UX Research Methods and the Path to User Empathy
How can designers move beyond personal insights to understand the problems users face? We introduce time-tested UX research methods that inspire user empathy and lead to better user experiences.


By Micah Bowers
Micah helps businesses craft meaningful engagement through branding, illustration, and design.
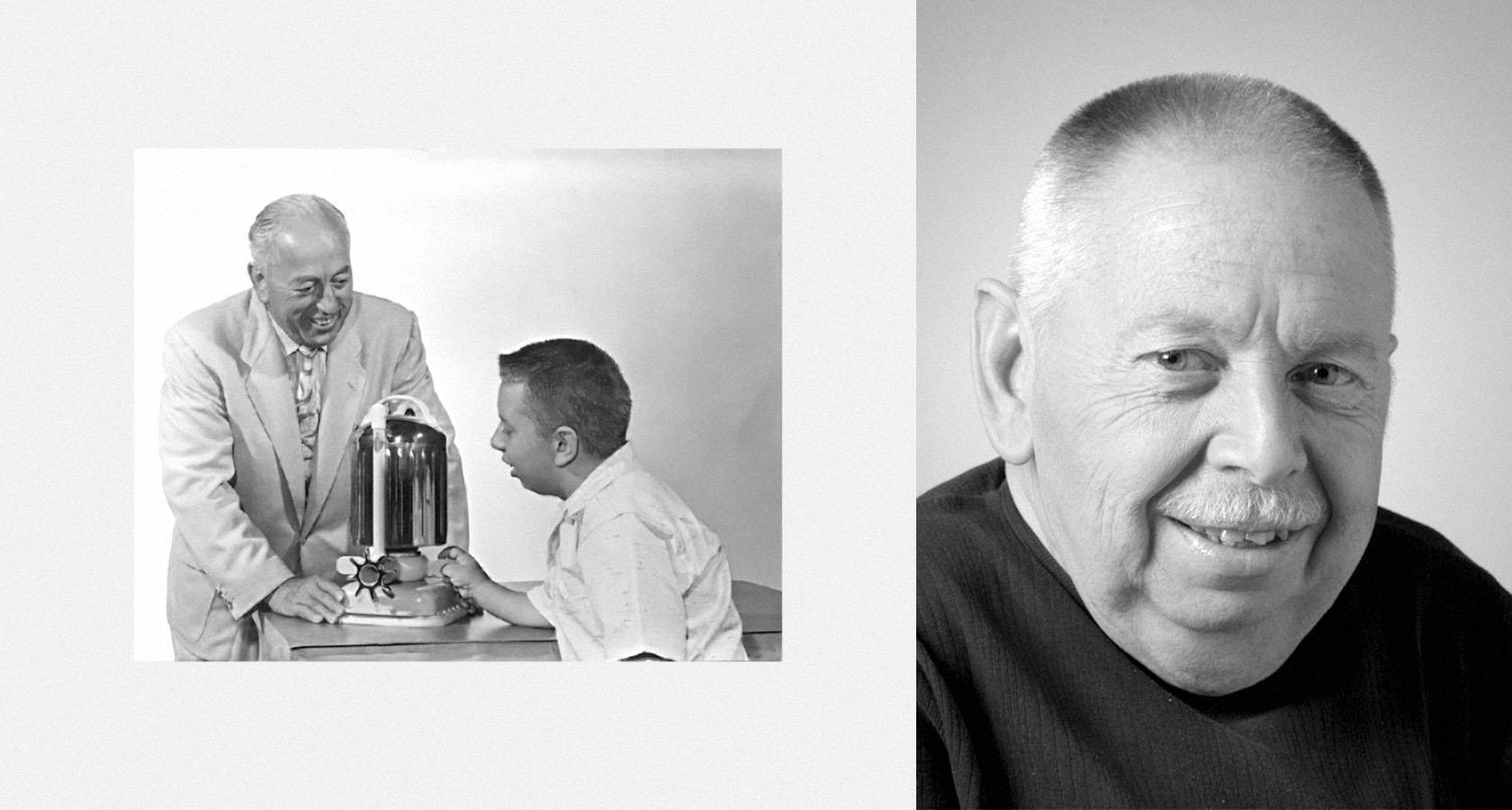
In 1941, a baby boy named Ken was born in Oakland, CA. Ken’s dad, Candido, was an Italian immigrant and inventor who, along with his brothers, supplied the United States with lightweight airplane propellers during the First World War.
Unfortunately, baby Ken suffered from juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, a potentially fatal condition that can cause severe deformities. Doctors recommended hydrotherapy, but at the time, the only option was soaking in large tanks located in spas or hospitals.
Moved to ease his son’s suffering, Candido drew on his background in design and engineering to create a submersible pump capable of turning a home bathtub into a hydrotherapy tank. Lo and behold, it worked.
In fact, it worked so well that the family business shifted gears and began selling a portable version of the pump to health clubs and schools. A few years later, a self-contained pump/tub combo was marketed to homeowners under the family name—the Jacuzzi whirlpool bath.
And, Ken? Thanks to ongoing treatment in Jacuzzi tubs, his pain became manageable, and he spent the next 75 years of his life serving as a prominent advocate for people with disabilities.

Why Does User Empathy Matter in UX Design?
Candido Jacuzzi didn’t sit down one day to solve a theoretical design problem for a vague and faceless target customer. He observed his son’s struggle firsthand—heard his cries, saw his labored movements, and intimately understood the obstacles of his illness.
For today’s UX designers , there’s a lesson to be learned: The goal of our work is greater than gaining profitable advantages. Yes, profitability is important, but UX designers should strive for more by seeking to see problems through the eyes of the people they’re designing for.
To do this well, to move beyond rhetorical aspirations and deliver life-improving design solutions, requires a disciplined approach to UX research. In this article, we’ll introduce time-tested UX research methods that inspire user empathy and ultimately lead to better user experiences.
UX Research Types: A Bird’s-Eye View
Before diving in, we need to step way back and take a broad look at the different types of UX research. Doing so will provide context to the more specific methods examined later.
A word of caution: Without knowing how to classify the UX research you’re performing , you’re likely to misinterpret findings and arrive at design solutions that hinder users rather than help them.
Primary vs. Secondary Research
Primary research is original research that is completed by you or your design team. The tasks performed and insights gained during primary research relate back to the design problem you are attempting to solve.
Primary research typically takes place after secondary research has helped shed light on why the problem exists and what’s been done to address it in the past.
Secondary research is any research that was done by someone else, and it’s a great way for designers to familiarize themselves with the history of different design problems.
That said, the areas explored during secondary research needn’t relate directly to the design problem. Sometimes, seemingly unconnected topics can bring clarity and innovation.

Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
Quantitative research produces results with numerical values and answers questions like “How much, how often, and how many?”
The variables measured by quantitative research may be quite granular, and the findings can be powerfully illustrated with statistics and data visualizations. However, it’s important to understand that for all its numerical precision, quantitative research can’t explain why something is happening.
- Qualitative research (a.k.a. empirical research) yields insights that aren’t numerical and instead come in the form of people’s comments, preferences, observations, and feelings. This type of research is valuable because human behavior is rarely based on patterns of pure logic and reason.
Generative vs. Evaluative Research
Generative research is conducted during the beginning of the investigative process. It helps UX researchers clearly define a problem and generate a hypothesis for its solution.
Generative research includes both primary and secondary research, and it can be quantitative and qualitative.
The generative design process works much like a funnel: It’s broad in the beginning, using secondary research to understand a wide range of information.
Then, as the problem becomes clearer and the research objectives are established, the focus becomes narrower, using more primary research tools that are both quantitative and qualitative in nature.
Evaluative research is executed near the end of the research process, and it’s used to test and refine ideas until the best solution is reached. For digital products, evaluative research is a vital part of the development cycle, and it should be introduced during the early phases of the design process (i.e., concept sketching and prototyping).
UX Research Methods That Lead to User Empathy
Now that we understand the different types of research, we’re ready to inspect five UX research methods and show how they inspire empathetic insights into the lives of users.
Here, it’s important to restate that the aim of these methods is seeing problems through the eyes of users in order to deliver life-improving design solutions.
If this is lost and research becomes little more than a perfunctory checklist, valuable (and potentially profitable) insights will be overlooked.
1. User Interviews
What are they?
- In user interviews, a UX researcher questions people that use a product and records their answers. The nature of the questions depends on the intent of the research, but the main goal is to extract user insights that can be used for product ideation and improvement.
How do they lead to user empathy?
- UX designers may be tempted to draw design conclusions from personal insights and experiences. User interviews are an affordable resource that helps designers avoid this tendency and maintain an important mindset: “I’m designing for the user. The user is not me.”
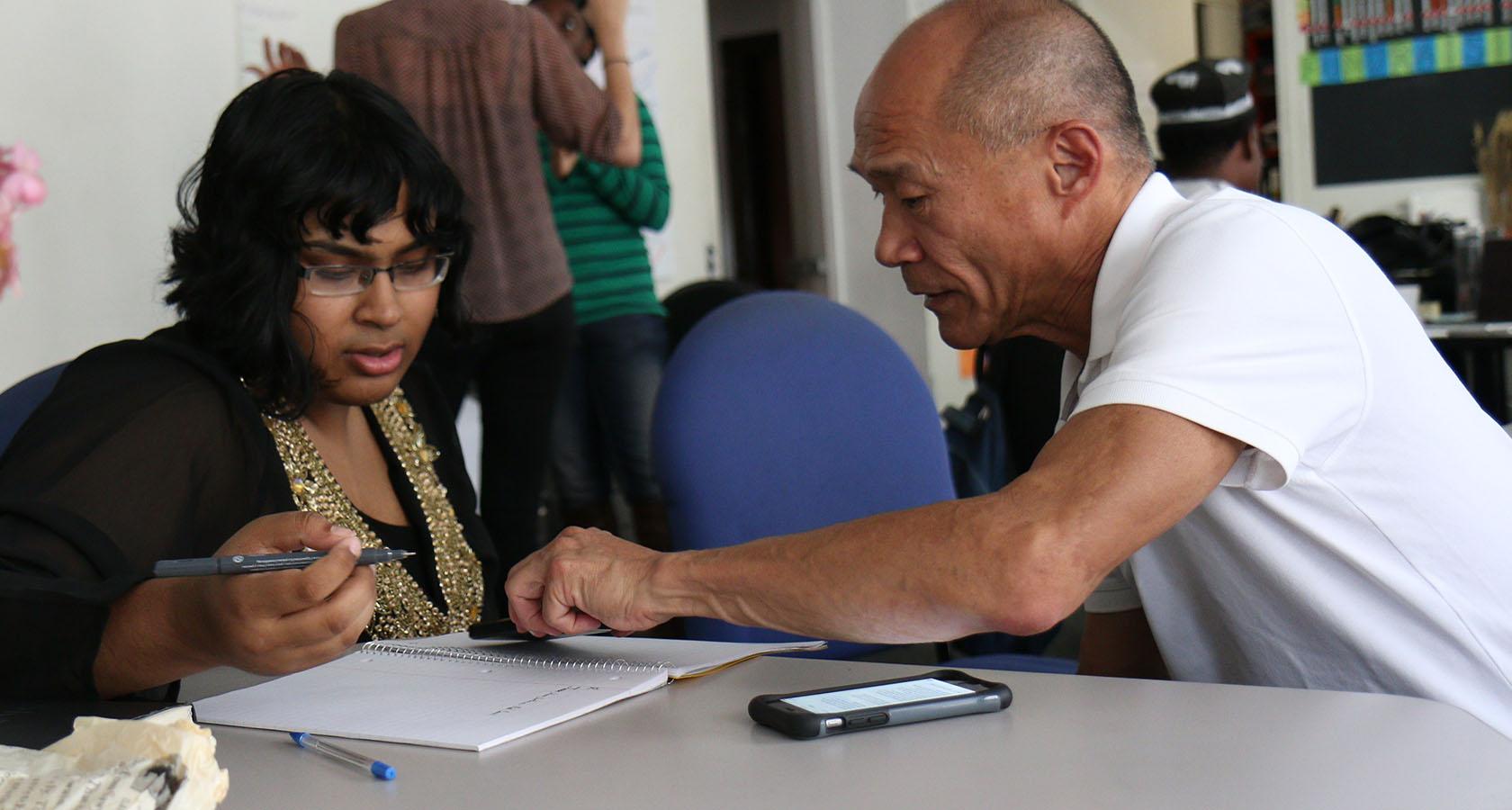

2. Ethnography
What is it?
- Want to know how users behave in their natural environment? Watch them. Ethnography is the firsthand observation of users as they interact with things in the world around them, and it’s an effective way for UX researchers to learn if a product is actually useful or hindered by design flaws.
How does it lead to user empathy?
- Testing a product in a controlled environment has its place, but the real world presents all manner of unforeseeable obstacles. Ethnography allows UX researchers to witness how everyday hurdles impact a product’s user experience. Then, researchers can pass their findings along to be included in the design problem-solving process.
3. User Surveys
A survey is a set of questions that evaluate users’ preferences, opinions, and attitudes about a product. Surveys are given to a sample audience that is representative of a larger population, and two types of questions are asked: closed and open.
Closed questions provide users with a fixed set of responses (i.e., yes/no, multiple choice, numerical scale, etc.), whereas open questions allow users to answer however they’d like.

- Surveys are a great way to get unfiltered feedback from users. By examining survey responses, UX designers can learn who users are, the problems they face, and what they honestly think about a product.
4. Contextual Inquiry
- A contextual inquiry is a hybrid UX research method where users are interviewed and observed while performing a task in its natural setting. However, it is the user (not the researcher) who takes on the role of expert and does most of the talking, explaining the steps of a process as it occurs.
- When people interact with something a lot, they develop an intimate knowledge of its strengths and weaknesses. Contextual inquiry helps researchers adopt a learning posture and allow users to explain how products are actually used day-to-day, workarounds and shortcomings included.
5. Card Sorting
Card sorting is a relatively simple technique that provides insight into how users structure data in their minds.
In an open card sort, people are given a deck of randomly shuffled cards and asked to organize them in whatever way they deem sensible. Once the cards are sorted, they are then asked to explain the reasoning behind their arrangement.
During a closed card sort, participants are asked to place cards from a deck into pre-existing groups, and their word associations are documented by researchers.

How does this UX research method lead to user empathy?
People with extensive product knowledge (e.g., designers, marketers, executives) tend to organize product information in ways that flow logically from their own in-depth understanding.
However, users are not privy to this insider knowledge and are likely to search for word associations that they can make sense of. Card sorting identifies what these associations are and reveals UX patterns that emerge from them.
Plan Before Embarking on Research Projects
Though we’ve primarily focused on the link between UX research methods and user empathy, we owe a word of acknowledgment to an overlooked aspect of the research process—planning.
In one respect, research is no different than any other design discipline: To do it well requires planning.
With planning, the goals and methodology of a UX research project are made crystal clear, and project stakeholders become much more likely to support any time and resources that are requested.
Without planning, UX research will lack focus and may intimidate or frustrate stakeholders, which can lead to unnecessary pushback and second-guessing.
Thankfully, research plans don’t need to be long. Aim for one page , and limit yourself to brief summaries of essential details like:
- Project Title
- Author Information
- Stakeholder Information
- Project Overview
- Research Objectives
- Research Methods
- Important Research Questions
- Target User Profile
- Relevant Supporting Data
If needed, you can expand this format, but a one-page plan is a useful tool that will help keep stakeholders on the same page as research progresses.

Commit to UX Research
UX design problems are complicated. Why? Because they involve the unpredictable phenomenon of human behavior. As designers, we’re always in search of order, always seeking simplicity. When it comes to digital products, order and simplicity are virtues, but they aren’t a starting point. If we think we can fully anticipate the needs of users based on past design solutions, we will miss opportunities to create products and experiences that truly delight.
The only way to avoid this is a commitment to research. Without research, or with a shallow commitment to research, designers are essentially saying to users, “We know what’s best for you. Keep quiet, and take what you’re given.”

While it seems obvious that no one wants to be treated this way, obstacles to UX research are abundant. Whether it be budgets, dubious stakeholders, or bull-headed designers, empathy-centric research often gets marginalized. The fallout almost always has a negative impact on users, and ultimately, a product’s profitability.
With this in mind, let us remain vigilant in our quest to see and synthesize problems through eyes that are not our own. We won’t create perfect products, but we will make progress and our designs will begin to improve the lives of the people we’re entrusted to help.
Further Reading on the Toptal Blog:
- Design Problem Statements: What They Are and How to Frame Them
- Know Your User: UX Statistics and Insights (With Infographic)
- Who, What, and Why: A Guide to User Testing Methods
- The Complete Guide to UX Research Methods
- Why Design Teams Need Psychological Safety
- The Value of User Research
Understanding the basics
What is ux research.
UX research is an investigation into the problems, needs, and experiences of users (people). A range of research types and methods exist, but the main goal is uncovering insights that can be passed along to UX designers and used to create more helpful/delightful user experiences.
What is user empathy?
User empathy is about seeing problems and experiences through the eyes of users. For UX researchers and designers, this means going beyond personal experiences. User empathy is important because UX designers must make decisions that are representative of and beneficial to the people they’re designing for.
What is key in user research?
The key to user research is an open, investigative mind that is free (as much as possible) of preconceived notions. If researchers and designers conduct (or interpret) research with the goal of supporting existing conclusions, they miss the opportunity to glean powerful empathetic insights.
What is empathy in design thinking?
Design thinking is a process of iteration and problem solving that helps designers better relate to users. The very first step in design thinking is to empathize. This means that researchers and designers must seek to study and understand user problems firsthand, in the environments in which they occur.
What is an empathy map?
An empathy map is a tool for visualizing and documenting what is known about a certain type of user. Empathy maps come in a variety of formats, but the standard format places the user information in the center of four quadrants: Says, Does, Thinks, Feels.
- UserResearch
- Product Design
Micah Bowers
Vancouver, WA, United States
Member since January 3, 2016
About the author
World-class articles, delivered weekly.
By entering your email, you are agreeing to our privacy policy .
Toptal Designers
- Adobe Creative Suite Experts
- Agile Designers
- AI Designers
- Art Direction Experts
- Augmented Reality Designers
- Axure Experts
- Brand Designers
- Creative Directors
- Dashboard Designers
- Digital Product Designers
- E-commerce Website Designers
- Full-Stack Designers
- Information Architecture Experts
- Interactive Designers
- Mobile App Designers
- Mockup Designers
- Presentation Designers
- Prototype Designers
- SaaS Designers
- Sketch Experts
- Squarespace Designers
- User Flow Designers
- User Research Designers
- Virtual Reality Designers
- Visual Designers
- Wireframing Experts
- View More Freelance Designers
Join the Toptal ® community.
Complete Beginner’s Guide to UX Research
In an industry devoted to the people who use our products, services, and applications, research is paramount. We ask questions. We take notes. We learn everything we can about the target audience, and then iteratively test our work throughout the design process.
UX research—or as it’s sometimes called, design research—serves many purposes throughout the design process. It helps us identify and prove or disprove our assumptions, find commonalities across our target audience members, and recognize their needs, goals, and mental models. Overall, research informs our work, improves our understanding, and make our work better.
In this Complete Beginner’s Guide, we’ll look at the many elements of design research, from interviews and observations, to usability testing and A/B testing. Readers will get a head start on how to use these design research techniques in their work, and improve experiences for all users.
Table of Contents
What is ux research, common methodologies, daily tasks and deliverables, people to follow.
- Tools of the Trade
Associations and Conferences
- UX Research Books
UX research encompasses a variety of investigative methods used to add context and insight to the design process. Unlike other sub-fields of UX, research did not develop out of some other field or fields. It merely translated from other forms of research. In other words, UX practitioners have borrowed many techniques from academics, scientists, market researchers, and others. However, there are still types of research that are fairly unique to the UX world.
The main goal of design research is to inform the design process from the perspective of the end user. It is research that prevents us from designing for one user: ourselves. It’s fairly well accepted that the purposes of UX and user-centered design are to design with the end-user in mind; and it’s research that tells us who that person is, in what context they’ll use this product or service, and what they need from us.
UX research has two parts: gathering data, and synthesizing that data in order to improve usability. At the start of the project, design research is focused on learning about project requirements from stakeholders, and learning about the needs and goals of the end users. Researchers will conduct interviews, collect surveys, observe prospects or current users, and review existing literature, data, or analytics. Then, iteratively throughout the design process, the research focus shifts to usability and sentiment. Researchers may conduct usability tests or A/B tests, interview users about the process, and generally test assumptions that will improve the designs.
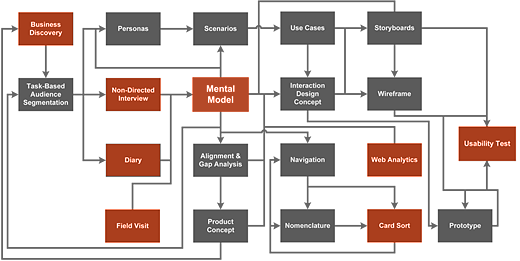
One example of a user research process, diagrammed. Young, Indi. 2008. Mental Models: Aligning Design Strategy with Human Behavior. New York: Rosenfeld Media.
We can also divide UX research methods into two camps: quantitative and qualitative.
- Quantitative research is any research that can be measured numerically. It answers questions such as “ how many people clicked here” or “ what percentage of users are able to find the call to action?” It’s valuable in understanding statistical likelihoods and what is happening on a site or in an app.
- Qualitative research is sometimes called “soft” research. It answers questions like “why didn’t people see the call to action” and “what else did people notice on the page?” and often takes the form of interviews or conversations. Qualitative research helps us understand why people do the things they do
Though researchers may specialize in specific types of interviews or tests, most are capable of conducting a wide variety of techniques. All user researchers collect valuable information that helps us design in an informed, contextual, user-centered manner.
The various types of UX research range from in-person interviews to unmoderated A/B tests (and everything in between), though they are consistent in that they all stem from the same key methodologies: observation, understanding, and analysis.
Observation
The first step to conducting research is learning to observe the world around us. Much like beginning photographers, beginning researchers need to learn how to see. They need to notice nervous tics that may signal that their interviewees are stressed or uncertain, and pick up on seemingly minor references that may reflect long-held beliefs or thoughts that should be further probed.
Observation may seem like a simple skill, but it can be clouded by unconscious biases—which everyone has. Design researchers train themselves to observe and take notes so that they can later find patterns across seemingly diverse groups of people.
Understanding
Much like observation, understanding is something we do all the time in our daily lives. We strive to understand our coworkers, our families, and our friends, often trying to grasp a point of contention or an unfamiliar concept. But for UX researchers, understanding has less to do with disagreements and more to do with mental models .
A mental model is the image that someone has in their mind when they think of a particular phrase or situation. For example, if someone owns an SUV, their mental model of “car” will likely differ from the mental model a smart car owner. The mental model informs the decisions we make; in the case of the car owners, when asked “how long does it take to drive to Winnipeg,” their answers will vary based on the gas mileage their vehicles get, among other things.
Design researchers need to understand the mental models of the people they interview or test, for two reasons. First, we all speak in shorthand at times. Researchers must recognize that shorthand based on the mental model of the speaker. Second, if the researcher can accurately identify the user’s mental model, he or she can share this information with the design team, and design to accommodate the model.
Research on its own can be valuable, but in order to use the insights to inform design, it needs to be analyzed and ultimately presented to a larger team. Analysis is the process by which the researcher identifies patterns in the research, proposes possible rationale or solutions, and makes recommendations.
Some analysis techniques include creating personas or scenarios, describing mental models, or providing charts and graphs that represent statistics and user behaviors. Although the techniques described here are focused predominantly on conducting research, it’s important to remember that research is only valuable if it is shared . It does no one any good when it’s locked away in a cabinet, or forgotten in the excitement of design.
Every UX project is different, and the tasks that one researcher takes on will differ from those appropriate in another setting. Some of the most popular forms of research are interviews, surveys and questionnaires, card sorts, usability tests, tree tests, and A/B tests .
One-on-one interviews are a tried and true method of communication between a researcher and a user or stakeholder. There are three main types of interviews, each of which is used in a different context and with different goals.
Directed interviews are the most common sort. These are typical question-and-answer interviews, where a researcher asks specific questions. This can be useful when conducting interviews with a large number of users, or when looking to compare and contrast answers from various users.
Non-directed interviews are the best way to learn about touchier subjects, where users or stakeholders may be put off by direct questions. With a non-directed interview, the interviewer sets up some rough guidelines and opens a conversation with the interviewee. The interviewer will mostly listen during this “conversation,” speaking only to prompt the user or stakeholder to provide additional detail or explain concepts.
Ethnographic interviews involve observing what people do as they go about their days in their “natural habitats.” In this sort of interview, the user shows the interviewee how they accomplish certain tasks, essentially immersing the interviewer in their work or home culture. This can help researchers understand the gaps between what people actually do, and what they say they do. It can also shed light on things that users do when they are feeling most comfortable.
Surveys and Questionnaires
Questionnaires and surveys are an easy way to gather a large amount of information about a group, while spending minimal time. These are a great research choice for projects that have a large and diverse group of users, or a group that is concerned with anonymity. A researcher can create a survey using tools like Wufoo or Google Docs , email it out, and receive hundreds of responses in just minutes.
There are downsides to surveys and questionnaires though. The researcher can’t interact directly with the respondents, and therefore can’t help with interpreting questions or framing them if the wording isn’t quite perfect; and researchers typically have a limited ability for follow up. Surveys see a far higher response rate when they do not require a login or contact information, and this anonymity makes it impossible to ask for clarification or further details.
Card sorts are sometimes done as part of either an interview or a usability test. In a card sort, a user is provided with a set of terms, and asked to categorize them. In a closed card sort, the user is also given the category names; in an open card sort the user creates whatever categories he or she feels are most appropriate.
The goal of a card sort is to explore relationships between content, and better understand the hierarchies that a user perceives. Many content strategists and information architects rely on card sorts to test out hierarchy theories, or kickstart work on a site map.
Usability Tests
Usability testing involves asking potential or current users of a product or service to complete a set of tasks and then observing their behavior to determine the usability of the product or service. This can be done using a live version of a site or app, a prototype or work-in-progress, or even using clickable wireframes or paper and pencil.
While there are many variations and styles of usability tests , there are three that are commonly used: moderated, unmoderated, and guerrilla.
Moderated usability tests are the most traditional type of test. They can happen in person, or via screenshare and video. Whole usability labs are set up, complete with one-way mirrors for stakeholders to observe, for the purpose of conducting moderated usability tests. In a moderated test an unbiased facilitator talks with the user, reading aloud the tasks and prompting the user to think aloud as he or she accomplishes the tasks. The facilitator’s role is to act as a conduit between stakeholders and the user, phrasing questions to evaluate the effectiveness of a design and testing assumptions while helping the user feel comfortable with the process.
Unmoderated usability tests , sometimes also known as asynchronous research, is conducted online, at the user’s convenience. The tasks and instructions are delivered via video or recorded audio, and the user clicks a button to begin the test and record his or her screen and audio. Just like in the moderated test, users are encouraged to speak their thoughts aloud, though there is no facilitator to ask follow up questions. Unmoderated tests are available through numerous online sites and can be significantly cheaper than moderated tests.
Guerrilla testing is a modern, lightweight take on traditional tests. Instead of renting a lab, guerrilla research is typically done out in the community; users are found at coffee shops or subway stations and asked to complete basic tasks with a website or service, in exchange for a few dollars, a coffee, or just out of the goodness of their hearts. While guerrilla testing is a great option , particularly on a budget, it is best used only for products or services with a large user base. More niche products will struggle to find reliable information from the random selection acquired in guerrilla testing.
Just as card sorts are a great way to gather information before a website’s architecture has been created, tree tests are helpful in validating that architecture. In a tree test, users are given a task and shown the top level of a site map. Then, much like in a usability test, they are asked to talk through where they would go to accomplish the task. However, unlike in a usability test, the user doesn’t see a screen when they choose a site section. Instead, they will see the next level of the architecture. The goal is to identify whether information is categorized correctly and how appropriately the nomenclature reflects the sections of the site.
A/B testing is another way of learning what actions users take. An A/B test is typically chosen as the appropriate research form when designers are struggling to choose between two competing elements. Whether the options are two styles of content, a button vs. a link, or two approaches to a home page design, an A/B test requires randomly showing each version to an equal number of users, and then reviewing analytics on which version better accomplished a specific goal. A/B testing is particularly valuable when comparing a revised screen to an older version, or when collecting data to prove an assumption.
Many people have contributed greatly to the field of experience design research. Here are just a few that readers may choose to follow, to learn more. If you are just starting your journey into user experience / UX Design you may be a bit confused by all the terms and methodologies that our out there. https://www.ukmeds.co.uk/ is here to help with their beginner’s guide to UX!
Tools of the trade
User Research has the potential to be a sizable undertaking, sometimes to the point that budgetary and scheduling concerns scare people away. Fortunately, today we often see a more casual, habitual approach. The tools we have available are responsible for much of that shift.
Ethnio was the first moderated remote research software when it launched, and it’s still going strong. Ethnio finds users who are currently using a site or app, and (with their permission) allows interviewers to ask them questions about their experience as they go. It automates many elements of the typical in-person test, including real-time notifications, and paying participants with Amazon gift cards. Ethnio has a fourteen day free trial, and four pricing options, to accommodate businesses of every size.
Learn more about Ethnio
Optimal Workshop
Optimal Workshop has everything! The full Workshop is a bundle of four research tools, all of which are also available sold separately (and very affordably). Treejack is great for remotely testing information architecture, either to test the nomenclature or the hierarchies themselves. Optimal Sort provides online card sorting, to see how users choose to organize content. Chalkmark offers heat maps of click patterns across a site, and Reframer is a tool for taking notes and identifying themes easily. All come highly recommended.
Learn more about Optimal Workshop
SurveyMonkey
Surveys and questionnaires are great ways to gather information, but they’re most useful when hundreds of responses can be seen at once. Enter SurveyMonkey, an online survey-creation and reporting tool, which allows people to customize and brand their own surveys and then send them out via social media, embed them into websites, or integrate with mass mailings. SurveyMonkey also allows for easy analysis and reporting when the results come in. It’s available as a free Basic version, or for a monthly fee with additional features.
Learn more about SurveyMonkey
UsabilityHub
For quick design iterations, gut checks, and clear user feedback, UsabilityHub is an incredible resource for low budget teams. With a super-simple interface (yay!) and fast turn-around times, iterative testing and research is a few clicks away through UsabilityHub.
Learn more about UsabilityHub
UserTesting.com
When it’s not possible to schedule a real-time test with users, UserTesting.com is a great way to see how people use a site. Researchers can create a series of tasks, and then receive videos from participants—either pre-chosen, or randomly selected. Researchers are able to see a video of the participant using the site, and speaking aloud to explain what they’re doing. UserTesting.com offers Basic and Pro options, and prices accordingly.
Learn more about UserTesting.com
The good news is, whatever you need, UserZoom has it. Usability testing, both moderated and unmoderated, remote testing for mobile and desktop, benchmarking, card sorting, tree testing, surveys, and rankings: they’ve got it! The bad news, as can be expected with any product this robust, is that it can be overwhelming to learn, and it is expensive. Still, for organizations with the budget to handle it, UserZoom is a solid, effective choice.
Learn more about UserZoom
In a way, all usability conferences are design research conferences. While the other areas of UX tend to have conferences that cater to their factions, trends, or best practices, researchers are by nature generalists, who seek out ways to learn more about humans and usability. To that end, we recommend a little bit of everything, to keep researchers up to speed.
UI Conference
UIE (User Interface Engineering) puts on an annual conference, bringing together thought leaders and tried-and-true concepts for UX practitioners to learn as much as they can from one another. One great thing about this conference is UIE’s commitment to helping people attend, whether in person or virtually. More information available at: ui.uie.com/
World Usability Conference
At World Usability Conference, the talks cover all areas of usability, user experience, and customer experience management. People come from around the world, across all industries, to find where we have more similarities than differences. More information available at: www.worldusabilitycongress.com
Design + Research + Society
Held in Brighton, England, the DRS Conference responds to the questions, “How can design research help frame and address the societal problems that face us?”; “How can design research be a creative and active force for rethinking ideas about Design?”; and “How can design research shape our lives in more responsible, meaningful, and open ways?” By focusing on how design research impacts people in today’s society, they turn a light on the human side of our designs. More information available at: www.designresearchsociety.org/cpages/conferences
The User Experience Professionals Association is open to everyone working in UX. They provide networking and professional development opportunities for UX practitioners around the world, by way of local chapters. If you live in a city, there’s a good chance there’s a UXPA chapter to join! Local chapters often host conferences, sponsor events, and create a network for local UX professionals. More information available at: uxpa.org
UX Research books
There are many books that focus on interviews, usability testing, A/B testing, and other specific areas of design research. These are just a smattering of books that cover the big picture.

- Make Design Decisions with a Purpose
- Creating Personas
- The Ethics of UX Research
- Five Tips for Conducting Scientific Research in the UX World
- Running a Successful User Workshop
UX Booth is trusted by over 100,000 user experience professionals. Start your subscription today for free.

We stand with Ukraine and our team members from Ukraine. Here are ways you can help

A Community Of Over 800,000
The Parallel Journey of Physical Product Design and UX/UI Design
My story of how I dived deep into UX when creating soft toys from scratch without even realising that…

Hiring Conversational Designers with Aaron Cooper, Banner Health’s Sr. Dir. of Digital Experience
- April 18, 2024
Share this link
From design thinking to ai thinking.
- Artificial Intelligence , Design , Design Theory , Things UX People Like
- The article outlines a paradigm shift from Design Thinking to AI Thinking, emphasizing the integration of LLMs into various sectors to enhance problem-solving through conversational interfaces.
Neurodesign: 7 Tips for Deeper Emotional Engagement
- April 16, 2024
- The article delves into seven neurodesign strategies aimed at enhancing emotional engagement with digital products, backed by examples and key benefits associated with their implementation.
Conversational ai is changing the nature of every job at every company starting yesterday.

The Disruption of Customer Experience: How Conversational AI is upping UX and CX standards
4.29 average rating.
- By transforming the way humans interact with technologies and making them more accessible to the public, conversational AI is raising the bar for customer experience.
- One of the most tangible impacts of conversational AI has been on customer support and sales conversion. Thanks to the automation of conversations, the load on human staff is reduced, which leads to greater customer and employee experience.
- As technological development advances, more opportunities to make good use of conversational AI will emerge. Nevertheless, it’s also necessary to not underestimate potential challenges related to legacy systems, data availability, shortage of conversational AI specialists.
A Six-Minute Breakdown of Gartner’s Top Conversational AI Platforms
There’s a ton of noise, promises and exaggerations flying around. Here’s a breakdown of the sixteen conversational AI platforms in Gartner’s 2019 Market Guide.

Lean Knowledge Management with Roger Forsgren, former Chief Knowledge Officer at NASA
- April 11, 2024

How to Think About UX Research Failures
- Research Methods and Techniques , The Evolution of Research , Things UX People Like , UX Education
A framework for diagnosing a study with conflicting or misleading results, and what to do about it.
- The article examines how UX research studies can fail due to issues in design, analysis, and generalization, using case studies to highlight each category’s importance in maintaining research integrity and relevance.
- April 9, 2024

Knowledge Management Challenges and Building Advanced Digital Assistants at Morgan Stanley
- April 4, 2024

60-second science
Eye Treatment Stretches Mouse Sight Beyond Visible Spectrum
Did you know UX Magazine hosts the most popular podcast about conversational AI?
Join 740,000 designers, thinkers, and doers.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. check our privacy policy and.
Integrations
What's new?
Prototype Testing
Live Website Testing
Feedback Surveys
Interview Studies
Card Sorting
Tree Testing
In-Product Prompts
Participant Management
Automated Reports
Templates Gallery
Choose from our library of pre-built mazes to copy, customize, and share with your own users
Browse all templates
Financial Services
Tech & Software
Product Designers
Product Managers
User Researchers
By use case
Concept & Idea Validation
Wireframe & Usability Test
Content & Copy Testing
Feedback & Satisfaction
Content Hub
Educational resources for product, research and design teams
Explore all resources
Question Bank
Research Maturity Model
Guides & Reports
Help Center
Future of User Research Report
The Optimal Path Podcast
User Research
Jan 10, 2023
The UX research trends shaping the industry in 2023 (+ expert insights)
Take a look at the top seven UX research trends that will shape the industry and how we build products in 2023 and beyond.

Giada Gastaldello
Content Marketing Manager at Maze
There's no doubt that 2023 will be a year of challenges and opportunities for the research industry.
UX research is no longer a nice to have and many organizations see the value of research in informing product and business decisions. But in the context of all the economic uncertainty and budget cuts facing the tech industry, now is the time for UX leaders to think more strategically about how to maximize the impact of research across the organization.
As the research field continues to evolve, UX professionals that keep up with the latest industry trends will be better equipped to empower the entire organization to leverage customer insights and build products that meet customers' shifting needs over time.
In this article, we'll look at some of the most influential user research trends shaping 2023. To identify these trends, we interviewed industry experts and surveyed over 600 product professionals as part of our Continuous Research Report 2023 to learn how product teams conduct research to inform their decision-making. Here’s the trends we identified:
- Continuous research is becoming a well-established practice
- Companies are scaling research through democratization
- The UX researcher role is shifting from technical executor to educator
- Organizations are using customer insights to make informed decisions and drive business growth
- Product professionals are thinking more deeply about how to build inclusive products
- Product teams are using qualitative and quantitative research to inform decisions
- UX tools are making user research more efficient and effective
Let's unpack each one of these UX research trends one by one.
🎧 Prefer video?
If you'd like a TL;DR version of the key research trends for 2023, check out our YouTube video below for a quick runthrough of the need-to-know facts.
1. Continuous research is becoming a well-established practice
With the rise of product-led growth (PLG), more and more organizations understand the value of UX research and the importance of creating products for and with their customers. As our Continuous Research Report shows, 82% of product organizations have at least one dedicated UX researcher and are starting to involve customers continuously throughout the product development process.
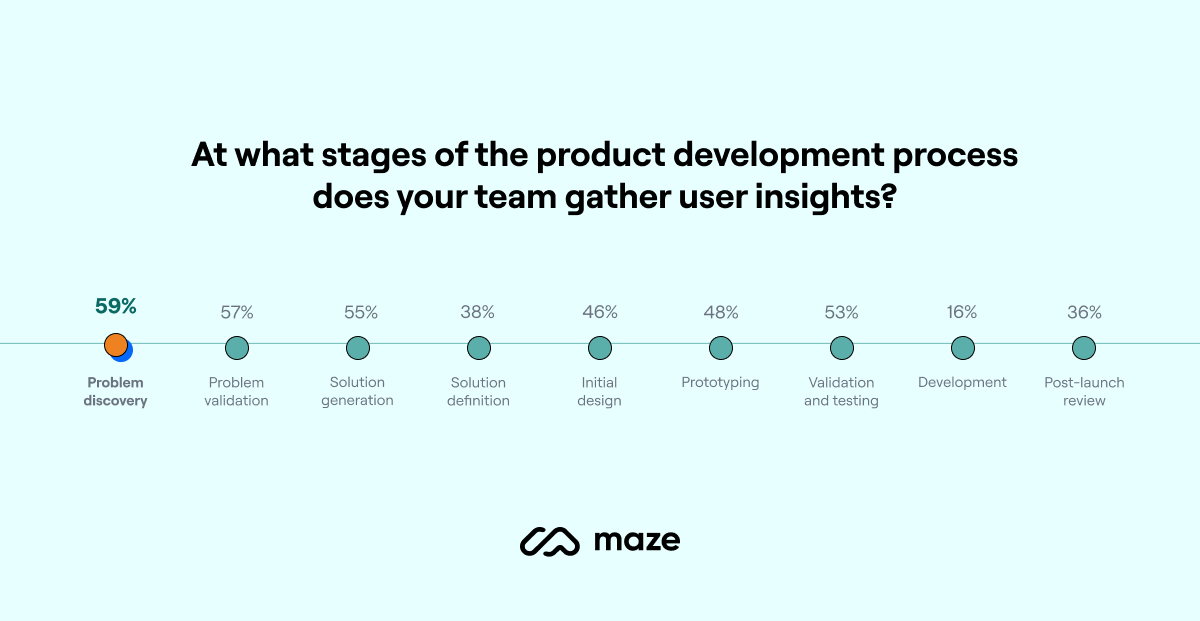
"A few years ago, there was a lot of discussion in the industry about getting buy-in for research and involving stakeholders in the research process," says Lucy Denton , Head of Design at Dovetail. "It's great to see how far the industry has come in terms of understanding the value of research. Companies are investing more in research which means they're investing more in customer-centricity and building for the customer."
Most product professionals (83%) agree that research should be conducted at each stage of the product life cycle. Yet 60% of product teams connect with customers once per month or less—despite product decisions being made almost daily.
In practice: To ensure your product thrives in 2023, adopt continuous product discovery practices to collect frequent feedback and build products that evolve as customers' needs evolve. Learn how to get started in our guide to continuous product discovery .
2. Companies are scaling research through democratization
The appetite for user insights is growing, and companies are faced with the challenge of scaling research. 78% of the audience we surveyed believe their company could do more research—yet time, budget limitations, and access to research participants are the main challenges hindering product teams from running more studies.
Researchers can't cover all the research questions the organization has, so more and more companies are scaling the impact of research by empowering different teams to engage in the research process and get access to the insights they need to make informed decisions.
With 64% of respondents saying their organization has a democratized culture—where researchers, designers, product managers, and marketers conduct research—we believe research democratization will be key to achieving continuous product discovery and building organizations that learn .
Research is all about learning. It doesn't matter who's learning in an organization—we want to enable teams to make better decisions. It's no longer about advocating for research to take place. It's really about, 'how do we educate people to do research or learn better?' That's what's driving the shift across the industry over time.

Roberta Dombrowski , VP of User Research at User Interviews
In practice: Scaling the impact of research by empowering everyone to play a more active role in research is an ongoing process. Check out our Scaling Research Playbook to learn how to successfully democratize research with insights from over 30 UX leaders.
3. The UX researcher role is shifting from technical executor to educator
As organizations scale their research practice, the role of the user researcher becomes not only a purely technical role but a facilitation role responsible for empowering the organization in its learning.
"One of the biggest hurdles we've seen as we've tried to upscale the number of people who can do their own research and answer their questions is, 'how do we instill confidence?'", explains Rachel Ny , Senior User Researcher at Atlassian. "The goal is to upskill people to a level where they feel confident that they're making the right decisions—whether in the middle of an interview or making their research plan .”
The role of the researcher has evolved to empower product teams and other stakeholders. This is a huge shift from the original definition of a UX researcher as a detective of problems to an ally of product teams capable of enabling more research and smooth decision-making for the product.

Shrut Kirti Saksena , Senior User Experience Researcher at Adobe
In practice: Whether you're looking to advance your career as a researcher or build a UX team , research is no longer just about technical skills. As customer needs become more critical to the business strategy, UX researchers will take on new responsibilities, including running strategic research , collaborating with different teams, and becoming mentors for their organizations.
🔭 Envisioning the future of the research industry
Learn more about the findings of our Continuous Research Report and the shift happening in research today in this episode of The Optimal Path, featuring our CEO & Co-founder, Jonathan Widawski. Tune in .
4. Organizations are using customer insights to make informed decisions and drive business growth
Another key trend highlighted in the report that we'll see continuing and expanding in the near future is that research helps organizations improve decision-making and positively impacts customer satisfaction, product adoption, user activation, and revenue.
74% of respondents reported that research is effective or partially effective in determining decision-making at their organizations, and 14% said it's highly effective. In particular, product teams who conduct research more often, weekly or daily, report more effective decision-making than teams who run research less often, quarterly or yearly.
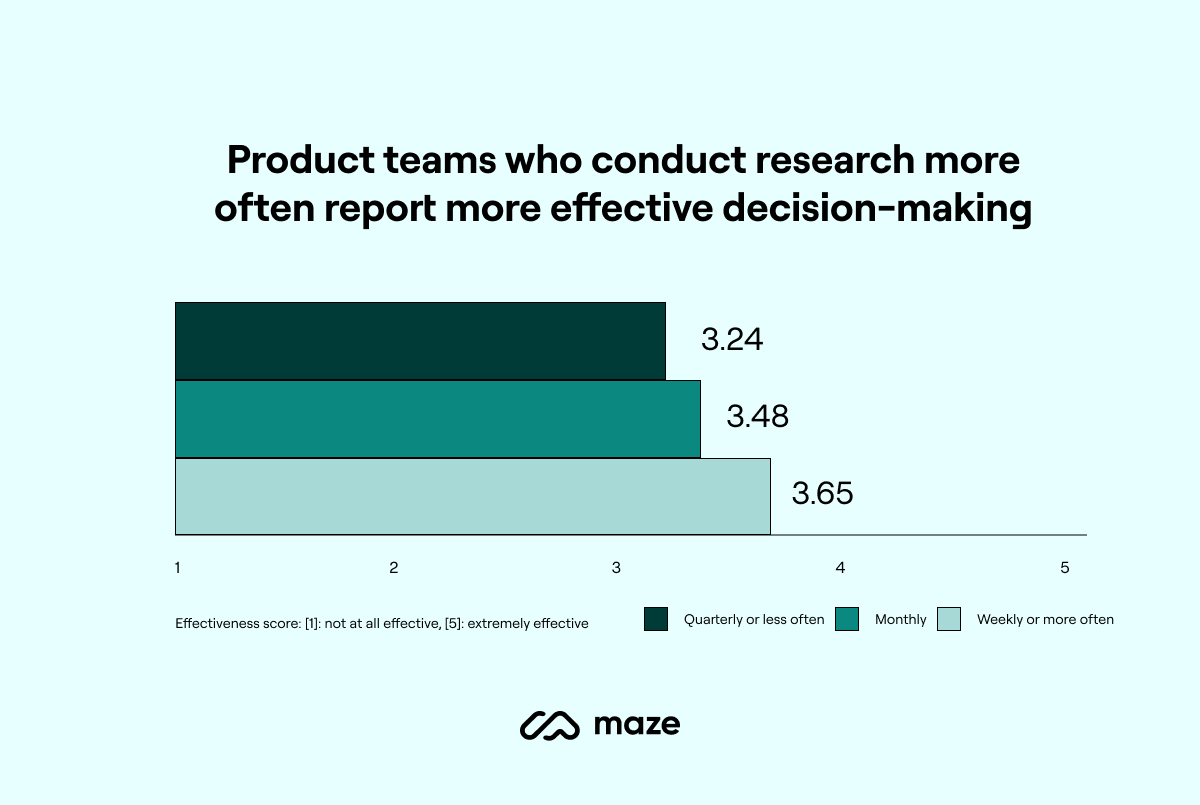
"Product and UX professionals are using research findings to inform their decisions. Once you have more information about the pros and cons of the options you're facing, there's a higher chance that the whole team has higher confidence in decision-making," says Xiangyi Tang , Head of User Research at Pitch. "Product organizations need to truly understand their customers to be competitive. With continuous research, they can constantly course-correct to work on the right problem and provide the right solution."
In practice: Continuous research will continue to be a powerful tool to inform decision-making, even more so in uncertain market conditions. Collect customer insights throughout the product development process to mitigate risk, react effectively to changes in the market, and leverage research to drive business growth .
Make feedback the foundation of your decision-making
With Maze, you can make the right product decisions faster and with confidence by infusing them with user insights generated across the entire product development cycle.
5. Product professionals are thinking more deeply about how to build inclusive products
A UX trend that will continue in 2023 is the focus on inclusivity and accessibility. Inclusive design is the process of creating solutions and experiences that are usable and open to all—regardless of age, language, ability, or culture.
"The reason why inclusive design is necessary is starting to resonate," says Melanie Buset , User Research Manager at Spotify. "If your product is designed inclusively, more people will feel comfortable, enabled, and excited to interact with it. And if more people are satisfied with your product, that leads to more usage and profits overall."
Major tech companies, including Apple , Microsoft , and Airbnb , are paving the way to inclusivity and have created their own "inclusive design manifestos" to design solutions that benefit everyone. Our industry report also shows that 29% of product teams conduct usability testing.
In practice: Create solutions that benefit more users by conducting research with a diverse user group early and often in the design process. Other inclusive design principles you can follow are hiring a diverse team and inviting experts to lead workshops and educate product teams on how to embed inclusivity in their work from day one.
If you'd like to learn more, read our guide Inclusive Design: Creating Better Experiences for All .
6. Product teams are using qualitative and quantitative research to inform decisions
So far, we’ve seen that more and more businesses see the value of engaging with their customers to understand their needs, pain points, and motivations and make the right product decisions.
To obtain customer insights throughout the product life cycle, product teams are turning to various research methods—the most frequently used being user interviews, surveys, product analytics, competitive analysis, and unmoderated usability tests.
Roberta Dombrowski , VP of User Research at User Interviews, explains, "many orgs lead with qualitative research first and 1-on-1 interviews when they're introducing research to their teams, and that's because it's easier to talk to a customer—it's something we naturally do. It's much harder to do a full product analysis with quantitative data and a card sort study."
Overall, our research shows that qualitative methods are more frequently used than quantitative methods (63% vs. 51%). Yet the best results come from a combination of these methods. While quantitative research helps you understand what your users are doing, qualitative research tells you why they’re doing it.
In practice: Incorporate mixed methods into the research process and combine qualitative and quantitative data to uncover deeper insights and ensure you're making the right product and business decisions.
7. UX tools are making research more efficient and effective
To stay ahead of the competition, product organizations need to gather high-quality insights at scale—this is where the right UX tools come in. According to our report, one main challenge for product teams conducting research is having access to the right tools.
With the global pandemic and the rise of remote research, the need for digital tools that support user research teams is higher than ever. If we look at the 2022 UX Research Tools Map or 2022 Design Tools Survey , the UX tools landscape has kept growing in the past few years, and platforms are now offering new features and functionalities to support researchers and People Who Do Research (PWDR).
At Maze , for example, we're focusing on creating an end-to-end solution for product research. Our tool offers new solutions for recruiting survey participants, product research and reporting to help teams build the habit of continuous product discovery and foster more efficient product collaboration.
In practice: The range of UX research tools is expanding, covering everything from recruiting participants to usability tests and generating reports. Check out our list of the best UX research tools for 2023 to choose the best ones for your needs.
Picturing the future of UX research
The future is customer-centric, and user research is evolving to empower anyone in the organization to connect to customers on an ongoing basis. Research is becoming a continuous function that isn't confined to one stage of the product development process but extends across it—from discovery research to post-launch reviews.
User research is a fascinating field because it constantly evolves to meet customer needs more effectively and create business value. While the last years were challenging due to the pandemic and uncertain economy, we also saw great opportunities for the UX industry. By adopting a continuous product discovery mindset, organizations can uncover customer needs and motivation and constantly improve their product as they build.
"There are lots of opportunities as we expand and grow the research craft to go beyond just the research team and implement it into every stage of the product life cycle," states Rachel Ny , Senior User Researcher at Atlassian.
I think growth will happen in terms of understanding the purpose of research, aligning around the need for it, and where we are in terms of our knowledge base. Ultimately research is a way to start building the knowledge base that allows you to make the right decisions in the product life cycle.

Rachel Ny , Senior User Researcher at Atlassian

Pulse UX Blog
Theory, Analysis and Reviews on UX User Experience Research and Design
Home Mission About Charles L. Mauro CHFP
« Updates From Mauro Usability Science - Critical Analysis of Maeda Design in Tech Report 2017 »
User Interface Design and UX Design: 80+ Important Research Papers Covering Peer-Reviewed and Informal Studies
Charles Mauro CHFP
Important peer-reviewed and informally published recent research on user interface design and user experience (UX) design.
For the benefit of clients and colleagues we have culled a list of approximately 70 curated recent research publications dealing with user interface design, UX design and e-commerce optimization.
In our opinion these publications represent some of the best formal research thinking on UI and UX design. These papers are also among the most widely downloaded and cited formal research on UI / UX design. We have referenced many of these studies in our work at MauroNewMedia.

Pay walls: As you will note in reviewing the following links and abstracts, most of the serious research on UI / UX design and optimization is located behind pay walls controlled by major publishers. However, in the end, good data is well worth the investment. Many links and other cited references are, of course, free.
Important disclaimer: We do not receive any form of compensation for citing any of the following content. Either Charles L Mauro CHFP or Paul Thurman MBA has personally reviewed all papers and links in this list. Some of these references were utilized in the recent NYTECH UX talk given by Paul Thurman MBA titled: Critical New UX Design Optimization Research
In addition to historical research papers, we frequently receive requests from colleagues, clients and journalists for recommended reading lists on topics covering our expertise in UX design, usability research and human factors engineering. These requests prompted us to pull from our research library (yes, we still have real books) 30+ books which our professional staff felt should be considered primary conceptual literature for anyone well-read in the theory and practice of UX design and research. Please follow the for PulseUX’s compilation of the 30+ Best UX Design and Research Books of All Time
Title: The influence of hedonic and utilitarian motivations on user engagement: The case of online shopping experiences
Abstract User experience seeks to promote rich, engaging interactions between users and systems. In order for this experience to unfold, the user must be motivated to initiate an interaction with the technology. This study explored hedonic and utilitarian motivations in the context of user engagement with online shopping. Factor analysis was performed to identify a parsimonious set of factors from the Hedonic and Utilitarian Shopping Motivation Scale and the User Engagement Scale based on responses from 802 shoppers. Multiple linear regression was used to test hypotheses with hedonic and utilitarian motivations (Idea, Social, Adventure/Gratification, Value and Achievement Shopping) and attributes of user engagement (Aesthetics, Focused Attention, Perceived Usability, and Endurability). Results demonstrate the salience of Adventure/Gratification Shopping and Achievement Shopping Motivations to specific variables of user engagement in the e-commerce environment and provide considerations for the inclusion of different types of motivation into models of engaging user experiences. Abstract Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: New Support for Marketing Analytics
Abstract Consumer surveys and myriad other forms of research have long been the grist for marketing decisions at large companies. But many firms have been reluctant to embrace the high-tech approach to data gathering and number crunching that falls under the rubric of marketing analytics, which uses advanced techniques to transform the tracking of promotional efforts, customer preferences, and industry developments into sophisticated branding and advertising campaigns. Fueled in part by Tom Peters and Robert Waterman’s seminal 1982 book In Search of Excellence , which coined the phrase “paralysis through analysis,” skepticism about the approach remains widespread, even in the face of a number of positive research results over the years. This new study, involving Fortune 1000 companies, offers yet more ammunition for supporters of marketing analytics. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Booz & Company Inc. All rights reserved.
Title: Video game values: Human-computer interaction and games
Abstract Current human–computer interaction (HCI) research into video games rarely considers how they are different from other forms of software. This leads to research that, while useful concerning standard issues of interface design, does not address the nature of video games as games specifically. Unlike most software, video games are not made to support external, user-defined tasks, but instead define their own activities for players to engage in. We argue that video games contain systems of values which players perceive and adopt, and which shape the play of the game. A focus on video game values promotes a holistic view of video games as software, media, and as games specifically, which leads to a genuine video game HCI. Abstract Copyright © 2006 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: When fingers do the talking: a study of text messaging
Abstract SMS or text messaging is an area of growth in the communications field. The studies described below consisted of a questionnaire and a diary study. The questionnaire was designed to examine texting activities in 565 users of the mobile phone. The diary study was carried out by 24 subjects over a period of 2 weeks. The findings suggest that text messaging is being used by a wide range of people for all kinds of activities and that for some people it is the preferred means of communication. These studies should prove interesting for those examining the use and impact of SMS. Abstract Copyright © 2004 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Understanding factors affecting trust in and satisfaction with mobile banking in Korea: A modified DeLone and McLean’s model perspective
Abstract As mobile technology has developed, mobile banking has become accepted as part of daily life. Although many studies have been conducted to assess users’ satisfaction with mobile applications, none has focused on the ways in which the three quality factors associated with mobile banking – system quality, information quality and interface design quality – affect consumers’ trust and satisfaction. Our proposed research model, based on DeLone and McLean’s model, assesses how these three external quality factors can impact satisfaction and trust. We collected 276 valid questionnaires from mobile banking customers, then analyzed them using structural equation modeling. Our results show that system quality and information quality significantly influence customers’ trust and satisfaction, and that interface design quality does not. We present herein implications and suggestions for further research. Abstract Copyright © 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.

Title: What is beautiful is usable
Abstract An experiment was conducted to test the relationships between users’ perceptions of a computerized system’s beauty and usability. The experiment used a computerized application as a surrogate for an Automated Teller Machine (ATM). Perceptions were elicited before and after the participants used the system. Pre-experimental measures indicate strong correlations between system’s perceived aesthetics and perceived usability. Post-experimental measures indicated that the strong correlation remained intact. A multivariate analysis of covariance revealed that the degree of system’s aesthetics affected the post-use perceptions of both aesthetics and usability, whereas the degree of actual usability had no such effect. The results resemble those found by social psychologists regarding the effect of physical attractiveness on the valuation of other personality attributes. The findings stress the importance of studying the aesthetic aspect of human–computer interaction (HCI) design and its relationships to other design dimensions. Abstract Copyright © 2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: UX Curve: A method for evaluating long-term user experience
Abstract The goal of user experience design in industry is to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty through the utility, ease of use, and pleasure provided in the interaction with a product. So far, user experience studies have mostly focused on short-term evaluations and consequently on aspects relating to the initial adoption of new product designs. Nevertheless, the relationship between the user and the product evolves over long periods of time and the relevance of prolonged use for market success has been recently highlighted. In this paper, we argue for the cost-effective elicitation of longitudinal user experience data. We propose a method called the “UX Curve” which aims at assisting users in retrospectively reporting how and why their experience with a product has changed over time. The usefulness of the UX Curve method was assessed in a qualitative study with 20 mobile phone users. In particular, we investigated how users’ specific memories of their experiences with their mobile phones guide their behavior and their willingness to recommend the product to others. The results suggest that the UX Curve method enables users and researchers to determine the quality of long-term user experience and the influences that improve user experience over time or cause it to deteriorate. The method provided rich qualitative data and we found that an improving trend of perceived attractiveness of mobile phones was related to user satisfaction and willingness to recommend their phone to friends. This highlights that sustaining perceived attractiveness can be a differentiating factor in the user acceptance of personal interactive products such as mobile phones. The study suggests that the proposed method can be used as a straightforward tool for understanding the reasons why user experience improves or worsens in long-term product use and how these reasons relate to customer loyalty. Abstract Copyright 2011 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Heuristic evaluation: Comparing ways of finding and reporting usability problems
Abstract Research on heuristic evaluation in recent years has focused on improving its effectiveness and efficiency with respect to user testing. The aim of this paper is to refine a research agenda for comparing and contrasting evaluation methods. To reach this goal, a framework is presented to evaluate the effectiveness of different types of support for structured usability problem reporting. This paper reports on an empirical study of this framework that compares two sets of heuristics, Nielsen’s heuristics and the cognitive principles of Gerhardt-Powals, and two media of reporting a usability problem, i.e. either using a web tool or paper. The study found that there were no significant differences between any of the four groups in effectiveness, efficiency and inter-evaluator reliability. A more significant contribution of this research is that the framework used for the experiments proved successful and should be reusable by other researchers because of its thorough structure. Abstract Copyright © 2006 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Socio-technical systems: From design methods to systems engineering
Abstract It is widely acknowledged that adopting a socio-technical approach to system development leads to systems that are more acceptable to end users and deliver better value to stakeholders. Despite this, such approaches are not widely practised. We analyse the reasons for this, highlighting some of the problems with the better known socio-technical design methods. Based on this analysis we propose a new pragmatic framework for socio-technical systems engineering (STSE) which builds on the (largely independent) research of groups investigating work design, information systems, computer-supported cooperative work, and cognitive systems engineering. STSE bridges the traditional gap between organisational change and system development using two main types of activity: sensitisation and awareness; and constructive engagement. From the framework, we identify an initial set of interdisciplinary research problems that address how to apply socio-technical approaches in a cost-effective way, and how to facilitate the integration of STSE with existing systems and software engineering approaches. Abstract Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Five reasons for scenario-based design
Abstract Scenarios of human–computer interaction help us to understand and to create computer systems and applications as artifacts of human activity—as things to learn from, as tools to use in one’s work, as media for interacting with other people. Scenario-based design of information technology addresses five technical challenges: scenarios evoke reflection in the content of design work, helping developers coordinate design action and reflection. Scenarios are at once concrete and flexible, helping developers manage the fluidity of design situations. Scenarios afford multiple views of an interaction, diverse kinds and amounts of detailing, helping developers manage the many consequences entailed by any given design move. Scenarios can also be abstracted and categorized, helping designers to recognize, capture and reuse generalizations and to address the challenge that technical knowledge often lags the needs of technical design. Finally, scenarios promote work-oriented communication among stakeholders, helping to make design activities more accessible to the great variety of expertise that can contribute to design, and addressing the challenge that external constraints designers and clients face often distract attention from the needs and concerns of the people who will use the technology. Abstract Copyright © 2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Needs, affect, and interactive products – Facets of user experience
Abstract Subsumed under the umbrella of User Experience (UX), practitioners and academics of Human–Computer Interaction look for ways to broaden their understanding of what constitutes “pleasurable experiences” with technology. The present study considered the fulfilment of universal psychological needs, such as competence, relatedness, popularity, stimulation, meaning, security, or autonomy, to be the major source of positive experience with interactive technologies. To explore this, we collected over 500 positive experiences with interactive products (e.g., mobile phones, computers). As expected, we found a clear relationship between need fulfilment and positive affect, with stimulation, relatedness, competence and popularity being especially salient needs. Experiences could be further categorized by the primary need they fulfil, with apparent qualitative differences among some of the categories in terms of the emotions involved. Need fulfilment was clearly linked to hedonic quality perceptions, but not as strongly to pragmatic quality (i.e., perceived usability), which supports the notion of hedonic quality as “motivator” and pragmatic quality as “hygiene factor.” Whether hedonic quality ratings reflected need fulfilment depended on the belief that the product was responsible for the experience (i.e., attribution). Abstract Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: The role of social presence in establishing loyalty in e-Service environments
Abstract Compared to offline shopping, the online shopping experience may be viewed as lacking human warmth and sociability as it is more impersonal, anonymous, automated and generally devoid of face-to-face interactions. Thus, understanding how to create customer loyalty in online environments (e-Loyalty) is a complex process. In this paper a model for e-Loyalty is proposed and used to examine how varied conditions of social presence in a B2C e-Services context influence e-Loyalty and its antecedents of perceived usefulness, trust and enjoyment. This model is examined through an empirical study involving 185 subjects using structural equation modeling techniques. Further analysis is conducted to reveal gender differences concerning hedonic elements in the model on e-Loyalty. Abstract Copyright © 2006 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: A framework for evaluating the usability of mobile phones based on multi-level, hierarchical model of usability factors
Abstract As a mobile phone has various advanced functionalities or features, usability issues are increasingly challenging. Due to the particular characteristics of a mobile phone, typical usability evaluation methods and heuristics, most of which are relevant to a software system, might not effectively be applied to a mobile phone. Another point to consider is that usability evaluation activities should help designers find usability problems easily and produce better design solutions. To support usability practitioners of the mobile phone industry, we propose a framework for evaluating the usability of a mobile phone, based on a multi-level, hierarchical model of usability factors, in an analytic way. The model was developed on the basis of a set of collected usability problems and our previous study on a conceptual framework for identifying usability impact factors. It has multi-abstraction levels, each of which considers the usability of a mobile phone from a particular perspective. As there are goal-means relationships between adjacent levels, a range of usability issues can be interpreted in a holistic as well as diagnostic way. Another advantage is that it supports two different types of evaluation approaches: task-based and interface-based. To support both evaluation approaches, we developed four sets of checklists, each of which is concerned, respectively, with task-based evaluation and three different interface types: Logical User Interface (LUI), Physical User Interface (PUI) and Graphical User Interface (GUI). The proposed framework specifies an approach to quantifying usability so that several usability aspects are collectively measured to give a single score with the use of the checklists. A small case study was conducted in order to examine the applicability of the framework and to identify the aspects of the framework to be improved. It showed that it could be a useful tool for evaluating the usability of a mobile phone. Based on the case study, we improved the framework in order that usability practitioners can use it more easily and consistently. Abstract Copyright © 2011 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Understanding the most satisfying and unsatisfying user experiences: Emotions, psychological needs, and context
Abstract The aim of this research was to study the structure of the most satisfying and unsatisfying user experiences in terms of experienced emotions, psychological needs, and contextual factors. 45 university students wrote descriptions of their most satisfying and unsatisfying recent user experiences and analyzed those experiences using the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS) method for experienced emotions, a questionnaire probing the salience of 10 psychological needs, and a self-made set of rating scales for analyzing context. The results suggested that it was possible to capture variations in user experiences in terms of experienced emotions, fulfillment of psychological needs, and context effectively by using psychometric rating scales. The results for emotional experiences showed significant differences in 16 out of 20 PANAS emotions between the most satisfying and unsatisfying experiences. The results for psychological needs indicated that feelings of autonomy and competence emerged as highly salient in the most satisfying experiences and missing in the unsatisfying experiences. High self-esteem was also notably salient in the most satisfying experiences. The qualitative results indicated that most of the participants’ free-form qualitative descriptions, especially for the most unsatisfying user experiences, gave important information about the pragmatic aspects of the interaction, but often omitted information about hedonic and social aspects of user experience. Abstract Copyright © 2011 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: The Usability Metric for User Experience
Abstract The Usability Metric for User Experience (UMUX) is a four-item Likert scale used for the subjective assessment of an application’s perceived usability. It is designed to provide results similar to those obtained with the 10-item System Usability Scale, and is organized around the ISO 9241-11 definition of usability. A pilot version was assembled from candidate items, which was then tested alongside the System Usability Scale during usability testing. It was shown that the two scales correlate well, are reliable, and both align on one underlying usability factor. In addition, the Usability Metric for User Experience is compact enough to serve as a usability module in a broader user experience metric. Abstract Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.

Title: User acceptance of mobile Internet: Implication for convergence technologies
Abstract Using the Technology Acceptance Model as a conceptual framework and a method of structural equation modeling, this study analyzes the consumer attitude toward Wi-Bro drawing data from 515 consumers. Individuals’ responses to questions about whether they use/accept Wi-Bro were collected and combined with various factors modified from the Technology Acceptance Model.
The result of this study show that users’ perceptions are significantly associated with their motivation to use Wi-Bro. Specifically, perceived quality and perceived availability are found to have significant effect on users’ extrinsic and intrinsic motivation. These new factors are found to be Wi-Bro-specific factors, playing as enhancing factors to attitudes and intention. Abstract Copyright © 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Understanding purchasing behaviors in a virtual economy: Consumer behavior involving virtual currency in Web 2.0 communities
Abstract This study analyzes consumer purchasing behavior in Web 2.0, expanding the technology acceptance model (TAM), focusing on which variables influence the intention to transact with virtual currency. Individuals’ responses to questions about attitude and intention to transact in Web 2.0 were collected and analyzed with various factors modified from the TAM. The results of the proposed model show that subjective norm is a key behavioral antecedent to using virtual currency. In the extended model, the moderating effects of subjective norm on the relations among the variables were found to be significant. The new set of variables is virtual environment-specific, acting as factors enhancing attitudes and behavioral intentions in Web 2.0 transactions. Abstract Copyright © 2008 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Fundamentals of physiological computing
Abstract This review paper is concerned with the development of physiological computing systems that employ real-time measures of psychophysiology to communicate the psychological state of the user to an adaptive system. It is argued that physiological computing has enormous potential to innovate human–computer interaction by extending the communication bandwidth to enable the development of ‘smart’ technology. This paper focuses on six fundamental issues for physiological computing systems through a review and synthesis of existing literature, these are (1) the complexity of the psychophysiological inference, (2) validating the psychophysiological inference, (3) representing the psychological state of the user, (4) designing explicit and implicit system interventions, (5) defining the biocybernetic loop that controls system adaptation, and (6) ethical implications. The paper concludes that physiological computing provides opportunities to innovate HCI but complex methodological/conceptual issues must be fully tackled during the research and development phase if this nascent technology is to achieve its potential. Abstract Copyright © 2008 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Modelling user experience with web sites: Usability, hedonic value, beauty and goodness
Abstract Recent research into user experience has identified the need for a theoretical model to build cumulative knowledge in research addressing how the overall quality or ‘goodness’ of an interactive product is formed. An experiment tested and extended Hassenzahl’s model of aesthetic experience. The study used a 2 × 2 × (2) experimental design with three factors: principles of screen design, principles for organizing information on a web page and experience of using a web site. Dependent variables included hedonic perceptions and evaluations of a web site as well as measures of task performance, navigation behaviour and mental effort. Measures, except Beauty, were sensitive to manipulation of web design. Beauty was influenced by hedonic attributes (identification and stimulation), but Goodness by both hedonic and pragmatic (user-perceived usability) attributes as well as task performance and mental effort. Hedonic quality was more stable with experience of web-site use than pragmatic quality and Beauty was more stable than Goodness. Abstract Copyright © 2008 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Sample Size In Usability Studies
Abstract Usability studies are a cornerstone activity for developing usable products. Their effectiveness depends on sample size, and determining sample sizehas been a research issue in usability engineering for the past 30 years. In 2010, Hwang and Salvendy reported a meta study on the effectiveness of usability evaluation, concluding that a sample size of 10±2 is sufficient for discovering 80% of usability problems (not five, as suggested earlier by Nielsen in 2000). Here, I show the Hwang and Salvendy study ignored fundamental mathematical properties of the problem, severely limiting the validity of the 10±2 rule, then look to reframe the issue of effectiveness and sample-size estimation to the practices and requirements commonly encountered in industrial-scale usability studies. Abstract Copyright © 2013 ACM, Inc. Title: An experimental study of learner perceptions of the interactivity of web-based instruction
Abstract An effectively designed interaction mechanism creates a shortcut for human–computer interaction. Most studies in this area have concluded that the higher the level of interactivity, the better, especially regarding interactive websites applied in the fields of business and education. Previous studies have also suggested that designs with a higher level of interactivity result in higher learner evaluations of websites. However, little research has examined learner perceptions as they interact with web-based instruction (WBI) systems in a situation with limited time. To assist learners in acquiring knowledge quickly, the interactivity design must make the web learning environment easier to use by reducing the complexity of the interface. The aim of the present study is to explore learner perceptions of three WBI systems with different interaction levels under time limitations. This study was therefore designed to provide a new framework to design systems with different degrees of interactivity, and to examine learners’ perceptions of these interaction elements. Three WBI systems were developed with different degrees of interactivity from high to low, and a between-subject experiment was conducted with 45 subjects. The results of the experiment indicate that a higher level of interactivity does not necessarily guarantee a higher perception of interactivity in a short-term learning situation. Therefore, the instructors must pay attention to modifying or selecting appropriate interactive elements that are more suitable for various learning stages. The findings provide insights for designers to adopt different degrees of interactivity in their designs that will best fulfill various learners’ needs. Abstract Copyright © 2011 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.

Title: Age differences in the perception of social presence in the use of 3D virtual world for social interaction
Abstract 3D virtual worlds are becoming increasingly popular as tool for social interaction, with the potential of augmenting the user’s perception of physical and social presence. Thus, this technology could be of great benefit to older people, providing home-bound older users with access to social, educational and recreational resources. However, so far there have been few studies looking into how older people engage with virtual worlds, as most research in this area focuses on younger users. In this study, an online experiment was conducted with 30 older and 30 younger users to investigate age differences in the perception of presence in the use of virtual worlds for social interaction. Overall, we found that factors such as navigation and prior experience with text messaging tools played a key role in older people’s perception of presence. Both physical and social presence was found to be linked to the quality of social interaction for users of both age groups. In addition, older people displayed proxemic behavior which was more similar to proxemic behavior in the physical world when compared to younger users. Abstract Copyright © 2012 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Human error and information systems failure: the case of the London ambulance service computer-aided despatch system project
Abstract Human error and systems failure have been two constructs that have become linked in many contexts. In this paper we particularly focus on the issue of failure in relation to that group of software systems known as information systems. We first review the extant theoretical and empirical work on this topic. Then we discuss one particular well-known case — that of the London ambulance service computer-aided despatch system (Lascad) project — and use it as a particularly cogent example of the features of information systems failure. We maintain that the tendency to analyse information systems failure solely from a technological standpoint is limiting, that the nature of information systems failure is multi-faceted, and hence cannot be adequately understood purely in terms of the immediate problems of systems construction. Our purpose is also to use the generic material on IS failure and the specific details of this particular case study to critique the issues of safety, criticality, human error and risk in relation to systems not currently well considered in relation to these areas. Abstract Copyright © 1999 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.

Title: Feminist HCI meets facebook: Performativity and social networking sites
Abstract In this paper, I reflect on a specific product of interaction design, social networking sites. The goals of this paper are twofold. One is to bring a feminist reflexivity, to HCI, drawing on the work of Judith Butler and her concepts of peformativity, citationality, and interpellation. Her approach is, I argue, highly relevant to issues of identity and self-representation on social networking sites; and to the co-constitution of the subject and technology. A critical, feminist HCI must ask how social media and other HCI institutions, practices, and discourses are part of the processes by which sociotechnical configurations are constructed. My second goal is to examine the implications of such an approach by applying it to social networking sites (SNSs) drawing the empirical research literature on SNSs, to show how SNS structures and policies help shape the subject and hide the contingency of subject categories. Abstract Copyright © 2011 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: A survey of methods for data fusion and system adaptation using autonomic nervous system responses in physiological computing
Abstract Physiological computing represents a mode of human–computer interaction where the computer monitors, analyzes and responds to the user’s psychophysiological activity in real-time. Within the field, autonomic nervous system responses have been studied extensively since they can be measured quickly and unobtrusively. However, despite a vast body of literature available on the subject, there is still no universally accepted set of rules that would translate physiological data to psychological states. This paper surveys the work performed on data fusion and system adaptation using autonomic nervous system responses in psychophysiology and physiological computing during the last ten years. First, five prerequisites for data fusion are examined: psychological model selection, training set preparation, feature extraction, normalization and dimension reduction. Then, different methods for either classification or estimation of psychological states from the extracted features are presented and compared. Finally, implementations of system adaptation are reviewed: changing the system that the user is interacting with in response to cognitive or affective information inferred from autonomic nervous system responses. The paper is aimed primarily at psychologists and computer scientists who have already recorded autonomic nervous system responses and now need to create algorithms to determine the subject’s psychological state. Abstract Copyright © 2012 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Positive mood induction procedures for virtual environments designed for elderly people
Abstract Positive emotions have a significant influence on mental and physical health. Their role in the elderly’s wellbeing has been established in numerous studies. It is therefore worthwhile to explore ways in which elderly people can increase the number of positive experiences in their daily lives. This paper describes two Virtual Environments (VEs) that were used as mood induction procedures (MIPs) for this population. In addition, the VEs’ efficacy at increasing joy and relaxation in elderly users is analyzed. The VEs contain exercises for generating positive-autobiographic memories, mindfulness and slow breathing rhythms. The total sample comprised 18 participants over 55 years old who used the VEs on two occasions. Twelve of them used the joy environment, while 16 used the relaxation environment. Moods before and after each session were assessed using Visual Analogical Scales. After using both VEs, results indicated significant increases in joy and relaxation and significant decreases in sadness and anxiety. The participants also indicated low levels of difficulty of use and high levels of satisfaction and sense of presence. Hence, the VEs demonstrate their usefulness at promoting positive affects and enhancing the wellbeing of elderly people. Abstract Copyright © 2012 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: The effects of trust, security and privacy in social networking: A security-based approach to understand the pattern of adoption
Abstract Social network services (SNS) focus on building online communities of people who share interests and/or activities, or who are interested in exploring the interests and activities of others. This study examines security, trust, and privacy concerns with regard to social networking Websites among consumers using both reliable scales and measures. It proposes an SNS acceptance model by integrating cognitive as well as affective attitudes as primary influencing factors, which are driven by underlying beliefs, perceived security, perceived privacy, trust, attitude, and intention. Results from a survey of SNS users validate that the proposed theoretical model explains and predicts user acceptance of SNS substantially well. The model shows excellent measurement properties and establishes perceived privacy and perceived security of SNS as distinct constructs. The finding also reveals that perceived security moderates the effect of perceived privacy on trust. Based on the results of this study, practical implications for marketing strategies in SNS markets and theoretical implications are recommended accordingly. Abstract Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Usability testing: what have we overlooked?
Abstract For more than a decade, the number of usability test participants has been a major theme of debate among usability practitioners and researchers keen to improve usability test performance. This paper provides evidence suggesting that the focus be shifted to task coverage instead. Our data analysis of nine commercial usability test teams participating in the CUE-4 study revealed no significant correlation between the percentage of problems found or of new problems and number of test users, but correlations of both variables and number of user tasks used by each usability team were significant. The role of participant recruitment on usability test performance and future research directions are discussed. Abstract Copyright © 2013 ACM, Inc.
Title: Predicting online grocery buying intention: a comparison of the theory of reasoned action and the theory of planned behavior
Abstract This paper tests the ability of two consumer theories—the theory of reasoned action and the theory of planned behavior—in predicting consumer online grocery buying intention. In addition, a comparison of the two theories is conducted. Data were collected from two web-based surveys of Danish ( n =1222) and Swedish ( n =1038) consumers using self-administered questionnaires. These results suggest that the theory of planned behavior (with the inclusion of a path from subjective norm to attitude) provides the best fit to the data and explains the highest proportion of variation in online grocery buying intention. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Decomposition and crossover effects in the theory of planned behavior: A study of consumer adoption intentions
Abstract The Theory of Planned Behavior, an extension of the well-known Theory of Reasoned Action, is proposed as a model to predict consumer adoption intention. Three variations of the Theory of Planned Behavior are examined and compared to the Theory of Reasoned Action. The appropriateness of each model is assessed with data from a consumer setting. Structural equation modelling using maximum likelihood estimation for the four models revealed that the traditional forms of the Theory of Reasoned Action and the Theory of Planned Behavior fit the data adequately. Decomposing the belief structures and allowing for crossover effects in the Theory of Planned Behavior resulted in improvements in model prediction. The application of each model to theory development and management intervention is explored. Abstract Copyright © 1995 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Knowledge and the Prediction of Behavior: The Role of Information Accuracy in the Theory of Planned Behavior
Abstract The results of the present research question the common assumption that being well informed is a prerequisite for effective action to produce desired outcomes. In Study 1 ( N = 79), environmental knowledge had no effect on energy conservation, and in Study 2 ( N = 79), alcohol knowledge was unrelated to drinking behavior. Such disappointing correlations may result from an inappropriate focus on accuracy of information at the expense of its relevance to and support for the behavior. Study 3 ( N = 85) obtained a positive correlation between knowledge and pro-Muslim behavior, but Study 4 ( N = 89) confirmed the proposition that this correlation arose because responses on the knowledge test reflected underlying attitudes. Study 4 also showed that the correlation could become positive or negative by appropriate selection of questions for the knowledge test. The theory of planned behavior (Ajzen, 1991 ), with its focus on specific actions, predicted intentions and behavior in all four studies. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Informa plc

Link: h ttp://www.businessinsider.com/ron-johnson-apple-store-j-c-penney-2011-11
People come to the Apple Store for the experience — and they’re willing to pay a premium for that. There are lots of components to that experience, but maybe the most important — and this is something that can translate to any retailer — is that the staff isn’t focused on selling stuff, it’s focused on building relationships and trying to make people’s lives better. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Business Insider, Inc. All rights reserved.
Title : Naturalizing aesthetics: Brain areas for aesthetic appraisal across sensory modalities
Abstract We present here the most comprehensive analysis to date of neuroaesthetic processing by reporting the results of voxel-based meta-analyses of 93 neuroimaging studies of positive-valence aesthetic appraisal across four sensory modalities. The results demonstrate that the most concordant area of activation across all four modalities is the right anterior insula, an area typically associated with visceral perception, especially of negative valence (disgust, pain, etc.). We argue that aesthetic processing is, at its core, the appraisal of the valence of perceived objects. This appraisal is in no way limited to artworks but is instead applicable to all types of perceived objects. Therefore, one way to naturalize aesthetics is to argue that such a system evolved first for the appraisal of objects of survival advantage, such as food sources, and was later co-opted in humans for the experience of artworks for the satisfaction of social needs. Abstract Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=the-neuroscience-of-beauty
Studies from neuroscience and evolutionary biology challenge this separation of art from non-art. Human neuroimaging studies have convincingly shown that the brain areas involved in aesthetic responses to artworks overlap with those that mediate the appraisal of objects of evolutionary importance, such as the desirability of foods or the attractiveness of potential mates. Hence, it is unlikely that there are brain systems specific to the appreciation of artworks; instead there are general aesthetic systems that determine how appealing an object is, be that a piece of cake or a piece of music. Abstract © 2013 Scientific American, a Division of Nature America, Inc.
Link: http://blogs.scientificamerican.com/symbiartic/2011/10/03/need-proof-that-were-visual-beings/
This video offers proof that humans are visual beings. Abstract © 2013 Scientific American, a Division of Nature America, Inc.
Link: http://hbr.org/web/slideshows/five-charts-that-changed-business/1-slide
Once in a while, a chart so deftly captures an important strategic insight that it becomes an iconic part of management thinking and a tool that shows up in MBA classrooms and corporate boardrooms for years to come. As HBR prepares for its 90th anniversary, in 2012, their editors have combed the magazine archives and other sources to select five charts that changed the shape of strategy. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved.
Link: http://www.strategy-business.com/article/04412
It is a widely accepted and rarely challenged tenet of marketing that companies can sustain competitive advantage only through “new and improved” product differentiation based on unique features and benefits. What a mistake. By paying attention to what consumers really want, companies can attract new customers and create a distinctive brand. Abstract © 2013 Booz & Company Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://www.economist.com/node/17723028
If you can have everything in 57 varieties, making decisions becomes hard work. Many of these options have improved life immeasurably in the rich world, and to a lesser extent in poorer parts. They are testimony to human ingenuity and innovation. Free choice is the basis on which markets work, driving competition and generating economic growth. It is the cornerstone of liberal democracy. The 20th century bears the scars of too many failed experiments in which people had no choice. But amid all the dizzying possibilities, a nagging question lurks: is so much extra choice unambiguously a good thing? Abstract Copyright © The Economist Newspaper Limited 2013. All rights reserved.
Link: http://e.businessinsider.com/public/1099804
Mobile apps are becoming more important to people, not less important, according to this chart plucked from a big presentation on the internet. It’s an interesting trend because it shows how mobile behavior is different than traditional desktop computing behavior when it comes to the web. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Business Insider, Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://blogs.scientificamerican.com/scicurious-brain/2012/07/30/you-want-that-well-i-want-it-too-the-neuroscience-of-mimetic-desire/
Mimetic desire is more than jealously wanting something because someone else has it. Rather, it’s about valuing something because someone else values it . And it’s pretty easy to transmit the value. Just writing about Person A’s activities and habits and showing it to Person B will make Person B start to think Person A must have seen something good about the Toyota Camry…maybe his next car…
But what is behind this contagion of desires? Abstract © 2013 Scientific American, a Division of Nature America, Inc.

Link: http://www.united-academics.org/magazine/27212/visual-memory-blindness/
A well-known pheonomenon in psychology has been the ‘inattentional blindness’ principle. In fact, you might know it from experience: it means that people tend to fail seeing things in their visible fields when they have to focus on a task. Until now, it was thought that in order to cause the effect, a cluttered visual field is required. Recent research shows that the effect is present though in many more situations. Abstract Copyright United Academics 2012 Coypright – All rights Reserved
Link: http://www.businessinsider.com/18-24-texting-2011-9
Chart of the Day: According to the Pew Internet project , people in the 18-24 year-old range are sending and receiving 110 texts per day on average. The median number of texts sent/received by that group is 50 per day. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Business Insider, Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://www.businessinsider.com/chart-of-the-day-facebook-time-2011-9
Chart of the Day: A new report on social media from Nielsen shows U.S. users spent 53.5 billion minutes on Facebook in May, which is more time than was spent on the next four biggest sites. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Business Insider, Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=your-brain-on-facebook
A recent study showed that certain brain areas expand in people who have greater numbers of friends on Facebook . There was a problem, though. The study, in Proceedings of the Royal Society B , was unable to resolve the question of whether “friending” plumps up the brain areas or whether people with a type of robustness in brain physiology are just natural social butterflies. But with the help of a few monkeys in England, teenagers everywhere may now have more ammunition to use against parents. Abstract © 2013 Scientific American, a Division of Nature America, Inc.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/196.abstract.html?etoc
Although advances in technology now enable people to communicate ‘anytime, anyplace’, it is not clear how citizens can be motivated to actually do so. This paper evaluates the impact of three principles of psychological empowerment, namely perceived self-efficacy, sense of community and causal importance, on public transport passengers’ motivation to report issues and complaints while on the move. A week-long study with 65 participants revealed that self-efficacy and causal importance increased participation in short bursts and increased perceptions of service quality over longer periods. Finally, we discuss the implications of these findings for citizen participation projects and reflect on design opportunities for mobile technologies that motivate citizen participation. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/208.abstract.html?etoc
This review paper argues that users of personal information management systems have three particularly pressing requirements, for which current systems do not fully cater: (i) To combat information overload, as the volume of information increases. (ii) To ease context switching, in particular, for users who face frequent interrupts in their work. (iii) To be supported in information integration, across a variety of applications. To meet these requirements, four broad technological approaches should be adopted in an incremental fashion: (i) The deployment of a unified file system to manage all information objects, including files, emails and webpage URLs. (ii) The use of tags to categorize information; implemented in a way which is backward-compatible with existing hierarchical file systems. (iii) The use of context to aid information retrieval; built upon existing file and tagging systems rather than creating a parallel context management system. (iv) The deployment of semantic technologies, coupled with the harvesting of all useful metadata. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/238.abstract.html?etoc
Projective techniques are used in psychology and consumer research to provide information about individuals’ motivations, thoughts and feelings. This paper reviews the use of projective techniques in marketing research and user experience (UX) research and discusses their potential role in understanding users, their needs and values, and evaluating UX in practical product development contexts. A projective technique called sentence completion is evaluated through three case studies. Sentence completion produces qualitative data about users’ views in a structured form. The results are less time-consuming to analyze than interview results. Compared with quantitative methods such as AttrakDiff, the results are more time consuming to analyze, but more information is retrieved on negative feelings. The results show that sentence completion is useful in understanding users’ perceptions and that the technique can be used to complement other methods. Sentence completion can also be used online to reach wider user groups. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/256.abstract.html?etoc
Cognitive load (CL) is experienced during critical tasks and also while engaged emotional states are induced either by the task itself or by extraneous experiences. Emotions irrelevant to the working memory representation may interfere with the processing of relevant tasks and can influence task performance and behavior, making the accurate detection of CL from nonverbal information challenging. This paper investigates automatic CL detection from facial features, physiology and task performance under affective interference. Data were collected from participants (n=20) solving mental arithmetic tasks with emotional stimuli in the background, and a combined classifier was used for detecting CL levels. Results indicate that the face modality for CL detection was more accurate under affective interference, whereas physiology and task performance were more accurate without the affective interference. Multimodal fusion improved detection accuracies, but it was less accurate under affective interferences. More specifically, the accuracy decreased with an increasing intensity of emotional arousal. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/269.abstract.html?etoc
In the field of virtual reality (VR), many efforts have been made to analyze presence, the sense of being in the virtual world. However, it is only recently that functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has been used to study presence during an automatic navigation through a virtual environment. In the present work, our aim was to use fMRI to study the sense of presence during a VR-free navigation task, in comparison with visualization of photographs and videos (automatic navigations through the same environment). The main goal was to analyze the usefulness of fMRI for this purpose, evaluating whether, in this context, the interaction between the subject and the environment is performed naturally, hiding the role of technology in the experience. We monitored 14 right-handed healthy females aged between 19 and 25 years. Frontal, parietal and occipital regions showed their involvement during free virtual navigation. Moreover, activation in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex was also shown to be negatively correlated to sense of presence and the postcentral parietal cortex and insula showed a parametric increased activation according to the condition-related sense of presence, which suggests that stimulus attention and self-awareness processes related to the insula may be linked to the sense of presence. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/285.abstract.html?etoc
Unlike visual stimuli, little attention has been paid to auditory stimuli in terms of emotion prediction with physiological signals. This paper aimed to investigate whether auditory stimuli can be used as an effective elicitor as visual stimuli for emotion prediction using physiological channels. For this purpose, a well-controlled experiment was designed, in which standardized visual and auditory stimuli were systematically selected and presented to participants to induce various emotions spontaneously in a laboratory setting. Numerous physiological signals, including facial electromyogram, electroencephalography, skin conductivity and respiration data, were recorded when participants were exposed to the stimulus presentation. Two data mining methods, namely decision rules and k-nearest neighbor based on the rough set technique, were applied to construct emotion prediction models based on the features extracted from the physiological data. Experimental results demonstrated that auditory stimuli were as effective as visual stimuli in eliciting emotions in terms of systematic physiological reactivity. This was evidenced by the best prediction accuracy quantified by the F1 measure (visual: 76.2% vs. auditory: 76.1%) among six emotion categories (excited, happy, neutral, sad, fearful and disgusted). Furthermore, we also constructed culture-specific (Chinese vs. Indian) prediction models. The results showed that model prediction accuracy was not significantly different between culture-specific models. Finally, the implications of affective auditory stimuli in human–computer interaction, limitations of the study and suggestions for further research are discussed. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289614000087
The deliberate practice view has generated a great deal of scientific and popular interest in expert performance. At the same time, empirical evidence now indicates that deliberate practice, while certainly important, is not as important as Ericsson and colleagues have argued it is. In particular, we (Hambrick, Oswald, Altmann, Meinz, Gobet, & Campitelli, 2014) found that individual differences in accumulated amount of deliberate practice accounted for about one-third of the reliable variance in performance in chess and music, leaving the majority of the reliable variance unexplained and potentially explainable by other factors. Ericsson’s (2014) defense of the deliberate practice view, though vigorous, is undercut by contradictions, oversights, and errors in his arguments and criticisms, several of which we describe here. We reiterate that the task now is to develop and rigorously test falsifiable theories of expert performance that take into account as many potentially relevant constructs as possible. Abstract © 2014 Elsevier Inc.
Link: http://techcrunch.com/2013/02/05/amazon-to-launch-virtual-currency-amazon-coins-in-its-appstore-in-may/
Amazon has just announced a new virtual currency for Kindle Fire owners to use on in-app purchases, app purchases, etc. in the Amazon Appstore. Abstract © 2013 AOL Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smj.2284/abstract
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2014/05/09/iwc.iwu016.abstract.html?papetoc
Wizard of Oz (WOZ) is a well-established method for simulating the functionality and user experience of future systems. Using a human wizard to mimic certain operations of a potential system is particularly useful in situations where extensive engineering effort would otherwise be needed to explore the design possibilities offered by such operations. The WOZ method has been widely used in connection with speech and language technologies, but advances in sensor technology and pattern recognition as well as new application areas such as human–robot interaction have made it increasingly relevant to the design of a wider range of interactive systems. In such cases, achieving acceptable performance at the user interface level often hinges on resource-intensive improvements such as domain tuning, which are better done once the overall design is relatively stable. Although WOZ is recognized as a valuable prototyping technique, surprisingly little effort has been put into exploring it from a methodological point of view. Starting from a survey of the literature, this paper presents a systematic investigation and analysis of the design space for WOZ for language technology applications, and proposes a generic architecture for tool support that supports the integration of components for speech recognition and synthesis as well as for machine translation. This architecture is instantiated in WebWOZ—a new web-based open-source WOZ prototyping platform. The viability of generic support is explored empirically through a series of evaluations. Researchers from a variety of backgrounds were able to create experiments, independent of their previous experience with WOZ. The approach was further validated through a number of real experiments, which also helped to identify a number of possibilities for additional support, and flagged potential issues relating to consistency in wizard performance. Abstract 2014 Oxford University Press
Link: http://www.thinkwithgoogle.com/insights/library/studies/the-new-multi-screen-world-study/
This paper studies how business models can be designed to tap effectively into open innovation labor markets with heterogeneously motivated workers. Using data on open source software, we show that motivations are diverse, and demonstrate how managers can strategically influence the flow of code contributions and their impact on project performance. Unlike previous literature using survey data, we exploit the observed pattern of project membership and code contributions—the “revealed preference” of developers—to infer the motivations driving their decision to contribute. Developers strongly sort along key dimensions of the business model chosen by project managers, especially the degree of openness of the project license. The results indicate an important role for intrinsic motivation, reputation, and labor market signaling, and a more limited role for reciprocity. Abstract 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
updated on 5/13
Title: Developing elements of user experience for mobile phones and services: survey, interview, and observation approaches
Abstract The term user experience (UX) encompasses the concepts of usability and affective engineering. However, UX has not been defined clearly. In this study, a literature survey, user interview and indirect observation were conducted to develop definitions of UX and its elements. A literature survey investigated 127 articles that were considered to be helpful to define the concept of UX. An in-depth interview targeted 14 hands-on workers in the Korean mobile phone industry. An indirect observation captured daily experiences of eight end-users with mobile phones. This study collected various views on UX from academia, industry, and end-users using these three approaches. As a result, this article proposes definitions of UX and its elements: usability, affect, and user value. These results are expected to help design products or services with greater levels of UX. Abstract Copyright 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Title: Why different people prefer different systems for different tasks: An activity perspective on technology adoption in a dynamic user environment
Abstract In a contemporary user environment, there are often multiple information systems available for a certain type of task. Based on the premises of Activity Theory, this study examines how user characteristics, system experiences, and task situations influence an individual’s preferences among different systems in terms of user readiness to interact with each. It hypothesizes that system experiences directly shape specific user readiness at the within-subject level, user characteristics and task situations make differences in general user readiness at the between-subject level, and task situations also affect specific user readiness through the mediation of system experiences. An empirical study was conducted, and the results supported the hypothesized relationships. The findings provide insights on how to enhance technology adoption by tailoring system development and management to various task contexts and different user groups. Abstract Copyright 2011 ASIS&T
Title: A review of factors influencing user satisfaction in information retrieval
Abstract The authors investigate factors influencing user satisfaction in information retrieval. It is evident from this study that user satisfaction is a subjective variable, which can be influenced by several factors such as system effectiveness, user effectiveness, user effort, and user characteristics and expectations. Therefore, information retrieval evaluators should consider all these factors in obtaining user satisfaction and in using it as a criterion of system effectiveness. Previous studies have conflicting conclusions on the relationship between user satisfaction and system effectiveness; this study has substantiated these findings and supports using user satisfaction as a criterion of system effectiveness. Abstract Copyright 2010 ASIS&T
Title: The development and evaluation of a survey to measure user engagement
Abstract Facilitating engaging user experiences is essential in the design of interactive systems. To accomplish this, it is necessary to understand the composition of this construct and how to evaluate it. Building on previous work that posited a theory of engagement and identified a core set of attributes that operationalized this construct, we constructed and evaluated a multidimensional scale to measure user engagement. In this paper we describe the development of the scale, as well as two large-scale studies (N=440 and N=802) that were undertaken to assess its reliability and validity in online shopping environments. In the first we used Reliability Analysis and Exploratory Factor Analysis to identify six attributes of engagement: Perceived Usability, Aesthetics, Focused Attention, Felt Involvement, Novelty, and Endurability. In the second we tested the validity of and relationships among those attributes using Structural Equation Modeling. The result of this research is a multidimensional scale that may be used to test the engagement of software applications. In addition, findings indicate that attributes of engagement are highly intertwined, a complex interplay of user-system interaction variables. Notably, Perceived Usability played a mediating role in the relationship between Endurability and Novelty, Aesthetics, Felt Involvement, and Focused Attention. Abstract Copyright 2009 ASIS&T
Title: Exploring user engagement in online news interactions
Abstract This paper describes a qualitative study of online news reading and browsing. Thirty people participated in a quasi-experimental study in which they were asked to browse a news website and select three stories to discuss at a social gathering. Semi-structured interviews were conducted post-task to understand participants’ perceptions of what makes online news reading and browsing engaging or non-engaging. Findings as presented within the experience-based framework of user engagement and demonstrate the complexity of users’ interactions with information content and systems in online news environments. This study extends the model of user engagement and contributes new insights into user’s experience in casual-leisure settings, such as online news, which has implications for other information domains. Abstract Copyright 2011 by American Society for Information Science and Technology
Abstract This chapter of The Fabric of Mobile Services: Software Paradigms and Business Demands contains sections titled: New Services and User Experience, User-Centered Simplicity and Experience, Methodologies for Simplicity and User Experience, and Case Studies: Simplifying Paradigms Abstract Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Title: The Right Angle: Visual Portrayal of Products Affects Observers’ Impressions of Owners
Abstract Consumer products have long been known to influence observers’ impressions of product owners. The angle at which products are visually portrayed in advertisements, however, may be an overlooked factor in these effects. We hypothesize and find that portrayals of the same product from different viewpoints can prime different associations that color impressions of product and owner in parallel ways. In Study 1, automobiles were rated higher on status- and power-related traits (e.g., dominant , powerful ) when portrayed head-on versus in side profile, an effect found for sport utility vehicles (SUVs)—a category with a reputation for dominance—but not sedans. In Study 2, these portrayal-based associations influenced the impressions formed about the product’s owner: a target person was rated higher on status- and power-related traits when his SUV was portrayed head-on versus in side profile. These results suggest that the influence of visual portrayal extends beyond general evaluations of products to affect more specific impressions of products and owners alike, and highlight that primed traits are likely to influence impressions when compatible with other knowledge about the target. Abstract Copyright 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc
Title: The Counterfeit Self: The Deceptive Costs of Faking It
Abstract Although people buy counterfeit products to signal positive traits, we show that wearing counterfeit products makes individuals feel less authentic and increases their likelihood of both behaving dishonestly and judging others as unethical. In four experiments, participants wore purportedly fake or authentically branded sunglasses. Those wearing fake sunglasses cheated more across multiple tasks than did participants wearing authentic sunglasses, both when they believed they had a preference for counterfeits (Experiment 1a) and when they were randomly assigned to wear them (Experiment 1b). Experiment 2 shows that the effects of wearing counterfeit sunglasses extend beyond the self, influencing judgments of other people’s unethical behavior. Experiment 3 demonstrates that the feelings of inauthenticity that wearing fake products engenders—what we term the counterfeit selfmediate the impact of counterfeits on unethical behavior. Finally, we show that people do not predict the impact of counterfeits on ethicality; thus, the costs of counterfeits are deceptive. Abstract Copyright 2010 Francesca Gino, Michael I. Norton, and Dan Ariely3
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/5/389.full.html?etoc
Menus are a key mechanism for organizing different commands in graphical user interfaces. Nowadays low-cost devices that allow using different interaction techniques in remote interfaces have become widespread. Nevertheless, their corresponding menus are direct adaptations from traditional ones. As a consequence, they are inaccurate and slow, and also produce tiredness. In this paper, we design, implement and evaluate a menu selection technique for remote interfaces, the Body Menu. This technique permits whole-body interaction and is specifically designed to take advantage of the proprioception sense. The Body Menu attaches virtual menu items to different parts of the body and selects them when the users reach these zones with their hands. We use the Microsoft Kinect to implement this system. Additionally, we compared it with the most representative menus, studied the best number of body parts to be used and analyzed how children interact with it. Abstract © 2013 Oxford University Publishing.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/5/403.full.html?etoc
We present the evaluation of an interactive audio map system that enables blind and partially sighted users to explore and navigate city maps from the safety of their home using simulated 3D audio and synthetic speech alone. We begin with a review of existing literature in the areas of spatial knowledge and wayfinding, auditory displays and auditory map systems, before describing how this research builds on and differentiates itself from this body of work. One key requirement was the ability to quantify the effectiveness of the audio map, so we describe the design and implementation of the evaluation, which took the form of a game downloaded by participants to their own computers. The results demonstrate that participants (blind, partially sighted and sighted) have acquired detailed spatial knowledge and also that the availability of positional audio cues significantly improves wayfinding performance. Abstract © 2013 Oxford University Publishing.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/5/417.full.html?etoc
Delegation is the practice of sharing authority with another individual to enable them to complete a specific task as a proxy. Practices to permit delegation can range from formal to informal arrangements and can involve spontaneous yet finely balanced notions of trust between people. This paper argues that delegation is a ubiquitous yet an unsupported feature of socio-technical computer systems and that this lack of support illustrates a particular neglect to the everyday financial practices of the more vulnerable people in society. Our contribution is to provide a first exploration of the domain of person-to-person delegation in digital payments, a particularly pressing context. We first report qualitative data collected across several studies concerning banking practices of individuals over 80 years of age. We then use analytical techniques centred upon identification of stakeholders, their concerns and interactions, to characterize the delegation practices we observed. We propose a Concerns Matrix as a suitable representation to capture conflicts in the needs of individuals in such complex socio-technical systems, and finally propose a putative design response in the form of a Helper Card. Abstract © 2013 Oxford University Publishing..
Link: Why We Love Beautiful Things
Great design, the management expert Gary Hamel once said, is like Justice Potter Stewart’s famous definition of pornography — you know it when you see it. You want it, too: brain scan studies reveal that the sight of an attractive product can trigger the part of the motor cerebellum that governs hand movement. Instinctively, we reach out for attractive things; beauty literally moves us. © 2013 New York Times
Link: http://www.bris.ac.uk/news/2013/9478.html
A new study has analysed tens of thousands of articles available to readers of online news and created a model to find out ‘what makes people click’. The aim of the study was to model the reading preferences for the audiences of 14 online news outlets using machine learning techniques. The models, describing the appeal of an article to each audience, were developed by linear functions of word frequencies. The models compared articles that became “most popular” on a given day in a given outlet with articles that did not. The research dentified the most attractive keywords, as well as the least attractive ones, and explained the choices readers made. Abstract © 2013 University of Bristol.
Title: Pointing and Selecting with Facial Activity
Abstract The aim of this paper was to evaluate the use of three facial actions (i.e. frowning, raising the eyebrows, and smiling) in selecting objects on a computer screen when gaze was used for pointing. Dwell time is the most commonly used selection technique in gaze-based interaction, and thus, a dwell time of 400 ms was used as a reference selection technique. A wireless, head-mounted prototype device that carried out eye tracking and contactless, capacitive measurement of facial actions was used for the interaction task. Participants (N=16) performed point-and-select tasks with three pointing distances (i.e. 60, 120 and 240 mm) and three target sizes (i.e. 25, 30 and 40 mm). Task completion times, pointing errors and throughput values based on Fitts’ law were used to compare the selection techniques. The participants also rated the techniques with subjective ratings scales. The results showed that the different techniques performed equally well in many respects. However, throughput values varied from 8.38 bits/s (raising the eyebrows) to 15.33 bits/s (smiling) and were comparable to or, in the case of smiling, better than in earlier research with similar interaction techniques. The dwell time was found to be the least accurate selection technique in terms of the magnitudes of point-and-select errors. Smiling technique was rated as more accurate to use than the frowning or the raising techniques. The results give further support for methods that combine facial behavior to eye tracking when interacting with technology.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Outi Tuisku1, Ville Rantanen, Oleg Špakov, Veikko Surakka and Jukka Lekkala
Title: Modeling Traditional Literacy, Internet Skills and Internet Usage: An Empirical Study
Abstract This paper focuses on the relationships among traditional literacy (reading, writing and understanding text), medium-related Internet skills (consisting of operational and formal skills), content-related Internet skills (consisting of information and strategic skills) and Internet usage types (information- and career-directed Internet use and entertainment use). We conducted a large-scale survey that resulted in a dataset of 1008 respondents. The results reveal the following: (i) traditional literacy has a direct effect on formal and information Internet skills and an indirect effect on strategic Internet skills and (ii) differences in types of Internet usage are indirectly determined by traditional literacy and directly affected by Internet skills, such that higher levels of strategic Internet skills result in more information- and career-directed Internet use. Traditional literacy is a pre-condition for the employment of Internet skills, and Internet skills should not be considered an easy means of disrupting historically grounded inequalities caused by differences in traditional literacy.
Abstract Copyright 2014 A.J.A.M. van Deursen and J.A.G.M. van Dijk
Title: Life Is Too Short to RTFM: How Users Relate to Documentation and Excess Features in Consumer Products
Abstract This paper addresses two common problems that users of various products and interfaces encounter—over-featured interfaces and product documentation. Over-featured interfaces are seen as a problem as they can confuse and over-complicate everyday interactions. Researchers also often claim that users do not read product documentation, although they are often exhorted to ‘RTFM’ (read the field manual). We conducted two sets of studies with users which looked at the issues of both manuals and excess features with common domestic and personal products. The quantitative set was a series of questionnaires administered to 170 people over 7 years. The qualitative set consisted of two 6-month longitudinal studies based on diaries and interviews with a total of 15 participants. We found that manuals are not read by the majority of people, and most do not use all the features of the products that they own and use regularly. Men are more likely to do both than women, and younger people are less likely to use manuals than middle-aged and older ones. More educated people are also less likely to read manuals. Over-featuring and being forced to consult manuals also appears to cause negative emotional experiences. Implications of these findings are discussed.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Alethea L. Blackler, Rafael Gomez, Vesna Popovic and M. Helen Thompson
Title: Effect of Age on Human–Computer Interface Control Via Neck Electromyography
Abstract The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of age on visuomotor tracking using submental and anterior neck surface electromyography (sEMG) to assess feasibility of computer control via neck musculature, which allows people with little remaining motor function to interact with computers. Thirty-two healthy adults participated: 16 younger adults aged 18–29 years and 16 older adults aged 69–85 years. Participants modulated sEMG to achieve targets presented at different amplitudes using real-time visual feedback. Root mean squared (RMS) error was used to quantify tracking performance. RMS error was increased for older adults relative to younger adults. Older adults demonstrated more RMS error than younger adults as a function of increasing target amplitude. The differential effects of age found on static tracking performance in anterior neck musculature suggest more difficult translation of human–computer interfaces controlled using anterior neck musculature for static tasks to older populations.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Gabrielle L. Hands and Cara E. Stepp
Title: Should I Stay or Should I Go? Improving Event Recommendation in the Social Web
Abstract This paper focuses on the recommendation of events in the Social Web, and addresses the problem of finding if, and to which extent, certain features, which are peculiar to events, are relevant in predicting the users’ interests and should thereby be taken into account in recommendation. We consider, in particular, three ‘additional’ features that are usually shown to users within social networking environments: reachability from the user location, the reputation of the event in the community and the participation of the user’s friends. Our study is aimed at evaluating whether adding this information to the description of the event type and topic, and including in the user profile the information on the relevance of these factors, can improve our capability to predict the user’s interest. We approached the problem by carrying out two surveys with users, who were asked to express their interest in a number of events. We then trained, by means of linear regression, a scoring function defined as a linear combination of the different factors, whose goal was to predict the user scores. We repeated this experiment under different hypotheses on the additional factors, in order to assess their relevance by comparing the predictive capabilities of the resulting functions. The compared results of our experiments show that additional factors, if properly weighted, can improve the prediction accuracy with an error reduction of 4.1%. The best results were obtained by combining content-based factors and additional factors in a proportion of ∼10:4.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Federica Cena, Silvia Likavec, Ilaria Lombardi and Claudia Picardi
Title: “I Need to Be Explicit: You’re Wrong”: Impact of Face Threats on Social Evaluations in Online Instructional Communication
Abstract Online instructional communication, as found in ask-an-expert forums, e-learning discussion boards or online help desks, creates situations that threaten the recipient’s face. This study analyzed the evaluation of face-threatening acts with a 1×3 design. An online forum thread confronted a layperson with an expert who either (a) addressed the layperson’s misconceptions directly and frankly, (b) mitigated face threats through explicit hints about the need to be direct or (c) communicated politely and indirectly. College students read these dialogues and assessed the expert communicator’s facework, recipient orientation, credibility and likability. Results showed that polite experts were evaluated most positively; explicit hints did not improve perceptions of face-threatening acts. This implies that users of instructional forums prefer communicators to be polite even when face threats are necessary. We discuss practical implications for different online instruction contexts and make suggestions for further research.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Regina Jucks, Lena Päuler and Benjamin Brummernhenrich
Title: The Potential of a Text-Based Interface as a Design Medium: An Experiment in a Computer Animation Environment
Abstract Since the birth of the concept of direct manipulation, the graphical user interface has been the dominant means of controlling digital objects. In this research, we hypothesize that the benefits of a text-based interface involve multiple tradeoffs, and we explore the potential of text as a medium of design from three perspectives: (i) the perceived level of control of the designed object, (ii) a tool for realizing creative ideas and (iii) an effective form for a highly learnable user interface. Our experiment in a computer animation environment shows that (i) participants did feel a high level of control of characters, (ii) creativity was both restricted and facilitated depending on the task and (iii) natural language expedited the learning of a new interface language. Our research provides experimental proof of the effect of a text-based interface and offers guidelines for the design of future computer-aided design applications.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Sangwon Lee and Jin Yan
Title: Framing a Set: Understanding the Curatorial Character of Personal Digital Bibliographies
Abstract We articulate a model of curatorship that emphasizes framing the character of the curated set as the focus of curatorial activity. This curatorial character is structured through the articulation, via mechanisms of selection, description and arrangement, of coherent classificatory principles. We describe the latest stage of a continuing project to examine the curatorial character of personal digital bibliographies, such as Pinterest boards, Flickr galleries and GoodReads shelves, and to support the design of such curatorially expressive personal collections. In the study reported here, 24 participants created personal bibliographies using either a structured design process, with explicit tasks for selecting, describing and arranging collection items, or an unstructured process that did not separate these activities. Our findings lead to a more complex understanding of personal collections as curatorial, expressive artifacts. We explore the role of cohesion as a quality that facilitates expression of the curatorial frame, and we find that when designers read source materials as a part of a set, they are more likely to write cohesive collections. Our findings also suggest that the curatorial act involves both the definition of abstract classificatory principles and their instantiation in a specific material environment. We describe various framing devices that facilitate these reading and writing activities, and we suggest design directions for supporting curatorial reading and writing tasks.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Melanie Feinberg, Ramona Broussard and Eryn Whitworth
Title: Identifying Problems Associated with Focus and Context Awareness in 3D Modelling Tasks
Abstract Creating complex 3D models is a challenging process. One of the main reasons for this is that 3D models are usually created using software developed for conventional 2D displays which lack true depth perspective, and therefore do not support correct perception of spatial placement and depth-ordering of displayed content. As a result, modellers often have to deal with many overlapping components of 3D models (e.g. vertices, edges, faces, etc.) on a 2D display surface. This in turn causes them to have difficulties in distinguishing distances, maintaining position and orientation awareness, etc. To better understand the nature of these problems, which can collectively be defined as ‘focus and context awareness’ problems, we have conducted a pilot study with a group of novice 3D modellers, and a series of interviews with a group of professional 3D modellers. This article presents these two studies, and their findings, which have resulted in identifying a set of focus and context awareness problems that modellers face in creating 3D models using conventional modelling software. The article also provides a review of potential solutions to these problems in the related literature.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Masood Masoodian, Azmi bin Mohd Yusof and Bill Rogers
Abstract The goal of user experience design in industry is to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty through the utility, ease of use, and pleasure provided in the interaction with a product. So far, user experience studies have mostly focused on short-term evaluations and consequently on aspects relating to the initial adoption of new product designs. Nevertheless, the relationship between the user and the product evolves over long periods of time and the relevance of prolonged use for market success has been recently highlighted. In this paper, we argue for the cost-effective elicitation of longitudinal user experience data. We propose a method called the “UX Curve” which aims at assisting users in retrospectively reporting how and why their experience with a product has changed over time. The usefulness of the UX Curve method was assessed in a qualitative study with 20 mobile phone users. In particular, we investigated how users’ specific memories of their experiences with their mobile phones guide their behavior and their willingness to recommend the product to others. The results suggest that the UX Curve method enables users and researchers to determine the quality of long-term user experience and the influences that improve user experience over time or cause it to deteriorate. The method provided rich qualitative data and we found that an improving trend of perceived attractiveness of mobile phones was related to user satisfaction and willingness to recommend their phone to friends. This highlights that sustaining perceived attractiveness can be a differentiating factor in the user acceptance of personal interactive products such as mobile phones. The study suggests that the proposed method can be used as a straightforward tool for understanding the reasons why user experience improves or worsens in long-term product use and how these reasons relate to customer loyalty.
Abstract Copyright 2011 Sari Kujalaa, Virpi Rotob, Kaisa Väänänen-Vainio-Mattilaa, Evangelos Karapanosc and Arto Sinneläa
Title: Researching Young Children’s Everyday Uses of Technology in the Family Home
Abstract Studies of the everyday uses of technology in family homes have tended to overlook the role of children and, in particular, young children. A study that was framed by an ecocultural approach focusing on children’s play and learning with toys and technologies is used to illustrate some of the methodological challenges of conducting research with young children in the home. This theoretical framework enabled us to identify and develop a range of methods that illuminated the home’s unique mix of inhabitants, learning opportunities and resources and to investigate parents’ ethnotheories, or cultural beliefs, that gave rise to the complex of practices, values and attitudes and their intersections with technology and support for learning in the home. This resulted in a better understanding of the role of technology in the lives of these 3- and 4-year-old children.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Lydia Plowman
Title: Measuring web usability using item response theory: Principles, features and opportunities
Abstract Usability is considered a critical issue on the web that determines either the success or the failure of a company. Thus, the evaluation of usability has gained substantial attention. However, most current tools for usability evaluation have some limitations, such as excessive generality and a lack of reliability and validity. The present work proposes the construction of a tool to measure usability in e-commerce websites using item response theory (IRT). While usability issues have only been considered in theoretical or empirical contexts, in this study, we discuss them from a mathematical point of view using IRT. In particular, we develop a standardised scale to measure usability in e-commerce websites. This study opens a new field of research in the ergonomics of interfaces with respect to the development of scales using IRT.
Abstract Copyright 2011 Rafael Tezzaa, Antonio Cezar Borniaa and Dalton Francisco de Andrade
Title: Everything Science Knows Right Now About Standing Desks
Abstract If it wasn’t already clear through common sense, it’s become painfully clear through science that sitting all day is terrible for your health. What’s especially alarming about this evidence is that extra physical activity doesn’t seem to offset the costs of what researchers call “prolonged sedentary time.” Just as jogging and tomato juice don’t make up for a night of smoking and drinking, a little evening exercise doesn’t erase the physical damage done by a full work day at your desk.
In response some people have turned to active desks—be it a standing workspace or even a treadmill desk—but the research on this recent trend has been too scattered to draw clear conclusions on its benefits (and potential drawbacks). At least until now. A trio of Canada-based researchers has analyzed the strongest 23 active desk studies to draw some conclusions on how standing and treadmill desks impact both physiological health and psychological performance. Abstract Copyright 2015 Eric Jaffe
Send Us Your Research References: If you have interesting and relevant research references post, post content as comment below for possible inclusion in next year’s updated list.
Other Content from PulseUX: Here are 2 other references from widely read and quoted long-form posts you may find interesting.

Angry Birds UX: Why Angry Birds is so successful and popular: a cognitive teardown of the user experience (1.5 million page views). https://live-mauro-usability-science.pantheonsite.io/blog/why-angry-birds-is-so-successful-a-cognitive-teardown-of-the-user-experience/

Apple v. Samsung: Impact and Implications for Product Design, User Interface Design (UX), Software Development and the Future of High-Technology Consumer Products https://live-mauro-usability-science.pantheonsite.io/blog/apple-v-samsung-implications-for-product-design-user-interface-ux-design-software-development-and-the-future-of-high-technology-consumer-products/
Charles L Mauro CHFP President / Founder MauroNewMedia
Find out more about Charles L Mauro Find out more about MauroNewMedia Follow Pulse>UX on Twitter @PulseUX
Subscribe to email updates
- Pingback: Why Flappy Bird Is / Was So Successful And Popular But So Difficult To Learn: A Cognitive Teardown Of The User Experience (UX)
- Pingback: Wishing You and Your Technology Success in 2014… and Goodbye to Engelbart from MauroNewMedia
Fantastic site. A lot of helpful info here. I’m sending it to some buddies ans additionally sharing in delicious. And naturally, thanks on your sweat!
you are truly a just right webmaster. The site loading speed is incredible. It kind of feels that you’re doing any distinctive trick. In addition, The contents are masterwork. you have done a great activity in this matter!
This is such an intriguing post, thank you for sharing it!
This is a comment from Bing using Python.
pelicula mexicana red social hi5 red social the social network en español red social mas usada en mexico
Thanks, I have just been looking for information about this subject for a long time and yours is the best I’ve discovered till now. However, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you certain in regards to the supply?
Post a Comment
Subscribe to email updates.
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
21 UX case studies to learn from in 2024

UX case studies are the heart of your design portfolio. They offer a peek into your design process, showcasing how you tackle challenges, your methods, and your results. For recruiters, these case studies serve as a metric for evaluating your skills, problem-solving abilities, and talent.

If you’re considering creating your own UX case study in 2024 but don’t know where to start, you’re in the right place. This article aims to inspire you with 21 carefully hand-picked UX case study examples, each offering valuable lessons.
But before we dive into these examples, let’s address a question that might be lingering: Is a UX case study truly worth the effort?
Is it worth creating a UX case study?
The short answer is yes.
Remember how in math class, showing your workings was even more important than getting the correct answer? UX case studies are like that for designers. They are more than just showcasing the final product (the polished website or app); they detail the steps taken to get there (the research, user testing, and design iterations). By showing your design process, you give potential employers or clients a peek into your thought process and problem-solving skills.
A well-laid-out case study has many benefits, including the following:
Building credibility
As case studies provide evidence of your expertise and past successes, they can build credibility and trust with potential employers or clients.
Educational value
By showing your design process, you provide valuable insights and learnings for other designers and stakeholders.
Differentiation
A compelling case study can leave a lasting impression on potential recruiters and clients, helping you stand out.
Iterative improvement
A case study is like a roadmap of each project, detailing the highs, lows, failures, and successes. This information allows you to identify areas for improvement, learn from mistakes, and refine your approach in subsequent projects.
Now that you know why a stand-out case study is so important, let’s look at 21 examples to help you get creative. The case studies will fall under five categories:
- Language learning app
- Learning app
- Travel agency app
- Intelly healthcare app
- Cox Automotive
- Swiftwash laundry
- Wayfaro trip planner
- New York Times app redesign
- Disney+ app redesign
- Fitbit redesign
- Ryanair app redesign
- Forbes app redesign
- Enhancing virtual teaching with Google Meet
- Airbnb’s global check-in tool
- Spotify home shortcuts
- AI-powered spatial banking for Apple Vision Pro
- Sage Express
In this section, we’ll explore case studies that take us through the complete design journey of creating a digital product from scratch.
1. Language learning app
If you’re a designer looking to get your foot in the door, this is one case study you need to check out. It’s so well detailed that it helped this designer land their first role as a UX designer:
Created by Christina Sa, this case study tackles the all-too-common struggle of learning a new language through a mobile app. It takes us through the process of designing a nontraditional learning app that focuses on building a habit by teaching the Korean language using Korean media such as K-pop, K-drama, and K-webtoon.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Key takeaway
This case study shows how a structured design process, user-centered approach, and effective communication can help you stand out. The creator meticulously laid out their design process from the exploratory research phase to the final prototype, even detailing how the case study changed their view on the importance of a design process.
If you’re searching for a comprehensive case study that details every step of the design process, look no further. This one is for you:
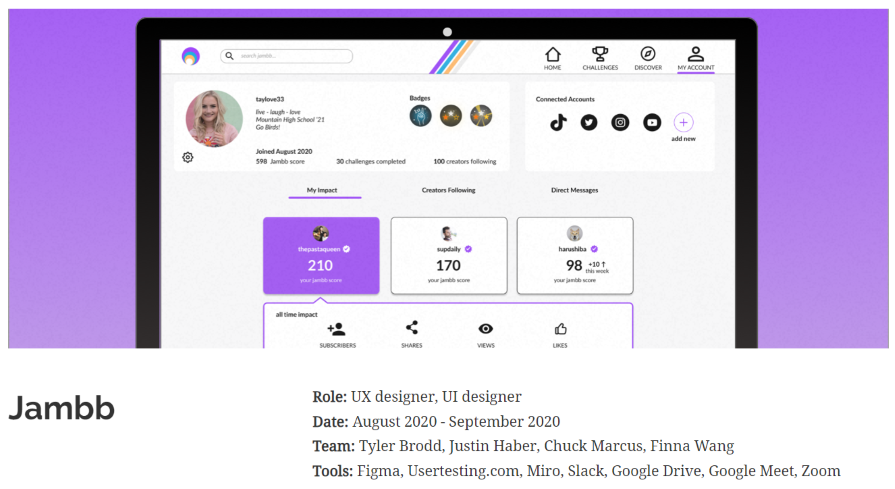
This impressive case study by Finna Wang explores the creation of a fan-focused responsive platform for Jambb, an already existing social platform. The creator starts by identifying the problem and then defines the project scope before diving into the design process.
This case study shows us the importance of an iterative problem-solving approach. It identifies a problem (pre-problem statement), creates a solution, tests the solution, and then revises the problem statement based on the new findings.
3. Learning app
If you need a highly visual case study that takes you through every step of the design process in an engaging way, this one is for you:
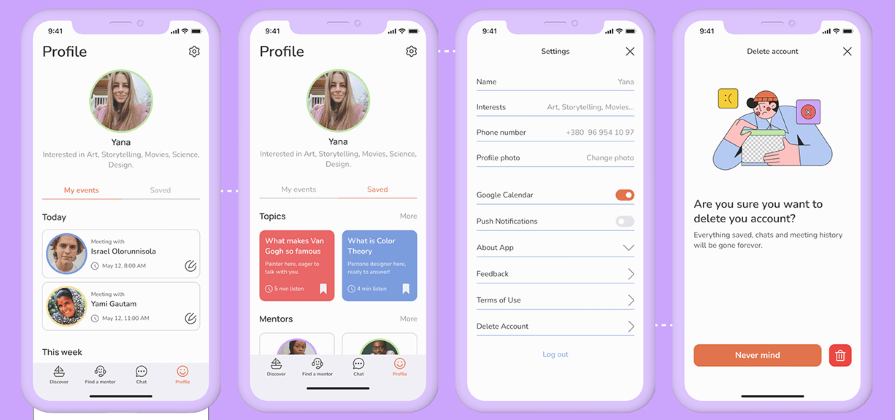
This case study walks us through the design of a platform where users can find experts to explain complex topics to them in a simple and friendly manner. It starts by defining the scope of work, then progresses through research, user journeys, information architecture, user flow, initial design, and user testing, before presenting the final solution.
This case study demonstrates effective ways to keep readers engaged while taking them through the steps of a design process. By incorporating illustrations and data visualization, the designer communicates complex information in an engaging manner, without boring the readers.
If you’re in search of a case study that details the design process but is also visually appealing, you should give this one a look:
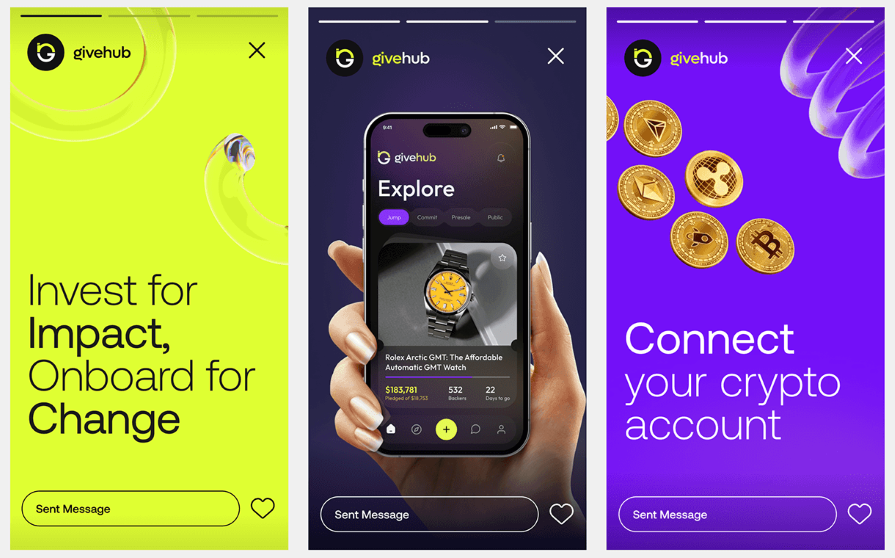
This case study by Orbix Studio takes us through the process of designing GiveHub, a fundraising app that helps users set up campaigns for causes they’re passionate about. It starts with an overview of the design process, then moves on to identifying the challenges and proposing solutions, before showing us how the solutions are brought to life.
This case study illustrates how a visually engaging design and clear organization can make your presentation easy to grasp.
5. Travel agency app
This case study is quite popular on Behance, and it’s easy to see why:
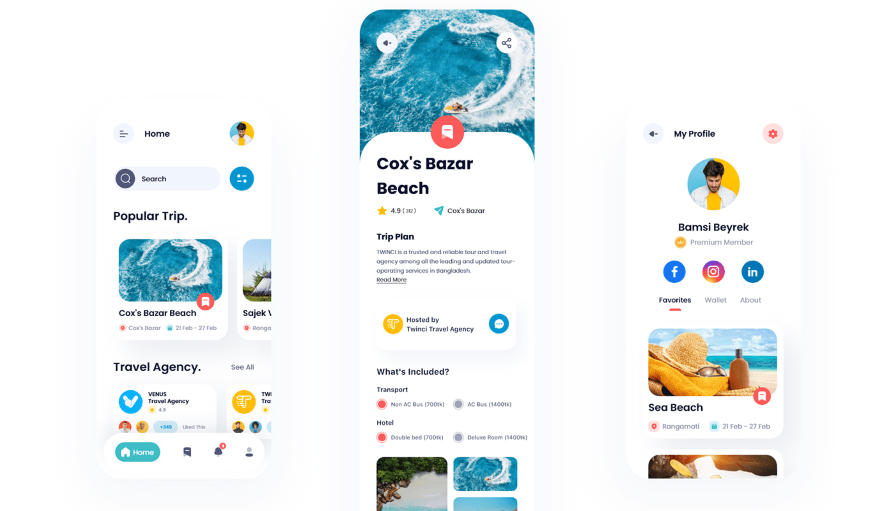
The case study takes us through the process of creating a travel app that lets users compare travel packages from various travel agencies or groups. The creators set out a clear problem statement, propose a solution, and then show us the step-by-step implementation process. The incorporation of data visualization tools makes this case study easy to digest.
This is another case study that shows the importance of using a clearly defined design process. Going by its popularity on Behance, you can tell that the step-by-step process breakdown was well worth the effort.
6. Intelly healthcare app
If you’re looking for a UX case study that explores the design journey for both mobile and desktop versions of an app, this is one you should check out:
This case study explores the process of creating Intelly, an app that transforms patient care with telemedicine, prescription management, and real-time tracking. The case study begins with a clear design goal, followed by a layout of existing problems and design opportunities. The final design is a mobile app for patients and a desktop app for doctors.
This case study highlights the importance of proactive problem-solving and creative thinking in the design process. The creators laid out some key problems, identified design opportunities in them, and effectively leveraged them to create an app.
7. Cox Automotive
If you prefer a results-oriented case study, you’ll love this one:

This case study delves into how Cox Automotive’s Manheim division, used LogRocket to optimize their customers’ digital experience for remote car auctions. It starts by highlighting the three key outcomes before giving us an executive summary of the case study. The rest of the case study takes us through the process of achieving the highlighted outcomes.
A key takeaway from this case study is the significance of using user data and feedback to enhance the digital experience continuously. Cox Automotive used LogRocket to identify and address user-reported issues, gain insights into customer behaviors, and make data-driven decisions to optimize their product.
These case studies are more focused on the visual aspects of the design process, teaching us a thing or two about presentation and delivery.
If you love a case study that scores high on aesthetics with vivid colors, cool illustrations, and fun animations, you need to check this one out:
This case study takes us on a visual journey of creating Rebank, a digital product aimed at revolutionizing the baking industry. It starts with the research process, moves on to branding and style, and then takes us through the different screens, explaining what each one offers.
This case study illustrates the value of thinking outside the box. Breaking away from the conventional design style of financial products makes it a stand-out case study.
9. Swiftwash Laundry
If you’re looking for a case study that prioritizes aesthetics and visual appeal, you should check this one out:

This case study by Orbix Studio gives us a peek into how they created Swiftwash, a laundry service app. It takes us through the steps involved in creating an intuitive, user-friendly, and visually appealing interface.
If there’s one thing to take away from this case study, it’s the value of presenting information in a straightforward manner. Besides being easy on the eye, this case study is also easy to digest. The creators lay out the problem and detail the steps taken to achieve a solution, in an easy-to-follow way, while maintaining a high visual appeal.
10. Wayfaro trip planner
If you’re looking for a concise case study with clean visuals, you should definitely check this one out:
This Behance case study takes us through the design of Wayfaro, a trip planner app that allows users to plan their itineraries for upcoming journeys. The creators dive straight into the visual design process, showing us aspects such as branding and user flow, and explaining the various features on each screen.
This case study shows us the power of an attractive presentation. Not only is the mobile app design visually appealing, but the design process is presented in a sleek and stylish manner.
App redesign
These case studies delve into the redesign of existing apps, offering valuable insights into presentation techniques and problem-solving approaches.
11. New York Times app redesign
If you’re looking for an app redesign case study that’s impactful yet concise, this one is for you:
This study details the creation of “Timely,” a design feature to address issues with the NYT app such as irrelevant content, low usage, and undesirable coverage. It takes us through the process of identifying the problem, understanding audience needs, creating wireframes, and prototyping.
This case study shows us that you don’t always need to overhaul the existing app when redesigning. It suggests a solution that fits into the current information setup, adding custom graphics to the mobile app. Starting with a simple problem statement, it proposes a solution to address the app’s issues without changing what customers already enjoy.
12. Disney+ app redesign
If you’re looking for an engaging case study that’s light on information, you should check out this one:

This case study by Andre Carioca dives right into giving the user interface a little facelift to make it more fun and engaging. By employing compelling storytelling and appealing visuals, the creator crafts a narrative that’s a delight to read.
Given how popular this case study is on Behance, you can tell that the designer did something right. It shows how injecting a little playfulness can elevate your case study and make it more delightful.
13. Fitbit redesign
If you want an in-depth case study that doesn’t bore you to sleep, this one is for you:
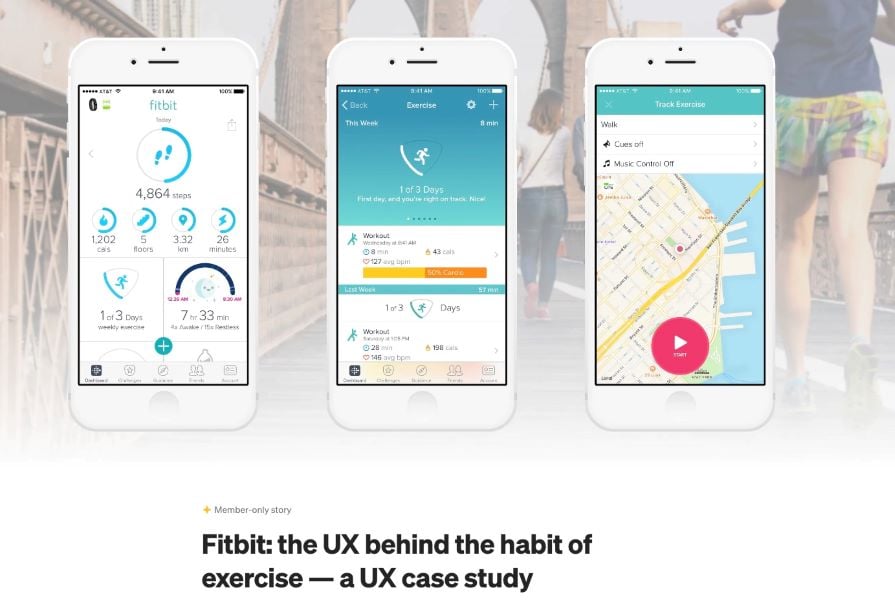
This case study by Stacey Wang takes us through the process of redesigning Fitbit, a wearable fitness tracker. The creator starts by understanding personas and what users expect from a fitness tracker.
Next was the development of use cases and personas. Through a series of guerrilla tests, they were able to identify user pain points. The redesign was centered around addressing these pain points.
This case study highlights the importance of clear organization and strong visual communication. The creator goes in-depth into the intricacies of redesigning the Fitbit app, highlighting every step, without boring the readers.
14. Ryanair app redesign
If you’re bored of the usual static case studies and need something more interactive, this app redesign is what you’re looking for:
This case study takes us through the process of giving the Ryanair app a fresh look. Besides the clean aesthetics and straightforward presentation, the incorporation of playful language and interactive elements makes this case study captivating.
This case study shows how adding a bit of interactivity to your presentation can elevate your work.
15. Forbes app redesign
This case study starts by explaining why the redesign was needed and dives deep into analyzing the current app. The creator then takes us through the research and ideation phases and shares their proposed solution. After testing the solution, they made iterations based on the results.
When it comes to redesigning an existing product, it’s a good idea to make a strong case for why the redesign was needed in the first place.
UX research
These case studies are centered around UX research, highlighting key research insights to enhance your design process.
16. Enhancing virtual teaching with Google Meet
This case study by Amanda Rosenburg, Head of User Experience Research, Google Classroom shows us how listening to user feedback can help make our products more useful and inclusive to users.

To improve the virtual teaching experience on Google Meet, the team spent a lot of time getting feedback from teachers. They then incorporated this feedback into the product design, resulting in new functionality like attendance taking, hand raising, waiting rooms, and polls. Not only did these new features improve the user experience for teachers and students, but they also created a better user experience for all Google Meet users.
When there isn’t room for extensive user research and you need to make quick improvements to the user experience, it’s best to go straight to your users for feedback.
17. Airbnb’s global check-in tool
This case study by Vibha Bamba, Design Lead on Airbnb’s Host Success team, shows us how observing user behaviors inspired the creation of a global check-in tool:
By observing interactions between guests and hosts, the Airbnb team discovered a design opportunity. This led to the creation of visual check-in guides for Airbnb guests, which they can access both offline and online.
There’s a lot to be learned from observing user behavior. Don’t limit yourself to insights obtained from periodic research. Instead, observe how people interact with your product in their daily lives. The insights obtained from such observations can help unlock ingenious design opportunities.
18. Spotify Home Shortcuts
This case study by Nhi Ngo, a Senior User Researcher at Spotify shows us the importance of a human perspective in a data-driven world:
When the Spotify team set out to develop and launch the ML-powered Shortcuts feature on the home tab, they hit a brick wall with the naming. A/B tests came back inconclusive. In the end, they had to go with the product designer’s suggestion of giving the feature a name that would create a more human and personal experience for users.
This led to the creation of a humanistic product feature that evoked joy in Spotify’s users and led to the incorporation of more time-based features in the model, making the content more time-sensitive for users.
Although data-driven research is powerful, it doesn’t hold all the answers. So in your quest to uncover answers through research, never lose sight of the all-important human perspective.
Artificial intelligence
The following case studies are centered around the design of AI-powered products.
19. AI-powered spatial banking for Apple Vision Pro
If you want to be wowed by a futuristic case study that merges artificial intelligence with spatial banking, you should check this out:
In this revolutionary case study, UXDA designers offer a sneak peek into the future with a banking experience powered by AI. They unveil their vision of AI-powered spatial banking on the visionOS platform, showcasing its features and their AI use cases.
This case study shows us the importance of pushing boundaries to create innovative experiences that cater to user needs and preferences.

20. Sage Express
If what you need is an AI case study that isn’t information-dense, this one is for you:
This case study by Arounda takes us through the design of Sage Express, an AI-powered data discovery tool that automatically extracts patterns, tendencies, and insights from data. It outlines the challenge, proposes a solution, and details the journey of bringing the proposed solution to life. But it doesn’t stop there: it also shows the actual results of the design using tangible metrics.
This case study underscores the importance of showing your outcomes in tangible form. You’ve worked hard on a project, but what were the actual results?
If you’re looking for a clean and well-structured AI case study, this will be helpful:
This case study takes us through the process of creating Delfi, an AI-driven banking financial report system. It details the entire design process from onboarding to prototype creation.
If there’s one thing to learn from this case study, it’s how a well-structured presentation can simplify complex information. Although the case study is heavy on financial data, the organized layout not only enhances visual appeal but also aids comprehension.
This article has shown you 21 powerful case study examples across various niches, each providing valuable insights into the design process. These case studies demonstrate the importance of showcasing the design journey, not just the final polished product.
When creating your own case study, remember to walk your users through the design process, the challenges you faced, and your solutions. This gives potential recruiters and clients a glimpse of your creativity and problem-solving skills.
And finally, don’t forget to add that human touch. Let your personality shine through and don’t be afraid to inject a little playfulness and storytelling where appropriate. By doing so, you can craft a case study that leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Header image source: IconScout
LogRocket : Analytics that give you UX insights without the need for interviews
LogRocket lets you replay users' product experiences to visualize struggle, see issues affecting adoption, and combine qualitative and quantitative data so you can create amazing digital experiences.
See how design choices, interactions, and issues affect your users — get a demo of LogRocket today .
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Service design in action: Creating memorable experiences for small businesses
Service design can help our organizations innovate customer experience and build brand loyalty — and it’s great for small businesses.

Combating addictive design is the UX challenge of 2024
Digital addiction is bad for your mental and physical health. Learn what trends encourage this concerning behavior and how to avoid it.
What is DesignOps? The essentials of DesignOps
DesignOps is a set of best practices and principles that aims to streamline the effectiveness of design teams.

Using Zeplin for design handoff: How does it compare to Figma Dev Mode?
Let’s compare Zeplin with Figma Dev Mode to find out which suits design handoff better for your software product team!

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Top Articles
- Experiences
- Embracing Neurodiversity in UX Design: Crafting Inclusive Digital Environments
For many neurodiverse individuals, navigating digital spaces can be a challenging or even an overwhelming experience.
Therefore, UX designers must prioritize creating inclusive digital environments that cater to the diverse cognitive needs of all users. Embracing neurodiversity in UX design can help us unlock a world of possibilities, in which everyone can access and engage with digital products seamlessly, regardless of their neurological differences.
In this article, we’ll explore the significance of neurodiversity in UX design and take a look at practical strategies for UX designers to create digital products that accommodate a wide range of cognitive experiences.
Understanding Neurodiversity in Relation to Technology
Neurodiversity refers to natural , including conditions such as adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, dyslexia, and others. These unique brain-wiring patterns can influence variations in human cognition , including conditions such as autism, adult attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), dyslexia, and others. These unique brain-wiring patterns can influence how people perceive, process, and interact with digital user interfaces.
Neurodiverse individuals often face barriers when interacting with technology such as sensory overload, difficulty processing complex information, or challenges with navigation and focus.
These barriers can lead to frustration, exclusion, and a diminished user experience. However, by understanding the principles of neuro-inclusive design and implementing design best practices, UX designers have the power to break down these barriers and create digital spaces that are truly inclusive and accessible.
Respecting neurodiversity also means conveying the necessary information and creating a relaxing, soothing user experience, especially when the user is making payments or performing other tasks that require the user’s full attention. As another example, we must share information in ways that every visitor can easily understand. Plus, if you have PCI-compliant hosting , you can share personalized information, explaining why it’s significant while considering different cognitive abilities. Everyone appreciates learning about their online experiences.
What Is the Difference Between Neurodiverse and Neurotypical?
The terms neurodiverse and neurotypical refer to differences in the wiring of people’s brains and how they process information . Understanding the distinctions between these two terms is essential in embracing neurodiversity in UX design. Let’s consider some key differences, as follows:
- cognitive processing —Neurodiverse individuals might have unique strengths , challenges, and ways of processing information in comparison to neurotypical individuals. For example, some people might excel in pattern recognition or attention to detail, while others might struggle with social cues or sensory processing.
- sensory experiences —Neurodiverse individuals might have heightened or diminished sensory experiences , which can impact how they perceive and respond to stimuli such as sounds, colors, textures, or patterns.
- communication and social interactions —Neurotypical individuals often follow established social norms and communication patterns, while neurodiverse individuals could have different approaches to social interactions, communication styles, or interpretations of nonverbal cues.
- learning and problem-solving —Neurodiverse individuals might have different learning styles , problem-solving approaches, or ways of organizing and processing information in comparison to neurotypical individuals.
Why Should We Design with Neurodiversity in Mind?
Designing with neurodiversity in mind is essential because it acknowledges and embraces the wide range of human cognitive differences. Without inclusivity in the digital age , even simple actions such as signing up for a Web site can be a problem for a large swath of the neurodiverse group, which according to recent research represents up to 15 to 20% of the worldwide population .
Keeping inclusivity in mind when designing user experiences helps us create digital environments that are accessible , usable, and enjoyable for everyone, not just the neurotypical majority.
This inclusive approach not only improves the user experience for a broader audience but also reflects a commitment to equity and diversity , ensuring that our digital products support all users in engaging with technology effectively and comfortably.
Principles of Neuro-Inclusive Design
Creating digital environments that are truly inclusive for neurodiverse individuals requires a thoughtful and intentional approach: accepting, respecting, and accommodating these neurological differences.
These principles collectively emphasize the importance of empathy , flexibility, and inclusivity in designing digital spaces. Whether for educational environments, workplaces, or public spaces, the focus is on accommodating a diverse range of sensory needs , learning preferences, and ways of interacting with the environment.
Let’s consider three fundamental principles of neuro-inclusive design that should guide our design process.
1. Customizable User Interfaces
One of the core principles of neuro-inclusive design">neuro-inclusive design is offering customizable user interfaces that let users tailor the digital experience to their specific needs and preferences. This includes providing ways of adjusting font sizes, color schemes , and contrast levels, as well as personalized settings for audio, visual, and tactile feedback. Plus, adaptable layouts and navigation options can empower users to navigate digital spaces in ways that align with their cognitive strengths.
2. Thoughtful Color Schemes
Color plays a crucial role in digital design, but it can also pose challenges for neurodiverse individuals. Certain color combinations can cause visual strain, confusion, or even physical discomfort. In contrast, neuro-inclusive design emphasizes the importance of avoiding problematic color pairings and incorporating palettes that are friendly to users with color-deficient vision . Plus, using color effectively for highlighting and emphasis, while minimizing unnecessary distractions can enhance the overall user experience for all.
3. Structured Navigation
A clear, consistent information architecture is essential for neurodiverse users, who might struggle in navigating complex digital environments. On platforms such as a SaaS digital payments solution , it’s necessary to streamline the process and provide brief but informative instructions . With every click you require the user to perform, you’re decreasing the inclusivity of your platform.
Neuro-inclusive design principles prioritize the creation of easy-to-learn, predictable navigation patterns, while minimizing cognitive load through techniques such as chunking and progressive disclosure . By providing structured, logical workflows, designers can reduce the mental effort that navigating digital spaces requires, making the experience more enjoyable and accessible for all users.
Winning Strategies for Inclusive Design
Adhering to inclusive-design best practices is crucial for UX designers whose aim is to create truly neuro-inclusive digital experiences. These best practices ensure the effective implementation of the principles of neuro-inclusive design and result in accessible and enjoyable products for all users, including those who are neurodiverse. Now, let’s explore some essential neuro-inclusive design best practices, as follows:
- user research and testing with neurodiverse participants —Involving neurodiverse individuals throughout the design process is vital. Conducting user research and usability testing with participants who represent a range of neurocognitive profiles provides invaluable insights into their unique needs, challenges, and preferences.
- implementing accessible design principles —A fundamental best practice for neuro-inclusive UX design is adherence to established accessibility guidelines such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). These guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for creating digital experiences that are perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for users with various abilities and disabilities, including those who are neurodiverse.
- clear, concise content that uses plain language —Neurodiverse individuals could experience difficulties processing complex or ambiguous information. Therefore, presenting content in a clear, concise, straightforward manner is crucial, as is using plain language that is easy to understand.
- multiple modalities for input and output —Offering different means of data input and output such as voice, text, and visuals lets digital products accommodate a wider range of cognitive preferences and abilities. This approach lets users interact with digital user interfaces in ways that align with their strengths and preferred modes of communication and information processing. You can even use artificial intelligence (AI) to help users. Data shows that AI is helping businesses increase productivity by up to 40% , making it a great tool for this purpose.
- minimizing distractions and sensory overload —Sensory overload can be a significant barrier for many neurodiverse individuals. Best practices include minimizing distractions such as unnecessary animations, loud sounds, and cluttered user interfaces, and providing options for users to control and adjust sensory elements according to their preferences.
- feedback mechanisms for continuous improvement —Implementing feedback mechanisms such as user surveys or forums or providing dedicated channels for reporting accessibility issues can help UX designers continuously improve their products and services. This continuous feedback loop ensures that our designs remain responsive to the evolving needs and perspectives of neurodiverse users.
The digital world has the potential to become a truly inclusive space in which everyone can access and engage with technology seamlessly, regardless of their cognitive differences.
Embracing neurodiversity in UX design is not just a matter of compliance or meeting legal requirements. It represents a powerful statement of inclusivity and the recognition that cognitive differences are a natural part of the human experience.
No Comments
Join the discussion, magnus eriksen.
Freelance Copywriter and Ecommerce SEO Specialist
New York, New York

Other Articles by Magnus Eriksen
- Designing for Mobile Accessibility: Enhancing the User Experience on Small Screens
- Designing Empathetic Healthcare User Interfaces: Enhancing Usability and Accessibility
- Enhancing User Engagement Through Interactive, Virtual Real-Estate Tours
- 5 Immersive Ecommerce Design Tips to Help Increase Engagement
Other Articles on Accessibility
- Inclusive Digital Experiences: Redesign Strategies for Addressing Diverse Abilities and Accessibility Challenges, Part 1
- Fostering Inclusive Design in Industrial Automation, Part 2
- How to Design an Accessible Web Site for People with Color-Deficient Vision
New on UXmatters
- Designing Our Relationship with AI
- Creating a UX Playbook for Onboarding Users to Your Product
- The Crucial Dance: Enhancing Designer-Developer Collaboration for Exceptional Products
- 15 Essential UX Design Principles and Practices for Developers
Share this article
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: Why People Really Buy Upcycled Products
- Sara Caprioli,
- Christoph Fuchs,
- Bram Van den Bergh

Creativity is more of a selling point than sustainability.
Researchers who analyzed consumer feedback from Etsy discovered that what consumers value most about upcycled products is not their sustainability but their creativity. Their findings offer some guidelines for companies who hope to design and successfully market upcycled products: 1) Designers should consider using components from other industries to enhance the appeal of their products and encourage cross-industry collaboration; 2) Product designers and managers should identify new uses for product components; 3) Marketers should emphasize creativity, as well as sustainability, in their messaging about upcycled products; and 4) Companies can boost the appeal of new products by emphasizing design elements that remind consumers of upcycled products.
Upcycling — the creation of new products by reusing one or more components from ones — is having a moment.
- SC Sara Caprioli is a postdoctoral researcher at the TUM School of Management in Germany. Her work focuses on the effects of creativity and artificial intelligence on human behavior.
- CF Christoph Fuchs is a professor of marketing at the University of Vienna in Austria. His research is situated at the interface of marketing, technology, and human behavior.
- BB Bram Van den Bergh is professor of marketing at the Rotterdam School of Management, Erasmus University Rotterdam. His research focuses on decision making and persuasion.
Partner Center
Skip navigation

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
The picture-superiority effect: harness the power of visuals.

April 26, 2024 2024-04-26
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
You may have heard the popular saying: a picture is worth a thousand words . Pictures can communicate concepts better than words alone, partly because people tend to remember information better when presented visually. This is known as the picture-superiority effect.
In This Article:
What is the picture-superiority effect, why images matter, factors affecting the picture-superiority effect, 3 ways to leverage the picture-superiority effect, should you use images instead of words.
Definition : The picture-superiority effect refers to the fact that people tend to remember pictures better than words.
This phenomenon is well documented in cognitive psychology. One of the most popular theories for why pictures are more memorable than words belongs to the psychologist Allan Paivio. Paivo believed that the picture-superiority effect occurs because any visual is stored in two ways in memory — (1) as an image, and (2) as a word or phrase that describes the image. In contrast, words are stored in only one way — the word itself. While the mind can generate images for words, this process is not automatic and requires significant cognitive effort, making it less common.
Thus, Paivio’s theory says that images are more memorable than words because they have more representation in memory.

Visuals play an important role in UX design. They can illustrate concepts, showcase products, and communicate the company’s brand.
In ecommerce contexts, product images and marketing visuals ensure that users are more likely to remember the product , its value proposition, and the associated brand attributes. They help the company stand out from its competitors. One of our participants in a recent usability study of our consulting pages said,
“I know it seems almost mundane, but those simple things [imagery] help me organize my thoughts [...] it helps me remember you better [...] I found myself being attracted to a particular marketing group because their graphics educated me more than their nomenclature did. I didn't have to read it. I could just visually go through it. [...] So I actually selected them for training.”
Imagery can also help people grasp complex concepts. When people need to remember a complex concept or a process, they often rely on visuals stored in their memory.

UX practitioners can leverage the picture-superiority effect when communicating user-research insights. Visual artifacts, like maps and personas, help team members and stakeholders remember user-research insights. Memorable research findings are more likely to be referenced and used in everyday decision making.
The strength of the picture-superiority effect depends on several factors, including:
- Discoverability: People must discover and look at a visual for it to be memorable. French psychologist Paul Fraisse found that the picture-superiority effect diminishes if people don’t view an image long enough. The longer a person views an image, the more likely they are to remember it.
- Clarity: The more concrete and literal the visual is, the more memorable it will be. The mind can interpret and assign a label to a literal image more easily than to an abstract one. The more abstract the image, the more difficult its interpretation, and the lower its memorability.
- Familiarity : The more familiar a person is with a concept, the easier it will be to comprehend a visual of it and associate a word with it. People with minimal experience with a concept or object may not recognize an image of it and, therefore, will struggle to find a word to assign to it. The image will have lower memorability.
- Uniqueness : The more unique the visual is (relative to other visuals present), the more memorable it will be.

Designers can leverage the picture-superiority effect by making some strategic choices when creating or choosing visuals for their designs.
#1: Place Visuals Where Users Spend Time
To boost discoverability, designers should:
- Place important visuals where users spend time . Analytics can help you identify where and how long people spend on different pages, screens, or web properties. On many websites, the homepage receives the most views. Therefore, it is particularly important to place meaningful visuals on your website’s homepage, if you want to boost the memorability of your products.
- Place high-value, information-carrying visuals above the fold . We know users spend 80% of their time above the page fold on websites. Save visuals that support the brand but don’t carry much information for the area below the fold.
- Ensure that visuals persist to give users the best chance of remembering them. Some websites feature an autoforwarding carousel of images. For example, Garmin’s homepage carousel (pictured below) auto-forwards approximately every four seconds. This risks that users do not have enough time to comprehend (and remember) the visuals.
#2 Choose Literal Images over Abstract Ones
To ensure images are clear and familiar, avoid abstract visuals. Abstract visuals do not depict a recognizable, clear object, and as a result, don’t evoke a clear word when perceived; therefore, they are difficult to remember.

For example, the Adobe Podcast AI product homepage features an illustration highlighting a key feature called Mic Check . However, the illustration is too abstract to comprehend.
In contrast, the ChatGPT homepage (pictured below) features screenshots of the product on mobile and desktop; this illustration makes it easy for users to understand the product capabilities.

#3: Pick Unique Imagery
Images that differ from the imagery around them are more likely to be noticed, processed, and therefore, remembered. In contrast, images that are too similar may be associated with similar words and may be harder to distinguish from each other and recall.
For example, Google uses heavily branded icons for each service in its cloud-based software suite. The visuals for Meet , Chat , Drive , and Calendar are too similar, decreasing the picture-superiority effect.

While uniqueness is important, your images should not be visually jarring. To maintain overall visual cohesion, visuals should use similar color palettes, saturation, or photo crops The Google Drive icons above use the same color palette and saturation; however, the shapes and color placement are nearly identical; as a result, the icons are too similar to be easily distinguishable from each other.
Unique imagery applies not only to your product; your visuals should also be distinct from your competitors’ visuals. When visuals on your competitors’ products are too similar to your own, users may struggle to remember your product.
For example, Nortably.ai uses visuals and visual-design elements that are highly similar to those on Dovetail.com. The result is that both designs (and the corresponding products) are less memorable overall. This is one reason we advise designers not to blindly copy the designs of their competitors .

Some people mistakenly use the picture-superiority effect to justify replacing text with images, such as incorporating icons in a user interface without text labels. However, words still matter! Adding text labels provides redundancy and will strengthen comprehension and memorability. In addition, labels will ensure that your icons will be comprehended correctly and will increase the target size , making it easier for people to click on those icons.
When the picture-superiority effect is effectively leveraged in interface design, users are more likely to leave with a more accurate and positive impression of your website, product, or brand. While visuals can add information and increase memorability, text is still required for good usability and conveying a clear message.
Allan Paivio and Kalman Csapo. 1973. Picture superiority in free recall: Imagery or dual coding? Cognitive Psychology 5, 2 (1973), 176–206.
Joyce M. Oates and Lynne M. Reder. 2010. Memory for pictures: Sometimes a picure is not worth a single word. In Successful Remembering and Successful Forgetting: A Festschrift in Honor of Robert A. Bjork . Psychology Press, 447–462.
Paul Fraisse. 1968. Motor and verbal reaction times to words and drawings. Psychonomic Science 12, 6 (1968), 235–236. DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.3758/bf03331287
Brady, T.F. et al. (2008) Visual long-term memory has a massive storage capacity for object details | proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, PNAS.org . Available at: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.0803390105
Related Courses
The human mind and usability.
Use psychology to predict and explain how your customers think and act
Interaction
Persuasive and Emotional Design
Create delightful experiences that touch, convince, or excite your audience
Visual Design Fundamentals
What every team member needs to know about creating user interfaces using essential principles, techniques, and methods of visual design
Related Topics
- Psychology and UX Psychology and UX
- Visual Design
Learn More:

Why the UX Team Doesn't Get the Credit
Tanner Kohler · 4 min

What is Whitespace?
Kelley Gordon · 3 min

How to Use the Zeigarnik Effect in UX
Feifei Liu · 5 min
Related Articles:
Memory Recognition and Recall in User Interfaces
Raluca Budiu · 8 min
How Chunking Helps Content Processing
Kate Moran · 6 min
Photos as Web Content
Jakob Nielsen · 4 min
Big Pictures on Small Screens: Remove, Resize or Reorganize
Amy Schade · 7 min
Spatial Memory: Why It Matters for UX Design
Page Laubheimer · 9 min
Working Memory and External Memory
Raluca Budiu · 7 min
Our approach
- Responsibility
- Infrastructure
- Try Meta AI
RECOMMENDED READS
- 5 Steps to Getting Started with Llama 2
- The Llama Ecosystem: Past, Present, and Future
- Introducing Code Llama, a state-of-the-art large language model for coding
- Meta and Microsoft Introduce the Next Generation of Llama
- Today, we’re introducing Meta Llama 3, the next generation of our state-of-the-art open source large language model.
- Llama 3 models will soon be available on AWS, Databricks, Google Cloud, Hugging Face, Kaggle, IBM WatsonX, Microsoft Azure, NVIDIA NIM, and Snowflake, and with support from hardware platforms offered by AMD, AWS, Dell, Intel, NVIDIA, and Qualcomm.
- We’re dedicated to developing Llama 3 in a responsible way, and we’re offering various resources to help others use it responsibly as well. This includes introducing new trust and safety tools with Llama Guard 2, Code Shield, and CyberSec Eval 2.
- In the coming months, we expect to introduce new capabilities, longer context windows, additional model sizes, and enhanced performance, and we’ll share the Llama 3 research paper.
- Meta AI, built with Llama 3 technology, is now one of the world’s leading AI assistants that can boost your intelligence and lighten your load—helping you learn, get things done, create content, and connect to make the most out of every moment. You can try Meta AI here .
Today, we’re excited to share the first two models of the next generation of Llama, Meta Llama 3, available for broad use. This release features pretrained and instruction-fine-tuned language models with 8B and 70B parameters that can support a broad range of use cases. This next generation of Llama demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of industry benchmarks and offers new capabilities, including improved reasoning. We believe these are the best open source models of their class, period. In support of our longstanding open approach, we’re putting Llama 3 in the hands of the community. We want to kickstart the next wave of innovation in AI across the stack—from applications to developer tools to evals to inference optimizations and more. We can’t wait to see what you build and look forward to your feedback.
Our goals for Llama 3
With Llama 3, we set out to build the best open models that are on par with the best proprietary models available today. We wanted to address developer feedback to increase the overall helpfulness of Llama 3 and are doing so while continuing to play a leading role on responsible use and deployment of LLMs. We are embracing the open source ethos of releasing early and often to enable the community to get access to these models while they are still in development. The text-based models we are releasing today are the first in the Llama 3 collection of models. Our goal in the near future is to make Llama 3 multilingual and multimodal, have longer context, and continue to improve overall performance across core LLM capabilities such as reasoning and coding.
State-of-the-art performance
Our new 8B and 70B parameter Llama 3 models are a major leap over Llama 2 and establish a new state-of-the-art for LLM models at those scales. Thanks to improvements in pretraining and post-training, our pretrained and instruction-fine-tuned models are the best models existing today at the 8B and 70B parameter scale. Improvements in our post-training procedures substantially reduced false refusal rates, improved alignment, and increased diversity in model responses. We also saw greatly improved capabilities like reasoning, code generation, and instruction following making Llama 3 more steerable.

*Please see evaluation details for setting and parameters with which these evaluations are calculated.
In the development of Llama 3, we looked at model performance on standard benchmarks and also sought to optimize for performance for real-world scenarios. To this end, we developed a new high-quality human evaluation set. This evaluation set contains 1,800 prompts that cover 12 key use cases: asking for advice, brainstorming, classification, closed question answering, coding, creative writing, extraction, inhabiting a character/persona, open question answering, reasoning, rewriting, and summarization. To prevent accidental overfitting of our models on this evaluation set, even our own modeling teams do not have access to it. The chart below shows aggregated results of our human evaluations across of these categories and prompts against Claude Sonnet, Mistral Medium, and GPT-3.5.

Preference rankings by human annotators based on this evaluation set highlight the strong performance of our 70B instruction-following model compared to competing models of comparable size in real-world scenarios.
Our pretrained model also establishes a new state-of-the-art for LLM models at those scales.

To develop a great language model, we believe it’s important to innovate, scale, and optimize for simplicity. We adopted this design philosophy throughout the Llama 3 project with a focus on four key ingredients: the model architecture, the pretraining data, scaling up pretraining, and instruction fine-tuning.
Model architecture
In line with our design philosophy, we opted for a relatively standard decoder-only transformer architecture in Llama 3. Compared to Llama 2, we made several key improvements. Llama 3 uses a tokenizer with a vocabulary of 128K tokens that encodes language much more efficiently, which leads to substantially improved model performance. To improve the inference efficiency of Llama 3 models, we’ve adopted grouped query attention (GQA) across both the 8B and 70B sizes. We trained the models on sequences of 8,192 tokens, using a mask to ensure self-attention does not cross document boundaries.
Training data
To train the best language model, the curation of a large, high-quality training dataset is paramount. In line with our design principles, we invested heavily in pretraining data. Llama 3 is pretrained on over 15T tokens that were all collected from publicly available sources. Our training dataset is seven times larger than that used for Llama 2, and it includes four times more code. To prepare for upcoming multilingual use cases, over 5% of the Llama 3 pretraining dataset consists of high-quality non-English data that covers over 30 languages. However, we do not expect the same level of performance in these languages as in English.
To ensure Llama 3 is trained on data of the highest quality, we developed a series of data-filtering pipelines. These pipelines include using heuristic filters, NSFW filters, semantic deduplication approaches, and text classifiers to predict data quality. We found that previous generations of Llama are surprisingly good at identifying high-quality data, hence we used Llama 2 to generate the training data for the text-quality classifiers that are powering Llama 3.
We also performed extensive experiments to evaluate the best ways of mixing data from different sources in our final pretraining dataset. These experiments enabled us to select a data mix that ensures that Llama 3 performs well across use cases including trivia questions, STEM, coding, historical knowledge, etc.
Scaling up pretraining
To effectively leverage our pretraining data in Llama 3 models, we put substantial effort into scaling up pretraining. Specifically, we have developed a series of detailed scaling laws for downstream benchmark evaluations. These scaling laws enable us to select an optimal data mix and to make informed decisions on how to best use our training compute. Importantly, scaling laws allow us to predict the performance of our largest models on key tasks (for example, code generation as evaluated on the HumanEval benchmark—see above) before we actually train the models. This helps us ensure strong performance of our final models across a variety of use cases and capabilities.
We made several new observations on scaling behavior during the development of Llama 3. For example, while the Chinchilla-optimal amount of training compute for an 8B parameter model corresponds to ~200B tokens, we found that model performance continues to improve even after the model is trained on two orders of magnitude more data. Both our 8B and 70B parameter models continued to improve log-linearly after we trained them on up to 15T tokens. Larger models can match the performance of these smaller models with less training compute, but smaller models are generally preferred because they are much more efficient during inference.
To train our largest Llama 3 models, we combined three types of parallelization: data parallelization, model parallelization, and pipeline parallelization. Our most efficient implementation achieves a compute utilization of over 400 TFLOPS per GPU when trained on 16K GPUs simultaneously. We performed training runs on two custom-built 24K GPU clusters . To maximize GPU uptime, we developed an advanced new training stack that automates error detection, handling, and maintenance. We also greatly improved our hardware reliability and detection mechanisms for silent data corruption, and we developed new scalable storage systems that reduce overheads of checkpointing and rollback. Those improvements resulted in an overall effective training time of more than 95%. Combined, these improvements increased the efficiency of Llama 3 training by ~three times compared to Llama 2.
Instruction fine-tuning
To fully unlock the potential of our pretrained models in chat use cases, we innovated on our approach to instruction-tuning as well. Our approach to post-training is a combination of supervised fine-tuning (SFT), rejection sampling, proximal policy optimization (PPO), and direct preference optimization (DPO). The quality of the prompts that are used in SFT and the preference rankings that are used in PPO and DPO has an outsized influence on the performance of aligned models. Some of our biggest improvements in model quality came from carefully curating this data and performing multiple rounds of quality assurance on annotations provided by human annotators.
Learning from preference rankings via PPO and DPO also greatly improved the performance of Llama 3 on reasoning and coding tasks. We found that if you ask a model a reasoning question that it struggles to answer, the model will sometimes produce the right reasoning trace: The model knows how to produce the right answer, but it does not know how to select it. Training on preference rankings enables the model to learn how to select it.
Building with Llama 3
Our vision is to enable developers to customize Llama 3 to support relevant use cases and to make it easier to adopt best practices and improve the open ecosystem. With this release, we’re providing new trust and safety tools including updated components with both Llama Guard 2 and Cybersec Eval 2, and the introduction of Code Shield—an inference time guardrail for filtering insecure code produced by LLMs.
We’ve also co-developed Llama 3 with torchtune , the new PyTorch-native library for easily authoring, fine-tuning, and experimenting with LLMs. torchtune provides memory efficient and hackable training recipes written entirely in PyTorch. The library is integrated with popular platforms such as Hugging Face, Weights & Biases, and EleutherAI and even supports Executorch for enabling efficient inference to be run on a wide variety of mobile and edge devices. For everything from prompt engineering to using Llama 3 with LangChain we have a comprehensive getting started guide and takes you from downloading Llama 3 all the way to deployment at scale within your generative AI application.
A system-level approach to responsibility
We have designed Llama 3 models to be maximally helpful while ensuring an industry leading approach to responsibly deploying them. To achieve this, we have adopted a new, system-level approach to the responsible development and deployment of Llama. We envision Llama models as part of a broader system that puts the developer in the driver’s seat. Llama models will serve as a foundational piece of a system that developers design with their unique end goals in mind.

Instruction fine-tuning also plays a major role in ensuring the safety of our models. Our instruction-fine-tuned models have been red-teamed (tested) for safety through internal and external efforts. Our red teaming approach leverages human experts and automation methods to generate adversarial prompts that try to elicit problematic responses. For instance, we apply comprehensive testing to assess risks of misuse related to Chemical, Biological, Cyber Security, and other risk areas. All of these efforts are iterative and used to inform safety fine-tuning of the models being released. You can read more about our efforts in the model card .
Llama Guard models are meant to be a foundation for prompt and response safety and can easily be fine-tuned to create a new taxonomy depending on application needs. As a starting point, the new Llama Guard 2 uses the recently announced MLCommons taxonomy, in an effort to support the emergence of industry standards in this important area. Additionally, CyberSecEval 2 expands on its predecessor by adding measures of an LLM’s propensity to allow for abuse of its code interpreter, offensive cybersecurity capabilities, and susceptibility to prompt injection attacks (learn more in our technical paper ). Finally, we’re introducing Code Shield which adds support for inference-time filtering of insecure code produced by LLMs. This offers mitigation of risks around insecure code suggestions, code interpreter abuse prevention, and secure command execution.
With the speed at which the generative AI space is moving, we believe an open approach is an important way to bring the ecosystem together and mitigate these potential harms. As part of that, we’re updating our Responsible Use Guide (RUG) that provides a comprehensive guide to responsible development with LLMs. As we outlined in the RUG, we recommend that all inputs and outputs be checked and filtered in accordance with content guidelines appropriate to the application. Additionally, many cloud service providers offer content moderation APIs and other tools for responsible deployment, and we encourage developers to also consider using these options.
Deploying Llama 3 at scale
Llama 3 will soon be available on all major platforms including cloud providers, model API providers, and much more. Llama 3 will be everywhere .
Our benchmarks show the tokenizer offers improved token efficiency, yielding up to 15% fewer tokens compared to Llama 2. Also, Group Query Attention (GQA) now has been added to Llama 3 8B as well. As a result, we observed that despite the model having 1B more parameters compared to Llama 2 7B, the improved tokenizer efficiency and GQA contribute to maintaining the inference efficiency on par with Llama 2 7B.
For examples of how to leverage all of these capabilities, check out Llama Recipes which contains all of our open source code that can be leveraged for everything from fine-tuning to deployment to model evaluation.
What’s next for Llama 3?
The Llama 3 8B and 70B models mark the beginning of what we plan to release for Llama 3. And there’s a lot more to come.
Our largest models are over 400B parameters and, while these models are still training, our team is excited about how they’re trending. Over the coming months, we’ll release multiple models with new capabilities including multimodality, the ability to converse in multiple languages, a much longer context window, and stronger overall capabilities. We will also publish a detailed research paper once we are done training Llama 3.
To give you a sneak preview for where these models are today as they continue training, we thought we could share some snapshots of how our largest LLM model is trending. Please note that this data is based on an early checkpoint of Llama 3 that is still training and these capabilities are not supported as part of the models released today.

We’re committed to the continued growth and development of an open AI ecosystem for releasing our models responsibly. We have long believed that openness leads to better, safer products, faster innovation, and a healthier overall market. This is good for Meta, and it is good for society. We’re taking a community-first approach with Llama 3, and starting today, these models are available on the leading cloud, hosting, and hardware platforms with many more to come.
Try Meta Llama 3 today
We’ve integrated our latest models into Meta AI, which we believe is the world’s leading AI assistant. It’s now built with Llama 3 technology and it’s available in more countries across our apps.
You can use Meta AI on Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, Messenger, and the web to get things done, learn, create, and connect with the things that matter to you. You can read more about the Meta AI experience here .
Visit the Llama 3 website to download the models and reference the Getting Started Guide for the latest list of all available platforms.
You’ll also soon be able to test multimodal Meta AI on our Ray-Ban Meta smart glasses.
As always, we look forward to seeing all the amazing products and experiences you will build with Meta Llama 3.
Our latest updates delivered to your inbox
Subscribe to our newsletter to keep up with Meta AI news, events, research breakthroughs, and more.
Join us in the pursuit of what’s possible with AI.

Product experiences
Foundational models
Latest news
Meta © 2024
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
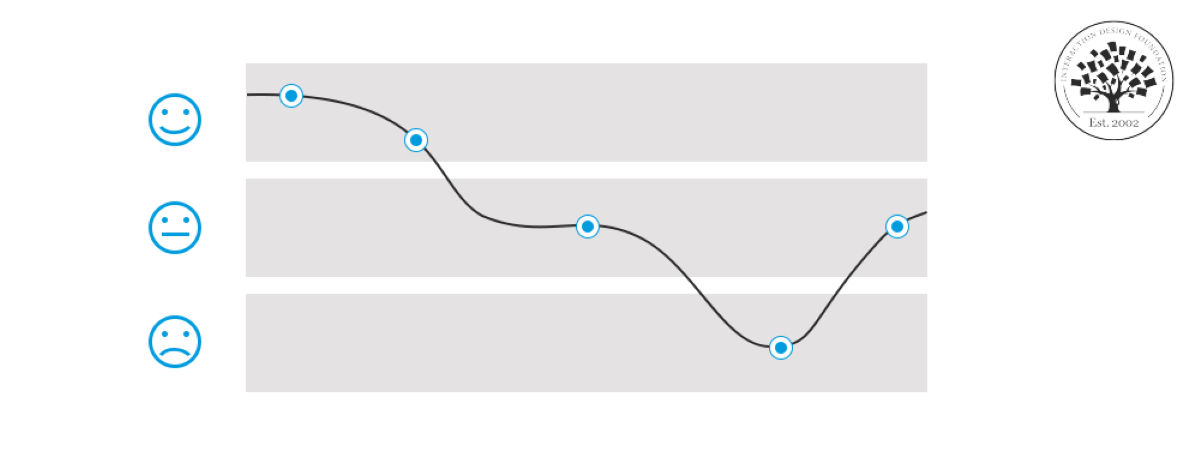

How to Create Effective Journey Maps: Learnings from the IxDF Course
A low conversion rate (below 2%) usually means a website struggles to keep visitors interested. Journey mapping helps identify why visitors leave quickly and tracks every step of a user's interaction with a website. The goal is simple: to create a smooth, enjoyable journey to make users return. Learn the secrets of journey maps with the IxDF course, Journey mapping . This course shows you how to pinpoint improvement areas effectively and how to enhance user satisfaction and loyalty.
Have you ever found yourself lost on a website, unsure where to click next? Frustrating digital experiences make us want to give up and leave. This is why journey mapping is so important. It's a strategic approach in UX design that lays out a user's path through a product or service. When you understand each step a user takes, you can create more intuitive and enjoyable experiences.
In journey mapping, you plot a course to guide users from one point to another. This method reveals the pain points and moments of delight in a user's product interaction. When you smooth out these critical junctures, you can craft solutions that meet and exceed user expectations.
“ Good design is obvious. Great design is transparent.” - Joe Sparano
Journey mapping equips us with the insights needed to refine the user experience and create first encounters with your product, both positive and memorable. Since 94% of first impressions relate to a website's design, it’s critical to make an excellent first impression through a well-mapped user journey. A solid understanding of journey mapping principles can transform a confusing or mediocre user experience into one that’s engaging and seamless.
To create seamless user journeys, you must understand the journey mapping process in detail. Look at the fundamental aspects you should explore to craft better digital experiences.
Journey Mapping: The Essentials
Journey mapping enables teams to visualize the user's experience from initial contact through various interactions to the final goal. Let’s run through the basics.
What is Journey Mapping?
Journey mapping creates a detailed visualization of a user's experience with a product or service. It maps out each step a user takes. It highlights their feelings, motivations and challenges. This process helps you identify pain points and opportunities to enhance the user experience.
Watch Matt Snyder, Head of Product & Design at Hivewire, discuss journey mapping in UX.
- Transcript loading…
Why Journey Mapping Matters
Journey mapping matters because it shows where users face struggles and frustrations. If you understand these issues, you can make your websites or services better. This means happier customers who are more likely to return and recommend the product/service to others.
Consider the process users follow to book a flight online. The user's journey begins with the search for flights. Here, they might encounter their first obstacle: a confusing interface. This moment could lead to frustration. It may push them towards a competitor's website. Journey mapping would reveal this pain point and allow you to simplify the search process.
Next, the user selects a flight. If the site bombards them with too many upsell options, like seat upgrades or extra baggage, it might overwhelm them. A well-designed journey map would highlight this issue. It may suggest a more streamlined and helpful upsell process, not pushy.
Finally, the user reaches the payment section. A complex checkout process with unclear pricing and surprise charges can deter them from completing the purchase. Journey mapping pinpoints this critical moment. You may have to recommend a clearer, more concise checkout flow.
If you map out this journey, your design team can:
Simplify the flight search interface to reduce initial frustration.
Streamline the upsell process to enhance the user experience without overwhelming them.
Revise the checkout process for clarity and ease. You must encourage the completion of the purchase.
Watch this quick video that explains the power of mapping.
How Journey Mapping Improves UX
Journey mapping provides a clear framework to analyze and optimize each touchpoint in the user's journey. It allows you to:
Identify and eliminate barriers that cause frustration or abandonment.
Enhance features that users find valuable.
Design with a holistic understanding of the user's experience.
Journey Mapping Variations
Journey mapping comes in different forms. Each one offers unique insights into the user experience. These variations can help you apply the right approach to your UX challenges. You’ll learn about these variations in detail in our journey mapping course.
Experience Maps
Experience maps are the broadest form of journey maps. They map out the overall human experience in different situations. You can use these maps for more than product or service interactions. Their goal is to get a broad understanding of human behaviors and feelings.
For example, consider mapping the common experience of commuting. This could include various methods like walking or biking to public transport. Experience maps can help you spot common issues and chances for improvement. They prepare you for more detailed studies.
Example of an Experience map for ordering a car through an app. It shows the actions, problems, emotions, quotes and opportunities that relate to the user.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey maps narrow the focus. They focus on how a person interacts with a specific product or service. These maps help us understand a customer's experience with a business.
A customer journey map includes the following elements.
Customer persona : This defines a typical customer. You create a character that represents a part of your customer base.
Phases : Stages of the customer journey. It typically includes Awareness, Research, Consideration, Purchase and Support.
Touchpoints : These are all interaction points between the customer and your brand across different phases. This interaction may happen through marketing materials, digital presence, staff interactions, purchase process and post-purchase follow-up.
Customer thoughts, actions and emotions : Detail what customers think, do and feel at each touchpoint. Use surveys and direct feedback for accuracy.
Opportunities : You list the chances to improve the customer's experience, solve any issues they face and make their journey smoother.
For instance, with a music streaming app like Spotify, a customer journey map would show how a user finds, chooses and uses the app. It would point out their main steps and where they might have problems.
An example of a customer journey map for a music streaming app. It tracks interactions from the initial visit to the response. It also highlights emotions and thoughts at each stage.
© Draft.io, Fair Use
Service Blueprints
Service blueprints build on what we learn from customer journey maps . Unlike journey maps, which focus on the customer's experience, service blueprints give us a peek into how the service works behind the scenes. They show how different parts of the service work together to support the customer's journey.
The anatomy of a service blueprint showing all the key processes in different phases. (described below)
A service blueprint maps out five key areas:
Physical evidence: This is anything the customer can see, touch or interact with, like a website or a product. It includes all the physical parts of the service.
Customer's actions: These are the steps customers take when they use the service. The service needs these actions to meet the customer's needs.
Frontstage: This area is all about what the customer interacts with directly. It's the part of the service the customer sees and uses.
Backstage: These are the parts of the service that happen out of the customer's view. They support the frontstage but remain hidden to the customer.
Supporting actions: These are the behind-the-scenes processes that make sure the service operates smoothly.
The Role of Research in Effective Journey Mapping
You need comprehensive data—both qualitative and quantitative—to create an accurate and useful journey map. This process involves understanding the problems your users face and the potential solutions. Here’s an overview of key steps to collect the necessary information.
Research Problems and Solutions
Identify the problems and opportunities within the user experience. You must look at the issue from two angles: the problem space and the solution space.
In the problem space, you aim to understand the user's challenges, needs and pain points. You typically do this through qualitative user research , such as user observation and interviews. Quantitative methods like surveys can also contribute. You don’t need to consider the existing solutions.
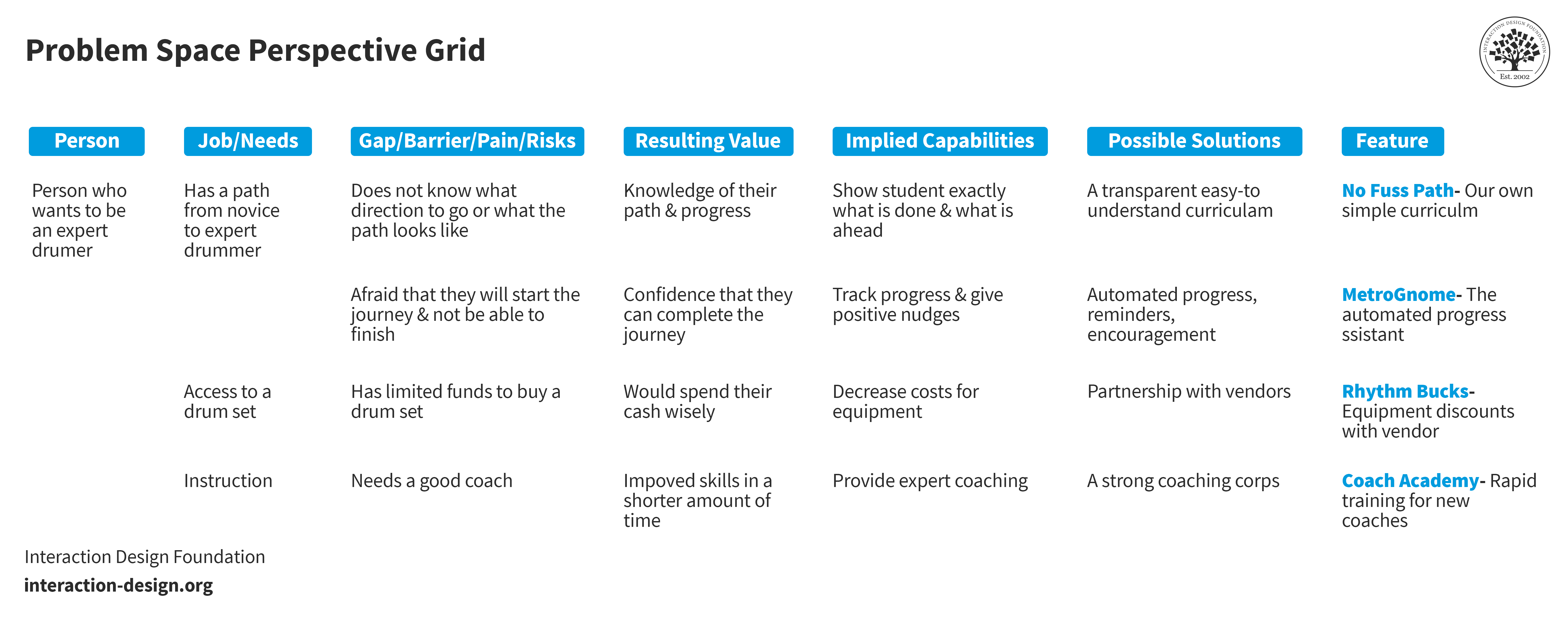
A straightforward perspective grid for a person aiming to become an expert drummer. This individual needs a clear path, access to drums and some instruction.
In the solution space, you ideate potential solutions to problems you identified. This shift requires a creative approach. You aim to explore various ideas that effectively address users’ needs and evaluate those in usability sessions or A/B testing.
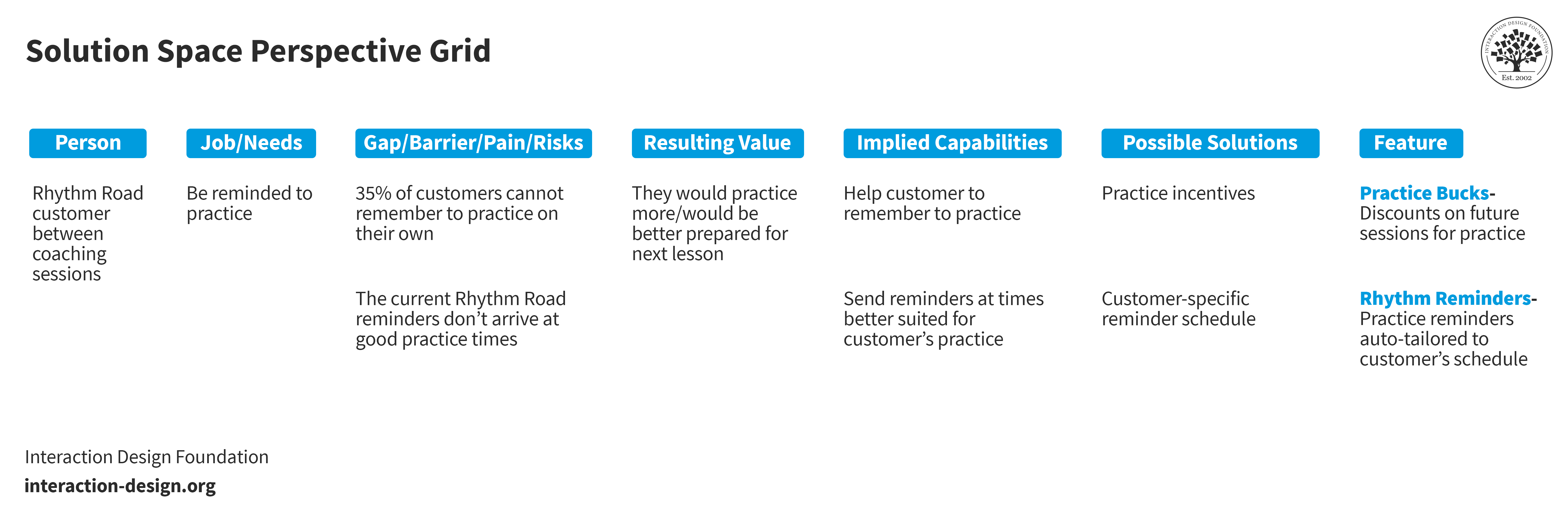
A simple perspective grid for a Rhythm Road customer. This customer is between coaching sessions. They need help from Rhythm Road to remember to practice.
Organize Your Research
A perspective grid helps you organize and synthesize the data collected from your research. You can use it to ensure the remainder of the journey mapping process proceeds smoothly. It allows you to categorize insights based on different user perspectives or personas . This step helps you understand the experiences and expectations of your user base.
To create a perspective grid, list your user personas along one axis and the stages of their journey along the other. Fill in each cell with the Gaps/Barriers/Pain/Risks relevant to that persona at each stage. This visualization helps you identify commonalities and differences across the journey.
How to Create Journey Map Variations
Each journey map variation helps you achieve specific goals. Let's explore how to create experience maps, customer journey maps and service design blueprints.
How to Create an Experience Map
An Experience Map involves a five-step approach.
Plan your experience map : Determine the scope. Decide who needs to participate in the workshop. Consider a cross-disciplinary team for better insights.
Customer research : Gather factual data along with user stories and analytics. This step helps you fill knowledge gaps.
Run the workshop : An all-day event where diverse voices collaborate. You must plan the event for productive outcomes.
Create your experience map : Turn the workshop findings into a visual map. This map should outline general common experiences related to your field.
Use your experience map : Apply what you learned to make decisions and improvements in your organization.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map
Follow these seven steps to map out the detailed interactions users have with your organization:
Define your objectives : Determine what you aim to achieve with the map.
Gather Information : Understand your customers’ behaviors, needs and how they interact with your product.
Identify customer touchpoints : Note how customers interact with your product. Then, understand how these touchpoints affect their experience.
Outline key stages of customer experience : From the customer's perspective, map the sequence of events. Document all events from initial contact to post-purchase support.
Start mapping : Use diagrams or digital tools to visualize the journey. Include touchpoints, emotional responses and any other relevant factors.
Validate your results : Get feedback from customers and internal teams to ensure accuracy.
Analyze your map : Compare it against your goals to see if it meets customer expectations.
How to Create a Service Design Blueprint
Service design focuses on the internal workings of a service. It outlines frontstage and backstage actions. Here’s how to develop a Service Design Blueprint:
Find support : Assemble a cross-disciplinary team and secure stakeholder buy-in.
Define the goal : Set a clear scope and business objective for the blueprint.
Gather research : Unlike customer journey mapping, a blueprint requires more internal research. It includes direct observations and employee interviews.
Map the blueprint : Organize a workshop to determine the five elements encountered throughout the service delivery.
Refine and distribute : Enhance the blueprint with contextual details. Then, distribute it to stakeholders to communicate the internal processes.
The Role of a Journey Mapping Workshop (and How to Do It Right)
The effectiveness of journey mapping hinges on a detailed and well-organized journey mapping workshop. This is when teams work together to understand and improve customer experiences.
Here’s how to navigate the pre-workshop preparation and conduct the workshop.
Before the Journey -Mapping Workshop
Preparation is key. Assemble a diverse team to bring a wide range of views. Prioritize the customer personas and scenarios you'll focus on to maintain a clear focus. Share existing research with all participants to get everyone on the same page. They should understand the journey's context.
Build a Collaborative Team
Journey mapping thrives on collaboration. Include people from various departments to ensure a holistic view of the customer journey. Don’t forget to invite stakeholders who will decide on the final approach. This team will help you create the map and implement its findings.
Prioritize Actors and Scenarios
Focus on specific customer personas and how they interact with your service. It helps you create a more targeted and actionable journey map. If you cover multiple personas or scenarios, plan how to manage this complexity.
Share and Analyze Existing Research
Compile and review all data related to the journey. This may include user experience studies, marketing analysis and customer feedback. Share information before the workshop to help everyone understand the starting point.
Assign Pre-Workshop Tasks
Assign homework to make the participants well-prepared. It includes background reading and key questions related to the journey. This pre-engagement makes the workshop more effective.
During the Journey-Mapping Workshop
The workshop should be an active and engaging process. It starts with building a basic understanding. Then, you map the customer's experience and brainstorm ways to improve it.
Establish the Foundation
You bring everyone on the same page to begin. Everyone should understand journey mapping principles, existing research and input methods. Use engaging activities like trivia to refresh key concepts and energize the group.
Map the Current State
The team would create an assumption-based map of the current journey. This should reflect the team’s collective understanding. Offer attendees a template to identify pain points with ease:
" requires ______ to achieve ______."
" requires ______, allowing them to ______."
For instance: "Bob requires an easier method to compare choices, allowing him to avoid feeling swamped."
Note : It’s important to avoid using the first person , like "As a I want...". This format can be repetitive and time-consuming in documents full of user stories. It also shifts important information into sentences that make them harder to scan and understand. More importantly, you must not assume the user's perspective as that can lead developers to project their own experiences and biases onto users.
Make the map open to revisions. Use customer interviews for this phase to validate assumptions and gain fresh insights.
Vision the Future State
Use the identified pain points to brainstorm ideas to improve the customer journey. Encourage teams to think big and use metaphors in their ideas. This prevents them from focusing too early on specific solutions, like features. Sketch and critique potential future interactions to translate these ideas into tangible designs.
You need the positive aspects on green sticky notes. You can mark areas for improvement on yellow ones. The critiques help refine the ideas.
Now, merge the best elements from these individual sketches into a unified future-state flow. You can then share this consolidated journey with the whole workshop team. It will help you paint a picture of what the improved customer experience could look like.
After the Journey -Mapping Workshop
The work doesn’t end when the workshop does. Quickly share the outcomes and next steps to maintain momentum. Further test and refine the ideas generated during the workshop. It’ll bring meaningful changes to the customer journey.
Share Workshop Insights
Document and distribute the workshop's findings to all participants and stakeholders. This includes:
The journey maps created
Identified pain points
Future state designs
Keep everyone informed for continued engagement and support in implementing changes.
Bring Ideas to Life
Translate the workshop's conceptual ideas into prototypes for user testing . This iterative design and feedback process helps refine the solutions into actionable improvements to the customer journey.
Continuously Refine the Process
With each workshop, gather feedback on what worked and what didn’t to improve future sessions. This continuous improvement ensures that journey mapping remains a productive and insightful tool for your organization.
This might seem like a lot, but if you want to learn about how to set up workshops, the journey mapping course can help you. You’ll learn how to:
Increase understanding
Create visions
Guide evaluations
Plan experiments
Build a workshop plan
About the Journey Mapping Course
Journey mapping is a 7-week course that will help you solve complex design problems with simple, user-friendly solutions. You’ll learn the right journey-mapping process for your goals and master data collection and analysis with a perspective grid. Create key journey maps: experience maps, customer journey maps and service blueprints. Gain skills to run a journey mapping workshop and turn insights into real solutions.
This course will help you if you want to design smooth shopping experiences, easy signup flows or engaging apps. Start with journey mapping basics. Understand its power and role in UX design. Learn to identify, read and use various journey maps. Gain data gathering and analysis skills. Then, finish with the ability to create journey maps and lead workshops.
Make sure to benefit from practical techniques and downloadable templates. Participate in three hands-on exercises in the " Build Your Portfolio: Journey Mapping Project. " These activities solidify your learning. They also offer an option to create a case study for your portfolio.
Learn from four industry experts:
Indi Young , founder of Adaptive Path, brings her deep understanding of data gathering in journey mapping. She wrote two books, Practical Empathy and Mental Models .
Kai Wang shares insights from his experiences at CarMax and CapitalOne. She emphasizes journey mapping's organizational impact.
Head of Product & Design at Hivewire , Matt Snyder, presents journey mapping as an effective product development tool. He teaches the application of a perspective grid for smoother data-rich processes.
Christian Briggs , Senior Product Designer and Design Educator, guides you through this course with his extensive experience in digital product design and journey mapping.
This course caters to budding and intermediate designers eager to refine complex user experiences. It's ideal for:
Aspiring UX/ UI designers seeking foundational design skills.
Junior to mid-level designers aiming for advanced challenges and strategic team roles.
Product managers focused on crafting intricate experiences.
Join a global design community that shares knowledge. Collaborate, learn and grow with peers to enhance your design skills and career prospects.
Course Overview
Weekly lessons : We release each week with no deadlines.
Learning time : Approximately 9 hours and 54 minutes over the span of 7 weeks.
Where to Learn More
Enrollment for the Journey Mapping course is now open. It’s included in an IxDF membership.
To become a member, sign up here .
Read our article Customer Journey Maps — Walking a Mile in Your Customer’s Shoes .
Learn more about website conversion rates .
Read web design statistics from WebFX .
Journey Mapping

Get Weekly Design Insights
What you should read next, master mobile experiences: 5 key discoveries from the ixdf course.
Interaction Design Foundation Reviews: Answers to frequently asked questions by members
- 2 weeks ago
10 UI Designer Portfolio Examples

What Tech Job is Right for Me? A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating Your Career Path

- 3 weeks ago
How to Succeed as a Designer on Agile Teams: Embrace Imperfection
Your Guide to Hamburger Menus
How to Design with AI: 5 Insights from the IxDF Course
Tree Testing: A Complete Guide
The Role of Micro-interactions in Modern UX

How to Design UI Forms in 2024: Your Best Guide
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Get weekly UX articles, videos, and upcoming training events straight to your inbox. Research-based articles about user experience (UX), interaction design, web usability, user testing, and UI/GUI design by Nielsen Norman Group authors, including Jakob Nielsen, Don Norman, Bruce 'Tog' Tognazzini, and other group members.
The following user-experience articles published in 2021 were the ones our audience read the most: The 6 Levels of UX Maturity Our UX-maturity model has 6 stages that cover processes, design, research, leadership support, and longevity of UX. Use our quiz to get an idea of your organization's UX maturity. Mapping User Stories in Agile
UX (user experience) research is the systematic study of target users and their requirements, to add realistic contexts and insights to design processes. UX researchers adopt various methods to uncover problems and design opportunities. Doing so, they reveal valuable information which can be fed into the design process.
Journal of User Experience (JUX) is a peer-reviewed, international, online publication dedicated to promoting and enhancing the practice, research, and education of user experience (UX) design and evaluation.The journal aims to provide UX practitioners and researchers with a forum to share:Empirical findings and case studies Emerging methods and tools from within the user experience profession ...
📃 Articles. Improve your UX Research process with our curated short reads on the best UX Research practices.
With new articles published regularly, UX Daily is the world's largest online resource on UX Design by the Interaction Design Foundation. ... In 9 chapters, we'll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more! Download free ebook Go. A valid email address is ...
A Guide to Using User-Experience Research Methods. Kelley Gordon and Christian Rohrer. August 21, 2022. Summary: Modern day UX research methods answer a wide range of questions. To help you know when to use which user research method, each of 20 methods is mapped across 3 dimensions and over time within a typical product-development process.
The article highlights the author's realization of the parallels between physical product design, particularly in the creation of soft toys, and UX/UI design, showcasing how principles like research, prototyping, teamwork, and empathy are fundamental to both domains.
UX research includes two main types: quantitative (statistical data) and qualitative (insights that can be observed but not computed), done through observation techniques, task analysis, and other feedback methodologies. The UX research methods used depend on the type of site, system, or app being developed.
What is UX Research? Usually the first stage of a design sprint, UX Research focusses on asking questions using a variety investigative techniques to deliver actionable insights which the team can then use to design a solution. While it may sound academic, UX research as Ben Ralph says is "less of being a scientist and more of being a detective ...
2. Senior Designer Bundle: Become a design leader with systems to help you build a meaningful career & grow your designers. Join 500+ aspiring leaders. 3. UX Portfolio Critique: Get a 20-minute video review of your portfolio. A checklist of actionable things to fix, in less than 48 hours. Get a personalised portfolio critique here. 4.
In this article, we'll introduce time-tested UX research methods that inspire user empathy and ultimately lead to better user experiences. UX Research Types: A Bird's-Eye View. Before diving in, we need to step way back and take a broad look at the different types of UX research. Doing so will provide context to the more specific methods ...
What all user research has in common is that it helps place people at the center of your design process and your products. You use user research to inspire your design, to evaluate your solutions, and to measure your impact. User research (and other kinds of research) is often divided into quantitative and qualitative methods.
Overall, research informs our work, improves our understanding, and make our work better. In this Complete Beginner's Guide, we'll look at the many elements of design research, from interviews and observations, to usability testing and A/B testing. Readers will get a head start on how to use these design research techniques in their work ...
The article examines how UX research studies can fail due to issues in design, analysis, and generalization, using case studies to highlight each category's importance in maintaining research integrity and relevance. Share on twitter Share on linkedin. Share on facebook. Share on reddit ...
The field of user experience has a wide range of research methods available, ranging from tried-and-true methods such as lab-based usability testing to those that have been more recently developed, such as unmoderated UX assessments. While it's not realistic to use the full set of methods on a given project, nearly all projects would benefit ...
Here's the trends we identified: Continuous research is becoming a well-established practice. Companies are scaling research through democratization. The UX researcher role is shifting from technical executor to educator. Organizations are using customer insights to make informed decisions and drive business growth.
Recent research into user experience has identified the need for a theoretical model to build cumulative knowledge in research addressing how the overall quality or 'goodness' of an interactive product is formed. An experiment tested and extended Hassenzahl's model of aesthetic experience. The study used a 2 × 2 × (2) experimental ...
Free UX/UI Design books, articles & topic overviews written by leading designers, bestselling authors, and Ivy League professors. Reviews / Why join our community? ... In 9 chapters, we'll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more! Download free ebook Go.
UX Research. Enhancing virtual teaching with Google Meet; Airbnb's global check-in tool; Spotify home shortcuts; Artificial Intelligence. AI-powered spatial banking for Apple Vision Pro; Sage Express; Delfi; UX design. In this section, we'll explore case studies that take us through the complete design journey of creating a digital product ...
For many neurodiverse individuals, navigating digital spaces can be a challenging or even an overwhelming experience.. Therefore, UX designers must prioritize creating inclusive digital environments that cater to the diverse cognitive needs of all users. Embracing neurodiversity in UX design can help us unlock a world of possibilities, in which everyone can access and engage with digital ...
Anna Andersen. Apr 25. UX Collective. We believe designers are thinkers as much as they are makers. Curated stories on UX, Visual & Product Design. https://linktr.ee/uxc. More information. Followers. 468K. Elsewhere.
UX Research Cheat Sheet. Susan Farrell. February 12, 2017. Summary: User research can be done at any point in the design cycle. This list of methods and activities can help you decide which to use when. User-experience research methods are great at producing data and insights, while ongoing activities help get the right things done.
Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.. In 9 chapters, we'll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
Researchers who analyzed consumer feedback from Etsy discovered that what consumers value most about upcycled products is not their sustainability but their creativity. Their findings offer some ...
UX practitioners can leverage the picture-superiority effect when communicating user-research insights. Visual artifacts, like maps and personas, help team members and stakeholders remember user-research insights. Memorable research findings are more likely to be referenced and used in everyday decision making.
Today, we're introducing Meta Llama 3, the next generation of our state-of-the-art open source large language model. Llama 3 models will soon be available on AWS, Databricks, Google Cloud, Hugging Face, Kaggle, IBM WatsonX, Microsoft Azure, NVIDIA NIM, and Snowflake, and with support from hardware platforms offered by AMD, AWS, Dell, Intel, NVIDIA, and Qualcomm.
15 Guiding Principles for UX Researchers. We've found that a lot of first time UX researchers have similar questions and concerns when they start working in UX design. So, we thought we'd round up and tackle some of the most common questions to form a set of useful principles for UX researchers. Of course, this isn't a complete guide to ...
Share and Analyze Existing Research. Compile and review all data related to the journey. This may include user experience studies, marketing analysis and customer feedback. Share information before the workshop to help everyone understand the starting point. Assign Pre-Workshop Tasks. Assign homework to make the participants well-prepared.