Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


Religious Tourism Studies: Evolution, Progress, and Future Prospects

2019, Tourism Recreation Research
This review study examines evolving themes in the scholarly literature on religious tourism and identifies research gaps that provide a basis for future investigations. The researchers evaluate a total of 84 studies of religion-induced tourism using content and thematic analyses. The findings show a plurality of approaches, both disciplinary and interdisciplinary, that extend to diverse methods, themes, applications, geographical foci and manifestations of the phenomenon. Understandings of religious tourism have evolved beyond pilgrimage and now encompass the meaningfulness of a destination. Recent explorations have extended beyond visitor motivations to consider their identities, such as individual religious affiliations and religiosity. The current paper contributes to knowledge by embracing infrastructure and the activities which occur in and around religious places as a legitimate study domain.
Related Papers
Amfiteatru Economic
MADALINA TALA
Religious tourism, sometimes called spiritual tourism, has gained an increasing role throughout the world. Due to its initial component, pilgrimage, it is often considered the oldest form of tourism, dating thousands of years back. Travels to the ancient holy places didn't have today's logistical support, but they had the same human motivation: faith. This faith, sometimes extreme, was the basis for shaping religions. Religions' variety and complexity can be justified through human typology, the environment in which their adepts live, culture, and last but not least, society's stage of development. The present paper wishes to investigate aspects related to religious tourism, identify some features it must react to, and highlight its determinants as well. Information is based on an up-to-date documentation, difficult to obtain in a field which hasn't been thoroughly investigated. The results refer to some original aspects, such as identifying the stakeholders of r...
Journal of Heritage Tourism
Peter Wiltshier
International Journal of Religious Tourism and Pilgrimage
Dr Razaq Raj
This discussion paper explores the topic of religious tourism and pilgrimage, examining it from a tourism industry perspective, reflecting on definitions, motivations and scale of the ‘product’ as reported at a global level. Mindful of the fact that international records of religious tourism are scant to say the least, this is an attempt to bring together definitions, classifications and data which come from a variety of sources. The paper draws together understandings from different religious traditions, presenting data and motivations on a variety of pilgrimage types. As the paper demonstrates, this ‘niche’ product is indeed enormous, and if industry projections are correct, is set to become an even more important element of international travel and tourism.
Silvia Beltramo
Maximiliano E. Korstanje
Advances in Hospitality, Tourism, and the Services Industry
Carlo Perelli
José Álvarez García
This paper reviews the academic literature related to religious tourism through a bibliometric study and citations of articles indexed in the multidisciplinary database Web of Science (WoS). Through an advanced search by terms, a representative set of 103 documents that form the ad-hoc basis of the analysis were selected. In view of the results, it is concluded that the United States is at the forefront of research, with almost 20% of the articles affiliated to one of its centres, mainly university centres. Publications on religious tourism are currently in an exponential growth stage, supported by the annual increase in the number of citations received. These papers are published in a small number of journals well positioned in their JCR category, classified within the field of Social Sciences Research.
Annals of Tourism Research
Mark N K Saunders
Current Issues in Tourism
David Airey
RELATED PAPERS
Journal of the South African Veterinary Association
Trevor Waner
OPUS Uluslararası Toplum Araştırmaları Dergisi
ferman erim
JURNAL PENDIDIKAN ILMU SOSIAL
Triani Widyanti
Tijarah: Jurnal Ekonomi dan Bisnis
Rizki khoirul Annisa
Revista Brasileira de Terapia Intensiva
José Mario Meira Teles
Revista de Innovación y Buenas Prácticas Docentes
Magdalena Campos
Polly Schaafsma
Aline BEDHA
Daniel Cardeira
Solid-State Electronics
ChemistrySelect
Mahmood D. Aljabri
Mustafa Ökmen
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
The Journal of Japan Atherosclerosis Society
Mitsuko Takenaga
Journal of chemical information and modeling
Nancy Baker
Physical Review C
Rui Ferreira Marques
Review of Quantitative Finance and Accounting
Jungshik Hur
JURNAL PENGABDIAN KEPADA MASYARAKAT
Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference “Business Cooperation as a Resource of Sustainable Economic Development and Investment Attraction” (ISPCBC 2019)
Nikolay Lomakin
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP
Maria Júlia Paes Silva
Vincent C Hu
Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis
Susana Camarero
BMC Oral Health
Osama Felemban
arXiv (Cornell University)
Mario Pichler
Environmental Health Perspectives
Jean McClellan
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Spiritual Tourism: A Review and Synthesis
- Conference paper
- First Online: 05 August 2023
- Cite this conference paper

- Eva Lang 4 ,
- Alexander Josiassen 4 , 5 &
- Florian Kock 4
Included in the following conference series:
- Sustainability, Economics, Innovation, Globalisation and Organisational Psychology Conference
213 Accesses
While traditionally interlinked with religiosity, spirituality is today used more broadly to include esoteric, mystic, and New Age beliefs and practices that centre on the individualistic search for meaning and purpose. Spiritual well-being, an outcome of spiritual experiences, has been linked to feelings of inner harmony and direction and thus to reduced stress and higher levels of life satisfaction. Tourism scholars have acknowledged the potential of tourism to provide spiritual experiences and thereby contribute to consumers’ well-being (e.g., Moal-Ulvoas G, Ann Tour Res 66:151–158, 2017). However, academics’ and tourism managers’ understanding and ability to leverage spirituality is considerably limited by two key shortcomings. Firstly, there is a lack of consensus regarding the definition of spiritual tourism, resulting in substantial conceptual ambiguity. Second, researchers disagree on the boundaries between religious and spiritual tourism, which has further complicated the understanding of the concept. These shortcomings leave tourism practitioners ill-equipped to understand and leverage the growing interest in spiritual tourism (Moufakkir O and Noureddine S, Ann Tour Res 70:108–119, 2018; Vada S et al, Tour Manag Perspect 33:100631, 2020). Setting out to address these shortcomings, the present study systematically reviews the body of literature on spiritual tourism and synthesizes the findings along central research themes. Anchored in this review, the study also advances a more nuanced, and much needed, delimitation between religiosity and spirituality in tourism. Based on the findings, the authors identify gaps in the current literature on spiritual tourism and suggest avenues for future research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Andriotis, K. (2009). Sacred site experience. A phenomenological study. Annals of Tourism Research, 36 (1), 64–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2008.10.003
Article Google Scholar
Buzinde, C. N., Kalavar, J. M., Kohli, N., & Manuel-Navarrete, D. (2014). Emic understandings of Kumbh Mela pilgrimage experiences. Annals of Tourism Research, 49 , 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2014.08.001
Cheer, J. M., Belhassen, Y., & Kujawa, J. (2017). The search for spirituality in tourism: Toward a conceptual framework for spiritual tourism. Tourism Management Perspectives, 24 , 252–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2017.07.018
Collins-Kreiner, N. (2010). Researching pilgrimage: Continuity and transformations. Annals of Tourism Research, 37 (2), 440–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2009.10.016
Collins-Kreiner, N. (2020). Religion and tourism: A diverse and fragmented field in need of a holistic agenda. Annals of Tourism Research, 82 , 102892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2020.102892
de Meezenbroek, E. J., Garssen, B., van den Berg, M., van Dierendonck, D., Visser, A., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2012). Measuring spirituality as a universal human experience: A review of spirituality questionnaires. Journal of Religion and Health, 51 (2), 336–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-010-9376-1
Digance, J. (2003). Pilgrimage at contested sites. Annals of Tourism Research, 30 (1), 143–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-7383(02)00028-2
Fedele, A. (2013). Looking for Mary Magdalene: Alternative pilgrimage and ritual creativity at Catholic shrines in France . Oxford University Press.
Google Scholar
Gilbert, E. (2007). Eat, pray, love: One woman’s search for everything . A&C Black.
Hall, M. C. (2006). Travel and journeying on the sea of faith: Perspectives from religious humanism. In D. J. Timothy & D. H. Olsen (Eds.), Tourism, religion and spiritual journeys . Routledge.
Heelas, P., & Woodhead, L. (2005). The spiritual revolution: Why religion is giving way to spirituality . Blackwell.
Hill, P. C., Pargament, K. I., Hood, R. W., Mccullough, M. E., Swyers, J. P., Larson, D. B., & Zinnbauer, B. J. (2000). Conceptualizing religion and spirituality: Points of commonality, points of departure. Journal for the Theory of Social Behaviour, 30 (1), 51–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-5914.00119
Holman, C. (2011). Surfing for a shaman: Analyzing an ayahuasca website. Annals of Tourism Research, 38 (1), 90–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2010.05.005
Houtman, D., & Aupers, S. (2007). The spiritual turn and the decline of tradition: The spread of post-Christian spirituality in 14 Western Countries, 1981–2000. Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion, 46 (3), 305–320. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-5906.2007.00360.x
Jarratt, D., & Sharpley, R. (2017). Tourists at the seaside: Exploring the spiritual dimension. Tourist Studies, 17 (4), 349–368. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468797616687560
Jiang, T., Ryan, C., & Zhang, C. (2018). The spiritual or secular tourist? The experience of Zen meditation in Chinese temples. Tourism Management, 65 , 187–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2017.10.008
Kato, K., & Progano, R. N. (2017). Spiritual (walking) tourism as a foundation for sustainable destination development: Kumano-kodo pilgrimage, Wakayama, Japan. Tourism Management Perspectives, 24 , 243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2017.07.017
Kim, B., Kim, S. S., & King, B. (2016). The sacred and the profane: Identifying pilgrim traveler value orientations using means-end theory. Tourism Management, 56 , 142–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.04.003
Komppula, R., & Gartner, W. C. (2013). Hunting as a travel experience: An auto-ethnographic study of hunting tourism in Finland and the USA. Tourism Management, 35 , 168–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2012.06.014
Kujawa, J. (2017). Spiritual tourism as a quest. Tourism Management Perspectives, 24 , 193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2017.07.011
Laing, J., Wheeler, F., Reeves, K., & Frost, W. (2014). Assessing the experiential value of heritage assets: A case study of a Chinese heritage precinct, Bendigo, Australia. Tourism Management, 40 , 180–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2013.06.004
Lin, L. P. (Lynn), & Hsieh, W. K. (2022). Exploring how perceived resilience and restoration affected the wellbeing of Matsu pilgrims during COVID-19. Tourism Management, 90 , 104473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2021.104473
Miao, L., Im, J., So, K. K. F., & Cao, Y. (2022). Post-pandemic and post-traumatic tourism behavior. Annals of Tourism Research, 95 , 103410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2022.103410
Moal-Ulvoas, G. (2017). Positive emotions and spirituality in older travelers. Annals of Tourism Research, 66 , 151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2017.07.020
Moal-Ulvoas, G., & Taylor, V. A. (2014). The spiritual benefits of travel for senior tourists. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 13 (6), 453–462. https://doi.org/10.1002/cb.v13.6 ; https://doi.org/10.1002/cb.1495
Moufahim, M., & Lichrou, M. (2019). Pilgrimage, consumption and rituals: Spiritual authenticity in a Shia Muslim pilgrimage. Tourism Management, 70 (August 2018), 322–332. https://doi.org/10.1002/cb.v13.610.1002/cb.1495
Moufakkir, O., & Noureddine, S. (2018). Examining the spirituality of spiritual tourists: A Sahara desert experience. Annals of Tourism Research, 70 , 108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2017.09.003
Nilsson, M., & Tesfahuney, M. (2016). Performing the “post-secular” in Santiago de Compostela. Annals of Tourism Research, 57 , 18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2015.11.001
Norman, A. (2011). Spiritual tourism: Travel and religious practice in western society . Bloomsbury Publishing.
Norman, A., & Pokorny, J. J. (2017). Meditation retreats: Spiritual tourism well-being interventions. Tourism Management Perspectives, 24 , 201–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2017.07.012
Palmatier, R. W., Houston, M. B., & Hulland, J. (2018). Review articles: Purpose, process, and structure. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 46 (1), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-017-0563-4
Paloutzian, R. F., & Park, C. L. (2014). Handbook of the psychology of religion and spirituality . Guilford Publications.
Piedmont, R. (1999). Does spirituality represent the sixth factor of personality? Spiritual transcendence and the five-factor model. Journal of Personality, 67 (6), 985–1013.
Puczkó, L., & Smith, M. (2012). An analysis of tourism QOL domains from the demand side. In Handbook of tourism and quality-of-life research (pp. 263–277). Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Reed, P. G. (1992). An emerging paradigm for the investigation of spirituality in nursing. Research in Nursing and Health, 15 , 349–357.
Rinschede, G. (1992). Forms of religious tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 19 (1), 51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/0160-7383(92)90106-Y
Sharpley, R., & Jepson, D. (2011). Rural tourism: A spiritual experience? Annals of Tourism Research, 38 (1), 52–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2010.05.002
Sheldrake, P. (2009). A brief history of spirituality . John Wiley & Sons.
Singleton, A. (2017). The summer of the spirits: Spiritual tourism to America’s foremost village of spirit mediums. Annals of Tourism Research, 67 , 48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2017.08.002
Sirgy, M. J., Kruger, P. S., Lee, D. J., & Yu, G. B. (2011). How does a travel trip affect tourists’ life satisfaction? Journal of Travel Research, 50 (3), 261–275. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287510362784
Stausberg, M. (2014). Religion and spirituality in tourism. In A. A. Lew, C. M. Hall, & A. M. Williams (Eds.), The Wiley Blackwell companion to tourism (pp. 349–360). Wiley.
Terzidou, M., Scarles, C., & Saunders, M. N. K. (2018). The complexities of religious tourism motivations: Sacred places, vows and visions. Annals of Tourism Research, 70 , 54–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2018.02.011
The World Academy of Science. (2022). ICSTED 2022: 16 . International conference on spiritual tourism and economic development . Waset.Org. https://waset.org/spiritual-tourism-and-economic-development-conference-in-november-2022-in-paris
Uysal, M., Sirgy, M. J., Woo, E., & Kim, H. L. (2016). Quality of life (QOL) and well-being research in tourism. Tourism Management, 53 , 244–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2015.07.013
Vada, S., Prentice, C., Scott, N., & Hsiao, A. (2020). Positive psychology and tourist well-being: A systematic literature review. Tourism Management Perspectives, 33 , 100631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2019.100631
Walton, J. K. (2009). Prospects in tourism history: Evolution, state of play and future developments. Tourism Management, 30 (6), 783–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2009.05.010
Wang, S., & Blasco, D. (2022). East meets West: Spiritual tourism in Chinese protected areas. Annals of Tourism Research Empirical Insights, 3 (1), 100035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annale.2022.100035
Wang, Y. C., Chen, P. J., Shi, H., & Shi, W. (2021). Travel for mindfulness through Zen retreat experience: A case study at Donghua Zen Temple. Tourism Management, 83 (September 2020), 104211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104211
Willson, G. B., McIntosh, A. J., & Zahra, A. L. (2013). Tourism and spirituality: A phenomenological analysis. Annals of Tourism Research, 42 , 150–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2013.01.016
World Tourism Organization [WASET]. (2015). First UNWTO International Conference on Spiritual Tourism for Sustainable Development – Ninh Binh Province, Viet Nam, 21–22 November 2013 . https://doi.org/10.18111/9789284416738
Zheng, C., Zhang, J., Qiu, M., Guo, Y., & Zhang, H. (2020). From mixed emotional experience to spiritual meaning: Learning in dark tourism places. Tourism Geographies, 22 (1), 105–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616688.2019.1618903
Zinnbauer, B. J., Pargament, K. I., Cole, B., Rye, M. S., Butter, E. M., Belavich, T. G., Hipp, K. M., Scott, A. B., & Kadar, J. L. (1997). Religion and spirituality: Unfuzzying the fuzzy. Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion, 36 (4), 549. https://doi.org/10.2307/1387689
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Copenhagen Business School, Frederiksberg, Denmark
Eva Lang, Alexander Josiassen & Florian Kock
James Cook University, Singapore, Singapore
Alexander Josiassen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Eva Lang .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Centre for International Trade and Business in Asia, James Cook University, Singapore, Singapore
Emiel L. Eijdenberg
Malobi Mukherjee
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Lang, E., Josiassen, A., Kock, F. (2023). Spiritual Tourism: A Review and Synthesis. In: Eijdenberg, E.L., Mukherjee, M., Wood, J. (eds) Innovation-Driven Business and Sustainability in the Tropics. SEIGOP 2023. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2909-2_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2909-2_9
Published : 05 August 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-2908-5
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-2909-2
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, the perspective of religious and spiritual tourism research: a systematic mapping study.
Journal of Islamic Marketing
ISSN : 1759-0833
Article publication date: 1 October 2018
Issue publication date: 18 October 2018
Religious tourism is a form of tourism where people of a particular faith travel to visit places of religious significance in their faith. Previous research into the various aspects of religious and spiritual tourism (RST) has been noticeably extended. The purpose of this study is to perform systematic mapping to provide trends and classification regarding the recent publications in the area of RST.
Design/methodology/approach
This study collected 181 papers from five scientific databases, from which 122 were selected to be classified according to six properties: research type, research focus, research method, investigated religion, publication type and time.
The analysis of these data resulted in a map of the research field, which was presented under three perspectives: the distribution and trends over time of each classification property and the relationship between them. Besides the visual map, the full list of classified papers is available. The results showed that the number of publications is increasing every year, which shows a growing interest in this field. Moreover, the primary research focuses were destination, demand and marketing. Top three journals were found to be International Journal of Tourism Research , Tourism Recreation Research and Journal of Heritage Tourism . Furthermore, evaluation research, solution proposals and opinion papers were the main research types in the area. In addition, the majority of studies focused on Christianity and Islam. Finally, survey, discussion paper, interview and case study were the predominantly used research methods.
Originality/value
The mapping study delivers the first systematic summary of RST research.
- Literature review
- Religious tourism
- Spiritual tourism
- Systematic mapping study
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely acknowledge the anonymous reviewer for giving constructive criticisms for improving the overall character of this review paper. The remarks given by the reviewer has certainly helped the authors in fine-tuning this paper, which may be of interest to the readers. This paper is based on the second chapter of PhD dissertation of fourth author under the title of “Modelling Dynamics of Religious Tourism Networks: A Future-Oriented Approach” in the Faculty of Management, University of Tehran, Iran.
Heidari, A. , Yazdani, H.R. , Saghafi, F. and Jalilvand, M.R. (2018), "The perspective of religious and spiritual tourism research: a systematic mapping study", Journal of Islamic Marketing , Vol. 9 No. 4, pp. 747-798. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-02-2017-0015
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2018, Emerald Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Environ Res Public Health

Research on the Development of Religious Tourism and the Sustainable Development of Rural Environment and Health
Hsiao-hsien lin.
1 Department of Leisure Industry Management, National Chin-Yi University of Technology, Taichung 41170, Taiwan
2 Department of Tourism Management, Athena lnstitute of Holidtic Wellness, Wuyi University, No 26, Wuyi Avenue, Wuyishan 354300, China
3 Institute of Physical Education and Health, Yulin Normal University, 1303 Jiaoyu East Rd., Yulin 537000, China; wt.moc.oohay@861961g
Jao-Chuan Lin
4 Department of Marine Leisure Management, National Kaohsiung University of Science and Technology, Kaohsiung 811213, Taiwan; wt.ude.tsukn@lcj
Zhou-Fu Liang
5 School of Environmental and Life Sciences, Nanning Normal University, No. 175 Mingxiu East Road, Xixiangtang District, Nanning 530001, China
Associated Data
No data support.
The purpose of the research is to explore how to reach a consensus on the development of cultural tourism and the sustainability of the entire rural environment from the perspective of different rights holders. Using Beigang Township in Taiwan as a case study, we first conducted a questionnaire survey and analyzed 600 respondents by statistical verifications method, then used an interview method to compile suggestions from experts and scholars, and finally conducted a field survey to collect actual information. After summarizing, organizing, and analyzing all the data, the study was examined in a multivariate manner. This study concludes that creating parking spaces, providing a comfortable resting place, facilitating the exchange of ideas, and improving the environmental literacy of the public will increase the public attention to issues such as village visibility, people interaction, ancient architecture, culture and totems, public health and transportation, and entrepreneurial development, as well as address the concerns of local residents and some men and people over 31–40 years old. By doing so, we can improve community building and security, enrich cultural resources, build and develop sufficient industries, stabilize prices, obtain a safe and hygienic village environment, increase the desire to revisit, become a recommendation for family travel, and achieve the goal of sustainable development of rural environment and health.
1. Introduction
Cultural tourism has gradually become an important source of income for the tourism industry. It is also a tourism asset that countries are investing in and developing one after another. Sites, architecture, art, festivals, religions, pilgrimages, etc., cultural relics or behaviors that can be remembered can be called cultural tourism resources [ 1 ]. However, general tourism resources will gradually be consumed due to the time and degree of use [ 2 ], and maintenance cost is required. However, religious beliefs and culture will not be exploited and consumed for development purposes, resulting in the exploitation or depletion of cultural resources that are increasingly impure. Instead, because of the uniqueness of local religious beliefs and culture, they are recognized by the public and attract more believers to worship them [ 3 ], which in turn adds to the mystery of local culture and makes local religious beliefs and culture more valued and preserved by the public [ 4 ]. It can be seen that religious cultural tourism resources are sustainable and have considerable potential for improving the current situation of rural development.
Religious culture is a unique belief in Chinese society. The belief in gods and goddesses arises when people face unpredictable natural or man-made disasters, or events beyond their ability, and seek spiritual support in the hope that the gods will bless them and their families to be safe, secure, and even prosperous [ 5 ]. Wude Temple was founded in 1955 and has a history of more than 30 years. It has become a famous temple of wealth on both sides of the Taiwan Strait [ 6 ].
Because of the frequent transmission of cultural deeds, the temple has won the trust of the faithful. In less than half a century, more than 6000 branches have been established on both sides of the Taiwan Strait, making the belief in the god of wealth one of the most rapidly developing beliefs in Taiwan [ 7 ]. Since 2010, the current authorities have combined the concept of cultural and creative industries to transform the operation of the temple with an innovative commercial management model. Blue Ocean strategy, intelligent innovation, and online platforms are applied to adapt to the competitiveness. Facilities and activities such as robots, five-way gods of wealth cards, cafes, and the Triacademy attract more consumers [ 8 ]. Despite natural disasters in 2019–2020 and Taiwan’s overall economic downturn, the Lunar New Year Festival attracted more than 100,000 people [ 9 ]. Successive national holidays have brought in tens of thousands of people. On average, the temple attracts at least 4 million worshippers each year [ 10 ], indirectly creating more than a million business opportunities. This shows that Wude Temple has established itself in the hearts of the Taiwanese people and has become an indispensable part of their faith, bringing new opportunities for economic development to Beigang, which was originally an agricultural area.
Although religious beliefs and culture are specific to a region and have a unique appeal, they can attract people’s interest to experience or participate in them, leading to tourism or consumer behavior and indirectly generating the flow of people and capital. However, while tourism development is a major contributor to the economic development of villages, there are always oversights in management decisions and can have positive and negative impacts on the economy, society, and the environment [ 11 , 12 , 13 ], affecting local sustainable development.
Moreover, the impact of tourism development is not instantaneous but requires time to prove, and usually occurs after the end of tourism activities [ 12 , 14 , 15 ]. Especially with the development of Internet technology and software technology [ 16 ], coupled with the impact of the COVID-19 epidemic [ 17 ], people have begun to change their behaviors and choices in tourism activities. In order to understand the changes generated by the development, exploring from the perspective of the residents can provide insight into the real state of local changes [ 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 ], and exploring from the experience of tourists can understand the real effectiveness and shortcomings of tourism development promotion [ 21 , 22 , 23 ]. Religious and cultural promotion of tourism development can unite society, give people spiritual support, promote economic circulation, and improve the community environment, but it can also cause an increase in local social events, inflate consumer costs, leave behind waste, and cause air and environmental pollution. Therefore, in order to achieve sustainable village development, we must not capture the views of a single target group but must ensure that both residents and visitors have a basic understanding of environmental literacy and a consensus on sustainable development, in order to achieve the goal of promoting sustainable economic development in villages through religious culture. By exploring the development dilemma from both residents’ and visitors’ perspectives, not only can we obtain a more nuanced view of the problem [ 18 , 22 , 23 ], but we can also obtain a consensus between them to solve the di-lemma they face.
Furthermore, according to the literature in the National Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations in Taiwan, although the current research on religion, culture, and tourism are mostly qualitative in terms of investigating cultural characteristics and assets [ 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ], followed by the awareness of religious activities [ 2 , 16 , 27 ], and cultural creativity and merchandise [ 28 ], the most quantitative research is on the impact of religious and cultural tourism [ 29 , 30 ]. However, there are only two studies on the Wude Temple of the God of Wealth in Beigang, Yunlin, and only qualitative studies on religious culture [ 5 ] and temple business model [ 8 ], and no other studies have been conducted to investigate the impact of religious culture development on local tourism development.
Therefore, the main purpose of this study was to understand the impact of religious and cultural tourism activities on the development of rural communities and the surrounding environment. From the perspective of environmental perceptions of people from different backgrounds, the study aimed to present the views on the impact of development on the current situation of local communities and the surrounding environment after the promotion of tourism activities with cultural resources in rural areas, to identify the shortcomings of development, and to propose suggestions for improvement towards the goal of common prosperity.
1.1. The Importance of Environmental Literacy to the Development of Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism is the act of using cultural artifacts, historical relics, and ancestral cultural creations as resources to attract tourists to travel and spend money. Culture is an inseparable tourism asset for the tourism industry [ 31 ]. However, cultural tourism cannot be properly developed without a beautiful natural environment, convenient traffic planning and transportation, and sales services of related industries and commodities in the vicinity [ 32 ]. It is clear that the promotion of cultural tourism still requires the integration of local economic, social, and environmental resources, and joint planning and development in order to effectively promote cultural tourism.
However, tourism development cannot be achieved overnight as it requires public recognition and cooperation for effective planning and development [ 18 , 22 , 23 ]. There has been a long-standing positive and negative debate on tourism development [ 11 , 12 , 13 ], which has not yet been properly resolved. The main reason is that tourist travel or consumption behavior has an impact on local economic, social, and environmental conditions, while residents continue to change the existing economic, social, and environmental conditions in order to obtain rich rewards and improve their quality of life [ 23 ]. As the global environment becomes more and more degraded and the problems arising from tourist behavior become more and more serious, individuals and society recognize the interaction between their living environment and the surrounding natural environment and the need to focus on individual or collective solutions to present or future environmental problems [ 33 ] and, therefore, begin to advocate environmental education and to appreciate its value deeply.
The value of environmental education is to enhance people’s environmental awareness and sensitivity, knowledge of environmental concepts, environmental values and attitudes, environmental action skills, as well as environmental action experiences [ 34 ]. In addition to the goals of technological integration, proactive participation in the problem-solving, balanced world and local perspectives, sustainable development, and international cooperation [ 35 ], environmental literacy should be cultivated so that citizens have basic environmental values and can effectively judge the strengths and weaknesses of development and help improve the current situation to achieve sustainable development. This shows that although culture may be damaged by tourism development if people can improve their knowledge of environmental education, be sensitive to tourism development, and develop environmental literacy, they will be able to reduce the negative impacts of tourism development and achieve the goal of sustainable development.
1.2. Establishment of Environmental Literacy Helps People Develop Cultural Tourism
Tourism is a global industry and a major economic source, but with global climate change, the problem of carbon emission and waste pollution from tourism activities is becoming more and more serious, so governments have started to pay attention to this problem actively [ 36 ]. The best way to solve the problems caused by tourism development is to improve the direction of development decisions and raise the level of environmental literacy of the people [ 37 ] so that decision-makers and the public can move toward a sustainable attitude toward tourism development decisions. It can be seen that exploring the current state of tourism development with people’s current attitude toward environmental literacy is a good way to examine the effectiveness and shortcomings of sustainable development of tourism decisions.
Tourism is generally seen as an important means of promoting local economic development [ 10 ], increasing local employment opportunities, improving local infrastructure, tax revenues, foreign investment, etc., and thus attracting more industries to the area [ 38 ], which not only contributes to the local economy but is also very beneficial to the economic positioning of the area [ 39 ]. The economic impact is easier to measure, has a more robust methodology, and is more convenient and reliable in terms of the amount of data available, and the economy is also the core interest of tourism development policy [ 40 ], so the issue of economic impact has been emphasized earlier than social and environmental impact.
The economic impact can be examined in terms of the price of people, industrial construction, and village development [ 16 ], which can lead to entrepreneurship and employment opportunities, increased wage income, increased tourism construction, increased tourism industries, the integration of local specialty industries, increased leisure opportunities, integrity of public facility maintenance, tourism development feedback to the community, convenience of public transportation, increased local health standards, development protection policy settings, development of creative goods and increased expenditure costs, and increased land and housing prices [ 16 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 ]. Therefore, the researcher believes that the most accurate economic impact factors can be obtained by examining employment, wages, consumption, construction, industry, facilities, prices, incentives, health, cultural and creative activities, community feedback, and policy coordination.
The social impact is brought about by the intervention of tourism development, which can positively promote cultural and lifestyle communication, reduce population outflow, and maintain a more robust social structure, as well as contribute to the preservation of local culture due to the importance of tourism; a tendency for social relations to become increasingly indifferent and self-serving, and the negative effects are the change in the local social system, the possible deviation of individual behavior, the growing coldness and utilitarianism of social relations, and the local social conflicts due to racial discrimination [ 42 ]. These include improved material living conditions, diversification of occupational structures, decreasing trends of out-migration, narrowing of racial barriers, increased community openness, increased community conflicts, and seasonal unemployment generation and crime [ 43 ]. It will also influence the popularity of tourism, improve the quality of local tourism services and activities, increase leisure opportunities, encourage participation in community tourism affairs, provide sufficient local tourism indicators and options for recreational facilities, strengthen tourism development organizations, attract young people to return to their hometowns, preserve indigenous cultures, raise expenditure costs, increase land and housing prices, highlight local architectural features, make visitors feel friendly, interact well with residents, and increase cultural exchanges across the strait, and provide sufficient police and security personnel, and increase the willingness of people to revisit or purchase property in the area [ 20 , 21 , 44 ]. Therefore, the researcher believes that the most accurate social impact factors can be obtained by looking at tourism facilities, community building, living atmosphere, cultural security, and then exploring the aspects of popularity, service and activity quality, policy participation, tourism organization planning, cultural and architectural characteristics, security maintenance, community building, and public interaction.
There are two sources of environmental impacts, the first is the impact of the tourism activity itself, and the other is the impact of the facilities provided for the tourism activity [ 45 ]. The physical environment can be divided into the human-made environment and the natural environment, including soil erosion, vegetation destruction, and ecosystem changes [ 21 , 46 ]. The impact of the man-made environment includes traffic congestion, noise, and garbage caused by the increase of population, and the lack of space and environment resulting in the overload of physical facilities [ 16 , 20 ], and the impact of a large number of new era buildings forming an incongruous landscape with the existing facilities [ 43 ]. Therefore, researchers believe that the most accurate environmental impact factors can be obtained by looking at tourism and leisure facilities, natural ecosystems [ 21 , 22 , 23 ], public transportation, parking and open space, environmental quality of tourists, garbage, motor vehicle fumes, water, and air quality.
1.3. Analyze the Importance of the Relationship between Perceptions of Tourism Shocks and Willingness to Re-Tourism to Establish Rural Health and Environmental Sustainability
Tourism development can promote the local economy, enhance the living conditions and quality of life of local residents, and improve existing facilities and infrastructure to increase tourists’ willingness to visit and spend money there [ 23 , 38 , 40 ]. A good experience of the effectiveness of decision-making and development will help residents to actively cooperate and generate the will to continuously promote participation in tourism decision-making [ 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 ], and a good tourism consumption experience will also increase tourists’ willingness to participate in tourism [ 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 ]. The perceptions of decision effectiveness [ 54 , 55 ] and the current status of rural tourism development may also vary among different rights holders, genders, and ages [ 38 , 54 , 56 , 57 ].
Based on the above arguments, it is concluded that since villages can promote local economy through tourism development, improve community environment and facilities, enhance tourism conditions, and improve the quality of services and facilities, it will have a certain influence on the current situation of residents’ quality of life and tourists’ willingness to travel. Therefore, the researcher believes that there is a correlation between tourism impact perception and the desire to revisit or purchase a property.
2. Research Methods
2.1. research process and framework.
This study was designed to Beigang Wude Temple as a case and investigates the effect of Taiwan’s religious and cultural tourism for the development of rural tourism. Firstly, we collected relevant literature and conducted a questionnaire survey targeting local residents and tourists in Beigang from December 2020 to January 2021. A total of 800 questionnaires were distributed, and 600 valid questionnaires were retrieved, with a return rate of about 75%. The data were statistically analyzed using SPSS 22.0 software, and then descriptive analysis was conducted. Based on the analysis results, the field survey method was used to collect field information, and the interview method was used to collect the opinions of experts, seniors, and travelers, and the research paper was constructed by the sequence of summarization, organization, and analysis [ 20 ]. Finally, the multivariate verification analysis method was used to integrate the information of different research subjects, research theories, and methods, and to obtain accurate knowledge and meanings by comparing the research results from multiple perspectives and multiple data [ 20 , 58 , 59 ].
According to the above-mentioned literature [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 ], the study investigated the economic, social, and environmental-related aspects and issues from the perception perspectives of different backgrounds, and the specific research framework is shown in Figure 1 .

Study framework.
According to the above framework, the research hypothesis is:
The development of religious and cultural tourism has no significant impact on the current economic development of the village.
There is no significant impact of religious and cultural tourism development on the social development of villages.
There is no significant impact of religious and cultural tourism development on village environment development.
There was no significant correlation between the impact of economic development and the willingness to revisit.
There was no significant correlation between the impact of social development and the willingness to revisit.
There was no significant correlation between environmental development impacts and the desire to revisit.
2.2. Research Tools
With reference to the literature on tourism impact [ 16 , 21 , 55 , 56 , 57 ], the economic, social, and environmental dimensions were categorized, and the subcomponents of the economic, social, and environmental dimensions were differentiated. The cognitive scale was designed using a five-point Likert scale, with a score of 5 for strongly agree, 4 for agree, 3 for generally agree, 2 for disagree, and 1 for strongly disagree, with the higher the score, the higher the cognitive level, and vice versa.
Reliability analysis can examine whether the measurement tool is reliable and stable. The α reliability coefficient method was used in this survey questionnaire, and SPSS 22.0 software was used to analyze the reliability of the questionnaire. Meanwhile, the coefficient value of Cronbach’s α is between 0 and 1, and the larger the α value, the better the correlation and the higher the reliability [ 60 ]. In general, an α value below 0.6 indicates that the internal consistency of the questionnaire is poor, an α value between 0.6 and 0.8 indicates that it is good, and if it is greater than 0.8, it indicates that the internal consistency of the questionnaire is very good [ 61 ]. The analysis showed that the Cronbach’s α coefficient was greater than 0.8 for economic, social, and environmental dimensions, so the reliability of the study questionnaire was higher for the economic dimension, as shown in Table 1 .
Classification table of tourism impact dimensions.
2.3. Research and Analysis
The purpose of this study was to investigate the impact of religious culture on the development of village tourism in Beigang Wude Temple. Quantitative research can get the opinions of most people, but cannot get detailed questions [ 62 , 63 ]. Although qualitative research can only represent the suggestions of a small number of people, with the answers provided by representative people, deeper and subtle insights can be obtained [ 64 ]. Mixed research methods can make up for shortcomings [ 65 ]. In order to obtain the most factual suggestions for improvement, the study first asked five industry members, scholars, and citizens who are familiar with the local development process and have relevant professional backgrounds and created an outline of the interviews by referring to the issues on which at least three people had a consensus. Based on the results of the questionnaire analysis, we then applied focused interviews to seek the opinions of professionals, scholars, and citizens who are familiar with the local development process and have relevant professional backgrounds, to obtain more factual truths and construct the best recommendations as shown in Table 2 .
Background information of the interviewees and outline of the interview.
Lastly, field surveys and interviews were conducted to collect actual information, and after summarizing, organizing, and analyzing all the data, a multivariate review was conducted.
The survey started in 2020, and the initial visitors were distributed all over the country. Due to limitations in manpower, material resources, and funding, field surveys were conducted first to observe the current status of village development and residents’ opinions. In addition, factors such as local farming, young people working outside the village, and the fact that the COVID-19 epidemic was not yet under control limited the initial collection of samples. Although the information was subsequently collected through a combination of online questionnaire platforms, the information collected by the researcher was flawed due to differences in respondents’ cooperation and proficiency in using 3C products. The limitations of the study will be presented in this paper, and we encourage subsequent researchers to correct them to improve on the study.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. background analysis.
The analysis revealed that there was not much difference in the status of the respondents (45.5% of residents and 54.5% of tourists), but most of them were women (40.9%), aged between 21 and 50 (74.2%), mainly residents of central (48.5%) and southern (42.4%) areas, and mostly used their own cars for transportation (89.4%). Most of the spending amount was less than 35.71 USD (75.8%), mainly for prayers, donations, joss paper, and incense (72.8%), as shown in Table 3 .
Background disguised analysis table.
3.2. Analysis of the Awareness of the Impact of Religious and Cultural Tourism on Village Development
Culture is an indispensable trace of human civilization, and faith is a source of inspiration for most people. Religious and cultural concepts of the immutability and equality of all beings have been the means of transmitting the correct social values and fostering environmental and cultural awareness in our country from ancient times to the present [ 57 ]. Therefore, based on the premise of environmental awareness, exploring people’s views on promoting cultural tourism and maintaining the overall environment of rural communities [ 34 , 66 , 67 ] can be a sound proposal for sustainable rural development. However, development has positive and negative impacts on the economic, social, and environmental levels [ 12 , 16 ], and different backgrounds may lead to different perspectives, and acquiring different perspectives is beneficial for obtaining the best suggestions for improvement [ 16 , 23 , 55 , 56 , 57 ].
The questionnaire was designed based on the literature, and a Likert scale was used, with 1 meaning strongly disagree and 5 meaning strongly agree. The basic statistical tests were used to explore people’s perceptions of the current status of village development, and then the t-test and ANOVA tests were used to explore the perception differences among different status, gender, and age, and then the interview information was compared and explored in a multivariate verification method [ 20 , 58 ].
3.2.1. Analysis of the Awareness of the Impact of Religious and Cultural Tourism on the Village Economy
It was found that most people believed that the development of cultural tourism in Wude Temple has combined with local specialty industries (4.24), increased entrepreneurship and employment opportunities (3.95), and indirectly improved the standard of medical and health care (4.09). However, the effectiveness of the existing tourism development in giving back to the community (3.53) was not perceived, and the quality of public facilities (4.11) and public transportation (3.18) remained poor, which is not entirely consistent with the literature [ 14 , 21 , 53 , 54 , 55 ]. In addition, there was a significant difference in the perception of the current status of public facilities maintenance in communities with feedback from tourism development ( p < 0.01), and residents felt worse about the effectiveness of public facilities maintenance; the older they were, the worse they felt, as shown in Table 4 . Based on the above description, Hypothesis 1 was not confirmed.
Analysis of the awareness of the impact of religious and cultural tourism on the village economy.
* p < 0.01.
Although environmental education has been included in the basic curriculum of Taiwan national education for many years, and students have been cultivating a sense of environmental conservation for many years, coupled with the Chinese culture’s promotion of the concept of benevolence and love, and the religion’s promotion of the awareness of equality of all beings, Taiwanese people are well aware of ecological and environmental conservation. However, the overall economic development of rural areas is insufficient, and all industries are still waiting to be developed. Although the people have the awareness of ecological and environmental conservation, they still hope to continue to develop rural cultural tourism activities by combining local religious customs (4.24), ecological environment, and agricultural products, so as to attract believers and tourists to visit the villages and create a large number of business opportunities, and to improve employment and entrepreneurship opportunities (3.95), medical and health care, as well as to improve the quality of life (4.09). However, since most of the existing public temple cultural institutions in Taiwan are private organizations with self-funded operations, and in order to avoid suspicion, officials seldom take the initiative to communicate with each other on development planning issues, and the degree of cooperation is low, as a result, the feedback received by villages is not effective (3.53), and the quality of public facilities (4.11) and public transportation remains poor (3.18). As a result, most people feel strongly about changes in the integration of special industries, entrepreneurship and employment opportunities, and the standard of medical and health care, but feel poorly about the effectiveness of the development of feedback villages, public transportation, and public facilities.
While the public has a wealth of environmental awareness and experience, policies need to be discussed, decisions need to be driven by human and resources, and results need to be proven over time so visitors who stay for a short period will not be able to accurately judge the difference between before and after changes. Moreover, as tourism development extends over time, the magnitude of change increases and only those who have lived here for a long time will be able to feel it deeply. Therefore, residents believe that the development of tourism does not give back to the community (residents < tourists; 3.77:4.39) and maintain public facilities (residents < tourists; 3.60:4.25), and the older they are, the worse they feel (20 under > 21–30 > 31–40 > over 51 > 41–50). Based on the above description, the analysis results obtained cannot be in line with the Institute of Research Hypothesis 1.
3.2.2. Analysis of the Awareness of the Impact of Religious and Cultural Tourism on Village Society
It was found that most people thought that the development of cultural tourism in Wude Temple was helpful in enhancing the visibility of local tourism (4.47), friendly interaction between residents and tourists (3.91), and preservation of unique village humanistic architecture or landscape totems (4.17). However, the result is not entirely consistent with the literature [ 16 , 23 , 55 , 56 , 57 ], as police, firefighters, and security personnel (3.47), as well as tourism indicators (4.05), are not well planned, and architectural features (3.3) are gradually disappearing. The results are in line with the literature [ 16 , 55 , 56 , 57 ]. The issue of open space is significantly divided by gender ( p < 0.01), and men believe that parking and open space facilities need to be improved, while people aged 31–40 are more sensitive to the issues of social participation and development of tourism organizations, as shown in Table 5 . Based on the above description, Hypothesis 2 was not confirmed.
Analysis of the awareness of the impact of religious and cultural tourism on village society.
Most of the villages are remote areas where crowds do not easily gather. Promoting tourism development with religious, agricultural, and cultural specialties can effectively enhance local visibility (4.47). While residents expect to improve their quality of life and achieve long-term development, they do not want to lose their existing living habits (3.91), cultural cus-toms and features, and tourists do not want to lose their original village style and tourism features (4.17). However, due to the aging population, the outflow of young people (3.47), the small size of the village, and the limited space available for consumption (4.05), a large number of modern entertainment and consumption facilities have been built to meet the needs of tourists, forcing the demolition of existing buildings (3.3). Therefore, most people think that the visibility, preservation of unique village architecture or landscape totems, and interaction between residents and tourists are effective, while tourism indicators and police, firefighters, and security personnel are insufficient, and architectural features are gradually disappearing.
Since most people in Taiwan are highly educated and nurtured by sound professional knowledge and environmental teaching, they possess basic knowledge and have a high degree of environmental awareness and sensitivity. Most of the believers and cultural tourism tourists are family tourists, and there is little unused space in the rural areas. Excluding the living space of the existing residents, the shopping areas and stalls occupy the area, and the parking spaces for tourists are chaotic, resulting in tourists who are mainly male (father or elder brother) drivers often face the difficulty of finding a parking place (female > male; 3.56:3.97). Therefore, male citizens are more sensitive to the issue of parking and leisure facilities, while citizens aged 31–40 are more sensitive to the issue of social participation and the development of tourism organizations (31–40 > 20 under > over 51 > 21–30 > 41–50). Based on the above description, the analysis results obtained cannot be in line with the Institute of Research Hypothesis 2.
3.2.3. Analysis of the Awareness of the Impact of Religious and Cultural Tourism on the Village Environment
It was found that most people thought that the cultural tourism development of Wude Temple helped preserve the historical scenery and relics (4.00) and that the temple authorities provided sufficient space for public toilets (4.00). However, the planning of transportation outside the temple (3.06) was inconvenient, and the public trash cans were not clearly set up and insufficient (3.39), which is not exactly the same as in the literature [ 16 , 23 , 55 , 56 , 57 ]. Although respondents of different status and gender had the same opinion, the older they were, the worse they felt about the planning of public toilets and the effectiveness of historical scenery and maintenance of monuments, as shown in Table 6 . Based on the above description, Hypothesis 3 was not confirmed.
Analysis of the awareness of the impact of religious and cultural tourism on the village environment.
Although the ecological environment, history, customs, and ancient architecture are important tourism resources, the unique local religious culture is also a unique rural tour-ism feature. However, rural villages are scattered and have little space for tourism development, and the number is small and dense so maintaining resources (4.00) and providing a good public environment and sanitary space (4.00) is the key to improving the quality of tourism and services as well as sustainable development. However, because the main tourist activity space is far away from the road outside, the residential houses and the surrounding stores are crowded (3.06), the activity area is narrow and the available space for planning is limited (3.39). Therefore, most people think that the historical scenery and historical sites are well maintained, and the public toilets are well planned, but the public garbage cans are not well set up and insufficient in number, and the transportation is inconvenient.
Nevertheless, due to the limited building space available in the village temples, the lack of public space around them, the intermingling of residential and tourist areas, the aging population, the proliferation of elderly tourists, the outflow of young people, and the loss of labor force, it is impossible to provide adequate and complete public toilet facilities to satisfy the elderly worshippers (tourists). Moreover, the longer historical scenery and relics exist, the more precious they become, but the more easily they are damaged. Changes in scenery or resources can be experienced and felt by people who have lived there for a long time in a different time and context (20 under > 21–30 > 31–40 > 41–50 > over 51). Therefore, the older people are, the more deeply they feel that public restrooms are inadequate and that historical landscapes and monuments are not well maintained. Based on the above description, the analysis results obtained cannot be in line with the Institute of Research Hypothesis 3.
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Village Development Impact and Perception of Re-Tourism or Property Purchase Intention
Ultimately, tourism development aims to promote village development, improve existing facilities and infrastructure, meet the needs of tourists, and promote sustainable visitation and tourism consumption [ 23 , 38 , 40 , 55 ], which are sustainable development goals. Therefore, it is important to investigate the impact of village development on perceptions and willingness to revisit or purchase property to understand the key factors of people’s willingness to revisit or purchase properties. Therefore, the Pearson correlation analysis was used to examine the correlation between the impact on cognition and the willingness to revisit or purchase properties.
3.3.1. Correlation between Economic Impact and Perception of Re-Tourism Willingness
It was found that there was a significant relationship between industrial development, private property prices, community development and the willingness to revisit or purchase properties ( p < 0.001), and the effectiveness of industrial development (0.686), community development (0.618), and private property prices (0.588) influenced the willingness to recommend friends and relatives to travel and experience, and the results were not identical in the literature [ 23 , 38 , 40 , 55 ], as shown in Table 7 . Based on the above description, Hypothesis 4 was no confirmed.
Correlation analysis of the economic impact and re-tourism intention.
** p < 0.001.
Although tourism development is currently advocated to be environmentally friendly and to move toward sustainable tourism development, for villages with religious culture and agricultural industry as development resources, having adequate industrial development, sound community development, and stable prices for people’s livelihoods are still the main keys to attracting people. Based on the above description, the analysis results obtained cannot be in line with the Institute of Research Hypothesis 4.
3.3.2. Correlation between Society Impact and Perception of Re-Tourism Willingness
It was found that there was a significant correlation ( p < 0.001) between community building, the culture of life, cultural security and the willingness to revisit or purchase property, and the effectiveness of community building (0.686), cultural security (0.618), and culture of life (0.588) affected the willingness to recommend friends and relatives to travel and experience, and the results were not identical in the literature [ 19 , 34 , 36 , 51 ], as shown in Table 8 . Based on the above description, Hypothesis 5 was no confirmed.
Correlation analysis of society impact and re-tourism intention.
Since villages have limited space for tourism development, organizing volunteers or bringing in manpower to maintain culture and law and order, deeply cultivating local human customs and cultural characteristics, using existing space for community building, as well as proper planning of tourism highlights, will be the basis for people to recommend their friends and relatives to visit the villages. Based on the above description, resulting in the analysis results obtained cannot be in line with the Institute of Research Hypothesis 5.
3.3.3. Correlation between Environment Impact and Perception of Re-Tourism Willingness
A significant correlation ( p < 0.001) was found between village environment, public health, and the willingness to revisit or purchase properties, and the effectiveness of public health (0.752) and village environment (0.317) influenced people’s attractiveness and willingness to re-engage in local activities and the results were not identical in the literature [ 23 , 38 , 40 , 55 ], as shown in Table 9 . Based on the above description, Hypothesis 6 was no confirmed.
Correlation analysis of the environmental impact and re-tourism intention.
* p < 0.01. ** p < 0.001.
The environment and sanitary conditions of tourism are the main factors for people to consider in their travel activities, especially in the current poor travel environment surrounded by viruses, a safe and sanitary travel environment is a key consideration. Therefore, maintaining a clean and safe public sanitary space in the village environment is a key factor to attract tourists to visit again and recommend their friends and relatives to visit with them. Based on the above description, the analysis results obtained cannot be in line with the Institute of Research Hypothesis 6.
4. Conclusions
Survey results show that although cultural tourism helps villages to improve their reputation, preserve historical sites, increase the integration of special industries, promote interaction among people, increase entrepreneurship and employment opportunities, and improve the standard of public toilets and medical sanitation, problems such as the lack of tourism feedback, inadequate village development, low number of public garbage cans, unclear settings, inconvenient transportation, insufficient public facilities, tourism indicators, and police and fire safety personnel, and the disappearance of local architecture have yet to be solved.
It was concluded that creating parking spaces, providing a comfortable resting place for tourists, creating an open exchange of ideas, and raising public awareness and consciousness of the environment would increase the importance of public issues such as village visibility, citizen interaction, ancient architecture, culture and totems, public health and transportation, and entrepreneurial development in the village, as well as address the concerns of local residents and some men and people over the age of 31–40. It will also improve community building and security, enrich cultural resources, provide adequate industrial infrastructure and development, stabilize prices, and achieve a safe and sanitary public environment, thus increasing the desire of people to revisit and making the village a recommended destination for family travel, and achieving the goal of sustainable development of rural environment and health.
Based on the above results, the following suggestions are made:

4.1. Local Government
Development does not only depend on local rural characteristics and tourism resources but also requires administrative and financial support from government agencies in order to have proper development space and community planning.
If the local government can entrust experts and scholars to conduct field Tacha, reforming surrounding tourist moving lines, link temples and cultural organizations, to collect the views of residents, aid to promote the depth of cultural tourism.
4.2. Local Authorities
Development does not rely solely on government resources and enthusiastic public input, but also on talents with professional knowledge and skills, in order to continuously explore local characteristics, create uninterrupted tourism appeal, and achieve sustainable development goals.
If local governments or tourism development organizations can refer to the suggestions of local cultural organizations and professionals, conserve local cultural assets, and use resources to develop tourism activities or products, they can create tourism highlights.
4.3. Policy Makers
Visionary leaders are critical but gathering more information and recruiting more expertise can lead to innovative, sound, and trend-aligned decisions.
If government agencies can invite existing villagers, organize community volunteer organizations, set up entrepreneurial technology courses, encourage residents to participate, and combine local high school courses and manpower, it can solve the problem of insufficient development manpower.
4.4. Suggestions for Future Research
Since the study mainly takes Beigang Wude Temple as a case study, it explores the influence of Taiwan’s religious and cultural tourism on the development of rural tourism, and the different cultural customs and characteristics of different regions may also cause different village development impacts.
Therefore, the researchers believe that it is recommended that future researchers continue to explore religious and cultural tourism or related issues based on differences in different countries, regions, different rights, and ages, and understand the understanding and differences of peers on this topic in order to improve related research flaws.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-H.L. and Z.-F.L.; methodology, H.-H.L.; software, Y.L.; validation, J.-C.L., Y.L.; formal analysis, H.-H.L.; investigation, J.-C.L.; resources, Z.-F.L.; data curation, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-H.L. and Z.-F.L.; writing—review and editing, H.-H.L.; visualization, H.-H.L.; supervision, H.-H.L.; project administration, Z.-F.L.; funding acquisition, J.-C.L., Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All subjects in the study were anonymously labeled and agreed to participate in the survey.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
religious tourism Recently Published Documents
Total documents.
- Latest Documents
- Most Cited Documents
- Contributed Authors
- Related Sources
- Related Keywords
THE EMERGENCE OF A NEW RELIGIOUS TRAVEL SEGMENT: UMRAH DO IT YOURSELF TRAVELLERS (DIY)
This research examines the rise of a new religious travel segment – the Umrah Do It Yourself (DIY) travellers. While Hajj is the fifth pillar of Islam, Umrah is a minor Muslim pilgrimage that can be undertaken at any time of the year, while still playing a crucial role in the completion of Hajj rituals. In the past, Umrah was managed by an authorised travel agent, who makes all the necessary pilgrimage preparations, from flights to trip itineraries. Recent years have seen an upsurge in travellers who prefer not to utilise the services of such agencies, but instead, to make their own arrangements. The decision by the Saudi Arabian government to launch a Tourist e-Visa in September 2019 has opened a window of opportunity for the legalization of Umrah DIY journeys. The objectives of this study are (i) to explore the travel motives that contribute to the success of the Umrah DIY, and (ii) to explore the factors that support and facilitate the decision for the Umrah DIY. The data were obtained via 20 semi-structured interviews with Umrah DIY travellers. The findings show that flexibility, spirituality, and budget have a crucial impact on travel motivation. Additionally, the findings suggest that information sources, travel quality, companionship/new friendship, and familiarity facilitate the choice of Umrah DIY travel. This research contributes to the growing scholarship on the Muslim travel market beyond Hajj and to studies on independent religious travel. Findings provide an opportunity for suppliers and industry participants to understand the travel motives of this new segment as a basis for producing relevant religious tourism products and services.
EVALUATION OF ARCHITECTURAL COMPONENTS IN BAYUNG GEDE VILLAGE SETTLEMENT, BALI AS A TOURISM OF SPECIAL INTEREST
<p>Special interest tourism is one of the efforts to provide alternative tourist attractions and sustainable tourism development in Bali. Visits of both domestic and foreign tourists to Bali in the last 4 years (2015-2019) have increased by an average of 8%. Now the tourism sector in Bali, especially in Bangli Regency, is starting to investigate or explore the possible development of tourist attractions through the development of tourist villages. In this case, the development of special tourism, including the tourist village of Bayung Gede, Bangli is very dependent on the architectural components of traditional settlements and the traditions of the residents in it as a source of attraction and main attraction for tourists. However, the influence of tourism has led to the transformation of traditional settlements. In this case, the transformation has given rise to a paradoxical phenomenon where on the one hand traditional housing attracts tourists, on the other hand the presence of tourists has led to a transformation of the traditional settlements of an area. The purpose of this study is to examine the architectural components of the Bayung Gede Village settlement as a tourism potential based on special interest tourism and then to find out how far the tourism architectural potential is found and how strong the Bayung Gede Village settlement icon is as a special interest DTW. The method used is a qualitative-exploratory and descriptive method. The results show that the traditional settlement of Bayung Gede Village contains elements of special interest tourism such as elements of novelty seeking, quality seeking, enriching, rewarding, adventuring and learning, so that it has the potential as religious tourism (the existence of four types of graves), culture (settlement and residential layout) and citrus plantation sector agro-tourism in improving the economic sector of the community. Investigation and inventory of Bayung Gede traditional housing is an effort to find a village icon that has prestige that can attract tourists to visit and be able to compete with other tourist villages.</p>
Prospect of Pilgrimage Tourism in Namo Buddha Area, Kavre
This paper tries to find out the prospect of pilgrimage tourism at Namo Buddha, Kavre, Nepal. There is found limited academic work on pilgrimage tourism in Nepal; however, no evidence of study could be traced on Namo Buddha that is based on pilgrimage tourism perspective. A pilgrimage is an ancient form of religious travel where people make a journey to the place of their belief for experiencing spirituality. Namo Buddha is one of the sacred Buddhist shrines and important pilgrimage sites for Buddhists as they believe the relics of the previous life of Lord Buddha are kept at Namo Buddha Stūpa. Namo Buddha stūpa is also considered to be one of the holiest stūpas in Nepal including Svayambhu Stūpa (Svayambhu Mahachaitya) and the Bodhnath Stūpa (Khasti Mahachaitya). This stūpa commemorates the Buddha Śakyamuni’s sacrifice of his body to a starving tigress and her cubs in his previous life. Nepali people call this site Namo Buddha, Newars call Namo Buddha as Namura and Tibetans call it as Takmo Lu Jin. The place has a huge potential to attract both Buddhist and Hindu pilgrims including international tourists from all over the world. This place offers other attractions and activities besides pilgrimage-based elements such as sightseeing of heritage town; spectacular Himalayan ranges; paddy field terrains; hilly forests; soft adventures experience; and so on. Religious tourism and pilgrimage tourism are interchangeably used in this study and the paper is based on both the primary and secondary data. Exploratory research has been carried out to examine the religious and economic benefits of pilgrims at this site. It also tried to investigate locals’ perspectives on pilgrimage tourism development. Meanwhile, this paper not only studied prospects of pilgrimage tourism in Namo Buddha but also attempted to find out and highlight how the Covid-19 pandemic has impacted the destination.
Role of Technology on Religious Tourism in Turkey
The religious tourism sector is a booming industry and attracts a sizable number of tourists around the world. While several factors play an important role in increasing the number of tourists for religious purposes, technology plays a vital role in managing and boasting religious tourism in a country. The authors aim to see this in the context of Turkey, a country that is a bridge between East and West, possessing a number of religious touristic sites and attracting a large number of tourists. The profile of the country and the role of technology in increasing tourism in Turkey also suggest improvements in the technological landscape of the country to increase and facilitate the religious tourists.
Construction of the Wali Pitu’s Sacredness and Islamic Veneration in Balinese Hindu Civilization
<p class="abstrak">This article explains the <em>Wali Pitu</em> (the seven saints) as a new form of veneration dynamics in Indonesia, which was built by the sacredness of Bali as the heart of Hindu culture in Indonesia. This phenomenon is unique and interesting, because the seven tombs of Muslim saints are venerated by Hindus of the region. This study uses a qualitative approach with the case-study method, extracting data as documentation from the notes of Toyyib Zaen Arifin during the expedition to search the seven graves, and interviews with members of the Manaqib al-Jamali, guidance, organizers and religious tourism congregations, as well as several caretakers of the tombs. This article describes the sacred construction of the discovery of the seven sainthoods tombs and their cults and their dynamics as a new form of the veneration of saints in Indonesia, one that differs from the other forms of veneration in Java which has been deeply rooted for a long time, such as the <em>Wali Songo</em> (the nine saints).</p><p class="abstrak" align="left"> </p><p><em>Artikel ini berupaya menjelaskan Wali Pitu (tujuh wali) sebagai bentuk baru dinamika venerasi di Indonesia yang dibangun oleh sakralitas Bali sebagai jantung peradaban Hindu. Fenomena ini sangat unik dan menarik dimana kedua korpus yang diteliti sangat kontradiktif namun menjadi sebuah realitas nyata, dimana tujuh makam wali Muslim ditemukan di Bali sebagai jantung peradaban Hindu. Menggunakan pendekatan kualitatif dengan metode studi kasus, penggalian data berupa dokumentasi dari hasil catatan Toyyib Zaen Arifin selama ekspedisi pencarian tujuh makam wali, dan wawancara kepada anggota manaqib al-Jamali, pembimbing, penyelenggara dan jama’ah wisata religi, serta beberapa juru kunci makam Wali Pitu. Artikel ini menjelaskan konstruksi sakralitas atas penemuan tujuh makam wali dan pengkultusannya serta dinamikanya sebagai wujud baru venerasi orang suci di Indonesia yang berbeda dengan venerasi sebelumnya di Jawa yang sudah mengakar kuat sejak lama (Wali Songo).</em></p>
Situasi Kebahasaan pada Lanskap Linguistik di Masjid Tiban Malang
This study investigates the phenomenon of the public linguistic landscape, which reveals the use of language in the Tiban Mosque in Malang, East Java. The goal of this research was to describe the language contestation practiced in the Tiban mosque. Furthermore, the purpose of this research is to describe the function of language in the linguistic landscape at the Tiban Malang mosque. The collected data was then classified as monolingual, bilingual, or multilingual. The qualitative descriptive method is used in this linguistic landscape study. Data is collected by observing the location, photographing the object building, and documenting it. According to the findings of this study, the linguistic landscape in the vicinity of the Tiban Malang Mosque is dominated by monolingual and bilingual speakers. This is used to make it easier for visitors and tourists to visit the Tiban mosque's religious tourism area.
Religious and museum tourism to Museum of the Holy Father John Paul II Family Home in Wadowice
The research was aimed at identifying changes in tourist traffic – religious tourism and museum tourism to the Museum of the Holy Father John Paul II Family Home in Wadowice in 1996–2019. The museum was opened in 1984 in the house where Karol Wojtyła, Pope John Paul II, was born in 1920. The thorough reconstruction between 2010 and 2014 resulted in the establishment of a museum with a modern multimedia narrative exhibition. In recent years, the museum has been visited by more than 200 thousand tourists a year, including 40 thousand foreigners from more than 100 countries worldwide. During the years 1996–2019 the number of international tourists rose more than twice. The greatest boom in the visits to the museum was noted in 2005 and was associated with the disease, death, funeral, and increasing worship of Pope John Paul II. Following decreased interest in visits to the museum during the period of 2010–2014, which was due to the museum renovation, a revival and increase in visits to the museum was observed again. Changes that were observed in the museum during the last twenty-five years were identified, among other things, thanks to field research involving observations and interviews with museum curators and staff. Analyses of tourist visits to the museum were based on detailed data provided by the museum managers. In the elaboration of the collected research results descriptive-analytical, dynamic-comparative and cartographic methods were used.
Religious tourism in municipalities in the state of Amazonas
Risk, faith and religious tourism in second modernity: visits to mount athos in the covid-19 era, collaborative planning for the environmental sustainability of the hajj.
Every year, millions of Muslim worshippers visit Mecca in Saudi Arabia to perform the Hajj which is the fifth and final pillar of Islam. Mecca hosts more than 2,300,000 people from around 183 different countries and cultures every year. In 2016, these numbers were forecast to grow to 2,500,000 in 2020. This goal, however, has not been achieved due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic has forced the government to severely reduce the number of pilgrims in 2020 to just 10,000 people. Ultimately, this situation is temporary and visitor numbers should continue to rise. Tourism, especially religious tourism such as the Hajj, is expected to boost the economy and create new jobs for Saudi youth in the services sector. Yet, despite the many benefits of the pilgrimage, the Hajj itself has several severe adverse environmental impacts. The activities of Hajj generate considerable solid and liquid waste, use large quantities of scarce fresh water and produce high levels of greenhouse gasses (GHGs).
Export Citation Format
Share document.
100+ Tourism Research Topics: Trends and Future Directions

Tourism research stands at the crossroads of exploration and understanding, dissecting the intricacies of an industry that transcends geographical boundaries. In this blog, we delve into the realm of tourism research topics, examining their importance, trends, popular areas of study, challenges faced by researchers, and the future directions that the field is poised to take.
Key Trends in Tourism Research
Table of Contents
- Sustainable Tourism
Sustainable tourism has become a cornerstone of research in recent years, reflecting the global shift towards eco-conscious travel. Researchers are delving into the intricate balance between satisfying the wanderlust of tourists and preserving the environment.
Initiatives such as wildlife conservation, eco-friendly accommodations, and community engagement are key focus areas.
Technology in Tourism
The pervasive influence of technology on tourism cannot be overstated. From online booking platforms to virtual reality experiences, researchers are exploring the impact of technology on travel behavior.
Emerging areas of study include the use of artificial intelligence in personalized travel recommendations and the implications of augmented reality for enhancing tourist attractions.
What is the Importance of Tourism Research for Students?
Tourism research holds significant importance for students pursuing studies in various disciplines, including tourism management, hospitality, business, sociology, and environmental studies. Here are some key reasons why tourism research is valuable for students:
Academic Enrichment
- Increases Understanding: By conducting study on the tourist business, students may increase their comprehension of the intricate relationships between the economic, social, cultural, and environmental facets of the sector.
- Application of Theoretical information: This increases the practical relevance of their education by giving them the chance to apply the theoretical information they have learned in the classroom to real-world situations.
Skill Development
- Research Skills: Gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data are just a few of the vital research skills that come from conducting tourist research. These abilities are adaptable and useful in a range of work environments.
- Communication abilities: Through research papers, presentations, and conversations, students learn how to effectively express their results, which improves both their writing and spoken communication abilities.
Industry Insights
- Current Trends and Issues: Research allows students to stay abreast of current trends, challenges, and emerging issues in the tourism industry. This awareness is crucial for adapting to the dynamic nature of the field.
- In-Depth Knowledge: By delving into specific tourism research topics, students gain in-depth knowledge of particular sectors within the industry, positioning themselves as experts in specialized areas.
Career Opportunities
- Competitive Advantage: Having experience in tourism research can provide students with a competitive advantage in the job market. Employers value candidates who can bring a research-driven perspective to decision-making.
- Diverse Career Paths: Whether in academia, policy-making, destination management, or market analysis, a background in tourism research opens doors to a variety of career paths within the broader field of tourism and hospitality.
Contributions to Sustainable Practices
- Environmental and Social Responsibility: Tourism research often focuses on sustainable practices. Students, through their research, can contribute ideas and solutions for promoting responsible tourism, minimizing negative impacts on the environment and local communities.
Global Perspective
- Cultural Awareness: Researching diverse tourism topics exposes students to various cultures, traditions, and perspectives. This global perspective is crucial in an industry where interactions with people from different backgrounds are common.
Problem-Solving Skills
- Analytical Thinking: Research involves analyzing complex issues and developing solutions. This cultivates students’ analytical thinking and problem-solving skills, valuable attributes in any professional setting.
Personal Growth
- Confidence Building: Successfully conducting research and presenting findings builds students’ confidence in their abilities. It empowers them to tackle challenges and approach tasks with a systematic mindset.
In summary, tourism research is a multifaceted learning experience that goes beyond textbooks, providing students with the skills, knowledge, and perspectives needed for a successful and impactful career in the tourism industry or related fields.
100+ Tourism Research Topics: Category Wise
- Impact of Technology on Travel
- Cultural Tourism and Heritage Preservation
- Dark Tourism: Ethics and Motivations
- Community-Based Tourism for Socioeconomic Development
- Wildlife Tourism and Conservation
- Gastronomic Tourism: Culinary Experiences
- Adventure Tourism: Risk and Reward
- Medical Tourism: Trends and Implications
- Religious Tourism and Pilgrimages
- LGBTQ+ Tourism: Diversity in Travel
- Film Tourism: Influence on Destination Choice
- Cruise Tourism: Environmental Impact
- Rural Tourism: Exploring Off-the-Beaten-Path
- Urban Tourism and City Planning
- Educational Tourism: Learning Journeys
- Wellness Tourism: Mind and Body Retreats
- Space Tourism: Future Frontiers
- Luxury Tourism and Experiential Travel
- Sports Tourism: Events and Impact
- Volunteer Tourism: Traveling for a Cause
- Accessible Tourism: Inclusive Travel
- Niche Tourism: Unusual Destinations
- The Psychology of Tourist Behavior
- Destination Marketing and Branding
- Over-tourism: Challenges and Solutions
- Impacts of Climate Change on Tourism
- Cruise Tourism: Cultural Interactions
- Heritage Tourism Management
- Tourism and Globalization
- Impact of Political Instability on Tourism
- COVID-19 and Tourism: Recovery Strategies
- Solo Travel: Trends and Safety Concerns
- E-Tourism: Online Booking Trends
- Responsible Tourism Practices
- Agritourism: Farm and Rural Experiences
- Wildlife Sanctuaries: Balancing Conservation and Tourism
- Backpacking Culture: Trends and Challenges
- Tourism Entrepreneurship and Innovation
- Social Media Influencers in Tourism
- Geotourism: Exploring Geological Wonders
- Virtual Reality in Tourism Experiences
- Tourism Policy and Regulation
- Sustainable Transportation in Tourism
- Wellness Retreats: Trends and Impacts
- Coastal and Marine Tourism
- Historical Tourism and Interpretation
- Space-Archaeology and Cultural Heritage Tourism
- Cross-Cultural Communication in Tourism
- Slow Tourism: Embracing the Journey
- Geopolitics and Tourism
- Adventure Sports Tourism: Risk Management
- Wellness Tourism: The Spa Industry
- Religious Festivals and Tourism
- Volunteer Tourism: Cultural Exchange
- Impacts of Terrorism on Tourism
- Tourism and Gender Equality
- Dark Sky Tourism: Stargazing Adventures
- Social Justice in Tourism
- Music Tourism: Festivals and Events
- Cruise Tourism: Port Infrastructure
- Urban Regeneration through Tourism
- Wellness Tourism: Mindful Travel
- Cultural Appropriation in Tourism
- Sports Mega-Events and Tourism
- Virtual Tourism: Exploring from Home
- Tourism Education and Training
- Destination Resilience to Crises
- Adventure Tourism: Environmental Stewardship
- Slow Food Movement and Culinary Tourism
- Accessible Tourism: Technology Solutions
- Adventure Tourism: Cultural Immersion
- Experiential Learning in Tourism
- Tourism and Biodiversity Conservation
- Indigenous Tourism: Empowerment and Challenges
- Film-Induced Tourism: Pop Culture Impact
- Ephemeral Tourism Events
- Adventure Tourism: Cultural Sensitivity
- Slum Tourism: Ethical Considerations
- Tourism and Water Conservation
- Space Tourism: Ethical Considerations
- Rural Tourism: Community Engagement
- Wellness Tourism: Mind-Body Connection
- Tourism and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Adventure Tourism: Extreme Sports
- The Role of Festivals in Tourism
- Cultural Tourism and Social Inclusion
- Wellness Tourism: Alternative Therapies
- Tourism and Human Rights
- Heritage Conservation and Tourism
- Adventure Tourism: Risk Perception
- Virtual Reality Museums and Tourism
- Responsible Wildlife Tourism
- Tourism and Disaster Management
- Festivals as Cultural Tourism Attractions
- Adventure Tourism: Psychological Benefits
- Wellness Tourism: Eco-Friendly Retreats
- Tourism and Aging Population
- Culinary Tourism: Fusion Cuisine
- Adventure Tourism: Cross-Cultural Interactions
Challenges and Opportunities in Tourism Research
Data collection and analysis.
While technology has streamlined data collection, challenges persist in ensuring data accuracy and relevance. Researchers are exploring advanced methodologies, such as big data analytics and machine learning, to overcome these hurdles and derive meaningful insights.
Globalization and Tourism
The globalization of the tourism industry poses both challenges and opportunities. Researchers are scrutinizing the impact of global trends on local economies, cultural identities, and the environment. Striking a balance between global and local interests is a complex task that requires careful consideration.
Future Directions in Tourism Research
Emerging tourism destinations.
The landscape of tourist destinations is ever-evolving. Researchers are turning their attention to emerging destinations, investigating the factors that contribute to their rise and the implications for the broader tourism industry.
This includes understanding the appeal of off-the-beaten-path locations and the potential challenges associated with their sudden popularity.
Post-Pandemic Tourism
The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped the tourism industry in unprecedented ways. Researchers are exploring the long-term effects of the pandemic on travel behavior, destination preferences, and the overall structure of the tourism sector.
Strategies for recovery and resilience are also under the microscope as the industry adapts to the new normal.
Resources for Tourism Research Topics
- Academic Journals and Publications: Leading academic journals in tourism research, such as the “Journal of Sustainable Tourism” and the “Annals of Tourism Research,” provide a wealth of knowledge for researchers. These publications cover a wide array of topics, from sustainable practices to cultural tourism.
- Conferences and Events: Attending conferences and events, such as the “International Conference on Tourism Research” and the “World Tourism Forum,” offers researchers the opportunity to engage with peers, present their work, and stay abreast of the latest developments in the field.
- Online Databases and Research Platforms: Online databases, including Google Scholar, ResearchGate, and Tourism Management Database , provide access to a vast repository of research articles, theses, and reports. These platforms facilitate collaboration and information exchange among researchers.
In conclusion, the landscape of tourism research topics is vast and dynamic, reflecting the multifaceted nature of the tourism industry. As researchers continue to explore sustainable practices, emerging trends, and the post-pandemic landscape, the importance of their work cannot be overstated.
By navigating the challenges and embracing the opportunities presented, tourism researchers contribute to a more informed and resilient industry, ensuring that the joy of travel remains accessible for generations to come.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Key findings about COVID-19 restrictions that affected religious groups around the world in 2020

During the COVID-19 pandemic , countries around the world restricted large gatherings to reduce the spread of the virus. Religious events, including in-person worship services, were banned in many places. In every region of the globe, at least some religious groups protested these regulations.
Pew Research Center’s 13th annual report on restrictions on religion in 2020 includes a new analysis of how public health measures related to the coronavirus affected religious groups the year the pandemic took hold globally. The report also shows that overall government restrictions and social hostilities relating to religion remained fairly stable from 2019 to 2020.
The study analyzes 198 countries and territories and is based on policies and events in 2020, the most recent year for which data is available.
These are the key findings from the report.
This post is based on Pew Research Center’s 13th annual report that analyzes the extent to which governments and societies around the world impinge on religious beliefs and practices. The studies are part of the Pew-Templeton Global Religious Futures project, which analyzes religious change and its impact on societies around the world.
To measure global restrictions on religion in 2020 – the most recent year for which data is available – the study rates 198 countries and territories by their levels of government restrictions on religion and social hostilities involving religion. The new study is based on the same 10-point indexes used in the previous studies.
- The Government Restrictions Index (GRI) measures government laws, policies and actions that restrict religious beliefs and practices.
- The Social Hostilities Index (SHI) measures acts of religious hostility by private individuals, organizations or groups in society.
To track these indicators of government restrictions and social hostilities, researchers combed through more than a dozen publicly available, widely-cited sources of information, including the U.S. Department of State’s annual Reports on International Religious Freedom and annual reports from the U.S. Commission on International Religious Freedom, as well as reports and databases from a variety of European and United Nations bodies and several independent, nongovernmental organizations. (Read the methodology for more details on sources used in the study.)
For the section on the COVID-19 pandemic, which is new in this year’s report, coders collected information from the same set of sources used for the annual tracking of restrictions on religion. To supplement these sources, coders electronically searched English-language newspaper websites for each country and territory analyzed, using terms related to religious restrictions and COVID-19 to find relevant news articles. Coders also reviewed English-language global news sites and reports on COVID-19 produced by organizations including think tanks and university research centers. (For a list of the global news sites and organizations, read the methodology .)
To keep the data sources for the GRI and SHI consistent from year to year, incidents that appeared only in the newspaper websites used for the COVID-19 section are not included in either of those indexes. However, incidents related to COVID-19 were included in the GRI and SHI analyses when they appeared in the primary and secondary sources traditionally used for the indexes.
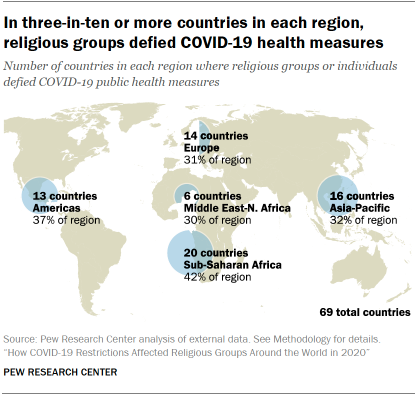
In 69 countries (35% of the total analyzed), one or more religious groups defied public health measures that were imposed during the pandemic. In Canada , for example, several congregations continued holding services despite restrictions on large gatherings to limit the spread of the coronavirus. Leaders of the Free Grace Baptist Church and Free Reformed Church in Chillwack, British Columbia, argued that restrictions on gatherings violated their rights and freedoms. And in the United States , a pastor in Louisiana challenged the governor’s stay-at-home orders by holding services at his church, telling the hundreds of attendees that they had “nothing to fear but fear itself.”
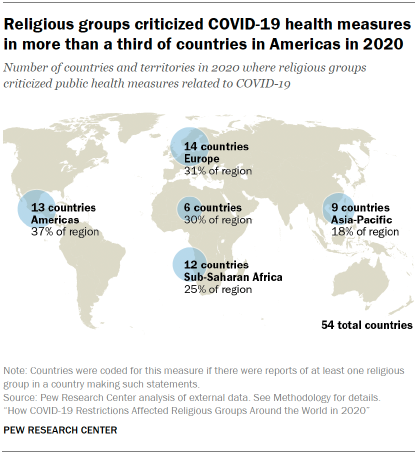
Religious groups criticized government-mandated public health measures in 54 countries (27% of all analyzed), often stating the rules were a violation of religious freedom. In 45 countries (23%), religious groups claimed that limits on large gatherings targeted them unfairly when compared with shops, restaurants or other businesses. In Belgium , for instance, about 100 Catholics asked the Council of State to nullify the suspension of all religious gatherings (other than funerals), arguing it was unfair that large crowds were allowed to go to shops but not to Mass. They argued that the rule was “disproportionate and violates religious freedom as guaranteed in the [country’s] Constitution.”
In nearly a quarter of countries, governments used physical force, such as arrests and raids, to make religious groups comply with COVID-19 public health measures. In Comoros , Gabon and Nepal , police used tear gas to disperse religious gatherings that violated COVID-19 lockdown rules. In the United States, police in New Jersey arrested 15 people at a rabbi’s funeral that violated the state’s stay-at-home order. (The arrests came after some mourners became disorderly and argumentative when police tried to turn the crowd away, according to media reports .) In South Korea, authorities raided the headquarters of the Shincheonji Church of Jesus , largely because it violated restrictions on public gatherings and its leader refused to share membership lists with authorities so they could track the spread of the virus. And in India , two Christians died after being beaten in police custody; they had been accused of violating COVID-19 curfews in the state of Tamil Nadu.
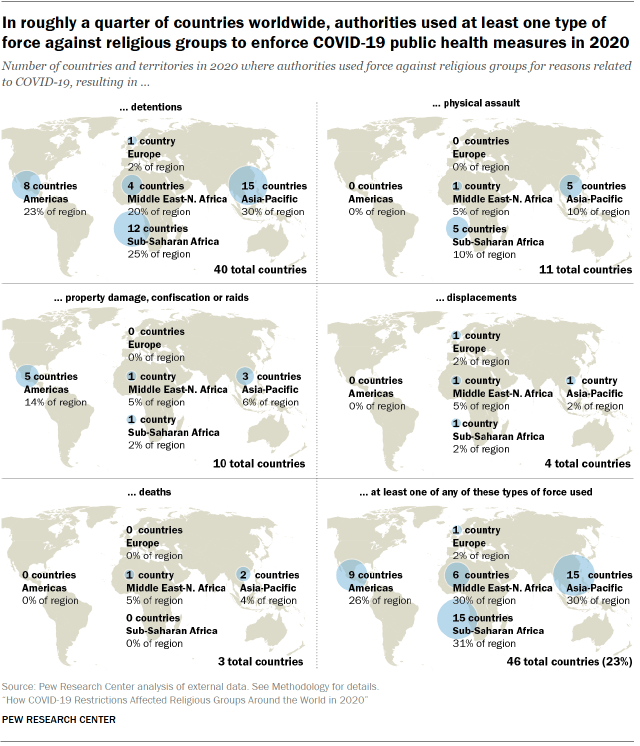
Authorities and social groups in several countries blamed religious groups for spreading the virus. In 18 countries, authorities linked religious groups or gatherings to the spread of COVID-19. And in 39 countries (20% of all studied) private individuals or groups attributed the spread of the virus to religious groups. In Pakistan, Shiite Muslims of Hazara ethnicity who returned from a pilgrimage to Iran were accused by officials in the country’s western province of spreading COVID-19, according to the U.S. Commission on International Religious Freedom . In Cambodia , which has a Buddhist majority, the Ministry of Health in March 2020 began drawing attention to Muslims by including a special category about them in infection rate data, after reports emerged that Cambodian Muslims had contracted COVID-19 at a religious gathering in Malaysia before returning to Cambodia. Afterward, some Muslims said they faced suspicion and discrimination. Some Cambodian merchants reportedly refused to sell goods to Muslims, while other non-Muslims wore masks only in the presence of Muslims.
Private groups or individuals also used conspiracy theories or other inflammatory speech to blame specific religious groups for the spread of the virus. In 23 countries, such comments targeted Jews. In France, social media users shared antisemitic tropes with caricatures of a former Jewish health minister that depicted her poisoning a well – an insinuation that Jews were responsible for the pandemic (and a reference to a trope that dates back to the 14th-century Black Plague).
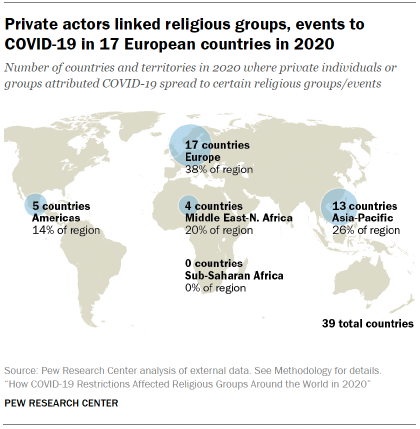
Muslims were targeted by such inflammatory speech in 15 countries. In India, for example, Islamophobic hashtags like #CoronaJihad circulated widely on social media. Meanwhile, Christian groups were accused in nine countries of having spread COVID-19. In Turkey , an Armenian Orthodox church’s door was set on fire , and a man told police he did it because “they [Armenian Christians] brought the coronavirus” to Turkey, according to news reports.
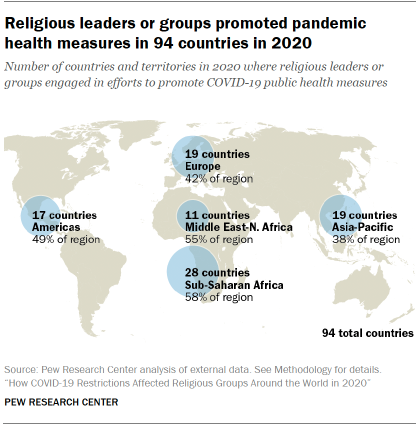
Despite the frictions over limits on large gatherings, religious groups or leaders promoted one or more types of public health measures, such as social distancing and hand-washing, in 94 (or 47%) of the countries analyzed. In Lesotho, for example, both evangelical Protestant and Catholic churches helped raise awareness about the pandemic and encouraged people to take precautions. And in Albania , religious leaders assisted the government’s health measures and canceled religious gatherings for two months.
Overall, scores captured in the Center’s Government Restrictions Index (GRI) and Social Hostilities Index (SHI) remained fairly stable in 2020. The median score on the GRI – which includes laws, policies and actions by government officials that impinge on religious beliefs and practices – fell from 2.9 in 2019 to 2.8 in 2020. And the median score on the SHI, which includes religion-related hostilities by private individuals and organizations, increased slightly from 1.7 in 2019 to 1.8 in 2020. (Scores on both indexes range from 0 to 10).
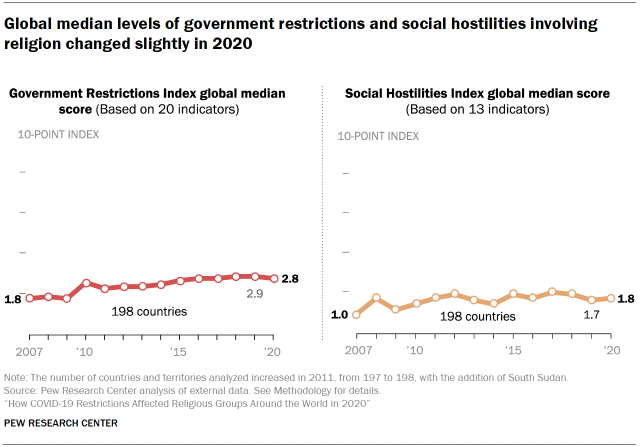
Meanwhile, the number of countries with either “high” or “very high” levels of government restrictions remained the same, at 57 countries (29%) from 2019 to 2020, a peak number for the study. At the same time, the number of countries with “high” or “very high” levels of social hostilities fell from 43 countries (22%) in 2019 to 40 countries (20%) in 2020, which was below the peak of 65 countries (33%) recorded in 2012.
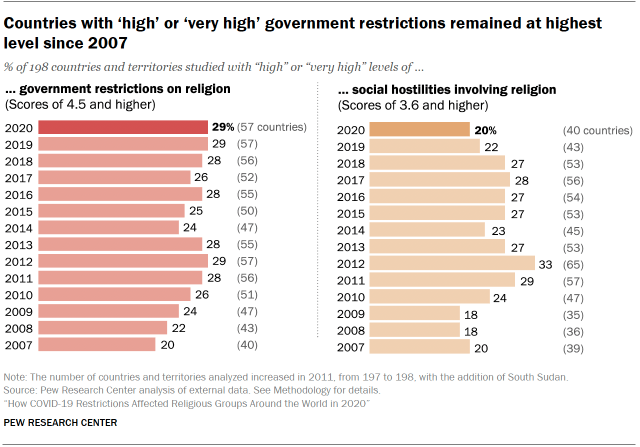
Note: For a list of the global news sites and organizations used and more details on sources used in the study , read the methodology .
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Global Health
- Health Policy
- Religion & Government
- Religious Freedom & Restrictions

Samirah Majumdar is a research associate focusing on religion research at Pew Research Center
How Americans View the Coronavirus, COVID-19 Vaccines Amid Declining Levels of Concern
Online religious services appeal to many americans, but going in person remains more popular, about a third of u.s. workers who can work from home now do so all the time, how the pandemic has affected attendance at u.s. religious services, mental health and the pandemic: what u.s. surveys have found, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

COMMENTS
Abstract. This review study examines evolving themes in the scholarly literature on religious tourism and. identifies research gaps that provide a basis for future investigations. The researchers ...
Thus, the tourism industry has identified a new niche known as religious tourism. Research interest in religious tourism is steadily increasing (Durán-Sánchez, Álvarez-García, del Río-Rama, & Oliveira, ... Gisbert Rinschede in the paper, which is part of a special issue of Annals of Tourism Research, dedicated to the topic in 1992, gives a ...
This review study examines evolving themes in the scholarly literature on religious tourism and identifies research gaps that provide a basis for future investigations. The researchers evaluate a total of 84 studies of religion-induced tourism using content and thematic analyses. The findings show a plurality of approaches, both disciplinary ...
Main themes in the current religious & tourism research. In this section, a traditional review was undertaken by analyzing the latest papers written on the topic in the past 10 years. ... She is also a resource editor of the "Annals of Tourism Research" and published many papers on the topics of Tourism. Recommended articles. References (65 ...
A total of 410 journals published articles on the topic of religion and tourism, another reflection of the fragmented nature of the topic. Fig. 6 reflects the top 25. The two most prolific journals on the topic were the Annals of Tourism Research (with 39 articles, or 5.026%) and Tourism Management (with 33 articles, or 4.
Although some studies and research refer to both the field of sustainable tourism and that of religious tourism, still few studies elucidate the impact of sustainable tourism development (Sharpley, 2020) and interrelate the role of religious tourism as a means for rethinking the sustainability-oriented vision as a strategy of land development ...
Annals of Tourism Research, dedicated to the topic in 1992, gives a brief systematic overview of the different forms of religious tourism: short-term religious tourism and long-term religious ...
This review study examines evolving themes in the scholarly literature on religious tourism and identifies research gaps that provide a basis for future investigations. The researchers evaluate a total of 84 studies of religion-induced tourism using ... This discussion paper explores the topic of religious tourism and pilgrimage, examining it ...
Compared to nature-based, cultural, and recreational tourism, religious tourism is a relatively new concept in tourism research and has received less empirical attention (Almuhrzi & Alsawafi, 2017).The term religious tourism refers to a wide range of activities that visitors partake in to improve their own sense of meaning, identity, and purpose (Norman & Pokorny, 2017).
Religious tourism is a significant and growing field of tourism that overlaps with cultural tourism. It has the potential to improve the quality of life of those who live in places of faith or along routes of spiritual interest. ... This research topic connects current traditions, the identity dimension, and community practices that still ...
Originality of the research - The authors developed a Conceptual Model of Spiritual Tourism with. seven themes: Meaning/Purpose of life, Consciousne ss, Transcendence, Spiritual resources, Self ...
Tourism's contribution to travellers' overall life satisfaction is a growing stream of research (e.g., Puczkó & Smith, 2012; Sirgy et al., 2011; Vada et al., 2020).Over the last few decades, tourism scholars have demonstrated that leisure travel can enhance well-being and quality of life (for a review, see Uysal et al., 2016), making tourism a vital resource in times of major challenges ...
The perspective of religious and spiritual tourism research: a systematic mapping study - Author: Ali Heidari, Hamid Reza Yazdani, Fatemeh Saghafi, Mohammad Reza Jalilvand. Religious tourism is a form of tourism where people of a particular faith travel to visit places of religious significance in their faith. Previous research into the various ...
Therefore, the researchers believe that it is recommended that future researchers continue to explore religious and cultural tourism or related issues based on differences in different countries, regions, different rights, and ages, and understand the understanding and differences of peers on this topic in order to improve related research flaws.
Research interest in religious tourism is steadily increasing (Durán-Sánchez, Álvarez-García, del Río-Rama, & Oliveira, 2018). The current paper is not the single paper that reviews research in religious tourism (see for example Durán-Sánchez et al., 2018; Rashid, 2018), however, this is the first paper in literature that seeks to ...
The research was aimed at identifying changes in tourist traffic - religious tourism and museum tourism to the Museum of the Holy Father John Paul II Family Home in Wadowice in 1996-2019. The museum was opened in 1984 in the house where Karol Wojtyła, Pope John Paul II, was born in 1920.
This paper reviews the academic literature related to religious tourism through a bibliometric study and citations of articles indexed in the multidisciplinary database Web of Science (WoS). Through an advanced search by terms, a representative set of 103 documents that form the ad-hoc basis of the analysis were selected. In view of the results, it is concluded that the United States is at the ...
Providing researchers and students of tourism, religious studies, anthropology and related subjects with an important review of the topic, this book aims to bridge the ever-widening gap between specialists within the religious, tourism, management and education sectors.
The purpose of the research is to explore how to reach a consensus on the development of cultural tourism and the sustainability of the entire rural environment from the perspective of different rights holders. Using Beigang Township in Taiwan as a case study, we first conducted a questionnaire survey and analyzed 600 respondents by statistical verifications method, then used an interview ...
In summary, tourism research is a multifaceted learning experience that goes beyond textbooks, providing students with the skills, knowledge, and perspectives needed for a successful and impactful career in the tourism industry or related fields. 100+ Tourism Research Topics: Category Wise. Sustainable Tourism; Impact of Technology on Travel
Religious tourism has developed in post-communist Romania, after decades of restrictions on the manifestation of the population's religiosity. ... existing literature by incorporating travel experience into QOL domains and also taps on the possibility to expand the research topic into more contemporary modes of travel, including meditation ...
Religious tourism. Government data indicates that tourist destinations featuring religion, such as Mount Jiuhua, a Buddhist sacred site, and Mount Wudang, a Taoist holy place with around 200 temples, experienced large increases in visitors between 2010 and 2019. These gains correspond with an overall boom in domestic tourism in China.
In every region of the globe, at least some religious groups protested these regulations. Pew Research Center's 13th annual report on restrictions on religion in 2020 includes a new analysis of how public health measures related to the coronavirus affected religious groups the year the pandemic took hold globally. The report also shows that ...