
What (Exactly) Is A Research Proposal?
A simple explainer with examples + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Whether you’re nearing the end of your degree and your dissertation is on the horizon, or you’re planning to apply for a PhD program, chances are you’ll need to craft a convincing research proposal . If you’re on this page, you’re probably unsure exactly what the research proposal is all about. Well, you’ve come to the right place.
Overview: Research Proposal Basics
- What a research proposal is
- What a research proposal needs to cover
- How to structure your research proposal
- Example /sample proposals
- Proposal writing FAQs
- Key takeaways & additional resources
What is a research proposal?
Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it’s worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face).
The most important word here is “ convince ” – in other words, your research proposal needs to sell your research idea (to whoever is going to approve it). If it doesn’t convince them (of its suitability and manageability), you’ll need to revise and resubmit . This will cost you valuable time, which will either delay the start of your research or eat into its time allowance (which is bad news).

What goes into a research proposal?
A good dissertation or thesis proposal needs to cover the “ what “, “ why ” and” how ” of the proposed study. Let’s look at each of these attributes in a little more detail:
Your proposal needs to clearly articulate your research topic . This needs to be specific and unambiguous . Your research topic should make it clear exactly what you plan to research and in what context. Here’s an example of a well-articulated research topic:
An investigation into the factors which impact female Generation Y consumer’s likelihood to promote a specific makeup brand to their peers: a British context
As you can see, this topic is extremely clear. From this one line we can see exactly:
- What’s being investigated – factors that make people promote or advocate for a brand of a specific makeup brand
- Who it involves – female Gen-Y consumers
- In what context – the United Kingdom
So, make sure that your research proposal provides a detailed explanation of your research topic . If possible, also briefly outline your research aims and objectives , and perhaps even your research questions (although in some cases you’ll only develop these at a later stage). Needless to say, don’t start writing your proposal until you have a clear topic in mind , or you’ll end up waffling and your research proposal will suffer as a result of this.
Need a helping hand?
As we touched on earlier, it’s not good enough to simply propose a research topic – you need to justify why your topic is original . In other words, what makes it unique ? What gap in the current literature does it fill? If it’s simply a rehash of the existing research, it’s probably not going to get approval – it needs to be fresh.
But, originality alone is not enough. Once you’ve ticked that box, you also need to justify why your proposed topic is important . In other words, what value will it add to the world if you achieve your research aims?
As an example, let’s look at the sample research topic we mentioned earlier (factors impacting brand advocacy). In this case, if the research could uncover relevant factors, these findings would be very useful to marketers in the cosmetics industry, and would, therefore, have commercial value . That is a clear justification for the research.
So, when you’re crafting your research proposal, remember that it’s not enough for a topic to simply be unique. It needs to be useful and value-creating – and you need to convey that value in your proposal. If you’re struggling to find a research topic that makes the cut, watch our video covering how to find a research topic .

It’s all good and well to have a great topic that’s original and valuable, but you’re not going to convince anyone to approve it without discussing the practicalities – in other words:
- How will you actually undertake your research (i.e., your methodology)?
- Is your research methodology appropriate given your research aims?
- Is your approach manageable given your constraints (time, money, etc.)?
While it’s generally not expected that you’ll have a fully fleshed-out methodology at the proposal stage, you’ll likely still need to provide a high-level overview of your research methodology . Here are some important questions you’ll need to address in your research proposal:
- Will you take a qualitative , quantitative or mixed -method approach?
- What sampling strategy will you adopt?
- How will you collect your data (e.g., interviews, surveys, etc)?
- How will you analyse your data (e.g., descriptive and inferential statistics , content analysis, discourse analysis, etc, .)?
- What potential limitations will your methodology carry?
So, be sure to give some thought to the practicalities of your research and have at least a basic methodological plan before you start writing up your proposal. If this all sounds rather intimidating, the video below provides a good introduction to research methodology and the key choices you’ll need to make.
How To Structure A Research Proposal
Now that we’ve covered the key points that need to be addressed in a proposal, you may be wondering, “ But how is a research proposal structured? “.
While the exact structure and format required for a research proposal differs from university to university, there are four “essential ingredients” that commonly make up the structure of a research proposal:
- A rich introduction and background to the proposed research
- An initial literature review covering the existing research
- An overview of the proposed research methodology
- A discussion regarding the practicalities (project plans, timelines, etc.)
In the video below, we unpack each of these four sections, step by step.
Research Proposal Examples/Samples
In the video below, we provide a detailed walkthrough of two successful research proposals (Master’s and PhD-level), as well as our popular free proposal template.
Proposal Writing FAQs
How long should a research proposal be.
This varies tremendously, depending on the university, the field of study (e.g., social sciences vs natural sciences), and the level of the degree (e.g. undergraduate, Masters or PhD) – so it’s always best to check with your university what their specific requirements are before you start planning your proposal.
As a rough guide, a formal research proposal at Masters-level often ranges between 2000-3000 words, while a PhD-level proposal can be far more detailed, ranging from 5000-8000 words. In some cases, a rough outline of the topic is all that’s needed, while in other cases, universities expect a very detailed proposal that essentially forms the first three chapters of the dissertation or thesis.
The takeaway – be sure to check with your institution before you start writing.
How do I choose a topic for my research proposal?
Finding a good research topic is a process that involves multiple steps. We cover the topic ideation process in this video post.
How do I write a literature review for my proposal?
While you typically won’t need a comprehensive literature review at the proposal stage, you still need to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the key literature and are able to synthesise it. We explain the literature review process here.
How do I create a timeline and budget for my proposal?
We explain how to craft a project plan/timeline and budget in Research Proposal Bootcamp .
Which referencing format should I use in my research proposal?
The expectations and requirements regarding formatting and referencing vary from institution to institution. Therefore, you’ll need to check this information with your university.
What common proposal writing mistakes do I need to look out for?
We’ve create a video post about some of the most common mistakes students make when writing a proposal – you can access that here . If you’re short on time, here’s a quick summary:
- The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated).
- The research aims, objectives and questions don’t align.
- The research topic is not well justified.
- The study has a weak theoretical foundation.
- The research design is not well articulated well enough.
- Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
- Poor project planning and risk management.
- Not following the university’s specific criteria.
Key Takeaways & Additional Resources
As you write up your research proposal, remember the all-important core purpose: to convince . Your research proposal needs to sell your study in terms of suitability and viability. So, focus on crafting a convincing narrative to ensure a strong proposal.
At the same time, pay close attention to your university’s requirements. While we’ve covered the essentials here, every institution has its own set of expectations and it’s essential that you follow these to maximise your chances of approval.
By the way, we’ve got plenty more resources to help you fast-track your research proposal. Here are some of our most popular resources to get you started:
- Proposal Writing 101 : A Introductory Webinar
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : The Ultimate Online Course
- Template : A basic template to help you craft your proposal
If you’re looking for 1-on-1 support with your research proposal, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the proposal development process (and the entire research journey), step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
51 Comments
I truly enjoyed this video, as it was eye-opening to what I have to do in the preparation of preparing a Research proposal.
I would be interested in getting some coaching.
I real appreciate on your elaboration on how to develop research proposal,the video explains each steps clearly.
Thank you for the video. It really assisted me and my niece. I am a PhD candidate and she is an undergraduate student. It is at times, very difficult to guide a family member but with this video, my job is done.
In view of the above, I welcome more coaching.
Wonderful guidelines, thanks
This is very helpful. Would love to continue even as I prepare for starting my masters next year.
Thanks for the work done, the text was helpful to me
Bundle of thanks to you for the research proposal guide it was really good and useful if it is possible please send me the sample of research proposal
You’re most welcome. We don’t have any research proposals that we can share (the students own the intellectual property), but you might find our research proposal template useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-proposal-template/
Cheruiyot Moses Kipyegon
Thanks alot. It was an eye opener that came timely enough before my imminent proposal defense. Thanks, again
thank you very much your lesson is very interested may God be with you
I am an undergraduate student (First Degree) preparing to write my project,this video and explanation had shed more light to me thanks for your efforts keep it up.
Very useful. I am grateful.
this is a very a good guidance on research proposal, for sure i have learnt something
Wonderful guidelines for writing a research proposal, I am a student of m.phil( education), this guideline is suitable for me. Thanks
You’re welcome 🙂
Thank you, this was so helpful.
A really great and insightful video. It opened my eyes as to how to write a research paper. I would like to receive more guidance for writing my research paper from your esteemed faculty.
Thank you, great insights
Thank you, great insights, thank you so much, feeling edified
Wow thank you, great insights, thanks a lot
Thank you. This is a great insight. I am a student preparing for a PhD program. I am requested to write my Research Proposal as part of what I am required to submit before my unconditional admission. I am grateful having listened to this video which will go a long way in helping me to actually choose a topic of interest and not just any topic as well as to narrow down the topic and be specific about it. I indeed need more of this especially as am trying to choose a topic suitable for a DBA am about embarking on. Thank you once more. The video is indeed helpful.
Have learnt a lot just at the right time. Thank you so much.
thank you very much ,because have learn a lot things concerning research proposal and be blessed u for your time that you providing to help us
Hi. For my MSc medical education research, please evaluate this topic for me: Training Needs Assessment of Faculty in Medical Training Institutions in Kericho and Bomet Counties
I have really learnt a lot based on research proposal and it’s formulation
Thank you. I learn much from the proposal since it is applied
Your effort is much appreciated – you have good articulation.
You have good articulation.
I do applaud your simplified method of explaining the subject matter, which indeed has broaden my understanding of the subject matter. Definitely this would enable me writing a sellable research proposal.
This really helping
Great! I liked your tutoring on how to find a research topic and how to write a research proposal. Precise and concise. Thank you very much. Will certainly share this with my students. Research made simple indeed.
Thank you very much. I an now assist my students effectively.
Thank you very much. I can now assist my students effectively.
I need any research proposal
Thank you for these videos. I will need chapter by chapter assistance in writing my MSc dissertation
Very helpfull
the videos are very good and straight forward
thanks so much for this wonderful presentations, i really enjoyed it to the fullest wish to learn more from you
Thank you very much. I learned a lot from your lecture.
I really enjoy the in-depth knowledge on research proposal you have given. me. You have indeed broaden my understanding and skills. Thank you
interesting session this has equipped me with knowledge as i head for exams in an hour’s time, am sure i get A++
This article was most informative and easy to understand. I now have a good idea of how to write my research proposal.
Thank you very much.
Wow, this literature is very resourceful and interesting to read. I enjoyed it and I intend reading it every now then.
Thank you for the clarity
Thank you. Very helpful.
Thank you very much for this essential piece. I need 1o1 coaching, unfortunately, your service is not available in my country. Anyways, a very important eye-opener. I really enjoyed it. A thumb up to Gradcoach
What is JAM? Please explain.
Thank you so much for these videos. They are extremely helpful! God bless!
very very wonderful…
thank you for the video but i need a written example
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
The goal of a research proposal is twofold: to present and justify the need to study a research problem and to present the practical ways in which the proposed study should be conducted. The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews. They must provide persuasive evidence that a need exists for the proposed study. In addition to providing a rationale, a proposal describes detailed methodology for conducting the research consistent with requirements of the professional or academic field and a statement on anticipated outcomes and benefits derived from the study's completion.
Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005.
How to Approach Writing a Research Proposal
Your professor may assign the task of writing a research proposal for the following reasons:
- Develop your skills in thinking about and designing a comprehensive research study;
- Learn how to conduct a comprehensive review of the literature to determine that the research problem has not been adequately addressed or has been answered ineffectively and, in so doing, become better at locating pertinent scholarship related to your topic;
- Improve your general research and writing skills;
- Practice identifying the logical steps that must be taken to accomplish one's research goals;
- Critically review, examine, and consider the use of different methods for gathering and analyzing data related to the research problem; and,
- Nurture a sense of inquisitiveness within yourself and to help see yourself as an active participant in the process of conducting scholarly research.
A proposal should contain all the key elements involved in designing a completed research study, with sufficient information that allows readers to assess the validity and usefulness of your proposed study. The only elements missing from a research proposal are the findings of the study and your analysis of those findings. Finally, an effective proposal is judged on the quality of your writing and, therefore, it is important that your proposal is coherent, clear, and compelling.
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions:
- What do you plan to accomplish? Be clear and succinct in defining the research problem and what it is you are proposing to investigate.
- Why do you want to do the research? In addition to detailing your research design, you also must conduct a thorough review of the literature and provide convincing evidence that it is a topic worthy of in-depth study. A successful research proposal must answer the "So What?" question.
- How are you going to conduct the research? Be sure that what you propose is doable. If you're having difficulty formulating a research problem to propose investigating, go here for strategies in developing a problem to study.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failure to be concise . A research proposal must be focused and not be "all over the map" or diverge into unrelated tangents without a clear sense of purpose.
- Failure to cite landmark works in your literature review . Proposals should be grounded in foundational research that lays a foundation for understanding the development and scope of the the topic and its relevance.
- Failure to delimit the contextual scope of your research [e.g., time, place, people, etc.]. As with any research paper, your proposed study must inform the reader how and in what ways the study will frame the problem.
- Failure to develop a coherent and persuasive argument for the proposed research . This is critical. In many workplace settings, the research proposal is a formal document intended to argue for why a study should be funded.
- Sloppy or imprecise writing, or poor grammar . Although a research proposal does not represent a completed research study, there is still an expectation that it is well-written and follows the style and rules of good academic writing.
- Too much detail on minor issues, but not enough detail on major issues . Your proposal should focus on only a few key research questions in order to support the argument that the research needs to be conducted. Minor issues, even if valid, can be mentioned but they should not dominate the overall narrative.
Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sanford, Keith. Information for Students: Writing a Research Proposal. Baylor University; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences, Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Structure and Writing Style
Beginning the Proposal Process
As with writing most college-level academic papers, research proposals are generally organized the same way throughout most social science disciplines. The text of proposals generally vary in length between ten and thirty-five pages, followed by the list of references. However, before you begin, read the assignment carefully and, if anything seems unclear, ask your professor whether there are any specific requirements for organizing and writing the proposal.
A good place to begin is to ask yourself a series of questions:
- What do I want to study?
- Why is the topic important?
- How is it significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
- What problems will it help solve?
- How does it build upon [and hopefully go beyond] research already conducted on the topic?
- What exactly should I plan to do, and can I get it done in the time available?
In general, a compelling research proposal should document your knowledge of the topic and demonstrate your enthusiasm for conducting the study. Approach it with the intention of leaving your readers feeling like, "Wow, that's an exciting idea and I can’t wait to see how it turns out!"
Most proposals should include the following sections:
I. Introduction
In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project or it's the first step in getting approval to write a doctoral dissertation. Even if this is just a course assignment, treat your introduction as the initial pitch of an idea based on a thorough examination of the significance of a research problem. After reading the introduction, your readers should not only have an understanding of what you want to do, but they should also be able to gain a sense of your passion for the topic and to be excited about the study's possible outcomes. Note that most proposals do not include an abstract [summary] before the introduction.
Think about your introduction as a narrative written in two to four paragraphs that succinctly answers the following four questions :
- What is the central research problem?
- What is the topic of study related to that research problem?
- What methods should be used to analyze the research problem?
- Answer the "So What?" question by explaining why this is important research, what is its significance, and why should someone reading the proposal care about the outcomes of the proposed study?
II. Background and Significance
This is where you explain the scope and context of your proposal and describe in detail why it's important. It can be melded into your introduction or you can create a separate section to help with the organization and narrative flow of your proposal. Approach writing this section with the thought that you can’t assume your readers will know as much about the research problem as you do. Note that this section is not an essay going over everything you have learned about the topic; instead, you must choose what is most relevant in explaining the aims of your research.
To that end, while there are no prescribed rules for establishing the significance of your proposed study, you should attempt to address some or all of the following:
- State the research problem and give a more detailed explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction. This is particularly important if the problem is complex or multifaceted .
- Present the rationale of your proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing; be sure to answer the "So What? question [i.e., why should anyone care?].
- Describe the major issues or problems examined by your research. This can be in the form of questions to be addressed. Be sure to note how your proposed study builds on previous assumptions about the research problem.
- Explain the methods you plan to use for conducting your research. Clearly identify the key sources you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Describe the boundaries of your proposed research in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you plan to study, but what aspects of the research problem will be excluded from the study.
- If necessary, provide definitions of key concepts, theories, or terms.
III. Literature Review
Connected to the background and significance of your study is a section of your proposal devoted to a more deliberate review and synthesis of prior studies related to the research problem under investigation . The purpose here is to place your project within the larger whole of what is currently being explored, while at the same time, demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methodological approaches they have used, and what is your understanding of their findings and, when stated, their recommendations. Also pay attention to any suggestions for further research.
Since a literature review is information dense, it is crucial that this section is intelligently structured to enable a reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your proposed study in relation to the arguments put forth by other researchers. A good strategy is to break the literature into "conceptual categories" [themes] rather than systematically or chronologically describing groups of materials one at a time. Note that conceptual categories generally reveal themselves after you have read most of the pertinent literature on your topic so adding new categories is an on-going process of discovery as you review more studies. How do you know you've covered the key conceptual categories underlying the research literature? Generally, you can have confidence that all of the significant conceptual categories have been identified if you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations that are being made.
NOTE: Do not shy away from challenging the conclusions made in prior research as a basis for supporting the need for your proposal. Assess what you believe is missing and state how previous research has failed to adequately examine the issue that your study addresses. Highlighting the problematic conclusions strengthens your proposal. For more information on writing literature reviews, GO HERE .
To help frame your proposal's review of prior research, consider the "five C’s" of writing a literature review:
- Cite , so as to keep the primary focus on the literature pertinent to your research problem.
- Compare the various arguments, theories, methodologies, and findings expressed in the literature: what do the authors agree on? Who applies similar approaches to analyzing the research problem?
- Contrast the various arguments, themes, methodologies, approaches, and controversies expressed in the literature: describe what are the major areas of disagreement, controversy, or debate among scholars?
- Critique the literature: Which arguments are more persuasive, and why? Which approaches, findings, and methodologies seem most reliable, valid, or appropriate, and why? Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what an author says/does [e.g., asserts, demonstrates, argues, etc.].
- Connect the literature to your own area of research and investigation: how does your own work draw upon, depart from, synthesize, or add a new perspective to what has been said in the literature?
IV. Research Design and Methods
This section must be well-written and logically organized because you are not actually doing the research, yet, your reader must have confidence that you have a plan worth pursuing . The reader will never have a study outcome from which to evaluate whether your methodological choices were the correct ones. Thus, the objective here is to convince the reader that your overall research design and proposed methods of analysis will correctly address the problem and that the methods will provide the means to effectively interpret the potential results. Your design and methods should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
Describe the overall research design by building upon and drawing examples from your review of the literature. Consider not only methods that other researchers have used, but methods of data gathering that have not been used but perhaps could be. Be specific about the methodological approaches you plan to undertake to obtain information, the techniques you would use to analyze the data, and the tests of external validity to which you commit yourself [i.e., the trustworthiness by which you can generalize from your study to other people, places, events, and/or periods of time].
When describing the methods you will use, be sure to cover the following:
- Specify the research process you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results obtained in relation to the research problem. Don't just describe what you intend to achieve from applying the methods you choose, but state how you will spend your time while applying these methods [e.g., coding text from interviews to find statements about the need to change school curriculum; running a regression to determine if there is a relationship between campaign advertising on social media sites and election outcomes in Europe ].
- Keep in mind that the methodology is not just a list of tasks; it is a deliberate argument as to why techniques for gathering information add up to the best way to investigate the research problem. This is an important point because the mere listing of tasks to be performed does not demonstrate that, collectively, they effectively address the research problem. Be sure you clearly explain this.
- Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers and pitfalls in carrying out your research design and explain how you plan to address them. No method applied to research in the social and behavioral sciences is perfect, so you need to describe where you believe challenges may exist in obtaining data or accessing information. It's always better to acknowledge this than to have it brought up by your professor!
V. Preliminary Suppositions and Implications
Just because you don't have to actually conduct the study and analyze the results, doesn't mean you can skip talking about the analytical process and potential implications . The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you believe your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the subject area under investigation. Depending on the aims and objectives of your study, describe how the anticipated results will impact future scholarly research, theory, practice, forms of interventions, or policy making. Note that such discussions may have either substantive [a potential new policy], theoretical [a potential new understanding], or methodological [a potential new way of analyzing] significance. When thinking about the potential implications of your study, ask the following questions:
- What might the results mean in regards to challenging the theoretical framework and underlying assumptions that support the study?
- What suggestions for subsequent research could arise from the potential outcomes of the study?
- What will the results mean to practitioners in the natural settings of their workplace, organization, or community?
- Will the results influence programs, methods, and/or forms of intervention?
- How might the results contribute to the solution of social, economic, or other types of problems?
- Will the results influence policy decisions?
- In what way do individuals or groups benefit should your study be pursued?
- What will be improved or changed as a result of the proposed research?
- How will the results of the study be implemented and what innovations or transformative insights could emerge from the process of implementation?
NOTE: This section should not delve into idle speculation, opinion, or be formulated on the basis of unclear evidence . The purpose is to reflect upon gaps or understudied areas of the current literature and describe how your proposed research contributes to a new understanding of the research problem should the study be implemented as designed.
ANOTHER NOTE : This section is also where you describe any potential limitations to your proposed study. While it is impossible to highlight all potential limitations because the study has yet to be conducted, you still must tell the reader where and in what form impediments may arise and how you plan to address them.
VI. Conclusion
The conclusion reiterates the importance or significance of your proposal and provides a brief summary of the entire study . This section should be only one or two paragraphs long, emphasizing why the research problem is worth investigating, why your research study is unique, and how it should advance existing knowledge.
Someone reading this section should come away with an understanding of:
- Why the study should be done;
- The specific purpose of the study and the research questions it attempts to answer;
- The decision for why the research design and methods used where chosen over other options;
- The potential implications emerging from your proposed study of the research problem; and
- A sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship about the research problem.
VII. Citations
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used . In a standard research proposal, this section can take two forms, so consult with your professor about which one is preferred.
- References -- a list of only the sources you actually used in creating your proposal.
- Bibliography -- a list of everything you used in creating your proposal, along with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem.
In either case, this section should testify to the fact that you did enough preparatory work to ensure the project will complement and not just duplicate the efforts of other researchers. It demonstrates to the reader that you have a thorough understanding of prior research on the topic.
Most proposal formats have you start a new page and use the heading "References" or "Bibliography" centered at the top of the page. Cited works should always use a standard format that follows the writing style advised by the discipline of your course [e.g., education=APA; history=Chicago] or that is preferred by your professor. This section normally does not count towards the total page length of your research proposal.
Develop a Research Proposal: Writing the Proposal. Office of Library Information Services. Baltimore County Public Schools; Heath, M. Teresa Pereira and Caroline Tynan. “Crafting a Research Proposal.” The Marketing Review 10 (Summer 2010): 147-168; Jones, Mark. “Writing a Research Proposal.” In MasterClass in Geography Education: Transforming Teaching and Learning . Graham Butt, editor. (New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2015), pp. 113-127; Juni, Muhamad Hanafiah. “Writing a Research Proposal.” International Journal of Public Health and Clinical Sciences 1 (September/October 2014): 229-240; Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005; Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Punch, Keith and Wayne McGowan. "Developing and Writing a Research Proposal." In From Postgraduate to Social Scientist: A Guide to Key Skills . Nigel Gilbert, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), 59-81; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences , Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- << Previous: Writing a Reflective Paper
- Next: Generative AI and Writing >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How to Write a Research Proposal

Table of Contents

In academia, especially in social and behavioral sciences, writing a research proposal is an essential first step while planning a new research project. A research proposal is an initial pitch, or theoretical framework that serves to introduce the topic and anticipated results of a project, provide an overview of the methods to be used, and convince the reader that the proposed research can be conducted successfully. It is very essential to know how to write a research proposal, whether you are a student trying to fulfill course requirements or a researcher looking for funding for scholarly research. But writing a well-structured proposal is easier said than done.
To make things simpler for you, In this article, I explained the fundamentals of a research proposal, its structure, the steps involved in writing a research proposal, and common mistakes to avoid. Continue reading to gain a thorough understanding of the concept and purpose of a research proposal. This blog will also enable you to write the research proposal quickly, reducing the likelihood of rejection.
What is a Research Proposal?
In simpler terms, A research proposal is a document written to explain and justify your chosen research topic and the necessity to carry out that particular research by addressing the research problem. Likewise, a good research proposal should carry the proposed research's results and benefits, backed by convincing evidence.
Always keep your audience in mind while writing your research proposal. Your audience expects a concise summary and a detailed research methodology from you in the research proposal.
To begin, you must understand the purpose of a research proposal in order to effectively write a research proposal and also to receive swift approvals.
What is the purpose or importance of a research proposal?

A research proposal's purpose is to provide a detailed outline of the process that will be used to answer a specific research problem. Whereas the goal of the research proposal varies from person to person. In some cases, it may be to secure funding, while in others, it may be to obtain a meager approval from the committee or the supervisor to proceed with the research project. Regardless of your research proposal's end goal, you are supposed to write a research proposal that fulfills its intended purpose of presenting the best plan for your research.
While writing a research proposal, you should demonstrate how and why your proposed research is crucial for the domain, especially if it is social and behavioral sciences. It would help if you showed how your work is necessary by addressing some key points like:
- Bridging the gaps in the existing domain of research.
- Adding new and fresh perspectives to the existing understanding of the topic.
- Undervalued data in the current stats of the domain.
Furthermore, your research proposal must demonstrate that you, as an author, are capable of conducting the research and that the results will significantly contribute to the field of knowledge. To do so, include and explain your academic background and significance along with your previous accolades to demonstrate that you and your idea have academic merit.
What is the ideal length of a research proposal?
There are no hard and fast rules about how long a research proposal should be, and it varies dramatically from different institutions and publishers. However, as a standard domain practice, a research proposal is generally between 3000- 4000 words. A majority of globally reputed institutions follow the 3000- 3500 word limit.
Since the research proposal is written well before the research is conducted, you need to outline all the necessary elements your research will entail and accomplish. Once completed, your research proposal must resemble a concise version of a thesis or dissertation without results and a discussion section.
Structure of a research proposal

When you recognize a gap in the existing books of knowledge, you will address it by developing a research problem. A research problem is a question that researchers want to answer. It is the starting point for any research project, and it can be broad or narrow, depending on your objectives. Once you have a problem, it is followed by articulating a research question. After that, you can embark on the process of writing a research proposal.
Whether your goal is to secure funding or just approval, nevertheless, your research proposal needs to follow the basic outline of a research paper, containing all the necessary sections. Therefore, the structure of a research proposal closely resembles and follows a thesis or dissertation or any research paper. It should contain the following sections:
As is well known, the first thing that catches the reader's attention is a catchy title. Therefore, you should try to come up with a catchy yet informative title for your research proposal. Additionally, it should be concise and clear to reflect enough information about your research question.
To create a good research proposal, try writing the title to induce interest and information in your readers. Pro-Tip: Avoid using phrases such as “An investigation of …” or “A review of …” etc. . These have been overused for ages and may reflect your research title as a regular entry. On the other hand, concise and well-defined titles are always something readers like and stand higher chances for a proposal approval.
2. Abstract
Write your abstract in a brief yet very informative way. It should summarize the research you intend to conduct. Put an emphasis on the research question, research hypothesis , research design and methods, and the key findings of your proposed research.
If you wish to create a detailed proposal, try including a table of contents. It will help readers navigate easily and catch a glance at your entire proposal writing. Check out this guide if you want to learn more about how to write a research abstract for your scholarly research.
3. Introduction
All papers need a striking introduction to set the context of the research question. While framing your research proposal, ensure that the introduction provides rich background and relevant information about the research question.
Your entire research proposal hinges upon your research question. Thus, fit should come out clearly in the intro. Provide a general introduction without clear explanations, and it might render your research proposal insignificant.
Start your research proposal with the research problem, engage your audience with elements that relate to the problem, and then shed some light on the research question. Then, proceed with your study's evidence-based justification, and you'll find that the audience is sticking with your proposal narrative.
While writing your research proposal, ensure that you have covered the following:
- Purpose of your study.
- Background information and significance of your study.
- Introduction to the question, followed by an introduction to the paper.
- Brief mention of the critical issues that you will focus on.
- Declaration of independent and dependent variables of the research hypothesis. (You can learn more about the variables of the research hypothesis here .)
4. Literature Review
Writing a literature review is an important part of the research process. It provides the researcher with a summary of previous studies that have been conducted on a subject, and it helps the researcher determine what areas might need additional investigation in the existing research. Guidelines for the literature review vary for different institutions.
To effectively conduct and write a literature review check this guide . You can also use tools like SciSpace Copilot , our AI research assistant that makes reading academic papers a much easier task. You can use it to get simple explanations for complex text, maths, or tables. Copilot can be particularly helpful when you’re sifting through papers as you can quickly understand the abstract, get some context around the study, and identify if the paper is relevant to your project or not.
The literature review can either be kept as a separate section or incorporated into the introduction section. A separate section is always favorable and vital in gaining the research proposal approval. Additionally, a separate section for a literature review offers in-depth background data and demonstrates the relevance of your research question by emphasizing the gaps that have remained since the previous study.
Your research proposal’s literature review must contain and serve the following:

- To provide a reference of the studies and the researchers who have previously worked in the same domain.
- To provide the build path of your research question.
- To furnish a critical examination of the previous research works.
- To present the research issues about the current investigation.
- To convince the audience about the importance of your research in the relevant domain.
Need help you with your literature review? Try SciSpace Discover and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge.
Discover millions of peer-reviewed research articles and their full-text PDFs here. The articles can be compiled in one place and saved for later use to conduct a Hassel-free literature review.
5. Research Methodology
Research design and methods is the section where you explain how you will be conducting the proposed research. Ensure that you provide and include a sufficient explanation for the chosen methods. Additionally, include some points explaining how your chosen methods will help you get the desired or expected results.
Provide ample information to the readers about your research procedures so that they can easily comprehend the methodology and its expected results. Through your research methodology, you can easily show your audience whether the results you are promising can be achieved or not.
Most importantly, make sure the methodology you choose—whether qualitative or quantitative—is the best fit for your research. You should also be able to justify your choice.
Additionally, you should properly explain both the quantitative and qualitative components of your research if they are both used. For a qualitative approach, you must offer more elaborate and in-depth theoretical-based evidence. On the other hand, for the quantitative approach, you must describe the survey or lab setup, sample size, tools, and data collection methods.
Make sure you have plenty of explanations for the research methodology to support how you approached the research problem.
6. Expected Research Results
The expected research results section is where the researcher states what they expect to find in their research. The purpose of this section is to provide a summary of the study's goals, as well as give an overview of what the researcher expects will be found out. These results must orient the reader in sync with the methodology section and provide the answers to the research questions.
7. Limitations
The limitations section of an academic research paper is a section in which the writers of the paper discuss the weaknesses of their study. They do this by identifying problems with their methods, design, and implementation. This section should also discuss any other factors that may have affected the results or accuracy of the study. This section allows readers to understand how much confidence they can place in the findings, and how applicable they are to other contexts.
Furthermore, it will also showcase your honesty and complete understanding of the topic. Your research proposal’s limitations can include:
- Reasons for the chosen sample size.
- Justifications for the availability of resources at hand.
- Any unexpected error that might occur in the course of research as well.
8. Reference and Bibliography
If you don’t want your efforts to be tagged as plagiarized, ensure that you include the reference section at the end of the research proposal and follow the appropriate citation guidelines while citing different scholarly sources and various other researchers’ work.
For references, use both the in-text and footnote citations. List all the literature you have used to gather the information. However, in the bibliography, apart from including the references you have cited, you should include the sources that you didn't cite.
Reasons why research proposals get rejected

Research proposals often get rejected due to the smallest of mistakes. To keep the chances of getting your research proposal rejection at bay or a minimum, you should be aware of what grounds committees or supervisors often decide on rejection.
Follow through to understand the common reasons why research papers get rejected:
- The proposal stated a flawed hypothesis.
- The readers or the audience don't get convinced that the expected results will be anything new or unique.
- The research methodology lacks the details and may appear unrealistic.
- The research proposal lacks coherence in the problem statement, methodology, and results.
- Inadequate literature review.
- Inaccurate interpretation of expected results from the methodology.
- Plagiarized or copied sections of the research proposal.
Common mistakes to avoid

You must stay aware of the research proposal guidelines and best writing manners. To maximize the approval chances of your research proposal, you should try to avoid some common pitfalls like:
- Making it verbose
Try explaining the various sections of the research proposal economically. Ideally, you should strive to keep your writing as a concise, brief, and to the point as possible. The more concisely you explain the purpose and goal of your research proposal, the better.
- Focusing on minor issues than tackling the core
While writing the research proposal, you may feel every issue is important, and you should provide an explanatory note for that. However, stay wiser while selecting the importance of issues. Avoid falling into the trap of trivial issues, as it may distract your readers from the core issues.
- Failure to put a strong research argument
The easiest way your readers can undermine your research proposal is by stating it is far more subjective and sounds unrealistic. A potent research argument describing the gaps in the current field, its importance, significance, and contributions to your research is the foremost requirement of a good research proposal.
Remember, even though you are proposing the objective, academic way, the goal is to persuade the audience to provide you with the required research approval.
- Not citing correctly
Understand that when you are going for some research, its outcome will contribute to the existing pool of knowledge. Therefore, always cite some landmark works of your chosen research domain and connect your proposed work with it.
Providing such intricate details will establish your research's importance, relevance, and familiarity with the domain knowledge.
Before You Go,
You might also like.

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Education
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
By Danesh Ramuthi , Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Writing a Research Proposal
- First Online: 10 April 2022
Cite this chapter

- Fahimeh Tabatabaei 3 &
- Lobat Tayebi 3
789 Accesses
A research proposal is a roadmap that brings the researcher closer to the objectives, takes the research topic from a purely subjective mind, and manifests an objective plan. It shows us what steps we need to take to reach the objective, what questions we should answer, and how much time we need. It is a framework based on which you can perform your research in a well-organized and timely manner. In other words, by writing a research proposal, you get a map that shows the direction to the destination (answering the research question). If the proposal is poorly prepared, after spending a lot of energy and money, you may realize that the result of the research has nothing to do with the initial objective, and the study may end up nowhere. Therefore, writing the proposal shows that the researcher is aware of the proper research and can justify the significance of his/her idea.
- Research proposal
- Research strategy
- Research methodology
- Research design
- Problem formulation
- Sample size
- Random allocation
- Specific aims
- Review grants
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
A. Gholipour, E.Y. Lee, S.K. Warfield, The anatomy and art of writing a successful grant application: A practical step-by-step approach. Pediatr. Radiol. 44 (12), 1512–1517 (2014)
Article Google Scholar
L.S. Marshall, Research commentary: Grant writing: Part I first things first …. J. Radiol. Nurs. 31 (4), 154–155 (2012)
E.K. Proctor, B.J. Powell, A.A. Baumann, A.M. Hamilton, R.L. Santens, Writing implementation research grant proposals: Ten key ingredients. Implement. Sci. 7 (1), 96 (2012)
K.C. Chung, M.J. Shauver, Fundamental principles of writing a successful grant proposal. J. Hand Surg. Am. 33 (4), 566–572 (2008)
A.A. Monte, A.M. Libby, Introduction to the specific aims page of a grant proposal. Kline JA, editor. Acad. Emerg. Med. 25 (9), 1042–1047 (2018)
P. Kan, M.R. Levitt, W.J. Mack, R.M. Starke, K.N. Sheth, F.C. Albuquerque, et al., National Institutes of Health grant opportunities for the neurointerventionalist: Preparation and choosing the right mechanism. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 13 (3), 287–289 (2021)
A.M. Goldstein, S. Balaji, A.A. Ghaferi, A. Gosain, M. Maggard-Gibbons, B. Zuckerbraun, et al., An algorithmic approach to an impactful specific aims page. Surgery 169 (4), 816–820 (2021)
S. Engberg, D.Z. Bliss, Writing a grant proposal—Part 1. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 32 (3), 157–162 (2005)
D.Z. Bliss, K. Savik, Writing a grant proposal—Part 2. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 32 (4), 226–229 (2005)
D.Z. Bliss, Writing a grant proposal—Part 6. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 32 (6), 365–367 (2005)
J.C. Liu, M.A. Pynnonen, M. St John, E.L. Rosenthal, M.E. Couch, C.E. Schmalbach, Grant-writing pearls and pitfalls. Otolaryngol. Neck. Surg. 154 (2), 226–232 (2016)
R.J. Santen, E.J. Barrett, H.M. Siragy, L.S. Farhi, L. Fishbein, R.M. Carey, The jewel in the crown: Specific aims section of investigator-initiated grant proposals. J. Endocr. Soc. 1 (9), 1194–1202 (2017)
O.J. Arthurs, Think it through first: Questions to consider in writing a successful grant application. Pediatr. Radiol. 44 (12), 1507–1511 (2014)
M. Monavarian, Basics of scientific and technical writing. MRS Bull. 46 (3), 284–286 (2021)
Additional Resources
https://grants.nih.gov
https://grants.nih.gov/grants/oer.htm
https://www.ninr.nih.gov
https://www.niaid.nih.gov
http://www.grantcentral.com
http://www.saem.org/research
http://www.cfda.gov
http://www.ahrq.gov
http://www.nsf/gov
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Dentistry, Marquette University, Milwaukee, WI, USA
Fahimeh Tabatabaei & Lobat Tayebi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Tabatabaei, F., Tayebi, L. (2022). Writing a Research Proposal. In: Research Methods in Dentistry. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98028-3_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98028-3_4
Published : 10 April 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-98027-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-98028-3
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
How to write a research proposal?
Department of Anaesthesiology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Devika Rani Duggappa
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.
Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
Published on June 7, 2021 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023 by Pritha Bhandari.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about:
- Your overall research objectives and approach
- Whether you’ll rely on primary research or secondary research
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods
- The procedures you’ll follow to collect data
- Your data analysis methods
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research objectives and that you use the right kind of analysis for your data.
Table of contents
Step 1: consider your aims and approach, step 2: choose a type of research design, step 3: identify your population and sampling method, step 4: choose your data collection methods, step 5: plan your data collection procedures, step 6: decide on your data analysis strategies, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research design.
- Introduction
Before you can start designing your research, you should already have a clear idea of the research question you want to investigate.
There are many different ways you could go about answering this question. Your research design choices should be driven by your aims and priorities—start by thinking carefully about what you want to achieve.
The first choice you need to make is whether you’ll take a qualitative or quantitative approach.
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive , allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.
Quantitative research designs tend to be more fixed and deductive , with variables and hypotheses clearly defined in advance of data collection.
It’s also possible to use a mixed-methods design that integrates aspects of both approaches. By combining qualitative and quantitative insights, you can gain a more complete picture of the problem you’re studying and strengthen the credibility of your conclusions.
Practical and ethical considerations when designing research
As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics .
- How much time do you have to collect data and write up the research?
- Will you be able to gain access to the data you need (e.g., by travelling to a specific location or contacting specific people)?
- Do you have the necessary research skills (e.g., statistical analysis or interview techniques)?
- Will you need ethical approval ?
At each stage of the research design process, make sure that your choices are practically feasible.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research.
Types of quantitative research designs
Quantitative designs can be split into four main types.
- Experimental and quasi-experimental designs allow you to test cause-and-effect relationships
- Descriptive and correlational designs allow you to measure variables and describe relationships between them.
With descriptive and correlational designs, you can get a clear picture of characteristics, trends and relationships as they exist in the real world. However, you can’t draw conclusions about cause and effect (because correlation doesn’t imply causation ).
Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results. However, their controlled conditions may not always reflect how things work in the real world. They’re often also more difficult and expensive to implement.
Types of qualitative research designs
Qualitative designs are less strictly defined. This approach is about gaining a rich, detailed understanding of a specific context or phenomenon, and you can often be more creative and flexible in designing your research.
The table below shows some common types of qualitative design. They often have similar approaches in terms of data collection, but focus on different aspects when analyzing the data.
Your research design should clearly define who or what your research will focus on, and how you’ll go about choosing your participants or subjects.
In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from.
Defining the population
A population can be made up of anything you want to study—plants, animals, organizations, texts, countries, etc. In the social sciences, it most often refers to a group of people.
For example, will you focus on people from a specific demographic, region or background? Are you interested in people with a certain job or medical condition, or users of a particular product?
The more precisely you define your population, the easier it will be to gather a representative sample.
- Sampling methods
Even with a narrowly defined population, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every individual. Instead, you’ll collect data from a sample.
To select a sample, there are two main approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling . The sampling method you use affects how confidently you can generalize your results to the population as a whole.
Probability sampling is the most statistically valid option, but it’s often difficult to achieve unless you’re dealing with a very small and accessible population.
For practical reasons, many studies use non-probability sampling, but it’s important to be aware of the limitations and carefully consider potential biases. You should always make an effort to gather a sample that’s as representative as possible of the population.
Case selection in qualitative research
In some types of qualitative designs, sampling may not be relevant.
For example, in an ethnography or a case study , your aim is to deeply understand a specific context, not to generalize to a population. Instead of sampling, you may simply aim to collect as much data as possible about the context you are studying.
In these types of design, you still have to carefully consider your choice of case or community. You should have a clear rationale for why this particular case is suitable for answering your research question .
For example, you might choose a case study that reveals an unusual or neglected aspect of your research problem, or you might choose several very similar or very different cases in order to compare them.
Data collection methods are ways of directly measuring variables and gathering information. They allow you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study.
Survey methods
Surveys allow you to collect data about opinions, behaviors, experiences, and characteristics by asking people directly. There are two main survey methods to choose from: questionnaires and interviews .
Observation methods
Observational studies allow you to collect data unobtrusively, observing characteristics, behaviors or social interactions without relying on self-reporting.
Observations may be conducted in real time, taking notes as you observe, or you might make audiovisual recordings for later analysis. They can be qualitative or quantitative.
Other methods of data collection
There are many other ways you might collect data depending on your field and topic.
If you’re not sure which methods will work best for your research design, try reading some papers in your field to see what kinds of data collection methods they used.
Secondary data
If you don’t have the time or resources to collect data from the population you’re interested in, you can also choose to use secondary data that other researchers already collected—for example, datasets from government surveys or previous studies on your topic.
With this raw data, you can do your own analysis to answer new research questions that weren’t addressed by the original study.
Using secondary data can expand the scope of your research, as you may be able to access much larger and more varied samples than you could collect yourself.
However, it also means you don’t have any control over which variables to measure or how to measure them, so the conclusions you can draw may be limited.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As well as deciding on your methods, you need to plan exactly how you’ll use these methods to collect data that’s consistent, accurate, and unbiased.
Planning systematic procedures is especially important in quantitative research, where you need to precisely define your variables and ensure your measurements are high in reliability and validity.

Operationalization
Some variables, like height or age, are easily measured. But often you’ll be dealing with more abstract concepts, like satisfaction, anxiety, or competence. Operationalization means turning these fuzzy ideas into measurable indicators.
If you’re using observations , which events or actions will you count?
If you’re using surveys , which questions will you ask and what range of responses will be offered?
You may also choose to use or adapt existing materials designed to measure the concept you’re interested in—for example, questionnaires or inventories whose reliability and validity has already been established.
Reliability and validity
Reliability means your results can be consistently reproduced, while validity means that you’re actually measuring the concept you’re interested in.
For valid and reliable results, your measurement materials should be thoroughly researched and carefully designed. Plan your procedures to make sure you carry out the same steps in the same way for each participant.
If you’re developing a new questionnaire or other instrument to measure a specific concept, running a pilot study allows you to check its validity and reliability in advance.
Sampling procedures
As well as choosing an appropriate sampling method , you need a concrete plan for how you’ll actually contact and recruit your selected sample.
That means making decisions about things like:
- How many participants do you need for an adequate sample size?
- What inclusion and exclusion criteria will you use to identify eligible participants?
- How will you contact your sample—by mail, online, by phone, or in person?
If you’re using a probability sampling method , it’s important that everyone who is randomly selected actually participates in the study. How will you ensure a high response rate?
If you’re using a non-probability method , how will you avoid research bias and ensure a representative sample?
Data management
It’s also important to create a data management plan for organizing and storing your data.
Will you need to transcribe interviews or perform data entry for observations? You should anonymize and safeguard any sensitive data, and make sure it’s backed up regularly.
Keeping your data well-organized will save time when it comes to analyzing it. It can also help other researchers validate and add to your findings (high replicability ).
On its own, raw data can’t answer your research question. The last step of designing your research is planning how you’ll analyze the data.
Quantitative data analysis
In quantitative research, you’ll most likely use some form of statistical analysis . With statistics, you can summarize your sample data, make estimates, and test hypotheses.
Using descriptive statistics , you can summarize your sample data in terms of:
- The distribution of the data (e.g., the frequency of each score on a test)
- The central tendency of the data (e.g., the mean to describe the average score)
- The variability of the data (e.g., the standard deviation to describe how spread out the scores are)
The specific calculations you can do depend on the level of measurement of your variables.
Using inferential statistics , you can:
- Make estimates about the population based on your sample data.
- Test hypotheses about a relationship between variables.
Regression and correlation tests look for associations between two or more variables, while comparison tests (such as t tests and ANOVAs ) look for differences in the outcomes of different groups.
Your choice of statistical test depends on various aspects of your research design, including the types of variables you’re dealing with and the distribution of your data.
Qualitative data analysis
In qualitative research, your data will usually be very dense with information and ideas. Instead of summing it up in numbers, you’ll need to comb through the data in detail, interpret its meanings, identify patterns, and extract the parts that are most relevant to your research question.
Two of the most common approaches to doing this are thematic analysis and discourse analysis .
There are many other ways of analyzing qualitative data depending on the aims of your research. To get a sense of potential approaches, try reading some qualitative research papers in your field.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question . It defines your overall approach and determines how you will collect and analyze data.
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims, that you collect high-quality data, and that you use the right kind of analysis to answer your questions, utilizing credible sources . This allows you to draw valid , trustworthy conclusions.
Quantitative research designs can be divided into two main categories:
- Correlational and descriptive designs are used to investigate characteristics, averages, trends, and associations between variables.
- Experimental and quasi-experimental designs are used to test causal relationships .
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible. Common types of qualitative design include case study , ethnography , and grounded theory designs.
The priorities of a research design can vary depending on the field, but you usually have to specify:
- Your research questions and/or hypotheses
- Your overall approach (e.g., qualitative or quantitative )
- The type of design you’re using (e.g., a survey , experiment , or case study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., questionnaires , observations)
- Your data collection procedures (e.g., operationalization , timing and data management)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical tests or thematic analysis )
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
Operationalization means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioral avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalize the variables that you want to measure.
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, ethical considerations in research | types & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- 66 Ogoja Road, Abakaliki, Ebonyi State 23480 NG.
- Sun - Fri 24Hours Saturday CLOSED
- support [@] writersking.com
- +23480-6075-5653 Hot Line

- Data Collection/Analysis
- Hire Proposal Writers
- Hire Essay Writers
- Hire Paper Writers
- Proofreading Services
- Thesis/Dissertation Writers
- Virtual Supervisor
- Turnitin Checker
- Book Chapter Writer
- Hire Business Writing Services
- Hire Blog Writers
- Writers King TV
- Proposal Sample
- Chapter 1-3 Sample
- Term Paper Sample
- Report Assignment Sample
- Course work Sample
- Payment Options
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service/Use
- Business Guide
- Academic Writing Guide
- General Writing Guide
- Research News
- Writing Paper Samples
- January 25, 2022
- Category: Academic Writing Guide

7 Types of Research proposal and How to know what’s required of you
1.0 introduction.
A research proposal provides a detailed explanation of a proposed project about to be conducted by a researcher. The research proposal provides a summary of the information discussed in the project by reviewing the entire research process.
Content Outline
It is important to create research proposals to facilitate the smooth navigation of various research activities, in order to make research as effective as possible, to reduce labour, time and costs and to provide as much information as possible. As a result, a research proposal is a conceptual framework in which research is conducted to create a plan for data collection, measurement and analysis.
The research proposal comes in the form of a dissertation which provides a summary of the plan the researcher intends to implement. Consequently, the research proposal contains what researchers intend to do throughout the study period, from developing hypotheses and their practical significance to final data analysis . The research proposals aim to organize ideas, present the preparations in a logical way, emphasizing the relationship between each party and other departments, and explains the limitations of the research and related concepts.
As a result, research proposals include extensive literature reviews . This is necessary as they must provide the necessary information to demonstrate the need for the proposed research. In addition, the research proposal also provides detailed research methods that meet the professional or disciplinary requirements and the expected results and benefits of completing the research.
The research proposal guidelines are not as rigorous and formal as the main thesis as design elements and procedures for conducting the research are governed by standards within the predominant discipline. However, most research institutes provide detailed instructions or guidelines in writing a research proposal, which must be strictly adhered to.
Typically, most proposals are between six (6) and twelve (12) pages in length and not longer than 3500 words (not including references). However, this may differ across institutions. This article aims at identifying the various types of research proposals to assist you to know the type required of you. This will be of great help in preparing excellent proposals.
2.0 Types of Research Proposals
In all fields spanning across academic, government and private sectors, research scientists usually find competitive funding for research projects by creating and submitting research proposals for funding analysis.
Also, students across various institutions submit research proposals to conduct academic studies. As a result, there are several types of research proposals with each type being due to its own requirements or qualifications. These types of research proposals are discussed below.
Approval proposal:
This type of proposal is commonly written by students. It is submitted to your supervisor for approval and is written before undertaking a final project, dissertation or thesis. This is where the supervisor needs to ensure that your research is valuable and that the methodology employed can successfully be carried out by the student. It involves providing information on the research purpose, relevance, previous research in the field, how the research is conducted, the time and resources required.
Revised Proposal:
This is the type of proposal written when the funding for a proposed project is to be changed to a different amount other than the actual amount. As a result of this, the sponsor will require the researcher to submit a revised proposal to support the funding amount. This replaces ongoing proposals or not funded but not formally rejected by the sponsor. If the sponsor reduces the budget, the researcher must determine if the scope and objectives of the original project are met in the revised budget. If a proposal is rejected, then the researcher will need to prepare a new proposal.
Supplemental Proposal:
This is a type of proposal which provides support for proposals already approved and funded. It originates as a result of increases in the proposed budget of the study. The increase may occur during the current budget period and may include an extended scope of project approval. This is a type of research proposal is often required when the researcher needs additional funding.
Continuation Proposal:
This type of proposal is typical with a multiannual study award. The continuation proposal is requested when a researcher needs funding to continue the next stage of the project. At this stage, sponsors usually require progress reports and budgets before allocating additional funding. In some cases, it includes financial statements that show expenditures and any balance for the year. This type of research proposal only applies to projects already approved by the sponsor in the original award and which are a going concern.
Pre-proposal/Notice of Intent:
The purpose of the proposal is to promote the interests of potential sponsors where interested sponsors will subsequently request a complete proposal. This type of proposal is required if the sponsor wants to reduce the applicant’s effort to prepare a complete proposal.
The primary aim of the pre-proposal is to inform interested potential sponsors of the project. Typically, the proposal does not include cost estimates and are not expected to result in a study award. As a result, a pre-proposal usually take the form of a statement of intent or a brief summary. After considering a pre-proposal, the sponsor will notify the researcher if a full proposal is required.
Solicited Proposals:
Formal proposals are often solicited by sponsors through publishing specific program announcements which are disseminated through various means. These announcements often come in the form of Funding Opportunity Announcements (FOAs), Request for Proposals (RFPs) , Broad Agency Announcements (BAAs), etc. Researchers responding to the project announcement write proposals to comply with the sponsor’s project guidelines.
A typical example of a solicited proposal is the Request for Proposals (RFPs) which is a document that identifies specific research topics of particular interest to institutions seeking solutions. Interested researchers then present a proposal often referred to as a white paper that summarizes the solution to the problem. If a funding organization or company is interested, they can ask researchers to submit a complete proposal to consider funding.
Unsolicited Proposals:
These are proposals that are submitted by a researcher in response to a ‘general call’ for proposals that is issued by a research department or research institute or company in a field or area of study. Here you must prove the suitability of your research project, the importance of your research, its relevance to the organization, your qualifications as a researcher, the suitability of your research facility and the adequacy of your research budget.
3.0 How to Know the Type Required of You
Having gained knowledge of the various types of research proposals, it is important to determine which is relevant to your study. Generally, knowing the type of research proposal expected of you lies in the careful perusal of the accompanying guidelines and instructions. The guidelines lays out what is expected of the researcher and will act as a beacon in pinpointing the type of research proposal that is expected of the researcher.
Furthermore, the purpose of writing the research proposal is also a proper yardstick in determining the type of research proposal that is expected of you. For example, when writing in response to a Request for Proposals (RFP) we acknowledge that this is a solicited proposal. Nevertheless, it is important to note the intersection between the various types of research proposals as this will contribute significantly to the successful completion of an excellent research proposal.
4.0 Conclusion
Effective proposals not only clearly explain the research problem but also identify and analyzes the method used for the research. Successful research proposals should place their research in a broader field of study and explain why it is important. The structure of the proposal must be well planned with each section carefully written to avoid errors. This planning ensures the most effective structure which gives rise to persuasive content that will interest the target audience, thereby ensuring success.
How do one write a tourism related research proposal.
Drop your comment, question or suggestion for the post improvement Cancel reply

Find Us Today
Writers King LTD, Akachukwu Plaza,
66 Ogoja Road Abakaliki, Ebonyi State,
480101 Nigeria
Phone: 0806-075-5653
- Website: https://writersking.com/
- Email: support {@} writersking.com
- +2348060755653
Quick Links
Writing guide.
- Research Profiles
- Refererences
- Research Proposals
Articles on Research Funding
- Possible Funding Resources
- The Review Process
In this section, we will discuss the following:
- the basic types of research proposals ;
- the purpose of a research proposal ;
- the typical format for a research proposal ; and
- some general suggestions regarding proposal submission
Types of Research Proposals
In all sectors (academe, government, and the private sector), research scientists typically seek and obtain competitive funding for their research projects by writing and submitting research proposals for consideration by the funding source. There are two kinds of research proposals:
Solicited proposals are those that are written and submitted in response to the issuance of a “Request for Proposals” (RFP), a document that identifies a specific research problem of interest to the funding agency for which they are specifically seeking a solution. Interested investigator then submits a “concept” or “white paper” briefly outlining their proposed solution to the problem. If the funding agency or company is interested, they may then request that the investigator submit a full proposal for consideration of funding.
Unsolicited
Unsolicited proposals are those proposals that are submitted by an investigator in response to a “general call” for proposals that is issued by a funding agency or company in a field or area of study.
The majority of funding agencies issue calls for proposals which have firmly established deadlines and for which the format of the proposals is fairly well defined. Thus, it is vitally important at the outset after you have identified a funding source that you obtain all of the relevant information on the specific grant program and its requirements. Today most funding agencies have searchable websites where they post detailed information concerning their grant programs.
Back to Top
Purpose of a Research Proposal
The purpose of a proposal is to sell your idea to the funding agency. This means that the investigator must convince the funding agency that:
- The problem is significant and worthy of study
- The technical approach is novel and likely to yield results
- The investigator and his/her research team is/are the right group of individuals to carry out and accomplish the work described in the research proposal.
Typical Proposal Format
The title of your proposal should be short, accurate, and clear. A single sentence containing ten or fewer words is best. Don’t use acronyms and technical jargon as your reviewers may not come from your technical specialty. For example, “Web-GURU: Web-based Guide to Research for Undergraduates.”
As in a technical paper, the proposal abstract should “abstract” the project for the reader. It should be a brief (100 – 200 words), tightly worded summary of the project, its objectives, the problem’s significance, the project’s scope, the methods that will be employed, the identity and relevant technical expertise of the research team, and the results that are expected to result. Be sure to write this section last so that its content indeed abstracts your proposal.
Introduction
The introduction section should introduce the research problem, its significance, and the technical approach your work will take to investigate/solve the problem. It should introduce the research team that will carry out the work.
This section should present a concise review of the primary literature relevant to your proposed research efforts. As such it should:
- Cite the key literature sources
- Be up to date
- Critically appraise the literature
The background section should be constructed to inform the reader concerning where your study fits in? It should clearly state why your project should be done? Does your work:
- Take science in a bold new direction?
- Build on the prior work of others (whose?) in the field
- Address flaws in previous work (again, whose?)
- Develop infrastructure (instrumentation, methodology, collaborations) that will take science in exciting new directions
Preliminary Studies
If the project builds on past studies from your laboratory, then you should include a brief section outlining what you have already accomplished and explain how these results relate to the work outlined in the present proposal. If the ideas you are proposing are novel, then it is especially important to include this section and to present evidence supporting the probable success of your project.
Research Methodology
This section should outline your plan of attack. Specific information that should be contained in this section includes information on the research team and its technical expertise as it relates to the project, a realistic timeline, description of the specific experiments that will be accomplished together with alternate plans in case of potential difficulties/challenges. If more than one person will do the work described in the proposal then a division of labor should be provided together with an explanation of why each person is best qualified to do the work described. The timeline should define the length of the project and provide a schedule of who will do what specific tasks approximately when during the project period. Problems always arise in research. Things never go as anticipated. So, it is important to provide the reviewer with enough information to give them confidence that when problems arise, as they inevitably will, that you will be able to handle them in such a way that meaningful science results.
The budget should identify the anticipated cost for everything (salaries, materials, instrumentation, travel costs, etc.) that will be required in order to accomplish the research project. Usually budgets are prepared and submitted as tables with prescribed format. A budget justification typically accompanies the budget request. The budget justification is simply an explanation, item-by-item, stating why you must spend the money requested in order to carry out the experiments planned.
The most important point in preparing a budget is to make sure that you ask for what you really need. Some people underestimate the importance of working through a budget in advance of writing the actual grant proposal. This is really important because most grant programs provide grants with a certain set monetary value. It is critical to ask for the amount you really need because if you don’t ask for what you need you simply won’t be able to do the work and if you can’t carry out your project, it is highly unlikely that you will ever be able to obtain funding from that funding agency again in the near future. At the same time, it is important not to go overboard in padding your budgetary request. A thoughtful budget demonstrates that your project is well conceived and likely to yield quality results. If the reviewers feel that your budget is naïve or over-inflated, that can work against you – your project could be funded at a lower rate or certain items requested might simply be eliminated from the budget by the funding agency – so be sure to think through your budget requests carefully and make sure that all requests are thoughtfully justified.
There are two major components in a budget:
Direct costs are the costs that you incur that are directly attributable to the project. Examples of direct costs include personnel salary, fringe benefits, materials and supplies, major instrumentation, and travel costs. We will briefly examine each of these:
Personnel Salary
An important budget request in most grants is the salary for the personnel who will carry out the research on the project. Salary is usually requested for the principal investigator, postdoctoral students, graduate and undergraduate students. Some funding agencies will provide secretarial support. Academic faculty, who usually receive academic year ( 9-mos typically) salary from their institutions, often supplement their salary (summer salary) by carrying out external research programs.
Fringe Benefits
Fringe benefits refers to the costs incurred by your institution/employer in providing group health insurance, retirement, unemployment, workers compensation, FICA (Medicare), etc. Undergraduate salaries are not normally assessed fringe benefits when the student is supported during the academic year.
Materials and Supplies
Materials and supplies include a wide range of items such as laboratory supplies, chemical reagents, research animals, computer software and supplies, etc.
Major Instrumentation
A purchase is typically identified as major instrumentation rather than materials and supplies when the cost of the instrument exceeds a thousand dollars and when the device has an anticipated lifespan of more than a year. Examples of major instrumentation purchases include laptops (cost typically $2k), UV-vis instruments, desktop centrifuges, etc. When requesting major instrumentation it is important to specify the manufacturer and model of the specific instrument that you wish to purchase and to indicate what if any features this model has that make it uniquely required in order to accomplish your proposed work. If you do require a specific instrument, it is wise to obtain a quotation from the manufacturer. Since it may be six months or more before you begin your project be sure to inquire what the anticipated cost of the instrument will be at the time you anticipate purchasing it (i.e., allow for inflation).
Travel Costs
If you intend to attend a professional meeting in order to present the results of your research, you may include the anticipated cost of traveling to and attending the meeting in your budget request. You may include the cost of a round-trip coach class fare airplane ticket, meeting registration, hotel, ground transportation (taxi, car rental, etc.), and food. Many funding sources place strict limitations on travel so be sure to research this carefully before making your request.
Subcontractor Costs
If you are working on a collaborative project with an investigator at another institution, then you will need to include the costs that they will incur in carrying out the proposed work. Your collaborator is viewed as a subcontractor in terms of the grant proposal. Their institution may assess its own indirect costs and those will also need to be included in your budget request to the funding agency.
Indirect costs on the other hand are the facilities and administrative costs that are incurred by your institution/employer in support of your research activities. These include These are typically assessed as a percentage of the direct costs for the project. Indirect costs are often assessed on either a modified total direct costs basis (MTDC) or a total direct costs basis (TDC). MTDC rates do not include the costs of major instrumentation, student tuition, or subcontractors in the total for the direct costs on which the indirect costs are assessed while TDC includes all costs when assessing the indirect costs for the project. The MTDC and TDC rates are set by your institution so be sure to check with them to determine what the current rates are.
Curriculum Vitae for Principal Investigators
Most funding agencies require the principal investigator(s) to include some form of curriculum vitae. Curriculum vitae are the academic-version (extended) of a resume. They provide useful information on the education, technical expertise, and research productivity of the principal investigator. In an effort to ensure the brevity and uniformity of the information provided, many funding agencies require that this information be provided according to a specific format. Be sure to include only the information requested. Do not embellish your accomplishments.
This ancillary section should be used only to provide secondary information that is relevant to the research project. For example, if you are collaborating with another investigator, it is appropriate to obtain a letter from him/her indicating his/her willingness to collaborate and detailing what specific support (personnel, equipment, research materials, results, etc.) they are willing to provide for the research project. Some funding programs do not allow investigators to submit appendices so be sure to find out in advance whether or not you can submit supporting materials and what if any limitations there may be concerning these materials (content, page limits, etc.).
Human Subjects
If your project involves experimentation on either animals or people, you will need to obtain approval for your project through your institution’s office of Institutional Compliance.
General Suggestions
- Don’t be afraid to ask your advisor or other scientists if you can read copies of their successfully funded proposals.
- There is no substitute for a good idea. This means the idea should be important and technically sound. If the idea is of interest to you, it is likely going to be of interest to others. Your job is to clearly make the case that this is work worth funding by the particular funding agency and program to which you have applied. In terms of the work being technically sound, make sure that you research it before you begin writing. This may mean doing some preliminary experiments in order to obtain data that clearly demonstrate that your ideas will work. This is particularly important if your ideas are truly novel.
- Before you begin writing, map out your project. Identify the key experiments you will need to do. Determine who and what you will need in order to carry out these experiments and figure out how much it will cost to do the actual work (i.e., work out the budget). Be sure that the anticipated cost of your project fits the scope of the funding agency’s program.
- Read the application instructions thoroughly and follow them carefully. If you have any questions telephone or e-mail and ask. Don’t make any implicit assumptions about your reviewers including their technical expertise, what they know about you and your work, the conditions under which they will read your proposal, etc. If you don’t follow the directions, don’t be surprised if your proposal is returned to you un-reviewed.
- Write your proposal to address all of the review criteria of the grant program.
- Start writing your proposal well in advance of the deadline for submission.
- Presentation and written expression count. Think about the reviewer’s workload (see “ The Review Process ”) Don’t use a lot of technical jargon. Write simply and clearly. Use the spell checker and grammar checker. Don’t fault the reviewer’s for equating a poorly written and poorly proofed proposal with evidence of a sloppy scientist likely incapable of carrying out a quality project if funded.
- Ask your advisor, a friend, and/or colleague to review your proposal (be sure to provide them with a copy of the funding agency’s review criteria) before submitting it and when you receive their feedback modify your proposal accordingly.
- If your proposal is not funded, seek feedback. Don’t take the rejection of your proposal personally. Learn from it! Modify your proposal accordingly, and resubmit it. Perseverance is everything when it comes to research funding – just about everyone has at some point submitted a proposal that didn’t get funded.
- Mission, Vision, Strategic Priorities
- Postdoctoral Researchers
- Recognition
- Reporting Concerns/Suspected Violations
- RCA 2023 Schedule
- Institutional Official Responsibilities
- Research Council
- Research Integrity Services
- Sponsored Program Administration
- Research and Large Center Development
- Announcements
- Award Management
- Financial Management
- Effort Certification Policy
- Award Closeout
- Uniform Guidance Procurement
- Essentials for Project Directors/PIs
- Federal Agency Guidance on Notification and Reporting of Discrimination and Harassment
- Cayuse Research Suite
- UNH Research Support Matrix for Compliance & Safety
- IACUC Application Resources
- IACUC Application Review Process
- IACUC Meeting Schedule
- IACUC Membership
- Animal Care & Use FAQs
- Animal Resources Office
- Approval of Facilities Housing Vertebrate Animals
- Occupational Health Program for Animal Handlers
- Reporting Animal Care and/or Use Concerns
- Training for Animal Care and Use Personnel
- Animal Care & Use: In the News & Resources
- Cayuse Outside Interests
- Conflict of Interest FAQs
- FCOIR Training & Resources
- Financial Conflicts of Interest in Research
- Financial Conflicts of Interest in Research for PIs
- Disclosure Review Committee
- Controlled Substances
- Data Management Policy FAQs
- Data Management Training & Resources
- Regulation Overview
- Export Controls in an Academic Environment
- Export Compliance Advisory Committee
- Useful Links and Background Reading
- International Students and Scholars Foreign Hires
- Visiting Scientist Agreements
- International Travel & Activities
- Technology Control Plan (TCP)
- Export Controls Training
- Export Controls FAQs
- Export Controls & Sanctions News
- Foreign Influence
- HIPAA Training
- HIPAA & Health Privacy News
- IRB Application Resources
- IRB Application Review Process
- IRB Review Levels
- IRB Training
- IRB Meeting Schedule
- IRB Membership
- Recent Changes to Human Research Subjects Protections
- Does Your Activity Need IRB Review at UNH?
- Collaborations with Other Institutions
- Human Subjects FAQs
- Title IX Reporting Exception for Research
- NIH Clinical Trials Information
- NIH Required Human Subjects Training
- HIPAA Privacy Rule & Research
- Human Subjects: In the News & Resources
- Misconduct in Scholarly Activity
- Responsible Conduct of Research & Scholarly Activity Committee
- NIH RCR Training Requirement
- NSF RCR Training FAQs
- USDA NIFA RCR Training Requirement
- RCR Instruction at UNH
- RCR Training at UNH
- RCR Workshops
- Research Ethics Lecture Series
- RCR: In the News & Resources
- About EH&SO
- Air Quality
- Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC)
- Biological Safety Resources
- Biosafety Cabinets & Clean Benches
- Biosafety Training
- IBC Registration
- Bloodborne Pathogens
- Chemical Safety Committee
- Chemical Receipt & Transfer Form
- Removing Containers from Inventory
- Plans & Programs
- Emergency Procedures Resources
- Emergency Action & Fire Prevention
- Emergency Procedures for Spills of Radioactive Materials
- UNH Integrated Contingency Planning
- Radiation Safety Committee (RSC)
- Hazardous Materials Management Plan
- Hazardous Chemical Waste
- Universal Waste
- Radioactive Waste
- Incidents/Accidents with Biohazards
- Biohazardous Waste Disposal Procedures
- Scrap Electronics
- Hazardous Waste Management Programs
- Hazardous Waste Resources
- Shipment of Biohazardous Materials
- Regulatory & Carrier References
- Hazard Communication: Labeling
- Hazard Communication: Pictograms
- Hazard Communication: Safety Datasheets
- Exposure Monitoring
- Hazardous Building Materials
- Hearing Conservation
- Indoor Air Quality
- Thermal Stress (Heat Advisory)
- Occupational Safety Committee (OSC)
- Incident Reporting
- Confined Space Entry
- Contractor Safety
- Crane and Hoist Safety
- Ergonomic Desks
- Ergonomic Chairs
- Sit-Stand Workstations
- Back Safety
- Ergonomic Assessment Request
- Keyboard Ergonomics
- Material Handling
- Mouse Ergonomics
- Workstation Monitors
- Fall Protection
- Laboratory Ventilation Management Program
- Lockout/Tagout Control of Hazardous Energy
- Mobile Elevated Work Platform Safety
- Personal Protective Equipment
- Powered Industrial Trucks
- Respiratory Protection
- Occupational Safety Resources
- Water Shutdown Procedures
- Radiation Safety Program Management
- Radiation Forms
- Radioactive Permits
- Radiation Safety Training
- Radiation Dosimetry
- Radiation Surveys
- NH Rules for the Control of Radiation
- Radiation Safety Resources
- Assistant Authorized User
- Radioactive Waste Disposal Requests
- Radionuclide Safety Sheets
- Laser Safety Program Management & Registration
- Magnet Safety
- X-Ray Safety
- Research Fieldwork Safety Program
- UNHCEMS Tutorials
- EHS Training
- GHS Training
- UNH Manchester Safety Committee
- Law School Safety Committee Comment Form
- Proposal Preparation Checklist
Types of Proposals
- Proposal Components
- Develop a Budget
- Develop a Budget Justification
- Get Approvals
- Submit a Proposal
- Proposal Submission Guidelines
- Ongoing COVID-19 Data, Resources, and Funding Opportunities
- Funding Types
- Sponsor Types
- Internal (UNH) Funding Opportunities
- Current LSP Deadlines
- Early Career Researchers & Scholars
- Federal Sponsors and Other Search Resources for Graduate Students
- Federal Sponsors and Other Search Resources for Postdoctoral Fellows
- International Research & Scholarship
- NIH AREA (R15) Grants
- EPSCoR and IDeA
- Research Equipment, Instrumentation, and Infrastructure Funding Opportunities
- Publication and Subvention
- Small Business Grants - SBIR & STTR
- Search Strategies
- Search Tools
- Vision 2030: A Roadmap for Science & Engineering
- RLCD Programs - AY 2023-2024
- Workshops By Theme
- Workshop Resources
- Graduate Student Programs
- Research Development & Grant Writing News
- Collaborative Research Excellence (CoRE) Initiative
- Developing Broader Impacts and Outreach Activities
- DEIA and Belonging
- Proposal Development Services
- Proposal Writing & Development
- RD Digital Library
- UNH and DOE National Laboratories
- Support Team for the Administration of Research (STAR)
- UNH Research Faculty
- About Outreach and Engagement
- UNHInnovation
- Connections for Business
- Intellectual Property
- Data Management & Access
- Assistance, Services & Other Resources
- Collaborations and Agreements
- Core Facility & Campus Resources
- InterOperability Laboratory (IOL)
- Knowledge Base
- Research Area Experts
- Research Centers & Institutes
- Research Computing Center
- University Instrumentation Center
- Quick Links for Frequently Used Resources for Researchers
Follow us on Twitter Follow us on LinkedIn
Phone: (603) 862-1948 Email: [email protected]
Pre-Proposal Solicited Proposal Renewal and Continuation Proposals Limited Submissions Revised Budgets
Pre-Proposals
This type of proposal is requested when a sponsor wishes to minimize an applicant’s effort in preparing a full proposal. They are usually in the form of a letter of intent or a brief abstract of what the PI plans to do, how the PI will conduct the project and why this project has merit. A pre-proposal establishes a foundation for discussion; it does not commit the PI or the University to anything. However, since these proposals often do become the basis for negotiation for funding, if a budget is included in the submission, it should be routed for the appropriate University signatures. When requested by the sponsor, the pre-proposal may be used to determine how well the project fits the agency’s priorities. Also, the preliminary proposal may determine selection for the next stage of the application, help in the selection of possible reviewers and possibly offer a chance for feedback to the PI. After the preproposal is reviewed, the sponsor notifies the investigator if a full proposal is warranted. Broad Agency Announcements (BAA) usually associated with DOD, refer to pre-proposals or preliminary proposals as “White Papers”.
Solicited Proposal
Sponsors solicit formal proposals by publishing specific program announcements. These solicitations are often called Request for Proposals (RFPs), Funding Opportunity Announcements (FOAs), Broad Agency Announcements (BAAs), etc. Researchers responding to the program announcement write the proposal to meet the sponsor’s program guidelines. Deadlines may recur annually or several times a year.
A response to a Request for Proposal (RFP) is one type of solicited proposal. Most RFP’s have a stated deadline and are one-time solicitations for specific needs of the sponsor, not expected to recur. The proposed project must respond to the specific work statement in the Request for Proposal.
Solicited proposals must be routed through the University proposal routing process prior to submitting the proposal to the sponsor.
Renewal and Continuation Proposals
A competing renewal proposal (also called a competing continuation ) is a request for continued funding of a project for which the funding or project period is about to terminate. Such proposals are similar to "new" proposals and must be routed and approved in the same manner.
Noncompeting continuation proposals, which request the next year’s funding within a multi-year grant, generally consist of a progress report, budget, and other relevant materials such as research results, reprints, vitae for new personnel, etc. They sometimes include a financial status report showing the unobligated balance for the current year. Generally, sponsors require the signature of the institutional official and investigators. Noncompeting continuation proposals are routed through Sponsored Programs Administration, even if a budget is not required.
Research Performance Progress Reports (RPPR) is a federal-wide uniform progress report format for use by federal agencies that provide sponsored funding. RPPR is also used for noncompeting continuations. These reports to NSF are now submitted through Research.gov
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) requires use of the RPPR module to submit progress reports for Streamlined Non-competing Award Process (SNAP), fellowship, and multi-year funded awards. The RPPR is currently available to all institutions for non-SNAP progress reports, including those for complex and training awards. NIH will require all grantee institutions to use the RPPR for non-SNAP progress reports submitted on or after October 17, 2014. If you are unsure if this requirement applies to your NIH grant, your Notice of Award will specify whether an award uses SNAP. Note, “R” awards routinely use SNAP. In addition, the RPPR requirement also applies to all fellowship (“F”) awards.
Limited Solicitations
Occasionally, sponsors announce program-funding opportunities limiting the number of proposals that may be submitted by each institution. The UNH Research Development Office maintains a list of all limited submission programs on the Research Office website ( Current LSP Deadlines ) and sends a monthly email about upcoming opportunities to the Research Office “Principal Investigators & Project Directors” list. Faculty interested in submitting proposals should follow the limited submission pre-proposal process described here . The primary factors for selecting pre-proposals to go forward to the sponsor are the relevance to the program selection criteria; the potential for successfully competing in the sponsor’s competitive process, and the strategic advantage of the project to UNH. Those whose pre-proposals are selected as the institutional submission(s) will be notified and must then prepare a complete application to submit to the sponsor. See Limited Submission Programs for additional information.
Revised Budgets
When a sponsor wants to fund a proposed project at an amount different from that originally proposed, the sponsor asks the investigator to submit a "revised" budget supporting the amount to be funded. If the sponsor reduces the budget, the investigator must determine whether the originally proposed scope and objectives of the project can be met under the revised budget. If not, the investigator and sponsor must redefine the scope and objectives in writing before the University accepts the award.
If the original budget contained cost share or matching, the cost share or matching amount may need to change to reflect the budget revisions. These changes need institutional approval prior to resubmission.
View Proposals Knowledge Base
The Knowledge Base contains forms, instruction and training material, minutes, policies, tools and other resources to support your research efforts by topic area.
Contact Information
Sponsored Programs Administration Service Bldg., 2nd Floor 51 College Road Durham, NH 03824 Phone: 603-862-4865 Fax: 603-862-3564
FIND YOUR PRE-AWARD GRANT AND CONTRACT ADMINISTRATOR
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Methodology
Definition:
Research Methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to conduct research, investigate problems, and gather data and information for a specific purpose. It involves the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect , analyze , and interpret data to answer research questions or solve research problems . Moreover, They are philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process.
Structure of Research Methodology
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section:
I. Introduction
- Provide an overview of the research problem and the need for a research methodology section
- Outline the main research questions and objectives
II. Research Design
- Explain the research design chosen and why it is appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Discuss any alternative research designs considered and why they were not chosen
- Describe the research setting and participants (if applicable)
III. Data Collection Methods
- Describe the methods used to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations)
- Explain how the data collection methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or instruments used for data collection
IV. Data Analysis Methods
- Describe the methods used to analyze the data (e.g., statistical analysis, content analysis )
- Explain how the data analysis methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or software used for data analysis
V. Ethical Considerations
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise from the research and how they were addressed
- Explain how informed consent was obtained (if applicable)
- Detail any measures taken to ensure confidentiality and anonymity
VI. Limitations
- Identify any potential limitations of the research methodology and how they may impact the results and conclusions
VII. Conclusion
- Summarize the key aspects of the research methodology section
- Explain how the research methodology addresses the research question(s) and objectives
Research Methodology Types
Types of Research Methodology are as follows:
Quantitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data using statistical methods. This type of research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Qualitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Mixed-Methods Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research. This approach can be particularly useful for studies that aim to explore complex phenomena and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Case Study Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves in-depth examination of a single case or a small number of cases. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and anthropology to gain a detailed understanding of a particular individual or group.
Action Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves a collaborative process between researchers and practitioners to identify and solve real-world problems. Action research is often used in education, healthcare, and social work.
Experimental Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the manipulation of one or more independent variables to observe their effects on a dependent variable. Experimental research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Survey Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection of data from a sample of individuals using questionnaires or interviews. Survey research is often used to study attitudes, opinions, and behaviors.
Grounded Theory Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the development of theories based on the data collected during the research process. Grounded theory is often used in sociology and anthropology to generate theories about social phenomena.
Research Methodology Example
An Example of Research Methodology could be the following:
Research Methodology for Investigating the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Reducing Symptoms of Depression in Adults
Introduction:
The aim of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. To achieve this objective, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach.
Research Design:
The study will follow a pre-test and post-test design with two groups: an experimental group receiving CBT and a control group receiving no intervention. The study will also include a qualitative component, in which semi-structured interviews will be conducted with a subset of participants to explore their experiences of receiving CBT.
Participants:
Participants will be recruited from community mental health clinics in the local area. The sample will consist of 100 adults aged 18-65 years old who meet the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder. Participants will be randomly assigned to either the experimental group or the control group.
Intervention :
The experimental group will receive 12 weekly sessions of CBT, each lasting 60 minutes. The intervention will be delivered by licensed mental health professionals who have been trained in CBT. The control group will receive no intervention during the study period.
Data Collection:
Quantitative data will be collected through the use of standardized measures such as the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7). Data will be collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at a 3-month follow-up. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a subset of participants from the experimental group. The interviews will be conducted at the end of the intervention period, and will explore participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-tests, and mixed-model analyses of variance (ANOVA) to assess the effectiveness of the intervention. Qualitative data will be analyzed using thematic analysis to identify common themes and patterns in participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Ethical Considerations:
This study will comply with ethical guidelines for research involving human subjects. Participants will provide informed consent before participating in the study, and their privacy and confidentiality will be protected throughout the study. Any adverse events or reactions will be reported and managed appropriately.
Data Management:
All data collected will be kept confidential and stored securely using password-protected databases. Identifying information will be removed from qualitative data transcripts to ensure participants’ anonymity.
Limitations:
One potential limitation of this study is that it only focuses on one type of psychotherapy, CBT, and may not generalize to other types of therapy or interventions. Another limitation is that the study will only include participants from community mental health clinics, which may not be representative of the general population.
Conclusion:
This research aims to investigate the effectiveness of CBT in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. By using a randomized controlled trial and a mixed-methods approach, the study will provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the relationship between CBT and depression. The results of this study will have important implications for the development of effective treatments for depression in clinical settings.
How to Write Research Methodology
Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It’s an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are the steps to write a research methodology:
- Start by explaining your research question: Begin the methodology section by restating your research question and explaining why it’s important. This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods.
- Describe your research design: Explain the overall approach you used to conduct research. This could be a qualitative or quantitative research design, experimental or non-experimental, case study or survey, etc. Discuss the advantages and limitations of the chosen design.
- Discuss your sample: Describe the participants or subjects you included in your study. Include details such as their demographics, sampling method, sample size, and any exclusion criteria used.
- Describe your data collection methods : Explain how you collected data from your participants. This could include surveys, interviews, observations, questionnaires, or experiments. Include details on how you obtained informed consent, how you administered the tools, and how you minimized the risk of bias.
- Explain your data analysis techniques: Describe the methods you used to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, content analysis, thematic analysis, or discourse analysis. Explain how you dealt with missing data, outliers, and any other issues that arose during the analysis.
- Discuss the validity and reliability of your research : Explain how you ensured the validity and reliability of your study. This could include measures such as triangulation, member checking, peer review, or inter-coder reliability.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your research: Discuss any limitations of your study, including any potential threats to validity or generalizability. This helps readers understand the scope of your findings and how they might apply to other contexts.
- Provide a summary: End the methodology section by summarizing the methods and techniques you used to conduct your research. This provides a clear overview of your research methodology and helps readers understand the process you followed to arrive at your findings.
When to Write Research Methodology
Research methodology is typically written after the research proposal has been approved and before the actual research is conducted. It should be written prior to data collection and analysis, as it provides a clear roadmap for the research project.
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
The methodology should be written in a clear and concise manner, and it should be based on established research practices and standards. It is important to provide enough detail so that the reader can understand how the research was conducted and evaluate the validity of the results.
Applications of Research Methodology
Here are some of the applications of research methodology:
- To identify the research problem: Research methodology is used to identify the research problem, which is the first step in conducting any research.
- To design the research: Research methodology helps in designing the research by selecting the appropriate research method, research design, and sampling technique.
- To collect data: Research methodology provides a systematic approach to collect data from primary and secondary sources.
- To analyze data: Research methodology helps in analyzing the collected data using various statistical and non-statistical techniques.
- To test hypotheses: Research methodology provides a framework for testing hypotheses and drawing conclusions based on the analysis of data.
- To generalize findings: Research methodology helps in generalizing the findings of the research to the target population.
- To develop theories : Research methodology is used to develop new theories and modify existing theories based on the findings of the research.
- To evaluate programs and policies : Research methodology is used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies by collecting data and analyzing it.
- To improve decision-making: Research methodology helps in making informed decisions by providing reliable and valid data.
Purpose of Research Methodology
Research methodology serves several important purposes, including:
- To guide the research process: Research methodology provides a systematic framework for conducting research. It helps researchers to plan their research, define their research questions, and select appropriate methods and techniques for collecting and analyzing data.
- To ensure research quality: Research methodology helps researchers to ensure that their research is rigorous, reliable, and valid. It provides guidelines for minimizing bias and error in data collection and analysis, and for ensuring that research findings are accurate and trustworthy.
- To replicate research: Research methodology provides a clear and detailed account of the research process, making it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings.
- To advance knowledge: Research methodology enables researchers to generate new knowledge and to contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. It provides a means for testing hypotheses, exploring new ideas, and discovering new insights.
- To inform decision-making: Research methodology provides evidence-based information that can inform policy and decision-making in a variety of fields, including medicine, public health, education, and business.
Advantages of Research Methodology
Research methodology has several advantages that make it a valuable tool for conducting research in various fields. Here are some of the key advantages of research methodology:
- Systematic and structured approach : Research methodology provides a systematic and structured approach to conducting research, which ensures that the research is conducted in a rigorous and comprehensive manner.
- Objectivity : Research methodology aims to ensure objectivity in the research process, which means that the research findings are based on evidence and not influenced by personal bias or subjective opinions.
- Replicability : Research methodology ensures that research can be replicated by other researchers, which is essential for validating research findings and ensuring their accuracy.
- Reliability : Research methodology aims to ensure that the research findings are reliable, which means that they are consistent and can be depended upon.
- Validity : Research methodology ensures that the research findings are valid, which means that they accurately reflect the research question or hypothesis being tested.
- Efficiency : Research methodology provides a structured and efficient way of conducting research, which helps to save time and resources.
- Flexibility : Research methodology allows researchers to choose the most appropriate research methods and techniques based on the research question, data availability, and other relevant factors.
- Scope for innovation: Research methodology provides scope for innovation and creativity in designing research studies and developing new research techniques.
Research Methodology Vs Research Methods
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer

Eduinput- Online tutoring platform for Math, chemistry, Biology Physics
An online learning platform for Mcat, JEE, NEET and UPSC students
Research Proposal-Components, Types, Topics, Importance, and Applications

Table of Contents
What is Research Proposal?
A research proposal is a document that outlines the plan and rationale for conducting a research study. It serves as a blueprint for the entire research process and helps researchers communicate their objectives, methods, and expected outcomes effectively.
Components of a Research Proposal
The key components of a research proposal include:
- Title (Concise and informative title that reflects the essence of the research study)
- Abstract (Brief summary of the research proposal, highlighting its key objectives, methods, and expected outcomes)
- Introduction (Overview of the research topic, highlighting its significance and relevance)
- Research Objectives/Questions/Hypotheses (Clear and specific statements that outline the purpose of the study)
- Literature Review (Critical analysis of existing scholarly works related to the research topic)
- Research Methodology (Detailed explanation of the research design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques)
- Significance and Expected Outcomes (Explanation of the potential impact of the research and the expected results)
- Research Timeline (Proposed timeline that outlines the key milestones and activities of the research study)
- References (Comprehensive list of the sources cited in the research proposal)
Also learn about Action Proposal
Types of Research Proposals
Research proposals can vary depending on the field of study and the intended audience. Different types of research proposals can help you determine which format is most appropriate for your specific needs.
Whether responding to a solicitation, submitting an unsolicited proposal, or seeking continuation or renewal funding, each proposal type requires careful consideration and alignment with the sponsor’s objectives and guidelines.
Here are some common types of research proposals:
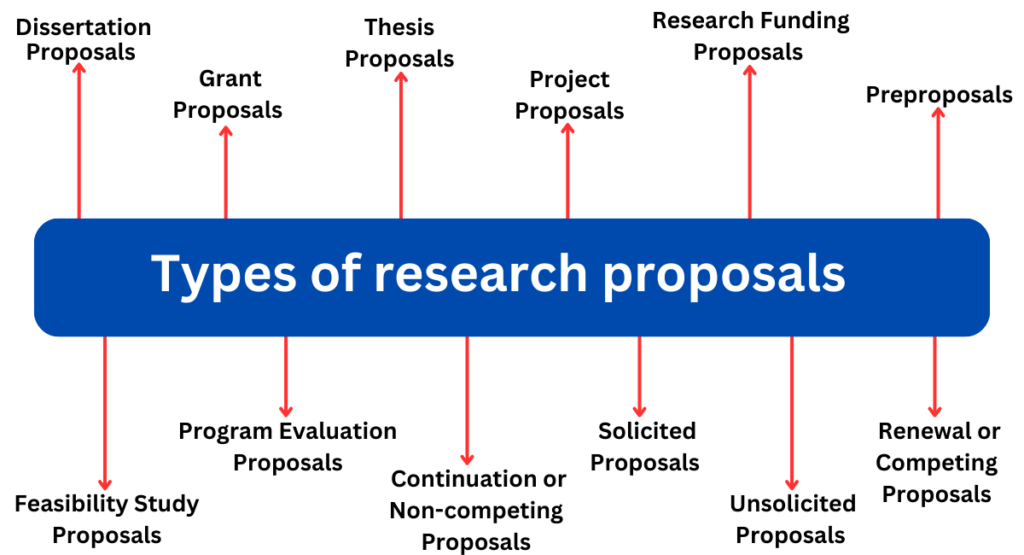
1. Solicited Proposals
Solicited proposals are submitted in response to a specific call or request issued by a sponsor. These calls, often referred to as Request for Proposals (RFP) or Request for Quotations (RFQ), outline the sponsor’s specific requirements, objectives, and evaluation criteria.
Solicited proposals must adhere to the provided guidelines and may include technical specifications and terms and conditions set by the sponsor. Broad Agency Announcements (BAAs) are similar but are not considered formal solicitations.
2. Unsolicited Proposals
Unsolicited proposals are submitted to a sponsor without a specific request or solicitation. In these cases, the investigator believes that the sponsor has an interest in the subject matter. Unsolicited proposals require the researcher to present a compelling case for the significance and relevance of their research, convincing the sponsor of the value and potential impact of the proposed study.
3. Preproposals
Preproposals are typically requested by sponsors who want to streamline the application process and minimize the effort required by applicants. Preproposals are in the form of a letter of intent or a brief abstract that outlines the main objectives and approach of the research.
After reviewing the preproposal, the sponsor informs the investigator if a full proposal is warranted. This process allows both the investigator and the sponsor to determine if it is worthwhile to proceed with a complete proposal submission.
4. Continuation or Non-competing Proposals
Continuation or non-competing proposals are submitted for multi-year projects that have already received funding from the sponsor for an initial period, typically one year. These proposals confirm the original proposal’s scope, objectives, and funding requirements for the subsequent period.
The sponsor’s decision to continue funding is contingent upon satisfactory work progress and the availability of funds.
5. Renewal or Competing Proposals
Renewal or competing proposals are submitted when an existing project is nearing its end, and the investigator requests continued support for the research. From the sponsor’s perspective, these proposals are treated similarly to unsolicited proposals, requiring a thorough presentation of the project’s achievements, impact, and future plans.
Renewal proposals must demonstrate the ongoing relevance and value of the research, highlighting the need for further funding to continue the project’s objectives.
6. Grant Proposals
Grant proposals are submitted to funding agencies, such as government bodies, foundations, or organizations, to secure financial support for research projects.
These proposals typically require a detailed description of the research project, including the objectives, methodology, expected outcomes, budget, and timeline. Grant proposals often follow specific guidelines provided by the funding agency.
7. Dissertation Proposals
Dissertation proposals are submitted by doctoral students as part of their research journey. These proposals outline the research topic, objectives, theoretical framework, methodology, and anticipated contributions to the field.
Dissertation proposals also typically include a literature review to establish the context and significance of the proposed research.
8. Project Proposals
Project proposals are common in academic and professional settings where research projects are undertaken. These proposals outline the objectives, scope, methodology, timeline, and expected outcomes of the project.
Project proposals often include details about the project team, resources required, and the potential impact of the project on stakeholders.
9. Thesis Proposals
Similar to dissertation proposals, thesis proposals are submitted by students pursuing a master’s degree. These proposals present the research topic, objectives, methodology, and expected contributions to the field.
Thesis proposals also include a literature review that highlights the existing knowledge and research gaps in the chosen area of study.
10. Research Funding Proposals
Research funding proposals are typically submitted by researchers or research teams within academic institutions or research organizations. These proposals aim to secure funding for ongoing or new research projects.
Research funding proposals often include a detailed description of the research objectives, methodology, expected outcomes, budget, and timeline. They may also require a justification for the need for funding and a demonstration of the potential impact of the research.
11. Feasibility Study Proposals
Feasibility study proposals are used to assess the practicality and viability of a research project before its full implementation. These proposals outline the research objectives, methodology, timeline, and expected outcomes, with a particular focus on evaluating the feasibility of conducting the research.
Feasibility study proposals often involve preliminary data collection or analysis to inform the decision-making process.
12. Program Evaluation Proposals
Program evaluation proposals are designed to assess the effectiveness, efficiency, and impact of a specific program, intervention, or policy. These proposals typically outline the evaluation objectives, methodology, data collection methods, analysis techniques, and expected outcomes.
Program evaluation proposals often require collaboration with relevant stakeholders and may involve both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
Steps in Developing a Research Proposal
Following steps are involved in Developing a Research Proposal:
- First of all identify a research topic . Select a research topic that aligns with your interests, expertise, and the existing gaps in knowledge.
- Review existing literature . Conduct a comprehensive literature review to understand the current state of knowledge in your research area and identify research gaps.
- Formulate research objectives/questions/hypotheses . Clearly define the research objectives, questions, or hypotheses that you aim to address in your study.
- Design research methodology . Determine the most appropriate research design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques for your study.
- Develop a research timeline . Create a timeline that outlines the key activities and milestones of your research project, ensuring a realistic and achievable plan.
- Consider ethical considerations and research limitations . Address any ethical concerns associated with your research, such as participant consent and data privacy. Also, acknowledge the potential limitations of your study.
- Write the research proposal . Compile all the components of the research proposal into a cohesive document, ensuring clarity, coherence, and adherence to guidelines.
Selecting Research Proposal Topics
Selecting a suitable research topic is important for the success of your research proposal. Consider the following tips when choosing your research topic:
- Choose an interesting topic . Select a research area aligned with your passions, experiences, or career aspirations to stay engaged and motivated throughout the process.
- Narrow down your topic . Refine your research question to a specific aspect or subtopic to maintain focus and avoid overwhelming amounts of information.
- Familiarize yourself with existing literature to gain insights, identify gaps in knowledge, and refine the scope of your research.
- Tailor your topic selection to meet the specific requirements and expectations outlined in your research assignment.
- Consult with professors or TAs for guidance, insights, and recommendations related to potential research topics within your field of study.
- Discuss your research ideas with classmates or friends to gain different perspectives, identify new angles, and prompt innovative approaches to your topic.
- Consider the “ who, what, when, where, and why ” questions.
- Why did you choose the topic? What aspects of the topic interest you? Do you have a particular opinion or stance on the issues involved?
- Who are the key information providers on this topic? Are there specific organizations, institutions, or experts affiliated with the topic?
- What are the major questions, debates, or issues surrounding the topic? Are there different viewpoints or perspectives to consider?
- Where is your topic significant? Does it have local, national, or international implications? Are there specific geographical regions or communities affected by the topic?
- When is/ was your topic important? Is it a current event or a historical issue? Are you interested in comparing your topic across different time periods?
Examples of Research Proposal Topics
- The impact of social media on mental health among adolescents
- Exploring the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing stress and anxiety
- Investigating the factors influencing consumer buying behavior in the e-commerce industry
- Assessing the effects of climate change on agricultural productivity in developing countries
- Investigating the Relationship between Exercise and Cognitive Function in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial.
- Exploring the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Enhancing Customer Experience in the Retail Industry.
- Understanding the Factors Influencing Employee Job Satisfaction and Engagement in the Workplace.
- Examining the Impact of Online Learning on Student Performance and Satisfaction in Higher Education.
- Investigating the Relationship between Parental Involvement and Academic Achievement among Elementary School Students.
- Analyzing the Effects of Early Childhood Education Programs on Long-term Academic Success and Socioeconomic Outcomes.
- Exploring the Factors Influencing Consumer Decision-making in Purchasing Organic Food Products.
- Investigating the Effects of Workplace Diversity on Organizational Performance and Innovation.
Importance and Impact of a Well-Written Research Proposal
Crafting a well-structured and compelling research proposal is essential for several reasons:
- A well-developed research proposal increases your chances of securing funding from organizations and institutions.
- Research proposals are often required for academic programs and can contribute to your academic and professional growth.
- A well-crafted research proposal provides a clear direction and plan for your research study, minimizing ambiguity and ensuring focused efforts.
- A thorough research proposal increases the likelihood of conducting impactful research that contributes to knowledge and addresses real-world problems.
Applications of Research Proposals
Research proposals serve as essential tools for planning and initiating research projects across various fields. They play a crucial role in academic, scientific, and professional settings. Here are some key applications of research proposals:

- In academic research , Research proposals are commonly used in academia to secure grants, scholarships, or to gain approval for research projects.
- Scientific Researchers in various scientific fields use research proposals to obtain funding, collaboration, and ethical clearance.
- In Business and industry , Research proposals are essential in business settings for conducting market research, product development, and process improvement initiatives.
- Research proposals enable non-profit organizations to gather data and evidence to support their mission and programs.
- Research proposals help government agencies gather information for policy development, program evaluation, and decision-making.
- Research proposals are used in healthcare settings to conduct clinical trials , study disease patterns, and evaluate treatment interventions.
- Research proposals assist environmental organizations in studying and addressing environmental issues such as climate change, pollution, and conservation.
- Research proposals are employed in educational settings to study teaching methodologies, curriculum development, and student outcomes.
- Research proposals are utilized in disciplines such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology to investigate human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices.
- In Technology and innovation , Research proposals support technological advancements by exploring new technologies, improving existing systems, and solving technological challenges.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get updates about new courses
NCERT solutions

9th Class 10th Class 11 Class 12 Class
Join the groups below to get updates.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Proposal. Definition: Proposal is a formal document or presentation that outlines a plan, idea, or project and seeks to persuade others to support or adopt it. Proposals are commonly used in business, academia, and various other fields to propose new initiatives, solutions to problems, research studies, or business ventures.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
Academic Research Proposal. This is the most common type of research proposal, which is prepared by students, scholars, or researchers to seek approval and funding for an academic research project. It includes all the essential components mentioned earlier, such as the introduction, literature review, methodology, and expected outcomes.
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Any type of research proposal follows the style, structure, and other writing conventions set by the relevant field of discipline. A research proposal outline's content typically varies in length, from 3 to 35 pages, with references (and appendices, if necessary). But like any academic activity, start the research proposal template writing ...
The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews.
A potent research argument describing the gaps in the current field, its importance, significance, and contributions to your research is the foremost requirement of a good research proposal. Remember, even though you are proposing the objective, academic way, the goal is to persuade the audience to provide you with the required research approval.
Writing a research proposal in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let's look at the explanation for each of the steps here: Step 1: Title and Abstract. Step 2: Introduction. Step 3: Research objectives. Step 4: Literature review.
A research proposal is a roadmap that brings the researcher closer to the objectives, takes the research topic from a purely subjective mind, and manifests an objective plan. It shows us what steps we need to take to reach the objective, what questions we should answer, and how much time we need. It is a framework based on which you can perform ...
e. A research proposal is a document proposing a research project, generally in the sciences or academia, and generally constitutes a request for sponsorship of that research. [1] Proposals are evaluated on the cost and potential impact of the proposed research, and on the soundness of the proposed plan for carrying it out. [2]
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer. [ 2] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about ...
A research proposal is a vital tool that can help scholars and university students complete a dissertation, receive funding for projects or fulfill course requirements. It outlines the importance of your inquiry and summarizes how you plan to investigate your research problem. Before developing a project, it's often valuable to learn some ...
Components of a Proposal. For each of the descriptions below, identify which component of the research proposal applies (title, abstract, table of contents, introduction, literature review, method ...
Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies. Other interesting articles.
A research proposal is a detailed plan which clearly outlines a suggested (or proposed) research project, its purpose, how the findings will add to the field of existing knowledge, and how the research will be ... TYPES OF RESEARCH While each discipline has some slightly different requirements for setting out a research proposal, the major
Also, students across various institutions submit research proposals to conduct academic studies. As a result, there are several types of research proposals with each type being due to its own requirements or qualifications. These types of research proposals are discussed below. Approval proposal: This type of proposal is commonly written by ...
The purpose of a proposal is to sell your idea to the funding agency. This means that the investigator must convince the funding agency that: The problem is significant and worthy of study. The technical approach is novel and likely to yield results. The investigator and his/her research team is/are the right group of individuals to carry out ...
A r esearch proposal is a document written by a researcher that provides a detailed description of. the pr oposed pr ogram. It is like an outline of the entire research process that gives a reader ...
Pre-Proposals. This type of proposal is requested when a sponsor wishes to minimize an applicant's effort in preparing a full proposal. They are usually in the form of a letter of intent or a brief abstract of what the PI plans to do, how the PI will conduct the project and why this project has merit. A pre-proposal establishes a foundation ...
Qualitative Research Methodology. This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Types of Research Proposals. Research proposals can vary depending on the field of study and the intended audience. Different types of research proposals can help you determine which format is most appropriate for your specific needs. Whether responding to a solicitation, submitting an unsolicited proposal, or seeking continuation or renewal ...