- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Critical Reviews

How to Write an Article Review (With Examples)
Last Updated: April 24, 2024 Fact Checked
Preparing to Write Your Review
Writing the article review, sample article reviews, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,101,737 times.
An article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of experts in the field. Experts also are often asked to review the work of other professionals. Understanding the main points and arguments of the article is essential for an accurate summation. Logical evaluation of the article's main theme, supporting arguments, and implications for further research is an important element of a review . Here are a few guidelines for writing an article review.
Education specialist Alexander Peterman recommends: "In the case of a review, your objective should be to reflect on the effectiveness of what has already been written, rather than writing to inform your audience about a subject."
Article Review 101
- Read the article very closely, and then take time to reflect on your evaluation. Consider whether the article effectively achieves what it set out to.
- Write out a full article review by completing your intro, summary, evaluation, and conclusion. Don't forget to add a title, too!
- Proofread your review for mistakes (like grammar and usage), while also cutting down on needless information.

- Article reviews present more than just an opinion. You will engage with the text to create a response to the scholarly writer's ideas. You will respond to and use ideas, theories, and research from your studies. Your critique of the article will be based on proof and your own thoughtful reasoning.
- An article review only responds to the author's research. It typically does not provide any new research. However, if you are correcting misleading or otherwise incorrect points, some new data may be presented.
- An article review both summarizes and evaluates the article.

- Summarize the article. Focus on the important points, claims, and information.
- Discuss the positive aspects of the article. Think about what the author does well, good points she makes, and insightful observations.
- Identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the text. Determine if there is enough data or research included to support the author's claims. Find any unanswered questions left in the article.

- Make note of words or issues you don't understand and questions you have.
- Look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with, so you can fully understand the article. Read about concepts in-depth to make sure you understand their full context.

- Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure you fully understand the article. The only way to write a good article review is to understand the article.

- With either method, make an outline of the main points made in the article and the supporting research or arguments. It is strictly a restatement of the main points of the article and does not include your opinions.
- After putting the article in your own words, decide which parts of the article you want to discuss in your review. You can focus on the theoretical approach, the content, the presentation or interpretation of evidence, or the style. You will always discuss the main issues of the article, but you can sometimes also focus on certain aspects. This comes in handy if you want to focus the review towards the content of a course.
- Review the summary outline to eliminate unnecessary items. Erase or cross out the less important arguments or supplemental information. Your revised summary can serve as the basis for the summary you provide at the beginning of your review.

- What does the article set out to do?
- What is the theoretical framework or assumptions?
- Are the central concepts clearly defined?
- How adequate is the evidence?
- How does the article fit into the literature and field?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject?
- How clear is the author's writing? Don't: include superficial opinions or your personal reaction. Do: pay attention to your biases, so you can overcome them.

- For example, in MLA , a citation may look like: Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly 50.3 (1994): 127-53. Print. [9] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.

- Your introduction should only be 10-25% of your review.
- End the introduction with your thesis. Your thesis should address the above issues. For example: Although the author has some good points, his article is biased and contains some misinterpretation of data from others’ analysis of the effectiveness of the condom.

- Use direct quotes from the author sparingly.
- Review the summary you have written. Read over your summary many times to ensure that your words are an accurate description of the author's article.

- Support your critique with evidence from the article or other texts.
- The summary portion is very important for your critique. You must make the author's argument clear in the summary section for your evaluation to make sense.
- Remember, this is not where you say if you liked the article or not. You are assessing the significance and relevance of the article.
- Use a topic sentence and supportive arguments for each opinion. For example, you might address a particular strength in the first sentence of the opinion section, followed by several sentences elaborating on the significance of the point.

- This should only be about 10% of your overall essay.
- For example: This critical review has evaluated the article "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS" by Anthony Zimmerman. The arguments in the article show the presence of bias, prejudice, argumentative writing without supporting details, and misinformation. These points weaken the author’s arguments and reduce his credibility.

- Make sure you have identified and discussed the 3-4 key issues in the article.

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.cmich.edu/writinghelp/articlereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548566/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://guides.library.queensu.ca/introduction-research/writing/critical
- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548565/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/593/2014/06/How_to_Summarize_a_Research_Article1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/how-to-review-a-journal-article
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

If you have to write an article review, read through the original article closely, taking notes and highlighting important sections as you read. Next, rewrite the article in your own words, either in a long paragraph or as an outline. Open your article review by citing the article, then write an introduction which states the article’s thesis. Next, summarize the article, followed by your opinion about whether the article was clear, thorough, and useful. Finish with a paragraph that summarizes the main points of the article and your opinions. To learn more about what to include in your personal critique of the article, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prince Asiedu-Gyan
Apr 22, 2022
Did this article help you?
Sammy James
Sep 12, 2017
Juabin Matey
Aug 30, 2017
Vanita Meghrajani
Jul 21, 2016
Nov 27, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
How to Write an Article Review: Tips and Examples

Did you know that article reviews are not just academic exercises but also a valuable skill in today's information age? In a world inundated with content, being able to dissect and evaluate articles critically can help you separate the wheat from the chaff. Whether you're a student aiming to excel in your coursework or a professional looking to stay well-informed, mastering the art of writing article reviews is an invaluable skill.
Short Description
In this article, our research paper writing service experts will start by unraveling the concept of article reviews and discussing the various types. You'll also gain insights into the art of formatting your review effectively. To ensure you're well-prepared, we'll take you through the pre-writing process, offering tips on setting the stage for your review. But it doesn't stop there. You'll find a practical example of an article review to help you grasp the concepts in action. To complete your journey, we'll guide you through the post-writing process, equipping you with essential proofreading techniques to ensure your work shines with clarity and precision!
What Is an Article Review: Grasping the Concept
A review article is a type of professional paper writing that demands a high level of in-depth analysis and a well-structured presentation of arguments. It is a critical, constructive evaluation of literature in a particular field through summary, classification, analysis, and comparison.
If you write a scientific review, you have to use database searches to portray the research. Your primary goal is to summarize everything and present a clear understanding of the topic you've been working on.
Writing Involves:
- Summarization, classification, analysis, critiques, and comparison.
- The analysis, evaluation, and comparison require the use of theories, ideas, and research relevant to the subject area of the article.
- It is also worth nothing if a review does not introduce new information, but instead presents a response to another writer's work.
- Check out other samples to gain a better understanding of how to review the article.
Types of Review
When it comes to article reviews, there's more than one way to approach the task. Understanding the various types of reviews is like having a versatile toolkit at your disposal. In this section, we'll walk you through the different dimensions of review types, each offering a unique perspective and purpose. Whether you're dissecting a scholarly article, critiquing a piece of literature, or evaluating a product, you'll discover the diverse landscape of article reviews and how to navigate it effectively.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Research Article Review
Distinguished by its focus on research methodologies, a research article review scrutinizes the techniques used in a study and evaluates them in light of the subsequent analysis and critique. For instance, when reviewing a research article on the effects of a new drug, the reviewer would delve into the methods employed to gather data and assess their reliability.
Science Article Review
In the realm of scientific literature, a science article review encompasses a wide array of subjects. Scientific publications often provide extensive background information, which can be instrumental in conducting a comprehensive analysis. For example, when reviewing an article about the latest breakthroughs in genetics, the reviewer may draw upon the background knowledge provided to facilitate a more in-depth evaluation of the publication.
Need a Hand From Professionals?
Address to Our Writers and Get Assistance in Any Questions!
Formatting an Article Review
The format of the article should always adhere to the citation style required by your professor. If you're not sure, seek clarification on the preferred format and ask him to clarify several other pointers to complete the formatting of an article review adequately.
How Many Publications Should You Review?
- In what format should you cite your articles (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.)?
- What length should your review be?
- Should you include a summary, critique, or personal opinion in your assignment?
- Do you need to call attention to a theme or central idea within the articles?
- Does your instructor require background information?
When you know the answers to these questions, you may start writing your assignment. Below are examples of MLA and APA formats, as those are the two most common citation styles.
Using the APA Format
Articles appear most commonly in academic journals, newspapers, and websites. If you write an article review in the APA format, you will need to write bibliographical entries for the sources you use:
- Web : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Journal : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Publication Year). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Newspaper : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Publication Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
Using MLA Format
- Web : Last, First Middle Initial. “Publication Title.” Website Title. Website Publisher, Date Month Year Published. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date, Month, Year Published: Page(s). Print.
- Journal : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Enhance your writing effortlessly with EssayPro.com , where you can order an article review or any other writing task. Our team of expert writers specializes in various fields, ensuring your work is not just summarized, but deeply analyzed and professionally presented. Ideal for students and professionals alike, EssayPro offers top-notch writing assistance tailored to your needs. Elevate your writing today with our skilled team at your article review writing service !
.jpg)
The Pre-Writing Process
Facing this task for the first time can really get confusing and can leave you unsure of where to begin. To create a top-notch article review, start with a few preparatory steps. Here are the two main stages from our dissertation services to get you started:
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow:
- Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
- Define the positive points — identify the strong aspects, ideas, and insightful observations the author has made.
- Find the gaps —- determine whether or not the author has any contradictions, gaps, or inconsistencies in the article and evaluate whether or not he or she used a sufficient amount of arguments and information to support his or her ideas.
- Identify unanswered questions — finally, identify if there are any questions left unanswered after reading the piece.
Step 2: Move on and review the article. Here is a small and simple guide to help you do it right:
- Start off by looking at and assessing the title of the piece, its abstract, introductory part, headings and subheadings, opening sentences in its paragraphs, and its conclusion.
- First, read only the beginning and the ending of the piece (introduction and conclusion). These are the parts where authors include all of their key arguments and points. Therefore, if you start with reading these parts, it will give you a good sense of the author's main points.
- Finally, read the article fully.
These three steps make up most of the prewriting process. After you are done with them, you can move on to writing your own review—and we are going to guide you through the writing process as well.
Outline and Template
As you progress with reading your article, organize your thoughts into coherent sections in an outline. As you read, jot down important facts, contributions, or contradictions. Identify the shortcomings and strengths of your publication. Begin to map your outline accordingly.
If your professor does not want a summary section or a personal critique section, then you must alleviate those parts from your writing. Much like other assignments, an article review must contain an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Thus, you might consider dividing your outline according to these sections as well as subheadings within the body. If you find yourself troubled with the pre-writing and the brainstorming process for this assignment, seek out a sample outline.
Your custom essay must contain these constituent parts:
- Pre-Title Page - Before diving into your review, start with essential details: article type, publication title, and author names with affiliations (position, department, institution, location, and email). Include corresponding author info if needed.
- Running Head - In APA format, use a concise title (under 40 characters) to ensure consistent formatting.
- Summary Page - Optional but useful. Summarize the article in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology, avoiding verbatim text or references.
- Title Page - Include the full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction - Set the stage with an engaging overview of the article.
- Body - Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References - Properly cite all sources used in your review.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page - If permitted, suggest further readings for in-depth exploration.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed by the professor) - Include visuals when requested by your professor for clarity.
Example of an Article Review
You might wonder why we've dedicated a section of this article to discuss an article review sample. Not everyone may realize it, but examining multiple well-constructed examples of review articles is a crucial step in the writing process. In the following section, our essay writing service experts will explain why.
Looking through relevant article review examples can be beneficial for you in the following ways:
- To get you introduced to the key works of experts in your field.
- To help you identify the key people engaged in a particular field of science.
- To help you define what significant discoveries and advances were made in your field.
- To help you unveil the major gaps within the existing knowledge of your field—which contributes to finding fresh solutions.
- To help you find solid references and arguments for your own review.
- To help you generate some ideas about any further field of research.
- To help you gain a better understanding of the area and become an expert in this specific field.
- To get a clear idea of how to write a good review.
View Our Writer’s Sample Before Crafting Your Own!
Why Have There Been No Great Female Artists?
Steps for Writing an Article Review
Here is a guide with critique paper format on how to write a review paper:
.webp)
Step 1: Write the Title
First of all, you need to write a title that reflects the main focus of your work. Respectively, the title can be either interrogative, descriptive, or declarative.
Step 2: Cite the Article
Next, create a proper citation for the reviewed article and input it following the title. At this step, the most important thing to keep in mind is the style of citation specified by your instructor in the requirements for the paper. For example, an article citation in the MLA style should look as follows:
Author's last and first name. "The title of the article." Journal's title and issue(publication date): page(s). Print
Abraham John. "The World of Dreams." Virginia Quarterly 60.2(1991): 125-67. Print.
Step 3: Article Identification
After your citation, you need to include the identification of your reviewed article:
- Title of the article
- Title of the journal
- Year of publication
All of this information should be included in the first paragraph of your paper.
The report "Poverty increases school drop-outs" was written by Brian Faith – a Health officer – in 2000.
Step 4: Introduction
Your organization in an assignment like this is of the utmost importance. Before embarking on your writing process, you should outline your assignment or use an article review template to organize your thoughts coherently.
- If you are wondering how to start an article review, begin with an introduction that mentions the article and your thesis for the review.
- Follow up with a summary of the main points of the article.
- Highlight the positive aspects and facts presented in the publication.
- Critique the publication by identifying gaps, contradictions, disparities in the text, and unanswered questions.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Make a summary of the article by revisiting what the author has written about. Note any relevant facts and findings from the article. Include the author's conclusions in this section.
Step 6: Critique It
Present the strengths and weaknesses you have found in the publication. Highlight the knowledge that the author has contributed to the field. Also, write about any gaps and/or contradictions you have found in the article. Take a standpoint of either supporting or not supporting the author's assertions, but back up your arguments with facts and relevant theories that are pertinent to that area of knowledge. Rubrics and templates can also be used to evaluate and grade the person who wrote the article.
Step 7: Craft a Conclusion
In this section, revisit the critical points of your piece, your findings in the article, and your critique. Also, write about the accuracy, validity, and relevance of the results of the article review. Present a way forward for future research in the field of study. Before submitting your article, keep these pointers in mind:
- As you read the article, highlight the key points. This will help you pinpoint the article's main argument and the evidence that they used to support that argument.
- While you write your review, use evidence from your sources to make a point. This is best done using direct quotations.
- Select quotes and supporting evidence adequately and use direct quotations sparingly. Take time to analyze the article adequately.
- Every time you reference a publication or use a direct quotation, use a parenthetical citation to avoid accidentally plagiarizing your article.
- Re-read your piece a day after you finish writing it. This will help you to spot grammar mistakes and to notice any flaws in your organization.
- Use a spell-checker and get a second opinion on your paper.
The Post-Writing Process: Proofread Your Work
Finally, when all of the parts of your article review are set and ready, you have one last thing to take care of — proofreading. Although students often neglect this step, proofreading is a vital part of the writing process and will help you polish your paper to ensure that there are no mistakes or inconsistencies.
To proofread your paper properly, start by reading it fully and checking the following points:
- Punctuation
- Other mistakes
Afterward, take a moment to check for any unnecessary information in your paper and, if found, consider removing it to streamline your content. Finally, double-check that you've covered at least 3-4 key points in your discussion.
And remember, if you ever need help with proofreading, rewriting your essay, or even want to buy essay , our friendly team is always here to assist you.
Need an Article REVIEW WRITTEN?
Just send us the requirements to your paper and watch one of our writers crafting an original paper for you.
What Is A Review Article?
How to write an article review, how to write an article review in apa format, related articles.
.webp)

Get Started
Take the first step and invest in your future.

Online Programs
Offering flexibility & convenience in 51 online degrees & programs.

Prairie Stars
Featuring 15 intercollegiate NCAA Div II athletic teams.

Find your Fit
UIS has over 85 student and 10 greek life organizations, and many volunteer opportunities.

Arts & Culture
Celebrating the arts to create rich cultural experiences on campus.

Give Like a Star
Your generosity helps fuel fundraising for scholarships, programs and new initiatives.

Bragging Rights
UIS was listed No. 1 in Illinois and No. 3 in the Midwest in 2023 rankings.
- Quick links Applicants & Students Important Apps & Links Alumni Faculty and Staff Community Admissions How to Apply Cost & Aid Tuition Calculator Registrar Orientation Visit Campus Academics Register for Class Programs of Study Online Degrees & Programs Graduate Education International Student Services Study Away Student Support Bookstore UIS Life Dining Diversity & Inclusion Get Involved Health & Wellness COVID-19 United in Safety Residence Life Student Life Programs UIS Connection Important Apps UIS Mobile App Advise U Canvas myUIS i-card Balance Pay My Bill - UIS Bursar Self-Service Email Resources Bookstore Box Information Technology Services Library Orbit Policies Webtools Get Connected Area Information Calendar Campus Recreation Departments & Programs (A-Z) Parking UIS Newsroom The Observer Connect & Get Involved Update your Info Alumni Events Alumni Networks & Groups Volunteer Opportunities Alumni Board News & Publications Featured Alumni Alumni News UIS Alumni Magazine Resources Order your Transcripts Give Back Alumni Programs Career Development Services & Support Accessibility Services Campus Services Campus Police Facilities & Services Registrar Faculty & Staff Resources Website Project Request Web Services Training & Tools Academic Impressions Career Connect CSA Reporting Cybersecurity Training Faculty Research FERPA Training Website Login Campus Resources Newsroom Campus Calendar Campus Maps i-Card Human Resources Public Relations Webtools Arts & Events UIS Performing Arts Center Visual Arts Gallery Event Calendar Sangamon Experience Center for Lincoln Studies ECCE Speaker Series Community Engagement Center for State Policy and Leadership Illinois Innocence Project Innovate Springfield Central IL Nonprofit Resource Center NPR Illinois Community Resources Child Protection Training Academy Office of Electronic Media University Archives/IRAD Institute for Illinois Public Finance
Request Info

How to Review a Journal Article

- Request Info Request info for.... Undergraduate/Graduate Online Study Away Continuing & Professional Education International Student Services General Inquiries
For many kinds of assignments, like a literature review , you may be asked to offer a critique or review of a journal article. This is an opportunity for you as a scholar to offer your qualified opinion and evaluation of how another scholar has composed their article, argument, and research. That means you will be expected to go beyond a simple summary of the article and evaluate it on a deeper level. As a college student, this might sound intimidating. However, as you engage with the research process, you are becoming immersed in a particular topic, and your insights about the way that topic is presented are valuable and can contribute to the overall conversation surrounding your topic.
IMPORTANT NOTE!!
Some disciplines, like Criminal Justice, may only want you to summarize the article without including your opinion or evaluation. If your assignment is to summarize the article only, please see our literature review handout.
Before getting started on the critique, it is important to review the article thoroughly and critically. To do this, we recommend take notes, annotating , and reading the article several times before critiquing. As you read, be sure to note important items like the thesis, purpose, research questions, hypotheses, methods, evidence, key findings, major conclusions, tone, and publication information. Depending on your writing context, some of these items may not be applicable.
Questions to Consider
To evaluate a source, consider some of the following questions. They are broken down into different categories, but answering these questions will help you consider what areas to examine. With each category, we recommend identifying the strengths and weaknesses in each since that is a critical part of evaluation.
Evaluating Purpose and Argument
- How well is the purpose made clear in the introduction through background/context and thesis?
- How well does the abstract represent and summarize the article’s major points and argument?
- How well does the objective of the experiment or of the observation fill a need for the field?
- How well is the argument/purpose articulated and discussed throughout the body of the text?
- How well does the discussion maintain cohesion?
Evaluating the Presentation/Organization of Information
- How appropriate and clear is the title of the article?
- Where could the author have benefited from expanding, condensing, or omitting ideas?
- How clear are the author’s statements? Challenge ambiguous statements.
- What underlying assumptions does the author have, and how does this affect the credibility or clarity of their article?
- How objective is the author in his or her discussion of the topic?
- How well does the organization fit the article’s purpose and articulate key goals?
Evaluating Methods
- How appropriate are the study design and methods for the purposes of the study?
- How detailed are the methods being described? Is the author leaving out important steps or considerations?
- Have the procedures been presented in enough detail to enable the reader to duplicate them?
Evaluating Data
- Scan and spot-check calculations. Are the statistical methods appropriate?
- Do you find any content repeated or duplicated?
- How many errors of fact and interpretation does the author include? (You can check on this by looking up the references the author cites).
- What pertinent literature has the author cited, and have they used this literature appropriately?
Following, we have an example of a summary and an evaluation of a research article. Note that in most literature review contexts, the summary and evaluation would be much shorter. This extended example shows the different ways a student can critique and write about an article.
Chik, A. (2012). Digital gameplay for autonomous foreign language learning: Gamers’ and language teachers’ perspectives. In H. Reinders (ed.), Digital games in language learning and teaching (pp. 95-114). Eastbourne, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
Be sure to include the full citation either in a reference page or near your evaluation if writing an annotated bibliography .
In Chik’s article “Digital Gameplay for Autonomous Foreign Language Learning: Gamers’ and Teachers’ Perspectives”, she explores the ways in which “digital gamers manage gaming and gaming-related activities to assume autonomy in their foreign language learning,” (96) which is presented in contrast to how teachers view the “pedagogical potential” of gaming. The research was described as an “umbrella project” consisting of two parts. The first part examined 34 language teachers’ perspectives who had limited experience with gaming (only five stated they played games regularly) (99). Their data was recorded through a survey, class discussion, and a seven-day gaming trial done by six teachers who recorded their reflections through personal blog posts. The second part explored undergraduate gaming habits of ten Hong Kong students who were regular gamers. Their habits were recorded through language learning histories, videotaped gaming sessions, blog entries of gaming practices, group discussion sessions, stimulated recall sessions on gaming videos, interviews with other gamers, and posts from online discussion forums. The research shows that while students recognize the educational potential of games and have seen benefits of it in their lives, the instructors overall do not see the positive impacts of gaming on foreign language learning.
The summary includes the article’s purpose, methods, results, discussion, and citations when necessary.
This article did a good job representing the undergraduate gamers’ voices through extended quotes and stories. Particularly for the data collection of the undergraduate gamers, there were many opportunities for an in-depth examination of their gaming practices and histories. However, the representation of the teachers in this study was very uneven when compared to the students. Not only were teachers labeled as numbers while the students picked out their own pseudonyms, but also when viewing the data collection, the undergraduate students were more closely examined in comparison to the teachers in the study. While the students have fifteen extended quotes describing their experiences in their research section, the teachers only have two of these instances in their section, which shows just how imbalanced the study is when presenting instructor voices.
Some research methods, like the recorded gaming sessions, were only used with students whereas teachers were only asked to blog about their gaming experiences. This creates a richer narrative for the students while also failing to give instructors the chance to have more nuanced perspectives. This lack of nuance also stems from the emphasis of the non-gamer teachers over the gamer teachers. The non-gamer teachers’ perspectives provide a stark contrast to the undergraduate gamer experiences and fits neatly with the narrative of teachers not valuing gaming as an educational tool. However, the study mentioned five teachers that were regular gamers whose perspectives are left to a short section at the end of the presentation of the teachers’ results. This was an opportunity to give the teacher group a more complex story, and the opportunity was entirely missed.
Additionally, the context of this study was not entirely clear. The instructors were recruited through a master’s level course, but the content of the course and the institution’s background is not discussed. Understanding this context helps us understand the course’s purpose(s) and how those purposes may have influenced the ways in which these teachers interpreted and saw games. It was also unclear how Chik was connected to this masters’ class and to the students. Why these particular teachers and students were recruited was not explicitly defined and also has the potential to skew results in a particular direction.
Overall, I was inclined to agree with the idea that students can benefit from language acquisition through gaming while instructors may not see the instructional value, but I believe the way the research was conducted and portrayed in this article made it very difficult to support Chik’s specific findings.
Some professors like you to begin an evaluation with something positive but isn’t always necessary.
The evaluation is clearly organized and uses transitional phrases when moving to a new topic.
This evaluation includes a summative statement that gives the overall impression of the article at the end, but this can also be placed at the beginning of the evaluation.
This evaluation mainly discusses the representation of data and methods. However, other areas, like organization, are open to critique.
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
Myths About Online High Schools: Everything You Need to Know
Reasons you should study geography: everything you need to know, the vtoman jump 1800 portable power station: the best of the best, key roles of a school superintendent: everything you need to know, why learners cheat: everything you need to know, top issues in education: everything you need to know, duties of a school principal: everything you need to know, private vs. public education: everything you need to know, choosing the perfect college: everything you need to know, common college freshmen fears: how to overcome them, how to write an article review (with sample reviews) .

An article review is a critical evaluation of a scholarly or scientific piece, which aims to summarize its main ideas, assess its contributions, and provide constructive feedback. A well-written review not only benefits the author of the article under scrutiny but also serves as a valuable resource for fellow researchers and scholars. Follow these steps to create an effective and informative article review:
1. Understand the purpose: Before diving into the article, it is important to understand the intent of writing a review. This helps in focusing your thoughts, directing your analysis, and ensuring your review adds value to the academic community.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification.
3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review’s introduction, briefly outline the primary themes and arguments presented by the author(s). Keep it concise but sufficiently informative so that readers can quickly grasp the essence of the article.
4. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses: In subsequent paragraphs, assess the strengths and limitations of the article based on factors such as methodology, quality of evidence presented, coherence of arguments, and alignment with existing literature in the field. Be fair and objective while providing your critique.
5. Discuss any implications: Deliberate on how this particular piece contributes to or challenges existing knowledge in its discipline. You may also discuss potential improvements for future research or explore real-world applications stemming from this study.
6. Provide recommendations: Finally, offer suggestions for both the author(s) and readers regarding how they can further build on this work or apply its findings in practice.
7. Proofread and revise: Once your initial draft is complete, go through it carefully for clarity, accuracy, and coherence. Revise as necessary, ensuring your review is both informative and engaging for readers.
Sample Review:
A Critical Review of “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health”
Introduction:
“The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is a timely article which investigates the relationship between social media usage and psychological well-being. The authors present compelling evidence to support their argument that excessive use of social media can result in decreased self-esteem, increased anxiety, and a negative impact on interpersonal relationships.
Strengths and weaknesses:
One of the strengths of this article lies in its well-structured methodology utilizing a variety of sources, including quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. This approach provides a comprehensive view of the topic, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the effects of social media on mental health. However, it would have been beneficial if the authors included a larger sample size to increase the reliability of their conclusions. Additionally, exploring how different platforms may influence mental health differently could have added depth to the analysis.
Implications:
The findings in this article contribute significantly to ongoing debates surrounding the psychological implications of social media use. It highlights the potential dangers that excessive engagement with online platforms may pose to one’s mental well-being and encourages further research into interventions that could mitigate these risks. The study also offers an opportunity for educators and policy-makers to take note and develop strategies to foster healthier online behavior.
Recommendations:
Future researchers should consider investigating how specific social media platforms impact mental health outcomes, as this could lead to more targeted interventions. For practitioners, implementing educational programs aimed at promoting healthy online habits may be beneficial in mitigating the potential negative consequences associated with excessive social media use.
Conclusion:
Overall, “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is an important and informative piece that raises awareness about a pressing issue in today’s digital age. Given its minor limitations, it provides valuable
3 Ways to Make a Mini Greenhouse ...
3 ways to teach yourself to play ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

3 Ways to Crack Your Neck

How to Paint a Desk

How to Culture Microworms: 14 Steps
3 Ways to Fool Your Opponent in Chess

4 Ways to Block Foul Language on YouTube

How to Build a Rat Rod: 14 Steps
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

How I fled bombed Aleppo to continue my career in science
Career Feature 08 MAY 24

Illuminating ‘the ugly side of science’: fresh incentives for reporting negative results

Hunger on campus: why US PhD students are fighting over food
Career Feature 03 MAY 24
Japan can embrace open science — but flexible approaches are key
Correspondence 07 MAY 24

US funders to tighten oversight of controversial ‘gain of function’ research
News 07 MAY 24

France’s research mega-campus faces leadership crisis
News 03 MAY 24

Mount Etna’s spectacular smoke rings and more — April’s best science images

Plagiarism in peer-review reports could be the ‘tip of the iceberg’
Nature Index 01 MAY 24
Recruitment of Principal Investigators by the School of Life Sciences, Peking University
The School of Life Sciences at Peking University is actively seeking talents, with an emphasis on bioinformatics/computational biology/AI/RNA biology.
Beijing (CN)
School of Life Sciences, Peking University
2024 Recruitment notice Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology: Shenzhen, China
The wide-ranging expertise drawing from technical, engineering or science professions...
Shenzhen,China
Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology
Head of Operational Excellence
In this key position, you’ll be responsible for ensuring efficiency and quality in journal workflows through continuous improvement and innovation.
United States (US) - Remote
American Physical Society
Rowland Fellowship
The Rowland Institute at Harvard seeks outstanding early-career experimentalists in all fields of science and engineering.
Cambridge, Massachusetts
Rowland Institute at Harvard
Postdoctoral Fellowship: Chemical and Cell Biology
The 2-year fellowship within a project that will combine biochemical, cell biological and chemical genetic approaches to elucidate migrasome biology
Umeå, Sweden
Umeå University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
How to Write an Effective Article Review – Updated 2024 Guide

Purpose of an Article Review
Importance of writing an effective review, read the article thoroughly, identify the main arguments, take notes on key points.
- Evaluate the Author's Credibility
- Assess the Article's Structure and Organization
Examine the Use of Evidence and Examples
Write a concise summary of the article.
- Include the Article's Main Points
Avoid Personal Opinions in the Summary
Identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Evaluate the Article's Logic and Reasoning
- Discuss the Article's Impact and Relevance
Start with an Engaging Introduction
Provide a brief overview of the article.
- Critique the Article's Strengths and Weaknesses
Offer Suggestions for Improvement
Conclude with a summary and recommendation, check for grammar and spelling errors, ensure clarity and coherence of writing, revise for proper formatting and citations, review the overall structure and flow, make final edits and revisions, submit the article review.
Writing an article review can be a challenging task, but it is an essential skill for academics, researchers, and anyone who needs to critically evaluate published work. An article review is a written piece that provides a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of a scholarly article, book, or other published material. It goes beyond a simple summary by offering a critical assessment of the work’s strengths, weaknesses, and overall contribution to the field. In this blog post, we will explore the steps involved in writing an effective article review.
I. Introduction
The primary purpose of an article review is to provide a critical evaluation of a published work. It serves as a means of engaging with the ideas and arguments presented by the author(s) and assessing their validity, significance, and potential impact on the field. An article review allows the reviewer to analyze the work’s merits, identify its limitations, and offer constructive feedback or suggestions for further research or discussion.
Writing an effective article review is crucial for several reasons. First, it demonstrates the reviewer’s ability to critically analyze and synthesize complex information. This skill is highly valued in academic and professional settings, where critical thinking and analytical skills are essential . Second, article reviews contribute to the ongoing scholarly discourse by providing informed perspectives and critiques that can shape future research and discussions. Finally, well-written article reviews can help readers determine whether a particular work is worth reading or exploring further, making them valuable resources for researchers and scholars in the field.
II. Understanding the Article

The first step in writing an article review is to read the article carefully and thoroughly. This may seem obvious, but it is crucial to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the work before attempting to critique it. During the initial reading, focus on grasping the main arguments, key points, and the overall structure of the article. Take note of any unfamiliar concepts, terminology, or references that may require further research or clarification.
As you read the article, pay close attention to the author’s central arguments or thesis statements. Identify the main claims, hypotheses, or research questions that the article attempts to address. Understanding the core arguments is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of the author’s reasoning and the validity of their conclusions.
While reading the article, it is helpful to take notes on the key points, supporting evidence, and any critical or thought-provoking ideas presented by the author(s). These notes will serve as a reference when you begin writing the review and will help you organize your thoughts and critique more effectively.
III. Analyzing the Article
Evaluate the author’s credibility.
When analyzing an article, it is essential to consider the author’s credibility and expertise in the field. Research the author’s background, qualifications, and previous publications to assess their authority on the subject matter. This information can provide valuable context and help you determine the weight and reliability of the arguments presented in the article.
Assess the Article’s Structure and Organization
Evaluate the overall structure and organization of the article. Is the information presented in a logical and coherent manner? Does the article follow a clear progression from introduction to conclusion? Assessing the structure can help you determine whether the author has effectively communicated their ideas and arguments.
Critically examine the evidence and examples used by the author(s) to support their arguments. Are the sources credible and up-to-date? Are the examples relevant and well-chosen? Evaluating the quality and appropriateness of the evidence can help you assess the strength and validity of the author’s claims.
IV. Summarizing the Article
Before delving into your critique, it is essential to provide a concise summary of the article . This summary should briefly outline the article’s main arguments, key points, and conclusions. The goal is to give the reader a clear understanding of the article’s content without adding any personal opinions or critiques at this stage.
Include the Article’s Main Points
In your summary, be sure to include the article’s main points and the evidence or examples used to support them. This will help the reader understand the context and the basis for the author’s arguments, which is crucial for your subsequent critique.
When summarizing the article, it is important to remain objective and avoid injecting personal opinions or critiques. The summary should be a neutral representation of the article’s content, leaving the analysis and evaluation for the critique section.
V. Critiquing the Article

After providing a summary, it is time to analyze and critique the article. Begin by identifying the article’s strengths and weaknesses . Strengths may include well-reasoned arguments, thorough research, innovative ideas, or significant contributions to the field. Weaknesses could include flawed logic, lack of evidence, oversimplification of complex issues, or failure to address counterarguments.
Evaluate the Article’s Logic and Reasoning
Carefully evaluate the author’s logic and reasoning throughout the article. Are the arguments well-supported and logically consistent? Do the conclusions follow naturally from the evidence presented? Identify any logical fallacies, contradictions, or gaps in reasoning that may undermine the author’s arguments.
Discuss the Article’s Impact and Relevance
Consider the article’s potential impact and relevance within the broader context of the field. How does it contribute to existing knowledge or challenge prevailing theories? Does it open up new avenues for research or discussion? Discussing the article’s impact and relevance can help readers understand its significance and importance.
VI. Writing the Article Review

Begin your article review with an engaging introduction that captures the reader’s attention and provides context for the review. Briefly introduce the article, its author(s), and the main topic or research area. You can also include a concise thesis statement that summarizes your overall evaluation or critique of the article.
After the introduction, provide a brief overview or summary of the article. This should be a condensed version of the summary you wrote earlier, highlighting the article’s main arguments, key points, and conclusions. Keep this section concise and focused, as the main critique will follow.
Critique the Article’s Strengths and Weaknesses
In the critique section, present your analysis of the article’s strengths and weaknesses. Discuss the author’s use of evidence, the validity of their arguments, and the overall quality of their reasoning. Support your critique with specific examples and references from the article. Be sure to provide balanced criticism, acknowledging both the positive and negative aspects of the work.
In addition to critiquing the article , consider offering constructive suggestions for improvement. These suggestions could address areas where the author’s arguments were weak or where additional research or discussion is needed. Your suggestions should be specific and actionable, aimed at enhancing the quality and impact of the work.
Conclude your article review by summarizing your main points and providing an overall recommendation or final assessment of the article. This recommendation could be to read or not read the article, to use it as a reference in a specific context, or to consider it as a starting point for further research or discussion.
VII. Editing and Proofreading
After you have completed your initial draft, it is essential to carefully proofread and edit your work. Check for any grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, or typos that may have been overlooked during the writing process. These small errors can detract from the overall quality and professionalism of your review.
In addition to checking for mechanical errors , ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and coherent. Review your sentences and paragraphs for clarity, and make sure that your ideas flow logically from one point to the next. Avoid ambiguous or confusing language that could make your critique difficult to understand.
Depending on the specific requirements or guidelines for your article review, you may need to revise your work to ensure proper formatting and citation styles. Check that you have correctly cited any references or quotes from the article you are reviewing, and that your formatting (e.g., headings, spacing, font) adheres to the specified guidelines.
VIII. Finalizing the Review

Before finalizing your article review , take a step back and review the overall structure and flow of your writing. Ensure that your introduction effectively sets the stage for your critique, and that your body paragraphs logically build upon one another, leading to a well-supported conclusion.
During this final review, consider whether your critique is balanced and objective, presenting both the strengths and weaknesses of the article in a fair and impartial manner. Also, check that you have provided sufficient evidence and examples to support your analysis and that your arguments are clearly articulated.
After reviewing the overall structure and flow, make any necessary final edits and revisions to your article review. This might involve reorganizing or reworking certain sections for better clarity, strengthening your arguments with additional evidence, or refining your writing style for greater impact.
Pay close attention to your choice of words and tone, ensuring that your critique remains respectful and professional, even when addressing the article’s shortcomings. Remember, the goal is to provide a constructive and well-reasoned analysis, not to disparage or attack the author’s work.
Once you are satisfied with your article review, it is time to submit it according to the appropriate guidelines or requirements . This might involve formatting your work in a specific style, adhering to word count or page limits, or following specific submission procedures.
If your article review is intended for publication, be sure to follow the guidelines provided by the journal or publication outlet. This may include submitting your work through an online portal, adhering to specific formatting requirements, or including additional materials such as an abstract or author biography.
Congratulations! By following these steps, you have successfully written a comprehensive and effective article review. Remember, the process of critically evaluating published work is an essential skill that not only demonstrates your ability to analyze and synthesize complex information but also contributes to the ongoing scholarly discourse within your field.
Writing an article review can be a challenging task, but it is a valuable exercise that sharpens your critical thinking, analytical, and communication skills. By carefully reading and understanding the article, assessing its strengths and weaknesses, and providing a well-reasoned critique, you contribute to the advancement of knowledge and foster a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
So, embrace the opportunity to write article reviews, and use each one as a platform to engage with the ideas and arguments presented by scholars and researchers. Your thoughtful and insightful critiques can shape future research, inspire new perspectives, and ultimately drive progress within your field of study.
- RESEARCH PAPER FOR SALE
- RESEARCH PAPER WRITER
- RESEARCH PROPOSAL WRITING SERVICES
- SCHOLARSHIP ESSAY HELP
- SPEECH HELP
- STATISTICS HOMEWORK HELP
- TERM PAPER WRITING HELP
- THESIS EDITING SERVICES
- THESIS PROPOSAL WRITING SERVICE
- TRIGONOMETRY HOMEWORK HELP
- ADMISSION ESSAY WRITING HELP
- BIOLOGY PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- BOOK REPORT WRITING HELP
- BUY BOOK REVIEW
- BUY COURSEWORKS
- BUY DISCUSSION POST
- BUY TERM PAPER
- CAPSTONE PROJECT WRITING SERVICE
- COURSEWORK WRITING SERVICE
- CRITIQUE MY ESSAY
- CUSTOM RESEARCH PAPER
- CUSTOMER CONDUCT
- DISSERTATION EDITING SERVICE
- DISSERTATION WRITERS
- DO MY DISSERTATION FOR ME
- DO MY POWERPOINT PRESENTATION
- EDIT MY PAPER
- English Research Paper Writing Service
- ENGLISH RESEARCH PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- ESSAY WRITING HELP
- ESSAYS FOR SALE
- GRADUATE PAPER WRITING SERVICE
- LAW ASSIGNMENT WRITING HELP
- MARKETING ASSIGNMENT WRITING HELP
- NON-PLAGIARIZED ESSAYS
- NURSING ASSIGNMENT HELP
- PAY FOR COURSEWORK
- PAY FOR ESSAYS
- PAY FOR LITERATURE REVIEW
- PAY FOR PAPERS
- PAY FOR RESEARCH PAPERS
- PERSONAL STATEMENT EDITING SERVICE
- PERSONAL STATEMENT WRITER
- PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING HELP
- PERSUASIVE ESSAY WRITING SERVICES
- PHD THESIS WRITING SERVICE
- PROOFREAD MY PAPER
- PSYCHOLOGY ESSAY WRITING SERVICES
- THESIS STATEMENT HELP
- WRITE MY ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY FOR ME
- WRITE MY CASE STUDY
- WRITE MY DISCUSSION BOARD POST
- WRITE MY LAB REPORT
How to Write an Effective Journal Article Review
- First Online: 01 January 2012
Cite this chapter

- Dennis Drotar PhD 2 ,
- Yelena P. Wu PhD 3 &
- Jennifer M. Rohan MA 4
5636 Accesses
2 Citations
The experience of reviewing manuscripts for scientific journals is an important one in professional development. Reviewing articles gives trainees familiarity with the peer review process in ways that facilitate their writing. For example, reviewing manuscripts can help students and early career psychologists understand what reviewers and editors look for in a peer-reviewed article and ways to critique and enhance a manuscript based on peer review. Experiences in review can facilitate early career faculty with early entry into and experience being a reviewer for a professional journal. The experience of journal reviews also gives students a broader connection to the field of science in areas of their primary professional interest. At the same time reviewing articles for scientific journals poses a number of difficult challenges (see Hyman, 1995; Drotar, 2000a, 2009a, 2009b, 2009c, 2009d, 2010, 2011; Lovejoy, Revenson, & France, 2011). The purpose of this chapter is to provide an introduction to the review process and give step by step guidance in conducting reviews for scientific journals. Interested readers might wish to read Lovejoy et al.’s (2011) primer for manuscript review, which contains annotated examples of reviews and an editor’s decision letter.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
American Psychological Association. (2010). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Google Scholar
American Psychological Association Science Student Council. (2007). A graduate students’ guide to involvement in the peer review process. Retrieved July 15, 2011, from http://www.apa.org/research/publishing/
APA Publications and Communications Working Group on Journal Article Reporting Standards. (2008). Reporting standards for research in psychology. Why do we need them? What do they need to be? American Psychologist, 63 , 839–851.
Article Google Scholar
Cumming, G., & Finch, S. (2008). Putting research in context: Understanding confidence intervals from one or more studies. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 (9), 903–916.
PubMed Google Scholar
Drotar, D. (2000a). Reviewing and editing manuscripts for scientific journals. In D. Drotar (Ed.), Handbook of research methods in clinical child and pediatric psychology (pp. 409–425). New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum.
Chapter Google Scholar
Drotar, D. (2000b). Training professional psychologists to write and publish. The utility of a writer’s workshop seminar. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 31 , 453–457.
Drotar, D. (2009a). Editorial: How to write effective reviews for the Journal of Pediatric Psychology . Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 , 113–117.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Drotar, D. (2009b). Editorial: Thoughts in improving the quality of manuscripts submitted to the Journal of Pediatric Psychology: How to write a convincing introduction. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 , 1–3.
Drotar, D. (2009c). Editorial: How to report methods in the Journal of Pediatric Psychology . Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 , 227–230.
Drotar, D. (2009d). How to write an effective results and discussion section for the Journal of Pediatric Psychology . Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 , 339–343.
Drotar, D. (2010). Editorial: Guidance for submission and review of multiple publications derived from the same study. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 35 , 225–230.
Drotar, D. (2011). Editorial: How to write more effective, user friendly reviews for the Journal of Pediatric Psychology . Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 36 , 1–3.
Durlak, J. A. (2009). How to select, calculate, and interpret effect sizes. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 , 917–928.
Fiske, D. W., & Fogg, L. (1990). But the reviewers are making different criticisms of my paper: Diversity and uniqueness in reviewer comments. American Psychologist, 40 , 591–598.
Holmbeck, G. N., & Devine, K. A. (2009). Editorial: An author’s checklist for measure development and validation manuscripts. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 (7), 691–696.
Hyman, R. (1995). How to critique a published article. Psychological Bulletin, 118 , 178–182.
Journal of Pediatric Psychology mentoring policy & suggestions for conducting mentored reviews (2009). Retrieved July 15, 2011, from http://www.oxfordjournals.org/our_journals/jpepsy/for_authors/msprep_submission.html
Lovejoy, T. I., Revenson, T. A., & France, C. R. (2011). Reviewing manuscripts for peer-review journals: A primer for novice and seasoned reviewers. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 42 , 1–13.
Palermo, T. M. (2010). Editorial: Exploring ethical issues in peer review for the Journal of Pediatric Psychology. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 35 (3), 221–224.
Routh, D. K. (1995). Confessions of an editor, including mistakes I have made. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 24 , 236–241.
Sternberg, R. J. (Ed.). (2006). Reviewing scientific works in psychology . Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Stinson, J. N., McGrath, P. J., & Yamada, J. T. (2003). Clinical trials in the Journal of Pediatric Psychology : Applying the CONSORT statement. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 28 , 159–167.
Weller, A. C. (2001). Editorial peer review: Its strengths and weaknesses . Medford, NY: Information Today, Inc.
Wu, Y. P., Nassau, J. H., & Drotar, D. (2011). Mentoring reviewers: The Journal of Pediatric Psychology experience. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 36 , 258–264.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Behavioral Medicine and Clinical Psychology, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, MLC 7039, 3333 Burnet Avenue, Cincinnati, OH, 45229-3039, USA
Dennis Drotar PhD
Division of Behavioral Medicine and Clinical Psychology, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 45229-3039, USA
Yelena P. Wu PhD
Division of Behavioral Medicine and Clinical Psychology, Department of Psychology, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 45229-3039, USA
Jennifer M. Rohan MA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dennis Drotar PhD .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
, Department of Psychology, University of North Carolina at Chapel H, Davie Hall, Campus Box 3270, Chapel Hill, 27599-3270, North Carolina, USA
Mitchell J. Prinstein
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Drotar, D., Wu, Y.P., Rohan, J.M. (2013). How to Write an Effective Journal Article Review. In: Prinstein, M. (eds) The Portable Mentor. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3994-3_11
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3994-3_11
Published : 25 July 2012
Publisher Name : Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN : 978-1-4614-3993-6
Online ISBN : 978-1-4614-3994-3
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science Behavioral Science and Psychology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

How to write a journal article review: Do the writing
- What's in this Guide
- What is a journal article?
- Create a template
- Choose your article to review
- Read your article carefully
Do the writing
- Remember to edit
- Additional resources
Start to write. Follow the instructions of your assessment, then structure your writing accordingly.
The four key parts of a journal article review are:
3. A critique, or a discussion about the key points of the journal article.
A critique is a discussion about the key points of the journal article. It should be a balanced discussion about the strengths and weaknesses of the key points and structure of the article.
You will also need to discuss if the author(s) points are valid (supported by other literature) and robust (would you get the same outcome if the way the information was gathered was repeated).
Example of part of a critique
4. A conclusion - a final evaluation of the article
1. Give an overall opinion of the text.
2. Briefly summarise key points and determine if they are valid, useful, accurate etc.
3. Remember, do not include new ideas or opinions in the conclusion.
Pathways and Academic Learning Support

- << Previous: Read your article carefully
- Next: Remember to edit >>
- Last Updated: Apr 27, 2023 4:28 PM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-a-journal-article-review
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
How to Write a Peer Review

When you write a peer review for a manuscript, what should you include in your comments? What should you leave out? And how should the review be formatted?
This guide provides quick tips for writing and organizing your reviewer report.
Review Outline
Use an outline for your reviewer report so it’s easy for the editors and author to follow. This will also help you keep your comments organized.
Think about structuring your review like an inverted pyramid. Put the most important information at the top, followed by details and examples in the center, and any additional points at the very bottom.
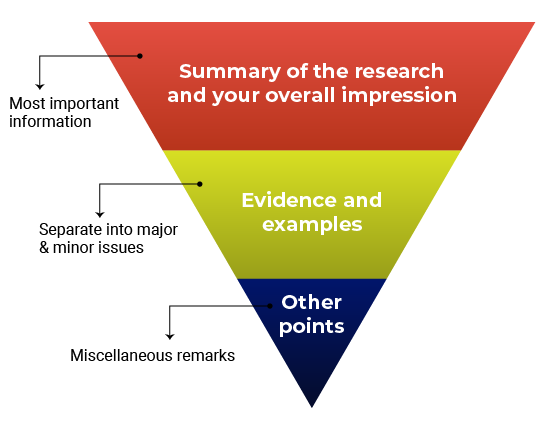
Here’s how your outline might look:
1. Summary of the research and your overall impression
In your own words, summarize what the manuscript claims to report. This shows the editor how you interpreted the manuscript and will highlight any major differences in perspective between you and the other reviewers. Give an overview of the manuscript’s strengths and weaknesses. Think about this as your “take-home” message for the editors. End this section with your recommended course of action.
2. Discussion of specific areas for improvement
It’s helpful to divide this section into two parts: one for major issues and one for minor issues. Within each section, you can talk about the biggest issues first or go systematically figure-by-figure or claim-by-claim. Number each item so that your points are easy to follow (this will also make it easier for the authors to respond to each point). Refer to specific lines, pages, sections, or figure and table numbers so the authors (and editors) know exactly what you’re talking about.
Major vs. minor issues
What’s the difference between a major and minor issue? Major issues should consist of the essential points the authors need to address before the manuscript can proceed. Make sure you focus on what is fundamental for the current study . In other words, it’s not helpful to recommend additional work that would be considered the “next step” in the study. Minor issues are still important but typically will not affect the overall conclusions of the manuscript. Here are some examples of what would might go in the “minor” category:
- Missing references (but depending on what is missing, this could also be a major issue)
- Technical clarifications (e.g., the authors should clarify how a reagent works)
- Data presentation (e.g., the authors should present p-values differently)
- Typos, spelling, grammar, and phrasing issues
3. Any other points
Confidential comments for the editors.
Some journals have a space for reviewers to enter confidential comments about the manuscript. Use this space to mention concerns about the submission that you’d want the editors to consider before sharing your feedback with the authors, such as concerns about ethical guidelines or language quality. Any serious issues should be raised directly and immediately with the journal as well.
This section is also where you will disclose any potentially competing interests, and mention whether you’re willing to look at a revised version of the manuscript.
Do not use this space to critique the manuscript, since comments entered here will not be passed along to the authors. If you’re not sure what should go in the confidential comments, read the reviewer instructions or check with the journal first before submitting your review. If you are reviewing for a journal that does not offer a space for confidential comments, consider writing to the editorial office directly with your concerns.
Get this outline in a template
Giving Feedback
Giving feedback is hard. Giving effective feedback can be even more challenging. Remember that your ultimate goal is to discuss what the authors would need to do in order to qualify for publication. The point is not to nitpick every piece of the manuscript. Your focus should be on providing constructive and critical feedback that the authors can use to improve their study.
If you’ve ever had your own work reviewed, you already know that it’s not always easy to receive feedback. Follow the golden rule: Write the type of review you’d want to receive if you were the author. Even if you decide not to identify yourself in the review, you should write comments that you would be comfortable signing your name to.
In your comments, use phrases like “ the authors’ discussion of X” instead of “ your discussion of X .” This will depersonalize the feedback and keep the focus on the manuscript instead of the authors.
General guidelines for effective feedback

- Justify your recommendation with concrete evidence and specific examples.
- Be specific so the authors know what they need to do to improve.
- Be thorough. This might be the only time you read the manuscript.
- Be professional and respectful. The authors will be reading these comments too.
- Remember to say what you liked about the manuscript!

Don’t
- Recommend additional experiments or unnecessary elements that are out of scope for the study or for the journal criteria.
- Tell the authors exactly how to revise their manuscript—you don’t need to do their work for them.
- Use the review to promote your own research or hypotheses.
- Focus on typos and grammar. If the manuscript needs significant editing for language and writing quality, just mention this in your comments.
- Submit your review without proofreading it and checking everything one more time.
Before and After: Sample Reviewer Comments
Keeping in mind the guidelines above, how do you put your thoughts into words? Here are some sample “before” and “after” reviewer comments
✗ Before
“The authors appear to have no idea what they are talking about. I don’t think they have read any of the literature on this topic.”
✓ After
“The study fails to address how the findings relate to previous research in this area. The authors should rewrite their Introduction and Discussion to reference the related literature, especially recently published work such as Darwin et al.”
“The writing is so bad, it is practically unreadable. I could barely bring myself to finish it.”
“While the study appears to be sound, the language is unclear, making it difficult to follow. I advise the authors work with a writing coach or copyeditor to improve the flow and readability of the text.”
“It’s obvious that this type of experiment should have been included. I have no idea why the authors didn’t use it. This is a big mistake.”
“The authors are off to a good start, however, this study requires additional experiments, particularly [type of experiment]. Alternatively, the authors should include more information that clarifies and justifies their choice of methods.”
Suggested Language for Tricky Situations
You might find yourself in a situation where you’re not sure how to explain the problem or provide feedback in a constructive and respectful way. Here is some suggested language for common issues you might experience.
What you think : The manuscript is fatally flawed. What you could say: “The study does not appear to be sound” or “the authors have missed something crucial”.
What you think : You don’t completely understand the manuscript. What you could say : “The authors should clarify the following sections to avoid confusion…”
What you think : The technical details don’t make sense. What you could say : “The technical details should be expanded and clarified to ensure that readers understand exactly what the researchers studied.”
What you think: The writing is terrible. What you could say : “The authors should revise the language to improve readability.”
What you think : The authors have over-interpreted the findings. What you could say : “The authors aim to demonstrate [XYZ], however, the data does not fully support this conclusion. Specifically…”
What does a good review look like?
Check out the peer review examples at F1000 Research to see how other reviewers write up their reports and give constructive feedback to authors.
Time to Submit the Review!
Be sure you turn in your report on time. Need an extension? Tell the journal so that they know what to expect. If you need a lot of extra time, the journal might need to contact other reviewers or notify the author about the delay.
Tip: Building a relationship with an editor
You’ll be more likely to be asked to review again if you provide high-quality feedback and if you turn in the review on time. Especially if it’s your first review for a journal, it’s important to show that you are reliable. Prove yourself once and you’ll get asked to review again!
- Getting started as a reviewer
- Responding to an invitation
- Reading a manuscript
- Writing a peer review
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…

- Research Process
Writing a good review article
- 3 minute read
- 77.7K views
Table of Contents
As a young researcher, you might wonder how to start writing your first review article, and the extent of the information that it should contain. A review article is a comprehensive summary of the current understanding of a specific research topic and is based on previously published research. Unlike research papers, it does not contain new results, but can propose new inferences based on the combined findings of previous research.
Types of review articles
Review articles are typically of three types: literature reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses.
A literature review is a general survey of the research topic and aims to provide a reliable and unbiased account of the current understanding of the topic.
A systematic review , in contrast, is more specific and attempts to address a highly focused research question. Its presentation is more detailed, with information on the search strategy used, the eligibility criteria for inclusion of studies, the methods utilized to review the collected information, and more.
A meta-analysis is similar to a systematic review in that both are systematically conducted with a properly defined research question. However, unlike the latter, a meta-analysis compares and evaluates a defined number of similar studies. It is quantitative in nature and can help assess contrasting study findings.
Tips for writing a good review article
Here are a few practices that can make the time-consuming process of writing a review article easier:
- Define your question: Take your time to identify the research question and carefully articulate the topic of your review paper. A good review should also add something new to the field in terms of a hypothesis, inference, or conclusion. A carefully defined scientific question will give you more clarity in determining the novelty of your inferences.
- Identify credible sources: Identify relevant as well as credible studies that you can base your review on, with the help of multiple databases or search engines. It is also a good idea to conduct another search once you have finished your article to avoid missing relevant studies published during the course of your writing.
- Take notes: A literature search involves extensive reading, which can make it difficult to recall relevant information subsequently. Therefore, make notes while conducting the literature search and note down the source references. This will ensure that you have sufficient information to start with when you finally get to writing.
- Describe the title, abstract, and introduction: A good starting point to begin structuring your review is by drafting the title, abstract, and introduction. Explicitly writing down what your review aims to address in the field will help shape the rest of your article.
- Be unbiased and critical: Evaluate every piece of evidence in a critical but unbiased manner. This will help you present a proper assessment and a critical discussion in your article.
- Include a good summary: End by stating the take-home message and identify the limitations of existing studies that need to be addressed through future studies.
- Ask for feedback: Ask a colleague to provide feedback on both the content and the language or tone of your article before you submit it.
- Check your journal’s guidelines: Some journals only publish reviews, while some only publish research articles. Further, all journals clearly indicate their aims and scope. Therefore, make sure to check the appropriateness of a journal before submitting your article.
Writing review articles, especially systematic reviews or meta-analyses, can seem like a daunting task. However, Elsevier Author Services can guide you by providing useful tips on how to write an impressive review article that stands out and gets published!

- Manuscript Preparation
What are Implications in Research?

How to write the results section of a research paper
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Scholarly Sources: What are They and Where can You Find Them?
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
How to Write an Article Review: Template & Examples
An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university, you shouldn’t confuse it with a response paper, which is a distinct assignment with other purposes (we’ll talk about it in detail below).
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
In this article, prepared by Custom-Writing experts, you’ll find:
- the intricacies of article review writing;
- the difference between an article review and similar assignments;
- a step-by-step algorithm for review composition;
- a couple of samples to guide you throughout the writing process.
So, if you wish to study our article review example and discover helpful writing tips, keep reading.

❓ What Is an Article Review?
- ✍️ Writing Steps
📑 Article Review Format
🔗 references.
An article review is an academic paper that summarizes and critically evaluates the information presented in your selected article.

The first thing you should note when approaching the task of an article review is that not every article is suitable for this assignment. Let’s have a look at the variety of articles to understand what you can choose from.
Popular Vs. Scholarly Articles
In most cases, you’ll be required to review a scholarly, peer-reviewed article – one composed in compliance with rigorous academic standards. Yet, the Web is also full of popular articles that don’t present original scientific value and shouldn’t be selected for a review.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Not sure how to distinguish these two types? Here is a comparative table to help you out.
Article Review vs. Response Paper
Now, let’s consider the difference between an article review and a response paper:
- If you’re assigned to critique a scholarly article , you will need to compose an article review .
- If your subject of analysis is a popular article , you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper .
The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of these two article types. Peer-reviewed, scholarly articles have clear-cut quality criteria, allowing you to conduct and present a structured assessment of the assigned material. Popular magazines have loose or non-existent quality criteria and don’t offer an opportunity for structured evaluation. So, they are only fit for a subjective response, in which you can summarize your reactions and emotions related to the reading material.
All in all, you can structure your response assignments as outlined in the tips below.
✍️ How to Write an Article Review: Step by Step
Here is a tried and tested algorithm for article review writing from our experts. We’ll consider only the critical review variety of this academic assignment. So, let’s get down to the stages you need to cover to get a stellar review.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 15% off your first order!
Read the Article
As with any reviews, reports, and critiques, you must first familiarize yourself with the assigned material. It’s impossible to review something you haven’t read, so set some time for close, careful reading of the article to identify:
- The author’s main points and message.
- The arguments they use to prove their points.
- The methodology they use to approach the subject.
In terms of research type , your article will usually belong to one of three types explained below.
Summarize the Article
Now that you’ve read the text and have a general impression of the content, it’s time to summarize it for your readers. Look into the article’s text closely to determine:
- The thesis statement , or general message of the author.
- Research question, purpose, and context of research.
- Supporting points for the author’s assumptions and claims.
- Major findings and supporting evidence.
As you study the article thoroughly, make notes on the margins or write these elements out on a sheet of paper. You can also apply a different technique: read the text section by section and formulate its gist in one phrase or sentence. Once you’re done, you’ll have a summary skeleton in front of you.
Evaluate the Article
The next step of review is content evaluation. Keep in mind that various research types will require a different set of review questions. Here is a complete list of evaluation points you can include.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Write the Text
After completing the critical review stage, it’s time to compose your article review.
The format of this assignment is standard – you will have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction should present your article and summarize its content. The body will contain a structured review according to all four dimensions covered in the previous section. The concluding part will typically recap all the main points you’ve identified during your assessment.
It is essential to note that an article review is, first of all, an academic assignment. Therefore, it should follow all rules and conventions of academic composition, such as:
- No contractions . Don’t use short forms, such as “don’t,” “can’t,” “I’ll,” etc. in academic writing. You need to spell out all those words.
- Formal language and style . Avoid conversational phrasing and words that you would naturally use in blog posts or informal communication. For example, don’t use words like “pretty,” “kind of,” and “like.”
- Third-person narrative . Academic reviews should be written from the third-person point of view, avoiding statements like “I think,” “in my opinion,” and so on.
- No conversational forms . You shouldn’t turn to your readers directly in the text by addressing them with the pronoun “you.” It’s vital to keep the narrative neutral and impersonal.
- Proper abbreviation use . Consult the list of correct abbreviations , like “e.g.” or “i.e.,” for use in your academic writing. If you use informal abbreviations like “FYA” or “f.i.,” your professor will reduce the grade.
- Complete sentences . Make sure your sentences contain the subject and the predicate; avoid shortened or sketch-form phrases suitable for a draft only.
- No conjunctions at the beginning of a sentence . Remember the FANBOYS rule – don’t start a sentence with words like “and” or “but.” They often seem the right way to build a coherent narrative, but academic writing rules disfavor such usage.
- No abbreviations or figures at the beginning of a sentence . Never start a sentence with a number — spell it out if you need to use it anyway. Besides, sentences should never begin with abbreviations like “e.g.”
Finally, a vital rule for an article review is properly formatting the citations. We’ll discuss the correct use of citation styles in the following section.
When composing an article review, keep these points in mind:
- Start with a full reference to the reviewed article so the reader can locate it quickly.
- Ensure correct formatting of in-text references.
- Provide a complete list of used external sources on the last page of the review – your bibliographical entries .
You’ll need to understand the rules of your chosen citation style to meet all these requirements. Below, we’ll discuss the two most common referencing styles – APA and MLA.
Article Review in APA
When you need to compose an article review in the APA format , here is the general bibliographical entry format you should use for journal articles on your reference page:
- Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year of Publication). Name of the article. Name of the Journal, volume (number), pp. #-#. https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy
Horigian, V. E., Schmidt, R. D., & Feaster, D. J. (2021). Loneliness, mental health, and substance use among US young adults during COVID-19. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 53 (1), pp. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2020.1836435
Your in-text citations should follow the author-date format like this:
- If you paraphrase the source and mention the author in the text: According to Horigian et al. (2021), young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic.
- If you paraphrase the source and don’t mention the author in the text: Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al., 2021).
- If you quote the source: As Horigian et al. (2021) point out, there were “elevated levels of loneliness, depression, anxiety, alcohol use, and drug use among young adults during COVID-19” (p. 6).
Note that your in-text citations should include “et al.,” as in the examples above, if your article has 3 or more authors. If you have one or two authors, your in-text citations would look like this:
- One author: “According to Smith (2020), depression is…” or “Depression is … (Smith, 2020).”
- Two authors: “According to Smith and Brown (2020), anxiety means…” or “Anxiety means (Smith & Brown, 2020).”
Finally, in case you have to review a book or a website article, here are the general formats for citing these source types on your APA reference list.
Article Review in MLA
If your assignment requires MLA-format referencing, here’s the general format you should use for citing journal articles on your Works Cited page:
- Author’s last name, First name. “Title of an Article.” Title of the Journal , vol. #, no. #, year, pp. #-#.
Horigian, Viviana E., et al. “Loneliness, Mental Health, and Substance Use Among US Young Adults During COVID-19.” Journal of Psychoactive Drugs , vol. 53, no. 1, 2021, pp. 1-9.
In-text citations in the MLA format follow the author-page citation format and look like this:
- According to Horigian et al., young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (6).
- Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al. 6).
Like in APA, the abbreviation “et al.” is only needed in MLA if your article has 3 or more authors.
If you need to cite a book or a website page, here are the general MLA formats for these types of sources.
✅ Article Review Template
Here is a handy, universal article review template to help you move on with any review assignment. We’ve tried to make it as generic as possible to guide you in the academic process.
📝 Article Review Examples
The theory is good, but practice is even better. Thus, we’ve created three brief examples to show you how to write an article review. You can study the full-text samples by following the links.
📃 Men, Women, & Money
This article review examines a famous piece, “Men, Women & Money – How the Sexes Differ with Their Finances,” published by Amy Livingston in 2020. The author of this article claims that men generally spend more money than women. She makes this conclusion from a close analysis of gender-specific expenditures across five main categories: food, clothing, cars, entertainment, and general spending patterns. Livingston also looks at men’s approach to saving to argue that counter to the common perception of women’s light-hearted attitude to money, men are those who spend more on average.
📃 When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism
This is a review of Jonathan Heidt’s 2016 article titled “When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism,” written as an advocacy of right-wing populism rising in many Western states. The author illustrates the case with the election of Donald Trump as the US President and the rise of right-wing rhetoric in many Western countries. These examples show how nationalist sentiment represents a reaction to global immigration and a failure of globalization.
📃 Sleep Deprivation
This is a review of the American Heart Association’s article titled “The Dangers of Sleep Deprivation.” It discusses how the national organization concerned with the American population’s cardiovascular health links the lack of high-quality sleep to far-reaching health consequences. The organization’s experts reveal how a consistent lack of sleep leads to Alzheimer’s disease development, obesity, type 2 diabetes, etc.
✏️ Article Review FAQ
A high-quality article review should summarize the assigned article’s content and offer data-backed reactions and evaluations of its quality in terms of the article’s purpose, methodology, and data used to argue the main points. It should be detailed, comprehensive, objective, and evidence-based.
The purpose of writing a review is to allow students to reflect on research quality and showcase their critical thinking and evaluation skills. Students should exhibit their mastery of close reading of research publications and their unbiased assessment.
The content of your article review will be the same in any format, with the only difference in the assignment’s formatting before submission. Ensure you have a separate title page made according to APA standards and cite sources using the parenthetical author-date referencing format.
You need to take a closer look at various dimensions of an assigned article to compose a valuable review. Study the author’s object of analysis, the purpose of their research, the chosen method, data, and findings. Evaluate all these dimensions critically to see whether the author has achieved the initial goals. Finally, offer improvement recommendations to add a critique aspect to your paper.
- Scientific Article Review: Duke University
- Book and Article Reviews: William & Mary, Writing Resources Center
- Sample Format for Reviewing a Journal Article: Boonshoft School of Medicine
- Research Paper Review – Structure and Format Guidelines: New Jersey Institute of Technology
- Article Review: University of Waterloo
- Article Review: University of South Australia
- How to Write a Journal Article Review: University of Newcastle Library Guides
- Writing Help: The Article Review: Central Michigan University Libraries
- Write a Critical Review of a Scientific Journal Article: McLaughlin Library
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
How to Write an Article Review: Practical Tips and Examples
Table of contents
- 1 What Is an Article Review?
- 2 Different Types of Article Review
- 3.1 Critical review
- 3.2 Literature review
- 3.3 Mapping review/systematic map
- 3.4 Meta-analysis
- 3.5 Overview
- 3.6 Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
- 3.7 Rapid review
- 3.8 Scoping review
- 3.9 Systematic review
- 3.10 Umbrella review
- 4 Formatting
- 5 How To Write An Article Review
- 6 Article Review Outline
- 7 10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
- 8 An Article Review Example
What Is an Article Review?
Before you get started, learn what an article review is. It can be defined as a work that combines elements of summary and critical analysis. If you are writing an article review, you should take a close look at another author’s work. Many experts regularly practice evaluating the work of others. The purpose of this is to improve writing skills.
This kind of work belongs to professional pieces of writing because the process of crafting this paper requires reviewing, summarizing, and understanding the topic. Only experts are able to compose really good reviews containing a logical evaluation of a paper as well as a critique.
Your task is not to provide new information. You should process what you have in a certain publication.
Different Types of Article Review
In academic writing, the landscape of article reviews is diverse and nuanced, encompassing a variety of formats that cater to different research purposes and methodologies. Among these, three main types of article reviews stand out due to their distinct approaches and applications:
- Narrative. The basic focus here is the author’s personal experience. Judgments are presented through the prism of experiences and subsequent realizations. Besides, the use of emotional recollections is acceptable.
- Evidence. There is a significant difference from the narrative review. An in-depth study of the subject is assumed, and conclusions are built on arguments. The author may consider theories or concrete facts to support that.
- Systematic. The structure of the piece explains the approach to writing. The answer to what’s a systematic review lies on the surface. The writer should pay special attention to the chronology and logic of the narrative.
Understanding 10 Common Types
Don`t rush looking at meta-analysis vs. systematic review. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with other formats and topics of texts. This will allow you to understand the types of essays better and select them based on your request. For this purpose, we`ll discuss the typology of reviews below.
Critical review
The critical review definition says that the author must be objective and have arguments for each thought. Sometimes, amateur authors believe that they should “criticize” something. However, it is important to understand the difference since objectivity and the absence of emotional judgments are prioritized. The structure of this type of review article is as follows:
- Introduction;
- Conclusion.
“Stuffing” of the text is based on such elements as methodology, argumentation, evidence, and theory base. The subject of study is stated at the beginning of the material. Then follows the transition to the main part (facts). The final word summarizes all the information voiced earlier.
It is a mistake to believe that critical reviews are devoid of evaluation. The author’s art lies in maneuvering between facts. Smooth transition from one argument to another and lays out the conclusions in the reader. That is why such texts are used in science. The critical reviews meaning is especially tangible in medical topics.
Literature review
Literature is the basis for this type of work ─ books, essays, and articles become a source of information. Thus, the author should rethink the voiced information. After that, it is possible to proceed to conclusions. The methodology aims to find interconnections, repetitions, and even “gaps” in the literature. One important item is the referencing of sources. Footnotes are possible in the work itself or the list of resources used.
These types of research reviews often explore myths since there are often inconsistencies in mythology. Sometimes, there is contrary information. In this case, the author has to gather all existing theories. The essence does not always lie in the confirmation of facts. There are other different types of reviews for this purpose. In literary reviews, the object of study may be characters or traditions. This is where the author’s space for discovery opens up. Inconsistencies in the data can tell important details about particular periods or cultures. At the same time, patterns reveal well-established facts. Make sure to outline your work before you write. This will help you with essay writing .
Mapping review/systematic map
A mapping review, also known as a systematic map, is a unique approach to surveying and organizing existing literature, providing a panoramic view of the research landscape. This paper systematically categorizes and maps out the available literature on a particular topic, emphasizing breadth over depth. Its primary goal is to present a comprehensive visual representation of the research distribution, offering insights into the overall scope of a subject.
One of the strengths of systematic reviews is that they deeply focus on a research question with detailed analysis and synthesis, while mapping review prioritizes breadth. It identifies and categorizes a broad range of studies without necessarily providing in-depth critique or content synthesis. This approach allows for a broader understanding of the field, making it especially useful in the early stages of research. Mapping reviews excel in identifying gaps in the existing body of literature.
By systematically mapping the distribution of research, researchers can pinpoint areas where studies are scarce or nonexistent, helping to guide future research directions. This makes mapping reviews a valuable tool for researchers seeking to contribute meaningfully to a field by addressing unexplored or underexplored areas.
Meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a powerful statistical technique. It systematically combines the results of multiple studies to derive comprehensive and nuanced insights. This method goes beyond the limitations of individual studies, offering a more robust understanding of a particular phenomenon by synthesizing data from diverse sources.
Meta-analysis employs a rigorous methodology. It involves the systematic collection and statistical integration of data from multiple studies. This methodological rigor ensures a standardized and unbiased approach to data synthesis. It is applied across various disciplines, from medicine and psychology to social sciences, providing a quantitative assessment of the overall effect of an intervention or the strength of an association.
In evidence-based fields, where informed decision-making relies on a thorough understanding of existing research, meta-analysis plays a pivotal role. It offers a quantitative overview of the collective evidence, helping researchers, policymakers, and practitioners make more informed decisions. By synthesizing results from diverse studies, meta-analysis contributes to the establishment of robust evidence-based practices, enhancing the reliability and credibility of findings in various fields. To present your research findings in the most readable way possible, learn how to write a summary of article .
If the key purpose of systematic review is to maximize the disclosure of facts, the opposite is true here. Imagine a video shot by a quadcopter from an altitude. The viewer sees a vast area of terrain without focusing on individual details. Overviews follow the same principle. The author gives a general picture of the events or objects described.
These types of reviews often seem simple. However, the role of the researcher becomes a very demanding one. The point is not just to list facts. Here, the search for information comes to the fore. After all, it is such reports that, in the future, will provide the basis for researching issues more narrowly. In essence, you yourself create a new source of information ─ students who worry that somebody may critique the author’s article love this type of material. However, there are no questions for the author; they just set the stage for discussions in different fields.
An example of this type of report would be a collection of research results from scientists. For example, statistics on the treatment of patients with certain diseases. In such a case, reference is made to scientific articles and doctrines. Based on this information, readers can speak about the effectiveness of certain treatment methods.
Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
One of the next types of review articles represents a meticulous effort to synthesize and analyze qualitative studies within a specific research domain.
The focus is synthesizing qualitative studies, employing a systematic and rigorous approach to extract meaningful insights. Its significance lies in its ability to provide a nuanced understanding of complex phenomena, offering a qualitative lens to complement quantitative analyses. Researchers can uncover patterns, themes, and contextual nuances that may elude traditional quantitative approaches by systematically reviewing and synthesizing qualitative data.
Often, you may meet discussion: is a systematic review quantitative or qualitative? The application of qualitative systematic reviews extends across diverse research domains, from healthcare and social sciences to education and psychology. For example, this approach can offer a comprehensive understanding of patient experiences and preferences in healthcare. In social sciences, it can illuminate cultural or societal dynamics. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for researchers exploring, interpreting, and integrating qualitative findings to enrich their understanding of complex phenomena within their respective fields.
Rapid review
If you don’t know how to write an article review , try starting with this format. It is the complete opposite of everything we talked about above. The key advantage and feature is speed. Quick overviews are used when time is limited. The focus can go to individual details (key). Often, the focus is still on the principal points.
Often, these types of review papers are critically needed in politics. This method helps to communicate important information to the reader quickly. An example can be a comparison of the election programs of two politicians. The author can show the key differences. Or it can make an overview based on the theses of the opponents’ proposals on different topics.
Seeming simplicity becomes power. Such texts allow the reader to make a quick decision. The author’s task is to understand potential interests and needs. Then, highlight and present the most important data as concisely as possible. In addition to politics, such reports are often used in communications, advertising, and marketing. Experienced writers mention the one-minute principle. This means you can count on 60 seconds of the reader’s attention. If you managed to hook them ─ bravo, you have done the job!
Scoping review
If you read the official scoping review definition, you may find similarities with the systematic type of review. However, recall is a sequential and logical study in the second case. It’s like you stack things on a shelf by color, size, and texture.
This type of review can be more difficult to understand. The basic concept is to explore what is called the field of subjects. This means, on the one hand, exploring a particular topic through the existing data about it. The author tries to find gaps or patterns by drawing on sources of information.
Another good comparison between systematic and this type of review is imagining as if drawing a picture. In the first case, you will think through every nuance and detail, why it is there, and how it “moves the story.” In the second case, it is as if you are painting a picture with “broad strokes.” In doing so, you can explain your motives for choosing the primary color. For example: “I chose the emerald color because all the cultural publications say it’s a trend”. The same goes for texts.
Systematic review
Sometimes, you may encounter a battle: narrative review vs. systematic review. The point is not to compare but to understand the different types of papers. Once you understand their purpose, you can present your data better and choose a more readable format. The systematic approach can be called the most scientific. Such a review relies on the following steps:
- Literature search;
- Evaluating the information;
- Data processing;
- Careful analysis of the material.
It is the fourth point that is key. The writer should carefully process the information before using it. However, 80% of your work’s result depends on this stage’s seriousness.
A rigorous approach to data selection produces an array of factual data. That is why this method is so often used in science, education, and social fields. Where accuracy is important. At the same time, the popularity of this approach is growing in other directions.
Systematic reviews allow for using different data and methodologies,, but with one important caveat ─ if the author manages to keep the narrative structured and explain the reason for certain methods. It is not about rigor. The task of this type of review is to preserve the facts, which dictates consistency and rationality.
Umbrella review
An umbrella review is a distinctive approach that involves the review of existing reviews, providing a comprehensive synthesis of evidence on a specific topic. The methodology of an umbrella review entails systematically examining and summarizing findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
This method ensures a rigorous and consolidated analysis of the existing evidence. The application of an umbrella review is broad, spanning various fields such as medicine, public health, and social sciences. It is particularly useful when a substantial body of systematic reviews exists, allowing researchers to draw overarching conclusions from the collective findings.
It allows the summarization of existing reviews and provides a new perspective on individual subtopics of the main object of study. In the context of the umbrella method, the comparison “bird’s eye view” is often cited. A bird in flight can see the whole panorama and shift its gaze to specific objects simultaneously. What becomes relevant at a particular moment? The author will face the same task.
On the one hand, you must delve into the offshoots of the researched topic. On the other hand, focus on the topic or object of study as a whole. Such a concept allows you to open up new perspectives and thoughts.

Different types of formatting styles are used for article review writing. It mainly depends on the guidelines that are provided by the instructor, sometimes, professors even provide an article review template that needs to be followed.
Here are some common types of formatting styles that you should be aware of when you start writing an article review:
- APA (American Psychological Association) – An APA format article review is commonly used for social sciences. It has guidelines for formatting the title, abstract, body paragraphs, and references. For example, the title of an article in APA format is in sentence case, whereas the publication title is in title case.
- MLA (Modern Language Association): This is a formatting style often used in humanities, such as language studies and literature. There are specific guidelines for the formatting of the title page, header, footer, and citation style.
- Chicago Manual of Style: This is one of the most commonly used formatting styles. It is often used for subjects in humanities and social sciences, but also commonly found in a newspaper title. This includes guidelines for formatting the title page, end notes, footnotes, publication title, article citation, and bibliography.
- Harvard Style: Harvard style is commonly used for social sciences and provides specific guidelines for formatting different sections of the pages, including publication title, summary page, website publisher, and more.
To ensure that your article review paper is properly formatted and meets the requirements, it is crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for the formatting style you are using. This helps you write a good article review.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
How To Write An Article Review
There are several steps that must be followed when you are starting to review articles. You need to follow these to make sure that your thoughts are organized properly. In this way, you can present your ideas in a more concise and clear manner. Here are some tips on how to start an article review and how to cater to each writing stage.
- Read the Article Closely: Even before you start to write an article review, it’s important to make sure that you have read the specific article thoroughly. Write down the central points and all the supporting ideas. It’s important also to note any questions or comments that you have about the content.
- Identify the Thesis: Make sure that you understand the author’s main points, and identify the main thesis of the article. This will help you focus on your review and ensure that you are addressing all of the key points.
- Formulate an Introduction: The piece should start with an introduction that has all the necessary background information, possibly in the first paragraph or in the first few paragraphs. This can include a brief summary of the important points or an explanation of the importance.
- Summarize the Article : Summarize the main points when you review the article, and make sure that you include all supporting elements of the author’s thesis.
- Start with Personal Critique : Now is the time to include a personal opinion on the research article or the journal article review. Start with evaluating all the strengths and weaknesses of the reviewed article. Discuss all of the flaws that you found in the author’s evidence and reasoning. Also, point out whether the conclusion provided by the author was well presented or not.
- Add Personal Perspective: Offer your perspective on the original article, do you agree or disagree with the ideas that the article supports or not. Your critical review, in your own words, is an essential part of a good review. Make sure you address all unanswered questions in your review.
- Conclude the Article Review : In this section of the writing process, you need to be very careful and wrap up the whole discussion in a coherent manner. This is should summarize all the main points and offer an overall assessment.
Make sure to stay impartial and provide proof to back up your assessment. By adhering to these guidelines, you can create a reflective and well-structured article review.
Article Review Outline
Here is a basic, detailed outline for an article review you should be aware of as a pre-writing process if you are wondering how to write an article review.
Introduction
- Introduce the article that you are reviewing (author name, publication date, title, etc.) Now provide an overview of the article’s main topic
Summary section
- Summarize the key points in the article as well as any arguments Identify the findings and conclusion
Critical Review
- Assess and evaluate the positive aspects and the drawbacks
- Discuss if the authors arguments were verified by the evidence of the article
- Identify if the text provides substantial information for any future paper or further research
- Assess any gaps in the arguments
- Restate the thesis statement
- Provide a summary for all sections
- Write any recommendations and thoughts that you have on the article
- Never forget to add and cite any references that you used in your article
10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
Have you ever written such an assignment? If not, study the helpful tips for composing a paper. If you follow the recommendations provided here, the process of writing a summary of the article won’t be so time-consuming, and you will be able to write an article in the most effective manner.
The guidelines below will help to make the process of preparing a paper much more productive. Let’s get started!
- Check what kind of information your work should contain. After answering the key question “What is an article review?” you should learn how to structure it the right way. To succeed, you need to know what your work should be based on. An analysis with insightful observations is a must for your piece of writing.
- Identify the central idea: In your first reading, focus on the overall impression. Gather ideas about what the writer wants to tell, and consider whether he or she managed to achieve it.
- Look up unfamiliar terms. Don’t know what certain words and expressions mean? Highlight them, and don’t forget to check what they mean with a reliable source of information.
- Highlight the most important ideas. If you are reading it a second time, use a highlighter to highlight the points that are most important to understanding the passage.
- Write an outline. A well-written outline will make your life a lot easier. All your thoughts will be grouped. Detailed planning helps not to miss anything important. Think about the questions you should answer when writing.
- Brainstorm headline ideas. When choosing a project, remember: it should reflect the main idea. Make it bold and concise.
- Check an article review format example. You should check that you know how to cite an article properly. Note that citation rules are different in APA and MLA formats. Ask your teacher which one to prioritize.
- Write a good introduction. Use only one short paragraph to state the central idea of the work. Emphasize the author’s key concepts and arguments. Add the thesis at the end of the Introduction.
- Write in a formal style. Use the third person, remembering that this assignment should be written in a formal academic writing style.
- Wrap up, offer your critique, and close. Give your opinion on whether the author achieved his goals. Mention the shortcomings of the job, if any, and highlight its strengths.
If you have checked the tips and you still doubt whether you have all the necessary skills and time to prepare this kind of educational work, follow one more tip that guarantees 100% success- ask for professional assistance by asking the custom writing service PapersOwl to craft your paper instead of you. Just submit an order online and get the paper completed by experts.

An Article Review Example
If you have a task to prepare an analysis of a certain piece of literature, have a look at the article review sample. There is an article review example for you to have a clear picture of what it must look like.
Journal Article on Ayn Rand’s Works Review Example
“The purpose of the article is to consider the features of the poetics of Ayn Rand’s novels “Atlas Shrugged,” “We the living,” and “The Fountainhead.” In the analysis of the novels, the structural-semantic and the method of comparative analysis were used.
With the help of these methods, genre features of the novels were revealed, and a single conflict and a cyclic hero were identified.
In-depth reading allows us to more fully reveal the worldview of the author reflected in the novels. It becomes easier to understand the essence of the author’s ideas about the connection between being and consciousness, embodied in cyclic ideas and images of plot twists and heroes. The author did a good job highlighting the strong points of the works and mentioning the reasons for the obvious success of Ayn Rand.“
You can also search for other relevant article review examples before you start.
In conclusion, article reviews play an important role in evaluating and analyzing different scholarly articles. Writing a review requires critical thinking skills and a deep understanding of the article’s content, style, and structure. It is crucial to identify the type of article review and follow the specific guidelines for formatting style provided by the instructor or professor.
The process of writing an article review requires several steps, such as reading the article attentively, identifying the thesis, and formulating an introduction. By following the tips and examples provided in this article, students can write a worthy review that demonstrates their ability to evaluate and critique another writer’s work.
Learning how to write an article review is a critical skill for students and professionals alike. Before diving into the nitty-gritty of reviewing an article, it’s important to understand what an article review is and the elements it should include. An article review is an assessment of a piece of writing that summarizes and evaluates a work. To complete a quality article review, the author should consider the text’s purpose and content, its organization, the author’s style, and how the article fits into a larger conversation. But if you don’t have the time to do all of this work, you can always purchase a literature review from Papers Owl .
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Article Review
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples

People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Struggling to write a review that people actually want to read? Feeling lost in the details and wondering how to make your analysis stand out?
You're not alone!
Many writers find it tough to navigate the world of article reviews, not sure where to start or how to make their reviews really grab attention.
No worries!
In this blog, we're going to guide you through the process of writing an article review that stands out. We'll also share tips, and examples to make this process easier for you.
Let’s get started.
- 1. What is an Article Review?
- 2. Types of Article Reviews
- 3. Article Review Format
- 4. How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
- 5. Article Review Outline
- 6. Article Review Examples
- 7. Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
What is an Article Review?
An article review is a critical evaluation and analysis of a piece of writing, typically an academic or journalistic article.
It goes beyond summarizing the content; it involves an in-depth examination of the author's ideas, arguments, and methodologies.
The goal is to provide a well-rounded understanding of the article's strengths, weaknesses, and overall contribution to the field.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Types of Article Reviews
Article reviews come in various forms, each serving a distinct purpose in the realm of academic or professional discourse. Understanding these types is crucial for tailoring your approach.
Here are some common types of article reviews:
Journal Article Review
A journal article review involves a thorough evaluation of scholarly articles published in academic journals.
It requires summarizing the article's key points, methodology, and findings, emphasizing its contributions to the academic field.
Take a look at the following example to help you understand better.
Example of Journal Article Review
Research Article Review
A research article review focuses on scrutinizing articles with a primary emphasis on research.
This type of review involves evaluating the research design, methodology, results, and their broader implications.
Discussions on the interpretation of results, limitations, and the article's overall contributions are key.
Here is a sample for you to get an idea.
Example of Research Article Review
Science Article Review
A science article review specifically addresses articles within scientific disciplines. It includes summarizing scientific concepts, hypotheses, and experimental methods.
The type of review assesses the reliability of the experimental design, and evaluates the author's interpretation of findings.
Take a look at the following example.
Example of Science Article Review
Critical Review
A critical review involves a balanced critique of a given article. It encompasses providing a comprehensive summary, highlighting key points, and engaging in a critical analysis of strengths and weaknesses.
To get a clearer idea of a critical review, take a look at this example.
Critical Review Example
Article Review Format
When crafting an article review in either APA or MLA format, it's crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for citing sources.
Below are the bibliographical entries for different types of sources in both APA and MLA styles:
How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
Writing an effective article review involves a systematic approach. Follow this step-by-step process to ensure a comprehensive and well-structured analysis.
Step 1: Understand the Assignment
Before diving into the review, carefully read and understand the assignment guidelines.
Pay attention to specific requirements, such as word count, formatting style (APA, MLA), and the aspects your instructor wants you to focus on.
Step 2: Read the Article Thoroughly
Begin by thoroughly reading the article. Take notes on key points, arguments, and evidence presented by the author.
Understand the author's main thesis and the context in which the article was written.
Step 3: Create a Summary
Summarize the main points of the article. Highlight the author's key arguments and findings.
While writing the summary ensure that you capture the essential elements of the article to provide context for your analysis.
Step 4: Identify the Author's Thesis
In this step, pinpoint the author's main thesis or central argument. Understand the purpose of the article and how the author supports their position.
This will serve as a foundation for your critique.
Step 5: Evaluate the Author's Evidence and Methodology
Examine the evidence provided by the author to support their thesis. Assess the reliability and validity of the methodology used.
Consider the sources, data collection methods, and any potential biases.
Step 6: Analyze the Author's Writing Style
Evaluate the author's writing style and how effectively they communicate their ideas.
Consider the clarity of the language, the organization of the content, and the overall persuasiveness of the article.
Step 7: Consider the Article's Contribution
Reflect on the article's contribution to its field of study. Analyze how it fits into the existing literature, its significance, and any potential implications for future research or applications.
Step 8: Write the Introduction
Craft an introduction that includes the article's title, author, publication date, and a brief overview.
State the purpose of your review and your thesis—the main point you'll be analyzing in your review.
Step 9: Develop the Body of the Review
Organize your review by addressing specific aspects such as the author's thesis, methodology, writing style, and the article's contribution.
Use clear paragraphs to structure your analysis logically.
Step 10: Conclude with a Summary and Evaluation
Summarize your main points and restate your overall assessment of the article.
Offer insights into its strengths and weaknesses, and conclude with any recommendations for improvement or suggestions for further research.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Article Review Outline
Creating a well-organized outline is an essential part of writing a coherent and insightful article review.
This outline given below will guide you through the key sections of your review, ensuring that your analysis is comprehensive and logically structured.
Refer to the following template to understand outlining the article review in detail.
Article Review Format Template
Article Review Examples
Examining article review examples can provide valuable insights into the structure, tone, and depth of analysis expected.
Below are sample article reviews, each illustrating a different approach and focus.
Example of Article Review
Sample of article review assignment pdf
Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
Crafting an effective article review involves a combination of critical analysis, clarity, and structure.
Here are some valuable tips to guide you through the process:
- Start with a Clear Introduction
Kick off your article review by introducing the article's main points and mentioning the publication date, which you can find on the re-title page. Outline the topics you'll cover in your review.
- Concise Summary with Unanswered Questions
Provide a short summary of the article, emphasizing its main ideas. Highlight any lingering questions, known as "unanswered questions," that the article may have triggered. Use a basic article review template to help structure your thoughts.
- Illustrate with Examples
Use examples from the article to illustrate your points. If there are tables or figures in the article, discuss them to make your review more concrete and easily understandable.
- Organize Clearly with a Summary Section
Keep your review straightforward and well-organized. Begin with the start of the article, express your thoughts on what you liked or didn't like, and conclude with a summary section. This follows a basic plan for clarity.
- Constructive Criticism
When providing criticism, be constructive. If there are elements you don't understand, frame them as "unanswered questions." This approach shows engagement and curiosity.
- Smoothly Connect Your Ideas
Ensure your thoughts flow naturally throughout your review. Use simple words and sentences. If you have questions about the article, let them guide your review organically.
- Revise and Check for Clarity
Before finishing, go through your review. Correct any mistakes and ensure it sounds clear. Check if you followed your plan, used simple words, and incorporated the keywords effectively. This makes your review better and more accessible for others.
In conclusion , writing an effective article review involves a thoughtful balance of summarizing key points, and addressing unanswered questions.
By following a simple and structured approach, you can create a review that not only analyzes the content but also adds value to the reader's understanding.
Remember to organize your thoughts logically, use clear language, and provide examples from the article to support your points.
Ready to elevate your article reviewing skills? Explore the valuable resources and expert assistance at MyPerfectWords.com.
Our team of experienced writers is here to help you with article reviews and other school tasks.
So why wait? Place your " write my essays online " request today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
Page Content
Overview of the review report format, the first read-through, first read considerations, spotting potential major flaws, concluding the first reading, rejection after the first reading, before starting the second read-through, doing the second read-through, the second read-through: section by section guidance, how to structure your report, on presentation and style, criticisms & confidential comments to editors, the recommendation, when recommending rejection, additional resources, step by step guide to reviewing a manuscript.
When you receive an invitation to peer review, you should be sent a copy of the paper's abstract to help you decide whether you wish to do the review. Try to respond to invitations promptly - it will prevent delays. It is also important at this stage to declare any potential Conflict of Interest.
The structure of the review report varies between journals. Some follow an informal structure, while others have a more formal approach.
" Number your comments!!! " (Jonathon Halbesleben, former Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Informal Structure
Many journals don't provide criteria for reviews beyond asking for your 'analysis of merits'. In this case, you may wish to familiarize yourself with examples of other reviews done for the journal, which the editor should be able to provide or, as you gain experience, rely on your own evolving style.
Formal Structure
Other journals require a more formal approach. Sometimes they will ask you to address specific questions in your review via a questionnaire. Or they might want you to rate the manuscript on various attributes using a scorecard. Often you can't see these until you log in to submit your review. So when you agree to the work, it's worth checking for any journal-specific guidelines and requirements. If there are formal guidelines, let them direct the structure of your review.
In Both Cases
Whether specifically required by the reporting format or not, you should expect to compile comments to authors and possibly confidential ones to editors only.

Following the invitation to review, when you'll have received the article abstract, you should already understand the aims, key data and conclusions of the manuscript. If you don't, make a note now that you need to feedback on how to improve those sections.
The first read-through is a skim-read. It will help you form an initial impression of the paper and get a sense of whether your eventual recommendation will be to accept or reject the paper.
Keep a pen and paper handy when skim-reading.
Try to bear in mind the following questions - they'll help you form your overall impression:
- What is the main question addressed by the research? Is it relevant and interesting?
- How original is the topic? What does it add to the subject area compared with other published material?
- Is the paper well written? Is the text clear and easy to read?
- Are the conclusions consistent with the evidence and arguments presented? Do they address the main question posed?
- If the author is disagreeing significantly with the current academic consensus, do they have a substantial case? If not, what would be required to make their case credible?
- If the paper includes tables or figures, what do they add to the paper? Do they aid understanding or are they superfluous?
While you should read the whole paper, making the right choice of what to read first can save time by flagging major problems early on.
Editors say, " Specific recommendations for remedying flaws are VERY welcome ."
Examples of possibly major flaws include:
- Drawing a conclusion that is contradicted by the author's own statistical or qualitative evidence
- The use of a discredited method
- Ignoring a process that is known to have a strong influence on the area under study
If experimental design features prominently in the paper, first check that the methodology is sound - if not, this is likely to be a major flaw.
You might examine:
- The sampling in analytical papers
- The sufficient use of control experiments
- The precision of process data
- The regularity of sampling in time-dependent studies
- The validity of questions, the use of a detailed methodology and the data analysis being done systematically (in qualitative research)
- That qualitative research extends beyond the author's opinions, with sufficient descriptive elements and appropriate quotes from interviews or focus groups
Major Flaws in Information
If methodology is less of an issue, it's often a good idea to look at the data tables, figures or images first. Especially in science research, it's all about the information gathered. If there are critical flaws in this, it's very likely the manuscript will need to be rejected. Such issues include:
- Insufficient data
- Unclear data tables
- Contradictory data that either are not self-consistent or disagree with the conclusions
- Confirmatory data that adds little, if anything, to current understanding - unless strong arguments for such repetition are made
If you find a major problem, note your reasoning and clear supporting evidence (including citations).
After the initial read and using your notes, including those of any major flaws you found, draft the first two paragraphs of your review - the first summarizing the research question addressed and the second the contribution of the work. If the journal has a prescribed reporting format, this draft will still help you compose your thoughts.
The First Paragraph
This should state the main question addressed by the research and summarize the goals, approaches, and conclusions of the paper. It should:
- Help the editor properly contextualize the research and add weight to your judgement
- Show the author what key messages are conveyed to the reader, so they can be sure they are achieving what they set out to do
- Focus on successful aspects of the paper so the author gets a sense of what they've done well
The Second Paragraph
This should provide a conceptual overview of the contribution of the research. So consider:
- Is the paper's premise interesting and important?
- Are the methods used appropriate?
- Do the data support the conclusions?
After drafting these two paragraphs, you should be in a position to decide whether this manuscript is seriously flawed and should be rejected (see the next section). Or whether it is publishable in principle and merits a detailed, careful read through.
Even if you are coming to the opinion that an article has serious flaws, make sure you read the whole paper. This is very important because you may find some really positive aspects that can be communicated to the author. This could help them with future submissions.
A full read-through will also make sure that any initial concerns are indeed correct and fair. After all, you need the context of the whole paper before deciding to reject. If you still intend to recommend rejection, see the section "When recommending rejection."
Once the paper has passed your first read and you've decided the article is publishable in principle, one purpose of the second, detailed read-through is to help prepare the manuscript for publication. You may still decide to recommend rejection following a second reading.
" Offer clear suggestions for how the authors can address the concerns raised. In other words, if you're going to raise a problem, provide a solution ." (Jonathon Halbesleben, Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Preparation
To save time and simplify the review:
- Don't rely solely upon inserting comments on the manuscript document - make separate notes
- Try to group similar concerns or praise together
- If using a review program to note directly onto the manuscript, still try grouping the concerns and praise in separate notes - it helps later
- Note line numbers of text upon which your notes are based - this helps you find items again and also aids those reading your review
Now that you have completed your preparations, you're ready to spend an hour or so reading carefully through the manuscript.
As you're reading through the manuscript for a second time, you'll need to keep in mind the argument's construction, the clarity of the language and content.
With regard to the argument’s construction, you should identify:
- Any places where the meaning is unclear or ambiguous
- Any factual errors
- Any invalid arguments
You may also wish to consider:
- Does the title properly reflect the subject of the paper?
- Does the abstract provide an accessible summary of the paper?
- Do the keywords accurately reflect the content?
- Is the paper an appropriate length?
- Are the key messages short, accurate and clear?
Not every submission is well written. Part of your role is to make sure that the text’s meaning is clear.
Editors say, " If a manuscript has many English language and editing issues, please do not try and fix it. If it is too bad, note that in your review and it should be up to the authors to have the manuscript edited ."
If the article is difficult to understand, you should have rejected it already. However, if the language is poor but you understand the core message, see if you can suggest improvements to fix the problem:
- Are there certain aspects that could be communicated better, such as parts of the discussion?
- Should the authors consider resubmitting to the same journal after language improvements?
- Would you consider looking at the paper again once these issues are dealt with?
On Grammar and Punctuation
Your primary role is judging the research content. Don't spend time polishing grammar or spelling. Editors will make sure that the text is at a high standard before publication. However, if you spot grammatical errors that affect clarity of meaning, then it's important to highlight these. Expect to suggest such amendments - it's rare for a manuscript to pass review with no corrections.
A 2010 study of nursing journals found that 79% of recommendations by reviewers were influenced by grammar and writing style (Shattel, et al., 2010).
1. The Introduction
A well-written introduction:
- Sets out the argument
- Summarizes recent research related to the topic
- Highlights gaps in current understanding or conflicts in current knowledge
- Establishes the originality of the research aims by demonstrating the need for investigations in the topic area
- Gives a clear idea of the target readership, why the research was carried out and the novelty and topicality of the manuscript
Originality and Topicality
Originality and topicality can only be established in the light of recent authoritative research. For example, it's impossible to argue that there is a conflict in current understanding by referencing articles that are 10 years old.
Authors may make the case that a topic hasn't been investigated in several years and that new research is required. This point is only valid if researchers can point to recent developments in data gathering techniques or to research in indirectly related fields that suggest the topic needs revisiting. Clearly, authors can only do this by referencing recent literature. Obviously, where older research is seminal or where aspects of the methodology rely upon it, then it is perfectly appropriate for authors to cite some older papers.
Editors say, "Is the report providing new information; is it novel or just confirmatory of well-known outcomes ?"
It's common for the introduction to end by stating the research aims. By this point you should already have a good impression of them - if the explicit aims come as a surprise, then the introduction needs improvement.
2. Materials and Methods
Academic research should be replicable, repeatable and robust - and follow best practice.
Replicable Research
This makes sufficient use of:
- Control experiments
- Repeated analyses
- Repeated experiments
These are used to make sure observed trends are not due to chance and that the same experiment could be repeated by other researchers - and result in the same outcome. Statistical analyses will not be sound if methods are not replicable. Where research is not replicable, the paper should be recommended for rejection.
Repeatable Methods
These give enough detail so that other researchers are able to carry out the same research. For example, equipment used or sampling methods should all be described in detail so that others could follow the same steps. Where methods are not detailed enough, it's usual to ask for the methods section to be revised.
Robust Research
This has enough data points to make sure the data are reliable. If there are insufficient data, it might be appropriate to recommend revision. You should also consider whether there is any in-built bias not nullified by the control experiments.
Best Practice
During these checks you should keep in mind best practice:
- Standard guidelines were followed (e.g. the CONSORT Statement for reporting randomized trials)
- The health and safety of all participants in the study was not compromised
- Ethical standards were maintained
If the research fails to reach relevant best practice standards, it's usual to recommend rejection. What's more, you don't then need to read any further.
3. Results and Discussion
This section should tell a coherent story - What happened? What was discovered or confirmed?
Certain patterns of good reporting need to be followed by the author:
- They should start by describing in simple terms what the data show
- They should make reference to statistical analyses, such as significance or goodness of fit
- Once described, they should evaluate the trends observed and explain the significance of the results to wider understanding. This can only be done by referencing published research
- The outcome should be a critical analysis of the data collected
Discussion should always, at some point, gather all the information together into a single whole. Authors should describe and discuss the overall story formed. If there are gaps or inconsistencies in the story, they should address these and suggest ways future research might confirm the findings or take the research forward.
4. Conclusions
This section is usually no more than a few paragraphs and may be presented as part of the results and discussion, or in a separate section. The conclusions should reflect upon the aims - whether they were achieved or not - and, just like the aims, should not be surprising. If the conclusions are not evidence-based, it's appropriate to ask for them to be re-written.
5. Information Gathered: Images, Graphs and Data Tables
If you find yourself looking at a piece of information from which you cannot discern a story, then you should ask for improvements in presentation. This could be an issue with titles, labels, statistical notation or image quality.
Where information is clear, you should check that:
- The results seem plausible, in case there is an error in data gathering
- The trends you can see support the paper's discussion and conclusions
- There are sufficient data. For example, in studies carried out over time are there sufficient data points to support the trends described by the author?
You should also check whether images have been edited or manipulated to emphasize the story they tell. This may be appropriate but only if authors report on how the image has been edited (e.g. by highlighting certain parts of an image). Where you feel that an image has been edited or manipulated without explanation, you should highlight this in a confidential comment to the editor in your report.
6. List of References
You will need to check referencing for accuracy, adequacy and balance.
Where a cited article is central to the author's argument, you should check the accuracy and format of the reference - and bear in mind different subject areas may use citations differently. Otherwise, it's the editor’s role to exhaustively check the reference section for accuracy and format.
You should consider if the referencing is adequate:
- Are important parts of the argument poorly supported?
- Are there published studies that show similar or dissimilar trends that should be discussed?
- If a manuscript only uses half the citations typical in its field, this may be an indicator that referencing should be improved - but don't be guided solely by quantity
- References should be relevant, recent and readily retrievable
Check for a well-balanced list of references that is:
- Helpful to the reader
- Fair to competing authors
- Not over-reliant on self-citation
- Gives due recognition to the initial discoveries and related work that led to the work under assessment
You should be able to evaluate whether the article meets the criteria for balanced referencing without looking up every reference.
7. Plagiarism
By now you will have a deep understanding of the paper's content - and you may have some concerns about plagiarism.
Identified Concern
If you find - or already knew of - a very similar paper, this may be because the author overlooked it in their own literature search. Or it may be because it is very recent or published in a journal slightly outside their usual field.
You may feel you can advise the author how to emphasize the novel aspects of their own study, so as to better differentiate it from similar research. If so, you may ask the author to discuss their aims and results, or modify their conclusions, in light of the similar article. Of course, the research similarities may be so great that they render the work unoriginal and you have no choice but to recommend rejection.
"It's very helpful when a reviewer can point out recent similar publications on the same topic by other groups, or that the authors have already published some data elsewhere ." (Editor feedback)
Suspected Concern
If you suspect plagiarism, including self-plagiarism, but cannot recall or locate exactly what is being plagiarized, notify the editor of your suspicion and ask for guidance.
Most editors have access to software that can check for plagiarism.
Editors are not out to police every paper, but when plagiarism is discovered during peer review it can be properly addressed ahead of publication. If plagiarism is discovered only after publication, the consequences are worse for both authors and readers, because a retraction may be necessary.
For detailed guidelines see COPE's Ethical guidelines for reviewers and Wiley's Best Practice Guidelines on Publishing Ethics .
8. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
After the detailed read-through, you will be in a position to advise whether the title, abstract and key words are optimized for search purposes. In order to be effective, good SEO terms will reflect the aims of the research.
A clear title and abstract will improve the paper's search engine rankings and will influence whether the user finds and then decides to navigate to the main article. The title should contain the relevant SEO terms early on. This has a major effect on the impact of a paper, since it helps it appear in search results. A poor abstract can then lose the reader's interest and undo the benefit of an effective title - whilst the paper's abstract may appear in search results, the potential reader may go no further.
So ask yourself, while the abstract may have seemed adequate during earlier checks, does it:
- Do justice to the manuscript in this context?
- Highlight important findings sufficiently?
- Present the most interesting data?
Editors say, " Does the Abstract highlight the important findings of the study ?"
If there is a formal report format, remember to follow it. This will often comprise a range of questions followed by comment sections. Try to answer all the questions. They are there because the editor felt that they are important. If you're following an informal report format you could structure your report in three sections: summary, major issues, minor issues.
- Give positive feedback first. Authors are more likely to read your review if you do so. But don't overdo it if you will be recommending rejection
- Briefly summarize what the paper is about and what the findings are
- Try to put the findings of the paper into the context of the existing literature and current knowledge
- Indicate the significance of the work and if it is novel or mainly confirmatory
- Indicate the work's strengths, its quality and completeness
- State any major flaws or weaknesses and note any special considerations. For example, if previously held theories are being overlooked
Major Issues
- Are there any major flaws? State what they are and what the severity of their impact is on the paper
- Has similar work already been published without the authors acknowledging this?
- Are the authors presenting findings that challenge current thinking? Is the evidence they present strong enough to prove their case? Have they cited all the relevant work that would contradict their thinking and addressed it appropriately?
- If major revisions are required, try to indicate clearly what they are
- Are there any major presentational problems? Are figures & tables, language and manuscript structure all clear enough for you to accurately assess the work?
- Are there any ethical issues? If you are unsure it may be better to disclose these in the confidential comments section
Minor Issues
- Are there places where meaning is ambiguous? How can this be corrected?
- Are the correct references cited? If not, which should be cited instead/also? Are citations excessive, limited, or biased?
- Are there any factual, numerical or unit errors? If so, what are they?
- Are all tables and figures appropriate, sufficient, and correctly labelled? If not, say which are not
Your review should ultimately help the author improve their article. So be polite, honest and clear. You should also try to be objective and constructive, not subjective and destructive.
You should also:
- Write clearly and so you can be understood by people whose first language is not English
- Avoid complex or unusual words, especially ones that would even confuse native speakers
- Number your points and refer to page and line numbers in the manuscript when making specific comments
- If you have been asked to only comment on specific parts or aspects of the manuscript, you should indicate clearly which these are
- Treat the author's work the way you would like your own to be treated
Most journals give reviewers the option to provide some confidential comments to editors. Often this is where editors will want reviewers to state their recommendation - see the next section - but otherwise this area is best reserved for communicating malpractice such as suspected plagiarism, fraud, unattributed work, unethical procedures, duplicate publication, bias or other conflicts of interest.
However, this doesn't give reviewers permission to 'backstab' the author. Authors can't see this feedback and are unable to give their side of the story unless the editor asks them to. So in the spirit of fairness, write comments to editors as though authors might read them too.
Reviewers should check the preferences of individual journals as to where they want review decisions to be stated. In particular, bear in mind that some journals will not want the recommendation included in any comments to authors, as this can cause editors difficulty later - see Section 11 for more advice about working with editors.
You will normally be asked to indicate your recommendation (e.g. accept, reject, revise and resubmit, etc.) from a fixed-choice list and then to enter your comments into a separate text box.
Recommending Acceptance
If you're recommending acceptance, give details outlining why, and if there are any areas that could be improved. Don't just give a short, cursory remark such as 'great, accept'. See Improving the Manuscript
Recommending Revision
Where improvements are needed, a recommendation for major or minor revision is typical. You may also choose to state whether you opt in or out of the post-revision review too. If recommending revision, state specific changes you feel need to be made. The author can then reply to each point in turn.
Some journals offer the option to recommend rejection with the possibility of resubmission – this is most relevant where substantial, major revision is necessary.
What can reviewers do to help? " Be clear in their comments to the author (or editor) which points are absolutely critical if the paper is given an opportunity for revisio n." (Jonathon Halbesleben, Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Recommending Rejection
If recommending rejection or major revision, state this clearly in your review (and see the next section, 'When recommending rejection').
Where manuscripts have serious flaws you should not spend any time polishing the review you've drafted or give detailed advice on presentation.
Editors say, " If a reviewer suggests a rejection, but her/his comments are not detailed or helpful, it does not help the editor in making a decision ."
In your recommendations for the author, you should:
- Give constructive feedback describing ways that they could improve the research
- Keep the focus on the research and not the author. This is an extremely important part of your job as a reviewer
- Avoid making critical confidential comments to the editor while being polite and encouraging to the author - the latter may not understand why their manuscript has been rejected. Also, they won't get feedback on how to improve their research and it could trigger an appeal
Remember to give constructive criticism even if recommending rejection. This helps developing researchers improve their work and explains to the editor why you felt the manuscript should not be published.
" When the comments seem really positive, but the recommendation is rejection…it puts the editor in a tough position of having to reject a paper when the comments make it sound like a great paper ." (Jonathon Halbesleben, Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Visit our Wiley Author Learning and Training Channel for expert advice on peer review.
Watch the video, Ethical considerations of Peer Review
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
- Open access
- Published: 17 August 2023
Data visualisation in scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics: a cross-sectional analysis
- Emily South ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2187-4762 1 &
- Mark Rodgers 1
Systematic Reviews volume 12 , Article number: 142 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
3636 Accesses
13 Altmetric
Metrics details
Scoping reviews and evidence maps are forms of evidence synthesis that aim to map the available literature on a topic and are well-suited to visual presentation of results. A range of data visualisation methods and interactive data visualisation tools exist that may make scoping reviews more useful to knowledge users. The aim of this study was to explore the use of data visualisation in a sample of recent scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics, with a particular focus on interactive data visualisation.
Ovid MEDLINE ALL was searched for recent scoping reviews and evidence maps (June 2020-May 2021), and a sample of 300 papers that met basic selection criteria was taken. Data were extracted on the aim of each review and the use of data visualisation, including types of data visualisation used, variables presented and the use of interactivity. Descriptive data analysis was undertaken of the 238 reviews that aimed to map evidence.
Of the 238 scoping reviews or evidence maps in our analysis, around one-third (37.8%) included some form of data visualisation. Thirty-five different types of data visualisation were used across this sample, although most data visualisations identified were simple bar charts (standard, stacked or multi-set), pie charts or cross-tabulations (60.8%). Most data visualisations presented a single variable (64.4%) or two variables (26.1%). Almost a third of the reviews that used data visualisation did not use any colour (28.9%). Only two reviews presented interactive data visualisation, and few reported the software used to create visualisations.
Conclusions
Data visualisation is currently underused by scoping review authors. In particular, there is potential for much greater use of more innovative forms of data visualisation and interactive data visualisation. Where more innovative data visualisation is used, scoping reviews have made use of a wide range of different methods. Increased use of these more engaging visualisations may make scoping reviews more useful for a range of stakeholders.
Peer Review reports
Scoping reviews are “a type of evidence synthesis that aims to systematically identify and map the breadth of evidence available on a particular topic, field, concept, or issue” ([ 1 ], p. 950). While they include some of the same steps as a systematic review, such as systematic searches and the use of predetermined eligibility criteria, scoping reviews often address broader research questions and do not typically involve the quality appraisal of studies or synthesis of data [ 2 ]. Reasons for conducting a scoping review include the following: to map types of evidence available, to explore research design and conduct, to clarify concepts or definitions and to map characteristics or factors related to a concept [ 3 ]. Scoping reviews can also be undertaken to inform a future systematic review (e.g. to assure authors there will be adequate studies) or to identify knowledge gaps [ 3 ]. Other evidence synthesis approaches with similar aims have been described as evidence maps, mapping reviews or systematic maps [ 4 ]. While this terminology is used inconsistently, evidence maps can be used to identify evidence gaps and present them in a user-friendly (and often visual) way [ 5 ].
Scoping reviews are often targeted to an audience of healthcare professionals or policy-makers [ 6 ], suggesting that it is important to present results in a user-friendly and informative way. Until recently, there was little guidance on how to present the findings of scoping reviews. In recent literature, there has been some discussion of the importance of clearly presenting data for the intended audience of a scoping review, with creative and innovative use of visual methods if appropriate [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. Lockwood et al. suggest that innovative visual presentation should be considered over dense sections of text or long tables in many cases [ 8 ]. Khalil et al. suggest that inspiration could be drawn from the field of data visualisation [ 7 ]. JBI guidance on scoping reviews recommends that reviewers carefully consider the best format for presenting data at the protocol development stage and provides a number of examples of possible methods [ 10 ].
Interactive resources are another option for presentation in scoping reviews [ 9 ]. Researchers without the relevant programming skills can now use several online platforms (such as Tableau [ 11 ] and Flourish [ 12 ]) to create interactive data visualisations. The benefits of using interactive visualisation in research include the ability to easily present more than two variables [ 13 ] and increased engagement of users [ 14 ]. Unlike static graphs, interactive visualisations can allow users to view hierarchical data at different levels, exploring both the “big picture” and looking in more detail ([ 15 ], p. 291). Interactive visualizations are often targeted at practitioners and decision-makers [ 13 ], and there is some evidence from qualitative research that they are valued by policy-makers [ 16 , 17 , 18 ].
Given their focus on mapping evidence, we believe that scoping reviews are particularly well-suited to visually presenting data and the use of interactive data visualisation tools. However, it is unknown how many recent scoping reviews visually map data or which types of data visualisation are used. The aim of this study was to explore the use of data visualisation methods in a large sample of recent scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics. In particular, we were interested in the extent to which these forms of synthesis use any form of interactive data visualisation.
This study was a cross-sectional analysis of studies labelled as scoping reviews or evidence maps (or synonyms of these terms) in the title or abstract.
The search strategy was developed with help from an information specialist. Ovid MEDLINE® ALL was searched in June 2021 for studies added to the database in the previous 12 months. The search was limited to English language studies only.
The search strategy was as follows:
Ovid MEDLINE(R) ALL
(scoping review or evidence map or systematic map or mapping review or scoping study or scoping project or scoping exercise or literature mapping or evidence mapping or systematic mapping or literature scoping or evidence gap map).ab,ti.
limit 1 to english language
(202006* or 202007* or 202008* or 202009* or 202010* or 202011* or 202012* or 202101* or 202102* or 202103* or 202104* or 202105*).dt.
The search returned 3686 records. Records were de-duplicated in EndNote 20 software, leaving 3627 unique records.
A sample of these reviews was taken by screening the search results against basic selection criteria (Table 1 ). These criteria were piloted and refined after discussion between the two researchers. A single researcher (E.S.) screened the records in EPPI-Reviewer Web software using the machine-learning priority screening function. Where a second opinion was needed, decisions were checked by a second researcher (M.R.).
Our initial plan for sampling, informed by pilot searching, was to screen and data extract records in batches of 50 included reviews at a time. We planned to stop screening when a batch of 50 reviews had been extracted that included no new types of data visualisation or after screening time had reached 2 days. However, once data extraction was underway, we found the sample to be richer in terms of data visualisation than anticipated. After the inclusion of 300 reviews, we took the decision to end screening in order to ensure the study was manageable.
Data extraction
A data extraction form was developed in EPPI-Reviewer Web, piloted on 50 reviews and refined. Data were extracted by one researcher (E. S. or M. R.), with a second researcher (M. R. or E. S.) providing a second opinion when needed. The data items extracted were as follows: type of review (term used by authors), aim of review (mapping evidence vs. answering specific question vs. borderline), number of visualisations (if any), types of data visualisation used, variables/domains presented by each visualisation type, interactivity, use of colour and any software requirements.
When categorising review aims, we considered “mapping evidence” to incorporate all of the six purposes for conducting a scoping review proposed by Munn et al. [ 3 ]. Reviews were categorised as “answering a specific question” if they aimed to synthesise study findings to answer a particular question, for example on effectiveness of an intervention. We were inclusive with our definition of “mapping evidence” and included reviews with mixed aims in this category. However, some reviews were difficult to categorise (for example where aims were unclear or the stated aims did not match the actual focus of the paper) and were considered to be “borderline”. It became clear that a proportion of identified records that described themselves as “scoping” or “mapping” reviews were in fact pseudo-systematic reviews that failed to undertake key systematic review processes. Such reviews attempted to integrate the findings of included studies rather than map the evidence, and so reviews categorised as “answering a specific question” were excluded from the main analysis. Data visualisation methods for meta-analyses have been explored previously [ 19 ]. Figure 1 shows the flow of records from search results to final analysis sample.
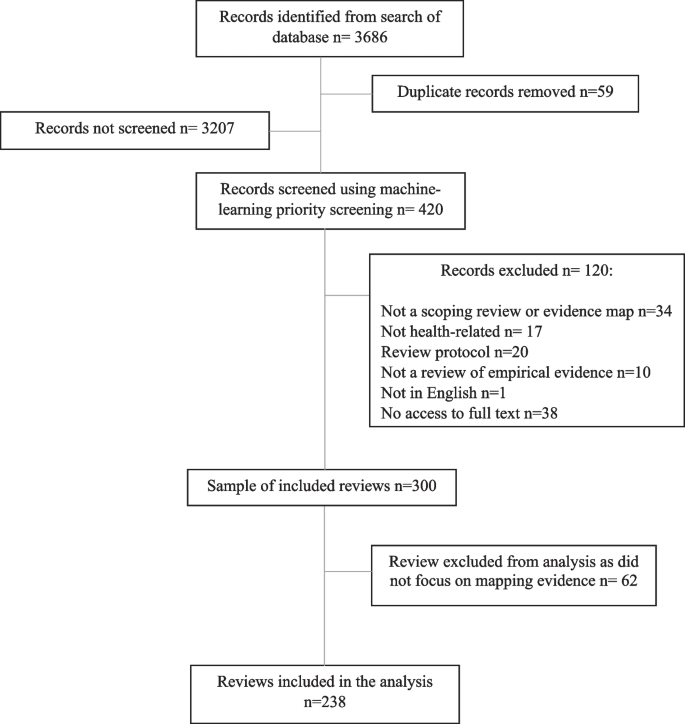
Flow diagram of the sampling process
Data visualisation was defined as any graph or diagram that presented results data, including tables with a visual mapping element, such as cross-tabulations and heat maps. However, tables which displayed data at a study level (e.g. tables summarising key characteristics of each included study) were not included, even if they used symbols, shading or colour. Flow diagrams showing the study selection process were also excluded. Data visualisations in appendices or supplementary information were included, as well as any in publicly available dissemination products (e.g. visualisations hosted online) if mentioned in papers.
The typology used to categorise data visualisation methods was based on an existing online catalogue [ 20 ]. Specific types of data visualisation were categorised in five broad categories: graphs, diagrams, tables, maps/geographical and other. If a data visualisation appeared in our sample that did not feature in the original catalogue, we checked a second online catalogue [ 21 ] for an appropriate term, followed by wider Internet searches. These additional visualisation methods were added to the appropriate section of the typology. The final typology can be found in Additional file 1 .
We conducted descriptive data analysis in Microsoft Excel 2019 and present frequencies and percentages. Where appropriate, data are presented using graphs or other data visualisations created using Flourish. We also link to interactive versions of some of these visualisations.
Almost all of the 300 reviews in the total sample were labelled by review authors as “scoping reviews” ( n = 293, 97.7%). There were also four “mapping reviews”, one “scoping study”, one “evidence mapping” and one that was described as a “scoping review and evidence map”. Included reviews were all published in 2020 or 2021, with the exception of one review published in 2018. Just over one-third of these reviews ( n = 105, 35.0%) included some form of data visualisation. However, we excluded 62 reviews that did not focus on mapping evidence from the following analysis (see “ Methods ” section). Of the 238 remaining reviews (that either clearly aimed to map evidence or were judged to be “borderline”), 90 reviews (37.8%) included at least one data visualisation. The references for these reviews can be found in Additional file 2 .
Number of visualisations
Thirty-six (40.0%) of these 90 reviews included just one example of data visualisation (Fig. 2 ). Less than a third ( n = 28, 31.1%) included three or more visualisations. The greatest number of data visualisations in one review was 17 (all bar or pie charts). In total, 222 individual data visualisations were identified across the sample of 238 reviews.
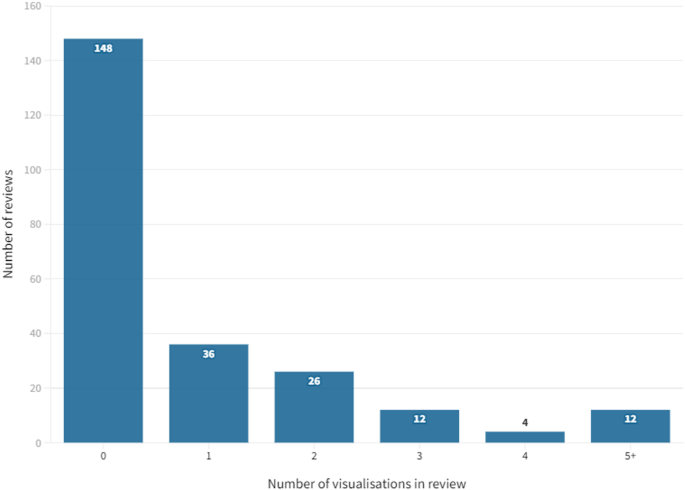
Number of data visualisations per review
Categories of data visualisation
Graphs were the most frequently used category of data visualisation in the sample. Over half of the reviews with data visualisation included at least one graph ( n = 59, 65.6%). The least frequently used category was maps, with 15.6% ( n = 14) of these reviews including a map.
Of the total number of 222 individual data visualisations, 102 were graphs (45.9%), 34 were tables (15.3%), 23 were diagrams (10.4%), 15 were maps (6.8%) and 48 were classified as “other” in the typology (21.6%).
Types of data visualisation
All of the types of data visualisation identified in our sample are reported in Table 2 . In total, 35 different types were used across the sample of reviews.
The most frequently used data visualisation type was a bar chart. Of 222 total data visualisations, 78 (35.1%) were a variation on a bar chart (either standard bar chart, stacked bar chart or multi-set bar chart). There were also 33 pie charts (14.9% of data visualisations) and 24 cross-tabulations (10.8% of data visualisations). In total, these five types of data visualisation accounted for 60.8% ( n = 135) of all data visualisations. Figure 3 shows the frequency of each data visualisation category and type; an interactive online version of this treemap is also available ( https://public.flourish.studio/visualisation/9396133/ ). Figure 4 shows how users can further explore the data using the interactive treemap.
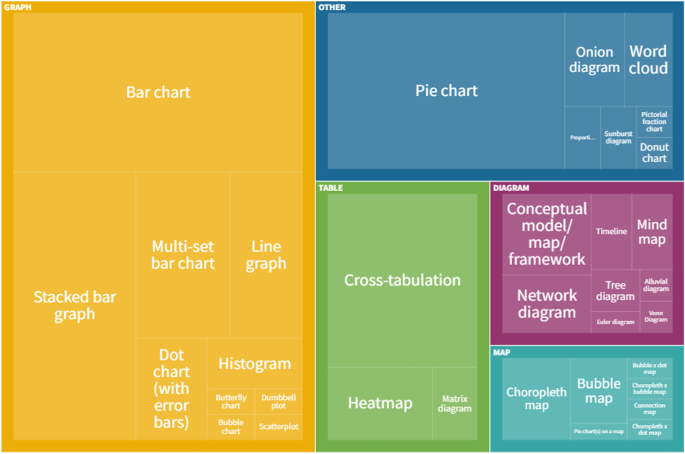
Data visualisation categories and types. An interactive version of this treemap is available online: https://public.flourish.studio/visualisation/9396133/ . Through the interactive version, users can further explore the data (see Fig. 4 ). The unit of this treemap is the individual data visualisation, so multiple data visualisations within the same scoping review are represented in this map. Created with flourish.studio ( https://flourish.studio )
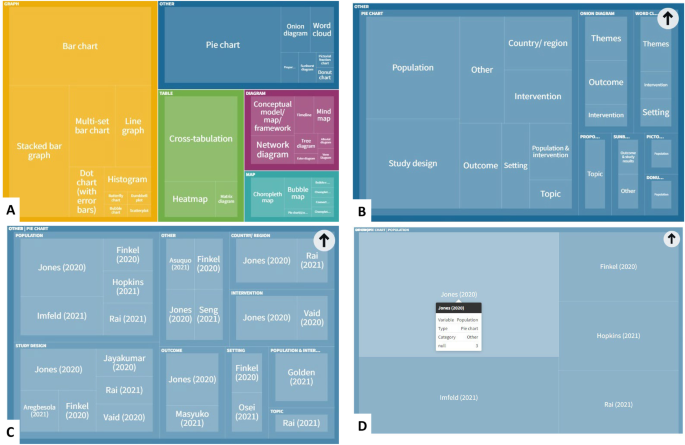
Screenshots showing how users of the interactive treemap can explore the data further. Users can explore each level of the hierarchical treemap ( A Visualisation category > B Visualisation subcategory > C Variables presented in visualisation > D Individual references reporting this category/subcategory/variable permutation). Created with flourish.studio ( https://flourish.studio )
Data presented
Around two-thirds of data visualisations in the sample presented a single variable ( n = 143, 64.4%). The most frequently presented single variables were themes ( n = 22, 9.9% of data visualisations), population ( n = 21, 9.5%), country or region ( n = 21, 9.5%) and year ( n = 20, 9.0%). There were 58 visualisations (26.1%) that presented two different variables. The remaining 21 data visualisations (9.5%) presented three or more variables. Figure 5 shows the variables presented by each different type of data visualisation (an interactive version of this figure is available online).
Variables presented by each data visualisation type. Darker cells indicate a larger number of reviews. An interactive version of this heat map is available online: https://public.flourish.studio/visualisation/10632665/ . Users can hover over each cell to see the number of data visualisations for that combination of data visualisation type and variable. The unit of this heat map is the individual data visualisation, so multiple data visualisations within a single scoping review are represented in this map. Created with flourish.studio ( https://flourish.studio )
Most reviews presented at least one data visualisation in colour ( n = 64, 71.1%). However, almost a third ( n = 26, 28.9%) used only black and white or greyscale.
Interactivity
Only two of the reviews included data visualisations with any level of interactivity. One scoping review on music and serious mental illness [ 22 ] linked to an interactive bubble chart hosted online on Tableau. Functionality included the ability to filter the studies displayed by various attributes.
The other review was an example of evidence mapping from the environmental health field [ 23 ]. All four of the data visualisations included in the paper were available in an interactive format hosted either by the review management software or on Tableau. The interactive versions linked to the relevant references so users could directly explore the evidence base. This was the only review that provided this feature.
Software requirements
Nine reviews clearly reported the software used to create data visualisations. Three reviews used Tableau (one of them also used review management software as discussed above) [ 22 , 23 , 24 ]. Two reviews generated maps using ArcGIS [ 25 ] or ArcMap [ 26 ]. One review used Leximancer for a lexical analysis [ 27 ]. One review undertook a bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer [ 28 ], and another explored citation patterns using CitNetExplorer [ 29 ]. Other reviews used Excel [ 30 ] or R [ 26 ].
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic and in-depth exploration of the use of data visualisation techniques in scoping reviews. Our findings suggest that the majority of scoping reviews do not use any data visualisation at all, and, in particular, more innovative examples of data visualisation are rare. Around 60% of data visualisations in our sample were simple bar charts, pie charts or cross-tabulations. There appears to be very limited use of interactive online visualisation, despite the potential this has for communicating results to a range of stakeholders. While it is not always appropriate to use data visualisation (or a simple bar chart may be the most user-friendly way of presenting the data), these findings suggest that data visualisation is being underused in scoping reviews. In a large minority of reviews, visualisations were not published in colour, potentially limiting how user-friendly and attractive papers are to decision-makers and other stakeholders. Also, very few reviews clearly reported the software used to create data visualisations. However, 35 different types of data visualisation were used across the sample, highlighting the wide range of methods that are potentially available to scoping review authors.
Our results build on the limited research that has previously been undertaken in this area. Two previous publications also found limited use of graphs in scoping reviews. Results were “mapped graphically” in 29% of scoping reviews in any field in one 2014 publication [ 31 ] and 17% of healthcare scoping reviews in a 2016 article [ 6 ]. Our results suggest that the use of data visualisation has increased somewhat since these reviews were conducted. Scoping review methods have also evolved in the last 10 years; formal guidance on scoping review conduct was published in 2014 [ 32 ], and an extension of the PRISMA checklist for scoping reviews was published in 2018 [ 33 ]. It is possible that an overall increase in use of data visualisation reflects increased quality of published scoping reviews. There is also some literature supporting our findings on the wide range of data visualisation methods that are used in evidence synthesis. An investigation of methods to identify, prioritise or display health research gaps (25/139 included studies were scoping reviews; 6/139 were evidence maps) identified 14 different methods used to display gaps or priorities, with half being “more advanced” (e.g. treemaps, radial bar plots) ([ 34 ], p. 107). A review of data visualisation methods used in papers reporting meta-analyses found over 200 different ways of displaying data [ 19 ].
Only two reviews in our sample used interactive data visualisation, and one of these was an example of systematic evidence mapping from the environmental health field rather than a scoping review (in environmental health, systematic evidence mapping explicitly involves producing a searchable database [ 35 ]). A scoping review of papers on the use of interactive data visualisation in population health or health services research found a range of examples but still limited use overall [ 13 ]. For example, the authors noted the currently underdeveloped potential for using interactive visualisation in research on health inequalities. It is possible that the use of interactive data visualisation in academic papers is restricted by academic publishing requirements; for example, it is currently difficult to incorporate an interactive figure into a journal article without linking to an external host or platform. However, we believe that there is a lot of potential to add value to future scoping reviews by using interactive data visualisation software. Few reviews in our sample presented three or more variables in a single visualisation, something which can easily be achieved using interactive data visualisation tools. We have previously used EPPI-Mapper [ 36 ] to present results of a scoping review of systematic reviews on behaviour change in disadvantaged groups, with links to the maps provided in the paper [ 37 ]. These interactive maps allowed policy-makers to explore the evidence on different behaviours and disadvantaged groups and access full publications of the included studies directly from the map.
We acknowledge there are barriers to use for some of the data visualisation software available. EPPI-Mapper and some of the software used by reviews in our sample incur a cost. Some software requires a certain level of knowledge and skill in its use. However numerous online free data visualisation tools and resources exist. We have used Flourish to present data for this review, a basic version of which is currently freely available and easy to use. Previous health research has been found to have used a range of different interactive data visualisation software, much of which does not required advanced knowledge or skills to use [ 13 ].
There are likely to be other barriers to the use of data visualisation in scoping reviews. Journal guidelines and policies may present barriers for using innovative data visualisation. For example, some journals charge a fee for publication of figures in colour. As previously mentioned, there are limited options for incorporating interactive data visualisation into journal articles. Authors may also be unaware of the data visualisation methods and tools that are available. Producing data visualisations can be time-consuming, particularly if authors lack experience and skills in this. It is possible that many authors prioritise speed of publication over spending time producing innovative data visualisations, particularly in a context where there is pressure to achieve publications.
Limitations
A limitation of this study was that we did not assess how appropriate the use of data visualisation was in our sample as this would have been highly subjective. Simple descriptive or tabular presentation of results may be the most appropriate approach for some scoping review objectives [ 7 , 8 , 10 ], and the scoping review literature cautions against “over-using” different visual presentation methods [ 7 , 8 ]. It cannot be assumed that all of the reviews that did not include data visualisation should have done so. Likewise, we do not know how many reviews used methods of data visualisation that were not well suited to their data.
We initially relied on authors’ own use of the term “scoping review” (or equivalent) to sample reviews but identified a relatively large number of papers labelled as scoping reviews that did not meet the basic definition, despite the availability of guidance and reporting guidelines [ 10 , 33 ]. It has previously been noted that scoping reviews may be undertaken inappropriately because they are seen as “easier” to conduct than a systematic review ([ 3 ], p.6), and that reviews are often labelled as “scoping reviews” while not appearing to follow any established framework or guidance [ 2 ]. We therefore took the decision to remove these reviews from our main analysis. However, decisions on how to classify review aims were subjective, and we did include some reviews that were of borderline relevance.
A further limitation is that this was a sample of published reviews, rather than a comprehensive systematic scoping review as have previously been undertaken [ 6 , 31 ]. The number of scoping reviews that are published has increased rapidly, and this would now be difficult to undertake. As this was a sample, not all relevant scoping reviews or evidence maps that would have met our criteria were included. We used machine learning to screen our search results for pragmatic reasons (to reduce screening time), but we do not see any reason that our sample would not be broadly reflective of the wider literature.
Data visualisation, and in particular more innovative examples of it, is currently underused in published scoping reviews on health topics. The examples that we have found highlight the wide range of methods that scoping review authors could draw upon to present their data in an engaging way. In particular, we believe that interactive data visualisation has significant potential for mapping the available literature on a topic. Appropriate use of data visualisation may increase the usefulness, and thus uptake, of scoping reviews as a way of identifying existing evidence or research gaps by decision-makers, researchers and commissioners of research. We recommend that scoping review authors explore the extensive free resources and online tools available for data visualisation. However, we also think that it would be useful for publishers to explore allowing easier integration of interactive tools into academic publishing, given the fact that papers are now predominantly accessed online. Future research may be helpful to explore which methods are particularly useful to scoping review users.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Organisation formerly known as Joanna Briggs Institute
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Munn Z, Pollock D, Khalil H, Alexander L, McLnerney P, Godfrey CM, Peters M, Tricco AC. What are scoping reviews? Providing a formal definition of scoping reviews as a type of evidence synthesis. JBI Evid Synth. 2022;20:950–952.
Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Colquhoun H, Garritty CM, Hempel S, Horsley T, Langlois EV, Lillie E, O’Brien KK, Tunçalp Ӧ, et al. Scoping reviews: reinforcing and advancing the methodology and application. Syst Rev. 2021;10:263.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18:143.
Sutton A, Clowes M, Preston L, Booth A. Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Health Info Libr J. 2019;36:202–22.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Miake-Lye IM, Hempel S, Shanman R, Shekelle PG. What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Syst Rev. 2016;5:28.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien K, Colquhoun H, Kastner M, Levac D, Ng C, Sharpe JP, Wilson K, et al. A scoping review on the conduct and reporting of scoping reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16:15.
Khalil H, Peters MDJ, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Alexander L, McInerney P, Godfrey CM, Munn Z. Conducting high quality scoping reviews-challenges and solutions. J Clin Epidemiol. 2021;130:156–60.
Lockwood C, dos Santos KB, Pap R. Practical guidance for knowledge synthesis: scoping review methods. Asian Nurs Res. 2019;13:287–94.
Article Google Scholar
Pollock D, Peters MDJ, Khalil H, McInerney P, Alexander L, Tricco AC, Evans C, de Moraes ÉB, Godfrey CM, Pieper D, et al. Recommendations for the extraction, analysis, and presentation of results in scoping reviews. JBI Evidence Synthesis. 2022;10:11124.
Google Scholar
Peters MDJ GC, McInerney P, Munn Z, Tricco AC, Khalil, H. Chapter 11: Scoping reviews (2020 version). In: Aromataris E MZ, editor. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI; 2020. Available from https://synthesismanual.jbi.global . Accessed 1 Feb 2023.
Tableau Public. https://www.tableau.com/en-gb/products/public . Accessed 24 January 2023.
flourish.studio. https://flourish.studio/ . Accessed 24 January 2023.
Chishtie J, Bielska IA, Barrera A, Marchand J-S, Imran M, Tirmizi SFA, Turcotte LA, Munce S, Shepherd J, Senthinathan A, et al. Interactive visualization applications in population health and health services research: systematic scoping review. J Med Internet Res. 2022;24: e27534.
Isett KR, Hicks DM. Providing public servants what they need: revealing the “unseen” through data visualization. Public Adm Rev. 2018;78:479–85.
Carroll LN, Au AP, Detwiler LT, Fu T-c, Painter IS, Abernethy NF. Visualization and analytics tools for infectious disease epidemiology: a systematic review. J Biomed Inform. 2014;51:287–298.
Lundkvist A, El-Khatib Z, Kalra N, Pantoja T, Leach-Kemon K, Gapp C, Kuchenmüller T. Policy-makers’ views on translating burden of disease estimates in health policies: bridging the gap through data visualization. Arch Public Health. 2021;79:17.
Zakkar M, Sedig K. Interactive visualization of public health indicators to support policymaking: an exploratory study. Online J Public Health Inform. 2017;9:e190–e190.
Park S, Bekemeier B, Flaxman AD. Understanding data use and preference of data visualization for public health professionals: a qualitative study. Public Health Nurs. 2021;38:531–41.
Kossmeier M, Tran US, Voracek M. Charting the landscape of graphical displays for meta-analysis and systematic reviews: a comprehensive review, taxonomy, and feature analysis. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20:26.
Ribecca, S. The Data Visualisation Catalogue. https://datavizcatalogue.com/index.html . Accessed 23 November 2021.
Ferdio. Data Viz Project. https://datavizproject.com/ . Accessed 23 November 2021.
Golden TL, Springs S, Kimmel HJ, Gupta S, Tiedemann A, Sandu CC, Magsamen S. The use of music in the treatment and management of serious mental illness: a global scoping review of the literature. Front Psychol. 2021;12: 649840.
Keshava C, Davis JA, Stanek J, Thayer KA, Galizia A, Keshava N, Gift J, Vulimiri SV, Woodall G, Gigot C, et al. Application of systematic evidence mapping to assess the impact of new research when updating health reference values: a case example using acrolein. Environ Int. 2020;143: 105956.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jayakumar P, Lin E, Galea V, Mathew AJ, Panda N, Vetter I, Haynes AB. Digital phenotyping and patient-generated health data for outcome measurement in surgical care: a scoping review. J Pers Med. 2020;10:282.
Qu LG, Perera M, Lawrentschuk N, Umbas R, Klotz L. Scoping review: hotspots for COVID-19 urological research: what is being published and from where? World J Urol. 2021;39:3151–60.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Rossa-Roccor V, Acheson ES, Andrade-Rivas F, Coombe M, Ogura S, Super L, Hong A. Scoping review and bibliometric analysis of the term “planetary health” in the peer-reviewed literature. Front Public Health. 2020;8:343.
Hewitt L, Dahlen HG, Hartz DL, Dadich A. Leadership and management in midwifery-led continuity of care models: a thematic and lexical analysis of a scoping review. Midwifery. 2021;98: 102986.
Xia H, Tan S, Huang S, Gan P, Zhong C, Lu M, Peng Y, Zhou X, Tang X. Scoping review and bibliometric analysis of the most influential publications in achalasia research from 1995 to 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8836395.
Vigliotti V, Taggart T, Walker M, Kusmastuti S, Ransome Y. Religion, faith, and spirituality influences on HIV prevention activities: a scoping review. PLoS ONE. 2020;15: e0234720.
van Heemskerken P, Broekhuizen H, Gajewski J, Brugha R, Bijlmakers L. Barriers to surgery performed by non-physician clinicians in sub-Saharan Africa-a scoping review. Hum Resour Health. 2020;18:51.
Pham MT, Rajić A, Greig JD, Sargeant JM, Papadopoulos A, McEwen SA. A scoping review of scoping reviews: advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5:371–85.
Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, McInerney P, Godfrey CM, Khalil H. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid Synth. 2020;18:2119–26.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, Moher D, Peters MDJ, Horsley T, Weeks L, et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:467–73.
Nyanchoka L, Tudur-Smith C, Thu VN, Iversen V, Tricco AC, Porcher R. A scoping review describes methods used to identify, prioritize and display gaps in health research. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019;109:99–110.
Wolffe TAM, Whaley P, Halsall C, Rooney AA, Walker VR. Systematic evidence maps as a novel tool to support evidence-based decision-making in chemicals policy and risk management. Environ Int. 2019;130:104871.
Digital Solution Foundry and EPPI-Centre. EPPI-Mapper, Version 2.0.1. EPPI-Centre, UCL Social Research Institute, University College London. 2020. https://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/cms/Default.aspx?tabid=3790 .
South E, Rodgers M, Wright K, Whitehead M, Sowden A. Reducing lifestyle risk behaviours in disadvantaged groups in high-income countries: a scoping review of systematic reviews. Prev Med. 2022;154: 106916.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Melissa Harden, Senior Information Specialist, Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, for advice on developing the search strategy.
This work received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York, York, YO10 5DD, UK
Emily South & Mark Rodgers
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Both authors conceptualised and designed the study and contributed to screening, data extraction and the interpretation of results. ES undertook the literature searches, analysed data, produced the data visualisations and drafted the manuscript. MR contributed to revising the manuscript, and both authors read and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Emily South .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Typology of data visualisation methods.
Additional file 2.
References of scoping reviews included in main dataset.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
South, E., Rodgers, M. Data visualisation in scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics: a cross-sectional analysis. Syst Rev 12 , 142 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02309-y
Download citation
Received : 21 February 2023
Accepted : 07 August 2023
Published : 17 August 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02309-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Scoping review
- Evidence map
- Data visualisation
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

"Diagnosed with New Health": Social Security Policy Recommendations for People with Cycstic Fibrosis in Ohio Transitioning to a Longer Lifespan
Article sidebar.

Main Article Content
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a chronic, progressive, genetic, and life-limiting lung disease that impacts approximately 105,000 individuals globally, including 40,000 individuals in the United States. In 2019, a revolutionary new drug, elexacaftor/ivacaftor/tezacaftor (ETI), was approved to manage some of the major symptoms of CF and dramatically increase the lifespan of people with cystic fibrosis (pwCF). Many individuals with CF cannot work full time and require Medicaid, Supplemental Security Income (SSI), Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI), and other financial assistance programs to pay for treatments and medical expenses. Yet in recent years, pwCF who are on ETI have been increasingly losing benefits. A possible explanation for this is the effectiveness of ETI in improving lung function, creating the perception that pwCF are no longer disabled by their condition. Even with this “miracle" drug, pwCF continue to experience significant complications and vulnerabilities to their physical and mental health as well as limitations on daily living and employment. The compounded vulnerabilities these individuals experience leave them without a safety net. Social Security policies for pwCF require revisions to prevent further biopsychosocial damage to this population. Two policies will be recommended: leniency in redetermination, and CF education for those who make determination decisions.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
- Open access
- Published: 10 January 2024
Progress in the clinical effects and adverse reactions of ticagrelor
- Peng Wei 1 na1 ,
- Xiaoqing Wang 1 na1 ,
- Qiang Fu 2 &
- Bangming Cao 3
Thrombosis Journal volume 22 , Article number: 8 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1263 Accesses
Metrics details
Ticagrelor is a novel receptor antagonist that selectively binds to the P2Y12 receptor, thereby inhibiting adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-mediated platelet aggregation. Compared to clopidogrel, ticagrelor has the advantages of a fast onset, potent effects, and a reversible platelet inhibition function, which make this drug clinically suitable for treating acute coronary syndrome (ACS), especially acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
This review was performed to determine the basic characteristics, clinical effects, and adverse reactions of ticagrelor.
Relevant trials and reports were obtained from the MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases.
Ticagrelor is rapidly absorbed by the body after oral administration, exhibits inherent activity without requiring metabolic activation, and binds reversibly to the P2Y12 receptor. Ticagrelor has been recommended in ACS treatment guidelines worldwide due to its advantageous pharmacological properties and significant clinical benefits. Ticagrelor inhibits platelet aggregation, inhibits inflammatory response, enhances adenosine function, and has cardioprotective effects. However, ticagrelor also causes adverse reactions such as bleeding tendency, dyspnea, ventricular pause, gout, kidney damage, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in clinical treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to risk assessments when using ticagrelor.
Ticagrelor is a promising drug for the effective treatment of ACS. When using ticagrelor, individualized treatment should be provided based on the specific conditions of the patients to avoid serious adverse events.
Introduction
Since its approval in 2010, ticagrelor has been widely used as an antiplatelet agent for the treatment of clinical acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Ticagrelor is a novel P2Y12 receptor antagonist that is rapidly absorbed by the body after oral administration. Therefore, compared to traditional P2Y12 receptor inhibitors such as clopidogrel and prasugrel, ticagrelor has the advantages of a fast onset, high efficacy, and reversible platelet inhibition. Ticagrelor has been recognized worldwide because of its favorable pharmacological properties and significant clinical benefits, and it is the preferred antiplatelet drug for the treatment of ACS [ 1 ]. However, in-depth studies and the expansion of the drug’s clinical applications have gradually revealed that ticagrelor also induces various adverse reactions, including bleeding tendency, dyspnea, ventricular pause, gout, kidney damage, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), which can limit its use. The basic characteristics, clinical efficacy, and adverse reactions of ticagrelor are reviewed in this article to improve the clinical understanding of this drug. This article is based on previously conducted studies and did not involve human participants or animal experimentation.
Chemical characteristics and mechanism of ticagrelor
Ticagrelor is not a prodrug and therefore does not require metabolic activation to inhibit the P2Y12 receptor. Ticagrelor is a non-thiophene pyridine adenosine diphosphate (ADP) receptor antagonist that has a chemical structure similar to adenosine and belongs to the cyclopentyltriazolopyrimidine class of antiplatelet drugs [ 2 ]. Ticagrelor exerts its antiplatelet effects by suppressing the expression, binding, and activity of P2Y12, an ADP receptor found on platelet membranes.
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of ticagrelor
Effective blood concentrations of ticagrelor can be achieved within 1.5–3.0 h after oral administration. Ticagrelor is then transformed by liver enzymes into active metabolites [ 3 ] that synergistically generate antiplatelet effects in vivo [ 4 ]. The major metabolites of ticagrelor are AR-C124910XX and AR-C133913XX, which are mainly metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 [ 5 ]. AR-C124910XX has been identified as a ticagrelor active metabolite (TAM) because its potency in binding P2Y12 is similar to that of ticagrelor. Therefore, it is necessary to neutralize ticagrelor and TAM to effectively reverse the effects of ticagrelor therapy [ 6 ]. After repeated metabolism in the liver, ticagrelor and its metabolites are excreted in the feces, with only a small part excreted through the kidneys [ 7 ]. Moreover, ticagrelor shows faster, more effective antiplatelet effects than clopidogrel does in patients with chronic renal failure undergoing dialysis, indicating that ticagrelor can be used for antiplatelet therapy in patients with renal insufficiency [ 8 ]. The pharmacokinetic characteristics of ticagrelor are not significantly correlated with the patients’ age, gender, or ethnicity and are not affected by diet. The use of ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, has been found to overtly increase the mean maximum concentration and mean area under the plasma concentration-time curve of ticagrelor by 135% and 632%, respectively, indicating that the co-administration of ticagrelor and ketoconazole should be avoided [ 9 ]. Similarly, the simultaneous use of ticagrelor and other potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, including itraconazole, clarithromycin, ritonavir, and telithromycin, is contraindicated [ 10 ]. Opioids, such as fentanyl and morphine, have been demonstrated to impair the antiplatelet effects of ticagrelor, raising the risk of insufficient platelet inhibition and leading to thrombotic complications in patients with coronary artery disease [ 11 , 12 ]. Opioids may delay the absorption and effects of oral P2Y12 receptor antagonists in patients, resulting in reduced plasma concentrations, delayed antiplatelet action, and increased platelet reactivity [ 13 ]. Thus, ticagrelor should also not be taken concomitantly with opioids.
Pharmacodynamic investigations of ticagrelor have revealed its fast, potent, reversible inhibition of platelets. Notably, ticagrelor does not require metabolic activation in the live, as it is quickly activated after absorption, and its efficacy is not affected by liver function [ 14 ]. Studies have shown that the binding and dissociation reactions between the ticagrelor and the P2Y12 receptor are rapid and reversible [ 15 ]. Interestingly, ticagrelor has been shown to elevate extracellular adenosine levels in vitro by repressing the equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (ENT1), which is an adenosine transporter found in red blood cells [ 16 ]. Thus, ticagrelor can promote a series of adenosine-induced physiological responses, such as enhanced coronary blood flow and inhibited adenosine-dependent platelet aggregation.
Nonlinear mixed-effects modeling and simulations have been used to determine the exposure–response relationship between ticagrelor and platelet inhibition. In patients with stable coronary artery disease or a history of myocardial infarction (MI), 60 mg or 90 mg of ticagrelor administered twice daily can achieve near-maximal platelet inhibition, whereas doses less than 60 mg lead to weaker overall efficacy and greater differences between patients [ 17 ]. Furthermore, evidence has shown that crushed or chewed ticagrelor tablets lead to faster platelet inhibition than standard whole tablets [ 18 ]. Although the gastrointestinal absorption of crushed ticagrelor is superior to that of whole tablets, the platelet reactivity of ACS patients is still high in the first two hours after administration, which is a marker of thrombotic complications [ 19 ]. Intriguingly, it has been reported that the concomitant administration of cangrelor and crushed ticagrelor can improve the gap in platelet repression that results from administering ticagrelor alone, without any significant drug interactions [ 20 ].
Clinical efficacy of ticagrelor in disease treatment
Ticagrelor has been recommended in ACS treatment guidelines worldwide due to its advantageous pharmacological properties and significant clinical benefits [ 1 , 21 , 22 ]. The clinical therapeutic effects of ticagrelor are mainly attributed to its effective inhibition of the P2Y12 receptor, which inhibits platelet aggregation, suppresses inflammation, reinforces adenosine function, and enhances cardiovascular protection.
Antiplatelet effects of ticagrelor
The process of intracoronary thrombosis is characterized by the binding of ADP to the P2Y12 receptor on platelet surfaces, which triggers platelet activation. Therefore, the effective inhibition of the P2Y12 receptor has become the main approach to clinically treating coronary artery disease. Ticagrelor reduces thrombosis by selectively inhibiting the P2Y12 receptor, and numerous studies have shown that ticagrelor has potent antiplatelet effects, with a fast onset and small individual differences in effectiveness. Clopidogrel is a P2Y12 inhibitor that is widely used for antiplatelet therapy, but ticagrelor results in faster, stronger effects and a greater reduction of atherothrombotic events in ACS patients [ 23 ]. The well-known PLATO study, which involved a 12-month follow-up of patients with ST-segment elevation or non-ST-segment elevation ACS, showed a significantly lower incidence of major cardiovascular events in patients receiving ticagrelor than in those receiving clopidogrel, with no remarkable increase in bleeding risk [ 24 ]. In addition, the short-term efficacy of ticagrelor has been reported to be better than that of clopidogrel in patients with ACS: the occurrence of cardiovascular events decreased one month after ticagrelor administration (180 mg loading dose plus 90 mg twice daily maintenance dose), compared to clopidogrel administration (300 mg loading dose plus 75 mg daily maintenance dose); neither ticagrelor nor clopidogrel caused fatal bleeding [ 25 ]. More importantly, Liu et al. estimated the antiplatelet function of ticagrelor at different loading doses and found that non-ST-segment elevation ACS patients receiving a high loading dose of 360 mg and a maintenance dose of 90 mg twice daily exhibited faster, stronger platelet suppression than those treated with a conventional loading dose of 180 mg and a maintenance dose of 90 mg twice daily [ 26 ]. Compared to clopidogrel, ticagrelor significantly reduces ischemic events without increasing bleeding events in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), and it also reduces all-cause mortality by 51% among CABG patients [ 27 , 28 , 29 ]. Ticagrelor has also been reported to have a faster platelet inhibition rate and a higher degree of inhibition than clopidogrel in diabetic patients with stable coronary heart disease, with the responses being independent of diabetic status. The RESPOND study was the first to evaluate the reactivity of patients with stable coronary heart disease after administration of 300 mg clopidogrel; a crossover experiment based on reactivity showed that the patients’ platelet aggregation decreased from 59% to 35% after switching from clopidogrel to ticagrelor, whereas the it increased from 36% to 56% after switching from ticagrelor to clopidogrel [ 30 ]. These results indicate that ticagrelor is a potent alternative to clopidogrel.
Individuals treated with clopidogrel may exhibit resistance to the drug or variability in clopidogrel efficacy, which may be related to individual differences as well as CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms. The CYP2C19 loss of function (LoF) allele is associated with a significantly increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with stable coronary artery disease undergoing PCI and treated with clopidogrel [ 31 ]. However, compared to clopidogrel, ticagrelor significantly reduces the risk of major adverse cardiac events and cardiovascular death among ACS patients carrying the CYP2C19 LoF allele and undergoing PCI [ 32 ]. Stimpfle et al. [ 33 ] investigated CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms and confirmed that the efficacy of antiplatelet therapy significantly improved in patients with poor responses to clopidogrel after switching to ticagrelor. In addition, ticagrelor has been recommended over clopidogrel for ACS patients with ABCB1 gene polymorphisms [ 34 ]. In sum, ticagrelor is not affected by individual genetic polymorphisms, so it can be used for the treatment of clopidogrel-resistant patients. Of note, the CYP3A4*22 allele has been shown to significantly attenuate the elimination of ticagrelor, thereby enhancing its antiplatelet effect [ 35 ]. However, a study in a Chinese population have indicated that it is unnecessary to adjust the dose of ticagrelor according to the CYP3A4 genotype [ 36 ].
Anti-inflammatory effects of ticagrelor
Platelets not only participate in hemostasis and thrombosis but are also involved in the body’s inflammatory response. Antiplatelet drugs can inhibit platelet aggregation and suppress inflammation. The P2Y12 receptor is expressed on the surfaces of platelets and various inflammatory cells (e.g., neutrophils, dendritic cells, and monocyte-macrophages), so the activation of the P2Y12 receptor plays a key role in the activation and migration of inflammatory cells [ 37 , 38 ]. In early animal experiments, clopidogrel significantly delayed the occurrence and development of mouse aneurysms by reducing the expression of inflammatory factors and the infiltration of inflammatory cells [ 39 ]. Further, the ASCET study showed that blood levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin (IL), matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and cluster of differentiation 40 (CD40) ligands were markedly reduced in patients with coronary heart disease after one year of clopidogrel treatment [ 40 ]. Chen et al. [ 41 ] found lower high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) concentrations in patients with non-ST-segment elevation ACS who were treated with a combination of clopidogrel and aspirin than in patients treated with aspirin alone. In a recent study [ 42 ], ticagrelor treatment resulted in a great reduction of hs-CRP compared to clopidogrel, suggesting that ticagrelor has a stronger anti-inflammatory effect. The mechanism by which ticagrelor exerts its anti-inflammatory effect is still unclear, but it probably acts by blocking the formation of platelet-macrophage and platelet-neutrophil aggregates. Gasecka et al. [ 43 ] reported that the fragments released by activated platelets during ACS are platelet-derived extracellular vesicles (PEVs); they are likely to be involved in inflammation and thrombosis and potentially in the development and progression of atherosclerosis. PEVs released by activated platelets (positive for CD61, P-selectin, and phosphatidylserine) are referred to as PEVs+. Notably, ticagrelor has been found to attenuate inflammation and thrombosis by decreasing the concentration of PEVs+.
Adenosine-like effects of ticagrelor
Ticagrelor can inhibit the uptake of adenosine by red blood cells, increase the concentration of extracellular adenosine, and enhance the activity of adenosine to produce a series of biological effects, including platelet inhibition, vasodilation, and myocardial protection [ 44 ]. Van Giezen et al. [ 45 ] reported that this inhibitory effect of ticagrelor on adenosine uptake could result in increased extracellular adenosine concentrations. In subsequent animal experiments, ticagrelor and dipyridamole were found to significantly and dose-dependently increase intracoronary adenosine-mediated blood flow in open-chest canine models. Wittfeldt et al. [ 46 ] obtained similar results from clinical randomized double-blind trials: ticagrelor significantly and dose-dependently increased the coronary blood flow velocity and area under the velocity curve when compared with a placebo. Similarly, in a prospective, single-center, single-blind study by Alexopoulos et al. [ 47 ], the ticagrelor group exhibited a significant increase in coronary blood flow velocity compared to the prasugrel group. Taken together, these findings suggest that ticagrelor plays an active role in the adenosine-mediated increases in coronary blood flow.
Animal experiments conducted by Wang et al. [ 48 ] and Birnbaum et al. [ 49 ] revealed that ticagrelor has a unique cardioprotective mechanism that clopidogrel does not. H-FABP can be used to determine myocardial infarct size in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and to evaluate their cardiovascular prognoses. Studies have shown that the increased levels of hs-TnT and h-FABP after PCI are significantly lower with ticagrelor administration than with clopidogrel administration, thus proving the myocardial protective effect of ticagrelor [ 50 ]. Compared to clopidogrel, pretreatment with a loading dose of ticagrelor can significantly reduce the incidence of perioperative MI associated with PCI. A multivariate analysis revealed a negative correlation between ticagrelor use and perioperative MI associated with PCI, indicating that ticagrelor treatment is an independent protective predictor of perioperative MI [ 51 ]. This cardioprotective effect is mediated by adenosine and can be completely reversed by adenosine receptor antagonists. Ticagrelor has been found to increases adenosine levels in two ways: 1) by blocking human equilibrium nucleoside transporters to inhibit adenosine reuptake; and 2) through the increased release of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is then converted to adenosine [ 52 ]. In short, ticagrelor not only inhibits adenosine reuptake but also induces human red blood cells to release ATP in a dose-dependent manner. The ATP released is rapidly decomposed into adenosine by the enzymes in endothelial cells, white blood cells, and red blood cells, which thereby causes transient ventricular block and endothelium-dependent vasodilation [ 53 ]. However, increased adenosine levels can cause some adverse reactions, such as dyspnea, bradycardia, gout, kidney damage, and TTP. For example, by acting on the A1 and A2A receptors on the C fibers of the vagus nerve, adenosine provokes bronchial constriction and eventually leads to dyspnea [ 54 ]. Bradycardia and ventricular pauses are side effects of adenosine-related stimulation of the adenosine A1 receptor present in heart tissue [ 55 ].
Ticagrelor-related adverse reactions
Numerous ACS patients now benefit from the advantageous antiplatelet effects of ticagrelor. However, due to the pharmacological properties and increasing clinical application of ticagrelor, some adverse reactions of using this drug in antiplatelet therapy, including bleeding tendency, dyspnea, ventricular pause, gout, kidney damage, and TTP, are now receiving considerable attention as part of efforts to make timely adjustments to ensure the safety and maximum clinical benefits of ticagrelor. Moreover, the PROGRESS trial has suggested that, compared to telephone follow-ups, clinical follow-ups in a dedicated outpatient clinic contribute to the decreased incidence of adverse reactions caused by ticagrelor [ 56 ]. Notably, a recent study showed that low doses of ticagrelor are safe for long-term antiplatelet therapy, and appropriate patient selection can help avoid or reduce the occurrence rates of some adverse effects of ticagrelor [ 57 ].
Bleeding tendency
Ticagrelor reduces the risk of ischemia but increases the tendency to hemorrhage. Bleeding is the most significant adverse reaction that occurs during the use of antiplatelet drugs, leading to complications, death, and increased healthcare costs. It is also more difficult to stop bleeding during events such as injury or surgery in patients taking ticagrelor due to the inhibition of platelet activity. The specific bleeding events associated with ticagrelor include nose bleeding, subcutaneous hemorrhage, gastrointestinal bleeding, and intracranial hemorrhage. The DISPERS study demonstrated an increased risk of minor bleeding but few major bleeding events with ticagrelor (administered at 50, 100, or 200 mg twice daily) compared to clopidogrel (administered at 400 mg daily) [ 58 ]. The PLATO study showed no significant difference in terms of major bleeding between the ticagrelor group (180 mg loading dose, 90 mg loading dose twice daily thereafter) and the clopidogrel group (300-600 mg loading dose, 75 mg loading dose twice daily thereafter) ; however, major bleeding not related to coronary-artery bypass grafting were higher in the ticagrelor group than in the clopidogrel group, and ticagrelor resulted in an increased risk of intracranial haemorrhage, with a 10-fold increase in the incidence of fatal intracranial hemorrhage (0.1% vs. 0.01%) [ 24 ]. For STEMI patients aged under 75 years treated with fibrinolytic therapy in TREAT trial, the rates of major bleeding (1.6% vs 2.1%; P = 0.21), Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) types 3 to 5 bleeding (1.6% vs 2.0%; P = 0.43), fatal bleeding (0.3% vs 0.2%; P = 0.55), and intracranial bleeding (0.3% vs 0.2%; P = 0.76) were similar between the ticagrelor and the clopidogrel groups, respectively [ 59 ]. A meta-analysis was recently conducted to assess the efficacy and safety of ticagrelor in Asian patients with ACS in real-world practice, as compared to clopidogrel; the findings indicated that ticagrelor can reduce the risk of major adverse cardiac events by reducing the risk of stroke, without increasing the rates of major bleeding [ 60 ].
However, compared with clopidogrel, ticagrelor is associated with a significantly high incidence of clinically relevant bleeding complications as part of dual or triple antithrombotic therapy. It has been found that the combination of aspirin and ticagrelor (n = 5853) is superior to aspirin alone (n = 10,722) in preventing stroke recurrence or death within 90 days of treatment initiation, but it increases the risk of major bleeding [ 61 ]. In patients receiving triple therapy (TT), ticagrelor may increase thromboembolic and ischemic cardiac events [ 62 ]. In a systematic review analyzing 5,659 patients who underwent dual antiplatelet therapy or TT, the use of ticagrelor was associated with a higher rate of clinically significant bleeding than clopidogrel was [ 62 ]. In addition, the administration of ticagrelor in TT is related to an increased risk of intracranial bleeding, as well as complications such as neurological deficits [ 63 , 64 ]. Considering this, bridge anticoagulation should be applied with caution when ticagrelor is used in dual antiplatelet therapy or TT.
In TWILIGHT, a double-blind trial, patients with an ischemic event who underwent PCI and completed three months of dual antiplatelet therapy were considered, and ticagrelor monotherapy was associated with a lower incidence of clinically relevant bleeding than ticagrelor plus aspirin. Further, the incidence of the primary endpoint BARC type 2, 3, or 5 bleeding was 4.0% among patients randomly assigned to receive ticagrelor plus placebo and 7.1% among patients assigned to receive ticagrelor plus aspirin (hazard ratio = 0.56; 95% CI = 0.45–0.68; P < 0.001) [ 65 ].
Platelet transfusion is usually performed for bleeding caused by antiplatelet drugs, but this may not be effective for ticagrelor-caused bleeding. According to a report, the use of 17 units of platelets failed to counteract bleeding due to tegretol in a 65-year-old male emergency patient [ 66 ]. Martin et al. [ 67 ] found that an increase in platelets could not restore the platelet aggregation function in ticagrelor samples, perhaps because ticagrelor and its metabolites inhibit fresh platelets and thereby prevent infused platelets from achieving a good antibleeding effect against ticagrelor. Notably, antibody fragments that exhibit high-affinity binding to ticagrelor, including MEDI2452 and PB2452, can act as antidotes in reversing the antiplatelet effects of ticagrelor [ 68 , 69 ]. Antiplatelet therapy is thus a double-edged sword, with an increase in thrombotic events in low responders and an increased risk of bleeding in high responders. Therefore, clinical medication should be differentiated, the risk of ischemia and bleeding should be assessed, and ticagrelor doses should be appropriately adjusted to avoid administering large doses to people with a high risk of bleeding. The importance of individualized treatment should be emphasized when striving for maximum clinical benefit and a minimal risk of bleeding. The ongoing POPular AGE test by Qaderdan et al. [ 70 ] is an evaluation of the clinical net benefits of new antiplatelet drugs, and the results may provide further references for clinical drug selection for the elderly.
Dyspnea is the most common adverse reaction associated with the clinical use of ticagrelor. The PLATO study showed that dyspnea is likelier to develop in patients treated with ticagrelor than in those treated with clopidogrel (13.8% vs. 7.8%, P < 0.001) [ 24 ]. Furthermore, Caldeira et al. [ 71 ] reported that ticagrelor causes a higher incidence of dyspnea than clopidogrel or prasugrel. Dyspnea tends to be mild to moderate in most patients, often occurs in the early stages of treatment, lasts from days to weeks, is generally self-limiting, and has no significant effects on blood oxygen saturation, vital capacity, functional residual capacity, or diffusion function [ 72 ]. Most patients continue to take medication, and their symptoms are gradually relieved without targeted treatment; the symptoms of dyspnea disappear after drug withdrawal [ 73 ]. At present, the pathogenesis of dyspnea caused by ticagrelor is unclear. The main mechanisms may be related to the delay in adenosine metabolism caused by the ticagrelor-induced inhibition of adenosine uptake by erythrocytes and the delayed adenosine clearance [ 74 ]. Ticagrelor can significantly increase coronary blood flow [ 45 ] and coronary blood flow velocity [ 46 ] by restraining adenosine uptake, which enhances adenosine-induced dyspnea. This dyspnea symptom can be reversed by theophylline drugs [ 75 ]. Other researchers have speculated that dyspnea is correlated with the inhibition ofP2Y12 in neuronal cells.
Compared to clopidogrel, ticagrelor treatment has been found to increase the risk of dyspnea in patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [ 76 ]. Therefore, ticagrelor should be used with caution when treating patients with asthma and COPD. Studies have also shown that high doses of ticagrelor remarkably increase the probability of dyspnea [ 77 ], which suggests that dyspnea is ticagrelor dose-related. Consequently, reducing the dose might reduce or relieve the symptoms of dyspnea, and the appropriate dose should be determined according to the actual situation of each patient.
Ventricular pause
The ventricular pause associated with ticagrelor mostly occurs at night, for short durations, and with mild symptoms [ 78 ]. The PLATO trial revealed a significant increase in the incidence of ventricular pauses in patients receiving ticagrelor, as compared to clopidogrel, but no statistical difference was noted after one month of treatment [ 24 ]. Nicol et al. [ 79 ] reported a case of ventricular pause caused by oral ticagrelor therapy for nonsustained tachycardia, and Scirica et al. [ 80 ] found a significantly greater proportion of ventricular pauses among patients treated with ticagrelor (5.8%) than those treated with clopidogrel (3.6%) in the first week after randomization. Furthermore, some adverse reactions, such as atrioventricular block and atrial fibrillation, have been reported due to the use of ticagrelor [ 81 , 82 , 83 ].
The mechanism of ventricular pause induced by ticagrelor remains to be further explored. Some scholars have supported the understanding that P2Y12 inhibitors directly affect the self-discipline or conductivity of the heart [ 80 ], while others have suggested a relationship between the occurrence of early ventricular pauses and changes in adenosine metabolism in the body [ 44 , 45 , 47 ]. The increased adenosine concentrations in the sinoatrial node and atrioventricular compartment may aggravate vagus nerve-mediated nocturnal bradycardia, thereby explaining the nocturnal pause caused by ticagrelor.
Gout is a possible adverse reaction to long-term treatment with ticagrelor. In the PLATO study in 2009, plasma uric acid concentration increased by 14% after ticagrelor administration for 1–2 months and decreased significantly after one month of withdrawal [ 24 ]. Further, Butler et al. found that serum uric acid increased significantly after five days of ticagrelor treatment, although no adverse reactions were caused by elevated uric acid. In recent study, patients undergoing long-term treatment with ticagrelor were twice as likely to develop gout as those in the placebo group [ 84 ].
The specific mechanism governing gout may be as follows: first, ticagrelor is metabolized by the kidney, with ticagrelor and its active metabolites inhibiting urate transporter-1 and organic cation transporter-1 [ 85 ], both of which play important roles in the absorption and reacceptance of uric acid [ 86 , 87 ]. This affects the metabolism of uric acid in the kidney and increases the chance of uric acid exposure. Second, ticagrelor inhibits the equilibrium type nucleoside transporters and suppresses the absorption of adenosine [ 88 ], resulting in an increased concentration of adenosine. Uric acid is a metabolite of adenosine and adenosine can cause ischemia, hypoxia, and inflammation, eventually leading to hyperuricemia and gout [ 89 ].
Ticagrelor-related gout is easily overlooked during long-term medication. Clinicians should regularly check patients’ plasma uric acid concentration and watch out for the symptoms of arthritis and gout caused by elevated uric acid. Clinically, uric acid abnormalities caused by medication alone can be treated in accordance with the protocols for drug-induced hyperuricemia, along with drug replacement. Patients with ACS and hyperuricemia can receive prophylactic treatment and intensive uric acid-lowering therapy in the early stages of taking ticagrelor to prevent drug-related adverse events.
Kidney damage
Clopidogrel exhibits low reactivity in patients with chronic kidney disease [ 90 , 91 ]; therefore, ticagrelor treatment is more advantageous in patients with impaired renal function [ 27 ]. However, studies have shown that patients treated with ticagrelor have a slightly higher risk of renal adverse reactions than those treated with clopidogrel. Clinically, the creatinine levels of some patients who received ticagrelor were found to be slightly higher than the levels before administration [ 5 , 24 , 92 ]. Van Vuren et al. reported that a patient with rhabdomyolysis due to elevated serum concentrations of rosuvastatin as a result of worsening renal function due to ticagrelor [ 93 ]. In the PLATO study [ 94 ], the plasma creatinine concentration increased by more than 30% in about a quarter of the ticagrelor-treated patients, and by more than 50% in some ticagrelor-treated patients. The mechanism of action underlying the increase in creatinine concentration is not clear, but it may be related to the extension of the adenosine half-life and the alteration of adenosine metabolism by ticagrelor. Enhanced adenosine concentration reduces glomerular filtration pressure and changes renal blood flow, resulting in elevated creatinine levels. At the same time, creatinine concentration increases with the elevation of uric acid (an adenosine metabolite) in the early stages of ticagrelor treatment [ 78 ]. Although adjusting the ticagrelor dose in response to elevated creatinine levels is not recommended in clinical applications, the guidelines of the European Medicines Agency state that patients should be tested for kidney function within one month of the initial use of ticagrelor. In patients with additional risk factors, creatinine concentration should be promptly determined to evaluate the long-term effects of ticagrelor on renal function.
TTP is a rare and lethal disorder that has been reported to be correlated with clopidogrel. FDA database results revealed that clopidogrel is the most common agent related to TTP, and the incidence of clopidogrel-associated TTP is four times higher than that of idiopathic TTP, indicating a causal-and-effect relationship [ 95 ]. Bennett et al. [ 96 ] studied the incidence of TTP in 11 patients during or soon after clopidogrel therapy and reported the possibility of TTP occurring at the beginning of clopidogrel treatment. Ticagrelor has not previously been correlated with TTP, but recent studies have indicated that TTP may be a rare adverse reaction to the drug. Doğan et al. [ 97 ] identified a case of ticagrelor-related TTP after the first month of ticagrelor use. Further, Wang et al. [ 98 ] reported that a patient with STEMI who incurred ticagrelor-induced TTP after two months of treatment with ticagrelor recovered quickly due to plasmapheresis and then died when ticagrelor was reused; this suggests that ticagrelor might be a contributor to TTP.
Ticagrelor is a novel P2Y12 receptor inhibitor that has many advantages in antiplatelet therapy. ACS patients can benefit from a series of biological effects resulting from the increased adenosine concentration induced by ticagrelor. However, adverse reactions can arise during clinical treatment, such as bleeding tendency, dyspnea, ventricular pause, gout, kidney damage, and TTP. Therefore, to avoid serious adverse events, individualized treatment should be provided based on the specific conditions of each patient when using ticagrelor. Based on the results of the ISAR-Reaction V randomized trial, the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines recommend that prasugrel be prioritized over ticagrelor for patients with non-ST segment elevation ACS undergoing PCI. However, the findings of this research are influenced by a bias that is difficult to estimate owing to various reasons. Moreover, studies have shown that the use of ticagrelor was related to improved outcomes compared with clopidogrel and prasugrel [ 99 ]. Further studies are needed to determine the prioritization of ticagrelor and prasugrel.
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Amsterdam EA, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non–ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(24):2645–87.
Article Google Scholar
Husted S, van Giezen JJ. Ticagrelor: the first reversibly binding oral P2Y12 receptor antagonist. Cardiovasc Ther. 2009;27(4):259–74.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Li Y, Landqvist C, Grimm SW. Disposition and metabolism of ticagrelor, a novel P2Y12 receptor antagonist, in mice, rats, and marmosets. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011;39(9):1555–67.
Storey RF. Pharmacology and clinical trials of reversibly-binding P2Y12 inhibitors. Thromb Haemost. 2011;105(Suppl 1):S75–81.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Teng R. Ticagrelor: Pharmacokinetic, Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacogenetic Profile: an update. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2015;54(11):1125–38.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sandinge AS, et al. Quantification of unbound concentration of ticagrelor in plasma as a proof of mechanism biomarker of the reversal agent, MEDI2452. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(7):e0201202.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Butler K, Teng R. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of ticagrelor in volunteers with severe renal impairment. J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;52(9):1388–98.
Jeong KH, et al. Platelet reactivity after receiving clopidogrel compared with ticagrelor in patients with Kidney Failure treated with hemodialysis: a randomized crossover study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;65(6):916–24.
Teng R, Butler K. Effect of the CYP3A inhibitors, diltiazem and ketoconazole, on ticagrelor pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers. J Drug Assess. 2013;2(1):30–9.
Ferri N, Corsini A, Bellosta S. Pharmacology of the new P2Y12 receptor inhibitors: insights on pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. Drugs. 2013;73(15):1681–709.
Kuczyńska K, Boncler M. Emerging role of Fentanyl in Antiplatelet Therapy. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020;76(3):267–75.
PubMed Google Scholar
Franchi F, et al. Effects of Methylnaltrexone on Ticagrelor-Induced Antiplatelet effects in Coronary Artery Disease patients treated with Morphine. JACC: Cardiovasc Interventions. 2019;12(16):1538–49.
Google Scholar
Iglesias JF, Valgimigli M, Carbone F, Lauriers N, Masci PG, Degrauwe S. Comparative effects of fentanyl versus morphine on platelet inhibition induced by ticagrelor in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: full results of the PERSEUS randomized trial. Cardiol J. 2022;29(4):591–600.
Gurbel PA, et al. Randomized double-blind assessment of the ONSET and OFFSET of the antiplatelet effects of ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in patients with stable coronary artery Disease: the ONSET/OFFSET study. Circulation. 2009;120(25):2577–85.
JJ VANG, et al. Ticagrelor binds to human P2Y(12) independently from ADP but antagonizes ADP-induced receptor signaling and platelet aggregation. J Thromb Haemost. 2009;7(9):1556–65.
Aungraheeta R, et al. Inverse agonism at the P2Y12 receptor and ENT1 transporter blockade contribute to platelet inhibition by ticagrelor. Blood. 2016;128(23):2717–28.
Astrand M, et al. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling of platelet response to ticagrelor in stable coronary artery Disease and prior Myocardial Infarction patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019;85(2):413–21.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Venetsanos D, et al. Chewed ticagrelor tablets provide faster platelet inhibition compared to integral tablets: the inhibition of platelet aggregation after administration of three different ticagrelor formulations (IPAAD-Tica) study, a randomised controlled trial. Thromb Res. 2017;149:88–94.
Marian MJ, et al. Effects of Crushed Ticagrelor Versus Eptifibatide Bolus Plus Clopidogrel in Troponin-negative Acute Coronary Syndrome patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a Randomized Clinical Trial. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8(23):e012844.
Franchi F, et al. Platelet inhibition with Cangrelor and Crushed Ticagrelor in patients with ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation. 2019;139(14):1661–70.
Hochholzer W, Neumann FJ. [The new 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation] Dtsch Med Wochenschr, 2016. 141(11): p. 782-5.
Anderson JL et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA focused update incorporated into the ACCF/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines J Am Coll Cardiol, 2013. 61(23): p. e179-347.
Franchi F, et al. Impact of escalating loading dose regimens of Ticagrelor in patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention: results of a prospective Randomized Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Investigation. Volume 8. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions; 2015. pp. 1457–67. 11.
Wallentin L, et al. Ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(11):1045–57.
Wang Q, Lin W. Application of ticagrelor in the treatment of acute coronary syndrome. Shandong Med. 2015;55(7):77–9.
CAS Google Scholar
Liu HL, et al. Design and rationale of the APELOT Trial: a randomized, Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase IV Study to evaluate the Antiplatelet Effect of different loading dose of Ticagrelor in patients with Non-ST Acute Coronary Syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Med (Baltim). 2016;95(22):e3756.
Article CAS Google Scholar
James S, et al. Ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in acute coronary syndromes in relation to renal function: results from the platelet inhibition and patient outcomes (PLATO) trial. Circulation. 2010;122(11):1056–67.
Cannon CP, et al. Comparison of ticagrelor with clopidogrel in patients with a planned invasive strategy for acute coronary syndromes (PLATO): a randomised double-blind study. Lancet. 2010;375(9711):283–93.
Held C, et al. Ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing coronary artery bypass Surgery: results from the PLATO (platelet inhibition and patient outcomes) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(6):672–84.
Gurbel PA, et al. Response to ticagrelor in clopidogrel nonresponders and responders and effect of switching therapies: the RESPOND study. Circulation. 2010;121(10):1188–99.
Biswas M, Kali SK. Association of CYP2C19 loss-of-function alleles with major adverse Cardiovascular events of Clopidogrel in stable coronary artery Disease patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: Meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021;35(6):1147–59.
Biswas M, et al. Risk of major adverse cardiovascular events of CYP2C19 loss-of-function genotype guided prasugrel/ticagrelor vs clopidogrel therapy for acute coronary syndrome patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis. Platelets. 2021;32(5):591–600.
Stimpfle F, et al. Impact of point-of-care testing for CYP2C19 on platelet inhibition in patients with acute coronary syndrome and early dual antiplatelet therapy in the emergency setting. Thromb Res. 2014;134(1):105–10.
Biswas M, et al. Effects of the ABCB1 C3435T single nucleotide polymorphism on major adverse cardiovascular events in acute coronary syndrome or coronary artery Disease patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention and treated with clopidogrel: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2020;19(12):1605–16.
Holmberg MT, et al. CYP3A4*22 impairs the elimination of Ticagrelor, but has no significant effect on the Bioactivation of Clopidogrel or Prasugrel. Volume 105. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics; 2019. pp. 448–57. 2.
Liu S, et al. Effect of CYP3A4(*)1G and CYP3A5(*)3 polymorphisms on Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Ticagrelor in healthy Chinese subjects. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:176.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Badrnya S, et al. Platelets directly enhance neutrophil transmigration in response to oxidised low-density lipoprotein. Thromb Haemost. 2012;108(4):719–29.
Webster CM, et al. Microglial P2Y12 deficiency/inhibition protects against brain ischemia. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(8):e70927.
Liu O, et al. Clopidogrel, a platelet P2Y12 receptor inhibitor, reduces vascular inflammation and angiotensin II induced-abdominal aortic Aneurysm progression. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(12):e51707.
Solheim S, et al. No difference in the effects of clopidogrel and aspirin on inflammatory markers in patients with coronary Heart Disease. Thromb Haemost. 2006;96(5):660–4.
Chen YG, et al. Effect of aspirin plus clopidogrel on inflammatory markers in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. Chin Med J (Engl). 2006;119(1):32–6.
Liu S, et al. Effect of CYP3A4( ∗ )1G and CYP3A5( ∗ )3 polymorphisms on Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Ticagrelor in healthy Chinese subjects. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:176.
Gasecka A, et al. P2Y12 antagonist ticagrelor inhibits the release of procoagulant extracellular vesicles from activated platelets. Cardiol J. 2019;26(6):782–9.
Nylander S, et al. Ticagrelor inhibits human platelet aggregation via adenosine in addition to P2Y12 antagonism. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11(10):1867–76.
van Giezen JJ, et al. Ticagrelor inhibits adenosine uptake in vitro and enhances adenosine-mediated hyperemia responses in a canine model. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2012;17(2):164–72.
Wittfeldt A, et al. Ticagrelor enhances adenosine-induced coronary vasodilatory responses in humans. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61(7):723–7.
Alexopoulos D, et al. Differential effect of ticagrelor versus prasugrel on coronary blood flow velocity in patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: an exploratory study. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6(3):277–83.
Wang K, et al. Adjunctive treatment with ticagrelor, but not clopidogrel, added to tPA enables sustained coronary artery recanalisation with recovery of myocardium perfusion in a canine Coronary Thrombosis model. Thromb Haemost. 2010;104(3):609–17.
Birnbaum Y, Ling S, Nanhwan, MK, Kodakandla M, Ye Y. Ticagrelor, but not clopidogrel, protects the heart and limits myocardial infarct size. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(12):A22.
Shabaiek A, et al. Role of Cardiac myocytes Heart fatty acid binding protein depletion (H-FABP) in early Myocardial Infarction in Human Heart (autopsy study). Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2016;4(1):17–21.
Zhang YR, Xue ZK, Chen KY. Loading doses of ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in preventing periprocedural Myocardial Infarction in Asian patients with acute coronary syndrome . 2021. 36(2): p. 122–9.
Kubisa MJ, et al. Ticagrelor - toward more efficient platelet inhibition and beyond. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018;14:129–40.
Ohman J, et al. Ticagrelor induces adenosine triphosphate release from human red blood cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;418(4):754–8.
Unverdorben M, et al. Dyspnea related to reversibly-binding P2Y12 inhibitors: a review of the pathophysiology, clinical presentation and diagnostics. Int J Cardiol. 2016;202:167–73.
Mustafa SJ, et al. Adenosine receptors and the heart: role in regulation of coronary blood flow and cardiac electrophysiology. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;193:161–88.
Crisci M, et al. Improving adherence to Ticagrelor in patients after Acute Coronary Syndrome: results from the PROGRESS trial. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(3):294–301.
Cesaro A, et al. Low-dose Ticagrelor in patients with high ischemic risk and previous Myocardial Infarction: a multicenter prospective real-world Observational Study. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020;76(2):173–80.
Husted S, Emanuelsson H, Heptinstall S, Sandset PM, Wickens M, Peters G. Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and safety of the oral reversible P2Y12 antagonist AZD6140 with aspirin in patients with atherosclerosis: a double-blind comparison to clopidogrel with aspirin. Eur Heart J. 2006;27(9):1038–47.
Berwanger O, Lopes RD, Moia DDF, Fonseca FA, Jiang L, Goodman SG, et al. Ticagrelor versus Clopidogrel in patients With STEMI treated With fibrinolysis: TREAT Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(22):2819–2828.
Galimzhanov AM, Azizov BS. Ticagrelor for Asian patients with acute coronary syndrome in real-world practice: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Indian Heart J. 2019;71(1):15–24.
Lun R, et al. Comparison of Ticagrelor vs Clopidogrel in Addition to aspirin in patients with minor ischemic Stroke and transient ischemic Attack: a Network Meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79(2):141–8.
Andreou I, et al. Ticagrelor Versus Clopidogrel as Part of Dual or Triple Antithrombotic Therapy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2018;32(3):287–94.
Farooq MU. Ticagrelor: a safe option as part of triple therapy? Clin Pract. 2020;10(1):1221.
Fu A, et al. Ticagrelor in Triple Antithrombotic Therapy: predictors of ischemic and bleeding Complications. Clin Cardiol. 2016;39(1):19–23.
Mehran R et al. Ticagrelor with or without aspirin in high-risk patients after PCI . N Engl J Med, 2019.
Godier A, Taylor G, Gaussem P. Inefficacy of platelet transfusion to reverse ticagrelor. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(2):196–7.
Martin AC, et al. The effectiveness of platelet supplementation for the reversal of ticagrelor-induced inhibition of platelet aggregation: an in-vitro study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2016;33(5):361–7.
Almquist J, et al. Unraveling the pharmacokinetic interaction of ticagrelor and MEDI2452 (Ticagrelor antidote) by mathematical modeling. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2016;5(6):313–23.
Bhatt DL, et al. Antibody-based ticagrelor reversal Agent in healthy volunteers. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(19):1825–33.
Qaderdan K, et al. Ticagrelor or prasugrel versus clopidogrel in elderly patients with an acute coronary syndrome: optimization of antiplatelet treatment in patients 70 years and older–rationale and design of the POPular AGE study. Am Heart J. 2015;170(5):981–985e1.
Caldeira D, Pinto FJ, Ferreira JJ. Dyspnea and reversibility profile of P2Y(1)(2) antagonists: systematic review of new antiplatelet Drugs. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2014;14(4):303–11.
Mehran R, et al. Cessation of dual antiplatelet treatment and cardiac events after percutaneous coronary intervention (PARIS): 2 year results from a prospective observational study. Lancet. 2013;382(9906):1714–22.
Gaubert M, et al. Effect of ticagrelor-related dyspnea on compliance with therapy in acute coronary syndrome patients. Int J Cardiol. 2014;173(1):120–1.
Armstrong D, et al. Characterization of the adenosine pharmacology of ticagrelor reveals therapeutically relevant inhibition of equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2014;19(2):209–19.
Lindholm D, et al. Design and rationale of TROCADERO: a TRial of caffeine to Alleviate DyspnEa related to ticagrelOr. Am Heart J. 2015;170(3):465–70.
Butler K, Maya J, Teng R. Effect of ticagrelor on pulmonary function in healthy elderly volunteers and Asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease patients. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013;29(5):569–77.
Cannon CP, et al. Safety, tolerability, and initial efficacy of AZD6140, the first reversible oral adenosine diphosphate receptor antagonist, compared with clopidogrel, in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome: primary results of the DISPERSE-2 trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50(19):1844–51.
Dobesh PP, Oestreich JH. Ticagrelor: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, clinical efficacy, and safety. Pharmacotherapy. 2014;34(10):1077–90.
Nicol M, et al. Side effects of ticagrelor: sinus node dysfunction with ventricular pause. Int J Cardiol. 2015;191:56–7.
Scirica BM, et al. The incidence of bradyarrhythmias and clinical bradyarrhythmic events in patients with acute coronary syndromes treated with ticagrelor or clopidogrel in the PLATO (platelet inhibition and patient outcomes) trial: results of the continuous electrocardiographic assessment substudy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(19):1908–16.
Baker NC, Nadour W, Friehling M. Clinically significant ticagrelor induced conduction abnormalities following percutaneous coronary intervention. Int J Cardiol. 2016;214:21–2.
Zhang N, et al. Another side effect of ticagrelor: atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. 2016;212:242–4.
Goldberg A, et al. Life-threatening complete atrioventricular block associated with ticagrelor therapy. Int J Cardiol. 2015;182:379–80.
Bonaca MP, et al. Long-term use of ticagrelor in patients with prior Myocardial Infarction. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(19):1791–800.
Butler K, Teng R. Evaluation and characterization of the effects of ticagrelor on serum and urinary uric acid in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012;91(2):264–71.
Enomoto A, et al. Molecular identification of a renal urate anion exchanger that regulates blood urate levels. Nature. 2002;417(6887):447–52.
Ichida K, et al. Urate transport via human PAH transporter hOAT1 and its gene structure. Kidney Int. 2003;63(1):143–55.
Cattaneo M, Faioni EM. Why does Ticagrelor induce dyspnea? Thromb Haemost. 2012;108(6):1031–6.
Zhang N, et al. Ticagrelor-related gout: an underestimated side effect. Int J Cardiol. 2015;192:11–3.
Htun P, et al. Low responsiveness to clopidogrel increases risk among CKD patients undergoing coronary intervention. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22(4):627–33.
Morel O, et al. Cardiovascular mortality in chronic Kidney Disease patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention is mainly related to impaired P2Y12 inhibition by clopidogrel. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(4):399–408.
Washam JB, et al. Pharmacotherapy in chronic Kidney Disease patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;131(12):1123–49.
van Vuren AJ, de Jong B, Bootsma HP, Van der Veen MJ, Feith GW. Ticagrelor-induced renal failure leading to statin-induced rhabdomyolysis. Neth J Med. 2015;73(3):136–8.
DiNicolantonio JJ, Serebruany VL. Angiotensin receptor blockers worsen renal function and dyspnea on ticagrelor: a potential ticagrelor-angiotensin receptor blocker interaction? Clin Cardiol. 2012;35(11):647–8.
Jacob S, et al. Ticlopidine-, clopidogrel-, and prasugrel-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a 20-year review from the Southern Network on adverse reactions (SONAR). Semin Thromb Hemost. 2012;38(8):845–53.
Bennett CL, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura associated with clopidogrel. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(24):1773–7.
Doğan A, et al. Ticagrelor-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Anatol J Cardiol. 2017;17(1):73–4.
Wang X, et al. Ticagrelor-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a case report and review of the literature. Med (Baltim). 2018;97(26):e11206.
Welsh RC, et al. Outcomes among Clopidogrel, Prasugrel, and Ticagrelor in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction patients who underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention from the TOTAL trial. Can J Cardiol. 2019;35(10):1377–85.
Download references
This work was supported by Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent, China (Number: QNRC2016382) and Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, China (Number: 2020JJA140216).
Author information
Peng Wei and Xiaoqing Wang contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Cardiology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People’s Hospital, Shanghai, 200233, China
Peng Wei & Xiaoqing Wang
Department of Cardiology, Xuzhou Central Hospital, Xuzhou, 221009, Jiangsu, China
Department of Gerontology, The Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, No. 18# Zhongshan 2 Road, Baise, 533000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
Bangming Cao
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
PW and XW designed the research and wrote the manuscript. QF revised the manuscript. BMC participated in designing the research and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Qiang Fu or Bangming Cao .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Wei, P., Wang, X., Fu, Q. et al. Progress in the clinical effects and adverse reactions of ticagrelor. Thrombosis J 22 , 8 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12959-023-00559-3
Download citation
Received : 17 May 2022
Accepted : 02 November 2023
Published : 10 January 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12959-023-00559-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Acute coronary syndrome
- Clinical effect
- Adverse reaction
Thrombosis Journal
ISSN: 1477-9560
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]

- Entertainment
- Investigations
- Latest Headlines
- What Are They Hiding?
- 2024 Election
- Clark County
- Nation and World
- Science and Technology
- Road Warrior
- Las Vegas Weather
- East Valley
- North Las Vegas
- Summerlin/Centennial Hills
- Remembering Oct. 1, 2017
- Deborah Wall
- Natalie Burt
- Remembering Jeff German
- Police Accountability
- Alpine Fire
- 100 Years of Growth
- Dangerous Driving
- Raiders News
- Golden Knights
- UNLV Football
- UNLV Basketball
- Nevada Preps
- Sports Betting 101
- Las Vegas Sportsbooks
- National Finals Rodeo
- Where Are They Now?
- On TV/Radio
- MMA and UFC
- Casinos & Gaming
- Conventions
- Inside Gaming
- Entrepreneurs
- Real Estate News
- Business Press
- Sheldon Adelson (1933-2021)
- Debra J. Saunders
- Michael Ramirez cartoons
- Victor Joecks
- Richard A. Epstein
- Victor Davis Hanson
- Drawing Board
- Homicide Tracker
- Faces of Death Row
- Kats’ Cool Hangs
- Arts & Culture
- Home and Garden
- Las Vegas Hiking Guide
- RJ Magazine
- Today’s Obituaries
- Submit an obit
- Dealer News
- Classifieds
- Place a Classified Ad
- Provided Content
- Real Estate Millions
- Internships
- Service Directory
- Transportation
- Merchandise
- Legal Information
- Real Estate Classifieds
- Garage Sales
- Contests and Promotions
- Best of Las Vegas
- Nevada State Bank
- Verizon Business
- P3 Health Partners
- Adult Health
- Star Nursery
- Partner Articles
- Ignite Funding
- Supplements
- Travel Nevada
- Subscriptions
- Newsletters
- Advertise with Us
- >> Crime
Can’t have Vegas become ‘crime-ridden’ like other cities, Metro sheriff says
As Las Vegas continues to grow, Sheriff Kevin McMahill wants to make sure the valley doesn’t become a hotbed for crime like some other American metropolitan areas.

As Las Vegas continues to grow, Sheriff Kevin McMahill wants to make sure the Las Vegas Valley doesn’t become a hotbed for crime like what has occurred in some other American metropolitan areas.
“Regardless of where I go, I get a lot of questions about keeping Las Vegas safe and making sure that we don’t become crime-ridden like some of these other cities that we see in America,” McMahill said during a Wednesday interview with Las Vegas Review-Journal reporters.
As the elected top cop who oversees the Metropolitan Police Department and its more than 6,000 employees, McMahill shared his thoughts on a number of issues including traffic fatalities, violent and nonviolent crime, his priorities, failures — he has repeatedly referred to last year’s spike in vehicle thefts as a failure — and areas of concern.
He also compares Las Vegas with similarly sized cities around the country and wants to ensure the city doesn’t become like some of the metropolitan areas that have had well-documented struggles with crime in recent years.
“I don’t want to be Denver, I can tell you that,” said McMahill, who is from Denver and was there recently. “I don’t want to be San Francisco, I can tell you that, and the list goes on and on and on.”
A married father of five who rose up through Metro’s ranks over almost three decades, eventually becoming undersheriff before retiring in 2020, then being elected sheriff in 2022, McMahill said it’s his responsibility as an elected official “to make sure that the city doesn’t decay into something that is not recognizable anymore.”
Part of making sure that doesn’t happen, he said, is his focus on three top priorities.
“Violent crime and traffic fatalities are at the very top of my list,” McMahill said. “Also, the third tier of that is the wellness of my police officers. Those are the top three things that I’m focused in on as the sheriff this particular year.
“And the better that I do at all of those, the better our community is going to be,” he said.
Positive strides
McMahill spoke of the homicide rate in Metro’s jurisdiction. As of Wednesday morning, he said, 40 homicides had occurred so far this year in Metro’s jurisdiction, which at that point was about a 22 percent decrease in killings over the same time in 2023, he said.
Another homicide, the fatal shooting of a teen boy, happened Saturday.
McMahill lauded the rate at which homicides are solved by Metro. As of the week that ended May 3, according to the most recently posted statistics on Metro’s website, the department had a 92 percent homicide clearance rate.
“We’re solving almost every homicide that occurs in our jurisdiction,” McMahill said.
McMahill highlighted the reduction in robberies.
That crime was down 19.4 percent in 2023 over the previous year, he said in his 2024 State of the Department speech earlier this year.
And in the roughly first four months of this year, it was down just over 12 percent, according to Metro stats.
‘Not giving up on it’
But one of the thorns in McMahill’s side has been vehicle thefts, which has been spiking across the country thanks in part to a social media trend that helped fuel the thefts nationwide of Kia and Hyundai vehicles.
“The other big one I’d just like to highlight for you, is what I talked about as our failure last year, was our auto theft,” McMahill said, noting that stolen vehicles were up 36.5 percent in 2023.
He said that a singular approach of only arresting and jailing such thieves doesn’t work, and that other measures — educating drivers, helping them to make their cars harder to steal — must be part of the solution.
He spoke of a recent event hosted by Metro and Hyundai in the parking lot of Metro’s headquarters in which more than 1,800 vehicles got anti-theft updates and 7,000 steering wheel locks given out.
According to Metro’s latest statistics, vehicle thefts were down by just over 18 percent between Jan. 1 and the beginning of May compared with the same time in 2023.
“I’m not giving up on it, even though it seems to be that one thing that keeps smacking me around the head a little bit, as far as a number that I can’t seem to make disappear,” McMahill said of vehicle thefts, adding that “we will continue to focus in on reducing that.”
Contact Brett Clarkson at [email protected]


A dispute between two neighbors outside their homes turned deadly when one neighbor allegedly shot the other man, who later died on his driveway, police said.

Jovan Wright Bullock, 16, was shot and killed outside his home in the central valley, police said.

Las Vegas police were investigating a killing in a central valley neighborhood.

A man was fatally shot in an apartment and his body was disposed at a nearby vacant lot of by a man who helped the accused killer, according to police.

Hundreds of unsealed court documents reveal the contentious custody battle between Ashley Prince and Dennis Houston leading up to a fatal shooting in April.

A 33-year-old man suspected in a series of Arts District burglaries was taken into custody, according to a news release.

A Las Vegas woman was arrested Thursday for her alleged participation in the U.S. Capitol riot after the 2020 presidential election.

Officers were diverted from another call and sped down West Charleston Boulevard to the April 8 shooting scene at the Prince Law Group in City National Bank building.

A Clark County grand jury indicted three men accused of trafficking nearly 45 pounds of fentanyl, the illicit opioid said to be many more times more powerful than morphine.

The Clark County coroner’s office identified a teenager found shot to death inside a car parked in a central valley neighborhood.

Soft Matter
Review on novel targeted enzyme drug delivery systems: enzymosomes.

* Corresponding authors
a School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Om Sterling Global University, Hisar, Haryana, India E-mail: [email protected]
b Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Starex University, Gurugram, India
The goal of this review is to present enzymosomes as an innovative means for site-specific drug delivery. Enzymosomes make use of an enzyme's special characteristics, such as its capacity to accelerate the reaction rate and bind to a particular substrate at a regulated rate. Enzymosomes are created when an enzyme forms a covalent linkage with a liposome or lipid vesicle surface. To construct enzymosomes with specialized activities, enzymes are linked using acylation, direct conjugation, physical adsorption, and encapsulation techniques. By reducing the negative side effects of earlier treatment techniques and exhibiting efficient medication release, these cutting-edge drug delivery systems improve long-term sickness treatments. They could be a good substitute for antiplatelet medication, gout treatment, and other traditional medicines. Recently developed supramolecular vesicular delivery systems called enzymosomes have the potential to improve drug targeting, physicochemical characteristics, and ultimately bioavailability in the pharmaceutical industry. Enzymosomes have advantages over narrow–therapeutic index pharmaceuticals as focusing on their site of action enhances both their pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiles. Additionally, it reduces changes in normal enzymatic activity, which enhances the half-life of an enzyme and accomplishes enzyme activity on specific locations.

- This article is part of the themed collection: Soft Matter Recent Review Articles, 2024
Article information
Download citation, permissions.
D. Kumar, K. Sachdeva, R. Tanwar and S. Devi, Soft Matter , 2024, Advance Article , DOI: 10.1039/D4SM00301B
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Drake and Kendrick Lamar’s feud — the biggest beef in recent rap history — explained
Police are investigating a shooting outside rapper Drake’s mansion in Toronto that left a security guard seriously wounded. Authorities did not confirm whether Drake was at home at the time of the shooting, but said his team is cooperating. The shooting happened around 2 a.m. Tuesday in the affluent Bridle Path neighborhood of Toronto. (May 7)
Rapper Kendrick Lamar appears at the MTV Video Music Awards, on Aug. 27, 2017, in Inglewood, Calif., left, and Canadian rapper Drake appears at the premiere of the series “Euphoria,” in Los Angeles on June 4, 2019. (AP Photo)
- Copy Link copied
In one of the biggest beefs in recent hip-hop history, Drake and Kendrick Lamar are feuding — to the point that police were asked about their feud after a security guard was shot outside Drake’s Toronto mansion on Tuesday. But it wasn’t always this way.
Over a decade ago, the pair collaborated on a few songs: On Drake’s 2011 track “Buried Alive Interlude,” on Lamar’s 2012 release “Poetic Justice,” and on A$AP Rocky’s “(Expletive) ’ Problems” that same year.
That didn’t last very long. In 2013, Pulitzer Prize winner Lamar was featured on Big Sean’s “Control,” in which he called out a slew of contemporary rappers including Drake, J. Cole, Meek Mill, Pusha T, A$AP Rocky, Big K.R.I.T., Wale, Pusha T and even Big Sean among them.
“I got love for you all, but I’m trying to murder you,” he rapped. “Trying to make sure your core fans never heard of you.”
Drake responded in a Billboard cover story, saying “I know good and well that Kendrick’s not murdering me, at all, in any platform.” Shortly afterward, at the 2013 BET Hip-Hop Awards , Lamar took another jab at Drake.
Over the next few years, the rappers launched disses at each other with less frequency. Drake had other beefs with other performers, like Meek Mill in 2015, and most infamously Pusha T in 2018, where the latter rapper dropped “The Story of Adidon,” revealing Drake is a father .
In October 2023, J. Cole perhaps accidentally reignited the beef on “First Person Shooter” with Drake. He rapped “Love when they argue the hardest MC / Is it K-Dot? Is it Aubrey? Or me?” referencing Lamar and Drake’s birth name, Aubrey Graham. “We the big three like we started a league / but right now, I feel like Muhammad Ali.”
Which brings us to the current moment. Here’s a timeline of the developments in recent weeks — it should be noted that diss tracks between rappers often include exaggerated truths and unsubstantiated rumors for dramatic effect, and that police have not said the feud led to Tuesday’s shooting.
March 22: Lamar disses Drake on Future and Metro Boomin’s “Like That”
“The big three,” Lamar raps, referencing J. Cole’s boast. “It’s just big me.”
He references Drake’s 2023 album “For All the Dogs,” and also compares himself to Prince and Drake to Michael Jackson: “Prince outlived Mike Jack.”
J. Cole soon releases a response, “7 Minute Drill,” but quickly apologizes for it onstage at his Dreamville Festival in Raleigh, N.C.
April 13: Drake’s “Push Ups” leaks
Drake’s response is leaked and later premiered by DJ Akademiks. “You ain’t in no Big Three, SZA got you wiped down, Travis got you wiped down, Savage got you wiped down,” he raps about Lamar.
It also assumed Drake takes aim at Future, Metro Boomin, Rick Ross and The Weeknd — Ross releases a response track shortly afterward.
April 24: Drake responds with a second, AI-assisted diss track, “Taylor Made Freestyle”
Drake’s second diss track used artificial intelligence technology to include verses from Tupac and Snoop Dogg, two of Lamar’s influences. In his own verse, Drake accuses Lamar of delaying his response track because of the imminent release of Taylor Swift ‘s “The Tortured Poets Department.” (Lamar collaborated with Swift on “Bad Blood.”)
Tupac’s estate threatened to sue Drake in response, so he removed the song from his social channels.
Snoop Dogg responded to the news in a video on Instagram . “They did what? When? How? Are you sure?” he said. “I’m going back to bed. Good night.”
April 30: Lamar hits back with a nearly six-and-a-half-minute track, “Euphoria”
This is where it gets more complicated. Lamar’s “Euphoria” hits like an opus, unleashing a slew of allegations against Drake. He comes after Drake’s skills as a rapper, use of AI, appearance, racial identity, and parenting .
“I got a son to raise, but I can see you know nothin’ ’bout that,” Lamar raps.
The title is a reference to the HBO series “Euphoria,” of which Drake is an executive producer.
Lamar teases that he’ll go “back-to-back” with his tracks.
May 3: Lamar drops a follow-up, “6:16 in LA”
In Lamar’s next diss, titled after a time and location like Drake is wont to do, Lamar targets the company Drizzy keeps. “Have you ever thought that OVO was working for me? / Fake bully, I hate bullies,” he raps, referencing Drake’s record label. “You must be a terrible person / Everyone inside your team is whispering that you deserve it.”
According to Billboard, the song was produced by Sounwave and Jack Antonoff — the latter notably Swift’s longtime producer. It also samples Al Green’s “What a Wonderful Thing Love Is,” on which one of Drake’s relatives played guitar.
May 3: Drake launches “Family Matters”
Drake hits back with a music video and a nearly eight-minute response, in which he alleges abuse and infidelity in Lamar’s relationship with his fiancee.
May 4: Lamar responds with “Meet the Grahams”
Almost immediately afterward, Lamar releases “Meet the Grahams,” which begins with the rapper addressing Drake’s son: “I’m sorry that man is your father.” Lamar also addresses Drake’s parents, and “a baby girl,” alleging that Drake has a secret daughter.
He also labels Drake a “predator,” without elaborating.
May 4: Less than 24 hours later, Lamar drops “Not Like Us”
Hours later, Lamar doubles down, releasing “Not Like Us,” produced by DJ Mustard.
“Say, Drake, I hear you like ’em young / You better not ever go to cell block one,” Lamar raps.
May 5: Drake softens his blows on “The Heart Part 6”
Referencing Lamar’s “The Heart” series, Drake drops “The Heart Part 6” in response. In the song, which samples Aretha Franklin’s “Prove It,” Drake challenges Lamar’s allegations, doubles down on his own against him, and says that he does not have a secret daughter.
He sounds notably lethargic on the song — potentially taking a final bow with verses like, “You know, at least your fans are gettin’ some raps out of you / I’m happy I could motivate you.”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3. Identify the article. Start your review by referring to the title and author of the article, the title of the journal, and the year of publication in the first paragraph. For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.
Journal Article Review. Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Before getting started on the critique, it is important to review the article thoroughly and critically. To do this, we recommend take notes, annotating, and reading the article several times before critiquing. As you read, be sure to note important items like the thesis, purpose, research questions, hypotheses, methods, evidence, key findings ...
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification. 3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review's introduction, briefly ...
This guide contains key resources for writing a journal article review.. Click the links below or the guide tabs above to find the following information. find out what a journal article is; learn how to use a template to get you started; explore strategies on how to choose the article for review; learn how to read a journal article effectively and make notes ...
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
Read the Article Thoroughly. The first step in writing an article review is to read the article carefully and thoroughly. This may seem obvious, but it is crucial to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the work before attempting to critique it. During the initial reading, focus on grasping the main arguments, key points, and the overall ...
The most critical characteristics of an effective review are clarity, specificity, constructiveness, and thoroughness (Hyman, 1995 ). A journal article review should inform the managing editor and author of the primary strengths and weaknesses of a manuscript in a focused way (see Table 11.1 ).
A review article can also be called a literature review, or a review of literature. It is a survey of previously published research on a topic. It should give an overview of current thinking on the topic. And, unlike an original research article, it will not present new experimental results. Writing a review of literature is to provide a ...
Author Hub | A Guide to Peer Reviewing Journal Articles 9/12 4. Writing your review Once you have read the article and made notes on both your broad and detailed impressions, you have the raw material for writing your review. Many reviewers choose to summarise their thoughts in the first paragraphs of the review, and then, in the second half
3. A critique, or a discussion about the key points of the journal article. A critique is a discussion about the key points of the journal article. It should be a balanced discussion about the strengths and weaknesses of the key points and structure of the article.. You will also need to discuss if the author(s) points are valid (supported by other literature) and robust (would you get the ...
Think about structuring your review like an inverted pyramid. Put the most important information at the top, followed by details and examples in the center, and any additional points at the very bottom. Here's how your outline might look: 1. Summary of the research and your overall impression. In your own words, summarize what the manuscript ...
Therefore, make sure to check the appropriateness of a journal before submitting your article. Writing review articles, especially systematic reviews or meta-analyses, can seem like a daunting task. However, Elsevier Author Services can guide you by providing useful tips on how to write an impressive review article that stands out and gets ...
Both a reaction paper and an article review will start with a content summary. ️. For scholarly material, you will present a structured review after the summary. ️. For popular magazine content, you will write a response that sums up your emotions, thoughts, and reactions that the material aroused.
Summarize the Article: Summarize the main points when you review the article, and make sure that you include all supporting elements of the author's thesis. Start with Personal Critique: Now is the time to include a personal opinion on the research article or the journal article review. Start with evaluating all the strengths and weaknesses ...
If you don't spot any major flaws, take a break from the manuscript, giving you time to think. Consider the article from your own perspective. When you sit down to write the review, again make sure you familiarize yourself with any journal-specific guidelines (these will be noted in the journal's guide for authors). 3.
Step 2: Read the Article Thoroughly. Begin by thoroughly reading the article. Take notes on key points, arguments, and evidence presented by the author. Understand the author's main thesis and the context in which the article was written.
The fundamental rationale of writing a review article is to make a readable synthesis of the best literature sources on an important research inquiry or a topic. This simple definition of a review article contains the following key elements: ... McAlister et al. analyzed review articles in 6 medical journals, and disclosed that in less than one ...
Briefly summarize what the paper is about and what the findings are. Try to put the findings of the paper into the context of the existing literature and current knowledge. Indicate the significance of the work and if it is novel or mainly confirmatory. Indicate the work's strengths, its quality and completeness.
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
how to review a journal article l step by step guideWhether you're publishing a journal article review or completing one for a class, your critique should be...
6 minutes ago. The Voice semifinals took place Monday night with performances by the Top 9 artists - Asher HaVon, Bryan Olesen, Josh Sanders, Karen Waldrup, Maddi Jane, Madison Curbelo, Nathan ...
Scoping reviews and evidence maps are forms of evidence synthesis that aim to map the available literature on a topic and are well-suited to visual presentation of results. A range of data visualisation methods and interactive data visualisation tools exist that may make scoping reviews more useful to knowledge users. The aim of this study was to explore the use of data visualisation in a ...
ABOUT CSWR. The Columbia Social Work Review was founded in 2003 and is an annual peer-reviewed journal for up-and-coming scholars in the field of social work to share their research with faculty, fellow students, and the wider scholarly community.The mission of the Columbia Social Work Review is to publish original academic writing on social work practice, education, research, policy and ...
Background Ticagrelor is a novel receptor antagonist that selectively binds to the P2Y12 receptor, thereby inhibiting adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-mediated platelet aggregation. Compared to clopidogrel, ticagrelor has the advantages of a fast onset, potent effects, and a reversible platelet inhibition function, which make this drug clinically suitable for treating acute coronary syndrome (ACS ...
Updated May 13, 2024 - 9:08 am. As Las Vegas continues to grow, Sheriff Kevin McMahill wants to make sure the Las Vegas Valley doesn't become a hotbed for crime like what has occurred in some ...
The goal of this review is to present enzymosomes as an innovative means for site-specific drug delivery. Enzymosomes make use of an enzyme's special characteristics, such as its capacity to accelerate the reaction rate and bind to a particular substrate at a regulated rate. Enzymosomes are created when an enzyme f Soft Matter Recent Review Articles, 2024
In one of the biggest beefs in recent hip-hop history, Drake and Kendrick Lamar are feuding — to the point that police were asked about their feud after a security guard was shot outside Drake's Toronto mansion on Tuesday. But it wasn't always this way. Over a decade ago, the pair collaborated on a few songs: On Drake's 2011 track "Buried Alive Interlude," on Lamar's 2012 release ...