- UNC Libraries
- HSL Subject Research
- Qualitative Research Resources
- Writing Up Your Research

Qualitative Research Resources: Writing Up Your Research
Created by health science librarians.

- What is Qualitative Research?
- Qualitative Research Basics
- Special Topics
- Training Opportunities: UNC & Beyond
- Help at UNC
- Qualitative Software for Coding/Analysis
- Software for Audio, Video, Online Surveys
- Finding Qualitative Studies
- Assessing Qualitative Research
About this Page
Writing conventions for qualitative research, sample size/sampling:.
- Integrating Qualitative Research into Systematic Reviews
- Publishing Qualitative Research
- Presenting Qualitative Research
- Qualitative & Libraries: a few gems
- Data Repositories
Why is this information important?
- The conventions of good writing and research reporting are different for qualitative and quantitative research.
- Your article will be more likely to be published if you make sure you follow appropriate conventions in your writing.
On this page you will find the following helpful resources:
- Articles with information on what journal editors look for in qualitative research articles.
- Articles and books on the craft of collating qualitative data into a research article.
These articles provide tips on what journal editors look for when they read qualitative research papers for potential publication. Also see Assessing Qualitative Research tab in this guide for additional information that may be helpful to authors.
Belgrave, L., D. Zablotsky and M.A. Guadagno.(2002). How do we talk to each other? Writing qualitative research for quantitative readers . Qualitative Health Research , 12(10),1427-1439.
Hunt, Brandon. (2011) Publishing Qualitative Research in Counseling Journals . Journal of Counseling and Development 89(3):296-300.
Fetters, Michael and Dawn Freshwater. (2015). Publishing a Methodological Mixed Methods Research Article. Journal of Mixed Methods Research 9(3): 203-213.
Koch, Lynn C., Tricia Niesz, and Henry McCarthy. (2014). Understanding and Reporting Qualitative Research: An Analytic Review and Recommendations for Submitting Authors. Rehabilitation Counseling Bulletin 57(3):131-143.
Morrow, Susan L. (2005) Quality and Trustworthiness in Qualitative Research in Counseling Psychology ; Journal of Counseling Psychology 52(2):250-260.
Oliver, Deborah P. (2011) "Rigor in Qualitative Research." Research on Aging 33(4): 359-360.
Sandelowski, M., & Leeman, J. (2012). Writing usable qualitative health research findings . Qual Health Res, 22(10), 1404-1413.
Schoenberg, Nancy E., Miller, Edward A., and Pruchno, Rachel. (2011) The qualitative portfolio at The Gerontologist : strong and getting stronger. Gerontologist 51(3): 281-284.
Weaver-Hightower, M. B. (2019). How to write qualitative research . [e-book]
Sidhu, Kalwant, Roger Jones, and Fiona Stevenson (2017). Publishing qualitative research in medical journals. Br J Gen Pract ; 67 (658): 229-230. DOI: 10.3399/bjgp17X690821 PMID: 28450340
- This article is based on a workshop on publishing qualitative studies held at the Society for Academic Primary Care Annual Conference, Dublin, July 2016.
Smith, Mary Lee.(1987) Publishing Qualitative Research. American Educational Research Journal 24(2): 173-183.
Tong, Allison, Sainsbury, Peter, Craig, Jonathan ; Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups , International Journal for Quality in Health Care , Volume 19, Issue 6, 1 December 2007, Pages 349–357, https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzm042 .
Tracy, Sarah. (2010) Qualitative Quality: Eight 'Big-Tent' Criteria for Excellent Qualitative Research. Qualitative Inquiry 16(10):837-51.
Because reviewers are not always familiar with qualitative methods, they may ask for explanation or justification of your methods when you submit an article. Because different disciplines,different qualitative methods, and different contexts may dictate different approaches to this issue, you may want to consult articles in your field and in target journals for publication. Additionally, here are some articles that may be helpful in thinking about this issue.
Bonde, Donna. (2013). Qualitative Interviews: When Enough is Enough . Research by Design.
Guest, Greg, Arwen Bunce, and Laura Johnson. (2006) How Many Interviews are Enough?: An Experiment with Data Saturation and Variability. Field Methods 18(1): 59-82.
Morse, Janice M. (2015) "Data Were Saturated..." Qualitative Health Research 25(5): 587-88 . doi:10.1177/1049732315576699.
Nelson, J. (2016) "Using Conceptual Depth Criteria: Addressing the Challenge of Reaching Saturation in Qualitative Research." Qualitative Research, December. doi:10.1177/1468794116679873.
Patton, Michael Quinn. (2015) "Chapter 5: Designing Qualitative Studies, Module 30 Purposeful Sampling and Case Selection. In Qualitative Research & Evaluation Methods: Integrating Theory and Practice, Fourth edition, pp. 264-72. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE Publications, Inc. ISBN: 978-1-4129-7212-3
Small, Mario Luis. (2009) 'How Many Cases Do I Need?': On Science and the Logic of Case-Based Selection in Field-Based Research. Ethnography 10(1): 538.
Search the UNC-CH catalog for books about qualitative writing . Selected general books from the catalog are listed below. If you are a researcher at another institution, ask your librarian for assistance locating similar books in your institution's catalog or ordering them via InterLibrary Loan.
Oft quoted and food for thought
- Morse, J. M. (1997). " Perfectly healthy, but dead": the myth of inter-rater reliability. DOI:10.1177/104973239700700401 Editorial
- Silberzahn, R., Uhlmann, E. L., Martin, D. P., Anselmi, P., Aust, F., Awtrey, E., ... & Carlsson, R. (2018). Many analysts, one data set: Making transparent how variations in analytic choices affect results. Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychologi
- << Previous: Assessing Qualitative Research
- Next: Integrating Qualitative Research into Systematic Reviews >>
- Last Updated: May 14, 2024 12:50 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.unc.edu/qual

Chapter 2. Research Design
Getting started.
When I teach undergraduates qualitative research methods, the final product of the course is a “research proposal” that incorporates all they have learned and enlists the knowledge they have learned about qualitative research methods in an original design that addresses a particular research question. I highly recommend you think about designing your own research study as you progress through this textbook. Even if you don’t have a study in mind yet, it can be a helpful exercise as you progress through the course. But how to start? How can one design a research study before they even know what research looks like? This chapter will serve as a brief overview of the research design process to orient you to what will be coming in later chapters. Think of it as a “skeleton” of what you will read in more detail in later chapters. Ideally, you will read this chapter both now (in sequence) and later during your reading of the remainder of the text. Do not worry if you have questions the first time you read this chapter. Many things will become clearer as the text advances and as you gain a deeper understanding of all the components of good qualitative research. This is just a preliminary map to get you on the right road.

Research Design Steps
Before you even get started, you will need to have a broad topic of interest in mind. [1] . In my experience, students can confuse this broad topic with the actual research question, so it is important to clearly distinguish the two. And the place to start is the broad topic. It might be, as was the case with me, working-class college students. But what about working-class college students? What’s it like to be one? Why are there so few compared to others? How do colleges assist (or fail to assist) them? What interested me was something I could barely articulate at first and went something like this: “Why was it so difficult and lonely to be me?” And by extension, “Did others share this experience?”
Once you have a general topic, reflect on why this is important to you. Sometimes we connect with a topic and we don’t really know why. Even if you are not willing to share the real underlying reason you are interested in a topic, it is important that you know the deeper reasons that motivate you. Otherwise, it is quite possible that at some point during the research, you will find yourself turned around facing the wrong direction. I have seen it happen many times. The reason is that the research question is not the same thing as the general topic of interest, and if you don’t know the reasons for your interest, you are likely to design a study answering a research question that is beside the point—to you, at least. And this means you will be much less motivated to carry your research to completion.
Researcher Note
Why do you employ qualitative research methods in your area of study? What are the advantages of qualitative research methods for studying mentorship?
Qualitative research methods are a huge opportunity to increase access, equity, inclusion, and social justice. Qualitative research allows us to engage and examine the uniquenesses/nuances within minoritized and dominant identities and our experiences with these identities. Qualitative research allows us to explore a specific topic, and through that exploration, we can link history to experiences and look for patterns or offer up a unique phenomenon. There’s such beauty in being able to tell a particular story, and qualitative research is a great mode for that! For our work, we examined the relationships we typically use the term mentorship for but didn’t feel that was quite the right word. Qualitative research allowed us to pick apart what we did and how we engaged in our relationships, which then allowed us to more accurately describe what was unique about our mentorship relationships, which we ultimately named liberationships ( McAloney and Long 2021) . Qualitative research gave us the means to explore, process, and name our experiences; what a powerful tool!
How do you come up with ideas for what to study (and how to study it)? Where did you get the idea for studying mentorship?
Coming up with ideas for research, for me, is kind of like Googling a question I have, not finding enough information, and then deciding to dig a little deeper to get the answer. The idea to study mentorship actually came up in conversation with my mentorship triad. We were talking in one of our meetings about our relationship—kind of meta, huh? We discussed how we felt that mentorship was not quite the right term for the relationships we had built. One of us asked what was different about our relationships and mentorship. This all happened when I was taking an ethnography course. During the next session of class, we were discussing auto- and duoethnography, and it hit me—let’s explore our version of mentorship, which we later went on to name liberationships ( McAloney and Long 2021 ). The idea and questions came out of being curious and wanting to find an answer. As I continue to research, I see opportunities in questions I have about my work or during conversations that, in our search for answers, end up exposing gaps in the literature. If I can’t find the answer already out there, I can study it.
—Kim McAloney, PhD, College Student Services Administration Ecampus coordinator and instructor
When you have a better idea of why you are interested in what it is that interests you, you may be surprised to learn that the obvious approaches to the topic are not the only ones. For example, let’s say you think you are interested in preserving coastal wildlife. And as a social scientist, you are interested in policies and practices that affect the long-term viability of coastal wildlife, especially around fishing communities. It would be natural then to consider designing a research study around fishing communities and how they manage their ecosystems. But when you really think about it, you realize that what interests you the most is how people whose livelihoods depend on a particular resource act in ways that deplete that resource. Or, even deeper, you contemplate the puzzle, “How do people justify actions that damage their surroundings?” Now, there are many ways to design a study that gets at that broader question, and not all of them are about fishing communities, although that is certainly one way to go. Maybe you could design an interview-based study that includes and compares loggers, fishers, and desert golfers (those who golf in arid lands that require a great deal of wasteful irrigation). Or design a case study around one particular example where resources were completely used up by a community. Without knowing what it is you are really interested in, what motivates your interest in a surface phenomenon, you are unlikely to come up with the appropriate research design.
These first stages of research design are often the most difficult, but have patience . Taking the time to consider why you are going to go through a lot of trouble to get answers will prevent a lot of wasted energy in the future.
There are distinct reasons for pursuing particular research questions, and it is helpful to distinguish between them. First, you may be personally motivated. This is probably the most important and the most often overlooked. What is it about the social world that sparks your curiosity? What bothers you? What answers do you need in order to keep living? For me, I knew I needed to get a handle on what higher education was for before I kept going at it. I needed to understand why I felt so different from my peers and whether this whole “higher education” thing was “for the likes of me” before I could complete my degree. That is the personal motivation question. Your personal motivation might also be political in nature, in that you want to change the world in a particular way. It’s all right to acknowledge this. In fact, it is better to acknowledge it than to hide it.
There are also academic and professional motivations for a particular study. If you are an absolute beginner, these may be difficult to find. We’ll talk more about this when we discuss reviewing the literature. Simply put, you are probably not the only person in the world to have thought about this question or issue and those related to it. So how does your interest area fit into what others have studied? Perhaps there is a good study out there of fishing communities, but no one has quite asked the “justification” question. You are motivated to address this to “fill the gap” in our collective knowledge. And maybe you are really not at all sure of what interests you, but you do know that [insert your topic] interests a lot of people, so you would like to work in this area too. You want to be involved in the academic conversation. That is a professional motivation and a very important one to articulate.
Practical and strategic motivations are a third kind. Perhaps you want to encourage people to take better care of the natural resources around them. If this is also part of your motivation, you will want to design your research project in a way that might have an impact on how people behave in the future. There are many ways to do this, one of which is using qualitative research methods rather than quantitative research methods, as the findings of qualitative research are often easier to communicate to a broader audience than the results of quantitative research. You might even be able to engage the community you are studying in the collecting and analyzing of data, something taboo in quantitative research but actively embraced and encouraged by qualitative researchers. But there are other practical reasons, such as getting “done” with your research in a certain amount of time or having access (or no access) to certain information. There is nothing wrong with considering constraints and opportunities when designing your study. Or maybe one of the practical or strategic goals is about learning competence in this area so that you can demonstrate the ability to conduct interviews and focus groups with future employers. Keeping that in mind will help shape your study and prevent you from getting sidetracked using a technique that you are less invested in learning about.
STOP HERE for a moment
I recommend you write a paragraph (at least) explaining your aims and goals. Include a sentence about each of the following: personal/political goals, practical or professional/academic goals, and practical/strategic goals. Think through how all of the goals are related and can be achieved by this particular research study . If they can’t, have a rethink. Perhaps this is not the best way to go about it.
You will also want to be clear about the purpose of your study. “Wait, didn’t we just do this?” you might ask. No! Your goals are not the same as the purpose of the study, although they are related. You can think about purpose lying on a continuum from “ theory ” to “action” (figure 2.1). Sometimes you are doing research to discover new knowledge about the world, while other times you are doing a study because you want to measure an impact or make a difference in the world.
Basic research involves research that is done for the sake of “pure” knowledge—that is, knowledge that, at least at this moment in time, may not have any apparent use or application. Often, and this is very important, knowledge of this kind is later found to be extremely helpful in solving problems. So one way of thinking about basic research is that it is knowledge for which no use is yet known but will probably one day prove to be extremely useful. If you are doing basic research, you do not need to argue its usefulness, as the whole point is that we just don’t know yet what this might be.
Researchers engaged in basic research want to understand how the world operates. They are interested in investigating a phenomenon to get at the nature of reality with regard to that phenomenon. The basic researcher’s purpose is to understand and explain ( Patton 2002:215 ).
Basic research is interested in generating and testing hypotheses about how the world works. Grounded Theory is one approach to qualitative research methods that exemplifies basic research (see chapter 4). Most academic journal articles publish basic research findings. If you are working in academia (e.g., writing your dissertation), the default expectation is that you are conducting basic research.
Applied research in the social sciences is research that addresses human and social problems. Unlike basic research, the researcher has expectations that the research will help contribute to resolving a problem, if only by identifying its contours, history, or context. From my experience, most students have this as their baseline assumption about research. Why do a study if not to make things better? But this is a common mistake. Students and their committee members are often working with default assumptions here—the former thinking about applied research as their purpose, the latter thinking about basic research: “The purpose of applied research is to contribute knowledge that will help people to understand the nature of a problem in order to intervene, thereby allowing human beings to more effectively control their environment. While in basic research the source of questions is the tradition within a scholarly discipline, in applied research the source of questions is in the problems and concerns experienced by people and by policymakers” ( Patton 2002:217 ).
Applied research is less geared toward theory in two ways. First, its questions do not derive from previous literature. For this reason, applied research studies have much more limited literature reviews than those found in basic research (although they make up for this by having much more “background” about the problem). Second, it does not generate theory in the same way as basic research does. The findings of an applied research project may not be generalizable beyond the boundaries of this particular problem or context. The findings are more limited. They are useful now but may be less useful later. This is why basic research remains the default “gold standard” of academic research.
Evaluation research is research that is designed to evaluate or test the effectiveness of specific solutions and programs addressing specific social problems. We already know the problems, and someone has already come up with solutions. There might be a program, say, for first-generation college students on your campus. Does this program work? Are first-generation students who participate in the program more likely to graduate than those who do not? These are the types of questions addressed by evaluation research. There are two types of research within this broader frame; however, one more action-oriented than the next. In summative evaluation , an overall judgment about the effectiveness of a program or policy is made. Should we continue our first-gen program? Is it a good model for other campuses? Because the purpose of such summative evaluation is to measure success and to determine whether this success is scalable (capable of being generalized beyond the specific case), quantitative data is more often used than qualitative data. In our example, we might have “outcomes” data for thousands of students, and we might run various tests to determine if the better outcomes of those in the program are statistically significant so that we can generalize the findings and recommend similar programs elsewhere. Qualitative data in the form of focus groups or interviews can then be used for illustrative purposes, providing more depth to the quantitative analyses. In contrast, formative evaluation attempts to improve a program or policy (to help “form” or shape its effectiveness). Formative evaluations rely more heavily on qualitative data—case studies, interviews, focus groups. The findings are meant not to generalize beyond the particular but to improve this program. If you are a student seeking to improve your qualitative research skills and you do not care about generating basic research, formative evaluation studies might be an attractive option for you to pursue, as there are always local programs that need evaluation and suggestions for improvement. Again, be very clear about your purpose when talking through your research proposal with your committee.
Action research takes a further step beyond evaluation, even formative evaluation, to being part of the solution itself. This is about as far from basic research as one could get and definitely falls beyond the scope of “science,” as conventionally defined. The distinction between action and research is blurry, the research methods are often in constant flux, and the only “findings” are specific to the problem or case at hand and often are findings about the process of intervention itself. Rather than evaluate a program as a whole, action research often seeks to change and improve some particular aspect that may not be working—maybe there is not enough diversity in an organization or maybe women’s voices are muted during meetings and the organization wonders why and would like to change this. In a further step, participatory action research , those women would become part of the research team, attempting to amplify their voices in the organization through participation in the action research. As action research employs methods that involve people in the process, focus groups are quite common.
If you are working on a thesis or dissertation, chances are your committee will expect you to be contributing to fundamental knowledge and theory ( basic research ). If your interests lie more toward the action end of the continuum, however, it is helpful to talk to your committee about this before you get started. Knowing your purpose in advance will help avoid misunderstandings during the later stages of the research process!
The Research Question
Once you have written your paragraph and clarified your purpose and truly know that this study is the best study for you to be doing right now , you are ready to write and refine your actual research question. Know that research questions are often moving targets in qualitative research, that they can be refined up to the very end of data collection and analysis. But you do have to have a working research question at all stages. This is your “anchor” when you get lost in the data. What are you addressing? What are you looking at and why? Your research question guides you through the thicket. It is common to have a whole host of questions about a phenomenon or case, both at the outset and throughout the study, but you should be able to pare it down to no more than two or three sentences when asked. These sentences should both clarify the intent of the research and explain why this is an important question to answer. More on refining your research question can be found in chapter 4.
Chances are, you will have already done some prior reading before coming up with your interest and your questions, but you may not have conducted a systematic literature review. This is the next crucial stage to be completed before venturing further. You don’t want to start collecting data and then realize that someone has already beaten you to the punch. A review of the literature that is already out there will let you know (1) if others have already done the study you are envisioning; (2) if others have done similar studies, which can help you out; and (3) what ideas or concepts are out there that can help you frame your study and make sense of your findings. More on literature reviews can be found in chapter 9.
In addition to reviewing the literature for similar studies to what you are proposing, it can be extremely helpful to find a study that inspires you. This may have absolutely nothing to do with the topic you are interested in but is written so beautifully or organized so interestingly or otherwise speaks to you in such a way that you want to post it somewhere to remind you of what you want to be doing. You might not understand this in the early stages—why would you find a study that has nothing to do with the one you are doing helpful? But trust me, when you are deep into analysis and writing, having an inspirational model in view can help you push through. If you are motivated to do something that might change the world, you probably have read something somewhere that inspired you. Go back to that original inspiration and read it carefully and see how they managed to convey the passion that you so appreciate.
At this stage, you are still just getting started. There are a lot of things to do before setting forth to collect data! You’ll want to consider and choose a research tradition and a set of data-collection techniques that both help you answer your research question and match all your aims and goals. For example, if you really want to help migrant workers speak for themselves, you might draw on feminist theory and participatory action research models. Chapters 3 and 4 will provide you with more information on epistemologies and approaches.
Next, you have to clarify your “units of analysis.” What is the level at which you are focusing your study? Often, the unit in qualitative research methods is individual people, or “human subjects.” But your units of analysis could just as well be organizations (colleges, hospitals) or programs or even whole nations. Think about what it is you want to be saying at the end of your study—are the insights you are hoping to make about people or about organizations or about something else entirely? A unit of analysis can even be a historical period! Every unit of analysis will call for a different kind of data collection and analysis and will produce different kinds of “findings” at the conclusion of your study. [2]
Regardless of what unit of analysis you select, you will probably have to consider the “human subjects” involved in your research. [3] Who are they? What interactions will you have with them—that is, what kind of data will you be collecting? Before answering these questions, define your population of interest and your research setting. Use your research question to help guide you.
Let’s use an example from a real study. In Geographies of Campus Inequality , Benson and Lee ( 2020 ) list three related research questions: “(1) What are the different ways that first-generation students organize their social, extracurricular, and academic activities at selective and highly selective colleges? (2) how do first-generation students sort themselves and get sorted into these different types of campus lives; and (3) how do these different patterns of campus engagement prepare first-generation students for their post-college lives?” (3).
Note that we are jumping into this a bit late, after Benson and Lee have described previous studies (the literature review) and what is known about first-generation college students and what is not known. They want to know about differences within this group, and they are interested in ones attending certain kinds of colleges because those colleges will be sites where academic and extracurricular pressures compete. That is the context for their three related research questions. What is the population of interest here? First-generation college students . What is the research setting? Selective and highly selective colleges . But a host of questions remain. Which students in the real world, which colleges? What about gender, race, and other identity markers? Will the students be asked questions? Are the students still in college, or will they be asked about what college was like for them? Will they be observed? Will they be shadowed? Will they be surveyed? Will they be asked to keep diaries of their time in college? How many students? How many colleges? For how long will they be observed?
Recommendation
Take a moment and write down suggestions for Benson and Lee before continuing on to what they actually did.
Have you written down your own suggestions? Good. Now let’s compare those with what they actually did. Benson and Lee drew on two sources of data: in-depth interviews with sixty-four first-generation students and survey data from a preexisting national survey of students at twenty-eight selective colleges. Let’s ignore the survey for our purposes here and focus on those interviews. The interviews were conducted between 2014 and 2016 at a single selective college, “Hilltop” (a pseudonym ). They employed a “purposive” sampling strategy to ensure an equal number of male-identifying and female-identifying students as well as equal numbers of White, Black, and Latinx students. Each student was interviewed once. Hilltop is a selective liberal arts college in the northeast that enrolls about three thousand students.
How did your suggestions match up to those actually used by the researchers in this study? It is possible your suggestions were too ambitious? Beginning qualitative researchers can often make that mistake. You want a research design that is both effective (it matches your question and goals) and doable. You will never be able to collect data from your entire population of interest (unless your research question is really so narrow to be relevant to very few people!), so you will need to come up with a good sample. Define the criteria for this sample, as Benson and Lee did when deciding to interview an equal number of students by gender and race categories. Define the criteria for your sample setting too. Hilltop is typical for selective colleges. That was a research choice made by Benson and Lee. For more on sampling and sampling choices, see chapter 5.
Benson and Lee chose to employ interviews. If you also would like to include interviews, you have to think about what will be asked in them. Most interview-based research involves an interview guide, a set of questions or question areas that will be asked of each participant. The research question helps you create a relevant interview guide. You want to ask questions whose answers will provide insight into your research question. Again, your research question is the anchor you will continually come back to as you plan for and conduct your study. It may be that once you begin interviewing, you find that people are telling you something totally unexpected, and this makes you rethink your research question. That is fine. Then you have a new anchor. But you always have an anchor. More on interviewing can be found in chapter 11.
Let’s imagine Benson and Lee also observed college students as they went about doing the things college students do, both in the classroom and in the clubs and social activities in which they participate. They would have needed a plan for this. Would they sit in on classes? Which ones and how many? Would they attend club meetings and sports events? Which ones and how many? Would they participate themselves? How would they record their observations? More on observation techniques can be found in both chapters 13 and 14.
At this point, the design is almost complete. You know why you are doing this study, you have a clear research question to guide you, you have identified your population of interest and research setting, and you have a reasonable sample of each. You also have put together a plan for data collection, which might include drafting an interview guide or making plans for observations. And so you know exactly what you will be doing for the next several months (or years!). To put the project into action, there are a few more things necessary before actually going into the field.
First, you will need to make sure you have any necessary supplies, including recording technology. These days, many researchers use their phones to record interviews. Second, you will need to draft a few documents for your participants. These include informed consent forms and recruiting materials, such as posters or email texts, that explain what this study is in clear language. Third, you will draft a research protocol to submit to your institutional review board (IRB) ; this research protocol will include the interview guide (if you are using one), the consent form template, and all examples of recruiting material. Depending on your institution and the details of your study design, it may take weeks or even, in some unfortunate cases, months before you secure IRB approval. Make sure you plan on this time in your project timeline. While you wait, you can continue to review the literature and possibly begin drafting a section on the literature review for your eventual presentation/publication. More on IRB procedures can be found in chapter 8 and more general ethical considerations in chapter 7.
Once you have approval, you can begin!
Research Design Checklist
Before data collection begins, do the following:
- Write a paragraph explaining your aims and goals (personal/political, practical/strategic, professional/academic).
- Define your research question; write two to three sentences that clarify the intent of the research and why this is an important question to answer.
- Review the literature for similar studies that address your research question or similar research questions; think laterally about some literature that might be helpful or illuminating but is not exactly about the same topic.
- Find a written study that inspires you—it may or may not be on the research question you have chosen.
- Consider and choose a research tradition and set of data-collection techniques that (1) help answer your research question and (2) match your aims and goals.
- Define your population of interest and your research setting.
- Define the criteria for your sample (How many? Why these? How will you find them, gain access, and acquire consent?).
- If you are conducting interviews, draft an interview guide.
- If you are making observations, create a plan for observations (sites, times, recording, access).
- Acquire any necessary technology (recording devices/software).
- Draft consent forms that clearly identify the research focus and selection process.
- Create recruiting materials (posters, email, texts).
- Apply for IRB approval (proposal plus consent form plus recruiting materials).
- Block out time for collecting data.
- At the end of the chapter, you will find a " Research Design Checklist " that summarizes the main recommendations made here ↵
- For example, if your focus is society and culture , you might collect data through observation or a case study. If your focus is individual lived experience , you are probably going to be interviewing some people. And if your focus is language and communication , you will probably be analyzing text (written or visual). ( Marshall and Rossman 2016:16 ). ↵
- You may not have any "live" human subjects. There are qualitative research methods that do not require interactions with live human beings - see chapter 16 , "Archival and Historical Sources." But for the most part, you are probably reading this textbook because you are interested in doing research with people. The rest of the chapter will assume this is the case. ↵
One of the primary methodological traditions of inquiry in qualitative research, ethnography is the study of a group or group culture, largely through observational fieldwork supplemented by interviews. It is a form of fieldwork that may include participant-observation data collection. See chapter 14 for a discussion of deep ethnography.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and research design that focuses on an individual case (e.g., setting, institution, or sometimes an individual) in order to explore its complexity, history, and interactive parts. As an approach, it is particularly useful for obtaining a deep appreciation of an issue, event, or phenomenon of interest in its particular context.
The controlling force in research; can be understood as lying on a continuum from basic research (knowledge production) to action research (effecting change).
In its most basic sense, a theory is a story we tell about how the world works that can be tested with empirical evidence. In qualitative research, we use the term in a variety of ways, many of which are different from how they are used by quantitative researchers. Although some qualitative research can be described as “testing theory,” it is more common to “build theory” from the data using inductive reasoning , as done in Grounded Theory . There are so-called “grand theories” that seek to integrate a whole series of findings and stories into an overarching paradigm about how the world works, and much smaller theories or concepts about particular processes and relationships. Theory can even be used to explain particular methodological perspectives or approaches, as in Institutional Ethnography , which is both a way of doing research and a theory about how the world works.
Research that is interested in generating and testing hypotheses about how the world works.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
An approach to research that is “multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives." ( Denzin and Lincoln 2005:2 ). Contrast with quantitative research .
Research that contributes knowledge that will help people to understand the nature of a problem in order to intervene, thereby allowing human beings to more effectively control their environment.
Research that is designed to evaluate or test the effectiveness of specific solutions and programs addressing specific social problems. There are two kinds: summative and formative .
Research in which an overall judgment about the effectiveness of a program or policy is made, often for the purpose of generalizing to other cases or programs. Generally uses qualitative research as a supplement to primary quantitative data analyses. Contrast formative evaluation research .
Research designed to improve a program or policy (to help “form” or shape its effectiveness); relies heavily on qualitative research methods. Contrast summative evaluation research
Research carried out at a particular organizational or community site with the intention of affecting change; often involves research subjects as participants of the study. See also participatory action research .
Research in which both researchers and participants work together to understand a problematic situation and change it for the better.
The level of the focus of analysis (e.g., individual people, organizations, programs, neighborhoods).
The large group of interest to the researcher. Although it will likely be impossible to design a study that incorporates or reaches all members of the population of interest, this should be clearly defined at the outset of a study so that a reasonable sample of the population can be taken. For example, if one is studying working-class college students, the sample may include twenty such students attending a particular college, while the population is “working-class college students.” In quantitative research, clearly defining the general population of interest is a necessary step in generalizing results from a sample. In qualitative research, defining the population is conceptually important for clarity.
A fictional name assigned to give anonymity to a person, group, or place. Pseudonyms are important ways of protecting the identity of research participants while still providing a “human element” in the presentation of qualitative data. There are ethical considerations to be made in selecting pseudonyms; some researchers allow research participants to choose their own.
A requirement for research involving human participants; the documentation of informed consent. In some cases, oral consent or assent may be sufficient, but the default standard is a single-page easy-to-understand form that both the researcher and the participant sign and date. Under federal guidelines, all researchers "shall seek such consent only under circumstances that provide the prospective subject or the representative sufficient opportunity to consider whether or not to participate and that minimize the possibility of coercion or undue influence. The information that is given to the subject or the representative shall be in language understandable to the subject or the representative. No informed consent, whether oral or written, may include any exculpatory language through which the subject or the representative is made to waive or appear to waive any of the subject's rights or releases or appears to release the investigator, the sponsor, the institution, or its agents from liability for negligence" (21 CFR 50.20). Your IRB office will be able to provide a template for use in your study .
An administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under the auspices of the institution with which it is affiliated. The IRB is charged with the responsibility of reviewing all research involving human participants. The IRB is concerned with protecting the welfare, rights, and privacy of human subjects. The IRB has the authority to approve, disapprove, monitor, and require modifications in all research activities that fall within its jurisdiction as specified by both the federal regulations and institutional policy.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Qualitative research: methods and examples
Last updated
13 April 2023
Reviewed by
Qualitative research involves gathering and evaluating non-numerical information to comprehend concepts, perspectives, and experiences. It’s also helpful for obtaining in-depth insights into a certain subject or generating new research ideas.
As a result, qualitative research is practical if you want to try anything new or produce new ideas.
There are various ways you can conduct qualitative research. In this article, you'll learn more about qualitative research methodologies, including when you should use them.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a broad term describing various research types that rely on asking open-ended questions. Qualitative research investigates “how” or “why” certain phenomena occur. It is about discovering the inherent nature of something.
The primary objective of qualitative research is to understand an individual's ideas, points of view, and feelings. In this way, collecting in-depth knowledge of a specific topic is possible. Knowing your audience's feelings about a particular subject is important for making reasonable research conclusions.
Unlike quantitative research , this approach does not involve collecting numerical, objective data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is used extensively in education, sociology, health science, history, and anthropology.
- Types of qualitative research methodology
Typically, qualitative research aims at uncovering the attitudes and behavior of the target audience concerning a specific topic. For example, “How would you describe your experience as a new Dovetail user?”
Some of the methods for conducting qualitative analysis include:
Focus groups
Hosting a focus group is a popular qualitative research method. It involves obtaining qualitative data from a limited sample of participants. In a moderated version of a focus group, the moderator asks participants a series of predefined questions. They aim to interact and build a group discussion that reveals their preferences, candid thoughts, and experiences.
Unmoderated, online focus groups are increasingly popular because they eliminate the need to interact with people face to face.
Focus groups can be more cost-effective than 1:1 interviews or studying a group in a natural setting and reporting one’s observations.
Focus groups make it possible to gather multiple points of view quickly and efficiently, making them an excellent choice for testing new concepts or conducting market research on a new product.
However, there are some potential drawbacks to this method. It may be unsuitable for sensitive or controversial topics. Participants might be reluctant to disclose their true feelings or respond falsely to conform to what they believe is the socially acceptable answer (known as response bias).
Case study research
A case study is an in-depth evaluation of a specific person, incident, organization, or society. This type of qualitative research has evolved into a broadly applied research method in education, law, business, and the social sciences.
Even though case study research may appear challenging to implement, it is one of the most direct research methods. It requires detailed analysis, broad-ranging data collection methodologies, and a degree of existing knowledge about the subject area under investigation.
Historical model
The historical approach is a distinct research method that deeply examines previous events to better understand the present and forecast future occurrences of the same phenomena. Its primary goal is to evaluate the impacts of history on the present and hence discover comparable patterns in the present to predict future outcomes.
Oral history
This qualitative data collection method involves gathering verbal testimonials from individuals about their personal experiences. It is widely used in historical disciplines to offer counterpoints to established historical facts and narratives. The most common methods of gathering oral history are audio recordings, analysis of auto-biographical text, videos, and interviews.
Qualitative observation
One of the most fundamental, oldest research methods, qualitative observation , is the process through which a researcher collects data using their senses of sight, smell, hearing, etc. It is used to observe the properties of the subject being studied. For example, “What does it look like?” As research methods go, it is subjective and depends on researchers’ first-hand experiences to obtain information, so it is prone to bias. However, it is an excellent way to start a broad line of inquiry like, “What is going on here?”
Record keeping and review
Record keeping uses existing documents and relevant data sources that can be employed for future studies. It is equivalent to visiting the library and going through publications or any other reference material to gather important facts that will likely be used in the research.
Grounded theory approach
The grounded theory approach is a commonly used research method employed across a variety of different studies. It offers a unique way to gather, interpret, and analyze. With this approach, data is gathered and analyzed simultaneously. Existing analysis frames and codes are disregarded, and data is analyzed inductively, with new codes and frames generated from the research.
Ethnographic research
Ethnography is a descriptive form of a qualitative study of people and their cultures. Its primary goal is to study people's behavior in their natural environment. This method necessitates that the researcher adapts to their target audience's setting.
Thereby, you will be able to understand their motivation, lifestyle, ambitions, traditions, and culture in situ. But, the researcher must be prepared to deal with geographical constraints while collecting data i.e., audiences can’t be studied in a laboratory or research facility.
This study can last from a couple of days to several years. Thus, it is time-consuming and complicated, requiring you to have both the time to gather the relevant data as well as the expertise in analyzing, observing, and interpreting data to draw meaningful conclusions.
Narrative framework
A narrative framework is a qualitative research approach that relies on people's written text or visual images. It entails people analyzing these events or narratives to determine certain topics or issues. With this approach, you can understand how people represent themselves and their experiences to a larger audience.
Phenomenological approach
The phenomenological study seeks to investigate the experiences of a particular phenomenon within a group of individuals or communities. It analyzes a certain event through interviews with persons who have witnessed it to determine the connections between their views. Even though this method relies heavily on interviews, other data sources (recorded notes), and observations could be employed to enhance the findings.
- Qualitative research methods (tools)
Some of the instruments involved in qualitative research include:
Document research: Also known as document analysis because it involves evaluating written documents. These can include personal and non-personal materials like archives, policy publications, yearly reports, diaries, or letters.
Focus groups: This is where a researcher poses questions and generates conversation among a group of people. The major goal of focus groups is to examine participants' experiences and knowledge, including research into how and why individuals act in various ways.
Secondary study: Involves acquiring existing information from texts, images, audio, or video recordings.
Observations: This requires thorough field notes on everything you see, hear, or experience. Compared to reported conduct or opinion, this study method can assist you in getting insights into a specific situation and observable behaviors.
Structured interviews : In this approach, you will directly engage people one-on-one. Interviews are ideal for learning about a person's subjective beliefs, motivations, and encounters.
Surveys: This is when you distribute questionnaires containing open-ended questions
- What are common examples of qualitative research?
Everyday examples of qualitative research include:
Conducting a demographic analysis of a business
For instance, suppose you own a business such as a grocery store (or any store) and believe it caters to a broad customer base, but after conducting a demographic analysis, you discover that most of your customers are men.
You could do 1:1 interviews with female customers to learn why they don't shop at your store.
In this case, interviewing potential female customers should clarify why they don't find your shop appealing. It could be because of the products you sell or a need for greater brand awareness, among other possible reasons.
Launching or testing a new product
Suppose you are the product manager at a SaaS company looking to introduce a new product. Focus groups can be an excellent way to determine whether your product is marketable.
In this instance, you could hold a focus group with a sample group drawn from your intended audience. The group will explore the product based on its new features while you ensure adequate data on how users react to the new features. The data you collect will be key to making sales and marketing decisions.
Conducting studies to explain buyers' behaviors
You can also use qualitative research to understand existing buyer behavior better. Marketers analyze historical information linked to their businesses and industries to see when purchasers buy more.
Qualitative research can help you determine when to target new clients and peak seasons to boost sales by investigating the reason behind these behaviors.
- Qualitative research: data collection
Data collection is gathering information on predetermined variables to gain appropriate answers, test hypotheses, and analyze results. Researchers will collect non-numerical data for qualitative data collection to obtain detailed explanations and draw conclusions.
To get valid findings and achieve a conclusion in qualitative research, researchers must collect comprehensive and multifaceted data.
Qualitative data is usually gathered through interviews or focus groups with videotapes or handwritten notes. If there are recordings, they are transcribed before the data analysis process. Researchers keep separate folders for the recordings acquired from each focus group when collecting qualitative research data to categorize the data.
- Qualitative research: data analysis
Qualitative data analysis is organizing, examining, and interpreting qualitative data. Its main objective is identifying trends and patterns, responding to research questions, and recommending actions based on the findings. Textual analysis is a popular method for analyzing qualitative data.
Textual analysis differs from other qualitative research approaches in that researchers consider the social circumstances of study participants to decode their words, behaviors, and broader meaning.
Learn more about qualitative research data analysis software
- When to use qualitative research
Qualitative research is helpful in various situations, particularly when a researcher wants to capture accurate, in-depth insights.
Here are some instances when qualitative research can be valuable:
Examining your product or service to improve your marketing approach
When researching market segments, demographics, and customer service teams
Identifying client language when you want to design a quantitative survey
When attempting to comprehend your or someone else's strengths and weaknesses
Assessing feelings and beliefs about societal and public policy matters
Collecting information about a business or product's perception
Analyzing your target audience's reactions to marketing efforts
When launching a new product or coming up with a new idea
When seeking to evaluate buyers' purchasing patterns
- Qualitative research methods vs. quantitative research methods
Qualitative research examines people's ideas and what influences their perception, whereas quantitative research draws conclusions based on numbers and measurements.
Qualitative research is descriptive, and its primary goal is to comprehensively understand people's attitudes, behaviors, and ideas.
In contrast, quantitative research is more restrictive because it relies on numerical data and analyzes statistical data to make decisions. This research method assists researchers in gaining an initial grasp of the subject, which deals with numbers. For instance, the number of customers likely to purchase your products or use your services.
What is the most important feature of qualitative research?
A distinguishing feature of qualitative research is that it’s conducted in a real-world setting instead of a simulated environment. The researcher is examining actual phenomena instead of experimenting with different variables to see what outcomes (data) might result.
Can I use qualitative and quantitative approaches together in a study?
Yes, combining qualitative and quantitative research approaches happens all the time and is known as mixed methods research. For example, you could study individuals’ perceived risk in a certain scenario, such as how people rate the safety or riskiness of a given neighborhood. Simultaneously, you could analyze historical data objectively, indicating how safe or dangerous that area has been in the last year. To get the most out of mixed-method research, it’s important to understand the pros and cons of each methodology, so you can create a thoughtfully designed study that will yield compelling results.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
Research Paper Guide
Qualitative Research Method
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
16 min read

People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
There are various methods for conducting scientific research. The two broad approaches to data collection include qualitative and quantitative research methods.
However, it is not easy to decide which one to choose while writing a research paper .
If you know the basic difference between both methods, you will produce a well-written and structured paper.
In this blog, we have explored what is qualitative research, its nature, purpose, and methods of data collection. By reading this, students can gain a good understanding of qualitative research, enhancing their ability to conduct in-depth studies.
So keep reading!
- 1. What is Qualitative Research - Definition
- 2. Qualitative Research Methods
- 3. Types of Qualitative Research
- 4. Steps in Conducting Qualitative Research
- 5. Qualitative Research vs Quantitative Research
- 6. Qualitative Research Topics
- 7. Qualitative Research Examples
What is Qualitative Research - Definition
Qualitative research is a research methodology that aims to explore and understand the complexities of human behavior, emotions, and experiences through non-numerical data.
Unlike quantitative research, which deals in numbers and statistics, qualitative research is all about revealing the stories, and perspectives that make us uniquely human.
Let's dive deeper and discover why it's a powerful tool in the researcher's arsenal.
Purpose of Qualitative Research Design
Qualitative research simplifies the understanding of complex human behavior and experiences. Its purpose is to:
- Explore Complex Phenomena: Qualitative research allows us to delve deep into intricate human experiences and behaviors.
- Understand Motivations: It helps uncover the 'whys' behind actions, shedding light on underlying motivations.
- Capture Richness: By collecting narratives and stories, qualitative research captures the richness of human life.
- Generate Hypotheses: It often serves as a foundation for hypothesis generation in further quantitative studies.
- Inform Decision-Making: Qualitative findings guide decisions in fields like psychology, sociology, and market research.
- Contextualize Quantitative Data: It provides context to quantitative data, explaining the 'how' and 'why' behind the numbers.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
The following are the main characteristics of qualitative research.
- The real-world setting is the first important characteristic. It involves various qualitative research methods to study the behavior of participants.
- Researchers play an essential role in choosing a method and making a plan for conducting research.
- All qualitative approaches have their significance and are used for different scenarios.
- Qualitative research questions are beneficial for complex reasoning to get the right results.
- It is also used to explain the outcome of quantitative research methods.
- The role of participants is essential as it brings meaning to the study.
- Qualitative research is flexible and can be changed at any stage of the research work.
- It also describes the research problem by developing a complex cause-and-effect relationship between the variables.
- Data analysis in qualitative research is an ongoing process.
- Conclusions can be drawn based on the outcomes of the research process.
- Participants are selected from a particular and relevant group.
Qualitative Research Methods

A detailed description of the major qualitative approaches to collecting data is given below.
In-depth Interview
In-depth interviews involve one-on-one conversations to gather detailed information about a specific topic. This method allows researchers to explore participants' motivations, inspirations, and body language.
Interviews can be conducted face-to-face, via email, or over the phone for flexibility.
Focus Groups
Focus groups consist of small group discussions (5-15 participants) on specific topics, ideal for 'what,' 'why,' and 'how' questions about society and the environment. They can be conducted in-person or online, offering versatility in data collection.
Direct Observation
Direct observation collects subjective data through the five senses without interference. It focuses on characteristics, not measurements, often in public settings where privacy isn't a concern.
Open-Ended Surveys
Open-ended surveys use structured or unstructured questions to collect information on respondents' opinions and beliefs, providing insights into their perspectives.
Participant Observation
Participant observation involves researchers actively participating in events while observing people in natural settings, offering firsthand experience and insights.
Literature Review
The literature review method interprets words and images from published works to analyze social life. It examines word usage in context to draw inferences and identify meanings.
Types of Qualitative Research

The following is a comprehensive overview of the types of qualitative research methods.
The case study research method has now become the most valuable method of conducting research. It has evolved in recent years and is used to explain an entity in detail.
Moreover, it also involves a thorough understanding of different types of data sources. These include interviews, documents, reports, and observations. Mainly, this research type is used in different areas like education, social sciences, etc.
Ethnographic Research
The ethnographic research method is the most familiar and in-depth observational method. It focuses on people and their behaviors in the natural environment.
Here, a researcher needs to adapt to the environment and society of the target audience to conduct better research. It helps to get a first-hand experience of the natural setting, including the customs, traditions, and culture of the subjects.
This type of research is a challenging and time-consuming process as it can last from days to years. However, geographical constraints can be an issue while collecting data.
Grounded Theory
While other methods discuss and focus on an event or activity. The grounded theory method deeply looks into the explanation and the main theory behind the event.
It requires the researcher to observe the interviews and documents to build a theory. Moreover, it usually starts with a question or collection of data. However, the sample sizes in this method are usually larger than in other methods.
Phenomenological Method
This type is used in the description of an event, phenomenon, and activity. Here, methods like interviews, reading documents, visiting places, and watching videos are used.
This will help to add new insights to the existing data analysis by checking its reliability and validity.
Check out the video to learn more about the phenomenological method of qualitative research!
Narrative Method
The narrative method is used to gather data from subjects through interviews or documents. Later, the gathered information is used to derive answers and suggestions for future research.
Historical Method
The historical method involves the examination of past events to draw conclusions and predictions about the future. The steps included in the method are formulating a plan, gathering data, and analyzing the sources.
Steps in Conducting Qualitative Research
Conducting qualitative research is a systematic process that involves several key steps to ensure the collection of meaningful data.
Here's a chronological guide to conducting qualitative research:
Step 1: Define Research Objectives
Begin by clearly defining the research objectives and questions. What do you want to learn, explore, or understand through your qualitative research? This step sets the direction for your study.
Step 2: Select a Research Design
Choose an appropriate research design based on your objectives. Common designs include case studies, ethnography, grounded theory, or phenomenology. The design informs your data collection and analysis methods.
Step 3: Sampling Methods
Decide on your sampling strategy. Will you use purposive sampling to select specific participants who are most relevant to your research question? Or will you employ snowball sampling to find participants through referrals?
Step 4: Data Collection Techniques
Determine the data collection techniques that align with your research design. Depending on your approach, this may involve conducting in-depth interviews, facilitating focus groups, observing participants, or analyzing existing documents and content.
Step 5: Plan Interviews and Questions
If conducting interviews, create interview guides with open-ended questions. These questions should allow participants to share their thoughts, experiences, and perspectives freely. Ensure that questions are related to your research objectives.
Step 6: Conducting Data Collection
Collect data according to your chosen methods. For interviews, arrange and conduct interviews with participants, ensuring a comfortable and open environment. If using other techniques, follow the procedures outlined in your research design.
Step 7: Data Recording and Management
Record data meticulously. This may involve audio or video recordings, note-taking, or transcribing interviews. Organize and store data securely to maintain confidentiality.
Step 8: Data Analysis
Qualitative data can be in the form of interviews, transcripts, surveys, videos, audio, etc. The steps involved in qualitative data analysis are given below.
- Organize the Data: This can be done by transcribing interviews or making detailed notes.
- Review the Data: Examine the data, ideas, and patterns.
- Establish a Data Coding System: Generate a set of codes that you can apply to classify your data.
- Assign Codes to the Data: For qualitative survey analysis, create codes, and add them to your system.
- Identify Themes: Link the codes together into cohesive themes.
Similarly, the following are different approaches to analyzing qualitative data.
- Content Analysis – It is used to categorize common words and ideas.
- Thematic Analysis – thematic analysis in qualitative research is used to identify and interpret different themes and patterns.
- Textual Analysis – This type of analysis is used to examine the structure, content, and design of text.
- Discourse Analysis – It is used to study how a language is used to achieve specific results.
Step 9: Validity and Reliability
Ensure the validity and reliability of your findings. Consistently apply your chosen analysis methods and cross-check interpretations with colleagues or participants to validate your results.
Step 10: Ethical Considerations
Throughout the research process, uphold ethical principles. Protect the privacy and anonymity of participants, obtain informed consent, and address any ethical concerns that may arise.
Qualitative Research vs Quantitative Research
Qualitative and quantitative research are two distinct approaches to conducting research. Here are the main differences between qualitative vs. quantitative research.
Looking for a more detailed comparison between these 2 types of research? Check out our qualitative vs. quantitative research blog.
Qualitative Research Topics
To write an amazing qualitative research paper, here are some interesting topics for you.
- The Impact of Parental Involvement on Children's Education
- Social Isolation and Loneliness Among the Elderly
- Factors Influencing Consumer Choices in Sustainable Fashion
- Coping Mechanisms for Stress Among College Students
- Experiences of Immigrant Workers in Low-Wage Jobs
- The Role of Music in Expressing Emotions and Well-being
- Perceptions of Mental Health Stigma in Ethnic Communities
- Exploring the Transition to Parenthood: Challenges and Joys
- How Cultural Differences Influence Conflict Resolution Styles
- The Influence of Family Dynamics on Eating Habits and Nutrition in Children
We have also compiled a list of research paper topics in case you need more unique ideas.
Qualitative Research Examples
Check out the examples of qualitative research to get a better idea of writing a qualitative research study.
Qualitative Research Example
Qualitative Research Paper Sample
Qualitative Research Limitations
The following discussed are the qualitative research limitations.
- The qualitative research data involve fewer expenses and time.
- It does not have large-scale data.
- It requires a lot of time to manage, gather, and analyze data.
- It is not possible to verify the results as it is open-ended research.
- It is difficult to analyze the credibility and validity of data because of its subjective nature.
- Expert knowledge of the area is necessary to understand the collected information.
In Conclusion, the qualitative research method shows the idea and perception of your targeted audience. However, not every student is able to choose the right approach while writing a research paper. It requires a thorough understanding of both qualitative research and quantitative research methods.
This is where the professional help from MyPerfectWords.com comes in. We offer custom essay writing help with your academic assignments.
Contact our customer support and place " write my research paper " order today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the two methods in research study.
There are two types of studies that involve observing people during a study, participant observation and non-participant observation.
Why is qualitative research better?
Because qualitative research includes the ability to gain unique insights through deep exploration. Survey respondents are able to disclose their experiences, thoughts, and feelings without constraint or influence from an outside source.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
18 Qualitative Research Examples

Qualitative research is an approach to scientific research that involves using observation to gather and analyze non-numerical, in-depth, and well-contextualized datasets.
It serves as an integral part of academic, professional, and even daily decision-making processes (Baxter & Jack, 2008).
Methods of qualitative research encompass a wide range of techniques, from in-depth personal encounters, like ethnographies (studying cultures in-depth) and autoethnographies (examining one’s own cultural experiences), to collection of diverse perspectives on topics through methods like interviewing focus groups (gatherings of individuals to discuss specific topics).
Qualitative Research Examples
1. ethnography.
Definition: Ethnography is a qualitative research design aimed at exploring cultural phenomena. Rooted in the discipline of anthropology , this research approach investigates the social interactions, behaviors, and perceptions within groups, communities, or organizations.
Ethnographic research is characterized by extended observation of the group, often through direct participation, in the participants’ environment. An ethnographer typically lives with the study group for extended periods, intricately observing their everyday lives (Khan, 2014).
It aims to present a complete, detailed and accurate picture of the observed social life, rituals, symbols, and values from the perspective of the study group.
Example of Ethnographic Research
Title: “ The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity “
Citation: Evans, J. (2010). The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity. Peter Lang.
Overview: This study by Evans (2010) provides a rich narrative of young adult male identity as experienced in everyday life. The author immersed himself among a group of young men, participating in their activities and cultivating a deep understanding of their lifestyle, values, and motivations. This research exemplified the ethnographic approach, revealing complexities of the subjects’ identities and societal roles, which could hardly be accessed through other qualitative research designs.
Read my Full Guide on Ethnography Here
2. Autoethnography
Definition: Autoethnography is an approach to qualitative research where the researcher uses their own personal experiences to extend the understanding of a certain group, culture, or setting. Essentially, it allows for the exploration of self within the context of social phenomena.
Unlike traditional ethnography, which focuses on the study of others, autoethnography turns the ethnographic gaze inward, allowing the researcher to use their personal experiences within a culture as rich qualitative data (Durham, 2019).
The objective is to critically appraise one’s personal experiences as they navigate and negotiate cultural, political, and social meanings. The researcher becomes both the observer and the participant, intertwining personal and cultural experiences in the research.
Example of Autoethnographic Research
Title: “ A Day In The Life Of An NHS Nurse “
Citation: Osben, J. (2019). A day in the life of a NHS nurse in 21st Century Britain: An auto-ethnography. The Journal of Autoethnography for Health & Social Care. 1(1).
Overview: This study presents an autoethnography of a day in the life of an NHS nurse (who, of course, is also the researcher). The author uses the research to achieve reflexivity, with the researcher concluding: “Scrutinising my practice and situating it within a wider contextual backdrop has compelled me to significantly increase my level of scrutiny into the driving forces that influence my practice.”
Read my Full Guide on Autoethnography Here
3. Semi-Structured Interviews
Definition: Semi-structured interviews stand as one of the most frequently used methods in qualitative research. These interviews are planned and utilize a set of pre-established questions, but also allow for the interviewer to steer the conversation in other directions based on the responses given by the interviewee.
In semi-structured interviews, the interviewer prepares a guide that outlines the focal points of the discussion. However, the interview is flexible, allowing for more in-depth probing if the interviewer deems it necessary (Qu, & Dumay, 2011). This style of interviewing strikes a balance between structured ones which might limit the discussion, and unstructured ones, which could lack focus.
Example of Semi-Structured Interview Research
Title: “ Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review “
Citation: Puts, M., et al. (2014). Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review. Annals of oncology, 25 (3), 564-577.
Overview: Puts et al. (2014) executed an extensive systematic review in which they conducted semi-structured interviews with older adults suffering from cancer to examine the factors influencing their adherence to cancer treatment. The findings suggested that various factors, including side effects, faith in healthcare professionals, and social support have substantial impacts on treatment adherence. This research demonstrates how semi-structured interviews can provide rich and profound insights into the subjective experiences of patients.
4. Focus Groups
Definition: Focus groups are a qualitative research method that involves organized discussion with a selected group of individuals to gain their perspectives on a specific concept, product, or phenomenon. Typically, these discussions are guided by a moderator.
During a focus group session, the moderator has a list of questions or topics to discuss, and participants are encouraged to interact with each other (Morgan, 2010). This interactivity can stimulate more information and provide a broader understanding of the issue under scrutiny. The open format allows participants to ask questions and respond freely, offering invaluable insights into attitudes, experiences, and group norms.
Example of Focus Group Research
Title: “ Perspectives of Older Adults on Aging Well: A Focus Group Study “
Citation: Halaweh, H., Dahlin-Ivanoff, S., Svantesson, U., & Willén, C. (2018). Perspectives of older adults on aging well: a focus group study. Journal of aging research .
Overview: This study aimed to explore what older adults (aged 60 years and older) perceived to be ‘aging well’. The researchers identified three major themes from their focus group interviews: a sense of well-being, having good physical health, and preserving good mental health. The findings highlight the importance of factors such as positive emotions, social engagement, physical activity, healthy eating habits, and maintaining independence in promoting aging well among older adults.
5. Phenomenology
Definition: Phenomenology, a qualitative research method, involves the examination of lived experiences to gain an in-depth understanding of the essence or underlying meanings of a phenomenon.
The focus of phenomenology lies in meticulously describing participants’ conscious experiences related to the chosen phenomenon (Padilla-Díaz, 2015).
In a phenomenological study, the researcher collects detailed, first-hand perspectives of the participants, typically via in-depth interviews, and then uses various strategies to interpret and structure these experiences, ultimately revealing essential themes (Creswell, 2013). This approach focuses on the perspective of individuals experiencing the phenomenon, seeking to explore, clarify, and understand the meanings they attach to those experiences.
Example of Phenomenology Research
Title: “ A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology: current state, promise, and future directions for research ”
Citation: Cilesiz, S. (2011). A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology: Current state, promise, and future directions for research. Educational Technology Research and Development, 59 , 487-510.
Overview: A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology by Sebnem Cilesiz represents a good starting point for formulating a phenomenological study. With its focus on the ‘essence of experience’, this piece presents methodological, reliability, validity, and data analysis techniques that phenomenologists use to explain how people experience technology in their everyday lives.
6. Grounded Theory
Definition: Grounded theory is a systematic methodology in qualitative research that typically applies inductive reasoning . The primary aim is to develop a theoretical explanation or framework for a process, action, or interaction grounded in, and arising from, empirical data (Birks & Mills, 2015).
In grounded theory, data collection and analysis work together in a recursive process. The researcher collects data, analyses it, and then collects more data based on the evolving understanding of the research context. This ongoing process continues until a comprehensive theory that represents the data and the associated phenomenon emerges – a point known as theoretical saturation (Charmaz, 2014).
Example of Grounded Theory Research
Title: “ Student Engagement in High School Classrooms from the Perspective of Flow Theory “
Citation: Shernoff, D. J., Csikszentmihalyi, M., Shneider, B., & Shernoff, E. S. (2003). Student engagement in high school classrooms from the perspective of flow theory. School Psychology Quarterly, 18 (2), 158–176.
Overview: Shernoff and colleagues (2003) used grounded theory to explore student engagement in high school classrooms. The researchers collected data through student self-reports, interviews, and observations. Key findings revealed that academic challenge, student autonomy, and teacher support emerged as the most significant factors influencing students’ engagement, demonstrating how grounded theory can illuminate complex dynamics within real-world contexts.
7. Narrative Research
Definition: Narrative research is a qualitative research method dedicated to storytelling and understanding how individuals experience the world. It focuses on studying an individual’s life and experiences as narrated by that individual (Polkinghorne, 2013).
In narrative research, the researcher collects data through methods such as interviews, observations , and document analysis. The emphasis is on the stories told by participants – narratives that reflect their experiences, thoughts, and feelings.
These stories are then interpreted by the researcher, who attempts to understand the meaning the participant attributes to these experiences (Josselson, 2011).
Example of Narrative Research
Title: “Narrative Structures and the Language of the Self”
Citation: McAdams, D. P., Josselson, R., & Lieblich, A. (2006). Identity and story: Creating self in narrative . American Psychological Association.
Overview: In this innovative study, McAdams et al. (2006) employed narrative research to explore how individuals construct their identities through the stories they tell about themselves. By examining personal narratives, the researchers discerned patterns associated with characters, motivations, conflicts, and resolutions, contributing valuable insights about the relationship between narrative and individual identity.
8. Case Study Research
Definition: Case study research is a qualitative research method that involves an in-depth investigation of a single instance or event: a case. These ‘cases’ can range from individuals, groups, or entities to specific projects, programs, or strategies (Creswell, 2013).
The case study method typically uses multiple sources of information for comprehensive contextual analysis. It aims to explore and understand the complexity and uniqueness of a particular case in a real-world context (Merriam & Tisdell, 2015). This investigation could result in a detailed description of the case, a process for its development, or an exploration of a related issue or problem.
Example of Case Study Research
Title: “ Teacher’s Role in Fostering Preschoolers’ Computational Thinking: An Exploratory Case Study “
Citation: Wang, X. C., Choi, Y., Benson, K., Eggleston, C., & Weber, D. (2021). Teacher’s role in fostering preschoolers’ computational thinking: An exploratory case study. Early Education and Development , 32 (1), 26-48.
Overview: This study investigates the role of teachers in promoting computational thinking skills in preschoolers. The study utilized a qualitative case study methodology to examine the computational thinking scaffolding strategies employed by a teacher interacting with three preschoolers in a small group setting. The findings highlight the importance of teachers’ guidance in fostering computational thinking practices such as problem reformulation/decomposition, systematic testing, and debugging.
Read about some Famous Case Studies in Psychology Here
9. Participant Observation
Definition: Participant observation has the researcher immerse themselves in a group or community setting to observe the behavior of its members. It is similar to ethnography, but generally, the researcher isn’t embedded for a long period of time.
The researcher, being a participant, engages in daily activities, interactions, and events as a way of conducting a detailed study of a particular social phenomenon (Kawulich, 2005).
The method involves long-term engagement in the field, maintaining detailed records of observed events, informal interviews, direct participation, and reflexivity. This approach allows for a holistic view of the participants’ lived experiences, behaviours, and interactions within their everyday environment (Dewalt, 2011).
Example of Participant Observation Research
Title: Conflict in the boardroom: a participant observation study of supervisory board dynamics
Citation: Heemskerk, E. M., Heemskerk, K., & Wats, M. M. (2017). Conflict in the boardroom: a participant observation study of supervisory board dynamics. Journal of Management & Governance , 21 , 233-263.
Overview: This study examined how conflicts within corporate boards affect their performance. The researchers used a participant observation method, where they actively engaged with 11 supervisory boards and observed their dynamics. They found that having a shared understanding of the board’s role called a common framework, improved performance by reducing relationship conflicts, encouraging task conflicts, and minimizing conflicts between the board and CEO.
10. Non-Participant Observation
Definition: Non-participant observation is a qualitative research method in which the researcher observes the phenomena of interest without actively participating in the situation, setting, or community being studied.
This method allows the researcher to maintain a position of distance, as they are solely an observer and not a participant in the activities being observed (Kawulich, 2005).
During non-participant observation, the researcher typically records field notes on the actions, interactions, and behaviors observed , focusing on specific aspects of the situation deemed relevant to the research question.
This could include verbal and nonverbal communication , activities, interactions, and environmental contexts (Angrosino, 2007). They could also use video or audio recordings or other methods to collect data.
Example of Non-Participant Observation Research
Title: Mental Health Nurses’ attitudes towards mental illness and recovery-oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units: A non-participant observation study
Citation: Sreeram, A., Cross, W. M., & Townsin, L. (2023). Mental Health Nurses’ attitudes towards mental illness and recovery‐oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units: A non‐participant observation study. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing .
Overview: This study investigated the attitudes of mental health nurses towards mental illness and recovery-oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units. The researchers used a non-participant observation method, meaning they observed the nurses without directly participating in their activities. The findings shed light on the nurses’ perspectives and behaviors, providing valuable insights into their attitudes toward mental health and recovery-focused care in these settings.
11. Content Analysis
Definition: Content Analysis involves scrutinizing textual, visual, or spoken content to categorize and quantify information. The goal is to identify patterns, themes, biases, or other characteristics (Hsieh & Shannon, 2005).
Content Analysis is widely used in various disciplines for a multitude of purposes. Researchers typically use this method to distill large amounts of unstructured data, like interview transcripts, newspaper articles, or social media posts, into manageable and meaningful chunks.
When wielded appropriately, Content Analysis can illuminate the density and frequency of certain themes within a dataset, provide insights into how specific terms or concepts are applied contextually, and offer inferences about the meanings of their content and use (Duriau, Reger, & Pfarrer, 2007).
Example of Content Analysis
Title: Framing European politics: A content analysis of press and television news .
Citation: Semetko, H. A., & Valkenburg, P. M. (2000). Framing European politics: A content analysis of press and television news. Journal of Communication, 50 (2), 93-109.
Overview: This study analyzed press and television news articles about European politics using a method called content analysis. The researchers examined the prevalence of different “frames” in the news, which are ways of presenting information to shape audience perceptions. They found that the most common frames were attribution of responsibility, conflict, economic consequences, human interest, and morality.
Read my Full Guide on Content Analysis Here
12. Discourse Analysis
Definition: Discourse Analysis, a qualitative research method, interprets the meanings, functions, and coherence of certain languages in context.
Discourse analysis is typically understood through social constructionism, critical theory , and poststructuralism and used for understanding how language constructs social concepts (Cheek, 2004).
Discourse Analysis offers great breadth, providing tools to examine spoken or written language, often beyond the level of the sentence. It enables researchers to scrutinize how text and talk articulate social and political interactions and hierarchies.
Insight can be garnered from different conversations, institutional text, and media coverage to understand how topics are addressed or framed within a specific social context (Jorgensen & Phillips, 2002).
Example of Discourse Analysis
Title: The construction of teacher identities in educational policy documents: A critical discourse analysis
Citation: Thomas, S. (2005). The construction of teacher identities in educational policy documents: A critical discourse analysis. Critical Studies in Education, 46 (2), 25-44.
Overview: The author examines how an education policy in one state of Australia positions teacher professionalism and teacher identities. While there are competing discourses about professional identity, the policy framework privileges a narrative that frames the ‘good’ teacher as one that accepts ever-tightening control and regulation over their professional practice.
Read my Full Guide on Discourse Analysis Here
13. Action Research
Definition: Action Research is a qualitative research technique that is employed to bring about change while simultaneously studying the process and results of that change.
This method involves a cyclical process of fact-finding, action, evaluation, and reflection (Greenwood & Levin, 2016).
Typically, Action Research is used in the fields of education, social sciences , and community development. The process isn’t just about resolving an issue but also developing knowledge that can be used in the future to address similar or related problems.
The researcher plays an active role in the research process, which is normally broken down into four steps:
- developing a plan to improve what is currently being done
- implementing the plan
- observing the effects of the plan, and
- reflecting upon these effects (Smith, 2010).
Example of Action Research
Title: Using Digital Sandbox Gaming to Improve Creativity Within Boys’ Writing
Citation: Ellison, M., & Drew, C. (2020). Using digital sandbox gaming to improve creativity within boys’ writing. Journal of Research in Childhood Education , 34 (2), 277-287.
Overview: This was a research study one of my research students completed in his own classroom under my supervision. He implemented a digital game-based approach to literacy teaching with boys and interviewed his students to see if the use of games as stimuli for storytelling helped draw them into the learning experience.
Read my Full Guide on Action Research Here
14. Semiotic Analysis
Definition: Semiotic Analysis is a qualitative method of research that interprets signs and symbols in communication to understand sociocultural phenomena. It stems from semiotics, the study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation (Chandler, 2017).
In a Semiotic Analysis, signs (anything that represents something else) are interpreted based on their significance and the role they play in representing ideas.
This type of research often involves the examination of images, sounds, and word choice to uncover the embedded sociocultural meanings. For example, an advertisement for a car might be studied to learn more about societal views on masculinity or success (Berger, 2010).
Example of Semiotic Research
Title: Shielding the learned body: a semiotic analysis of school badges in New South Wales, Australia
Citation: Symes, C. (2023). Shielding the learned body: a semiotic analysis of school badges in New South Wales, Australia. Semiotica , 2023 (250), 167-190.
Overview: This study examines school badges in New South Wales, Australia, and explores their significance through a semiotic analysis. The badges, which are part of the school’s visual identity, are seen as symbolic representations that convey meanings. The analysis reveals that these badges often draw on heraldic models, incorporating elements like colors, names, motifs, and mottoes that reflect local culture and history, thus connecting students to their national identity. Additionally, the study highlights how some schools have shifted from traditional badges to modern logos and slogans, reflecting a more business-oriented approach.
15. Qualitative Longitudinal Studies
Definition: Qualitative Longitudinal Studies are a research method that involves repeated observation of the same items over an extended period of time.
Unlike a snapshot perspective, this method aims to piece together individual histories and examine the influences and impacts of change (Neale, 2019).
Qualitative Longitudinal Studies provide an in-depth understanding of change as it happens, including changes in people’s lives, their perceptions, and their behaviors.
For instance, this method could be used to follow a group of students through their schooling years to understand the evolution of their learning behaviors and attitudes towards education (Saldaña, 2003).
Example of Qualitative Longitudinal Research
Title: Patient and caregiver perspectives on managing pain in advanced cancer: a qualitative longitudinal study
Citation: Hackett, J., Godfrey, M., & Bennett, M. I. (2016). Patient and caregiver perspectives on managing pain in advanced cancer: a qualitative longitudinal study. Palliative medicine , 30 (8), 711-719.
Overview: This article examines how patients and their caregivers manage pain in advanced cancer through a qualitative longitudinal study. The researchers interviewed patients and caregivers at two different time points and collected audio diaries to gain insights into their experiences, making this study longitudinal.
Read my Full Guide on Longitudinal Research Here
16. Open-Ended Surveys
Definition: Open-Ended Surveys are a type of qualitative research method where respondents provide answers in their own words. Unlike closed-ended surveys, which limit responses to predefined options, open-ended surveys allow for expansive and unsolicited explanations (Fink, 2013).
Open-ended surveys are commonly used in a range of fields, from market research to social studies. As they don’t force respondents into predefined response categories, these surveys help to draw out rich, detailed data that might uncover new variables or ideas.
For example, an open-ended survey might be used to understand customer opinions about a new product or service (Lavrakas, 2008).
Contrast this to a quantitative closed-ended survey, like a Likert scale, which could theoretically help us to come up with generalizable data but is restricted by the questions on the questionnaire, meaning new and surprising data and insights can’t emerge from the survey results in the same way.
Example of Open-Ended Survey Research
Title: Advantages and disadvantages of technology in relationships: Findings from an open-ended survey
Citation: Hertlein, K. M., & Ancheta, K. (2014). Advantages and disadvantages of technology in relationships: Findings from an open-ended survey. The Qualitative Report , 19 (11), 1-11.
Overview: This article examines the advantages and disadvantages of technology in couple relationships through an open-ended survey method. Researchers analyzed responses from 410 undergraduate students to understand how technology affects relationships. They found that technology can contribute to relationship development, management, and enhancement, but it can also create challenges such as distancing, lack of clarity, and impaired trust.
17. Naturalistic Observation
Definition: Naturalistic Observation is a type of qualitative research method that involves observing individuals in their natural environments without interference or manipulation by the researcher.
Naturalistic observation is often used when conducting research on behaviors that cannot be controlled or manipulated in a laboratory setting (Kawulich, 2005).
It is frequently used in the fields of psychology, sociology, and anthropology. For instance, to understand the social dynamics in a schoolyard, a researcher could spend time observing the children interact during their recess, noting their behaviors, interactions, and conflicts without imposing their presence on the children’s activities (Forsyth, 2010).
Example of Naturalistic Observation Research
Title: Dispositional mindfulness in daily life: A naturalistic observation study
Citation: Kaplan, D. M., Raison, C. L., Milek, A., Tackman, A. M., Pace, T. W., & Mehl, M. R. (2018). Dispositional mindfulness in daily life: A naturalistic observation study. PloS one , 13 (11), e0206029.
Overview: In this study, researchers conducted two studies: one exploring assumptions about mindfulness and behavior, and the other using naturalistic observation to examine actual behavioral manifestations of mindfulness. They found that trait mindfulness is associated with a heightened perceptual focus in conversations, suggesting that being mindful is expressed primarily through sharpened attention rather than observable behavioral or social differences.
Read my Full Guide on Naturalistic Observation Here
18. Photo-Elicitation
Definition: Photo-elicitation utilizes photographs as a means to trigger discussions and evoke responses during interviews. This strategy aids in bringing out topics of discussion that may not emerge through verbal prompting alone (Harper, 2002).
Traditionally, Photo-Elicitation has been useful in various fields such as education, psychology, and sociology. The method involves the researcher or participants taking photographs, which are then used as prompts for discussion.
For instance, a researcher studying urban environmental issues might invite participants to photograph areas in their neighborhood that they perceive as environmentally detrimental, and then discuss each photo in depth (Clark-Ibáñez, 2004).
Example of Photo-Elicitation Research
Title: Early adolescent food routines: A photo-elicitation study
Citation: Green, E. M., Spivak, C., & Dollahite, J. S. (2021). Early adolescent food routines: A photo-elicitation study. Appetite, 158 .
Overview: This study focused on early adolescents (ages 10-14) and their food routines. Researchers conducted in-depth interviews using a photo-elicitation approach, where participants took photos related to their food choices and experiences. Through analysis, the study identified various routines and three main themes: family, settings, and meals/foods consumed, revealing how early adolescents view and are influenced by their eating routines.
Features of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a research method focused on understanding the meaning individuals or groups attribute to a social or human problem (Creswell, 2013).
Some key features of this method include:
- Naturalistic Inquiry: Qualitative research happens in the natural setting of the phenomena, aiming to understand “real world” situations (Patton, 2015). This immersion in the field or subject allows the researcher to gather a deep understanding of the subject matter.
- Emphasis on Process: It aims to understand how events unfold over time rather than focusing solely on outcomes (Merriam & Tisdell, 2015). The process-oriented nature of qualitative research allows researchers to investigate sequences, timing, and changes.
- Interpretive: It involves interpreting and making sense of phenomena in terms of the meanings people assign to them (Denzin & Lincoln, 2011). This interpretive element allows for rich, nuanced insights into human behavior and experiences.
- Holistic Perspective: Qualitative research seeks to understand the whole phenomenon rather than focusing on individual components (Creswell, 2013). It emphasizes the complex interplay of factors, providing a richer, more nuanced view of the research subject.
- Prioritizes Depth over Breadth: Qualitative research favors depth of understanding over breadth, typically involving a smaller but more focused sample size (Hennink, Hutter, & Bailey, 2020). This enables detailed exploration of the phenomena of interest, often leading to rich and complex data.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research
Qualitative research centers on exploring and understanding the meaning individuals or groups attribute to a social or human problem (Creswell, 2013).
It involves an in-depth approach to the subject matter, aiming to capture the richness and complexity of human experience.
Examples include conducting interviews, observing behaviors, or analyzing text and images.
There are strengths inherent in this approach. In its focus on understanding subjective experiences and interpretations, qualitative research can yield rich and detailed data that quantitative research may overlook (Denzin & Lincoln, 2011).
Additionally, qualitative research is adaptive, allowing the researcher to respond to new directions and insights as they emerge during the research process.
However, there are also limitations. Because of the interpretive nature of this research, findings may not be generalizable to a broader population (Marshall & Rossman, 2014). Well-designed quantitative research, on the other hand, can be generalizable.
Moreover, the reliability and validity of qualitative data can be challenging to establish due to its subjective nature, unlike quantitative research, which is ideally more objective.
Compare Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methodologies in This Guide Here
In conclusion, qualitative research methods provide distinctive ways to explore social phenomena and understand nuances that quantitative approaches might overlook. Each method, from Ethnography to Photo-Elicitation, presents its strengths and weaknesses but they all offer valuable means of investigating complex, real-world situations. The goal for the researcher is not to find a definitive tool, but to employ the method best suited for their research questions and the context at hand (Almalki, 2016). Above all, these methods underscore the richness of human experience and deepen our understanding of the world around us.
Angrosino, M. (2007). Doing ethnographic and observational research. Sage Publications.
Areni, C. S., & Kim, D. (1994). The influence of in-store lighting on consumers’ examination of merchandise in a wine store. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 11 (2), 117-125.
Barker, C., Pistrang, N., & Elliott, R. (2016). Research Methods in Clinical Psychology: An Introduction for Students and Practitioners. John Wiley & Sons.
Baxter, P. & Jack, S. (2008). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report, 13 (4), 544-559.
Berger, A. A. (2010). The Objects of Affection: Semiotics and Consumer Culture. Palgrave Macmillan.
Bevan, M. T. (2014). A method of phenomenological interviewing. Qualitative health research, 24 (1), 136-144.
Birks, M., & Mills, J. (2015). Grounded theory: A practical guide . Sage Publications.
Bryman, A. (2015) . The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research. Sage Publications.
Chandler, D. (2017). Semiotics: The Basics. Routledge.
Charmaz, K. (2014). Constructing grounded theory. Sage Publications.
Cheek, J. (2004). At the margins? Discourse analysis and qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research, 14(8), 1140-1150.
Clark-Ibáñez, M. (2004). Framing the social world with photo-elicitation interviews. American Behavioral Scientist, 47(12), 1507-1527.
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative and Mixed Methods Approaches. Sage Publications.
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2017). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Sage publications.
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A., Huby, G., Avery, A., & Sheikh, A. (2011). The case study approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 11(100), 1-9.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2011). The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Research. Sage.
Dewalt, K. M., & Dewalt, B. R. (2011). Participant observation: A guide for fieldworkers. Rowman Altamira.
Doody, O., Slevin, E., & Taggart, L. (2013). Focus group interviews in nursing research: part 1. British Journal of Nursing, 22(1), 16-19.
Durham, A. (2019). Autoethnography. In P. Atkinson (Ed.), Qualitative Research Methods. Oxford University Press.
Duriau, V. J., Reger, R. K., & Pfarrer, M. D. (2007). A content analysis of the content analysis literature in organization studies: Research themes, data sources, and methodological refinements. Organizational Research Methods, 10(1), 5-34.
Evans, J. (2010). The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity. Peter Lang.
Farrall, S. (2006). What is qualitative longitudinal research? Papers in Social Research Methods, Qualitative Series, No.11, London School of Economics, Methodology Institute.
Fielding, J., & Fielding, N. (2008). Synergy and synthesis: integrating qualitative and quantitative data. The SAGE handbook of social research methods, 555-571.
Fink, A. (2013). How to conduct surveys: A step-by-step guide . SAGE.
Forsyth, D. R. (2010). Group Dynamics . Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Fugard, A. J. B., & Potts, H. W. W. (2015). Supporting thinking on sample sizes for thematic analyses: A quantitative tool. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 18 (6), 669–684.
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research. Aldine de Gruyter.
Gray, J. R., Grove, S. K., & Sutherland, S. (2017). Burns and Grove’s the Practice of Nursing Research E-Book: Appraisal, Synthesis, and Generation of Evidence. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Greenwood, D. J., & Levin, M. (2016). Introduction to action research: Social research for social change. SAGE.
Harper, D. (2002). Talking about pictures: A case for photo elicitation. Visual Studies, 17 (1), 13-26.
Heinonen, T. (2012). Making Sense of the Social: Human Sciences and the Narrative Turn. Rozenberg Publishers.
Heisley, D. D., & Levy, S. J. (1991). Autodriving: A photoelicitation technique. Journal of Consumer Research, 18 (3), 257-272.
Hennink, M. M., Hutter, I., & Bailey, A. (2020). Qualitative Research Methods . SAGE Publications Ltd.
Hsieh, H. F., & Shannon, S. E. (2005). Three Approaches to Qualitative Content Analysis. Qualitative Health Research, 15 (9), 1277–1288.
Jorgensen, D. L. (2015). Participant Observation. In Emerging Trends in the Social and Behavioral Sciences: An Interdisciplinary, Searchable, and Linkable Resource. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Jorgensen, M., & Phillips, L. (2002). Discourse Analysis as Theory and Method . SAGE.
Josselson, R. (2011). Narrative research: Constructing, deconstructing, and reconstructing story. In Five ways of doing qualitative analysis . Guilford Press.
Kawulich, B. B. (2005). Participant observation as a data collection method. Forum: Qualitative Social Research, 6 (2).
Khan, S. (2014). Qualitative Research Method: Grounded Theory. Journal of Basic and Clinical Pharmacy, 5 (4), 86-88.
Koshy, E., Koshy, V., & Waterman, H. (2010). Action Research in Healthcare . SAGE.
Krippendorff, K. (2013). Content Analysis: An Introduction to its Methodology. SAGE.
Lannon, J., & Cooper, P. (2012). Humanistic Advertising: A Holistic Cultural Perspective. International Journal of Advertising, 15 (2), 97–111.
Lavrakas, P. J. (2008). Encyclopedia of survey research methods. SAGE Publications.
Lieblich, A., Tuval-Mashiach, R., & Zilber, T. (2008). Narrative research: Reading, analysis and interpretation. Sage Publications.
Mackey, A., & Gass, S. M. (2015). Second language research: Methodology and design. Routledge.
Marshall, C., & Rossman, G. B. (2014). Designing qualitative research. Sage publications.
McAdams, D. P., Josselson, R., & Lieblich, A. (2006). Identity and story: Creating self in narrative. American Psychological Association.
Merriam, S. B., & Tisdell, E. J. (2015). Qualitative Research: A Guide to Design and Implementation. Jossey-Bass.
Mick, D. G. (1986). Consumer Research and Semiotics: Exploring the Morphology of Signs, Symbols, and Significance. Journal of Consumer Research, 13 (2), 196-213.
Morgan, D. L. (2010). Focus groups as qualitative research. Sage Publications.
Mulhall, A. (2003). In the field: notes on observation in qualitative research. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 41 (3), 306-313.
Neale, B. (2019). What is Qualitative Longitudinal Research? Bloomsbury Publishing.
Nolan, L. B., & Renderos, T. B. (2012). A focus group study on the influence of fatalism and religiosity on cancer risk perceptions in rural, eastern North Carolina. Journal of religion and health, 51 (1), 91-104.
Padilla-Díaz, M. (2015). Phenomenology in educational qualitative research: Philosophy as science or philosophical science? International Journal of Educational Excellence, 1 (2), 101-110.
Parker, I. (2014). Discourse dynamics: Critical analysis for social and individual psychology . Routledge.
Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice . Sage Publications.
Polkinghorne, D. E. (2013). Narrative configuration in qualitative analysis. In Life history and narrative. Routledge.
Puts, M. T., Tapscott, B., Fitch, M., Howell, D., Monette, J., Wan-Chow-Wah, D., Krzyzanowska, M., Leighl, N. B., Springall, E., & Alibhai, S. (2014). Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review. Annals of oncology, 25 (3), 564-577.
Qu, S. Q., & Dumay, J. (2011). The qualitative research interview . Qualitative research in accounting & management.
Ali, J., & Bhaskar, S. B. (2016). Basic statistical tools in research and data analysis. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia, 60 (9), 662–669.
Rosenbaum, M. S. (2017). Exploring the social supportive role of third places in consumers’ lives. Journal of Service Research, 20 (1), 26-42.
Saldaña, J. (2003). Longitudinal Qualitative Research: Analyzing Change Through Time . AltaMira Press.
Saldaña, J. (2014). The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers. SAGE.
Shernoff, D. J., Csikszentmihalyi, M., Shneider, B., & Shernoff, E. S. (2003). Student engagement in high school classrooms from the perspective of flow theory. School Psychology Quarterly, 18 (2), 158-176.
Smith, J. A. (2015). Qualitative Psychology: A Practical Guide to Research Methods . Sage Publications.
Smith, M. K. (2010). Action Research. The encyclopedia of informal education.
Sue, V. M., & Ritter, L. A. (2012). Conducting online surveys . SAGE Publications.
Van Auken, P. M., Frisvoll, S. J., & Stewart, S. I. (2010). Visualising community: using participant-driven photo-elicitation for research and application. Local Environment, 15 (4), 373-388.
Van Voorhis, F. L., & Morgan, B. L. (2007). Understanding Power and Rules of Thumb for Determining Sample Sizes. Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 3 (2), 43–50.
Wodak, R., & Meyer, M. (2015). Methods of Critical Discourse Analysis . SAGE.
Zuber-Skerritt, O. (2018). Action research for developing educational theories and practices . Routledge.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 30 January 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organisation?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography, action research, phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasise different aims and perspectives.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves ‘instruments’ in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analysing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organise your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorise your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analysing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasise different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analysing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analysing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalisability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalisable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labour-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organisation to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, January 30). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Qualitative Research Methods: Types, Analysis + Examples
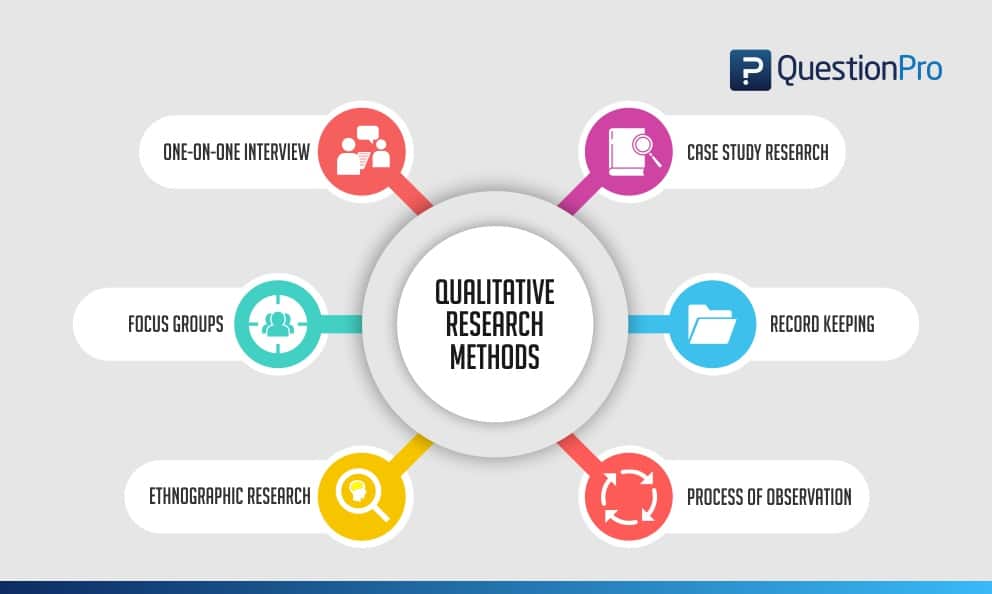
Qualitative research is based on the disciplines of social sciences like psychology, sociology, and anthropology. Therefore, the qualitative research methods allow for in-depth and further probing and questioning of respondents based on their responses. The interviewer/researcher also tries to understand their motivation and feelings. Understanding how your audience makes decisions can help derive conclusions in market research.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is defined as a market research method that focuses on obtaining data through open-ended and conversational communication .
This method is about “what” people think and “why” they think so. For example, consider a convenience store looking to improve its patronage. A systematic observation concludes that more men are visiting this store. One good method to determine why women were not visiting the store is conducting an in-depth interview method with potential customers.
For example, after successfully interviewing female customers and visiting nearby stores and malls, the researchers selected participants through random sampling . As a result, it was discovered that the store didn’t have enough items for women.
So fewer women were visiting the store, which was understood only by personally interacting with them and understanding why they didn’t visit the store because there were more male products than female ones.
Gather research insights
Types of qualitative research methods with examples
Qualitative research methods are designed in a manner that helps reveal the behavior and perception of a target audience with reference to a particular topic. There are different types of qualitative research methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, ethnographic research, content analysis, and case study research that are usually used.
The results of qualitative methods are more descriptive, and the inferences can be drawn quite easily from the obtained data .
Qualitative research methods originated in the social and behavioral research sciences. Today, our world is more complicated, and it is difficult to understand what people think and perceive. Online research methods make it easier to understand that as it is a more communicative and descriptive analysis .
The following are the qualitative research methods that are frequently used. Also, read about qualitative research examples :

1. One-on-one interview
Conducting in-depth interviews is one of the most common qualitative research methods. It is a personal interview that is carried out with one respondent at a time. This is purely a conversational method and invites opportunities to get details in depth from the respondent.
One of the advantages of this method is that it provides a great opportunity to gather precise data about what people believe and their motivations . If the researcher is well experienced, asking the right questions can help him/her collect meaningful data. If they should need more information, the researchers should ask such follow-up questions that will help them collect more information.
These interviews can be performed face-to-face or on the phone and usually can last between half an hour to two hours or even more. When the in-depth interview is conducted face to face, it gives a better opportunity to read the respondents’ body language and match the responses.
2. Focus groups
A focus group is also a commonly used qualitative research method used in data collection. A focus group usually includes a limited number of respondents (6-10) from within your target market.
The main aim of the focus group is to find answers to the “why, ” “what,” and “how” questions. One advantage of focus groups is you don’t necessarily need to interact with the group in person. Nowadays, focus groups can be sent an online survey on various devices, and responses can be collected at the click of a button.
Focus groups are an expensive method as compared to other online qualitative research methods. Typically, they are used to explain complex processes. This method is very useful for market research on new products and testing new concepts.
3. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research is the most in-depth observational research method that studies people in their naturally occurring environment.
This method requires the researchers to adapt to the target audiences’ environments, which could be anywhere from an organization to a city or any remote location. Here, geographical constraints can be an issue while collecting data.
This research design aims to understand the cultures, challenges, motivations, and settings that occur. Instead of relying on interviews and discussions, you experience the natural settings firsthand.
This type of research method can last from a few days to a few years, as it involves in-depth observation and collecting data on those grounds. It’s a challenging and time-consuming method and solely depends on the researcher’s expertise to analyze, observe, and infer the data.
4. Case study research
T he case study method has evolved over the past few years and developed into a valuable quality research method. As the name suggests, it is used for explaining an organization or an entity.
This type of research method is used within a number of areas like education, social sciences, and similar. This method may look difficult to operate; however , it is one of the simplest ways of conducting research as it involves a deep dive and thorough understanding of the data collection methods and inferring the data.
5. Record keeping
This method makes use of the already existing reliable documents and similar sources of information as the data source. This data can be used in new research. This is similar to going to a library. There, one can go over books and other reference material to collect relevant data that can likely be used in the research.
6. Process of observation
Qualitative Observation is a process of research that uses subjective methodologies to gather systematic information or data. Since the focus on qualitative observation is the research process of using subjective methodologies to gather information or data. Qualitative observation is primarily used to equate quality differences.
Qualitative observation deals with the 5 major sensory organs and their functioning – sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing. This doesn’t involve measurements or numbers but instead characteristics.
Explore Insightfully Contextual Inquiry in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research: data collection and analysis
A. qualitative data collection.
Qualitative data collection allows collecting data that is non-numeric and helps us to explore how decisions are made and provide us with detailed insight. For reaching such conclusions the data that is collected should be holistic, rich, and nuanced and findings to emerge through careful analysis.
- Whatever method a researcher chooses for collecting qualitative data, one aspect is very clear the process will generate a large amount of data. In addition to the variety of methods available, there are also different methods of collecting and recording the data.
For example, if the qualitative data is collected through a focus group or one-to-one discussion, there will be handwritten notes or video recorded tapes. If there are recording they should be transcribed and before the process of data analysis can begin.
- As a rough guide, it can take a seasoned researcher 8-10 hours to transcribe the recordings of an interview, which can generate roughly 20-30 pages of dialogues. Many researchers also like to maintain separate folders to maintain the recording collected from the different focus group. This helps them compartmentalize the data collected.
- In case there are running notes taken, which are also known as field notes, they are helpful in maintaining comments, environmental contexts, environmental analysis , nonverbal cues etc. These filed notes are helpful and can be compared while transcribing audio recorded data. Such notes are usually informal but should be secured in a similar manner as the video recordings or the audio tapes.
B. Qualitative data analysis
Qualitative data analysis such as notes, videos, audio recordings images, and text documents. One of the most used methods for qualitative data analysis is text analysis.
Text analysis is a data analysis method that is distinctly different from all other qualitative research methods, where researchers analyze the social life of the participants in the research study and decode the words, actions, etc.
There are images also that are used in this research study and the researchers analyze the context in which the images are used and draw inferences from them. In the last decade, text analysis through what is shared on social media platforms has gained supreme popularity.
Characteristics of qualitative research methods

- Qualitative research methods usually collect data at the sight, where the participants are experiencing issues or research problems . These are real-time data and rarely bring the participants out of the geographic locations to collect information.
- Qualitative researchers typically gather multiple forms of data, such as interviews, observations, and documents, rather than rely on a single data source .
- This type of research method works towards solving complex issues by breaking down into meaningful inferences, that is easily readable and understood by all.
- Since it’s a more communicative method, people can build their trust on the researcher and the information thus obtained is raw and unadulterated.
Qualitative research method case study
Let’s take the example of a bookstore owner who is looking for ways to improve their sales and customer outreach. An online community of members who were loyal patrons of the bookstore were interviewed and related questions were asked and the questions were answered by them.
At the end of the interview, it was realized that most of the books in the stores were suitable for adults and there were not enough options for children or teenagers.
By conducting this qualitative research the bookstore owner realized what the shortcomings were and what were the feelings of the readers. Through this research now the bookstore owner can now keep books for different age categories and can improve his sales and customer outreach.
Such qualitative research method examples can serve as the basis to indulge in further quantitative research , which provides remedies.
When to use qualitative research
Researchers make use of qualitative research techniques when they need to capture accurate, in-depth insights. It is very useful to capture “factual data”. Here are some examples of when to use qualitative research.
- Developing a new product or generating an idea.
- Studying your product/brand or service to strengthen your marketing strategy.
- To understand your strengths and weaknesses.
- Understanding purchase behavior.
- To study the reactions of your audience to marketing campaigns and other communications.
- Exploring market demographics, segments, and customer care groups.
- Gathering perception data of a brand, company, or product.
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research methods vs quantitative research methods
The basic differences between qualitative research methods and quantitative research methods are simple and straightforward. They differ in:
- Their analytical objectives
- Types of questions asked
- Types of data collection instruments
- Forms of data they produce
- Degree of flexibility
LEARN MORE ABOUR OUR SOFTWARE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS
Data Information vs Insight: Essential differences
May 14, 2024

Pricing Analytics Software: Optimize Your Pricing Strategy
May 13, 2024

Relationship Marketing: What It Is, Examples & Top 7 Benefits
May 8, 2024

The Best Email Survey Tool to Boost Your Feedback Game
May 7, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Qualitative Research Questions
Try Qualtrics for free
How to write qualitative research questions.
11 min read Here’s how to write effective qualitative research questions for your projects, and why getting it right matters so much.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a blanket term covering a wide range of research methods and theoretical framing approaches. The unifying factor in all these types of qualitative study is that they deal with data that cannot be counted. Typically this means things like people’s stories, feelings, opinions and emotions , and the meanings they ascribe to their experiences.
Qualitative study is one of two main categories of research, the other being quantitative research. Quantitative research deals with numerical data – that which can be counted and quantified, and which is mostly concerned with trends and patterns in large-scale datasets.
What are research questions?
Research questions are questions you are trying to answer with your research. To put it another way, your research question is the reason for your study, and the beginning point for your research design. There is normally only one research question per study, although if your project is very complex, you may have multiple research questions that are closely linked to one central question.
A good qualitative research question sums up your research objective. It’s a way of expressing the central question of your research, identifying your particular topic and the central issue you are examining.
Research questions are quite different from survey questions, questions used in focus groups or interview questions. A long list of questions is used in these types of study, as opposed to one central question. Additionally, interview or survey questions are asked of participants, whereas research questions are only for the researcher to maintain a clear understanding of the research design.
Research questions are used in both qualitative and quantitative research , although what makes a good research question might vary between the two.
In fact, the type of research questions you are asking can help you decide whether you need to take a quantitative or qualitative approach to your research project.
Discover the fundamentals of qualitative research
Quantitative vs. qualitative research questions
Writing research questions is very important in both qualitative and quantitative research, but the research questions that perform best in the two types of studies are quite different.
Quantitative research questions
Quantitative research questions usually relate to quantities, similarities and differences.
It might reflect the researchers’ interest in determining whether relationships between variables exist, and if so whether they are statistically significant. Or it may focus on establishing differences between things through comparison, and using statistical analysis to determine whether those differences are meaningful or due to chance.
- How much? This kind of research question is one of the simplest. It focuses on quantifying something. For example:
How many Yoruba speakers are there in the state of Maine?
- What is the connection?
This type of quantitative research question examines how one variable affects another.
For example:
How does a low level of sunlight affect the mood scores (1-10) of Antarctic explorers during winter?
- What is the difference? Quantitative research questions in this category identify two categories and measure the difference between them using numerical data.
Do white cats stay cooler than tabby cats in hot weather?
If your research question fits into one of the above categories, you’re probably going to be doing a quantitative study.
Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions focus on exploring phenomena, meanings and experiences.
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research isn’t about finding causal relationships between variables. So although qualitative research questions might touch on topics that involve one variable influencing another, or looking at the difference between things, finding and quantifying those relationships isn’t the primary objective.
In fact, you as a qualitative researcher might end up studying a very similar topic to your colleague who is doing a quantitative study, but your areas of focus will be quite different. Your research methods will also be different – they might include focus groups, ethnography studies, and other kinds of qualitative study.
A few example qualitative research questions:
- What is it like being an Antarctic explorer during winter?
- What are the experiences of Yoruba speakers in the USA?
- How do white cat owners describe their pets?
Qualitative research question types
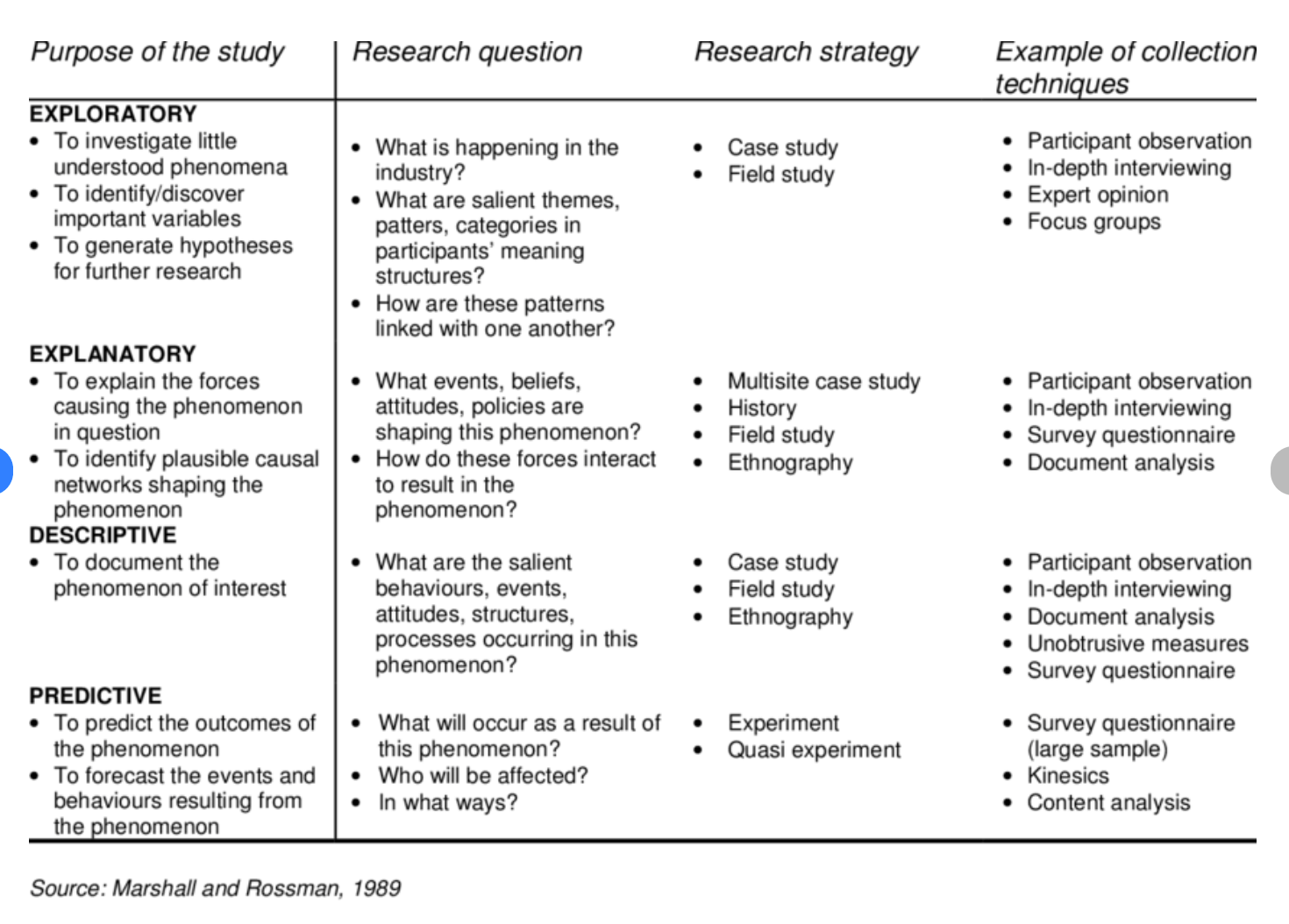
Marshall and Rossman (1989) identified 4 qualitative research question types, each with its own typical research strategy and methods.
- Exploratory questions
Exploratory questions are used when relatively little is known about the research topic. The process researchers follow when pursuing exploratory questions might involve interviewing participants, holding focus groups, or diving deep with a case study.
- Explanatory questions
With explanatory questions, the research topic is approached with a view to understanding the causes that lie behind phenomena. However, unlike a quantitative project, the focus of explanatory questions is on qualitative analysis of multiple interconnected factors that have influenced a particular group or area, rather than a provable causal link between dependent and independent variables.
- Descriptive questions
As the name suggests, descriptive questions aim to document and record what is happening. In answering descriptive questions , researchers might interact directly with participants with surveys or interviews, as well as using observational studies and ethnography studies that collect data on how participants interact with their wider environment.
- Predictive questions
Predictive questions start from the phenomena of interest and investigate what ramifications it might have in the future. Answering predictive questions may involve looking back as well as forward, with content analysis, questionnaires and studies of non-verbal communication (kinesics).
Why are good qualitative research questions important?
We know research questions are very important. But what makes them so essential? (And is that question a qualitative or quantitative one?)
Getting your qualitative research questions right has a number of benefits.
- It defines your qualitative research project Qualitative research questions definitively nail down the research population, the thing you’re examining, and what the nature of your answer will be.This means you can explain your research project to other people both inside and outside your business or organization. That could be critical when it comes to securing funding for your project, recruiting participants and members of your research team, and ultimately for publishing your results. It can also help you assess right the ethical considerations for your population of study.
- It maintains focus Good qualitative research questions help researchers to stick to the area of focus as they carry out their research. Keeping the research question in mind will help them steer away from tangents during their research or while they are carrying out qualitative research interviews. This holds true whatever the qualitative methods are, whether it’s a focus group, survey, thematic analysis or other type of inquiry.That doesn’t mean the research project can’t morph and change during its execution – sometimes this is acceptable and even welcome – but having a research question helps demarcate the starting point for the research. It can be referred back to if the scope and focus of the project does change.
- It helps make sure your outcomes are achievable
Because qualitative research questions help determine the kind of results you’re going to get, it helps make sure those results are achievable. By formulating good qualitative research questions in advance, you can make sure the things you want to know and the way you’re going to investigate them are grounded in practical reality. Otherwise, you may be at risk of taking on a research project that can’t be satisfactorily completed.
Developing good qualitative research questions
All researchers use research questions to define their parameters, keep their study on track and maintain focus on the research topic. This is especially important with qualitative questions, where there may be exploratory or inductive methods in use that introduce researchers to new and interesting areas of inquiry. Here are some tips for writing good qualitative research questions.
1. Keep it specific
Broader research questions are difficult to act on. They may also be open to interpretation, or leave some parameters undefined.
Strong example: How do Baby Boomers in the USA feel about their gender identity?
Weak example: Do people feel different about gender now?

2. Be original
Look for research questions that haven’t been widely addressed by others already.
Strong example: What are the effects of video calling on women’s experiences of work?
Weak example: Are women given less respect than men at work?
3. Make it research-worthy
Don’t ask a question that can be answered with a ‘yes’ or ‘no’, or with a quick Google search.
Strong example: What do people like and dislike about living in a highly multi-lingual country?
Weak example: What languages are spoken in India?
4. Focus your question
Don’t roll multiple topics or questions into one. Qualitative data may involve multiple topics, but your qualitative questions should be focused.
Strong example: What is the experience of disabled children and their families when using social services?
Weak example: How can we improve social services for children affected by poverty and disability?
4. Focus on your own discipline, not someone else’s
Avoid asking questions that are for the politicians, police or others to address.
Strong example: What does it feel like to be the victim of a hate crime?
Weak example: How can hate crimes be prevented?
5. Ask something researchable
Big questions, questions about hypothetical events or questions that would require vastly more resources than you have access to are not useful starting points for qualitative studies. Qualitative words or subjective ideas that lack definition are also not helpful.
Strong example: How do perceptions of physical beauty vary between today’s youth and their parents’ generation?
Weak example: Which country has the most beautiful people in it?
Related resources
Qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, business research methods 12 min read, qualitative research interviews 11 min read, market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research
Patrik aspers.
1 Department of Sociology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
2 Seminar for Sociology, Universität St. Gallen, St. Gallen, Switzerland
3 Department of Media and Social Sciences, University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway
What is qualitative research? If we look for a precise definition of qualitative research, and specifically for one that addresses its distinctive feature of being “qualitative,” the literature is meager. In this article we systematically search, identify and analyze a sample of 89 sources using or attempting to define the term “qualitative.” Then, drawing on ideas we find scattered across existing work, and based on Becker’s classic study of marijuana consumption, we formulate and illustrate a definition that tries to capture its core elements. We define qualitative research as an iterative process in which improved understanding to the scientific community is achieved by making new significant distinctions resulting from getting closer to the phenomenon studied. This formulation is developed as a tool to help improve research designs while stressing that a qualitative dimension is present in quantitative work as well. Additionally, it can facilitate teaching, communication between researchers, diminish the gap between qualitative and quantitative researchers, help to address critiques of qualitative methods, and be used as a standard of evaluation of qualitative research.
If we assume that there is something called qualitative research, what exactly is this qualitative feature? And how could we evaluate qualitative research as good or not? Is it fundamentally different from quantitative research? In practice, most active qualitative researchers working with empirical material intuitively know what is involved in doing qualitative research, yet perhaps surprisingly, a clear definition addressing its key feature is still missing.
To address the question of what is qualitative we turn to the accounts of “qualitative research” in textbooks and also in empirical work. In his classic, explorative, interview study of deviance Howard Becker ( 1963 ) asks ‘How does one become a marijuana user?’ In contrast to pre-dispositional and psychological-individualistic theories of deviant behavior, Becker’s inherently social explanation contends that becoming a user of this substance is the result of a three-phase sequential learning process. First, potential users need to learn how to smoke it properly to produce the “correct” effects. If not, they are likely to stop experimenting with it. Second, they need to discover the effects associated with it; in other words, to get “high,” individuals not only have to experience what the drug does, but also to become aware that those sensations are related to using it. Third, they require learning to savor the feelings related to its consumption – to develop an acquired taste. Becker, who played music himself, gets close to the phenomenon by observing, taking part, and by talking to people consuming the drug: “half of the fifty interviews were conducted with musicians, the other half covered a wide range of people, including laborers, machinists, and people in the professions” (Becker 1963 :56).
Another central aspect derived through the common-to-all-research interplay between induction and deduction (Becker 2017 ), is that during the course of his research Becker adds scientifically meaningful new distinctions in the form of three phases—distinctions, or findings if you will, that strongly affect the course of his research: its focus, the material that he collects, and which eventually impact his findings. Each phase typically unfolds through social interaction, and often with input from experienced users in “a sequence of social experiences during which the person acquires a conception of the meaning of the behavior, and perceptions and judgments of objects and situations, all of which make the activity possible and desirable” (Becker 1963 :235). In this study the increased understanding of smoking dope is a result of a combination of the meaning of the actors, and the conceptual distinctions that Becker introduces based on the views expressed by his respondents. Understanding is the result of research and is due to an iterative process in which data, concepts and evidence are connected with one another (Becker 2017 ).
Indeed, there are many definitions of qualitative research, but if we look for a definition that addresses its distinctive feature of being “qualitative,” the literature across the broad field of social science is meager. The main reason behind this article lies in the paradox, which, to put it bluntly, is that researchers act as if they know what it is, but they cannot formulate a coherent definition. Sociologists and others will of course continue to conduct good studies that show the relevance and value of qualitative research addressing scientific and practical problems in society. However, our paper is grounded in the idea that providing a clear definition will help us improve the work that we do. Among researchers who practice qualitative research there is clearly much knowledge. We suggest that a definition makes this knowledge more explicit. If the first rationale for writing this paper refers to the “internal” aim of improving qualitative research, the second refers to the increased “external” pressure that especially many qualitative researchers feel; pressure that comes both from society as well as from other scientific approaches. There is a strong core in qualitative research, and leading researchers tend to agree on what it is and how it is done. Our critique is not directed at the practice of qualitative research, but we do claim that the type of systematic work we do has not yet been done, and that it is useful to improve the field and its status in relation to quantitative research.
The literature on the “internal” aim of improving, or at least clarifying qualitative research is large, and we do not claim to be the first to notice the vagueness of the term “qualitative” (Strauss and Corbin 1998 ). Also, others have noted that there is no single definition of it (Long and Godfrey 2004 :182), that there are many different views on qualitative research (Denzin and Lincoln 2003 :11; Jovanović 2011 :3), and that more generally, we need to define its meaning (Best 2004 :54). Strauss and Corbin ( 1998 ), for example, as well as Nelson et al. (1992:2 cited in Denzin and Lincoln 2003 :11), and Flick ( 2007 :ix–x), have recognized that the term is problematic: “Actually, the term ‘qualitative research’ is confusing because it can mean different things to different people” (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :10–11). Hammersley has discussed the possibility of addressing the problem, but states that “the task of providing an account of the distinctive features of qualitative research is far from straightforward” ( 2013 :2). This confusion, as he has recently further argued (Hammersley 2018 ), is also salient in relation to ethnography where different philosophical and methodological approaches lead to a lack of agreement about what it means.
Others (e.g. Hammersley 2018 ; Fine and Hancock 2017 ) have also identified the treat to qualitative research that comes from external forces, seen from the point of view of “qualitative research.” This threat can be further divided into that which comes from inside academia, such as the critique voiced by “quantitative research” and outside of academia, including, for example, New Public Management. Hammersley ( 2018 ), zooming in on one type of qualitative research, ethnography, has argued that it is under treat. Similarly to Fine ( 2003 ), and before him Gans ( 1999 ), he writes that ethnography’ has acquired a range of meanings, and comes in many different versions, these often reflecting sharply divergent epistemological orientations. And already more than twenty years ago while reviewing Denzin and Lincoln’ s Handbook of Qualitative Methods Fine argued:
While this increasing centrality [of qualitative research] might lead one to believe that consensual standards have developed, this belief would be misleading. As the methodology becomes more widely accepted, querulous challengers have raised fundamental questions that collectively have undercut the traditional models of how qualitative research is to be fashioned and presented (1995:417).
According to Hammersley, there are today “serious treats to the practice of ethnographic work, on almost any definition” ( 2018 :1). He lists five external treats: (1) that social research must be accountable and able to show its impact on society; (2) the current emphasis on “big data” and the emphasis on quantitative data and evidence; (3) the labor market pressure in academia that leaves less time for fieldwork (see also Fine and Hancock 2017 ); (4) problems of access to fields; and (5) the increased ethical scrutiny of projects, to which ethnography is particularly exposed. Hammersley discusses some more or less insufficient existing definitions of ethnography.
The current situation, as Hammersley and others note—and in relation not only to ethnography but also qualitative research in general, and as our empirical study shows—is not just unsatisfactory, it may even be harmful for the entire field of qualitative research, and does not help social science at large. We suggest that the lack of clarity of qualitative research is a real problem that must be addressed.
Towards a Definition of Qualitative Research
Seen in an historical light, what is today called qualitative, or sometimes ethnographic, interpretative research – or a number of other terms – has more or less always existed. At the time the founders of sociology – Simmel, Weber, Durkheim and, before them, Marx – were writing, and during the era of the Methodenstreit (“dispute about methods”) in which the German historical school emphasized scientific methods (cf. Swedberg 1990 ), we can at least speak of qualitative forerunners.
Perhaps the most extended discussion of what later became known as qualitative methods in a classic work is Bronisław Malinowski’s ( 1922 ) Argonauts in the Western Pacific , although even this study does not explicitly address the meaning of “qualitative.” In Weber’s ([1921–-22] 1978) work we find a tension between scientific explanations that are based on observation and quantification and interpretative research (see also Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 ).
If we look through major sociology journals like the American Sociological Review , American Journal of Sociology , or Social Forces we will not find the term qualitative sociology before the 1970s. And certainly before then much of what we consider qualitative classics in sociology, like Becker’ study ( 1963 ), had already been produced. Indeed, the Chicago School often combined qualitative and quantitative data within the same study (Fine 1995 ). Our point being that before a disciplinary self-awareness the term quantitative preceded qualitative, and the articulation of the former was a political move to claim scientific status (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 ). In the US the World War II seem to have sparked a critique of sociological work, including “qualitative work,” that did not follow the scientific canon (Rawls 2018 ), which was underpinned by a scientifically oriented and value free philosophy of science. As a result the attempts and practice of integrating qualitative and quantitative sociology at Chicago lost ground to sociology that was more oriented to surveys and quantitative work at Columbia under Merton-Lazarsfeld. The quantitative tradition was also able to present textbooks (Lundberg 1951 ) that facilitated the use this approach and its “methods.” The practices of the qualitative tradition, by and large, remained tacit or was part of the mentoring transferred from the renowned masters to their students.
This glimpse into history leads us back to the lack of a coherent account condensed in a definition of qualitative research. Many of the attempts to define the term do not meet the requirements of a proper definition: A definition should be clear, avoid tautology, demarcate its domain in relation to the environment, and ideally only use words in its definiens that themselves are not in need of definition (Hempel 1966 ). A definition can enhance precision and thus clarity by identifying the core of the phenomenon. Preferably, a definition should be short. The typical definition we have found, however, is an ostensive definition, which indicates what qualitative research is about without informing us about what it actually is :
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives. (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 :2)
Flick claims that the label “qualitative research” is indeed used as an umbrella for a number of approaches ( 2007 :2–4; 2002 :6), and it is not difficult to identify research fitting this designation. Moreover, whatever it is, it has grown dramatically over the past five decades. In addition, courses have been developed, methods have flourished, arguments about its future have been advanced (for example, Denzin and Lincoln 1994) and criticized (for example, Snow and Morrill 1995 ), and dedicated journals and books have mushroomed. Most social scientists have a clear idea of research and how it differs from journalism, politics and other activities. But the question of what is qualitative in qualitative research is either eluded or eschewed.
We maintain that this lacuna hinders systematic knowledge production based on qualitative research. Paul Lazarsfeld noted the lack of “codification” as early as 1955 when he reviewed 100 qualitative studies in order to offer a codification of the practices (Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 :239). Since then many texts on “qualitative research” and its methods have been published, including recent attempts (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ) similar to Lazarsfeld’s. These studies have tried to extract what is qualitative by looking at the large number of empirical “qualitative” studies. Our novel strategy complements these endeavors by taking another approach and looking at the attempts to codify these practices in the form of a definition, as well as to a minor extent take Becker’s study as an exemplar of what qualitative researchers actually do, and what the characteristic of being ‘qualitative’ denotes and implies. We claim that qualitative researchers, if there is such a thing as “qualitative research,” should be able to codify their practices in a condensed, yet general way expressed in language.
Lingering problems of “generalizability” and “how many cases do I need” (Small 2009 ) are blocking advancement – in this line of work qualitative approaches are said to differ considerably from quantitative ones, while some of the former unsuccessfully mimic principles related to the latter (Small 2009 ). Additionally, quantitative researchers sometimes unfairly criticize the first based on their own quality criteria. Scholars like Goertz and Mahoney ( 2012 ) have successfully focused on the different norms and practices beyond what they argue are essentially two different cultures: those working with either qualitative or quantitative methods. Instead, similarly to Becker ( 2017 ) who has recently questioned the usefulness of the distinction between qualitative and quantitative research, we focus on similarities.
The current situation also impedes both students and researchers in focusing their studies and understanding each other’s work (Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 :239). A third consequence is providing an opening for critiques by scholars operating within different traditions (Valsiner 2000 :101). A fourth issue is that the “implicit use of methods in qualitative research makes the field far less standardized than the quantitative paradigm” (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 :9). Relatedly, the National Science Foundation in the US organized two workshops in 2004 and 2005 to address the scientific foundations of qualitative research involving strategies to improve it and to develop standards of evaluation in qualitative research. However, a specific focus on its distinguishing feature of being “qualitative” while being implicitly acknowledged, was discussed only briefly (for example, Best 2004 ).
In 2014 a theme issue was published in this journal on “Methods, Materials, and Meanings: Designing Cultural Analysis,” discussing central issues in (cultural) qualitative research (Berezin 2014 ; Biernacki 2014 ; Glaeser 2014 ; Lamont and Swidler 2014 ; Spillman 2014). We agree with many of the arguments put forward, such as the risk of methodological tribalism, and that we should not waste energy on debating methods separated from research questions. Nonetheless, a clarification of the relation to what is called “quantitative research” is of outmost importance to avoid misunderstandings and misguided debates between “qualitative” and “quantitative” researchers. Our strategy means that researchers, “qualitative” or “quantitative” they may be, in their actual practice may combine qualitative work and quantitative work.
In this article we accomplish three tasks. First, we systematically survey the literature for meanings of qualitative research by looking at how researchers have defined it. Drawing upon existing knowledge we find that the different meanings and ideas of qualitative research are not yet coherently integrated into one satisfactory definition. Next, we advance our contribution by offering a definition of qualitative research and illustrate its meaning and use partially by expanding on the brief example introduced earlier related to Becker’s work ( 1963 ). We offer a systematic analysis of central themes of what researchers consider to be the core of “qualitative,” regardless of style of work. These themes – which we summarize in terms of four keywords: distinction, process, closeness, improved understanding – constitute part of our literature review, in which each one appears, sometimes with others, but never all in the same definition. They serve as the foundation of our contribution. Our categories are overlapping. Their use is primarily to organize the large amount of definitions we have identified and analyzed, and not necessarily to draw a clear distinction between them. Finally, we continue the elaboration discussed above on the advantages of a clear definition of qualitative research.
In a hermeneutic fashion we propose that there is something meaningful that deserves to be labelled “qualitative research” (Gadamer 1990 ). To approach the question “What is qualitative in qualitative research?” we have surveyed the literature. In conducting our survey we first traced the word’s etymology in dictionaries, encyclopedias, handbooks of the social sciences and of methods and textbooks, mainly in English, which is common to methodology courses. It should be noted that we have zoomed in on sociology and its literature. This discipline has been the site of the largest debate and development of methods that can be called “qualitative,” which suggests that this field should be examined in great detail.
In an ideal situation we should expect that one good definition, or at least some common ideas, would have emerged over the years. This common core of qualitative research should be so accepted that it would appear in at least some textbooks. Since this is not what we found, we decided to pursue an inductive approach to capture maximal variation in the field of qualitative research; we searched in a selection of handbooks, textbooks, book chapters, and books, to which we added the analysis of journal articles. Our sample comprises a total of 89 references.
In practice we focused on the discipline that has had a clear discussion of methods, namely sociology. We also conducted a broad search in the JSTOR database to identify scholarly sociology articles published between 1998 and 2017 in English with a focus on defining or explaining qualitative research. We specifically zoom in on this time frame because we would have expect that this more mature period would have produced clear discussions on the meaning of qualitative research. To find these articles we combined a number of keywords to search the content and/or the title: qualitative (which was always included), definition, empirical, research, methodology, studies, fieldwork, interview and observation .
As a second phase of our research we searched within nine major sociological journals ( American Journal of Sociology , Sociological Theory , American Sociological Review , Contemporary Sociology , Sociological Forum , Sociological Theory , Qualitative Research , Qualitative Sociology and Qualitative Sociology Review ) for articles also published during the past 19 years (1998–2017) that had the term “qualitative” in the title and attempted to define qualitative research.
Lastly we picked two additional journals, Qualitative Research and Qualitative Sociology , in which we could expect to find texts addressing the notion of “qualitative.” From Qualitative Research we chose Volume 14, Issue 6, December 2014, and from Qualitative Sociology we chose Volume 36, Issue 2, June 2017. Within each of these we selected the first article; then we picked the second article of three prior issues. Again we went back another three issues and investigated article number three. Finally we went back another three issues and perused article number four. This selection criteria was used to get a manageable sample for the analysis.
The coding process of the 89 references we gathered in our selected review began soon after the first round of material was gathered, and we reduced the complexity created by our maximum variation sampling (Snow and Anderson 1993 :22) to four different categories within which questions on the nature and properties of qualitative research were discussed. We call them: Qualitative and Quantitative Research, Qualitative Research, Fieldwork, and Grounded Theory. This – which may appear as an illogical grouping – merely reflects the “context” in which the matter of “qualitative” is discussed. If the selection process of the material – books and articles – was informed by pre-knowledge, we used an inductive strategy to code the material. When studying our material, we identified four central notions related to “qualitative” that appear in various combinations in the literature which indicate what is the core of qualitative research. We have labeled them: “distinctions”, “process,” “closeness,” and “improved understanding.” During the research process the categories and notions were improved, refined, changed, and reordered. The coding ended when a sense of saturation in the material arose. In the presentation below all quotations and references come from our empirical material of texts on qualitative research.
Analysis – What is Qualitative Research?
In this section we describe the four categories we identified in the coding, how they differently discuss qualitative research, as well as their overall content. Some salient quotations are selected to represent the type of text sorted under each of the four categories. What we present are examples from the literature.
Qualitative and Quantitative
This analytic category comprises quotations comparing qualitative and quantitative research, a distinction that is frequently used (Brown 2010 :231); in effect this is a conceptual pair that structures the discussion and that may be associated with opposing interests. While the general goal of quantitative and qualitative research is the same – to understand the world better – their methodologies and focus in certain respects differ substantially (Becker 1966 :55). Quantity refers to that property of something that can be determined by measurement. In a dictionary of Statistics and Methodology we find that “(a) When referring to *variables, ‘qualitative’ is another term for *categorical or *nominal. (b) When speaking of kinds of research, ‘qualitative’ refers to studies of subjects that are hard to quantify, such as art history. Qualitative research tends to be a residual category for almost any kind of non-quantitative research” (Stiles 1998:183). But it should be obvious that one could employ a quantitative approach when studying, for example, art history.
The same dictionary states that quantitative is “said of variables or research that can be handled numerically, usually (too sharply) contrasted with *qualitative variables and research” (Stiles 1998:184). From a qualitative perspective “quantitative research” is about numbers and counting, and from a quantitative perspective qualitative research is everything that is not about numbers. But this does not say much about what is “qualitative.” If we turn to encyclopedias we find that in the 1932 edition of the Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences there is no mention of “qualitative.” In the Encyclopedia from 1968 we can read:
Qualitative Analysis. For methods of obtaining, analyzing, and describing data, see [the various entries:] CONTENT ANALYSIS; COUNTED DATA; EVALUATION RESEARCH, FIELD WORK; GRAPHIC PRESENTATION; HISTORIOGRAPHY, especially the article on THE RHETORIC OF HISTORY; INTERVIEWING; OBSERVATION; PERSONALITY MEASUREMENT; PROJECTIVE METHODS; PSYCHOANALYSIS, article on EXPERIMENTAL METHODS; SURVEY ANALYSIS, TABULAR PRESENTATION; TYPOLOGIES. (Vol. 13:225)
Some, like Alford, divide researchers into methodologists or, in his words, “quantitative and qualitative specialists” (Alford 1998 :12). Qualitative research uses a variety of methods, such as intensive interviews or in-depth analysis of historical materials, and it is concerned with a comprehensive account of some event or unit (King et al. 1994 :4). Like quantitative research it can be utilized to study a variety of issues, but it tends to focus on meanings and motivations that underlie cultural symbols, personal experiences, phenomena and detailed understanding of processes in the social world. In short, qualitative research centers on understanding processes, experiences, and the meanings people assign to things (Kalof et al. 2008 :79).
Others simply say that qualitative methods are inherently unscientific (Jovanović 2011 :19). Hood, for instance, argues that words are intrinsically less precise than numbers, and that they are therefore more prone to subjective analysis, leading to biased results (Hood 2006 :219). Qualitative methodologies have raised concerns over the limitations of quantitative templates (Brady et al. 2004 :4). Scholars such as King et al. ( 1994 ), for instance, argue that non-statistical research can produce more reliable results if researchers pay attention to the rules of scientific inference commonly stated in quantitative research. Also, researchers such as Becker ( 1966 :59; 1970 :42–43) have asserted that, if conducted properly, qualitative research and in particular ethnographic field methods, can lead to more accurate results than quantitative studies, in particular, survey research and laboratory experiments.
Some researchers, such as Kalof, Dan, and Dietz ( 2008 :79) claim that the boundaries between the two approaches are becoming blurred, and Small ( 2009 ) argues that currently much qualitative research (especially in North America) tries unsuccessfully and unnecessarily to emulate quantitative standards. For others, qualitative research tends to be more humanistic and discursive (King et al. 1994 :4). Ragin ( 1994 ), and similarly also Becker, ( 1996 :53), Marchel and Owens ( 2007 :303) think that the main distinction between the two styles is overstated and does not rest on the simple dichotomy of “numbers versus words” (Ragin 1994 :xii). Some claim that quantitative data can be utilized to discover associations, but in order to unveil cause and effect a complex research design involving the use of qualitative approaches needs to be devised (Gilbert 2009 :35). Consequently, qualitative data are useful for understanding the nuances lying beyond those processes as they unfold (Gilbert 2009 :35). Others contend that qualitative research is particularly well suited both to identify causality and to uncover fine descriptive distinctions (Fine and Hallett 2014 ; Lichterman and Isaac Reed 2014 ; Katz 2015 ).
There are other ways to separate these two traditions, including normative statements about what qualitative research should be (that is, better or worse than quantitative approaches, concerned with scientific approaches to societal change or vice versa; Snow and Morrill 1995 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2005 ), or whether it should develop falsifiable statements; Best 2004 ).
We propose that quantitative research is largely concerned with pre-determined variables (Small 2008 ); the analysis concerns the relations between variables. These categories are primarily not questioned in the study, only their frequency or degree, or the correlations between them (cf. Franzosi 2016 ). If a researcher studies wage differences between women and men, he or she works with given categories: x number of men are compared with y number of women, with a certain wage attributed to each person. The idea is not to move beyond the given categories of wage, men and women; they are the starting point as well as the end point, and undergo no “qualitative change.” Qualitative research, in contrast, investigates relations between categories that are themselves subject to change in the research process. Returning to Becker’s study ( 1963 ), we see that he questioned pre-dispositional theories of deviant behavior working with pre-determined variables such as an individual’s combination of personal qualities or emotional problems. His take, in contrast, was to understand marijuana consumption by developing “variables” as part of the investigation. Thereby he presented new variables, or as we would say today, theoretical concepts, but which are grounded in the empirical material.
Qualitative Research
This category contains quotations that refer to descriptions of qualitative research without making comparisons with quantitative research. Researchers such as Denzin and Lincoln, who have written a series of influential handbooks on qualitative methods (1994; Denzin and Lincoln 2003 ; 2005 ), citing Nelson et al. (1992:4), argue that because qualitative research is “interdisciplinary, transdisciplinary, and sometimes counterdisciplinary” it is difficult to derive one single definition of it (Jovanović 2011 :3). According to them, in fact, “the field” is “many things at the same time,” involving contradictions, tensions over its focus, methods, and how to derive interpretations and findings ( 2003 : 11). Similarly, others, such as Flick ( 2007 :ix–x) contend that agreeing on an accepted definition has increasingly become problematic, and that qualitative research has possibly matured different identities. However, Best holds that “the proliferation of many sorts of activities under the label of qualitative sociology threatens to confuse our discussions” ( 2004 :54). Atkinson’s position is more definite: “the current state of qualitative research and research methods is confused” ( 2005 :3–4).
Qualitative research is about interpretation (Blumer 1969 ; Strauss and Corbin 1998 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2003 ), or Verstehen [understanding] (Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 ). It is “multi-method,” involving the collection and use of a variety of empirical materials (Denzin and Lincoln 1998; Silverman 2013 ) and approaches (Silverman 2005 ; Flick 2007 ). It focuses not only on the objective nature of behavior but also on its subjective meanings: individuals’ own accounts of their attitudes, motivations, behavior (McIntyre 2005 :127; Creswell 2009 ), events and situations (Bryman 1989) – what people say and do in specific places and institutions (Goodwin and Horowitz 2002 :35–36) in social and temporal contexts (Morrill and Fine 1997). For this reason, following Weber ([1921-22] 1978), it can be described as an interpretative science (McIntyre 2005 :127). But could quantitative research also be concerned with these questions? Also, as pointed out below, does all qualitative research focus on subjective meaning, as some scholars suggest?
Others also distinguish qualitative research by claiming that it collects data using a naturalistic approach (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 :2; Creswell 2009 ), focusing on the meaning actors ascribe to their actions. But again, does all qualitative research need to be collected in situ? And does qualitative research have to be inherently concerned with meaning? Flick ( 2007 ), referring to Denzin and Lincoln ( 2005 ), mentions conversation analysis as an example of qualitative research that is not concerned with the meanings people bring to a situation, but rather with the formal organization of talk. Still others, such as Ragin ( 1994 :85), note that qualitative research is often (especially early on in the project, we would add) less structured than other kinds of social research – a characteristic connected to its flexibility and that can lead both to potentially better, but also worse results. But is this not a feature of this type of research, rather than a defining description of its essence? Wouldn’t this comment also apply, albeit to varying degrees, to quantitative research?
In addition, Strauss ( 2003 ), along with others, such as Alvesson and Kärreman ( 2011 :10–76), argue that qualitative researchers struggle to capture and represent complex phenomena partially because they tend to collect a large amount of data. While his analysis is correct at some points – “It is necessary to do detailed, intensive, microscopic examination of the data in order to bring out the amazing complexity of what lies in, behind, and beyond those data” (Strauss 2003 :10) – much of his analysis concerns the supposed focus of qualitative research and its challenges, rather than exactly what it is about. But even in this instance we would make a weak case arguing that these are strictly the defining features of qualitative research. Some researchers seem to focus on the approach or the methods used, or even on the way material is analyzed. Several researchers stress the naturalistic assumption of investigating the world, suggesting that meaning and interpretation appear to be a core matter of qualitative research.
We can also see that in this category there is no consensus about specific qualitative methods nor about qualitative data. Many emphasize interpretation, but quantitative research, too, involves interpretation; the results of a regression analysis, for example, certainly have to be interpreted, and the form of meta-analysis that factor analysis provides indeed requires interpretation However, there is no interpretation of quantitative raw data, i.e., numbers in tables. One common thread is that qualitative researchers have to get to grips with their data in order to understand what is being studied in great detail, irrespective of the type of empirical material that is being analyzed. This observation is connected to the fact that qualitative researchers routinely make several adjustments of focus and research design as their studies progress, in many cases until the very end of the project (Kalof et al. 2008 ). If you, like Becker, do not start out with a detailed theory, adjustments such as the emergence and refinement of research questions will occur during the research process. We have thus found a number of useful reflections about qualitative research scattered across different sources, but none of them effectively describe the defining characteristics of this approach.
Although qualitative research does not appear to be defined in terms of a specific method, it is certainly common that fieldwork, i.e., research that entails that the researcher spends considerable time in the field that is studied and use the knowledge gained as data, is seen as emblematic of or even identical to qualitative research. But because we understand that fieldwork tends to focus primarily on the collection and analysis of qualitative data, we expected to find within it discussions on the meaning of “qualitative.” But, again, this was not the case.
Instead, we found material on the history of this approach (for example, Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 ; Atkinson et al. 2001), including how it has changed; for example, by adopting a more self-reflexive practice (Heyl 2001), as well as the different nomenclature that has been adopted, such as fieldwork, ethnography, qualitative research, naturalistic research, participant observation and so on (for example, Lofland et al. 2006 ; Gans 1999 ).
We retrieved definitions of ethnography, such as “the study of people acting in the natural courses of their daily lives,” involving a “resocialization of the researcher” (Emerson 1988 :1) through intense immersion in others’ social worlds (see also examples in Hammersley 2018 ). This may be accomplished by direct observation and also participation (Neuman 2007 :276), although others, such as Denzin ( 1970 :185), have long recognized other types of observation, including non-participant (“fly on the wall”). In this category we have also isolated claims and opposing views, arguing that this type of research is distinguished primarily by where it is conducted (natural settings) (Hughes 1971:496), and how it is carried out (a variety of methods are applied) or, for some most importantly, by involving an active, empathetic immersion in those being studied (Emerson 1988 :2). We also retrieved descriptions of the goals it attends in relation to how it is taught (understanding subjective meanings of the people studied, primarily develop theory, or contribute to social change) (see for example, Corte and Irwin 2017 ; Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 :281; Trier-Bieniek 2012 :639) by collecting the richest possible data (Lofland et al. 2006 ) to derive “thick descriptions” (Geertz 1973 ), and/or to aim at theoretical statements of general scope and applicability (for example, Emerson 1988 ; Fine 2003 ). We have identified guidelines on how to evaluate it (for example Becker 1996 ; Lamont 2004 ) and have retrieved instructions on how it should be conducted (for example, Lofland et al. 2006 ). For instance, analysis should take place while the data gathering unfolds (Emerson 1988 ; Hammersley and Atkinson 2007 ; Lofland et al. 2006 ), observations should be of long duration (Becker 1970 :54; Goffman 1989 ), and data should be of high quantity (Becker 1970 :52–53), as well as other questionable distinctions between fieldwork and other methods:
Field studies differ from other methods of research in that the researcher performs the task of selecting topics, decides what questions to ask, and forges interest in the course of the research itself . This is in sharp contrast to many ‘theory-driven’ and ‘hypothesis-testing’ methods. (Lofland and Lofland 1995 :5)
But could not, for example, a strictly interview-based study be carried out with the same amount of flexibility, such as sequential interviewing (for example, Small 2009 )? Once again, are quantitative approaches really as inflexible as some qualitative researchers think? Moreover, this category stresses the role of the actors’ meaning, which requires knowledge and close interaction with people, their practices and their lifeworld.
It is clear that field studies – which are seen by some as the “gold standard” of qualitative research – are nonetheless only one way of doing qualitative research. There are other methods, but it is not clear why some are more qualitative than others, or why they are better or worse. Fieldwork is characterized by interaction with the field (the material) and understanding of the phenomenon that is being studied. In Becker’s case, he had general experience from fields in which marihuana was used, based on which he did interviews with actual users in several fields.
Grounded Theory
Another major category we identified in our sample is Grounded Theory. We found descriptions of it most clearly in Glaser and Strauss’ ([1967] 2010 ) original articulation, Strauss and Corbin ( 1998 ) and Charmaz ( 2006 ), as well as many other accounts of what it is for: generating and testing theory (Strauss 2003 :xi). We identified explanations of how this task can be accomplished – such as through two main procedures: constant comparison and theoretical sampling (Emerson 1998:96), and how using it has helped researchers to “think differently” (for example, Strauss and Corbin 1998 :1). We also read descriptions of its main traits, what it entails and fosters – for instance, an exceptional flexibility, an inductive approach (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :31–33; 1990; Esterberg 2002 :7), an ability to step back and critically analyze situations, recognize tendencies towards bias, think abstractly and be open to criticism, enhance sensitivity towards the words and actions of respondents, and develop a sense of absorption and devotion to the research process (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :5–6). Accordingly, we identified discussions of the value of triangulating different methods (both using and not using grounded theory), including quantitative ones, and theories to achieve theoretical development (most comprehensively in Denzin 1970 ; Strauss and Corbin 1998 ; Timmermans and Tavory 2012 ). We have also located arguments about how its practice helps to systematize data collection, analysis and presentation of results (Glaser and Strauss [1967] 2010 :16).
Grounded theory offers a systematic approach which requires researchers to get close to the field; closeness is a requirement of identifying questions and developing new concepts or making further distinctions with regard to old concepts. In contrast to other qualitative approaches, grounded theory emphasizes the detailed coding process, and the numerous fine-tuned distinctions that the researcher makes during the process. Within this category, too, we could not find a satisfying discussion of the meaning of qualitative research.
Defining Qualitative Research
In sum, our analysis shows that some notions reappear in the discussion of qualitative research, such as understanding, interpretation, “getting close” and making distinctions. These notions capture aspects of what we think is “qualitative.” However, a comprehensive definition that is useful and that can further develop the field is lacking, and not even a clear picture of its essential elements appears. In other words no definition emerges from our data, and in our research process we have moved back and forth between our empirical data and the attempt to present a definition. Our concrete strategy, as stated above, is to relate qualitative and quantitative research, or more specifically, qualitative and quantitative work. We use an ideal-typical notion of quantitative research which relies on taken for granted and numbered variables. This means that the data consists of variables on different scales, such as ordinal, but frequently ratio and absolute scales, and the representation of the numbers to the variables, i.e. the justification of the assignment of numbers to object or phenomenon, are not questioned, though the validity may be questioned. In this section we return to the notion of quality and try to clarify it while presenting our contribution.
Broadly, research refers to the activity performed by people trained to obtain knowledge through systematic procedures. Notions such as “objectivity” and “reflexivity,” “systematic,” “theory,” “evidence” and “openness” are here taken for granted in any type of research. Next, building on our empirical analysis we explain the four notions that we have identified as central to qualitative work: distinctions, process, closeness, and improved understanding. In discussing them, ultimately in relation to one another, we make their meaning even more precise. Our idea, in short, is that only when these ideas that we present separately for analytic purposes are brought together can we speak of qualitative research.
Distinctions
We believe that the possibility of making new distinctions is one the defining characteristics of qualitative research. It clearly sets it apart from quantitative analysis which works with taken-for-granted variables, albeit as mentioned, meta-analyses, for example, factor analysis may result in new variables. “Quality” refers essentially to distinctions, as already pointed out by Aristotle. He discusses the term “qualitative” commenting: “By a quality I mean that in virtue of which things are said to be qualified somehow” (Aristotle 1984:14). Quality is about what something is or has, which means that the distinction from its environment is crucial. We see qualitative research as a process in which significant new distinctions are made to the scholarly community; to make distinctions is a key aspect of obtaining new knowledge; a point, as we will see, that also has implications for “quantitative research.” The notion of being “significant” is paramount. New distinctions by themselves are not enough; just adding concepts only increases complexity without furthering our knowledge. The significance of new distinctions is judged against the communal knowledge of the research community. To enable this discussion and judgements central elements of rational discussion are required (cf. Habermas [1981] 1987 ; Davidsson [ 1988 ] 2001) to identify what is new and relevant scientific knowledge. Relatedly, Ragin alludes to the idea of new and useful knowledge at a more concrete level: “Qualitative methods are appropriate for in-depth examination of cases because they aid the identification of key features of cases. Most qualitative methods enhance data” (1994:79). When Becker ( 1963 ) studied deviant behavior and investigated how people became marihuana smokers, he made distinctions between the ways in which people learned how to smoke. This is a classic example of how the strategy of “getting close” to the material, for example the text, people or pictures that are subject to analysis, may enable researchers to obtain deeper insight and new knowledge by making distinctions – in this instance on the initial notion of learning how to smoke. Others have stressed the making of distinctions in relation to coding or theorizing. Emerson et al. ( 1995 ), for example, hold that “qualitative coding is a way of opening up avenues of inquiry,” meaning that the researcher identifies and develops concepts and analytic insights through close examination of and reflection on data (Emerson et al. 1995 :151). Goodwin and Horowitz highlight making distinctions in relation to theory-building writing: “Close engagement with their cases typically requires qualitative researchers to adapt existing theories or to make new conceptual distinctions or theoretical arguments to accommodate new data” ( 2002 : 37). In the ideal-typical quantitative research only existing and so to speak, given, variables would be used. If this is the case no new distinction are made. But, would not also many “quantitative” researchers make new distinctions?
Process does not merely suggest that research takes time. It mainly implies that qualitative new knowledge results from a process that involves several phases, and above all iteration. Qualitative research is about oscillation between theory and evidence, analysis and generating material, between first- and second -order constructs (Schütz 1962 :59), between getting in contact with something, finding sources, becoming deeply familiar with a topic, and then distilling and communicating some of its essential features. The main point is that the categories that the researcher uses, and perhaps takes for granted at the beginning of the research process, usually undergo qualitative changes resulting from what is found. Becker describes how he tested hypotheses and let the jargon of the users develop into theoretical concepts. This happens over time while the study is being conducted, exemplifying what we mean by process.
In the research process, a pilot-study may be used to get a first glance of, for example, the field, how to approach it, and what methods can be used, after which the method and theory are chosen or refined before the main study begins. Thus, the empirical material is often central from the start of the project and frequently leads to adjustments by the researcher. Likewise, during the main study categories are not fixed; the empirical material is seen in light of the theory used, but it is also given the opportunity to kick back, thereby resisting attempts to apply theoretical straightjackets (Becker 1970 :43). In this process, coding and analysis are interwoven, and thus are often important steps for getting closer to the phenomenon and deciding what to focus on next. Becker began his research by interviewing musicians close to him, then asking them to refer him to other musicians, and later on doubling his original sample of about 25 to include individuals in other professions (Becker 1973:46). Additionally, he made use of some participant observation, documents, and interviews with opiate users made available to him by colleagues. As his inductive theory of deviance evolved, Becker expanded his sample in order to fine tune it, and test the accuracy and generality of his hypotheses. In addition, he introduced a negative case and discussed the null hypothesis ( 1963 :44). His phasic career model is thus based on a research design that embraces processual work. Typically, process means to move between “theory” and “material” but also to deal with negative cases, and Becker ( 1998 ) describes how discovering these negative cases impacted his research design and ultimately its findings.
Obviously, all research is process-oriented to some degree. The point is that the ideal-typical quantitative process does not imply change of the data, and iteration between data, evidence, hypotheses, empirical work, and theory. The data, quantified variables, are, in most cases fixed. Merging of data, which of course can be done in a quantitative research process, does not mean new data. New hypotheses are frequently tested, but the “raw data is often the “the same.” Obviously, over time new datasets are made available and put into use.
Another characteristic that is emphasized in our sample is that qualitative researchers – and in particular ethnographers – can, or as Goffman put it, ought to ( 1989 ), get closer to the phenomenon being studied and their data than quantitative researchers (for example, Silverman 2009 :85). Put differently, essentially because of their methods qualitative researchers get into direct close contact with those being investigated and/or the material, such as texts, being analyzed. Becker started out his interview study, as we noted, by talking to those he knew in the field of music to get closer to the phenomenon he was studying. By conducting interviews he got even closer. Had he done more observations, he would undoubtedly have got even closer to the field.
Additionally, ethnographers’ design enables researchers to follow the field over time, and the research they do is almost by definition longitudinal, though the time in the field is studied obviously differs between studies. The general characteristic of closeness over time maximizes the chances of unexpected events, new data (related, for example, to archival research as additional sources, and for ethnography for situations not necessarily previously thought of as instrumental – what Mannay and Morgan ( 2015 ) term the “waiting field”), serendipity (Merton and Barber 2004 ; Åkerström 2013 ), and possibly reactivity, as well as the opportunity to observe disrupted patterns that translate into exemplars of negative cases. Two classic examples of this are Becker’s finding of what medical students call “crocks” (Becker et al. 1961 :317), and Geertz’s ( 1973 ) study of “deep play” in Balinese society.
By getting and staying so close to their data – be it pictures, text or humans interacting (Becker was himself a musician) – for a long time, as the research progressively focuses, qualitative researchers are prompted to continually test their hunches, presuppositions and hypotheses. They test them against a reality that often (but certainly not always), and practically, as well as metaphorically, talks back, whether by validating them, or disqualifying their premises – correctly, as well as incorrectly (Fine 2003 ; Becker 1970 ). This testing nonetheless often leads to new directions for the research. Becker, for example, says that he was initially reading psychological theories, but when facing the data he develops a theory that looks at, you may say, everything but psychological dispositions to explain the use of marihuana. Especially researchers involved with ethnographic methods have a fairly unique opportunity to dig up and then test (in a circular, continuous and temporal way) new research questions and findings as the research progresses, and thereby to derive previously unimagined and uncharted distinctions by getting closer to the phenomenon under study.
Let us stress that getting close is by no means restricted to ethnography. The notion of hermeneutic circle and hermeneutics as a general way of understanding implies that we must get close to the details in order to get the big picture. This also means that qualitative researchers can literally also make use of details of pictures as evidence (cf. Harper 2002). Thus, researchers may get closer both when generating the material or when analyzing it.
Quantitative research, we maintain, in the ideal-typical representation cannot get closer to the data. The data is essentially numbers in tables making up the variables (Franzosi 2016 :138). The data may originally have been “qualitative,” but once reduced to numbers there can only be a type of “hermeneutics” about what the number may stand for. The numbers themselves, however, are non-ambiguous. Thus, in quantitative research, interpretation, if done, is not about the data itself—the numbers—but what the numbers stand for. It follows that the interpretation is essentially done in a more “speculative” mode without direct empirical evidence (cf. Becker 2017 ).
Improved Understanding
While distinction, process and getting closer refer to the qualitative work of the researcher, improved understanding refers to its conditions and outcome of this work. Understanding cuts deeper than explanation, which to some may mean a causally verified correlation between variables. The notion of explanation presupposes the notion of understanding since explanation does not include an idea of how knowledge is gained (Manicas 2006 : 15). Understanding, we argue, is the core concept of what we call the outcome of the process when research has made use of all the other elements that were integrated in the research. Understanding, then, has a special status in qualitative research since it refers both to the conditions of knowledge and the outcome of the process. Understanding can to some extent be seen as the condition of explanation and occurs in a process of interpretation, which naturally refers to meaning (Gadamer 1990 ). It is fundamentally connected to knowing, and to the knowing of how to do things (Heidegger [1927] 2001 ). Conceptually the term hermeneutics is used to account for this process. Heidegger ties hermeneutics to human being and not possible to separate from the understanding of being ( 1988 ). Here we use it in a broader sense, and more connected to method in general (cf. Seiffert 1992 ). The abovementioned aspects – for example, “objectivity” and “reflexivity” – of the approach are conditions of scientific understanding. Understanding is the result of a circular process and means that the parts are understood in light of the whole, and vice versa. Understanding presupposes pre-understanding, or in other words, some knowledge of the phenomenon studied. The pre-understanding, even in the form of prejudices, are in qualitative research process, which we see as iterative, questioned, which gradually or suddenly change due to the iteration of data, evidence and concepts. However, qualitative research generates understanding in the iterative process when the researcher gets closer to the data, e.g., by going back and forth between field and analysis in a process that generates new data that changes the evidence, and, ultimately, the findings. Questioning, to ask questions, and put what one assumes—prejudices and presumption—in question, is central to understand something (Heidegger [1927] 2001 ; Gadamer 1990 :368–384). We propose that this iterative process in which the process of understanding occurs is characteristic of qualitative research.
Improved understanding means that we obtain scientific knowledge of something that we as a scholarly community did not know before, or that we get to know something better. It means that we understand more about how parts are related to one another, and to other things we already understand (see also Fine and Hallett 2014 ). Understanding is an important condition for qualitative research. It is not enough to identify correlations, make distinctions, and work in a process in which one gets close to the field or phenomena. Understanding is accomplished when the elements are integrated in an iterative process.
It is, moreover, possible to understand many things, and researchers, just like children, may come to understand new things every day as they engage with the world. This subjective condition of understanding – namely, that a person gains a better understanding of something –is easily met. To be qualified as “scientific,” the understanding must be general and useful to many; it must be public. But even this generally accessible understanding is not enough in order to speak of “scientific understanding.” Though we as a collective can increase understanding of everything in virtually all potential directions as a result also of qualitative work, we refrain from this “objective” way of understanding, which has no means of discriminating between what we gain in understanding. Scientific understanding means that it is deemed relevant from the scientific horizon (compare Schütz 1962 : 35–38, 46, 63), and that it rests on the pre-understanding that the scientists have and must have in order to understand. In other words, the understanding gained must be deemed useful by other researchers, so that they can build on it. We thus see understanding from a pragmatic, rather than a subjective or objective perspective. Improved understanding is related to the question(s) at hand. Understanding, in order to represent an improvement, must be an improvement in relation to the existing body of knowledge of the scientific community (James [ 1907 ] 1955). Scientific understanding is, by definition, collective, as expressed in Weber’s famous note on objectivity, namely that scientific work aims at truths “which … can claim, even for a Chinese, the validity appropriate to an empirical analysis” ([1904] 1949 :59). By qualifying “improved understanding” we argue that it is a general defining characteristic of qualitative research. Becker‘s ( 1966 ) study and other research of deviant behavior increased our understanding of the social learning processes of how individuals start a behavior. And it also added new knowledge about the labeling of deviant behavior as a social process. Few studies, of course, make the same large contribution as Becker’s, but are nonetheless qualitative research.
Understanding in the phenomenological sense, which is a hallmark of qualitative research, we argue, requires meaning and this meaning is derived from the context, and above all the data being analyzed. The ideal-typical quantitative research operates with given variables with different numbers. This type of material is not enough to establish meaning at the level that truly justifies understanding. In other words, many social science explanations offer ideas about correlations or even causal relations, but this does not mean that the meaning at the level of the data analyzed, is understood. This leads us to say that there are indeed many explanations that meet the criteria of understanding, for example the explanation of how one becomes a marihuana smoker presented by Becker. However, we may also understand a phenomenon without explaining it, and we may have potential explanations, or better correlations, that are not really understood.
We may speak more generally of quantitative research and its data to clarify what we see as an important distinction. The “raw data” that quantitative research—as an idealtypical activity, refers to is not available for further analysis; the numbers, once created, are not to be questioned (Franzosi 2016 : 138). If the researcher is to do “more” or “change” something, this will be done by conjectures based on theoretical knowledge or based on the researcher’s lifeworld. Both qualitative and quantitative research is based on the lifeworld, and all researchers use prejudices and pre-understanding in the research process. This idea is present in the works of Heidegger ( 2001 ) and Heisenberg (cited in Franzosi 2010 :619). Qualitative research, as we argued, involves the interaction and questioning of concepts (theory), data, and evidence.
Ragin ( 2004 :22) points out that “a good definition of qualitative research should be inclusive and should emphasize its key strengths and features, not what it lacks (for example, the use of sophisticated quantitative techniques).” We define qualitative research as an iterative process in which improved understanding to the scientific community is achieved by making new significant distinctions resulting from getting closer to the phenomenon studied. Qualitative research, as defined here, is consequently a combination of two criteria: (i) how to do things –namely, generating and analyzing empirical material, in an iterative process in which one gets closer by making distinctions, and (ii) the outcome –improved understanding novel to the scholarly community. Is our definition applicable to our own study? In this study we have closely read the empirical material that we generated, and the novel distinction of the notion “qualitative research” is the outcome of an iterative process in which both deduction and induction were involved, in which we identified the categories that we analyzed. We thus claim to meet the first criteria, “how to do things.” The second criteria cannot be judged but in a partial way by us, namely that the “outcome” —in concrete form the definition-improves our understanding to others in the scientific community.
We have defined qualitative research, or qualitative scientific work, in relation to quantitative scientific work. Given this definition, qualitative research is about questioning the pre-given (taken for granted) variables, but it is thus also about making new distinctions of any type of phenomenon, for example, by coining new concepts, including the identification of new variables. This process, as we have discussed, is carried out in relation to empirical material, previous research, and thus in relation to theory. Theory and previous research cannot be escaped or bracketed. According to hermeneutic principles all scientific work is grounded in the lifeworld, and as social scientists we can thus never fully bracket our pre-understanding.
We have proposed that quantitative research, as an idealtype, is concerned with pre-determined variables (Small 2008 ). Variables are epistemically fixed, but can vary in terms of dimensions, such as frequency or number. Age is an example; as a variable it can take on different numbers. In relation to quantitative research, qualitative research does not reduce its material to number and variables. If this is done the process of comes to a halt, the researcher gets more distanced from her data, and it makes it no longer possible to make new distinctions that increase our understanding. We have above discussed the components of our definition in relation to quantitative research. Our conclusion is that in the research that is called quantitative there are frequent and necessary qualitative elements.
Further, comparative empirical research on researchers primarily working with ”quantitative” approaches and those working with ”qualitative” approaches, we propose, would perhaps show that there are many similarities in practices of these two approaches. This is not to deny dissimilarities, or the different epistemic and ontic presuppositions that may be more or less strongly associated with the two different strands (see Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ). Our point is nonetheless that prejudices and preconceptions about researchers are unproductive, and that as other researchers have argued, differences may be exaggerated (e.g., Becker 1996 : 53, 2017 ; Marchel and Owens 2007 :303; Ragin 1994 ), and that a qualitative dimension is present in both kinds of work.
Several things follow from our findings. The most important result is the relation to quantitative research. In our analysis we have separated qualitative research from quantitative research. The point is not to label individual researchers, methods, projects, or works as either “quantitative” or “qualitative.” By analyzing, i.e., taking apart, the notions of quantitative and qualitative, we hope to have shown the elements of qualitative research. Our definition captures the elements, and how they, when combined in practice, generate understanding. As many of the quotations we have used suggest, one conclusion of our study holds that qualitative approaches are not inherently connected with a specific method. Put differently, none of the methods that are frequently labelled “qualitative,” such as interviews or participant observation, are inherently “qualitative.” What matters, given our definition, is whether one works qualitatively or quantitatively in the research process, until the results are produced. Consequently, our analysis also suggests that those researchers working with what in the literature and in jargon is often called “quantitative research” are almost bound to make use of what we have identified as qualitative elements in any research project. Our findings also suggest that many” quantitative” researchers, at least to some extent, are engaged with qualitative work, such as when research questions are developed, variables are constructed and combined, and hypotheses are formulated. Furthermore, a research project may hover between “qualitative” and “quantitative” or start out as “qualitative” and later move into a “quantitative” (a distinct strategy that is not similar to “mixed methods” or just simply combining induction and deduction). More generally speaking, the categories of “qualitative” and “quantitative,” unfortunately, often cover up practices, and it may lead to “camps” of researchers opposing one another. For example, regardless of the researcher is primarily oriented to “quantitative” or “qualitative” research, the role of theory is neglected (cf. Swedberg 2017 ). Our results open up for an interaction not characterized by differences, but by different emphasis, and similarities.
Let us take two examples to briefly indicate how qualitative elements can fruitfully be combined with quantitative. Franzosi ( 2010 ) has discussed the relations between quantitative and qualitative approaches, and more specifically the relation between words and numbers. He analyzes texts and argues that scientific meaning cannot be reduced to numbers. Put differently, the meaning of the numbers is to be understood by what is taken for granted, and what is part of the lifeworld (Schütz 1962 ). Franzosi shows how one can go about using qualitative and quantitative methods and data to address scientific questions analyzing violence in Italy at the time when fascism was rising (1919–1922). Aspers ( 2006 ) studied the meaning of fashion photographers. He uses an empirical phenomenological approach, and establishes meaning at the level of actors. In a second step this meaning, and the different ideal-typical photographers constructed as a result of participant observation and interviews, are tested using quantitative data from a database; in the first phase to verify the different ideal-types, in the second phase to use these types to establish new knowledge about the types. In both of these cases—and more examples can be found—authors move from qualitative data and try to keep the meaning established when using the quantitative data.
A second main result of our study is that a definition, and we provided one, offers a way for research to clarify, and even evaluate, what is done. Hence, our definition can guide researchers and students, informing them on how to think about concrete research problems they face, and to show what it means to get closer in a process in which new distinctions are made. The definition can also be used to evaluate the results, given that it is a standard of evaluation (cf. Hammersley 2007 ), to see whether new distinctions are made and whether this improves our understanding of what is researched, in addition to the evaluation of how the research was conducted. By making what is qualitative research explicit it becomes easier to communicate findings, and it is thereby much harder to fly under the radar with substandard research since there are standards of evaluation which make it easier to separate “good” from “not so good” qualitative research.
To conclude, our analysis, which ends with a definition of qualitative research can thus both address the “internal” issues of what is qualitative research, and the “external” critiques that make it harder to do qualitative research, to which both pressure from quantitative methods and general changes in society contribute.
Acknowledgements
Financial Support for this research is given by the European Research Council, CEV (263699). The authors are grateful to Susann Krieglsteiner for assistance in collecting the data. The paper has benefitted from the many useful comments by the three reviewers and the editor, comments by members of the Uppsala Laboratory of Economic Sociology, as well as Jukka Gronow, Sebastian Kohl, Marcin Serafin, Richard Swedberg, Anders Vassenden and Turid Rødne.
Biographies
is professor of sociology at the Department of Sociology, Uppsala University and Universität St. Gallen. His main focus is economic sociology, and in particular, markets. He has published numerous articles and books, including Orderly Fashion (Princeton University Press 2010), Markets (Polity Press 2011) and Re-Imagining Economic Sociology (edited with N. Dodd, Oxford University Press 2015). His book Ethnographic Methods (in Swedish) has already gone through several editions.
is associate professor of sociology at the Department of Media and Social Sciences, University of Stavanger. His research has been published in journals such as Social Psychology Quarterly, Sociological Theory, Teaching Sociology, and Music and Arts in Action. As an ethnographer he is working on a book on he social world of big-wave surfing.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Patrik Aspers, Email: [email protected] .
Ugo Corte, Email: [email protected] .
- Åkerström M. Curiosity and serendipity in qualitative research. Qualitative Sociology Review. 2013; 9 (2):10–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Alford, Robert R. 1998. The craft of inquiry. Theories, methods, evidence . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Alvesson M, Kärreman D. Qualitative research and theory development . Mystery as method . London: SAGE Publications; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Aspers, Patrik. 2006. Markets in Fashion, A Phenomenological Approach. London Routledge.
- Atkinson P. Qualitative research. Unity and diversity. Forum: Qualitative Social Research. 2005; 6 (3):1–15. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Outsiders. Studies in the sociology of deviance . New York: The Free Press; 1963. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Whose side are we on? Social Problems. 1966; 14 (3):239–247. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Sociological work. Method and substance. New Brunswick: Transaction Books; 1970. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. The epistemology of qualitative research. In: Richard J, Anne C, Shweder RA, editors. Ethnography and human development. Context and meaning in social inquiry. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1996. pp. 53–71. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Tricks of the trade. How to think about your research while you're doing it. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker, Howard S. 2017. Evidence . Chigaco: University of Chicago Press.
- Becker H, Geer B, Hughes E, Strauss A. Boys in White, student culture in medical school. New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers; 1961. [ Google Scholar ]
- Berezin M. How do we know what we mean? Epistemological dilemmas in cultural sociology. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 (2):141–151. [ Google Scholar ]
- Best, Joel. 2004. Defining qualitative research. In Workshop on Scientific Foundations of Qualitative Research , eds . Charles, Ragin, Joanne, Nagel, and Patricia White, 53-54. http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2004/nsf04219/nsf04219.pdf .
- Biernacki R. Humanist interpretation versus coding text samples. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 (2):173–188. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blumer H. Symbolic interactionism: Perspective and method. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1969. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brady H, Collier D, Seawright J. Refocusing the discussion of methodology. In: Henry B, David C, editors. Rethinking social inquiry. Diverse tools, shared standards. Lanham: Rowman and Littlefield; 2004. pp. 3–22. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown AP. Qualitative method and compromise in applied social research. Qualitative Research. 2010; 10 (2):229–248. [ Google Scholar ]
- Charmaz K. Constructing grounded theory. London: Sage; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Corte, Ugo, and Katherine Irwin. 2017. “The Form and Flow of Teaching Ethnographic Knowledge: Hands-on Approaches for Learning Epistemology” Teaching Sociology 45(3): 209-219.
- Creswell JW. Research design. Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method approaches. 3. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidsson D. The myth of the subjective. In: Davidsson D, editor. Subjective, intersubjective, objective. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1988. pp. 39–52. [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin NK. The research act: A theoretical introduction to Ssociological methods. Chicago: Aldine Publishing Company Publishers; 1970. [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin NK, Lincoln YS. Introduction. The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In: Denzin NK, Lincoln YS, editors. Collecting and interpreting qualitative materials. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications; 2003. pp. 1–45. [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin NK, Lincoln YS. Introduction. The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In: Denzin NK, Lincoln YS, editors. The Sage handbook of qualitative research. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications; 2005. pp. 1–32. [ Google Scholar ]
- Emerson RM, editor. Contemporary field research. A collection of readings. Prospect Heights: Waveland Press; 1988. [ Google Scholar ]
- Emerson RM, Fretz RI, Shaw LL. Writing ethnographic fieldnotes. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Esterberg KG. Qualitative methods in social research. Boston: McGraw-Hill; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fine, Gary Alan. 1995. Review of “handbook of qualitative research.” Contemporary Sociology 24 (3): 416–418.
- Fine, Gary Alan. 2003. “ Toward a Peopled Ethnography: Developing Theory from Group Life.” Ethnography . 4(1):41-60.
- Fine GA, Hancock BH. The new ethnographer at work. Qualitative Research. 2017; 17 (2):260–268. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fine GA, Hallett T. Stranger and stranger: Creating theory through ethnographic distance and authority. Journal of Organizational Ethnography. 2014; 3 (2):188–203. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flick U. Qualitative research. State of the art. Social Science Information. 2002; 41 (1):5–24. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flick U. Designing qualitative research. London: SAGE Publications; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Frankfort-Nachmias C, Nachmias D. Research methods in the social sciences. 5. London: Edward Arnold; 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Franzosi R. Sociology, narrative, and the quality versus quantity debate (Goethe versus Newton): Can computer-assisted story grammars help us understand the rise of Italian fascism (1919- 1922)? Theory and Society. 2010; 39 (6):593–629. [ Google Scholar ]
- Franzosi R. From method and measurement to narrative and number. International journal of social research methodology. 2016; 19 (1):137–141. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gadamer, Hans-Georg. 1990. Wahrheit und Methode, Grundzüge einer philosophischen Hermeneutik . Band 1, Hermeneutik. Tübingen: J.C.B. Mohr.
- Gans H. Participant Observation in an Age of “Ethnography” Journal of Contemporary Ethnography. 1999; 28 (5):540–548. [ Google Scholar ]
- Geertz C. The interpretation of cultures. New York: Basic Books; 1973. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilbert N. Researching social life. 3. London: SAGE Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaeser A. Hermeneutic institutionalism: Towards a new synthesis. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 :207–241. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaser, Barney G., and Anselm L. Strauss. [1967] 2010. The discovery of grounded theory. Strategies for qualitative research. Hawthorne: Aldine.
- Goertz G, Mahoney J. A tale of two cultures: Qualitative and quantitative research in the social sciences. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goffman E. On fieldwork. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography. 1989; 18 (2):123–132. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goodwin J, Horowitz R. Introduction. The methodological strengths and dilemmas of qualitative sociology. Qualitative Sociology. 2002; 25 (1):33–47. [ Google Scholar ]
- Habermas, Jürgen. [1981] 1987. The theory of communicative action . Oxford: Polity Press.
- Hammersley M. The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research & Method in Education. 2007; 30 (3):287–305. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammersley, Martyn. 2013. What is qualitative research? Bloomsbury Publishing.
- Hammersley M. What is ethnography? Can it survive should it? Ethnography and Education. 2018; 13 (1):1–17. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammersley M, Atkinson P. Ethnography . Principles in practice . London: Tavistock Publications; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heidegger M. Sein und Zeit. Tübingen: Max Niemeyer Verlag; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heidegger, Martin. 1988. 1923. Ontologie. Hermeneutik der Faktizität, Gesamtausgabe II. Abteilung: Vorlesungen 1919-1944, Band 63, Frankfurt am Main: Vittorio Klostermann.
- Hempel CG. Philosophy of the natural sciences. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall; 1966. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hood JC. Teaching against the text. The case of qualitative methods. Teaching Sociology. 2006; 34 (3):207–223. [ Google Scholar ]
- James W. Pragmatism. New York: Meredian Books; 1907. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jovanović G. Toward a social history of qualitative research. History of the Human Sciences. 2011; 24 (2):1–27. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kalof L, Dan A, Dietz T. Essentials of social research. London: Open University Press; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Katz J. Situational evidence: Strategies for causal reasoning from observational field notes. Sociological Methods & Research. 2015; 44 (1):108–144. [ Google Scholar ]
- King G, Keohane RO, Sidney S, Verba S. Scientific inference in qualitative research. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1994. Designing social inquiry. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamont M. Evaluating qualitative research: Some empirical findings and an agenda. In: Lamont M, White P, editors. Report from workshop on interdisciplinary standards for systematic qualitative research. Washington, DC: National Science Foundation; 2004. pp. 91–95. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamont M, Swidler A. Methodological pluralism and the possibilities and limits of interviewing. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 (2):153–171. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lazarsfeld P, Barton A. Some functions of qualitative analysis in social research. In: Kendall P, editor. The varied sociology of Paul Lazarsfeld. New York: Columbia University Press; 1982. pp. 239–285. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lichterman, Paul, and Isaac Reed I (2014), Theory and Contrastive Explanation in Ethnography. Sociological methods and research. Prepublished 27 October 2014; 10.1177/0049124114554458.
- Lofland J, Lofland L. Analyzing social settings. A guide to qualitative observation and analysis. 3. Belmont: Wadsworth; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lofland J, Snow DA, Anderson L, Lofland LH. Analyzing social settings. A guide to qualitative observation and analysis. 4. Belmont: Wadsworth/Thomson Learning; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Long AF, Godfrey M. An evaluation tool to assess the quality of qualitative research studies. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2004; 7 (2):181–196. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lundberg G. Social research: A study in methods of gathering data. New York: Longmans, Green and Co.; 1951. [ Google Scholar ]
- Malinowski B. Argonauts of the Western Pacific: An account of native Enterprise and adventure in the archipelagoes of Melanesian New Guinea. London: Routledge; 1922. [ Google Scholar ]
- Manicas P. A realist philosophy of science: Explanation and understanding. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Marchel C, Owens S. Qualitative research in psychology. Could William James get a job? History of Psychology. 2007; 10 (4):301–324. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McIntyre LJ. Need to know. Social science research methods. Boston: McGraw-Hill; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Merton RK, Barber E. The travels and adventures of serendipity . A Study in Sociological Semantics and the Sociology of Science. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mannay D, Morgan M. Doing ethnography or applying a qualitative technique? Reflections from the ‘waiting field‘ Qualitative Research. 2015; 15 (2):166–182. [ Google Scholar ]
- Neuman LW. Basics of social research. Qualitative and quantitative approaches. 2. Boston: Pearson Education; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ragin CC. Constructing social research. The unity and diversity of method. Thousand Oaks: Pine Forge Press; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ragin, Charles C. 2004. Introduction to session 1: Defining qualitative research. In Workshop on Scientific Foundations of Qualitative Research , 22, ed. Charles C. Ragin, Joane Nagel, Patricia White. http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2004/nsf04219/nsf04219.pdf
- Rawls, Anne. 2018. The Wartime narrative in US sociology, 1940–7: Stigmatizing qualitative sociology in the name of ‘science,’ European Journal of Social Theory (Online first).
- Schütz A. Collected papers I: The problem of social reality. The Hague: Nijhoff; 1962. [ Google Scholar ]
- Seiffert H. Einführung in die Hermeneutik. Tübingen: Franke; 1992. [ Google Scholar ]
- Silverman D. Doing qualitative research. A practical handbook. 2. London: SAGE Publications; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Silverman D. A very short, fairly interesting and reasonably cheap book about qualitative research. London: SAGE Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Silverman D. What counts as qualitative research? Some cautionary comments. Qualitative Sociology Review. 2013; 9 (2):48–55. [ Google Scholar ]
- Small ML. “How many cases do I need?” on science and the logic of case selection in field-based research. Ethnography. 2009; 10 (1):5–38. [ Google Scholar ]
- Small, Mario L 2008. Lost in translation: How not to make qualitative research more scientific. In Workshop on interdisciplinary standards for systematic qualitative research, ed in Michelle Lamont, and Patricia White, 165–171. Washington, DC: National Science Foundation.
- Snow DA, Anderson L. Down on their luck: A study of homeless street people. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Snow DA, Morrill C. New ethnographies: Review symposium: A revolutionary handbook or a handbook for revolution? Journal of Contemporary Ethnography. 1995; 24 (3):341–349. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss AL. Qualitative analysis for social scientists. 14. Chicago: Cambridge University Press; 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss AL, Corbin JM. Basics of qualitative research. Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. 2. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Swedberg, Richard. 2017. Theorizing in sociological research: A new perspective, a new departure? Annual Review of Sociology 43: 189–206.
- Swedberg R. The new 'Battle of Methods'. Challenge January–February. 1990; 3 (1):33–38. [ Google Scholar ]
- Timmermans S, Tavory I. Theory construction in qualitative research: From grounded theory to abductive analysis. Sociological Theory. 2012; 30 (3):167–186. [ Google Scholar ]
- Trier-Bieniek A. Framing the telephone interview as a participant-centred tool for qualitative research. A methodological discussion. Qualitative Research. 2012; 12 (6):630–644. [ Google Scholar ]
- Valsiner J. Data as representations. Contextualizing qualitative and quantitative research strategies. Social Science Information. 2000; 39 (1):99–113. [ Google Scholar ]
- Weber, Max. 1904. 1949. Objectivity’ in social Science and social policy. Ed. Edward A. Shils and Henry A. Finch, 49–112. New York: The Free Press.
- Open access
- Published: 17 May 2024
A qualitative exploration of health care workers’ approaches to relational harm reduction in HIV primary care settings
- Emma Sophia Kay 1 ,
- Stephanie L. Creasy 2 ,
- Jessica Townsend 1 &
- Mary Hawk 2
Harm Reduction Journal volume 21 , Article number: 97 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Structural harm reduction is an approach to care for people who use drugs (PWUD) that incorporates services and resources (e.g., naloxone, sterile syringes). As conceptualized in our previous research, harm reduction is also “relational,” encompassing a patient-provider relationship that is non-judgmental and respectful of patients’ autonomy. Little is known about health care workers’ (HCW) knowledge or attitudes towards harm reduction beyond structural strategies, whose availability and legality vary across geographical settings. To operationalize how relational harm reduction is both characterized and employed in HIV care settings, where nearly half of patients have a diagnosed substance use disorder, we qualitatively explored HCWs’ knowledge of and use of harm reduction via individual in-depth interviews.
Our study sample included three HIV clinics, one in Birmingham, Alabama (AL) and two in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania (PA). We conducted individual interviews with n = 23 health care workers via Zoom, using a semi-structured interview guide to probe for questions around health care workers’ attitudes towards and experiences with providing care to PWH who use drugs and their knowledge of and attitudes towards relational and structural harm reduction. Data was analyzed in Dedoose using thematic analysis.
Qualitative analyses revealed two primary themes, Continuum of Relational Harm Reduction in Practice and Limited Harm Reduction Training . Nearly all HCWs ( n = 19, 83%) described a patient interaction or expressed a sentiment that corresponded with the principles of relational harm reduction. Yet, over half of participants ( n = 14, 61%) used language to describe PWH who use drugs that was stigmatizing or described an interaction that was antithetical to the principles of relational harm reduction. Five HCWs, all from Birmingham, were unaware of the term ‘harm reduction.’ Few HCWs had any harm reduction training, with most learning about harm reduction from webinars/conferences or on the job.
Our findings suggest that relational harm reduction in HIV care settings is practiced along a continuum, and that a range of behaviors exist even within individual HCWs (e.g., used stigmatizing terms such as “addict” but also described patient interactions that reflected patients’ autonomy). Given that harm reduction is typically described as a structural approach, a broader definition of harm reduction that is not dependent on policy-dependent resources is needed.
Introduction
Harm reduction is an approach to care developed by people who use drugs (PWUD) for PWUD that incorporates not only services and resources (e.g., naloxone, sterile syringes, fentanyl test strips—structural harm reduction), but also patient-provider relationships that are non-judgmental and respectful of patients’ autonomy, defined as relational harm reduction [ 1 ]. Harm reduction is aimed at minimizing harm associated with drug use, rather than requiring abstinence. In a previous study, we outlined a set of six harm reduction principles in medical settings, which can be used to guide health care workers’ (HCW) interactions with patients [ 1 ] (See Table 1 for a list of the relational harm reduction principles and their definitions.) The purpose of this work was to operationalize ways that HCW can apply long-standing harm reduction principles in the context of their work. As these principles are the foundation of health care workers’ communication with PWUD, we define the operationalization of these principles as “relational” harm reduction, while we refer to drug overdose prevention strategies and other tangible services as “structural” harm reduction. While the two forms of harm reduction should ideally be paired in practice, we delineate them here to underscore that the ways in which care is delivered is as important as the specific services provided. Moreover, there is variability of structural harm reduction services across different political contexts (e.g., seven states, including Alabama, one of our study locations, have failed to legalize sterile syringe programs to date [ 2 ]), while relational harm reduction can be practiced in any political context.
A recent editorial by the director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) urges HCWs to provide compassionate, non-stigmatizing care to PWUD, noting the alternative may exacerbate drug use [ 3 ]. Continued conflation of drug use as “abuse,” which implies that any drug use is wrong, pervades social messaging [ 4 ]. Indeed, research shows that HCWs are not immune from this social messaging, with some providers regarding PWUD as “criminal” [ 5 ]. To avoid experiences of stigma and discrimination when receiving health care services, PWUD may seek to avoid stigma by concealing their drug use from HCWs, minimizing symptoms of pain, and even delaying care altogether [ 6 , 7 ]. PWUD may even avoid calling emergency medical services for fear of arrest [ 8 ]. These negative experiences in healthcare settings decrease trust in the medical system, raising risk of adverse health outcomes such as death from injection-related infections [ 7 ], relying on non-prescription medication to alleviate pain [ 9 ], and leaving the hospital against medical advice [ 10 ]. However, patients who feel respected by and trust their HCWs are more likely to experience positive health outcomes [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ]. For PWUD, greater trust in their provider is associated with positive expectations for their interactions with their providers and is mediated by perceived provider support for harm reduction [ 11 ]. PWUD also cite the harm reduction principles of humanism, pragmatism, autonomy, individualism, incrementalism, and autonomy without termination [ 1 ], as well as ongoing support, reliability, and provider expertise in treating substance use disorder [ 12 ], as cornerstones of strong patient-provider relationships.
To better serve the needs of PWUD, scholars and providers have recommended integrating harm reduction into primary care and other settings that do not explicitly serve PWUD and have recognized the importance of the patient-provider relationship as a form of harm reduction [ 13 ]. Indeed, harm reduction has been recognized as one of the key components of the US Department of Health and Human Services’ Overdose Prevention Strategy [ 14 ], and the Health and Medicine panel of the National Academy of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine has recommended incorporating harm reduction strategies into infectious disease and opioid use disorder care [ 15 ]. Since the elimination of the X-Waiver in 2023, any provider can prescribe buprenorphine without having to register with the Drug Enforcement Administration [ 16 ], a requirement that was previously noted as a significant barrier to prescribing medication for opioid use disorder (MOUD) [ 17 ]. Yet, despite the importance of integrating harm reduction principles into health care settings, little is known about what this looks like in practice. Extant literature is focused on HCWs’ knowledge of structural harm reduction services. For example, a previous scoping review focusing on harm reduction for people who use opioids identified 25 studies that examined physicians’ knowledge and perceptions of harm reduction for people who use opioids [ 18 ]. Knowledge gaps include those related to prescribing medication for opioid use disorder and using naloxone, and uncertainly about their legality. Physicians’ perceptions of harm reduction highlighted the prevalence of stigma and concerns about medication diversion [ 18 ]. Finally, the scoping review revealed system and institutional barriers to the provision of high-quality care for PWUD, such as those related to insurance coverage, reimbursement, and organizational policies. Similarly, a survey of Veterans Affairs providers identified low levels of knowledge regarding use of naloxone [ 19 ].
While these studies illustrate medical providers’ knowledge of structural harm reduction strategies such as MOUD and naloxone, little is known about how providers, including those working in social and administrative services, operationalize the principles of harm reduction into practice, i.e., relational harm reduction. Thus, in the current paper, we qualitatively explore HCW’s knowledge of and use of harm reduction via individual in-depth interviews, to operationalize how relational harm reduction is both characterized and employed in healthcare settings. As the current work is part of our larger study aimed at developing a harm reduction intervention for people with HIV (PWH) who use drugs, we focused on HCWs practicing in HIV care settings (citation redacted for peer review).
Sample and recruitment
Our study sample included three HIV clinics, one in Birmingham, Alabama (AL) and two in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania (PA). We leveraged internal electronic messaging used by each site to disseminate information about the HCW interviews. IRB-approved recruitment messaging and a confidential link to the REDCap survey were included in the email messages, which were sent by site-level champions. HCWs were eligible if they (1) worked at one of these sites for at least one year and (2) provided “direct patient engagement” to PWH or PWUD at high risk for HIV acquisition. Eligible roles included front desk, clinical research coordinator, service coordinator, pharmacy, social worker, counselor/therapist, nurse, dietician, medical assistant, medical technician, advanced practice provider, physician assistant, and clinician. We included a wide range of HCWs rather than just licensed medical providers (e.g., clinician, nurse) to encompass the range of positions found at an HIV clinic, as modern HIV care is akin to a medical home model with coordinated medical and social services [ 20 , 21 ]. We defined “drugs” as inclusive of illicit drugs and prescription drugs used in ways other than they were prescribed; we did not include alcohol or marijuana use, as these substances have been shown to carry less stigma than prescription drug misuse or use of drugs that are nationally criminalized [ 22 , 23 ].
Individual interviews with n = 23 HCWs were conducted over a four-month period between November 2022 and March 2023. Interviews lasted between 30 and 60 min (average = 45 min). To maximize availability of the five study team members who led the qualitative interviews across Birmingham and Pittsburgh, interviews were conducted over HIPAA-compliant Zoom. Each of these study team members, including the PIs, three Co-Is, and a study coordinator, provided their availability on Microsoft Bookings. Interested HCWs could then sign up for an available time slot with a particular interviewer, thereby streamlining the recruitment process.
Data collection
We used a semi-structured interview guide to explore health care workers’ attitudes towards and experiences with providing care to PWH who use drugs and their knowledge of and attitudes towards relational and structural harm reduction. We collected demographic information around participants’ racial and ethnic identity and gender identity, job title, and years of practice, including years specifically devoted to working with PWH, which we used to characterize the participant population in aggregate. Interviews were audio-recorded with participant permission and professionally transcribed verbatim. All identifying information was removed from study transcripts; each transcript was labeled with a numerical subject identification number and the information linking subject identification numbers with names was kept separate from the research records. All study activities were approved by the [name redacted] IRB.
Deidentified transcript data were uploaded into Dedoose [ 24 ] for analysis. We used a codebook thematic analysis to code the data, an approach to thematic analysis that fits within the positivist paradigm [ 25 , 26 ]. One of the PIs (first author) read through each of the transcripts and familiarized themselves with the data. They reviewed field notes composed by study team members who conducted the interviews, which provided valuable critical reflection and interviewer feedback to inform analysis [ 27 ]. Then, this PI, in addition to four other members of the study team with expertise in qualitative analysis, independently coded three transcripts to identify broad themes. This team of five then met to discuss initial codes and resolve any discrepancies.
This list of initial codes was used to create a coding framework. We analyzed the data using both deductive coding from our interview guide (see Supplemental File) as well as inductive coding, achieving code saturation, which is typically attained from between 9 and 17 interviews with homogenous populations, well under our sample of n = 23 [ 28 ]. The first author and three other team members coded the remaining transcripts using this framework, meeting every two weeks and iteratively adding sub-codes and modifying the codebook using processes of adjudication. Five transcripts were double-coded (23%) and compared for consistency, following scholars’ recommendation to double-code between 10 and 25% of transcripts [ 29 ]. The final set of codes was combined into themes with the input of the full study team.
Twelve interviews were completed with health care workers in Birmingham, and 11 were completed with health care workers in Pittsburgh. Table 2 provides an overview of self-reported HCW characteristics.
HCWs had a wide variety of ways that they both understood and practiced relational harm reduction in the HIV care setting with PWUD, with some not utilizing these harm reduction principles at all. We characterized this range of behaviors and attitudes, our primary analytical theme, The Continuum of Relational Harm Reduction in Practice. This primary theme had three subthemes: Use of Relational Harm Reduction characterized behaviors that corresponded to one or more of the six harm reduction principles. Antithetical to Relational Harm Reduction was characterized by HCWs who described an interaction that was at odds with the six principles of relational harm reduction. HCWs with No Knowledge of Harm Reduction were not familiar with harm reduction or its principles and had not integrated these principles into practice. An interrelated primary theme on Limited Harm Reduction Training was identified, in which HCWs discussed how they learned about harm reduction and source(s) of knowledge and highlighted the need for more training in this area. This theme helped to contextualize the primary theme by illustrating the extent to which the HCWs in our sample had been exposed to harm reduction education.
Illustrative quotes from both AL and PA are included for each subtheme to provide thick description and establish credibility of our findings [ 30 ]. Theme and subtheme prevalence is also provided; however, the importance of each theme or subtheme is not directly related to its prevalence. For each quote, we include both the location and HCW number; thus, for example, PA.1 would be the first HCW we interviewed who works at a Pittsburgh study site. We also provide participants’ specific job titles for each quote. Since there are a limited number of HCWs within each job category at our study sites, we do not include descriptives such as gender or race to protect participants’ confidentiality. [48]
Theme 1: continuum of relational harm reduction in practice
Subtheme 1. use of relational harm reduction.
Nearly all HCWs ( n = 19, 83%) described a patient interaction or expressed a sentiment that corresponded with one or more principles of relational harm reduction. These examples are further characterized and described below. While some of their harm reduction principles have natural overlap with each other (e.g., autonomy and individualism), we have identified principles that best reflect each illustrative quote.
Meeting patients where they are
Some HCWs described how they allowed patients to guide and lead their interactions rather than imposing a set agenda, as in the case of the following HCW who exemplified multiple principles of harm reduction (individualism, incrementalism, and pragmatism) in their commitment to assisting patients in their desired care plans:
I believe we do harm reduction every day…not showing or casting any kind of judgment on a patient, meeting them where they are and just listening, just trying to guide them through where you can and where they allow you to. (PA.7; Pharmacist)
This sentiment was expressed across HCW types in ways that reflected their respective job responsibilities. HCWs working in social services described how they helped patients access wraparound social services like housing or how they used motivational interviewing to “meet patients where they’re at.” This quote highlights the principles of autonomy and individualism.
I really just try to meet the patient where they’re at and with them making a decision on where they’re deciding to go next… And for me, I think, it’s always really just being here as a listening ear to the patient and making sure that they understand that I heard what they said and really try to figure out what can I do to help their experience be a little bit better and– even if it’s just for a moment. (AL 11; Therapist)
HCWs working in medical services focused on aspects of clinical care, as in the following quote that exemplifies both relational harm reduction (individualism and pragmatism) and structural harm reduction (MOUD induction):
I’m pretty good at kind of coaching patients through how to do it at home and, you know, they have good contact information with us should anything happen, should they need to talk to us. I kinda go over the different induction options with them, whether they wanna do traditional high dose or, um, low dose induction, and kind of just figure out what works for the patient. (PA.1; Clinician)
Knowing patients as humans
Most HCWs emphasized the importance of humanizing their patients (i.e., humanism) and getting to know them as people. This involved asking patients about their lives outside of their health condition(s) and creating a space where patients felt comfortable sharing personal details. An AL HCW discussed how they get to know their patients and their personal lives:
I feel like I know them on a more personal level. I know they’re aunties and their uncles and their dogs and their cats and, you know, everything about them because we talk all the time… I love that part [the personal connection]. (AL.3; Medical Social Worker)
A PA HCW shared how they start clinical visits by catching up:
You know, my first thing was, you know, “How have you been doing…We’ll get to your vitals and, you know, going over your medications, but how are you? Um, you know, how was your week?” You know, and it’s just, like, starting off like, “…I wanna make sure you’re okay.” (PA.2; Physician Assistant)
One HCW described this humanizing approach as “more important than what ailments our patients have.” HCWs also enjoyed having close relationships with patients. A PA HCW described their relationships with patient as a “privilege”: “When you see someone periodically every four to six months for years and you’re walking a journey with them, I consider a privilege to do. It’s very rewarding, and they– I think it’s mutual” (PA.10; Clinician). An AL HCW described their patients as more than “a number on a page”:
I really enjoy that patient interaction, is really getting to know people, versus see a number on a page. I really enjoy that aspect of even just finding a little snippet out about somebody. And since some of the people I see have been here in research for many years…when I see them sitting, they’ll be like, “Oh, hey, so-and-so” …some of my participants are still in other studies, so when they come in for a visit, they now know my face. We will speak. And they’re not just another person in the clinic. (AL.8; Clinical Research Coordinator)
Open communication
HCWs underscored the importance of creating an environment of mutual trust with patients where they felt comfortable disclosing drug use. This trust and open communication are hallmarks of the principle of pragmatism, which acknowledges that some patients will use drugs and the role of the HCW is to assist patients rather than offer judgments on their behaviors. This open communication also allows HCWs to give patients more tailored care that acknowledges the various circumstances in patients’ lives that can affect their health:
Um, you know, it should always be a no-judgment zone. You know, don’t pass judgments. You know, yeah, we want to know what’s going on with you, and it’s important for you to be honest because it only will allow us to, you know, individualize your care based off of what you’re dealing with. (PA.2; Physician Assistant)
HCWs also recognized the multiple and complex challenges that some patients faced and acted like “cheerleaders” whenever patients experienced setbacks, which relates to the principle of incrementalism:
Interviewer : What if they don’t make any progress at all or go backwards? HCW : So I have some patients that are like that, and they’re like, “I almost didn’t come into my visit today because I was so upset that I have made no progress.” And I was– and then I just thank them for being honest, and that, you know, we can try again. …and then I talk about like, “Why did you not make progress? Like, was there a reason?” And they’re, you know, their mom died, and they got evicted. You know, and it’s like, “Okay. You had other things going on is reasonable that you were stressed out and that wasn’t the first thing on your list.” (AL.3; Medical Social Worker)
Always having the door open
HCWs discussed the importance of maintaining continuity of care with patients and not terminating anyone from care for continued drug use, which aligns with the principle of accountability without termination. An AL HCW shared how she was committed to “[getting] through this together” with patients:
One thing that I do like about our [Clinic] is they will, like, never terminate anyone. So a person– you know, like, they have all these other drugs in their subsystem, but they’re still able to come back. … I’ve had so many patients who’ve gone through treatment and relapsed again. I’m like, “It’s okay. You know, we’ll get through it together. You know, we can always try again. Like, you’re still here, and that’s the point. (AL.5; Clinician)
HCWs emphasized that their goal was to help patients, rather than “punish [them] for normal human behavior.” The only instances in which patients were terminated from care involved threats of violence or extreme verbal abuse:
Interviewer : Is there ever a point that you get to where you have to fire a patient? HCW : If they threaten physical abuse in the clinic, or, you know, “I’m gonna kill.” You know, they’re really awful. Make racist comments to the front staff or, or just really do something totally egregious. If it’s moderately egregious, they get a warning letter, if it’s something awful, then they get a letter like, “You’re dismissed. Here are the other options for your care.” (PA.10; Clinician)
Subtheme 2. Antithetical to relational harm reduction
Despite most participants integrating some aspect of relational harm reduction in their practice, over half ( n = 14, 61%) also used language to describe PWH who use drugs that was stigmatizing or described an interaction that was antithetical to the six principles of relational harm reduction enumerated in Table 1 —humanism, pragmatism, individualism, autonomy, incrementalism, and accountability without termination. These participants included HCWs from both AL and PA and encompassed a range of HCW types.
Substance use stigma
Substance use stigma was evident among nearly half of the HCWs ( n = 10; 43%), although this was found to varying degrees. Some used stigmatizing terms like “addict,” but otherwise did not describe patients in a way that stigmatized their drug use. Others characterized PWUD in a broadly negative sense that went beyond terminology, such as in the following quote from a PA HCW: … “Your mother’s an addict too and you know, half your family are addicts, so it’s, it’s just–I think that’s probably the biggest thing is the social chaos. It, uh, kind of– kind of flies around people who have problems with addiction.” (PA.2, Clinician). For other HCWs, stigma was evident in the way they framed abstinence as “bettering yourself,” becoming a “productive member of society,” etc., without consideration of around whether abstinence aligned with the patient’s own goals or what these goals looked like in general. As an example, one HCW described their work with PWUD and a need for these to patients to “change”:
A lot of them, from whom I’ve spoken with, they don’t like change. They just kinda want everything to remain the same. And unfortunately, in life, you know, you’re gonna have change… unfortunately, sometimes, they fall by the wayside. And they need that force to kind of pick them back up and to help them guide them along a little bit to come back on the narrow path. (PA.6; Medical Assistant and Health Coach)
Other HCWs made negative generalizations about PWUD’s ability to take their HIV medication as directed, as well as their health in general:
The substance use interferes with their ability to take their medication as directed, and it also interferes with their ability to eat in a way that’s generally healthy…it seems to be that people with active substance use will have higher viral loads and lower CD4 counts which is indicative of not taking the medication every day. (AL.10, Registered Dietician)
Similarly, a nurse from AL described PWH who use drugs as unable to stay adherent to HIV medication:
So they will prioritize their next fix over trying to stay as healthy as possible or not transmitting HIV to someone else. And they’ll actually trade sex for that next fix, and they’re not biologically suppressed, so.” (AL.1, Nurse)
In these examples, substance use stigma is evident in the ways that HCWs describe PWUD and minimize their individualism and autonomy by making sweeping (and negative) generalizations.
Characterizing abstinence as the end goal for all PWUD
A key tenet of harm reduction is an understanding that patients’ goals might not reflect that of HCWs’, and that abstinence may not be the goal for all PWUD. However, some HCWs ( n = 7; 30%), primarily in AL, described harm reduction as a kind of stepping-stone on the way to abstinence, implying that abstinence is the only acceptable outcome for patients:
I mean, harm reduction is a part of soberness. I feel like it’s the first step to getting people to a point where they’re willing to contemplate changing, and making them more aware of what they’re actually doing…because in order to practice harm reduction, you have to be aware that you need to. And if you’re aware that you need to, then you’re aware of what you’re doing, and you’re aware that it could cause problems. And if you get to that point, then you might be willing to talk about further initiatives for change. (AL.3; Medical Social Worker)
This emphasis on abstinence was seen in the way some HCWs couched patients as “taking advantage” of harm reduction, despite it being a medical resource:
The only time I have a problem with [harm reduction] is when I think people are, like, really taking advantage of it, that they’re just manipulating the system because they know we’re harm reduction. I don’t see that in the majority of our patients, but, you know, I definitely have seen it a few times, and it makes me, like, upset because I’m like, “We’re doing everything we can do for you, and you’re still, like, either not listening or not, like, doing what you, you need to be doing.” (PA.8; Nurse)
Similarly, several AL HCWs felt there should be a limit to harm reduction. One HCW was uncertain about the role of Suboxone and whether it should be taken indefinitely:
I do believe that the end goal [of harm reduction] could at least could be abstinence because I feel like, you’re addicted to opioids, and you want to get off that to kind of switch Suboxone, and to me, that’s like, “Okay, you’re taking the steps towards, um, you know, being abstinent and–” but it like kind of stops there. It’s like, you just take Suboxone for the rest of your life…I don’t know. And I feel like the [clinic] doesn’t really stress the importance of abstinence. They are really just strictly harm reduction, which is fine, but I think there also needs to be like a second, um, part of it of abstinence. (AL.12; Social Worker)
Another AL HCW shared this sentiment, feeling like there should be a limit to harm reduction: “There’s a little bit of a fine line with harm reduction. And I think some of our patients may feel like we need to just give them whatever they want.” (AL.1, Nurse).
Subtheme 3. No knowledge of harm reduction
Though reflecting a minority of participants, several HCWs ( n = 5, 22%; all from Birmingham, AL) were unfamiliar with the term “harm reduction.” However, after being given a standardized definition from the interviewer, some HCWs were able to relate it back to their work. For example, a dietician shared how they could use harm reduction in their practice:
I kind of use harm reduction in nutrition because I hope to help people balance, right? So people who don’t want to give up sodas, for example, maybe we can think of something else they could do to, to, you know, reduce that harm, like, walking more, whatever. (AL.10; Registered Dietician)
Similarly, an administrative HCW working with dental patients identified how harm reduction could relate to dental care for PWUD, noting that patients could decrease drug use to protect their dental health: “It’s not like, you know, like, “Oh, you gotta stop [using drugs] tomorrow,” no. But, like, you know, “Step by step, you know, start, like, you know, thinking about, you know, your, your, your smile.” (AL.6, Medical Technician).
Theme 2: limited harm reduction training
A minority of HCWs in our study had been exposed to harm reduction education ( n = 7; 30%). None of the HCWs had received any formal training in harm reduction while in school, while just one clinician from AL had received training through a fellowship. Most HCWs had little experience working with PWUD prior to their current roles and were not familiar with harm reduction outside of structural services, despite most HCWs describing interactions with patients that aligned with one or more principles of relational harm reduction. Overall, HCWs in AL had less exposure to harm reduction than HCWs in PA. In fact, only three HCWs (two clinicians, one nurse) in AL had ever received any harm reduction education. This education came from a fellowship, webinars, conferences, and even social media. As AL.5 noted, X (formerly known as Twitter) was their primary source of information post-fellowship:
Yeah, a lot of it has been me, um, just reading on my own and following– I mean, frankly, a lot of it I get through Twitter. A lot of the people I follow on Twitter are harm reductionists, addiction medicine docs, infectious disease docs who do addiction medicine work. That’s where I’ve learned a lot about clinical practice policy
AL HCWs also discussed the importance of exposing more medical students to harm reduction to “destigmatize” working with PWUD:
And you’re right, it’s not really trained. At least I wasn’t trained, in the way that I practice now, when I was in residency or fellowship. There was no substance use clinic that I could shadow at or kind of rotate through when I was in training. And I wish there was. And we certainly have the fellows come and experience [Clinic] now when we have residents and PA students. We try to get as many learners as possible for this reason, that we want to open their eyes…to this whole kind of population in need that is, and it’s really satisfying work. (AL.5; Clinician)
HCWs in PA (n = 5) described receiving structural harm reduction education at multiple levels of influence, including the healthcare network (healthcare network-wide trainings), organization (learning on-the-job), and patient levels (learning about harm reduction from the patients themselves). These HCWs came from a variety of backgrounds, including a counselor, nurse, benefit services coordinator, clinical research coordinator, and clinician. A clinician described how their work with patients made them a better harm reductionist and demonstrated use of both structural and relational harm reduction in their practice:
Just constantly be getting feedback from the people you’re helping and what they think about something as simple as, like, really, “I hate this brand of syringes. Like, they keep breaking. They don’t [plunge], and, like, that kinda feedback. Really trying to make it comfortable for everybody and just learn as you go. (PA.9; Clinician)
This same clinician further discussed that they, like their colleagues, had “picked [harm reduction] up along the way:
…Like a lot of people in addiction medicine, kind of picked it up experientially, just like a lot of people back in the day with HIV when it wasn’t part of any kind of training. It was just, you know, something people did… So I just kind of picked it up along the way. (PA.9; clinician)
One HCW characterized harm reduction as being innate rather than something that needed to be taught:
I guess [harm reduction]’s not something that can be taught…it’s all about, you know, caring about the next person, no matter what they’re dealing with, wanting to see everybody succeed, even, like, professionally. (PA.2; Physician Assistant)
These qualitative findings reveal the extent to which relational harm reduction exists as a continuum in HIV care settings. Harm reduction can even occur along a continuum for a single HCW, as evidenced by individual HCWs in our study who used stigmatizing terms such as “addict” or “drug abuse,” for example, but who also described patient interactions that reflected principles of relational harm reduction. These contradictions highlight the complexity of providing harm reduction care and the fact that no HCW is “perfect.” Interestingly, we did not identify any place- or HCW role-based trends in HCWs’ use of relational harm reduction and integration of the six principles in practice, suggesting that this continuum may exist despite variation in legality of harm reduction services (e.g., syringe services not legal in AL but are legal in Pittsburgh, PA).
Our study also identified the need for more relational harm reduction training. Few HCWs had received any formal education in either relational or structural harm reduction. AL HCWs were primarily self-taught and discussed the paucity of training, which is likely a result of having fewer resources for PWUD, including a lack of legalized sterile syringe programs (SSPs) [ 2 ]. However, even HCWs in Pittsburgh, where SSPs operate legally [ 31 ], primarily learned on-the-job rather than via a formal training program. Interestingly, while PA HCWs spoke about learning of the ethos of harm reduction from their clients, AL HCWs did not identify clients as a source of harm reduction knowledge. Another difference between the two groups of HCWs was that only PA HCWs discussed harm reduction as an innate method of caring for PWUD. While it is difficult to speculate on the reasons for these setting-based differences that are not a direct reflection of policy context, it may be that policy-level differences had a downstream effect, such that AL HCWs felt less empowered or confident as harm reductionists given more limited resources. However, some HCWs who stated that they were not familiar with or had not been trained in harm reduction were able to provide examples of relational harm reduction in practice, suggesting that some HCWs may be practicing harm reduction without recognizing it as such. Given that harm reduction is typically described as a structural approach, a broader definition of harm reduction that is not dependent on policy-dependent resources is needed.
HCWs emphasized the importance of getting to know their patients as human beings beyond their health diagnoses (humanism). This led to enhanced patient comfort and a sense of fulfillment for HCWs. A personalized relationship has been identified as one of the strongest independent predictors of adherence to antiretroviral therapy for PWH [ 32 ]. The importance of the patient-provider relationship and the significance of providers earning patients’ trust in harm reduction and substance use treatment settings has also been recognized in extant literature [ 33 , 34 , 35 ]. Yet, less is known about the extent to which humanism impacts substance use-related health outcomes. Additional research is needed to explore this potential relationship.
Harm reduction does not preclude abstinence and may be a treatment goal for some PWUD. The emphasis on abstinence for all PWUD among some HCWs in our study, and even the suggestion that MOUD should be a time-limited healthcare service despite the wide evidence base to the contrary [ 36 ], is reflective of a larger cultural emphasis on sobriety and the widespread criminalization of drug use. Scholars have noted that moralism pervades anti-harm reductionist views, and that, despite an economic and medical evidence base supporting harm reduction [ 37 ], a belief that drug use is “immoral” diminishes support for harm reduction policies and programs [ 38 ]. Favoring abstinence may also decrease support for harm reduction programs [ 39 ]. Yet, as our study demonstrates, support for harm reduction and attitudes towards abstinence may not always be linearly related, and harm reduction often exists on a continuum. Even organizations that officially incorporate harm reduction may still favor abstinence and stigmatize people who are actively using drugs. For example, a qualitative study of staff and residents at a housing first program described how abstinence was characterized as “improving one’s life” and emphasized the importance of “getting clean” [ 40 ]. Participants also spoke about the disconnect between policy and practice, in which abstinence was not required for program entry but substance use onsite was not tolerated and could lead to dismissal [ 40 ]. Similarly, while all HIV clinics included in our study directly provided or referred patients to harm reduction services, abstinence was prioritized among some of the HCWs and clearly pervaded their interactions with patients.
Limitations
These qualitative findings reflect the perspective of HIV HCWs in Birmingham, AL and Pittsburgh, PA, and may not reflect the attitudes of HCWs who work outside of HIV clinics or elsewhere in the United States. Recruitment language shared with HCWs stated that “the aim of this study is to understand the ways that harm reduction care and stigma experienced in healthcare settings affect clinical outcomes for people living with HIV who use drugs.” As a result, HCWs who elected to participate in the interviews may have been more knowledgeable about harm reduction than those who did not. These perspectives may therefore not be representative of those of HCWs less familiar with harm reduction work. However, results demonstrated a wide range of harm reduction approaches and variable familiarity with the concept, suggesting that our sample was fairly heterogeneous.
Our study is the first, to our knowledge, that explores how HIV HCWs utilize relational harm reduction in HIV primary care settings. With this work we seek to amplify voices of those with lived experiences by explicating ways that the long-standing principles of harm reduction, which were developed by PWUD for PWUD, can be translated to and practiced in healthcare settings regardless of policy contexts that may enable or inhibit structural harm reductions strategies such as syringe services or MOUD. Our findings suggest that relational harm reduction in our study settings is practiced along a continuum. Some HCWs were experienced in integrating relational harm reduction into their interactions with patients, while several HCWs were entirely unaware of harm reduction. Interestingly, we also found that even strong harm reductionists shared sentiments or used language in opposition to harm reduction principles, suggesting that even experienced HCWs could benefit from additional training. Given the health benefits associated with harm reduction care, additional research is needed to identify ways to strengthen harm reduction approaches in HIV settings.
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
Antiretroviral Therapy
Health Care Worker
Medication for Opioid Use Disorder
Pennsylvania
People With HIV
People Who Use Drugs
Syringe Service Program
Substance Use Disorder
Hawk M, Coulter R, Egan J, Friedman M, Tula M, Kinsky S. Harm reduction principles for Healthcare Settings. Harm Reduct J. 2017;14:70.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kaiser Family Foundation. Sterile Syringe Exchange Programs 2022 [ https://www.kff.org/ .
Volkow ND. Stigma and the toll of addiction. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(14):1289–90.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Zwick J, Appleseth H, Arndt S. Stigma: how it affects the substance use disorder patient. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2020;15(1):50.
Wakeman SE, Pham-Kanter G, Donelan K. Attitudes, practices, and preparedness to care for patients with substance use disorder: results from a survey of general internists. Subst Abus. 2016;37(4):635–41.
Biancarelli DL, Biello KB, Childs E, Drainoni M, Salhaney P, Edeza A, et al. Strategies used by people who inject drugs to avoid stigma in healthcare settings. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019;198:80–6.
Meyerson BE, Russell DM, Kichler M, Atkin T, Fox G, Coles HB. I don’t even want to go to the doctor when I get sick now: Healthcare experiences and discrimination reported by people who use drugs, Arizona 2019. Int J Drug Policy. 2021;93:103112.
Ellis K, Walters S, Friedman SR, Ouellet LJ, Ezell J, Rosentel K, et al. Breaching Trust: a qualitative study of Healthcare experiences of people who use drugs in a rural setting. Front Sociol. 2020;5:593925.
Chan Carusone S, Guta A, Robinson S, Tan DH, Cooper C, O’Leary B, et al. Maybe if I stop the drugs, then maybe they’d care?—hospital care experiences of people who use drugs. Harm Reduct J. 2019;16(1):16.
Simon R, Snow R, Wakeman S. Understanding why patients with substance use disorders leave the hospital against medical advice: a qualitative study. Subst Abus. 2020;41(4):519–25.
O’Brien TC, Feinberg J, Gross R, Albarracín D. Supportive environments during the substance use disorder epidemic in the rural United States: provider support for interventions and expectations of interactions with providers. Soc Sci Med. 2022;294:114691.
King C, Collins D, Patten A, Nicolaidis C, Englander H. Trust in Hospital Physicians among patients with Substance Use Disorder referred to an Addiction Consult Service: a mixed-methods study. J Addict Med. 2022;16(1):41–8.
Chang JE, Lindenfeld Z, Hagan H. Integrating harm reduction into Medical Care: lessons from three models. J Am Board Family Medicine: JABFM. 2023;36(3):449–61.
Article Google Scholar
US Department of Health and Human Services. Overdose Prevention Strategy 2023 [ https://www.hhs.gov/overdose-prevention/harm-reduction .
National Academies of Sciences E, and Medicine. Opportunities to improve opioid Use Disorder and Infectious Disease services: integrating responses to a dual epidemic. Washington, DC: The National Academies; 2020.
Google Scholar
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Waiver Elimination (MAT Act) 2023 [ https://www.samhsa.gov/medications-substance-use-disorders/waiver-elimination-mat-act .
Lanham HJ, Papac J, Olmos DI, Heydemann EL, Simonetti N, Schmidt S, et al. Survey of barriers and facilitators to Prescribing Buprenorphine and Clinician perceptions on the drug Addiction Treatment Act of 2000 Waiver. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(5):e2212419–e.
Gugala E, Briggs O, Moczygemba LR, Brown CM, Hill LG. Opioid harm reduction: a scoping review of Physician and System-Level gaps in Knowledge, Education, and practice. Substance Abuse. 2022;43(1):972–87.
Winograd RP, Davis CS, Niculete M, Oliva E, Martielli RP. Medical providers’ knowledge and concerns about Opioid Overdose Education and Take-Home Naloxone Rescue Kits within Veterans Affairs Health Care Medical Treatment settings. Substance Abuse. 2017;38(2):135–40.
Beane SN, Culyba RJ, DeMayo M, Armstrong W. Exploring the medical home in Ryan White HIV care settings: a pilot study. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2014;25(3):191–202.
Pappas G, Yujiang J, Seiler N, Malcarney M-B, Horton K, Shaikh I, et al. Perspectives on the role of patient-centered medical homes in HIV Care. Am J Public Health. 2014;104(7):e49–53.
Reid M. A qualitative review of cannabis stigmas at the twilight of prohibition. J Cannabis Res. 2020;2(1):46.
Krendl AC, Perry BL. Addiction onset and offset characteristics and public stigma toward people with common substance dependencies: a large national survey experiment. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2022;237:109503.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Dedoose Version 9.0.17. Los Angeles, CA: SocioCultural Research Consultants, LLC; 2021.
Braun V, Clarke V. Toward good practice in thematic analysis: avoiding common problems and be(com)ing a knowing researcher. Int J Transgender Health. 2023;24(1):1–6.
Braun V, Clarke V. One size fits all? What counts as quality practice in (reflexive) thematic analysis? Qualitative Res Psychol. 2021;18(3):328–52.
Phillippi J, Lauderdale J. A guide to Field Notes for qualitative research: Context and Conversation. Qual Health Res. 2017;28(3):381–8.
Hennink M, Kaiser BN. Sample sizes for saturation in qualitative research: a systematic review of empirical tests. Soc Sci Med. 2022;292:114523.
O’Connor C, Joffe H. Intercoder Reliability in Qualitative Research: debates and practical guidelines. Int J Qualitative Methods. 2020;19:1609406919899220.
Creswell JW, Miller DL. Determining validity in qualitative Inquiry. Theory into Pract. 2000;39(3):124–30.
Department of Health of Allegheny County. Chapter 851: Needle Exchange Programs 2007 [ https://ecode360.com/8773299#8773299 .
Beach MC, Keruly J, Moore RD. Is the quality of the patient-provider relationship associated with better adherence and health outcomes for patients with HIV? J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(6):661–5.
Gressler LE, Natafgi NM, DeForge B, Shaneman-Robinson B, Welsh C, Shaya F. What motivates people with substance use disorders to pursue treatment? A patient-centered approach to understanding patient experiences and patient-provider interactions. J Subst Use. 2019;24(6):587–99.
Kosakowski S, Benintendi A, Lagisetty P, Larochelle MR, Bohnert ASB, Bazzi AR. Patient perspectives on improving patient-provider relationships and Provider Communication during Opioid Tapering. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(7):1722–8.
Frankeberger J, Gagnon K, Withers J, Hawk M. Harm reduction principles in a Street Medicine Program: a qualitative study. Cult Med Psychiatry. 2023;47(4):1005–21.
Medicine Division; Board on Health Sciences Policy, Health M. Committee on medication-assisted treatment for opioid use disorder. Medications for opioid Use Disorder Save lives. Washington, D.C.: National Academies; 2019.
National Institute on Drug Abuse. Harm Reduction 2022 [ https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/harm-reduction .
Stoljar N. Disgust or dignity? The Moral basis of harm reduction. Health Care Anal. 2020;28(4):343–51.
Javadi R, Lagana K, Krowicki T, Bennett D, Schindler B. Attitudes toward harm reduction among substance use treatment professionals in Philadelphia. J Subst Use. 2022;27(5):459–64.
Pauly B, Wallace B, Barber K. Turning a blind eye: implementation of harm reduction in a transitional programme setting. Drugs: Educ Prev Policy. 2018;25(1):21–30.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding for this study was provided by the US National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Drug Abuse (1R01DA054832-01). The funder had no role in the design of the study, data collection, data analyses, interpretation of data, or preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Nursing, University of Alabama at Birmingham, 1701 University Blvd., Birmingham, Alabama, AL, 35294, USA
Emma Sophia Kay & Jessica Townsend
Department of Behavioral and Community Health Sciences, School of Public Health, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
Stephanie L. Creasy & Mary Hawk
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ESK and MH are MPIs on the award that funded this research. ESK composed the initial manuscript draft. ESK and SLC analyzed the qualitative data. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Emma Sophia Kay .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was approved via expedited review by the University of Pittsburgh Institutional Review Board (STUDY21090002).
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kay, E.S., Creasy, S.L., Townsend, J. et al. A qualitative exploration of health care workers’ approaches to relational harm reduction in HIV primary care settings. Harm Reduct J 21 , 97 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12954-024-01021-x
Download citation
Received : 26 March 2024
Accepted : 10 May 2024
Published : 17 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12954-024-01021-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Harm Reduction Journal
ISSN: 1477-7517
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 09 May 2024
Overlooked by the obstetric gaze – how women with persistent health problems due to severe perineal trauma experience encounters with healthcare services: a qualitative study
- Katharina Tjernström 1 ,
- Inger Lindberg 1 ,
- Maria Wiklund 2 &
- Margareta Persson 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 610 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
124 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
During the first year postpartum, about 25 per cent of Swedish women with severe perineal trauma (SPT), i.e., a third- or fourth-degree perineal laceration at childbirth, are unsatisfied with their healthcare contacts. Further, there is a lack of research on the more long-term experiences of healthcare encounters among women with persistent SPT-related health problems. This study explores how women with self-reported persistent SPT-related health problems experience their contact with healthcare services 18 months to five years after childbirth when the SPT occurred.
In this descriptive qualitative study, a purposive sample of twelve women with self-reported persistent health problems after SPT were individually interviewed from November 2020 – February 2022. The data was analysed using inductive qualitative content analysis.
Our results showed a paradoxical situation for women with persistent health problems due to SPT. They struggled with their traumatised body, but healthcare professionals rejected their health problems as postpartum normalities. This paradox highlighted the women’s difficulties in accessing postpartum healthcare, rehabilitation, and sick leave, which left them with neglected healthcare needs, diminished emotional well-being, and loss of financial and social status. Our results indicated that these health problems did not diminish over time. Consequently, the women had to search relentlessly for a ‘key person’ in healthcare who acknowledged their persistent problems as legitimate to access needed care, rehabilitation, and sick leave, thus feeling empowered.
Conclusions
Our study revealed that women with persistent SPT-related health problems experienced complex health challenges. Additionally, their needs for medical care, rehabilitation, and sick leave were largely neglected. Thus, the study highlights an inequitable provision of SPT-related healthcare services in Sweden, including regional disparities in access to care. Hence, the authors suggest that Swedish national guidelines for SPT-related care need to be developed and implemented, applying a woman-centered approach, to ensure equitable, effective, and accessible healthcare.
Peer Review reports
Intrapartum and postpartum healthcare should ideally be high-quality, evidence-based, and a positive experience stemming from woman-centred care with a holistic approach based on human rights [ 1 ]. This approach acknowledges each woman’s articulated needs and expectations in her social, emotional, physical, spiritual, and cultural context [ 2 ]. Nevertheless, during the first year postpartum, about one in four Swedish women with severe perineal trauma (SPT) [ 3 ], i.e., a third- or fourth-degree perineal laceration involving the anal sphincter muscle and anorectal mucosa at vaginal childbirth [ 4 ], are dissatisfied with their care and one in three women report ongoing health problems related to their SPT. Women with SPT may suffer from various physiological and psychological consequences such as pain [ 5 , 6 ] , incontinence [ 7 ], defecation problems [ 8 ], vaginal prolapse [ 5 ], sexual dysfunction [ 9 ] or depression and anxiety [ 10 , 11 , 12 ].
Reducing physical symptoms is essential to support emotional and social recovery after any perineal trauma [ 13 , 14 ]. Women with SPT emphasise that professional, competent, and respectful attitudes from healthcare professionals (HCPs), including individual and adapted information, facilitate, and promote their postpartum recovery. Thus, the HCPs’ competence and knowledge of treatment options is a prerequisite for women to access needed care [ 15 ]. An additional problem in the Swedish context is the lack of national recommendations or guidelines, which enables each of the 21 regions to develop own regional and local guidelines. An audit of the existing regional and local guidelines for prevention and care of SPT shows an unexpected diversity or lack of evidence-based recommendations [ 16 ]. However, dissatisfaction with access to healthcare has been expressed by women with persistent, i.e., beyond one year postpartum, SPT-related health problems [ 6 , 17 ]. Furthermore, women criticise inadequate or absent support [ 6 , 18 ], poor information and education [ 6 , 10 , 18 ], and lack of follow-up care regarding SPT and its potential psychological and social consequences [ 6 , 10 ]. Postpartum care focuses more on the baby than the mother’s well-being [ 18 , 19 ]. Also, the available treatment options are perceived as limited and outdated by those with access to needed care [ 17 , 18 ]. Moreover, women with SPT describe that some HCPs tend to normalise their SPT-related problems [ 10 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 ], and women are met in unprofessional and disrespectful ways [ 17 , 23 ], where HCPs are perceived as ignorant, nonchalant, and questioning women’s symptoms [ 10 , 17 ]. Previous research [ 24 ] indicates an institutional objectification of women with SPT by Swedish healthcare providers hindering access to healthcare, sick leave, and occupational rehabilitation after SPT. In contrast, women also report being acknowledged and liberated when HCPs have a professional and empathic approach and provide continuity of care that enables access to care for persistent SPT-related health problems [ 17 , 18 , 19 , 25 ]. Thus, several women who sustained an SPT during childbirth do not experience access to needed and necessary care, a fact that needs further exploration.
Globally, sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) are crucial for individual health and gender equality [ 26 ]. Current issues within SRHR and midwifery are controlled by the institutional power in health institutions, i.e., medical power [ 27 ], connected to the still-existing economic and educational disadvantages of women globally, which are also feminist issues [ 26 , 28 ]. As midwife stands for ‘with woman’ [ 28 ], gender or feminist approaches are used in advancing midwifery theory [ 27 , 29 ] and various aspects of SRHR topics such as breastfeeding promotion [ 30 ], birth plans [ 31 ] and attitudes towards contraceptives [ 32 ]. In midwifery and feminist approaches, the biological material body and the socially constructed gendered body are viewed as intertwined [ 33 ]. Moreover, midwifery care is recommended to be woman-centred [ 1 , 2 ], focusing on the individual woman’s needs and transferring control from the institution to the woman herself. However, despite the different organisations of sexual and reproductive healthcare between countries, international research shows similar results regarding women’s diverging experiences with postpartum SPT-related healthcare [ 6 , 15 , 17 , 18 ].
In sum, there is growing evidence showing that many women with persisting health problems caused by SPT are often, but not always, met with mistrust and ignorance when seeking care for their problems. Even though there may be national, regional, or local protocols or guidelines for care after SPT, women with persistent SPT-related problems still raise their voices about the difficulty of getting access to competent quality care. This indicates a potential gender bias [ 34 ] and a need for gender theoretical perspectives in midwifery [ 28 ], as utilized in this study. Additionally, few studies explore the care-seeking experience among this group of women in a longer time perspective after childbirth when the SPT occurred.
The aim of this study is to explore how women with self-reported persistent SPT-related health problems experience their contact with healthcare services 18 months to five years after childbirth when the SPT occurred.
Study design and context
The present study is part of a larger research project investigating the long-term consequences of SPT on quality of life, working life, and healthcare contacts. This study had an inductive qualitative interview study design applying qualitative content analysis to analyse data [ 35 , 36 , 37 ]. This method searches for patterns, e.g., by identifying similarities and differences in the data. The researchers obtain an in-depth understanding of the studied phenomenon through abstraction and interpretation [ 36 ]; thus, an appropriate method to apply to capture women’s experiences of their healthcare encounters when seeking medical help and support. Throughout the research process, the recommendations for qualitative research according to ‘Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research’ (COREQ) were followed [ 38 ].
Sweden has 21 partly independent regions primarily responsible for providing healthcare services to the population. Healthcare services are tax-funded, and the regions have extensive autonomy to decide upon the healthcare services within each region based on the frameworks of the Health and Medical Service Act [ 39 ]. Additionally, within the Swedish social security system, 480 days of paid parental leave are allocated to each child in Sweden and can be utilised by their legal guardian(s) until the child is twelve years old. Of these 480 days, 60 days are specifically assigned to each parent, and the remaining days are split between parents as desired. The financial compensation is based on the parent’s income and is financed by taxes [ 40 ].
In Sweden, midwives are the primary care providers to women with normal pregnancies, births, and postpartum care. In case of complications to pregnancy and childbirth, midwives collaborate with other medical professionals, especially obstetricians. For example, midwives suture first- and second-degree perineal lacerations, while obstetricians are responsible for all SPT repairs [ 41 ]. Generally, in Sweden, women who sustain an SPT during childbirth are offered a check-up with the obstetrician responsible for the repair before discharge and should also have a follow-up with an obstetrician or sometimes a physiotherapist within the postnatal period. Thereafter, women with no mayor initial healing problems are advised to contact relevant healthcare services if any health issues related to the SPT should arise in the future. Women presenting with complicated healing are treated accordingly. Additionally, women with second- to fourth-degree perineal lacerations are assessed with questionnaires three times during the first year postpartum by the National Perineal Laceration Register. However, there are no recommendations in Sweden for prolonged check-ups for women with SPT after the postnatal period and no guidelines on organised check-ups for women with prolonged symptoms due to SPT exist [ 42 , 43 ].
Women with persistent SPT-related health problems and characteristics were purposively recruited to achieve a heterogeneous sample reflecting multiple experiences. An overview of inclusion and exclusion criteria can be found in Table 1 .
The closed Swedish Facebook community ‘Förlossningsskadad? Du är inte ensam!’ [‘Injured at childbirth? You are not alone!’] functioned as a recruitment platform for a national sample of women reporting persistent SPT-related health problems. The Facebook community is secluded to women with SPT and started in 2014. During the data collection period (Nov 2020 – Feb 2022), the group had over 7,600 members; today, the community has grown to include over 9,500 members [ 44 ].
In late November 2020, the administrators of the Facebook community pinned a digital poster with study information and a link to the study homepage in the group feed. The study homepage contained written information on the research project and contact details for the research group if any women wanted additional information about the study. Interested potential participants contacted the research group via a contact form on the homepage, and the first author (KT) confirmed that the potential participants met the inclusion criteria via telephone. Thirteen participants from different parts of Sweden showed interest in participating and left their contact information. One woman never responded to our efforts to reach her. The remaining twelve women fulfilled the inclusion criteria and were invited to an interview. Before the interview, the women answered a digital survey on background data (such as demographic data, education, employment, sick leave, and childbirth history) distributed via REDCap ® , a web-based application to create secure online questionnaires and research databases [ 45 ]. The interviews were finalised in February 2022.
Data collection
We collected data via individual open-ended interviews [ 46 ], supported by a semi-structured interview guide [see Additional file 1 ]. The interview guide, developed by KT and MP with input from MW and IL, was based on literature reviews, our awareness of gender as a social construct [ 33 ], and the clinical pre-understanding within the research group. After a pilot interview conducted by KT (not included in the data), minor adjustments were made to the interview guide. The final interview guide covered the topics of everyday life experiences, work, and general functioning. However, despite the mentioned interview topics, the emergent study design and the ability to speak freely about what was perceived as important for their daily functioning, the contacts with healthcare services was brought up in vivid and extensive narratives by all participants as part of their descriptions of their challenges in everyday life and their ability to function at work. Hence, the experiences the women made of the healthcare services played an important role for the women in their daily management of SPT-related health problems.
As data collection occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic, all participants were interviewed digitally via Zoom ® [ 47 , 48 ]. With the participant’s consent, the interviews were audio-recorded via Zoom ® and a separate digital recorder (as backup). Any Zoom video files automatically generated were deleted directly after the termination of the interview to protect participants’ identities. The first author interviewed all women; in two interviews, co-authors (IL or MW) also attended. The authors had no professional or personal affiliation with the enrolled participants . Detailed interviews ranging from 29 – 112 minutes (median: 61.5 minutes) gave extensive data. All interviews were performed in Swedish and transcribed verbatim. After that, the first author validated the transcripts for accuracy by reviewing the text while listening to the recordings.
Authors’ pre-understanding and theoretical positionality
The research group comprises three midwives (KT, IL, MP) and one physiotherapist (MW). We all have extensive professional experiences from clinical practice in primary and in-patient care, where three authors (KT, IL, MP) have specific professional experiences of caring for women with SPT. Additionally, we are women, feminists, and mothers with various birth experiences. Further, the group holds expertise in gender studies and qualitative research within midwifery science, such as perineal trauma and medical sociology. Hence, we stem from a social constructivist research standpoint and utilise ourselves as co-constructors in the analysis process. As feminist researchers, we apply a gender theoretical lens to the data.
Data analysis
The interviews were analysed using qualitative content analysis with an inductive and stepwise approach focusing on the manifest and latent content [ 35 , 36 , 37 ]. The interviews, transcripts, and analysis steps were performed in Swedish.
The analytical procedure started with reading the transcripts multiple times while highlighting text, meaning units, with content relevant to the aim of this study. Then, identified meaning units were condensed, focusing on preserving their core meaning and labelled with manifest codes [ 35 , 36 , 37 ]. Initially, KT coded one interview and triangulated those codes with the principal investigator (MP). KT then coded the rest of the interviews. In the next step, similar codes were clustered, forming subcategories based on the manifest content. Moving towards an interpretation of the content, categories were created by the abstraction of subcategories. This was done by KT and MP separately and then triangulated to identify significant concepts. Next, the preliminary categories and subcategories were triangulated with the whole research group until a consensus was obtained. To answer the question of ‘what?’ and ‘how?’ within the data, the latent content and thread of meaning were identified by clustering and abstracting the emerging findings to form subthemes and a theme [ 36 , 37 ]. The emerging findings were also peer-reviewed and discussed at a research seminar. The finalisation of the analysis resulted in an overarching theme and four subthemes. The translation of categories, subthemes, theme and inserted citations from Swedish into English was performed as a last step. The translation and choice of words were discussed between authors (all knowledgeable in English) to reach a consensus and minimise translation bias.
During the coding process, the researchers used MAXQDA ® [ 49 ], a software for organising, transcribing, analysing, and visualising qualitative research data, and Microsoft Excel ® [ 50 ] as aids to organise the codes.
Demographics of included participants
The background characteristics of the twelve participants in the final sample are presented in Table 2 .
The participants identified themselves as cis women, i.e., their gender identity matched their sex assigned at birth [ 51 ], and are thus referred to as ‘women’ in this paper. All women were in a partner relationship. The women reported a broad spectrum of physical and phycological health problems following the SPT at childbirth, e.g., urine or anal incontinence, pain in the lower abdomen, sexual dysfunction, and depression. Thirty per cent of the women had full-time employment, and the proportion of parental leave varied from 12% to 100% (three women had an ongoing parental leave with subsequent children at the interview). Further, 60% of the women had a sedentary occupation. Five women had been on sick leave after reconstructive surgery, and five reported sick leave for other reasons than their SPT.
The analysis resulted in one theme, ‘Overlooked by the obstetric gaze – living the paradox of a normalised but traumatised postpartum body’, with related subthemes ‘Questioning whether it’s all in my head’, ‘Fighting persistently for access and legitimacy in no (wo)man's-land’, ‘Facing multidimensional losses when no help in sight’, and ‘Depending on other’s advocacy to navigate an arbitrary system’. An overview of the findings is presented in Table 3 . The findings are presented as an overarching theme and thereafter, the related subthemes and categories. Citations from the participants illustrate the findings. All women have been allocated pseudonyms in the result presentation.
Overlooked by the obstetric gaze – living the paradox of a normalised but traumatised postpartum body
The latent theme ‘Overlooked by the obstetric gaze – living the paradox of a normalised but traumatised postpartum body’ represented the women’s experiences of healthcare encounters covering HCPs’ diminishing attitudes towards women’s persistent SPT-related health problems and the women’s difficulties accessing healthcare and sick leave. We interpreted that the women were assessed by the HCPs’ ‘obstetric gaze’, i.e., a medical gaze in postpartum healthcare normalising their persistent health problems and judging the women’s lower abdomen as ‘fine’ by their looks. The obstetric gaze put the women in a paradoxical situation where HCPs normalised tangible symptoms to be a natural part of childbirth. With no medical legitimacy of the health problems, the women also felt labelled as ‘hysterical’ (exaggerating health problems) by the HCPs. As a result, on the one hand, they had to continue facing persistent and tangible health problems such as incontinence, pain or prolapses. On the other hand, no acknowledgement by HCPs of their health problems led them to question whether their problems were merely a product of their imagination and, thus, only existed ‘in their head’. The theme also comprised women’s struggle for legitimacy in a gendered healthcare system - a no-(wo)man's land. They experienced that healthcare services and social insurance systems were challenging to access and demanded a tenacious and extensive fight to obtain legitimacy for their health problems. Consequently, the women had to put up with neglected healthcare needs, negatively impacting their physical and emotional well-being, and financial and social status when no medical help or rehabilitation was available. However, some women had encountered an HCP who was empathic and understanding, hence not guided by the obstetric gaze. Such encounters legitimised persistent problems and were crucial for accessing needed care, sick leave, and rehabilitation.
Questioning whether it’s all in my head
The subtheme ‘Questioning whether it’s all in my head’ focused on the women’s experiences of facing ignoration and no confirmation of perceived health problems and thus being labelled as a hysterical woman. The related categories referred to a normalisation process that the women experienced in their encounters with HCPs, which made them question their bodily perceptions. Furthermore, the women felt accused of exaggerating symptoms because their persistent SPT-related health problems did not match HPCs’ views of acceptable postpartum symptoms. Thus, it could be understood that the women found themselves in a paradox of suffering from tangible physical consequences after SPT, which were normalised by HCPs and their ‘obstetric gaze’.
Facing HCP's ignoration of perceived problems
The women experienced the HCPs defining their persistent health problems after the SPT as ‘normal’. The HCPs assured the women that their problems would disappear with time or that transient motherhood-related aspects, such as breastfeeding or fragile vaginal mucosa, were the cause of the problem. One woman expressed:
“Then I felt, ‘It should not feel like this; this is something wrong’, and I sought medical attention and was seen by multiple physicians […] They thought my vaginal mucous membrane was not ready for intercourse. I was still breastfeeding, so they thought I should stop breastfeeding. Then maybe the mucous membrane would be restored, which was causing me the pain. I was not listened to at all. I was treated very poorly by one physician in particular, and despite second opinions and so on, nobody… nobody took me seriously.” (Linda)
Consequently, the women perceived that their concerns were ignored. They also learned that the HCPs saw their prolonged physical problems after SPT as an inevitable part of childbirth, which the women should accept. One woman resigned:
“But then [the physician] says something like this: ’Well, that's completely normal’, but I felt like, ‘Yes, but it doesn't feel normal'.” (Emma)
After the genital and pelvic floor examinations, the HCPs often guaranteed the women that ‘everything looked fine’, i.e., reinforcing the normality of the genital area. Although the women described to the HCPs that they struggled with SPT-related problems, their concerns were met with a comment on the physical appearance rather than a comprehensive examination of the pelvic floor's functionality.
One woman responded:
“They think ‘everything looks fine’ and ‘everything looks good and repaired’. I still have problems. I was also referred to a surgeon, who did a rectoscopy, and ‘it looked so nice’. Then, I was referred to a urotherapist to learn how to pinch my muscles because ‘everything would be so good’. She helped me get a second opinion in XX [town], where they discovered that there was still damage." (Jin)
Another woman expressed:
”I couldn’t care less what it [genital area] looks like. Nobody will be down there watching. I only need it [genital area] to function as intended.” (Anna)
Consequently, the women felt ignored and unheard in their contact with healthcare services. They perceived that HCPs did not listen to them, leaving them feeling invisible, sometimes even having severe health problems.
“I was hospitalised with sepsis before someone listened to me.” (Josefin)
Being labelled as a hysterical woman
The women also experienced being labelled as the ‘hysterical woman’ who exaggerated their persistent symptoms and had mental health problems. The women described how the HCPs accused them of imagining their SPT-related health problems. One woman indignantly revealed that the HCP she encountered said, 'These problems only exist in your head’ (Joanna), i.e., suggesting that the perceived symptoms did not exist and rejecting the health concerns. Hence, this attitude made some women believe their problems were a product of their imagination and sometimes made them even question their sanity.
Moreover, the HCPs’ condescending attitudes towards the women made them feel dismissed and devalued. For example, the women shared that HCPs laughed at them or were rough or cold during the examination. Moreover, HCPs expressed that they had ‘seen worse’ (Amanda). Some women also conveyed that they were advised ‘to drink some wine to feel better’ (Elin) when discussing painful intercourses due to their SPT-related health problems.
“You are constantly dismissed, ‘No, but everything looks fine, you have no problems’. Then you start to think you’re imagining things. And then you may not dare to talk about the injuries.” (Jin)
Fighting persistently for access and legitimacy in no (wo)man's-land
The subtheme ‘Fighting persistently for access and legitimacy in no (wo)man's-land’ referred to the women’s experience of gender constructs related to inaccessible healthcare services and their often year-long struggles to access this gendered healthcare and linked social insurance systems. The difficulties in accessing care created negative attitudes towards the healthcare services, making the women wish for general improvements in women’s healthcare.
Struggling to access the gendered healthcare and social insurance systems
The women pointed out that after giving birth, they needed more extensive information on their injury, precautions, available help (follow-up care or re-operation), and sick leave. To overcome the lack of required information, they had to request or actively search for it on their own, which also led to uncertainty about where and when to seek further help if needed.
“I was sent home with a brochure and a pat on the shoulder.” (Amanda)
The women also experienced a lack of adequate healthcare services targeted at their SPT-related health problems. For example, many women did not have access to a pelvic floor clinic or had to travel long distances to see specialists. Hence, their place of residence decided the quality of care the women received. Moreover, some women problematised the organisation of postpartum care as they missed out on follow-up care and even, in some cases, were denied follow-up care or referrals to specialised care were lost. As a result, some women had no opportunity to talk to the operating physician or experienced no follow-up care, although they requested it.
“They said it can take up to a year to get better. So, when that year had passed, and before starting to work again, I called different places in the hospital and asked: What should I do now? […] It took several months before I got an appointment with the surgeon for an assessment. And then I had to get a second opinion. So, it took like seven months before I got an appointment at [a specialist clinic].” (Hawa)
For the women, access to healthcare services, sick leave certificates, and HCPs’ dismissive attitudes were perceived as gender-related, i.e., difficulties in obtaining help from women’s healthcare services would not exist if the services were more women-oriented. One woman illustrated this by expressing: ‘If men gave birth to babies, the situation would not be like this’ (Joanna). Moreover, they perceived that women’s healthcare services were not prioritised. They explicitly stated that the absence of sick leave certificates and benefits was related to their gender. The women were expected to cope without sick leave benefits because vaginal and perineal lacerations of any scope were viewed as a natural part of childbirth, a normal process of a woman’s body. Thus, sequelae thereof did not exist or were taboo in society.
“Everything that happens during and after childbirth and related injuries has been a taboo discussion topic, so it has been completely ‘normal’ to suffer from persistent pain.” (Anna)
“I have applied for compensation from the national patient insurance. I got rejection after rejection; nothing has gone wrong. I was told: 'You simply must expect these things in childbirth. And a caesarean section is not less risky'.” (Hawa)
Thus, the women argued that society and the government did not invest needed resources in women’s healthcare. In addition, those few women receiving a short period of sick cash benefits had it immediately after giving birth or after re-operation, but not for prolonged problems. Further, the women noted that they were not offered sick leave certificates due to persistent physical SPT-related health problems but instead due to mental issues, such as depression or anxiety.
“I've heard about women who have been mentally unwell and have hurt their children. So maybe physicians get cautious and put women on sick leave if they say, ‘I'm not feeling mentally well’. Then they act quickly because they think it's so important. But they don't think about the physical injuries because that's part of [childbirth].” (Jenny)
However, the women shared how they fought long and hard for acknowledgement and care and made demands; for many, this process had covered years. They had to repeatedly insist that something was wrong and felt pressure to prove their health problems to the HCPs. In some women, this led to their persistent problems being diagnosed and acknowledged after several years of delay. The struggle for care involved countless visits and referrals to different HCPs, demanding much strength and persistence, which exhausted them. Sometimes, the sequelae had to develop into an acute health situation, or some women decided to pay for private care to access the proper treatment and rehabilitation. Further, with time, they also became explicit about their demands for sick leave certificates and benefits.
“Well, it [short sick leave period because of birth traumas] just feels like scorn. To me, it is not a sufficient length of sick leave.” (Elin)
Wishing for improvement in women's healthcare
The perceived lack of adequate care and rehabilitation, access to sick leave benefits, and HCPs’ attitude negatively influenced the women’s opinions on healthcare services, especially postpartum healthcare. In addition, the women perceived many HCPs as unprofessional, indifferent, and unstructured. As a result, the women mistrusted the HCPs and lost hope in healthcare services. Thus, they were reluctant to seek further care and were anxious about receiving proper treatment or that HCPs would miss important things.
“I am not being listened to in women's healthcare. This is partly why I feel so disappointed.” (Linda) “You just don't trust the healthcare system. […] Some people have been struggling with their injuries for like 18 years. But the [specialist clinic] – I finally received fantastic treatment, and what if it could be available everywhere [in Sweden]?” (Hawa)
Moreover, the women described a struggle for their rights when deciding whether to report the HCPs to the authorities and pointed out the need to improve women’s healthcare. Reporting HCPs was perceived as complicated as the women did not want to blame specific individuals. The women saw that the major problem lay within the healthcare system and with individual HCPs.
“In the end, I met a fantastic person [healthcare professional]. She wanted me to report the mistreatment when I eventually had the strength. Because no one listened when I said I was ill. So, she has offered to help me if I want to, but I don't know if I have the strength to file a complaint.” (Josefin)
A wish to improve women’s healthcare services was articulated, especially regarding personal follow-up care beyond one year postpartum and the possibility of full-time or part-time sick leave certificates and benefits for persistent problems on equal terms. This wish also strengthened their decision not to give up searching for help and to raise their voices to help themselves and other women.
“I received physiotherapy and the follow-up surveys [the Perineal Laceration Register] during the first year, but thereafter I would have liked to have an annual follow-up for the next years to ensure the status and potential re-operations. […] I can google, but I want to have that information in dialog with a living person, but you do not get that.” (Jenny)
Partaking in developing educational material for HCPs or starting a career within women’s healthcare were some women’s ways to contribute and increase competency in persistent SPT-related health problems.
“One of my strategies since I got the injury is also to try to influence. Being able to be involved and influence what postpartum care should consist of.” (Jin)
Facing multidimensional losses when no help in sight
The subtheme ‘Facing multidimensional losses when no help in sight’ covered physical and mental health consequences and the financial and social losses the participating women faced when no support or access to needed care and rehabilitation was provided.
Being physically victimised by HCP's malpractice
The women’s experiences covered either being misdiagnosed during the suturing after birth or in the following years when seeking help for persistent SPT-related health problems. Further, they shared how physicians had incorrectly sutured vaginal and perineal muscles after childbirth, leading the women to live with incontinence, pain, prolapses, or sexual dysfunction if their vaginas were sutured too tight. They also described how they endured infections, wound ruptures, sepsis, necrosis, and re-operations. Additionally, the women perceived a general lack of competency regarding communication and persistent SPT-related health problems, including problems related to sex life and sexual functioning, besides a more specific lack regarding suturing techniques and ultrasound examinations.
“I was referred to a specialist clinic. And they found out that all the muscles were separated, the internal and external sphincters were torn, and my pinching ability was kind of weak. So, it was quite the opposite, really, quite the opposite. None of what the other physician had said was true [laughs]. Absolutely incredible. And she is supposed to be a specialist.” (Hawa)
Aching inside
Living with troubled postpartum bodies and the absence of HCPs’ legitimation of the women´s problems made them struggle mentally, feeling speechless and silenced. This neglect reinforced irritation, anger, distress, bitterness, and disappointment towards the HCPs and the healthcare services. One woman illustrated the emotional struggle in this way:
“It's just that the health services don’t believe you, which makes you feel terrible. It's a big deal that no one listens.” (Josefin)
Moreover, the women felt uncertain about their health status due to a default medical diagnosis with concerns for their future and which staff to trust. Consequently, some had to bite the bullet, put up with their situation, and try to think positively. Other women were denying or diminishing their SPT-related health problems, accepting that their symptoms would improve, even disappear or that their condition was ‘normal’ as they had been told. Further, the women described despair because their neglected health problems caused by their SPT made them feel exposed, unsure, and hopeless. In some, this desperation resulted in a mental breakdown, a fear of losing custody of their child due to mental illness or suicidal thoughts.
“Something broke inside of me that day. I felt entirely omitted; I was close to leaving my son and committing suicide. Nobody understood how bad everything was.” (Elin)
Additionally, the women suffered emotionally when motherhood was crushed. Their partner had to take the primary responsibility for the family, and the children had to come in second place as the mothers suffered from various physical and mental health problems. As a result, the women felt they missed their children’s development and could not use their parental social security benefits as desired.
“I feel devasted because people tell me, ‘You are on maternity leave’. I’m not on maternity leave; I’m sick. I should be on sick leave.” (Jaanika)
Suffering financial and societal losses
Moreover, the women suffered financially and societally due to persistent health problems. Some women were denied financial compensation from Patient Insurance (a national insurance system where patients can seek compensation for care injuries). The Social Security Agency and the HCPs were perceived as obstacles to receiving sick cash benefits. They noted that ‘extensive’ health problems were required to receive sick cash benefits and that their health problems paradoxically were not seen as extensive or even a problem per se by the HCPs; hence, no sick leave certificates were issued.
“He [the physician] tried to argue and clarify my pain situation in the sick leave certificate to meet the requirements for a sick leave benefit at the Social Security Agency. I was in so much pain and had to lie down to breastfeed. But, no, ‘If you can manage to hold the baby when breastfeeding, then you are on maternity leave, not sick leave benefit’ [mimicking the official at the Social Security Agency who rejected the certificate and consequently also the sick cash benefit]”. (Jaanika)
Furthermore, the women were set back financially and societally because they could not work full-time due to their persistent health problems. Therefore, some women chose to compensate for their work absence with part-time parental benefits to diminish their working hours and cover their inability to work due to persistent SPT-related health problems. Without a sick leave certificate, i.e., the physicians or the officials at the Social Security Agency’s acknowledgement of a ‘true’ health problem, partners or other relatives were obliged to adjust their work schedules to support or unburden the woman’s suffering and inability to work full-time. This reduction in working hours for the SPT-affected women and, in some cases, their partners was expressed to potentially negatively affect their upcoming careers and pensions. As a result, the women experienced being caught between stools in the social insurance systems:
“[…] You end up in a position where you are neither on sick leave nor unemployment benefits and at the same time cannot perform any offered work [due to persistent problems]. But multiple societal bodies demand and expect you to be a part of the working force, and nobody really listens.” (Elin)
Depending on other’s advocacy to navigate an arbitrary system
The last subtheme, ‘Depending on other’s advocacy to navigate an arbitrary system’, highlights the women’s experiences of, often by chance, finding a single devoted professional, i.e., a ‘key person’, to access needed care and rehabilitation. Such a ‘key person’ was vital to recognising persistent problems, legitimating symptoms, and enabling access to needed care, sick leave, and rehabilitation. The women who finally had legitimation for their health problems described that the medical diagnosis also came with a feeling of sanity and empowerment, relieving them of their paradoxical situation.
Encountering a ‘key person’ to receive needed care
A support system was a prerequisite for enduring their health problems and finding the strength to fight for access to care. This system could be a partner, other family members, or friends who gave the women power and courage, but most importantly – encountering a professional who saw their problems and provided referrals or other options to obtain the needed help and support. In most cases, women would search for years for competent HCPs, such as midwives, physicians, or physiotherapists, who would listen and acknowledge persistent problems. This ‘key person’ showed empathy and trustworthiness, creating relief and security. Further, the ‘key person’ was portrayed as competent, attentive, professional, and respectful. The ‘key persons’ also shared women’s outrage at the mistreatment and default healthcare they endured. Additionally, these ‘key persons’ were surprised that the women were not on sick cash benefits due to their symptoms and that they had to compensate for their financial situation with parental benefits or reduced working hours and lower salaries. Consequently, finding this ‘key person’, often by chance or word of mouth, was crucial for accessing care and marked a significant turning point in the women’s recovery.
“I sought help from another midwife, as I felt something was wrong. This midwife referred me to the physiotherapist, who referred me to a specialist, who then referred me to surgery and rehabilitation.” (Malin)
Some women received follow-up care for their persistent SPT-related health problems during the first year postpartum. If persistent problems occurred and were acknowledged, the women were offered different surgical approaches with various outcomes, consultations by colon specialists, physiotherapy, and psychiatric care. They were grateful for the help they received but felt more comprehensive care was needed.
Feeling sane and empowered
Confirmation of persistent SPT-related health problems was expressed as liberating, strengthening and, as one woman put it, a ‘win’ (Elin). Receiving a medical diagnosis and appurtenant treatment was relieving because the medical confirmation of the symptoms released a considerable burden. These women described being acknowledged, and the diagnosis proved that health problems existed, and the struggles were not in vain. Furthermore, it explicitly stated to everyone, including themselves, that they were not ‘crazy’, ‘imagining things’ or ‘hysterical’.
“So, my laceration has been classified as an injury caused by the healthcare services. This was somehow a confirmation. It's not just that it's in my head, but it has been established that it is a medical injury, and it could have been avoided.” (Jin)
Alongside feelings of sanity and being legitimised, the women experienced empowerment. The women felt supported and confident. Thus, finding an agency to address the taboo of their SPT by talking openly about it and helping others in the same situation was also seen as therapeutic. Further, the legitimation of the sequelae and access to appropriate care gave them time to heal and process their trauma. Receiving sick leave certificates and benefits was seen as a part of the empowerment and legitimacy of their persistent SPT-related health problems, reducing stress, and easing the financial burden. Furthermore, access to occupational rehabilitation and understanding at work became available. Thus, the women who had received the help they needed after a struggle to obtain it were hopeful about the future and possible recovery.
“I have regained my authority to speak up. It [SPT-related health problems] should be out in the open, not withheld.” (Jaanika)
Our main finding was that women with persistent health problems due to SPT at childbirth were caught in a paradox of living in a normalised but traumatised body, and their health problems were rejected as postpartum normalities. Furthermore, our results elucidated the difficulties in accessing postpartum healthcare, rehabilitation, and sick leave benefits. Therefore, the women struggled with neglected healthcare needs, diminished emotional well-being, and loss of financial and social status. Our study highlighted experiences up to 5 years after sustaining SPT, which showed that some women’s SPT-related health problems do not diminish with time. They faced challenges functioning in daily life, at work, and in society. In contrast, finding a ‘key person’, i.e., a professional who acknowledged the women’s persistent problems as legitimate, was a prerequisite for accessing all the needed care and sick leave and enhancing empowerment for the women. Thus, this ‘key person’ was not blinded by the obstetric gaze and instead used their agency and advocacy as support.
In the following, we will discuss our findings related to other empirical studies and problematise them with theoretical reflections.
The paradox of normalising the postpartum body
In our findings, the paradox arose when the HCPs dismissed physical health problems after SPT despite women’s perceived symptoms. Central in this context was a normalisation process where health problems were regarded as ‘normal’ by HCPs, a phenomenon also found in prior research on SPT [ 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 ]. The HCPs’ normalisation of women’s health problems can also be found regarding other medical conditions affecting women, such as pelvic organ prolapse [ 52 ], menstrual pain [ 53 ], endometriosis [ 54 ] or nausea and vomiting during pregnancy [ 55 ]. In light of the medicalisation of women’s healthcare, where the medical field has sought to pathologise natural bodily processes such as pregnancy and childbirth [ 33 ], actual medical conditions such as persistent SPT-related health problems are paradoxically normalised. Our findings, therefore, highlight the need to challenge HCPs’ views of what constitutes a ‘normal postpartum body’ or ‘normal postpartum symptoms’ after sustaining SPT.
The key to healthcare
In the context of denied legitimacy of health problems and neglected needs, it appeared that the women became dependent on the goodwill of a ‘key person’, personified as the respectful, competent, and empathetic HCP. Prior research on SPT has also found women struggling with accessing healthcare [ 6 , 17 ] and specific HCPs as enablers of care [ 12 ]. The dependency on a ‘key person’ to access adequate care might highlight a structural problem within the provision of postpartum SPT-related healthcare. Globally, there are a few national guidelines on SPT management and prevention [ 56 ]. Additionally, no national guidelines regarding postpartum care of SPT exist in Sweden, and pelvic floor teams are only available in some Swedish regions [ 16 ]. In our study, the women lacked information, and competent HCPs were hard to find or located far away. Other studies have shown poor patient information and education as a postpartum problem [ 6 , 10 , 18 ], indicating a need to develop targeted oral and written information on wound healing and recovery. Further, women in Australia describe similar challenges to accessing SPT-related healthcare when having persistent SPT-related health problems [ 18 ]. The absence of national Australian guidelines may have led to inconsistent care, failing to meet women’s healthcare needs. Further, women from rural areas have had additional difficulties accessing needed care. In 2021, a clinical standard for SPT was implemented in Australia, comprising care standards for follow-up [ 57 ]. Thus, to improve the national situation in Sweden, more research and resources must be allocated to develop evidence-based recommendations, preferably internationally accepted guidelines [ 56 ]. Moreover, the accessibility of SPT-related healthcare, such as pelvic floor clinics, needs to be expanded so that women can easily meet their ‘key person’ if required.
Woman-(de)centred care?
We found that HCPs were obstructed by their obstetric gaze when assessing women with persistent SPT-related health problems. Obstetric gaze derives from the medical gaze notions [ 58 ], suggesting a gaze that splits the individual from the body, constructing the care-seeker as a medical object or condition instead of an individual with a social context. This gaze blinded HCPs who normalised obvious health problems. Recent advances in women’s healthcare in industrial countries and midwifery research show development towards continuity of care models with a woman-centred approach in different caseload-midwifery projects and informed choice regarding place of childbirth [ 28 , 59 , 60 , 61 ]. Wom e n-centred care [ 2 ] is a widespread care philosophy within midwifery that advocates for providing individualised care to women. Further, wom a n-centred care emphasises the individual woman’s healthcare needs and situation, incorporating the concepts of choice, control, continuity of caregiver, and self-determination. It can be argued that the obstetric gaze obstructed HCPs in providing wom a n-centred care because they did not acknowledge the women’s healthcare needs. Consequently, the women did not have control over their health situation. Making women feel empowered [ 2 , 62 ] is crucial in woman-centred care. Hence, the ‘key persons’ in our study managed to provide wom a n-centred care where acknowledgement of problems as real medical problems and access to care made the women experience empowerment. Therefore, we argue that guidelines regarding follow-up care after SPT should ideally be developed with wom a n-centred care as its core.
Everything looks fine
The biomedical model has traditionally focused on normality and abnormality rather than health [ 63 ]. Theoretically, the ‘obstetric gaze’ is closely tied to the ‘medical gaze’ and the ‘male gaze’, referring to the biomedical paradigm and its power [ 27 , 58 ]. In our study, the obstetric gaze judged the women’s persistent health problems due to SPT as ‘normal’ and the appearance of their genital area as ‘fine’, which created a paradoxical situation regarding the legitimacy of their ongoing health problems after SPT. Generally, the healthcare sector is critiqued for reducing the body to only incorporating organs and tissue, i.e., focusing on physical symptoms [ 27 ].
The women in our study, of which most showed more than one significant symptom after SPT, noted that HCPs would comment on the physical appearance of the perineal area rather than its functionality by telling them that ‘everything looked fine’. The focus on looks rather than functionality regarding SPT-related health problems aligns with the findings presented by others [ 17 ]. Having women describe how their persistent physical pelvic floor problems after SPT during childbirth are trivialised, normalised, questioned, and labelled as mental health issues is of utmost concern. This implies the need for rapid improvements in HCPs’ knowledge and organisation of care but also raises the question of what is considered a normal status and recovery after any perineal laceration in the short- and long-term perspective. A similar discursive focus on women’s appearance instead of their health problems has also been found among HCPs when women seek care for chronic pain [ 64 ]. The sentence ‘Everything looks fine’ can be interpreted as an objectifying, gendered discourse in an obstetric context. This discourse may reinforce the obstetric gaze and, in the broader sense, the medical gaze [ 58 ]. The Swedish Health and Medical Care Act [ 39 ] advocates for the respectful treatment of patients. Hence, it is noteworthy that the women experienced being judged by the looks of their genital area in their medical encounters rather than HCPs addressing the functionality. Such treatment does not align with the legislation and calls for a discourse analysis of the attitudes of HCPs towards women with persistent SPT-related health problems and their experiences of providing care for affected women.
Being subjected to obstetric gaslighting
In light of the women’s perception of their dismissal as dramatic, illegitimate, and irrational patients, we argue that they faced so-called ‘gaslighting’ in an obstetric context [ 65 , 66 ]. Thus, the women experienced being offered sick leave for mental problems instead of their perceived physical health problems, depicting them as hysterical women who exaggerated their condition. Gaslighting is a concept used in medicine in general [ 66 ] and in obstetrics regarding traumatic childbirth experiences [ 65 ]. The concept of hysteria, i.e., a prior medical diagnosis and historical concept theoretically linked to femininity [ 67 , 68 ] and ‘obstetric gaslighting’ [ 65 ], has also been found in research on women’s chronic pain [ 64 ] and endometriosis [ 69 ]. Men with chronic pain are perceived as brave, and women in pain are hysterical, emotional, whining, malingering, or imagining pain [ 64 ]. Further, women with endometriosis are viewed as ‘reproductive bodies’ with a proneness for hysteria [ 69 ]. Obstetric gaslighting, enforced by the normalisation of SPT-related health problems and the gendered stereotype of women as hysterical patients, puts women with SPT in an inferior position towards HCPs and can, therefore, be interpreted as a demonstration of institutional power [ 65 ]. Hence, being overlooked by the obstetric gaze might constitute a form of obstetric gaslighting, a concept that has not been applied to SPT before.
Implications and significance
Our study indicated that women continue to have problems accessing healthcare for persistent SPT-related health problems several years postpartum. Additionally, women with persistent SPT-related health problems often depended on a ‘key person’ with the competence to open the doors to comprehensive care, as shown in our findings. The Swedish Government launched a multi-million project from 2015 to 2022 to improve and promote women’s health [ 70 ]. Despite this investment, the depicted experiences of the included women reflect upon remaining structural and clinical problems within Swedish healthcare, which need further attention, investigation, and actions. Additionally, there are considerable differences in reported satisfaction and prevalence of complications at the one-year follow-up between the regions [ 3 ], indicating that there are suboptimal healthcare services. With a significant variation in satisfaction and recovery at one year, there are reasons to believe that women with prolonged problems may experience problems getting access to needed care.
Our study also showed that SPT-related healthcare services are not available on equal terms to women with persistent SPT-related health problems. In general, many women within this group had problems accessing care and sick leave for years. However, depending on where the women reside, not all women have access to specialised care. This inequity may be explained by Sweden having 21 self-governing health regions, and in the absence of national guidelines regarding SPT care and follow-up, the healthcare provision for affected women varies. To secure access to postpartum care for women with SPT in general and those with different prerequisites within this group, implementation studies are needed to develop and evaluate the effect of national guidelines for follow-up care regarding SPT.
Strengths and limitations
This study has strengths and limitations that need to be addressed. A significant strength, enhancing credibility and transferability, was providing a clear context and thick descriptions of our results, where we thoroughly portrayed the women’s voices using quotations [ 35 ]. Further, our detailed account of the study context, data collection, and data analysis process facilitated the transferability of our study. Including three women born outside of Sweden added to the variety of the sample and thus improved credibility because qualitative research often overlooks immigrants' experiences. However, the migrant women spoke Swedish well enough to participate in an interview, indicating that they have been living in Sweden for some time and might be familiar with the healthcare system. Finally, the credibility and dependability of this study were also strengthened by the frequent use of interdisciplinary triangulation between the authors throughout data analysis and the writing process, as well as peer review at a research seminar.
A potential limitation was that this study may not have fully explored the situation of women with fourth-degree lacerations or those with lower education, as most participants had third-degree perineal lacerations and higher education. Further, we could not include non-binary persons and same-sex or single parents, which may be a weakness; consequently, future studies should focus on the under-represented participant groups and migrant women needing an interpreter. Additionally, all women responded voluntarily to the study invitation. Thus, our participants might be particularly outspoken about their problems or interested in raising their voices or experiences. However, they represented a variety of persistent SPT-related health problems of various severity, and some had been able to get access to medical help, whereas others had not. Additionally, our findings cohered to similar studies [ 12 , 17 ] covering shorter periods after the SPT, which may indicate that the experiences of the challenging search for needed help remain over time. Therefore, our findings may reflect other women’s experiences seeking care for SPT-related health problems and may be transferable to other women’s experiences with persistent health problems of a rare condition.
The data for this study was comprehensive and rich. Information power in qualitative research is an ongoing discussion, and the number of participants and their representativity can be seen as a limitation of credibility and transferability [ 71 , 72 ]. Graneheim, Lindgren and Lundman [ 36 ] argue that sample size should be determined by the study’s aim and the data’s quality so that variations in experiences can be captured. They do, therefore, not recommend a specific number of participants, but others do [ 71 ]. With this in mind, the authors believe that the women’s detailed descriptions of the included concepts and the extensive length of the conducted interviews enabled us to achieve sufficient information power based on the richness of the data [ 72 ].
By qualitatively exploring how women with persistent SPT-related health problems experienced their healthcare encounters, we interpreted that they faced a paradox of being reassured of normality by HCPs despite reporting sequelae symptoms. Thus, women’s needs for medical care, rehabilitation, and sick leave were largely neglected. Further, our study might indicate a structural problem within women’s postpartum healthcare, indicating that access to care depended on encountering a ‘key person’, a professional who acknowledged persistent problems as real symptoms. Access to quality care provided with a professional attitude was essential for the future well-being of women with persistent SPT-related health problems. Thus, it should not depend on meeting a single ‘key person’. Therefore, national guidelines for long-term postpartum care of persistent SPT-related health problems must be developed in Sweden. Additionally, to ensure that healthcare services meet the individual needs of women with persistent SPT-related health problems, it is crucial to consider arranging the organisation and availability of quality care for these women from a woman-centred perspective.
Availability of data and materials
The original recordings and transcripts from the current study are not publicly available due to securing the individual privacy and confidentiality of the participants. Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Healthcare professionals
Interquartile range
Strategic Research Area Health Care Science
- Severe perineal trauma
Sexual and reproductive health and rights
World Health Organisation
World Health Organization (WHO). WHO recommendations: Intrapartum care for a positive childbirth experience. Geneva: WHO; 2018. Cited 2024 Feb 14. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241550215 .
Leap N. Woman-centred or women-centred care: does it matter? Br J Midwifery. 2009;17(1):12–6.
Article Google Scholar
Uustal E. Bristning vid förlossning grad 3 - 4. Årsrapport från GynOp-registret avseende operationer utförda år 2022. [Laceration at childbirth, grade 3 - 4, Annual Report of surgeries 2022]. Umeå: The Swedish National Quality Register of Gynecological Surgery; 2023. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://www.gynop.se/rapporter/arsrapporter/ .
World Health Organization (WHO). International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems (ICD) 10th revision. Geneva: WHO; 2019. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://icd.who.int/browse10/2019/en .
d’Almeida I. Women’s experiences following obstetric anal sphincter injury. J Pelvic Obstet Gynaecol Physiother. 2020;127:39–50.
Google Scholar
Darmody E, Bradshaw C, Atkinson S. Women’s experience of obstetric anal sphincter injury following childbirth: An integrated review. Midwifery. 2020;91:102820.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
LaCross A, Groff M, Smaldone A. Obstetric anal sphincter injury and anal incontinence following vaginal birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Midwifery Women’s Health. 2015;60(1):37–47.
Samarasekera DN, Bekhit MT, Wright Y, Lowndes RH, Stanley KP, Preston JP, et al. Long-term anal continence and quality of life following postpartum anal sphincter injury. Colorectal Dis. 2008;10(8):793–9.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Andreucci CB, Bussadori JC, Pacagnella RC, Chou D, Filippi V, Say L, et al. Sexual life and dysfunction after maternal morbidity: a systematic review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2015;15:307.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Beck CT. Effects of fourth-degree perineal lacerations on women’s physical and mental health. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2021;50(2):133–42.
Keighley MR, Perston Y, Bradshaw E, Hayes J, Keighley DM, Webb S. The social, psychological, emotional morbidity and adjustment techniques for women with anal incontinence following Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injury: use of a word picture to identify a hidden syndrome. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16(1):275.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lindqvist M, Lindberg I, Nilsson M, Uustal E, Persson M. “Struggling to settle with a damaged body” - A Swedish qualitative study of women’s experiences one year after obstetric anal sphincter muscle injury (OASIS) at childbirth. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2019;19:36–41.
Shoorab NJ, Taghipour A, Mirteimouri M, Roudsari RL. Social recovery: a neglected dimension of caring for women with perineal trauma in Iran. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2020;25(4):333–40.
Jahani Shoorab N, Mirteimouri M, Taghipour A, Latifnejad Roudsari R. Women’s experiences of emotional recovery from childbirth-related perineal trauma: a qualitative content analysis. Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2019;7(3):181–91.
PubMed Google Scholar
Swedish Agency for Health Technology Assessment and Assessment of Social Services. Practices to improve detection of perineal tears and women’s views and experiences of healthcare providers following sustained perineal tear. A systematic review. 2021. Report No.: 323.
Persson M, Lindberg I, Ohman A. Regional and clinical guidelines for prevention and care of obstetric anal sphincter injuries - A critical frame analysis. Midwifery. 2023;119:103608.
Huber M, Tunon K, Lindqvist M. “From hell to healed” - A qualitative study on women’s experience of recovery, relationships and sexuality after severe obstetric perineal injury. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2022;33:100736.
Priddis HS, Schmied V, Kettle C, Sneddon A, Dahlen HG. “A patchwork of services”–caring for women who sustain severe perineal trauma in New South Wales–from the perspective of women and midwives. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2014;14:236.
Priddis H, Schmied V, Dahlen H. Women’s experiences following severe perineal trauma: a qualitative study. BMC Womens Health. 2014;14(1):32.
Williams A, Lavender T, Richmond DH, Tincello DG. Women’s experiences after a third-degree obstetric anal sphincter tear: a qualitative study. Birth. 2005;32(2):129–36.
Herron-Marx S, Williams A, Hicks C. A Q methodology study of women’s experience of enduring postnatal perineal and pelvic floor morbidity. Midwifery. 2007;23(3):322–34.
Crookall R, Fowler G, Wood C, Slade P. A systematic mixed studies review of women’s experiences of perineal trauma sustained during childbirth. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74(9):2038–52.
Priddis H, Dahlen H, Schmied V. Women’s experiences following severe perineal trauma: a meta-ethnographic synthesis. J Adv Nurs. 2013;69(4):748–59.
Tjernström K, Lindberg I, Wiklund M, Persson M. Negotiating the ambiguity of an (in)authentic working life: a grounded theory study into severe perineal trauma. BMC Women’s Health. 2023;23(1):47.
Lindqvist M, Persson M, Nilsson M, Uustal E, Lindberg I. “A worse nightmare than expected” - a Swedish qualitative study of women’s experiences two months after obstetric anal sphincter muscle injury. Midwifery. 2018;61:22–8.
United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2022. New York City: United Nations; 2022. Cited 2024 Feb 24. Available from: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2022/ .
Fahy K, Foureur M, Hastie C. Birth territory and midwifery guardianship : theory for practice, education, and research. Edinburgh: Books for Midwives; 2008.
Walsh D, Christianson M, Stewart M. Why midwives should be feminists. Midirs Midwifery Digest. 2015;25(2):154–60.
Buchanan K, Newnham E, Geraghty S, Whitehead L. Navigating midwifery solidarity: a feminist participatory action research framework. Women Birth. 2023;36(1):e169–74.
Benoit B, Goldberg L, Campbell-Yeo M. Infant feeding and maternal guilt: The application of a feminist phenomenological framework to guide clinician practices in breast feeding promotion. Midwifery. 2016;34:58–65.
Westergren A, Edin K, Walsh D, Christianson M. Autonomous and dependent-The dichotomy of birth: a feminist analysis of birth plans in Sweden. Midwifery. 2019;68:56–64.
Alspaugh A, Barroso J, Reibel M, Phillips S. Women’s contraceptive perceptions, beliefs, and attitudes: an integrative review of qualitative research. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2020;65(1):64–84.
Davis DL, Walker K. Re-discovering the material body in midwifery through an exploration of theories of embodiment. Midwifery. 2010;26(4):457–62.
Govender V, Penn-Kekana L. Gender biases and discrimination: a review of health care interpersonal interactions. Global Public Health. 2008;3(sup1):90–103.
Graneheim UH, Lundman B. Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures and measures to achieve trustworthiness. Nurse Educ Today. 2004;24(2):105–12.
Graneheim UH, Lindgren BM, Lundman B. Methodological challenges in qualitative content analysis: a discussion paper. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;56:29–34.
Lindgren BM, Lundman B, Graneheim UH. Abstraction and interpretation during the qualitative content analysis process. Int J Nurs Stud. 2020;108:103632.
Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19(6):349–57.
Ministry of Health and Social Affairs. Hälso- och sjukvårdslag (2017:30) [Health and Medical Care Act]. Stockholm: The Swedish Riksdag; 2017. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://www.riksdagen.se/sv/dokument-och-lagar/dokument/svensk-forfattningssamling/halso-och-sjukvardslag-201730_sfs-2017-30/ .
The Swedish Social Insurance Agency. Parental benefits. 2023. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://www.forsakringskassan.se/english/parents/when-the-child-is-born/parental-benefit .
The Swedish Association of Midwives. Kompetensbeskrivning för legitimerad barnmorska [Description of competences for registered midwives]. Stockholm: The Swedish Association of Midwives; 2018. Updated 2019 Jan. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://storage.googleapis.com/barnmorskeforbundet-se/uploads/2020/04/Kompetensbeskrivning-for-legitimerad-barnmorska.pdf .
Bäckenbottenutbildning [Pelvic floor education]. Utbildningsmaterial: Uppföljning [Educational material: Follow-up]. 2022. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://backenbottenutbildning.se/index.php/utbildningsmaterial/uppfoljning .
GynOp [The Swedish National Quality Register of Gynecological Surgery]. About GynOp. 2023. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://www.gynop.se/home/about-gynop/ .
Öhman H, Schesny S, Bearth L, Löwendahl J. Förlossningsskadad? Du är inte ensam! [Injured at childbirth? You are not alone!’]. 2014. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://www.facebook.com/groups/forlossningsskadad/ .
Vanderbilt University. About REDCap. Nashville: Vanderbilt; 2023. Updated 2023. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://projectredcap.org/about/ .
Kvale S, Brinkmann S. Interviews: learning the craft of qualitative research interviewing. 2nd ed. Los Angeles: Sage Publications; 2009.
Keen S, Lomeli-Rodriguez M, Joffe H. From challenge to opportunity: virtual qualitative research during COVID-19 and beyond. Int J Qual Methods. 2022;21:16094069221105076.
Thunberg S, Arnell L. Pioneering the use of technologies in qualitative research - A research review of the use of digital interviews. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2022;25(6):757–68.
MAXQDA. Why MAXQDA? Berlin: VERBI Software GmbH; 2024. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://www.maxqda.com/why-maxqda .
Microsoft. Microsoft Excel. Redmond: Microsoft; 2024. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://www.microsoft.com/sv-se/microsoft-365/excel?market=se .
Griffin GA. Dictionary of Gender Studies. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2017.
Book Google Scholar
Abhyankar P, Uny I, Semple K, Wane S, Hagen S, Wilkinson J, et al. Women’s experiences of receiving care for pelvic organ prolapse: a qualitative study. BMC Womens Health. 2019;19(1):45.
Scott KD, Hintz EA, Harris TM. “Having pain is normal”: How talk about chronic pelvic and genital pain reflects messages from menarche. Health Commun. 2022;37(3):296–306.
Pettersson A, Bertero CM. How women with endometriosis experience health care encounters. Womens Health Rep (New Rochelle). 2020;1(1):529–42.
Heitmann K, Svendsen HC, Sporsheim IH, Holst L. Nausea in pregnancy: attitudes among pregnant women and general practitioners on treatment and pregnancy care. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2016;34(1):13–20.
Roper JC, Amber N, Wan OYK, Sultan AH, Thakar R. Review of available national guidelines for obstetric anal sphincter injury. Int Urogynecol J. 2020;31(11):2247–59.
The Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. Third and Fourth Degree Perineal Tears Clinical Care Standard. Sydney: The Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care; 2021. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/standards/clinical-care-standards/third-and-fourth-degree-perineal-tears-clinical-care-standard .
Foucault M, Sheridan A. The birth of the clinic: an archaeology of medical perception. 3rd ed. London: Routledge; 2003.
Scarf VL, Rossiter C, Vedam S, Dahlen HG, Ellwood D, Forster D, et al. Maternal and perinatal outcomes by planned place of birth among women with low-risk pregnancies in high-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Midwifery. 2018;62:240–55.
Offerhaus P, Jans S, Hukkelhoven C, de Vries R, Nieuwenhuijze M. Women’s characteristics and care outcomes of caseload midwifery care in the Netherlands: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20(1):517.
Forster DA, McLachlan HL, Davey MA, Biro MA, Farrell T, Gold L, et al. Continuity of care by a primary midwife (caseload midwifery) increases women’s satisfaction with antenatal, intrapartum and postpartum care: results from the COSMOS randomised controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16:28.
Brady S, Lee N, Gibbons K, Bogossian F. Woman-centred care: an integrative review of the empirical literature. Int J Nurs Stud. 2019;94:107–19.
Findlay D. The medical gaze: medical models, power, and women’s health. Atlantis. 1992;18(1&2):104–24.
Samulowitz A, Gremyr I, Eriksson E, Hensing G. “Brave Men” and “Emotional Women”: a theory-guided literature review on gender bias in health care and gendered norms towards patients with chronic pain. Pain Res Manag. 2018;2018:6358624.
Fielding-Singh P, Dmowska A. Obstetric gaslighting and the denial of mothers’ realities. Soc Sci Med (1982). 2022;301:114938.
Sebring JCH. Towards a sociological understanding of medical gaslighting in western health care. Sociol Health Ill. 2021;43(9):1951–64.
Jones CE. Wandering wombs and “female troubles”: the hysterical origins, symptoms, and treatments of endometriosis. Women Stud. 2015;44(8):1083–113.
Tasca C, Rapetti M, Carta MG, Fadda B. Women and hysteria in the history of mental health. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. 2012;8:110–9.
Young K, Fisher J, Kirkman M. “Do mad people get endo or does endo make you mad?”: Clinicians’ discursive constructions of Medicine and women with endometriosis. Fem Psychol. 2019;29(3):337–56.
The Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs. Överenskommelse om en förbättrad förlossningsvård och insatser för kvinnors hälsa [Agreement on improving maternity care and women's health] [Internet]. Stockholm: The Swedish Government; 2015. S2015/07777/FS. [cited 2024 Maj 8]. Available from: https://www.regeringen.se/overenskommelser-och-avtal/2015/12/overenskommelse-om-en-forbattrad-forlossningsvard-och-insatser-for-kvinnors-halsa/ .
Boddy CR. Sample size for qualitative research. Qual Mark Res. 2016;19(4):426–32.
Malterud K, Siersma VD, Guassora AD. Sample size in qualitative interview studies: guided by information power. Qual Health Res. 2016;26(13):1753–60.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We want to thank the participating women for generously sharing their experiences.
Open access funding provided by Umea University. This work was supported by the Research Lift (SWE: Forskningslyftet) and Strategic Research Area Health Care Science (SFO-V), Umeå University. The funders had no specific role in the conceptualisation, design, data collection, analysis, publication decision, or manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Nursing, Umeå University, 901 87, Umeå, Sweden
Katharina Tjernström, Inger Lindberg & Margareta Persson
Department of Community Medicine and Rehabilitation, Section of Physiotherapy, Umeå University, 901 87, Umeå, Sweden
Maria Wiklund
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
KT: conceptualisation; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; validation; visualisation; writing - original draft; writing - review & editing. IL: conceptualisation; methodology; supervision; visualisation; writing - review & editing. MW: conceptualisation; methodology; supervision; visualisation; writing - review & editing. MP: conceptualisation; data curation; funding acquisition; methodology; project administration; supervision; visualisation; writing - review & editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Katharina Tjernström .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The Swedish Ethical Review Authority approved the study. An amendment to the original ethical approval of the research project to further explore the experiences of encounters with healthcare services was obtained (Dnr: 2020-035410908 and Dnr: 2022-02784-02). The study was undertaken in compliance with research ethics guidelines. All participation was voluntary, and participants received oral and written information about the study and provided written informed consent before the interviews. No interview questions were mandatory, and the women decided if and how detailed they wanted to share their experiences.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
12913_2024_11037_moesm1_esm.pdf.
Additional file 1. Semi-structured interview guide for individual interviews; contains interview questions aimed at highlighting the experience of everyday life and working life after suffering 3 rd or 4 th degree perineal laceration at childbirth (i.e., severe perineal trauma [SPT]).
Additional file 2. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative studies (COREQ): 32-item checklist.
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Tjernström, K., Lindberg, I., Wiklund, M. et al. Overlooked by the obstetric gaze – how women with persistent health problems due to severe perineal trauma experience encounters with healthcare services: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 610 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11037-5
Download citation
Received : 11 September 2023
Accepted : 23 April 2024
Published : 09 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11037-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Persistent health problems
- Qualitative content analysis
- Healthcare encounters
- Postpartum healthcare
- Normalisation
- Access to care
- Empowerment
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Exploring Quantitative Biological Major, Trace, and Ultratrace Elements Composition and Qualitative Primary-Secondary Metabolites in Lamiaceae Medicinal Plants from Turkey
- Open access
- Published: 14 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Enes Tekman 1 ,
- Tugay Asgarlı 2 ,
- Hafize Yuca 2 ,
- Alptuğ Atila 3 ,
- Ömer Çeçen 4 &
- Songül Karakaya 1
35 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Medicinal plants comprise a spectrum of constituents, encompassing both organic and inorganic elements. Elemental composition of 27 species of medicinal plants of Lamiaceae (including 17 endemic) family grown in Turkey was carried out by ICP-MS. The following elements were determined in analysed samples: Na, Mg, Al, K, Ca, Sc, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Zn, As, Rb, Sr, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Sm, U, Se. Quantitative analysis of specific primary and secondary metabolites was carried out. Na and K are major constituents in plants. The concentrations of Na range from 332,495.590 g/kg (in sample 10SA) to 279,690.674 g/kg (in sample 4SA), while those of K vary from 67,492.456 g/kg (in sample 15SA) to 3347.612 g/kg (in sample 1A). Some metals such as Al, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Zn, As, Se, Rb, Sr, Cs, and Ba were also detected. Flavonoids, carbohydrates and tannins were present in all sample. Saponins were found in all samples except 1C and 2O. Coumarin were detected in samples 2N, 1 T, 1O, 1Z, 3SA, 1C, 4SA, 6SA, 8SA, 1 M, 11SA, 13SA, 2O, 14SA, 1H, and 16SI. Lipids were present in samples 6S, 9S, 1A, 10S, 1 M, 11SA, 12SA, 13SA, 14SA, and 16SI. Plants contain essential, rare earth, and trace elements at mg/kg concentrations, while major elements such as K and Na are present in high levels. Toxic element As (arsenic) was detected in all analyzed plants, but in most samples, its concentration was below the threshold set by World Health Organization.
Graphical Abstract
Similar content being viewed by others
Evaluation of essential and non-essential elemental composition of commonly used medicinal plants from district Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan

Investigation of Heavy Metal Level and Mineral Nutrient Status in Widely Used Medicinal Plants’ Leaves in Turkey: Insights into Health Implications
Heavy metals and trace elements detected in the leaves of medicinal plants collected in the southeast part of Turkey
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Medicinal plants comprise a spectrum of constituents, encompassing both organic and inorganic elements. The presence of macronutrients and trace (micro-) elements in medicinal plants serves as a rich source, playing a pivotal role in preventing a myriad of diseases [ 1 ]. Herbal remedies derived from medicinal plants have been employed as therapeutic agents since ancient times. Various plant components, including leaves, flowers, stems, roots, seeds, and bark, are utilized either individually or in synergistic combinations for their medicinal properties. The efficacy of these plants lies in their bioactive phytochemical constituents, which elicit specific physiological responses in the human body. Phytochemicals can be broadly categorized into two groups based on their functions within the plant. Primary metabolites (PMs), such as sugars, amino acids, proteins, lipids, and chlorophyll, are essential for basic growth processes. In contrast, secondary metabolites (SMs), including alkaloids, essential oils, flavonoids, tannins, terpenoids, saponins, phenolic compounds, and cardiac glycosides, play a crucial role in the plant's defense mechanisms against herbivores and other inter-species threats. These SMs contribute to the intricate pharmacological profile of medicinal plants, making them valuable resources in traditional and modern medicine alike. SMs in plants serve not only as a diverse array of natural products but also play a crucial role in fortifying the plant's defense mechanisms against pathogenic assaults and environmental stressors. Possessing noteworthy biological activities, these plant SM are gaining prominence as key components in medicinal formulations and food additives, catering to therapeutic, aromatic, and culinary needs. Research into plant secondary metabolites has witnessed a steady rise over the past five decades [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ].
In the realm of agricultural science, prevailing challenges affecting global crop production encompass issues related to nutrient management, the presence of heavy and toxic metals, and the quest for optimal plant productivity. Plants, enduring for numerous decades, exhibit a diverse composition of elements in varying proportions. The elements present in plants are broadly categorized as either macronutrients, including Ca, K, Mg, N, P, and S, or micronutrients such as B, Cu, Cl, Fe, Mn, Mo, Na, and Zn. These elements play a pivotal role in the developmental processes and growth of plants, underscoring their significance in the agricultural landscape [ 6 ]. Plants frequently assimilate nutrients in quantities surpassing their immediate requirements, necessitating the storage of these excess nutrients within plant tissues until they are needed. Despite the selective uptake of essential micro- and macronutrients and the implementation of sophisticated exclusion mechanisms, plants unavoidably absorb elements that possess toxicity [ 7 ]. Elements exist in various forms in nature, and their presence is indispensable for the body to execute diverse functions. Trace elements hold paramount importance in facilitating cellular functions at biological, chemical, and molecular levels. These elements play a pivotal role in orchestrating important biochemical reactions by serving as cofactors for numerous enzymes and acting as central components for stabilizing the structures of enzymes and proteins. Certain elements exert control over crucial biological processes by binding to molecules on the receptor sites of cell membranes or by altering the membrane structure to impede the entry of specific molecules into the cell. The functions of trace elements exhibit a dual nature; at normal levels, they are crucial for stabilizing cellular structures, yet in deficiency states, they may stimulate alternative pathways, leading to various diseases. Disruptions in the balance of trace elements can lead to the onset of pathological conditions and diseases [ 8 , 9 ].
The Lamiaceae , commonly known as the mint family, exhibits a broad distribution across various natural ecosystems, encompassing 236 genera. Characterized by square stems in cross-section, opposite leaves, and zygomorphic flowers with five united petals and sepals, these aromatic plants are cultivated for their straightforward propagation through methods such as stem cutting [ 10 ]. The Lamiaceae (Labiatae) family boasts numerous medicinal plants of considerable value. Within this family, there are an estimated 6900 to 7200 species. Among the most prolific genera are Salvia (with approximately 900 species), Scutellaria (360 species), Stachys (300 species), Plectranthus (300 species), Hyptis (280 species), Teucrium (250 species), Vitex (250 species), Thymus (220 species), and Nepeta (200 species) [ 11 ]. Lamiaceae stands as the third-largest family in terms of taxon number and the fourth-largest based on species count in Turkey. With 48 genera and a total of 782 taxa (603 species, 179 subspecies, and varieties), 346 of these taxa (comprising 271 species, 75 subspecies, and varieties) are endemic, constituting approximately 44% of the family's diversity in the country (data updated as of February 1, 2017). Additionally, there are 23 hybrid species, 19 of which exhibit endemism (82%). These findings underscore Turkey's significance as one of the primary centers of diversity for Lamiaceae in the Old World. The flora of Turkey holds significant importance for the Lamiaceae family [ 10 , 12 ]. Lamiaceae is celebrated for housing a variety of active secondary metabolites that hold substantial biological and economic significance. These compounds encompass volatile oils containing monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, triterpenes, phenolic acids, flavonoids, and other substances, each contributing diverse properties [ 13 ].
The majority of species within this plant family are known for their aromatic qualities and contain essential oils, rendering them highly valuable in the fields of cosmetics, perfumery, agriculture, food, and medicine [ 14 ]. Throughout history, the species belonging to the Lamiaceae family have held a storied tradition of utilization for flavoring, food preservation, and medicinal applications, owing to their dual benefits of healing and preventative attributes. It is widely acknowledged that each species possesses a unique and intricate blend of bioactive compounds, where each component plays a role in its overall bioactivity. These plants are highly esteemed for their capability to produce an extensive array of secondary metabolites, showcasing potent antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antiviral, and anticancer activities [ 15 ].
The trace elements are presently recognized and classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) into three groups: essential elements, elements considered likely to be essential, and elements with potential toxicity. Man necessitates essential trace elements in quantities spanning from 50 µg to 18 mg per day, wherein they function as catalytic or structural components within larger molecules [ 16 ]. In our study, the major elements identified in Lamiaceae plants are sodium (Na) and potassium (K). Sodium and potassium play indispensable roles in human health, serving as crucial ions within the body and being intricately linked to numerous physiological and pathophysiological processes [ 17 ].
In this research, we undertook an evaluation of various elements in 27 (including 17 endemic) herb species belonging to the Lamiaceae family, gathered in Turkey, utilizing ICP-MS analysis. Moreover, a quantitative analysis of specific primary and secondary metabolites was carried out. A substantial number of the analyzed herbs are readily available and widely utilized voluntarily by the entire population of the country.
Material and Method
Plant materials.
The names of the plants used, the localities where they were collected, their herbarium numbers and endemism status are given in Table 1 . A map showcasing the plant collecting sites across Turkey is presented in Fig. 1 .
A map showcasing the plant collecting sites across Turkey
The extraction process utilized in the study involved a mobile maceration technique, wherein 10 g of the dried flowering above-ground parts of each plant were meticulously weighed and then transformed into powder form. Subsequently, this powdered plant material was subjected to a mobile maceration process with 150 ml methanol (after 8 h, it was filtered and 150 ml of methanol was added again and this process was continued for 3 days), which typically involves soaking the plant material in a solvent at room temperature for a specific duration. During the mobile maceration process, the powdered plant material was immersed in a suitable solvent. The choice of solvent can vary depending on the specific compounds being targeted for extraction and their solubility characteristics. Commonly used solvents for maceration with methanol. The duration of maceration typically ranged from 3 to 8 h at room temperature. This duration allows sufficient time for the solvent to penetrate the plant material and extract the desired compounds. After the designated maceration period, the filtrates obtained from each day's extraction were systematically combined. Subsequently, the combined filtrates underwent evaporation using a rotavapor. Rotavapor, short for rotary evaporator, is a common laboratory instrument used for gentle evaporation of solvents from a mixture under reduced pressure. This process helps concentrate the extracted compounds, leaving behind a more concentrated extract for further analysis. Overall, the mobile maceration process employed in the study involved soaking the powdered plant material in a solvent for a specific duration at room temperature to facilitate the extraction of bioactive compounds. This method allows for efficient extraction while preserving the integrity of the extracted compounds. At the conclusion of each day, the filtrates were systematically amalgamated and subjected to evaporation using a rotavapor.
Qualitative Analysis of Secondary and Primary Metabolites
Detection of alkaloids.
The methanolic extract of each species was weighed 0.5 g, 10 ml of 70% ethanol solution (containing 6% H 2 SO 4 ) was added, boiled for 1 min and was cooled. Some of the extract was separated into 2 tubes and Mayer and Dragendorff reagents were added. The samples were checked for the appearance of precipitates and further experiments were continued for the samples in which precipitates were observed. After this control, the ethanol extract was alkalinized with a 25% Na 2 CO 3 solution. Then, extracted with 15 ml of chloroform, the chloroformed layer was taken into a clean separating funnel and extracted with 15 ml of 10% acetic acid solution. The acetic acid phase was divided into three separate tubes and one tube was kept as a control, the second tube added Mayer's reagents and the third tube added Dragendorff's reagents. It was checked for the precipitate formation [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Detection of Flavonoids
The methanolic extract of each species was weighed 0.5 g and extracted with water. The test solution was extracted with ethyl acetate into a separatory funnel and the ethyl acetate phase was capsulated and dried in a water bath. The residue remaining in the capsule was dissolved with a mixture of HCl:MeOH:H 2 O (1:1:1) and transferred to a test tube. After adding Mg powder, the color was observed and the flavonoid was identified [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Detection of Cardioactive Heterosides
The methanolic extract of each species was weighed 0.5 g and prepared as a solution with 10 ml 70% ethanol. Add 1 ml of concentrated lead subacetate solution to the solution, mixed and filtered. The filtrate was extracted with 10 ml of chloroform, the chloroform layer was separated, taken into a capsule and evaporated. Add 3 ml of 3.5% glacial acetic acid solution of FeCl 3 to the capsule and carefully transfer to 2 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid in a test tube to form a layer. The colors seen on the surface of the separation and in the acetic acid layers were observed [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Detection of Saponosides
The methanolic extract of each species was taken 0.5 g and placed in a test tube with 10 ml of hot water. After cooling, the tube was shaken strongly for 10 s. If saponoside was present, a 1–10 cm high foam layer was observed which remained stable for at least 10 min. Then 1–2 drops of 2N HCl were added and the persistence of the foam layer was observed. The methanolic extract of 0.5 g of each species was dissolved in chloroform and filtered. Add an equal volume of concentrated H 2 SO 4 to the filtrate. The presence of fluorescence color in the chloroform layer and in the acidic layer was observed. The reaction is based on the coloration of the [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Detection of Anthocyanosides
The methanol extract of each species was extracted in 50% ethanol. The extract was filtered, the filtrate was separated into five portions and the following reactions were performed:
The addition of diluted H 2 SO 4 resulted in the formation of red color.
First NaOH solution was added, then diluted HCl was added and the colors were observed.
The precipitate was observed with a 10% lead acetate solution.
Added a volume of amyl alcohol, shaken and observed the coloration of the layers [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Detection of Tannins
The methanol extract of each species was taken in a spatula to make an aqueous extract. The extract was divided into 3 parts and the following reactions were applied:
2 ml of 1% 1% saline gelatin solution (saturated with NaCl) was added and the precipitate was observed.
Tannins give a color reaction with iron salts. This reaction was determined with 5% FeCl 3 . Olive green and blue-black color formation was observed.
Brominated water was added and the precipitate were observed [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Detection of Anthracene Heterosides
The methanol extract of each species was taken at 0.5 g and boiled with diluted H 2 SO 4 . After filtering while hot, the filtrate was cooled. The extract was extracted with ether to eliminate the ether layer and shaken with 10% ammonia solution. The color in the underlying ammonia layer was observed [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Detection of Coumarin
The methanol extract of each species was taken 0.5 g, extracted in 10 ml ethanol and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated to dryness in a capsule and 1N NaOH solution was added. It was transferred into a tube and checked for fluorescence color at UV 366 nm [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Detection of Starch
The methanol extract of each species was taken 0.5 g and aqueous extract was prepared. Add a few drops of 0.1 N Iodine solution. The formation of purple color was checked [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Detection of Lipid
The extract of each species was made with petroleum ether and 5 ml was taken in a glass tube. It was concentrated in a water bath and applied as a stain on a filter paper. The filter paper was allowed to dry in an oven at 100 °C for 5 min. The oily stain was observed on the paper [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Detection of Carbohydrates
The methanol extract of each species was weighed 1 g and 6 ml of water was added to make an aqueous extract. It was filtered and the filtrate was divided into 3 tubes. The following experiments were applied to the solutions in the tubes respectively:
2 ml of Fehling A and 2 ml of Fehling B solutions were added to an empty tube and mixed. Then the test solution was added to it. The tube was heated and red colored precipitate.
1–2 drops of 15% solution of 1-naphthol in ethanol was added to 1 ml of the test solution. To this mixture, 1 ml of concentrated H 2 SO 4 . Purple ring formation was observed between the two layers.
Add a few crystals of resorcin to 1 ml of test solution. To this 1 ml of concentrated HCl was added and kept in a water bath. The presence of red color was observed [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Detection of Cyanogenetic Heterosites
0.5 g of the methanol extract of each species was taken into a flask and some water was added. The filter paper was wetted first with picric acid and then with sodium carbonate solution. The wetted filter paper was dropped into the flask. The flask was heated and red color formation was observed on the yellow colored filter paper [ 18 , 19 , 20 ].
ICP-MS Analysis of 21 Elements
The determination of elemental concentrations in the solution was carried out using an Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometer (ICP-MS), specifically the Agilent 7800 series provided by Agilent Technologies in Japan. For sample introduction, a glass MicroMist nebulizer from U-series in Australia and a double-pass quartz spray chamber from the USA were employed. The plasma system included a quartz torch (2.5 mm) and nickel components, including a sample cone and skimmer cone for the x-lens. Before sample analysis, all quartz and nickel components underwent a meticulous cleaning process. Quartz and glass elements were soaked in a 5–10% HNO 3 solution overnight, thoroughly rinsed with distilled water, dried in an oven, and then installed on the device. Nickel components, such as sample and skimmer cone pieces, underwent ultrasonic baths in pure water, 5% HNO 3 solution, and distilled water successively for five minutes each. Following this, they were cleaned with a cotton ball, rinsed thoroughly with distilled water, and dried in the oven before installation on the device. Before analysis, the device underwent a 45-min helium gas purge. Activation was followed by adjusting parameters, including Plasma gas (15 L/min), auxiliary gas (1 L/min), carrier gas (1 L/min), makeup/dilution gas (1 L/min), and carrier gas pressure (1.45 kPa). The plasma gas, auxiliary gas, carrier gas, and makeup/dilution gas were Argon (Ar).Torch axis, resolution axis, EM, standard lenses tune, plasma correction, full spectrum, and performance report tests were carried out sequentially. Calibration of the device utilized a tuning solution (1 µg/L Ce, Co, Li, Mg, Tl, Y). The values obtained during tuning were scrutinized to identify any deviations in the device. Standard solutions, prepared from stock solutions, were then analyzed, and calibration curves were verified within the standard reference range (0–10, 25, 50, 100, 250, 500 g/kg, mg/kg, and µg/kg for Na, Mg, Al, K, Ca, Sc, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Zn, As, Se, Rb, Sr, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Sm, and U elements.
Qualitative Analysis of Secondary Metabolites
The qualitative analysis of primary and secondary metabolites for the samples is detailed in Table 2 . Flavonoids were identified in all samples, while tannins were present in every sample. Saponins were found in all samples except 1C and 2O. Coumarin was detected in various samples, including 2N, 1 T, 1O, 1Z, 3SA, 1C, 4SA, 6SA, 8SA, 1 M, 11SA, 13SA, 2O, 14SA, 1H, and 16SI. Cardioactive heterosides were absent in all samples. Starch was identified solely in samples 4SA and 10SA. Lipids were present in samples 6S, 9S, 1A, 10S, 1 M, 11SA, 12SA, 13SA, 14SA, and 16SI, while carbohydrates were observed in all samples. Notably, no alkaloids, anthocyanosides, anthracene heterosides, or cyanogenetic heterosides were detected among the samples. The qualitative analysis data of primary and secondary metabolites for the methanolic extracts were provided in Table 2 .
Elemental Analysis
The analysis of the elemental composition of methanol extracts revealed notable variations in element concentrations, as outlined in Table 3 . Using ICP-MS, the methanol extracts were investigated for the presence of 21 elements, including Na, Mg, Al, K, Ca, Sc, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Zn, As, Rb, Sr, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Sm, U, and Se. The results indicated elevated levels of Na [ranging from 332,495.590 g/kg (in sample 10SA) to 279,690.674 g/kg (in sample 4SA) g/kg] and K [ranging from 67,492.456 g/kg (in sample 15SA) to 3347.612 g/kg (in sample 1A)]. Some heavy metals such as Al, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Zn, As, Se, Rb, Sr, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Sm (except samples 1SI, 2SA-12SA), and U (including samples 15SA and 16 SI) were also detected.
A comprehensive review of literature from 2002 to 2018 revealed various classes of secondary metabolites in this family, including flavonoids, fatty derivatives, and sterols [ 13 ].
In a review article, a total of 217 articles were selected from the initial search focusing on Lamiaceae , specifically those recognizing Mexican genera and species. The bioactive constituents identified in these genera predominantly include terpenes (both volatile and non-volatile) and phenolic compounds, particularly flavonoids in the form of glycosides and aglycones [ 22 ].
A review provided an overview of Nepeta species, focusing on their phytochemical characteristics. Terpenoids and phenolic compounds were predominantly identified through the application of chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques [ 23 ]. In another review, major constituents as nepetalactones, iridoids and their glucosides, diterpenes, triterpenes, and flavonoids, as well as essential oil, have been identified within Nepeta species [ 24 ]. The phytochemical composition and trace elements of Nepeta suavis were examined in an analysis. The findings unveiled the existence of bioactive components, including flavonoids, alkaloids, phenols, saponins, and tannins. Furthermore, the herb proved to be a rich reservoir of essential minerals such as Na, K, Ca, Mg, Zn, Fe, and P [ 25 ]. The volatile oils stand out as the primary constituents of the Thymus genus. In addition to these, the genus is rich in flavonoids, phenylpropanoids, tannins, organic acids, terpenoids, and phytosterols [ 26 ]. The Origanum genus exhibits chemical variations. Oregano, recognized for its distinctive flavor, is primarily associated with several plant species known for producing essential oils rich in carvacrol. Additionally, the genus consists of a diverse range of compounds, including terpenes, phenols such as phenolic acids, and flavonoids [ 27 ]. Numerous chemical constituents have been elucidated within the Sideritis genus, encompassing terpenes, flavonoids, essential oils, iridoids, coumarins, lignans, and sterols. Diterpenes, flavonoids, and essential oils are consistently present in nearly every species, serving as the primary components responsible for the pharmacological activity [ 28 ].
In a study, the aerial parts of Sideritis and Origanum species were analyzed for mineral contents, flavonoids, total phenols, and anthocyanins. K was found to be high in both plant species. In Sideritis , K contents ranged from 10,184.91 mg/kg ( Sideritis libanotica subsp. linearis ) to 17,182.86 mg/kg ( S. hispida ), while in Origanum , they ranged from 10,265.40 mg/kg ( Origanum majorana ) to 21,293.79 mg/kg ( O. vulgare ). Crude protein contents in Sideritis varied between 1.55% ( S. libanotica subsp. linearis ) and 7.83% ( S. perfoliata ), whereas protein contents in Origanum species ranged from 1.99% ( O. leptocladum ) to 5.51% ( O. vulgare ). Flavonoid contents in Sideritis plants ranged from 246.34 ( S. libatotica subsp. linearis ) to 2013.33 ( S. hololeuca ), and in Origanum plants, they varied from 345.38 ( O. onites ) to 1730.47 ( O. majorana ). For Origanum , K contents ranged between 10,265.40 mg/kg ( O. majorana ) and 21,293.79 mg/kg ( O. vulgare ) [ 29 ].
The terpenoids and flavonoids constitute the primary secondary metabolite constituents of Salvia , with over 80% being terpenoids, particularly abietane and clerodane diterpenoids. Notably, sesquiterpenoids and triterpenoids are relatively scarce in Salvia species. Numerous studies highlight the presence of flavonoids, triterpenoids, and monoterpenes, particularly in the flowers and leaves, while diterpenoids are predominantly found in the roots. However, literature surveys indicate that certain American Salvia species also contain diterpenoids in aerial parts, and in some Salvia species, triterpenoids and flavones are present in the roots [ 30 ]
In a research, Salvia officinalis , S. sclarea , S. pratensis , and S. nemorosa originating from Hungary and Transylvania were investigated for their tannin and flavonoid content. Significant differences (p < 0.05) were observed in tannin content between Hungarian and Transylvanian S. officinalis and flavonoid content between Hungarian and Transylvanian S. sclarea . Chromium content was notably high in all examined species. The element concentrations also differed significantly in aqueous extracts, with distinct dissolution rates. Notably, Hungarian S. officinalis exhibited elevated concentrations of Al, Fe, Mn, and Ti, possibly linked to soil pollution. Zinc accumulation was highest in Transylvanian S. officinalis and S. pratensis , while Hungarian S. nemorosa demonstrated elevated Li content. Chromium content was notably high in Hungarian S. officinalis and S. sclarea . Dissolution rates of elements varied widely among sage teas, showcasing significant differences in element concentrations (Al, B, Ba, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Na, P, S, Zn) and dissolution characteristics based on the sample and the element studied [ 31 ].
The genus Ziziphora has been extensively studied, and previous reports in the literature highlight its species as rich sources of valuable bioactive compounds, including sterols, fatty acids, caffeoyl derivatives, and flavonoids. Notably, among the different groups of natural compounds, flavonoids, flavones, and their derivatives exhibit the highest frequency in the separated and characterized bioactive compounds, contributing significantly to each profile [ 32 ].
In literature, studies have indicated that Cyclotrichium essential oils are abundant in phenolic and alcoholic compounds, along with monoterpenes. Phenolic compounds are widely believed to be abundant in most Cyclotrichium species. C. origanifolium is rich in flavonoid [ 33 ]. According to our knowledge, this is the first elemental analysis conducted on the Cyclotrichium genus.
A comprehensive review aimed to provide an in-depth summary of the genus Ajuga L. Currently, more than 280 chemical constituents have been isolated and characterized from Ajuga species, with neo-clerodane diterpenes and diterpenoids, phytoecdysteroids, flavonoids, and iridoids identified as the major bioactive compounds [ 34 ]. This study represents the inaugural investigation into the elemental analysis of Ajuga chamaepitys .
In a comprehensive literature review on the genus Marrubium , chemical characteristics were investigated. The biological effects of the plants are often attributed to the presence of diterpenes, sterols, phenylpropanoids, and flavonoids [ 35 ].
Hyssop ( Hyssopus sp. ) genus has been known with volatile oils. The genus also containe flavonoid in leaves, flowers, stalks, and roots during full flowering. Furthermore, hyssop seeds have fatty acid content in oil [ 36 ].
In a study conducted similarly to our research, the elemental composition of 45 medicinal plant species belonging to the Lamiaceae family in the Republic of Moldova was investigated. Various elements, including essential, rare earth, and trace elements (measured in μg/L), as well as major elements such as Ca, Cl, K, Mg, and Na (measured in mg/L), were determined in the analyzed samples. Despite the presence of the toxic element As in all plants, its concentration in the majority of samples was below the limit set [ 37 ].
The study conducted in Pakistan, aimed to investigate the phytochemical, and elemental aspects of five crucial medicinal plants from the Lamiaceae family, namely Mentha longifolia , M. piperita , M. spicata , Ocimum basilicum , and Rosmarinus officinalis , collected in Peshawar district. Quantitative analysis of macro- and microminerals identified 13 elements (C, N, O, Mg, K, P, S, Ca, Al, Si, Fe, Cl, and Na) present in varying amounts among species. Methanol extracts from leaves were analyzed for phytochemical constituents such as saponins, flavonoids, tannins, terpenoids, phlobatannins, steroids, and anthraquinones [ 38 ].
Another research aimed to analyze the elemental content of six medicinal plant species from the Lamiaceae family, predominantly found in the western part of Romania. The findings indicate that these medicinal plants are rich sources of nutrients, with high potassium (K) content, followed by calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), and zinc (Zn) [ 39 ].
A study explored the mineral elements of extract from N. italica subsp. cadmea . Mineral elements (P, Mg, K, Fe, Cu) were found in the extract [ 40 ]. A paper focused on the analysis of trace elements in the Indian medicinal plant Nepeta hindostana . The plant was identified as a rich source of essential trace elements as Na, K, Mg, Zn, Fe, and Mn [ 41 ].
A study investigated the concentrations of eleven mineral and trace elements (Mg, Ca, K, Fe, Mn, Al, Zn, Cu, Cd, Ni, and Pb) in various Thymus species in Turkey, including the Thymus cilicicus . The elemental concentrations (mg/g) in T. cilicicus were found to be 0.40 ± 0.02 (Pb), 0.20 ± 0.10 (Ni), 0.04 ± 0.01 (Cd), 10.70 ± 2.30 (Cu), 40.80 ± 4.70 (Zn), 191.0 ± 8.0 (Al), 19.0 ± 2.0 (Mn), 189.0 ± 2.0 (Fe), 12,250.0 ± 672.0 (K), 14,417.0 ± 1909.0 (Ca), and 4127.0 ± 1200.0 (Mg). T. cilicicus stands out as particularly rich in essential elements, with the highest concentrations observed for Ca, K, and Mg [ 42 ].
In a study, elemental concentrations in Ziziphora medicinal plants were analyzed. Samples were collected from the Eynali mountain region in the north of Tabriz, Iran. The study revealed varying concentrations of Al, Ca, K, Mg, Mn, Na, V, Cl, and Ti elements in powdered Ziziphora plants. Notably, Ziziphora plants exhibited richness in essential elements such as Mg, K, and Ca, all of importance for human health. Importantly, the concentration of the potentially toxic element, Al, was determined to be below the levels permitted by the World Health Organization (WHO) [ 43 ].
In research, to rationalize its medicinal applications and establish a biogeochemical link, the mineral elements (Na, K, Ca, Mg, Zn, Mn, Cu, Fe, Cr) present in the leaves and roots of Ajuga bracteosa were investigated. The herb exhibited comparatively higher amounts of chromium (25 mg per 100 g in leaves and 20 mg in roots), which may be associated with its traditional use as a remedy for diabetes. Additionally, the herb contains significantly higher levels of potassium (139 mg per 100 g in leaves and 159 mg in roots) compared to sodium (21 mg per 100 g in leaves and 29 mg in roots), suggesting a potential correlation with its use in managing hypertension [ 44 ].
According to our knowledge, this is the first elemental analysis conducted on the Marrubium globosum. In another study, instrumental neutron activation analysis identified twenty-two chemical elements in Marrubium vulgare . The study revealed that K was the dominant chemical element in the plant, constituting 4.40% of the mass. Ca and Fe mass fractions were also relatively high. Importantly, potential toxic elements in this Lamiaceae plant were found to be within the safety limits recommended by WHO/FAO [ 45 ].
A study considered four harvest heights (15, 25, 35, and 45 cm from the tip of the Hyssopus officinalis ) along with the residual stalks. Dependent variables included the accumulated content of elements (N, K, P, Ca, Mg, Cu, Zn, and Pb) at different heights. Results revealed that moving from the upper shoots towards the ground led to an increase in Mg, Ca, Cu, Zn, and Pb content by 22.67%, 43.74%, 12.87%, 39.02%, and 85.04%, respectively. Conversely, a downward trend was observed for N (50.16%) and K (6.41%) content, while an upward trend was noted for P (29.06%) content. In residual stalks, moving from upper shoots to the ground resulted in decreased Mg, Ca, Cu, Zn, and Pb contents by 1.01%, 21.03%, 9.11%, 17.02%, and 51.06%, respectively. However, N and P contents increased by 60.59% and 3.15%, respectively, with a 34.74% increase in P content [ 46 ].
The comprehensive analysis of primary and secondary metabolites, alongside elemental composition evaluation of methanol extracts, offers profound insights into the characteristics and potential functionalities of the samples. The ubiquitous presence of flavonoids and tannins across all samples hints at the antioxidant capabilities and potentially broader health-promoting effects of the plants under study. Flavonoids, renowned for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, stand as focal points in numerous health studies. Conversely, tannins, recognized for antimicrobial and antiviral attributes, contribute to the overall pharmacological profile of these plants. The absence of cardioactive heterosides suggests a lack of pronounced effects on cardiac function, which could be advantageous or constraining depending on the intended application of these botanicals. The detection of coumarin in varied samples sparks interest due to its diverse pharmacological spectrum, encompassing anticoagulant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial facets. This discovery implies that the plants may harbor therapeutic potential extending beyond mere antioxidant capacities. The presence of lipids in several samples and the occurrence of starch in select ones accentuate the nutritional diversity inherent in these botanicals. Lipids, vital constituents of cellular membranes, and starch, a pivotal energy source, contribute to the overall nutritional value of these plants. Regarding elemental composition, the elevated levels of sodium and potassium throughout the samples hint at their potential mineral richness. However, the identification of heavy metals like aluminum, chromium, and arsenic raises concerns regarding potential toxicity, particularly in samples exhibiting higher concentrations of these elements. The provided text offers a comprehensive overview of studies focusing on the Lamiaceae family, exploring the elemental composition and phytochemical characteristics of various plant species within this family. These studies shed light on the diverse array of bioactive compounds present in Lamiaceae plants, ranging from essential minerals to secondary metabolites like flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolic compounds. One notable aspect highlighted in the text is the prevalence of essential elements such as K, Ca, Mg, and Fe across different Lamiaceae species. These elements play crucial roles in various physiological processes, including enzymatic reactions, cellular signalling, and structural support. The abundance of these minerals underscores the potential nutritional significance of Lamiaceae plants in human diets. Additionally, the presence of bioactive compounds like flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolic compounds underscores the therapeutic potential of Lamiaceae plants. These compounds have been associated with various pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. The diverse chemical profile of Lamiaceae plants suggests their potential utility in traditional medicine and as sources of novel therapeutic agents. Furthermore, the studies discussed in the text also address the elemental variability among different Lamiaceae species, as well as the influence of environmental factors on elemental composition. Understanding these variations is crucial for assessing the nutritional quality and potential health benefits of Lamiaceae plants, as well as for elucidating their ecological roles and adaptation strategies. Overall, the findings presented in the text underscore the importance of interdisciplinary approaches in studying plant chemistry and ecology. Integrating elemental analysis with phytochemical profiling provides valuable insights into the nutritional, medicinal, and ecological significance of Lamiaceae plants, ultimately contributing to our understanding of their roles in human health and natural ecosystems.
In summary, these findings underscore the intricate nature of plant metabolites and emphasize the necessity for exhaustive analysis in deciphering their potential health implications. Further investigations, encompassing pharmacological and toxicological inquiries, are imperative for a comprehensive understanding of the therapeutic prospects and safety profiles associated with these botanicals.
In conclusion, the comprehensive analysis of 27 medicinal plant species from the Lamiaceae family in Turkey revealed a diverse spectrum of constituents, encompassing both organic and inorganic elements. The elemental composition, including 18 endemic species, was determined using ICP/MS, highlighting the presence of essential, rare earth, and trace elements at mg/kg concentrations. Major elements such as Na and K were found in elevated levels, demonstrating the richness of these plants in important nutrients. Despite the widespread detection of the toxic element As (arsenic), the concentrations in most samples remained below the World Health Organization's established threshold, assuring the safety of these medicinal plants. The inclusion of specific primary and secondary metabolites, such as flavonoids, tannins, saponins, coumarin, starch, lipids, and carbohydrates, further underscored the diverse chemical composition of these plants. Overall, this study provides valuable insights into the elemental and chemical profiles of medicinal plants from the Lamiaceae family, contributing to our understanding of their potential therapeutic properties and nutritional benefits. The presence of essential elements in trace amounts, coupled with the relatively low levels of toxic elements, reinforces the potential of these plants as valuable resources for traditional and modern medicine.
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
Jyothsna S, Manjula G, Suthari S, Rao AN (2020) Qualitative elemental analysis of selected potential anti-asthmatic medicinal plant taxa using EDXRF technique. Heliyon 6(2):e03260
Bourgaud F, Gravot A, Milesi S, Gontier E (2001) Production of plant secondary metabolites: a historical perspective. Plant Sci 161:839–851
Article CAS Google Scholar
Saxena HO, Soni A, Mohammad N, Choubey SK (2014) Phytochemical screening and elemental analysis in different plant parts of Uraria picta Desv.: a Dashmul species. J Chem Pharm Res 6:756–760
Google Scholar
Tiwari R, Rana CS (2015) Plant secondary metabolites: a review. Int J Eng Res Gen Sci 3:661–670
Yang L, Wen K-S, Ruan X et al (2018) Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 23:762
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Singh VK, Sharma N, Verma ON et al (2021) application of LIBS to elemental analysis and mapping of plant samples. Spectrosc 42:99–113
CAS Google Scholar
Conn S, Gilliham M (2010) Comparative physiology of elemental distributions in plants. Ann Bot 105:1081–1102
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Prashanth L, Kattapagari KK, Chitturi RT et al (2015) A review on role of essential trace elements in health and disease. J Dr YSR Univ Health Sci 4:75–85
Article Google Scholar
Skalnaya MG, Skalny AV (2018) Essential trace elements in human health: a physician’s view. Tomsk Publ House Tomsk State Univ 224:1–222
Ebadollahi A, Ziaee M, Palla F (2020) Essential oils extracted from different species of the Lamiaceae plant family as prospective bioagents against several detrimental pests. Molecules 25:1556
Karpiński TM (2020) Essential oils of Lamiaceae family plants as antifungals. Biomolecules 10:103
Selvi S, Polat R, Cakilcioglu U et al (2022) An ethnobotanical review on medicinal plants of the Lamiaceae family in Turkey. Turk J Bot 46:283–332
Hamed AN, Attia E, Desoukey SY (2021) A review on various classes of secondary metabolites and biological activities of Lamiaceae (Labiatae) (2002–2018). J Adv Biomed Pharm Sci 4:16–31
Valerio F, Mezzapesa GN, Ghannouchi A et al (2021) Characterization and antimicrobial properties of essential oils from four wild taxa of Lamiaceae family growing in Apulia. Agronomy 11:1431
Carović-StanKo K, PeteK M, Grdiša M et al (2016) Medicinal plants of the family Lamiaceae as functional foods-a review. Czech J Food Sci 34:377–390
Aliasgharpour M, Rahnamaye Farzami M (2013) Trace elements in human nutrition: a review. Int J Med Investig 2(3):115–128
Pohl HR, Wheeler JS, Murray HE (2013) Sodium and potassium in health and disease. In: Sigel A, Sigel H, Sigel RKO (eds) Interrelations between essential metal ions and human diseases. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 29–47
Chapter Google Scholar
Karakaya S (2016) Investigations on Ferulago trachycarpa Boiss., F. blancheana Post., F.pachyloba (Fenzl) Boiss. and F. bracteata Boiss. & Haussk. (Apiaceae). Doctoral Thesis, Ankara University, Health Sciences Institute
Tanker M, Tanker N (1991) Farmakognozi, Ankara Üniversitesi Basımevi. A.Ü. Ecz. Fak. Yayınları, Ankara
Yuca H, Civas A, Tekman E et al (2023) Qualitative and quantitative phytochemicals of essential oils and extracts of Thymbra spicata subsp. spicata L. as a spice for diabetes mellitus. Flavour Fragr J 38:378–391. https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.3753
Brown RJ, Milton MJ (2005) Analytical techniques for trace element analysis: an overview. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 24(3):266–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2004.11.0
Hernandez-Leon A, Moreno-Pérez GF, Martínez-Gordillo M et al (2021) Lamiaceae in Mexican species, a great but scarcely explored source of secondary metabolites with potential pharmacological effects in pain relief. Molecules 26:7632
Suntar I, Nabavi SM, Barreca D et al (2018) Pharmacological and chemical features of Nepeta L. genus: its importance as a therapeutic agent. Phytother Res 32:185–198. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5946
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Formisano C, Rigano D, Senatore F et al (2008) Volatile constituents of aerial parts of three endemic Centaurea species from Turkey: Centaurea amanicola Hub.-Mor., Centaurea consanguinea DC. and Centaurea ptosimopappa Hayek and their antibacterial activities. Nat Prod Res 22:833–839. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786410701218259
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Hussain J, Khan FU, Ullah R et al (2009) Evaluation of the chemical composition and trace elements analysis of Nepeta suavis and Phlomis bracteosa belonging to family Labitae. Am Eurasian J Agric Env Sci 6:651–656
Li X, He T, Wang X et al (2019) Traditional uses, chemical constituents and biological activities of plants from the genus Thymus . Chem Biodivers 16:e1900254. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201900254
Marrelli M, Statti GA, Conforti F (2018) Origanum spp.: an update of their chemical and biological profiles. Phytochem Rev 17:873–888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-018-9566-0
González-Burgos E, Carretero ME, Gómez-Serranillos MP (2011) Sideritis spp.: Uses, chemical composition and pharmacological activities—a review. J Ethnopharmacol 135:209–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.03.014
Dursun N, Dogu S, Gezgin S et al (2016) Mineral contents and chemical properties of some Sideritis and Origanum species. J Agroaliment Process Technol 22:220–225
Wu Y-B, Ni Z-Y, Shi Q-W et al (2012) Constituents from Salvia species and their biological activities. Chem Rev 112:5967–6026. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200058f
Szentmihályi K, Then M, Csedó (2004) Comparative study on tannins, flavonoids, terpenes and mineral elements of some Salvia species. Acta Hortic 463–470. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2004.629.60
Mohammadhosseini M (2017) The ethnobotanical, phytochemical and pharmacological properties and medicinal applications of essential oils and extracts of different Ziziphora species. Ind Crops Prod 105:164–192
Yazdanshenas H, Tafrihi M (2022) The biological and therapeutic potentials of Cyclotrichium genus: a systematic review. Int J Environ Health Res 32:2589–2599. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2021.1977784
Luan F, Han K, Li M et al (2019) Ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology of species from the genus Ajuga L.: a systematic review. Am J Chin Med 47:959–1003. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X19500502
Meyre-Silva C, Cechinel-Filho V (2010) A review of the chemical and pharmacological aspects of the genus Marrubium . Curr Pharm Des 16:3503–3518. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161210793563392
Jankovskỳ M, Landa T (2002) Genus Hyssopus L.-recent knowledge. Hort SciPrague 29:119–123
Zinicovscaia I, Gundorina S, Vergel K et al (2020) Elemental analysis of Lamiaceae medicinal and aromatic plants growing in the Republic of Moldova using neutron activation analysis. Phytochem Lett 35:119–127
Shah SM, Amin M, Gul B, Begum M (2020) Ethnoecological, elemental, and phytochemical evaluation of five plant species of Lamiacea e in Peshawar, Pakistan. Scientifica 2020:1–8
Tomescu A, Rus C, Pop G et al (2015) Researches regarding proximate and selected elements composition of some medicinal plants belonging to the Lamiaceae family. Lucr Ştiinţ 58:175–180
Kaska A, Cicek M, Mammadov R (2019) Biological activities, phenolic constituents and mineral element analysis of two endemic medicinal plants from Turkey: Nepeta italica subsp. cadmea and Teucrium sandrasicum . South Afr J Bot 124:63–70
Koche D (2010) Trace element analysis and vitamins from an Indian medicinal plant Nepeta hindostana (ROTH) Haines. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 3:53–54
Kucukbay F, Kuyumcu E (2010) Determination of trace element contents of Thymus species from Turkey. Turk J Chem 34:911–920
Jooybari BS, Soltanpour H, Uchbelagh DR (2022) Multi element analysis of Ziziphora medicinal plant by instrumental neutron activation analysis. Presented at the 1st İnternational and 28th National Conference on Nuclear Science and Technology, Iran
Ahmed D, Chaudhary MA (2009) Medicinal and nutritional aspects of various trace metals determined in Ajuga bracteosa . J Appl Sci Res 5:864–869
Nedjimi B, Beladel B (2016) Instrumental neutron activation analysis of Marrubium vulgare L., a valuable medicinal herb. Radiochim Acta 104:285–289. https://doi.org/10.1515/ract-2015-2406
Saebi A, Minaei S, Mahdavian AR, Ebadi M-T (2021) Precision Harvesting of medicinal plants: elements and ash content of Hyssop ( Hyssopus officinalis L.) as affected by harvest height. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:753–762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02171-2
Download references
Acknowledgements
Enes TEKMAN extends appreciation for the scholarship granted by the Turkish Scientific and Technical Research Council (TÜBİTAK) and acknowledges the assistance received during their postgraduate program.
Open access funding provided by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Türkiye (TÜBİTAK).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Pharmaceutical Botany, Faculty of Pharmacy, Ataturk University, 25240, Erzurum, Turkey
Enes Tekman & Songül Karakaya
Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Ataturk University, 25240, Erzurum, Turkey
Tugay Asgarlı & Hafize Yuca
Department of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Ataturk University, 25240, Erzurum, Turkey
Alptuğ Atila
Department of Plant and Animal Production, Vocational School of Technical Sciences, Karamanoğlu Mehmetbey University, 70200, Karaman, Turkey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization: E.T., T.A., H.Y., A.A., Ö.Ç., S.K. Data curation: E.T., T.A., H.Y., A.A., Ö.Ç., S.K. Formal analysis and investigation: E.T., T.A., H.Y., A.A., S.K. Software: H.Y., S.K. Supervision: S.K. Resourches: Ö.Ç. Writing original draft: E.T., H.Y., S.K. Review and editing: H.Y., S.K. The manuscript has been checked and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Songül Karakaya .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval.
There is no ethics approval.
Competing Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Tekman, E., Asgarlı, T., Yuca, H. et al. Exploring Quantitative Biological Major, Trace, and Ultratrace Elements Composition and Qualitative Primary-Secondary Metabolites in Lamiaceae Medicinal Plants from Turkey. Biol Trace Elem Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04219-z
Download citation
Received : 15 March 2024
Accepted : 02 May 2024
Published : 14 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04219-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Elemental analysis
- Medicinal plants
- Metabolites
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PAPER 45 research problem. For example, the purpose of this study is to examine the prevalence of the use of synthetic marijuana use among preteens which will lead to a prevention and intervention model to be used in community centers citywide. Significance of the Study
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Examples of Qualitative Research. You have probably seen examples of qualitative research before, but you might not have paid particular attention to how they were produced or realized that the accounts you were reading were the result of hours, months, even years of research "in the field." A good qualitative researcher will present the ...
JARS-Qual, developed in 2018, mark the first time APA Style has included qualitative standards. They outline what should be reported in qualitative research manuscripts to make the review process easier. The seventh edition of the Publication Manual also includes content on qualitative studies, including standards for journal article ...
However, for many research projects, there are different sorts of questions that need answering, some requiring quantitative methods, and some requiring qualitative methods. If the question is a qualitative one, then the most appropriate and rigorous way of answering it is to use qualitative methods. For instance, if you
For the reasons explained above, qualitative research does not require specific sample sizes, nor does it require that the sample size be determined a priori [1, 14, 27, 37-39]. Sample size can only be a useful quality indicator when related to the research purpose, the chosen methodology and the composition of the sample, i.e. who was ...
Purpose - This paper aims to offer junior scholars a front-to-back guide to writing an academic, theoretically positioned, qualitative research article in the social sciences. Design/methodology ...
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervening or introducing treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypothenar to further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences ...
Qualitative research, conducted thoughtfully, is internally consistent, rigorous, and helps us answer important questions about people and their lives (Lincoln & Guba, 1985). These fundamental epistemological foundations are key for developing the right research mindset before designing and conducting qualitative research. ... For example ...
How to search for and evaluate qualitative research, integrate qualitative research into systematic reviews, report/publish qualitative research. Includes some Mixed Methods resources. ... Sample Size/Sampling: Because reviewers are not always familiar with qualitative methods, they may ask for explanation or justification of your methods when ...
The usually small sample size in qualitative research depends on the information richness of the data, the variety of participants (or other units), the broadness of the research question and the phenomenon, the data collection method (e.g., individual or group interviews) and the type of sampling strategy.
qualitative research involves collecting and/or working with text, images, or sounds. An outcome-oriented definition such as that proposed by Nkwi et al. avoids (typically inaccurate) generalizations and the unnecessary (and, for the most part, inaccurate) dichotomous positioning of qualitative research with respect to its quantitative coun -
Qualitative research methods are a huge opportunity to increase access, equity, inclusion, and social justice. Qualitative research allows us to engage and examine the uniquenesses/nuances within minoritized and dominant identities and our experiences with these identities. Qualitative research allows us to explore a specific topic, and through ...
Qualitative research: methods and examples. Qualitative research is an excellent way to gain insight into real-world problems. This research type can explain various aspects of individuals in a target group, such as their traits, behaviors, and motivations. Qualitative research involves gathering and evaluating non-numerical information to ...
The steps involved in qualitative data analysis are given below. Organize the Data: This can be done by transcribing interviews or making detailed notes. Review the Data: Examine the data, ideas, and patterns. Establish a Data Coding System: Generate a set of codes that you can apply to classify your data.
Qualitative Research Examples. 1. Ethnography. Definition: Ethnography is a qualitative research design aimed at exploring cultural phenomena. Rooted in the discipline of anthropology, this research approach investigates the social interactions, behaviors, and perceptions within groups, communities, or organizations.
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive, allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.. Qualitative research example If you want to generate new ideas for online teaching strategies, a qualitative approach would make the most sense. You can use this type of research to explore exactly what teachers and students struggle ...
Qualitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data. The findings of qualitative research are expressed in words and help in understanding individuals' subjective perceptions about an event, condition, or subject. This type of research is exploratory and is used to generate hypotheses or theories ...
Revised on 30 January 2023. Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which ...
Qualitative research is defined as a market research method that focuses on obtaining data through open-ended and conversational communication. This method is about "what" people think and "why" they think so. For example, consider a convenience store looking to improve its patronage.
5. Ask something researchable. Big questions, questions about hypothetical events or questions that would require vastly more resources than you have access to are not useful starting points for qualitative studies. Qualitative words or subjective ideas that lack definition are also not helpful.
The findings of this research revealed that flexibility, cost-effectiveness, electronic research availability, ease of connection to the Internet, and well-designed class interface were students' positive experiences. The students' negative experiences were caused by delayed feedback from instructors, unavailable technical support from ...
Qualitative research is a widely used term for resear ch that does not subject research findings to. quantification or quantitative analysis. Qualitative research examines the attitudes ...
What is qualitative research? If we look for a precise definition of qualitative research, and specifically for one that addresses its distinctive feature of being "qualitative," the literature is meager. In this article we systematically search, identify and analyze a sample of 89 sources using or attempting to define the term ...
Sample sizes for saturation in qualitative research: a systematic review of empirical tests. Soc Sci Med. 2022;292:114523. Article PubMed Google Scholar O'Connor C, Joffe H. Intercoder Reliability in Qualitative Research: debates and practical guidelines. Int J Qualitative Methods. 2020;19:1609406919899220.
Sample size for qualitative research. Qual Mark Res. 2016;19(4):426-32. Article Google Scholar ... 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons ...
Problem areas of determining the sample size in qualitative research: a model proposal. Hasan Tutar, Mehmet Şahin, Teymur Sarkhanov. Pages 315-336. Article preview. select article Book review: Qualitative research in education: a review for physics education and other sub-sciences.
For example, qualitative research indicates that popularity indicators often constitute powerful cues that increase an article's perceived relevance, importance, or appeal (Costera Meijer and Groot Kormelink Citation 2020).
Quantitative analysis of specific primary and secondary metabolites was carried out. Na and K are major constituents in plants. The concentrations of Na range from 332,495.590 g/kg (in sample 10SA) to 279,690.674 g/kg (in sample 4SA), while those of K vary from 67,492.456 g/kg (in sample 15SA) to 3347.612 g/kg (in sample 1A).
However, the authors are confident that data saturation was reached, as no new themes emerged in the latter interviews. Additionally, the aim of qualitative research is to explore issues of context and depth, rather than generalisability and the authors were able to recruit patients for interviews in line with the pre-specified purposive sample.