
Textual Analysis: Definition, Types & 10 Examples
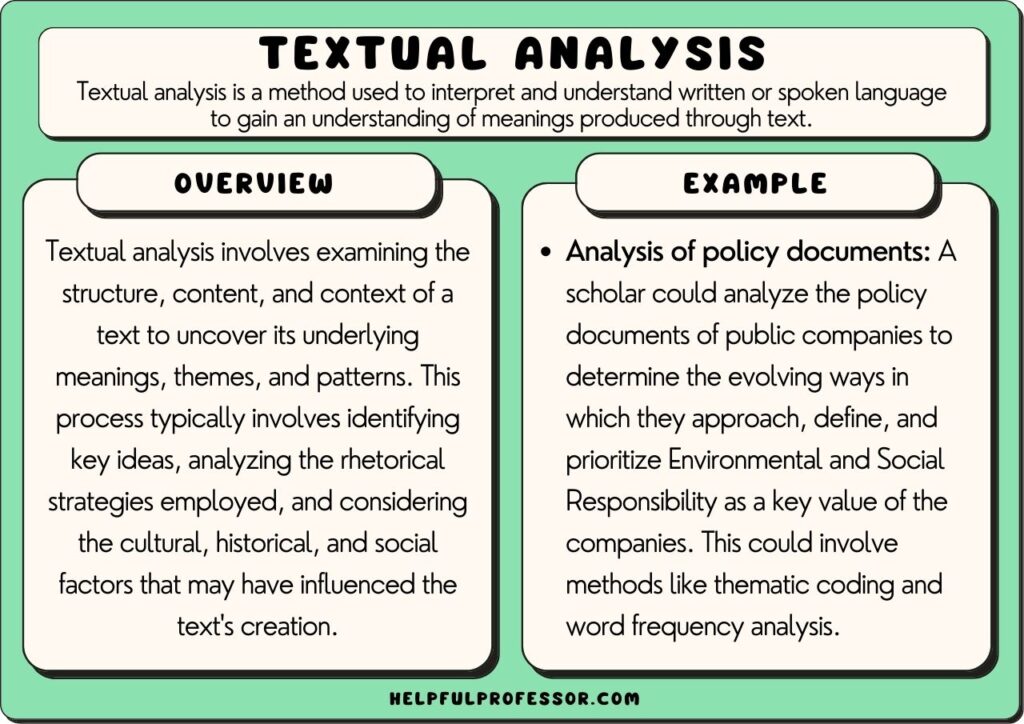
Textual analysis is a research methodology that involves exploring written text as empirical data. Scholars explore both the content and structure of texts, and attempt to discern key themes and statistics emergent from them.
This method of research is used in various academic disciplines, including cultural studies, literature, bilical studies, anthropology , sociology, and others (Dearing, 2022; McKee, 2003).
This method of analysis involves breaking down a text into its constituent parts for close reading and making inferences about its context, underlying themes, and the intentions of its author.
Textual Analysis Definition
Alan McKee is one of the preeminent scholars of textual analysis. He provides a clear and approachable definition in his book Textual Analysis: A Beginner’s Guide (2003) where he writes:
“When we perform textual analysis on a text we make an educated guess at some of the most likely interpretations that might be made of the text […] in order to try and obtain a sense of the ways in which, in particular cultures at particular times, people make sense of the world around them.”
A key insight worth extracting from this definition is that textual analysis can reveal what cultural groups value, how they create meaning, and how they interpret reality.
This is invaluable in situations where scholars are seeking to more deeply understand cultural groups and civilizations – both past and present (Metoyer et al., 2018).
As such, it may be beneficial for a range of different types of studies, such as:
- Studies of Historical Texts: A study of how certain concepts are framed, described, and approached in historical texts, such as the Bible.
- Studies of Industry Reports: A study of how industry reports frame and discuss concepts such as environmental and social responsibility.
- Studies of Literature: A study of how a particular text or group of texts within a genre define and frame concepts. For example, you could explore how great American literature mythologizes the concept of the ‘The American Dream’.
- Studies of Speeches: A study of how certain politicians position national identities in their appeals for votes.
- Studies of Newspapers: A study of the biases within newspapers toward or against certain groups of people.
- Etc. (For more, see: Dearing, 2022)
McKee uses the term ‘textual analysis’ to also refer to text types that are not just written, but multimodal. For a dive into the analysis of multimodal texts, I recommend my article on content analysis , where I explore the study of texts like television advertisements and movies in detail.
Features of a Textual Analysis
When conducting a textual analysis, you’ll need to consider a range of factors within the text that are worthy of close examination to infer meaning. Features worthy of considering include:
- Content: What is being said or conveyed in the text, including explicit and implicit meanings, themes, or ideas.
- Context: When and where the text was created, the culture and society it reflects, and the circumstances surrounding its creation and distribution.
- Audience: Who the text is intended for, how it’s received, and the effect it has on its audience.
- Authorship: Who created the text, their background and perspectives, and how these might influence the text.
- Form and structure: The layout, sequence, and organization of the text and how these elements contribute to its meanings (Metoyer et al., 2018).
Textual Analysis Coding Methods
The above features may be examined through quantitative or qualitative research designs , or a mixed-methods angle.
1. Quantitative Approaches
You could analyze several of the above features, namely, content, form, and structure, from a quantitative perspective using computational linguistics and natural language processing (NLP) analysis.
From this approach, you would use algorithms to extract useful information or insights about frequency of word and phrase usage, etc. This can include techniques like sentiment analysis, topic modeling, named entity recognition, and more.
2. Qualitative Approaches
In many ways, textual analysis lends itself best to qualitative analysis. When identifying words and phrases, you’re also going to want to look at the surrounding context and possibly cultural interpretations of what is going on (Mayring, 2015).
Generally, humans are far more perceptive at teasing out these contextual factors than machines (although, AI is giving us a run for our money).
One qualitative approach to textual analysis that I regularly use is inductive coding, a step-by-step methodology that can help you extract themes from texts. If you’re interested in using this step-by-step method, read my guide on inductive coding here .
See more Qualitative Research Approaches Here
Textual Analysis Examples
Title: “Discourses on Gender, Patriarchy and Resolution 1325: A Textual Analysis of UN Documents” Author: Nadine Puechguirbal Year: 2010 APA Citation: Puechguirbal, N. (2010). Discourses on Gender, Patriarchy and Resolution 1325: A Textual Analysis of UN Documents, International Peacekeeping, 17 (2): 172-187. doi: 10.1080/13533311003625068
Summary: The article discusses the language used in UN documents related to peace operations and analyzes how it perpetuates stereotypical portrayals of women as vulnerable individuals. The author argues that this language removes women’s agency and keeps them in a subordinate position as victims, instead of recognizing them as active participants and agents of change in post-conflict environments. Despite the adoption of UN Security Council Resolution 1325, which aims to address the role of women in peace and security, the author suggests that the UN’s male-dominated power structure remains unchallenged, and gender mainstreaming is often presented as a non-political activity.
Title: “Racism and the Media: A Textual Analysis” Author: Kassia E. Kulaszewicz Year: 2015 APA Citation: Kulaszewicz, K. E. (2015). Racism and the Media: A Textual Analysis . Dissertation. Retrieved from: https://sophia.stkate.edu/msw_papers/477
Summary: This study delves into the significant role media plays in fostering explicit racial bias. Using Bandura’s Learning Theory, it investigates how media content influences our beliefs through ‘observational learning’. Conducting a textual analysis, it finds differences in representation of black and white people, stereotyping of black people, and ostensibly micro-aggressions toward black people. The research highlights how media often criminalizes Black men, portraying them as violent, while justifying or supporting the actions of White officers, regardless of their potential criminality. The study concludes that news media likely continues to reinforce racism, whether consciously or unconsciously.
Title: “On the metaphorical nature of intellectual capital: a textual analysis” Author: Daniel Andriessen Year: 2006 APA Citation: Andriessen, D. (2006). On the metaphorical nature of intellectual capital: a textual analysis. Journal of Intellectual capital , 7 (1), 93-110.
Summary: This article delves into the metaphorical underpinnings of intellectual capital (IC) and knowledge management, examining how knowledge is conceptualized through metaphors. The researchers employed a textual analysis methodology, scrutinizing key texts in the field to identify prevalent metaphors. They found that over 95% of statements about knowledge are metaphor-based, with “knowledge as a resource” and “knowledge as capital” being the most dominant. This study demonstrates how textual analysis helps us to understand current understandings and ways of speaking about a topic.
Title: “Race in Rhetoric: A Textual Analysis of Barack Obama’s Campaign Discourse Regarding His Race” Author: Andrea Dawn Andrews Year: 2011 APA Citation: Andrew, A. D. (2011) Race in Rhetoric: A Textual Analysis of Barack Obama’s Campaign Discourse Regarding His Race. Undergraduate Honors Thesis Collection. 120 . https://digitalcommons.butler.edu/ugtheses/120
This undergraduate honors thesis is a textual analysis of Barack Obama’s speeches that explores how Obama frames the concept of race. The student’s capstone project found that Obama tended to frame racial inequality as something that could be overcome, and that this was a positive and uplifting project. Here, the student breaks-down times when Obama utilizes the concept of race in his speeches, and examines the surrounding content to see the connotations associated with race and race-relations embedded in the text. Here, we see a decidedly qualitative approach to textual analysis which can deliver contextualized and in-depth insights.
Sub-Types of Textual Analysis
While above I have focused on a generalized textual analysis approach, a range of sub-types and offshoots have emerged that focus on specific concepts, often within their own specific theoretical paradigms. Each are outlined below, and where I’ve got a guide, I’ve linked to it in blue:
- Content Analysis : Content analysis is similar to textual analysis, and I would consider it a type of textual analysis, where it’s got a broader understanding of the term ‘text’. In this type, a text is any type of ‘content’, and could be multimodal in nature, such as television advertisements, movies, posters, and so forth. Content analysis can be both qualitative and quantitative, depending on whether it focuses more on the meaning of the content or the frequency of certain words or concepts (Chung & Pennebaker, 2018).
- Discourse Analysis : Emergent specifically from critical and postmodern/ poststructural theories, discourse analysis focuses closely on the use of language within a social context, with the goal of revealing how repeated framing of terms and concepts has the effect of shaping how cultures understand social categories. It considers how texts interact with and shape social norms, power dynamics, ideologies, etc. For example, it might examine how gender is socially constructed as a distinct social category through Disney films. It may also be called ‘critical discourse analysis’.
- Narrative Analysis: This approach is used for analyzing stories and narratives within text. It looks at elements like plot, characters, themes, and the sequence of events to understand how narratives construct meaning.
- Frame Analysis: This approach looks at how events, ideas, and themes are presented or “framed” within a text. It explores how these frames can shape our understanding of the information being presented. While similar to discourse analysis, a frame analysis tends to be less associated with the loaded concept of ‘discourse’ that exists specifically within postmodern paradigms (Smith, 2017).
- Semiotic Analysis: This approach studies signs and symbols, both visual and textual, and could be a good compliment to a content analysis, as it provides the language and understandings necessary to describe how signs make meaning in cultural contexts that we might find with the fields of semantics and pragmatics . It’s based on the theory of semiotics, which is concerned with how meaning is created and communicated through signs and symbols.
- Computational Textual Analysis: In the context of data science or artificial intelligence, this type of analysis involves using algorithms to process large amounts of text. Techniques can include topic modeling, sentiment analysis, word frequency analysis, and others. While being extremely useful for a quantitative analysis of a large dataset of text, it falls short in its ability to provide deep contextualized understandings of words-in-context.
Each of these methods has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of method depends on the research question, the type of text being analyzed, and the broader context of the research.
See More Examples of Analysis Here
Strengths and Weaknesses of Textual Analysis
When writing your methodology for your textual analysis, make sure to define not only what textual analysis is, but (if applicable) the type of textual analysis, the features of the text you’re analyzing, and the ways you will code the data. It’s also worth actively reflecting on the potential weaknesses of a textual analysis approach, but also explaining why, despite those weaknesses, you believe this to be the most appropriate methodology for your study.
Chung, C. K., & Pennebaker, J. W. (2018). Textual analysis. In Measurement in social psychology (pp. 153-173). Routledge.
Dearing, V. A. (2022). Manual of textual analysis . Univ of California Press.
McKee, A. (2003). Textual analysis: A beginner’s guide. Textual analysis , 1-160.
Mayring, P. (2015). Qualitative content analysis: Theoretical background and procedures. Approaches to qualitative research in mathematics education: Examples of methodology and methods , 365-380. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9181-6_13
Metoyer, R., Zhi, Q., Janczuk, B., & Scheirer, W. (2018, March). Coupling story to visualization: Using textual analysis as a bridge between data and interpretation. In 23rd International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces (pp. 503-507). doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3172944.3173007
Smith, J. A. (2017). Textual analysis. The international encyclopedia of communication research methods , 1-7.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Textual Analysis – Types, Examples and Guide
Textual Analysis – Types, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

Textual Analysis
Textual analysis is the process of examining a text in order to understand its meaning. It can be used to analyze any type of text, including literature , poetry, speeches, and scientific papers. Textual analysis involves analyzing the structure, content, and style of a text.
Textual analysis can be used to understand a text’s author, date, and audience. It can also reveal how a text was constructed and how it functions as a piece of communication.
Textual Analysis in Research
Textual analysis is a valuable tool in research because it allows researchers to examine and interpret text data in a systematic and rigorous way. Here are some ways that textual analysis can be used in research:
- To explore research questions: Textual analysis can be used to explore research questions in various fields, such as literature, media studies, and social sciences. It can provide insight into the meaning, interpretation, and communication patterns of text.
- To identify patterns and themes: Textual analysis can help identify patterns and themes within a set of text data, such as analyzing the representation of gender or race in media.
- To evaluate interventions: Textual analysis can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, such as analyzing the language and messaging of public health campaigns.
- To inform policy and practice: Textual analysis can provide insights that inform policy and practice, such as analyzing legal documents to inform policy decisions.
- To analyze historical data: Textual analysis can be used to analyze historical data, such as letters, diaries, and newspapers, to provide insights into historical events and social contexts.
Textual Analysis in Cultural and Media Studies
Textual analysis is a key tool in cultural and media studies as it enables researchers to analyze the meanings, representations, and discourses present in cultural and media texts. Here are some ways that textual analysis is used in cultural and media studies:
- To analyze representation: Textual analysis can be used to analyze the representation of different social groups, such as gender, race, and sexuality, in media and cultural texts. This analysis can provide insights into how these groups are constructed and represented in society.
- To analyze cultural meanings: Textual analysis can be used to analyze the cultural meanings and symbols present in media and cultural texts. This analysis can provide insights into how culture and society are constructed and understood.
- To analyze discourse: Textual analysis can be used to analyze the discourse present in cultural and media texts. This analysis can provide insights into how language is used to construct meaning and power relations.
- To analyze media content: Textual analysis can be used to analyze media content, such as news articles, TV shows, and films, to understand how they shape our understanding of the world around us.
- To analyze advertising : Textual analysis can be used to analyze advertising campaigns to understand how they construct meanings, identities, and desires.
Textual Analysis in the Social Sciences
Textual analysis is a valuable tool in the social sciences as it enables researchers to analyze and interpret text data in a systematic and rigorous way. Here are some ways that textual analysis is used in the social sciences:
- To analyze interview data: Textual analysis can be used to analyze interview data, such as transcribed interviews, to identify patterns and themes in the data.
- To analyze survey responses: Textual analysis can be used to analyze survey responses to identify patterns and themes in the data.
- To analyze social media data: Textual analysis can be used to analyze social media data, such as tweets and Facebook posts, to identify patterns and themes in the data.
- To analyze policy documents: Textual analysis can be used to analyze policy documents, such as government reports and legislation, to identify discourses and power relations present in the policy.
- To analyze historical data: Textual analysis can be used to analyze historical data, such as letters and diaries, to provide insights into historical events and social contexts.
Textual Analysis in Literary Studies
Textual analysis is a key tool in literary studies as it enables researchers to analyze and interpret literary texts in a systematic and rigorous way. Here are some ways that textual analysis is used in literary studies:
- To analyze narrative structure: Textual analysis can be used to analyze the narrative structure of a literary text, such as identifying the plot, character development, and point of view.
- To analyze language and style: Textual analysis can be used to analyze the language and style used in a literary text, such as identifying figurative language, symbolism, and rhetorical devices.
- To analyze themes and motifs: Textual analysis can be used to analyze the themes and motifs present in a literary text, such as identifying recurring symbols, themes, and motifs.
- To analyze historical and cultural context: Textual analysis can be used to analyze the historical and cultural context of a literary text, such as identifying how the text reflects the social and political context of its time.
- To analyze intertextuality: Textual analysis can be used to analyze the intertextuality of a literary text, such as identifying how the text references or is influenced by other literary works.
Textual Analysis Methods
Textual analysis methods are techniques used to analyze and interpret various types of text, including written documents, audio and video recordings, and online content. These methods are commonly used in fields such as linguistics, communication studies, sociology, psychology, and literature.
Some common textual analysis methods include:
Content Analysis
This involves identifying patterns and themes within a set of text data. This method is often used to analyze media content or other types of written materials, such as policy documents or legal briefs.
Discourse Analysis
This involves examining how language is used to construct meaning in social contexts. This method is often used to analyze political speeches or other types of public discourse.
Critical Discourse Analysis
This involves examining how power and social relations are constructed through language use, particularly in political and social contexts.
Narrative Analysis
This involves examining the structure and content of stories or narratives within a set of text data. This method is often used to analyze literary texts or oral histories.
This involves analyzing the meaning of signs and symbols within a set of text data. This method is often used to analyze advertising or other types of visual media.
Text mining
This involves using computational techniques to extract patterns and insights from large sets of text data. This method is often used in fields such as marketing and social media analysis.
Close Reading
This involves a detailed and in-depth analysis of a particular text, focusing on the language, style, and literary techniques used by the author.
How to Conduct Textual Analysis
Here are some general steps to conduct textual analysis:
- Choose your research question: Define your research question and identify the text or set of texts that you want to analyze.
- F amiliarize yourself with the text: Read and re-read the text, paying close attention to its language, structure, and content. Take notes on key themes, patterns, and ideas that emerge.
- Choose your analytical approach: Select the appropriate analytical approach for your research question, such as close reading, thematic analysis, content analysis, or discourse analysis.
- Create a coding scheme: If you are conducting content analysis, create a coding scheme to categorize and analyze the content of the text. This may involve identifying specific words, themes, or ideas to code.
- Code the text: Apply your coding scheme to the text and systematically categorize the content based on the identified themes or patterns.
- Analyze the data: Once you have coded the text, analyze the data to identify key patterns, themes, or trends. Use appropriate software or tools to help with this process if needed.
- Draw conclusions: Draw conclusions based on your analysis and answer your research question. Present your findings and provide evidence to support your conclusions.
- R eflect on limitations and implications: Reflect on the limitations of your analysis, such as any biases or limitations of the selected method. Also, discuss the implications of your findings and their relevance to the broader research field.
When to use Textual Analysis
Textual analysis can be used in various research fields and contexts. Here are some situations when textual analysis can be useful:
- Understanding meaning and interpretation: Textual analysis can help understand the meaning and interpretation of text, such as literature, media, and social media.
- Analyzing communication patterns: Textual analysis can be used to analyze communication patterns in different contexts, such as political speeches, social media conversations, and legal documents.
- Exploring cultural and social contexts: Textual analysis can be used to explore cultural and social contexts, such as the representation of gender, race, and identity in media.
- Examining historical documents: Textual analysis can be used to examine historical documents, such as letters, diaries, and newspapers.
- Evaluating marketing and advertising campaigns: Textual analysis can be used to evaluate marketing and advertising campaigns, such as analyzing the language, symbols, and imagery used.
Examples of Textual Analysis
Here are a few examples:
- Media Analysis: Textual analysis is frequently used in media studies to examine how news outlets and social media platforms frame and present news stories. Researchers can use textual analysis to examine the language and images used in news articles, tweets, and other forms of media to identify patterns and biases.
- Customer Feedback Analysis: Textual analysis is often used by businesses to analyze customer feedback, such as online reviews or social media posts, to identify common themes and areas for improvement. This allows companies to make data-driven decisions and improve their products or services.
- Political Discourse Analysis: Textual analysis is commonly used in political science to analyze political speeches, debates, and other forms of political communication. Researchers can use this method to identify the language and rhetoric used by politicians, as well as the strategies they employ to appeal to different audiences.
- Literary Analysis: Textual analysis is a fundamental tool in literary criticism, allowing scholars to examine the language, structure, and themes of literary works. This can involve close reading of individual texts or analysis of larger literary movements.
- Sentiment Analysis: Textual analysis is used to analyze social media posts, customer feedback, or other sources of text data to determine the sentiment of the text. This can be useful for businesses or organizations to understand how their brand or product is perceived in the market.
Purpose of Textual Analysis
There are several specific purposes for using textual analysis, including:
- To identify and interpret patterns in language use: Textual analysis can help researchers identify patterns in language use, such as common themes, recurring phrases, and rhetorical devices. This can provide insights into the values and beliefs that underpin the text.
- To explore the cultural context of the text: Textual analysis can help researchers understand the cultural context in which the text was produced, including the historical, social, and political factors that shaped the language and messages.
- To examine the intended and unintended meanings of the text: Textual analysis can help researchers uncover both the intended and unintended meanings of the text, and to explore how the language is used to convey certain messages or values.
- To understand how texts create and reinforce social and cultural identities: Textual analysis can help researchers understand how texts contribute to the creation and reinforcement of social and cultural identities, such as gender, race, ethnicity, and nationality.
Applications of Textual Analysis
Here are some common applications of textual analysis:
Media Studies
Textual analysis is frequently used in media studies to analyze news articles, advertisements, and social media posts to identify patterns and biases in media representation.
Literary Criticism
Textual analysis is a fundamental tool in literary criticism, allowing scholars to examine the language, structure, and themes of literary works.
Political Science
Textual analysis is commonly used in political science to analyze political speeches, debates, and other forms of political communication.
Marketing and Consumer Research
Textual analysis is used to analyze customer feedback, such as online reviews or social media posts, to identify common themes and areas for improvement.
Healthcare Research
Textual analysis is used to analyze patient feedback and medical records to identify patterns in patient experiences and improve healthcare services.
Social Sciences
Textual analysis is used in various fields within social sciences, such as sociology, anthropology, and psychology, to analyze various forms of data, including interviews, field notes, and documents.
Linguistics
Textual analysis is used in linguistics to study language use and its relationship to social and cultural contexts.
Advantages of Textual Analysis
There are several advantages of textual analysis in research. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Systematic and objective: Textual analysis is a systematic and objective method of analyzing text data. It enables researchers to analyze text data in a consistent and rigorous way, minimizing the risk of bias or subjectivity.
- Versatile : Textual analysis can be used to analyze a wide range of text data, including interview transcripts, survey responses, social media data, policy documents, and literary texts.
- Efficient : Textual analysis can be a more efficient method of data analysis compared to manual coding or other methods of qualitative analysis. With the help of software tools, researchers can process large volumes of text data more quickly and accurately.
- Allows for in-depth analysis: Textual analysis enables researchers to conduct in-depth analysis of text data, uncovering patterns and themes that may not be visible through other methods of data analysis.
- Can provide rich insights: Textual analysis can provide rich and detailed insights into complex social phenomena. It can uncover subtle nuances in language use, reveal underlying meanings and discourses, and shed light on the ways in which social structures and power relations are constructed and maintained.
Limitations of Textual Analysis
While textual analysis can provide valuable insights into the ways in which language is used to convey meaning and create social and cultural identities, it also has several limitations. Some of these limitations include:
- Limited Scope : Textual analysis is only able to analyze the content of written or spoken language, and does not provide insights into non-verbal communication such as facial expressions or body language.
- Subjectivity: Textual analysis is subject to the biases and interpretations of the researcher, as well as the context in which the language was produced. Different researchers may interpret the same text in different ways, leading to inconsistencies in the findings.
- Time-consuming: Textual analysis can be a time-consuming process, particularly if the researcher is analyzing a large amount of text. This can be a limitation in situations where quick analysis is necessary.
- Lack of Generalizability: Textual analysis is often used in qualitative research, which means that its findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. This limits the ability to draw conclusions that are applicable to a wider range of contexts.
- Limited Accessibility: Textual analysis requires specialized skills and training, which may limit its accessibility to researchers who are not trained in this method.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Cluster Analysis – Types, Methods and Examples

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Discriminant Analysis – Methods, Types and...

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

MANOVA (Multivariate Analysis of Variance) –...

Observational Research – Methods and Guide
11 Different Types of Text Analysis Explained
By Grégory Gossart
Unlock the secrets of text analysis with our comprehensive guide. Explore 11 different types of text analysis explained in detail. From sentiment analysis to stylometry, delve into the nuances of language interpretation and extraction of meaningful insights.
What is text analysis?
Why is text analysis important, benefits of using text analysis, 11 different types of text analysis, future of text analysis, examples of text analysis in use, how to get started with text analysis.
Text analysis is like a helpful tool that lets us dig deeper into what's written. It's all about understanding the stories and information hidden in the words we read.
In a world full of information, text analysis acts as a guide. It helps us make sense of feelings, discover themes, and find patterns in the words people use. It's like a key to unlocking the meaning behind what's written.
Insightful Discoveries: Text analysis reveals hidden insights and trends in large volumes of text, helping us see beyond the surface.
Efficient Understanding: It streamlines the process of understanding sentiments, themes, and patterns, making it easier to grasp the core of any written content.
In our journey, we'll explore 11 different types of text analysis. Each type is like a unique lens, offering a distinct way to understand and interpret written words. From simple statistical analysis to more advanced methods like sentiment analysis, we'll uncover the tools that make text analysis a versatile skill.
1 - Statistical Text Analysis
Definition: Statistical Text Analysis serves as a textual archaeologist, delving into the fundamental elements of a text. It uncovers character count, word count, sentence count, paragraph count, and explores the evolution of these metrics, like the average characters or words per sentence.
Examples: Imagine using Statistical Text Analysis to dissect an article. You could swiftly gather insights into its length, structure, and how the complexity of sentences changes over time.
Benefits: It provides a foundational understanding of the text's structure, aiding in quick assessments of its length and complexity.
Limitations: Yet, it might overlook the more intricate nuances and deeper layers of meaning within the language.
2 - Word Frequency Analysis
Definition: Word Frequency Analysis, a companion to Statistical Text Analysis, is like a word detective. It specifically focuses on counting how often words appear in a text, aiding in the identification of keywords and their prominence.
Examples: Consider using this to analyze social media comments, pinpointing which words people use the most and gaining insights into popular topics.
Benefits: It's a fantastic tool for extracting keywords and understanding the emphasis of certain terms within a text.
Limitations: Yet, it might miss the context and broader patterns present in the language.
3 - Lexical Analysis
Definition: Lexical Analysis, our language sculptor, focuses on breaking down a text into its individual tokens, or words. It's like dissecting the building blocks of language to understand their arrangement and meaning.
Additional Insight: This process also helps identify stop words, common words often removed from text analysis because they don't contribute much value. It's akin to sifting through the clutter to unveil the essence of meaningful words.
Examples: Picture using Lexical Analysis to study poetry, deciphering the beauty and intended emotions by understanding not just the words but also recognizing and filtering out the less meaningful ones.
Benefits: Provides a deep understanding of language construction, aiding in interpreting meaning beyond surface-level metrics.
Limitations: May not capture the broader context, concentrating more on the intricacies of individual words.
4 - Semantic Analysis
Definition: Semantic Analysis acts as the interpreter of meaning, going beyond the surface to understand the context and intent behind words. It's like the detective who unravels the deeper layers of a story.
Examples: Imagine using Semantic Analysis to explore a news article. It helps unveil not just what's written but also the underlying meaning and intended messages.
Benefits: Provides a holistic understanding of the text, capturing the nuances and context that mere words may not convey.
Limitations: Yet, it may struggle with highly nuanced or ambiguous language, as it grapples with deciphering the intricacies of intent.
5 - Syntactic Analysis
Definition: Syntactic Analysis is the architect of language, focusing on sentence structure, grammar, and the arrangement of words. It's like understanding the blueprint that shapes the meaning of sentences.
Examples: Visualize using Syntactic Analysis to dissect a complex sentence. It helps unveil the grammatical structure, allowing a deeper understanding of how each part contributes to the overall meaning.
Benefits: Provides insights into the organization of sentences, aiding in the interpretation of complex ideas.
Limitations: However, it may struggle with creative expressions that intentionally deviate from traditional grammatical structures.
6 - Topic Modeling
Definition: Topic Modeling is like the curator of themes, uncovering the main subjects within a collection of texts. It's akin to distilling the essence of what a body of text is all about.
Examples: Envision using Topic Modeling to analyze a set of research papers. It identifies the recurring themes, offering a snapshot of the primary subjects explored in the collection.
Benefits: Enables a quick overview of the main topics in a large text corpus, aiding in categorization and understanding overarching themes.
Limitations: Yet, it may struggle with nuanced or evolving topics, as it might oversimplify complex subjects.
7 - Sentiment Analysis
Definition: Sentiment Analysis is the emotion interpreter, determining the emotional tone behind words. It's like having a keen listener who can understand if a piece of text is happy, sad, or neutral.
Examples: Imagine using Sentiment Analysis to evaluate product reviews. It discerns whether customers are expressing joy, dissatisfaction, or indifference.
Benefits: Provides insights into how people feel about a particular subject, helping businesses gauge customer opinions and sentiments.
Limitations: Yet, it may struggle with sarcasm or complex emotions expressed in language.
8 - Stylometry
Definition: Stylometry is the literary fingerprint reader, analyzing writing styles to identify unique patterns and characteristics. It's like recognizing an author's signature woven into the fabric of their writing.
Examples: Picture using Stylometry to attribute anonymous texts to specific authors. It discerns the distinctive elements that make each writer's style unique.
Benefits: Provides a forensic lens for identifying authors, understanding writing patterns, and even detecting plagiarism.
Limitations: However, it may struggle with highly collaborative works or intentional style alterations.
9 - Plagiarism Detection
Definition: Plagiarism Detection is the vigilant sentinel, scrutinizing texts to identify instances of copied or unoriginal content. It's like a watchful guardian ensuring the integrity of written work.
Examples: Envision using Plagiarism Detection to review academic papers. It swiftly identifies any sections that resemble existing works, safeguarding against unintentional plagiarism.
Benefits: Safeguards the originality of content, ensuring the integrity of academic and professional writings.
Limitations: Yet, it may face challenges in detecting more sophisticated forms of plagiarism, such as paraphrasing.
10 - Cohesion Analysis
Definition: Cohesion Analysis is the language harmonizer, exploring how sentences and paragraphs connect to create a unified text. It's like ensuring the smooth flow of a river of words.
Examples: Picture using Cohesion Analysis to refine an essay. It examines how sentences link together, ensuring a seamless and logical progression of ideas.
Benefits: Enhances the clarity and coherence of written or spoken language, fostering a more engaging and understandable communication.
Limitations: However, it may struggle with unconventional or intentionally disjointed writing styles.
11 - Corpus Linguistics
Definition: Corpus Linguistics is the linguistic explorer, analyzing large collections of texts to uncover patterns, trends, and linguistic phenomena. It's like studying the vast tapestry of language to reveal its secrets.
Examples: Picture using Corpus Linguistics to study language evolution. It analyzes a large body of texts across different time periods to observe changes in vocabulary and usage.
Benefits: Enables the investigation of language on a grand scale, providing insights into linguistic evolution, usage patterns, and language variation.
Limitations: However, it may struggle with capturing the dynamic and evolving nature of language in real-time.
As we conclude our journey through the diverse landscapes of text analysis, we've unraveled the intricacies of understanding, interpreting, and extracting meaning from written and spoken language. From the foundational elements of Statistical Text Analysis and Word Frequency Analysis to the nuanced realms of Sentiment Analysis, Stylometry, and beyond, each level unveils a unique facet of the enchanted world of language.
The future holds promises of even more advanced tools and techniques, leveraging the power of artificial intelligence to refine our understanding of language. As technology evolves, so too will our ability to analyze, interpret, and derive meaningful insights from the vast sea of textual information.
From deciphering customer sentiments in product reviews to ensuring the originality of academic works through Plagiarism Detection, the applications of text analysis are vast. Businesses, researchers, and individuals alike harness the power of these techniques to gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and navigate the complexities of language.
For those looking to embark on their own journey into text analysis, numerous resources await. Online courses, tutorials, and software tools can serve as guides through the enchanting realms we've explored.
Embarking on the journey of text analysis doesn't require a magic wand but a curious mind and the right tools. Here's your guide to stepping into the enchanting realms of deciphering written language:
Learn the Basics: Familiarize yourself with the foundational concepts of text analysis, such as statistical metrics, word frequency, and syntactic structures. Online platforms, tutorials, and introductory courses can be your trusty companions.
Choose Your Tools: Select the tools that align with your goals. For beginners, user-friendly platforms like Prose Analyzer provide a seamless entry point. As you advance, explore more sophisticated tools based on your specific needs.
Dive into Tutorials: Tutorials are the treasure maps guiding you through the terrains of text analysis. Follow step-by-step guides to understand the practical application of different methods and techniques.
Explore Real-world Examples: The best way to master text analysis is by immersing yourself in real-world examples. Analyze articles, social media posts, or any written content that piques your interest. Apply your newfound skills to uncover hidden meanings.
Join the Community: Text analysis is an ever-evolving field, and there's a vibrant community of enthusiasts eager to share knowledge. Participate in forums, discussions, and online communities to learn from experienced practitioners and exchange ideas.
Stay Updated: The magic of text analysis lies in its continuous evolution. Stay updated on the latest tools, techniques, and advancements in the field. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant blogs, and attend webinars to keep your skills sharp.
With Prose Analyzer, elevate your writing skills effortlessly — all with one click.
Related articles, how to analyze text online: a comprehensive guide for digital insights.
Unraveling the meaning hidden within written content. Explore sentiments, extract keywords, and understand statistical patterns for powerful insights.
Decoding Essay Length: A Practical Guide to Writing Success
Discover the ideal length for your essays. Our guide helps you effectively navigate essay lengths for clear, impactful communication.

The Power of Analysis: Tips and Tricks for Writing Analysis Essays: Home
Crystal sosa.

Helpful Links
- Super Search Webpage Where to start your research.
- Scribbr Textual analysis guide.
- Analyzing Texts Prezi Presentation A prezi presentation on analyzing texts.
- Writing Essays Guide A guide to writing essays/
- Why is it important?
- Explanation & Example
- Different Types of Analysis Essays
Text analysis and writing analysis texts are important skills to develop as they allow individuals to critically engage with written material, understand underlying themes and arguments, and communicate their own ideas in a clear and effective manner. These skills are essential in academic and professional settings, as well as in everyday life, as they enable individuals to evaluate information and make informed decisions.
What is Text Analysis?
Text analysis is the process of examining and interpreting a written or spoken text to understand its meaning, structure, and context. It involves breaking down the text into its constituent parts, such as words, phrases, and sentences, and analyzing how they work together to convey a particular message or idea.
Text analysis can be used to explore a wide range of textual material, including literature, poetry, speeches, and news articles, and it is often employed in academic research, literary criticism, and media analysis. By analyzing texts, we can gain deeper insights into their meanings, uncover hidden messages and themes, and better understand the social and cultural contexts in which they were produced.
What is an Analysis Essay?
An analysis essay is a type of essay that requires the writer to analyze and interpret a particular text or topic. The goal of an analysis essay is to break down the text or topic into smaller parts and examine each part carefully. This allows the writer to make connections between different parts of the text or topic and develop a more comprehensive understanding of it.
In “The Yellow Wallpaper,” Charlotte Perkins Gilman uses the first-person point of view and vivid descriptions of the protagonist’s surroundings to convey the protagonist’s psychological deterioration. By limiting the reader’s understanding of the story’s events to the protagonist’s perspective, Gilman creates a sense of claustrophobia and paranoia, mirroring the protagonist’s own feelings. Additionally, the use of sensory language, such as the “smooch of rain,” and descriptions of the “yellow wallpaper” and its “sprawling flamboyant patterns,” further emphasize the protagonist’s sensory and emotional experience. Through these techniques, Gilman effectively communicates the protagonist’s descent into madness and the effects of societal oppression on women’s mental health.
There are several different types of analysis essays, including:
Literary Analysis Essays: These essays examine a work of literature and analyze various literary devices such as character development, plot, theme, and symbolism.
Rhetorical Analysis Essays: These essays examine how authors use language and rhetoric to persuade their audience, focusing on the author's tone, word choice, and use of rhetorical devices.
Film Analysis Essays: These essays analyze a film's themes, characters, and visual elements, such as cinematography and sound.
Visual Analysis Essays: These essays analyze visual art, such as paintings or sculptures, and explore how the artwork's elements work together to create meaning.
Historical Analysis Essays: These essays analyze historical events or documents and examine their causes, effects, and implications.
Comparative Analysis Essays: These essays compare and contrast two or more works, focusing on similarities and differences between them.
Process Analysis Essays: These essays explain how to do something or how something works, providing a step-by-step analysis of a process.
Analyzing Texts
- General Tips
- How to Analyze
- What to Analyze
When writing an essay, it's essential to analyze your topic thoroughly. Here are some suggestions for analyzing your topic:
Read carefully: Start by reading your text or prompt carefully. Make sure you understand the key points and what the text or prompt is asking you to do.
Analyze the text or topic thoroughly: Analyze the text or topic thoroughly by breaking it down into smaller parts and examining each part carefully. This will help you make connections between different parts of the text or topic and develop a more comprehensive understanding of it.
Identify key concepts: Identify the key concepts, themes, and ideas in the text or prompt. This will help you focus your analysis.
Take notes: Take notes on important details and concepts as you read. This will help you remember what you've read and organize your thoughts.
Consider different perspectives: Consider different perspectives and interpretations of the text or prompt. This can help you create a more well-rounded analysis.
Use evidence: Use evidence from the text or outside sources to support your analysis. This can help you make your argument stronger and more convincing.
Formulate your thesis statement: Based on your analysis of the essay, formulate your thesis statement. This should be a clear and concise statement that summarizes your main argument.
Use clear and concise language: Use clear and concise language to communicate your ideas effectively. Avoid using overly complicated language that may confuse your reader.
Revise and edit: Revise and edit your essay carefully to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Understanding the assignment: Make sure you fully understand the assignment and the purpose of the analysis. This will help you focus your analysis and ensure that you are meeting the requirements of the assignment.
Read the essay multiple times: Reading the essay multiple times will help you to identify the author's main argument, key points, and supporting evidence.
Take notes: As you read the essay, take notes on key points, quotes, and examples. This will help you to organize your thoughts and identify patterns in the author's argument.
Take breaks: It's important to take breaks while reading academic essays to avoid burnout. Take a break every 20-30 minutes and do something completely different, like going for a walk or listening to music. This can help you to stay refreshed and engaged.
Highlight or underline key points: As you read, highlight or underline key points, arguments, and evidence that stand out to you. This will help you to remember and analyze important information later.
Ask questions: Ask yourself questions as you read to help you engage critically with the text. What is the author's argument? What evidence do they use to support their claims? What are the strengths and weaknesses of their argument?
Engage in active reading: Instead of passively reading, engage in active reading by asking questions, making connections to other readings or personal experiences, and reflecting on what you've read.
Find a discussion partner: Find someone to discuss the essay with, whether it's a classmate, a friend, or a teacher. Discussing the essay can help you to process and analyze the information more deeply, and can also help you to stay engaged.
- Identify the author's purpose and audience: Consider why the author wrote the essay and who their intended audience is. This will help you to better understand the author's perspective and the purpose of their argument.
Analyze the structure of the essay: Consider how the essay is structured and how this supports the author's argument. Look for patterns in the organization of ideas and the use of transitions.
Evaluate the author's use of evidence: Evaluate the author's use of evidence and how it supports their argument. Consider whether the evidence is credible, relevant, and sufficient to support the author's claims.
Consider the author's tone and style: Consider the author's tone and style and how it contributes to their argument. Look for patterns in the use of language, imagery, and rhetorical devices.
Consider the context : Consider the context in which the essay was written, such as the author's background, the time period, and any societal or cultural factors that may have influenced their perspective.
Evaluate the evidence: Evaluate the evidence presented in the essay and consider whether it is sufficient to support the author's argument. Look for any biases or assumptions that may be present in the evidence.
Consider alternative viewpoints: Consider alternative viewpoints and arguments that may challenge the author's perspective. This can help you to engage critically with the text and develop a more well-rounded understanding of the topic.

- Last Updated: Jun 21, 2023 1:01 PM
- URL: https://odessa.libguides.com/analysis

Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, textual analysis – how to engage in textual analysis.
- © 2023 by Jennifer Janechek - IBM Quantum

As a reader, a developing writer, and an informed student and citizen, you need to be able to locate, understand, and critically analyze others’ purposes in communicating information. Being able to identify and articulate the meaning of other writers’ arguments and theses enables you to engage in intelligent, meaningful, and critical knowledge exchanges. Ultimately, regardless of the discipline you choose to participate in, textual analysis —the summary, contextualization, and interpretation of a writer’s effective or ineffective delivery of their perspective on a topic, statement of thesis, and development of an argument—will be an invaluable skill. Your ability to critically engage in knowledge exchanges—through the analysis of others’ communication—is integral to your success as a student and as a citizen.

Step 1: What Is The Thesis?
In order to learn how to better recognize a thesis in a written text, let’s consider the following argument:
So far, [Google+] does seem better than Facebook, though I’m still a rookie and don’t know how to do even some basic things.
It’s better in design terms, and also much better with its “circles” allowing you to target posts to various groups.
Example: following that high school reunion, the overwhelming majority of my Facebook friends list (which I’m barely rebuilding after my rejoin) are people from my own hometown. None of these people are going to care too much when my new book comes out from Edinburgh. Likewise, not too many of you would care to hear inside jokes about our old high school teachers, or whatever it is we banter about.
Another example: people I know only from exchanging a couple of professional emails with them ask to be Facebook friends. I’ve never met these people and have no idea what they’re really like, even if they seem nice enough on email. Do I really want to add them to my friends list on the same level as my closest friends, brothers, valued colleagues, etc.? Not yet. But then there’s the risk of offending people if you don’t add them. On Google+ you can just drop them in the “acquaintances” circle, and they’ll never know how they’re classified.
But they won’t be getting any highly treasured personal information there, which is exactly the restriction you probably want for someone you’ve never met before.
I also don’t like too many family members on my Facebook friends list, because frankly they don’t need to know everything I’m doing or chatting about with people. But on Google+ this problem will be easily manageable. (Harman)
The first sentence, “[Google+] does seem better than Facebook” (Harman), doesn’t communicate the writer’s position on the topic; it is merely an observation . A position, also called a “claim,” often includes the conjunction “because,” providing a reason why the writer’s observation is unique, meaningful, and critical.https://www.youtube.com/embed/rwSFfnlwtjY?rel=0&feature=youtu.beTherefore, if the writer’s sentence, “[Google+] does seem better than Facebook” (Harman), is simply an observation, then in order to identify the writer’s position, we must find the answer to “because, why?” One such answer can be found in the author’s rhetorical question/answer, “Do I really want to add them to my friends list on the same level as my closest friends, brothers, valued colleagues, etc.? Not yet” (Harman). The writer’s “because, why?” could be “because Google+ allows me to manage old, new, and potential friends and acquaintances using separate circles, so that I’m targeting posts to various, separate groups.” Therefore, the writer’s thesis—their position—could be something like, “Google+ is better than Facebook because its design enables me to manage my friends using separate circles, so that I’m targeting posts to various, separate groups instead of posting the same information for everyone I’ve added to my network.”
In addition to communicating a position on a particular topic, a writer’s thesis outlines what aspects of the topic they will address. Outlining intentions within a thesis is not only acceptable, but also one of a writer’s primary obligations, since the thesis relates their general argument. In a sense, you could think of the thesis as a responsibility to answer the question, “What will you/won’t you be claiming and why?”
To explain this further, let’s consider another example. If someone were to ask you what change you want to see in the world, you probably wouldn’t readily answer “world peace,” even though you (and many others) may want that. Why wouldn’t you answer that way? Because such an answer is far too broad and ambiguous to be logically argued. Although world peace may be your goal, for logic’s sake, you would be better off articulating your answer as “a peaceful solution to the violence currently occurring on the border of southern Texas and Mexico,” or something similarly specific. The distinction between the two answers should be clear: the first answer, “world peace,” is broad, ambiguous, and not a fully developed claim (there wouldn’t be many, if any, people who would disagree with this statement); the second answer is narrower, more specific, and a fully developed claim. It confines the argument to a particular example of violence, but still allows you to address what you want, “world peace,” on a smaller, more manageable, and more logical scale.
Since a writer’s thesis functions as an outline of what they will address in an argument, it is often organized in the same manner as the argument itself. Let’s return to the argument about Google+ for an example. If the author stated their position as suggested—“Google+ is better than Facebook because its design enables me to manage my friends using separate circles, so that I’m targeting posts to various, separate groups instead of posting the same information I’ve added to my network”—we would expect them to first address the similarities and differences between the designs of Google+ and Facebook, and then the reasons why they believe Google+ is a more effective way of sharing information. The organization of their thesis should reflect the overall order of their argument. Such a well-organized thesis builds the foundation for a cohesive and persuasive argument.
Textual Analysis: How is the Argument Structured?
“Textual analysis” is the term writers use to describe a reader’s written explanation of a text. The reader’s textual analysis ought to include a summary of the author’s topic, an analysis or explanation of how the author’s perspective relates to the ongoing conversation about that particular topic, an interpretation of the effectiveness of the author’s argument and thesis , and references to specific components of the text that support his or her analysis or explanation.
An effective argument generally consists of the following components:
- A thesis. Communicates the writer’s position on a particular topic.
- Acknowledgement of opposition. Explains existing objections to the writer’s position.
- Clearly defined premises outlining reasoning. Details the logic of the writer’s position.
- Evidence of validating premises. Proves the writer’s thorough research of the topic.
- A conclusion convincing the audience of the argument’s soundness/persuasiveness. Argues the writer’s position is relevant, logical, and thoroughly researched and communicated.
An effective argument also is specifically concerned with the components involved in researching, framing, and communicating evidence:
- The credibility and breadth of the writer’s research
- The techniques (like rhetorical appeals) used to communicate the evidence (see “The Rhetorical Appeals”)
- The relevance of the evidence as it reflects the concerns and interests of the author’s targeted audience
To identify and analyze a writer’s argument, you must critically read and understand the text in question. Focus and take notes as you read, highlighting what you believe are key words or important phrases. Once you are confident in your general understanding of the text, you’ll need to explain the author’s argument in a condensed summary. One way of accomplishing this is to ask yourself the following questions:
- What topic has the author written about? (Explain in as few words as possible.)
- What is the author’s point of view concerning their topic?
- What has the author written about the opposing point of view? (Where does it appear as though the author is “giving credit” to the opposition?)
- Does the author offer proof (either in reference to another published source or from personal experience) supporting their stance on the topic?
- As a reader, would you say that the argument is persuasive? Can you think of ways to strengthen the argument? Using which evidence or techniques?
Your articulation of the author’s argument will most likely derive from your answers to these questions. Let’s reconsider the argument about Google+ and answer the reflection questions listed above:
The author’s topic is two social networks—Google+ and Facebook.
The author is “for” the new social network Google+.
The author makes a loose allusion to the opposing point of view in the explanation, “I’m still a rookie and don’t know how to do even some basic things” (Harman). (The author alludes to his inexperience and, therefore, the potential for the opposing argument to have more merit.)
Yes, the author offers proof from personal experience, particularly through their first example: “following that high school reunion, the overwhelming majority of my Facebook friends list (which I’m barely rebuilding after my rejoin) are people from my hometown” (Harman). In their second example, they cite that “[o]n Google+ you can just drop [individuals] in the ‘acquaintances’ circle, and they’ll never even know how they’re classified” (Harman) in order to offer even more credible proof, based on the way Google+ operates instead of personal experience.
Yes, I would say that this argument is persuasive, although if I wanted to make it even stronger, I would include more detailed information about the opposing point of view. A balanced argument—one that fairly and thoroughly articulates both sides—is often more respected and better received because it proves to the audience that the writer has thoroughly researched the topic prior to making a judgment in favor of one perspective or another.

Works Cited
Harman, Graham. Object-Oriented Philosophy. WordPress, n.d. Web. 15 May 2012.
Related Articles:
Annotating the margins, textual analysis - how to analyze ads, suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Jennifer Janechek
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Textual Analysis – Definition, Approaches & Fields
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Textual communication surrounds a large part of the methodology used by researchers to analyze and interpret texts by studying their style, content, structure, purpose, and underlying meaning. Besides analyzing the text, textual analysis gives us a better and more detailed idea of how people communicate and represent their experiences and perspectives through writing. This article will outline the different approaches to textual analysis and in what fields of study it is commonly used.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Textual Analysis – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Textual analysis
- 3 What are the approaches to textual analysis?
- 4 Different fields of textual analysis
Textual Analysis – In a Nutshell
- Text can be defined simply as any instance of language in any medium that makes sense to someone who knows the language, e.g., newspaper articles and transcripts of spoken interviews and observations.
- The purpose of textual analysis is to describe the functions, content, and structure of messages contained in a text.
- This type of analysis is used in different fields, including literary studies (where it is most common), social sciences, and cultural and media studies.
Definition: Textual analysis
Textual analysis is a broad term that entails various research methods, which allow to analyze, describe, and interpret the characteristics of a recorded message. There are four main approaches typically used in academic writing. Nevertheless, textual analysis is also used in other fields, such as in cultural and media studies, social sciences, and literary studies.
An example of textual analysis is brand monitoring to determine social opinion on your brand in various contexts.
What are the approaches to textual analysis?
There are four main approaches to textual analysis, which are listed and discussed below:
1. Rhetorical criticism
Rhetorical criticism is the systematic method of describing, analyzing, interpreting, and evaluating the persuasive force of messages within texts. At its core, rhetorical criticism is simply analyzing the use of rhetoric.
The process of rhetorical criticism has four steps :
- Select the text to study
- Choose the type of rhetorical criticism
- Analyze the chosen text using the chosen method
- Write a critical essay
The process of rhetorical criticism serves essential functions , including:
- Helping in understanding the historical, cultural, and social contexts
- Researchers can use it to evaluate society as a form of social criticism
- Helps illuminate the purpose of persuasive messages
- Teaching people what makes effective persuasion and how persuasion works
2. Content analysis
Content analysis is the analysis of specific message characteristics in a piece of text. It is usually considered unobtrusive since the analyzed texts already exist and are not being produced on request.
Content analysis can be both qualitative and quantitative, as described below:
- Quantitative – A systematic step-by-step procedure used to test hypotheses and answer research questions
- Qualitative – An approach that is more interested in the meanings of messages than the frequency of the occurrence of message variables.
The goals of content analysis include:
- Understanding the intentions of groups and individuals
- Identifying bias and propaganda
- Finding connections in how concepts are communicated
- Identifying communication differences in different contexts
3. Interaction analysis
Interaction analysis is the process of evaluating processes, determining the data requirements of each, and generating a matrix of what data is used by what process.
An interaction analysis involves two general tasks:
- Obtain a sample of interaction : When gathering a sample, the researchers’ choices affect the quality and type of data collected. Their choices determine if the interaction will be natural or structured, whether the location will be in a laboratory or another area, and the exact methods used to collect data.
- Analyzing the sample : Specific analysis of the collected samples will depend on the researchers’ goals and the form of the collected data.
4. Performance Studies
Performance studies is an approach that uses performance as the lens to study the world. There are six primary steps to undertaking a performance study:

Different fields of textual analysis
Textual analysis is a critical component of research in various fields of study, as discussed below.
Textual analysis in cultural and media studies
Researchers in cultural and media studies take media and cultural objects and treat them as texts to be analyzed.
- Media content
- Music videos
- Social media content.
Researchers in this field usually seek to connect contemporary culture and politics with text elements. In this context, the analysis is usually qualitative and creative. The different aspects of a text that a researcher may analyze include:
- The relationship with other relevant texts
- The design elements
- The word choice
- The location of the text
- The intended audience
Textual analysis in social sciences
Textual analysis in the social sciences is usually applied to texts like surveys, interview transcripts, and different media types to draw conclusions about social relations.
In this field, textual analysis usually takes a more quantitative approach, where certain text features’ frequency is measured numerically.
A researcher may investigate which words in a particular language are used most commonly, or which colors feature most in different advertisements aimed at different demographics.
Common methods of analyzing text in this field include discourse analysis, content analysis , and thematic analysis .
Textual analysis in literary studies
One of the most common uses of textual analysis is found in literary studies. Almost all works in this field – poems, plays, stories, novels – involve a comprehensive analysis. As this field deals with literary texts, a greater emphasis is usually placed on deliberately constructed elements such as the narrator’s voice and the rhyming scheme. In understanding these elements, the researcher lends more meaning to the text.
Textual analysis in this field also explores what the text reveals from the perspective through which the text was written, and finds new and unexpected ways to analyze classic pieces of text.
How do you write a textual analysis?
To write this analysis, the writer should analyze the structure, characters, setting, citations of a text, and central idea and themes. Consider the what, who, why, and where of the text you are analyzing.
What are the common approaches to textual analysis?
There are four primary textual analysis approaches:
- Rhetorical criticism
- Content analysis
- Interaction analysis
- Performance studies
What are the key features of textual analysis?
The key features of a textual analysis essay include:
- The summary and context of a text
- A statement of intent
- An explanation of the text’s continuing relevance
Why do we need to analyze texts?
The analysis helps extract a deeper meaning from a specific text and discover different perspectives in context.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
16.3 Glance at Genre: Print or Textual Analysis
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define key terms and organizational patterns of textual analysis.
- Explain how genre conventions are shaped by purpose, culture, and expectation.
As a genre —or literary category in which works feature similar forms, styles, or subject matter—textual analysis is less of a genre in itself and more of an exploration and interpretation of other genres. That is, textual analysis is explanatory and interpretive. When you receive an assignment to analyze a text, you focus on the elements that give it meaning. Usually your instructor will assign a specific writing task: to analyze and explain certain aspects of a text, to compare or contrast certain elements within a single text or in two or more texts, or to relate certain text elements to historical context or current events (as student writer Gwyn Garrison has done in the Annotated Student Sample ). These writing tasks thus explore genre characteristics of fiction, drama, poetry, literary nonfiction, film, and other forms of literary language.
When you write a textual analysis, ask yourself questions such as these:
- In what ways can this text be read?
- What are some different ways of reading it?
- Which reading makes the most sense to me?
- Which passages in the text support this reading?
- Whom does my analysis need to convince? (Who is my audience?)
Textual Analysis and Interpretive Communities
How you read and analyze a text depends on who you are. Who you are depends on the influences that have shaped you, or the communities to which you belong. Everyone belongs to various communities: families, social and economic groups (e.g., students or teachers, middle or working class), organizations (e.g., Democratic or Republican Party, Masons, Habitat for Humanity), geographic locales (e.g., rural or urban, north or south), and institutions (e.g., school, church, fraternity). Your membership in one or more communities may determine how you view and respond to the world. The communities that influence you most are called interpretive communities ; they influence the meaning you make of the world. People who belong to the same community may well have similar assumptions and therefore are likely to analyze texts in similar ways.
Before writing an interpretive or textual analysis essay, it is helpful to ask, Who am I when writing this piece? Be aware of your age, gender, race, ethnic identity, economic class, geographic location, educational level, or political or religious persuasion. Ask to what extent and for what purpose any of these identities emerges in your writing. Readers will examine the biases you may bring to your work, understanding that everyone views the world—and, consequently, texts—from their own vantage point.
College is, of course, a large interpretive community. The various smaller communities that exist within it are called disciplines: English, history, biology, business, art, and so on. Established ways of interpreting texts exist within disciplines. Often when you write a textual analysis, you will do so from the perspective of a traditional academic interpretive community or from the perspective of one who challenges that community.
Whether you deliberately identify yourself and any biases you might bring with you in your essay depends on the assignment you are given. Some assignments ask you to remove your personal perspective as much as possible from your writing, others ask that you acknowledge and explain it, and others fall somewhere in between.
Conventions of Textual Analysis
When asked to analyze or interpret a literary work, whether fiction or nonfiction, you will likely focus on some of these literary elements to explain how an author uses them to make meaning.
- Alliteration: literary device consisting of repetition of initial consonant sounds. (“Away from the steamy sidewalk, the children sat in a circle.”)
- Analysis: close examination and explanation of a text, supported by reasoning and evidence.
- Antagonist: character or force opposing the main character (protagonist) in a story.
- Climax: moment of emotional or intellectual intensity or a point in the plot when one opposing force overcomes another and the conflict is resolved.
- Epiphany: flash of intuitive understanding by the narrator or a character in a story.
- Figurative language: language that suggests special meanings or effects. Similes and metaphors are examples of figurative, rather than literal, language. (“She stands like a tree, solid and rooted.”)
- Imagery: language that appeals to one (or more) of the five senses. (“The cicadas hummed nonstop all day, but never loud enough to dull the roar of the leaf blowers.)
- Metaphor: direct comparison between two unlike things. (“She is a sly fox in her undercover work for the government.”)
- Narrator: someone who tells a story. A character narrator is a part of the story, whereas an omniscient narrator tells a story about others.
- Persona: mask to disguise or cover the author’s real self when presenting a story or other literary work.
- Plot: sequence of events in a story or play.
- Point of view: vantage point from which a story or event is perceived and told. The most frequently used points of view are first person and third person. In first person, the narrator is a character or observer in the story (fiction) or the author of it (nonfiction). In third person, the narrator has no part in the story other than telling it.
- Protagonist: main character or hero in a story.
- Rhyme: repetition of sounds, usually at the ends of lines in poems, but also occurring at other intervals in a line.
- Rhythm: rise and fall of stressed sounds within sentences, paragraphs, and stanzas.
- Simile: indirect comparison of unlike things using the word as or like . (“When he does undercover work, he is as sly as a fox.”)
- Symbol: object that represents itself and something else at the same time. A red rose is both a rose of a certain color and the suggestion of something romantic.
- Theme: meaning or thesis of a literary text.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/16-3-glance-at-genre-print-or-textual-analysis
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Textual Analysis | Guide, 3 Approaches & Examples
Textual Analysis | Guide, 3 Approaches & Examples
Published on 7 May 2022 by Jack Caulfield .
Textual analysis is a broad term for various research methods used to describe, interpret and understand texts. All kinds of information can be gleaned from a text – from its literal meaning to the subtext, symbolism, assumptions, and values it reveals.
The methods used to conduct textual analysis depend on the field and the aims of the research. It often aims to connect the text to a broader social, political, cultural, or artistic context.
Table of contents
What is a text, textual analysis in cultural and media studies, textual analysis in the social sciences, textual analysis in literary studies.
The term ‘text’ is broader than it seems. A text can be a piece of writing, such as a book, an email message, or a transcribed conversation. But in this context, a text can also be any object whose meaning and significance you want to interpret in depth: a film, an image, an artifact, even a place.
The methods you use to analyse a text will vary according to the type of object and the purpose of your analysis:
- Analysis of a short story might focus on the imagery, narrative perspective, and structure of the text.
- To analyse a film, not only the dialogue but also the cinematography and use of sound could be relevant to the analysis.
- A building might be analysed in terms of its architectural features and how it is navigated by visitors.
- You could analyse the rules of a game and what kind of behaviour they are designed to encourage in players.
While textual analysis is most commonly applied to written language, bear in mind how broad the term ‘text’ is and how varied the methods involved can be.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
In the fields of cultural studies and media studies, textual analysis is a key component of research. Researchers in these fields take media and cultural objects – for example, music videos, social media content, billboard advertising – and treat them as texts to be analysed.
Usually working within a particular theoretical framework (e.g., postcolonial theory, media theory, semiotics), researchers seek to connect elements of their texts with issues in contemporary politics and culture. They might analyse many different aspects of the text:
- Word choice
- Design elements
- Location of the text
- Target audience
- Relationship with other texts
Textual analysis in this context is usually creative and qualitative in its approach. Researchers seek to illuminate something about the underlying politics or social context of the cultural object they’re investigating.
In the social sciences, textual analysis is often applied to texts such as interview transcripts and surveys , as well as to various types of media. Social scientists use textual data to draw empirical conclusions about social relations.
Textual analysis in the social sciences sometimes takes a more quantitative approach , where the features of texts are measured numerically. For example, a researcher might investigate how often certain words are repeated in social media posts, or which colours appear most prominently in advertisements for products targeted at different demographics.
Some common methods of analysing texts in the social sciences include content analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Textual analysis is the most important method in literary studies. Almost all work in this field involves in-depth analysis of texts – in this context, usually novels, poems, stories, or plays.
Because it deals with literary writing, this type of textual analysis places greater emphasis on the deliberately constructed elements of a text: for example, rhyme and metre in a poem, or narrative perspective in a novel. Researchers aim to understand and explain how these elements contribute to the text’s meaning.
However, literary analysis doesn’t just involve discovering the author’s intended meaning. It often also explores potentially unintended connections between different texts, asks what a text reveals about the context in which it was written, or seeks to analyse a classic text in a new and unexpected way.
Some well-known examples of literary analysis show the variety of approaches that can be taken:
- Eve Kosofky Sedgwick’s book Between Men analyses Victorian literature in light of more contemporary perspectives on gender and sexuality.
- Roland Barthes’ S/Z provides an in-depth structural analysis of a short story by Balzac.
- Harold Bloom’s The Anxiety of Influence applies his own ‘influence theory’ to an analysis of various classic poets.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, May 07). Textual Analysis | Guide, 3 Approaches & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 15 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/textual-analysis-explained/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, content analysis | a step-by-step guide with examples, what is ethnography | meaning, guide & examples, critical discourse analysis | definition, guide & examples.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

10: Writing Argument Analysis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 27206
.jpg?revision=2)
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
Learning Outcomes
- Write an analysis of an argument's appeal to emotion
- Write an analysis of an argument's appeal to trust
- Connect an assessment of an argument's logical structure to an assessment of the effectiveness of its rhetorical appeals
- Give constructive feedback on an argument analysis essay
- Describe how the visual features of an image can reinforce the message of a visual argument.
- 10.1: How Argument Analysis Essays are Structured An argument analysis should summarize the argument and discuss how well any appeals to trust and emotion are likely to work with readers.
- 10.2: Analyzing an Argument's Situation (Kairos, or the Rhetorical Situation) Examining the author, audience, context, purpose, constraints, and genre of the argument can help us understand what shapes it.
- 10.3: Generating Ideas for an Argument Analysis Paper We can generate material by asking ourselves questions about an argument's logical structure, its appeals to emotion, and its appeals to trust.
- 10.4: Reviewing an Argument Analysis Essay We can ask ourselves certain questions as we read and give feedback on an argument analysis essay.
- 10.5.1: Annotated Brief Sample Argument Analysis
- 10.6.1: Annotated Longer Sample Argument Analysis
- 10.8.1: Annotated Sample Visual Argument Analysis

Find Study Materials for
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English Literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Social Studies
- Browse all subjects
- Read our Magazine
Create Study Materials
A text is any kind of written content. Periodicals, novels, scientific and literary papers, advertisements, and even text messages are kinds of texts. To analyze a text is to identify and explore every aspect of it. The art and science behind this is textual analysis . The topic of textual analysis is as broad as it is deep, so prepare to immerse yourself in the written word.

Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free.
Textual Analysis
Want to get better grades, get free, full access to:.
- Explanations
- Study Planner
- Textbook solutions
- StudySmarter AI
- Textbook Solutions
- 5 Paragraph Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Cues and Conventions
- English Grammar
- English Language Study
- Essay Prompts
- Essay Writing Skills
- Global English
- History of English Language
- International English
- Key Concepts in Language and Linguistics
- Language Acquisition
- Language Analysis
- Language and Social Groups
- Lexis and Semantics
- Linguistic Terms
- Listening and Speaking
- Multiple Choice Questions
- Research and Composition
- Rhetorical Analysis Essay
- Single Paragraph Essay
- Sociolinguistics
- Summary Text
- Synthesis Essay
- Character Analysis
- Citation Analysis
- Text Structure Analysis
- Vocabulary Assessment
Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen.
Textual Analysis Definition
Analyzing a text isn’t merely for class assignments or as part of standardized tests.
Textual analysis is a method of studying a text in order to understand the author's deliberate meaning.
This may sound grandiose but think of it this way: when you analyze part of a novel and write your conclusions, you are writing and explaining your understanding of it. You should always aim to help others to understand the meanings or possible meanings of the text.
To accomplish this goal, you can use textual analysis to identify the who, what, when, where, why, and how of a text by asking the following questions:
Who wrote it and for whom? Consider the author and audience.
What was written? Consider what type of text you are analyzing, e.g., is it an informative newspaper article or a speech?
When was it written and read? Consider the historical context .
Where was it written and read? Consider the place and culture in which the text was written.
Why was it written and read? Consider the author's intention behind writing the text.
How was it written? Consider the purpose of a text. Often, a textual analysis of “how” will analyze the text's structure, central idea , characters, setting, vocabulary, rhetoric , and citations.
The question “how?” is often the starting point for writing a literary analysis. While the other five modalities focus more on objective history, the how begins to explore a more personalized view of the text, such as the word choice of the text itself, which is largely interpreted by the reader. A more historical or scientific essay will often focus more on the first five modalities to support its points.
Textual Analysis with a Thesis
Textual analysis with a thesis explores “how” a text conveys an idea, but in an even bigger way. The most in-depth form of textual analysis uses a thesis to explore not only the factual aspects of a text but also the parts people don't agree on.
For instance, a thesis analysis might explore how well the writer accomplishes their goal, not merely how. Often, this complex form of analysis will compare the text in question with other relevant texts in order to draw a conclusion about it.
While identifying the who, what, when where, why, and how helps us to understand a text, a textual analysis with a thesis helps us to understand the bigger picture around a text. This could include information about the author’s life work, a literary genre, a period in time, or how that text relates to a modern reader or movement.
A textual analysis with a thesis always draws a conclusion that could be contested. However, you should attempt to argue your point in a way that makes it as resilient as possible to counter-arguments.
Different Types of Textual Analysis
A textual analysis often comes in the form of an essay with a thesis, but textual analysis can also be found anywhere. If at any point you analyze the who, what, when, where, why, and how of a text, it is a textual analysis. As such, a textual analysis essay is made up of a variety of interlinking analyses!
Textual Analysis Essay is the targeted exploration of a text using a thesis.
A textual analysis may also come in the form of a history or a deconstruction .
A history analysis is the explanation and analysis of a single text, with a focus on its place in time.
A deconstruction analysis is the break down of a scene, rhetorical device, character, or any other piece of a text into its constituents (i.e., the parts that make it up). A deconstruction is focused on the parts of the whole.
In short, anything that aims to classify or decode a text is a piece of textual analysis.
Structure of a Textual Analysis Essay
When writing a textual analysis essay, keep these five things in mind: summary and context , statement of intent , evidence , and the bigger picture .
Summary and Context
Textual analysis will summarize and contextualize the text, usually in or near the introduction. A textual analysis might introduce the temporal, cultural, or geographical context of the text. Depending on your audience, you might also include a summary of the text itself in order to jog their memory and remind them of the critical details you will be discussing.
Statement of Intent
Textual analysis will include some sort of statement of intent. If the analyst is focusing on the history of the text, they might include why the contents of the text are important to preserve. In the case of an essay, the analyst will include a thesis statement explaining why the text should be interpreted a certain way.
Textual analysis will have some form of evidence . If the analyst is focusing on the history of a text, the analyst will frequently cite the historical text or related histories. In a deconstruction of a text, the analyst will repeatedly cite the focal text. In an essay, the analyst will use evidence from the text to support a thesis.
The Bigger Picture
Textual analysis will speak to the bigger picture, usually in the conclusion. Without generalizing or making sweeping conclusions about "society" or "the world," be sure to cover the text’s future or continuing relevance. Include this in your conclusion, alongside other avenues for future analysis. Remember: the bulk of your essay is meant to contribute to the conversation on the text.

How to Write a Textual Analysis Essay
Approach your textual analysis from the top down. Is the text you are analyzing nonfiction or fiction?
Nonfiction is any written work that is about facts and true events.
Examples of nonfiction include memoirs, diaries, autobiographies and biographies, scientific papers, news articles, journals, and magazines.
Fiction is any written work invented by someone's imagination.
Any work that includes an imagined reality is a work of fiction, including any work that includes imaginative elements such as historical fiction.
Other fiction examples include novels, novellas, short stories, fables and myths, epic poems and sagas, and many screenplays and scripts.
Once you know whether the written work is fiction or nonfiction, move on to your analysis.
Philosophical, religious, and spiritual texts blur the lines between fiction and nonfiction because reality itself is disputed in these types of texts. Analyses of these highly contended topics are often found in writing assignments because there are many aspects that can be questioned.
How to Analyze Nonfiction
When analyzing nonfiction, you are more likely to focus on the who, what, when, where, and why of a text. This is because nonfiction deals with the realities of the world.
Your analysis of nonfiction could be very simple and draw close comparisons to an explanation. However, if you are writing an essay, your analysis will be more complicated because you will be using objective realities, facts, and evidence to support a conclusion.
You would analyze the who, what, when, where, and why of a climate report to support your thesis that America needs to address global climate change.
When analyzing nonfiction, you will also analyze the author’s rhetoric to explore how.
Rhetoric is the convincing way an author makes a point. It can also be described as a rhetorical mode.
Some examples of rhetoric that a nonfiction author might employ are classification, illustration/example, analogy, classical appeals, lines of reason, and objective description. You should analyze multiple rhetorical modes to be as convincing as possible.
How to Analyze Fiction
When analyzing fiction, you are more likely to focus on how a text conveys an idea. This is because a writer has invented all aspects of the story. The story the author has written has its own answers to the questions "who?" (the characters), "what?" (the story), "when?" (the period), "where?" (the setting), "why?" (the themes), and "how?" (the narrator).

So, when you unpack the how of a piece of fiction, you are unpacking an entire fictional reality as well. Every aspect of this reality has been constructed by the author using words. This leaves a lot for you to analyze, including the author's relationship between their own reality and their fictional reality. Textual analysis is really like exploring an all-new world!
When analyzing fiction, you should analyze the author’s rhetoric and whether the author's choice of rhetorical modes is effective. Some examples of rhetoric that a fiction author might employ are themes, mood, descriptions, specialized word choice, syntax, and narration.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Textual Analysis
Because textual analysis is such a broad category of writing, you will find that the strengths and weaknesses of textual analysis lie with specific textual analyses rather than the form of textual analysis itself.
When writing your own textual analysis, keep these do's and do not's in mind:
Do: Use Primary Sources
A primary source could be the text you are analyzing itself or a review, article, or interview regarding the text written near the time the text was first introduced. Primary sources are a great way to understand the historical context of a text and will bolster your introduction and body paragraphs.
Do Not: Use Opinions as Evidence
Your evidence should be objective and logical. Unless your thesis involves how well a text was received, people's opinions are not a great source of support for your essay.
Do: Cite your Sources
When you are drawing a debatable conclusion, remember to cite your sources. Evidence is only helpful if it is verifiable.
Do Not: Try to Cover Every Aspect of the Text
Focus on one or just a few aspects. As a student, you will never write a textual analysis, or even a history, that covers every aspect of a text. If you try, you will end up writing a bland, short summary or a history that probably adds very little to the conversation surrounding the text. Instead of analyzing all of Alice's Adventures in Wonderland (1865) at once, for example, analyze a few of Alice's encounters that show Lewis Carroll's love of numbers.
Textual Analysis Example
Here is an example of how to analyze a short excerpt from a story, something you are likely to be asked on standardized and timed tests, as well as in your take-home essays.
In this case, the writer presents a textual analysis of a passage from the opening narration of Charles Dickens's A Christmas Carol (1843):
Text Passage: "Marley was dead: to begin with. There is no doubt whatever about that. The register of his burial was signed by the clergyman, the clerk, the undertaker, and the chief mourner. Scrooge signed it: and Scrooge’s name was good upon ’Change, for anything he chose to put his hand to.' Old Marley was as dead as a door-nail."
Textual Analysis:
In this passage, Dickens employs a curt style to set the tone for Scrooge’s own brusque ways. This brusqueness begins at the start of the narrative, in his abrupt handling of Marley’s funeral. Punctuation is an important part of this style, including the colon, which tightly and emphatically joins “dead” and “to begin with.” Frequent periods also add to this pervasive sense of finality. Dickens finally employs figurative language to drive the point home when the narrator refers to Marley being “dead as a doornail.” This passage directs the reader to think of Marley as gone and departed, the way that Scrooge does. This tactic of misdirection pays off with a surprise when the reader learns that Marley is anything but gone and departed.
In the example, the writer of the textual analysis has chosen to focus on the following aspects to analyze how the text was written and explain and uncover the author's meaning in the passage from A Christmas Carol :
- Punctuation
- Figurative language
Textual Analysis - Key Takeaways
- Textual analysis is a method of studying a text in order to understand the various meanings by identifying the who, what, when, where, why, and how of a text.
- The most in-depth form of textual analysis uses a thesis.
- Textual analysis will include context and summary of a text, a statement of intent, evidence from the text and usually other sources.
- When analyzing nonfiction, you are more likely to focus on the who, what, when, where, and why of a text. When analyzing fiction, you are more likely to focus on the how of a text.
- For both nonfiction and fiction texts, you will analyze the author’s rhetoric to explore how.
Frequently Asked Questions about Textual Analysis
--> what is textual analysis.
Textual analysis is a method of studying a text in order to understand the various meanings.
--> How do you write a textual analysis?
To write a textual analysis, consider the who, what, when, where, why, and how of the text you are analyzing. Analyze the structure, central idea, characters, setting, vocabulary, rhetoric, and citations of a text.
--> What are the four key features of a textual analysis?
A textual analysis will:
- Summarize and contextualize a text.
- Include some sort of statement of intent.
- Provide evidence.
- Explain the text's continuing relevance.
--> What type of research is textual analysis?
Textual analysis is not a form of research, but rather uses research to analyze a text.
--> How do you write a textual analysis essay?
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards.
Textual analysis is a method of studying a text in order to _____ the author’s deliberate meaning.
To accomplish its goal, textual analysis identifies the _____ of a text.
An essay that aims to deconstruct a text is a piece of textual analysis.True or false?
Your score:

Join the StudySmarter App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Learn with 116 textual analysis flashcards in the free studysmarter app.
Already have an account? Log in
Understand.
All the above: who, what, when, where, why, how.
How does textual analysis differ from film analysis?
Textual analysis is the analysis of the written word. Film is a visual media.
An essay that aims to deconstruct a text is a piece of textual analysis.
True or false?
A textual analysis will include some sort of statement of _____.
Does a textual analysis use evidence?

of the users don't pass the Textual Analysis quiz! Will you pass the quiz?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free english cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our StudySmarter App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Smart Note-Taking

Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
This is still free to read, it's not a paywall.
You need to register to keep reading, create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Entdecke Lernmaterial in der StudySmarter-App


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Textual analysis is a research methodology that involves exploring written text as empirical data. Scholars explore both the content and structure of texts, and attempt to discern key themes and statistics emergent from them. This method of research is used in various academic disciplines, including cultural studies, literature, bilical studies ...
Textual analysis is a broad term for various research methods used to describe, interpret and understand texts. All kinds of information can be gleaned from a text - from its literal meaning to the subtext, symbolism, assumptions, and values it reveals. The methods used to conduct textual analysis depend on the field and the aims of the ...
Textual analysis is the process of examining a text in order to understand its meaning. It can be used to analyze any type of text, including literature, poetry, speeches, and scientific papers. Textual analysis involves analyzing the structure, content, and style of a text. Textual analysis can be used to understand a text's author, date ...
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis, nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
10 - Cohesion Analysis. Definition: Cohesion Analysis is the language harmonizer, exploring how sentences and paragraphs connect to create a unified text. It's like ensuring the smooth flow of a river of words. Examples: Picture using Cohesion Analysis to refine an essay.
Develop a writing project focused on textual analysis. Complete the stages of the writing process, including generating ideas, drafting, reviewing, revising, rewriting, and editing. Integrate the writer's ideas with ideas of others. Collaborate in the peer review process. When analyzing a text, writers usually focus on the content of the text ...
Always keep in mind, however, that a textual analysis is not about whether you like a text; it is about the meaning of the text—how the author created it and intended it to be understood. Any written work can be analyzed as a text. But an editorial or opinion piece or something written, for example, as part of an ongoing argument of ...
An analysis essay is a type of essay that requires the writer to analyze and interpret a particular text or topic. The goal of an analysis essay is to break down the text or topic into smaller parts and examine each part carefully. This allows the writer to make connections between different parts of the text or topic and develop a more ...
Textual Analysis - How to Engage in Textual Analysis. As a reader, a developing writer, and an informed student and citizen, you need to be able to locate, understand, and critically analyze others' purposes in communicating information. Being able to identify and articulate the meaning of other writers' arguments and theses enables you ...
The term regularly used for the development of the central idea of a literary analysis essay is the body. In this section you present the paragraphs (at least 3 paragraphs for a 500-750 word essay) that support your thesis statement. Good literary analysis essays contain an explanation of your ideas and evidence from the text (short story,
While the Textual Analysis Essay's thesis takes a stance on the effectiveness of the methods used in Pappano's essay, it does not explicitly take a stance on Pappano's argument. ... both types of essays. By this point in the term, you know that each main point in the body must work to prove, explain, or illustrate the thesis statement ...
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting the thesis, a body analyzing ...
Literary analysis involves examining all the parts of a novel, play, short story, or poem—elements such as character, setting, tone, and imagery—and thinking about how the author uses those elements to create certain effects. A literary essay isn't a book review: you're not being asked whether or not you liked a book or whether you'd ...
Textual analysis is a broad term that entails various research methods, which allow to analyze, describe, and interpret the characteristics of a recorded message. There are four main approaches typically used in academic writing. Nevertheless, textual analysis is also used in other fields, such as in cultural and media studies, social sciences ...
How to Write a Literary Analysis. These 4 steps will help prepare you to write an in-depth literary analysis that offers new insight to both old and modern classics. 1. Read the text and identify literary devices. As you conduct your literary analysis, you should first read through the text, keeping an eye on key elements that could serve as ...
Define key terms and organizational patterns of textual analysis. Explain how genre conventions are shaped by purpose, culture, and expectation. As a genre —or literary category in which works feature similar forms, styles, or subject matter—textual analysis is less of a genre in itself and more of an exploration and interpretation of other ...
8.1: Literary Analysis Arguments. Analysis means to break something down in order to better understand how it works. To analyze a literary work is to pull it apart and look at its discrete components to see how those components contribute to the meaning and/or effect of the whole. Thus, a literary analysis argument considers what has been ...
Textual analysis is a broad term for various research methods used to describe, interpret and understand texts. All kinds of information can be gleaned from a text - from its literal meaning to the subtext, symbolism, assumptions, and values it reveals. The methods used to conduct textual analysis depend on the field and the aims of the ...
Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap. City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative. Table of contents. Example 1: Poetry. Example 2: Fiction. Example 3: Poetry. Attribution. The following examples are essays where student writers focused on close-reading a literary work.
reader to trust it (e.g. in textual analysis, it often helps to find one or two key or representative passages to quote and focus on); and if summarized, it needs to be summarized accurately and fairly. 5. Analysis: the work of breaking down, interpreting, and commenting upon the data, of saying what can be
Write an analysis of an argument's appeal to emotion. Write an analysis of an argument's appeal to trust. Connect an assessment of an argument's logical structure to an assessment of the effectiveness of its rhetorical appeals. Give constructive feedback on an argument analysis essay. Describe how the visual features of an image can reinforce ...
2 Research your topic. Once you know your topic, you can begin collecting data and evidence to discuss it. If your analytical essay is about a creative work, you may want to spend time reviewing or evaluating that work, such as watching a film closely or studying the details of a painting.
Different Types of Textual Analysis. A textual analysis often comes in the form of an essay with a thesis, but textual analysis can also be found anywhere. If at any point you analyze the who, what, when, where, why, and how of a text, it is a textual analysis. As such, a textual analysis essay is made up of a variety of interlinking analyses!