, the Elephant Calf Students watch a short, downloadable video segment about elephants and identify the techniques used to persuade listeners to feel certain ways about what they see. This lesson is designed for grades 6-8. It includes support materials and a suggestion for assessment.

Persuasion Rubric

About this printout
Use this rubric to assess the effectiveness of a student's essay, speech, poster, or any type of assignment that incorporates persuasion.
Teaching with this printout
More ideas to try, related resources.
Grading rubrics can be of great benefit to both you and your students. For you, a rubric saves time and decreases subjectivity. Specific criteria are explicitly stated, facilitating the grading process and increasing your objectivity. For students, the use of grading rubrics helps them meet or exceed expectations, to view the grading process as being “fair,” and helps them set goals for future learning. In order to help your students meet or exceed expectations of the assignment, be sure to discuss the rubric with your students when you assign a persuasion project. It is helpful to show them examples of pieces that meet and do not meet the expectations. As an added benefit, because the criteria are explicitly stated in the rubric, the use of it decreases the likelihood that students will be confused about the grade they receive. The explicitness of the expectations helps students know exactly why they lost points on the assignment and aids them in setting goals for future improvement. Use the Visuals/Delivery category to grade audio and visual elements in speeches, PowerPoint presentations, blogs, posters, skits, podcasts, or any other assignment where visuals and delivery play roles. If your assignment does not require speech or visuals, simply disregard this part of the rubric.
- Routinely have students score peers’ work using the rubric as the assessment tool. This increases their level of awareness of the traits that distinguish successful persuasive projects from those that fail to meet the criteria.
- Alter some expectations or add additional traits on the rubric as needed. For example, if the assignment is to create a persuasive podcast, criteria such as articulation, communication, sound effects, and audio clarity may be added. You may also adapt the criteria to make it more rigorous for advanced learners and less stringent for lower level learners. In addition, you may want to include content-specific criteria for your subject area.
- After you and your students have used the rubric, have them work in groups to make suggested alterations to the rubric to more precisely match their needs or the parameters of a specific persuasive assignment. For example, if you wanted them to work in cooperative groups to write and present persuasive skits, possible criteria could include teamwork and the length of the skit.
- Lesson Plans
- Student Interactives
- Strategy Guides
Through a classroom game and resource handouts, students learn about the techniques used in persuasive oral arguments and apply them to independent persuasive writing activities.
The Persuasion Map is an interactive graphic organizer that enables students to map out their arguments for a persuasive essay or debate.
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K
- Chess (Gr. 1-4)
- TV (Gr. 1-4)
- Metal Detectors (Gr. 2-6)
- Tetris (Gr. 2-6)
- Seat Belts (Gr. 2-6)
- The Coliseum (Gr. 2-6)
- The Pony Express (Gr. 2-6)
- Wintertime (Gr. 2-6)
- Reading (Gr. 3-7)
- Black Friday (Gr. 3-7)
- Hummingbirds (Gr. 3-7)
- Worst Game Ever? (Gr. 4-8)
- Carnivorous Plants (Gr. 4-8)
- Google (Gr. 4-8)
- Honey Badgers (Gr. 4-8)
- Hyperinflation (Gr. 4-8)
- Koko (Gr. 4-8)
- Mongooses (Gr. 5-9)
- Trampolines (Gr. 5-9)
- Garbage (Gr. 5-9)
- Maginot Line (Gr. 5-9)
- Asian Carp (Gr. 5-9)
- Tale of Two Countries (Gr. 6-10)
- Kevlar (Gr. 7-10)
- Tigers (Gr. 7-11)
- Statue of Liberty (Gr. 8-10)
- Submarines (Gr. 8-12)
- Castles (Gr. 9-13)
- Gutenberg (Gr. 9-13)
- Author's Purpose Practice 1
- Author's Purpose Practice 2
- Author's Purpose Practice 3
- Fact and Opinion Practice 1
- Fact and Opinion Practice 2
- Fact and Opinion Practice 3
- Idioms Practice Test 1
- Idioms Practice Test 2
- Figurative Language Practice 1
- Figurative Language Practice 2
- Figurative Language Practice 3
- Figurative Language Practice 4
- Figurative Language Practice 5
- Figurative Language Practice 6
- Figurative Language Practice 7
- Figurative Language Practice 8
- Figurative Language Practice 9
- Figurative Language of Edgar Allan Poe
- Figurative Language of O. Henry
- Figurative Language of Shakespeare
- Genre Practice 1
- Genre Practice 2
- Genre Practice 3
- Genre Practice 4
- Genre Practice 5
- Genre Practice 6
- Genre Practice 7
- Genre Practice 8
- Genre Practice 9
- Genre Practice 10
- Irony Practice 1
- Irony Practice 2
- Irony Practice 3
- Making Inferences Practice 1
- Making Inferences Practice 2
- Making Inferences Practice 3
- Making Inferences Practice 4
- Making Inferences Practice 5
- Main Idea Practice 1
- Main Idea Practice 2
- Point of View Practice 1
- Point of View Practice 2
- Text Structure Practice 1
- Text Structure Practice 2
- Text Structure Practice 3
- Text Structure Practice 4
- Text Structure Practice 5
- Story Structure Practice 1
- Story Structure Practice 2
- Story Structure Practice 3
- Author's Purpose
- Characterizations
- Context Clues
- Fact and Opinion
- Figurative Language
- Grammar and Language Arts
- Poetic Devices
- Point of View
- Predictions
- Reading Comprehension
- Story Structure
- Summarizing
- Text Structure
- Character Traits
- Common Core Aligned Unit Plans
- Teacher Point of View
- Teaching Theme
- Patterns of Organization
- Project Ideas
- Reading Activities
- How to Write Narrative Essays
- How to Write Persuasive Essays
- Narrative Essay Assignments
- Narrative Essay Topics
- Persuasive Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics
- Rubrics for Writing Assignments
- Learn About Sentence Structure
- Grammar Worksheets
- Noun Worksheets
- Parts of Speech Worksheets
- Punctuation Worksheets
- Sentence Structure Worksheets
- Verbs and Gerunds
- Examples of Allitertion
- Examples of Hyperbole
- Examples of Onomatopoeia
- Examples of Metaphor
- Examples of Personification
- Examples of Simile
- Figurative Language Activities
- Figurative Language Examples
- Figurative Language Poems
- Figurative Language Worksheets
- Learn About Figurative Language
- Learn About Poetic Devices
- Idiom Worksheets
- Online Figurative Language Tests
- Onomatopoeia Worksheets
- Personification Worksheets
- Poetic Devices Activities
- Poetic Devices Worksheets
- About This Site
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Understanding CCSS Standards
- What's New?
Ereading Worksheets
Free reading worksheets, activities, and lesson plans., site navigation.
- Learn About Author’s Purpose
- Author’s Purpose Quizzes
- Character Types Worksheets and Lessons
- List of Character Traits
- Differentiated Reading Instruction Worksheets and Activities
- Fact and Opinion Worksheets
- Irony Worksheets
- Animal Farm Worksheets
- Literary Conflicts Lesson and Review
- New Home Page Test
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 2 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 5 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 6 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 10 Worksheet
- Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass
- Sister Carrie
- The Count of Monte Cristo
- The Odyssey
- The War of the Worlds
- The Wizard of Oz
- Mood Worksheets
- Context Clues Worksheets
- Inferences Worksheets
- Main Idea Worksheets
- Making Predictions Worksheets
- Nonfiction Passages and Functional Texts
- Setting Worksheets
- Summarizing Worksheets and Activities
- Short Stories with Questions
- Story Structure Activities
- Story Structure Worksheets
- Tone Worksheets
- Types of Conflict Worksheets
- Reading Games
- Figurative Language Poems with Questions
- Hyperbole and Understatement Worksheets
- Simile and Metaphor Worksheets
- Simile Worksheets
- Hyperbole Examples
- Metaphor Examples
- Personification Examples
- Simile Examples
- Understatement Examples
- Idiom Worksheets and Tests
- Poetic Devices Worksheets & Activities
- Alliteration Examples
- Allusion Examples
- Onomatopoeia Examples
- Onomatopoeia Worksheets and Activities
- Genre Worksheets
- Genre Activities
- Capitalization Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Contractions Worksheets and Activities
- Double Negative Worksheets
- Homophones & Word Choice Worksheets
- ‘Was’ or ‘Were’
- Simple Subjects & Predicates Worksheets
- Subjects, Predicates, and Objects
- Clauses and Phrases
- Type of Sentences Worksheets
- Sentence Structure Activities
- Comma Worksheets and Activities
- Semicolon Worksheets
- End Mark Worksheets
- Noun Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Verb Worksheets and Activities
- Pronoun Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Adverbs & Adjectives Worksheets, Lessons, & Tests
- Preposition Worksheets and Activities
- Conjunctions Worksheets and Activities
- Interjections Worksheets
- Parts of Speech Activities
- Verb Tense Activities
- Past Tense Worksheets
- Present Tense Worksheets
- Future Tense Worksheets
- Point of View Activities
- Point of View Worksheets
- Teaching Point of View
- Cause and Effect Example Paragraphs
- Chronological Order
- Compare and Contrast
- Order of Importance
- Problem and Solution
- Text Structure Worksheets
- Text Structure Activities
- Essay Writing Rubrics
- Narrative Essay Topics and Story Ideas
- Narrative Essay Worksheets & Writing Assignments
- Persuasive Essay and Speech Topics
Persuasive Essay Worksheets & Activities
- Writing Narrative Essays and Short Stories
- Writing Persuasive Essays
- All Reading Worksheets
- Understanding Common Core State Standards
- Remote Learning Resources for Covid-19 School Closures
- What’s New?
- Ereading Worksheets | Legacy Versions
- Online Figurative Language Practice
- Online Genre Practice Tests
- Online Point of View Practice Tests
- 62 School Project Ideas
- 2nd Grade Reading Worksheets
- 3rd Grade Reading Worksheets
- 4th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 5th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 6th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 7th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 8th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 9th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 10th Grade Reading Worksheets
- Membership Billing
- Membership Cancel
- Membership Checkout
- Membership Confirmation
- Membership Invoice
- Membership Levels
- Your Profile
Want Updates?
84 comments.
Thank you so much. This has truly helped me in my exams and throughout the beneficial journey of my school year.
Ellen Davis
How will I be able to check my work, when I print it out to work on them? Where are the answers?
I guess it depends on what you are working on. On what are you working?
Kareema Coles
Ummm the pdf version is not working…is the link still valid?
Which link?
This is an amazing website with fabulous ideas and printable ready to go lessons!!! Thank you so much! I wish I could meet you!!!
Thank you very much for this amazing resource and great ideas. They are extremely comprehensive and well designed. Thank you very much for your kind consideration and not adding a Price-tag to your valuable resources. Highly appreciated.
Sandra Conner
Thank you so much for sharing your knowledge and your work with us. As teachers, we are always in need of fresh material. I teach college level creative writing classes, and your worksheets help my students. Sometimes I change the essay topics to fit their particular age group or interest, but having these examples laid out for us and made available for use in our classrooms is wonderful.
Lifesaver! Thank you for the great ideas and guidance. I am a new teacher, and finding this site has made a true turn around in my instruction. Thank you, thank you, thank you!!!
Thank you for these great step by step resources
Macca Malbrán
Despite all the negative comments above, you should keep up for the ones (like me) who are absolutely grateful for these material.
Thanks for sharing! Best.
I give this website 3stares only for the info but in general 1star
I give your comment 0 stars because your position lacks support or evidence of any kind. Complete some of these worksheets and begin your argument again.
that’s stupid from where do u get the worksheets
I wrote them.
I did not see any activities that required the student to write an entire essay.
https://www.ereadingworksheets.com/writing/persuasive-essay-topics/
Lamar Mohamed
Thank you for this information! They helped me in my exam so much!
These are fantastic resources! Thank you so much for sharing them. I only wish I had found them earlier in the school year!
There’s always next year…
Thank you so much for all you do for teachers. I love an use practically everything on your Website!
That’s awesome. Thanks for visiting my website.
I really like this website
Shenard McDougal
How can a teacher get the answers to the worksheets?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe Now
Popular content.
- Author's Purpose Worksheets
- Characterization Worksheets
- Common Core Lesson and Unit Plans
- Online Reading Practice Tests
- Plot Worksheets
- Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- Summary Worksheets
- Theme Worksheets
New and Updated Pages
- Capitalization Worksheets
- Contractions Worksheets
- Double Negatives Worksheets
- Homophones & Word Choice Worksheets
BECOME A MEMBER!

Start Here: Teaching Middle School Public Forum

In Public Forum Debate , students work in pairs of two to debate both sides of a topic. Public Forum is one of the most popular events and is a great entry point for new students and judges.
Topics are based on current events and change frequently, which gives students the opportunity to learn about a variety of subjects and keeps debates exciting and new.
Students present prepared cases, then engage in rebuttal and questioning periods with limited prep.
Students Will Be Able To:
- Write a persuasive speech that features complete arguments with a claim, data, warrant, and impact.
- Present information, findings, and supporting evidence clearly, concisely, and logically such that listeners can follow the line of reasoning.
- Find, cut, cite, and organize evidence that supports their claims.
- Evaluate a speaker’s point of view, reasoning, and use of evidence and rhetoric, identifying any fallacious reasoning or exaggerated or distorted evidence.
- Listen effectively and respond to attacks against their arguments with limited prep using logic and/or evidence.
- Complete a full Public Forum round.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Enter your email to access a sample of our “Start Here: Teaching Middle School Public Forum” collection.
100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
There is a small but important difference between planning a persuasive speech and writing a persuasive essay. First, if you are planning a persuasive speech, you should think about a topic that can engage your audience. For this reason, you may want to consider a few topics before settling on the one that allows you to be more descriptive and entertaining.
Another important factor when picking a persuasive speech topic is to choose one that can provoke your audience. If you stir up a little emotion in your audience members, you'll keep their attention. The list below is provided to help you brainstorm. Choose a topic from this list or use the list to generate an idea of your own.
- Studying martial arts is good for mind and health.
- Competitive sports can teach us about life.
- Reality shows are exploiting people.
- Community service should be a graduation requirement for all high school students.
- The characteristics that make a person a hero.
- It's important to grow things in a garden.
- Violent video games are dangerous.
- Lyrics in a song can impact our lives.
- Traveling and studying abroad are positive experiences.
- Journal writing is therapeutic.
- You should spend time with your grandparents.
- A laptop is better than a tablet.
- Religion and science can go hand in hand.
- School uniforms are good.
- All-female colleges and all-male colleges are bad.
- Multiple choice tests are better than essay tests .
- We should not spend money on space exploration.
- Open-book tests are as effective as closed-book tests.
- Security cameras keep us safer.
- Parents should have access to students' grades.
- Small classes are better than big classes.
- You need to start saving for retirement now.
- Credit cards are harmful to college students.
- We should have a royal family.
- We should protect endangered animals.
- Texting while driving is dangerous.
- You can write a novel.
- Recycling should be required in the U.S.
- State colleges are better than private colleges.
- Private colleges are better than state colleges.
- We should do away with penny coins.
- Fast food containers hurt the environment.
- Plastic straws are harmful to the environment.
- You can eat and enjoy healthy snacks.
- You can become a millionaire.
- Dogs are better pets than cats.
- You should own a bird.
- It's unethical to keep birds in cages.
- Liberal arts degrees prepare graduates to be better workers than other degrees.
- Hunting animals should be banned.
- Football is a dangerous sport.
- School days should start later.
- Night school is better than day school.
- Technical training is better than a college degree.
- Immigration laws should be more lenient.
- Students should be able to choose their schools.
- Everyone should learn to play a musical instrument.
- Grass lawns should be prohibited.
- Sharks should be protected.
- We should do away with cars and go back to horse and carriage for transportation.
- We should use more wind power.
- We should pay more taxes.
- We should do away with taxes.
- Teachers should be tested like students.
- We should not interfere in the affairs of other countries.
- Every student should join a club.
- Homeschooling is better than traditional schooling.
- People should stay married for life.
- Smoking in public should be illegal.
- College students should live on campus .
- Parents should let students fail.
- Giving to charity is good.
- Education makes us happier people.
- The death penalty should be outlawed.
- Bigfoot is real.
- We should increase train travel to save the environment.
- We should read more classic books.
- Fame is bad for young children.
- Athletes should stay loyal to teams.
- We should reform our prisons.
- Juvenile offenders should not go to boot camps.
- Abraham Lincoln was the best president.
- Abraham Lincoln gets too much credit.
- Students should be allowed to have cell phones in elementary, middle, and high school.
- College student-athletes should be paid for playing.
- Elderly citizens on fixed income should receive free public transportation.
- Colleges and universities should be free to attend.
- All American citizens should complete one year of community service.
- Students should be required to take Spanish classes.
- Every student should be required to learn at least one foreign language .
- Marijuana should be legal for recreational use nationwide.
- Commercial testing of products on animals should no longer be allowed.
- High school students should be required to participate in at least one team sport.
- The drinking age in the U.S. should be 25.
- Replacing fossil fuels with cheaper alternative energy options should be mandated.
- Churches need to contribute their share of taxes.
- The Cuba embargo should be maintained by the U.S.
- America should replace income taxes with a nationwide flat tax.
- Once they reach the age of 18, all U.S. citizens should be automatically registered to vote .
- Doctor-assisted suicide should be legal.
- Spammers—people who bombard the internet with unsolicited email—should be banned from sending junk mail.
- Every automobile driver should be required to take a new driver's test every three years.
- Electroshock treatment is not a humane form of therapy.
- Global warming is not real.
- Single-parent adoption should be encouraged and promoted.
- Gun companies should be held accountable for gun crimes.
- Human cloning is not moral.
- Religion does not belong in public education.
- Juveniles should not be tried as adults.
- American workers should be guaranteed a three-day weekend by law.
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- Middle School Debate Topics
- 40 Writing Topics for Argumentative and Persuasive Essays
- High School Debate Topics
- Controversial Speech Topics
- How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Preparing an Argument Essay: Exploring Both Sides of an Issue
- 30 Writing Topics: Persuasion
- Speech Topics to Meet Oral Communication Standards
- The Best Summer Plans for High School Students
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- 50 Topics for Impromptu Student Speeches
- 12 Interesting Ethical Topics for Essay Papers
- Impromptu Speech Activities
- How Much Damage Do Bad Grades Do?
- What Is a Blue Book?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reason 3 ( Provide one reason as to why listeners should act or think the way your thesis suggests.) Example 1 - Support for the reason given above. Example 2 - Support for the reason given above. The most important part of a persuasive speech is the conclusion, second to the introduction and thesis statement.
middle school (6-8) persuasive/argument writing prompts information contained herein belongs exc duplication of this material is strictly forbidden without the express prior written duplicate one (1) copy of this material exclusively for your personal use. this material non or to limit any legal or equitable remedies appurtenant hereto.
Ideas for your persuasive speech outline 1. Structure of your persuasive speech. The opening and closing of speech are the most important. Consider these carefully when thinking about your persuasive speech outline. A strong opening ensures you have the audience's attention from the start and gives them a positive first impression of you.
Harvey Milk's "The Hope" Speech. Sample lines: "Some people are satisfied. And some people are not. You see there is a major difference—and it remains a vital difference—between a friend and a gay person, a friend in office and a gay person in office. Gay people have been slandered nationwide.
Here are Melissa's simple steps for using this debate-style discussion strategy in your classroom: Give students a thought-provoking or humorous prompt. Play music as students think, research, jot notes, and (if possible) walk around the room. Stop the music and have students get into groups of two or three.
Before your students use this tool independently, model its use for them. Choose a simple topic (such as, "Sixth Grade is the Best Grade" or "Why Our Lunch Period Should be Longer"). Then, fill in the Persuasion Map while discussing the process aloud, displaying the tool so that all students can see it. Review students' completed maps ...
Key Takeaways: For middle school students, acquiring the critical-thinking and communication skills they need to evaluate both sides of a debate and write persuasive essays isn't always easy. With Junior Scholastic's free Social Studies Debate Kit, learning how to debate and craft an effective argument essay will be an exciting and ...
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you. You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your ...
10. Argue why homework should be limited to weekends only. 101 Writing Prompts for Middle School Students. 11. Convince your friends to sign up to be in the talent show. 12. Persuade your family to have a "no-screen" day every week. 13. Write a letter persuading your parents to buy you a new pet.
Persuasion Map: Students can use this online interactive tool to map out an argument for their persuasive essay.: Persuasive Strategy Presentation: This handy PowerPoint presentation helps students master the definition of each strategy used in persuasive writing.: Check the Strategies: Students can apply what they know about persuasive writing strategies by evaluating a persuasive piece and ...
Have them write a 6-8 minute speech in outline form to persuade the class. Each student will then deliver this speech in front of the class while the rest of the students take notes and prepare to give the speaker feedback on the speech. The voice and the body are the best tools — every student is a natural persuader!
ÐÏ à¡± á> þÿ :
Of course it's much easier to use persuasive speech if you pick a statement that you strongly agree or disagree with, but if you're struggling for ideas then take a look at the following ideas. 100 Examples of Persuasive Speech Topics. 1: The death penalty should be removed in all states. 2. The modern world is causing global warming to ...
Persuasive Writing Differs From Argument Writing. At the middle school level, students need to understand persuasive and argument writing in a concrete way. Therefore, I keep it simple by explaining that both types of writing involve a claim. However, in persuasive writing, the supporting details are based on opinions, feelings, and emotions ...
If it really cannot be avoided, then make an outline as to help you keep track of where you are heading in the speech. You may also see on how to make a leadership speech if you're into that sort of thing. 4. Illustrate. Show and don't tell. You have to make them visualize the scene and not just tell them about it.
A rubric in student language written for middle school students to self-assess a persuasive speech Learning Goals. Use this rubric to self-assess your persuasive speech as you work on it. title "Persuasive Speech Rubric" 2024 by Barbara Beard under license "Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial" Version History Cite this work
This lesson is designed for grades 5-8. This page is a resource for teachers who wish to consider using trailers to teach students about persuasive texts and techniques. Students analyze the persuasive techniques found in junk mail. Designed for grades 6-8. Nine learning activities to develop persuasive writing skills. Designed for middle school.
Routinely have students score peers' work using the rubric as the assessment tool. This increases their level of awareness of the traits that distinguish successful persuasive projects from those that fail to meet the criteria. Alter some expectations or add additional traits on the rubric as needed. For example, if the assignment is to ...
Students practice arguing both sides of a four different topics. Arguing Both Sides Worksheet 2 - Here's another persuasive essay worksheet to help students practice approaching writing prompts logically. In this double-sided worksheet students practice arguing both sides of a selection of topics.
Teaching Persuasive Writing. In this session, participants visit two middle-level classrooms to see how teachers can help young writers develop effective and authentic persuasive pieces based on their own experiences and interests - for example, using cell phones in schools or altering their homework schedule. View Transcript.
Public Forum is one of the most popular events and is a great entry point for new students and judges. Topics are based on current events and change frequently, which gives students the opportunity to learn about a variety of subjects and keeps debates exciting and new. Students present prepared cases, then engage in rebuttal and questioning ...
We should pay more taxes. We should do away with taxes. Teachers should be tested like students. We should not interfere in the affairs of other countries. Every student should join a club. Homeschooling is better than traditional schooling. People should stay married for life. Smoking in public should be illegal.
Learning how to write persuasively is an essential part of your students' literary development. There are structures to adopt, and certain vocabulary has to be used to create the desired effect. Our persuasive text planning template is a fantastic resource to help engage your students and get them familiar with the persuasive writing form. This resource is set out in the persuasive structure ...