
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


17.9: The West as History- the Turner Thesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 10013

- American YAWP
- Stanford via Stanford University Press
.png?revision=1)
In 1893, the American Historical Association met during that year’s World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago. The young Wisconsin historian Frederick Jackson Turner presented his “frontier thesis,” one of the most influential theories of American history, in his essay “The Significance of the Frontier in American History.”
Turner looked back at the historical changes in the West and saw, instead of a tsunami of war and plunder and industry, waves of “civilization” that washed across the continent. A frontier line “between savagery and civilization” had moved west from the earliest English settlements in Massachusetts and Virginia across the Appalachians to the Mississippi and finally across the Plains to California and Oregon. Turner invited his audience to “stand at Cumberland Gap [the famous pass through the Appalachian Mountains], and watch the procession of civilization, marching single file—the buffalo following the trail to the salt springs, the Indian, the fur trader and hunter, the cattle-raiser, the pioneer farmer—and the frontier has passed by.” 26
Americans, Turner said, had been forced by necessity to build a rough-hewn civilization out of the frontier, giving the nation its exceptional hustle and its democratic spirit and distinguishing North America from the stale monarchies of Europe. Moreover, the style of history Turner called for was democratic as well, arguing that the work of ordinary people (in this case, pioneers) deserved the same study as that of great statesmen. Such was a novel approach in 1893.
But Turner looked ominously to the future. The Census Bureau in 1890 had declared the frontier closed. There was no longer a discernible line running north to south that, Turner said, any longer divided civilization from savagery. Turner worried for the United States’ future: what would become of the nation without the safety valve of the frontier? It was a common sentiment. Theodore Roosevelt wrote to Turner that his essay “put into shape a good deal of thought that has been floating around rather loosely.” 27
The history of the West was many-sided and it was made by many persons and peoples. Turner’s thesis was rife with faults, not only in its bald Anglo-Saxon chauvinism—in which nonwhites fell before the march of “civilization” and Chinese and Mexican immigrants were invisible—but in its utter inability to appreciate the impact of technology and government subsidies and large-scale economic enterprises alongside the work of hardy pioneers. Still, Turner’s thesis held an almost canonical position among historians for much of the twentieth century and, more importantly, captured Americans’ enduring romanticization of the West and the simplification of a long and complicated story into a march of progress.

The Significance of the Frontier in American History
- December 31, 1893
Introduction
In 1890 the U.S. Census Bureau announced that the contiguous frontier line separating wilderness from civilization in the United States no longer existed. Three years later, Frederick Jackson Turner, a young professor at the University of Wisconsin, delivered a scholarly paper, “The Significance of the Frontier in American History,” before the American Historical Association in Chicago during the World’s Columbian Exposition (Chicago World’s Fair). In it Turner argued that “the existence of an area of free land, its continuous recession, and the advance of American settlement westward explain American development.” The frontier line “between savagery and civilization” had moved west from the earliest English settlements in Massachusetts and Virginia across the Appalachians to the Mississippi and finally across the plains to California and Oregon. Settlers had been forced by necessity to build a rough-hewn civilization on the frontier, and the resourcefulness and strength of character that required had given America its individualistic and democratic spirit, and distinguished North America from the monarchies of Europe.
Turner’s paper was widely distributed and enormously influential, and it remains perhaps the single most important piece of American historical writing. Scholars since have criticized Turner’s facts and interpretation, but at the time, his words raised concerns about the future of American government and society. Would the American character degrade without the stimulus of the frontier, especially at a time of rapid industrialization? Should the United States seek a new frontier and compete with the European nations now scrambling to gain or maintain colonial empires?
Source: Frederick Jackson Turner, “The Significance of the Frontier in American History,” address to the American Historical Association, in The Frontier in American History(New York: Henry Holt and Co., 1920), 1–38, available at http://www.gutenberg.org/files/22994/22994-h/22994-h.htm .
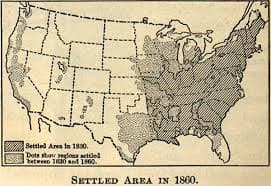
In a recent bulletin of the Superintendent of the Census for 1890 appear these significant words: “Up to and including 1880 the country had a frontier of settlement, but at present the unsettled area has been so broken into by isolated bodies of settlement that there can hardly be said to be a frontier line. In the discussion of its extent, its westward movement, etc., it cannot, therefore, any longer have a place in the census reports.” This brief official statement marks the closing of a great historic movement. Up to our own day American history has been in a large degree the history of the colonization of the Great West. The existence of an area of free land, its continuous recession, and the advance of American settlement westward, explain American development.
Behind institutions, behind constitutional forms and modifications, lie the vital forces that call these organs into life and shape them to meet changing conditions. The peculiarity of American institutions is the fact that they have been compelled to adapt themselves to the changes of an expanding people—to the changes involved in crossing a continent, in winning a wilderness, and in developing at each area of this progress out of the primitive economic and political conditions of the frontier into the complexity of city life. Said Calhoun in 1817, “We are great, and rapidly—I was about to say fearfully—growing!” [1] So saying, he touched the distinguishing feature of American life. All peoples show development; the germ theory of politics has been sufficiently emphasized. [2] In the case of most nations, however, the development has occurred in a limited area; and if the nation has expanded, it has met other growing peoples whom it has conquered. But in the case of the United States we have a different phenomenon. Limiting our attention to the Atlantic Coast, we have the familiar phenomenon of the evolution of institutions in a limited area, such as the rise of representative government[,] into complex organs; the progress from primitive industrial society, without division of labor, up to manufacturing civilization. But we have in addition to this a recurrence of the process of evolution in each western area reached in the process of expansion. Thus American development has exhibited not merely advance along a single line, but a return to primitive conditions on a continually advancing frontier line, and a new development for that area. American social development has been continually beginning over again on the frontier. This perennial rebirth, this fluidity of American life, this expansion westward with its new opportunities, its continuous touch with the simplicity of primitive society, furnish the forces dominating American character. The true point of view in the history of this nation is not the Atlantic Coast, it is the Great West. Even the slavery struggle, which is made so exclusive an object of attention by writers like Professor von Holst, occupies [3] its important place in American history because of its relation to westward expansion.
In this advance, the frontier is the outer edge of the wave—the meeting point between savagery and civilization. Much has been written about the frontier from the point of view of border warfare and the chase, but as a field for the serious study of the economist and the historian it has been neglected.
The American frontier is sharply distinguished from the European frontier—a fortified boundary line running through dense populations. The most significant thing about the American frontier is that it lies at the hither edge of free land. In the census reports it is treated as the margin of that settlement which has a density of two or more to the square mile. The term is an elastic one, and for our purposes does not need sharp definition. We shall consider the whole frontier belt including the Indian country and the outer margin of the “settled area” of the census reports. This paper will make no attempt to treat the subject exhaustively; its aim is simply to call attention to the frontier as a fertile field for investigation, and to suggest some of the problems which arise in connection with it. . . .
It was this nationalizing tendency of the West that transformed the democracy of Jefferson into the national republicanism of Monroe and the democracy of Andrew Jackson. The West of the War of 1812, the West of Clay, and Benton and Harrison, and Andrew Jackson, [4] shut off by the Middle States and the mountains from the coast sections, had a solidarity of its own with national tendencies. On the tide of the Father of Waters, [5] North and South met and mingled into a nation. Interstate migration went steadily on—a process of cross-fertilization of ideas and institutions. The fierce struggle of the sections over slavery on the western frontier does not diminish the truth of this statement; it proves the truth of it. Slavery was a sectional trait that would not down, but in the West it could not remain sectional. It was the greatest of frontiersmen who declared: “I believe this Government can not endure permanently half slave and half free. It will become all of one thing or all of the other.” [6] Nothing works for nationalism like intercourse within the nation. Mobility of population is death to localism, and the western frontier worked irresistibly in unsettling population. The effect reached back from the frontier and affected profoundly the Atlantic Coast and even the Old World.
But the most important effect of the frontier has been in the promotion of democracy here and in Europe. As has been indicated, the frontier is productive of individualism. Complex society is precipitated by the wilderness into a kind of primitive organization based on the family. The tendency is antisocial. It produces antipathy to control, and particularly to any direct control. The tax gatherer is viewed as a representative of oppression. Prof. Osgood, in an able article, [7] has pointed out that the frontier conditions prevalent in the colonies are important factors in the explanation of the American Revolution, where individual liberty was sometimes confused with absence of all effective government. The same conditions aid in explaining the difficulty of instituting a strong government in the period of the confederacy. The frontier individualism has from the beginning promoted democracy. The frontier states that came into the Union in the first quarter of a century of its existence came in with democratic suffrage provisions, [8] and had reactive effects of the highest importance upon the older states whose peoples were being attracted there. An extension of the franchise became essential. It was western New York that forced an extension of suffrage in the constitutional convention of that state in 1821; and it was western Virginia that compelled the tide-water region to put a more liberal suffrage provision in the constitution framed in 1830, and to give to the frontier region a more nearly proportionate representation with the tide-water aristocracy. The rise of democracy as an effective force in the nation came in with western preponderance under Jackson and William Henry Harrison, and it meant the triumph of the frontier—with all of its good and with all of its evil elements. An interesting illustration of the tone of frontier democracy in 1830 comes from the same debates in the Virginia convention already referred to. [9] . . .
So long as free land exists, the opportunity for a competency exists, and economic power secures political power. But the democracy born of free land, strong in selfishness and individualism, intolerant of administrative experience and education, and pressing individual liberty beyond its proper bounds, has its dangers as well as its benefits. Individualism in America has allowed a laxity in regard to governmental affairs which has rendered possible the spoils system and all the manifest evils that follow from the lack of a highly developed civic spirit. [10] In this connection may be noted also the influence of frontier conditions in permitting lax business honor, inflated paper currency and wild-cat banking. The colonial and revolutionary frontier was the region whence emanated many of the worst forms of an evil currency. The West in the War of 1812 repeated the phenomenon on the frontier of that day, while the speculation and wild-cat banking of the period of the crisis of 1837 occurred on the new frontier belt of the next tier of states. Thus each one of the periods of lax financial integrity coincides with periods when a new set of frontier communities had arisen, and coincides in area with these successive frontiers for the most part. The recent Populist agitation is a case in point. [11] Many a state that now declines any connection with the tenets of the Populists, itself adhered to such ideas in an earlier stage of the development of the state. A primitive society can hardly be expected to show the intelligent appreciation of the complexity of business interests in a developed society. The continual recurrence of these areas of paper-money agitation is another evidence that the frontier can be isolated and studied as a factor in American history of the highest importance.
The East has always feared the result of an unregulated advance of the frontier, and has tried to check and guide it. The English authorities would have checked settlement at the headwaters of the Atlantic tributaries. . . .
From the conditions of frontier life came intellectual traits of profound importance. The works of travelers along each frontier from colonial days onward describe certain common traits, and these traits have, while softening down, still persisted as survivals in the place of their origin, even when a higher social organization succeeded. The result is that to the frontier the American intellect owes its striking characteristics. That coarseness and strength combined with acuteness and inquisitiveness; that practical, inventive turn of mind, quick to find expedients; that masterful grasp of material things, lacking in the artistic but powerful to effect great ends; that restless, nervous energy; that dominant individualism, working for good and for evil, and withal that buoyancy and exuberance which comes with freedom—these are traits of the frontier, or traits called out elsewhere because of the existence of the frontier. Since the days when the fleet of Columbus sailed into the waters of the New World, America has been another name for opportunity, and the people of the United States have taken their tone from the incessant expansion which has not only been open but has even been forced upon them. He would be a rash prophet who should assert that the expansive character of American life has now entirely ceased. Movement has been its dominant fact, and, unless this training has no effect upon a people, the American energy will continually demand a wider field for its exercise. But never again will such gifts of free land offer themselves. For a moment, at the frontier, the bonds of custom are broken and unrestraint is triumphant. There is no tabula rasa. [12] The stubborn American environment is there with its imperious summons to accept its conditions; the inherited ways of doing things are also there; and yet, in spite of environment, and in spite of custom, each frontier did indeed furnish a new field of opportunity, a gate of escape from the bondage of the past; and freshness, and confidence, and scorn of older society, impatience of its restraints and its ideas, and indifference to its lessons, have accompanied the frontier. What the Mediterranean Sea was to the Greeks, breaking the bond of custom, offering new experiences, calling out new institutions and activities, that, and more, the ever retreating frontier has been to the United States directly, and to the nations of Europe more remotely. And now, four centuries from the discovery of America, at the end of a hundred years of life under the Constitution, the frontier has gone, and with its going has closed the first period of American history.
- 1. John C. Calhoun (1782–1850), then a congressman from South Carolina. Turner quotes from Calhoun’s speech “On the Bill to Set Aside the Bank Bill Dividends,” February 4, 1817.
- 2. Proponents of the germ theory believed that political habits are determined by innate racial attributes.
- 3. Hermann Eduard von Holst (1841–1904) was a German American historian.
- 4. Henry Clay (1777–1852), Thomas Hart Benton (1782–1858), William Henry Harrison (1773–1841) and Andrew Jackson (1767–1845), the latter two American presidents, were from what was then regarded as the West.
- 5. Commonly used term for the Mississippi River.
- 6. Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), in his famous House Divided speech, June 16, 1858, while running for the U.S. Senate.
- 7. Herbert L. Osgood (1855–1918) was an American historian of colonial American history
- 8. Up through 1814, Vermont, Kentucky, Tennessee, Ohio, and Louisiana.
- 9. A convention called to revise the state constitution of Virginia, in which the underrepresentation of the western, or frontier, counties was a central topic
- 10. The spoils system was the practice in which a political party, after winning an election, gave government civil service jobs and other favors to its supporters, friends, and relatives
- 11. The Populist movement, and the Populist Party, sought to curtail what its adherents regarded as the excess power of the corporate and financial establishment. See The Farmers’ Movement.
- 12. Tabula rasa = blank slate.
Mormonism and Jesuitism
The folly of colonization, see our list of programs.
Conversation-based seminars for collegial PD, one-day and multi-day seminars, graduate credit seminars (MA degree), online and in-person.
Check out our collection of primary source readers
Our Core Document Collection allows students to read history in the words of those who made it. Available in hard copy and for download.
The American Yawp Reader
17. conquering the west.

American anthropologist and ethnographer Frances Densmore records the Blackfoot chief Mountain Chief in 1916 for the Bureau of American Ethnology.
Introduction
Native Americans long dominated the vastness of the American West. Indigenous Americans had lived in North America for over ten millennia and, into the late-nineteenth century, perhaps as many as 250,000 natives still inhabited the American West. But then unending waves of American settlers, the American military, and the unstoppable onrush of American capital conquered all. The United States removed native groups to ever-shrinking reservations, incorporated the West first as territories and then as states, and, for the first time in its history, controlled the enormity of land between the two oceans. The history of the late-nineteenth-century West is many-sided. Tragedy for some, triumph for others, the many intertwined histories of the American West marked a pivotal transformation in the history of the United States. The following sources explore the long American “conquest” of the West.
1. Chief Joseph on Indian Affairs (1877, 1879)
A branch of the Nez Percé tribe, from the Pacific Northwest, refused to be moved to a reservation and attempted to flee to Canada but were pursued by the U.S. Cavalry, attacked, and forced to return. The following is a transcript of Chief Joseph’s surrender, as recorded by Lieutenant Wood, Twenty-first Infantry, acting aide-de-camp and acting adjutant-general to General Oliver O. Howard, in 1877.
2. William T. Hornady on the Extermination of the American Bison (1889)
William T. Hornady, Superintendent of the National Zoological Park, wrote a detailed account of the near-extinction of the American bison in the late-nineteenth century.
3. Chester A. Arthur on American Indian Policy (1881)
The following is extracted from President Chester A. Arthur’s First Annual Message to Congress, delivered December 6, 1881.
4. Frederick Jackson Turner, “Significance of the Frontier in American History” (1893)
Perhaps the most influential essay by an American historian, Frederick Jackson Turner’s address to the American Historical Association on “The Significance of the Frontier in American History” defined for many Americans the relationship between the frontier and American culture and contemplated what might follow “the closing of the frontier.”
5. Turning Hawk and American Horse on the Wounded Knee Massacre (1890/1891)
On February 11, 1891, a Sioux delegation met with the Commissioner of Indian Affairs in Washington D.C. and gave their account of the Wounded Knee Massacre six weeks prior.
6. Laura C. Kellogg on Indian Education (1913)
The United States used education to culturally assimilate Native Americans. Laura Cornelius Kellogg, an Oneida author, performer, and activist who helped found the Society of American Indians (SAI) in 1913, criticized the cultural chauvinism of American policy. Speaking to the SAI, she challenged her Indian audience to embrace modern American democracy while maintaining their own identity.

7. Helen Hunt Jackson on a Century of Dishonor (1881)
In 1881, Helen Hunt Jackson published A Century of Dishonor, a history of the injustices visited upon Native Americans. Exposing the many wrongs perpetrated by her country, she hoped “to redeem the name of the United States from the stain of a century of dishonor.”
Tom Torlino (1882, 1885)
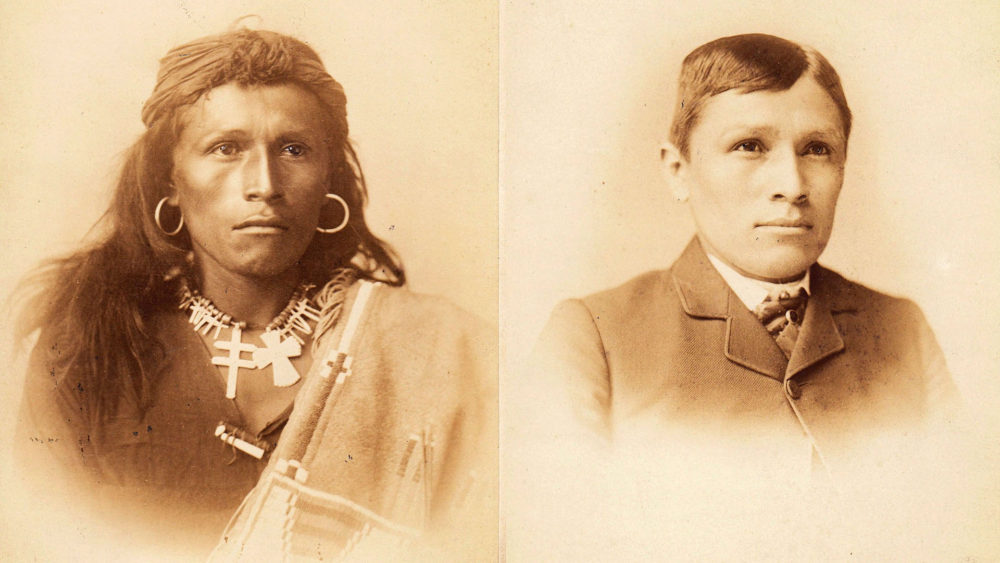

Source: Carlisle Indian School Digital Resource Center .
Tom Torlino, a member of the Navajo Nation, entered the Carlisle Indian School, a Native American boarding school founded by the United States government in 1879, on October 21, 1882 and departed on August 28, 1886. Torlino’s student file contained photographs from 1882 and 1885.
Frances Densmore and Mountain Chief (1916)
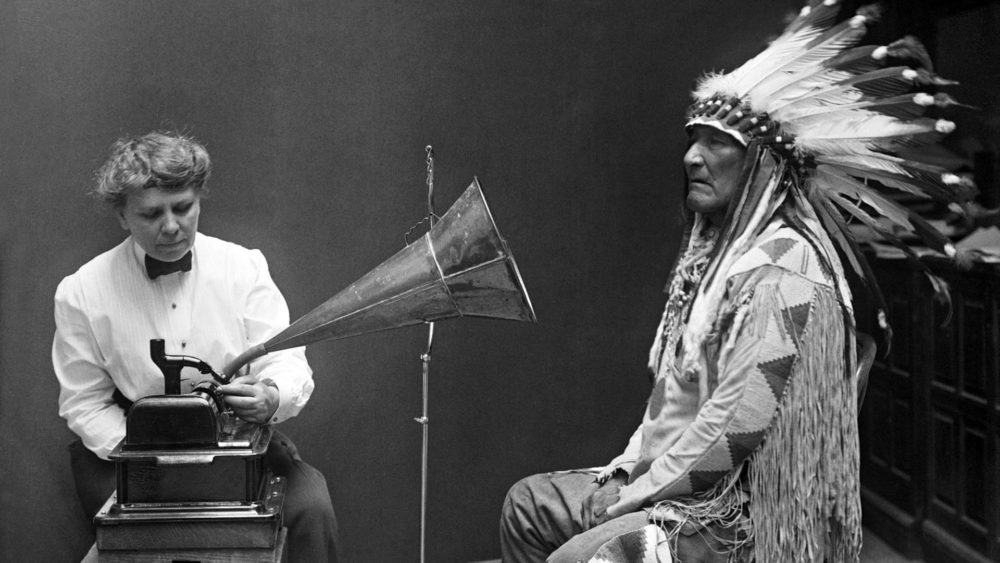

Source: Library of Congress.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

Conquering the West
Assignment: the turner thesis.
Frederick Jackson Turner was a famous American historian in the 1890s. He wrote a very influential article called “The Significance of the Frontier in American History.” It quickly became known as the “ Turner Thesis. ” Read the Turner Thesis and in a paragraph or two (250-300 words) answer the following:
- What is the Turner Thesis? (What is the frontier and why is it significant to the development of American history?)
- What specific quotes, passages, and lines from the document led you to that conclusion?
- Turner Thesis Assignment. Authored by : Chris Thomas. Provided by : Reynolds Community College. License : CC BY: Attribution
Was Frederick Jackson Turner’s Frontier Thesis Myth or Reality?
Two scholars debate this question.
Written by: (Claim A) Andrew Fisher, William & Mary; (Claim B) Bradley J. Birzer, Hillsdale College
Suggested sequencing.
- Use this Point-Counterpoint with the Frederick Jackson Turner, “The Significance of the Frontier in American History,” 1893 Primary Source to give students more background on individualism and western expansion.
Issue on the Table
Was Turner’s thesis a myth about the individualism of the American character and the influence of the West or was it essentially correct in explaining how the West and the advancing frontier contributed to the shaping of individualism in the American character?
Instructions
Read the two arguments in response to the question, paying close attention to the supporting evidence and reasoning used for each. Then, complete the comparison questions that follow. Note that the arguments in this essay are not the personal views of the scholars but are illustrative of larger historical debates.
Every nation has a creation myth, a simple yet satisfying story that inspires pride in its people. The United States is no exception, but our creation myth is all about exceptionalism. In his famous essay, “The Significance of the Frontier in American History,” Frederick Jackson Turner claimed that the process of westward expansion had transformed our European ancestors into a new breed of people endowed with distinctively American values and virtues. In particular, the frontier experience had supposedly fostered democracy and individualism, underpinned by the abundance of “free land” out West. “So long as free land exists,” Turner wrote, “the opportunity for a competency exists, and economic power secures political power.” It was a compelling articulation of the old Jeffersonian Dream. Like Jefferson’s vision, however, Turner’s thesis excluded much of the nation’s population and ignored certain historical realities concerning American society.
Very much a man of his times, Turner filtered his interpretation of history through the lens of racial nationalism. The people who counted in his thesis, literally and figuratively, were those with European ancestry—and especially those of Anglo-Saxon origins. His definition of the frontier, following that of the U.S. Census, was wherever population density fell below two people per square mile. That effectively meant “where white people were scarce,” in the words of historian Richard White; or, as Patricia Limerick puts it, “where white people got scared because they were scarce.” American Indians only mattered to Turner as symbols of the “savagery” that white pioneers had to beat back along the advancing frontier line. Most of the “free land” they acquired in the process came from the continent’s vast indigenous estate, which, by 1890, had been reduced to scattered reservations rapidly being eroded by the Dawes Act. Likewise, Mexican Americans in the Southwest saw their land base and economic status whittled away after the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo that nominally made them citizens of the United States. Chinese immigrants, defined as perpetual aliens under federal law, could not obtain free land through the Homestead Act. For all these groups, Euro-American expansion and opportunity meant the contraction or denial of their own ability to achieve individual advancement and communal stability.
Turner also exaggerated the degree of social mobility open to white contemporaries, not to mention their level of commitment to an ideology of rugged individualism. Although plenty of Euro-Americans used the homestead laws to get their piece of free land, they often struggled to make that land pay and to keep it in the family. During the late nineteenth century, the commoditization and industrialization of American agriculture caught southern and western farmers in a crushing cost-price squeeze that left many wrecked by debt. To combat this situation, they turned to cooperative associations such as the Grange and the National Farmers’ Alliance, which blossomed into the Populist Party at the very moment Turner was writing about the frontier as the engine of American democracy. Perhaps it was, but not in the sense he understood. Populists railed against the excess of individualism that bred corruption and inequality in Gilded Age America. Even cowboys, a pillar of the frontier myth, occasionally tried to organize unions to improve their wages and working conditions. Those seeking a small stake of their own—what Turner called a “competency”— in the form of their own land or herds sometimes ran afoul of concentrated capital, as during the Johnson County War of 1892. The big cattlemen of the Wyoming Stockgrowers Association had no intention of sharing the range with pesky sodbusters and former cowboys they accused of rustling. Their brand of individualism had no place for small producers who might become competitors.
Turner took such troubles as a sign that his prediction had come true. With the closing of the frontier, he said, the United States would begin to see greater class conflict in the form of strikes and radical politics. There was lots of free land left in 1890, though; in fact, approximately 1 million people filed homestead claims between 1901 and 1913, compared with 1.4 million between 1862 and 1900. That did not prevent the country from experiencing serious clashes between organized labor and the corporations that had come to dominate many industries. Out west, socialistic unions such as the Western Federation of Miners and the Industrial Workers of the World challenged not only the control that companies had over their employees but also their influence in the press and politics. For them, Turner’s dictum that “economic power secures political power” would have held a more sinister meaning. It was the rise of the modern corporation, not the supposed fading of the frontier, that narrowed the meanings of individualism and opportunity as Americans had previously understood them.
Young historian Frederick Jackson Turner presented his academic paper, “The Significance of the Frontier in American History,” at the World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago on July 12, 1893. He was the final presenter of that hot and humid day, but his essay ranks among the most influential arguments ever made regarding American history.
Turner was trained at the University of Wisconsin (his home state) and Johns Hopkins University, then the center of Germanic-type graduate studies—that is, it was scientific and objectivist rather than idealist or liberal. Turner rebelled against that purely scientific approach, but not by much. In 1890, the U.S. Census revealed that the frontier (defined as fewer than two people per square mile) was closed. There was no longer an unbroken frontier line in the United States, although frontier conditions lasted in certain parts of the American West until 1920. Turner lamented this, believing the most important phase of American history was over.
No one publicly commented on the essay at the time, but the American Historical Association reprinted it in its annual report the following year, and within a decade, it became known as the “Turner Thesis.”
What is most prominent in the Turner Thesis is the proposition that the United States is unique in its heritage; it is not a European clone, but a vital mixture of European and American Indian. Or, as he put it, the American character emerged through an intermixing of “savagery and civilization.” Turner attributed the American character to the expansion to the West, where, he said, American settlers set up farms to tame the frontier. “The existence of an area of free land, its continuous recession, and the advance of American settlement westward, explain American development.” As people moved west in a “perennial rebirth,” they extended the American frontier, the boundary “between savagery and civilization.”
The frontier shaped the American character because the settlers who went there had to conquer a land difficult for farming and devoid of any of the comforts of life in urban parts of the East: “The frontier is the line of most rapid and effective Americanization. The wilderness masters the colonist. It finds him a European in dress, industries, tools, modes of travel, and thought. It takes him from the railroad car and puts him in the birch canoe. It strips off the garments of civilization and arrays him in the hunting shirt and the moccasin. It puts him in the log cabin of the Cherokee and Iroquois and runs an Indian palisade around him. Before long he has gone to planting Indian corn and plowing with a sharp stick; he shouts the war cry and takes the scalp in orthodox Indian fashion. In short, at the frontier the environment is at first too strong for the man. He must accept the conditions which it furnishes, or perish, and so he fits himself into the Indian clearings and follows the Indian trails.”
Politically and socially, according to Turner, the American character—including traits that prioritized equality, individualism, and democracy—was shaped by moving west and settling the frontier. “The tendency,” Turner wrote, “is anti-social. [The frontier] produces antipathy to control, and particularly to any direct control.” Those hardy pioneers on the frontier spread the ideas and practice of democracy as well as modern civilization. By conquering the wilderness, Turner stressed, they learned that resources and opportunity were seemingly boundless, meant to bring the ruggedness out of each individual. The farther west the process took them, the less European the Americans as a whole became. Turner saw the frontier as the progenitor of the American practical and innovative character: “That coarseness and strength combined with acuteness and acquisitiveness; that practical, inventive turn of mind, quick to find expedients; that masterful grasp of material things, lacking the artistic but powerful to effect great ends; that restless, nervous energy; that dominant individualism, working for good and for evil, and withal that buoyancy and exuberance which comes with freedom – these are trains of the frontier.”
Turner’s thesis, to be sure, viewed American Indians as uncivilized. In his vision, they cannot compete with European technology, and they fall by the wayside, serving as little more than a catalyst for the expansion of white Americans. This near-absence of Indians from Turner’s argument gave rise to a number of critiques of his thesis, most prominently from the New Western Historians beginning in the 1980s. These more recent historians sought to correct Turner’s “triumphal” myth of the American West by examining it as a region rather than as a process. For Turner, the American West is a progressive process, not a static place. There were many Wests, as the process of conquering the land, changing the European into the American, happened over and over again. What would happen to the American character, Turner wondered, now that its ability to expand and conquer was over?
Historical Reasoning Questions
Use Handout A: Point-Counterpoint Graphic Organizer to answer historical reasoning questions about this point-counterpoint.
Primary Sources (Claim A)
Cooper, James Fenimore. Last of the Mohicans (A Leatherstocking Tale) . New York: Penguin, 1986.
Turner, Frederick Jackson. “The Significance of the Frontier in American History.” http://sunnycv.com/steve/text/civ/turner.html
Primary Sources (Claim B)
Suggested resources (claim a).
Cronon, William, George Miles, and Jay Gitlin, eds. Under an Open Sky: Rethinking America’s Western Past . New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 1992.
Faragher, John Mack. Women and Men on the Overland Trail . New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2001.
Grossman, Richard R, ed. The Frontier in American Culture: Essays by Richard White and Patricia Nelson Limerick . Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1994.
Limerick, Patricia Nelson. The Legacy of Conquest: The Unbroken Past of the American West . New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 1987.
Limerick, Patricia Nelson, Clyde A. Milner II, and Charles E. Rankin, eds. Trails: Toward a New Western History . Lawrence, KS: University Press of Kansas, 1991.
Milner II, Clyde A. A New Significance: Re-envisioning the History of the American West . New York: Oxford University Press, 1996.
Nugent, Walter. Into the West: The Story of Its People . New York: Knopf, 1991.
Slotkin, Richard. The Fatal Environment: The Myth of the Frontier in the Age of Industrialization, 1800-1890 . Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press, 1998.
Suggested Resources (Claim B)
Billington, Ray Allen, and Martin Ridge. Westward Expansion: A History of the American Frontier . Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, 2001.
Etulain, Richard, ed. Does the Frontier Experience Make America Exceptional? New York: Bedford/St. Martin’s, 1999.
Mondi. Megan. “’Connected and Unified?’: A More Critical Look at Frederick Jackson Turner’s America.” Constructing the Past , 7 no. 1:Article 7. http://digitalcommons.iwu.edu/constructing/vol7/iss1/7
Nelson, Robert. “Public Lands and the Frontier Thesis.” Atlas of the Historical Geography of the United States , Digital Scholarship Lab, University of Richmond, 2014. http://dsl.richmond.edu/fartherafield/public-lands-and-the-frontier-thesis/
More from this Category

Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness
In our resource history is presented through a series of narratives, primary sources, and point-counterpoint debates that invites students to participate in the ongoing conversation about the American experiment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Frederick Jackson Turner, "Significance of the Frontier in American History" (1893) Perhaps the most influential essay by an American historian, Frederick Jackson Turner's address to the American Historical Association on "The Significance of the Frontier in American History" defined for many Americans the relationship between the frontier and American culture and contemplated what ...
In 1893, the American Historical Association met during that year's World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago. The young Wisconsin historian Frederick Jackson Turner presented his "frontier thesis," one of the most influential theories of American history, in his essay "The Significance of the Frontier in American History."
The young Wisconsin historian Frederick Jackson Turner presented his "frontier thesis," one of the most influential theories of American history, in his essay "The Significance of the Frontier in American History." Turner looked back at the historical changes in the West and saw, instead of a tsunami of war and plunder and industry ...
The Frontier Thesis, also known as Turner's Thesis or American frontierism, is the argument advanced by historian Frederick Jackson Turner in 1893 that the settlement and colonization of the rugged American frontier was decisive in forming the culture of American democracy and distinguishing it from European nations. He stressed the process of "winning a wilderness" to extend the frontier line ...
The young Wisconsin historian Frederick Jackson Turner presented his "frontier thesis," one of the most influential theories of American history, in his essay, "The Significance of the Frontier in American History.". Turner looked back at the historical changes in the West and saw, instead of a tsunami of war and plunder and industry ...
Frederick Jackson Turner ___Frederick Jackson Turner___ The Significance of the Frontier in American History ... [Footnote in address as reprinted in Turner, The Frontier in American History, 1920] 1 In 1817 John C. Calhoun represented South Carolina in the U.S. House. Later in the year he was appointed Secretary of War by President
The Significance of the Frontier in American History" is a seminal essay by the American historian Frederick Jackson Turner which advanced the Frontier thesis of American history. Turner's thesis had a significant impact on how people in the late 19th and early 20th centuries understood American identity, character, and national growth.
Frederick Jackson Turner, "The Significance of the Frontier in American History" 1893 This brief official statement marks the closing of a great historic movement. Up to our own day American history has been in a large degree the history of the colonization of the Great West. The existence of an area of free land, its continuous recession, and ...
Three years later, Frederick Jackson Turner, a young professor at the University of Wisconsin, delivered a scholarly paper, "The Significance of the Frontier in American History," before the American Historical Association in Chicago during the World's Columbian Exposition (Chicago World's Fair).
Frederick Jackson Turner be lieved that America, with all its shortcomings, was more democratic and offered more opportunity to the common man than any other nation in the world. Turner's the ory explained how the frontier in teracted with all the other primary influences to produce a unique de mocracy and a distinctive Ameri can character.
Frederick Jackson Turner's Frontier Thesis 1 5 1 II The Frontier Thesis was Turner's answer to the challenge of putting his ideas about history into practice. Its meaning, then, does not simply lie in a new interpretation of the past, but in a new use of the past for the present. This implied building a theory whose very structure would
Perhaps the most influential essay by an American historian, Frederick Jackson Turner's address to the American Historical Association on "The Significance of the Frontier in American History" defined for many Americans the relationship between the frontier and American culture and contemplated what might follow "the closing of the ...
Chester A. Arthur on American Indian Policy (1881) Frederick Jackson Turner, "Significance of the Frontier in American History" (1893) Turning Hawk and American Horse on the Wounded Knee Massacre (1890/1891) Helen Hunt Jackson on a Century of Dishonor (1881) Laura C. Kellogg on Indian Education (1913) 18. Life in Industrial America
Summary. Last Updated September 5, 2023. "The Significance of the Frontier in American History" was written by Frederick Jackson Turner, delivered as a conference paper at the annual meeting of ...
Frederick Jackson Turner (born November 14, 1861, Portage, Wisconsin, U.S.—died March 14, 1932, San Marino, California) was an American historian best known for the " frontier thesis.". The single most influential interpretation of the American past, it proposed that the distinctiveness of the United States was attributable to its long ...
Perhaps the most influential essay by an American historian, Frederick Jackson Turner's address to the American Historical Association on "The Significance of the Frontier in American History" defined for many Americans the relationship between the frontier and American culture and contemplated what might follow "the closing of the frontier."
2014 Reprint of 1894 Edition. Full facsimile of the original edition. The "Frontier Thesis" or "Turner Thesis," is the argument advanced by historian Frederick Jackson Turner in 1894 that American democracy was formed by the American Frontier. He stressed the process-the moving frontier line-and the impact it had on pioneers going through the process.
Thus, fundamentally trans- formed as a people, Americans built their commitment to democracy, es-. caped the perils of class conflict, and overran a continent. Now, in the 1890s, the frontier was gone, and a new foundation for American life must some-. how be discovered. So ran Turner's argument.
Assignment: The Turner Thesis. Frederick Jackson Turner was a famous American historian in the 1890s. He wrote a very influential article called "The Significance of the Frontier in American History.". It quickly became known as the " Turner Thesis. " Read the Turner Thesis and in a paragraph or two (250-300 words) answer the following:
In their work on Turner's formative period, Ray A. Billington and Fulmer Mood have shown that the Frontier Thesis, formulated in 1893 in "The Significance of the Frontier in American History," is not so much a brilliant early effort by a young scholar as a mature study in which Turner gave his ideas an organization that proved to be final.
Turner, The Frontier in American History (New York, 1921), 2. 2 A number of excellent analyses and evaluations of the Turner thesis have been made. Among the most significant are the following: Avery 0. Craven, "Frederick Jackson Turner," in The Marcus W. Jernegan Essays in American Historiography (Chicago,
Young historian Frederick Jackson Turner presented his academic paper, "The Significance of the Frontier in American History," at the World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago on July 12, 1893. He was the final presenter of that hot and humid day, but his essay ranks among the most influential arguments ever made regarding American history.