Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips

How to Write a Narrative Essay | Example & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A narrative essay tells a story. In most cases, this is a story about a personal experience you had. This type of essay , along with the descriptive essay , allows you to get personal and creative, unlike most academic writing .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a narrative essay for, choosing a topic, interactive example of a narrative essay, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about narrative essays.
When assigned a narrative essay, you might find yourself wondering: Why does my teacher want to hear this story? Topics for narrative essays can range from the important to the trivial. Usually the point is not so much the story itself, but the way you tell it.
A narrative essay is a way of testing your ability to tell a story in a clear and interesting way. You’re expected to think about where your story begins and ends, and how to convey it with eye-catching language and a satisfying pace.
These skills are quite different from those needed for formal academic writing. For instance, in a narrative essay the use of the first person (“I”) is encouraged, as is the use of figurative language, dialogue, and suspense.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Narrative essay assignments vary widely in the amount of direction you’re given about your topic. You may be assigned quite a specific topic or choice of topics to work with.
- Write a story about your first day of school.
- Write a story about your favorite holiday destination.
You may also be given prompts that leave you a much wider choice of topic.
- Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself.
- Write about an achievement you are proud of. What did you accomplish, and how?
In these cases, you might have to think harder to decide what story you want to tell. The best kind of story for a narrative essay is one you can use to talk about a particular theme or lesson, or that takes a surprising turn somewhere along the way.
For example, a trip where everything went according to plan makes for a less interesting story than one where something unexpected happened that you then had to respond to. Choose an experience that might surprise the reader or teach them something.
Narrative essays in college applications
When applying for college , you might be asked to write a narrative essay that expresses something about your personal qualities.
For example, this application prompt from Common App requires you to respond with a narrative essay.
In this context, choose a story that is not only interesting but also expresses the qualities the prompt is looking for—here, resilience and the ability to learn from failure—and frame the story in a way that emphasizes these qualities.
An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” is shown below.
Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works.
Since elementary school, I have always favored subjects like science and math over the humanities. My instinct was always to think of these subjects as more solid and serious than classes like English. If there was no right answer, I thought, why bother? But recently I had an experience that taught me my academic interests are more flexible than I had thought: I took my first philosophy class.
Before I entered the classroom, I was skeptical. I waited outside with the other students and wondered what exactly philosophy would involve—I really had no idea. I imagined something pretty abstract: long, stilted conversations pondering the meaning of life. But what I got was something quite different.
A young man in jeans, Mr. Jones—“but you can call me Rob”—was far from the white-haired, buttoned-up old man I had half-expected. And rather than pulling us into pedantic arguments about obscure philosophical points, Rob engaged us on our level. To talk free will, we looked at our own choices. To talk ethics, we looked at dilemmas we had faced ourselves. By the end of class, I’d discovered that questions with no right answer can turn out to be the most interesting ones.
The experience has taught me to look at things a little more “philosophically”—and not just because it was a philosophy class! I learned that if I let go of my preconceptions, I can actually get a lot out of subjects I was previously dismissive of. The class taught me—in more ways than one—to look at things with an open mind.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
If you’re not given much guidance on what your narrative essay should be about, consider the context and scope of the assignment. What kind of story is relevant, interesting, and possible to tell within the word count?
The best kind of story for a narrative essay is one you can use to reflect on a particular theme or lesson, or that takes a surprising turn somewhere along the way.
Don’t worry too much if your topic seems unoriginal. The point of a narrative essay is how you tell the story and the point you make with it, not the subject of the story itself.
Narrative essays are usually assigned as writing exercises at high school or in university composition classes. They may also form part of a university application.
When you are prompted to tell a story about your own life or experiences, a narrative essay is usually the right response.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write a Narrative Essay | Example & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved April 16, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/narrative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an expository essay, how to write a descriptive essay | example & tips, how to write your personal statement | strategies & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 3 great narrative essay examples + tips for writing.
General Education

A narrative essay is one of the most intimidating assignments you can be handed at any level of your education. Where you've previously written argumentative essays that make a point or analytic essays that dissect meaning, a narrative essay asks you to write what is effectively a story .
But unlike a simple work of creative fiction, your narrative essay must have a clear and concrete motif —a recurring theme or idea that you’ll explore throughout. Narrative essays are less rigid, more creative in expression, and therefore pretty different from most other essays you’ll be writing.
But not to fear—in this article, we’ll be covering what a narrative essay is, how to write a good one, and also analyzing some personal narrative essay examples to show you what a great one looks like.
What Is a Narrative Essay?
At first glance, a narrative essay might sound like you’re just writing a story. Like the stories you're used to reading, a narrative essay is generally (but not always) chronological, following a clear throughline from beginning to end. Even if the story jumps around in time, all the details will come back to one specific theme, demonstrated through your choice in motifs.
Unlike many creative stories, however, your narrative essay should be based in fact. That doesn’t mean that every detail needs to be pure and untainted by imagination, but rather that you shouldn’t wholly invent the events of your narrative essay. There’s nothing wrong with inventing a person’s words if you can’t remember them exactly, but you shouldn’t say they said something they weren’t even close to saying.
Another big difference between narrative essays and creative fiction—as well as other kinds of essays—is that narrative essays are based on motifs. A motif is a dominant idea or theme, one that you establish before writing the essay. As you’re crafting the narrative, it’ll feed back into your motif to create a comprehensive picture of whatever that motif is.
For example, say you want to write a narrative essay about how your first day in high school helped you establish your identity. You might discuss events like trying to figure out where to sit in the cafeteria, having to describe yourself in five words as an icebreaker in your math class, or being unsure what to do during your lunch break because it’s no longer acceptable to go outside and play during lunch. All of those ideas feed back into the central motif of establishing your identity.
The important thing to remember is that while a narrative essay is typically told chronologically and intended to read like a story, it is not purely for entertainment value. A narrative essay delivers its theme by deliberately weaving the motifs through the events, scenes, and details. While a narrative essay may be entertaining, its primary purpose is to tell a complete story based on a central meaning.
Unlike other essay forms, it is totally okay—even expected—to use first-person narration in narrative essays. If you’re writing a story about yourself, it’s natural to refer to yourself within the essay. It’s also okay to use other perspectives, such as third- or even second-person, but that should only be done if it better serves your motif. Generally speaking, your narrative essay should be in first-person perspective.
Though your motif choices may feel at times like you’re making a point the way you would in an argumentative essay, a narrative essay’s goal is to tell a story, not convince the reader of anything. Your reader should be able to tell what your motif is from reading, but you don’t have to change their mind about anything. If they don’t understand the point you are making, you should consider strengthening the delivery of the events and descriptions that support your motif.
Narrative essays also share some features with analytical essays, in which you derive meaning from a book, film, or other media. But narrative essays work differently—you’re not trying to draw meaning from an existing text, but rather using an event you’ve experienced to convey meaning. In an analytical essay, you examine narrative, whereas in a narrative essay you create narrative.
The structure of a narrative essay is also a bit different than other essays. You’ll generally be getting your point across chronologically as opposed to grouping together specific arguments in paragraphs or sections. To return to the example of an essay discussing your first day of high school and how it impacted the shaping of your identity, it would be weird to put the events out of order, even if not knowing what to do after lunch feels like a stronger idea than choosing where to sit. Instead of organizing to deliver your information based on maximum impact, you’ll be telling your story as it happened, using concrete details to reinforce your theme.

3 Great Narrative Essay Examples
One of the best ways to learn how to write a narrative essay is to look at a great narrative essay sample. Let’s take a look at some truly stellar narrative essay examples and dive into what exactly makes them work so well.
A Ticket to the Fair by David Foster Wallace
Today is Press Day at the Illinois State Fair in Springfield, and I’m supposed to be at the fairgrounds by 9:00 A.M. to get my credentials. I imagine credentials to be a small white card in the band of a fedora. I’ve never been considered press before. My real interest in credentials is getting into rides and shows for free. I’m fresh in from the East Coast, for an East Coast magazine. Why exactly they’re interested in the Illinois State Fair remains unclear to me. I suspect that every so often editors at East Coast magazines slap their foreheads and remember that about 90 percent of the United States lies between the coasts, and figure they’ll engage somebody to do pith-helmeted anthropological reporting on something rural and heartlandish. I think they asked me to do this because I grew up here, just a couple hours’ drive from downstate Springfield. I never did go to the state fair, though—I pretty much topped out at the county fair level. Actually, I haven’t been back to Illinois for a long time, and I can’t say I’ve missed it.
Throughout this essay, David Foster Wallace recounts his experience as press at the Illinois State Fair. But it’s clear from this opening that he’s not just reporting on the events exactly as they happened—though that’s also true— but rather making a point about how the East Coast, where he lives and works, thinks about the Midwest.
In his opening paragraph, Wallace states that outright: “Why exactly they’re interested in the Illinois State Fair remains unclear to me. I suspect that every so often editors at East Coast magazines slap their foreheads and remember that about 90 percent of the United States lies between the coasts, and figure they’ll engage somebody to do pith-helmeted anthropological reporting on something rural and heartlandish.”
Not every motif needs to be stated this clearly , but in an essay as long as Wallace’s, particularly since the audience for such a piece may feel similarly and forget that such a large portion of the country exists, it’s important to make that point clear.
But Wallace doesn’t just rest on introducing his motif and telling the events exactly as they occurred from there. It’s clear that he selects events that remind us of that idea of East Coast cynicism , such as when he realizes that the Help Me Grow tent is standing on top of fake grass that is killing the real grass beneath, when he realizes the hypocrisy of craving a corn dog when faced with a real, suffering pig, when he’s upset for his friend even though he’s not the one being sexually harassed, and when he witnesses another East Coast person doing something he wouldn’t dare to do.
Wallace is literally telling the audience exactly what happened, complete with dates and timestamps for when each event occurred. But he’s also choosing those events with a purpose—he doesn’t focus on details that don’t serve his motif. That’s why he discusses the experiences of people, how the smells are unappealing to him, and how all the people he meets, in cowboy hats, overalls, or “black spandex that looks like cheesecake leotards,” feel almost alien to him.
All of these details feed back into the throughline of East Coast thinking that Wallace introduces in the first paragraph. He also refers back to it in the essay’s final paragraph, stating:
At last, an overarching theory blooms inside my head: megalopolitan East Coasters’ summer treats and breaks and literally ‘getaways,’ flights-from—from crowds, noise, heat, dirt, the stress of too many sensory choices….The East Coast existential treat is escape from confines and stimuli—quiet, rustic vistas that hold still, turn inward, turn away. Not so in the rural Midwest. Here you’re pretty much away all the time….Something in a Midwesterner sort of actuates , deep down, at a public event….The real spectacle that draws us here is us.
Throughout this journey, Wallace has tried to demonstrate how the East Coast thinks about the Midwest, ultimately concluding that they are captivated by the Midwest’s less stimuli-filled life, but that the real reason they are interested in events like the Illinois State Fair is that they are, in some ways, a means of looking at the East Coast in a new, estranging way.
The reason this works so well is that Wallace has carefully chosen his examples, outlined his motif and themes in the first paragraph, and eventually circled back to the original motif with a clearer understanding of his original point.
When outlining your own narrative essay, try to do the same. Start with a theme, build upon it with examples, and return to it in the end with an even deeper understanding of the original issue. You don’t need this much space to explore a theme, either—as we’ll see in the next example, a strong narrative essay can also be very short.

Death of a Moth by Virginia Woolf
After a time, tired by his dancing apparently, he settled on the window ledge in the sun, and, the queer spectacle being at an end, I forgot about him. Then, looking up, my eye was caught by him. He was trying to resume his dancing, but seemed either so stiff or so awkward that he could only flutter to the bottom of the window-pane; and when he tried to fly across it he failed. Being intent on other matters I watched these futile attempts for a time without thinking, unconsciously waiting for him to resume his flight, as one waits for a machine, that has stopped momentarily, to start again without considering the reason of its failure. After perhaps a seventh attempt he slipped from the wooden ledge and fell, fluttering his wings, on to his back on the window sill. The helplessness of his attitude roused me. It flashed upon me that he was in difficulties; he could no longer raise himself; his legs struggled vainly. But, as I stretched out a pencil, meaning to help him to right himself, it came over me that the failure and awkwardness were the approach of death. I laid the pencil down again.
In this essay, Virginia Woolf explains her encounter with a dying moth. On surface level, this essay is just a recounting of an afternoon in which she watched a moth die—it’s even established in the title. But there’s more to it than that. Though Woolf does not begin her essay with as clear a motif as Wallace, it’s not hard to pick out the evidence she uses to support her point, which is that the experience of this moth is also the human experience.
In the title, Woolf tells us this essay is about death. But in the first paragraph, she seems to mostly be discussing life—the moth is “content with life,” people are working in the fields, and birds are flying. However, she mentions that it is mid-September and that the fields were being plowed. It’s autumn and it’s time for the harvest; the time of year in which many things die.
In this short essay, she chronicles the experience of watching a moth seemingly embody life, then die. Though this essay is literally about a moth, it’s also about a whole lot more than that. After all, moths aren’t the only things that die—Woolf is also reflecting on her own mortality, as well as the mortality of everything around her.
At its core, the essay discusses the push and pull of life and death, not in a way that’s necessarily sad, but in a way that is accepting of both. Woolf begins by setting up the transitional fall season, often associated with things coming to an end, and raises the ideas of pleasure, vitality, and pity.
At one point, Woolf tries to help the dying moth, but reconsiders, as it would interfere with the natural order of the world. The moth’s death is part of the natural order of the world, just like fall, just like her own eventual death.
All these themes are set up in the beginning and explored throughout the essay’s narrative. Though Woolf doesn’t directly state her theme, she reinforces it by choosing a small, isolated event—watching a moth die—and illustrating her point through details.
With this essay, we can see that you don’t need a big, weird, exciting event to discuss an important meaning. Woolf is able to explore complicated ideas in a short essay by being deliberate about what details she includes, just as you can be in your own essays.

Notes of a Native Son by James Baldwin
On the twenty-ninth of July, in 1943, my father died. On the same day, a few hours later, his last child was born. Over a month before this, while all our energies were concentrated in waiting for these events, there had been, in Detroit, one of the bloodiest race riots of the century. A few hours after my father’s funeral, while he lay in state in the undertaker’s chapel, a race riot broke out in Harlem. On the morning of the third of August, we drove my father to the graveyard through a wilderness of smashed plate glass.
Like Woolf, Baldwin does not lay out his themes in concrete terms—unlike Wallace, there’s no clear sentence that explains what he’ll be talking about. However, you can see the motifs quite clearly: death, fatherhood, struggle, and race.
Throughout the narrative essay, Baldwin discusses the circumstances of his father’s death, including his complicated relationship with his father. By introducing those motifs in the first paragraph, the reader understands that everything discussed in the essay will come back to those core ideas. When Baldwin talks about his experience with a white teacher taking an interest in him and his father’s resistance to that, he is also talking about race and his father’s death. When he talks about his father’s death, he is also talking about his views on race. When he talks about his encounters with segregation and racism, he is talking, in part, about his father.
Because his father was a hard, uncompromising man, Baldwin struggles to reconcile the knowledge that his father was right about many things with his desire to not let that hardness consume him, as well.
Baldwin doesn’t explicitly state any of this, but his writing so often touches on the same motifs that it becomes clear he wants us to think about all these ideas in conversation with one another.
At the end of the essay, Baldwin makes it more clear:
This fight begins, however, in the heart and it had now been laid to my charge to keep my own heart free of hatred and despair. This intimation made my heart heavy and, now that my father was irrecoverable, I wished that he had been beside me so that I could have searched his face for the answers which only the future would give me now.
Here, Baldwin ties together the themes and motifs into one clear statement: that he must continue to fight and recognize injustice, especially racial injustice, just as his father did. But unlike his father, he must do it beginning with himself—he must not let himself be closed off to the world as his father was. And yet, he still wishes he had his father for guidance, even as he establishes that he hopes to be a different man than his father.
In this essay, Baldwin loads the front of the essay with his motifs, and, through his narrative, weaves them together into a theme. In the end, he comes to a conclusion that connects all of those things together and leaves the reader with a lasting impression of completion—though the elements may have been initially disparate, in the end everything makes sense.
You can replicate this tactic of introducing seemingly unattached ideas and weaving them together in your own essays. By introducing those motifs, developing them throughout, and bringing them together in the end, you can demonstrate to your reader how all of them are related. However, it’s especially important to be sure that your motifs and clear and consistent throughout your essay so that the conclusion feels earned and consistent—if not, readers may feel mislead.
5 Key Tips for Writing Narrative Essays
Narrative essays can be a lot of fun to write since they’re so heavily based on creativity. But that can also feel intimidating—sometimes it’s easier to have strict guidelines than to have to make it all up yourself. Here are a few tips to keep your narrative essay feeling strong and fresh.
Develop Strong Motifs
Motifs are the foundation of a narrative essay . What are you trying to say? How can you say that using specific symbols or events? Those are your motifs.
In the same way that an argumentative essay’s body should support its thesis, the body of your narrative essay should include motifs that support your theme.
Try to avoid cliches, as these will feel tired to your readers. Instead of roses to symbolize love, try succulents. Instead of the ocean representing some vast, unknowable truth, try the depths of your brother’s bedroom. Keep your language and motifs fresh and your essay will be even stronger!
Use First-Person Perspective
In many essays, you’re expected to remove yourself so that your points stand on their own. Not so in a narrative essay—in this case, you want to make use of your own perspective.
Sometimes a different perspective can make your point even stronger. If you want someone to identify with your point of view, it may be tempting to choose a second-person perspective. However, be sure you really understand the function of second-person; it’s very easy to put a reader off if the narration isn’t expertly deployed.
If you want a little bit of distance, third-person perspective may be okay. But be careful—too much distance and your reader may feel like the narrative lacks truth.
That’s why first-person perspective is the standard. It keeps you, the writer, close to the narrative, reminding the reader that it really happened. And because you really know what happened and how, you’re free to inject your own opinion into the story without it detracting from your point, as it would in a different type of essay.
Stick to the Truth
Your essay should be true. However, this is a creative essay, and it’s okay to embellish a little. Rarely in life do we experience anything with a clear, concrete meaning the way somebody in a book might. If you flub the details a little, it’s okay—just don’t make them up entirely.
Also, nobody expects you to perfectly recall details that may have happened years ago. You may have to reconstruct dialog from your memory and your imagination. That’s okay, again, as long as you aren’t making it up entirely and assigning made-up statements to somebody.
Dialog is a powerful tool. A good conversation can add flavor and interest to a story, as we saw demonstrated in David Foster Wallace’s essay. As previously mentioned, it’s okay to flub it a little, especially because you’re likely writing about an experience you had without knowing that you’d be writing about it later.
However, don’t rely too much on it. Your narrative essay shouldn’t be told through people explaining things to one another; the motif comes through in the details. Dialog can be one of those details, but it shouldn’t be the only one.
Use Sensory Descriptions
Because a narrative essay is a story, you can use sensory details to make your writing more interesting. If you’re describing a particular experience, you can go into detail about things like taste, smell, and hearing in a way that you probably wouldn’t do in any other essay style.
These details can tie into your overall motifs and further your point. Woolf describes in great detail what she sees while watching the moth, giving us the sense that we, too, are watching the moth. In Wallace’s essay, he discusses the sights, sounds, and smells of the Illinois State Fair to help emphasize his point about its strangeness. And in Baldwin’s essay, he describes shattered glass as a “wilderness,” and uses the feelings of his body to describe his mental state.
All these descriptions anchor us not only in the story, but in the motifs and themes as well. One of the tools of a writer is making the reader feel as you felt, and sensory details help you achieve that.
What’s Next?
Looking to brush up on your essay-writing capabilities before the ACT? This guide to ACT English will walk you through some of the best strategies and practice questions to get you prepared!
Part of practicing for the ACT is ensuring your word choice and diction are on point. Check out this guide to some of the most common errors on the ACT English section to be sure that you're not making these common mistakes!
A solid understanding of English principles will help you make an effective point in a narrative essay, and you can get that understanding through taking a rigorous assortment of high school English classes !

Melissa Brinks graduated from the University of Washington in 2014 with a Bachelor's in English with a creative writing emphasis. She has spent several years tutoring K-12 students in many subjects, including in SAT prep, to help them prepare for their college education.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

- Scriptwriting
What is a Narrative Essay — Examples, Format & Techniques
I was in the Amazon jungle the first time I wrote a narrative essay, enlightened and enraptured by the influence of ayahuasca. That’s not true. I’ve never been to South America nor have I ever taken ayahuasca. The purpose of that opening is to show how to craft a narrative essay intro — hook, line, and sinker. Narrative essays rely on hooking the reader, and enticing them to read on. But what is a narrative essay? We’re going to break down everything you need to know about these essays — definition, examples, tips and tricks included. By the end, you’ll be ready to craft your own narrative essay for school or for publication.
What’s a Narrative Essay?
First, let’s define narrative essay.
Narrative essays share a lot of similarities with personal essays, but whereas the former can be fictional or non-fictional, the latter are strictly non-fictional. The goal of the narrative essay is to use established storytelling techniques, like theme , conflict , and irony , in a uniquely personal way.
The responsibility of the narrative essayist is to make the reader feel connected to their story, regardless of the topic. This next video explores how writers can use structural elements and techniques to better engage their readers.
Personal Narrative Essay Examples With Essay Pro
Narrative essays rely on tried and true structure components, including:
- First-person POV
- Personal inspiration
- Focus on a central theme
By keeping these major tenets in mind, you’ll be better prepared to recognize weaknesses and strengths in your own works.
NARRATIVE ESSAY DEFINITION
What is a narrative essay.
A narrative essay is a prose-written story that’s focused on the commentary of a central theme. Narrative essays are generally written in the first-person POV, and are usually about a topic that’s personal to the writer. Everything in these essays should take place in an established timeline, with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
Famous Narrative Essay Examples
- Ticker to the Fair by David Foster Wallace
- After Life by Joan Didion
- Here is a Lesson in Creative Writing by Kurt Vonnegut
Narrative Writing Explained
How to start a narrative essay.
When you go to sleep at night, what do you think of? Flying squirrels? Lost loved ones? That time you called your teacher ‘mom’? Whatever it is, that’s what you need to write about. There’s a reason those ideas and moments have stuck with you over time. Your job is to figure out why.
Once you realize what makes a moment important to you, it’s your job to make it important to the reader too. In this next video, Academy Award-nominated filmmaker J. Christian Jensen explains the power of the personal narrative.
Narrative Writing and the Personal Narrative Essay • Video by TEDx Talks
Anything and everything can be the topic of your essay. It could be as benign as a walk to school or as grandiose as a trip to the moon — so long as that narrative exists within reality. Give your thoughts and opinions on the matter too — don’t be afraid to say “this is what I think” so long as it’s supported by storytelling techniques. Remember, never limit yourself as a writer, just keep in mind that certain topics will be harder to make engaging than others.
Narrative Essay Outline
How to write a narrative essay.
First step, game plan. You’re going to want to map out the story from beginning to end, then mark major story beats in your document.
Like all stories, your narrative essay needs a clear beginning, middle, and end. Each section should generally conform to a specifically outlined structure. For reference, check out the outline below.
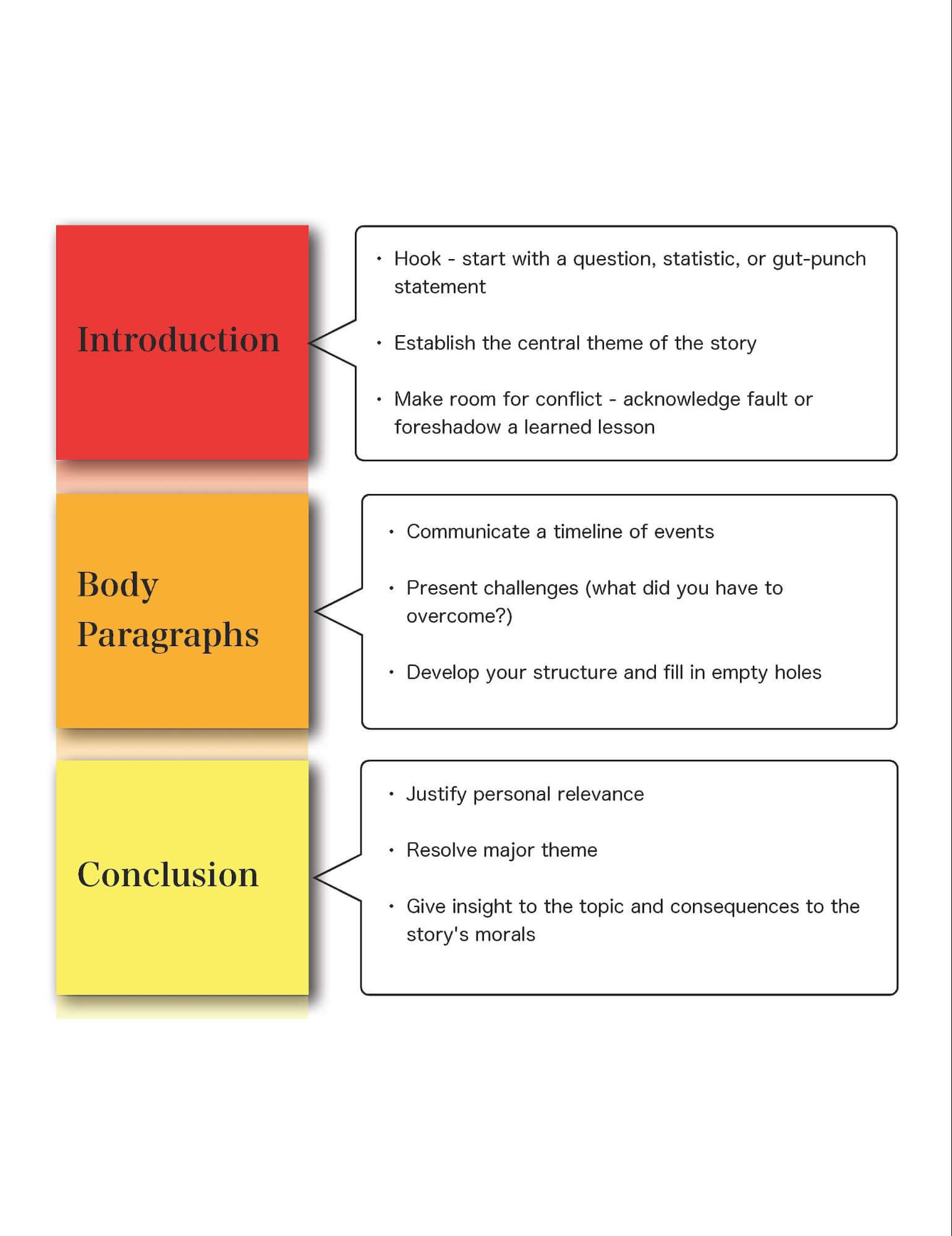
Narrative Essay Format • How to Write a Narrative Essay Step by Step
Make sure to reference back to this outline throughout the writing process to make sure you have all your major beats covered.
Purpose of narrative essay writing
Narrative essays give writers the ability to freely express themselves within the structure of a traditional story. Nearly all universities ask applicants to submit a narrative essay with their formal application. This is done for two reasons: they allow institutions to judge the linguistic and grammar capabilities of its applicants, as well as their raw creative side.
If you’re considering studying creative writing in an undergraduate or graduate program, then you’re going to write A LOT of narrative style essays. This process may seem indomitable; How am I supposed to write hundreds of pages about… me? But by the end, you’ll be a better writer and you’ll have a better understanding of yourself.
One thing that all successful essayists have in common is that they make radical, often defiant statements on the world at large. Think Ralph Waldo Emerson, Virginia Woolf, and Langston Hughes for example.
Being a professional essayist isn’t easy, and it’s near-impossible to be one who makes a lot of money. Many essayists work as professors, editors, and curriculum designers as well.
This next video features the late, award-winning essayist Brian Doyle. He explains all the things you need to hear when thinking about writing a story.
Narrative Essay Examples “Lecture” via Boston University
We can learn a lot from the way Doyle “opens” his stories. My favorite is how he begins with the statement, “I met the Dalai Lama once.” How can we not be interested in learning more?
This brings us all the way back to the beginning. Start with a hook, rattle off the line, then reel in the sinker. If you entice the reader, develop a personal plot, and finish with a resolute ending, you’ll have a lot of success in essay writing.
Up Next
Narrative essay topics.
We've curated a collection of narrative essay topics that will spark your creativity and bring your experiences to life. Dive into the rich tapestry of your memories, explore the unique threads of your life, and let your narrative unfold.
Up Next: Narrative Essay Topics →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- Is Film School Worth It — Why You Should or Shouldn’t Go
- How to Write a Poem — A Step-by-Step Guide
- What is a Character Flaw — And Why Writers Love Them
- How to Become a Movie Critic — Career Tips Explained
- What is an Indie Film — Definition & History Explained
- 1 Pinterest
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Narrative Essay? How to Write It (with Examples)

Narrative essays are a type of storytelling in which writers weave a personal experience into words to create a fascinating and engaging narrative for readers. A narrative essay explains a story from the author’s point of view to share a lesson or memory with the reader. Narrative essays, like descriptive essays , employ figurative language to depict the subject in a vivid and creative manner to leave a lasting impact on the readers’ minds. In this article, we explore the definition of narrative essays, list the key elements to be included, and provide tips on how to craft a narrative that captivates your audience.
Table of Contents
What is a narrative essay, choosing narrative essay topics, key elements in a narrative essay, creating a narrative essay outline, types of narrative essays, the pre-writing stage, the writing stage, the editing stage, narrative essay example, frequently asked questions.
Narrative essays are often based on one’s personal experience which allows the author to express himself/herself in compelling ways for the reader. They employ storytelling elements to convey the plot and captivate the reader while disclosing the story’s theme or purpose. The author must always have a purpose or theme in mind when writing a narrative essay. These essays may be assigned to high school students to assess their ability to create captivating stories based on personal experiences, or they may be required as part of a college application to assess the applicant’s personal traits. Narrative essays might be based on true events with minor tweaks for dramatic purposes, or they can be adapted from a fictional scenario. Whatever the case maybe, the goal is to tell a story, a good story!
In narrative essays, the emphasis is not so much on the narrative itself as it is on how you explain it. Narrative essay topics cover a range of experiences, from noteworthy to mundane, but when storytelling elements are used well, even a simple account can have weight. Notably, the skills required for narrative writing differ significantly from those needed for formal academic essays, and we will delve deeper into this in the next section.
You can talk about any narrative, but consider whether it is fascinating enough, has enough twists and turns, or teaches a lesson (It’s a plus if the story contains an unexpected twist at the end). The potential topics for a narrative essay are limitless—a triumphant story, a brief moment of introspection, or a voyage of self-discovery. These essays provide writers with the opportunity to share a fragment of their lives with the audience, enriching both the writer’s and the reader’s experiences. Narrative essay examples could be a write-up on “What has been your biggest achievement in life so far and what did it teach you?” or “Describe your toughest experience and how you dealt with it?”.

While narrative essays allow you to be creative with your ideas, language, and format, they must include some key components to convey the story clearly, create engaging content and build reader interest. Follow these guidelines when drafting your essay:
- Tell your story using the first person to engage users.
- Use sufficient sensory information and figurative language.
- Follow an organized framework so the story flows chronologically.
- Include interesting plot components that add to the narrative.
- Ensure clear language without grammar, spelling, or word choice errors.
Narrative essay outlines serve as the foundational structure for essay composition, acting as a framework to organize thoughts and ideas prior to the writing process. These outlines provide writers with a means to summarize the story, and help in formulating the introduction and conclusion sections and defining the narrative’s trajectory.
Unlike conventional essays that strictly adhere to the five-paragraph structure, narrative essays allow for more flexibility as the organization is dictated by the flow of the story. The outline typically encompasses general details about the events, granting writers the option to prioritize writing the body sections first while deferring the introduction until later stages of the writing process. This approach allows for a more organic and fluid writing process. If you’re wondering how to start writing a narrative essay outline, here is a sample designed to ensure a compelling and coherent narrative:
Introduction
- Hook/Opening line: The introduction should have an opening/hook sentence that is a captivating quote, question, or anecdote that grabs the reader’s attention.
- Background: Briefly introduce the setting, time, tone, and main characters.
- Thesis statement: State clearly the main theme or lesson acquired from the experience.
- Event 1 (according to occurrence): Describe the first major event in detail. Introduce the primary characters and set the story context; include sensory elements to enrich the narrative and give the characters depth and enthusiasm.
- Event 2: Ensure a smooth transition from one event to the next. Continue with the second event in the narrative. For more oomph, use suspense or excitement, or leave the plot with cliffhanger endings. Concentrate on developing your characters and their relationships, using dialog to bring the story to life.
- Event 3: If there was a twist and suspense, this episode should introduce the climax or resolve the story. Keep the narrative flowing by connecting events logically and conveying the feelings and reactions of the characters.
- Summarize the plot: Provide a concise recap of the main events within the narrative essay. Highlight the key moments that contribute to the development of the storyline. Offer personal reflections on the significance of the experiences shared, emphasizing the lasting impact they had on the narrator. End the story with a clincher; a powerful and thought-provoking sentence that encapsulates the essence of the narrative. As a bonus, aim to leave the reader with a memorable statement or quote that enhances the overall impact of the narrative. This should linger in the reader’s mind, providing a satisfying and resonant conclusion to the essay.
There are several types of narrative essays, each with their own unique traits. Some narrative essay examples are presented in the table below.
How to write a narrative essay: Step-by-step guide
A narrative essay might be inspired by personal experiences, stories, or even imaginary scenarios that resonate with readers, immersing them in the imaginative world you have created with your words. Here’s an easy step-by-step guide on how to write a narrative essay.
- Select the topic of your narrative
If no prompt is provided, the first step is to choose a topic to write about. Think about personal experiences that could be given an interesting twist. Readers are more likely to like a tale if it contains aspects of humor, surprising twists, and an out-of-the-box climax. Try to plan out such subjects and consider whether you have enough information on the topic and whether it meets the criteria of being funny/inspiring, with nice characters/plot lines, and an exciting climax. Also consider the tone as well as any stylistic features (such as metaphors or foreshadowing) to be used. While these stylistic choices can be changed later, sketching these ideas early on helps you give your essay a direction to start.
- Create a framework for your essay
Once you have decided on your topic, create an outline for your narrative essay. An outline is a framework that guides your ideas while you write your narrative essay to keep you on track. It can help with smooth transitions between sections when you are stuck and don’t know how to continue the story. It provides you with an anchor to attach and return to, reminding you of why you started in the first place and why the story matters.

- Compile your first draft
A perfect story and outline do not work until you start writing the draft and breathe life into it with your words. Use your newly constructed outline to sketch out distinct sections of your narrative essay while applying numerous linguistic methods at your disposal. Unlike academic essays, narrative essays allow artistic freedom and leeway for originality so don’t stop yourself from expressing your thoughts. However, take care not to overuse linguistic devices, it’s best to maintain a healthy balance to ensure readability and flow.
- Use a first-person point of view
One of the most appealing aspects of narrative essays is that traditional academic writing rules do not apply, and the narration is usually done in the first person. You can use first person pronouns such as I and me while narrating different scenarios. Be wary of overly using these as they can suggest lack of proper diction.
- Use storytelling or creative language
You can employ storytelling tactics and linguistic tools used in fiction or creative writing, such as metaphors, similes, and foreshadowing, to communicate various themes. The use of figurative language, dialogue, and suspense is encouraged in narrative essays.
- Follow a format to stay organized
There’s no fixed format for narrative essays, but following a loose format when writing helps in organizing one’s thoughts. For example, in the introduction part, underline the importance of creating a narrative essay, and then reaffirm it in the concluding paragraph. Organize your story chronologically so that the reader can follow along and make sense of the story.
- Reread, revise, and edit
Proofreading and editing are critical components of creating a narrative essay, but it can be easy to become weighed down by the details at this stage. Taking a break from your manuscript before diving into the editing process is a wise practice. Stepping away for a day or two, or even just a few hours, provides valuable time to enhance the plot and address any grammatical issues that may need correction. This period of distance allows for a fresh perspective, enabling you to approach the editing phase with renewed clarity and a more discerning eye.
One suggestion is to reconsider the goals you set out to cover when you started the topic. Ask yourself these questions:
- Is there a distinct beginning and end to your story?
- Does your essay have a topic, a memory, or a lesson to teach?
- Does the tone of the essay match the intended mood?
Now, while keeping these things in mind, modify and proofread your essay. You can use online grammar checkers and paraphrase tools such as Paperpal to smooth out any rough spots before submitting it for publication or submission.
It is recommended to edit your essay in the order it was written; here are some useful tips:
- Revise the introduction
After crafting your narrative essay, review the introduction to ensure it harmonizes with the developed narrative. Confirm that it adeptly introduces the story and aligns seamlessly with the conclusion.
- Revise the conclusion and polish the essay
The conclusion should be the final element edited to ensure coherence and harmony in the entire narrative. It must reinforce the central theme or lesson outlined initially.
- Revise and refine the entire article
The last step involves refining the article for consistent tone, style, and tense as well as correct language, grammar, punctuation, and clarity. Seeking feedback from a mentor or colleague can offer an invaluable external perspective at this stage.
Narrative essays are true accounts of the writer’s personal experiences, conveyed in figurative language for sensory appeal. Some narrative essay topic examples include writing about an unforgettable experience, reflecting on mistakes, or achieving a goal. An example of a personal narrative essay is as follows:
Title: A Feline Odyssey: An Experience of Fostering Stray Kittens
Introduction:
It was a fine summer evening in the year 2022 when a soft meowing disrupted the tranquility of my terrace. Little did I know that this innocent symphony would lead to a heartwarming journey of compassion and companionship. Soon, there was a mama cat at my doorstep with four little kittens tucked behind her. They were the most unexpected visitors I had ever had.
The kittens, just fluffs of fur with barely open eyes, were a monument to life’s fragility. Their mother, a street-smart feline, had entrusted me with the care of her precious offspring. The responsibility was sudden and unexpected, yet there was an undeniable sense of purpose in the air , filling me with delight and enthusiasm.
As the days unfolded, my terrace transformed into a haven for the feline family. Cardboard boxes became makeshift cat shelters and my once solitary retreat was filled with purrs and soothing meows. The mother cat, Lily, who initially observ ed me from a safe distance, gradually began to trust my presence as I offered food and gentle strokes.
Fostering the kittens was a life-changing , enriching experience that taught me the true joy of giving as I cared for the felines. My problems slowly faded into the background as evenings were spent playing with the kittens. Sleepless nights turned into a symphony of contented purring, a lullaby filled with the warmth of trust and security . Although the kittens were identical, they grew up to have very distinct personalities, with Kuttu being the most curious and Bobo being the most coy . Every dawn ushered in a soothing ritual of nourishing these feline companions, while nights welcomed their playful antics — a daily nocturnal delight.
Conclusion:
As the kittens grew, so did the realization that our paths were destined to part. Finally, the day arrived when the feline family, now confident and self-reliant, bid farewell to my terrace. It was a bittersweet moment, filled with a sense of love and accomplishment and a tinge of sadness.
Fostering Kuttu, Coco, Lulu, and Bobo became one of the most transformative experiences of my life. Their arrival had brought unexpected joy, teaching me about compassion and our species’ ability to make a difference in the world through love and understanding. The terrace, once a quiet retreat, now bore the echoes of a feline symphony that had touched my heart in ways I could have never imagined.

The length of a narrative essay may vary, but it is typically a brief to moderate length piece. Generally, the essay contains an introductory paragraph, two to three body paragraphs (this number can vary), and a conclusion. The entire narrative essay could be as short as five paragraphs or much longer, depending on the assignment’s requirements or the writer’s preference.
You can write a narrative essay when you have a personal experience to share, or a story, or a series of events that you can tell in a creative and engaging way. Narrative essays are often assigned in academic settings as a form of writing that allows students to express themselves and showcase their storytelling skills. However, you can also write a narrative essay for personal reflection, entertainment, or to communicate a message.
A narrative essay usually follows a three-part structure: – Introduction (To set the stage for the story) – Body paragraphs (To describe sequence of events with details, descriptions, and dialogue) – Conclusion (To summarize the story and reflect on the significance)
Paperpal is an AI academic writing assistant that helps authors write better and faster with real-time writing suggestions and in-depth checks for language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of published scholarly articles and 20+ years of STM experience, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to Paperpal Copilot and premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks, submission readiness and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
Webinar: how to use generative ai tools ethically in your academic writing.
- 7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Chemistry Terms: 7 Commonly Confused Words in Chemistry Manuscripts
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
What is a Descriptive Essay? How to Write It (with Examples)
You may also like, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid....
Narrative Essay with Tips - a Detailed Guide

Defining What Is a Narrative Essay
We can explain a narrative essay definition as a piece of writing that tells a story. It's like a window into someone's life or a page torn from a diary. Similarly to a descriptive essay, a narrative essay tells a story, rather than make a claim and use evidence. It can be about anything – a personal experience, a childhood memory, a moment of triumph or defeat – as long as it's told in a way that captures the reader's imagination.
You might ask - 'which sentence most likely comes from a narrative essay?'. Let's take this for example: 'I could hear the waves crashing against the shore, their rhythm a soothing lullaby that carried me off to sleep.' You could even use such an opening for your essay when wondering how to start a narrative essay.
To further define a narrative essay, consider it storytelling with a purpose. The purpose of a narrative essay is not just to entertain but also to convey a message or lesson in first person. It's a way to share your experiences and insights with others and connect with your audience. Whether you're writing about your first love, a harrowing adventure, or a life-changing moment, your goal is to take the reader on a journey that will leave them feeling moved, inspired, or enlightened.
So if you're looking for a way to express yourself creatively and connect with others through your writing, try your hand at a narrative essay. Who knows – you might just discover a hidden talent for storytelling that you never knew you had!
Meanwhile, let's delve into the article to better understand this type of paper through our narrative essay examples, topic ideas, and tips on constructing a perfect essay.
Types of Narrative Essays
If you were wondering, 'what is a personal narrative essay?', know that narrative essays come in different forms, each with a unique structure and purpose. Regardless of the type of narrative essay, each aims to transport the reader to a different time and place and to create an emotional connection between the reader and the author's experiences. So, let's discuss each type in more detail:
- A personal narrative essay is based on one's unique experience or event. Personal narrative essay examples include a story about overcoming a fear or obstacle or reflecting on a particularly meaningful moment in one's life.
- A fictional narrative is a made-up story that still follows the basic elements of storytelling. Fictional narratives can take many forms, from science fiction to romance to historical fiction.
- A memoir is similar to personal narratives but focuses on a specific period or theme in a person's life. Memoirs might be centered around a particular relationship, a struggle with addiction, or a cultural identity. If you wish to describe your life in greater depth, you might look at how to write an autobiography .
- A literacy narrative essay explores the writer's experiences with literacy and how it has influenced their life. The essay typically tells a personal story about a significant moment or series of moments that impacted the writer's relationship with reading, writing, or communication.
You might also be interested in discovering ' HOW TO WRITE AN AUTOBIOGRAPHY '
Pros and Cons of Narrative Writing
Writing a narrative essay can be a powerful tool for self-expression and creative storytelling, but like any form of writing, it comes with its own set of pros and cons. Let's explore the pros and cons of narrative writing in more detail, helping you to decide whether it's the right writing style for your needs.
- It can be a powerful way to convey personal experiences and emotions.
- Allows for creative expression and unique voice
- Engages the reader through storytelling and vivid details
- It can be used to teach a lesson or convey a message.
- Offers an opportunity for self-reflection and growth
- It can be challenging to balance personal storytelling with the needs of the reader
- It may not be as effective for conveying factual information or arguments
- It may require vulnerability and sharing personal details that some writers may find uncomfortable
- It can be subjective, as the reader's interpretation of the narrative may vary
If sharing your personal stories is not your cup of tea, you can buy essays online from our expert writers, who will customize the paper to your particular writing style and tone.
20 Excellent Narrative Essay Topics and How to Choose One
Choosing a good topic among many narrative essay ideas can be challenging, but some tips can help you make the right choice. Here are some original and helpful tips on how to choose a good narrative essay topic:
- Consider your own experiences: One of the best sources of inspiration for a narrative essay is your own life experiences. Consider moments that have had a significant impact on you, whether they are positive or negative. For example, you could write about a memorable trip or a challenging experience you overcame.
- Choose a topic relevant to your audience: Consider your audience and their interests when choosing a narrative essay topic. If you're writing for a class, consider what topics might be relevant to the course material. If you're writing for a broader audience, consider what topics might be interesting or informative to them.
- Find inspiration in literature: Literature can be a great source of inspiration for a narrative essay. Consider the books or stories that have had an impact on you, and think about how you can incorporate elements of them into your own narrative. For example, you could start by using a title for narrative essay inspired by the themes of a favorite novel or short story.
- Focus on a specific moment or event: Most narrative essays tell a story, so it's important to focus on a specific moment or event. For example, you could write a short narrative essay about a conversation you had with a friend or a moment of realization while traveling.
- Experiment with different perspectives: Consider writing from different perspectives to add depth and complexity to your narrative. For example, you could write about the same event from multiple perspectives or explore the thoughts and feelings of a secondary character.
- Use writing prompts: Writing prompts can be a great source of inspiration if you struggle to develop a topic. Consider using a prompt related to a specific theme, such as love, loss, or growth.
- Choose a topic with rich sensory details: A good narrative essay should engage the senses and create a vivid picture in the reader's mind. Choose a topic with rich sensory details that you can use to create a vivid description. For example, you could write about a bustling city's sights, sounds, and smells.
- Choose a topic meaningful to you: Ultimately, the best narrative essays are meaningful to the writer. Choose a topic that resonates with you and that you feel passionate about. For example, you could write about a personal goal you achieved or a struggle you overcame.
Here are some good narrative essay topics for inspiration from our experts:
- A life-changing event that altered your perspective on the world
- The story of a personal accomplishment or achievement
- An experience that tested your resilience and strength
- A time when you faced a difficult decision and how you handled it
- A childhood memory that still holds meaning for you
- The impact of a significant person in your life
- A travel experience that taught you something new
- A story about a mistake or failure that ultimately led to growth and learning
- The first day of a new job or school
- The story of a family tradition or ritual that is meaningful to you
- A time when you had to confront a fear or phobia
- A memorable concert or music festival experience
- An experience that taught you the importance of communication or listening
- A story about a time when you had to stand up for what you believed in
- A time when you had to persevere through a challenging task or project
- A story about a significant cultural or societal event that impacted your life
- The impact of a book, movie, or other work of art on your life
- A time when you had to let go of something or someone important to you
- A memorable encounter with a stranger that left an impression on you
- The story of a personal hobby or interest that has enriched your life
Narrative Format and Structure
The narrative essay format and structure are essential elements of any good story. A well-structured narrative can engage readers, evoke emotions, and create lasting memories. Whether you're writing a personal essay or a work of fiction, the following guidelines on how to write a narrative essay can help you create a compelling paper:

- Introduction : The introduction sets the scene for your story and introduces your main characters and setting. It should also provide a hook to capture your reader's attention and make them want to keep reading. When unsure how to begin a narrative essay, describe the setting vividly or an intriguing question that draws the reader in.
- Plot : The plot is the sequence of events that make up your story. It should have a clear beginning, middle, and end, with each part building on the previous one. The plot should also have a clear conflict or problem the protagonist must overcome.
- Characters : Characters are the people who drive the story. They should be well-developed and have distinct personalities and motivations. The protagonist should have a clear goal or desire, and the antagonist should provide a challenge or obstacle to overcome.
- Setting : The setting is the time and place the story takes place. It should be well-described and help to create a mood or atmosphere that supports the story's themes.
- Dialogue : Dialogue is the conversation between characters. It should be realistic and help to reveal the characters' personalities and motivations. It can also help to move the plot forward.
- Climax : The climax is the highest tension or conflict point in the story. It should be the turning point that leads to resolving the conflict.
- Resolution : The resolution is the end of the story. It should provide a satisfying conclusion to the conflict and tie up any loose ends.
Following these guidelines, you can create a narrative essay structure that engages readers and leaves a lasting impression. Remember, a well-structured story can take readers on a journey and make them feel part of the action.
Want to Be Like an Expert Writer?
Order now and let our narrative essay service turn your experiences into a captivating and unforgettable tale
Narrative Essay Outline
Here is a detailed narrative essay outline from our custom term paper writing :
Introduction
A. Hook: Start with an attention-grabbing statement, question, or anecdote that introduces the topic and draws the reader in. Example: 'The sun beat down on my skin as I stepped onto the stage, my heart pounding with nervous excitement.'
B. Background information: Provide context for the story, such as the setting or the characters involved. Example: 'I had been preparing for this moment for weeks, rehearsing my lines and perfecting my performance for the school play.'
C. Thesis statement: State the essay's main point and preview the events to come. Example: 'This experience taught me that taking risks and stepping outside my comfort zone can lead to unexpected rewards and personal growth.'
Body Paragraphs
A. First event: Describe the first event in the story, including details about the setting, characters, and actions. Example: 'As I delivered my first lines on stage, I felt a rush of adrenaline and a sense of pride in my hard work paying off.'
B. Second event: Describe the second event in the story, including how it builds on the first event and moves the story forward. Example: 'As the play progressed, I became more comfortable in my role and connecting with the other actors on stage.'
C. Turning point: Describe the turning point in the story, when something unexpected or significant changes the course of events. Example: 'In the final act, my character faced a difficult decision that required me to improvise and trust my instincts.'
D. Climax: Describe the story's climax, the highest tension or conflict point. Example: 'As the play reached its climax, I delivered my final lines with confidence and emotion, feeling a sense of accomplishment and fulfillment.'
A. Restate thesis: Summarize the essay's main point and how the events in the story support it. Example: 'Through this experience, I learned that taking risks and pushing past my comfort zone can lead to personal growth and unexpected rewards.'
B. Reflection: Reflect on the significance of the experience and what you learned from it. Example: 'Looking back, I realize that this experience not only taught me about acting and performance but also about the power of perseverance and self-belief.'
C. Call to action: if you're still wondering how to write an essay conclusion , consider ending it with a call to action or final thought that leaves the reader with something to consider or act on. Example: 'I encourage everyone to take risks and embrace new challenges because you never know what kind of amazing experiences and growth they may lead to.
You might also be interested in getting detailed info on ' HOW TO WRITE AN ESSAY CONCLUSION '
Narrative Essay Examples
Are you looking for inspiration for your next narrative essay? Look no further than our narrative essay example. Through vivid storytelling and personal reflections, this essay takes the reader on a journey of discovery and leaves them with a powerful lesson about the importance of compassion and empathy. Use this sample from our expert essay writer as a guide for crafting your own narrative essay, and let your unique voice and experiences shine through.
Narrative Essay Example for College
College professors search for the following qualities in their students:
- the ability to adapt to different situations,
- the ability to solve problems creatively,
- and the ability to learn from mistakes.
Your work must demonstrate these qualities, regardless of whether your narrative paper is a college application essay or a class assignment. Additionally, you want to demonstrate your character and creativity. Describe a situation where you have encountered a problem, tell the story of how you came up with a unique approach to solving it, and connect it to your field of interest. The narrative can be exciting and informative if you present it in such fashion.
Narrative Essay Example for High School
High school is all about showing that you can make mature choices. You accept the consequences of your actions and retrieve valuable life lessons. Think of an event in which you believe your actions were exemplary and made an adult choice. A personal narrative essay example will showcase the best of your abilities. Finally, use other sources to help you get the best results possible. Try searching for a sample narrative essay to see how others have approached it.
Final Words
So now that you know what is a narrative essay you might want to produce high-quality paper. For that let our team of experienced writers help. Our research paper writing service offers a range of professional writing services that cater to your unique needs and requirements, from narrative essays to medical personal statement , also offering dissertation help and more.
With our flexible pricing options and fast turnaround times, you can trust that you'll receive great value for your investment. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you succeed in your academic writing journey.
Unlock Your Potential with Our Essays!
Order now and take the first step towards achieving your academic goals
What Is A Narrative Essay?
How to start a narrative essay, how to write a good narrative essay, related articles.
%20(2).webp)
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Narrative Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Modes of Discourse—Exposition, Description, Narration, Argumentation (EDNA)—are common paper assignments you may encounter in your writing classes. Although these genres have been criticized by some composition scholars, the Purdue OWL recognizes the widespread use of these approaches and students’ need to understand and produce them.
What is a narrative essay?
When writing a narrative essay, one might think of it as telling a story. These essays are often anecdotal, experiential, and personal—allowing students to express themselves in a creative and, quite often, moving ways.
Here are some guidelines for writing a narrative essay.
- If written as a story, the essay should include all the parts of a story.
This means that you must include an introduction, plot, characters, setting, climax, and conclusion.
- When would a narrative essay not be written as a story?
A good example of this is when an instructor asks a student to write a book report. Obviously, this would not necessarily follow the pattern of a story and would focus on providing an informative narrative for the reader.
- The essay should have a purpose.
Make a point! Think of this as the thesis of your story. If there is no point to what you are narrating, why narrate it at all?
- The essay should be written from a clear point of view.
It is quite common for narrative essays to be written from the standpoint of the author; however, this is not the sole perspective to be considered. Creativity in narrative essays oftentimes manifests itself in the form of authorial perspective.
- Use clear and concise language throughout the essay.
Much like the descriptive essay, narrative essays are effective when the language is carefully, particularly, and artfully chosen. Use specific language to evoke specific emotions and senses in the reader.
- The use of the first person pronoun ‘I’ is welcomed.
Do not abuse this guideline! Though it is welcomed it is not necessary—nor should it be overused for lack of clearer diction.
- As always, be organized!
Have a clear introduction that sets the tone for the remainder of the essay. Do not leave the reader guessing about the purpose of your narrative. Remember, you are in control of the essay, so guide it where you desire (just make sure your audience can follow your lead).

Crafting Compelling Narrative Essays: Storytelling Techniques for Students

Narrative essays offer a unique platform for students to convey their stories, experiences, and viewpoints. Unlike other forms of academic writing that demand strict adherence to factual information and formal structure, narrative essays provide a creative avenue for personal expression. They allow writers to connect with their readers through the art of storytelling, bringing to life their experiences, observations, and insights. This article aims to guide students in harnessing the power of storytelling to create compelling narrative essays. By mastering certain storytelling techniques, students can transform their essays from mere collections of events to captivating stories that resonate with their audience.

Understanding Narrative Essays
A narrative essay is essentially a story told from a personal perspective. It involves characters, a setting, a plot, and often a moral or conclusion drawn from the events narrated. Unlike expository or argumentative essays, narrative essays typically focus on personal experiences and are less rigid in structure and style. This freedom allows for greater creativity and expression, making them a favorite among students and a common assignment in academic settings.
The essence of a narrative essay lies in its storytelling aspect. It’s not just about presenting facts but about weaving these facts into a coherent and engaging story. The challenge for students is to maintain the balance between being informative and creative, which is where storytelling techniques play a crucial role. A narrative essay should not only inform the reader but also connect with them on an emotional level. This connection is what makes narrative essays stand out and is often what students aim to achieve when they seek help from services like Writepaper , which guides them in crafting impactful narratives.

Storytelling Elements in Narrative Essays
Effective storytelling in narrative essays revolves around several key elements:
1. Character. Every narrative essay needs a protagonist, often the writer themselves. Developing a well-rounded character with relatable traits and emotions is essential for creating a connection with the reader. 2. Setting. The backdrop of the story sets the tone and context. Whether it’s a physical location, a historical period, or a cultural background, the setting can significantly influence the mood of the essay. 3. Plot. This is the sequence of events in the essay. A well-structured plot with a clear beginning, middle, and end helps keep the reader engaged. Including a climax or a turning point makes the narrative more compelling. 4. Conflict. The challenges or problems faced by the characters are crucial in creating suspense and interest. Conflict can be external (against other characters or forces) or internal (within the character’s mind). 5. Resolution. How the conflict is resolved forms the crux of the narrative. The resolution brings closure to the story and often carries the underlying message or moral of the essay. Each of these elements contributes to the overall effectiveness of the narrative essay, making the story engaging and memorable for the reader.
Developing a Strong Narrative Voice
The narrative voice is the perspective through which the story is told, and it plays a crucial role in how the story is received by the reader. A strong, distinctive narrative voice can make an essay stand out. To develop this voice, students should consider the following:
1. Choose the Right Perspective. First-person narratives create intimacy, while third-person narratives offer more flexibility in describing events and characters. 2. Be Authentic. The voice should reflect the writer’s personality and experiences. An authentic voice resonates more with readers. 3. Consider Tone and Style. The tone should match the content of the essay. A serious story might require a formal tone, while a humorous one can be more casual and conversational. Developing a unique narrative voice takes practice, but it significantly impacts the essay’s tone and the reader’s engagement.
Creating Vivid Descriptions
Descriptive language is a powerful tool in narrative essays, enabling writers to create vivid imagery and engage the reader’s senses. Here are some techniques for crafting vivid descriptions:
• Use Sensory Details. Describe what is seen, heard, smelled, tasted, or touched to paint a clear picture in the reader’s mind. • Show, Don’t Tell. Instead of stating facts, show them through descriptions and actions. For example, instead of saying, “It was a stormy night,” describe the howling wind and torrential rain. • Be Specific. General descriptions can be dull. Specific details add depth and authenticity to the narrative. Balancing descriptive writing with the narrative’s pace is key. Overly detailed descriptions can slow down the story, while too few can leave it feeling flat and unengaging.
Building Emotional Connection
An emotional connection with the reader is what elevates a narrative essay from good to great. This connection is achieved when the reader feels invested in the story and can empathize with the characters and their experiences.
Here are strategies to build this connection:
• Use Relatable Experiences. Choose topics or situations that are likely to resonate with your audience. Sharing common human experiences, such as triumphs and failures, can evoke a sense of empathy. • Express Emotions. Clearly expressing the emotions experienced by the characters, especially the narrator, helps readers connect on an emotional level. Show how the events affected the characters emotionally, not just physically. • Create Tension and Release. Building tension, be it through conflict, challenges, or uncertainty, and then providing a release keeps readers engaged and creates an emotional payoff. By focusing on these elements, students can make their narratives more impactful and emotionally engaging, fostering a deeper connection with their readers.
Structuring Your Narrative Essay
A well-structured narrative essay helps maintain clarity and ensures that the story flows logically. The structure typically involves:
1. Introduction. Set the scene and introduce the characters and the premise. Begin with a hook to capture the reader’s attention. 2. Body. This is where the plot unfolds. Describe the events in a logical sequence, and include the conflict and build-up to the climax. 3. Conclusion. Offer a resolution to the conflict and reflect on the story’s significance. End with a closing statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Good structure is essential for guiding the reader through the story without confusion, keeping them engaged from start to finish.
Editing and Refining Your Essay
Editing and refining are crucial stages in crafting a compelling narrative essay. This process involves:
• Reviewing Content. Ensure that all the elements of a good story are present and effectively conveyed. Check for clarity in the narrative and consistency in the characters and plot. • Proofreading. Pay attention to grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors. These can distract from the story and affect the essay’s overall quality. • Seeking Feedback. Getting feedback from peers, teachers, or a mentor can provide new insights and help identify areas that need improvement. Editing and refining can transform a good narrative essay into an excellent one, making this stage as important as the initial writing process.
Final Thoughts
Crafting a compelling narrative essay involves more than just recounting events; it requires skillful storytelling, emotional engagement, clear structure, and careful editing. By employing these techniques, students can elevate their narrative essays, making them not just assignments to be completed but stories to be cherished and remembered. Just as one might turn to the best paper writing service for guidance in academic writing, mastering the art of narrative essay writing requires practice, feedback, and a willingness to learn and grow as a storyteller.
In conclusion, narrative essays offer a unique opportunity for students to express themselves creatively and connect with their readers. By utilizing storytelling techniques effectively, students can create essays that are not only academically successful but also personally fulfilling and engaging for their audience.
Narrative Essay
Narrative Essay Examples
10+ Interesting Narrative Essay Examples Plus Writing Tips!

People also read
Narrative Essay - A Complete Writing Guide with Examples
Writing a Personal Narrative Essay: Everything You Need to Know
Best Narrative Essay Topics 2023 for Students
Crafting a Winning Narrative Essay Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
Many students struggle with crafting engaging and impactful narrative essays. They often find it challenging to weave their personal experiences into coherent and compelling stories.
If you’re having a hard time, don't worry!
We’ve compiled a range of narrative essay examples that will serve as helpful tools for you to get started. These examples will provide a clear path for crafting engaging and powerful narrative essays.
So, keep reading and find our expertly written examples!
- 1. Narrative Essay Definition
- 2. Narrative Essay Examples
- 3. Narrative Essay Examples for Students
- 4. Narrative Essay Topics
- 5. Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative Essay Definition
Writing a narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that revolves around personal experiences, aiming to immerse the reader in the author's world. It's a piece of writing that delves into the depths of thoughts and feelings.
In a narrative essay, life experiences take center stage, serving as the main substance of the story. It's a powerful tool for writers to convey a personal journey, turning experiences into a captivating tale. This form of storytelling is an artful display of emotions intended to engage readers, leaving the reader feeling like they are a part of the story.
By focusing on a specific theme, event, emotions, and reflections, a narrative essay weaves a storyline that leads the reader through the author's experiences.
The Essentials of Narrative Essays
Let's start with the basics. The four types of essays are argumentative essays , descriptive essays , expository essays , and narrative essays.
The goal of a narrative essay is to tell a compelling tale from one person's perspective. A narrative essay uses all components you’d find in a typical story, such as a beginning, middle, and conclusion, as well as plot, characters, setting, and climax.
The narrative essay's goal is the plot, which should be detailed enough to reach a climax. Here's how it works:
- It's usually presented in chronological order.
- It has a function. This is typically evident in the thesis statement's opening paragraph.
- It may include speech.
- It's told with sensory details and vivid language, drawing the reader in. All of these elements are connected to the writer's major argument in some way.
Before writing your essay, make sure you go through a sufficient number of narrative essay examples. These examples will help you in knowing the dos and don’ts of a good narrative essay.
It is always a better option to have some sense of direction before you start anything. Below, you can find important details and a bunch of narrative essay examples. These examples will also help you build your content according to the format.
Here is a how to start a narrative essay example:
Sample Narrative Essay
The examples inform the readers about the writing style and structure of the narration. The essay below will help you understand how to create a story and build this type of essay in no time.
Here is another narrative essay examples 500 words:
Narrative Essay Examples for Students
Narrative essays offer students a platform to express their experiences and creativity. These examples show how to effectively structure and present personal stories for education.
Here are some helpful narrative essay examples:
Narrative Essay Examples Middle School
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 7
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 8
Grade 11 Narrative Essay Examples
Narrative Essay Example For High School
Narrative Essay Example For College
Personal Narrative Essay Example
Descriptive Narrative Essay Example
3rd Person Narrative Essay Example
Narrative Essay Topics
Here are some narrative essay topics to help you get started with your narrative essay writing.
- When I got my first bunny
- When I moved to Canada
- I haven’t experienced this freezing temperature ever before
- The moment I won the basketball finale
- A memorable day at the museum
- How I talk to my parrot
- The day I saw the death
- When I finally rebelled against my professor
Need more topics? Check out these extensive narrative essay topics to get creative ideas!
Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative essays give you the freedom to be creative, but it can be tough to make yours special. Use these tips to make your story interesting:
- Share your story from a personal viewpoint, engaging the reader with your experiences.
- Use vivid descriptions to paint a clear picture of the setting, characters, and emotions involved.
- Organize events in chronological order for a smooth and understandable narrative.
- Bring characters to life through their actions, dialogue, and personalities.
- Employ dialogue sparingly to add realism and progression to the narrative.
- Engage readers by evoking emotions through your storytelling.
- End with reflection or a lesson learned from the experience, providing insight.
Now you have essay examples and tips to help you get started, you have a solid starting point for crafting compelling narrative essays.
However, if storytelling isn't your forte, you can always turn to our essay writing service for help.
Our writers are specialists that can tackle any type of essay with great skill. With their experience, you get a top-quality, 100% plagiarism free essay everytime.
So, let our narrative essay writing service make sure your narrative essay stands out. Order now!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Spring Sale: Get 15% off selected writing courses, only through April 19! Learn more »

It is hard to describe the art of storytelling, but you know good storytelling it when you read it. You read a passage of prose and it raises your arm hairs, makes your blood tingle, gets your heart racing; suddenly you’re swept up in the experience of beautiful writing.
Indeed, writers seem to possess a certain magic of storytelling—but anyone can learn the tricks of the trade. From story structures to style advice, this article covers the storytelling techniques that make readers laugh, weep, gasp, and stay up past their bedtimes.
Along the way, we discuss the key elements of storytelling, and we answer the question “Why is storytelling important?” But first, let’s dissect the art of storytelling itself. How do writers tell great stories?
Storytelling Contents
Story Versus Situation
- Point of View
- Style & Word Choice
20 Storytelling Techniques
Why is storytelling important, storytelling definition.
What is storytelling? It depends on whom you ask. A sociologist will tell you it’s mankind’s way of preserving history and identity; an anthropologist will say that it’s what distinguishes man from the rest of the animal kingdom.
Storytelling is the process of weaving language into a concrete narrative, with the purpose of creating rich, believable experiences.
For writers, storytelling is the process of weaving language into a concrete narrative, with the purpose of creating rich, believable experiences. To do this, storytellers tie together character and plot, resulting in stories that act as metaphors for the human experience.
In other words, storytellers don’t just relay facts: they use words in a way that the reader or listener can sit inside the story itself as though they were really there.
This is true regardless of genre—writers of sci-fi, fantasy, and horror create stories just as believable as writers of literary fiction . Nonfiction authors and poets also demonstrate mastery over the art of storytelling, though they may use different storytelling techniques.
The reader can sit inside the story itself as though they were really there.
The magic of storytelling is found in the power of stories themselves. Many writers, however, confuse “story” with “situation,” having not been taught the difference between these two concepts.
Here’s a breakdown of the difference between storytelling and situation-telling, as explained by our instructor Jeff Lyons .
https://writers.com/stories-vs-situations-how-to-know-your-story-will-work-in-any-genre
7 Elements of Storytelling
No matter the tale, every work of prose (and many poems) rely on these 7 elements of storytelling.
Plot is the skeleton of storytelling. You can have a gorgeous prose style with deeply relatable characters, but without a logical flow of events, your story will confuse the reader. For a story to emulate real life, it needs to follow a real-life series of plot points.
Now, this doesn’t mean that your story needs to follow chronological order. Many stories experiment with the order of events, or they jump over decades of time, or they weave together the present with the past. There’s no need to stick to one timeline: time is a thread, and can be interwoven to create rich tapestries.
Your characters write your plot; your plot doesn’t write your characters.
Nonetheless, your reader needs to follow the plot to understand your story. And remember: your characters write your plot; your plot doesn’t write your characters.
For more advice on crafting effective plots, take a look at these articles on:
- Freytag’s Pyramid
- How to Write a Story Outline
2. Character
Equally important to the art of storytelling is the characters that populate your work. Every event that takes place in your story is defined by your characters’ thoughts, feelings, and actions. Although some plot points are outside of their control, it’s your characters’ responses to conflict that make a story worth reading.
Writers must consider how the reader will connect with the story’s characters. If those characters have depth, understandable motives, and relatable flaws, the reader will feel much more engrossed in the story. Stephen King sums this up nicely when he writes:
“I try to create sympathy for my characters, then turn the monsters loose.” —Stephen King
Once we relate to the story’s characters, we care about what happens to them, and we’re willing to follow them along their personal journeys. Each character of your story—including your protagonist, antagonist, secondary and tertiary characters—should feel like real, flesh-and-blood human beings.
For more advice on writing realistic characters, take a look at these articles:
- Character Development Definition, Questions, & 40 Character Traits
- Character Development Advice
- How to Write Dialogue
- Crafting Your Protagonist
- Writing An Antagonist
- Foil Characters
- Static Vs Dynamic Characters
- Round Vs Flat Characters
- Anti Hero Characters
You might also benefit from this Character Development PDF .
3. Point-of-View
Point-of-View (POV) defines who is communicating to the reader , and from what vantage point. The story’s narrator influences how the story is told and what information the reader has access to.
Writers have 5 points of view to choose from:
- First Person (“I”): The narrator is the protagonist, and we view the story from their perspective. This is generally the most intimate storytelling POV.
- First Person Peripheral (“I”): The narrator is a close acquaintance of the protagonist, and we view the story from their perspective. An example of this is Nick Carraway, narrator of The Great Gatsby .
- Second Person (“You”): The narrator casts the reader as the story’s protagonist. This is a way to make the reader intimate with the story’s events, but it’s a hard sell—stories are rarely written in the 2nd person.
- Third Person Limited (“He/She/They”): The narrator tells the story from the vantage point of one or a few protagonists. The narrator only knows what the protagonist also knows.
- Third Person Omniscient (“He/She/They”): The narrator tells the story from multiple vantage points. The narrator knows more than any character in the story knows, and the narrator often weaves this knowledge together to craft a deeper, more holistic story.
A story’s point of view will affect the storytelling techniques and strategies that the author uses. Bear in mind, too, that a story can switch between different POVs. Learn more about POV at our article What is Point of View in Literature ?
At its most basic, setting is where your story takes place, but setting can serve many more functions than just this. The relationship that your characters have to their setting influences the story’s pace, plot, conflict, and even its themes.
Your characters will, in some way or another, be defined by their setting. The personality of someone from Cheyenne, Wyoming will differ greatly from a character who grew up in Hell’s Kitchen, New York City, and both of these people will experience the world differently than someone who grew up in Seoul, South Korea. Setting implies culture, worldview, and language, even if your character tries to push back against their upbringing.
Your characters will, in some way or another, be defined by their setting.
Setting also influences dialogue and action. An argument at the dinner table will (probably) sound different than an argument in a restaurant; a fist fight in a parking lot will go a different route than a fist fight in an office.
Finally, setting can build symbolism . If your protagonist lives in a rundown, ramshackle house, this house can represent his ramshackle life; a character that lives in a gentrified apartment building in an otherwise poor neighborhood might be equally ritzy and oblivious to the world around her.
Just be careful not to stereotype—setting is just one of many influences on a character’s psyche and worldview. For more advice on writing setting, take a look at our article What is the Setting of a Story?
5. Style & Word Choice
One of the more intangible elements of storytelling, style refers to the unique way that an author tells their story.
Style occurs at both a line-level and a global level. At the line-level, style is influenced by a story’s word choice, syntax, sentence structure, sentence length, and the observational details that the author includes.
At the global level, style is influenced by the story’s pacing, the way the story presents information, the length of scenes and chapters, and the author’s own literary influences.
All of these things culminate in the author’s thumbprint. There’s no singular reason why a novel by Haruki Murakami is so vividly distinct from a novel by Margaret Atwood. All of the aforementioned elements coalesce into something unique and intangible, but nonetheless present in the atmosphere of the author’s work.
Style isn’t forced: it develops naturally as the author grows into their storytelling role. For advice on honing your style, read our articles:
- The Importance of Word Choice in Writing
- How to Write a Compelling Story
- What is Tone in Literature?
- How to Avoid Cliches in Writing
6. Conflict
Every story has conflict. Conflict is the lifeblood of storytelling: without it, your characters don’t undergo any growth or finish any journey.
Conflict can manifest itself in many ways. The protagonist wants something, but has to overcome certain obstacles to get it; or they want something, but an antagonist stands in the way; or an antagonist uproots the protagonist’s life; or the protagonist seeks a life of their own, but doesn’t know how to build one.
The road to resolving conflict is never easy, but that’s what makes great stories!
In any case, conflict has to do with the protagonist having certain needs, desires, or struggles. Great stories involve the protagonist having to undergo personal journeys in order to get what they need. The road to resolving conflict is never easy, but that’s what makes great stories!
For more on conflict, take a look at our article What is Conflict in a Story?
Also check out What Does Your Character Want? Conflict is closely related to theme, which we discuss below.
The aforementioned elements of storytelling culminate in theme. At its simplest, theme answers the question “What is this story about?”
The story’s plot, characters, and conflicts revolve around certain abstract issues. Romeo & Juliet , for example, revolves around the themes of love, fate, and family; A Tale of Two Cities has themes of war, revolution, justice, and power & corruption.
In other words, theme describes the central ideas that a piece of writing explores. And, because a story is propelled by conflict, theme and conflict are closely intertwined. If the protagonist’s needs are jeopardized because of the government, the theme might be “justice” or “power & corruption.” Or, if the protagonist’s needs aren’t being met because they’ve just survived an apocalypse, the theme might be “the environment” or “man vs. nature.”
The job of the storyteller isn’t to resolve those themes: themes should be open-ended, debatable, and thought-provoking. Two readers may have vastly different, yet equally defensible, interpretations of a theme. Rather, the storyteller’s job is to present clear conflicts, flawed characters, and navigable plots; theme, often, follows on its own accord.
To learn more about theme and read some theme examples, read our article What is Theme?
In addition to these elements of storytelling, writers use the following storytelling techniques to craft engaging, compelling stories.
Storytelling Techniques
The elements of storytelling answer what storytellers do at a global level. But when it comes to actually crafting the story—stringing one word after another to move the reader along—what do storytellers do?
Below are some tried-and-true methods of telling engaging stories. Note that this list is not exhaustive: us writers have been refining the art of storytelling for millennia, and this is just a sample of the many tools at our disposal.
Backstory describes the history of a character or setting. By providing relevant historical detail, the author gives contexts for certain conflicts and relationships that exist within the main narrative.
The relationship between backstory and narration can be difficult to refine, because too much backstory will slow down the pace of the work at large. Like most storytelling techniques, be economical—you shouldn’t provide more backstory than necessary.
That said, backstory can span chapters of the text, if needed. By providing valuable insight into a character’s psyche and motives, backstory helps the reader understand the decisions that character makes and the problems they face.
Deus Ex Machina
Deus Ex Machina is a plot device where something outside of the protagonist’s control interferes with the story, usually resolving the story’s conflict. This term comes from the Latin for “God from the machine,” and it refers to a convention of Ancient Greek plays in which an actor, playing as a god, was mechanically lowered onto the stage.
Deus Ex Machina can take many forms. Perhaps a natural disaster kills the antagonist, or two friends discover they’re actually long lost sisters, or an actual god intervenes on the protagonist’s behalf. In any case, Deus Ex Machinas never occur by the protagonist’s own volition.
Generally, Deus Ex Machina is frowned upon as an easy way out of conflict. Rather than giving the protagonist agency, the author has decided to interrupt the protagonist’s journey and personal growth. At the same time, Deus Ex Machina can create new artistic possibilities, especially if the author is writing in genres like absurdism, surrealism, or magical realism .
Ethos, pathos, and logos are three storytelling strategies often associated with rhetoric, but they apply just as readily to the art of storytelling.
In creative writing, Ethos describes the author’s credibility as a storyteller. Ethos is built from both the author’s reputation and from their ability to relay facts accurately, without harmful bias or intentionally misleading the reader.
Now, authors need to have a credible ethos, but narrators don’t. Remember that Point of View is one of the essential elements of storytelling. One way that writers can twist Ethos is by writing an unreliable narrator —someone who distorts facts, misleads the reader, and creates their own reality. Pulling off an effective unreliable narrator can prove difficult, but it can also create some very entertaining twists in the story.
To learn more about ethos, pathos, and logos, check out our article on rhetorical devices .
Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing refers to moments in the story that predict later events. When the narrator foreshadows, they usually hint at the story’s climax, but any future plot point is fair game for foreshadowing.
The best foreshadowing is memorable, but subtle enough that you don’t realize it’s foreshadowing until later. For example, in The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald, the drunk Miss Baedeker foreshadows Gatsby’s death when she complains of getting her “head stuck in a pool.”
A more ostensible example is Gatsby’s relationship to the green light on Daisy’s property. He reaches out to the green light but can never hold it, much like he reaches out to Daisy but can never hold her. You may note that this is also an example of symbolism, and indeed, foreshadowing can coincide with many other literary devices.
In Media Res
*Record Scratch* “Yep, that’s me. You’re probably wondering how I got here.”
In Media Res (Latin: in the middle of things) is a plot device in which the story begins in the middle, rather than at the beginning. By doing this, the author throws the reader directly into the story’s conflict. Eventually, the inciting incident and character backstories are provided.
The In Media Res strategy helps generate intrigue for the story, its plot, and its characters. Rather than set up the conflict in chapters of exposition, we are launched directly into the drama.
Some famous stories that begin In Media Res include The Odyssey by Homer, The Gambler by Fyodor Dostoevsky, The Handmaid’s Tale by Margaret Atwood, and Wuthering Heights by Emily Brontë.
Literary Devices
Literary devices are methods of creating deeper meanings within a text. By harnessing the power of comparison, connection, and sound, writers use literary devices to take their work beyond a literal meaning . Literary devices create nuance and depth, making them essential to the art of storytelling.
Try your hand at different literary devices from this article.
https://writers.com/common-literary-devices
Logos is the use of logic and reasoning to persuade the reader. While Logos most commonly presents itself in rhetorical essays and arguments, it also has its place in creative writing.
Authors will most often use logos in relation to the story’s themes. For example, the novel To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee is about racial justice in the United States. When lawyer Atticus Finch defends the wrongfully accused Tom Robinson, he uses logos to appeal to the courts that Tom is innocent.
But Atticus’ logical appeal isn’t just to the courts, it’s to the readers themselves. When Tom is convicted anyway and later killed, the reader understands exactly how society disregards Logos when it comes to the plight of black men. Through these plot points, the novel intricately examines its themes of justice, and how justice is not evenly distributed in American society.
A MacGuffin describes a character’s motives. Every character is chasing something in particular, whether that be a physical object or an abstract concept. Items like The Holy Grail or the Rings of Power are MacGuffins, and so are ideas like love, revenge, and stability.
MacGuffins are one of the most open-ended storytelling techniques, because a character’s motives can be virtually anything. Additionally, a MacGuffin can be both openly stated or obscure. In Pulp Fiction , for example, the movie’s MacGuffin is a briefcase, but the contents of that briefcase are never revealed, highlighting the movie’s senseless violence in the pursuit of nothing.
If the story’s MacGuffin is a physical object, that object often symbolizes something deeper for the main characters. Nonetheless, your characters can pursue whatever they want, just as people in real life pursue their own mysterious MacGuffins.
Mythology provides a powerful reservoir of storytelling for modern day authors. By “mythology,” we’re referring to any set of stories, narratives, folklore, poems, and epics particular to a certain culture, with the intent of relating that culture’s religious and moral beliefs.
References to ancient myth abound in both classic and contemporary literature. This is for three reasons:
- First, mythologies are commonly read stories. You can connect with the reader using myth as a stepping stone, especially if that myth is widely familiar.
- Second, myths act as their own symbols. If you reference the story of Icarus, your reader will know you are referencing the tragedy of Hubris.
- Third, mythology allows the reader to create relevant cultural contexts. Haruki Murakami often incorporates Japanese folklore into his work, and the novel Beauty is a Wound by Eka Kurniawan relies heavily on Indonesian mythology.
Pathos is an appeal to the reader’s emotions. Because the experience of reading relies so much on the reader’s own empathy, harnessing the power of pathos is key to the art of storytelling.
Storytellers generate pathos simply by writing relatable characters. When the reader connects with a character as if they were a real human being, the reader also feels that character’s pain, struggles, and triumphs. Always assume that your reader wants to connect with your characters, that they want to feel your story pour salt in the wound. This is equally true for your antagonist, assuming that antagonist is also a human being.
Think about the things that everyday, ordinary people yearn for. Maybe it’s stability, love, a sense of belonging; maybe they relate to stories of natural disaster, unrequited love, or being a misfit. Consider your reader and what they might connect with, and make Pathos your doorway into the reader’s heart.
A quibble is a technicality that, though minor, often resolves the plot in a major way.
Let’s say your protagonist makes a bet with someone, and they lose that bet. The price they pay for that bet is death. Your protagonist may save their own life by arguing that the bet should follow the exact verbal agreement that they made—and by invoking this technicality, your protagonist manages to evade death entirely.
Of course, quibbles can go against the protagonist’s wishes, too. In Macbeth , the Three Witches tell Macbeth that “none of woman born” can kill him. Macbeth assumes this to mean he is invincible, but he is later killed by Macduff, who was C-sectioned rather than “born from” a woman.
If written haphazardly, a quibble can be just as convenient as a Deus Ex Machina. Nonetheless, quibbles often surprise the reader, as they chip at the seeming absoluteness of fate.
Red Herrings
In both rhetoric and literature, a red herring is something that distracts the reader. You will most often see red herrings in mystery novels, as the novelist is trying to prevent the reader from solving the mystery until the very end.
Red herrings are one of the more versatile storytelling techniques, as they take many different forms. A red herring can be a clue falsely pinned to an innocent person; it can be a forced confession, or an unreliable narrator falsifying the past, or even a coincidence that the writer didn’t intend.
Although red herrings are a fun twist to the art of storytelling, use them sparingly. As an author, you have an implicit contract with the reader to tell your story faithfully; too many distractions and misleading elements will make the reader lose faith in your storytelling.
Rhetorical Questions
A rhetorical question is a question that’s posed for the sake of asking, rather than the sake of being answered. In other words, it’s a question meant to provoke the reader.
Rhetorical questions are often open-ended. While a narrator can pose rhetorical questions, they usually come from a character in the story.
A famous example of this is in Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar , when Caesar asks Brutus “Et tu, Brute?” This question has no answer—after all, Caesar is about to die—but it prompts the reader to think about Brutus’ betrayal of trust and friendship.
In everyday speech, we use rhetorical questions all the time. Who knows? Why not? Is the sky blue? Rhetorical questions can help make your dialogue seem more human, and it can also provoke your reader’s thoughts and emotions.
Rule of Threes
The Rule of Threes states that readers best respond to information that’s presented in lists of three. This applies to everything, from basic descriptions to global, structural elements in a story.
The Rule of Threes happens at the line level, especially with description. If I tell you my cat is “young, fluffy, and orange,” those three images give you a solid description. If I tell you my cat is “young, fluffy, loud, stubborn, fast, destructive, capricious, and orange,” I’ve overloaded my description with adjectives, and you won’t know what part of that information is essential .
The Rule of Threes also applies to story structures. Many stories have, at most, three main characters. Many plots have three main events: an inciting incident, a climax, and a falling action (or response to the climax). If a novel has sections, it often has three sections; if a style has multiple settings, it usually has three main ones.
This is not a hard and fast rule—in fact, most rules in writing are suggestions. Nonetheless, your writing will lose the reader’s attention and brainspace if it presents too much information. The Rule of Threes is not immutable, and you don’t need 3 of everything.
But, when it comes to the central elements of your work, try to keep it to three discrete items. Otherwise, you might lose your grip on the magic of storytelling.
Show, Don’t Tell
What is storytelling without the show, don’t tell rule? “Show, don’t tell” is a way of using imagery to relay an experience to the reader, rather than spoon feeding that experience through literal description. The effect is that your reader becomes immersed in the story, perceiving everything that your characters perceive as though they were really there.
“Don’t tell me the moon is shining; show me the glint of light on broken glass.” —Anton Chekhov
To master the show, don’t tell rule, read through our in-depth article.
https://writers.com/show-dont-tell-writing
Stream of Consciousness
Stream of Consciousness is a writing technique in which a character’s thoughts are written directly onto the page, without any filter or editing. The author, assuming the persona of their character, observes their thoughts and impartially transcribes those thoughts into narration and internal dialogue.
Because stream of consciousness attempts to capture the idiosyncrasies of human thought, the prose itself can be difficult to follow. Authors may write using free association, frequent repetition, disjointed imagery, and a keen focus on senses and emotions. The prose often follows a nonlinear fashion, it may use punctuation frenetically, and it certainly won’t have the polished, edited feel of a typical manuscript.
To be clear: this is perhaps the most difficult of storytelling techniques to master. If you want to write stream of consciousness, start by simply keeping a personal journal , observing the nature of your own thoughts as they flow onto the page. It’s also worth reading the masters of the technique, like James Joyce, William Faulkner, and Virginia Woolf.
The Everyday
Even characters in sci-fi, fantasy, and thriller novels have quotidian, everyday lives. Providing a glimpse into their everyday lives helps make the story more accessible to the reader.
What do those everyday details look like? A daily commute, a morning shower, a stop at the grocery store after work. It can also be everyday annoyances: swatting at mosquitoes in the evening, holding your breath when you walk past a sewer grate, forgetting not to scratch at the rash on your wrist, etc.
What do these boring, everyday tasks do? One, they humanize your characters, giving them relatable behaviors that act as windows to their worlds. Two, these tasks show the reader what everyday life looks like before the inciting incident . Once the protagonist’s life becomes upended by something major, we now relate to the character on a personal level and want them to succeed on their journey.
Just be careful not to provide too many everyday details that your story loses sight of its plot. The reader doesn’t need to see every moment in a typical day of your protagonist’s life—and, unless it’s extremely relevant, don’t start your story with your protagonist waking up, as this is an overdone cliché.
A trope is a theme or archetype that shows up regularly in a genre of work. Tropes give structure to a story, providing a kind of scaffolding that the author can manipulate and build from, creating a story both fresh and readable. In genre fiction, tropes are essential to the art of storytelling.
Tropes are commonly misconstrued as clichés, but that’s not the case. For example, a trope in the romance genre is the “meet-cute,” where two soon-to-be-lovers meet each other in a unique and adorable situation. While this trope recurs throughout romance fiction, writers are free to experiment with the meet-cute in their own original ways.
If you intend to write genre fiction, or even to pull from different genres in your own literary work, it’s important to familiarize yourself with that genre’s tropes. The wiki TV Tropes is a fantastic resource for this, covering tropes in both film and literature.
Vernacular refers to regional dialects. Like “the everyday,” vernacular helps humanize your characters, while also establishing a sense of place in your story.
If your characters are strongly immersed in the culture of their upbringing, do some research on the vernacular of that place. For example, a character who grew up in Wisconsin should say “bubbler,” not “water fountain.”
Language, and even just the English language, is fantastically diverse. Using vernacular in your characters’ dialogue makes them feel more flesh-and-blood, and it also provides some entertaining moments in language and storytelling.
Wordplay makes for enjoyable, engaging storytelling. Twists of phrase create memorable moments of narration and dialogue, keeping the reader glued to the page.
Wordplay comes in many different forms. Puns, malapropisms, neologisms, oxymorons, kennings, onomatopoeias, portmanteaus, zeugmas, and contronyms are just some of the ways that writers have fun with language.
Additionally, sound devices like alliteration and rhyme also create memorable, meaningful moments in language.
Way before the printing press and the invention of modern prose, storytellers told their tales orally and entirely in verse. The epic poem was a way of sharing stories, and because pencil and paper were scarce in antiquity, storytellers had to memorize their work. These wordplay devices were ways of memorizing stories, allowing the storyteller to move through the plot while keeping the listener entertained.
Thus, these tools are freely at the writer’s disposal, and storytellers are encouraged to use them. Wordplay is essential to the magic of storytelling, so harness the magic of words!
To learn more about wordplay, check out our article: Word Play: Examples of a Play on Words
The above elements and techniques coalesce into the power of storytelling. But, why is storytelling important?
In short, storytelling is the closest that writers come to creating real worlds, characters, and events. When a story is told well and meaningfully, the reader is transported into a world of the writer’s own making—a world with its own rules, laws, physics, relationships, and ideas. In this world, the writer can twist emotions, make powerful statements, and entertain the reader in beautiful ways.
But for the reader to access this world, the writer needs to use storytelling techniques. Storytelling is a portal into a different dimension, or a doorway into an unexplored house, or a bridge across a river, or a rocketship to different planets.
You must transport your reader if you want to persuade, inspire, or provoke them.
Whatever the metaphor, you must transport your reader if you want to persuade, inspire, or provoke them. This is what makes writers both fantastically powerful and fantastically human.
Wield the Art of Storytelling at Writers.com
The instructors at Writers.com have mastered these storytelling techniques, and they’re ready to show you the craft. Gain meaningful feedback and insight on your work, and harness the magic of storytelling in one of our upcoming courses .
Sean Glatch
[…] Capturing the Art of Storytelling: Techniques & Tips […]
very useful your article
Wisconsin native here. Bubbler is a southeastern Wisconsin term. It was probably originally a Milwaukee area term. Most wisconsinites outside that area have never heard the term bubbler and instead use drinking fountain or water fountain. I grew up in Wisconsin and never heard of it until we moved down into the southern part of the state. My kids came home from their first day of school and asked if I’d ever heard of a bubbler and I hadn’t. 🙂
Thanks, Steve! I’m a Milwaukee native myself, and thought it was a statewide thing. It’s always fun to say “bubbler” outside the state and have people look really, really confused.
It’s even more fun to use it in different countries and get people REALLY REALLY confused.
[…] Metaphors, analogies, and vivid descriptions can be employed to illustrate abstract ideas and engage readers in a way that straightforward explanations […]
[…] look at each of these items and more. Creating real, flesh-and-blood people is essential to great storytelling, so let’s explore the alchemy of turning words into real people—creating characters from […]
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Telling a Story in Academic Writing
Storytelling is the most engaging way to communicate. In storytelling, writers use a variety of methods to maintain an appealing pace, to create human connections with their readers, and to help readers visualize their ideas. These same techniques are effective across all types of writing. They can be used to make writing assignments more engaging, more readable, and more persuasive.
When you build plot, you think of your writing as a sequence of connected events where anticipation (tension) rises toward a final climactic event, and ends with a resolution. For an academic argument, you can use the traditional narrative arc as a basic structure. The following shows how these narrative arcs of story structure might map onto academic paper.
- Story: “This is the background you need to know to understand what’s coming next.”
- Academic Writing: Introduce the issue and the argument you want to develop.
Rising action
- Story: “First this happened. Then this happened. Then this happened.”
- Academic Writing: To build tension, arrange your arguments to build in strength. How each point builds upon the previous one should be clear. For example, in a literature review, you would arrange the previous research to show how and why you came to your own research question. (You might think of this format like a detective story. The problems, successes, or omissions in previous research serve as the “clues” that led you to your own research project).
- Story: “All of that led to this big event.”
- Academic Writing: At the climax, reveal your most convincing reasoning and evidence.
- Story: “Here’s how everything came together at the end.”
- Academic Writing: In the final phase, summarize your arguments and emphasizing the significance of the issue.
Balance Action with Commentary
Academic writing with too much action - where the writer presents facts and descriptions, one after the other - reads like a rapid-fire list of statements. This kind of writing doesn’t give the reader time to process and reflect on the information. Make sure that you include analysis, reflection, and other commentary to build the right pace for your readers.
In contrast, academic writing with too much commentary feels slow and plodding and often has so much discussion that the reader loses sight of the writer’s goal. Make sure that you provide only the most important commentary. Then move on.
Instead of . . .
“ So and so argues this… so and so claims this… so and so analyzes this… “ or “One definition of the topic is x. Another is y. The definition proposed by z is….” or “There are multiple approaches to the topic. X looks at this . . ., Y views this. . ., Z combines this. . .”
“ There are many approaches to the topic. X looks at this . . ., which establishes important criteria for the field but avoids finding a consensus about issue M. Y’s research adds to the conversation about fundamental criteria for assessing these clinical situations. However, the author also takes a critical look at the disagreements underlying certain existing criteria. In contrast, rather than establishing criteria, Z investigates systemic assumptions in the field that lead practitioners to weigh some criteria more heavily than others.”
Focus on Pacing
Use active voice.
When writers use active voice they focus their sentences on an actor and the action – the two most important parts of storytelling. For more information on using active voice, check out our resource, Active and passive voice .
Ideally, to avoid unintentional bias in our measurements, information regarding the source population of each specimen was withheld from the observer.
We strived to avoid unintentional bias in our measurements. To that end, we withheld from observers, information about each specimen’s source population.
Vary sentence and paragraph length
Blair shone in his extracurricular activities at school. During his time at university he produced a magazine, joined in the production of other publications, and, in addition, participated in the college’s acapella group, but his academic performance reports suggested that he neglected his academic studies. His parents could not afford to send him to university without him winning another scholarship, and thus they concluded from his poor results that he would not be able to win one. His family decided that Blair should join the Imperial Police instead of finishing school.
Blair shone in his extracurricular activities at school. During his time at university he produced a magazine and also joined in the production of other publications. In addition, he participated in the college’s acapella group. Despite these achievements, his parents could not afford to send him to university without him winning another scholarship. Judging from Blair’s poor results, his family concluded that he would not be able to win. They thought Blair should join the Imperial Police instead.
Omit clutter
Too many unnecessary words in a sentence can not only lead to confusion, but also slow the pace and make text feel onerous and tiresome.
It has been found that CO2 and H2O formation has been reduced at high temperatures.
Less CO2 and H2O form at higher temperatures.
Humanize your Writing
Stories are powerful because, in one way or another, they place human concerns as their focus. To remind your readers of the human concerns that your research paper addresses, put human elements into your writing.
Use characters as your subjects
When a sentence describes an action completed by a person, that person should be the subject of the sentence. This small change in structure provides your sentences with characters and their actions, adding human elements to the paper.
Fetal DNA has been found in maternal plasma but exists as a minor fraction among a high background of maternal DNA. Even with highly precise single counting methods such as digital PCR, a large number of DNA molecules and hence maternal plasma volume would need to be analyzed to achieve the necessary analytical precision.
Researchers have found fetal DNA in maternal plasma, but it exists as a minor fraction among a high background of maternal DNA. Hence, even with highly precise, single molecule counting methods, such as digital PCR, geneticists must analyze a large number of DNA molecules and maternal plasma to achieve the necessary analytical precision.
Use the first person (I/we )
First person provides a human connection and improves clarity. It lets the reader know clearly who did what.
Here, instead of using approaches that target specific gene loci, the use of a locus-independent method would greatly increase the number of target molecules from the aneuploidy chromosome that could be analyzed within the same fixed volume of plasma.
Try . . .
Here, we chose not to use approaches that target specific gene loci. Rather, by using a locus-independent method, we could greatly increase the number of target molecules from the aneuploidy chromosome, and, with this increase, improve our analysis within the same fixed volume of plasma.
Add Metaphor
When we use one object, experience, or event to help symbolize and represent a different one, we are using metaphor. Through metaphor, writers use a concept familiar to the reader to help explain something that is unfamiliar. Metaphor helps a reader understand a concept from two pathways – literal and visual – and increases engagement.
Beyond treating individual letters as physical objects, the human brain may also perceive a text in its entirety as a kind of physical landscape, similar to the mental maps we create of terrain. For example, in the physical world we might recall that we passed the red farmhouse near the start of a trail we hiked. In a similar way, in text, we remember that we read about Mr. Darcy rebuffing Elizabeth Bennett on the bottom of the left-hand page in one of the earlier chapters.
VIDEO COURSE
Finish your draft in our 3-month master class. Sign up now to watch a free lesson!
Learn How to Write a Novel
Finish your draft in our 3-month master class. Enroll now for daily lessons, weekly critique, and live events. Your first lesson is free!

Blog • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Oct 31, 2022
10 Personal Narrative Examples to Inspire Your Writing
Personal narratives are short pieces of creative nonfiction that recount a story from someone’s own experiences. They can be a memoir, a thinkpiece, or even a polemic — so long as the piece is grounded in the writer's beliefs and experiences, it can be considered a personal narrative.
Despite the nonfiction element, there’s no single way to approach this topic, and you can be as creative as you would be writing fiction. To inspire your writing and reveal the sheer diversity of this type of essay, here are ten great examples personal narratives from recent years:
1. “Only Disconnect” by Gary Shteyngart

Personal narratives don’t have to be long to be effective, as this thousand-word gem from the NYT book review proves. Published in 2010, just as smartphones were becoming a ubiquitous part of modern life, this piece echoes many of our fears surrounding technology and how it often distances us from reality.
In this narrative, Shteyngart navigates Manhattan using his new iPhone—or more accurately, is led by his iPhone, completely oblivious to the world around him. He’s completely lost to the magical happenstance of the city as he “follow[s] the arrow taco-ward”. But once he leaves for the country, and abandons the convenience of a cell phone connection, the real world comes rushing back in and he remembers what he’s been missing out on.
The downfalls of technology is hardly a new topic, but Shteyngart’s story remains evergreen because of how our culture has only spiraled further down the rabbit hole of technology addiction in the intervening years.
What can you learn from this piece?
Just because a piece of writing is technically nonfiction, that doesn’t mean that the narrative needs to be literal. Shteyngart imagines a Manhattan that physically changes around him when he’s using his iPhone, becoming an almost unrecognizable world. From this, we can see how a certain amount of dramatization can increase the impact of your message—even if that wasn’t exactly the way something happened.

FREE COURSE
How to Craft a Killer Short Story
From pacing to character development, master the elements of short fiction.
2. “Why I Hate Mother's Day” by Anne Lamott
The author of the classic writing text Bird by Bird digs into her views on motherhood in this piece from Salon. At once a personal narrative and a cultural commentary, Lamott explores the harmful effects that Mother’s Day may have on society —how its blind reverence to the concept of motherhood erases women’s agency and freedom to be flawed human beings.
Lamott points out that not all mothers are good, not everyone has a living mother to celebrate, and some mothers have lost their children, so have no one to celebrate with them. More importantly, she notes how this Hallmark holiday erases all the people who helped raise a woman, a long chain of mothers and fathers, friends and found family, who enable her to become a mother. While it isn’t anchored to a single story or event (like many classic personal narratives), Lamott’s exploration of her opinions creates a story about a culture that puts mothers on an impossible pedestal.
In a personal narrative essay, lived experience can be almost as valid as peer-reviewed research—so long as you avoid making unfounded assumptions. While some might point out that this is merely an opinion piece, Lamott cannily starts the essay by grounding it in the personal, revealing how she did not raise her son to celebrate Mother’s Day. This detail, however small, invites the reader into her private life and frames this essay as a story about her —and not just an exercise in being contrary.
3. “The Crane Wife” by CJ Hauser
Days after breaking off her engagement with her fiance, CJ Hauser joins a scientific expedition on the Texas coast r esearching whooping cranes . In this new environment, she reflects on the toxic relationship she left and how she found herself in this situation. She pulls together many seemingly disparate threads, using the expedition and the Japanese myth of the crane wife as a metaphor for her struggles.
Hauser’s interactions with the other volunteer researchers expand the scope of the narrative from her own mind, reminding her of the compassion she lacked in her relationship. In her attempts to make herself smaller, less needy, to please her fiance, she lost sight of herself and almost signed up to live someone else’s life, but among the whooping cranes of Texas, she takes the first step in reconnecting with herself.
With short personal narratives, there isn’t as much room to develop characters as you might have in a memoir so the details you do provide need to be clear and specific. Each of the volunteer researchers on Hauser’s expedition are distinct and recognizable though Hauser is economical in her descriptions.
For example, Hauser describes one researcher as “an eighty-four-year-old bachelor from Minnesota. He could not do most of the physical activities required by the trip, but had been on ninety-five Earthwatch expeditions, including this one once before. Warren liked birds okay. What Warren really loved was cocktail hour.”
In a few sentences, we get a clear picture of Warren's fun-loving, gregarious personality and how he fits in with the rest of the group.

How to Develop Characters
In 10 days, learn to develop complex characters readers will love.
4. “The Trash Heap Has Spoken” by Carmen Maria Machado
The films and TV shows of the 80s and 90s—cultural touchstones that practically raised a generation—hardly ever featured larger women on screen. And if they did, it was either as a villain or a literal trash heap. Carmen Maria Machado grew up watching these cartoons, and the absence of fat women didn’t faze her. Not until puberty hit and she went from a skinny kid to a fuller-figured teen. Suddenly uncomfortable in her skin, she struggled to find any positive representation in her favorite media.
As she gets older and more comfortable in her own body, Machado finds inspiration in Marjory the Trash Heap from Fraggle Rock and Ursula, everyone’s favorite sea witch from The Little Mermaid —characters with endless power in the unapologetic ways they inhabit their bodies. As Machado considers her own body through the years, it’s these characters she returns to as she faces society’s unkind, dismissive attitudes towards fat women.
Stories shape the world, even if they’re fictional. Some writers strive for realism, reflecting the world back on itself in all its ugliness, but Carmen Maria Machado makes a different point. There is power in being imaginative and writing the world as it could be, imagining something bigger, better, and more beautiful. So, write the story you want to see, change the narrative, look at it sideways, and show your readers how the world could look.
5. “Am I Disabled?” by Joanne Limburg
The titular question frames the narrative of Joanne Limburg’s essay as she considers the implications of disclosing her autism. What to some might seem a mundane occurrence—ticking ‘yes’, ‘no’, or ‘prefer not to say’ on a bureaucratic form—elicits both philosophical and practical questions for Limburg about what it means to be disabled and how disability is viewed by the majority of society.
Is the labor of disclosing her autism worth the insensitive questions she has to answer? What definition are people seeking, exactly? Will anyone believe her if she says yes? As she dissects the question of what disability is, she explores the very real personal effects this has on her life and those of other disabled people.
Limburg’s essay is written in a style known as the hermit crab essay , when an author uses an existing document form to contain their story. You can format your writing as a recipe, a job application, a resume, an email, or a to-do list – the possibilities are as endless as your creativity. The format you choose is important, though. It should connect in some way to the story you’re telling and add something to the reader’s experience as well as your overall theme.

FREE RESOURCE
Literary Devices Cheatsheet
Master these 40+ devices to level up your writing skills.
6. “Living Like Weasels” by Annie Dillard

While out on a walk in the woods behind her house, Annie Dillard encounters a wild weasel. In the short moment when they make eye contact, Dillard takes an imaginary journey through the weasel’s mind and wonders if the weasel’s approach to life is better than her own.
The weasel, as Dillard sees it, is a wild creature with jaws so powerful that when it clamps on to something, it won’t let go, even into death. Necessity drives it to be like this, and humanity, obsessed with choice, might think this kind of life is limiting, but the writer believes otherwise. The weasel’s necessity is the ultimate freedom, as long as you can find the right sort, the kind that will have you holding on for dear life and refusing to let go.
Make yourself the National Geographic explorer of your backyard or neighborhood and see what you can learn about yourself from what you discover. Annie Dillard, queen of the natural personal essay, discovers a lot about herself and her beliefs when meeting a weasel.
What insight can you glean from a blade of grass, for example? Does it remind you that despite how similar people might be, we are all unique? Do the flights of migrating birds give you perspective on the changes in your own life? Nature is a potent and never-ending spring of inspiration if you only think to look.

Show, Don't Tell
Master the golden rule of writing in 10 five-minute lessons.
7. “Love In Our Seventies” by Ellery Akers
“ And sometimes, when I lift the gray hair at the back of your neck and kiss your shoulder, I think, This is it.”
In under 400 words, poet Ellery Akers captures the joy she has found in discovering romance as a 75-year-old . The language is romantic, but her imagery is far from saccharine as she describes their daily life and the various states in which they’ve seen each other: in their pajamas, after cataract surgeries, while meditating. In each singular moment, Akers sees something she loves, underscoring an oft-forgotten truth. Love is most potent in its smallest gestures.
Personal narrative isn’t a defined genre with rigid rules, so your essay doesn’t have to be an essay. It can be a poem, as Akers’ is. The limitations of this form can lead to greater creativity as you’re trying to find a short yet evocative way to tell a story. It allows you to focus deeply on the emotions behind an idea and create an intimate connection with your reader.
8. “What a Black Woman Wishes Her Adoptive White Parents Knew” by Mariama Lockington

Mariama Lockington was adopted by her white parents in the early 80s, long before it was “trendy” for white people to adopt black children. Starting with a family photograph, the writer explores her complex feelings about her upbringing , the many ways her parents ignored her race for their own comfort, and how she came to feel like an outsider in her own home. In describing her childhood snapshots, she takes the reader from infancy to adulthood as she navigates trying to live as a black woman in a white family.
Lockington takes us on a journey through her life through a series of vignettes. These small, important moments serve as a framing device, intertwining to create a larger narrative about race, family, and belonging.
With this framing device, it’s easy to imagine Lockington poring over a photo album, each picture conjuring a different memory and infusing her story with equal parts sadness, regret, and nostalgia. You can create a similar effect by separating your narrative into different songs to create an album or episodes in a TV show. A unique structure can add an extra layer to your narrative and enhance the overall story.
9. “Drinking Chai to Savannah” by Anjali Enjeti
On a trip to Savannah with her friends, Anjali Enjeti is reminded of a racist incident she experienced as a teenager . The memory is prompted by her discomfort of traveling in Georgia as a South Asian woman and her friends’ seeming obliviousness to how others view them. As she recalls the tense and traumatic encounter she had in line at a Wendy’s and the worry she experiences in Savannah, Enjeti reflects on her understanding of otherness and race in America.
Enjeti paints the scene in Wendy’s with a deft hand. Using descriptive language, she invokes the five senses to capture the stress and fear she felt when the men in line behind her were hurling racist sentiments.
She writes, “He moves closer. His shadow eclipses mine. His hot, tobacco-tinged breath seeps over the collar of my dress.” The strong, evocative language she uses brings the reader into the scene and has them experience the same anxiety she does, understanding why this incident deeply impacted her.
10. “Siri Tells A Joke” by Debra Gwartney
One day, Debra Gwartney asks Siri—her iPhone’s digital assistant—to tell her a joke. In reply, Siri recites a joke with a familiar setup about three men stuck on a desert island. When the punchline comes, Gwartney reacts not with laughter, but with a memory of her husband , who had died less than six months prior.
In a short period, Gwartney goes through a series of losses—first, her house and her husband’s writing archives to a wildfire, and only a month after, her husband. As she reflects on death and the grief of those left behind in the wake of it, she recounts the months leading up to her husband’s passing and the interminable stretch after as she tries to find a way to live without him even as she longs for him.
A joke about three men on a deserted island seems like an odd setup for an essay about grief. However, Gwartney uses it to great effect, coming back to it later in the story and giving it greater meaning. By the end of her piece, she recontextualizes the joke, the original punchline suddenly becoming deeply sad. In taking something seemingly unrelated and calling back to it later, the essay’s message about grief and love becomes even more powerful.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

The Redemption Arc: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
Learn what it takes to redeem a character with these four tips.

How Many Sentences Are in a Paragraph?
From fiction to nonfiction works, the length of a paragraph varies depending on its purpose. Here's everything you need to know.
Narrative Structure: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
What's the difference between story structure and narrative structure? And how do you choose the right narrative structure for you novel?

What is the Proust Questionnaire? 22 Questions to Write Better Characters
Inspired by Marcel Proust, check out the questionnaire that will help your characters remember things past.

What is Pathos? Definition and Examples in Literature
Pathos is a literary device that uses language to evoke an emotional response, typically to connect readers with the characters in a story.

How to Start a Children’s Book: Coming Up with Your Big Idea
If you've ever dreamed of writing a children's book but aren't sure where to start, check out this post to learn more about how you can create the perfect story for kids.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
Bring your stories to life
Our free writing app lets you set writing goals and track your progress, so you can finally write that book!

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
The Art of Storytelling
This essay about the intricate craft of storytelling, explores its timeless appeal and the elements that contribute to its magic. It emphasizes the importance of authenticity in connecting with audiences, the structured framework that guides narratives, and the universal language of imagery and symbolism. From the art of narrative weaving to the power of symbolism, storytelling serves as a conduit for empathy, connection, and transformation. Through its exploration of these themes, the essay underscores the profound impact storytelling has on individuals and societies alike, inviting readers to appreciate its artistry and significance.
How it works
Storytelling, a timeless tradition passed down through generations, transcends mere words on a page. It is an intricate tapestry woven from threads of imagination, emotion, and experience. From the flicker of a campfire to the glow of a cinema screen, the essence of storytelling lies in its ability to transport us to realms both familiar and fantastical, leaving an indelible mark on our hearts and minds.
Central to the magic of storytelling is the alchemy of narrative weaving. Like a master artisan, the storyteller deftly intertwines elements of plot, character, and setting to create a rich tapestry of imagery and emotion.
Each thread carefully chosen, each stitch meticulously placed, until the story comes to life in all its vivid splendor. Whether it’s a tale of heroism, romance, or adventure, the art of narrative weaving captivates and enchants, drawing us into worlds of wonder and possibility.
Yet, beyond the surface allure of plot and spectacle, lies the beating heart of authenticity. Authentic storytelling speaks to the soul, resonating with truths universal and timeless. It is the raw honesty of human experience laid bare, the vulnerability of shared emotion that binds us together in our common humanity. For it is in the authenticity of storytelling that we find not only entertainment, but also catharsis, empathy, and connection.
Moreover, the architecture of storytelling is a labyrinthine maze of structure and form. From the inciting incident to the climax and resolution, the narrative arc guides us on a journey of discovery and transformation. It is the scaffolding upon which the story is built, the framework that gives shape and meaning to the unfolding tale. Yet, within this structure lies the freedom of creativity, the boundless expanse of imagination where anything is possible.
Furthermore, the power of storytelling lies in its ability to transcend the confines of language and culture. Through the universal language of imagery and symbolism, stories speak to the heart in ways that words alone cannot. Whether it’s a metaphorical motif or a subtle gesture, symbolism adds depth and complexity to the narrative, inviting interpretation and introspection. It is through the interplay of symbols and archetypes that the story resonates on a deeper level, touching something primal and profound within us all.
In essence, storytelling is more than mere entertainment; it is a sacred art form that speaks to the very essence of what it means to be human. From the ancient myths of old to the modern epics of today, stories have the power to inspire, to provoke, and to transform. As we continue to journey through the labyrinth of narrative possibility, let us remember the alchemy of storytelling and the profound impact it has on our lives and our world.
Cite this page
The Art of Storytelling. (2024, Apr 14). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-art-of-storytelling/
"The Art of Storytelling." PapersOwl.com , 14 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-art-of-storytelling/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Art of Storytelling . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-art-of-storytelling/ [Accessed: 16 Apr. 2024]
"The Art of Storytelling." PapersOwl.com, Apr 14, 2024. Accessed April 16, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-art-of-storytelling/
"The Art of Storytelling," PapersOwl.com , 14-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-art-of-storytelling/. [Accessed: 16-Apr-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Art of Storytelling . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-art-of-storytelling/ [Accessed: 16-Apr-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
NPR in Turmoil After It Is Accused of Liberal Bias
An essay from an editor at the broadcaster has generated a firestorm of criticism about the network on social media, especially among conservatives.

By Benjamin Mullin and Katie Robertson
NPR is facing both internal tumult and a fusillade of attacks by prominent conservatives this week after a senior editor publicly claimed the broadcaster had allowed liberal bias to affect its coverage, risking its trust with audiences.
Uri Berliner, a senior business editor who has worked at NPR for 25 years, wrote in an essay published Tuesday by The Free Press, a popular Substack publication, that “people at every level of NPR have comfortably coalesced around the progressive worldview.”
Mr. Berliner, a Peabody Award-winning journalist, castigated NPR for what he said was a litany of journalistic missteps around coverage of several major news events, including the origins of Covid-19 and the war in Gaza. He also said the internal culture at NPR had placed race and identity as “paramount in nearly every aspect of the workplace.”
Mr. Berliner’s essay has ignited a firestorm of criticism of NPR on social media, especially among conservatives who have long accused the network of political bias in its reporting. Former President Donald J. Trump took to his social media platform, Truth Social, to argue that NPR’s government funding should be rescinded, an argument he has made in the past.
NPR has forcefully pushed back on Mr. Berliner’s accusations and the criticism.
“We’re proud to stand behind the exceptional work that our desks and shows do to cover a wide range of challenging stories,” Edith Chapin, the organization’s editor in chief, said in an email to staff on Tuesday. “We believe that inclusion — among our staff, with our sourcing, and in our overall coverage — is critical to telling the nuanced stories of this country and our world.” Some other NPR journalists also criticized the essay publicly, including Eric Deggans, its TV critic, who faulted Mr. Berliner for not giving NPR an opportunity to comment on the piece.
In an interview on Thursday, Mr. Berliner expressed no regrets about publishing the essay, saying he loved NPR and hoped to make it better by airing criticisms that have gone unheeded by leaders for years. He called NPR a “national trust” that people rely on for fair reporting and superb storytelling.
“I decided to go out and publish it in hopes that something would change, and that we get a broader conversation going about how the news is covered,” Mr. Berliner said.
He said he had not been disciplined by managers, though he said he had received a note from his supervisor reminding him that NPR requires employees to clear speaking appearances and media requests with standards and media relations. He said he didn’t run his remarks to The New York Times by network spokespeople.
When the hosts of NPR’s biggest shows, including “Morning Edition” and “All Things Considered,” convened on Wednesday afternoon for a long-scheduled meet-and-greet with the network’s new chief executive, Katherine Maher , conversation soon turned to Mr. Berliner’s essay, according to two people with knowledge of the meeting. During the lunch, Ms. Chapin told the hosts that she didn’t want Mr. Berliner to become a “martyr,” the people said.
Mr. Berliner’s essay also sent critical Slack messages whizzing through some of the same employee affinity groups focused on racial and sexual identity that he cited in his essay. In one group, several staff members disputed Mr. Berliner’s points about a lack of ideological diversity and said efforts to recruit more people of color would make NPR’s journalism better.
On Wednesday, staff members from “Morning Edition” convened to discuss the fallout from Mr. Berliner’s essay. During the meeting, an NPR producer took issue with Mr. Berliner’s argument for why NPR’s listenership has fallen off, describing a variety of factors that have contributed to the change.
Mr. Berliner’s remarks prompted vehement pushback from several news executives. Tony Cavin, NPR’s managing editor of standards and practices, said in an interview that he rejected all of Mr. Berliner’s claims of unfairness, adding that his remarks would probably make it harder for NPR journalists to do their jobs.
“The next time one of our people calls up a Republican congressman or something and tries to get an answer from them, they may well say, ‘Oh, I read these stories, you guys aren’t fair, so I’m not going to talk to you,’” Mr. Cavin said.
Some journalists have defended Mr. Berliner’s essay. Jeffrey A. Dvorkin, NPR’s former ombudsman, said Mr. Berliner was “not wrong” on social media. Chuck Holmes, a former managing editor at NPR, called Mr. Berliner’s essay “brave” on Facebook.
Mr. Berliner’s criticism was the latest salvo within NPR, which is no stranger to internal division. In October, Mr. Berliner took part in a lengthy debate over whether NPR should defer to language proposed by the Arab and Middle Eastern Journalists Association while covering the conflict in Gaza.
“We don’t need to rely on an advocacy group’s guidance,” Mr. Berliner wrote, according to a copy of the email exchange viewed by The Times. “Our job is to seek out the facts and report them.” The debate didn’t change NPR’s language guidance, which is made by editors who weren’t part of the discussion. And in a statement on Thursday, the Arab and Middle Eastern Journalists Association said it is a professional association for journalists, not a political advocacy group.
Mr. Berliner’s public criticism has highlighted broader concerns within NPR about the public broadcaster’s mission amid continued financial struggles. Last year, NPR cut 10 percent of its staff and canceled four podcasts, including the popular “Invisibilia,” as it tried to make up for a $30 million budget shortfall. Listeners have drifted away from traditional radio to podcasts, and the advertising market has been unsteady.
In his essay, Mr. Berliner laid some of the blame at the feet of NPR’s former chief executive, John Lansing, who said he was retiring at the end of last year after four years in the role. He was replaced by Ms. Maher, who started on March 25.
During a meeting with employees in her first week, Ms. Maher was asked what she thought about decisions to give a platform to political figures like Ronna McDaniel, the former Republican Party chair whose position as a political analyst at NBC News became untenable after an on-air revolt from hosts who criticized her efforts to undermine the 2020 election.
“I think that this conversation has been one that does not have an easy answer,” Ms. Maher responded.
Benjamin Mullin reports on the major companies behind news and entertainment. Contact Ben securely on Signal at +1 530-961-3223 or email at [email protected] . More about Benjamin Mullin
Katie Robertson covers the media industry for The Times. Email: [email protected] More about Katie Robertson

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Interactive example of a narrative essay. An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt "Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself," is shown below. Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works. Narrative essay example.
Essay On Storytelling. Lyndsay Miller Ms. Williams English 12 10 November 2014 Storytelling Storytelling is the oral tradition of sharing stories and recounting events of the past. It is an ancient art form and is a dear form of human expression (What is). Most historians and psychologists alike agree that storytelling is one of the many things ...
A narrative essay is one of the most intimidating assignments you can be handed at any level of your education. Where you've previously written argumentative essays that make a point or analytic essays that dissect meaning, a narrative essay asks you to write what is effectively a story.. But unlike a simple work of creative fiction, your narrative essay must have a clear and concrete motif ...
Here is a PDF of all 650 prompts, and we also have a related lesson plan, From 'Lives' to 'Modern Love': Writing Personal Essays With Help From The New York Times. Below, a list that ...
Curating the best of the best of personal narratives and narrative essays from all over the web. Some are award-winning articles. Narratively. Long-form writing to celebrate humanity through storytelling. It publishes personal narrative essays written to provoke, inspire, and reflect, touching lesser-known and overlooked subjects. Narrative ...
The goal of the narrative essay is to use established storytelling techniques, like theme, conflict, and irony, in a uniquely personal way. The responsibility of the narrative essayist is to make the reader feel connected to their story, regardless of the topic. This next video explores how writers can use structural elements and techniques to ...
Step 1: Choose a Topic. Sometimes, you will be assigned a topic or prompt for your essay by your instructor. But other times, you need to choose a topic yourself. Select a personal experience or event that is meaningful to you and has a clear message or theme.
0 comment 2. Narrative essays are a type of storytelling in which writers weave a personal experience into words to create a fascinating and engaging narrative for readers. A narrative essay explains a story from the author's point of view to share a lesson or memory with the reader. Narrative essays, like descriptive essays, employ ...
A personal narrative essay is based on one's unique experience or event. Personal narrative essay examples include a story about overcoming a fear or obstacle or reflecting on a particularly meaningful moment in one's life. A fictional narrative is a made-up story that still follows the basic elements of storytelling. Fictional narratives can ...
A good example of this is when an instructor asks a student to write a book report. Obviously, this would not necessarily follow the pattern of a story and would focus on providing an informative narrative for the reader. ... The essay should be written from a clear point of view. It is quite common for narrative essays to be written from the ...
Effective storytelling in narrative essays revolves around several key elements: 1. Character. Every narrative essay needs a protagonist, often the writer themselves. Developing a well-rounded character with relatable traits and emotions is essential for creating a connection with the reader. 2. Setting. The backdrop of the story sets the tone ...
Narrative Essay Definition. Writing a narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that revolves around personal experiences, aiming to immerse the reader in the author's world. It's a piece of writing that delves into the depths of thoughts and feelings. In a narrative essay, life experiences take center stage, serving as the main substance of the story. It's a powerful tool for writers ...
Narrative essays share an important experience or life event through storytelling elements and the author's perspective. The story reveals a purpose through the events and details that are shared ...
Before you write your narrative essay, you can get a better idea of what to do with a narrative essay example. See real samples along with essential tips.
7 Elements of Storytelling. No matter the tale, every work of prose (and many poems) rely on these 7 elements of storytelling. 1. Plot. Plot is the skeleton of storytelling. You can have a gorgeous prose style with deeply relatable characters, but without a logical flow of events, your story will confuse the reader.
Storytelling, in particular oral storytelling, has also led to the development of language throughout the centuries and across cultures. ... His work is one of the best narrative essay examples of the 19th century. "My life is not an apology, but a life. It is for itself and not for a spectacle. I much prefer that it should be of a lower ...
Telling a Story in Academic Writing. Storytelling is the most engaging way to communicate. In storytelling, writers use a variety of methods to maintain an appealing pace, to create human connections with their readers, and to help readers visualize their ideas. These same techniques are effective across all types of writing.
Here's the structure that most American films use. It's a structure as old as storytelling itself, and storytellers have been using it for thousands of years. I'll refer to it as narrative structure. You can think of this approach to writing an essay as breaking down into three basic sections: Challenges + Effects. What I Did About Them.
Overview. Our Personal Narrative Essay Contest is inspired by The New York Times's Lives column, which ran from 1996 to 2017 and featured "short, powerful stories about meaningful life ...
Ten examples of amazing personal narrative essays to inspire your writing. Click to tweet! 1. "Only Disconnect" by Gary Shteyngart. Personal narratives don't have to be long to be effective, as this thousand-word gem from the NYT book review proves. Published in 2010, just as smartphones were becoming a ubiquitous part of modern life ...
3. Have a clear structure. There are many different ways to structure a story, but the three ingredients a story must have are a beginning, middle, and end. On a more granular level, a successful story will start with an inciting incident, lead into rising action, build to a climax and ultimately settle into a satisfying resolution.
Essay Example: Storytelling, a timeless tradition passed down through generations, transcends mere words on a page. It is an intricate tapestry woven from threads of imagination, emotion, and experience. From the flicker of a campfire to the glow of a cinema screen, the essence of storytelling
PAGES 6 WORDS 1740. Storytelling. A tale of fictitious or real events or narrative is defined as a story. For our hungry souls, the nourishment is stories. Palatable stories exist due to these elements of truth. There are many ways to tell a story to the latest Hollywood blockbuster from classic novels written by the greatest writers and to ...
The Power of Storytelling Essay examples. Decent Essays. 875 Words. 4 Pages. Open Document. Story telling is a uniquely human attribute. It is an imaginative process between the composer and responder that invites us, as the audience to engage vicariously with the experience of others. Stories or narratives have been shared in all culture as a ...
Enter a detailed storytelling prompt, and watch as words fill the page within seconds. Run free with this AI-generated story draft and transform it into a page-turner with your own voice and vision. As a Canva Free subscriber, you can enjoy a total of 50 lifetime uses with Magic Write. Upgrade to Canva Pro to unlock 500 uses per user per month.
In his essay, Mr. Berliner laid some of the blame at the feet of NPR's former chief executive, John Lansing, who said he was retiring at the end of last year after four years in the role. He was ...