The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Find This link opens in a new window
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window

Get Organized
- Lit Review Prep Use this template to help you evaluate your sources, create article summaries for an annotated bibliography, and a synthesis matrix for your lit review outline.
Synthesize your Information
Synthesize: combine separate elements to form a whole.
Synthesis Matrix
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other.
After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables.
By arranging your sources by theme or variable, you can see how your sources relate to each other, and can start thinking about how you weave them together to create a narrative.
- Step-by-Step Approach
- Example Matrix from NSCU
- Matrix Template
- << Previous: Summarize
- Next: Integrate >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 10:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review
Literature Syntheis 101
How To Synthesise The Existing Research (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | August 2023
One of the most common mistakes that students make when writing a literature review is that they err on the side of describing the existing literature rather than providing a critical synthesis of it. In this post, we’ll unpack what exactly synthesis means and show you how to craft a strong literature synthesis using practical examples.
This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp . In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step. If it’s your first time writing a literature review, you definitely want to use this link to get 50% off the course (limited-time offer).
Overview: Literature Synthesis
- What exactly does “synthesis” mean?
- Aspect 1: Agreement
- Aspect 2: Disagreement
- Aspect 3: Key theories
- Aspect 4: Contexts
- Aspect 5: Methodologies
- Bringing it all together
What does “synthesis” actually mean?
As a starting point, let’s quickly define what exactly we mean when we use the term “synthesis” within the context of a literature review.
Simply put, literature synthesis means going beyond just describing what everyone has said and found. Instead, synthesis is about bringing together all the information from various sources to present a cohesive assessment of the current state of knowledge in relation to your study’s research aims and questions .
Put another way, a good synthesis tells the reader exactly where the current research is “at” in terms of the topic you’re interested in – specifically, what’s known , what’s not , and where there’s a need for more research .
So, how do you go about doing this?
Well, there’s no “one right way” when it comes to literature synthesis, but we’ve found that it’s particularly useful to ask yourself five key questions when you’re working on your literature review. Having done so, you can then address them more articulately within your actual write up. So, let’s take a look at each of these questions.

1. Points Of Agreement
The first question that you need to ask yourself is: “Overall, what things seem to be agreed upon by the vast majority of the literature?”
For example, if your research aim is to identify which factors contribute toward job satisfaction, you’ll need to identify which factors are broadly agreed upon and “settled” within the literature. Naturally, there may at times be some lone contrarian that has a radical viewpoint , but, provided that the vast majority of researchers are in agreement, you can put these random outliers to the side. That is, of course, unless your research aims to explore a contrarian viewpoint and there’s a clear justification for doing so.
Identifying what’s broadly agreed upon is an essential starting point for synthesising the literature, because you generally don’t want (or need) to reinvent the wheel or run down a road investigating something that is already well established . So, addressing this question first lays a foundation of “settled” knowledge.
Need a helping hand?
2. Points Of Disagreement
Related to the previous point, but on the other end of the spectrum, is the equally important question: “Where do the disagreements lie?” .
In other words, which things are not well agreed upon by current researchers? It’s important to clarify here that by disagreement, we don’t mean that researchers are (necessarily) fighting over it – just that there are relatively mixed findings within the empirical research , with no firm consensus amongst researchers.
This is a really important question to address as these “disagreements” will often set the stage for the research gap(s). In other words, they provide clues regarding potential opportunities for further research, which your study can then (hopefully) contribute toward filling. If you’re not familiar with the concept of a research gap, be sure to check out our explainer video covering exactly that .

3. Key Theories
The next question you need to ask yourself is: “Which key theories seem to be coming up repeatedly?” .
Within most research spaces, you’ll find that you keep running into a handful of key theories that are referred to over and over again. Apart from identifying these theories, you’ll also need to think about how they’re connected to each other. Specifically, you need to ask yourself:
- Are they all covering the same ground or do they have different focal points or underlying assumptions ?
- Do some of them feed into each other and if so, is there an opportunity to integrate them into a more cohesive theory?
- Do some of them pull in different directions ? If so, why might this be?
- Do all of the theories define the key concepts and variables in the same way, or is there some disconnect? If so, what’s the impact of this ?
Simply put, you’ll need to pay careful attention to the key theories in your research area, as they will need to feature within your theoretical framework , which will form a critical component within your final literature review. This will set the foundation for your entire study, so it’s essential that you be critical in this area of your literature synthesis.
If this sounds a bit fluffy, don’t worry. We deep dive into the theoretical framework (as well as the conceptual framework) and look at practical examples in Literature Review Bootcamp . If you’d like to learn more, take advantage of our limited-time offer to get 60% off the standard price.

4. Contexts
The next question that you need to address in your literature synthesis is an important one, and that is: “Which contexts have (and have not) been covered by the existing research?” .
For example, sticking with our earlier hypothetical topic (factors that impact job satisfaction), you may find that most of the research has focused on white-collar , management-level staff within a primarily Western context, but little has been done on blue-collar workers in an Eastern context. Given the significant socio-cultural differences between these two groups, this is an important observation, as it could present a contextual research gap .
In practical terms, this means that you’ll need to carefully assess the context of each piece of literature that you’re engaging with, especially the empirical research (i.e., studies that have collected and analysed real-world data). Ideally, you should keep notes regarding the context of each study in some sort of catalogue or sheet, so that you can easily make sense of this before you start the writing phase. If you’d like, our free literature catalogue worksheet is a great tool for this task.
5. Methodological Approaches
Last but certainly not least, you need to ask yourself the question: “What types of research methodologies have (and haven’t) been used?”
For example, you might find that most studies have approached the topic using qualitative methods such as interviews and thematic analysis. Alternatively, you might find that most studies have used quantitative methods such as online surveys and statistical analysis.
But why does this matter?
Well, it can run in one of two potential directions . If you find that the vast majority of studies use a specific methodological approach, this could provide you with a firm foundation on which to base your own study’s methodology . In other words, you can use the methodologies of similar studies to inform (and justify) your own study’s research design .
On the other hand, you might argue that the lack of diverse methodological approaches presents a research gap , and therefore your study could contribute toward filling that gap by taking a different approach. For example, taking a qualitative approach to a research area that is typically approached quantitatively. Of course, if you’re going to go against the methodological grain, you’ll need to provide a strong justification for why your proposed approach makes sense. Nevertheless, it is something worth at least considering.
Regardless of which route you opt for, you need to pay careful attention to the methodologies used in the relevant studies and provide at least some discussion about this in your write-up. Again, it’s useful to keep track of this on some sort of spreadsheet or catalogue as you digest each article, so consider grabbing a copy of our free literature catalogue if you don’t have anything in place.

Bringing It All Together
Alright, so we’ve looked at five important questions that you need to ask (and answer) to help you develop a strong synthesis within your literature review. To recap, these are:
- Which things are broadly agreed upon within the current research?
- Which things are the subject of disagreement (or at least, present mixed findings)?
- Which theories seem to be central to your research topic and how do they relate or compare to each other?
- Which contexts have (and haven’t) been covered?
- Which methodological approaches are most common?
Importantly, you’re not just asking yourself these questions for the sake of asking them – they’re not just a reflection exercise. You need to weave your answers to them into your actual literature review when you write it up. How exactly you do this will vary from project to project depending on the structure you opt for, but you’ll still need to address them within your literature review, whichever route you go.
The best approach is to spend some time actually writing out your answers to these questions, as opposed to just thinking about them in your head. Putting your thoughts onto paper really helps you flesh out your thinking . As you do this, don’t just write down the answers – instead, think about what they mean in terms of the research gap you’ll present , as well as the methodological approach you’ll take . Your literature synthesis needs to lay the groundwork for these two things, so it’s essential that you link all of it together in your mind, and of course, on paper.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

excellent , thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- 6. Synthesize
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
Synthesis Visualization
Synthesis matrix example.
- 7. Write a Literature Review
- Synthesis Worksheet
About Synthesis
Approaches to synthesis.
You can sort the literature in various ways, for example:

How to Begin?
Read your sources carefully and find the main idea(s) of each source
Look for similarities in your sources – which sources are talking about the same main ideas? (for example, sources that discuss the historical background on your topic)
Use the worksheet (above) or synthesis matrix (below) to get organized
This work can be messy. Don't worry if you have to go through a few iterations of the worksheet or matrix as you work on your lit review!
Four Examples of Student Writing
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D . For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.

Long description of "Four Examples of Student Writing" for web accessibility
- Download a copy of the "Four Examples of Student Writing" chart

Click on the example to view the pdf.

From Jennifer Lim
- << Previous: 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- Next: 7. Write a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 10, 2024 4:46 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

Literature Reviews
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- Getting started
- Types of reviews
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
How to synthesize
Approaches to synthesis.
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
In the synthesis step of a literature review, researchers analyze and integrate information from selected sources to identify patterns and themes. This involves critically evaluating findings, recognizing commonalities, and constructing a cohesive narrative that contributes to the understanding of the research topic.
Here are some examples of how to approach synthesizing the literature:
💡 By themes or concepts
🕘 Historically or chronologically
📊 By methodology
These organizational approaches can also be used when writing your review. It can be beneficial to begin organizing your references by these approaches in your citation manager by using folders, groups, or collections.
Create a synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix allows you to visually organize your literature.
Topic: ______________________________________________
Topic: Chemical exposure to workers in nail salons
- << Previous: 4. Organize your results
- Next: 6. Write the review >>
- Last Updated: Apr 3, 2024 12:40 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/lit-reviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries


Library Guides
Literature reviews: synthesis.
- Criticality
Synthesise Information
So, how can you create paragraphs within your literature review that demonstrates your knowledge of the scholarship that has been done in your field of study?
You will need to present a synthesis of the texts you read.
Doug Specht, Senior Lecturer at the Westminster School of Media and Communication, explains synthesis for us in the following video:
Synthesising Texts
What is synthesis?
Synthesis is an important element of academic writing, demonstrating comprehension, analysis, evaluation and original creation.
With synthesis you extract content from different sources to create an original text. While paraphrase and summary maintain the structure of the given source(s), with synthesis you create a new structure.
The sources will provide different perspectives and evidence on a topic. They will be put together when agreeing, contrasted when disagreeing. The sources must be referenced.
Perfect your synthesis by showing the flow of your reasoning, expressing critical evaluation of the sources and drawing conclusions.
When you synthesise think of "using strategic thinking to resolve a problem requiring the integration of diverse pieces of information around a structuring theme" (Mateos and Sole 2009, p448).
Synthesis is a complex activity, which requires a high degree of comprehension and active engagement with the subject. As you progress in higher education, so increase the expectations on your abilities to synthesise.
How to synthesise in a literature review:
Identify themes/issues you'd like to discuss in the literature review. Think of an outline.
Read the literature and identify these themes/issues.
Critically analyse the texts asking: how does the text I'm reading relate to the other texts I've read on the same topic? Is it in agreement? Does it differ in its perspective? Is it stronger or weaker? How does it differ (could be scope, methods, year of publication etc.). Draw your conclusions on the state of the literature on the topic.
Start writing your literature review, structuring it according to the outline you planned.
Put together sources stating the same point; contrast sources presenting counter-arguments or different points.
Present your critical analysis.
Always provide the references.
The best synthesis requires a "recursive process" whereby you read the source texts, identify relevant parts, take notes, produce drafts, re-read the source texts, revise your text, re-write... (Mateos and Sole, 2009).
What is good synthesis?
The quality of your synthesis can be assessed considering the following (Mateos and Sole, 2009, p439):
Integration and connection of the information from the source texts around a structuring theme.
Selection of ideas necessary for producing the synthesis.
Appropriateness of the interpretation.
Elaboration of the content.
Example of Synthesis
Original texts (fictitious):
Synthesis:
Animal experimentation is a subject of heated debate. Some argue that painful experiments should be banned. Indeed it has been demonstrated that such experiments make animals suffer physically and psychologically (Chowdhury 2012; Panatta and Hudson 2016). On the other hand, it has been argued that animal experimentation can save human lives and reduce harm on humans (Smith 2008). This argument is only valid for toxicological testing, not for tests that, for example, merely improve the efficacy of a cosmetic (Turner 2015). It can be suggested that animal experimentation should be regulated to only allow toxicological risk assessment, and the suffering to the animals should be minimised.
Bibliography
Mateos, M. and Sole, I. (2009). Synthesising Information from various texts: A Study of Procedures and Products at Different Educational Levels. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 24 (4), 435-451. Available from https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178760 [Accessed 29 June 2021].
- << Previous: Structure
- Next: Criticality >>
- Last Updated: Nov 18, 2023 10:56 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/literature-reviews
CONNECT WITH US

Literature Review How To
- Things To Consider
- Synthesizing Sources
- Video Tutorials
- Books On Literature Reviews
What is Synthesis
What is Synthesis? Synthesis writing is a form of analysis related to comparison and contrast, classification and division. On a basic level, synthesis requires the writer to pull together two or more summaries, looking for themes in each text. In synthesis, you search for the links between various materials in order to make your point. Most advanced academic writing, including literature reviews, relies heavily on synthesis. (Temple University Writing Center)
How To Synthesize Sources in a Literature Review
Literature reviews synthesize large amounts of information and present it in a coherent, organized fashion. In a literature review you will be combining material from several texts to create a new text – your literature review.
You will use common points among the sources you have gathered to help you synthesize the material. This will help ensure that your literature review is organized by subtopic, not by source. This means various authors' names can appear and reappear throughout the literature review, and each paragraph will mention several different authors.
When you shift from writing summaries of the content of a source to synthesizing content from sources, there is a number things you must keep in mind:
- Look for specific connections and or links between your sources and how those relate to your thesis or question.
- When writing and organizing your literature review be aware that your readers need to understand how and why the information from the different sources overlap.
- Organize your literature review by the themes you find within your sources or themes you have identified.
- << Previous: Things To Consider
- Next: Video Tutorials >>
- Last Updated: Nov 30, 2018 4:51 PM
- URL: https://libguides.csun.edu/literature-review
Report ADA Problems with Library Services and Resources
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix
Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix
Published on July 4, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Synthesizing sources involves combining the work of other scholars to provide new insights. It’s a way of integrating sources that helps situate your work in relation to existing research.
Synthesizing sources involves more than just summarizing . You must emphasize how each source contributes to current debates, highlighting points of (dis)agreement and putting the sources in conversation with each other.
You might synthesize sources in your literature review to give an overview of the field or throughout your research paper when you want to position your work in relation to existing research.
Table of contents
Example of synthesizing sources, how to synthesize sources, synthesis matrix, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about synthesizing sources.
Let’s take a look at an example where sources are not properly synthesized, and then see what can be done to improve it.
This paragraph provides no context for the information and does not explain the relationships between the sources described. It also doesn’t analyze the sources or consider gaps in existing research.
Research on the barriers to second language acquisition has primarily focused on age-related difficulties. Building on Lenneberg’s (1967) theory of a critical period of language acquisition, Johnson and Newport (1988) tested Lenneberg’s idea in the context of second language acquisition. Their research seemed to confirm that young learners acquire a second language more easily than older learners. Recent research has considered other potential barriers to language acquisition. Schepens, van Hout, and van der Slik (2022) have revealed that the difficulties of learning a second language at an older age are compounded by dissimilarity between a learner’s first language and the language they aim to acquire. Further research needs to be carried out to determine whether the difficulty faced by adult monoglot speakers is also faced by adults who acquired a second language during the “critical period.”
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

To synthesize sources, group them around a specific theme or point of contention.
As you read sources, ask:
- What questions or ideas recur? Do the sources focus on the same points, or do they look at the issue from different angles?
- How does each source relate to others? Does it confirm or challenge the findings of past research?
- Where do the sources agree or disagree?
Once you have a clear idea of how each source positions itself, put them in conversation with each other. Analyze and interpret their points of agreement and disagreement. This displays the relationships among sources and creates a sense of coherence.
Consider both implicit and explicit (dis)agreements. Whether one source specifically refutes another or just happens to come to different conclusions without specifically engaging with it, you can mention it in your synthesis either way.
Synthesize your sources using:
- Topic sentences to introduce the relationship between the sources
- Signal phrases to attribute ideas to their authors
- Transition words and phrases to link together different ideas
To more easily determine the similarities and dissimilarities among your sources, you can create a visual representation of their main ideas with a synthesis matrix . This is a tool that you can use when researching and writing your paper, not a part of the final text.
In a synthesis matrix, each column represents one source, and each row represents a common theme or idea among the sources. In the relevant rows, fill in a short summary of how the source treats each theme or topic.
This helps you to clearly see the commonalities or points of divergence among your sources. You can then synthesize these sources in your work by explaining their relationship.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Synthesizing sources means comparing and contrasting the work of other scholars to provide new insights.
It involves analyzing and interpreting the points of agreement and disagreement among sources.
You might synthesize sources in your literature review to give an overview of the field of research or throughout your paper when you want to contribute something new to existing research.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
Topic sentences help keep your writing focused and guide the reader through your argument.
In an essay or paper , each paragraph should focus on a single idea. By stating the main idea in the topic sentence, you clarify what the paragraph is about for both yourself and your reader.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix. Scribbr. Retrieved April 6, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/synthesizing-sources/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, signal phrases | definition, explanation & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, how to find sources | scholarly articles, books, etc., "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- AIMS Public Health
- v.3(1); 2016

What Synthesis Methodology Should I Use? A Review and Analysis of Approaches to Research Synthesis
Kara schick-makaroff.
1 Faculty of Nursing, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Marjorie MacDonald
2 School of Nursing, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada
Marilyn Plummer
3 College of Nursing, Camosun College, Victoria, BC, Canada
Judy Burgess
4 Student Services, University Health Services, Victoria, BC, Canada
Wendy Neander
Associated data, additional file 1.
When we began this process, we were doctoral students and a faculty member in a research methods course. As students, we were facing a review of the literature for our dissertations. We encountered several different ways of conducting a review but were unable to locate any resources that synthesized all of the various synthesis methodologies. Our purpose is to present a comprehensive overview and assessment of the main approaches to research synthesis. We use ‘research synthesis’ as a broad overarching term to describe various approaches to combining, integrating, and synthesizing research findings.
We conducted an integrative review of the literature to explore the historical, contextual, and evolving nature of research synthesis. We searched five databases, reviewed websites of key organizations, hand-searched several journals, and examined relevant texts from the reference lists of the documents we had already obtained.
We identified four broad categories of research synthesis methodology including conventional, quantitative, qualitative, and emerging syntheses. Each of the broad categories was compared to the others on the following: key characteristics, purpose, method, product, context, underlying assumptions, unit of analysis, strengths and limitations, and when to use each approach.
Conclusions
The current state of research synthesis reflects significant advancements in emerging synthesis studies that integrate diverse data types and sources. New approaches to research synthesis provide a much broader range of review alternatives available to health and social science students and researchers.
1. Introduction
Since the turn of the century, public health emergencies have been identified worldwide, particularly related to infectious diseases. For example, the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) epidemic in Canada in 2002-2003, the recent Ebola epidemic in Africa, and the ongoing HIV/AIDs pandemic are global health concerns. There have also been dramatic increases in the prevalence of chronic diseases around the world [1] – [3] . These epidemiological challenges have raised concerns about the ability of health systems worldwide to address these crises. As a result, public health systems reform has been initiated in a number of countries. In Canada, as in other countries, the role of evidence to support public health reform and improve population health has been given high priority. Yet, there continues to be a significant gap between the production of evidence through research and its application in practice [4] – [5] . One strategy to address this gap has been the development of new research synthesis methodologies to deal with the time-sensitive and wide ranging evidence needs of policy makers and practitioners in all areas of health care, including public health.
As doctoral nursing students facing a review of the literature for our dissertations, and as a faculty member teaching a research methods course, we encountered several ways of conducting a research synthesis but found no comprehensive resources that discussed, compared, and contrasted various synthesis methodologies on their purposes, processes, strengths and limitations. To complicate matters, writers use terms interchangeably or use different terms to mean the same thing, and the literature is often contradictory about various approaches. Some texts [6] , [7] – [9] did provide a preliminary understanding about how research synthesis had been taken up in nursing, but these did not meet our requirements. Thus, in this article we address the need for a comprehensive overview of research synthesis methodologies to guide public health, health care, and social science researchers and practitioners.
Research synthesis is relatively new in public health but has a long history in other fields dating back to the late 1800s. Research synthesis, a research process in its own right [10] , has become more prominent in the wake of the evidence-based movement of the 1990s. Research syntheses have found their advocates and detractors in all disciplines, with challenges to the processes of systematic review and meta-analysis, in particular, being raised by critics of evidence-based healthcare [11] – [13] .
Our purpose was to conduct an integrative review of the literature to explore the historical, contextual, and evolving nature of research synthesis [14] – [15] . We synthesize and critique the main approaches to research synthesis that are relevant for public health, health care, and social scientists. Research synthesis is the overarching term we use to describe approaches to combining, aggregating, integrating, and synthesizing primary research findings. Each synthesis methodology draws on different types of findings depending on the purpose and product of the chosen synthesis (see Additional File 1 ).
3. Method of Review
Based on our current knowledge of the literature, we identified these approaches to include in our review: systematic review, meta-analysis, qualitative meta-synthesis, meta-narrative synthesis, scoping review, rapid review, realist synthesis, concept analysis, literature review, and integrative review. Our first step was to divide the synthesis types among the research team. Each member did a preliminary search to identify key texts. The team then met to develop search terms and a framework to guide the review.
Over the period of 2008 to 2012 we extensively searched the literature, updating our search at several time points, not restricting our search by date. The dates of texts reviewed range from 1967 to 2015. We used the terms above combined with the term “method* (e.g., “realist synthesis” and “method*) in the database Health Source: Academic Edition (includes Medline and CINAHL). This search yielded very few texts on some methodologies and many on others. We realized that many documents on research synthesis had not been picked up in the search. Therefore, we also searched Google Scholar, PubMed, ERIC, and Social Science Index, as well as the websites of key organizations such as the Joanna Briggs Institute, the University of York Centre for Evidence-Based Nursing, and the Cochrane Collaboration database. We hand searched several nursing, social science, public health and health policy journals. Finally, we traced relevant documents from the references in obtained texts.
We included works that met the following inclusion criteria: (1) published in English; (2) discussed the history of research synthesis; (3) explicitly described the approach and specific methods; or (4) identified issues, challenges, strengths and limitations of the particular methodology. We excluded research reports that resulted from the use of particular synthesis methodologies unless they also included criteria 2, 3, or 4 above.
Based on our search, we identified additional types of research synthesis (e.g., meta-interpretation, best evidence synthesis, critical interpretive synthesis, meta-summary, grounded formal theory). Still, we missed some important developments in meta-analysis, for example, identified by the journal's reviewers that have now been discussed briefly in the paper. The final set of 197 texts included in our review comprised theoretical, empirical, and conceptual papers, books, editorials and commentaries, and policy documents.
In our preliminary review of key texts, the team inductively developed a framework of the important elements of each method for comparison. In the next phase, each text was read carefully, and data for these elements were extracted into a table for comparison on the points of: key characteristics, purpose, methods, and product; see Additional File 1 ). Once the data were grouped and extracted, we synthesized across categories based on the following additional points of comparison: complexity of the process, degree of systematization, consideration of context, underlying assumptions, unit of analysis, and when to use each approach. In our results, we discuss our comparison of the various synthesis approaches on the elements above. Drawing only on documents for the review, ethics approval was not required.
We identified four broad categories of research synthesis methodology: Conventional, quantitative, qualitative, and emerging syntheses. From our dataset of 197 texts, we had 14 texts on conventional synthesis, 64 on quantitative synthesis, 78 on qualitative synthesis, and 41 on emerging syntheses. Table 1 provides an overview of the four types of research synthesis, definitions, types of data used, products, and examples of the methodology.
Although we group these types of synthesis into four broad categories on the basis of similarities, each type within a category has unique characteristics, which may differ from the overall group similarities. Each could be explored in greater depth to tease out their unique characteristics, but detailed comparison is beyond the scope of this article.
Additional File 1 presents one or more selected types of synthesis that represent the broad category but is not an exhaustive presentation of all types within each category. It provides more depth for specific examples from each category of synthesis on the characteristics, purpose, methods, and products than is found in Table 1 .
4.1. Key Characteristics
4.1.1. what is it.
Here we draw on two types of categorization. First, we utilize Dixon Woods et al.'s [49] classification of research syntheses as being either integrative or interpretive . (Please note that integrative syntheses are not the same as an integrative review as defined in Additional File 1 .) Second, we use Popay's [80] enhancement and epistemological models .
The defining characteristics of integrative syntheses are that they involve summarizing the data achieved by pooling data [49] . Integrative syntheses include systematic reviews, meta-analyses, as well as scoping and rapid reviews because each of these focus on summarizing data. They also define concepts from the outset (although this may not always be true in scoping or rapid reviews) and deal with a well-specified phenomenon of interest.
Interpretive syntheses are primarily concerned with the development of concepts and theories that integrate concepts [49] . The analysis in interpretive synthesis is conceptual both in process and outcome, and “the product is not aggregations of data, but theory” [49] , [p.12]. Interpretive syntheses involve induction and interpretation, and are primarily conceptual in process and outcome. Examples include integrative reviews, some systematic reviews, all of the qualitative syntheses, meta-narrative, realist and critical interpretive syntheses. Of note, both quantitative and qualitative studies can be either integrative or interpretive
The second categorization, enhancement versus epistemological , applies to those approaches that use multiple data types and sources [80] . Popay's [80] classification reflects the ways that qualitative data are valued in relation to quantitative data.
In the enhancement model , qualitative data adds something to quantitative analysis. The enhancement model is reflected in systematic reviews and meta-analyses that use some qualitative data to enhance interpretation and explanation. It may also be reflected in some rapid reviews that draw on quantitative data but use some qualitative data.
The epistemological model assumes that quantitative and qualitative data are equal and each has something unique to contribute. All of the other review approaches, except pure quantitative or qualitative syntheses, reflect the epistemological model because they value all data types equally but see them as contributing different understandings.
4.1.2. Data type
By and large, the quantitative approaches (quantitative systematic review and meta-analysis) have typically used purely quantitative data (i.e., expressed in numeric form). More recently, both Cochrane [81] and Campbell [82] collaborations are grappling with the need to, and the process of, integrating qualitative research into a systematic review. The qualitative approaches use qualitative data (i.e., expressed in words). All of the emerging synthesis types, as well as the conventional integrative review, incorporate qualitative and quantitative study designs and data.
4.1.3. Research question
Four types of research questions direct inquiry across the different types of syntheses. The first is a well-developed research question that gives direction to the synthesis (e.g., meta-analysis, systematic review, meta-study, concept analysis, rapid review, realist synthesis). The second begins as a broad general question that evolves and becomes more refined over the course of the synthesis (e.g., meta-ethnography, scoping review, meta-narrative, critical interpretive synthesis). In the third type, the synthesis begins with a phenomenon of interest and the question emerges in the analytic process (e.g., grounded formal theory). Lastly, there is no clear question, but rather a general review purpose (e.g., integrative review). Thus, the requirement for a well-defined question cuts across at least three of the synthesis types (e.g., quantitative, qualitative, and emerging).
4.1.4. Quality appraisal
This is a contested issue within and between the four synthesis categories. There are strong proponents of quality appraisal in the quantitative traditions of systematic review and meta-analysis based on the need for strong studies that will not jeopardize validity of the overall findings. Nonetheless, there is no consensus on pre-defined criteria; many scales exist that vary dramatically in composition. This has methodological implications for the credibility of findings [83] .
Specific methodologies from the conventional, qualitative, and emerging categories support quality appraisal but do so with caveats. In conventional integrative reviews appraisal is recommended, but depends on the sampling frame used in the study [18] . In meta-study, appraisal criteria are explicit but quality criteria are used in different ways depending on the specific requirements of the inquiry [54] . Among the emerging syntheses, meta-narrative review developers support appraisal of a study based on criteria from the research tradition of the primary study [67] , [84] – [85] . Realist synthesis similarly supports the use of high quality evidence, but appraisal checklists are viewed with scepticism and evidence is judged based on relevance to the research question and whether a credible inference may be drawn [69] . Like realist, critical interpretive syntheses do not judge quality using standardized appraisal instruments. They will exclude fatally flawed studies, but there is no consensus on what ‘fatally flawed’ means [49] , [71] . Appraisal is based on relevance to the inquiry, not rigor of the study.
There is no agreement on quality appraisal among qualitative meta-ethnographers with some supporting and others refuting the need for appraisal. [60] , [62] . Opponents of quality appraisal are found among authors of qualitative (grounded formal theory and concept analysis) and emerging syntheses (scoping and rapid reviews) because quality is not deemed relevant to the intention of the synthesis; the studies being reviewed are not effectiveness studies where quality is extremely important. These qualitative synthesis are often reviews of theoretical developments where the concept itself is what is important, or reviews that provide quotations from the raw data so readers can make their own judgements about the relevance and utility of the data. For example, in formal grounded theory, the purpose of theory generation and authenticity of data used to generate the theory is not as important as the conceptual category. Inaccuracies may be corrected in other ways, such as using the constant comparative method, which facilitates development of theoretical concepts that are repeatedly found in the data [86] – [87] . For pragmatic reasons, evidence is not assessed in rapid and scoping reviews, in part to produce a timely product. The issue of quality appraisal is unresolved across the terrain of research synthesis and we consider this further in our discussion.
4.2. Purpose
All research syntheses share a common purpose -- to summarize, synthesize, or integrate research findings from diverse studies. This helps readers stay abreast of the burgeoning literature in a field. Our discussion here is at the level of the four categories of synthesis. Beginning with conventional literature syntheses, the overall purpose is to attend to mature topics for the purpose of re-conceptualization or to new topics requiring preliminary conceptualization [14] . Such syntheses may be helpful to consider contradictory evidence, map shifting trends in the study of a phenomenon, and describe the emergence of research in diverse fields [14] . The purpose here is to set the stage for a study by identifying what has been done, gaps in the literature, important research questions, or to develop a conceptual framework to guide data collection and analysis.
The purpose of quantitative systematic reviews is to combine, aggregate, or integrate empirical research to be able to generalize from a group of studies and determine the limits of generalization [27] . The focus of quantitative systematic reviews has been primarily on aggregating the results of studies evaluating the effectiveness of interventions using experimental, quasi-experimental, and more recently, observational designs. Systematic reviews can be done with or without quantitative meta-analysis but a meta-analysis always takes place within the context of a systematic review. Researchers must consider the review's purpose and the nature of their data in undertaking a quantitative synthesis; this will assist in determining the approach.
The purpose of qualitative syntheses is broadly to synthesize complex health experiences, practices, or concepts arising in healthcare environments. There may be various purposes depending on the qualitative methodology. For example, in hermeneutic studies the aim may be holistic explanation or understanding of a phenomenon [42] , which is deepened by integrating the findings from multiple studies. In grounded formal theory, the aim is to produce a conceptual framework or theory expected to be applicable beyond the original study. Although not able to generalize from qualitative research in the statistical sense [88] , qualitative researchers usually do want to say something about the applicability of their synthesis to other settings or phenomena. This notion of ‘theoretical generalization’ has been referred to as ‘transferability’ [89] – [90] and is an important criterion of rigour in qualitative research. It applies equally to the products of a qualitative synthesis in which the synthesis of multiple studies on the same phenomenon strengthens the ability to draw transferable conclusions.
The overarching purpose of emerging syntheses is challenging the more traditional types of syntheses, in part by using data from both quantitative and qualitative studies with diverse designs for analysis. Beyond this, however, each emerging synthesis methodology has a unique purpose. In meta-narrative review, the purpose is to identify different research traditions in the area, synthesize a complex and diverse body of research. Critical interpretive synthesis shares this characteristic. Although a distinctive approach, critical interpretive synthesis utilizes a modification of the analytic strategies of meta-ethnography [61] (e.g., reciprocal translational analysis, refutational synthesis, and lines of argument synthesis) but goes beyond the use of these to bring a critical perspective to bear in challenging the normative or epistemological assumptions in the primary literature [72] – [73] . The unique purpose of a realist synthesis is to amalgamate complex empirical evidence and theoretical understandings within a diverse body of literature to uncover the operative mechanisms and contexts that affect the outcomes of social interventions. In a scoping review, the intention is to find key concepts, examine the range of research in an area, and identify gaps in the literature. The purpose of a rapid review is comparable to that of a scoping review, but done quickly to meet the time-sensitive information needs of policy makers.
4.3. Method
4.3.1. degree of systematization.
There are varying degrees of systematization across the categories of research synthesis. The most systematized are quantitative systematic reviews and meta-analyses. There are clear processes in each with judgments to be made at each step, although there are no agreed upon guidelines for this. The process is inherently subjective despite attempts to develop objective and systematic processes [91] – [92] . Mullen and Ramirez [27] suggest that there is often a false sense of rigour implied by the terms ‘systematic review’ and ‘meta-analysis’ because of their clearly defined procedures.
In comparison with some types of qualitative synthesis, concept analysis is quite procedural. Qualitative meta-synthesis also has defined procedures and is systematic, yet perhaps less so than concept analysis. Qualitative meta-synthesis starts in an unsystematic way but becomes more systematic as it unfolds. Procedures and frameworks exist for some of the emerging types of synthesis [e.g., [50] , [63] , [71] , [93] ] but are not linear, have considerable flexibility, and are often messy with emergent processes [85] . Conventional literature reviews tend not to be as systematic as the other three types. In fact, the lack of systematization in conventional literature synthesis was the reason for the development of more systematic quantitative [17] , [20] and qualitative [45] – [46] , [61] approaches. Some authors in the field [18] have clarified processes for integrative reviews making them more systematic and rigorous, but most conventional syntheses remain relatively unsystematic in comparison with other types.
4.3.2. Complexity of the process
Some synthesis processes are considerably more complex than others. Methodologies with clearly defined steps are arguably less complex than the more flexible and emergent ones. We know that any study encounters challenges and it is rare that a pre-determined research protocol can be followed exactly as intended. Not even the rigorous methods associated with Cochrane [81] systematic reviews and meta-analyses are always implemented exactly as intended. Even when dealing with numbers rather than words, interpretation is always part of the process. Our collective experience suggests that new methodologies (e.g., meta-narrative synthesis and realist synthesis) that integrate different data types and methods are more complex than conventional reviews or the rapid and scoping reviews.
4.4. Product
The products of research syntheses usually take three distinct formats (see Table 1 and Additional File 1 for further details). The first representation is in tables, charts, graphical displays, diagrams and maps as seen in integrative, scoping and rapid reviews, meta-analyses, and critical interpretive syntheses. The second type of synthesis product is the use of mathematical scores. Summary statements of effectiveness are mathematically displayed in meta-analyses (as an effect size), systematic reviews, and rapid reviews (statistical significance).
The third synthesis product may be a theory or theoretical framework. A mid-range theory can be produced from formal grounded theory, meta-study, meta-ethnography, and realist synthesis. Theoretical/conceptual frameworks or conceptual maps may be created in meta-narrative and critical interpretive syntheses, and integrative reviews. Concepts for use within theories are produced in concept analysis. While these three product types span the categories of research synthesis, narrative description and summary is used to present the products resulting from all methodologies.
4.5. Consideration of context
There are diverse ways that context is considered in the four broad categories of synthesis. Context may be considered to the extent that it features within primary studies for the purpose of the review. Context may also be understood as an integral aspect of both the phenomenon under study and the synthesis methodology (e.g., realist synthesis). Quantitative systematic reviews and meta-analyses have typically been conducted on studies using experimental and quasi-experimental designs and more recently observational studies, which control for contextual features to allow for understanding of the ‘true’ effect of the intervention [94] .
More recently, systematic reviews have included covariates or mediating variables (i.e., contextual factors) to help explain variability in the results across studies [27] . Context, however, is usually handled in the narrative discussion of findings rather than in the synthesis itself. This lack of attention to context has been one criticism leveled against systematic reviews and meta-analyses, which restrict the types of research designs that are considered [e.g., [95] ].
When conventional literature reviews incorporate studies that deal with context, there is a place for considering contextual influences on the intervention or phenomenon. Reviews of quantitative experimental studies tend to be devoid of contextual considerations since the original studies are similarly devoid, but context might figure prominently in a literature review that incorporates both quantitative and qualitative studies.
Qualitative syntheses have been conducted on the contextual features of a particular phenomenon [33] . Paterson et al. [54] advise researchers to attend to how context may have influenced the findings of particular primary studies. In qualitative analysis, contextual features may form categories by which the data can be compared and contrasted to facilitate interpretation. Because qualitative research is often conducted to understand a phenomenon as a whole, context may be a focus, although this varies with the qualitative methodology. At the same time, the findings in a qualitative synthesis are abstracted from the original reports and taken to a higher level of conceptualization, thus removing them from the original context.
Meta-narrative synthesis [67] , [84] , because it draws on diverse research traditions and methodologies, may incorporate context into the analysis and findings. There is not, however, an explicit step in the process that directs the analyst to consider context. Generally, the research question guiding the synthesis is an important factor in whether context will be a focus.
More recent iterations of concept analysis [47] , [96] – [97] explicitly consider context reflecting the assumption that a concept's meaning is determined by its context. Morse [47] points out, however, that Wilson's [98] approach to concept analysis, and those based on Wilson [e.g., [45] ], identify attributes that are devoid of context, while Rodgers' [96] , [99] evolutionary method considers context (e.g., antecedents, consequences, and relationships to other concepts) in concept development.
Realist synthesis [69] considers context as integral to the study. It draws on a critical realist logic of inquiry grounded in the work of Bhaskar [100] , who argues that empirical co-occurrence of events is insufficient for inferring causation. One must identify generative mechanisms whose properties are causal and, depending on the situation, may nor may not be activated [94] . Context interacts with program/intervention elements and thus cannot be differentiated from the phenomenon [69] . This approach synthesizes evidence on generative mechanisms and analyzes contextual features that activate them; the result feeds back into the context. The focus is on what works, for whom, under what conditions, why and how [68] .
4.6. Underlying Philosophical and Theoretical Assumptions
When we began our review, we ‘assumed’ that the assumptions underlying synthesis methodologies would be a distinguishing characteristic of synthesis types, and that we could compare the various types on their assumptions, explicit or implicit. We found, however, that many authors did not explicate the underlying assumptions of their methodologies, and it was difficult to infer them. Kirkevold [101] has argued that integrative reviews need to be carried out from an explicit philosophical or theoretical perspective. We argue this should be true for all types of synthesis.
Authors of some emerging synthesis approaches have been very explicit about their assumptions and philosophical underpinnings. An implicit assumption of most emerging synthesis methodologies is that quantitative systematic reviews and meta-analyses have limited utility in some fields [e.g., in public health – [13] , [102] ] and for some kinds of review questions like those about feasibility and appropriateness versus effectiveness [103] – [104] . They also assume that ontologically and epistemologically, both kinds of data can be combined. This is a significant debate in the literature because it is about the commensurability of overarching paradigms [105] but this is beyond the scope of this review.
Realist synthesis is philosophically grounded in critical realism or, as noted above, a realist logic of inquiry [93] , [99] , [106] – [107] . Key assumptions regarding the nature of interventions that inform critical realism have been described above in the section on context. See Pawson et al. [106] for more information on critical realism, the philosophical basis of realist synthesis.
Meta-narrative synthesis is explicitly rooted in a constructivist philosophy of science [108] in which knowledge is socially constructed rather than discovered, and what we take to be ‘truth’ is a matter of perspective. Reality has a pluralistic and plastic character, and there is no pre-existing ‘real world’ independent of human construction and language [109] . See Greenhalgh et al. [67] , [85] and Greenhalgh & Wong [97] for more discussion of the constructivist basis of meta-narrative synthesis.
In the case of purely quantitative or qualitative syntheses, it may be an easier matter to uncover unstated assumptions because they are likely to be shared with those of the primary studies in the genre. For example, grounded formal theory shares the philosophical and theoretical underpinnings of grounded theory, rooted in the theoretical perspective of symbolic interactionism [110] – [111] and the philosophy of pragmatism [87] , [112] – [114] .
As with meta-narrative synthesis, meta-study developers identify constructivism as their interpretive philosophical foundation [54] , [88] . Epistemologically, constructivism focuses on how people construct and re-construct knowledge about a specific phenomenon, and has three main assumptions: (1) reality is seen as multiple, at times even incompatible with the phenomenon under consideration; (2) just as primary researchers construct interpretations from participants' data, meta-study researchers also construct understandings about the primary researchers' original findings. Thus, meta-synthesis is a construction of a construction, or a meta-construction; and (3) all constructions are shaped by the historical, social and ideological context in which they originated [54] . The key message here is that reports of any synthesis would benefit from an explicit identification of the underlying philosophical perspectives to facilitate a better understanding of the results, how they were derived, and how they are being interpreted.
4.7. Unit of Analysis
The unit of analysis for each category of review is generally distinct. For the emerging synthesis approaches, the unit of analysis is specific to the intention. In meta-narrative synthesis it is the storyline in diverse research traditions; in rapid review or scoping review, it depends on the focus but could be a concept; and in realist synthesis, it is the theories rather than programs that are the units of analysis. The elements of theory that are important in the analysis are mechanisms of action, the context, and the outcome [107] .
For qualitative synthesis, the units of analysis are generally themes, concepts or theories, although in meta-study, the units of analysis can be research findings (“meta-data-analysis”), research methods (“meta-method”) or philosophical/theoretical perspectives (“meta-theory”) [54] . In quantitative synthesis, the units of analysis range from specific statistics for systematic reviews to effect size of the intervention for meta-analysis. More recently, some systematic reviews focus on theories [115] – [116] , therefore it depends on the research question. Similarly, within conventional literature synthesis the units of analysis also depend on the research purpose, focus and question as well as on the type of research methods incorporated into the review. What is important in all research syntheses, however, is that the unit of analysis needs to be made explicit. Unfortunately, this is not always the case.
4.8. Strengths and Limitations
In this section, we discuss the overarching strengths and limitations of synthesis methodologies as a whole and then highlight strengths and weaknesses across each of our four categories of synthesis.
4.8.1. Strengths of Research Syntheses in General
With the vast proliferation of research reports and the increased ease of retrieval, research synthesis has become more accessible providing a way of looking broadly at the current state of research. The availability of syntheses helps researchers, practitioners, and policy makers keep up with the burgeoning literature in their fields without which evidence-informed policy or practice would be difficult. Syntheses explain variation and difference in the data helping us identify the relevance for our own situations; they identify gaps in the literature leading to new research questions and study designs. They help us to know when to replicate a study and when to avoid excessively duplicating research. Syntheses can inform policy and practice in a way that well-designed single studies cannot; they provide building blocks for theory that helps us to understand and explain our phenomena of interest.
4.8.2. Limitations of Research Syntheses in General
The process of selecting, combining, integrating, and synthesizing across diverse study designs and data types can be complex and potentially rife with bias, even with those methodologies that have clearly defined steps. Just because a rigorous and standardized approach has been used does not mean that implicit judgements will not influence the interpretations and choices made at different stages.
In all types of synthesis, the quantity of data can be considerable, requiring difficult decisions about scope, which may affect relevance. The quantity of available data also has implications for the size of the research team. Few reviews these days can be done independently, in particular because decisions about inclusion and exclusion may require the involvement of more than one person to ensure reliability.
For all types of synthesis, it is likely that in areas with large, amorphous, and diverse bodies of literature, even the most sophisticated search strategies will not turn up all the relevant and important texts. This may be more important in some synthesis methodologies than in others, but the omission of key documents can influence the results of all syntheses. This issue can be addressed, at least in part, by including a library scientist on the research team as required by some funding agencies. Even then, it is possible to miss key texts. In this review, for example, because none of us are trained in or conduct meta-analyses, we were not even aware that we had missed some new developments in this field such as meta-regression [117] – [118] , network meta-analysis [119] – [121] , and the use of individual patient data in meta-analyses [122] – [123] .
One limitation of systematic reviews and meta-analyses is that they rapidly go out of date. We thought this might be true for all types of synthesis, although we wondered if those that produce theory might not be somewhat more enduring. We have not answered this question but it is open for debate. For all types of synthesis, the analytic skills and the time required are considerable so it is clear that training is important before embarking on a review, and some types of review may not be appropriate for students or busy practitioners.
Finally, the quality of reporting in primary studies of all genres is variable so it is sometimes difficult to identify aspects of the study essential for the synthesis, or to determine whether the study meets quality criteria. There may be flaws in the original study, or journal page limitations may necessitate omitting important details. Reporting standards have been developed for some types of reviews (e.g., systematic review, meta-analysis, meta-narrative synthesis, realist synthesis); but there are no agreed upon standards for qualitative reviews. This is an important area for development in advancing the science of research synthesis.
4.8.3. Strengths and Limitations of the Four Synthesis Types
The conventional literature review and now the increasingly common integrative review remain important and accessible approaches for students, practitioners, and experienced researchers who want to summarize literature in an area but do not have the expertise to use one of the more complex methodologies. Carefully executed, such reviews are very useful for synthesizing literature in preparation for research grants and practice projects. They can determine the state of knowledge in an area and identify important gaps in the literature to provide a clear rationale or theoretical framework for a study [14] , [18] . There is a demand, however, for more rigour, with more attention to developing comprehensive search strategies and more systematic approaches to combining, integrating, and synthesizing the findings.
Generally, conventional reviews include diverse study designs and data types that facilitate comprehensiveness, which may be a strength on the one hand, but can also present challenges on the other. The complexity inherent in combining results from studies with diverse methodologies can result in bias and inaccuracies. The absence of clear guidelines about how to synthesize across diverse study types and data [18] has been a challenge for novice reviewers.
Quantitative systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been important in launching the field of evidence-based healthcare. They provide a systematic, orderly and auditable process for conducting a review and drawing conclusions [25] . They are arguably the most powerful approaches to understanding the effectiveness of healthcare interventions, especially when intervention studies on the same topic show very different results. When areas of research are dogged by controversy [25] or when study results go against strongly held beliefs, such approaches can reduce the uncertainty and bring strong evidence to bear on the controversy.
Despite their strengths, they also have limitations. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses do not provide a way of including complex literature comprising various types of evidence including qualitative studies, theoretical work, and epidemiological studies. Only certain types of design are considered and qualitative data are used in a limited way. This exclusion limits what can be learned in a topic area.
Meta-analyses are often not possible because of wide variability in study design, population, and interventions so they may have a narrow range of utility. New developments in meta-analysis, however, can be used to address some of these limitations. Network meta-analysis is used to explore relative efficacy of multiple interventions, even those that have never been compared in more conventional pairwise meta-analyses [121] , allowing for improved clinical decision making [120] . The limitation is that network meta-analysis has only been used in medical/clinical applications [119] and not in public health. It has not yet been widely accepted and many methodological challenges remain [120] – [121] . Meta-regression is another development that combines meta-analytic and linear regression principles to address the fact that heterogeneity of results may compromise a meta-analysis [117] – [118] . The disadvantage is that many clinicians are unfamiliar with it and may incorrectly interpret results [117] .
Some have accused meta-analysis of combining apples and oranges [124] raising questions in the field about their meaningfulness [25] , [28] . More recently, the use of individual rather than aggregate data has been useful in facilitating greater comparability among studies [122] . In fact, Tomas et al. [123] argue that meta-analysis using individual data is now the gold standard although access to the raw data from other studies may be a challenge to obtain.
The usefulness of systematic reviews in synthesizing complex health and social interventions has also been challenged [102] . It is often difficult to synthesize their findings because such studies are “epistemologically diverse and methodologically complex” [ [69] , p.21]. Rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria may allow only experimental or quasi-experimental designs into consideration resulting in lost information that may well be useful to policy makers for tailoring an intervention to the context or understanding its acceptance by recipients.
Qualitative syntheses may be the type of review most fraught with controversy and challenge, while also bringing distinct strengths to the enterprise. Although these methodologies provide a comprehensive and systematic review approach, they do not generally provide definitive statements about intervention effectiveness. They do, however, address important questions about the development of theoretical concepts, patient experiences, acceptability of interventions, and an understanding about why interventions might work.
Most qualitative syntheses aim to produce a theoretically generalizable mid-range theory that explains variation across studies. This makes them more useful than single primary studies, which may not be applicable beyond the immediate setting or population. All provide a contextual richness that enhances relevance and understanding. Another benefit of some types of qualitative synthesis (e.g., grounded formal theory) is that the concept of saturation provides a sound rationale for limiting the number of texts to be included thus making reviews potentially more manageable. This contrasts with the requirements of systematic reviews and meta-analyses that require an exhaustive search.
Qualitative researchers debate about whether the findings of ontologically and epistemological diverse qualitative studies can actually be combined or synthesized [125] because methodological diversity raises many challenges for synthesizing findings. The products of different types of qualitative syntheses range from theory and conceptual frameworks, to themes and rich descriptive narratives. Can one combine the findings from a phenomenological study with the theory produced in a grounded theory study? Many argue yes, but many also argue no.
Emerging synthesis methodologies were developed to address some limitations inherent in other types of synthesis but also have their own issues. Because each type is so unique, it is difficult to identify overarching strengths of the entire category. An important strength, however, is that these newer forms of synthesis provide a systematic and rigorous approach to synthesizing a diverse literature base in a topic area that includes a range of data types such as: both quantitative and qualitative studies, theoretical work, case studies, evaluations, epidemiological studies, trials, and policy documents. More than conventional literature reviews and systematic reviews, these approaches provide explicit guidance on analytic methods for integrating different types of data. The assumption is that all forms of data have something to contribute to knowledge and theory in a topic area. All have a defined but flexible process in recognition that the methods may need to shift as knowledge develops through the process.
Many emerging synthesis types are helpful to policy makers and practitioners because they are usually involved as team members in the process to define the research questions, and interpret and disseminate the findings. In fact, engagement of stakeholders is built into the procedures of the methods. This is true for rapid reviews, meta-narrative syntheses, and realist syntheses. It is less likely to be the case for critical interpretive syntheses.
Another strength of some approaches (realist and meta-narrative syntheses) is that quality and publication standards have been developed to guide researchers, reviewers, and funders in judging the quality of the products [108] , [126] – [127] . Training materials and online communities of practice have also been developed to guide users of realist and meta-narrative review methods [107] , [128] . A unique strength of critical interpretive synthesis is that it takes a critical perspective on the process that may help reconceptualize the data in a way not considered by the primary researchers [72] .
There are also challenges of these new approaches. The methods are new and there may be few published applications by researchers other than the developers of the methods, so new users often struggle with the application. The newness of the approaches means that there may not be mentors available to guide those unfamiliar with the methods. This is changing, however, and the number of applications in the literature is growing with publications by new users helping to develop the science of synthesis [e.g., [129] ]. However, the evolving nature of the approaches and their developmental stage present challenges for novice researchers.
4.9. When to Use Each Approach
Choosing an appropriate approach to synthesis will depend on the question you are asking, the purpose of the review, and the outcome or product you want to achieve. In Additional File 1 , we discuss each of these to provide guidance to readers on making a choice about review type. If researchers want to know whether a particular type of intervention is effective in achieving its intended outcomes, then they might choose a quantitative systemic review with or without meta-analysis, possibly buttressed with qualitative studies to provide depth and explanation of the results. Alternately, if the concern is about whether an intervention is effective with different populations under diverse conditions in varying contexts, then a realist synthesis might be the most appropriate.
If researchers' concern is to develop theory, they might consider qualitative syntheses or some of the emerging syntheses that produce theory (e.g., critical interpretive synthesis, realist review, grounded formal theory, qualitative meta-synthesis). If the aim is to track the development and evolution of concepts, theories or ideas, or to determine how an issue or question is addressed across diverse research traditions, then meta-narrative synthesis would be most appropriate.
When the purpose is to review the literature in advance of undertaking a new project, particularly by graduate students, then perhaps an integrative review would be appropriate. Such efforts contribute towards the expansion of theory, identify gaps in the research, establish the rationale for studying particular phenomena, and provide a framework for interpreting results in ways that might be useful for influencing policy and practice.
For researchers keen to bring new insights, interpretations, and critical re-conceptualizations to a body of research, then qualitative or critical interpretive syntheses will provide an inductive product that may offer new understandings or challenges to the status quo. These can inform future theory development, or provide guidance for policy and practice.
5. Discussion
What is the current state of science regarding research synthesis? Public health, health care, and social science researchers or clinicians have previously used all four categories of research synthesis, and all offer a suitable array of approaches for inquiries. New developments in systematic reviews and meta-analysis are providing ways of addressing methodological challenges [117] – [123] . There has also been significant advancement in emerging synthesis methodologies and they are quickly gaining popularity. Qualitative meta-synthesis is still evolving, particularly given how new it is within the terrain of research synthesis. In the midst of this evolution, outstanding issues persist such as grappling with: the quantity of data, quality appraisal, and integration with knowledge translation. These topics have not been thoroughly addressed and need further debate.
5.1. Quantity of Data
We raise the question of whether it is possible or desirable to find all available studies for a synthesis that has this requirement (e.g., meta-analysis, systematic review, scoping, meta-narrative synthesis [25] , [27] , [63] , [67] , [84] – [85] ). Is the synthesis of all available studies a realistic goal in light of the burgeoning literature? And how can this be sustained in the future, particularly as the emerging methodologies continue to develop and as the internet facilitates endless access? There has been surprisingly little discussion on this topic and the answers will have far-reaching implications for searching, sampling, and team formation.
Researchers and graduate students can no longer rely on their own independent literature search. They will likely need to ask librarians for assistance as they navigate multiple sources of literature and learn new search strategies. Although teams now collaborate with library scientists, syntheses are limited in that researchers must make decisions on the boundaries of the review, in turn influencing the study's significance. The size of a team may also be pragmatically determined to manage the search, extraction, and synthesis of the burgeoning data. There is no single answer to our question about the possibility or necessity of finding all available articles for a review. Multiple strategies that are situation specific are likely to be needed.
5.2. Quality Appraisal
While the issue of quality appraisal has received much attention in the synthesis literature, scholars are far from resolution. There may be no agreement about appraisal criteria in a given tradition. For example, the debate rages over the appropriateness of quality appraisal in qualitative synthesis where there are over 100 different sets of criteria and many do not overlap [49] . These differences may reflect disciplinary and methodological orientations, but diverse quality appraisal criteria may privilege particular types of research [49] . The decision to appraise is often grounded in ontological and epistemological assumptions. Nonetheless, diversity within and between categories of synthesis is likely to continue unless debate on the topic of quality appraisal continues and evolves toward consensus.
5.3. Integration with Knowledge Translation
If research syntheses are to make a difference to practice and ultimately to improve health outcomes, then we need to do a better job of knowledge translation. In the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) definition of knowledge translation (KT), research or knowledge synthesis is an integral component [130] . Yet, with few exceptions [131] – [132] , very little of the research synthesis literature even mentions the relationship of synthesis to KT nor does it discuss strategies to facilitate the integration of synthesis findings into policy and practice. The exception is in the emerging synthesis methodologies, some of which (e.g., realist and meta-narrative syntheses, scoping reviews) explicitly involve stakeholders or knowledge users. The argument is that engaging them in this way increases the likelihood that the knowledge generated will be translated into policy and practice. We suggest that a more explicit engagement with knowledge users in all types of synthesis would benefit the uptake of the research findings.
Research synthesis neither makes research more applicable to practice nor ensures implementation. Focus must now turn seriously towards translation of synthesis findings into knowledge products that are useful for health care practitioners in multiple areas of practice and develop appropriate strategies to facilitate their use. The burgeoning field of knowledge translation has, to some extent, taken up this challenge; however, the research-practice gap continues to plague us [133] – [134] . It is a particular problem for qualitative syntheses [131] . Although such syntheses have an important place in evidence-informed practice, little effort has gone into the challenge of translating the findings into useful products to guide practice [131] .
5.4. Limitations
Our study took longer than would normally be expected for an integrative review. Each of us were primarily involved in our own dissertations or teaching/research positions, and so this study was conducted ‘off the sides of our desks.’ A limitation was that we searched the literature over the course of 4 years (from 2008–2012), necessitating multiple search updates. Further, we did not do a comprehensive search of the literature after 2012, thus the more recent synthesis literature was not systematically explored. We did, however, perform limited database searches from 2012–2015 to keep abreast of the latest methodological developments. Although we missed some new approaches to meta-analysis in our search, we did not find any new features of the synthesis methodologies covered in our review that would change the analysis or findings of this article. Lastly, we struggled with the labels used for the broad categories of research synthesis methodology because of our hesitancy to reinforce the divide between quantitative and qualitative approaches. However, it was very difficult to find alternative language that represented the types of data used in these methodologies. Despite our hesitancy in creating such an obvious divide, we were left with the challenge of trying to find a way of characterizing these broad types of syntheses.
6. Conclusion
Our findings offer methodological clarity for those wishing to learn about the broad terrain of research synthesis. We believe that our review makes transparent the issues and considerations in choosing from among the four broad categories of research synthesis. In summary, research synthesis has taken its place as a form of research in its own right. The methodological terrain has deep historical roots reaching back over the past 200 years, yet research synthesis remains relatively new to public health, health care, and social sciences in general. This is rapidly changing. New developments in systematic reviews and meta-analysis, and the emergence of new synthesis methodologies provide a vast array of options to review the literature for diverse purposes. New approaches to research synthesis and new analytic methods within existing approaches provide a much broader range of review alternatives for public health, health care, and social science students and researchers.
Acknowledgments
KSM is an assistant professor in the Faculty of Nursing at the University of Alberta. Her work on this article was largely conducted as a Postdoctoral Fellow, funded by KRESCENT (Kidney Research Scientist Core Education and National Training Program, reference #KRES110011R1) and the Faculty of Nursing at the University of Alberta.
MM's work on this study over the period of 2008-2014 was supported by a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Applied Public Health Research Chair Award (grant #92365).
We thank Rachel Spanier who provided support with reference formatting.
List of Abbreviations (in Additional File 1 )
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this article.
Authors' contributions: KSM co-designed the study, collected data, analyzed the data, drafted/revised the manuscript, and managed the project.
MP contributed to searching the literature, developing the analytic framework, and extracting data for the Additional File.
JB contributed to searching the literature, developing the analytic framework, and extracting data for the Additional File.
WN contributed to searching the literature, developing the analytic framework, and extracting data for the Additional File.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional Files: Additional File 1 – Selected Types of Research Synthesis
This Additional File is our dataset created to organize, analyze and critique the literature that we synthesized in our integrative review. Our results were created based on analysis of this Additional File.

Writing a Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- Step 1: Choosing a Topic
- Step 2: Finding Information
- Step 3: Evaluating Content
- Step 4: Taking Notes
- Step 5: Synthesizing Content
- Step 6: Writing the Review
- Step 7: Citing Your Sources
- Meet the Library Team
- Off-Campus & Mobile Access
- Research Help
- Other Helpful Guides
Tips on Synthesizing
By step 5 you are well into the literature review process. This next to last step is when you take a moment to reflect on the research you have, what you have learned, how the information fits into you topic, and what is the best way to present your findings.
Some tips on how to organize your research-
- Organize research by topic. Feel free to create subtopics as a means of connecting your research and ideas.
- Consider what points from each topic you want to address in your literature review. This is the time to start thinking about what areas you will discuss in your review and what pieces of research you will use to support your conclusions.
- After reviewing your notes, try summarizing the main points in one to two sentences.
- Draft an outline of your literature review. Start with a point, then list supporting arguments and resources. Repeat this process for each of your paper's main points.
- << Previous: Step 4: Taking Notes
- Next: Step 6: Writing the Review >>
- Last Updated: Apr 1, 2024 9:42 AM
- URL: https://libguides.llu.edu/literaturereview
Literature Review Basics
- What is a Literature Review?
- Synthesizing Research
- Using Research & Synthesis Tables
- Additional Resources

Synthesis: What is it?
First, let's be perfectly clear about what synthesizing your research isn't :
- - It isn't just summarizing the material you read
- - It isn't generating a collection of annotations or comments (like an annotated bibliography)
- - It isn't compiling a report on every single thing ever written in relation to your topic
When you synthesize your research, your job is to help your reader understand the current state of the conversation on your topic, relative to your research question. That may include doing the following:
- - Selecting and using representative work on the topic
- - Identifying and discussing trends in published data or results
- - Identifying and explaining the impact of common features (study populations, interventions, etc.) that appear frequently in the literature
- - Explaining controversies, disputes, or central issues in the literature that are relevant to your research question
- - Identifying gaps in the literature, where more research is needed
- - Establishing the discussion to which your own research contributes and demonstrating the value of your contribution
Essentially, you're telling your reader where they are (and where you are) in the scholarly conversation about your project.
Synthesis: How do I do it?
Synthesis, step by step.
This is what you need to do before you write your review.
- Identify and clearly describe your research question (you may find the Formulating PICOT Questions table at the Additional Resources tab helpful).
- Collect sources relevant to your research question.
- Organize and describe the sources you've found -- your job is to identify what types of sources you've collected (reviews, clinical trials, etc.), identify their purpose (what are they measuring, testing, or trying to discover?), determine the level of evidence they represent (see the Levels of Evidence table at the Additional Resources tab ), and briefly explain their major findings . Use a Research Table to document this step.
- Study the information you've put in your Research Table and examine your collected sources, looking for similarities and differences . Pay particular attention to populations , methods (especially relative to levels of evidence), and findings .
- Analyze what you learn in (4) using a tool like a Synthesis Table. Your goal is to identify relevant themes, trends, gaps, and issues in the research. Your literature review will collect the results of this analysis and explain them in relation to your research question.
Analysis tips
- - Sometimes, what you don't find in the literature is as important as what you do find -- look for questions that the existing research hasn't answered yet.
- - If any of the sources you've collected refer to or respond to each other, keep an eye on how they're related -- it may provide a clue as to whether or not study results have been successfully replicated.
- - Sorting your collected sources by level of evidence can provide valuable insight into how a particular topic has been covered, and it may help you to identify gaps worth addressing in your own work.
- << Previous: What is a Literature Review?
- Next: Using Research & Synthesis Tables >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 12:06 PM
- URL: https://usi.libguides.com/literature-review-basics

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 7: Synthesizing Sources
Learning objectives.
At the conclusion of this chapter, you will be able to:
- synthesize key sources connecting them with the research question and topic area.
7.1 Overview of synthesizing
7.1.1 putting the pieces together.
Combining separate elements into a whole is the dictionary definition of synthesis. It is a way to make connections among and between numerous and varied source materials. A literature review is not an annotated bibliography, organized by title, author, or date of publication. Rather, it is grouped by topic to create a whole view of the literature relevant to your research question.

Your synthesis must demonstrate a critical analysis of the papers you collected as well as your ability to integrate the results of your analysis into your own literature review. Each paper collected should be critically evaluated and weighed for “adequacy, appropriateness, and thoroughness” ( Garrard, 2017 ) before inclusion in your own review. Papers that do not meet this criteria likely should not be included in your literature review.
Begin the synthesis process by creating a grid, table, or an outline where you will summarize, using common themes you have identified and the sources you have found. The summary grid or outline will help you compare and contrast the themes so you can see the relationships among them as well as areas where you may need to do more searching. Whichever method you choose, this type of organization will help you to both understand the information you find and structure the writing of your review. Remember, although “the means of summarizing can vary, the key at this point is to make sure you understand what you’ve found and how it relates to your topic and research question” ( Bennard et al., 2014 ).
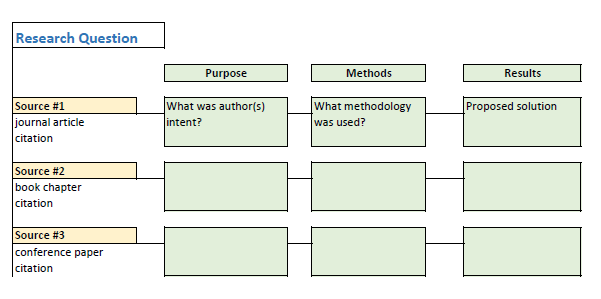
As you read through the material you gather, look for common themes as they may provide the structure for your literature review. And, remember, research is an iterative process: it is not unusual to go back and search information sources for more material.
At one extreme, if you are claiming, ‘There are no prior publications on this topic,’ it is more likely that you have not found them yet and may need to broaden your search. At another extreme, writing a complete literature review can be difficult with a well-trod topic. Do not cite it all; instead cite what is most relevant. If that still leaves too much to include, be sure to reference influential sources…as well as high-quality work that clearly connects to the points you make. ( Klingner, Scanlon, & Pressley, 2005 ).
7.2 Creating a summary table
Literature reviews can be organized sequentially or by topic, theme, method, results, theory, or argument. It’s important to develop categories that are meaningful and relevant to your research question. Take detailed notes on each article and use a consistent format for capturing all the information each article provides. These notes and the summary table can be done manually, using note cards. However, given the amount of information you will be recording, an electronic file created in a word processing or spreadsheet is more manageable. Examples of fields you may want to capture in your notes include:
- Authors’ names
- Article title
- Publication year
- Main purpose of the article
- Methodology or research design
- Participants
- Measurement
- Conclusions
Other fields that will be useful when you begin to synthesize the sum total of your research:
- Specific details of the article or research that are especially relevant to your study
- Key terms and definitions
- Strengths or weaknesses in research design
- Relationships to other studies
- Possible gaps in the research or literature (for example, many research articles conclude with the statement “more research is needed in this area”)
- Finally, note how closely each article relates to your topic. You may want to rank these as high, medium, or low relevance. For papers that you decide not to include, you may want to note your reasoning for exclusion, such as ‘small sample size’, ‘local case study,’ or ‘lacks evidence to support assertion.’
This short video demonstrates how a nursing researcher might create a summary table.
7.2.1 Creating a Summary Table

Summary tables can be organized by author or by theme, for example:
For a summary table template, see http://blogs.monm.edu/writingatmc/files/2013/04/Synthesis-Matrix-Template.pdf
7.3 Creating a summary outline
An alternate way to organize your articles for synthesis it to create an outline. After you have collected the articles you intend to use (and have put aside the ones you won’t be using), it’s time to identify the conclusions that can be drawn from the articles as a group.
Based on your review of the collected articles, group them by categories. You may wish to further organize them by topic and then chronologically or alphabetically by author. For each topic or subtopic you identified during your critical analysis of the paper, determine what those papers have in common. Likewise, determine which ones in the group differ. If there are contradictory findings, you may be able to identify methodological or theoretical differences that could account for the contradiction (for example, differences in population demographics). Determine what general conclusions you can report about the topic or subtopic as the entire group of studies relate to it. For example, you may have several studies that agree on outcome, such as ‘hands on learning is best for science in elementary school’ or that ‘continuing education is the best method for updating nursing certification.’ In that case, you may want to organize by methodology used in the studies rather than by outcome.
Organize your outline in a logical order and prepare to write the first draft of your literature review. That order might be from broad to more specific, or it may be sequential or chronological, going from foundational literature to more current. Remember, “an effective literature review need not denote the entire historical record, but rather establish the raison d’etre for the current study and in doing so cite that literature distinctly pertinent for theoretical, methodological, or empirical reasons.” ( Milardo, 2015, p. 22 ).
As you organize the summarized documents into a logical structure, you are also appraising and synthesizing complex information from multiple sources. Your literature review is the result of your research that synthesizes new and old information and creates new knowledge.
7.4 Additional resources:
Literature Reviews: Using a Matrix to Organize Research / Saint Mary’s University of Minnesota
Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources / Indiana University
Writing a Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix / Florida International University
Sample Literature Reviews Grid / Complied by Lindsay Roberts
Select three or four articles on a single topic of interest to you. Then enter them into an outline or table in the categories you feel are important to a research question. Try both the grid and the outline if you can to see which suits you better. The attached grid contains the fields suggested in the video .
Literature Review Table
Test yourself.
- Select two articles from your own summary table or outline and write a paragraph explaining how and why the sources relate to each other and your review of the literature.
- In your literature review, under what topic or subtopic will you place the paragraph you just wrote?
Image attribution
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students Copyright © by Linda Frederiksen is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Systematic reviews & evidence synthesis methods.
- Schedule a Consultation / Meet our Team
- What is Evidence Synthesis?
- Types of Evidence Synthesis
- Evidence Synthesis Across Disciplines
- Finding and Appraising Existing Systematic Reviews
- 0. Develop a Protocol
- 1. Draft your Research Question
- 2. Select Databases
- 3. Select Grey Literature Sources
- 4. Write a Search Strategy
- 5. Register a Protocol
- 6. Translate Search Strategies
- 7. Citation Management
- 8. Article Screening
- 9. Risk of Bias Assessment
- 10. Data Extraction
- 11. Synthesize, Map, or Describe the Results
- Open Access Evidence Synthesis Resources
What are Evidence Syntheses?
According to the Royal Society, 'evidence synthesis' refers to the process of bringing together information from a range of sources and disciplines to inform debates and decisions on specific issues. They generally include a methodical and comprehensive literature synthesis focused on a well-formulated research question. Their aim is to identify and synthesize all of the scholarly research on a particular topic, including both published and unpublished studies. Evidence syntheses are conducted in an unbiased, reproducible way to provide evidence for practice and policy-making, as well as to identify gaps in the research. Evidence syntheses may also include a meta-analysis, a more quantitative process of synthesizing and visualizing data retrieved from various studies.
Evidence syntheses are much more time-intensive than traditional literature reviews and require a multi-person research team. See this PredicTER tool to get a sense of a systematic review timeline (one type of evidence synthesis). Before embarking on an evidence synthesis, it's important to clearly identify your reasons for conducting one. For a list of types of evidence synthesis projects, see the Types of Evidence Synthesis tab.
How Does a Traditional Literature Review Differ From an Evidence Synthesis?
One commonly used form of evidence synthesis is a systematic review. This table compares a traditional literature review with a systematic review.
Video: Reproducibility and transparent methods (Video 3:25)
Reporting Standards
There are some reporting standards for evidence syntheses. These can serve as guidelines for protocol and manuscript preparation and journals may require that these standards are followed for the review type that is being employed (e.g. systematic review, scoping review, etc).
- PRISMA checklist Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) is an evidence-based minimum set of items for reporting in systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
- PRISMA-P Standards An updated version of the original PRISMA standards for protocol development.
- PRISMA - ScR Reporting guidelines for scoping reviews and evidence maps
- PRISMA-IPD Standards Extension of the original PRISMA standards for systematic reviews and meta-analyses of individual participant data.
- EQUATOR Network The EQUATOR (Enhancing the QUAlity and Transparency Of health Research) Network is an international initiative that seeks to improve the reliability and value of published health research literature by promoting transparent and accurate reporting and wider use of robust reporting guidelines. They provide a list of various standards for reporting in systematic reviews.
Video: Guidelines and reporting standards
PRISMA Flow Diagram
The PRISMA flow diagram depicts the flow of information through the different phases of an evidence synthesis. It maps the search (number of records identified), screening (number of records included and excluded), and selection (reasons for exclusion). Many evidence syntheses include a PRISMA flow diagram in the published manuscript.
See below for resources to help you generate your own PRISMA flow diagram.
- PRISMA Flow Diagram Tool
- PRISMA Flow Diagram Word Template
- << Previous: Schedule a Consultation / Meet our Team
- Next: Types of Evidence Synthesis >>
- Last Updated: Feb 14, 2024 4:20 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/evidence-synthesis
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.

- Herron School of Art
- Ruth Lilly Law
- Ruth Lilly Medical
- School of Dentistry
Literature Review - A Self-Guided Tutorial
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the question
- 2. Review discipline styles
- Searching article databases - video
- Finding the article full-text
- Citation chaining
- When to stop searching
- 4. Manage your references
- 5. Critically analyze and evaluate
- 6. Synthesize
- 7. Write literature review
Who's My Librarian?
Locate your University Library's subject librarian for personalized assistance.
Students doing research in specific areas may also request assistance at other IUPUI libraries:
- IU School of Dentistry Library
- Ruth Lilly Law Library
- Ruth Lilly Medical Library

You can sort the literature in various ways, for example:

Synthesis Matrix Example

From Jennifer Lim
- << Previous: 5. Critically analyze and evaluate
- Next: 7. Write literature review >>
- Last Updated: Jun 15, 2023 8:24 AM
- URL: https://iupui.libguides.com/literaturereview
Writing in the Health and Social Sciences: Literature Reviews and Synthesis Tools
- Journal Publishing
- Style and Writing Guides
- Readings about Writing
- Citing in APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Resources for Dissertation Authors
- Citation Management and Formatting Tools
- What are Literature Reviews?
- Conducting & Reporting Systematic Reviews
- Finding Systematic Reviews
- Tutorials & Tools for Literature Reviews
Systematic Literature Reviews: Steps & Resources
These steps for conducting a systematic literature review are listed below .
Also see subpages for more information about:
- The different types of literature reviews, including systematic reviews and other evidence synthesis methods
- Tools & Tutorials
Literature Review & Systematic Review Steps
- Develop a Focused Question
- Scope the Literature (Initial Search)
- Refine & Expand the Search
- Limit the Results
- Download Citations
- Abstract & Analyze
- Create Flow Diagram
- Synthesize & Report Results
1. Develop a Focused Question
Consider the PICO Format: Population/Problem, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome
Focus on defining the Population or Problem and Intervention (don't narrow by Comparison or Outcome just yet!)
"What are the effects of the Pilates method for patients with low back pain?"
Tools & Additional Resources:
- PICO Question Help
- Stillwell, Susan B., DNP, RN, CNE; Fineout-Overholt, Ellen, PhD, RN, FNAP, FAAN; Melnyk, Bernadette Mazurek, PhD, RN, CPNP/PMHNP, FNAP, FAAN; Williamson, Kathleen M., PhD, RN Evidence-Based Practice, Step by Step: Asking the Clinical Question, AJN The American Journal of Nursing : March 2010 - Volume 110 - Issue 3 - p 58-61 doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000368959.11129.79
2. Scope the Literature
A "scoping search" investigates the breadth and/or depth of the initial question or may identify a gap in the literature.
Eligible studies may be located by searching in:
- Background sources (books, point-of-care tools)
- Article databases
- Trial registries
- Grey literature
- Cited references
- Reference lists
When searching, if possible, translate terms to controlled vocabulary of the database. Use text word searching when necessary.
Use Boolean operators to connect search terms:
- Combine separate concepts with AND (resulting in a narrower search)
- Connecting synonyms with OR (resulting in an expanded search)
Search: pilates AND ("low back pain" OR backache )
Video Tutorials - Translating PICO Questions into Search Queries
- Translate Your PICO Into a Search in PubMed (YouTube, Carrie Price, 5:11)
- Translate Your PICO Into a Search in CINAHL (YouTube, Carrie Price, 4:56)
3. Refine & Expand Your Search
Expand your search strategy with synonymous search terms harvested from:
- database thesauri
- reference lists
- relevant studies
Example:
(pilates OR exercise movement techniques) AND ("low back pain" OR backache* OR sciatica OR lumbago OR spondylosis)
As you develop a final, reproducible strategy for each database, save your strategies in a:
- a personal database account (e.g., MyNCBI for PubMed)
- Log in with your NYU credentials
- Open and "Make a Copy" to create your own tracker for your literature search strategies
4. Limit Your Results
Use database filters to limit your results based on your defined inclusion/exclusion criteria. In addition to relying on the databases' categorical filters, you may also need to manually screen results.
- Limit to Article type, e.g.,: "randomized controlled trial" OR multicenter study
- Limit by publication years, age groups, language, etc.
NOTE: Many databases allow you to filter to "Full Text Only". This filter is not recommended . It excludes articles if their full text is not available in that particular database (CINAHL, PubMed, etc), but if the article is relevant, it is important that you are able to read its title and abstract, regardless of 'full text' status. The full text is likely to be accessible through another source (a different database, or Interlibrary Loan).
- Filters in PubMed
- CINAHL Advanced Searching Tutorial
5. Download Citations
Selected citations and/or entire sets of search results can be downloaded from the database into a citation management tool. If you are conducting a systematic review that will require reporting according to PRISMA standards, a citation manager can help you keep track of the number of articles that came from each database, as well as the number of duplicate records.
In Zotero, you can create a Collection for the combined results set, and sub-collections for the results from each database you search. You can then use Zotero's 'Duplicate Items" function to find and merge duplicate records.

- Citation Managers - General Guide
6. Abstract and Analyze
- Migrate citations to data collection/extraction tool
- Screen Title/Abstracts for inclusion/exclusion
- Screen and appraise full text for relevance, methods,
- Resolve disagreements by consensus
Covidence is a web-based tool that enables you to work with a team to screen titles/abstracts and full text for inclusion in your review, as well as extract data from the included studies.

- Covidence Support
- Critical Appraisal Tools
- Data Extraction Tools
7. Create Flow Diagram
The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagram is a visual representation of the flow of records through different phases of a systematic review. It depicts the number of records identified, included and excluded. It is best used in conjunction with the PRISMA checklist .

Example from: Stotz, S. A., McNealy, K., Begay, R. L., DeSanto, K., Manson, S. M., & Moore, K. R. (2021). Multi-level diabetes prevention and treatment interventions for Native people in the USA and Canada: A scoping review. Current Diabetes Reports, 2 (11), 46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-021-01414-3
- PRISMA Flow Diagram Generator (ShinyApp.io, Haddaway et al. )
- PRISMA Diagram Templates (Word and PDF)
- Make a copy of the file to fill out the template
- Image can be downloaded as PDF, PNG, JPG, or SVG
- Covidence generates a PRISMA diagram that is automatically updated as records move through the review phases
8. Synthesize & Report Results
There are a number of reporting guideline available to guide the synthesis and reporting of results in systematic literature reviews.
It is common to organize findings in a matrix, also known as a Table of Evidence (ToE).

- Reporting Guidelines for Systematic Reviews
- Download a sample template of a health sciences review matrix (GoogleSheets)
Steps modified from:
Cook, D. A., & West, C. P. (2012). Conducting systematic reviews in medical education: a stepwise approach. Medical Education , 46 (10), 943–952.
- << Previous: Citation Management and Formatting Tools
- Next: What are Literature Reviews? >>
- Last Updated: Mar 28, 2024 2:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/healthwriting
How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.
Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
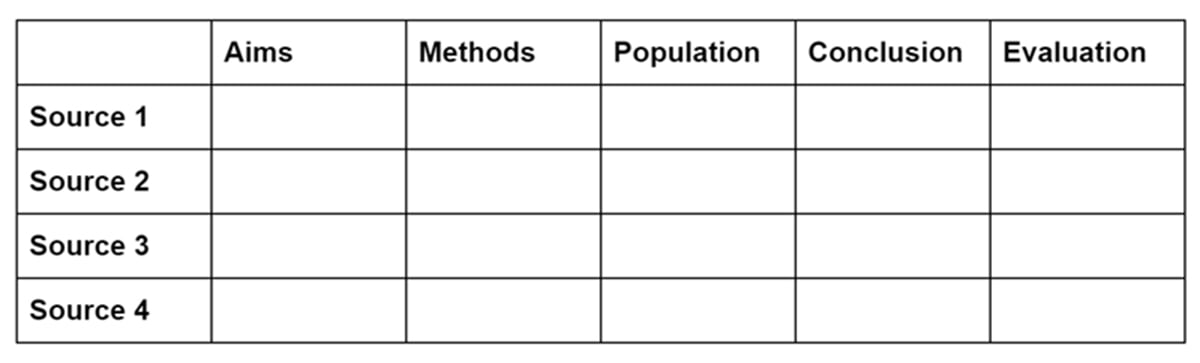
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
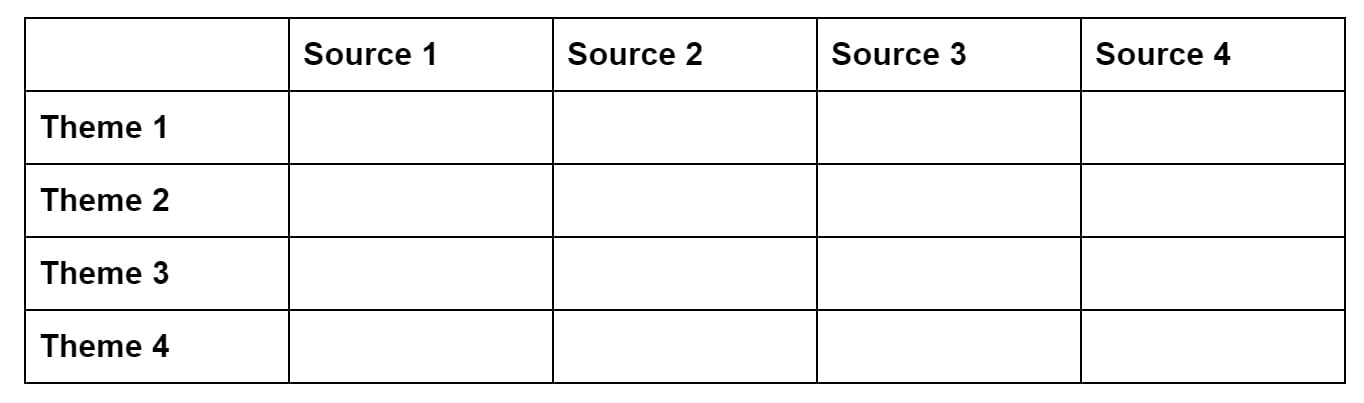
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
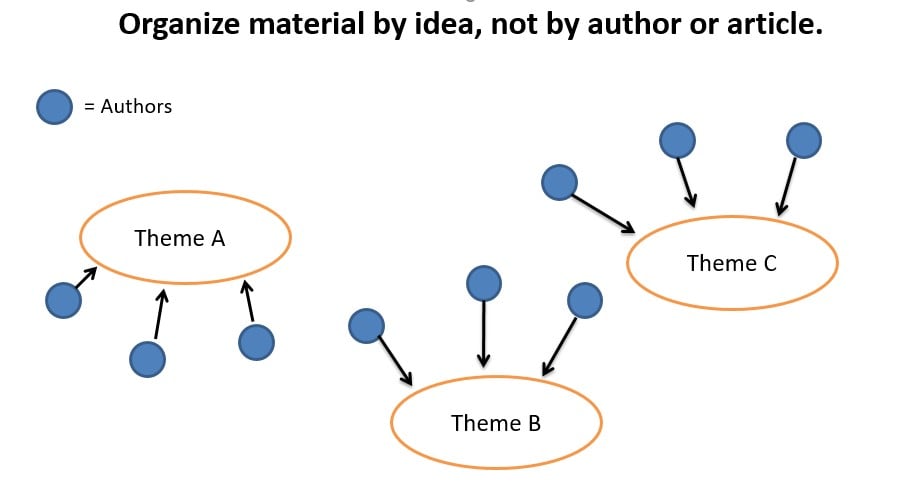
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay
Synthesising the literature as part of a literature review
Affiliation.
- 1 University of Manchester, England.
- PMID: 25783281
- DOI: 10.7748/ns.29.29.44.e8957
This article examines how to synthesise and critique research literature. To place the process of synthesising the research literature into context, the article explores the critiquing process by breaking it down into seven sequential steps. The article explains how and why these steps need to be kept in mind if a robust comprehensive literature search and analysis are to be achieved. The article outlines how to engage in the critiquing process and explains how the literature review needs to be assembled to generate a logical and reasoned debate to examine a topic of interest or research in more detail.
Keywords: Critical analysis; critique; evaluation; integrative review; literature review; literature search; research; research question; search strategy; synthesis.
- Research / standards*
- Research Design*
- Review Literature as Topic*

Write a Literature Review
- Find This link opens in a new window
Get Organized
- Lit Review Prep Use this template to help you evaluate your sources, create article summaries for an annotated bibliography, and a synthesis matrix for your lit review outline.
Synthesize your Information
Synthesize: combine separate elements to form a whole.
Synthesis Matrix
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other. After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix to help you see how they relate to each other, and apply to each of your themes or variables. By arranging your sources in a matrix by theme or variable, you can see how your sources relate to each other, and can start thinking about how you weave them together to create a narrative.
- Step-by-Step Approach
- Example Matrix from NSCU
- Matrix Template
- << Previous: Summarize
- Next: Integrate >>
- Last Updated: Oct 11, 2023 12:20 PM
- URL: https://libraryguides.goucher.edu/literature-review


Chapter 5: Writing a Summary and Synthesizing
5.5 Synthesis and Literature Reviews
Literature reviews : synthesis and research.
Why do we seek to understand the ways that authors or sources “converse” with one another? So that we can synthesize various perspectives on a topic to more deeply understand it.
In academic writing, this understanding of the “conversation” may become the content of an explanatory synthesis paper – a paper in which you, the writer, point out various various themes or key points from a conversation on a particular topic. Notice that the example of synthesis in “What Synthesis Is” acknowledges that guns and gun control inspire passionate responses in Americans, that more than one kind of weapon is involved in gun violence, that guns in America are both legally and illegally owned, and that there are many constituencies whose experience with guns needs to considered if sound gun-control policy is to be achieved. The writer of this synthesis isn’t “pretending” to be objective (“Although gun violence is a problem in American today, people who want to increase gun control clearly don’t understand the Second Amendment”); nor is the writer arguing a point or attempting to persuade the audience to accept one perspective. The writer is making a claim about gun control that demonstrates his or her deepest understanding of the issue.
Another assignment that you may complete that also applies your synthesis skills is a l iterature review . Literature reviews are often found in the beginning of scholarly journal articles to contextualize the author’s own research. Sometimes, literature reviews are done for their own sake; some scholarly articles are just Literature reviews.
Literature reviews (sometimes shortened to “lit reviews”) synthesize previous research that has been done on a particular topic, summarizing important works in the history of research on that topic. The literature review provides context for the author’s own new research. It is the basis and background out of which the author’s research grows. Context = credibility in academic writing. When writers are able to produce a literature review, they demonstrate the breadth of their knowledge about how others have already studied and discussed their topic.
- Literature reviews are most often arranged by topic or theme , much like a traditional explanatory synthesis paper.
- If one is looking at a topic that has a long history of research and scholarship, one may conduct a chronological literature review, one that looks at how the research topic has been studied and discussed in various time periods (i.e., what was published ten years ago, five years ago, and within the last year, for example).
- Finally, in some instances, one might seek to craft a literature review that is organized by discipline or field. This type of literature review could offer information about how different academic fields have examined a particular topic (i.e., what is the current research being done by biologists on this topic? What is the current research being done by psychologists on this topic? What is the current research being done by [ insert academic discipline] on this topic?).
A Literature Review offers only a report on what others have already written about. The Literature Review does not reflect the author’s own argument or contributions to the field of research. Instead, it indicates that the author has read others’ important contributions and understands what has come before him or her. Sometimes, literature reviews are stand alone assignments or publications. Sometimes, they fit into a larger essay or article (especially in many of the scholarly articles that you will read throughout college. For more information on how literature reviews are a part of scholarly articles, see chapter 10.5 )
A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing by Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Feedback/Errata
Comments are closed.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 24, Issue 2
- Five tips for developing useful literature summary tables for writing review articles
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0157-5319 Ahtisham Younas 1 , 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7839-8130 Parveen Ali 3 , 4
- 1 Memorial University of Newfoundland , St John's , Newfoundland , Canada
- 2 Swat College of Nursing , Pakistan
- 3 School of Nursing and Midwifery , University of Sheffield , Sheffield , South Yorkshire , UK
- 4 Sheffield University Interpersonal Violence Research Group , Sheffield University , Sheffield , UK
- Correspondence to Ahtisham Younas, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St John's, NL A1C 5C4, Canada; ay6133{at}mun.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2021-103417
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research. 1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis in reviews, the use of literature summary tables is of utmost importance. A literature summary table provides a synopsis of an included article. It succinctly presents its purpose, methods, findings and other relevant information pertinent to the review. The aim of developing these literature summary tables is to provide the reader with the information at one glance. Since there are multiple types of reviews (eg, systematic, integrative, scoping, critical and mixed methods) with distinct purposes and techniques, 2 there could be various approaches for developing literature summary tables making it a complex task specialty for the novice researchers or reviewers. Here, we offer five tips for authors of the review articles, relevant to all types of reviews, for creating useful and relevant literature summary tables. We also provide examples from our published reviews to illustrate how useful literature summary tables can be developed and what sort of information should be provided.
Tip 1: provide detailed information about frameworks and methods
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Tabular literature summaries from a scoping review. Source: Rasheed et al . 3
The provision of information about conceptual and theoretical frameworks and methods is useful for several reasons. First, in quantitative (reviews synthesising the results of quantitative studies) and mixed reviews (reviews synthesising the results of both qualitative and quantitative studies to address a mixed review question), it allows the readers to assess the congruence of the core findings and methods with the adapted framework and tested assumptions. In qualitative reviews (reviews synthesising results of qualitative studies), this information is beneficial for readers to recognise the underlying philosophical and paradigmatic stance of the authors of the included articles. For example, imagine the authors of an article, included in a review, used phenomenological inquiry for their research. In that case, the review authors and the readers of the review need to know what kind of (transcendental or hermeneutic) philosophical stance guided the inquiry. Review authors should, therefore, include the philosophical stance in their literature summary for the particular article. Second, information about frameworks and methods enables review authors and readers to judge the quality of the research, which allows for discerning the strengths and limitations of the article. For example, if authors of an included article intended to develop a new scale and test its psychometric properties. To achieve this aim, they used a convenience sample of 150 participants and performed exploratory (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) on the same sample. Such an approach would indicate a flawed methodology because EFA and CFA should not be conducted on the same sample. The review authors must include this information in their summary table. Omitting this information from a summary could lead to the inclusion of a flawed article in the review, thereby jeopardising the review’s rigour.
Tip 2: include strengths and limitations for each article
Critical appraisal of individual articles included in a review is crucial for increasing the rigour of the review. Despite using various templates for critical appraisal, authors often do not provide detailed information about each reviewed article’s strengths and limitations. Merely noting the quality score based on standardised critical appraisal templates is not adequate because the readers should be able to identify the reasons for assigning a weak or moderate rating. Many recent critical appraisal checklists (eg, Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool) discourage review authors from assigning a quality score and recommend noting the main strengths and limitations of included studies. It is also vital that methodological and conceptual limitations and strengths of the articles included in the review are provided because not all review articles include empirical research papers. Rather some review synthesises the theoretical aspects of articles. Providing information about conceptual limitations is also important for readers to judge the quality of foundations of the research. For example, if you included a mixed-methods study in the review, reporting the methodological and conceptual limitations about ‘integration’ is critical for evaluating the study’s strength. Suppose the authors only collected qualitative and quantitative data and did not state the intent and timing of integration. In that case, the strength of the study is weak. Integration only occurred at the levels of data collection. However, integration may not have occurred at the analysis, interpretation and reporting levels.
Tip 3: write conceptual contribution of each reviewed article
While reading and evaluating review papers, we have observed that many review authors only provide core results of the article included in a review and do not explain the conceptual contribution offered by the included article. We refer to conceptual contribution as a description of how the article’s key results contribute towards the development of potential codes, themes or subthemes, or emerging patterns that are reported as the review findings. For example, the authors of a review article noted that one of the research articles included in their review demonstrated the usefulness of case studies and reflective logs as strategies for fostering compassion in nursing students. The conceptual contribution of this research article could be that experiential learning is one way to teach compassion to nursing students, as supported by case studies and reflective logs. This conceptual contribution of the article should be mentioned in the literature summary table. Delineating each reviewed article’s conceptual contribution is particularly beneficial in qualitative reviews, mixed-methods reviews, and critical reviews that often focus on developing models and describing or explaining various phenomena. Figure 2 offers an example of a literature summary table. 4
Tabular literature summaries from a critical review. Source: Younas and Maddigan. 4

Tip 4: compose potential themes from each article during summary writing
While developing literature summary tables, many authors use themes or subthemes reported in the given articles as the key results of their own review. Such an approach prevents the review authors from understanding the article’s conceptual contribution, developing rigorous synthesis and drawing reasonable interpretations of results from an individual article. Ultimately, it affects the generation of novel review findings. For example, one of the articles about women’s healthcare-seeking behaviours in developing countries reported a theme ‘social-cultural determinants of health as precursors of delays’. Instead of using this theme as one of the review findings, the reviewers should read and interpret beyond the given description in an article, compare and contrast themes, findings from one article with findings and themes from another article to find similarities and differences and to understand and explain bigger picture for their readers. Therefore, while developing literature summary tables, think twice before using the predeveloped themes. Including your themes in the summary tables (see figure 1 ) demonstrates to the readers that a robust method of data extraction and synthesis has been followed.
Tip 5: create your personalised template for literature summaries
Often templates are available for data extraction and development of literature summary tables. The available templates may be in the form of a table, chart or a structured framework that extracts some essential information about every article. The commonly used information may include authors, purpose, methods, key results and quality scores. While extracting all relevant information is important, such templates should be tailored to meet the needs of the individuals’ review. For example, for a review about the effectiveness of healthcare interventions, a literature summary table must include information about the intervention, its type, content timing, duration, setting, effectiveness, negative consequences, and receivers and implementers’ experiences of its usage. Similarly, literature summary tables for articles included in a meta-synthesis must include information about the participants’ characteristics, research context and conceptual contribution of each reviewed article so as to help the reader make an informed decision about the usefulness or lack of usefulness of the individual article in the review and the whole review.
In conclusion, narrative or systematic reviews are almost always conducted as a part of any educational project (thesis or dissertation) or academic or clinical research. Literature reviews are the foundation of research on a given topic. Robust and high-quality reviews play an instrumental role in guiding research, practice and policymaking. However, the quality of reviews is also contingent on rigorous data extraction and synthesis, which require developing literature summaries. We have outlined five tips that could enhance the quality of the data extraction and synthesis process by developing useful literature summaries.
- Aromataris E ,
- Rasheed SP ,
Twitter @Ahtisham04, @parveenazamali
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
- Library Guides
- Literature Reviews
- Choosing a Type of Review
Literature Reviews: Choosing a Type of Review
Selecting a review type.

You'll want to think about the kind of review you are doing. Is it a selective or comprehensive review? Is the review part of a larger work or a stand-alone work ?
For example, if you're writing the Literature Review section of a journal article, that's a selective review which is part of a larger work. Alternatively, if you're writing a review article, that's a comprehensive review which is a stand-alone work. Thinking about this will help you develop the scope of the review.
Defining the Scope of Your Review
This exercise will help define the scope of your Literature Review, setting the boundaries for which literature to include and which to exclude.
A FEW GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS WHEN DEFINING SCOPE
- Which populations to investigate — this can include gender, age, socio-economic status, race, geographic location, etc., if the research area includes humans.
- What years to include — if researching the legalization of medicinal cannabis, you might only look at the previous 20 years; but if researching dolphin mating practices, you might extend many more decades.
- Which subject areas — if researching artificial intelligence, subject areas could be computer science, robotics, or health sciences
- How many sources — a selective review for a class assignment might only need ten, while a comprehensive review for a dissertation might include hundreds. There is no one right answer.
- There will be many other considerations that are more specific to your topic.
Most databases will allow you to limit years and subject areas, so look for those tools while searching. See the Searching Tips tab for information on how use these tools.
Four Common Types of Reviews
Literature review.
- Often used as a generic term to describe any type of review
- More precise definition: Published materials that provide an examination of published literature . Can cover wide range of subjects at various levels of comprehensiveness.
- Identifies gaps in research, explains importance of topic, hypothesizes future work, etc.
- Usually written as part of a larger work like a journal article or dissertation
SCOPING REVIEW
- Conducted to address broad research questions with the goal of understanding the extent of research that has been conducted.
- Provides a preliminary assessment of the potential size and scope of available research literature. It aims to identify the nature and extent of research evidence (usually including ongoing research)
- Doesn't assess the quality of the literature gathered (i.e. presence of literature on a topic shouldn’t be conflated w/ the quality of that literature)
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
- Common in the health sciences
- Goal: collect all literature that meets specific criteria (methodology, population, treatment, etc.) and then appraise its quality and synthesize it
- Follows strict protocol for literature collection, appraisal and synthesis
- Typically performed by research teams
- Takes 12-18 months to complete
- Often written as a stand alone work
META-ANALYSIS
- Goes one step further than a systematic review by statistically combining the results of quantitative studies to provide a more precise effect of the results.
- Evidence Synthesis Guide Learn more about Systematic Reviews, Scoping Reviews, Rapid Reviews, Umbrella Reviews, Meta-Analyses
Attribution
Thanks to Librarian Jamie Niehof at the University of Michigan for providing permission to reuse and remix this Literature Reviews guide.
Evidence Synthesis Guide
- Evidence Synthesis Guide Learn more about Systematic Reviews, Scoping Reviews, Rapid Reviews, Umbrella Reviews, and Meta-Analyses
Which Review is Right for You?

The Right Review tool has questions about your lit review process and plans. It offers a qualitative and quantitative option. At completion, you are given a lit review type recommendation.
More Review Types

This article by Sutton & Booth (2019) explores 48 distinct types of Literature Reviews:
- Last Updated: Apr 4, 2024 4:51 PM
- URL: https://info.library.okstate.edu/literaturereviews
- Open access
- Published: 12 December 2023
Examining the role of community resilience and social capital on mental health in public health emergency and disaster response: a scoping review
- C. E. Hall 1 , 2 ,
- H. Wehling 1 ,
- J. Stansfield 3 ,
- J. South 3 ,
- S. K. Brooks 2 ,
- N. Greenberg 2 , 4 ,
- R. Amlôt 1 &
- D. Weston 1
BMC Public Health volume 23 , Article number: 2482 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
1772 Accesses
21 Altmetric
Metrics details
The ability of the public to remain psychologically resilient in the face of public health emergencies and disasters (such as the COVID-19 pandemic) is a key factor in the effectiveness of a national response to such events. Community resilience and social capital are often perceived as beneficial and ensuring that a community is socially and psychologically resilient may aid emergency response and recovery. This review presents a synthesis of literature which answers the following research questions: How are community resilience and social capital quantified in research?; What is the impact of community resilience on mental wellbeing?; What is the impact of infectious disease outbreaks, disasters and emergencies on community resilience and social capital?; and, What types of interventions enhance community resilience and social capital?
A scoping review procedure was followed. Searches were run across Medline, PsycInfo, and EMBASE, with search terms covering both community resilience and social capital, public health emergencies, and mental health. 26 papers met the inclusion criteria.
The majority of retained papers originated in the USA, used a survey methodology to collect data, and involved a natural disaster. There was no common method for measuring community resilience or social capital. The association between community resilience and social capital with mental health was regarded as positive in most cases. However, we found that community resilience, and social capital, were initially negatively impacted by public health emergencies and enhanced by social group activities.
Several key recommendations are proposed based on the outcomes from the review, which include: the need for a standardised and validated approach to measuring both community resilience and social capital; that there should be enhanced effort to improve preparedness to public health emergencies in communities by gauging current levels of community resilience and social capital; that community resilience and social capital should be bolstered if areas are at risk of disasters or public health emergencies; the need to ensure that suitable short-term support is provided to communities with high resilience in the immediate aftermath of a public health emergency or disaster; the importance of conducting robust evaluation of community resilience initiatives deployed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Peer Review reports
For the general population, public health emergencies and disasters (e.g., natural disasters; infectious disease outbreaks; Chemical, Biological, Radiological or Nuclear incidents) can give rise to a plethora of negative outcomes relating to both health (e.g. increased mental health problems [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]) and the economy (e.g., increased unemployment and decreased levels of tourism [ 4 , 5 , 6 ]). COVID-19 is a current, and ongoing, example of a public health emergency which has affected over 421 million individuals worldwide [ 7 ]. The long term implications of COVID-19 are not yet known, but there are likely to be repercussions for physical health, mental health, and other non-health related outcomes for a substantial time to come [ 8 , 9 ]. As a result, it is critical to establish methods which may inform approaches to alleviate the longer-term negative consequences that are likely to emerge in the aftermath of both COVID-19 and any future public health emergency.
The definition of resilience often differs within the literature, but ultimately resilience is considered a dynamic process of adaptation. It is related to processes and capabilities at the individual, community and system level that result in good health and social outcomes, in spite of negative events, serious threats and hazards [ 10 ]. Furthermore, Ziglio [ 10 ] refers to four key types of resilience capacity: adaptive, the ability to withstand and adjust to unfavourable conditions and shocks; absorptive, the ability to withstand but also to recover and manage using available assets and skills; anticipatory, the ability to predict and minimize vulnerability; and transformative, transformative change so that systems better cope with new conditions.
There is no one settled definition of community resilience (CR). However, it generally relates to the ability of a community to withstand, adapt and permit growth in adverse circumstances due to social structures, networks and interdependencies within the community [ 11 ]. Social capital (SC) is considered a major determinant of CR [ 12 , 13 ], and reflects strength of a social network, community reciprocity, and trust in people and institutions [ 14 ]. These aspects of community are usually conceptualised primarily as protective factors that enable communities to cope and adapt collectively to threats. SC is often broken down into further categories [ 15 ], for example: cognitive SC (i.e. perceptions of community relations, such as trust, mutual help and attachment) and structural SC (i.e. what actually happens within the community, such as participation, socialising) [ 16 ]; or, bonding SC (i.e. connections among individuals who are emotionally close, and result in bonds to a particular group [ 17 ]) and bridging SC (i.e. acquaintances or individuals loosely connected that span different social groups [ 18 ]). Generally, CR is perceived to be primarily beneficial for multiple reasons (e.g. increased social support [ 18 , 19 ], protection of mental health [ 20 , 21 ]), and strengthening community resilience is a stated health goal of the World Health Organisation [ 22 ] when aiming to alleviate health inequalities and protect wellbeing. This is also reflected by organisations such as Public Health England (now split into the UK Health Security Agency and the Office for Health Improvement and Disparities) [ 23 ] and more recently, CR has been targeted through the endorsement of Community Champions (who are volunteers trained to support and to help improve health and wellbeing. Community Champions also reflect their local communities in terms of population demographics for example age, ethnicity and gender) as part of the COVID-19 response in the UK (e.g. [ 24 , 25 ]).
Despite the vested interest in bolstering communities, the research base establishing: how to understand and measure CR and SC; the effect of CR and SC, both during and following a public health emergency (such as the COVID-19 pandemic); and which types of CR or SC are the most effective to engage, is relatively small. Given the importance of ensuring resilience against, and swift recovery from, public health emergencies, it is critically important to establish and understand the evidence base for these approaches. As a result, the current review sought to answer the following research questions: (1) How are CR and SC quantified in research?; (2) What is the impact of community resilience on mental wellbeing?; (3) What is the impact of infectious disease outbreaks, disasters and emergencies on community resilience and social capital?; and, (4) What types of interventions enhance community resilience and social capital?
By collating research in order to answer these research questions, the authors have been able to propose several key recommendations that could be used to both enhance and evaluate CR and SC effectively to facilitate the long-term recovery from COVID-19, and also to inform the use of CR and SC in any future public health disasters and emergencies.
A scoping review methodology was followed due to the ease of summarising literature on a given topic for policy makers and practitioners [ 26 ], and is detailed in the following sections.
Identification of relevant studies
An initial search strategy was developed by authors CH and DW and included terms which related to: CR and SC, given the absence of a consistent definition of CR, and the link between CR and SC, the review focuses on both CR and SC to identify as much relevant literature as possible (adapted for purpose from Annex 1: [ 27 ], as well as through consultation with review commissioners); public health emergencies and disasters [ 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 ], and psychological wellbeing and recovery (derived a priori from literature). To ensure a focus on both public health and psychological research, the final search was carried across Medline, PsycInfo, and EMBASE using OVID. The final search took place on the 18th of May 2020, the search strategy used for all three databases can be found in Supplementary file 1 .
Selection criteria
The inclusion and exclusion criteria were developed alongside the search strategy. Initially the criteria were relatively inclusive and were subject to iterative development to reflect the authors’ familiarisation with the literature. For example, the decision was taken to exclude research which focused exclusively on social support and did not mention communities as an initial title/abstract search suggested that the majority of this literature did not meet the requirements of our research question.
The full and final inclusion and exclusion criteria used can be found in Supplementary file 2 . In summary, authors decided to focus on the general population (i.e., non-specialist, e.g. non-healthcare worker or government official) to allow the review to remain community focused. The research must also have assessed the impact of CR and/or SC on mental health and wellbeing, resilience, and recovery during and following public health emergencies and infectious disease outbreaks which affect communities (to ensure the research is relevant to the review aims), have conducted primary research, and have a full text available or provided by the first author when contacted.
Charting the data
All papers were first title and abstract screened by CH or DW. Papers then were full text reviewed by CH to ensure each paper met the required eligibility criteria, if unsure about a paper it was also full text reviewed by DW. All papers that were retained post full-text review were subjected to a standardised data extraction procedure. A table was made for the purpose of extracting the following data: title, authors, origin, year of publication, study design, aim, disaster type, sample size and characteristics, variables examined, results, restrictions/limitations, and recommendations. Supplementary file 3 details the charting the data process.
Analytical method
Data was synthesised using a Framework approach [ 32 ], a common method for analysing qualitative research. This method was chosen as it was originally used for large-scale social policy research [ 33 ] as it seeks to identify: what works, for whom, in what conditions, and why [ 34 ]. This approach is also useful for identifying commonalities and differences in qualitative data and potential relationships between different parts of the data [ 33 ]. An a priori framework was established by CH and DW. Extracted data was synthesised in relation to each research question, and the process was iterative to ensure maximum saturation using the available data.
Study selection
The final search strategy yielded 3584 records. Following the removal of duplicates, 2191 records remained and were included in title and abstract screening. A PRISMA flow diagram is presented in Fig. 1 .
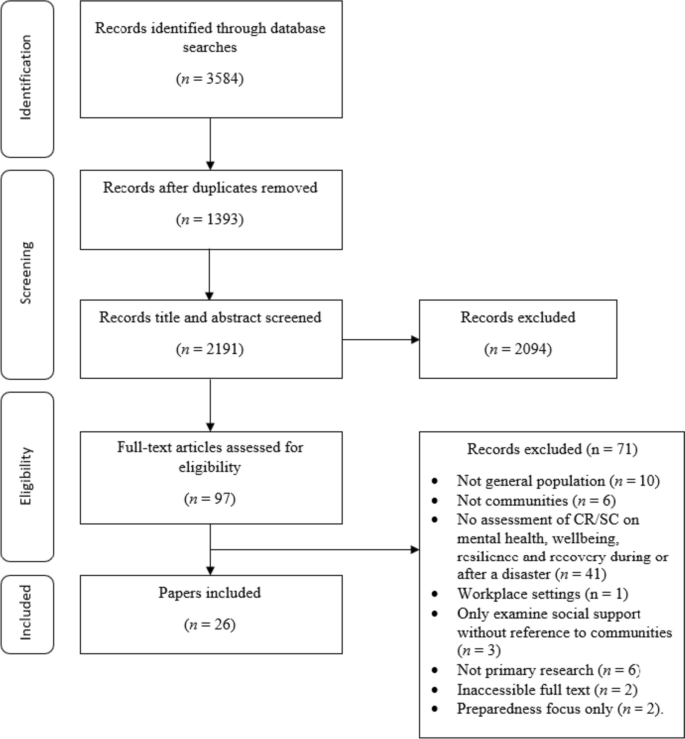
PRISMA flow diagram
At the title and abstract screening stage, the process became more iterative as the inclusion criteria were developed and refined. For the first iteration of screening, CH or DW sorted all records into ‘include,’ ‘exclude,’ and ‘unsure’. All ‘unsure’ papers were re-assessed by CH, and a random selection of ~ 20% of these were also assessed by DW. Where there was disagreement between authors the records were retained, and full text screened. The remaining papers were reviewed by CH, and all records were categorised into ‘include’ and ‘exclude’. Following full-text screening, 26 papers were retained for use in the review.
Study characteristics
This section of the review addresses study characteristics of those which met the inclusion criteria, which comprises: date of publication, country of origin, study design, study location, disaster, and variables examined.
Date of publication
Publication dates across the 26 papers spanned from 2008 to 2020 (see Fig. 2 ). The number of papers published was relatively low and consistent across this timescale (i.e. 1–2 per year, except 2010 and 2013 when none were published) up until 2017 where the number of papers peaked at 5. From 2017 to 2020 there were 15 papers published in total. The amount of papers published in recent years suggests a shift in research and interest towards CR and SC in a disaster/ public health emergency context.
Graph to show retained papers date of publication
Country of origin
The locations of the first authors’ institutes at the time of publication were extracted to provide a geographical spread of the retained papers. The majority originated from the USA [ 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 ], followed by China [ 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ], Japan [ 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 ], Australia [ 51 , 52 , 53 ], The Netherlands [ 54 , 55 ], New Zealand [ 56 ], Peru [ 57 ], Iran [ 58 ], Austria [ 59 ], and Croatia [ 60 ].
There were multiple methodological approaches carried out across retained papers. The most common formats included surveys or questionnaires [ 36 , 37 , 38 , 42 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 57 , 59 ], followed by interviews [ 39 , 40 , 43 , 51 , 52 , 60 ]. Four papers used both surveys and interviews [ 35 , 41 , 45 , 58 ], and two papers conducted data analysis (one using open access data from a Social Survey [ 44 ] and one using a Primary Health Organisations Register [ 56 ]).
Study location
The majority of the studies were carried out in Japan [ 36 , 42 , 44 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 ], followed by the USA [ 35 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 ], China [ 43 , 45 , 46 , 53 ], Australia [ 51 , 52 ], and the UK [ 54 , 55 ]. The remaining studies were carried out in Croatia [ 60 ], Peru [ 57 ], Austria [ 59 ], New Zealand [ 56 ] and Iran [ 58 ].
Multiple different types of disaster were researched across the retained papers. Earthquakes were the most common type of disaster examined [ 45 , 47 , 49 , 50 , 53 , 56 , 57 , 58 ], followed by research which assessed the impact of two disastrous events which had happened in the same area (e.g. Hurricane Katrina and the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in Mississippi, and the Great East Japan earthquake and Tsunami; [ 36 , 37 , 38 , 42 , 44 , 48 ]). Other disaster types included: flooding [ 51 , 54 , 55 , 59 , 60 ], hurricanes [ 35 , 39 , 41 ], infectious disease outbreaks [ 43 , 46 ], oil spillage [ 40 ], and drought [ 52 ].
Variables of interest examined
Across the 26 retained papers: eight referred to examining the impact of SC [ 35 , 37 , 39 , 41 , 46 , 49 , 55 , 60 ]; eight examined the impact of cognitive and structural SC as separate entities [ 40 , 42 , 45 , 48 , 50 , 54 , 57 , 59 ]; one examined bridging and bonding SC as separate entities [ 58 ]; two examined the impact of CR [ 38 , 56 ]; and two employed a qualitative methodology but drew findings in relation to bonding and bridging SC, and SC generally [ 51 , 52 ]. Additionally, five papers examined the impact of the following variables: ‘community social cohesion’ [ 36 ], ‘neighbourhood connectedness’ [ 44 ], ‘social support at the community level’ [ 47 ], ‘community connectedness’ [ 43 ] and ‘sense of community’ [ 53 ]. Table 1 provides additional details on this.
How is CR and SC measured or quantified in research?
The measures used to examine CR and SC are presented Table 1 . It is apparent that there is no uniformity in how SC or CR is measured across the research. Multiple measures are used throughout the retained studies, and nearly all are unique. Additionally, SC was examined at multiple different levels (e.g. cognitive and structural, bonding and bridging), and in multiple different forms (e.g. community connectedness, community cohesion).
What is the association between CR and SC on mental wellbeing?
To best compare research, the following section reports on CR, and facets of SC separately. Please see Supplementary file 4 for additional information on retained papers methods of measuring mental wellbeing.
- Community resilience
CR relates to the ability of a community to withstand, adapt and permit growth in adverse circumstances due to social structures, networks and interdependencies within the community [ 11 ].
The impact of CR on mental wellbeing was consistently positive. For example, research indicated that there was a positive association between CR and number of common mental health (i.e. anxiety and mood) treatments post-disaster [ 56 ]. Similarly, other research suggests that CR is positively related to psychological resilience, which is inversely related to depressive symptoms) [ 37 ]. The same research also concluded that CR is protective of psychological resilience and is therefore protective of depressive symptoms [ 37 ].
- Social capital
SC reflects the strength of a social network, community reciprocity, and trust in people and institutions [ 14 ]. These aspects of community are usually conceptualised primarily as protective factors that enable communities to cope and adapt collectively to threats.
There were inconsistencies across research which examined the impact of abstract SC (i.e. not refined into bonding/bridging or structural/cognitive) on mental wellbeing. However, for the majority of cases, research deems SC to be beneficial. For example, research has concluded that, SC is protective against post-traumatic stress disorder [ 55 ], anxiety [ 46 ], psychological distress [ 50 ], and stress [ 46 ]. Additionally, SC has been found to facilitate post-traumatic growth [ 38 ], and also to be useful to be drawn upon in times of stress [ 52 ], both of which could be protective of mental health. Similarly, research has also found that emotional recovery following a disaster is more difficult for those who report to have low levels of SC [ 51 ].
Conversely, however, research has also concluded that when other situational factors (e.g. personal resources) were controlled for, a positive relationship between community resources and life satisfaction was no longer significant [ 60 ]. Furthermore, some research has concluded that a high level of SC can result in a community facing greater stress immediately post disaster. Indeed, one retained paper found that high levels of SC correlate with higher levels of post-traumatic stress immediately following a disaster [ 39 ]. However, in the later stages following a disaster, this relationship can reverse, with SC subsequently providing an aid to recovery [ 41 ]. By way of explanation, some researchers have suggested that communities with stronger SC carry the greatest load in terms of helping others (i.e. family, friends and neighbours) as well as themselves immediately following the disaster, but then as time passes the communities recover at a faster rate as they are able to rely on their social networks for support [ 41 ].
Cognitive and structural social capital
Cognitive SC refers to perceptions of community relations, such as trust, mutual help and attachment, and structural SC refers to what actually happens within the community, such as participation, socialising [ 16 ].
Cognitive SC has been found to be protective [ 49 ] against PTSD [ 54 , 57 ], depression [ 40 , 54 ]) mild mood disorder; [ 48 ]), anxiety [ 48 , 54 ] and increase self-efficacy [ 59 ].
For structural SC, research is again inconsistent. On the one hand, structural SC has been found to: increase perceived self-efficacy, be protective of depression [ 40 ], buffer the impact of housing damage on cognitive decline [ 42 ] and provide support during disasters and over the recovery period [ 59 ]. However, on the other hand, it has been found to have no association with PTSD [ 54 , 57 ] or depression, and is also associated with a higher prevalence of anxiety [ 54 ]. Similarly, it is also suggested by additional research that structural SC can harm women’s mental health, either due to the pressure of expectations to help and support others or feelings of isolation [ 49 ].
Bonding and bridging social capital
Bonding SC refers to connections among individuals who are emotionally close, and result in bonds to a particular group [ 17 ], and bridging SC refers to acquaintances or individuals loosely connected that span different social groups [ 18 ].
One research study concluded that both bonding and bridging SC were protective against post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms [ 58 ]. Bridging capital was deemed to be around twice as effective in buffering against post-traumatic stress disorder than bonding SC [ 58 ].
Other community variables
Community social cohesion was significantly associated with a lower risk of post-traumatic stress disorder symptom development [ 35 ], and this was apparent even whilst controlling for depressive symptoms at baseline and disaster impact variables (e.g. loss of family member or housing damage) [ 36 ]. Similarly, sense of community, community connectedness, social support at the community level and neighbourhood connectedness all provided protective benefits for a range of mental health, wellbeing and recovery variables, including: depression [ 53 ], subjective wellbeing (in older adults only) [ 43 ], psychological distress [ 47 ], happiness [ 44 ] and life satisfaction [ 53 ].
Research has also concluded that community level social support is protective against mild mood and anxiety disorder, but only for individuals who have had no previous disaster experience [ 48 ]. Additionally, a study which separated SC into social cohesion and social participation concluded that at a community level, social cohesion is protective against depression [ 49 ] whereas social participation at community level is associated with an increased risk of depression amongst women [ 49 ].
What is the impact of Infectious disease outbreaks / disasters and emergencies on community resilience?
From a cross-sectional perspective, research has indicated that disasters and emergencies can have a negative effect on certain types of SC. Specifically, cognitive SC has been found to be impacted by disaster impact, whereas structural SC has gone unaffected [ 45 ]. Disaster impact has also been shown to have a negative effect on community relationships more generally [ 52 ].
Additionally, of the eight studies which collected data at multiple time points [ 35 , 36 , 41 , 42 , 47 , 49 , 56 , 60 ], three reported the effect of a disaster on the level of SC within a community [ 40 , 42 , 49 ]. All three of these studies concluded that disasters may have a negative impact on the levels of SC within a community. The first study found that the Deepwater Horizon oil spill had a negative effect on SC and social support, and this in turn explained an overall increase in the levels of depression within the community [ 40 ]. A possible explanation for the negative effect lays in ‘corrosive communities’, known for increased social conflict and reduced social support, that are sometimes created following oil spills [ 40 ]. It is proposed that corrosive communities often emerge due to a loss of natural resources that bring social groups together (e.g., for recreational activities), as well as social disparity (e.g., due to unequal distribution of economic impact) becoming apparent in the community following disaster [ 40 ]. The second study found that SC (in the form of social cohesion, informal socialising and social participation) decreased after the 2011 earthquake and tsunami in Japan; it was suggested that this change correlated with incidence of cognitive decline [ 42 ]. However, the third study reported more mixed effects based on physical circumstances of the communities’ natural environment: Following an earthquake, those who lived in mountainous areas with an initial high level of pre-community SC saw a decrease in SC post disaster [ 49 ]. However, communities in flat areas (which were home to younger residents and had a higher population density) saw an increase in SC [ 49 ]. It was proposed that this difference could be due to the need for those who lived in mountainous areas to seek prolonged refuge due to subsequent landslides [ 49 ].
What types of intervention enhance CR and SC and protect survivors?
There were mixed effects across the 26 retained papers when examining the effect of CR and SC on mental wellbeing. However, there is evidence that an increase in SC [ 56 , 57 ], with a focus on cognitive SC [ 57 ], namely by: building social networks [ 45 , 51 , 53 ], enhancing feelings of social cohesion [ 35 , 36 ] and promoting a sense of community [ 53 ], can result in an increase in CR and potentially protect survivors’ wellbeing and mental health following a disaster. An increase in SC may also aid in decreasing the need for individual psychological interventions in the aftermath of a disaster [ 55 ]. As a result, recommendations and suggested methods to bolster CR and SC from the retained papers have been extracted and separated into general methods, preparedness and policy level implementation.
General methods
Suggested methods to build SC included organising recreational activity-based groups [ 44 ] to broaden [ 51 , 53 ] and preserve current social networks [ 42 ], introducing initiatives to increase social cohesion and trust [ 51 ], and volunteering to increase the number of social ties between residents [ 59 ]. Research also notes that it is important to take a ‘no one left behind approach’ when organising recreational and social community events, as failure to do so could induce feelings of isolation for some members of the community [ 49 ]. Furthermore, gender differences should also be considered as research indicates that males and females may react differently to community level SC (as evidence suggests males are instead more impacted by individual level SC; in comparison to women who have larger and more diverse social networks [ 49 ]). Therefore, interventions which aim to raise community level social participation, with the aim of expanding social connections and gaining support, may be beneficial [ 42 , 47 ].
Preparedness
In order to prepare for disasters, it may be beneficial to introduce community-targeted methods or interventions to increase levels of SC and CR as these may aid in ameliorating the consequences of a public health emergency or disaster [ 57 ]. To indicate which communities have low levels of SC, one study suggests implementing a 3-item scale of social cohesion to map areas and target interventions [ 42 ].
It is important to consider that communities with a high level of SC may have a lower level of risk perception, due to the established connections and supportive network they have with those around them [ 61 ]. However, for the purpose of preparedness, this is not ideal as perception of risk is a key factor when seeking to encourage behavioural adherence. This could be overcome by introducing communication strategies which emphasise the necessity of social support, but also highlights the need for additional measures to reduce residual risk [ 59 ]. Furthermore, support in the form of financial assistance to foster current community initiatives may prove beneficial to rural areas, for example through the use of an asset-based community development framework [ 52 ].
Policy level
At a policy level, the included papers suggest a range of ways that CR and SC could be bolstered and used. These include: providing financial support for community initiatives and collective coping strategies, (e.g. using asset-based community development [ 52 ]); ensuring policies for long-term recovery focus on community sustainable development (e.g. community festival and community centre activities) [ 44 ]; and development of a network amongst cooperative corporations formed for reconstruction and to organise self-help recovery sessions among residents of adjacent areas [ 58 ].
This scoping review sought to synthesise literature concerning the role of SC and CR during public health emergencies and disasters. Specifically, in this review we have examined: the methods used to measure CR and SC; the impact of CR and SC on mental wellbeing during disasters and emergencies; the impact of disasters and emergencies on CR and SC; and the types of interventions which can be used to enhance CR. To do this, data was extracted from 26 peer-reviewed journal articles. From this synthesis, several key themes have been identified, which can be used to develop guidelines and recommendations for deploying CR and SC in a public health emergency or disaster context. These key themes and resulting recommendations are summarised below.
Firstly, this review established that there is no consistent or standardised approach to measuring CR or SC within the general population. This finding is consistent with a review conducted by the World Health Organization which concludes that despite there being a number of frameworks that contain indicators across different determinants of health, there is a lack of consensus on priority areas for measurement and no widely accepted indicator [ 27 ]. As a result, there are many measures of CR and SC apparent within the literature (e.g., [ 62 , 63 ]), an example of a developed and validated measure is provided by Sherrieb, Norris and Galea [ 64 ]. Similarly, the definitions of CR and SC differ widely between researchers, which created a barrier to comparing and summarising information. Therefore, future research could seek to compare various interpretations of CR and to identify any overlapping concepts. However, a previous systemic review conducted by Patel et al. (2017) concludes that there are nine core elements of CR (local knowledge, community networks and relationships, communication, health, governance and leadership, resources, economic investment, preparedness, and mental outlook), with 19 further sub-elements therein [ 30 ]. Therefore, as CR is a multi-dimensional construct, the implications from the findings are that multiple aspects of social infrastructure may need to be considered.
Secondly, our synthesis of research concerning the role of CR and SC for ensuring mental health and wellbeing during, or following, a public health emergency or disaster revealed mixed effects. Much of the research indicates either a generally protective effect on mental health and wellbeing, or no effect; however, the literature demonstrates some potential for a high level of CR/SC to backfire and result in a negative effect for populations during, or following, a public health emergency or disaster. Considered together, our synthesis indicates that cognitive SC is the only facet of SC which was perceived as universally protective across all retained papers. This is consistent with a systematic review which also concludes that: (a) community level cognitive SC is associated with a lower risk of common mental disorders, while; (b) community level structural SC had inconsistent effects [ 65 ].
Further examination of additional data extracted from studies which found that CR/SC had a negative effect on mental health and wellbeing revealed no commonalities that might explain these effects (Please see Supplementary file 5 for additional information)
One potential explanation may come from a retained paper which found that high levels of SC result in an increase in stress level immediately post disaster [ 41 ]. This was suggested to be due to individuals having greater burdens due to wishing to help and support their wide networks as well as themselves. However, as time passes the levels of SC allow the community to come together and recover at a faster rate [ 41 ]. As this was the only retained paper which produced this finding, it would be beneficial for future research to examine boundary conditions for the positive effects of CR/SC; that is, to explore circumstances under which CR/SC may be more likely to put communities at greater risk. This further research should also include additional longitudinal research to validate the conclusions drawn by [ 41 ] as resilience is a dynamic process of adaption.
Thirdly, disasters and emergencies were generally found to have a negative effect on levels of SC. One retained paper found a mixed effect of SC in relation to an earthquake, however this paper separated participants by area in which they lived (i.e., mountainous vs. flat), which explains this inconsistent effect [ 49 ]. Dangerous areas (i.e. mountainous) saw a decrease in community SC in comparison to safer areas following the earthquake (an effect the authors attributed to the need to seek prolonged refuge), whereas participants from the safer areas (which are home to younger residents with a higher population density) saw an increase in SC [ 49 ]. This is consistent with the idea that being able to participate socially is a key element of SC [ 12 ]. Overall, however, this was the only retained paper which produced a variable finding in relation to the effect of disaster on levels of CR/SC.
Finally, research identified through our synthesis promotes the idea of bolstering SC (particularly cognitive SC) and cohesion in communities likely to be affected by disaster to improve levels of CR. This finding provides further understanding of the relationship between CR and SC; an association that has been reported in various articles seeking to provide conceptual frameworks (e.g., [ 66 , 67 ]) as well as indicator/measurement frameworks [ 27 ]. Therefore, this could be done by creating and promoting initiatives which foster SC and create bonds within the community. Papers included in the current review suggest that recreational-based activity groups and volunteering are potential methods for fostering SC and creating community bonds [ 44 , 51 , 59 ]. Similarly, further research demonstrates that feelings of social cohesion are enhanced by general social activities (e.g. fairs and parades [ 18 ]). Also, actively encouraging activities, programs and interventions which enhance connectedness and SC have been reported to be desirable to increase CR [ 68 ]. This suggestion is supported by a recent scoping review of literature [ 67 ] examined community champion approaches for the COVID-19 pandemic response and recovery and established that creating and promoting SC focused initiatives within the community during pandemic response is highly beneficial [ 67 ]. In terms of preparedness, research states that it may be beneficial for levels of SC and CR in communities at risk to be assessed, to allow targeted interventions where the population may be at most risk following an incident [ 42 , 44 ]. Additionally, from a more critical perspective, we acknowledge that ‘resilience’ can often be perceived as a focus on individual capacity to adapt to adversity rather than changing or mitigating the causes of adverse conditions [ 69 , 70 ]. Therefore, CR requires an integrated system approach across individual, community and structural levels [ 17 ]. Also, it is important that community members are engaged in defining and agreeing how community resilience is measured [ 27 ] rather than it being imposed by system leads or decision-makers.
In the aftermath of the pandemic, is it expected that there will be long-term repercussions both from an economic [ 8 ] and a mental health perspective [ 71 ]. Furthermore, the findings from this review suggest that although those in areas with high levels of SC may be negatively affected in the acute stage, as time passes, they have potential to rebound at a faster rate than those with lower levels of SC. Ongoing evaluation of the effectiveness of current initiatives as the COVID-19 pandemic progresses into a recovery phase will be invaluable for supplementing the evidence base identified through this review.
- Recommendations
As a result of this review, a number of recommendations are suggested for policy and practice during public health emergencies and recovery.
Future research should seek to establish a standardised and validated approach to measuring and defining CR and SC within communities. There are ongoing efforts in this area, for example [ 72 ]. Additionally, community members should be involved in the process of defining how CR is measured.
There should be an enhanced effort to improve preparedness for public health emergencies and disasters in local communities by gauging current levels of SC and CR within communities using a standardised measure. This approach could support specific targeting of populations with low levels of CR/SC in case of a disaster or public health emergency, whilst also allowing for consideration of support for those with high levels of CR (as these populations can be heavily impacted initially following a disaster). By distinguishing levels of SC and CR, tailored community-centred approaches could be implemented, such as those listed in a guide released by PHE in 2015 [ 73 ].
CR and SC (specifically cognitive SC) should be bolstered if communities are at risk of experiencing a disaster or public health emergency. This can be achieved by using interventions which aim to increase a sense of community and create new social ties (e.g., recreational group activities, volunteering). Additionally, when aiming to achieve this, it is important to be mindful of the risk of increased levels of CR/SC to backfire, as well as seeking to advocate an integrated system approach across individual, community and structural levels.
It is necessary to be aware that although communities with high existing levels of resilience / SC may experience short-term negative consequences following a disaster, over time these communities might be able to recover at a faster rate. It is therefore important to ensure that suitable short-term support is provided to these communities in the immediate aftermath of a public health emergency or disaster.
Robust evaluation of the community resilience initiatives deployed during the COVID-19 pandemic response is essential to inform the evidence base concerning the effectiveness of CR/ SC. These evaluations should continue through the response phase and into the recovery phase to help develop our understanding of the long-term consequences of such interventions.
Limitations
Despite this review being the first in this specific topic area, there are limitations that must be considered. Firstly, it is necessary to note that communities are generally highly diverse and the term ‘community’ in academic literature is a subject of much debate (see: [ 74 ]), therefore this must be considered when comparing and collating research involving communities. Additionally, the measures of CR and SC differ substantially across research, including across the 26 retained papers used in the current review. This makes the act of comparing and collating research findings very difficult. This issue is highlighted as a key outcome from this review, and suggestions for how to overcome this in future research are provided. Additionally, we acknowledge that there will be a relationship between CR & SC even where studies measure only at individual or community level. A review [ 75 ] on articulating a hypothesis of the link to health inequalities suggests that wider structural determinants of health need to be accounted for. Secondly, despite the final search strategy encompassing terms for both CR and SC, only one retained paper directly measured CR; thus, making the research findings more relevant to SC. Future research could seek to focus on CR to allow for a comparison of findings. Thirdly, the review was conducted early in the COVID-19 pandemic and so does not include more recent publications focusing on resilience specifically in the context of COVID-19. Regardless of this fact, the synthesis of, and recommendations drawn from, the reviewed studies are agnostic to time and specific incident and contain critical elements necessary to address as the pandemic moves from response to recovery. Further research should review the effectiveness of specific interventions during the COVID-19 pandemic for collation in a subsequent update to this current paper. Fourthly, the current review synthesises findings from countries with individualistic and collectivistic cultures, which may account for some variation in the findings. Lastly, despite choosing a scoping review method for ease of synthesising a wide literature base for use by public health emergency researchers in a relatively tight timeframe, there are disadvantages of a scoping review approach to consider: (1) quality appraisal of retained studies was not carried out; (2) due to the broad nature of a scoping review, more refined and targeted reviews of literature (e.g., systematic reviews) may be able to provide more detailed research outcomes. Therefore, future research should seek to use alternative methods (e.g., empirical research, systematic reviews of literature) to add to the evidence base on CR and SC impact and use in public health practice.
This review sought to establish: (1) How CR and SC are quantified in research?; (2) The impact of community resilience on mental wellbeing?; (3) The impact of infectious disease outbreaks, disasters and emergencies on community resilience and social capital?; and, (4) What types of interventions enhance community resilience and social capital?. The chosen search strategy yielded 26 relevant papers from which we were able extract information relating to the aims of this review.
Results from the review revealed that CR and SC are not measured consistently across research. The impact of CR / SC on mental health and wellbeing during emergencies and disasters is mixed (with some potential for backlash), however the literature does identify cognitive SC as particularly protective. Although only a small number of papers compared CR or SC before and after a disaster, the findings were relatively consistent: SC or CR is negatively impacted by a disaster. Methods suggested to bolster SC in communities were centred around social activities, such as recreational group activities and volunteering. Recommendations for both research and practice (with a particular focus on the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic) are also presented.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Social Capital
Zortea TC, Brenna CT, Joyce M, McClelland H, Tippett M, Tran MM, et al. The impact of infectious disease-related public health emergencies on suicide, suicidal behavior, and suicidal thoughts. Crisis. 2020;42(6):474–87.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Davis JR, Wilson S, Brock-Martin A, Glover S, Svendsen ER. The impact of disasters on populations with health and health care disparities. Disaster Med Pub Health Prep. 2010;4(1):30.
Article Google Scholar
Francescutti LH, Sauve M, Prasad AS. Natural disasters and healthcare: lessons to be learned. Healthc Manage Forum. 2017;30(1):53–5.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Jones L, Palumbo D, Brown D. Coronavirus: How the pandemic has changed the world economy. BBC News; 2021. Accessible at: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-51706225 .
Below R, Wallemacq P. Annual disaster statistical review 2017. Brussels: CRED, Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters; 2018.
Google Scholar
Qiu W, Chu C, Mao A, Wu J. The impacts on health, society, and economy of SARS and H7N9 outbreaks in China: a case comparison study. J Environ Public Health. 2018;2018:2710185.
Worldometer. COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic. 2021.
Harari D, Keep M. Coronavirus: economic impact house of commons library. Briefing Paper (Number 8866); 2021. Accessible at: https://commonslibrary.parliament.uk/research-briefings/cbp-8866/ .
Nabavi N. Covid-19: pandemic will cast a long shadow on mental health, warns England’s CMO. BMJ. 2021;373:n1655.
Ziglio E. Strengthening resilience: a priority shared by health 2020 and the sustainable development goals. No. WHO/EURO: 2017-6509-46275-66939. World Health Organization; Regional Office for Europe; 2017.
Asadzadeh A, Kotter T, Salehi P, Birkmann J. Operationalizing a concept: the systematic review of composite indicator building for measuring community disaster resilience. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct. 2017;25:147.
Sherrieb K, Norris F, Galea S. Measuring capacities for community resilience. Soc Indicators Res. 2010;99(2):227.
Poortinga W. Community resilience and health: the role of bonding, bridging, and linking aspects of social capital. Health Place. 2011;18(2):286–95.
Ferlander S. The importance of different forms of social capital for health. Acta Sociol. 2007;50(2):115–28.
Nakagawa Y, Shaw R. Social capital: a missing link to disaster recovery. Int J Mass Emerge Disasters. 2004;22(1):5–34.
Grootaert C, Narayan D, Jones VN, Woolcock M. Measuring social capital: an integrated questionnaire. Washington, DC: World Bank Working Paper, No. 18; 2004.
Adler PS, Kwon SW. Social capital: prospects for a new concept. Acad Manage Rev. 2002;27(1):17–40.
Aldrich DP, Meyer MA. Social capital and community resilience. Am Behav Sci. 2015;59(2):254–69.
Rodriguez-Llanes JM, Vos F, Guha-Sapir D. Measuring psychological resilience to disasters: are evidence-based indicators an achievable goal? Environ Health. 2013;12(1):115.
De Silva MJ, McKenzie K, Harpham T, Huttly SR. Social capital and mental Illness: a systematic review. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2005;59(8):619–27.
Bonanno GA, Galea S, Bucciarelli A, Vlahov D. Psychological resilience after disaster: New York City in the aftermath of the september 11th terrorist attack. Psychol Sci. 2006;17(3):181.
World Health Organization. Health 2020: a European policy framework and strategy for the 21st century. World Health Organization. Regional Office for Europe; 2013.
Public Health England. Community-Centred Public Health: Taking a Whole System Approach. 2020.
SPI-B. The role of Community Champion networks to increase engagement in the context of COVID19: Evidence and best practice. 2021.
Public Health England. Community champions: A rapid scoping review of community champion approaches for the pandemic response and recovery. 2021.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
World Health Organisation. WHO health evidence network synthesis report: what quantitative and qualitative methods have been developed to measure health-related community resilience at a national and local level. 2018.
Hall C, Williams N, Gauntlett L, Carter H, Amlôt R, Peterson L et al. Findings from systematic review of public perceptions and responses. PROACTIVE EU. Deliverable 1.1. 2019. Accessible at: https://proactive-h2020.eu/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/PROACTIVE_20210312_D1.1_V5_PHE_Systematic-Review-of-Public-Perceptions-and-Responses_revised.pdf .
Weston D, Ip A, Amlôt R. Examining the application of behaviour change theories in the context of Infectious disease outbreaks and emergency response: a review of reviews. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1483.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Patel SS, Rogers MB, Amlôt R, Rubin GJ. What do we mean by ‘community resilience’? A systematic literature review of how it is defined in the literature. PLoS Curr. 2017;9:ecurrents.dis.db775aff25efc5ac4f0660ad9c9f7db2.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Brooks SK, Weston D, Wessely S, Greenberg N. Effectiveness and acceptability of brief psychoeducational interventions after potentially traumatic events: a systematic review. Eur J Psychotraumatology. 2021;12(1):1923110.
Pawson R, Greenhalgh T, Harvey G, Walshe K. Realist review-a new method of systematic review designed for complex policy interventions. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2005;10(1_suppl):21–34.
Gale NK, Heath G, Cameron E, Rashid S, Redwood S. Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13:1–8.
Bearman M, Dawson P. Qualitative synthesis and systematic review in health professions education. Med Educ. 2013;47(3):252–60.
Heid AR, Pruchno R, Cartwright FP, Wilson-Genderson M. Exposure to Hurricane Sandy, neighborhood collective efficacy, and post-traumatic stress symptoms in older adults. Aging Ment Health. 2017;21(7):742–50.
Hikichi H, Aida J, Tsuboya T, Kondo K, Kawachi I. Can community social cohesion prevent posttraumatic stress disorder in the aftermath of a disaster? A natural experiment from the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake and tsunami. Am J Epidemiol. 2016;183(10):902–10.
Lee J, Blackmon BJ, Cochran DM, Kar B, Rehner TA, Gunnell MS. Community resilience, psychological resilience, and depressive symptoms: an examination of the Mississippi Gulf Coast 10 years after Hurricane Katrina and 5 years after the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Disaster med. 2018;12(2):241–8.
Lee J, Blackmon BJ, Lee JY, Cochran DM Jr, Rehner TA. An exploration of posttraumatic growth, loneliness, depression, resilience, and social capital among survivors of Hurricane Katrina and the deepwater Horizon oil spill. J Community Psychol. 2019;47(2):356–70.
Lowe SR, Sampson L, Gruebner O, Galea S. Psychological resilience after Hurricane Sandy: the influence of individual- and community-level factors on mental health after a large-scale natural disaster. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0125761.
Rung AL, Gaston S, Robinson WT, Trapido EJ, Peters ES. Untangling the disaster-depression knot: the role of social ties after deepwater Horizon. Soc Sci Med. 2017;177:19–26.
Weil F, Lee MR, Shihadeh ES. The burdens of social capital: how socially-involved people dealt with stress after Hurricane Katrina. Soc Sci Res. 2012;41(1):110–9.
Hikichi H, Aida J, Matsuyama Y, Tsuboya T, Kondo K, Kawachi I. Community-level social capital and cognitive decline after a Natural Disaster: a natural experiment from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami. Soc Sci Med. 2018;257:111981.
Lau AL, Chi I, Cummins RA, Lee TM, Chou KL, Chung LW. The SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) pandemic in Hong Kong: effects on the subjective wellbeing of elderly and younger people. Aging Ment Health. 2008;12(6):746–60.
Sun Y, Yan T. The use of public health indicators to assess individual happiness in post-disaster recovery. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(21):4101.
Wong H, Huang Y, Fu Y, Zhang Y. Impacts of structural social capital and cognitive social capital on the psychological status of survivors of the yaan Earthquake. Appl Res Qual Life. 2018;14:1411–33.
Xiao H, Zhang Y, Kong D, Li S, Yang N. Social capital and sleep quality in individuals who self-isolated for 14 days during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in January 2020 in China. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e923921.
PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Matsuyama Y, Aida J, Hase A, Sato Y, Koyama S, Tsuboya T, et al. Do community- and individual-level social relationships contribute to the mental health of disaster survivors? A multilevel prospective study after the great East Japan earthquake. Soc Sci Med. 2016;151:187–95.
Ozaki A, Horiuchi S, Kobayashi Y, Inoue M, Aida J, Leppold C, Yamaoka K. Beneficial roles of social support for mental health vary in the Japanese population depending on disaster experience: a nationwide cross-sectional study. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018;246(4):213–23.
Sato K, Amemiya A, Haseda M, Takagi D, Kanamori M, Kondo K, et al. Post-disaster changes in Social Capital and Mental Health: a natural experiment from the 2016 Kumamoto Earthquake. Am J Epidemiol. 2020;189(9):910–21.
Tsuchiya N, Nakaya N, Nakamura T, Narita A, Kogure M, Aida J, Tsuji I, Hozawa A, Tomita H. Impact of social capital on psychological distress and interaction with house destruction and displacement after the great East Japan earthquake of 2011. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017;71(1):52–60.
Brockie L, Miller E. Understanding older adults’ resilience during the Brisbane floods: social capital, life experience, and optimism. Disaster Med Pub Health Prep. 2017;11(1):72–9.
Caldwell K, Boyd CP. Coping and resilience in farming families affected by drought. Rural Remote Health. 2009;9(2):1088.
PubMed Google Scholar
Huang Y, Tan NT, Liu J. Support, sense of community, and psychological status in the survivors of the Yaan earthquake. J Community Psychol. 2016;44(7):919–36.
Wind T, Fordham M, Komproe H. Social capital and post-disaster mental health. Glob Health Action. 2011;4(1):6351.
Wind T, Komproe IH. The mechanisms that associate community social capital with post-disaster mental health: a multilevel model. Soc Sci Med. 2012;75(9):1715–20.
Hogg D, Kingham S, Wilson TM, Ardagh M. The effects of spatially varying earthquake impacts on mood and anxiety symptom treatments among long-term Christchurch residents following the 2010/11 Canterbury Earthquakes, New Zealand. Health Place. 2016;41:78–88.
Flores EC, Carnero AM, Bayer AM. Social capital and chronic post-traumatic stress disorder among survivors of the 2007 earthquake in Pisco, Peru. Soc Sci Med. 2014;101:9–17.
Rafiey H, Alipour F, LeBeau R, Salimi Y, Ahmadi S. Exploring the buffering role of social capital in the development of posttraumatic stress symptoms among Iranian earthquake survivors. Psychol Trauma. 2019;14(6):1040–6.
Babcicky P, Seebauer S. The two faces of social capital in private Flood mitigation: opposing effects on risk perception, self-efficacy and coping capacity. J Risk Res. 2017;20(8):1017–37.
Bakic H, Ajdukovic D. Stability and change post-disaster: dynamic relations between individual, interpersonal and community resources and psychosocial functioning. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2019;10(1):1614821.
Rogers RW. A protection motivation theory of fear appeals and attitude change. J Psychol. 1975;91(1):93–114.
Lindberg K, Swearingen T. A reflective thrive-oriented community resilience scale. Am J Community Psychol. 2020;65(3–4):467–78.
Leykin D, Lahad M, Cohen O, Goldberg A, Aharonson-Daniel L. Conjoint community resiliency assessment measure-28/10 items (CCRAM28 and CCRAM10): a self-report tool for assessing community resilience. Am J Community Psychol. 2013;52:313–23.
Sherrieb K, Norris FH, Galea S. Measuring capacities for community resilience. Soc Indic Res. 2010;99:227–47.
Ehsan AM, De Silva MJ. Social capital and common mental disorder: a systematic review. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2015;69(10):1021–8.
Pfefferbaum B, Van Horn RL, Pfefferbaum RL. A conceptual framework to enhance community resilience using social capital. Clin Soc Work J. 2017;45(2):102–10.
Carmen E, Fazey I, Ross H, Bedinger M, Smith FM, Prager K, et al. Building community resilience in a context of climate change: the role of social capital. Ambio. 2022;51(6):1371–87.
Humbert C, Joseph J. Introduction: the politics of resilience: problematising current approaches. Resilience. 2019;7(3):215–23.
Tanner T, Bahadur A, Moench M. Challenges for resilience policy and practice. Working paper: 519. 2017.
Vadivel R, Shoib S, El Halabi S, El Hayek S, Essam L, Bytyçi DG. Mental health in the post-COVID-19 era: challenges and the way forward. Gen Psychiatry. 2021;34(1):e100424.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Pryor M. Social Capital Harmonised Standard. London: Government Statistical Service. 2021. Accessible at: https://gss.civilservice.gov.uk/policystore/social-capital/ .
Public Health England NE. A guide to community-centred approaches for health and wellbeing. 2015.
Hawe P. Capturing the meaning of ‘community’ in community intervention evaluation: some contributions from community psychology. Health Promot Int. 1994;9(3):199–210.
Uphoff EP, Pickett KE, Cabieses B, Small N, Wright J. A systematic review of the relationships between social capital and socioeconomic inequalities in health: a contribution to understanding the psychosocial pathway of health inequalities. Int J Equity Health. 2013;12:1–12.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This study was supported by the National Institute for Health Research Research Unit (NIHR HPRU) in Emergency Preparedness and Response, a partnership between Public Health England, King’s College London and the University of East Anglia. The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NIHR, Public Health England, the UK Health Security Agency or the Department of Health and Social Care [Grant number: NIHR20008900]. Part of this work has been funded by the Office for Health Improvement and Disparities, Department of Health and Social Care, as part of a Collaborative Agreement with Leeds Beckett University.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Behavioural Science and Insights Unit, Evaluation & Translation Directorate, Science Group, UK Health Security Agency, Porton Down, Salisbury, SP4 0JG, UK
C. E. Hall, H. Wehling, R. Amlôt & D. Weston
Health Protection Research Unit, Institute of Psychology, Psychiatry and Neuroscience, King’s College London, 10 Cutcombe Road, London, SE5 9RJ, UK
C. E. Hall, S. K. Brooks & N. Greenberg
School of Health and Community Studies, Leeds Beckett University, Portland Building, PD519, Portland Place, Leeds, LS1 3HE, UK
J. Stansfield & J. South
King’s Centre for Military Health Research, Institute of Psychology, Psychiatry and Neuroscience, King’s College London, 10 Cutcombe Road, London, SE5 9RJ, UK
N. Greenberg
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
DW, JSo and JSt had the main idea for the review. The search strategy and eligibility criteria were devised by CH, DW, JSo and JSt. CH conducted the database searches. CH and DW conducted duplicate, title and abstract and full text screening in accordance with inclusion criteria. CH conducted data extraction, CH and DW carried out the analysis and drafted the initial manuscript. All authors provided critical revision of intellectual content. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
Corresponding author.
Correspondence to D. Weston .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1., additional file 2., additional file 3., additional file 4., additional file 5., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Hall, C.E., Wehling, H., Stansfield, J. et al. Examining the role of community resilience and social capital on mental health in public health emergency and disaster response: a scoping review. BMC Public Health 23 , 2482 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-17242-x
Download citation
Received : 04 April 2022
Accepted : 16 November 2023
Published : 12 December 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-17242-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mental health
- Community cohesion
- Public health emergency
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 10 January 2024
A scoping review of theories, models and frameworks used or proposed to evaluate knowledge mobilization strategies
- Saliha Ziam ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8892-9572 1 ,
- Sèverine Lanoue 2 ,
- Esther McSween-Cadieux 2 ,
- Mathieu-Joël Gervais 3 ,
- Julie Lane 2 , 4 ,
- Dina Gaid 5 ,
- Laura Justine Chouinard 1 ,
- Christian Dagenais 6 ,
- Valéry Ridde 7 , 8 ,
- Emmanuelle Jean 9 ,
- France Charles Fleury 10 ,
- Quan Nha Hong 5 &
- Ollivier Prigent 2
Health Research Policy and Systems volume 22 , Article number: 8 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
2338 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
Evaluating knowledge mobilization strategies (KMb) presents challenges for organizations seeking to understand their impact to improve KMb effectiveness. Moreover, the large number of theories, models, and frameworks (TMFs) available can be confusing for users. Therefore, the purpose of this scoping review was to identify and describe the characteristics of TMFs that have been used or proposed in the literature to evaluate KMb strategies.
A scoping review methodology was used. Articles were identified through searches in electronic databases, previous reviews and reference lists of included articles. Titles, abstracts and full texts were screened in duplicate. Data were charted using a piloted data charting form. Data extracted included study characteristics, KMb characteristics, and TMFs used or proposed for KMb evaluation. An adapted version of Nilsen (Implement Sci 10:53, 2015) taxonomy and the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) taxonomy (Powell et al. in Implement Sci 10:21, 2015) guided data synthesis.
Of the 4763 search results, 505 were retrieved, and 88 articles were eligible for review. These consisted of 40 theoretical articles (45.5%), 44 empirical studies (50.0%) and four protocols (4.5%). The majority were published after 2010 ( n = 70, 79.5%) and were health related ( n = 71, 80.7%). Half of the studied KMb strategies were implemented in only four countries: Canada, Australia, the United States and the United Kingdom ( n = 42, 47.7%). One-third used existing TMFs ( n = 28, 31.8%). According to the adapted Nilsen taxonomy, process models ( n = 34, 38.6%) and evaluation frameworks ( n = 28, 31.8%) were the two most frequent types of TMFs used or proposed to evaluate KMb. According to the ERIC taxonomy, activities to “train and educate stakeholders” ( n = 46, 52.3%) were the most common, followed by activities to “develop stakeholder interrelationships” ( n = 23, 26.1%). Analysis of the TMFs identified revealed relevant factors of interest for the evaluation of KMb strategies, classified into four dimensions: context, process, effects and impacts.
Conclusions
This scoping review provides an overview of the many KMb TMFs used or proposed. The results provide insight into potential dimensions and components to be considered when assessing KMb strategies.
Peer Review reports
Contribution to the literature
The evaluation of KMb strategies is a critical dimension of the KMb process that is still poorly documented and warrants researchers’ attention.
Our review identified the most common theories, models and frameworks (TMFs) proposed or used to assess KMb strategies and the main components to consider when evaluating a KMb strategy.
By developing an integrative reference framework, this work contributes to improving organizations’ capacity to evaluate their KMb initiatives.
It is widely recognized that research evidence has the potential to inform, guide, and improve practices, decisions, and policies [ 1 ]. Unfortunately, for diverse reasons, the best available evidence is still too seldom taken into account and used [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]. The field of research on knowledge mobilization (KMb) has been growing rapidly since the early 2000s [ 2 , 3 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ]. Its purpose is to better understand how to effectively promote and support evidence use.
Knowledge mobilization is one of many terms and concepts developed over recent decades to describe processes, strategies, and actions to bridge the gap between research and practice. Other common terms often paired interchangeably with the term “knowledge” are “translation”, “transfer”, “exchange”, “sharing” and “dissemination”, among others. [ 12 , 13 ]. Some are more closely linked than others to specific fields or jurisdictions. For this study, we adopted the term knowledge mobilization (KMb) because it conveys the notions of complexity and multidirectional exchanges that characterize research-to-action processes. We used it as an umbrella concept that encompasses the efforts made to translate knowledge into concrete actions and beneficial impacts on populations [ 1 ]. Moreover, the term KMb is also used by research funding agencies in Canada to emphasize the medium- and long-term effects that research knowledge or research results can have on potential users [ 1 , 14 ].
KMb represents all processes from knowledge creation to action and includes all strategies implemented to facilitate these processes [ 14 ]. A KMb strategy is understood as a coordinated set of activities to support evidence use, such as dissemination activities to reach target audiences (for example, educational materials, practical guides, decision support tools) or activities to facilitate knowledge application in a specific context and support professional behaviour change (for example, community of practice, educational meetings, audits and feedback, reminders, deliberative dialogues) [ 15 ]. A KMb process may vary in intensity, complexity or actor engagement depending on the nature of the research knowledge and the needs and preferences of evidence users [ 7 ].
KMb is considered a complex process, in that numerous factors can facilitate or hinder its implementation and subsequent evidence use. The past two decades have seen the emergence of a deeper understanding of these factors [ 2 , 3 , 16 ]. These may be related to the knowledge mobilized (for example, relevance, reliability, clarity, costs), the individuals involved in the KMb process (for example, openness to change, values, time available, resources), the KMB strategies (for example, fit with stakeholder needs and preferences, regular interactions, trust relationships, timing), and organizational and political contexts (for example, culture of evidence use, leadership, resources) [ 2 , 6 , 17 , 18 ]. However, more studies are needed to understand which factors are more important in which contexts, and to evaluate the effects of KMb strategies.
On this last point, while essential, it is often very complex to study KMb impacts empirically to demonstrate the effectiveness of KMb strategies [ 19 , 20 , 21 ]. Partly for this reason, high-quality studies that evaluate process, mechanisms and effects of KMb strategies are still relatively rare [ 2 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 ]. As a result, knowledge about the effectiveness of different KMb strategies remains limited [ 10 , 17 , 19 , 23 , 26 , 27 , 28 ] and their development cannot be totally evidence informed [ 3 , 19 , 20 , 23 , 29 , 30 ], which may seem incompatible with the core values and principles of KMb.
The growing interest in KMb has led to an impressive proliferation of conceptual propositions, such as theories, models and frameworks (TMF) [ 2 , 3 , 9 , 11 , 12 , 31 , 32 ]. Many deplore the fact that these are poorly used [ 11 , 30 , 33 ] and insist on the need to test, refine and integrate existing ones [ 3 , 31 , 34 ]. Indeed, the conceptual and theoretical development of the field has outpaced its empirical development. This proliferation appears to have created confusion among certain users, such as organizations that need to evaluate their KMb strategies. Besides implementing and funding KMb strategies, knowledge organizations such as granting agencies, governments and public organizations, universities and health authorities are often required to demonstrate the impact of their strategies [ 21 , 35 , 36 ]. Yet this can be a significant challenge [ 20 , 23 , 29 ]. They may have difficulty knowing which TMFs to choose, in what context and how to use them effectively in their evaluation process [ 12 , 37 ].
Indeed, the evaluation of KMb strategies is still relatively poorly documented, with respect to the phases of their development and implementation. Our aim in this scoping review is to clarify, conceptually and methodologically, this crucial dimension of the KMb process. This would help organizations gain access to evidence-based, operational and easy-to-use evaluation toolkits for assessing the impacts of their KMb strategies.
To survey the available knowledge on evaluation practices for KMb strategies, we conducted a scoping review. According to Munn et al. [ 38 ], a scoping review is indicated to identify the types of available evidence and knowledge gaps, to clarify concepts in the literature and to identify key characteristics or factors related to a concept. This review methodology also allows for the inclusion of a diversity of publications, regardless of their nature or research design, to produce the most comprehensive evidence mapping possible [ 39 ]. The objective of the scoping review was to identify and describe the characteristics of theories, models and frameworks (TMFs) used or proposed to evaluate KMb strategies. The specific research questions were:
What TMFs to evaluate KMb strategies exist in the literature?
What KMb strategies do they evaluate (that is types of KMb objectives, activities, target audiences)?
What dimensions and components are included in these TMFs?
This scoping review was conducted based on the five steps outlined by Arksey and O’Malley [ 39 ]: (1) formulating the research questions; (2) identifying relevant studies; (3) selecting relevant studies; (4) extracting and charting data; and (5) analysing, collating, summarizing and presenting the data. Throughout the process, researchers and knowledge users (KMb practitioners) were involved in decisions regarding the research question, search strategy, selection criteria for studies and categories for data charting. We followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines [ 40 ]. No protocol was registered for this review.
Search strategy and information sources
The search strategy was developed, piloted and refined in consultation with our team’s librarian. Search terms included controlled vocabulary and keywords related to three main concepts: (1) knowledge mobilization (for example [knowledge or evidence or research] and transfer, translation, diffusion, dissemination, mobilization, implementation science, exchange, sharing, use, uptake, evidence-based practice, research-based evidence), (2) evaluation (for example, evaluat*, measur*, impact, outcome, assess, apprais*, indicator) and (3) TMF (for example, framework*, model*, method*, guide*, theor*). See Additional file 1 for the search terms and strategies used in the electronic searches.
The following databases were searched from January 2000 to August 2023: MEDLINE (Ovid), PsycInfo (Ovid), ERIC (ProQuest), Sociological Abstracts (ProQuest), Dissertations & Theses (Proquest), Érudit and Cairn. These databases were chosen to identify relevant references in the health, education and social fields. Several search strategies were tested by the librarian to optimize the retrieval of citations known to the investigators and to increase the likelihood that all relevant studies would be retrieved. We also searched reference lists of included articles and previous systematic reviews [ 11 , 12 , 15 , 41 ].
Eligibility criteria
A publication was considered eligible if it (1) presented or used a theory, model, or framework (TMF), (2) described dimensions or specific components to consider in the evaluation of KMb strategies, (3) presented or discussed KMb strategies or activities (any initiatives to improve evidence use), and (4) proposed outcomes that might result directly or indirectly from the KMb strategies. Studies were excluded from analysis if they (1) presented a TMF to assess the impact of research without mentioning KMb strategies or an intervention not related to KMb and (2) presented evaluation dimensions or components that could not be generalized. We considered publications in English or French. All types of articles and study designs were eligible, including study protocols.
Study selection
The results of the literature search were imported into Covidence, which the review team used for screening. After duplicate articles were removed, the titles and abstracts were screened independently by two of the three reviewers (EMC, MJG, GL). Publications identified as potentially relevant were retrieved in full text and screened independently by three reviewers (EMC, MJG, GL). Discrepancies regarding the inclusion of any publication were resolved through discussion and consensus among reviewers. The principal investigator (SZ) validated the final selection of articles.
Data synthesis
A data charting form was developed in Microsoft Excel and piloted by the research team. Data extracted included study characteristics (authors, authors’ country of affiliation, year, journal, discipline, article type, study setting, study aim), KMb strategies of interest, KMb objectives, KMb target audiences and TMFs used or proposed for KMb evaluation (existing or new TMF, specific dimensions or components of TMF and so on). Data were extracted by a single reviewer (SL, JC or OP) and validated by a second reviewer (SZ). Disagreements were discussed between reviewers and resolved by consensus. No quality appraisal of included studies was conducted, as this is optional in scoping reviews and the purpose was only to describe the content of identified TMFs [ 42 ].
Data analysis and presentation of results
Data were summarized according to study characteristics, KMb strategy characteristics (activities, objectives, target audiences), types of TMFs, and dimensions or components to consider for KMb evaluation. Disagreements during the process were discussed and resolved through consensus (SL, DG, SZ). A KMb strategy might have one or more objectives and include one or more activities. Thus, the objectives and activities of the KMb strategies extracted from the selected studies were summarized based on existing categorizations. The categorization of KMb objectives was inspired by Gervais et al. [ 15 ] and Farkas et al. [ 43 ] (Table 1 ).
The KMb activities were categorized according to the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) taxonomy [ 44 ]. The activities were first classified according to the full taxonomy and then grouped into the nine categories proposed by Waltz et al. [ 45 ] (Table 2 ).
The TMFs were categorized according to the categories of theoretical approaches described by Nilsen [ 32 ]: process models, evaluation frameworks, determinant frameworks and classic theories (Table 3 ). The category “implementation theories” originally described by Nilsen [ 32 ] was not used because we did not identify any article that fit this category. We also added a category named “logic models” due to the nature of the identified TMFs. Logic models are often used in theory-driven evaluation approaches and are usually developed to show the links among inputs (resources), activities and outputs (outcomes and short-, medium- and long-term effects) [ 46 ].
Finally, the content extracted from the TMFs was analysed using mainly an inductive method. This method allows, among other things, to develop a reference framework or a model from the emerging categories that are evident in the text data [ 50 ].
The classification of concepts is the result of multiple readings and interpretations. The concepts associated with each dimension of the framework were classified according to their meaning. Similar concepts were grouped together to form components. These grouped components were then associated with the subdimensions and main dimensions of the framework.
Search results
The searches yielded 4763 articles. Of those, 4258 were excluded during the title and abstract screening. Of the 505 full-text articles, we retained 88 in our final sample. The results of the search and selection processes (PRISMA flowchart) are summarized in Fig. 1 .
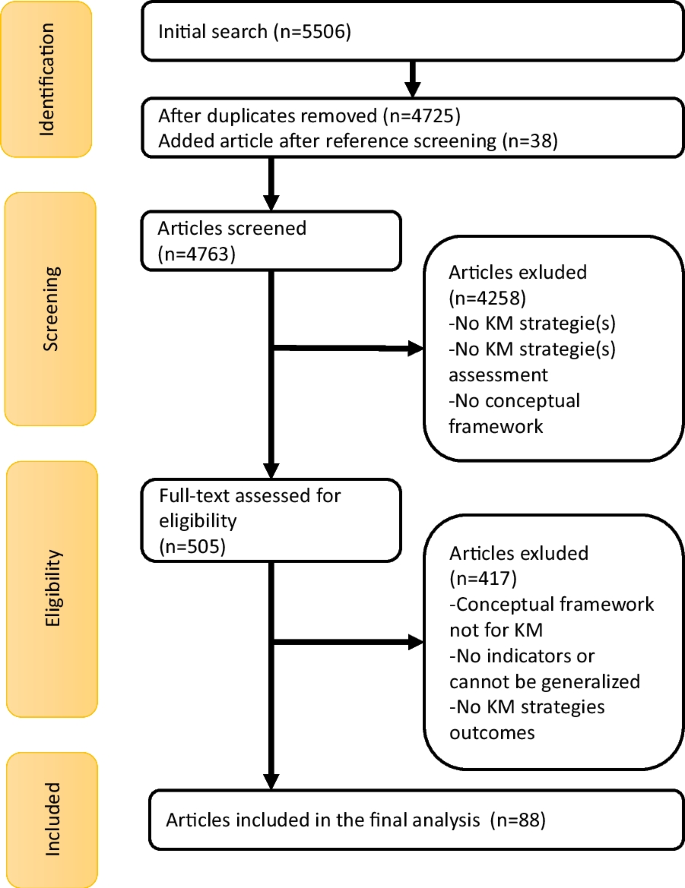
PRISMA flowchart summarizing search strategy and selection results [ 40 ]
Publication characteristics
Most articles were published after 2010 ( n = 70, 79.5%), with an average of 5 articles per year between 2010 and 2023 compared with an average of 2.1 articles per year between 2001 and 2009; there were no eligible articles from 2000. The search was conducted in August 2023, and only five articles were published in these 7 months of the year. Table 4 presents the main characteristics of the selected articles. A full list of the included articles with their main characteristics is presented in Additional file 2 .
The number of theoretical and empirical articles was relatively similar. Among the theoretical articles, 19 descriptive articles (21.6%) were aimed at describing a KMb strategy, a KMb infrastructure or a TMF related to a specific programme or context; 18 articles (20.5%) synthesized knowledge to propose a TMF (new or revised); and three articles conducted systematic reviews (3.4%).
The empirical articles category included studies with different methodological approaches (quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods). We will not report the details of the methodologies used, as this would result in a long list with few occurrences. The empirical articles can be divided into three categories: (1) studies that evaluated a TMF related to KMb ( n = 16, 18.2%), (2) studies that evaluated a KMb strategy ( n = 21, 23.9%) and (3) studies that evaluated both a KMb strategy and a TMF ( n = 7, 8.0%).
Most articles were related to healthcare ( n = 71, 80.7%). This field of study was divided into three subdomains. The healthcare and social services articles usually described or assessed a KMb strategy targeting health professionals’ practices in a variety of fields (for example, occupational therapy, dentistry, mental health, pharmacology, gerontology, nursing and so on). The health policy and systems articles usually described or assessed KMb strategies targeting decision-making processes, decision-makers or public health interventions and policies. The continuing education articles assessed training programmes for health professionals aimed at increasing knowledge and skills in a specific field. The articles in the general field described or discussed TMFs and KMb strategies that could be applied to multiple disciplines or contexts. Finally, the articles in the education field described or assessed a KMb strategy targeting education professionals.
Almost half of the articles ( n = 42, 47.7%) studied KMB strategies implemented in only four countries: Canada, Australia, the United States and the United Kingdom. Countries in South America, the Caribbean, Africa, Asia, the Middle East, China and Europe were underrepresented ( n = 8, 9.1%). The remaining 34 articles (38.6%) did not specify an implementation context and were mostly theoretical articles. Regarding the authors’ countries of affiliation, Canada, the United States, Australia and the United Kingdom were again the most represented countries, featuring in 85% of the articles ( n = 75).
What theories, models or frameworks exist in the literature to evaluate KMb strategies?
Several articles proposed a new TMF ( n = 37, 42.0%), and some articles proposed a logic model specifically developed to evaluate their KMb strategy ( n = 17, 19.3%). One-third of the articles used existing TMFs ( n = 28, 31.8%). A few articles only referred to existing TMFs but did not use them to guide a KMb strategy evaluation ( n = 6, 8.5%).
The identified TMFs were then categorized according to their theoretical approaches (adapted from Nilsen, [ 32 ]) (Table 5 ). Five articles used or proposed more than one TMF, and three TMFs could be classified in two categories. Several articles proposed or used a process model ( n = 34, 38.6%) or an evaluation framework ( n = 28, 31.8%); these were the two most frequently identified types of TMFs. Fewer articles proposed or used a logic model ( n = 17, 19.3%), a determinant framework ( n = 12, 13.6%) or a classic theory ( n = 7, 8.0%). The TMFs most often identified in the articles were the RE-AIM framework ( n = 5, 5.7%), the Knowledge-to-Action framework [ 9 ] ( n = 4, 4.5%), the Theory of Planned Behavior [ 51 ] ( n = 3, 3.4%) and the Expanded Outcomes framework for planning and assessing continuing medical education [ 52 ] ( n = 3, 3.4%). In total, we identified 87 different TMFs in the 88 articles. Only nine TMFS were retrieved in more than one article.
What KMb strategies do the TMFs evaluate (activities, objectives, target audience)?
Thirty-eight articles reported using more than one activity in their KMb strategy. According to the ERIC compilation, “Train and educate stakeholders” activities were the most common, followed by “Develop stakeholder interrelationships” and “Use evaluative and iterative strategies”. Table 6 presents the various types of activities and the number of articles that referred to each.
Of the 88 articles analysed, 18 (20.4%) did not specify a KMb objective. The remaining articles proposed one or more KMb strategy objectives. Specifically, 39 (36.4%) articles had one objective, 15 (17.0%) had two, three (3.4%) had three, and 13 (14.8%) had four or five. Table 7 presents the different types of objectives and the number of times they were identified.
The target audiences for KMb strategies were clearly specified in half of the articles ( n = 44, 50.0%). Generally, these were empirical articles that targeted specific professionals ( n = 36, 40.9%) or decision-makers ( n = 8, 9.1%). Just under one-third of the articles identified a broad target audience (for example, professionals and managers in the health system, a health organization) ( n = 26, 29.5%). Finally, 18 articles (20.4%) did not specify a target audience for KMb; these were most often theoretical articles.
What are the dimensions and components included in TMFs for evaluating KMb strategies?
The analysis of the identified TMFs revealed many factors of interest relevant for the evaluation of KMb strategies. These specific components were inductively classified into four main dimensions: context, process, effects and impacts (Fig. 2 ). The context dimension refers to the assessment of the conditions in place when the KMb strategy is implemented. These include both the external (that is, sociopolitical, economic, environmental and cultural characteristics) and internal environments (that is, characteristics of organizations, individuals and stakeholder partnerships). These factors are understood to influence the selection and tailoring of a KMb strategy. The process dimension refers to the assessment of the planning, levels and mechanisms of implementation, as well as to the characteristics of the KMb strategy implemented. The effects dimension refers to the assessment of outcomes following the KMb strategy implementation. The potential effects vary depending on the strategy’s objectives and can be either the immediate results of the KMb strategy or short-, medium- and long-term outcomes. The conceptual gradation of effects was generally represented in a similar way in the TMFs analysed, but the temporality of effects could vary. A medium-term outcome in one study could be understood as a long-term outcome in another. However, the majority of authors group these effects into three categories (Gervais et al. 2016: p. 6): (1) short-term effects, measured by success of KMb strategy measured by success of KMb strategy (number of people reached, satisfaction, participation and so on); (2) medium-term effects linked to changes in individual attitude and the use of knowledge; and (3) the long-term effects that result from achieving the KMb objective (for example, improved practices and services, changed collective behaviour, sustainable use of knowledge).
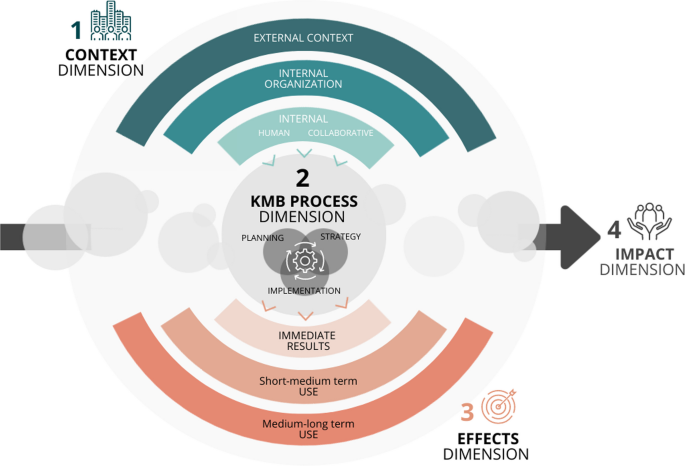
The main evaluation dimensions that emerged from the TMFs analysed
Finally, the impacts dimension refers to the ultimate effects of KMb products or interventions on end users, as measured by the organization (Phipps et al. [ 36 ], p. 34). The evaluation of these ultimate effects can be measured by the integration of a promising practice into organizational routines, by the effects on service users or by the effects on the health and well-being of communities and society in general.
This gradation shows the importance of measuring effects at different points in time, to take account of the time they take to appear and their evolving nature (Gervais et al., 2016: p. 6).
Most of the articles presented the dimensions that should be evaluated, whereas the empirical articles presented the dimensions but also used them in practice to evaluate a KMb strategy. Only five articles (5.7%) did not mention specific dimensions that could be classified.
Table 8 presents both the number of articles that presented dimensions to be evaluated and the number of articles that evaluated them in practice. These results showed that the effects dimension was both the most often named and the most evaluated in practice. The other three dimensions (context, process, impacts), while quite often mentioned as relevant to assess, were less often evaluated in practice. For example, only five articles (5.7%) reported having assessed the impacts dimension.
As previously mentioned, the components relevant for the evaluation of KMb strategies were extracted from the identified TMFs. Table 9 presents these components, which represent the more specific factors of interest for assessing context, process, effects and impacts.
Although often overlooked, the evaluation of KMb strategies is an essential step in guiding organizations seeking to determine whether the expected outcomes of their initiatives are being realized. Evaluation not only allows organizations to make adjustments if the initiatives are not producing the expected results, but also helps them to justify their funding of such initiatives. Evaluation is also essential if the KMb science is to truly inform KMb practice, such that the strategies developed are based on empirical data [ 30 ]. To make KMb evaluation more feasible, evaluation must be promoted and practices improved.
This scoping review meets the first objective of our project, which was to provide an overview of reference frameworks used or proposed for evaluating KM strategies, and to propose a preliminary version of a reference framework for evaluating KM strategies. Several key findings emerged from this scoping review:
Proliferation of theories, models and frameworks, but few frequently used
We are seeing a proliferation of TMFs in KMb and closely related fields [ 132 , 133 ]. Thus, the results of this scoping review support the argument that the conceptual and theoretical development of the field is outpacing its empirical development. Most of the reviewed articles (42.0%) proposed a new TMF rather than using existing ones. Furthermore, we identified relatively few empirical studies (50.0%) that focused on the evaluation of KMb strategies. Consequently, the TMFs used were poorly consolidated, which does not provide a solid empirical foundation to guide the evaluation of KMb strategies. Also, not all the TMFs proposed in the articles were specifically developed for evaluation; some were focused on KMb implementation processes. These may still provide elements to consider for evaluation, although they were not designed to propose specific indicators.
A scoping review published in 2018 identified 596 studies using 159 different KMb TMFs, 95 of which had been used only once [ 11 ]. Many authors reported that these are rarely reused and validated [ 11 , 30 , 33 ] and that it is important to test, refine and integrate existing ones [ 3 , 31 , 34 , 133 ]. A clear, collective and consistent use of existing TMFs is recommended and necessary to advance KMb science and closely related fields [ 12 , 31 ]. The systematic review by Strifler et al. [ 11 ] highlights the diversity of available TMFs and the difficulty users may experience when choosing TMFs to guide their KMb initiatives or evaluation process. Future work should focus on the development of tools to better support users of TMFs, especially those working in organizations. By consolidating a large number of TMFs, the results of this scoping review contribute to these efforts.
The importance of improving evaluation practices for complex multifaceted KMb strategies
Another noteworthy finding was the emphasis on the evaluation of strategies focused on education and professional training for practice improvement (52.3%). Relatively few of the reviewed articles looked at, for example, the evaluation of KMb strategies aimed at informing or influencing decision-making (13.6%), or KMb strategies targeting decision-makers (9.1%). These results reaffirm the importance of conducting more large-scale evaluations of complex and multifaceted KMb strategies. These involve a greater degree of interaction and engagement, are composed of networks of multiple actors, mobilize diverse sources of knowledge and have simultaneous multilevel objectives [ 19 , 134 ].
The fact that some KMb strategies are complex interventions implemented in complex contexts [ 134 ] presents a significant and recurring challenge to their evaluation. Methodological designs, approaches and tools are often ill-suited to capture the short-, medium- and long-term outcomes of KMb strategies, as well as to identify the mechanisms by which these outcomes were produced in a specific context. It is also difficult to link concrete changes in practice and decision-making to tangible longer-term impacts at the population level. Moreover, these impacts can take years to be achieved [ 36 ] and can be influenced by several other factors in addition to KMb efforts [ 2 , 19 , 24 ]. Comprehensive, dynamic and flexible evaluation approaches [ 135 , 136 , 137 ] using mixed methods [ 20 ] appear necessary to understand why, for whom, how, when and in what context KMb strategies achieve their objectives [ 2 , 21 , 25 ]. For instance, realist evaluation, which belongs to theory-based evaluation, may be an approach that addresses issues of causality without sacrificing complexity [ 134 , 138 , 139 ]. This evaluation approach aims to identify the underlying generative mechanisms that can explain how the outcomes were generated and what characteristics of the context affected, or not, those mechanisms. This approach is used to test and refine theory about how interventions with a similar logic of action actually work [ 139 ].
Large heterogeneity of methodologies used in empirical studies
Despite the growth of the KMb field, a recurring issue is the relatively limited number of high-quality studies that evaluate KMb outcomes and impacts. This observation is shared by many of the authors of our scoping articles [ 2 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 ]. Only a limited number of empirical articles met the selection criteria ( n = 44/88) in this scoping review. Synthesizing these studies is challenging due to the diversity of research designs used and the large number of potential evaluation components identified. In addition, most of the identified studies used TMFs and measurement tools that were not validated [ 20 , 29 ] and that were specifically developed for their study [ 16 , 25 , 140 ]. Moreover, these studies did not describe the methods used to justify their choice of evaluation dimensions and components [ 25 ], which greatly hinders the ability to draw inferences and develop generalizable theories through replication in similar studies [ 110 , 140 , 141 , 142 , 143 ]. The lack of a widely used evaluation approach across the field is therefore an important issue [ 16 , 20 ] also highlighted by this scoping review.
Our aim in this review was not to identify specific indicators or measurement tools (for example, questionnaires) for assessing KMb strategies, but rather to describe dimensions and component of TMFs used for KMb evaluation. However, a recent scoping review [ 144 ] looked at measurement tools and revealed that only two general potential tools have been identified to assess KMb activities in any sector or organization: the Level of Knowledge Use Survey (LOKUS) [ 145 ] and the Knowledge Uptake and Utilization Tool (KUUT) [ 95 ]. The authors also assert the importance of developing standardized tools and evaluation processes to facilitate comparison of KMb activities’ outcomes across organizations [ 144 ].
Lack of description and reporting of KMb strategies and evaluation
Another important finding from this review was the sparsity of descriptions of KMb strategies in the published articles. In general, the authors provided little information on the operationalization of their KMb strategies (for example, objectives, target audiences, details of activities implemented, implementation context, expected effects). The KMb strategy objectives and the implemented activities should be carefully selected and empirically, theoretically or pragmatically justified before the evaluation components and specific indicators can be determined [ 146 ].
To improve consistency in the field and to contribute to the development of KMb science, many authors reported the need to better describe and report KMb strategies and their context [ 8 , 54 , 146 , 147 , 148 , 149 , 150 ]. KMb strategies are often inconsistently labelled across studies, poorly described and rarely justified theoretically [ 146 , 150 , 151 ]. It was not possible in this scoping review to associate the evaluation components to be used with the objectives and types of KMb strategies, as too much information was missing in the articles. Over the past 10 years, several guidelines have been proposed to improve the reporting of interventions such as KMb strategies: the “Workgroup for Intervention Development and Evaluation Research (WIDER) recommendations checklist” [ 147 ], the “Standards for Reporting Implementation Studies (StaRI)” [ 150 ] and the “Template for Intervention Description and Replication (TIDieR)” [ 152 ]. These guidelines should be used more often to enhance the reporting of KMb strategies and help advance the field [ 153 ].
Implications for future research
This scoping review provides an overview of potential factors of interest for assessing the context, process, effects and impacts of a KMb strategy. It also proposes a preliminary inventory of potential dimensions and components to consider when planning the evaluation of a KMb strategy. Given the broad spectrum of factors of interest identified across studies, not all of them can be assessed in every context. Rather, they should be targeted according to the objectives of the evaluation, the nature of the KMb strategy and the resources available to conduct the evaluation. Thus, this inventory should not be understood as a prescriptive, normative and exhaustive framework, but rather as a toolbox to identify the most relevant factors to include in the evaluation of a given KMB strategy, and to address a need often expressed by organizations wishing to evaluate their KMb efforts.
Additional work is needed to validate and operationalize these dimensions, to identify relevant measurement tools related to the different components and to see how this inventory could support KMb evaluation practices in organizations.
This scoping review is the first stage of a larger research project aimed at improving organizations’ capacity to evaluate their KMb initiatives by developing an integrative, interdisciplinary and easy-to-use reference framework. In the second phase of the project, the relevance and clarity of the evaluation dimensions identified in the scoping review will be validated through a Delphi study with KMb specialists and researchers. The enriched framework will then be pilot tested in two organizations carrying out and evaluating KMb strategies, to adapt the framework to their needs and to further clarify how the dimensions can be measured in practice. In this third phase, guidance will be provided to help organizations adopt the framework and its support kit. The aim of the project is to go beyond proposing a theoretical framework, and to help build organizations’ capacity to evaluate KT strategies by proposing tools adapted to their realities.
Review limitations
Some limitations of this scoping review should be acknowledged. First, given the numerous different terms used to describe and conceptualize the science of using evidence, it is possible that our search strategy did not capture all relevant publications. However, to limit this risk, we manually searched the reference lists of the selected articles. Second, the literature search was limited to articles published in English or French, and the articles were mostly from high-income countries (for example, North America); therefore, the application of the identified concepts in this scoping review to other contexts should be further explored.
In addition, the search strategy focused on scientific publications to assess progress made in the field of knowledge mobilization strategy evaluation. The grey literature was not examined. It should be considered in future research to complete the overview of evaluation needs in the field of knowledge mobilization.
Finally, the paucity of information in the articles sometimes made it difficult to classify the TMFs according to the taxonomies [ 32 , 44 ], which may have led to possible misinterpretation. However, to limit the risk of errors, the categorization was performed by two reviewers and validated by a third in cases of uncertainty.
Given the increasing demand from organizations for the evaluation of KMb strategies, along with the poorly consolidated KMb research field, a scoping review was needed to identify the range, nature and extent of the literature. This scoping review enabled us to synthesize the breadth of the literature, provide an overview of the many theories, models and frameworks used, and identify and categorize the potential dimensions and components to consider when evaluating KMb initiatives. This scoping review is part of a larger research project, in which the next steps will be to validate the integrative framework and develop a support kit to facilitate its use by organizations involved in KMb.
Availability of data and materials
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is included within the article and its additional files.
Abbreviations
- Knowledge mobilization
- Theories, models, and frameworks
Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council. Guidelines for Effective Knowledge Mobilization. 2019. https://www.sshrc-crsh.gc.ca/funding-financement/policies-politiques/knowledge_mobilisation-mobilisation_des_connaissances-eng.aspx Accessed 28 Dec 2022.
Boaz A, Davies H, Fraser A, Nutley S. What works now? evidence-informed policy and practice. Bristol: Policy press; 2019.
Book Google Scholar
Curran JA, Grimshaw JM, Hayden JA, Campbell B. Knowledge translation research: the science of moving research into policy and practice. J Contin Educ Heal Prof. 2011;31(3):174–80.
Article Google Scholar
Global Commission on Evidence. The Evidence Commission report: A wake-up call and path forward for decision-makers, evidence intermediaries, and impact-oriented evidence producers. McMaster University; 2022 p. 144. https://www.mcmasterforum.org/networks/evidence-commission/report/english
Morris ZS, Wooding S, Grant J. The answer is 17 years, what is the question: understanding time lags in translational research. J R Soc Med. 2011;104(12):510–20.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Orton L, Lloyd-Williams F, Taylor-Robinson D, O’Flaherty M, Capewell S. The use of research evidence in public health decision making processes: systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(7): e21704.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Straus SE, Tetroe J, Graham ID, editors. Knowledge translation in health care: moving from evidence to practice. 2nd ed. Chichester, West Sussex ; Hoboken, NJ: Wiley/BMJ Books; 2013, 406
Barwick M, Dubrowski R, Petricca K. Knowledge translation: The rise of implementation. 2020; https://ktdrr.org/products/kt-implementation/KT-Implementation-508.pdf
Graham ID, Logan J, Harrison MB, Straus SE, Tetroe J, Caswell W, et al. Lost in knowledge translation: time for a map? J Continuing Educ Health Professions. 2006;26(1):13–24.
Grimshaw JM, Eccles MP, Lavis JN, Hill SJ, Squires JE. Knowledge translation of research findings. Implement Sci. 2012;7(1):50.
Strifler L, Cardoso R, McGowan J, Cogo E, Nincic V, Khan PA, et al. Scoping review identifies significant number of knowledge translation theories, models, and frameworks with limited use. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;100:92–102.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Esmail R, Hanson HM, Holroyd-Leduc J, Brown S, Strifler L, Straus SE, et al. A scoping review of full-spectrum knowledge translation theories, models, and frameworks. Implement Sci. 2020;15(1):11.
McKibbon KA, Lokker C, Wilczynski NL, Ciliska D, Dobbins M, Davis DA, et al. A cross-sectional study of the number and frequency of terms used to refer to knowledge translation in a body of health literature in 2006: a Tower of Babel? Implement Sci. 2010;5(1):16.
Fonds de recherche du Québec. Stratégie de mobilisation des connaissances 2014–2017. 2014. https://frq.gouv.qc.ca/en/mobilization-of-knowledge/ . Accessed 28 Dec 2022.
Gervais MJ, Souffez K, Ziam S. Quel impact avons-nous ? Vers l’élaboration d’un cadre pour rendre visibles les retombées du transfert des connaissances. TUC Revue francophone de recherche sur le transfert et l’utilisation des connaissances. 2016;1(2):21.
Google Scholar
Williams NJ, Beidas RS. Annual research review: the state of implementation science in child psychology and psychiatry: a review and suggestions to advance the field. J Child Psychol Psychiatr. 2019;60(4):430–50.
Mitton C, Adair CE, Mckenzie E, Patten SB, Perry BW. Knowledge transfer and exchange: review and synthesis of the literature. Milbank Q. 2007;85(4):729–68.
Oliver K, Innvar S, Lorenc T, Woodman J, Thomas J. A systematic review of barriers to and facilitators of the use of evidence by policymakers. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14(1):2.
Fazey I, Bunse L, Msika J, Pinke M, Preedy K, Evely AC, et al. Evaluating knowledge exchange in interdisciplinary and multi-stakeholder research. Glob Environ Chang. 2014;25:204–20.
Gervais MJ, Marion C, Dagenais C, Chiocchio F, Houlfort N. Dealing with the complexity of evaluating knowledge transfer strategies: guiding principles for developing valid instruments. Res Eval. 2016;25(1):62–9.
Reed MS, Bryce R, Machen R. Pathways to policy impact: a new approach for planning and evidencing research impact. Evid policy. 2018;14(3):431–58.
Kim C, Wilcher R, Petruney T, Krueger K, Wynne L, Zan T. A research utilisation framework for informing global health and development policies and programmes. Health Res Policy Sys. 2018;16(1):9.
Langer L, Tripney J, Gough D University of London, Social Science Research Unit, Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre. The science of using science: researching the use of research evidence in decision-making. 2016.
Rajić A, Young I, McEwen SA. Improving the utilization of research knowledge in agri-food public health: a mixed-method review of knowledge translation and transfer. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2013;10(5):397–412.
Scarlett J, Forsberg BC, Biermann O, Kuchenmüller T, El-Khatib Z. Indicators to evaluate organisational knowledge brokers: a scoping review. Health Res Policy Syst. 2020;18(1):93.
Bornbaum CC, Kornas K, Peirson L, Rosella LC. Exploring the function and effectiveness of knowledge brokers as facilitators of knowledge translation in health-related settings: a systematic review and thematic analysis. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):162.
Sarkies MN, Bowles KA, Skinner EH, Haas R, Lane H, Haines TP. The effectiveness of research implementation strategies for promoting evidence-informed policy and management decisions in healthcare: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):132.
Scott SD, Albrecht L, O’Leary K, Ball GD, Hartling L, Hofmeyer A, et al. Systematic review of knowledge translation strategies in the allied health professions. Implement Sci. 2012;7(1):70.
Dagenais C, Malo M, Robert É, Ouimet M, Berthelette D, Ridde V. Knowledge transfer on complex social interventions in public health: a scoping study. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(12): e80233.
Davies HT, Powell AE, Nutley SM. Mobilising knowledge to improve UK health care: learning from other countries and other sectors – a multimethod mapping study. Health Serv Deliv Res. 2015;3(27):1–190.
Damschroder LJ. Clarity out of chaos: use of theory in implementation research. Psychiatry Res. 2020;283: 112461.
Nilsen P. Making sense of implementation theories, models and frameworks. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):53.
Ellen ME, Panisset U, Araujo de Carvalho I, Goodwin J, Beard J. A knowledge translation framework on ageing and health. Health Policy. 2017;121(3):282–91.
Wensing M, Bosch M, Grol R. Developing and selecting interventions for translating knowledge to action. CMAJ. 2010;182(2):E85–8.
Bennet A, Bennet D, Fafard K, Fonda M, Lomond T, Messier L, et al. Knowledge mobilization in the social sciences and humanities: moving from research to action. Frost: MQI Press; 2007.
Phipps D, Cummins J, Pepler D, Craig W, Cardinal S. The Co-produced Pathway to Impact Describes Knowledge Mobilization Processes. JCES. 2016;9(1). https://jces.ua.edu/articles/258 . Accessed 17 Nov 2022.
Birken SA, Rohweder CL, Powell BJ, Shea CM, Scott J, Leeman J, et al. T-CaST: an implementation theory comparison and selection tool. Implement Sci. 2018;13(1):143.
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18(1):143.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73.
Moullin JC, Sabater-Hernandez D, Fernandez-Llimos F, Benrimoj SI. A systematic review of implementation frameworks of innovations in healthcare and resulting generic implementation framework. Health Res Policy Syst. 2015;13(101170481):16.
Pham MT, Rajić A, Greig JD, Sargeant JM, Papadopoulos A, McEwen SA. A scoping review of scoping reviews: advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res Synthesis Methods. 2014;5(4):371–85.
Farkas M, Jette AM, Tennstedt S, Haley SM, Quinn V. Knowledge dissemination and utilization in gerontology: an organizing framework. Gerontologist. 2003;43:47–56.
Powell BJ, Waltz TJ, Chinman MJ, Damschroder LJ, Smith JL, Matthieu MM, et al. A refined compilation of implementation strategies: results from the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) project. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):21.
Waltz TJ, Powell BJ, Matthieu MM, Damschroder LJ, Chinman MJ, Smith JL, et al. Use of concept mapping to characterize relationships among implementation strategies and assess their feasibility and importance: results from the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) study. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):109.
Smith JD, Li DH, Rafferty MR. The implementation research logic model: a method for planning, executing, reporting, and synthesizing implementation projects. Implement Sci. 2020;15(1):84.
Glasgow RE, Vogt TM, Boles SM. Evaluating the public health impact of health promotion interventions: the RE-AIM framework. Am J Public Health. 1999;89(9):1322–7.
Kitson A, Harvey G, McCormack B. Enabling the implementation of evidence based practice: a conceptual framework. Qual Health Care. 1998;7:149–58.
Sketris IS, Carter N, Traynor RL, Watts D, Kelly K, following contributing members of the CNODES Knowledge Translation Team: Pierre Ernst JG Brenda Hemmelgarn, Colleen Metge, Michael Paterson, Robert Platt W and Gary Teare. Building a framework for the evaluation of knowledge translation for the Canadian Network for Observational Drug Effect Studies. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2020;29 Suppl 1(d0r, 9208369):8–25.
Thomas DR. A general inductive approach for analyzing qualitative evaluation data. Am J Eval. 2006;27(2):237–46.
Ajzen I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process. 1991;50(2):179–211.
Moore DE, Green JS, Gallis HA. Achieving desired results and improved outcomes: integrating planning and assessment throughout learning activities. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2009;29(1):1–15.
Tschida JE, Drahota A. Fidelity to the ACT SMART Toolkit: an instrumental case study of implementation strategy fidelity. Implement Sci Commun. 2023;4(1):52.
Colquhoun H, Leeman J, Michie S, Lokker C, Bragge P, Hempel S, et al. Towards a common terminology: a simplified framework of interventions to promote and integrate evidence into health practices, systems, and policies. Implement Sci. 2014;9(1):781.
Bertone MP, Meessen B, Clarysse G, Hercot D, Kelley A, Kafando Y, et al. Assessing communities of practice in health policy: a conceptual framework as a first step towards empirical research. Health Res Policy Sys. 2013;11(1):39.
Gagliardi AR, Legare F, Brouwers MC, Webster F, Wiljer D, Badley E, et al. Protocol: developing a conceptual framework of patient mediated knowledge translation, systematic review using a realist approach. Implement Sci. 2011;6(101258411):25.
Sargeant J, Borduas F, Sales A, Klein D, Lynn B, Stenerson H. CPD and KT: models used and opportunities for synergy. J Contin Educ Heal Prof. 2011;31(3):167–73.
Stetler CB, Ritchie J, Rycroft-Malone J, Schultz A, Charns M. Improving quality of care through routine, successful implementation of evidence-based practice at the bedside: an organizational case study protocol using the Pettigrew and Whipp model of strategic change. Implement Sci. 2007;2(101258411):3.
Kok MO, Schuit AJ. Contribution mapping: a method for mapping the contribution of research to enhance its impact. Health Res Policy Syst. 2012;10(101170481):21.
Dadich A. From bench to bedside: methods that help clinicians use evidence-based practice. Aust Psychol. 2010;45(3):197–211.
Brown P, Bahri P. Engagement’ of patients and healthcare professionals in regulatory pharmacovigilance: establishing a conceptual and methodological framework. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2019;75(9):1181–92.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Dobbins M, Ciliska D, Cockerill R, Barnsley J, DiCenso A. A framework for the dissemination and utilization of research for health-care policy and practice. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs Presents Arch Online J Knowl Synthesis Nurs. 2002;9(1):149–60.
Gagliardi AR, Brouwers MC, Bhattacharyya OK. The guideline implementability research and application network (GIRAnet): an international collaborative to support knowledge exchange: study protocol. Implement Sci. 2012;7(101258411):26.
Brooks SP, Zimmermann GL, Lang M, Scott SD, Thomson D, Wilkes G, et al. A framework to guide storytelling as a knowledge translation intervention for health-promoting behaviour change. Implement sci commun. 2022;3(1):35.
Cullen L, Hanrahan K, Edmonds SW, Reisinger HS, Wagner M. Iowa implementation for sustainability framework. Implement Sci. 2022;17(1):1.
Labbé D, Mahmood A, Miller WC, Mortenson WB. Examining the impact of knowledge mobilization strategies to inform urban stakeholders on accessibility: a mixed-methods study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(5):1561.
Straus SE, Tetroe J, Graham ID, Zwarenstein M, Bhattacharyya O, Shepperd S. Monitoring use of knowledge and evaluating outcomes. Can Med Assoc J. 2010;182(2):E94–8.
Bennett S, Whitehead M, Eames S, Fleming J, Low S, Caldwell E. Building capacity for knowledge translation in occupational therapy: learning through participatory action research. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16(1):257.
Brown C, Rogers S. Measuring the effectiveness of knowledge creation as a means of facilitating evidence-informed practice in early years settings in one London Borough. Lond Rev Educ. 2014;12(3):245–60.
Talbott E, De Los RA, Kearns DM, Mancilla-Martinez J, Wang M. Evidence-based assessment in special education research: advancing the use of evidence in assessment tools and empirical processes. Except Child. 2023;89(4):467–87.
Rosella LC, Bornbaum C, Kornas K, Lebenbaum M, Peirson L, Fransoo R, et al. Evaluating the process and outcomes of a knowledge translation approach to supporting use of the Diabetes Population Risk Tool (DPoRT) in public health practice. Canadian J Program Eval. 2018;33(1):21–48.
Couineau AL, Forbes D. Using predictive models of behavior change to promote evidence-based treatment for PTSD. Psychol Trauma Theory Res Pract Policy. 2011;3(3):266–75.
Dufault M. Testing a collaborative research utilization model to translate best practices in pain management. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2004;1:S26-32.
Beckett K, Farr M, Kothari A, Wye L, le May A. Embracing complexity and uncertainty to create impact: exploring the processes and transformative potential of co-produced research through development of a social impact model. Health Res Policy Syst. 2018;16(1):118.
Kramer DM, Wells RP, Carlan N, Aversa T, Bigelow PP, Dixon SM, et al. Did you have an impact? A theory-based method for planning and evaluating knowledge-transfer and exchange activities in occupational health and safety. Int J Occup Saf Ergon. 2013;19(1):41–62.
Duhamel F, Dupuis F, Turcotte A, Martinez AM, Goudreau J. Integrating the illness beliefs model in clinical practice: a family systems nursing knowledge utilization model. J FAM NURS. 2015;21(2):322–48.
Wimpenny P, Johnson N, Walter I, Wilkinson JE. Tracing and identifying the impact of evidence-use of a modified pipeline model. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2008;5(1):3–12.
Ward V, Smith S, House A, Hamer S. Exploring knowledge exchange: a useful framework for practice and policy. Soc Sci Med. 2012;74(3):297–304.
Grooten L, Vrijhoef HJM, Alhambra-Borras T, Whitehouse D, Devroey D. The transfer of knowledge on integrated care among five European regions: a qualitative multi-method study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1):11.
Stetler CB. Updating the Stetler Model of research utilization to facilitate evidence-based practice. Nurs Outlook. 2001;49(6):272–9.
Ward V. Why, whose, what and how? A framework for knowledge mobilisers. Evid Policy J Res Debate Pract. 2017;13(3):477–97.
Levin RF, Fineout-Overholt E, Melnyk BM, Barnes M, Vetter MJ. Fostering evidence-based practice to improve nurse and cost outcomes in a community health setting: a pilot test of the advancing research and clinical practice through close collaboration model. Nurs Adm Q. 2011;35(1):21–33.
Currie M, King G, Rosenbaum P, Law M, Kertoy M, Specht J. A model of impacts of research partnerships in health and social services. Eval Program Plann. 2005;28(4):400–12.
Richard L, Chiocchio F, Essiembre H, Tremblay MC, Lamy G, Champagne F, et al. Communities of practice as a professional and organizational development strategy in local public health organizations in Quebec, Canada: an evaluation model. Healthc Policy. 2014;9(3):26–39.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rycroft-Malone J, Wilkinson J, Burton CR, Harvey G, McCormack B, Graham I, et al. Collaborative action around implementation in collaborations for leadership in applied health research and care: towards a programme theory. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2013;18(3 Suppl):13–26.
Gagliardi AR, Fraser N, Wright FC, Lemieux-Charles L, Davis D. Fostering knowledge exchange between researchers and decision-makers: exploring the effectiveness of a mixed-methods approach. Health Policy. 2008;86(1):53–63.
Paquette-Warren J, Harris SB, Naqshbandi Hayward M, Tompkins JW. Case study of evaluations that go beyond clinical outcomes to assess quality improvement diabetes programmes using the Diabetes Evaluation Framework for Innovative National Evaluations (DEFINE). J Eval Clin Pract. 2016;22(5):644–52.
Paquette-Warren J, Tyler M, Fournie M, Harris SB. The diabetes evaluation framework for innovative national evaluations (DEFINE): construct and content validation using a modified Delphi method. Can J diabetes. 2017;41(3):281–96.
Abbot ML, Lee KK, Rossiter MJ. Evaluating the effectiveness and functionality of professional learning communities in adult ESL Programs. TESL Canada J. 2018;35(2):1–25.
Ho K, Bloch R, Gondocz T, Laprise R, Perrier L, Ryan D, et al. Technology-enabled knowledge translation: frameworks to promote research and practice. J Contin Educ Heal Prof. 2004;24(2):90–9.
Yu X, Hu D, Li N, Xiao Y. Comprehensive evaluation on teachers’ knowledge sharing behavior based on the improved TOPSIS method. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022;2022(101279357):2563210.
Arora S, Kalishman SG, Thornton KA, Komaromy MS, Katzman JG, Struminger BB, et al. Project ECHO: a telementoring network model for continuing professional development. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2017;37(4):239–44.
Smidt A, Balandin S, Sigafoos J, Reed VA. The Kirkpatrick model: a useful tool for evaluating training outcomes. J Intellect Dev Disabil. 2009;34(3):266–74.
Jeffs L, Sidani S, Rose D, Espin S, Smith O, Martin K, et al. Using theory and evidence to drive measurement of patient, nurse and organizational outcomes of professional nursing practice. Int J Nurs Pract. 2013;19(2):141–8.
Skinner K. Developing a tool to measure knowledge exchange outcomes. Can J Program Eval. 2007;22(1):49–75.
Lavis J, Ross S, McLeod C, Gildiner A. Measuring the impact of health research. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2003;8(3):165–70.
Boyko JA, Lavis JN, Abelson J, Dobbins M, Carter N. Deliberative dialogues as a mechanism for knowledge translation and exchange in health systems decision-making. Soc Sci Med. 2012;75(11):1938–45.
Proctor E, Silmere H, Raghavan R, Hovmand P, Aarons G, Bunger A, et al. Outcomes for implementation research: conceptual distinctions, measurement challenges, and research agenda. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2011;38(2):65–76.
Gainforth HL, Latimer-Cheung AE, Athanasopoulos P, Martin Ginis KA. Examining the feasibility and effectiveness of a community-based organization implementing an event-based knowledge mobilization initiative to promote physical activity guidelines for people with spinal cord injury among support personnel. Health Promot Pract. 2015;16(1):55–62.
Glasgow RE, Harden SM, Gaglio B, Rabin B, Smith ML, Porter GC, et al. RE-AIM planning and evaluation framework: adapting to new science and practice with a 20-year review. Front Public Health. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2019.00064 .
Shelton RC, Chambers DA, Glasgow RE. An extension of RE-AIM to enhance sustainability: addressing dynamic context and promoting health equity over time. Front Public Health. 2020;8(101616579):134.
Bender BG, Simmons B, Konkoly N, Liu AH. The asthma toolkit bootcamp to improve rural primary care for pediatric asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9(8):3091-3097.e1.
de la Garza Iga FJ, Mejia Alvarez M, Cockroft JD, Rabin J, Cordon A, Elias Rodas DM, et al. Using the project ECHO TM model to teach mental health topics in rural Guatemala: an implementation science-guided evaluation. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2023;69(8):2031–41.
Alkin M, Taut S. Unbundling evaluation use. Stud Educ Eval. 2003;29(1):1–12.
Varallyay NI, Langlois EV, Tran N, Elias V, Reveiz L. Health system decision-makers at the helm of implementation research: development of a framework to evaluate the processes and effectiveness of embedded approaches. Health Res Policy Syst. 2020;18(1):64.
McCabe KE, Wallace A, Crosland A. A model for collaborative working to facilitate knowledge mobilisation in public health. Evid Policy. 2015;11(4):559–76.
Gonzales R, Handley MA, Ackerman S, O’sullivan PS. A framework for training health professionals in implementation and dissemination science. Acad Med. 2012;87(3):271–8.
Edgar L, Herbert R, Lambert S, MacDonald JA, Dubois S, Latimer M. The joint venture model of knowledge utilization: a guide for change in nursing. Nurs Leadersh. 2006;9(2):41–55.
Stetler CB, Damschroder LJ, Helfrich CD, Hagedorn HJ. A Guide for applying a revised version of the PARIHS framework for implementation. Implement Sci. 2011;6(101258411):99.
Brennan SE, Cumpston M, Misso ML, McDonald S, Murphy MJ, Green SE. Design and formative evaluation of the policy liaison initiative: a long-term knowledge translation strategy to encourage and support the use of cochrane systematic reviews for informing. Evid Policy. 2016;12(1):25–52.
Hinchcliff R, Senserrick T, Travaglia J, Greenfield D, Ivers R. The enhanced knowledge translation and exchange framework for road safety: a brief report on its development and potential impacts. Inj Prev. 2017;23(2):114–7.
Ye J, Woods D, Bannon J, Bilaver L, Kricke G, McHugh M, et al. Identifying contextual factors and strategies for practice facilitation in primary care quality improvement using an informatics-driven model: framework development and mixed methods case study. JMIR Hum Factors. 2022;9(2): e32174.
Brangan J, Quinn S, Spirtos M. Impact of an evidence-based practice course on occupational therapist’s confidence levels and goals. Occup Ther Health Care. 2015;29(1):27–38.
Bonetti D, Johnston M, Pitts NB, Deery C, Ricketts I, Tilley C, et al. Knowledge may not be the best target for strategies to influence evidence-based practice: using psychological models to understand RCT effects. Int J Behav Med. 2009;16(3):287–93.
Buckley LL, Goering P, Parikh SV, Butterill D, Foo EKH. Applying a “stages of change” model to enhance a traditional evaluation of a research transfer course. J Eval Clin Pract. 2003;9(4):385–90.
Boyko JA, Lavis JN, Dobbins M, Souza NM. Reliability of a tool for measuring theory of planned behaviour constructs for use in evaluating research use in policymaking. Health Res Policy Syst. 2011;24(9):29.
Imani-Nasab MH, Yazdizadeh B, Salehi M, Seyedin H, Majdzadeh R. Validity and reliability of the Evidence Utilisation in Policymaking Measurement Tool (EUPMT). Health Res Policy Syst. 2017;15(1):66.
Dwan KM, McInnes P, Mazumdar S. Measuring the success of facilitated engagement between knowledge producers and users: a validated scale. Evid Policy. 2015;11(2):239–52.
Haynes A, Rowbotham S, Grunseit A, Bohn-Goldbaum E, Slaytor E, Wilson A, et al. Knowledge mobilisation in practice: an evaluation of the Australian Prevention Partnership Centre. Health Res Policy Sys. 2020;18(1):13.
Haines M, Brown B, Craig J, D’Este C, Elliott E, Klineberg E, et al. Determinants of successful clinical networks: the conceptual framework and study protocol. Implement Sci. 2012;7(101258411):16.
Ko LK, Jang SH, Friedman DB, Glanz K, Leeman J, Hannon PA, et al. An application of the science impact framework to the cancer prevention and control research network from 2014–2018. Prev Med. 2019;12: 105821.
Leeman J, Sommers J, Vu M, Jernigan J, Payne G, Thompson D, et al. An evaluation framework for obesity prevention policy interventions. Prev Chronic Dis. 2012;9(101205018):E120.
Pettman TL, Armstrong R, Waters E, Allender S, Love P, Gill T, et al. Evaluation of a knowledge translation and exchange platform to advance non-communicable disease prevention. Evid Policy. 2016;12(1):109–26.
Yearwood AC. Applying a logical theory of change for strengthening research uptake in policy: a case study of the Evidence Informed Decision Making Network of the Caribbean. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2018;42: e91.
Thomson D, Brooks S, Nuspl M, Hartling L. Programme theory development and formative evaluation of a provincial knowledge translation unit. Health Res Policy Syst. 2019;17(1):40.
Garad R, Kozica-Olenski S, Teede HJ. Evaluation of a center of research excellence in polycystic ovary syndrome as a large-scale collaborative research translation initiative, including evaluating translation of guideline impact. Semin Reprod Med. 2018;36(1):42–9.
Reddy S, Wakerman J, Westhorp G, Herring S. Evaluating impact of clinical guidelines using a realist evaluation framework. J Eval Clin Pract. 2015;21(6):1114–20.
Van Eerd D, Moser C, Saunders R. A research impact model for work and health. Am J Ind Med. 2021;64(1):3–12.
Yip O, Huber E, Stenz S, Zullig LL, Zeller A, De Geest SM, et al. A contextual analysis and logic model for integrated care for frail older adults living at home: The INSPIRE Project. Int J Integr Care. 2021;21(2):9.
Guo R, Bain BA, Willer J. Application of a logic model to an evidence-based practice training program for speech-language pathologists and audiologists. J Allied Health. 2011;40(1):e23–8.
PubMed Google Scholar
McDonald S, Turner T, Chamberlain C, Lumbiganon P, Thinkhamrop J, Festin MR, et al. Building capacity for evidence generation, synthesis and implementation to improve the care of mothers and babies in South East Asia: methods and design of the SEA-ORCHID Project using a logical framework approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2010;10(100968545):61.
Tabak RG, Khoong EC, Chambers DA, Brownson RC. Bridging research and practice: models for dissemination and implementation research. Am J Prev Med. 2012;43(3):337–50.
Wensing M, Grol R. Knowledge translation in health: how implementation science could contribute more. BMC Med. 2019;17(1):88.
Kreindler SA. Advancing the evaluation of integrated knowledge translation. Health Res Policy Sys. 2018;16(1):104.
Best A, Holmes B. Systems thinking, knowledge and action: towards better models and methods. Evid Policy. 2010;6(2):145–59.
van Mil HGJ, Foegeding EA, Windhab EJ, Perrot N, van der Linden E. A complex system approach to address world challenges in food and agriculture. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2014;40(1):20–32.
Wehrens R. Beyond two communities – from research utilization and knowledge translation to co-production? Public Health. 2014;128(6):545–51.
Ridde V, Pérez D, Robert E. Using implementation science theories and frameworks in global health. BMJ Glob Health. 2020;5(4): e002269.
Salter KL, Kothari A. Using realist evaluation to open the black box of knowledge translation: a state-of-the-art review. Implement Sci. 2014;9(1):115.
Van Eerd D, Cole D, Keown K, Irvin E, Kramer D, Gibson B, et al. Report on knowledge transfer and exchange practices: A systematic review of the quality and types of instruments used to assess KTE implementation and impact. Toronto: Institute for Work & Health; 2011 p. 130. https://www.iwh.on.ca/sites/iwh/files/iwh/reports/iwh_sys_review_kte_evaluation_tools_2011_rev.pdf
Dobbins M, Robeson P, Ciliska D, Hanna S, Cameron R, O’Mara L, et al. A description of a knowledge broker role implemented as part of a randomized controlled trial evaluating three knowledge translation strategies. Implement Sci. 2009;4(1):23.
Rychetnik L, Bauman A, Laws R, King L, Rissel C, Nutbeam D, et al. Translating research for evidence-based public health: key concepts and future directions. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2012;66(12):1187–92.
Weiner BJ, Lewis CC, Stanick C, Powell BJ, Dorsey CN, Clary AS, et al. Psychometric assessment of three newly developed implementation outcome measures. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):108.
Bhawra J, Skinner K. Examination of tools associated with the evaluation of knowledge uptake and utilization: a scoping review. Eval Program Plann. 2020;83: 101875.
Lane JP, Stone VI, Nobrega A, Tomita M. Level Of Knowledge Use Survey (LOKUS): a validated instrument for tracking knowledge uptake and use. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2015;217:106–10.
Proctor EK, Powell BJ, McMillen JC. Implementation strategies: recommendations for specifying and reporting. Implement Sci. 2013;8(1):139.
Albrecht L, Archibald M, Arseneau D, Scott SD. Development of a checklist to assess the quality of reporting of knowledge translation interventions using the Workgroup for Intervention Development and Evaluation Research (WIDER) recommendations. Implement Sci. 2013;8(1):52.
Bragge P, Grimshaw JM, Lokker C, Colquhoun H, Albrecht L, Baron J, et al. AIMD - a validated, simplified framework of interventions to promote and integrate evidence into health practices, systems, and policies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17(1):38.
Kastner M, Makarski J, Hayden L, Lai Y, Chan J, Treister V, et al. Improving KT tools and products: development and evaluation of a framework for creating optimized, Knowledge-activated Tools (KaT). Implement Sci Commun. 2020;1(1):47.
Pinnock H, Barwick M, Carpenter CR, Eldridge S, Grandes G, Griffiths CJ, et al. Standards for Reporting Implementation Studies (StaRI) Statement. BMJ. 2017;6(356): i6795.
Lokker C, McKibbon KA, Colquhoun H, Hempel S. A scoping review of classification schemes of interventions to promote and integrate evidence into practice in healthcare. Implement Sci. 2015;10(1):27.
Hoffmann TC, Glasziou PP, Boutron I, Milne R, Perera R, Moher D, et al. Better reporting of interventions: template for intervention description and replication (TIDieR) checklist and guide. BMJ. 2014;7(348): g1687.
Wilson PM, Sales A, Wensing M, Aarons GA, Flottorp S, Glidewell L, et al. Enhancing the reporting of implementation research. Implement Sci. 2017;12(1):13.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Julie Desnoyers for designing and implementing the search strategy, Gabrielle Legendre for her contribution in the screening phase and Karine Souffez and Caroline Tessier for their input during the project.
This project was supported by an Insight Grant from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRC) and by the Équipe RENARD (FRQ-SC). The funding bodies had no role in the conduct of this scoping review.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Business Administration, Université TÉLUQ, Montreal, Canada
Saliha Ziam & Laura Justine Chouinard
Department of School and Social Adaptation Studies, Faculty of Education, Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Canada
Sèverine Lanoue, Esther McSween-Cadieux, Julie Lane & Ollivier Prigent
Department of Psychology, Université du Québec à Montréal, Montreal, Canada
Mathieu-Joël Gervais
Centre RBC d’expertise Universitaire en Santé Mentale, Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Canada
School of Rehabilitation, Faculty of Medicine, Université de Montréal, Montreal, Canada
Dina Gaid & Quan Nha Hong
Department of Psychology, Université de Montréal, Montreal, Canada
Christian Dagenais
Université Paris Cité, IRD (Institute for Research on Sustainable Development, CEPED, Paris, France
Valéry Ridde
Institute of Health and Development (ISED), Cheikh Anta Diop University, Dakar, Senegal
Public Health Intelligence and Knowledge Translation Division, Public Health Agency of Canada, Ottawa, Canada
Emmanuelle Jean
Coordinator of the Interregional Consortium of Knowledge in Health and Social Services (InterS4), Rimouski, Canada
France Charles Fleury
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
SZ, MJG, EMC, JL, CD, EJ, KS, VR and CT were involved in developing and designing the scoping review. EMC, MJG and GL (collaborator) screened articles in duplicate. SL, DG, LJC and OP extracted data from the included articles. SL and DG synthesized the data. SL, SZ and EMC drafted the manuscript. SZ led the project, supervised and assisted the research team at every stage, and secured the funding. All authors provided substantive feedback and approved the manuscript prior to submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Saliha Ziam .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Keywords and search strategy.
Additional file 2.
Summary of included articles.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ziam, S., Lanoue, S., McSween-Cadieux, E. et al. A scoping review of theories, models and frameworks used or proposed to evaluate knowledge mobilization strategies. Health Res Policy Sys 22 , 8 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-023-01090-7
Download citation
Received : 16 June 2023
Accepted : 07 December 2023
Published : 10 January 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-023-01090-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Knowledge translation
- Scoping review
Health Research Policy and Systems
ISSN: 1478-4505
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 02 January 2022
The roles, activities and impacts of middle managers who function as knowledge brokers to improve care delivery and outcomes in healthcare organizations: a critical interpretive synthesis
- Faith Boutcher 1 ,
- Whitney Berta 2 ,
- Robin Urquhart 3 &
- Anna R. Gagliardi 4
BMC Health Services Research volume 22 , Article number: 11 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
3903 Accesses
5 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Middle Managers (MMs) are thought to play a pivotal role as knowledge brokers (KBs) in healthcare organizations. However, the role of MMs who function as KBs (MM KBs) in health care is under-studied. Research is needed that contributes to our understanding of how MMs broker knowledge in health care and what factors influence their KB efforts.
We used a critical interpretive synthesis (CIS) approach to review both qualitative and quantitative studies to develop an organizing framework of how MMs enact the KB role in health care. We used compass questions to create a search strategy and electronic searches were conducted in MEDLINE, CINAHL, Social Sciences Abstracts, ABI/INFORM, EMBASE, PubMed, PsycINFO, ERIC and the Cochrane Library. Searching, sampling, and data analysis was an iterative process, using constant comparison, to synthesize the results.
We included 41 articles (38 empirical studies and 3 conceptual papers) that met the eligibility criteria. No existing review was found on this topic. A synthesis of the studies revealed 12 MM KB roles and 63 associated activities beyond existing roles hypothesized by extant theory, and we elaborate on two MM KB roles: 1) convincing others of the need for, and benefit of an innovation or evidence-based practice; and 2) functioning as a strategic influencer. We identified organizational and individual factors that may influence the efforts of MM KBs in healthcare organizations. Additionally, we found that the MM KB role was associated with enhanced provider knowledge, and skills, as well as improved organizational outcomes.
Our findings suggest that MMs do enact KB roles in healthcare settings to implement innovations and practice change. Our organizing framework offers a novel conceptualization of MM KBs that advances understanding of the emerging KB role that MMs play in healthcare organizations. In addition to roles, this study contributes to the extant literature by revealing factors that may influence the efforts and impacts of MM KBs in healthcare organizations. Future studies are required to refine and strengthen this framework.
Trial registration
A protocol for this review was not registered.
Peer Review reports
Contributions to the literature
MMs may play an important KB role in healthcare organizations.
Additional support for the MM KB role may help enhance quality of care in healthcare settings.
An improved understanding of MM KBs will contribute to this nascent area of inquiry in health care.
Health systems are under increasing pressure to improve performance including productivity, quality of care, and efficiency in service delivery. To promote optimal performance, health systems hold healthcare organizations such as hospitals accountable for the quality of care they provide through accountability agreements tied to performance targets [ 1 , 2 ]. Despite such incentives, healthcare organizations face considerable challenges in providing high-quality care and research continues to show that the quality of hospital-based care is less than ideal [ 3 , 4 , 5 ]. Some researchers contend that this is attributed, in part, to the challenges that healthcare organizations face when integrating new knowledge into practice. Some challenges include dedicating sufficient resources to adopt or implement evidence-informed innovations that enhance service delivery and optimize patient health and outcomes [ 6 ].
Healthcare organizations use knowledge translation (KT) approaches to promote the use of evidence-based practices intended to optimize quality of care. The use of knowledge brokers (KBs) is one such approach. KBs are defined as the human component of KT who work collaboratively with stakeholders to facilitate the transfer and exchange of knowledge in diverse settings, [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. KBs that facilitate the use of knowledge between people or groups have been referred to as opinion leaders, facilitators, champions, linking agents and change agents whose roles can be formal or informal [ 10 , 11 ]. These “influencer” roles are based on the premise that interpersonal contact improves the likelihood of behavioral change associated with use or adoption of new knowledge [ 12 ]. Research shows that KBs have had a positive effect on increasing knowledge and evidence-based practices among clinicians in hospitals, and on advocating for change on behalf of clinicians to executives [ 13 , 14 , 15 ]. However, greater insight is needed on how to equip and support KBs, so they effectively promote and enable clinicians to use evidence-based practices that improve quality of care [ 13 , 16 , 17 ].
Middle managers (MMs) play a pivotal role in facilitating high quality care and may play a brokerage role in the sharing and use of knowledge in healthcare organizations [ 18 , 19 ]. MMs are managers at the mid-level of an organization supervised by senior managers, and who, in turn, supervise frontline clinicians [ 20 ]. MMs facilitate the integration of new knowledge in healthcare organizations by helping clinicians appreciate the rationale for organizational changes and translating adoption decisions into on-the-ground implementation strategies [ 18 , 19 ]. Current research suggests that MMs may play an essential role as internal KBs because of their mid-level positions in healthcare organizations. Some researchers have called for a deeper understanding of the MM role in knowledge brokering, including how MMs enact internal KB roles [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 21 ].
To this end, further research is needed on who assumes the KB role and what they do. Prior research suggests that KBs may function across five key roles: knowledge manager, linking agent, capacity builder, facilitator, and evaluator, but it is not clear whether these roles are realized in all healthcare settings [ 7 , 21 , 22 ]. KBs are often distinguished as external or internal to the practice community that they seek to influence, and most studies have focused on external KBs with comparatively little research focused on the role of internal KBs [ 7 , 9 , 17 , 23 , 24 ]. To address this gap, we will focus on internal KBs (MMs) who hold a pivotal position because their credibility and detailed knowledge of local context allows them to overcome the barriers common to external KBs. One such barrier is resistance to advice from external sources unfamiliar with the local context [ 25 ].
With respect to what KBs do, two studies explored KB roles and activities, and generated frameworks that describe KB functions, processes, and outcomes in health care [ 7 , 22 ]. However, these frameworks are not specific to MMs and are limited in detail about KB roles and functions. This knowledge is required by healthcare organizations to develop KB capacity among MMs, who can then enhance quality of care. Therefore, the focus of this study was to synthesize published research on factors that influence the KB roles, activities, and impact of MMs in healthcare settings. In doing so, we will identify key concepts, themes, and the relationships among them to generate an organizing framework that categorizes how MMs function as KBs in health care to guide future policy, practice, and research.
We used a critical interpretive synthesis (CIS) to systematically review the complex body of literature on MM KBs. This included qualitative, quantitative, and theoretical papers. CIS offers an iterative, dynamic, recursive, and reflexive approach to qualitative synthesis. CIS was well-suited to review the MM KB literature than traditional systematic review methods because it integrates findings from diverse studies into a single, coherent framework based on new theoretical insights and interpretations [ 26 , 27 ]. A key feature that distinguishes CIS from other approaches to interpretive synthesis is the critical nature of the analysis that questions the way studies conceptualize and construct the topic under study and uses this as the basis for developing synthesizing arguments [ 26 ]. We ensured rigor by complying with the Enhancing Transparency in Reporting the Synthesis of Qualitative Research (ENTREQ) criteria (Additional file 1 ) and other criteria of trustworthiness [ 28 , 29 ]. We did not register a protocol for this review.
With a medical librarian, we developed a search strategy (Additional file 2 ) that complied with the evidence-based checklist for peer review of electronic search strategies [ 30 ]. We included Medical Subject Headings and keywords that captured the concepts of MMs (e.g., nurse administrator, manager), explicit or non-explicit KB roles (e.g., diffusion of innovation, dissemination, broker, and facilitator), evidence-based practice (e.g., knowledge, evidence) and setting (e.g., hospital, healthcare, or health care). We searched MEDLINE, CINAHL, Social Sciences Abstracts, ABI/INFORM, EMBASE, PubMed, PsycINFO, ERIC, and the Cochrane Library from January 1, 2001, to August 14, 2020. We searched from 2001 onward because the field of KT did not substantially investigate KBs until 2001 [ 7 , 21 ]. We reviewed the reference lists of eligible articles for additional relevant studies not identified by searches. As is typical of CIS, this was an iterative process allowing search terms to be expanded to optimize search results [ 26 , 31 ].
Eligibility
We generated eligibility criteria based on the PICO framework (population, intervention, comparisons, and outcomes) (Additional file 3 ). Populations refer to MMs functioning as KBs in hospitals or other healthcare settings but did not necessarily use those labels. Because the MM literature is emergent, we included settings other than hospitals (e.g., public health department, Veteran Affairs Medical Centres). We included studies involving clinical and non-clinical administrators, managers, directors, or operational leaders if those studies met all other inclusion criteria. The intervention of interest was how MM KBs operated in practice for the creation, use and sharing of knowledge, implementation of evidence-based practice(s), or innovation implementation. Study comparisons may have evaluated one or more MM KB roles, approaches and associated barriers, enablers and impacts alone or in comparison with other types of approaches for the sharing or implementation of knowledge, evidence, evidence-based practices, or innovations. Outcomes included but were not limited to MM KB effectiveness (change in knowledge, skills, policies and/or practices, care delivery, satisfaction in role), behaviors, and outcomes. Searches were limited to English language quantitative, randomized, or pragmatic controlled trials, case studies, surveys, quasi-experimental, qualitative, or mixed methods studies and conceptual papers. Systematic reviews were not eligible, but we screened references for additional eligible primary studies. Publications in the form of editorials, abstracts, protocols, unpublished theses, conference proceedings were not eligible.
FB and ARG independently screened 50 titles and abstracts according to the eligibility criteria and compared and discussed results. Based on discrepancies, they modified the eligibility criteria and discussed how to apply them. Thereafter, FB screened all remaining titles, and discussed all uncertainties with ARG and the research team. FB retrieved all potentially eligible articles. FB and ARG independently screened a sample of 25 full-text articles, and again discussed selection discrepancies to further standardize how eligibility criteria were applied. Thereafter, FB screened all remaining full-text items.
Quality appraisal
We employed quality appraisal tools relevant to different research designs: Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) [ 32 ], the Good Reporting of a Mixed Methods Study (GRAMMS) tool [ 33 ], Critical Appraisal of a Questionnaire Study [ 34 ], Revised Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) tool [ 35 ], and the Critical Appraisal Checklist for Quasi-Experimental Studies [ 36 ]. FB and ARG independently assessed and compared the quality of a sample of seven studies each. Thereafter, FB assessed the quality of the remaining 24 studies.
Data extraction
We developed a data extraction form to extract information on study characteristics (date of publication, country, purpose, research design) and MM KB characteristics, roles, activities, enablers, barriers, and impacts. To pilot test data extraction, FB and ARG independently extracted data from the same 25 articles, then compared results and discussed how to refine data extraction. Thereafter, FB extracted data from remaining articles, which was independently checked by ARG, and then reviewed by the research team.
Data analysis
FB and ARG conducted an initial reading and coding of a sample of articles independently. Codes were assigned to significant elements of data within the results and conclusions sections of the eligible articles and grouped into relevant categories with shared characteristics and organized into preliminary themes. This was an iterative process that involved ongoing consultation with the research team, who provided feedback on the codes and themes.
We created a matrix of MM KB roles and activities from extant MM and KB theory [ 7 , 18 , 22 , 37 ] and deductively mapped themes from included studies with the matrix to help inform the analysis and interpretation of our findings. As per CIS methodology, we developed an integrative grid (matrix table) where themes pertaining to MM KB roles and activities formed columns, and themes mapped to those roles/activities from individual studies formed rows [ 31 ]. The grid helped us integrate the evidence across studies and explore relationships between concepts and themes to inductively develop synthetic constructs [ 31 , 38 ]. Using a constant comparative approach, we critiqued the synthetic constructs with the full sample of papers to identify conceptual gaps in the available evidence in relation to our aims, and to ensure that the constructs were grounded in the data [ 31 , 38 ]. Our interpretive reflections on MM KB roles, activities, factors, and impacts led us to develop “synthetic arguments” and we used the arguments to structure our findings (attributes, roles, activities, impacts, enablers, barriers) in an organizing framework to capture our interpretation of how MMs function as KBs in healthcare organizations. We used NVivo 12 software to assist with data analysis.
Search results
The initial search yielded 9936 articles. Following removal of duplicates, 9760 titles were not eligible, and 176 items were retrieved as potentially relevant. Of those, 135 were excluded because the study design was ineligible (25), they did not examine MMs (27) or MM KBs (34), were not focused on the evaluation of an MM KB role (39), were editorials (4), or the publication was a duplicate (6). We included 41 articles for review (Fig. 1 PRISMA flow diagram). Additional file 4 includes all data extracted from included studies.
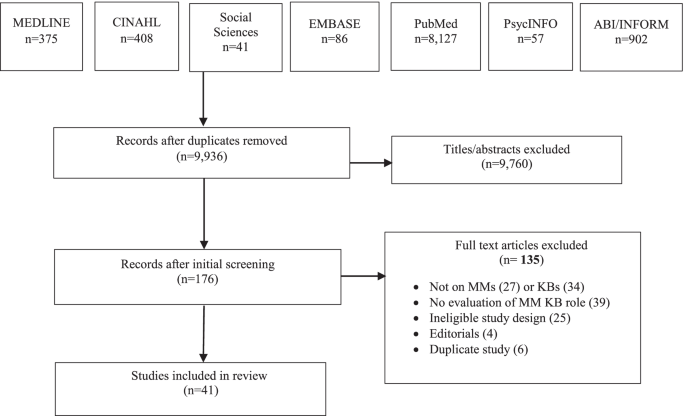
PRISMA flow diagram
Study characteristics
Eligible articles were published between 2003 and 2019. Three (7.3%) were conceptual and 38 (92.7%) were empirical studies. Conceptual articles discussed MM and KB theoretical constructs. Table 1 summarizes study characteristics. Studies examined the impacts of change efforts (47.3%), barriers to practice change (34.2%), and evaluation of KB interventions (18.4%). Most were qualitative (52.6%) and conducted in the United States (36.8%). Of study participants (34.2%) were MMs. In most studies, participants were nurses (63.1%) or allied health (13.2%) and based in hospitals (68.4%). Otherwise, (31.6%) were based in public health or occupational health departments, primary health care centers, Veterans Affairs Medical Centres, community care, and a senior’s care facility.
Quality assessment findings
A critical analysis of the included studies revealed issues related to research design, varying from data collected from heterogeneous healthcare settings and diverse types of MMs to the type of analyses completed (e.g., qualitative, mixed methods), to the strength of conclusions drawn from a few studies’ results (e.g., correlational, or causal). Fifteen (39.5%) studies met the criteria for quality. Twenty-three (60.5%) studies had minor methodological limitations (e.g., no research paradigm identified in qualitative studies, and mixed methods studies did not describe the integration of the two methods) (Additional file 5 ). These methodological flaws did not warrant exclusion of any studies as they provided relevant insights regarding the emerging framework.
MM KB attributes
Seven (18.4%) studies described MM KB attributes (Table 2 ). Of those, 4 (10.5%) identified MM attributes, 2 (5.2%) identified KB attributes, and 1 (2.6%) identified nurse knowledge broker attributes. MM KBs were described as confident, enthusiastic, and experienced with strong research skills [ 41 , 45 ]. They were also responsive and approachable, with an understanding of the complexity of an innovation and the organizational context [ 42 , 43 , 44 ].
MM KB roles and activities
Table 3 summarizes themes pertaining to roles and activities. A total of 63 activities were grouped in the following 12 MM KB roles: (1) gather data, (2) coordinate projects, (3) monitor and evaluate the progress of a project, (4) adjust implementation to organizational context, (5) disseminate information, (6) facilitate networks, (7) bridge the evidence-to-practice gap, (8) engage stakeholders, (9) convince others of the need for, and benefit of a project, (10) coach staff, (11) provide tools and resources and (12) function as a strategic influencer. Roles did not differ among MM KBs in hospital and non-hospital settings.
Table 4 summarizes the frequency of each of the 12 MM KB roles across included studies. The two most common MM KB roles were to monitor and evaluate the progress of a project (14, 36.8%) [ 40 , 41 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 54 , 57 , 60 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 ] and to convince others of the need for, and benefit of a project (12, 31.6%) [ 46 , 47 , 48 , 50 , 51 , 55 , 58 , 61 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 ]. For example, MM KBs played an important role in monitoring the progress of projects to evaluate and reinforce practice change [ 41 , 50 ]. To convince others of the need for, and benefit of a project and to promote staff buy-in, they held ongoing conversations with staff to help them understand the rationale for change, reinforce the message, and encourage staff to consistently maintain the innovations on their units [ 46 , 48 , 66 ]. The least common MM KB role was project coordination (4, 10.5%) [ 39 , 47 , 48 , 56 ].
Several of the identified MM KB roles aligned with five KB roles in prior published frameworks [ 7 , 22 ] and MM role theory [ 18 , 37 ] (Table 5 ). For example, 31 (81.6%) studies described MM KB roles of gather data, project coordination, disseminate information , and adjust implementation to organizational context , which aligned with the roles and activities of a KB knowledge manager. Twenty-nine (76.3%) studies described the MM KB roles of provide tools and resources, convince others of the need for and benefit of a project, and coach staff , which aligned with the roles and activities of a KB capacity builder. We found overlap between the MM KB roles and the four hypothesized roles in MM role theory: (1) disseminate and obtain information, (2) adapt information and the innovations, (3) mediate between strategy and day to day activities, and (4) selling innovation implementation) [ 18 , 37 ]. For example, we found that as capacity builders, MM KBs also mediated between strategy and day-to-day activities such as coaching staff and providing resources, and in the role of knowledge manager, MM KBs obtained, diffused, and synthesized information [ 18 , 37 ].
While MM KB roles identified in included studies aligned with the five previously identified KB roles, the CIS approach we employed identified 12 distinct roles that were further characterized based on corresponding activities associated with each of the 12 roles. Therefore, while this research agrees with prior work on MM KB roles, it represents a robust framework of MM KB roles and activities by elaborating the complexity of MM KB roles and activities.
We fully described two roles compared with prior frameworks: to convince others of the need for and benefit of a project, and function as a strategic influencer. To convince others of the need for and benefit of a project (e.g., a quality improvement, best practice guideline implementation, or innovation), MM KBs used tactics such as role modelling their commitment, providing the rationale for the change, being enthusiastic about its adoption, offering positive reinforcement, and providing emotional support [ 47 , 50 , 58 ]. The role of strategic influencer featured in 7 (18.4%) studies [ 39 , 48 , 52 , 56 , 62 , 65 , 68 ]. For example, MM KBs were influential at the executive level of the hospital, advocating for innovations among less involved team members and administrators, including the hospital board, were members of organizational decision-making groups for strategic planning, and served as an authoritative contact for initiatives.
Factors that influence MMs knowledge brokering
Table 6 summarizes the enablers and barriers of MM KB roles and activities, organized as individual or organizational factors. We identified four enablers at the organizational level: senior management support, availability of resources, engaged staff, and alignment to strategy. The most common was senior management support, featured in 12 (32.0%) studies. We found that senior management support enhanced the commitment of MM KBs to innovation implementation [ 16 , 17 , 19 , 44 , 45 , 52 , 61 , 63 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 ]. For example, senior managers empowered and supported MM KBs to make decisions by ensuring that the necessary structures and resources were in place, and by conveying that the implementation was an organizational priority [ 66 , 68 ]. We identified three individual-level facilitators: training and mentorship, personal attributes, and experience in the MM role. The most common facilitator was training and mentorship, featured in 8 (21.1%) studies. We found that training and mentorship with more experienced managers was important to the success of MM KBs and their projects, especially if they were new to their role [ 16 , 17 , 19 , 41 , 42 , 48 , 54 , 68 ].
Studies reported more barriers ( n = 8) than enablers ( n = 7). We found four organizational barriers: a lack of resources, lack of senior management support, staff resistance, and a lack of time. The most common barriers were lack of resources in 12 (32.0%) studies and lack of time in 12 (32.0%) studies. A lack of resources (budget constraints, limited staff) made it challenging for MM KBs to move their projects forward [ 39 , 42 , 44 , 47 , 52 , 55 , 57 , 64 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 ]. For example, inadequate funds interfered with obtaining appropriate resources and undermined the feasibility of implementing projects [ 47 , 55 ]. In addition, staffing issues created difficulty in engaging staff in project work and low staffing levels limited capacity to provide desired standards of care [ 42 , 64 ]. Additionally, a lack of protected time for data collection or other project work was identified as a significant barrier to implementing projects [ 17 , 19 , 39 , 42 , 44 , 47 , 52 , 55 , 57 , 64 , 68 , 71 ]. MM KBs also lacked the time to nurture, support and adequately coach staff [ 39 , 55 ].
We identified four individual-level barriers: lack of formal training, dissatisfaction with work life balance, being caught in the middle, and professional boundaries. The most common barriers were lack of formal training (8, 21.1%) and dissatisfaction with work life balance (8, 21.1%). For example, a lack of formal training resulted in MM KBs being unprepared for managerial roles and without the knowledge and skills to promote effective knowledge brokering and knowledge transfer with end users [ 17 , 39 , 41 , 42 , 55 , 57 , 69 , 71 ]. We also found that heavy workloads and conflicting priorities left MM KBs often dissatisfied with their work life balance and hindered their ability to successfully complete projects [ 42 , 44 , 51 , 52 , 57 , 61 , 64 , 71 ]. For example, because of multiple responsibilities and conflicting priorities, MM KBs were often pulled away to address problems or were so absorbed by administrative tasks that they had no time to complete project responsibilities [ 44 , 64 ].
Impact on service delivery and outcomes
Eight (21.1%) studies showed that MM KBs had some impact on organizational and provider outcomes [ 16 , 40 , 43 , 44 , 47 , 56 , 62 , 67 ]. One (2.6%) study reported that practice changes were greater when associated with higher MM leadership scores (OR 1.92 to 6.78) and when MMs worked to help create and sustain practice changes [ 40 ]. One (2.6%) study reported the impact of senior managers’ implementation of an evidence-based Hospital Elder Life Program on administrative outcomes (e.g., reduced length of stay and cost per patient), clinical outcomes (e.g., decreased episodes of delirium and reduced falls), and provider outcomes (e.g., increased knowledge and satisfaction) [ 67 ].
Two (5.3%) studies reported the impact of a Clinical Nurse Leader role on care processes at the service level in American hospitals. Benefits were evident in administrative outcomes such as RN hours per patient day (increased from 3.76 to 4.07) and in reduced surgical cancellation rates from 30 to 14%. There were also significantly improved patient outcomes in dementia care, pressure ulcer prevention, as well as ventilator-assisted pneumonia [ 56 , 62 ]. One (2.6%) study reported financial savings [ 56 ].
Four (10.5%) studies reported the effect of a KB strategy on health professionals’ knowledge, skills, and practices [ 16 , 43 , 44 , 47 ]. For example, Traynor et al. [ 44 ] found that participants who worked closely with a KB showed a statistically significant increase in knowledge and skill (average increase of 2.8 points out of a possible 36 (95% CI 2.0 to 3.6, p < 0.001) from baseline.
Organizing framework of MM KBs in healthcare organizations
We sought to capture the roles, activities, enablers, barriers and impacts of MM KBs across diverse healthcare settings in an organizing framework (Fig. 2 Organizing framework of MMs who function as knowledge brokers in healthcare organizations). From our interpretation of the published evidence, the findings across studies were categorized into 12 roles and 63 associated activities to represent specific ways in which MM KBs described their roles and activities during project implementation. Influencing factors were categorized into individual and organizational enablers and barriers that influence the efforts of MM KBs in healthcare organizations. While attributes were categorized as enablers, their level of importance as enablers emerged from our synthesis in how they operated in practice. The types of outcomes that we examined also varied between changes in care practice, processes, and competencies which we constructed into provider and organizational outcomes. Our emergent insights were used to construct four synthesizing arguments from the available literature: (1) MM KBs have attributes that equip and motivate them to implement practice change and innovations in healthcare organizations, (2) MMs enact KB roles and activities in healthcare organizations, (3) enablers and barriers influence the knowledge brokering efforts of MMs in healthcare settings; and (4) MM KB efforts impact healthcare service delivery. These synthesizing arguments were used to structure the organizing framework presented in Fig. 2 , which depicts how MM function as KBs in healthcare organizations and their impact on service delivery.
Organizing framework of MMs who function as knowledge brokers in healthcare organizations
We conducted a CIS to synthesize published research on factors that influence the roles, activities, and impacts of MM KBs in healthcare organizations. As per CIS, our output was an organizing framework (Fig. 2 ) that promotes expansive thinking about and extends knowledge of MM KBs in healthcare settings. We identified 63 activities organized within 12 distinct MM KB roles, which is far more comprehensive than any other study [ 7 , 22 ]. We build on prior frameworks and characterize further the roles of strategic influencer and convincing others of the need for, and benefit of an innovation or evidence-based practice. We identified organizational and individual enablers and barriers that may influence the efforts and impact of MM KBs in health care. Of note, a key enabler was senior leadership support while a key barrier for MM KBs was a lack of formal training in project implementation. Such factors should be closely considered when looking at how to strengthen the MM KB role in practice. Furthermore, we found that the MM KB role was associated with enhanced provider knowledge and skills, as well as improved clinical and organizational outcomes.
We offer a novel conceptualization of MM KBs in healthcare organizations that has, thus far, not been considered in the literature. Our theoretical insights (summarized in Fig. 2 ) are an important first step in understanding how individual and organizational factors may influence how MMs enact KB roles, and the impact they have on service delivery and associated outcomes. We found that the many MM KB roles and activities corresponded to the characterization of KB roles in the literature and substantiated MM role theory. Our findings corroborate previous studies and systematic reviews by confirming that MMs function as KBs and build on the MM and KB theoretical constructs previously identified in the literature [ 7 , 18 , 21 , 22 , 37 , 46 , 48 ]. Building on Birken and colleagues’ theory [ 37 ], we found significant overlap between MM and KB roles and activities. Figure 2 helps to define and analyze the intersection of these roles while distinguishing MM KB roles and activities more clearly from other administrative roles.
We contend that Fig. 2 has applicability across a range of healthcare settings and may be used by hospital administrators, policymakers, service providers, and researchers to plan projects and programs. It may be used as a resource in strategic planning, to re-structure clinical programs, build staff capacity, and optimize HR practices. For example, Fig. 2 could be used as a foundation to establish goals, objectives, or key performance indicators for a new or existing clinical program; refine job postings for MM roles to encompass optimal characteristics of candidates to enable KB activities; or identify new evaluation criteria for staff performance and training gaps in existing HR practices. It could also help decision makers take on pilot projects to formalize the KB role in healthcare.
Figure 2 is intended to foster further discussion of the role that MMs play in brokering knowledge in healthcare settings. It can be modified for specific applications, although we encourage retaining the basic structure (reflecting the synthesizing arguments). For example, the factors may change depending on specific localized healthcare contexts (i.e., acute care versus long-term care, or rehabilitation). Although the use of our framework in practice has yet to be evaluated, it may be strengthened with the results of additional mixed methods studies examining MM KBs as well as quasi-experimental studies applying adapted HR practices based upon our framework. As more studies are reported in the literature, the roles, activities, factors, and outcomes can be further refined, organized, and contextualized. Figure 2 can also be used as a guide for future studies examining how MMs enact the KB role across healthcare settings and systems, disciplines, and geographic locations.
Our synthesis provides new insights into the roles of MM KBs in healthcare settings. For example, we further elucidate two MM KB roles: 1) functioning as a strategic influencer; and 2) convincing others of the need for, and benefit of an innovation or evidence-based practice. These are important roles that MM KBs enact when preparing staff for implementation and corroborate Birken et al.’s hypothesized MM role of selling innovation implementation [ 18 , 37 ]. Our findings validate the organizational change literature that emphasizes the important information broker role MMs play in communicating with senior management and helping frontline staff achieve desired changes by bridging information gaps that might otherwise impede innovation implementation [ 37 ]. Our new conceptualization of how MM KBs navigate and enact their roles, and the impact they may have on service delivery and associated outcomes extends the findings of recent studies. These studies found that the role of MMs in organizational change is evolving and elements such as characteristics and context may influence their ability to facilitate organizational adaptation and lead the translation of new ideas [ 53 , 72 , 73 ]. However, further research is required to test and further explicate these relationships in the broader context of practice change.
Our synthesis both confirms and extends previous research by revealing organizational and individual factors that both enabled and hindered MM KBs efforts in healthcare organizations. An important organizational factor in our study was having senior management support. We found that MM KBs who had healthy supportive working relationships with their senior leaders led to project success. This support was critical because without it they experienced significant stress at being “caught in the middle” trying to address the needs of staff while also meeting the demands of senior management. Recent studies confirm our finding that senior management engagement is essential to MM KBs’ ability to implement innovations and underscores the need for senior leaders to be aware of, and acknowledge, the impact that excessive workload, competing demands, and role stress can play in their effectiveness [ 19 , 74 ].
The personal attributes of MM KBs as well as their level of experience were both important factors in how they operated in practice. We identified that key attributes of MM KBs contributed to their ability to drive implementation of initiatives and enhanced staff acceptance and motivation to implement practice change [ 75 , 76 ]. Our findings corroborate recent studies that highlight how the key attributes of effective champions (those that are intrinsic and cannot be taught) [ 77 , 78 , 79 ] may contribute to their ability to lead teams to successful implementation outcomes in healthcare organizations [ 80 , 81 , 82 ]. We also found that experienced MM KBs were well trained, knowledgeable, and better prepared to understand the practice context than novice MM KBs, but a lack of formal training in project implementation was an impediment for both. This emphasizes the importance of providing opportunities for professional development and training to prepare both novice and experienced MM KBs to successfully implement practice change. Our findings contribute to the growing knowledge base regarding what makes an effective MM KB. However, future research should focus on generating evidence, not only on the attributes of MM KBs, but also on how those attributes contribute to their organizational KB roles as well as the relationships among specific “attributes” and specific KB roles. More research is also needed to better understand how and what skills can be taught to boost the professional growth of MM KBs in health care.
Organizational theory and research may provide further insight into our findings and guidance for future research on the role of MM KBs in healthcare organizations. For example, the literature suggests that by increasing MMs’ appreciation of evidence-based practice, context, and implementation strategies may enhance their role in implementing evidence-based practices in healthcare organizations [ 18 , 83 , 84 ]. We found that MM KBs’ commitment to the implementation of an evidence-based project was influenced by the availability of resources, alignment with organizational priorities, a supportive staff and senior leadership. Extending from organizational theory and research, further investigation is needed to explore the nature of the relationship between these factors and the commitment of MM KBs to evidence-based practice implementation and subsequent outcomes.
When assessing the impact of MM KBs in hospitals, we found some evidence of changes in organizational and provider outcomes, suggesting MM KB impact on service delivery. Given that the available outcome data were limited, associational in nature, or poorly evaluated, it was challenging to identify strong thematic areas. Like our study, several systematic reviews also reported the lack of available outcome data [ 7 , 18 , 21 ]. This highlights an important area for research. Future research must include evaluation of the effectiveness of MM KBs and establish rigorous evidence of their impact on service delivery.
Our findings have important implications for policy and practice. MMs are an untapped KB resource who understand the challenges of implementing evidence-based practices in healthcare organizations. Both policy makers and administrators need to consider the preparation and training of MM KBs. As with other studies, our study found that providing MM KBs with opportunities for training and development may yield a substantial return on investment in terms of narrowing evidence-to-practice gaps in health care [ 48 ]. Thus, an argument can be made for recruiting and training MM KBs in health care. However, the lack of guidance on how to identify, determine and develop a curriculum to prepare MM KBs requires more research.
Our synthesis revealed numerous activities associated with 12 MM KB roles providing further insight into the MM role in healthcare settings. Our list of 63 activities (Table 2 ) has implications for practice. We found that MMs enact numerous KB roles and activities, in addition to their day-to day operational responsibilities, highlighting the complexity of the MM KB role. Senior leaders and administrators must acknowledge this complexity. A greater understanding of these KB roles and activities may lead to MM implementation effectiveness, to sustainable MM staffing models, and to organizational structures to support the KB efforts that many MMs are already doing informally. For example, senior leaders and administrators need to take the MM KB role seriously and explicitly include KB activities as a core function of existing MM job descriptions. To date, the KB role and associated activities are not typically or explicitly written into the formal job descriptions for MMs in healthcare settings, as their focus is primarily on operational responsibilities. A formal job description for MM KBs would improve the KB capacity of MMs by giving them the permission and recognition to implement KB-related functions. Our findings inform future research by more clearly articulating the MM KB roles and activities that may be essential to the implementation of evidence-based practice and highlights a much-needed area for future work.
Our study features both strengths and weaknesses. One strength in using CIS methodology was the ability to cast a wide net representing a range of research designs of included studies. This included studies in which MMs were required to be KBs by senior leaders or functioned explicitly as KBs. This enabled us to identify and include diverse studies that made valuable theoretical contributions to the development of an emerging framework, which goes beyond the extant theories summarized in the literature to date [ 18 ]. In contrast to prior systematic reviews of MM roles in implementing innovations [ 18 ], the CIS approach is both systematic and iterative with an interpretive approach to analysis and synthesis that allowed us to capture and critically analyze an in-depth depiction of how MMs may enact the KB role in healthcare organizations. Our synthesis also revealed numerous activities associated with the 12 identified MM KB roles. The resulting theoretical insights were merged into a new organizing framework (Fig. 2 ). These insights are an important first step in understanding how individual and organizational factors may influence how MMs enact KB roles, and the impact they have on service delivery.
Although CIS is an innovative method of synthesizing the literature and continues to evolve, it does have limitations. CIS has yet to be rigorously evaluated [ 85 , 86 ]. While there is some precedent guiding the steps to conduct a CIS, one weakness is that CIS is difficult to operationalize. Another weakness is that the steps to conduct CIS reviews are still being refined and can lack transparency. Therefore, we used standardized, evidence-based checklists and reporting tools to assess transparency and methodological quality, and an established methodology for coding and synthesis. We provided an audit trail of the interpretive process in line with the ENTREQ guidance. Still, there was a risk of methodological bias [ 28 , 85 , 86 ]. Another weakness of qualitative synthesis is its inability to access first order constructs that is the full set of participants’ accounts in each study. As reviewers, we can only work with the data provided in the papers and, therefore, the findings of any review cannot assess primary datasets [ 31 ]. Study retrieval was limited to journals that are indexed in the databases that were searched. We did not search the grey literature, assuming that most empirical research on MM KBs would be found in the indexed databases. Finally, we may have synthesized too small a sample of papers to draw definitive conclusions regarding different aspects of MMs as KBs.
Our study is a first step in advancing the theoretical and conceptual conversation regarding MM KBs by articulating the attributes, roles, activities, and factors influencing their efforts and impact. Through the generation of a novel organizing framework, we identify a potential combination of roles for those in MM positions who may also function as KBs in healthcare organizations. Our study is a timely contribution to the literature and offers an initial understanding of extant evidence of the KB role MMs play in health care. Our framework has utility for policymakers, administrators, and researchers to strengthen the MM role and, ultimately, improve quality of care.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
Middle Manager
Knowledge Broker
Middle managers who function as Knowledge brokers
Knowledge Translation
Critical Interpretive Synthesis
Quality Improvement
Enhancing Transparency in Reporting the Synthesis of Qualitative Research
Berenson RA, Rice Y. Beyond measurement and reward: methods of motivating quality improvement and accountability. Health Serv Res. 2015;2(2):155–65.
Google Scholar
Nunes R, Rego G, Brandao C. Healthcare regulation as a tool for public accountability. Medical Healthcare & Philosphy. 2009;12:257–64.
Article Google Scholar
Grimshaw JM, Eccles M, Lavis JN, Hill SJ, Squires JE. Knowledge translation of research findings. Implement Sci. 2012;7(50):1–17 Available from: http://www.implementationscience.com/content/7/1/50 .
McGlynn EA, Asch SM, Adams J, Keesey J, Hicks J, DeCristofaro A. The quality of health care delivered to adults in the United States. N England Journal of Medicine. 2003;348:2635–45. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsa022615 .
Squires JE, Graham ID, Grinspun D, Lavis J, Legare F, Bell R, et al. Inappropriateness of health care in Canada: a systematic review protocol. Systematic Review. 2019;8(50). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-019-0948-1 .
Innis J, Berta W. Routines for change: How managers can use absorptive capacity to adopt and implement evidence-based practice. Journal of Nursing Management. 2016;24(6). doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/jonm.12368 .
Bornbaum C, Kornas K, Pierson L, Rosella LC. Exploring the function and effectiveness of knowledge brokers as facilitators of knowledge translation in health-realted settings: a systematic review and thematic analysis. Implement Sci. 2015;10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-015-0351-9 .
Currie G, Burgess N, White L, Lockett A, Gladman J, Waring J. A qualitative study of the knowledge-brokering role of middle-level managers in service innovation: managing the translation gap in patient safety for older persons’ care. Health Services and Delivery Research. 2014;2(32). https://doi.org/10.3310/hsdr02320 .
Canadian Health Services Research Foundation. The theory and practice of knowledge brokering in Canada’s health system. 2003. Ottawa, Ontario: www.chsrf.ca .
Flodgren G, Parmelli E, Doumit G, Gattellari M, O’Brien MA, Grimshaw J, et al. Local opinion leaders: effects on professional practice and health care outcomes. Cochrane Database Systematic Review. 2011;8. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD00125 .
Soo S, Berta W, Baker G. Role of champions in the implementation of patient safety practice change. Healthcare Quarterly. 2009;12:123–8.
Thompson GN, Estabrooks CA, Degner LF. Clarifying the concepts in knowledge transfer: a literature review. J Adv Nurs. 2006;53(6):691.
Glegg S. Knowledge brokering as an intervention in paediatric rehabilitation practice. Int J Ther Rehabil. 2010;17(4):203–9.
Rivard LM, Russell DJ, Roxborough L, Ketelaar M, Bartlett DJ, Rosenbaum P. Promoting the use of measurement tools in practice: a mixed methods study of the activities and experiences of physical therapist knowledge brokers. Phys Ther. 2010;90(11):1580–90.
Russell D, Rivard LM, Walter SD, Rosebaum PL, Roxborough L, Cameron D, et al. Using knowledge brokers to facilitate the uptake of pediatric measurement tools into clinical practice: a before-after intervention study. Implementation Science. 2010;5(92).
Dobbins M, Traynor RL, Workentine S, Yousefi-Nooraie R, Yost J. Impact of an organization-wide knowledge translation strategy to support evidence- informed public health decision making. BMC Public Health. 2018;18:1412.
Dobbins M, Greco L, Yost J, Traynor R, Decorby-Watson K, et al. A description of a tailored knowledge translation intervention delivered by knowledge brokers within public health departments in Canada. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2019;17(63):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-019-0460-z .
Birkin S, Clary A, Tabriz AA, Turner K, Meza R, Zizzi A, et al. Middle managers’ role in implementing evidence-based practices in healthcare: a systematic review. Implementation Science. 2018;13(149): 1-14. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-018-0843-5 .
Urquhart R, Kendell C, Folkes A, Reiman T, Grunfeld E, Porter GA. Factors influencing middle mangers’ commitment to the implementation of innovation in cancer care. J Health Services Res Pol. 2019;24(2):91–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/1355819618804842 .
Burgess N, Currie G. The knowledge brokering role of the hybrid middle level manager: the case of healthcare. Br J Manag. 2013;24:S132–42.
Van Eerd D, Newman K, DeForge R, Urquhart R, Cornelissen E, Dainty KN. Knowledge brokering for healthy aging: a scoping review of potential approaches. Implement Sci. 2016;11:140. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-016-0504-5 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Glegg SM, Hoens A. Role domains of knowledge brokering: a model for the health care setting. JNPT. 2016;40:115–23. https://doi.org/10.1097/NPT.000000000000012 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Schleifer Taylor J, Verrier MC, Landry MD. What do we know about knowledge brokers in pediatric rehabilitation? A systematic search and narrative summary. Physiother Can. 2014;66(2):143–52.
Ward V, House A, Hamer S. Knowledge brokering: exploring the process of transferring knowledge into action. BMC Health Serv Res. 2009;9(12):1–6.
Cranley LA, Cummings GG, Profetto-McGrath J, Toth F, Estabrooks CA. Facilitation roles and characteristics associated with research use by healthcare professionals: a scoping review. BMJ Open. 2016;7. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014384 .
Dixon-Woods M, Cavers D, Agarwal S, Annandale E, Arthur A, Harvey J, et al. Conducting a critical interpretive synthesis of the literature on access to healthcare by vulnerable groups. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006;6:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-6-35 .
Kangasniemi M, Kallio H, Pietila AM. Towards environmentally responsible nursing: a critical interpretive synthesis. J Adv Nurs. 2013;70(7):1465–78.
Tong A, Flemming K, McInnes E, Oliver S, Craig J. Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ. BMC Medical Research Methodology. 2012;12(181) Available from: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/12/181 .
Shenton K. Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Educ Inf. 2004;22:63–75.
McGowan J, Sampson M, Lefebvre C. An evidence based checklist for the peer review of electronic search strategies (PRESS EBC). Evid Based Libr Inf Pract. 2010;5(1):149–54.
Flemming K. Synthesis of quantitiative and qualitative research: an example of critical interpretive synthesis. J Adv Nurs. 2010;66(1):201–17.
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research. (2017, April 15). Available from: http://www.equator-network.org .
O'Cathain A, Murphy E, Nicholl J. The quality of mixed methods studies in health services research. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2008;13(2):92–8.
Roever L. Critical appraisal of a questionnaire study. Evidence Based Medicine and Practice. 2016;1(2). Available from: https://doi.org/10.4172/ebmp.1000e110 .
Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden P, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revided publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing. 2015; 46(11):501–507. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3928/00220124-20151020-02 .
Tufanaru C, Munn Z, Aromataris E, Campbell J, Hoop L. Systematic reviews of effectiveness. In: Aromataris E, Munn Z, editors. Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewers Manual. The Joanna Briggs Institute. 2017. Available from: https://reviewersmanual.joannabriggs.org .
Birkin SA, DiMartino LD, Kirk MA, Lee S, McCelland M, Albert NA. Elaborating on theory with middle managers’ experience implementing healthcare innovations in practice. Implement Sci. 2016;11:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-015-0362-6 .
Johnson M, Tod A, Collins K, Brummell S. Prognostic communication in cancer: a critical interpretive synthesis of the literature. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2015;19(5):554–67.
Bullock A, Morris ZS, Atwell C. Collaboration between health services managers and researchers: making a difference. Original Research. 2012;17(2):2–10. https://doi.org/10.1258/jhsrp.2011.011099 .
Donahue KE, Halladay JR, Wise A, Reiter K, Lee SD, Ward K, et al. Facilitator of transforming primary care: a look under the Hood at practice leadership. Ann Fam Med. 2013;11:527–33. https://doi.org/10.1370/afm.1492 .
Kakyo TA, Xiao LD. Nurse managers’ experiences in continuous quality improvement in resource-poor healthcare settings. Nurs Health Sci. 2017;19:244–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/nhs.12338 .
Kitson A, Silverton H, Wiechula R, Zeitz K, Marcoionni D, Page T. Clinical nursing’, team members’ and service managers’ experiences of implementing evidence at a local level. J Nurs Manag. 2011;19:542–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2834.2011.01258 .
Schreiber J, Marchetti GF, Racicot B, Kaminski E. The use of knowledge translation program to increase use of standardized outcome measures in outpatient pediatric physical therapy clinic: administrative case report. American Physical Therapy Association. 2015;95(4):613–29. https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20130434 .
Traynor R, DeCorby K, Dobbins M. Knowledge brokering in public health: a tale of two studies. The Royal Society for Public Health. 2014;128:533–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2014.01.015 .
Catallo C. Should nurses be knowledge brokers? Competencies and organizational resources to support the role. Nurs Leadersh. 2015;28(1):24–37.
Engle RL, Lopez ER, Gormley KE, Chan JA, Charns MP, VanDeusen Lukas C. What roles do middle managers play in implementation of innovative practices? Health Care Manag Rev. 2017;42(1):14–27. https://doi.org/10.1097/HMR.0000000000000090 .
Hitch D, Rowan S, Nicola-Richmond K. A case study of knowledge brokerage in occupational therapy. MA Healthcare Ltd. 2014.
Urquhart R, Kendell C, Folkes A, Reiman T, Grunfeld E, Porter GA. Making it happen: middle managers’ roles in innovation implementation in health care. Worldviews Evid-Based Nurs. 2018;15(6):414–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/wvn.12324 .
Ploeg J, Skelly J, Rowan M, Edwards N, Davies B, Grinspun D. The role of nursing best practice champions in diffusing practice guidelines: a mixed methods study. Worldviews Evid-Based Nurs. 2010:238–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-6787.2010.00202 .
Fleiszer AR, Semenic SE, Ritchie JA, Richer MC, Denis JL. Nursing unit leaders’ influence on the long-term sustainability of evidence-based practice improvements. J Nurs Manag. 2015;24:309–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/jonm.12320 .
Jeffs L, Indar A, Harvey B, McShane J, Bookey-Bassett S, Flintoft V, et al. Enabling role of manager in engaging clinicians and staff in quality improvement. J Nurs Care Qual. 2016;31(4):367–72. https://doi.org/10.1097/NCQ.0000000000000196 .
Warshawsky NE, Lake SW, Bradford A. Nurse managers describe their practice environment. Nurs Admin Q. 2013;34(4):317–25. https://doi.org/10.1097/NAQ.0b013e3182a2f9c3 .
Gutberg J, Berta W. Understanding middle managers’ influence in implementing patient safety culture. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(582):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2533-4 .
Kislov R, Hodgson D, Boarden R. Professionals as knowledge brokers: the limits of Authority in Healthcare Collaboration. Public Adm. 2016;94(2):472–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/padm.12227 .
Shaw L, McDermid J, Kothari A, Lindsay R, Brake P, Page P. Knowledge brokering with injured workers: perspective of injured worker groups and health care professionals. Work. 2010;36:89–101. https://doi.org/10.3233/WOR-20101010 .
Wilson L, Orff S, Gerry T, Shirley BR, Tabor D, Caiazzo K, et al. Evolution of an innovative role: the clinical nurse leader. J Nurs Manag. 2013;21:175–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2834.2012.01454 .
Currie G, Burgess NA, Hayton JC. HR practices and knowledge brokering by hybrid middle managers in hospital settings: the influence of professional hierarchy. Human Resources Management. 2015;54(5):793–812. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm.21709 .
Waring J, Currie G, Crompton A, Bishop S. An exploratory study of knowledge sharing and learning for patient safety? Soc Sci Med. 2013;98:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2013.08.037 .
Girard A, Rochette A, Fillion B. Knowledge translation and improving practices in neurological rehabilitation: managers’ viewpoint. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice. 2013;19:60–7 10.1111/j.1365–2753.
Williams L, Burton C, Rycroft-Malone J. What works: a realist evaluation case study of intermediaries in infection control practice. J Adv Nurs. 2012;69(4):915–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2012.06084 .
Bradley EH, Holmboe ES, Mattera JA, Roumanis SA, Radford MJ, Krumholz HM. The roles of senior Management in Quality Improvement Efforts: what are the key components? J Healthc Manag. 2003;48(1):16–29.
Ott KM, Haddock KS, Fox SE, Shinn JK, Walters SE, Hardin JW. The clinical nurse leader: impact on practice outcomes in the veterans health administration. Nurs Econ. 2009;27(6):363–71.
PubMed Google Scholar
Schell WJ, Kuntz SW. Driving change from the middle: an exploration of the complementary roles and leadership Behaviours of clinical nurse leaders and engineers in healthcare process improvement. Eng Manag J. 2013;25(4):33–43.
Jeffs LP, Lo J, Beswick S, Campbell H. Implementing an organization-wide quality improvement initiative. Nursing Administrative Quarterly. 2013;37(3):222–30. https://doi.org/10.1097/NAQ.0b013e318295ec9f .
Lalleman PCB, Smid GAC, Lagerwey MD, Oldenhof L, Schuurmans MJ. Nurse middle managers’ dispositions of habitus: a Bourdieusian analysis of supporting role Behaviours in Dutch and American hospitals. Adv Nurs Sci. 2015;38(3):E1–E16. https://doi.org/10.1097/ANS.0000000000000083 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Birken SA, Lee S, Weiner BJ, Chin MH, Chiu M, Schaefer CT. From strategy to action: how top managers’ support increases middle managers’ commitment to innovation implementation in health care organization. Health Care Manag Rev. 2015;40(2):159–68. https://doi.org/10.1097/HMR.0000000000000018 .
Bradley EH, Webster TR, Schlesinger M, Baker D, Inouye SK. The roles of senior Management in Improving Hospital Experiences for frail older adults. J Healthc Manag. 2006;51(5):323–37.
Balding C. Embedding organisational quality improvement through middle manager ownership. International Journal of Health Care Quality Assurance. 2005;18(4):271–88. https://doi.org/10.1108/09526860510602541 .
Uvhagen H, Hasson H, Hansson J, von Knorring M. Leading top-down implementation processes: a qualitative study on the role of managers. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18:562.
Fryer A-K, Tucker AL, Singer SJ. The impact of middle manager affective commitment on perceived improvement program implementation success. Health Care Manag Rev. 2018;43(3):218–28.
Chang Chen H, Jones MK, Russell C. Exploring attitudes and barriers toward the use of evidence-based nursing among nurse managers in Taiwanese residential aged care facilities. J Gerontol Nurs. 2013;39(2):36–42.
Hansell V. Identifying the prevalence of influential factors on middle manager’s ability to lead organizational change within the context of community nursing and therapy services. Int J Healthcare Management. 2018;11(3):225–32.
Buick F, Blackman D, Johnson S. Enabling middle managers as change agents: why organizational support needs to change. Aust J Public Adm. 2017;77(2):222–35.
Breed M, Downing C, Ally H. Factors influencing motivation of nurse leaders in a private hospital group in Gauteng, South Africa: A quantitative study. Curationis. 2020;43(1): Available from: https://doi.org/10.4102/curationis.v43i1.2011 .
Kallas KD. Profile of an excellent nurse manager: identifying and developing health care team leaders. Nurse Admin Quarterly. 2014;38(3):261–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/NAQ.0000000000000032 .
Sellgren S, Ekvall G, Tomson G. Leadership styles in nursing management: preferred and perceived. J Nurs Manag. 2006;14:348–55.
Dobbins M, DeCorby K, Robeson P, Ciliska D, Hanna S, Cameron R, et al. A description of a knowledge broker role implemented as part of a randomized controlled trial evaluating three knowledge translation strategies. Implementation Science. 2009;4(23). Available from: http://www.implementationscience.com/content/4/1/23 .
Cook MJ. The attributes of effective clinical nurse leaders. Nurs Stand. 2001;15(35):33–6.
Gentry H, Prince-Paul M. The nurse influencer: a concept synthesis and analysis. Nurs Forum. 2020:1–7.
Demes JAE, Nickerson N, Farand L, Montekio VB, Torres P, Dube JG, et al. What are the characteristics of the champion that influence the implementation of quality improvement programs? Evaluation and Program Planning. 2020;80:101795.
Bonawitz K, Wetmore M, Heisler M, Dalton VK, Damschroder LJ, Forman J, et al. Champions in context: which attributes matter for change efforts in healthcare? Implementation Sci. 2020;15:62.
Bunce AE, Grub I, Davis JV, Cowburn S, Cohen D, Oakley J. Lessons learned about effective operationalization of champions as an implementation strategy: results from a qualitative process evaluation of a pragmatic trial. Implementation Sci. 2020;15:87.
Birkin SA, Currie G. Using organization theory to position middle-level managers as agents of evidence-based practice implementation. Implementation Sci. 2021;16:37.
Klein KI, Sorra JS. The challenge of innovation implementation. Acad Manag Rev. 1996;21(4):1055–80.
Tricco AC, Antony J, Soobiah C, Kastner M, MacDonald H, Cogo E, et al. Knowledge synthesis methods for integrating qualitative and quantitative data: a scoping review reveals poor operationalization of the methodological steps. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016a;73:29–35.
Tricco AC, Antony J, Soobiah C, Kastner M, MacDonald H, Cogo E, et al. Knowledge synthesis methods for generating or refining theory: a scoping review reveals that little guidance is available. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016b;73:36–42.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Baycrest Health Sciences, 3560 Bathurst Street, Toronto, Ontario, M6A 2E1, Canada
Faith Boutcher
Institute of Health Policy, Management and Evaluation, University of Toronto, Health Sciences Building Suite 425, 155 College Street, Toronto, Ontario, M5T 3M6, Canada
Whitney Berta
Department of Community Health and Epidemiology, Dalhousie University, Room 413, 5790 University Avenue, Halifax, Nova Scotia, B3H 1V7, Canada
Robin Urquhart
University Health Network, 13EN-228, 200 Elizabeth Street, Toronto, Ontario, M5G 2C4, Canada
Anna R. Gagliardi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
FB, ARG, WB, and RU conceptualized and planned the study, and developed the search strategy and data collection instruments. FB and ARG screened and reviewed articles. FB, ARG, WB and RU analyzed the data. All authors read and gave approval of the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Faith Boutcher .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
ENTREQ checklist
Additional file 2.
Search strategy
Additional file 3.
Eligibility criteria
Additional file 4.
Data extraction form for eligible studies
Additional file 5.
Quality appraisal tools and findings
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Boutcher, F., Berta, W., Urquhart, R. et al. The roles, activities and impacts of middle managers who function as knowledge brokers to improve care delivery and outcomes in healthcare organizations: a critical interpretive synthesis. BMC Health Serv Res 22 , 11 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-07387-z
Download citation
Received : 02 September 2021
Accepted : 07 December 2021
Published : 02 January 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-07387-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Middle managers
- Knowledge brokers
- Critical interpretive synthesis
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 11 June 2022
Factors impacting antenatal care utilization: a systematic review of 37 fragile and conflict-affected situations
- Kameela Miriam Alibhai ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5552-3015 1 ,
- Bianca R. Ziegler 2 ,
- Louise Meddings 1 ,
- Evans Batung 3 , 4 &
- Isaac Luginaah 3 , 4
Conflict and Health volume 16 , Article number: 33 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
12k Accesses
13 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
It is estimated that over 930 million people live in fragile and conflict-affected situations (FCAS) worldwide. These regions, characterized by violence, civil unrest, and war, are often governed by corrupt administrations who are unwilling to provide their citizens with basic human rights. Individuals living in FCAS face health inequities; however, women are disproportionally affected and face additional barriers to accessing sexual and reproductive services, including antenatal care (ANC). This systematic review aims to identify the factors that impact ANC usage in the 37 countries or regions classified as FCAS in 2020 by The World Bank.
Using the PRISMA guidelines, a systematic search of five databases (SCOPUS, Web of Science, PubMed, EMBASE, and CINAHL) was conducted. Results were limited to human studies, written in English, and published between January 2002 and January 2022. Studies that identified factors affecting utilization of ANC or maternal health services were included for review and critically appraised using the National Institute of Health’s Quality Assessment Tools. Findings were summarized using a narrative synthesis approach.
The database search yielded 26,527 studies. After title, abstract and full-text review, and exclusion of duplicate articles, 121 studies remained. Twenty-eight of the 37 FCAS were represented in the included studies. The studies highlighted that women in FCAS’ are still not meeting the World Health Organization’s 2002 recommendation of four ANC visits during pregnancy, a recommendation which has since been increased to eight visits. The most cited factors impacting ANC were socioeconomic status, education, and poor quality of ANC. Despite all studies being conducted in conflict-affected regions, only nine studies explicitly identified conflict as a direct barrier to accessing ANC.
This review demonstrated that there is a paucity in the literature examining the direct and indirect impacts of conflict on ANC utilization. Specifically, research should be conducted in the nine FCAS that are not currently represented in the literature. To mitigate the barriers that prevent utilization of maternal health services identified in this review, policy makers, women utilizing ANC, and global organizations should attempt to collaborate to enact policy change at the local level.
Introduction
As of 2022, it is estimated that over 930 million people live in fragile and conflict-affected situations (FCAS) worldwide and the number of individuals affected by conflict continues to rise [ 1 ]. FCAS are countries or regions characterized by a high propensity for recurring conflict or war. FCAS often have unstable and corrupt governments who are unwilling to provide basic resources and protect the human rights of their citizens [ 2 , 3 , 4 ]. In 2020, the World Bank classified 37 countries as fragile and conflict-affected in their annual list of FCAS.
Conflict presents as one of the world’s most significant threats to health [ 5 ]. Individuals living in FCAS suffer worse health on numerous outcomes including trauma and injuries, infectious and chronic disease, mental health, child health, and malnutrition [ 6 ]. Women, in particular, are heavily affected by ongoing conflict and violence as they obtain lower levels of education, do not have the autonomy to make decisions regarding their health, and experience abhorrent gender-based violence [ 7 , 8 ]. In FCAS, women face increased barriers to accessing a continuum of sexual, productive, and maternal health services, including antenatal care (ANC). This has negative impacts on maternal mortality rates (MMR) worldwide [ 6 ]. The United Nations created Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3.1 in 2015 to reduce the global MMR to less than 70 per 100,000 live births by 2030 [ 9 ], from an estimated rate of 211 per 100,000 live births in 2017 [ 10 ]. Although the MMR goal outlined in SDG 3.1 is considerably lower than the current global MMR, this difference is even greater when compared to the MMR of FCAS—583 per 100,000 live births as of 2017 [ 11 ]. To work towards achieving SDG 3.1, increased attention and interventions are needed to improve maternal health service utilization in FCAS, where the MMR are highest.
ANC has been cited by numerous studies as a type of maternal health service that, if utilized, has the potential to reduce maternal mortality [ 12 , 13 , 14 ]. ANC is care provided to pregnant women by healthcare practitioners to identify maternal risks, prevent and manage complications, encourage positive health behaviours, and build a therapeutic patient–provider relationship [ 15 ]. In 2002, the World Health Organization (WHO) created the first set of ANC recommendations, which consisted of one first trimester visit and three subsequent visits [ 13 ]. In 2016, the WHO’s ANC recommendations increased from four total visits to eight [ 16 ]. Studies conducted prior this new recommendation in FCAS have found that the majority of women in these regions are not meeting the ANC recommendations established in 2002 [ 17 ].
This systematic review is grounded in Andersen’s Model of Healthcare Utilization [ 18 ] (Fig. 1 ). This theoretical framework conceptualizes healthcare utilization as a function of the interaction between predisposing, enabling, and need factors that influence whether women are able to seek ANC as recommended. This model was used to create themes which were found to impact women’s ANC usage and to analyze the data extracted from included articles.
Andersen’s model of healthcare utilization (Andersen, 1995)
FCAS have been previously studied, as have the numerous health outcomes of individuals living in FCAS, including maternal health. However, the common factors that prevent women living in FCAS from accessing ANC have not been well studied. Furthermore, there is a paucity in the literature on the impact of conflict on health equity in FCAS, including the intersectional effect of gender within these situations [ 2 ]. This systematic review aims to better understand the access to maternal health services in FCAS and the factors that contribute to the inequitable gap in ANC utilization. For the purposes of this study, ANC will be defined as a visit to a healthcare practitioner to receive services, such as laboratory tests, scans, or advice regarding health behaviours, while pregnant. Visits at the time of childbirth will be excluded. Our specific objectives are to (1) identify the predisposing, enabling, and need factors which prevent and/or enable women living in FCAS from utilizing ANC according to Andersen’s Model of Healthcare Utilization [ 18 ]; and (2) identify the effects of persistent conflict on women’s access to and utilization of ANC in the 37 FCAS globally.
This systematic review was carried out to examine the barriers, facilitators, and overall factors that impact ANC usage in the 37 countries or regions classified as FCAS in 2020 by The World Bank (Fig. 2 ). A systematic review protocol was developed using the PRISMA checklist and uploaded to the International prospective register of systematic reviews (PROSPERO) on July 10th, 2020 (ID #: CRD42020180994).
The World Bank’s 2020 list of fragile and conflict-affected situations
Search strategy
A literature search of peer-reviewed articles was conducted using SCOPUS, Web of Science, PubMed, EMBASE, and CINAHL. All five databases were searched on January 11, 2022 using a combination of MeSH terms and keywords (Table 1 ). The search strategy was created with the help of a subject-specific librarian and adapted to each database. Search results were limited to human studies, written in English, and published between January 2002 and January 2022.
All relevant studies were imported into Covidence, a web-based systematic review software, which identifies and removes duplicates, streamlines screening of citations, and facilitates the resolution of conflicts between reviewers. Two reviewers (B.Z. and K.A.) individually screened all titles, abstracts, and full texts. Disputes were resolved through general discussion with the senior author (I.L) when necessary.
Study inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies were eligible for inclusion if they were conducted in a conflict-affected region of one of the 37 FCAS. To achieve this, the authors identified medium and high conflict zones within each FCAS, using the Humanitarian Data Exchange or the Armed Conflict Location and Event Data Project. Any studies that took place (1) in a low conflict area of an FCAS without widespread conflict or (2) in an unspecified region of an FCAS, were excluded. Studies that utilized nationwide data, such as the Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) and Multiple Indicator Cluster Studies (MICS), and took place in FCAS where conflict was not widespread, were excluded. This was done to ensure the data analyzed was focused on conflict-affected populations within FCAS. However, studies that utilized nationwide data were included if the FCAS had widespread conflict, such as Afghanistan. Studies published between January 2002 and January 2022 were eligible for inclusion. The year 2002 was chosen as this was when the WHO released their first set of recommendations for focused and goal-oriented ANC in an attempt to extend antenatal coverage in low- and middle-income countries [ 15 ]. Studies that identified barriers or facilitators of ANC use were included in the review. Data from women who were pregnant and had received a minimum of one ANC visit were also included in the review. Regarding study design, both quantitative and qualitative studies were eligible for inclusion. Poster presentations, conference abstracts, theses, and studies for which the full text could not be located were excluded from the review. Studies that only examined skilled birth were excluded as this type of care has been more widely studied in the context of FCAS and is not an outcome of interest in this review.
Data extraction
Two reviewers (B.Z and K.A.) independently extracted data from all included studies. Data extracted included: list of authors, year of publication, study design, methodology employed, geographic setting, patient demographics (i.e., age, marital status), type of care provided (i.e., ANC, skilled birth), factors affecting ANC (i.e., distance, education), outcomes of interest (i.e., number of ANC visits), overall conclusions, limitations, and future recommendations. Data was extracted into a standardized extraction form developed by one of the study authors (B.Z.) using Qualtrics, an online survey platform. All bibliographic information was imported into a reference manager, Zotero, to generate citations.
Quality assessment
Each source was critically appraised using the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Study Quality Assessment Tools [ 19 ]. The NIH tool utilized was specific to the study design of the article being reviewed. Studies were evaluated on the clarity of the research question, described eligibility criteria, choice of study population, sample size, outcomes measured, and type of statistical analysis employed. After the assessment, articles rated as either “good”, or “fair” were deemed to have high internal validity and were included in the review. Eight studies were classified as “poor” quality which would have caused them to be excluded, however, they were also excluded for other reasons including wrong geographic location. Discrepancies between reviewers were resolved through general discussion with the senior author (I.L.) when necessary.
Data synthesis
A narrative synthesis approach was employed to analyze the data extracted from all included articles. The factors that were found to affect ANC utilization across all included studies were inductively coded [ 20 ] by two independent authors (B.Z and K.A) according to Andersen’s Model of healthcare utilization. Factors were coded as either predisposing , enabling , need or other factor type. To gain cross-study synthesis, the geographic distribution of the studies, participant demographics, and primary outcomes measured were analyzed and the percentage of women who met the ANC recommendations were calculated whenever possible. Due to the inclusion of qualitative studies and of studies with varied designs and methodologies, the data collected was heterogenous and a meta-analysis could not be carried out.
The database search yielded 26,527 studies. After exclusion of 11,029 duplicate articles, and completion of title and abstract screening, a total of 739 studies were included for full text review. After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, 121 studies were retained for inclusion in the final dataset (Fig. 3 ). Due to the large number of full-text studies included in this review and the heterogeneity in the designs of the included studies, a thematic description of the results is presented. A description of each article is outlined in the Additional file 1 : Table S1.
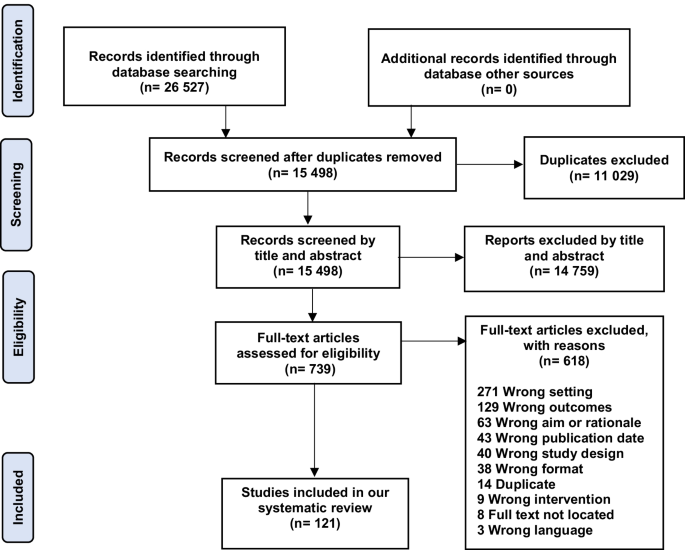
PRISMA diagram. *The total number of reasons for exclusion of the full texts exceeds 618 as some studies were excluded for multiple reasons (i.e., poor quality in addition to another factor)
The geographical spread of the studies included in this systematic review and the number of articles per country is outlined in Fig. 4 . The number of articles represented within Fig. 4 exceeds the total number of studies included as some articles examined ANC in multiple countries. Among the 121 articles included, ANC usage was examined in 123 settings: 77 articles in Africa, 15 articles in the Middle East, six articles in Southeast Asia, 11 articles in Central Asia, nine articles in Oceania, three articles in the Caribbean, one article in Palestine, and one article in Europe. Specifically, ANC was examined in 28 of the 37 regions identified as FCAS in 2020 by The World Bank. The nine FCAS for which no relevant studies were found include: Congo (Rep), Liberia, Central African Republic, Comoros, Venezuela, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, and Tuvalu. Thirty-two studies analyzed utilization of care in Nigeria, which highlights that ANC has been extensively studied in this country.
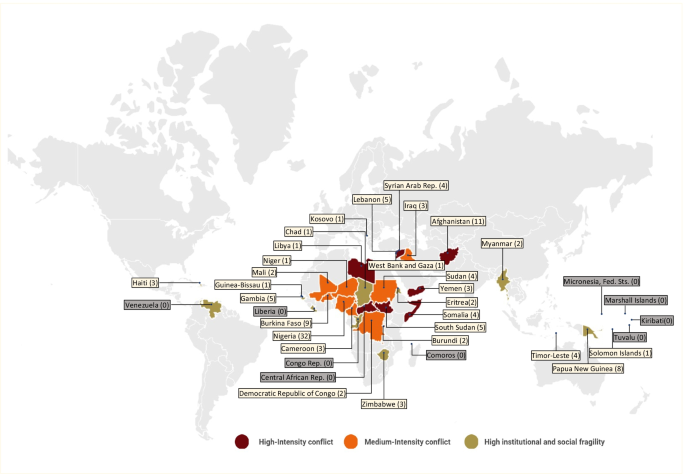
Geographic spread of articles (n = 99)
The studies included were published between 2002 and 2022, with most articles being published in 2014 or later (Fig. 5 ). The increasing number of studies over time indicates that research on ANC has been of interest since the Millennium Development Goals and SDGs targets on maternal mortality were established in 2000 and 2015, respectively.
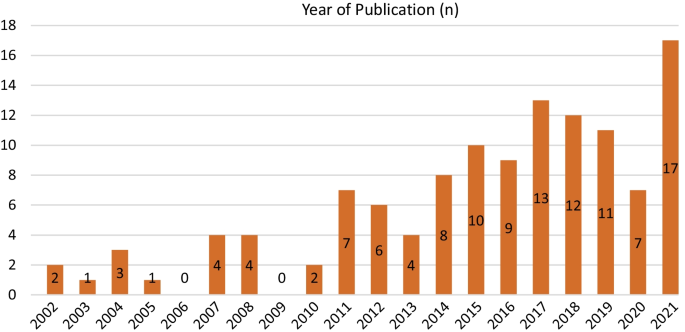
Publication year of included articles (n = 121)
Overall, the studies suggest that booking the first ANC visit late in pregnancy is very common in FCAS [ 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 ]. Many studies also indicate that while progress has been made, women in FCAS are not meeting the WHO 2002 recommendation of four ANC visits and are therefore not meeting the 2016 recommendation of eight ANC visits [ 26 , 27 ]. Table 2 identifies the factors that impact use of ANC in the 121 included articles. Seeing that many studies identified multiple factors that impact ANC utilization, the total number of factors highlighted in Table 2 exceeds 121. In accordance with Andersen’s model, predisposing factors include demographic, social, and contextual items such as education, employment, marital status, gender dynamics, religion, and culture [ 28 , 29 ]. Enabling factors include financial and organizational items such as conflict, structural resources, safety, distance from ANC resources, perceived poor quality of ANC, and socioeconomic status [ 28 , 29 ]. Additionally, need factors, which indicate a woman’s perceived need for ANC, include parity and previous complications. Finally, factors such as unwanted pregnancies, interventions (i.e., performance-based financing, home visits, mobile phone support and health education), and a husband’s education or employment were categorized as other . The most cited factors impacting ANC were socioeconomic status, poor quality of ANC, and education. Table 2 presents the 20 factors impacting ANC identified in the 121 included articles.
Predisposing
Demographic characteristics.
Demographic factors, including level of education, region of residence, marital status, age, religion, and ethnicity were cited 115 times as factors that impact ANC utilization. Education was the second most commonly cited factor that influenced ANC use in 49 studies (Table 2 ). Generally, women with no education or lower levels of education had decreased awareness and utilization of ANC during the first trimester and were less likely to receive the recommended number of ANC visits [ 30 ]. In contrast, women with higher levels of education were significantly more likely to book ANC early in pregnancy and to attend the recommended number of ANC visits [ 31 ]. Numerous studies also demonstrated that a husband’s level of education impacted a woman’s ANC usage [ 30 ]. It should be noted that this effect was smaller than the impact of a women’s educational attainment.
Region of residence and rurality were found to impact women’s utilization of ANC in 15 articles. The majority of studies found that, when compared to women living in rural areas, women living in urban areas within an FCAS were more likely to receive the recommended number of ANC visits and to have increased uptake of ANC overall [ 32 ].
Marital status was reported as a factor that influenced ANC utilization in 14 studies. In general, married women were more likely to use ANC as recommended compared to single women [ 33 , 34 ]. Specifically, the studies found that being married increased the likelihood of early initiation of ANC [ 33 ]. The type of marital union also impacted ANC usage, where women in polygamous marriages were more likely to utilize ANC services [ 34 ].
Maternal age was shown to be a factor influencing the timing and frequency of ANC utilization in 14 studies. Most studies, with the exception of Benage et al. [ 27 ] and Bashour et al. [ 35 ], found that younger women were less likely to seek ANC early in pregnancy, receive the four recommended ANC visits, and use ANC overall [ 36 ].
Religion was reported to be a factor influencing ANC utilization in nine studies, however, its impact was context dependent. De Allegri et al. [ 34 ], found a negative association between traditional African religions and ANC uptake. Conversely, a study by Nwakamma et al. [ 37 ], found that introducing and connecting women to ANC services through faith-based communities and leaders was an important factor in promoting ANC.
Finally, an individual’s employment status was reported to be both a facilitator and barrier to ANC uptake in eight studies. Failing et al. [ 38 ], found that women’s employment negatively impacted use of ANC, where women placed more importance on completing work responsibilities to survive financially than on take time off to receiving ANC. According to other studies, using ANC four times, as previously recommended by the WHO, was generally positively associated with women’s employment [ 17 , 39 , 40 ]. Additionally, numerous studies found that a husband’s occupation or employment status (categorized as other ) positively influenced women’s maternal healthcare utilization. To illustrate, Abimbola 2016 [ 30 ], found that a man’s occupation determines their wife’s socioeconomic status, which is an enabling factor that impacts ANC utilization [ 26 , 38 , 41 ].
Gender dynamics
Gender dynamics, which for the purposes of this study includes autonomy, decision-making abilities, and intimate partner violence, was found to impact ANC use in 26 studies. Women with higher autonomy, specifically financial autonomy, and increased decision-making abilities had greater uptake of ANC [ 42 , 43 ]. Receiving permission from the husband was cited as an additional barrier to accessing ANC in numerous studies [ 44 , 45 , 46 ]. Furthermore, women who did not experience intimate partner violence and who did not believe that wife-beating was acceptable were more likely to use ANC and meet the recommendation of four ANC visits [ 17 ].
Cultural and health beliefs
Cultural and health beliefs were reported to influence ANC uptake in 22 and 6 studies, respectively (Table 2 ). Culture was found to shape a woman’s beliefs about ANC and pregnancy, as well as her autonomy to make healthcare decisions [ 22 ]. For example, some women believed that their baby would be in danger or that enemies would bewitch them and cause them to miscarry if the pregnancy was disclosed too early, which resulted in late initiation of ANC [ 22 , 47 ]. Furthermore, in some traditions it is customary for a woman’s mother-in-law to decide whether or not she can receive care [ 46 , 48 ], which can further decrease ANC utilization. Women’s health beliefs, specifically those who believed that ANC was beneficial, were more likely to use maternal health services compared to those who believed ANC was only for curative purposes. Additionally, many women believed that pregnancy is a natural process and care should only be sought if one becomes ill or develops complications [ 49 , 50 ]. Therefore, the type of health belief that a woman held regarding the utility of ANC played a role in whether or not they utilized it.
Socioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status or financial difficulty was the most cited factor that prevented women from using ANC early and receiving the recommended number of visits. It was reported to influence ANC uptake in 68 of the 121 studies included in this review. The majority of studies found that women with higher socioeconomic status or wealth were more likely to utilize ANC in general, to initiate ANC early in pregnancy, and to receive the four recommended visits [ 26 , 38 , 41 ].
Distance & transport
Distance to the nearest ANC facility was the fourth most commonly cited reason for late or insufficient ANC uptake in 47 studies (Table 2 ). Women who lived closer to healthcare facilities or perceived the nearest healthcare facility as close to them, had higher levels of ANC usage. Unsurprisingly, those who lived further away from the nearest health facility were less likely to receive four ANC visits, initiate ANC early in their pregnancy, and use ANC overall [ 51 , 52 ]. Transportation was found to be a barrier of ANC uptake in 14 studies included (Table 2 ). Telfer et al. found unavailability of transportation to be one of the most important barriers preventing women from accessing ANC. Pregnant women also cited having to walk to the ANC facility and having inadequate modes of transportation (i.e., rickshaws, bicycles, motorbikes) as key barriers to accessing care. The high cost of transportation was also associated with fewer ANC visits and an overall lack of ANC utilization [ 30 , 64 ].
Poor quality of ANC
Poor Quality of ANC was reported to be a barrier to ANC uptake in 49 studies [ 53 , 59 ]. Women who believed they received low quality care were less likely to meet the WHO ANC recommendations [ 42 , 60 ]. Women cited lack of resources (e.g. ultrasound machines, providers etc.) [ 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 ], shortened hours of operation [ 27 , 60 ], long wait times [ 64 ], and a lack of trust in providers [ 65 , 66 ] as reasons for poor quality of care. Women also stated that healthcare providers were incompetent and had negative attitudes [ 43 , 50 ], which may explain the distrust they experienced [ 65 ].
Infrastructure and resources
Infrastructure or lack of resources was a factor reported to impact access to ANC in 11 studies. Studies found that women who perceived operational and infrastructure problems in their community (i.e., lack of electricity, running water, destroyed building infrastructure) were deterred from accessing ANC and faced poorer health outcomes as a result [ 61 , 67 ]. A study conducted by Mourtada et al. [ 63 ], found that as infrastructure destruction increased because of conflict, there was an associated decreased uptake of ANC.
Conflict & safety
Conflict and safety were reported as factors that directly impacted the uptake of ANC in nine and four studies [ 48 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 ], respectively. Women in zones of high conflict had poorer rates of ANC utilization. Due to prolonged conflict in FCAS, women felt unsafe or insecure travelling to ANC facilities, especially alone, and were therefore less likely to seek care as recommended [ 48 , 72 ]. This impact is intersectional as prolonged conflict negatively impacted education, fertility rate, availability of resources (e.g. machinery and providers), quality of care, and infrastructure, which in turn further decreased ANC utilization [ 48 , 68 , 69 ]. Increasing severity of conflict resulted in a decreased number of women in these areas meeting the WHO’s 2016 ANC recommendations. Finally, ANC was negatively impacted by a woman’s proximity to the conflict zone [ 70 ].
Parity, defined as the number of births a woman has had, was shown to be a factor that influenced ANC use in 21 studies. Women who did not have previous birth experience or who had low parity were more likely to initiate ANC early in pregnancy and to attend a greater number of ANC visits [ 73 ]. In contrast, women with higher parity were less likely to receive early ANC, attend the recommended number of visits, or meet the WHO’s ANC recommendations [ 17 , 74 , 75 ].
In 49 studies, women’s utilization of ANC was impacted by several other factors (Table 2 ). One commonly cited other factor was husband’s education and employment, where women whose partners had higher levels of education or formal employment had increased usage of ANC [ 38 ]. Unwanted pregnancies [ 45 , 73 , 76 ], stigma from the community or family members [ 36 , 50 , 74 ], community members advising against using formal ANC services [ 21 , 77 ], use of traditional healers [ 47 , 77 ], lack of awareness and knowledge [ 31 , 38 , 78 , 79 ] and performance-based financing interventions [ 80 , 81 ] were additional factors associated with delayed and less frequent use of ANC.
This review identified 20 factors that impacted ANC utilization across 28 of the 37 regions classified as fragile and conflict-affected by the World Bank in 2020. This is the first review, to our knowledge, that examines ANC utilization in FCAS, exclusively. Overall, the 121 studies included demonstrate that women in FCAS are not meeting the WHO recommendations for ANC use. When compared to women worldwide, those living in FCAS are significantly less likely to seek ANC early in pregnancy or attend a total of four ANC visits, which makes them even less likely to achieve the WHO’s 2016 recommendation of eight ANC visits [ 82 ].
Although all 121 studies examined ANC in FCAS, only nine studies (7.43%) identified conflict as a direct barrier to accessing care. We posit that while conflict was not a frequently cited barrier, it may largely explain women’s poor uptake of ANC. For example, in some FCAS, healthcare facilities are attacked, practitioners may be kidnapped, killed, or forced to flee to urban areas to ensure safety, and clinics often lack necessary resources [ 83 ]. These events may explain why women experience poor quality of ANC and cannot find care facilities in rural areas [ 6 , 84 , 85 ]. Furthermore, in regions of conflict, women may more often be raped by members of the militia. This leaves women less likely to seek ANC out of fear of experiencing violence when travelling to a healthcare facility alone [ 86 , 87 ]. This discussion highlights the intersectional relationship between conflict and the four most cited factors impacting ANC [ 6 , 88 , 89 , 90 ], namely education, gender dynamics, socioeconomic status, distance and quality of ANC.
Education was the most commonly cited predisposing factor affecting ANC utilization. Specifically, lack of education resulted in decreased utilization of ANC, which is consistent with literature on maternal healthcare utilization. In FCAS, students and teachers may be killed or displaced due to targeted attacks or recruitment initiatives by military groups [ 91 ]. This prevents schools from re-opening and decreases the number of students enrolled should schools reopen [ 91 ]. Women are often prematurely forced out of the education system to care for their family after their fathers and brothers are recruited into the military or because of unwanted pregnancies, secondary to rape. Women who are unable to obtain higher levels of education are less likely to know the benefits of ANC or the recommendations regarding timing and frequency of use [ 12 , 82 , 88 , 92 ].
Gender dynamics, which encompasses gender-based violence and lack of autonomy, was cited 26 times as a predisposing factor that impacts initiation and frequency of ANC. In conflict-affected areas, the gender dynamics are strained, which puts women at higher risk of experiencing sexual violence and military sexual slavery [ 93 , 94 ]. Should a woman become pregnant secondary to rape, she must ask for permission and financial support from her husband before seeking out necessary maternal care [ 12 , 96 ]. Lack of autonomy to make decisions about contraception use [ 8 , 97 , 98 ] may also increase the likelihood of unwanted pregnancies, which is an other factor negatively impacting ANC use [ 6 , 97 , 99 ]. Women who are granted permission to seek ANC may still be unable to access it due to safety concerns associated with transport or lack of infrastructure in regions of high conflict.
Socioeconomic status, an enabling factor, was the most cited factor impacting ANC use. In regions of conflict, employment opportunities are limited, which makes it difficult for women to obtain the financial resources to pay the service and transportation fees associated with ANC. As a result, women may accept employment opportunities that put them at risk of physical and sexual harm, which may cause prenatal complications [ 95 ]. Should these women succeed in accessing timely and cost-effective ANC, they may not be able to afford the medications needed to ensure a healthy pregnancy. Women with lower socioeconomic status are also less likely to obtain higher levels of education, have financial autonomy, or be employed [ 100 ], which are all known to impact ANC utilization.
Distance was the fourth most commonly cited factor affecting the use of ANC. Distance is commonly thought of as the geographical space between a woman’s home and the nearest health facility [ 43 ]. In FCAS, conflict results in displacement of communities and the destruction of roads, transport vehicles and healthcare facilities, which all contribute to the increased distance between residential communities and healthcare facilities [ 101 , 102 ]. Interestingly, this review found that perceived distance, which is how far a woman believes the nearest ANC facility is to her, also impacted uptake of ANC. Perceived distance is influenced by weather conditions, physical terrain, lack of transportation, and fear of travelling to healthcare facilities alone [ 8 , 103 ]. Overall, distance, both real and perceived, to the nearest healthcare facility was found to impact ANC utilization and these distances may be increased in regions of conflict.
Poor quality of ANC was the second most commonly cited enabling factor impacting ANC uptake during pregnancy [ 6 , 104 ]. Women reported experiencing long wait times and receiving care from providers who were unfriendly and “inept” [ 30 ]. Conflict directly affects resource allocation and contributes to a lack of providers, equipment, and medical resources, which may explain the poor quality of care [ 83 ]. Pregnant women in FCAS are a vulnerable population who are often unaware of the benefits of ANC [ 38 ]. When a woman feels she received poor quality ANC, it may reinforce the idea that ANC has little benefit and deter her from seeking it in the future. As such, the shortage of healthcare resources in FCAS as a result of conflict makes it difficult to provide women with high quality care which appears to have negative impacts on ANC utilization.
In order to start addressing the predisposing barriers that women living in FCAS face when seeking ANC, policies must be changed and region-specific interventions are needed. First, policies that prioritize girls’ access to education should be implemented to ensure they can continue with their studies if they become pregnant. Second, educational curricula should be modified to teach students the importance of using contraceptives and seeking ANC. It is also an opportunity to target cultural beliefs that claim use of ANC early in pregnancy can bewitch a child and lead to miscarriage. Third, there is a need to increase the employment opportunities for women. This will allow women to have increased financial autonomy and higher socioeconomic status, which are both positively related to ANC utilization [ 40 ]. If girls are educated and women are employed, the gender dynamics that are prevalent in FCAS may also be redefined.
To mitigate enabling factors, governments should provide safe and affordable transportation, cost-effective ANC services, and incentives to ANC providers. Providing transportation will help women feel safer when travelling through regions of conflict to seek ANC. Similarly, subsidizing the costs associated with ANC will help alleviate the financial burdens that women of low socioeconomic status face when seeking care. Performance-based financing schemes, which have been implemented in some FCAS [ 105 ], may financially incentivize healthcare workers to provide high quality, patient-centered ANC. It would be important, however, to ensure that a portion of the money practitioners receive is used to hire additional personnel and purchase necessary equipment, which will further ameliorate the quality of care provided.
Addressing the barriers that prevent uptake of ANC will require a grassroots approach and cooperation from several stakeholders, which may be complex, costly, and lengthy. Local policy makers, women utilizing ANC within FCAS, and global organizations, such as the WHO, should collaborate and discuss the local context, the effect of conflict on utilization of ANC, and the factors that impact its uptake. This will maximize the potential to create effective change to increase women’s access to and utilization of ANC in FCAS.
Limitations
This review has some limitations that must be considered. First, we excluded studies not published in English, conducted prior to 2002, and for which the full text could not be accessed. Considering English is not the official language in many of the FCAS analyzed, this review may be missing relevant studies. Second, our search string was created according to the World Bank’s 2020 list of FCAS; however, studies from as early as 2002 are included in this review. As such, some of the analyzed data may have been collected at a time when the region was not classified as fragile and conflict-affected and may not represent the current barriers women in these regions are facing. Third, the included studies are heterogeneous and differ in their study design, sample size, and overall quality, which ultimately prevented us from carrying out a meta-analysis. Furthermore, many studies used self-reported data, which is subject to recall and social desirability biases. Despite these limitations, we used systematic methodologies informed by the PRISMA guidelines to conduct this review and have ensured the quality of the research findings by including studies that were rated as fair or good according to the NIH’s Quality Assessment Tools. Finally, this review does not include studies that utilized nationwide data (i.e., DHS and MICS), which may identify other factors that limit use of ANC. However, elimination of those studies was done to ensure that the data analyzed was specific to conflict-affected populations.
The findings of this systematic review demonstrate that women living in FCAS worldwide face many barriers to accessing ANC. These women are not meeting the WHO 2016 recommendations of eight ANC visits, which is contributing to the high MMR in these regions. Although conflict was not commonly identified as a barrier to accessing maternal health services, it is likely that the frequently cited factors, namely socioeconomic status, distance, education, quality of ANC, and gender dynamics, are exacerbated by the effects of conflict.
Future research
Our findings revealed that research on the factors that affect utilization of ANC is needed in the nine FCAS that are not represented in the included studies. Additionally, it is evident that the direct and indirect impacts of conflict on women’s healthcare utilization have not been well studied. Future research is urgently needed to understand how conflict impacts ANC uptake if we hope to lower the global MMR and achieve SDG 3.1 by 2030.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
- Antenatal care
- Fragile and conflict-affected situations
Maternal mortality rate
Sustainable development goal
World Health Organization
The World Bank. Population, total—Fragile and conflict affected situations. Published online 2018. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL?locations=F1 .
Ranson K, Poletti T, Bornemisza O, Sondorp E. Conflict-affected fragile states. Published online 2007.
Bakrania S, Lucas B. The Impact of the financial crisis on conflict and state fragility in sub-Saharan Africa. 2009.
Bertocchi G, Guerzoni A. Growth, history, or institutions: What explains state fragility in sub-Saharan Africa? J Peace Res. 2012;49(6):769–83. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022343312452420 .
Article Google Scholar
Singh S, Orbinski JJ, Mills EJ. Conflict and health: a paradigm shift in global health and human rights. Confl Health. 2007;1(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-1505-1-1 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Garry S, Checchi F. Armed conflict and public health: into the 21st century. J Public Health. 1990;2019:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1093/pubmed/fdz095 .
Bafilemba F, Prendergast J. Congo stories: battling five centuries of exploitation and greed. 2018.
Ziegler BR. Pregnancy in Peril : the impact of conflict on antenatal care and skilled birth attendant utilization in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Burundi. Published online 2020.
The United Nations. Sustainable development goal. Published online 2015. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdg3 .
World Health Organization. Trends in maternal mortality 2000 to 2017: estimates by WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, World Bank Group and the United Nations Population Division: executive summary. World Health Organization; 2019,12 p.
The World Bank. Maternal mortality ratio (modeled estimate, per 100,000 live births). Published online 2017. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.STA.MMRT .
Atuoye KN, Amoyaw JA, Kuuire VZ, et al. Utilisation of skilled birth attendants over time in Nigeria and Malawi. Glob Public Health. 2017;12(6):728–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/17441692.2017.1315441 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Say L, Chou D, Gemmill A, et al. Global causes of maternal death: A WHO systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(6):323–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(14)70227-X .
The World Health Organization. Maternal mortality. Published online 2019. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/maternal-mortality .
The World Health Organization. WHO Antenatal care randomized trial: manual for the implementation of the new model. 2002.
The World Health Organization. WHO Recommendations on antenatal care for a positive pregnancy experience. 2016. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/250796/9789241549912-eng.pdf?sequence=1 .
Omer K, Afi NJ, Baba MC, et al. Seeking evidence to support efforts to increase use of antenatal care: a cross-sectional study in two states of Nigeria. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-014-0380-4 .
Andersen RM. Andersen and Newman framework of health services utilization. J Health Soc Behav. 1995;36:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/pme.12756 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
National Heart Blood and Lung Institute. Study quality assessment tools. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools .
Neuman WL, Robson K. Basics of social researh. 3rd ed. Toronto: Pearson Canada; 2014.
Google Scholar
Warri D, George A. Perceptions of pregnant women of reasons for late initiation of antenatal care: a qualitative interview study. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-020-2746-0 .
Ndidi E, Oseremen I. Reasons given by pregnant women for late initiation of antenatal care in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Ghana Med J. 2010. https://doi.org/10.4314/gmj.v44i2.68883 .
Kluckow H, Panisi L, Larui J, et al. Socio-demographic predictors of unintended pregnancy and late antenatal booking in Honiara, Solomon Islands. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2018;58(3):349–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajo.12782 .
Ebeigbe PN, Igberase GO. Antenatal care: a comparison of demographic and obstetric characteristics of early and late attenders in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Med Sci Monit. 2005;11(11):529–32.
Edie GEHE, Obinchemti TE, Tamufor EN, Njie MM, Njamen TN, Achidi EA. Perceptions of antenatal care services by pregnant women attending government health centres in the Buea health district, Cameroon: a cross sectional study. Pan Afr Med J. 2015;21:1–9. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2015.21.45.4858 .
Khanal V, da Cruz JLNB, Mishra SR, Karkee R, Lee AH. Under-utilization of antenatal care services in Timor-Leste: results from demographic and health survey 2009–2010. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-015-0646-5 .
Benage M, Gregg Greenough P, Vinck P, Omeira N, Pham P. An assessment of antenatal care among Syrian refugees in Lebanon. Confl Health. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-015-0035-8 .
Anderson RM. Revisiting the behavioral model and access to medical care: Does it matter? J Health Soc Behav. 1995;36(1):1–10.
Babitsch B, Gohl D, von Lengerke T. Re-revisiting Andersen’s behavioral model of health services use: a systematic review of studies from 1998–2011. Psycho-Soc Med. 2012. https://doi.org/10.3205/psm000089 .
Abimbola JM, Makanjuola AT, Ganiyu SA, Babatunde UMM, Adekunle DK, Olatayo AA. Pattern of utilization of ante-natal and delivery services in a semi-urban community of north-central Nigeria. Afr Health Sci. 2016;16(4):962–71. https://doi.org/10.4314/ahs.v16i4.12 .
Adam IF, Nakamura K, Kizuki M, Al Rifai R, Vanching U. Relationship between implementing interpersonal communication and mass education campaigns in emergency settings and use of reproductive healthcare services: Evidence from Darfur, Sudan. BMJ Open. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008285 .
Edu BC, Agan TU, Monjok E, Makowiecka K. Effect of free maternal health care program on health-seeking behavior of women during pregnancy, intra-partum and postpartum periods in Cross River State of Nigeria: a mixed method study. Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5(3):370–82. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2017.075 .
Ntambue AM, Malonga FK, Dramaix-Wilmet M, Ngatu RN, Donnen P. Better than nothing? Maternal, newborn, and child health services and perinatal mortality, Lubumbashi, democratic republic of the Congo: a cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-016-0879-y .
De Allegri M, Ridde V, Louis VR, et al. Determinants of utilisation of maternal care services after the reduction of user fees: a case study from rural Burkina Faso. Health Policy. 2011;99(3):210–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2010.10.010 .
Bashour H, Abdulsalam A, Al-Faisal W, Cheikha S. Patterns and determinants of maternity care in Damascus. East Mediterr Health J. 2008;14(3):595–604.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ebeigbe PN, Gharoro EP. Obstetric complications, intervention rates and maternofetal outcome in teenage nullipara in Benin City, Nigeria. Trop Doct. 2007;37(2):79–83. https://doi.org/10.1258/004947507780609356 .
Nwakamma IJ, Erinmwinhe A, Ajogwu A, Udoh A, Ada-Ogoh A. Mitigating gender and maternal and child health injustices through faith community-led initiatives. Int J MCH AIDS. 2019;8(2):146–55. https://doi.org/10.21106/ijma.326 .
Failing F, Ripa P, Tefuarani N, Vince J. A comparison of booked and unbooked mothers delivering at the Port Moresby General Hospital: a case-control study. P N G Med J. 2004;47(3–4):174–80.
El-Kak F, Chaaya M, Campbell O, Kaddour A. Patterns of antenatal care in low-versus high-risk pregnancies in Lebanon. East Mediterr Health J. 2004;10(3):268–76.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Oyetundeo and Elery. Factors influecing use of antenatal care and delivery services in Gwagwalada Area Council, Nigeria. Afr J Midwifery Women’s Health. 2014;8(4):195–202.
Alosaimi AN, Nwaru B, Luoto R, Al Serouri AW, Mouniri H. Using household socioeconomic indicators to predict the utilization of maternal and child health services among reproductive-aged women in rural Yemen. Glob Pediatr Health. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1177/2333794X19868926 .
Arnaert A, Ponzoni N, Debe Z, Meda MM, Nana NG, Arnaert S. Experiences of women receiving mhealth-supported antenatal care in the village from community health workers in rural Burkina Faso. Africa Digit Health. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1177/2055207619892756 .
Al-Mujtaba M, Cornelius LJ, Galadanci H, et al. Evaluating religious influences on the utilization of maternal health services among Muslim and Christian Women in North-Central Nigeria. BIOMED Res Int. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3645415 .
Telfer ML, Rowley JT, Walraven GEL. Experiences of mothers with antenatal, delivery and postpartum care in rural Gambia. Afr J Reprod Health. 2002;6(1):74–83. https://doi.org/10.2307/3583148 .
Sibanda EL, Bernays S, Weller IVD, Hakim JG, Cowan FM. “Well, not me, but other women do not register because”—Barriers to seeking antenatal care in the context of prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV among Zimbabwean women: a mixed-methods study. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-018-1898-7 .
Somé DT, Sombié I, Meda N. How decision for seeking maternal care is made——a qualitative study in two rural medical districts of Burkina Faso. Reprod Health. 2013;10(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4755-10-8 .
Laing SP, Sinmyee SV, Rafique K, Smith HE, Cooper MJ. Barriers to antenatal care in an urban community in the Gambia: an in-depth qualitative interview study. Afr J Reprod Health. 2017;21(3):62–9.
Wilunda C, Scanagatta C, Putoto G, et al. Barriers to utilisation of antenatal care services in South Sudan: a qualitative study in Rumbek North County. Reprod Health. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-017-0327-0 .
Haggaz A, Ahmed S, Adam I. Use of prenatal care services in Darfur, Sudan. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2008;103(3):252–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2008.06.010 .
Andrew EVW, Pell C, Angwin A, et al. Factors affecting attendance at and timing of formal antenatal care: results from a qualitative study in Madang, Papua New Guinea. PLoS ONE. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093025 .
Talhouk R, Mesmar S, Thieme A, et al. Syrian refugees and digital health in Lebanon: Opportunities for improving antenatal health. In: Conference on human factors in computing systems—proceedings. 2016;331–342. https://doi.org/10.1145/2858036.2858331 .
Tolefac PN, Halle-Ekane GE, Agbor VN, Sama CB, Ngwasiri C, Tebeu PM. Why do pregnant women present late for their first antenatal care consultation in Cameroon? Matern Health Neonatol Perinatol. 2017;3(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40748-017-0067-8 .
Okonofua F, Ogu R, Agholor K, et al. Qualitative assessment of women’s satisfaction with maternal health care in referral hospitals in Nigeria. Reprod Health. 2017;14(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-017-0305-6 .
Ifenne DI, Utoo BT. Gestational age at booking for antenatal care in a tertiary health facility in north-central, Nigeria. J Niger Med Assoc. 2012;53(4):236–9. https://doi.org/10.4103/0300-1652.107602 .
Rahmani Z, Brekke M. Antenatal and obstetric care in Afghanistan—a qualitative study among health care receivers and health care providers. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-13-166 .
Alam N, Chowdhury ME, Kouanda S, et al. The role of transportation to access maternal care services for women in rural Bangladesh and Burkina Faso: a mixed methods study. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2016;135:S45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2016.09.003 .
Donmozoun TS, Sombie I, Meda N. What prevent women for a sustainable use of maternal care in two medical districts of Burkina Faso? a qualitative study. Pan Afr Med J. 2014;18:1–6. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2014.18.43.2210 .
Wallace HJ, McDonald S, Belton S, et al. The decision to seek care antenatally and during labour and birth—Who and what influences this in Timor-Leste? A qualitative project exploring the perceptions of Timorese women and men. Midwifery. 2018;65:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2018.05.013 .
Shabila NP, Ahmed HM, Yasin MY. Women’s views and experiences of antenatal care in Iraq: a Q methodology study. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2393-14-43 .
Chol C, Hunter C, Debru B, Haile B, Negin J, Cumming RG. Stakeholders’ perspectives on facilitators of and barriers to the utilisation of and access to maternal health services in Eritrea: a qualitative study. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-018-1665-9 .
Alex M, Whitty-Rogers J. Experiences of pregnancy complications: Voices from central Haiti. Health Care Women Int. 2017;38(10):1034–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/07399332.2017.1350179 .
Lawry L, Canteli C, Rabenzanahary T, Pramana W. A mixed methods assessment of barriers to maternal, newborn and child health in gogrial west, south Sudan. Reprod Health. 2017;14(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-016-0269-y .
Mourtada R, Bottomley C, Houben F, Bashour H, Campbell OMR. A mixed methods analysis of factors affecting antenatal care content: a Syrian case study. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(3):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0214375 .
Jallow IK, Chou YJ, Liu TL, Huang N. Womens perception of antenatal care services in public and private clinics in the Gambia. Int J Qual Health Care. 2012;24(6):595–600. https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzs033 .
Badal NF, Yusuf UA, Egal J, et al. With knowledge and support, women can attend antenatal care: the views of women in IDP camps in Somaliland. 2015.
Gure F, Yusuf M, Foster AM. Exploring Somali women’s reproductive health knowledge and experiences: results from focus group discussions in Mogadishu. Reprod Health Matters. 2015;23(46):136–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhm.2015.11.018 .
Ekabua J, Ekabua K, Njoku C. Proposed framework for making focused antenatal care services accessible: a review of the Nigerian setting. ISRN Obstet Gynecol. 2011;2011:1–5. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/253964 .
Stojanovski K, Holla A, Hoxha I, Howell E, Janevic T. The influence of ethnicity and displacement on quality of antenatal care: the case of Roma, Ashkali, and Balkan Egyptian communities in Kosovo. Health Hum Rights. 2017;19(2):35–48.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mullany LC, Beyrer C, Lee TJ, et al. Access to essential maternal health interventions and human rights violations among vulnerable communities in eastern burma. PLoS Med. 2008;5(12):1689–98. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0050242 .
Leone T, Alburez-Gutierrez D, Ghandour R, Coast E, Giacaman R. Maternal and child access to care and intensity of conflict in the occupied Palestinian territory: a pseudo longitudinal analysis (2000–2014). Confl Health. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-019-0220-2 .
Solanke BL. Factors associated with use of maternal healthcare services during the Boko Haram insurgency in North-East Nigeria. Med Confl Surviv. 2018;34(3):158–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/13623699.2018.1511358 .
Mugo NS, Dibley MJ, Damundu EY, Alam A. “The system here isn’t on patients’ side”—perspectives of women and men on the barriers to accessing and utilizing maternal healthcare services in South Sudan. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2788-9 .
Othman S, Almahbashi T, Alabed AAA, Abdulwahed A. Factors affecting utilization of antenatal care services in Sana’a city, Yeman. Malays J Public Health Med. 2017;17(3):1–14.
Oyewale TO, Mavundla TR. Socioeconomic factors contributing to exclusion of women from maternal health benefit in Abuja, Nigeria. Curationis. 2015;38(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.4102/curationis.v38i1.1272 .
Teguete I, Maiga AW, Leppert PC. Maternal and neonatal outcomes of grand multiparas over two decades in Mali. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2012;91(5):580–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0412.2012.01372.x .
Ntambue AM, Dramaix-Wilmet M, Donnen P. Determinants of maternal health services utilization in urban settings of the Democratic Republic of Congo—a case study of Lubumbashi City. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2012;12(1):66.
Doctor HV, Findley SE, Ager A, et al. Using community-based research to shape the design and delivery of maternal health services in Northern Nigeria. Reprod Health Matters. 2012;20(39):104–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-8080(12)39615-8 .
Truppa C, Leresche E, Fuller AF, et al. Utilization of primary health care services among Syrian refugee and Lebanese women targeted by the ICRC program in Lebanon: a cross-sectional study. Confl Health. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-019-0190-4 .
Kiruja J, Osman F, Egal JA, Essén B, Klingberg-Allvin M, Erlandsson K. Maternal near-miss and death incidences—frequencies, causes and the referral chain in Somaliland: a pilot study using the WHO near-miss approach. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2017;12:30–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.srhc.2017.02.003 .
Steenland M, Robyn PJ, Compaore P, et al. Performance-based financing to increase utilization of maternal health services: evidence from Burkina Faso. SSM Popul Health. 2016;2017(3):179–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2017.01.001 .
Ashir GM, Doctor HV, Afenyadu GY. Performance based financing and uptake of maternal and child health services in yobe sate, northern Nigeria. Glob J Health Sci. 2013;5(3):34–41. https://doi.org/10.5539/gjhs.v5n3p34 .
Ziegler BR, Kansanga M, Sano Y, Kangmennaang J, Kpienbaareh D, Luginaah I. Antenatal care utilization in the fragile and conflict-affected context of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Soc Sci Med. 2020;262(July):113253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.113253 .
Ramos Jaraba SM, Quiceno Toro N, Ochoa Sierra M, et al. Health in conflict and post-conflict settings: reproductive, maternal and child health in Colombia. Confl Health. 2020;14(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-020-00273-1 .
Filippi V, Ronsmans C, Campbell OM, et al. Maternal health in poor countries: the broader context and a call for action. Lancet. 2006;368(9546):1535–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69384-7 .
Kpienbaareh D, Atuoye KN, Ngabonzima A, et al. Spatio-temporal disparities in maternal health service utilization in Rwanda: What next for SDGs? Soc Sci Med. 2019;226(March):164–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2019.02.040 .
Sami S, Mayai A, Sheehy G, et al. Maternal and child health service delivery in conflict-affected settings: a case study example from Upper Nile and Unity states, South Sudan. Confl Health. 2020;14(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-020-00272-2 .
Kelly JT, Betancourt TS, Mukwege D, Lipton R, VanRooyen MJ. Experiences of female survivors of sexual violence in eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo: a mixed-methods study. Confl Health. 2011;5(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-1505-5-25 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Daley P. Gender and genocide in burundi: the search for spaces of peace in the great Lakes region. 2008.
Baaz ME, Stern M. Why do soldiers rape? Masculinity, violence, and sexuality in the armed forces in the Congo (DRC). Int Stud Q. 2009;53(2):495–518. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2478.2009.00543.x .
Ezeh OK, Ogbo FA, Stevens GJ, et al. Factors Associated with the Early Initiation of Breastfeeding in Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS). Nutrients. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112765 .
Bell S. The quantitative impact of conflict on education. 2011.
Uvin P. Life after violence: a people’s story of Burundi. 2008.
Manjoo R, McRaith C. Gender-based violence and justice in conflict and post-conflict areas. Cornell Int Law J. 2011;44:11–31.
Wirtz AL, Pham K, Glass N, et al. Gender-based violence in conflict and displacement: qualitative findings from displaced women in Colombia. Confl Health. 2014;8(1):10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-1505-8-10 .
Alhusen JL, Ray E, Sharps P, Bullock L. Intimate partner violence during pregnancy: maternal and neonatal outcomes. J Womens Health. 2015;24(1):100–6. https://doi.org/10.1089/jwh.2014.4872 .
Gill MM, Ditekemena J, Loando A, et al. Addressing early retention in antenatal care among HIV-positive women through a simple intervention in Kinshasa, DRC: The Elombe “Champion” standard operating procedure. AIDS Behav. 2018;22(3):860–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-017-1770-1 .
Sano Y, Antabe R, Atuoye KN, Braimah JA, Galaa SZ, Luginaah I. Married women’s autonomy and post-delivery modern contraceptive use in the Democratic Republic of Congo. BMC Womens Health. 2018;18(1):4–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-018-0540-1 .
Tlapek SM. Women’s status and intimate partner violence in the Democratic Republic of Congo. J Interpers Violence. 2015;30(14):2526–40. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260514553118 .
Mkandawire P, Atari O, Kangmennaang J, Arku G, Luginaah I, Etowa J. Pregnancy intention and gestational age at first antenatal care (ANC) visit in Rwanda. Midwifery. 2018;2019(68):30–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2018.08.017 .
White D, Dynes M, Rubardt M, Sissoko K, Stephenson R. The influence of intra familial power on maternal health care in Mali: perspectives of women, men and mothers-in-law. Int Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2013;39(2):58–68. https://doi.org/10.1363/3905813 .
Ali R, Barra AF, Berg CN, Damania R, Nash JD, Russ J. Infrastructure in Conflict-Prone and Fragile Environments: Evidence from the Democratic Republic of Congo. Geneva: The World Bank; 2015. https://doi.org/10.1596/1813-9450-7273 .
Book Google Scholar
Mullany LC, Lee TJ, Yone L, et al. Impact of community-based maternal health workers on coverage of essential maternal health interventions among internally displaced communities in eastern Burma: The MOM project. PLoS Med. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000317 .
Ebener S, Guerra-Arias M, Campbell J, et al. The geography of maternal and newborn health: the state of the art. Int J Health Geogr. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12942-015-0012-x .
Simkhada B, Van Teijlingen ER, Porter M, Simkhada P. Factors affecting the utilization of antenatal care in developing countries: systematic review of the literature. J Adv Nurs. 2008;61(3):244–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04532.x .
Fakunle B, Okunlola MA, Fajola A, Ottih U, Ilesanmi AO. Community health insurance as a catalyst for uptake of family planning and reproductive health services: The Obio Cottage Hospital experience. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;34(6):501–3. https://doi.org/10.3109/01443615.2014.902044 .
Ibnouf AH, van den Borne HW, Maarse JA. Utilization of antenatal care services by Sudanese women in their reproductive age. Saudi Med J. 2007;28(5):737–43.
PubMed Google Scholar
Alenoghena IO, Isah EC, Isara AR. Maternal health services uptake and its determinants in public primary health care facilities in edo state, Nigeria. Niger Postgrad Med J. 2015;22(1):25–31.
Alhaidari T, Amso N, Jawad TM. Feasibility and acceptability of text messaging to support antenatal healthcare in Iraqi pregnant women: a pilot study. J Perinat Med. 2017;46(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1515/jpm-2016-0127 .
Balinska MA, Nesbitt R, Ghantous Z, Ciglenecki I, Staderini N. Reproductive health in humanitarian settings in Lebanon and Iraq: Results from four cross-sectional studies, 2014–2015. Confl Health. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-019-0210-4 .
Chi PC, Bulage P, Urdal H, Sundby J. A qualitative study exploring the determinants of maternal health service uptake in post-conflict Burundi and Northern Uganda. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-015-0449-8 .
Findley SE, Doctor HV, Ashir GM. Reinvigorating health systems and community-based services to improve maternal health outcomes: case study from northern Nigeria. J Prim Care Community Health. 2015;6(2):88–99. https://doi.org/10.1177/2150131914549383 .
Franco LM, Diop FP, Burgert CR, Kelley AG, Makinen M, Simparae CHT. Effects of mutual health organizations on use of priority health-care services in urban and rural Mali: a case-control study. Bull World Health Organ. 2008;86(11):830–8. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.08.051045 .
Gao X, Kelley DW. Understanding how distance to facility and quality of care affect maternal health service utilization in Kenya and Haiti: a comparative geographic information system study. Geospat Health. 2019;14(1):92–102. https://doi.org/10.4081/gh.2019.690 .
Ibrahim HK, El Borgy MD, Mohammed HO. Knowledge, attitude, and practices of pregnant women towards antenatal care in primary healthcare centers in Benghazi, Libya. J Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2014;89(3):119–26. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.EPX.0000455673.91730.50 .
Jibril UN, Saleh GN, Badaki O, Anyebe EE, Umar A, Kamal A. Health education intervention on knowledge and accessibility of pregnant women to antenatal care services in Edu, Kwara State, Nigeria. Int J Womens Health Reprod Sci. 2018;6(2):154–60. https://doi.org/10.15296/ijwhr.2018.26 .
Larsen GL, Lupiwa S, Kave HP, Gillieatt S, Alpers MP. Antenatal care in Goroka: issues and perceptions. P N G Med J. 2004;47(3–4):202–14.
Maraga S, Namosha E, Gouda H, Vallely L, Rare L, Phuanukoonnon S. Sociodemographic factors associated with maternal health care utilization in Wosera. East Sepik Province. 2011;54(3–4):154–63.
CAS Google Scholar
Okonofua F, Ntoimo L, Ogungbangbe J, Anjorin S, Imongan W, Yaya S. Predictors of women’s utilization of primary health care for skilled pregnancy care in rural Nigeria. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-018-1730-4 .
Rossier C, Muindi K, Soura A. Maternal health care utilization in Nairobi and Ouagadougou: evidence from HDSS. Glob Health Action. 2014;7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3402/gha.v7.24351 .
Turan JM, Tesfagiorghis M, Polan ML. Evaluation of a community intervention for promotion of safe motherhood in Eritrea. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2011;56(1):8–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1542-2011.2010.00001.x .
Vail J. Antenatal utilization, family planning and fertility preferences in Tari. P N G Med J. 2002;45(1–2):134–41.
Viswanathan K, Hansen PM, Hafizur RM. Can community health workers increase coverage of reproductive health services? J Epidemiol Community Health. 2012;66(10):894–900. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech-2011-200275 .
Adebangbe FT, Mturi AJ. Factors associated with the number of antenatal care visits among internally displaced women in northern Nigeria. Afr J Reprod Health. 2021;25(2):120–30.
Feng Y, Ahuru RR, Anser MK, Osabohien R, Ahmad M, Efegbere AH. Household economic wealth management and antenatal care utilization among business women in the reproductive-age. Afr J Reprod Health. 2021;25(6):143.
Laing SP, Guzek JM, Rassam DM, Ceesay IS, N’Dow JMO. Determinants of compliance with the World Health Organisation recommendations for pregnant women in an urban health centre in The Gambia. Afr J Reprod Health. 2020;24(3):24–32. https://doi.org/10.29063/ajrh2020/v24i3.3 .
Onalu C, Agwu P, Gobo B, Okoye U. Mortality experiences for women in riverine areas of the Niger delta and utilization of maternal health services. Health Soc Work. 2021;46(1):59–67. https://doi.org/10.1093/hsw/hlaa032 .
Oyovwe P, Woolhead G. Exploring health care professionals’ and women’s perspectives on the barriers to maternal health services: a qualitative study in Eku Town of Delta State, Nigeria. AIMS Public Health. 2021;8(1):154–71. https://doi.org/10.3934/publichealth.2021012 .
Somé A, Baguiya A, Coulibaly A, Bagnoa V, Kouanda S. Prevalence and factors associated with late first antenatal care visit in kaya health district, Burkina Fao. Afr J Reprod Health. 2020;24(2):19–26. https://doi.org/10.29063/ajrh2020/v24i2.2 .
Stanikzai MH, Wafa MH, Wasiq AW, Sayam H. Magnitude and determinants of antenatal care utilization in Kandahar City, Afghanistan. Obstet Gynecol Int. 2021;2021:e5201682. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5201682 .
Sui Y, Ahuru RR, Huang K, Anser MK, Osabohien R. Household socioeconomic status and antenatal care utilization among women in the reproductive-age. Front Public Health. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.724337 .
Kane S, Rial M, Kok M, Matere A, Dieleman M, Broerse JEW. Too afraid to go: fears of dignity violations as reasons for non-use of maternal health services in South Sudan. Reprod Health. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-018-0487-6 .
Lowe M, Chen DR, Huang SL. Social and cultural factors affecting maternal health in rural Gambia: an exploratory qualitative study. PLoS ONE. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163653 .
Meiksin R, Meekers D, Thompson S, Hagopian A, Mercer MA. Domestic violence, marital control, and family planning, maternal, and birth outcomes in Timor-Leste. Matern Child Health J. 2015;19(6):1338–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-014-1638-1 .
Ntoimo LFC, Okonofua FE, Igboin B, Ekwo C, Imongan W, Yaya S. Why rural women do not use primary health centres for pregnancy care: evidence from a qualitative study in Nigeria. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-019-2433-1 .
Igboanugo GM, Martin CH. What are pregnant women in a rural Niger Delta community’s perceptions of conventional maternity service provision? An exploratory qualitative study. Afr J Reprod Health. 2011;15(3):59–72.
Mohamed-Ahmed R, Aziz MA, Walker R. Antenatal care in Sudan: a qualitative study into accessibility and quality of maternal health services in Khartoum. Int J Childb. 2018;8(2):77–86. https://doi.org/10.1891/2156-5287.8.2.77 .
Bayo P, Belaid L, Ochola E, et al. Maternal and neonatal health care service utilisation in the wake of active conflict and socio-economic downturn in Torit County, Republic of South Sudan: a multimethod locally driven study. Afr J Reprod Health. 2021;25(3s):30–42.
Akseer N, Bhatti Z, Rizvi A, Salehi AS, Mashal T, Bhutta ZA. Coverage and inequalities in maternal and child health interventions in Afghanistan. BMC Public Health. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-3406-1 .
Galadanci HS, Ejembi CL, Iliyasu Z, Alagh B, Umar US. Maternal health in Northern Nigeria—a far cry from ideal. BJOG Int J Obstet Gynaecol. 2007;114(4):448–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2007.01229.x .
Merrell LK, Blackstone SR. Women’s empowerment as a mitigating factor for improved antenatal care quality despite impact of 2014 Ebola Outbreak in Guinea. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(21):8172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17218172 .
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mutowo J, Yazbek M, van der Wath A, Maree C. Barriers to using antenatal care services in a rural district in Zimbabwe. Int J Afr Nurs Sci. 2021;15:100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijans.2021.100319 .
Chittambo BR, Smith JE, Ehlers VJ. Community participation in providing antenatal services in Zimbabwe. Afr J Nurs Midwifery. 2003;5(1):9.
Edmond KM, Yousufi K, Anwari Z. Can community health worker home visiting improve care-seeking and maternal and newborn care practices in fragile states such as Afghanistan? A population-based intervention study. BMC Med. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-018-1092-9 .
Edmond KM, Foshanji AI, Naziri M. Conditional cash transfers to improve use of health facilities by mothers and newborns in conflict affected countries, a prospective population based intervention study from Afghanistan. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-019-2327-2 .
Rudasingwa M, Soeters R, Basenya O. The effect of performance-based financing on maternal healthcare use in Burundi: a two-wave pooled cross-sectional analysis. Glob Health Action. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1080/16549716.2017.1327241 .
Christou A, Alam A, Sadat Hofiani SM, et al. Understanding pathways leading to stillbirth: the role of care-seeking and care received during pregnancy and childbirth in Kabul province, Afghanistan. Women Birth J Aust Coll Midwives. 2020;33(6):544–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wombi.2020.02.012 .
Kim C, Tappis H, Natiq L, et al. Travel time, availability of emergency obstetric care, and perceived quality of care associated with maternal healthcare utilisation in Afghanistan: a multilevel analysis. Glob Public Health. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/17441692.2021.1873400 .
Jeremiah I, Kasso T, Oriji VK. Patients’ perception of antenatal care at the University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital. Niger J Med J Natl Assoc Resid Dr Niger. 2012;21(1):66–9.
King S, Passey M, Dickson R. Perceptions and use of maternal health services by women in rural coastal Madang Province. P N G Med J. 2013;56(1–2):5–13.
Hyzam D, Zou M, Boah M, et al. Health information and health-seeking behaviour in Yemen: perspectives of health leaders, midwives and mothers in two rural areas of Yemen. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2020;20(1):404. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-020-03101-9 .
Grenier L, Suhowatsky S, Kabue MM. Impact of group antenatal care (G-ANC) versus individual antenatal care (ANC) on quality of care, ANC attendance and facility-based delivery: a pragmatic cluster-randomized controlled trial in Kenya and Nigeria. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(10):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0222177 .
Currie S, Natiq L, Anwari Z, Tappis H. Assessing respectful maternity care in a fragile, conflict-affected context: observations from a 2016 national assessment in Afghanistan. Health Care Women Int. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/07399332.2021.1932890 .
Mourtada R, Bashour H, Houben F. A qualitative study exploring barriers to adequate uptake of antenatal care in pre-conflict Syria: low cost interventions are needed to address disparities in antenatal care. Contracept Reprod Med. 2021;6(1):17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40834-021-00156-7 .
Udenigwe O, Okonofua FE, Ntoimo LFC, Imongan W, Igboin B, Yaya S. “We have either obsolete knowledge, obsolete equipment or obsolete skills”: policy-makers and clinical managers’ views on maternal health delivery in rural Nigeria. Fam Med Community Health. 2021;9(3):e000994. https://doi.org/10.1136/fmch-2021-000994 .
Perry HB, King-Schultz LW, Aftab AS, Bryant JH. Health equity issues at the local level: socio-geography, access, and health outcomes in the service area of the Hôpital Albert Schweitzer-Haiti. Int J Equity Health. 2007;6:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-9276-6-7 .
Erismann S, Gami JP, Ouedraogo B, Revault D, Prytherch H, Lechthaler F. Effects of a four-year health systems intervention on the use of maternal and infant health services: results from a programme evaluation in two districts of rural Chad. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):2304. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-12330-2 .
Ekzayez A, Alhaj Ahmad Y, Alhaleb H, Checchi F. The impact of armed conflict on utilisation of health services in north-west Syria: an observational study. Confl Health. 2021;15(1):91. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-021-00429-7 .
Edmond K, Yousufi K, Naziri M. Mobile outreach health services for mothers and children in conflict-affected and remote areas: a population-based study from Afghanistan. Arch Child. 2020;105(1):18–25. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2019-316802 .
Nie J, Unger JA, Thompson S, Hofstee M, Gu J, Mercer MA. Does mobile phone ownership predict better utilization of maternal and newborn health services? A cross-sectional study in Timor-Leste. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-016-0981-1 .
O’Keefe D, Davis J, Yakuna G, Van Gemert C, Morgan C. Formal and informal maternal health care: comparing the service provision of health facilities and village health volunteers in East Sepik Province. P N G Med J. 2011;54(3–4):147–53.
Ye M, Bagagan C, Millogo O. Use of mobile phone to promote governance and equity within the health system: experience of rural health district in Burkina Faso. J Heal Commun. 2016;1(3):1–11. https://doi.org/10.4172/2472-1654.100017 .
Ouedraogo C, Vosti S, Wessells K, Arnold C, Faye M, Hess S. Out-of-pocket costs and time spent attending antenatal care services: a case study of pregnant women in selected rural communities in Zinder, Niger. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-06027-2 .
Samiah S, Stanikzai MH, Wasiq AW, Sayam H. Factors associated with late antenatal care initiation among pregnant women attending a comprehensive healthcare facility in Kandahar Province, Afghanistan. Indian J Public Health. 2021;65(3):298–301. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijph.IJPH_62_21 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research was supported by a Canadian Graduate Scholarship-Masters from the Social Science and Humanities Research Council and an Ontario Graduate Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Medicine, University of Ottawa, 451 Smyth Road, Ottawa, ON, K1H 8M5, Canada
Kameela Miriam Alibhai & Louise Meddings
DeGroote School of Medicine, McMaster University, 1280 Main Street W, Hamilton, ON, L8S 4L8, Canada
Bianca R. Ziegler
Department of Geography, Western University, 1151 Richmond Street, London, ON, N6A 3K7, Canada
Evans Batung & Isaac Luginaah
Environment Health and Hazards Lab, Western University, 1151 Richmond Street, London, ON, N6A 3K7, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
B.Z. developed the search string and developed the data extraction form. B.Z. and K.A. performed title, abstract, and full-text screening and independently extracted and coded the data. B.Z., L.M., and E.B. analyzed and interpreted the data. B.Z., K.A., L.M., and E.B. wrote the manuscript in consultation with I.L. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kameela Miriam Alibhai .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This systematic review did not require ethics approval as data was collected from publicly available documents.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: table s1..
Detailed description of included studies in this systematic review (n = 121).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Alibhai, K.M., Ziegler, B.R., Meddings, L. et al. Factors impacting antenatal care utilization: a systematic review of 37 fragile and conflict-affected situations. Confl Health 16 , 33 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-022-00459-9
Download citation
Received : 07 September 2021
Accepted : 06 May 2022
Published : 11 June 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-022-00459-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Maternal health
- Maternal mortality
- Sustainable development goals
Conflict and Health
ISSN: 1752-1505
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other. After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables. By arranging your sources by theme or ...
In this post, we'll unpack what exactly synthesis means and show you how to craft a strong literature synthesis using practical examples. This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp. In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step.
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D. For a web accessible version, click the link below the image. For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis).The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
How to synthesize. In the synthesis step of a literature review, researchers analyze and integrate information from selected sources to identify patterns and themes. This involves critically evaluating findings, recognizing commonalities, and constructing a cohesive narrative that contributes to the understanding of the research topic. Synthesis.
One way that seems particularly helpful in organizing literature reviews is the synthesis matrix. The synthesis matrix is a chart that allows a researcher to sort and categorize the different arguments presented on an issue. Across the top of the chart are the spaces to record sources, and along the side of the chart are the spaces to record ...
Synthesis is a complex activity, which requires a high degree of comprehension and active engagement with the subject. As you progress in higher education, so increase the expectations on your abilities to synthesise. How to synthesise in a literature review: Identify themes/issues you'd like to discuss in the literature review. Think of an ...
Synthesis writing is a form of analysis related to comparison and contrast, classification and division. On a basic level, synthesis requires the writer to pull together two or more summaries, looking for themes in each text. ... In a literature review you will be combining material from several texts to create a new text - your literature ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Review the information in the Resources box to learn about using a synthesis matrix. Create your own literature review synthesis matrix using the Word or Excel files available in the Activity box. Organize and synthesize literature related to your topic using your synthesis matrix
Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix. Published on July 4, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan. Revised on May 31, 2023. Synthesizing sources involves ... A literature review is a survey of scholarly knowledge on a topic. Our guide with examples, video, and templates can help you write yours. ...
Types of Research Synthesis: Key Characteristics: Purpose: Methods: Product: CONVENTIONAL Integrative Review: What is it? "The integrative literature review is a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated" [, p.356]. ...
of summaries of the works you read. A literature review is not an annotated bibliography. Your goal is to go one step further and integrate and synthesize what you find in the literature into something new. For example, let's say as you read you discover three major concepts that are important in the literature and relevant to your research.
By step 5 you are well into the literature review process. This next to last step is when you take a moment to reflect on the research you have, what you have learned, how the information fits into you topic, and what is the best way to present your findings. Some tips on how to organize your research-. Organize research by topic. Feel free to ...
Analyze what you learn in (4) using a tool like a Synthesis Table. Your goal is to identify relevant themes, trends, gaps, and issues in the research. Your literature review will collect the results of this analysis and explain them in relation to your research question. Analysis tips
A literature review is not an annotated bibliography, organized by title, author, or date of publication. Rather, it is grouped by topic to create a whole view of the literature relevant to your research question. Figure 7.1. Your synthesis must demonstrate a critical analysis of the papers you collected as well as your ability to integrate the ...
Traditional Literature Review: Systematic Review: Review Question/Topic. Topics may be broad in scope; the goal of the review may be to place one's own research within the existing body of knowledge, or to gather information that supports a particular viewpoint. Starts with a well-defined research question to be answered by the review.
Literature Review - A Self-Guided Tutorial. A self-guided tutorial that walks you through the process of conducting a Literature Review. ... This is the point where you sort articles by themes or categories in preparation for writing your lit review. You may find a synthesis matrix, like this one, or in the box below, helpful in understanding ...
These steps for conducting a systematic literature review are listed below. Also see subpages for more information about: What are Literature Reviews? The different types of literature reviews, including systematic reviews and other evidence synthesis methods; Conducting & Reporting Systematic Reviews; Finding Systematic Reviews; Tools & Tutorials
Step 1 Organize your sources. Step 2 Outline your structure. Step 3 Write paragraphs with topic sentences. Step 4 Revise, edit and proofread. When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own ...
Review Literature as Topic*. This article examines how to synthesise and critique research literature. To place the process of synthesising the research literature into context, the article explores the critiquing process by breaking it down into seven sequential steps. The article explains how and why these steps need to be ke ….
Synthesis Matrix. A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other. After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix to help you see how they relate to each other, and apply to each of your themes or variables. By arranging your sources in a matrix by theme ...
Literature reviews (sometimes shortened to "lit reviews") synthesize previous research that has been done on a particular topic, summarizing important works in the history of research on that topic. The literature review provides context for the author's own new research. It is the basis and background out of which the author's research ...
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research.1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis ...
LITERATURE REVIEW. Often used as a generic term to describe any type of review. More precise definition: Published materials that provide an examination of published literature. Can cover wide range of subjects at various levels of comprehensiveness. Identifies gaps in research, explains importance of topic, hypothesizes future work, etc.
This review presents a synthesis of literature which answers the following research questions: How are community resilience and social capital quantified in research?; What is the impact of community resilience on mental wellbeing?; What is the impact of infectious disease outbreaks, disasters and emergencies on community resilience and social ...
To survey the available knowledge on evaluation practices for KMb strategies, we conducted a scoping review. According to Munn et al. [], a scoping review is indicated to identify the types of available evidence and knowledge gaps, to clarify concepts in the literature and to identify key characteristics or factors related to a concept.This review methodology also allows for the inclusion of a ...
To investigate current practices and main research themes in fiction-based research, I conducted a critical review to classify and integrate existing studies, closely following best-practice recommendations for (methodological) literature reviews in the process (Aguinis et al., 2023; Celik et al., 2023; Hiebl, 2021; Koseoglu et al., 2022; Kunisch et al., 2023).
CIS offers an iterative, dynamic, recursive, and reflexive approach to qualitative synthesis. CIS was well-suited to review the MM KB literature than traditional systematic review methods because it integrates findings from diverse studies into a single, coherent framework based on new theoretical insights and interpretations [26, 27].
Search strategy. A literature search of peer-reviewed articles was conducted using SCOPUS, Web of Science, PubMed, EMBASE, and CINAHL. All five databases were searched on January 11, 2022 using a combination of MeSH terms and keywords (Table 1).The search strategy was created with the help of a subject-specific librarian and adapted to each database.