- Insert a picture in PowerPoint Article
- Edit pictures Article
- Add SmartArt to a slide Article
- Put a background picture on your slides Article
- Add a background picture to slides Article
- Use charts and graphs in your presentation Article
- Insert icons in PowerPoint Article


Use charts and graphs in your presentation
You can make a chart in PowerPoint or Excel. If you have lots of data to chart, create your chart in Excel , and then copy it into your presentation . This is also the best way if your data changes regularly and you want your chart to always reflect the latest numbers. In that case, when you copy and paste the chart, keep it linked to the original Excel file .
To create a simple chart from scratch in PowerPoint, click Insert > Chart and pick the chart you want.

Click Insert > Chart .
Click the chart type and then double-click the chart you want.
Tip: For help deciding which chart is best for your data, see Available chart types .
In the worksheet that appears, replace the placeholder data with your own information.

When you’ve finished, close the worksheet.
Create an org chart in PowerPoint
Create charts in Excel

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
Excel Visualization: A Guide to Clear Data Presentation for Beginners
I once struggled with dull data tables.
Numbers clustered in rows and columns become a blur. But with Excel visualization , you can empower your audience to make informed decisions based on the data presented. Excel charts and graphs replace chaos, revealing patterns and trends.
Convey ideas efficiently with the right visual. It’s not just about creating a chart; it’s about making data understandable and engaging.
In this article, I’ll guide you step-by-step on transforming your Excel data into insightful visuals.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of Excel Visualization
Excel provides various visualization options, whether 2D or 3D versions, standard, stacked, or 100% stacked options. It’s all about finding the right fit that best represents your data and message.
The Excel Charting Interface
Let’s start with creating a chart in Excel.
When you click on the Insert tab in Excel, you’ll see various chart types that you can use to visualize your data.

The Excel charting interface provides a wide range of options, from line and area charts to bar and column charts. When you click on a chart, the ‘ Chart Tools ’ contextual tab provides additional features for customizing your charts.
Types of Data for Visualization
Excel visualization data can be broadly categorized into numerical, categorical, and time-series data.
- Numerical data includes values that can be measured, such as sales figures or temperature readings.
- Categorical data includes information such as names, labels, or groups.
- Time-series data involves values measured over time, such as stock prices or website traffic.
Excel offers different chart types depending on your data type.
Selecting the Right Chart Type
Selecting the right chart type is half the battle for effective data visualization in Excel.
Pie charts are best for part-to-whole comparisons. Use line charts for time series or trends. Bar or column charts are the most suitable for categorical comparisons.
However, consider more advanced chart types for more complex data sets.
Scatter plots are excellent for correlation analysis , while histograms and box plots are ideal for distribution analysis of quantitative data.
It’s all about understanding your data and determining the best way to display it.
Steps for Visualizing Data in Excel – Creating Basic Charts
Creating basic charts in Excel is a fundamental skill for anyone looking to present data in a visual format.
Excel offers a variety of chart types, each with unique properties and use cases. The key to successful chart creation in Excel is understanding these different chart types and knowing how to present your data most effectively with them.
Organizing Your Data
Before you dive into creating Excel charts, it is crucial to organize your data correctly .
Well-organized data will make the charting process easier and the resulting charts more meaningful. Ensure your data is clean, error-free, and arranged clearly and logically.
This will make it easier to select the data for your charts and create visuals that effectively communicate your data analysis results.
Pie and Donut Chart
Pie charts are popular for showing the proportion of different categories within a whole. While visually appealing, they are often misused and can lead to misleading interpretations.
Generally, they are most effective when comparing a few categories representing parts of a whole.
On the other hand, donut charts are a variation of pie charts with a hole in the middle (as the name implies!). Like pie charts, they can display multiple data series, but they should be used sparingly.
To create a pie chart in Excel:
- Select the data you want to visualize
- From the “ Insert ” tab, choose “ Pie ” from the chart options.
- You can customize your chart by changing the colors, adding labels, and adjusting other settings in the “ Format Chart Area ” pane.
Here’s a video guide on how to create a donut chart:
Line and Area Chart
Line and area charts are handy when dealing with time-series data . These charts plot data points on a graph and connect them with a line, allowing you to see trends over time.
Check out this video for a step-by-step guide on how to create a line chart:
One of the business essentials when working with line and area charts is customizing the axis and gridlines. This can help make your chart more readable and meaningful .
The “ Format Axis ” pane allows you to customize the axis labels, adjust the scale, and add gridlines.
Column and Bar Graph
Bar and column charts are Excel’s most commonly used chart types. They are excellent for comparing different categories of data.
While bar charts and column charts are often used interchangeably, there is a difference: A bar chart presents data horizontally , while a column chart presents data vertically . This distinction can influence how easily your audience interprets the chart.
You can also choose between a stacked or clustered bar and column chart layout.
In a stacked chart , data series are stacked on each other, while in a clustered chart , they are placed side by side.
To create a bar or column chart:
- Select the data
- Then choose either “Bar” or “Column” from the chart options in the “ Insert ” tab
- Remember to format the chart and the axis labels to make the chart easier to understand
Advanced Charting Techniques
In this section, I’ll describe how to present complex data in a visually appealing and easily understandable format. Since each dataset is unique, treat these charts as ideas for meaningfully presenting your data.
Combination Charts
This type of chart combines the features of line and column charts, allowing you to present mixed data more comprehensively.
For example, when you have a target and actual data for comparison , a combination chart can be the perfect tool for visualization.
Clicking the Chart Design tab on the ribbon allows you to change the chart type and create a customized combination chart.

This allows you to have your target values in columns and the actual values marked along the line, which provides a clearer visualization of your data.
Trendlines and Data Analysis
Another essential feature of Excel charts is the ability to add trendlines. These can be linear, polynomial, or moving average trendlines.
A trendline graphically displays trends in your data , and you can extend it beyond the actual data to predict future values.
Along with trendlines, interpreting R-squared values is also crucial in data analysis. This will help you understand the relationship between your dependent and independent variables, thus enhancing your analysis results.
Check out our detailed how-to post on adding trendlines to Excel charts .
Conditional Formatting in Charts
Conditional formatting is another advanced charting technique in Excel that can enhance your data visualization. You can also add data bars, color scales, and icon sets.
These features allow you to customize your charts based on certain conditions, making it easier for your audience to understand your data. Applying these formatting options enables you to create more engaging and visually appealing charts for your data presentation.
Creating a Tornado Chart in Excel
Tornado charts are particularly effective when comparing and contrasting different variables . A well-crafted tornado chart can help you visualize how changes in several factors can impact a specific outcome – for example, the impact of inflation on NPV and IRR results.
Here’s a video showing you how to create a tornado chart:
Designing a Funnel Chart in Excel
Funnel Charts in Excel are highly effective tools for monitoring sales processes or any other process that narrows down over time.
Here are two quick methods for designing funnel charts in Excel:
Building a Waffle Chart in Excel
Waffle charts, also known as square pie or waffle bar charts, are a great way to visualize individual data points compared to the whole data set. They are a fun and engaging way to present percentages or proportions.
Here is a simple method for creating waffle charts:
Data Visualization Tips – Enhancing Chart Aesthetics
The aesthetics of your Excel chart play a significant role in how effectively your data is communicated.
A visually appealing chart is easier to understand and engages your audience. Enhancing chart aesthetics involves working with various chart elements and features, such as colors, styles, and data labels.
Adding data labels, for instance, provides additional information on your chart, making it easier to interpret.
Besides, you can customize the chart’s colors and styles to match your presentation theme or company branding.
Check out this post for more information on good dashboard design principles .
Working with Chart Elements
Working with chart elements can significantly improve the readability and effectiveness of your data visualization.
Some key chart elements you can manipulate include titles, legends, and data labels.
- Data labels provide additional context to your data and can be customized to suit your chart
- Modify axis labels and gridlines to adjust their appearance and improve readability. Check out this video on how to add gridlines to your Excel charts:
These chart elements can enhance your aesthetic appeal and make your data easier to interpret.
Customizing Chart Colors and Styles
Spicing up your Excel charts is easier than you think.
The ‘ Chart Design ‘ tab in the Excel ribbon allows you to alter your charts’ aesthetics significantly.
Navigate to the ‘ Chart Styles ‘ section, and you’ll see various styles for your chart.
Looking for a bit more customization? No problem! Simply click the ‘ Change Colors ‘ dropdown and choose a color scheme.

You can use Excel’s preset color schemes or create a custom color palette for brand consistency. Minor visual changes can significantly affect your chart’s overall look and feel.
3D Charts and Effects
Adding a third dimension to your charts can make them pop . But be careful.
While 3D effects can add a specific wow factor, they can also lead to misinterpretations of your data if they are not used properly.
To add 3D effects to your charts, click the ‘ Chart Styles ‘ and choose a style with 3D effects.
Remember, though, that 3D effects should be used sparingly and only when they can enhance the understanding of the data. Overuse of these effects can lead to cluttered, confusing charts. When it comes to 3D effects, less is often more .
Advanced Excel Graphics
Beyond the basic charts, Excel offers advanced graphics capabilities to take your data presentation to the next level.
This includes using Sparklines, shapes, and icons, among other features.
Sparklines are mini-charts within individual cells, each representing a row of data. They give a quick snapshot of trends, helping you understand your data at a glance.
Excel offers line, column, and win/loss types of Sparklines that you can add with the Quick Analysis tool.
Using Shapes and Icons

Remember to appropriately format these shapes and icons to convey the right message and not distract from the data.
Portraying a Story Through Data
Excel visualization is not just about creating charts or diagrams; it’s about telling a story with your data. This is where the concept of data storytelling comes in.
It’s about using visualization tools to highlight key points and trends in your data, making it easier for your audience to understand and absorb.
It’s not unlike creating a plot in a novel where rows and columns of data are the characters, and the chart is the narrative arc. Every element should convey your story effectively and compellingly, from simple bar charts to intricate trend analysis.
Exporting and Sharing Your Visualizations
Once you’ve created your data visualization in Excel, it’s important to know how to share it! This involves exporting the visual representation of data in a format that others can easily access.
Whether you’re sharing a simple bar graph or a complex infographic, the export method will depend on the intended use of the chart/graphic.
This process can be as simple as saving your chart as an image or embedding Excel visuals in PowerPoint presentations and documents.
Saving Charts as Images
One of the simplest ways to share visualizations is by saving them as images .
To do this, right-click the chart and select ‘Save as Picture.’ Several image formats are available, each with its uses.
For instance, JPEG is great for photographic images, while PNG is ideal for images with transparent backgrounds. However, it’s important to consider the resolution of your image. High resolution is crucial for clear, crisp images, especially if they’re intended for print.
Embedding Excel Visuals in Presentations and Documents
Embedding them in presentations and documents is another way to share your Excel visualizations.
This can be done in two ways: linking and embedding .
- Linking refers to connecting the original Excel file and the document where it’s inserted. Any changes made to the original file will automatically update in the document (assuming the link isn’t broken ).
- Embedding involves inserting a copy of the chart into the document. While this won’t update automatically, it ensures that the chart will always be available, regardless of the status of the original file.
Both methods have advantages and should be chosen based on your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common mistakes for beginners to avoid in data visualization with excel.
Common mistakes include overcrowding the chart with too much data, using inappropriate chart types, neglecting to label axes or data points clearly, and choosing colors or styles that reduce readability.
What are the best practices for presenting Excel data visually to a non-technical audience?
Focus on simplicity and clarity .
Use straightforward chart types, avoid technical jargon, and highlight key takeaways. Ensure your charts are well-labeled, and use annotations or callouts to draw attention to important data points.
What are some resources to learn more about Excel visualization?
For more tips and tricks, visit my YouTube channel . Alternatively, look at Chandoo’s training, where I learned many excellent dashboard design ideas.
Can Excel visualization help in career development?
Absolutely! Proficiency in Excel visualization is a valuable skill in many industries.
It’s especially relevant in fields like data science, finance, marketing, and others involving large amounts of data. Effectively communicating data through graphical representation can give you a significant advantage in your professional journey.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Try Process AI free
How to add a chart from microsoft excel to a powerpoint presentation.
In the world of presentations, visual aids are important. One such tool is a chart from Microsoft Excel in a PowerPoint presentation. This helps to show complex data in an appealing way, so your audience can understand the key messages quickly.
You can enhance your message by adding charts to PowerPoint . It’s easy! Open both Microsoft Excel and PowerPoint . Select the chart from Excel that you want to use. Then, press “Copy” under the “Home” tab or Ctrl+C.
Switch to your PowerPoint presentation . Put the chart where you want it. Then, press “Paste” under the “Home” tab or Ctrl+V. You’ll see the chart appear in the slide.
Any changes made in Excel will automatically update in PowerPoint too. Right-click the chart in PowerPoint to access formatting options. Choose colors, labels, titles, legends, fonts, and more. This enables you to customize the chart to match your design theme.
Following these steps, you can integrate charts from Microsoft Excel into your PowerPoint presentation without hassle. According to Microsoft, this process ensures data accuracy and dynamism.
Step 1: Exporting the chart from Microsoft Excel
Export your charts from Microsoft Excel to enhance your PowerPoint presentation! Here’s how:
- Open the Excel spreadsheet with the chart you want
- Select the entire chart (including labels and titles)
- Right-click and choose the “Copy” option
- Switch to your PowerPoint presentation
- Right-click where you want to insert the chart and select “Paste”
Remember, any changes made to the chart in Excel won’t be reflected automatically in PowerPoint, so make sure the chart is finalized before exporting.
Adding professionally designed visuals with data to your slides will make a lasting impression on your audience. So go ahead and try it out in your next presentation – they’ll thank you!
Step 2: Opening the PowerPoint presentation
- Achieving seamless integration of an Excel chart in a PowerPoint presentation requires just a few easy steps.
- First, make sure both the Excel file and PowerPoint presentation are saved in a place you can access on your computer.
- Then, open PowerPoint and select the File tab.
- Click Open to access your saved presentations.
- Having a well-organized file structure will also make locating and opening both files simpler.
- Follow these guidelines and you’ll be able to impress your audience with stunning data visualizations!
Step 3: Pasting the chart into the PowerPoint slide
- To paste a chart into PowerPoint, there are some steps to take. Start by opening your Excel file.
- Select the chart you want to add then press Ctrl + C or right-click and choose “Copy”.
- Switch to PowerPoint and go to the slide where you want to paste the chart. Press Ctrl + V or right-click and select “Paste”.
- To adjust size and position, click and drag the edges or corners.
- To customize the chart further, use PowerPoint’s formatting options like changing colors, fonts, or adding titles.
- Remember: pasting a chart from Excel preserves its link with the original data. This means any changes made in Excel will automatically update in your PowerPoint.
- For example, I once had to present sales data in a PowerPoint meeting. By following these steps, I was able to integrate an Excel chart into my slides. The audience was impressed with the clean and professional look which helped them understand the data better.
Step 4: Adjusting the chart in PowerPoint
It’s time to jazz up your PowerPoint chart! Follow these three steps for maximum visual impact.
- Formatting: Select the chart and head to the ‘Chart Tools’ tab. Adjust colors, fonts, and styles to match your presentation theme.
- Resizing and positioning: To resize, click the border and drag the corner handles. Use the ‘Format’ tab for precise measurements. Move the chart by clicking and dragging it.
- Data updates: Link an Excel spreadsheet to your chart by selecting it and clicking ‘Edit Data’. This keeps your data accurate and up-to-date.
Optimizing your chart will help you engage your audience. Amp up your presentation skills – start using these techniques now!
Incorporating Excel charts into PowerPoint presentations is a great way to improve data visualization. To do this, use the “Copy” and “Paste Special” functions. This maintains the formatting and data.
Link your chart to the original Excel file for real-time updates. This ensures your presentation is always up-to-date.
For a streamlined presentation, only select relevant data or portions of the chart.
These steps and tips will help you deliver effective presentations with ease.

No credit card required
Your projects are processes, Take control of them today.
- Editor's Choice: Tech Gifts for Mom
- Amazon Prime Tech Deals!
How to Add an Excel Chart to a PowerPoint Presentation
Copy and paste, or use the Link Data command
- Brock University
Charts add a little extra punch to your PowerPoint presentation instead of listing bullet points of data. Conveniently, charts created in Excel can be copied and pasted into your PowerPoint presentations. As an added bonus, update charts in your PowerPoint presentation when changes are made to the original Excel data.
Instructions in this article apply to PowerPoint for Microsoft 365, PowerPoint 2019, PowerPoint 2016, PowerPoint 2013, PowerPoint 2010, and Excel.
Copy Your Chart From Excel
Any chart that you create in Excel can be copied and pasted into any Microsoft Office app.
Open the Excel file that contains the chart you want to copy and select the chart.
Select Home > Copy .
There are other ways to copy the chart. Right-click on the chart and select Copy . Or, use the Ctrl + C shortcut.
Close Excel.
Choose How to Paste Your Chart
The chart you copied in Excel is stored on the Clipboard. Now it's time to paste it into a PowerPoint slide.
Open PowerPoint and navigate to the slide where you wish to paste the Excel chart.
Select Home and select the Paste down arrow. Or, right-click the slide. The different options for pasting a chart display.
Choose Use Destination Theme & Embed Workbook to paste your chart into PowerPoint with the ability to edit it in PowerPoint and match your presentation's color scheme.
Choose Keep Source Formatting & Embed Workbook to be able to edit it in PowerPoint and keep the original color scheme from Excel.
Choose Use Destination Theme & Link Data to be able to edit it by making changes to your original data in Excel. The chart will match your PowerPoint presentation's color scheme.
Choose Keep Source Formatting & Link Data to edit it by making changes to your original data in Excel. The chart will keep the original color scheme from Excel.
Choose Picture to paste a picture of your chart into PowerPoint. The picture cannot be edited and is not tied to any data.
Update Excel Charts in PowerPoint
If you chose to Link Data when pasting your Excel chart into PowerPoint, changes made to the original spreadsheet file will update the chart in PowerPoint.
To manually update chart data:
Select the chart in PowerPoint.
Select Chart Tools Design .
Select Refresh Data .
Microsoft Office Update Prompt
Each time you open a PowerPoint presentation that is linked to another Microsoft Office app, such as Excel or Word, you're prompted to update the links in the presentation file. If you trust the source of the presentation, choose Update Links . All links to other documents are updated with any new changes.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- Paste Links for Data, Charts, and Formulas in Excel, Word, PowerPoint
- How to Create a Timeline in PowerPoint
- How to Copy a PowerPoint Design Template to Another Presentation
- How to Insert PDF Files Into PowerPoint Presentations
- The 12 Best Tips for Using Excel for Android in 2024
- How to Link or Insert Excel Files to Word Documents
- How to Merge PowerPoints
- Copy Slides to Another PowerPoint Presentation
- How to Update PowerPoint on Windows and Mac
- How to Create a Column Chart in Excel
- Add Hyperlinks to PowerPoint Presentations
- How to Create an 8 Column Chart in Excel
- How to Make and Format a Column Chart in Excel
- Animate Specific Parts of a PowerPoint Chart
- How to Make a Gantt Chart in PowerPoint
- Creating Charts and Graphs From Table Data
Excel Charts In Powerpoint
Key takeaway:.
- Excel Charts in PowerPoint can be a powerful tool for enhancing presentations: Using Excel Charts in PowerPoint can help to present data in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand manner, making presentations more effective and engaging.
- Inserting Excel Charts in PowerPoint is simple and straightforward: Excel Charts can be easily inserted into PowerPoint using either the copy and paste method or the Excel Object insertion method, both of which are simple to execute and offer flexibility in terms of editing and customization.
- A few best practices can help ensure the best results when using Excel Charts in PowerPoint: Consistency in chart design, choosing appropriate chart types for data, and ensuring data accuracy are all key factors that can help make Excel Charts in PowerPoint more effective and impactful.
Have you ever wanted to use data visuals to make a point in a presentation? Excel Charts in PowerPoint makes it easy for you to create a professional, dynamic presentation that captivates your audience. With a few simple steps, you can turn data into powerful visuals to help bolster your message.
Overview of Excel Charts in PowerPoint
Excel charts are a powerful tool for creating visual representations of data. They can help communicate complex information quickly and effectively. When used in PowerPoint presentations, Excel charts can enhance the overall impact of the presentation and convey the information more clearly.
Here are six key features of using Excel charts in PowerPoint:
- Excel charts are easily customizable in PowerPoint. Users have access to a range of chart styles and formatting options that can be tailored to the specific needs of the presentation.
- Excel charts can be updated easily. Users can update charts directly within PowerPoint and the changes will be reflected in real-time. This saves time and effort, as there is no need to create new charts each time data is updated.
- Excel charts can be animated in PowerPoint. Animation can help to engage the audience and draw attention to important data points.
- Excel charts can be excellently manipulated in PowerPoint. Users can arrange the charts on the slide and resize them as desired to make them stand out or fit in with the overall design of the presentation.
- Excel charts are seamlessly integrated into the PowerPoint presentation. Users can embed the charts directly into the presentation without having to switch between different applications.
- Excel charts allow for data-driven presentation design. Users can create a presentation based on data insights and showcase the data in an easily digestible format using Excel charts.
In addition to these benefits, Excel charts offer a level of flexibility that allows users to create the precise visual representation needed to convey the data effectively.
It’s worth noting that Microsoft first introduced Excel charts in PowerPoint in 1993, and since then, they have become an integral feature of the software. The seamless integration of Excel and PowerPoint has been a core focus of Microsoft, and it is clear that users appreciate the convenience and functionality of using Excel charts in PowerPoint.
Benefits of using Excel Charts in PowerPoint
Excel Charts in PowerPoint: Professional Benefits Explored
Excel Charts in PowerPoint enhance the visual appeal of presentations, and assist in better data comprehension, especially in professional settings.
Advantages of Integrating Excel Charts in PowerPoint
- Excel Charts help in displaying complex data sets in a visually informative and easy-to-understand format.
- Excel Charts keep the data point consistent and ensure accuracy in presentation.
- Excel Charts allow for better presentation customization, including style, colors, and fonts.
- Excel Charts can be easily updated and edited to reflect new data sets.
- Excel Charts offer an efficient and impressive way to present quantitative information.
Unique Details about Excel Charts in PowerPoint Integration
Essentially, incorporating Excel Charts in PowerPoint means more than just inserting data from Excel, but using it as an embedded data sheet in the PowerPoint. Such integration guarantees data consistency and easy update, while allowing formatting changes to be done on both platforms simultaneously.
Suggestions for Enhancing PowerPoint Presentations with Excel Charts
Incorporation of clear and concise titles, axis labels, and legends make it significantly easier for audience comprehension. Similarly, it is essential to select the correct chart type for the data presentation in order to maximize visual impact, and also optimize colors for better visual appeal.
How to Insert Excel Charts in PowerPoint
Want to place Excel charts in PowerPoint? No worries! Copy and paste them , or use the Excel Object in PowerPoint. You’ll be able to add your data quickly and without difficulty. Easy-peasy!
Copying and Pasting Excel Charts in PowerPoint
Selecting and Placing Excel Charts in PowerPoint
To embed and display charts created in Excel within the presentation slides of PowerPoint, users should follow a simple procedure:
- Copy your desired chart from the Excel worksheet by either right-clicking on it or pressing ‘CTRL + C.’
- Then, go to your desired slide location in PowerPoint and select either ‘Paste’ or ‘Paste Special’ options from the ‘Home’ tab.
- Finally, adjust size and formatting options for each specific chart as necessary.
It is important to note that depending on the type of data visualization used to create a chart, adjusting colors or size may be necessary to cater to your audiences needs.
Ensuring clear visual aids can support powerful narratives helps make for more effective presentations. Making sure visuals are large enough for audience members to see and understand ensures that everyone can get the most out of all presentations they attend! When PowerPoint and Excel collide, it’s like the ultimate power couple. Inserting Excel charts into PowerPoint? Piece of cake, even for technologically-challenged individuals.
Inserting Excel Charts using Excel Object in PowerPoint
Inserting Excel Charts in PowerPoint using Excel Object is a seamless way to enhance your presentations with rich data visuals that are easy to update and manipulate. Here’s how you can do it in just 6 simple steps:
- Open both Microsoft Excel and PowerPoint applications.
- Select the chart you want to insert into PowerPoint from your Excel spreadsheet.
- Click on Copy or press Ctrl+C on your keyboard.
- Go to the slide where you want to insert the chart in your PowerPoint presentation.
- Press Ctrl+V on your keyboard
- Right-click and select Paste from the context menu.
- Your chart will now appear in your slides, and you can format it as desired using various design tools available in PowerPoint.
When pasting an Excel chart into a PowerPoint presentation, ensure that both applications are open simultaneously. Make sure there are no confidential data present while copying the charts.
Did you know that Excel charts embedded in PowerPoint presentations were introduced back in 1997 with Microsoft Office? The feature has evolved significantly over time with newer versions of Office offering more advanced visual design tools for charts!
Editing Excel charts in PowerPoint: where you can finally fix all those mistakes you made in your data entry.
Editing Excel Charts in PowerPoint
Make your Excel charts look great in your PowerPoint presentations! To do this, you need to edit them. In this section, we’ll show you how to refine your charts. It’s called “Editing Excel Charts in PowerPoint” .
We will also teach you “Updating Chart Data in PowerPoint from Excel” and “Customizing Chart Elements in PowerPoint” . Match the look and feel of your presentation with these solutions!
Updating Chart Data in PowerPoint from Excel
To update chart data in PowerPoint from Excel, you can edit the charts directly from the presentation.
Follow these 4 simple steps to Update Chart Data in PowerPoint from Excel using Semantic NLP variation:
- On the slide with the chart, click on it to select it.
- In the ribbon menu, choose “ Chart Tools ” and then select “ Design “.
- Click “ Edit Data ” to open up the Excel spreadsheet containing the chart’s data.
- Make necessary changes in the Excel sheet then click outside of the spreadsheet window to automatically update the chart in PowerPoint.
It is worth noting that this method applies equally for bar graphs, pie charts as well as other chart types.
Pro Tip: If you want to make only minor edits or updates like changing labels or numbers on a chart, you can just double-click directly on that part of the visual inside PowerPoint and make those changes there.
Get ready to take your PowerPoint presentation to the next level by giving your charts a makeover that even Cinderella would envy.
Customizing Chart Elements in PowerPoint
Customizing the visual elements of a chart in PowerPoint enables you to create a cohesive and compelling presentation.
Here is a 4-Step Guide to Customizing Chart Elements in PowerPoint :
- Select the chart, go to ‘Chart Tools’ and click on ‘Design.’
- To modify chart elements, click on ‘Add Chart Element’ and select options such as ‘Data Labels,’ ‘Legends,’ or ‘Axis.’
- You can customize colors, shapes, and formatting of various elements through the “Format” tab.
- Ensure that your modifications are saved by right-clicking in the chart area and choosing “Save As Template.”
Of significance, keep in mind that when adding data labels to charts for large datasets, consider using leader lines or remove clutter by only labeling critical values.
Pro Tip: When modifying chart elements in PowerPoint remember that your final goal is to produce engaging graphics that enhance your message. Because who needs boring bullet points when you can visually impress with Excel charts in PowerPoint?
Best Practices for Using Excel Charts in PowerPoint
To smoothly integrate Excel charts in PowerPoint, it’s best to use these tips:
- Make sure a consistent design for the charts .
- Choose the correct chart type for your data .
- Verify that the data in the charts is accurate .
Keep Chart Designs Consistent
Establishing Uniformity in Chart Design
Maintaining a uniform template for the design aspects of Excel charts is crucial when creating presentations using PowerPoint. This helps to achieve consistency and ensures that your charts match the overall look and feel of your presentation. Here are five steps to keep chart designs consistent:
- Establish a standard format: Determine a set of standard formatting guidelines for your charts that meet your organization’s branding requirements.
- Use chart templates: Create templates with predefined designs, color scheme, labels, and data sources so that these can be quickly applied without compromising on visual consistency.
- Follow naming conventions: Use descriptive titles or names for each chart element (axis, title, data series) to easily locate and modify them.
- Reuse elements: Reusing design elements such as colors, fonts, and styles across different charts contributes to uniformity in chart design throughout the presentation.
- Test before sharing: Always check each slide containing the charts before presenting it to ensure that you have achieved consistency in both form and function.
Exemplary Characteristics
It takes time to develop an intuitive understanding of chart design best practices since they involve both technical skills and aesthetic judgement. Ensure that your PowerPoint slides remain aesthetically pleasing while still conveying important information by establishing uniformity in your chart design.
Unexpected Event
Microsoft Excel has been around for almost 30 years. The first version was introduced on September 30th, 1985! Since then, excel has become one of the most commonly used tools across workplaces all over the world.
Don’t be that person who uses a pie chart for everything – it’s like wearing a suit to the beach.
Use Appropriate Chart Types for Data Representation
When creating charts in Excel for use in PowerPoint, it’s critical to choose appropriate chart types that accurately represent the data. This ensures viewers understand the information presented without confusion.
Here is a sample table that shows which chart types are best suited to represent various kinds of data:
It’s important to note that each chart type has unique properties and best suits specific data types. Using the wrong chart type can result in inaccurate or confusing representations of the data.
Every organization should have internal guidelines about how they display data using Excel charts. For instance, some companies may prefer column charts over bar charts for comparison purposes. Therefore, practitioners must adhere to the organization’s standards and select appropriate chart types accordingly.
An illuminating fact is that Joseph Priestley used charts to illustrate scientific data back in 1765 . His graph showed the rise and fall of different gases under controlled conditions. Graphs plotting natural phenomena still use his technique today because it provides an effective way of representing complex information simply and intuitively.
Because nothing says ‘professional’ like a chart with inaccurate data – except maybe a typo in your boss’s name on the PowerPoint slide.
Ensure Data Accuracy in Charts
With the increasing reliance of businesses on data to make decisions, charts are an essential tool in delivering precise insights. Accurate data charting is vital since it provides a structure for proper decision-making. Clear analysis of data can only occur when the correct points are entered into spreadsheets and graphs flawlessly.
Any mistakes in data collection or presentation can severely impact analytical decisions, which could culminate in missed opportunities. Therefore, an imperative would be to ensure that all inputs are consistently checked and double-checked before sharing a graphic representation.
In one instance, planning officers at a leading travel company embarked on designing business plans based on misinformation about customer trends acquired by wrongly inputted spreadsheet formulas. This led to significant revenue loss from underestimation of their target market over some time due to unaltered graphs used for analyses.
Some Facts About Excel Charts in PowerPoint:
- ✅ Excel Charts can be easily added to PowerPoint presentations. (Source: Microsoft)
- ✅ Data in PowerPoint charts can be easily updated in real-time using linked Excel files. (Source: GoSkills)
- ✅ There are several chart types availabe in Excel to choose from, such as Bar, Line, Pie, and Scatter. (Source: Exceljet)
- ✅ Charts in PowerPoint can be customized with colors, font styles, and other design elements to match the presentation theme. (Source: SlideModel)
- ✅ Excel Charts in PowerPoint can help presenters convey complex data in an easy-to-understand format. (Source: BrightCarbon)
FAQs about Excel Charts In Powerpoint
What are excel charts in powerpoint.
Excel Charts in PowerPoint refer to the feature where users can insert charts and tables created in Excel into PowerPoint slides to represent data visually through graphs and charts that help convey information with ease.
How do I insert an Excel Chart into a PowerPoint presentation?
To insert an Excel Chart into a PowerPoint presentation, open the slide where you want to insert the chart and click “Insert” from the ribbon menu. Then, select “Chart” and choose the type of chart you want to insert. From there, select the Excel file that contains the data you want to include in the chart, and drag the selection box to adjust the size of the chart as needed.
How can I update an Excel Chart in PowerPoint?
To update an Excel Chart in PowerPoint, select the chart and then click the “Edit Data” button from the ribbon. This will open the Excel sheet where the chart is located, allowing you to make changes to the data. Once you have made the changes, close the Excel sheet and the changes will be automatically updated in the PowerPoint presentation.
What types of Excel Charts can be inserted into PowerPoint?
Almost all types of charts available in Excel can be inserted into PowerPoint, including line charts, pie charts, bar charts, area charts, scatter charts, and more. The process of inserting each type of chart is slightly different, but the overall steps remain the same.
Can I customize the appearance of an Excel Chart in PowerPoint?
Yes, you can customize various aspects of an Excel Chart in PowerPoint. You can change the chart type, axis labels, color scheme, font style, and more. To customize the chart, select it and then click the “Chart Tools” menu on the ribbon, where you can make your changes.
Can I animate an Excel Chart in PowerPoint?
Yes, you can add animation to an Excel Chart in PowerPoint to make it more engaging and interactive. To do this, select the chart and then click the “Animations” tab on the ribbon. From there, choose the animation effect and timing that you want to apply to the chart.

Microsoft Excel
9 minute read
The Beginner’s Guide to Excel Charts

Kat Boogaard
Facebook Twitter LinkedIn WhatsApp Email

Join the Excel conversation on Slack
Ask a question or join the conversation for all things Excel on our Slack channel.
You’ve probably heard that Excel is a great tool for storing and analyzing a bunch of data. But, let’s face it—rows and rows of digits can be plain hard to look at. This is where our Excel chart tutorial comes in.
While spreadsheets themselves aren’t that interpretive and can be challenging to wade through, charts enable you to display that data and any trends or results in a visual way. In doing so, that seemingly complex data is far easier to digest, comprehend, and ultimately take action on.
Here's the amazing thing: Excel charts look awesome, but they really aren’t that complicated to create. And, the even better news? We’re here to walk you through the process step-by-step with an Excel chart tutorial.
Step up your Excel game
Download our print-ready shortcut cheatsheet for Excel.
Growth in email subscribers: An Excel charts case study
Meet Lucy. She works on the marketing team at her company and is primarily responsible for all of the email marketing campaigns.
She has to deliver a presentation to her organization’s leadership team, where she’ll highlight the growth of email subscribers over the past 12 months. She really wants to knock the presentation out of the park—because, when you boil it down, this information proves that she’s doing her job well.
Currently, she has the total number of email subscribers for each month of 2017 in a simple Excel spreadsheet that looks like this:
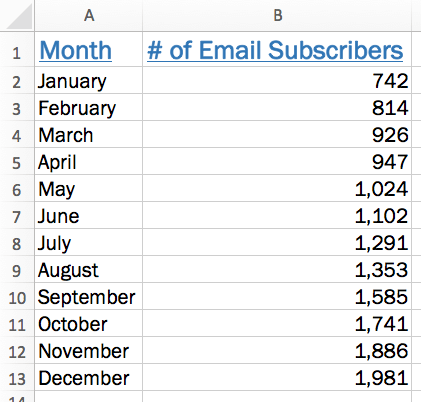
Sure, the numbers themselves show impressive growth, and she could simply spit out those digits during her presentation. But, she really wants to make an impact—so, she’s going to use an Excel chart to display the subscriber growth she’s worked so hard for.
How to build an Excel chart: A step-by-step Excel chart tutorial
1. get your data ready.
Before she dives right in with creating her chart, Lucy should take some time to scroll through her data and fix any errors that she spots—whether it’s a digit that looks off, a month spelled incorrectly, or something else.
Remember, the charts you build within Excel are going to pull directly from your data set. So, whatever errors you have there will also appear in your chart. Taking even just a little bit of time to check over your data could prevent you from having to go back and make changes after you see something off in your chart.
You should also ensure that you have descriptive column headers for your data. In this case, it’s pretty straightforward: Lucy has a column header for the month and a column header for the number of email subscribers.
TIP: Checking over data is pretty simple when you have a really small data set like Lucy, but it can become a little more cumbersome when you have hundreds or thousands of rows of data.
If you spot an issue, use Excel’s “find and replace” feature to correct all instances of that error. Go to the edit menu at the top of the page, and then type in the mistake you want to find and what it should be replaced with.
For example, if Lucy realized she spelled “September” as “Setpember” she could use this feature to replace all instances where it’s spelled incorrectly.
2. Insert chart and select chart type
With her data cleaned up, Lucy is ready to insert her chart into her spreadsheet. To do so, she’ll highlight all of the data (including column headers!) she wants included in her chart.
Once her data is highlighted, she’ll head to the “Insert” menu in the ribbon and select what type of chart she wants to use to display her data.
Excel offers tons of different types of charts to choose from, including:
- Scatter plot
- Numerous other more advanced charts
Want to learn more about column charts in particular? Check out this video.
If you’re unsure what type of chart to use, you can click the “Recommended Charts” button to see options that Excel suggests based on what appears in your data. This isn’t foolproof, but it can certainly help to give you some direction.
In this case, because Lucy wants to display a trend in her data over time, she knows that a line chart is probably her best bet. So, she selects a line chart from those options.
After doing so, her chart instantly appears within the same tab of her Excel workbook. That’s it—she’s just created her chart. Pretty easy, right?
3. Double-check your chart
Now with her chart is created, it's a good time for Lucy to take another quick peek and make sure nothing is unexpected or looks out of place.
In this case, since we’re working with such a small data set, it’s not a huge issue. But, when you’re working with a much larger set of data, mistakes can slip past much easier.
If you see a huge spike that you weren’t expecting or anything else that makes you hesitant, it’s best to return to your original data set to confirm there aren’t any errors that you didn’t catch the first time.
4. Customize your chart
At this point, the chart is created—and, you can stop here if you’re happy with it.
But, since Lucy works in marketing, she wants to make some changes to the colors to match her company’s branding, as well as add axis titles and a legend to make her point explicitly clear.
Let’s start by changing the colors. Here’s the important thing to remember about customizing a chart within Excel: You should click directly on the portion of the chart that you want to edit. So, if Lucy wants to change the line from orange to blue, she should click directly on the line—so that those formatting dots appear all around it.
When she’s clicked on the item that she wants to change, she’ll right-click on the line and select “Format Data Series.”
A quick note: The exact language here can vary depending on what portion of the chart you’re clicked into (for example, if you’re changing the white space around the chart, it’ll say “Format Chart Area”). In short, just look for the “Format” option.
After selecting “Format Data Series,” Lucy clicks the paint can for the color and then selects orange. Her line then changes from blue to orange.
To do so, she clicks within her chart and then visits the “Chart Design” tab in the ribbon (you must be clicked in your chart for this “Chart Design” tab to appear!). Within that menu, she’ll click “Add Chart Element” and select “Axis Titles”.
She’ll insert each axis title—the horizontal and the vertical—separately and enter the appropriate name for each. After doing so, they’ll appear on her chart.
Finally, Lucy wants to add a legend. It’s not really necessary on a data set like this (since there’s only one line displaying data). But, for clarity’s sake, we’ll go through the steps to add one.
Again, Lucy will click within the chart, head to the “Chart Design” tab, click the “Add Chart Element” button, and select “Legend.”
She’ll need to select where she’d like it to appear on her chart. This is all up to personal preference, so Lucy selects the right side of her chart.
When she does so, her new legend appears.
But, wait… what if you regret your chart choice?
Sometimes it can be hard to visualize what your data will look like in chart form until you’ve actually created the chart.
So, what happens if Lucy had created this line chart—but, after seeing it, she thinks that a bar chart would be better? Does she have to start all over again from scratch?
Absolutely not! Excel makes it easy to swap out the type of chart you’re using—even after it’s created.
To do so, click within the chart, go to the “Chart Design” tab, find the “Change Chart Type” button, and select the type of chart you want to swap to.
Take note that after doing so, you might have to reformat some of the colors selected (since Lucy chose to have lines displayed in orange when editing her line graph , that’s what’s showing up even in the column graph).
But, otherwise, swapping out your chart type is as easy as that.
Ready to build your own charts?
Charts are a great way to visualize your data and present it in a way that’s far more digestible than endless rows of digits. And, the best part? Excel charts really aren’t challenging to create.
Follow this step-by-step guide, and you’ll end up with a chart that summarizes your data in a way that’s painless to analyze.
Ready to try some advanced techniques? Check out this advanced Excel charts tutorial .
Ready to become a certified Excel ninja?
Start learning for free with GoSkills courses
Loved this? Subscribe, and join 451,660 others.
Get our latest content before everyone else. Unsubscribe whenever.

Kat is a writer specializing in career, self-development, and productivity topics. When she escapes her computer, she enjoys reading, hiking, golfing, and dishing out tips for prospective freelancers on her website.

Recommended
Excel Challenge 40: Create a Custom Excel Calculator
Would you like to build your own Excel calculator? It might be easier than you think! Take the challenge and see how our community members solved it.

Sort Functions in Excel — How to Use SORT and SORTBY
Excel sort functions are superior to manual sorting methods because they will automatically update the sort order without user intervention.

Excel Challenge 39: Generate Unique Random Values
What is the best way to generate random values in Excel? Better yet, can you make them unique? Put your skills to the test with this Excel challenge.
© 2024 GoSkills Ltd. Skills for career advancement

Excel Charts in PowerPoint
Introduction.
When it comes to creating impactful presentations, visual representation plays a crucial role in conveying complex information effectively. And what better way to enhance your PowerPoint slides than by using Excel charts? Excel charts not only add visual appeal to your presentations but also provide an easy-to-understand summary of your data. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of using Excel charts in PowerPoint and how they can elevate the quality of your presentations.
Key Takeaways
- Excel charts enhance the quality of PowerPoint presentations by providing visual appeal and summarizing data effectively.
- Using Excel charts allows for dynamic and interactive presentations, real-time updates, and data manipulation.
- Creating an Excel chart in PowerPoint involves selecting and importing data, choosing the right chart type, and customizing its appearance.
- Tips for effective chart presentation include keeping the design simple, using appropriate colors and fonts, and adding clear labels and titles.
- Enhancing Excel charts in PowerPoint can be done by adding animation, multimedia elements, or using advanced charting options for deeper analysis.
- Common challenges when using Excel charts include compatibility issues, troubleshooting errors, and ensuring consistency and accuracy in data representation.
- Using Excel charts effectively can result in impactful presentations that convey complex information clearly and engage the audience.
Benefits of using Excel charts in PowerPoint
When it comes to creating impactful presentations, incorporating data and visual representations can greatly enhance the effectiveness of your message. By using Excel charts in PowerPoint, you can take your presentations to the next level, making them not only informative but also engaging and visually appealing. Let's explore some of the key benefits of using Excel charts in PowerPoint:
Ability to create dynamic and interactive charts
One of the primary advantages of using Excel charts in PowerPoint is the ability to create dynamic and interactive visualizations. Excel provides a wide range of chart types, from basic bar and line charts to more advanced options like scatter plots and surface charts. These charts can be easily customized and linked to your PowerPoint slides, allowing you to present complex data in a visually appealing and user-friendly manner. By incorporating interactive features such as data filters and drill-down capabilities, you can empower your audience to explore the data on their own, leading to a more engaging and interactive presentation experience.
Allows for real-time updates and data manipulation
Another significant benefit of using Excel charts in PowerPoint is the seamless integration between the two programs. By linking your charts to the underlying Excel data, any updates or changes made to the data in Excel will automatically reflect in your PowerPoint presentation. This allows you to present real-time information without the need for manual updates or recreating the charts from scratch. Additionally, Excel's powerful data manipulation capabilities enable you to perform calculations, apply filters, and analyze data directly within the spreadsheet, providing you with greater flexibility and control over your presentation visuals.
Provides professional and visually appealing presentations
When it comes to creating presentations, aesthetics play a crucial role in capturing your audience's attention and conveying information effectively. Excel charts offer a wide range of customization options, including color schemes, chart styles, and formatting choices, allowing you to create visually appealing and professional-looking presentations. With the ability to choose from various chart layouts, add labels and annotations, and apply visual effects, you can transform raw data into visually compelling insights that leave a lasting impact on your audience.
In conclusion, utilizing Excel charts in PowerPoint provides numerous benefits for creating impactful presentations. From the ability to create dynamic and interactive charts to real-time updates and data manipulation capabilities, Excel charts enable you to present data in a visually appealing and professional manner. By leveraging these benefits, you can effectively communicate your message, engage your audience, and enhance the overall effectiveness of your presentations.
How to create an Excel chart in PowerPoint
Step-by-step guide on selecting and importing data.
Creating an Excel chart in PowerPoint is a simple process that starts with selecting and importing the data you want to visualize. Follow these steps:
- Step 1: Open Excel and enter your data into a spreadsheet.
- Step 2: Select the data you want to include in the chart by clicking and dragging over it.
- Step 3: Copy the selected data by pressing Ctrl+C or right-clicking and selecting "Copy".
- Step 4: Open PowerPoint and navigate to the slide where you want to insert the chart.
- Step 5: Paste the copied data into PowerPoint by pressing Ctrl+V or right-clicking and selecting "Paste".
- Step 6: PowerPoint will automatically detect the pasted data as an Excel chart and provide options for customizing it.
Choosing the right chart type for your data
Selecting the appropriate chart type is essential to effectively communicate your data. Consider the nature of your data and the message you want to convey. Follow these guidelines:
- Column and Bar charts: Use these chart types to compare values across different categories.
- Line charts: Use line charts to show trends over time or data progression.
- Pie and Donut charts: Use these chart types to visualize the composition or proportion of different parts in a whole.
- Area charts: Use area charts to display the cumulative values of different data series over time.
- Scatter and Bubble charts: Use these chart types to show relationships or correlations between multiple variables.
Customizing the chart appearance and layout
Once you have selected the appropriate chart type, it's important to customize its appearance and layout to enhance its visual impact. Follow these steps:
- Step 1: Click on the chart to activate the "Chart Tools" tab in the PowerPoint ribbon.
- Step 2: Use the options available in the "Design" and "Format" tabs to modify the chart's colors, fonts, labels, and other visual elements.
- Step 3: Experiment with different chart layouts and styles to find the one that best suits your data and presentation style.
- Step 4: Consider adding titles, axis labels, and data labels to provide context and clarify the information being conveyed.
- Step 5: Resize and position the chart on the slide to ensure it is easily visible and fits well with the overall design.
Tips for effective chart presentation in PowerPoint
Keeping the chart design simple and uncluttered.
One of the key aspects of effective chart presentation in PowerPoint is to keep the design simple and uncluttered. This helps in enhancing the clarity and understanding of the information being conveyed. Some tips to achieve simplicity in chart design include:
- Minimize the number of data points displayed on the chart.
- Remove unnecessary gridlines and borders.
- Avoid using excessive colors or embellishments.
- Ensure that the chart elements are properly aligned and spaced.
Using appropriate colors and fonts for readability
The choice of colors and fonts plays a crucial role in the readability of the chart. To ensure that the chart is easily legible, consider these suggestions:
- Use high contrasting colors for different data series or categories to make them visually distinguishable.
- Avoid using colors that are too bright or too dull, as they can strain the eyes or make the chart appear uninteresting.
- Choose a font that is easily readable and consistent throughout the presentation. Sans-serif fonts like Arial or Calibri are usually preferred for their clean and modern appearance.
- Ensure that the font size is appropriate for the size of the chart and the viewing distance.
Adding clear labels and titles for easy understanding
Clear labels and titles on the chart are essential to facilitate easy understanding of the information being presented. Consider these guidelines when adding labels and titles:
- Include a descriptive title that accurately reflects the content and purpose of the chart.
- Label the axes and data series clearly, using concise and meaningful descriptions.
- Avoid overcrowding the chart with labels, but ensure that important data points or values are appropriately labeled.
- Consider using data labels or callouts to highlight specific data points or provide additional context.
Enhancing Excel charts in PowerPoint
Excel charts are a powerful tool for visually representing data, but when it comes to making impactful presentations, adding a few extra touches can take your charts to the next level. In this chapter, we will explore some ways to enhance Excel charts in PowerPoint and make them more engaging and interactive.
Adding animation and transition effects to the chart
Animation and transition effects can bring your charts to life and help you grab your audience's attention. Here are a few ways to incorporate these effects into your Excel charts:
- Entrance animation: Make your chart elements appear on the slide one by one, creating a sense of anticipation and focus.
- Exit animation: Gradually fade out or move chart elements off the slide to create a smooth transition between slides.
- Emphasis animation: Highlight specific data points or elements within the chart to draw attention to key information.
- Motion path animation: Animate the movement of chart elements along a predefined path, adding visual interest and dynamic movement to your charts.
Incorporating multimedia elements like audio or video
Adding multimedia elements to your Excel charts can provide an immersive experience for your audience. Here are a few ways to incorporate audio or video into your charts:
- Audio narration: Record and insert audio narration to explain the chart or provide additional context.
- Video demonstration: Embed videos within your chart to showcase a product demo, illustrate a process, or provide a visual explanation.
- Interactive elements: Use hyperlinks or clickable buttons within your chart to trigger specific audio or video elements, allowing the audience to explore the chart at their own pace.
Using advanced charting options for deeper analysis
Excel offers a range of advanced charting options that can help you dive deeper into your data and uncover valuable insights. Here are a few advanced techniques you can use to enhance your Excel charts:
- Combining chart types: Combine different chart types, such as bar charts, line charts, and scatter plots, to better represent complex data relationships.
- Adding trendlines and error bars: Highlight trends and variability in your data by adding trendlines and error bars to your charts.
- Using secondary axes: Compare data series with different scales by adding a secondary axis to your chart, allowing for better visualization and analysis.
- Data filtering and sorting: Use Excel's data filtering and sorting capabilities to focus on specific data subsets within your chart and present information more effectively.
By leveraging these techniques, you can create visually striking Excel charts in PowerPoint that not only convey data effectively but also captivate and engage your audience.
Common challenges when using Excel charts in PowerPoint
Excel charts can be a powerful tool for visualizing data, but when it comes to transferring them to PowerPoint presentations, several common challenges can arise. Understanding and addressing these challenges is essential for ensuring a seamless integration of charts into your presentations.
Compatibility issues between different versions of Excel and PowerPoint
One of the primary challenges when using Excel charts in PowerPoint is compatibility between different versions of the two software programs. Excel and PowerPoint are frequently updated, and with each update, there is the potential for compatibility issues to arise.
To overcome this challenge, it is important to ensure that both Excel and PowerPoint are updated to the latest versions. This will help minimize potential compatibility problems and ensure a smooth transfer of charts between the two programs.
Troubleshooting errors and data discrepancies
Another challenge when using Excel charts in PowerPoint is troubleshooting errors and resolving data discrepancies. It is not uncommon for charts to display inaccurately or for errors to appear when transferring charts from Excel to PowerPoint.
To troubleshoot these errors, it is helpful to double-check the data in Excel and verify that it is accurate and properly formatted. Additionally, ensuring that the chart is correctly selected and copied in Excel before pasting it into PowerPoint can also help prevent data discrepancies.
Ensuring consistency and accuracy in data representation
Consistency and accuracy in data representation are crucial when using Excel charts in PowerPoint presentations. It is essential that the data in the chart is up-to-date, correctly labeled, and visually appealing.
To ensure consistency, it is recommended to use the same data source for both Excel and PowerPoint. This eliminates any discrepancies that may arise from using different data sources. Additionally, regularly reviewing and updating the data in the Excel chart and PowerPoint presentation will help maintain accuracy.
Furthermore, it is important to design the chart in a visually appealing manner, using appropriate colors, fonts, and chart styles. This will enhance the overall presentation and make the data more engaging and easy to understand for the audience.
By being aware of these common challenges and taking the necessary steps to address them, you can effectively use Excel charts in your PowerPoint presentations. Ensuring compatibility between different versions, troubleshooting errors, and maintaining consistency and accuracy in data representation will help you create impactful presentations that effectively communicate your data.
In conclusion, utilizing Excel charts in PowerPoint presentations offers numerous benefits that can greatly enhance the impact of your message. The ability to visually represent data in a clear and concise manner not only improves audience understanding but also adds credibility to your presentation. By harnessing the power of Excel charts, you can effectively communicate complex information, facilitate data analysis, and make your presentations more memorable. So, don't miss out on this valuable tool – start incorporating Excel charts into your PowerPoint presentations today and make a lasting impression on your audience.

Immediate Download
MAC & PC Compatible
Free Email Support
Related aticles

The Benefits of Excel Dashboards for Data Analysts

Unlock the Power of Real-Time Data Visualization with Excel Dashboards

Unlocking the Potential of Excel's Data Dashboard

Unleashing the Benefits of a Dashboard with Maximum Impact in Excel

Exploring Data Easily and Securely: Essential Features for Excel Dashboards

Unlock the Benefits of Real-Time Dashboard Updates in Excel

Unleashing the Power of Excel Dashboards

Understanding the Benefits and Challenges of Excel Dashboard Design and Development

Leverage Your Data with Excel Dashboards

Crafting the Perfect Dashboard for Excel

An Introduction to Excel Dashboards

How to Create an Effective Excel Dashboard
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.

Excel Charts In Powerpoint
April 9, 2024
Key Takeaway:
- Creating effective Excel charts for PowerPoint presentations involves selecting and organizing data in Excel, choosing the most suitable chart type, and customizing chart format options to enhance visual appeal and clarity.
- When inserting charts into PowerPoint, it is important to select the appropriate slide, use the “Paste Special” feature to insert the chart, and adjust the size and placement of the chart to fit the design of the presentation.
- To further enhance the appearance of charts in PowerPoint, users can alter the chart type, add chart elements such as titles and labels, and modify the style and color scheme of the chart. Adding animations to charts can also make them more engaging and effective in conveying information to audiences.
Do you want to supercharge your PowerPoint presentation with interactive charts? This article shows you how to create and edit Excel charts in PowerPoint to get the most out of your data. Whether you’re a professional or a student, these tips will help make your presentation a success!
Excel Chart Creation
Excel charts are mighty when it comes to displaying data in PowerPoint presentations. Let me guide you through the basics of making Excel charts that look great and get your message across. We’ll start by looking at how to pick and choose data in Excel , then choose a chart type that best shows your data . Lastly, we’ll go over changing the chart’s format to make it more eye-catching and powerful . After this section, you’ll be ready to make professional-grade Excel charts that make your presentations pop!
Choosing & Selecting Data in Excel
Before creating a chart in Excel, it is essential to select the right data. You need to identify if the data is organized in columns or rows and select the appropriate ones. Plus, the headers should be included to make the chart have correct labeling.
Did you know that traditional pie charts, where slices overlap , make it hard for viewers to accurately compare slice sizes? ( source: Forbes )
Picking the right chart type can help in effectively displaying the chosen data through visuals such as graphs and charts .
Selecting suitable chart type
It’s wise to build a table to compare chart types and their suitability for distinct data. For example, if you need to sum up categories and values, a stacked bar or column chart might be suitable. However, if you want to show how one variable affects another over time, a line graph might be more fitting.
It’s also essential to understand the different types of charts available. Excel offers various chart types, such as bar charts, pie charts, line graphs, scatter plots , etc. Each chart has a distinct purpose and can effectively display specific data.
I recall my friend presenting a pie chart in a presentation to represent their budget. The slices were too small and it caused confusion among the audience. This showed the importance of selecting the appropriate chart type that accurately displays the data.
Next, we’ll concentrate on customizing chart format.
Customizing Chart format
- Pick a chart style that fits your data type and presentation. You can choose from pre-designed templates or design your own. Then, modify it by formatting titles, legends, axis labels and data series.
- Formatting elements helps you emphasize certain trends or patterns in your data. Change colors, fonts, borders and effects to create a unique look.
- Adjust the axis to focus attention on specific data points or ranges.
For example, I had to present sales figures for various products at work. I used Excel charts but it wasn’t very clear. So, I customized my chart format by changing the colors of each product line graph.
Finally, ‘PowerPoint Chart Insertion’ . Here, we learn how to insert charts into PowerPoint slides.
PowerPoint Chart Insertion
I use PowerPoint a lot, so I understand the need for visually nice presentations. To make them look better, charts come in handy. Here, I will teach you how to add Excel charts to slides in PowerPoint. We’ll cover selecting slides, adjusting the size and position of the chart. This will help you make exciting and informative presentations that will get your message across to your viewers. So, let’s get started and learn how to create great charts with data from Excel in PowerPoint!
Selection of Slide in PowerPoint
Open your PowerPoint file and select the ‘Home’ tab. Click ‘New Slide’ for a list of layouts. Choose one that fits your content or edit an existing slide. Click the thumbnail and it’ll be added to your presentation.
Choose slides wisely . Think before selecting. It should be clear, functional and relevant. I once saw my boss choose a slide which was visually appealing but irrelevant to his topic. It confused the audience and reduced the impact of his message.
Now you have chosen the slide. Let’s move on to inserting charts from Excel into PowerPoint without losing any data or formatting. We’ll discuss in the next section.
Inserting Chart from Excel to PowerPoint
Inserting a chart from Excel into PowerPoint is simple! Follow these steps:
Adding charts from Excel makes PowerPoint presentations more dynamic. You can easily edit the charts without having to recreate them in PowerPoint. However, any changes made to the original data in Excel won’t appear in the PowerPoint presentation. To update the chart, you’ll need to edit it manually in PowerPoint.
A cautionary tale: Once, an analyst copied an out-of-date sales graph into their slideshow. This caused confusion as the data didn’t match what was discussed. This shows why it’s essential to make sure charts are up-to-date before including them in presentations.
Next heading: Adjusting Chart Size and Placement
Adjusting Chart Size and Placement
- Step 1: Pick a chart which needs adjusting.
- Step 2: Click on “Format,” then “Size.” Select the size you want from the options available. You can also drag the corners of the chart to resize it.
- Step 3: To move the chart, click it and drag it to the spot you desire.
You gotta make sure your chart is big enough for all to see and that it’s placed nicely in your presentation. When you resize, check if the chart’s size is proportionate to the other elements. And make sure the chart does not overlap with other elements on the slides.
Excel spreadsheets have lots of data. Avoid making slides cluttered with too much numbers. Instead, use graphic representations to make the numbers easier to understand.
Makespace.com’s report states that slide design will affect one-third of an audience’s decision to accept or reject a presentation’s message.
In the article “ PowerPoint Chart Formatting ,” you’ll know how to format Excel Charts within PowerPoint more proficiently.
PowerPoint Chart Formatting
If you’re a fan of formatting Excel charts, you know how much time it takes. Here’s what you need to know about formatting those charts in PowerPoint:
- First, choose the chart type that best represents your data.
- Then, add elements to help your audience understand better.
- Finally, modify the style and color to make it look cohesive and appealing.
With these tips, you’ll be creating stunning, informative charts in no time!
Altering Chart Type
To alter chart type, you need to know a few steps. First, click the chart you want to modify in PowerPoint. Then, locate the ‘Design’ tab at the top ribbon. After that, scroll through and choose a new type of chart for your data under the ‘Type’ group.
Charts are useful tools to show complex concepts in ways that engage audiences and help people understand. From money tracking to sales analysis or marketing reviews , charts are helpful for many different professions.
Excel charts can be confusing when picking which one to use or change. Different datasets mean different views on how to present the data visually. So, altering chart types is necessary for creating visuals for an audience. When modifying charts in PowerPoint, the right chart type is essential. It ensures the clarity of information presented, while still keeping the audience engaged.
Consider using multiple series if you have too many categories with one series due to legends’ challenge in Zoom meetings. Pie Charts are another good option when presenting information about proportional parts of a whole.
Lastly, adding chart elements includes formatting elements like titles and subtitles, as well as other styling options necessary for effective presentations, which help get stakeholder engagement and actionable insights.
Adding Chart Elements
What is Adding Chart Elements?
It’s adding extra features to a chart, such as labels or axes, to make it more informative and visually appealing. This helps communicate the message better to the audience.
Types of Chart Elements
You can add many different elements to a chart, like data labels, titles, legends, gridlines, error bars, trendlines , etc. You can pick the ones that fit best with your desired look and function.
Steps To Add Chart Elements
To add elements to your chart in PowerPoint: select the chart > go to “Chart Tools” > select “Layout” > check or uncheck the boxes for the elements you want.
Best Practices For Adding Chart Elements
Don’t clutter your slide with too many elements. Include only what’s necessary to communicate the info accurately and clearly. Use colors wisely and in a uniform way, so all the charts have a common design in the presentation.
Adding Chart Elements can make your presentation more interactive and dynamic. But, if you don’t use them well, you may miss out on opportunities to engage your audience fully.
In our next section, Modifying Chart Style and Color , we’ll learn about how style preferences affect the visual impact instantly. Color options are also very important for achieving branding through presentations.
Modifying Chart Style and Color
Click the chart you want to modify . You’ll see 3 buttons on the right .
Click the “Chart Styles” button for changing the style. Color, font size, background color, border thickness, etc. can be changed from these options.
Also use the “Format Chart Area” option to modify color and style. Different colors for parts of your chart, adjust outlines, and remove or add gridlines.
When making charts, remember to make them visually appealing and easy to read. Choose a design that enhances the message.
I used to work in a startup company. Making presentations was important. So I modified Chart Style and Color often to make the charts look professional.
Adding Animations to PowerPoint Charts is another trick . Fade-in and zoom-out effects can make charts interactive and captivating. Don’t overdo animations as they can distract from the meaning. Use them selectively depending on their suitability.
Adding Animations to PowerPoint Charts
PowerPoint is my go-to for creating engaging presentations. I love to add animated charts to liven up my slides. In this article, I’ll show you how to make your charts stand out. With some simple animation tricks, you can take your PowerPoint charts up a notch. We’ll discuss how to apply chart animations and add animation triggers. Plus, how to adjust animation settings to make your presentation look amazing. Let’s get started and turn plain PowerPoint charts into eye-catching animations!
Applying Chart Animations
Start by picking the chart you want to give animation to.
Go to the Animations tab in the Ribbon and click Add Animation .
Choose an animation effect which suits your needs from the drop-down menu. Get a preview by hovering over them with your mouse.
Change the animation settings as desired in the pane that shows up on the right side of the PowerPoint interface.
Test out your animations by pressing F5 or going into Slide Show mode.
Save and share your file.
It’s very important to ensure that the animations don’t take away from the presentation, but actually add to it. Don’t use too flashy or excessive effects that could distract or confuse your audience.
Animations can make data more interesting and captivating for viewers. A Constructivist Foundations study showed that animated visuals got higher ratings for clarity, attractiveness, and utility compared to static visuals.
Let’s move on to Adding Animation Triggers which will help us understand how adding interactivity through animations can engage audiences in our presentations.
Adding Animation Triggers
To add animation triggers, just follow 6 steps :
- Select a chart element to animate;
- Click the ‘Animations’ tab;
- Click ‘Add Animation’ ;
- Select from the drop-down menu;
- Click the arrow near the animation for ‘Effect Options’ ;
- In ‘Effect Tab’ , choose Trigger and select how to start the animation.
Floating objects, motion paths, growth/shrink effects – all these effects can be added by animation triggers. So, if you need to emphasise any data or key points, then adding an animation trigger could be the right choice.
Animation triggers are like switches to activate certain animated effects . This adds life to your presentations and makes them more attractive. It also helps in better communication of ideas and enhances audience engagement!
So, don’t miss out on this essential layer of depth by not adding animation triggers.
Now that we know how to add animation triggers, let’s find out more about adjusting animation settings in PowerPoint. After all, who doesn’t love options?
Adjusting Animation Settings
Click the chart to select it. Go to the “Animations” tab in the ribbon. Choose an animation from the dropdown list. Click “Effect Options” to customize the animation.
Make tweaks to duration, direction or trigger in the “Effect Options” dialog box. Preview the animation and make adjustments in the Animations tab.
Less is more when adjusting animation settings. Avoid too many animations to keep the focus on the core message . Use consistent timing across animations for a smoother flow. Publishing PowerPoint Charts is the next step to creating captivating presentations.
Publishing PowerPoint Charts
As a presenter, I’m always looking for ways to make my presentations more interesting and useful. Excel charts in PowerPoint are a great tool. But how can I publish the chart I created in Excel? In this part of the show, let’s look at different ways to post PowerPoint charts . We can:
- Export the chart to video files ,
- Save it as an image file ,
- And even share it on social media or online platforms .
This way, our data and insights can reach more people beyond our own devices.
Exporting Charts to Video Files
Open the PowerPoint with your charts. Right-click and choose ‘Save as Picture’ . In the dialog box, pick a file format like ‘.png’ or ‘.jpg’, then save. To make a video file of your charts, open a video editing software. Import the exported chart images and create the video.
Exporting Charts to Video Files is great when you need to show your data in a different way, like for an online tutorial or training program. But it won’t work if you need to update the data often. It’s better to use Excel charts in PowerPoint in that case.
Fun Fact: Visual aids like charts can help you remember up to 70% more info.
Saving Charts as Image Files
You can save charts as image files in formats such as PNG, JPEG, and GIF . To do this, right-click on the chart and click ‘Save As Picture’. Name the file appropriately for easy retrieval later.
This method is useful for transferring charts between softwares and devices. However, saving an image file freezes the chart data. Any changes to the original data won’t be reflected in the saved image.
Moreover, there may be a loss of resolution or clarity if enlarging the image significantly or if it was created at low resolution. So, check size and resolution options before saving the chart.
Saving charts as image files is essential for those who frequently use Excel or PowerPoint. It allows for easier sharing of information across platforms and devices. Additionally, regular checks on file size and resolution can prevent any loss of quality during the process.
I found this feature helpful during a presentation on sales data trends. By using images saved directly from Excel charts, I quickly inserted them into my PowerPoint slides without worrying about formatting errors. This helped me communicate my findings effectively to the audience.
Publishing Charts on Social Media or Web Platforms
- Step 1: Figure out the platform which is the best fit for you. There are many options, including LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram .
- Step 2: After you’ve created your charts in PowerPoint or Excel, make an image of them.
- Step 3: Export the chart as a JPEG or PNG file format.
- Step 4: Upload the chart to the relevant platform. Include a caption and hashtag if necessary.
Publishing charts online offers many advantages. It makes it easier for viewers to access and view the data. It also allows people to use, challenge, criticize, share, support, defend, improve, reject, or correct data points quickly. Through valid links from other platforms, this is much more convenient than downloading PDFs, Excel Sheets, or screenshots.
Don’t miss out on this chance to show off your data! Publish it online without hesitation.
Five Facts About Excel Charts in PowerPoint:
- ✅ Excel charts can be directly inserted into PowerPoint slides. (Source: Microsoft)
- ✅ Excel charts can be edited within PowerPoint using a user-friendly interface. (Source: PCMag)
- ✅ Excel charts in PowerPoint can be customized with various chart styles, colors, and design options. (Source: BrightCarbon)
- ✅ Excel charts in PowerPoint can be animated for more engaging and impactful presentations. (Source: SlideModel)
- ✅ Embedded Excel charts in PowerPoint update automatically when changes are made to the original data in Excel. (Source: Office Support)
FAQs about Excel Charts In Powerpoint
What is excel charts in powerpoint.
Excel Charts in PowerPoint is a feature that allows users to embed Excel charts directly into PowerPoint presentations. This makes it easy to present complex data in a more visual and understandable way.
How do I insert an Excel chart into PowerPoint?
To insert an Excel chart into PowerPoint, first open the Excel file containing the chart you want to use. Select the chart and copy it. Then go to your PowerPoint presentation, navigate to the slide where you want the chart to appear, and paste it in.
Can I edit the Excel chart within PowerPoint?
Yes, you can edit the Excel chart within PowerPoint. Simply double-click on the chart to open the Excel spreadsheet, make your changes, and then click “Save” to update the chart in your PowerPoint presentation.
Can I change the style or appearance of the Excel chart in PowerPoint?
Yes, you can change the style or appearance of the Excel chart in PowerPoint. With the chart selected, navigate to the “Chart Tools” tab and use the various formatting options to adjust colors, fonts, styles, and more.
What types of Excel charts can be embedded in PowerPoint?
Most types of Excel charts can be embedded in PowerPoint, including column, line, pie, bar, area, scatter, and more. However, some chart types, such as bubble charts or funnel charts, may not display correctly when copied into PowerPoint.
What are the benefits of using Excel Charts in PowerPoint?
Using Excel Charts in PowerPoint can make your presentations more impactful and engaging by allowing you to display complex data in a visual, easy-to-understand way. It also ensures that your information is up-to-date and accurate, as any changes made to the chart in Excel will automatically be reflected in your PowerPoint presentation.
- Testimonials
- Google Analytics & GTM Consulting
- Digital Analytics Training

Last Updated: December 23, 2023
This article will show you the best Excel charts for data analysis, presentation, and reporting.
You will learn about the various types of charts in Excel, from column charts, bar charts, line charts, and pie charts to stacked area charts.
Table of Contents
How to select the best Excel chart?
The type of Excel chart you select for your analysis and reporting depends upon the type of data you want to analyze and report and what you want to do with the data:
- Visualize data (make sense of data esp., big data).
- Classify and categorize data.
- Find a relationship among data.
- Understand the composition of data.
- Understand the distribution of data.
- Understand the overlapping of data.
- Determine patterns and trends.
- Detect outliers and other anomalies in data.
- Predict future trends.
- Tell meaningful and engaging stories to decision-makers
What are the most popular Excel charts and graphs types?
Following are the most popular Excel charts and graphs:
- Clustered column chart
- Combination chart
- Stacked column chart
- 100% stacked column chart
- Stacked area chart
- Number chart
- Gauge chart (Speedometer chart)
- Scatter chart
- Actual vs target chart
- Bullet chart
- Funnel chart
- Venn diagram
Sankey diagram

My step-by-step blueprint for selecting the best Excel charts for data analysis and reporting (40 pages)
Get the FREE e-book on Best Excel Charts For Data Analysis And Reporting (40 Pages)
Download the FREE ebook
When to use a Line chart
Following are the various scenarios where a line chart can be particularly helpful:
- Tracking trends over time.
- Handling many data points.
- Order of categories is important.
- Emphasizing changes between two variables.
- Spotting small changes or variations.
- Highlighting anomalies or outliers.
- Forecasting future trends.
- Showing rate of change.
- Time series analysis.
- Budget tracking.
- Performance analysis over specific intervals.
#1 Tracking trends over time
Use a line chart to observe trends (like (uptrend, downtrend, short-term trend, sideways trend, long term) over a period.

Start by understanding what each axis represents. Then, look at the trend of the line – whether it rises, falls, or stays consistent – to interpret the changes in data over time.
Line charts are great for showing long-term changes, such as trends over several months or years.
In a line chart, the axes are crucial in presenting the data.
The horizontal axis (x-axis) usually represents categories or time periods, while the vertical axis (y-axis) shows the values you’re measuring.
The relationship between these two axes allows a line chart to effectively display how one variable (the values on the y-axis) changes in relation to another (the categories or time periods on the x-axis).
This makes line charts particularly useful for tracking changes and trends over time.
#2 Handling many data points
If you have a lot of data points, a line chart can display it without looking cluttered, unlike bar or column charts, which might seem too crowded.
#3 Order of categories is important
Use a line chart instead of a clustered column chart if the order of categories is important.
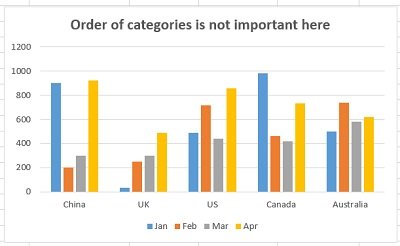
For example, if you want to show progress or changes over time, the line chart helps maintain the chronological order.
#4 Emphasizing changes between two variables
Line charts are perfect when you want to highlight how one variable changes in relation to another. The changes are plotted on the vertical axis against the horizontal axis.
Here’s a line chart that illustrates how one variable (Y-Values, the sine of X) changes in relation to another variable (X-Values).

#5 Spotting small changes or variations
Line charts are excellent for displaying data with small variations that might not be as noticeable in other chart types.
The chart shows Y-values that vary slightly around a sine wave pattern, plotted against X-values.
The line chart’s continuous nature makes it easier to spot these minor fluctuations, which could be lost or less apparent in other charts, like bar or column charts.
This demonstrates the effectiveness of line charts in revealing subtle changes and variations in data.
#6 Highlighting anomalies or outliers
Line charts can help spot unusual data points. If a line suddenly spikes or drops, it can indicate something significant, like a sudden increase in website traffic.

The line chart displayed above is designed to help spot unusual data points. It represents website traffic over 30 days.
On the 16th day, there’s a noticeable spike in traffic, which stands out distinctly against the otherwise consistent traffic levels.
The sudden increase in the chart can indicate something significant, like a successful marketing campaign, a viral post, or other events leading to increased website visits.
This example illustrates how line charts effectively highlight anomalies or unusual occurrences in data sets, allowing for quick identification of significant changes or events.
#7 Forecasting future trends
Line charts can be used for predictive analysis . By extending the line, you can forecast future trends based on past data.
The line chart shown above is designed for predictive analysis. It features original data (in blue) that follows a linear trend over 30 days.
Using this data, a linear regression model has been trained to forecast future trends. The model’s predictions are extended to 45 days and depicted in red on the chart.
The extended red line demonstrates the forecasted trend based on past data, visually representing expected future values.
This kind of analysis is useful for various applications, such as predicting sales, website traffic, or stock prices based on historical trends.
The chart effectively illustrates how extending the trend line in predictive models can help forecast future trends.
#8 Showing rate of change
Line charts are useful for illustrating the rate at which something changes.
For example, a steep line indicates a rapid change, while a gradual slope shows a slower change.

The line chart above illustrates the rate of change using two different types of growth.
The green line represents a rapid change, shown by a quadratic function (value = time²), which increases steeply as time progresses. This steep incline indicates a rapid rate of change.
In contrast, the orange line represents a slower change, modelled by a square root function (value = √time). This line has a more gradual slope, indicating a slower rate of change over the same time period.
This visualization effectively demonstrates how the steepness of a line in a chart can depict the rate at which values change: steeper lines suggest rapid changes.
At the same time, more gradual slopes indicate slower changes.
This is a fundamental concept in interpreting line charts, particularly in fields like economics, science, and engineering, where understanding the rate of change is crucial.
#9 Time series analysis
Line charts are essential for time series analysis, where you track the same variable over regular intervals, like daily temperature readings or monthly sales figures.
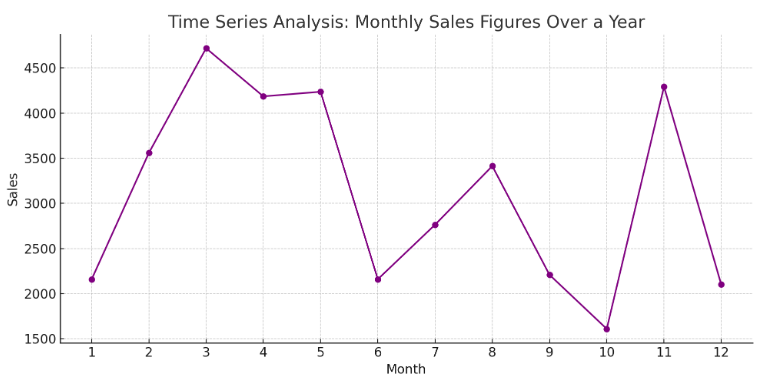
The line chart above is designed for time series analysis and depicts monthly sales figures over a year.
Each point on the chart represents sales data for a specific month, with the months on the horizontal axis and the corresponding sales figures on the vertical axis.
The connected points form a line that makes it easy to follow the sales trend throughout the year.
This type of visualization is particularly useful for identifying patterns, such as seasonal fluctuations or, unusual spikes or dips in sales.
Time series analysis like this is essential in many fields for tracking changes in variables over time and making informed decisions based on those trends.
#10 Budget tracking
Line charts can track expenses or revenues against a budget over time, helping to see areas over or under the budget quickly.
The above line chart tracks monthly expenses and revenues against a yearly budget. The red line represents monthly expenses, and the blue line represents monthly revenues.
The green dashed line indicates the set budget level for each month.
This visualization quickly assesses how expenses and revenues compare to the budget over time.
It’s easy to identify months where expenses exceed or fall below the budget and how revenues stand in relation to the budgeted amount.
Such a chart is particularly useful in financial management, providing a clear visual representation of fiscal health and highlighting areas needing attention or adjustment.
#11 Performance analysis over specific intervals
Line charts are great for comparing performance in different intervals, like comparing quarterly sales or academic scores year over year.
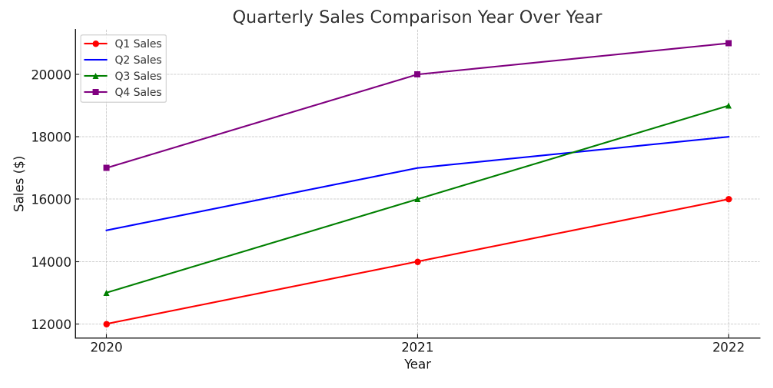
The line chart above compares quarterly sales figures year over year. It includes data for four quarters (Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4) across three years (2020, 2021, and 2022).
Each line represents the sales figures for a specific quarter across the different years, with distinct markers and colours for clarity.
This visualization makes it easy to compare the performance of each quarter year over year.
You can quickly see trends, such as which quarters showed growth or decline over the years.
This type of analysis is particularly valuable in business for assessing seasonal performance, planning future strategies, and understanding historical sales patterns.
When to use a Clustered column chart
Following are the various scenarios where a clustered column chart can be particularly helpful:
- Comparing multiple data series.
- Suitable for comparative analysis.
- Consistent units of measurement.
- Comparable data sizes.
- Displaying extremes.
- Focus on short-term trends.
- The order of categories is not important.
- Comparing subcategories within a main category.
- Visualizing part-to-whole relationships.
- Evaluating performance across different groups.
- Presenting survey results.

#1 Comparing multiple data series
A clustered column chart is ideal for comparing 2 to 4 data series. Avoid using it for just one series or more than four, as it can get cluttered.
Following is an example of a clustered column chart with just one data series:
The following chart contains just five data series, and it has already started looking cluttered:
The chart below contains 11 data series and is very difficult to read and understand:
If you want to create a column chart that contains a lot of data series, then you can try switching ‘row’ and ‘column’ of the chart and see whether it makes any difference:
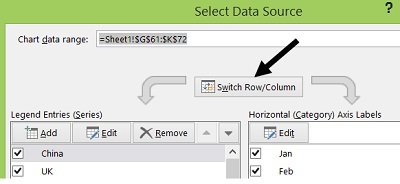
For example, after switching the row and column of the chart (with 11 data series), it looks like the one below:
Though it still looks cluttered, this chart is much easier to read and understand.
#2 Suitable for comparative analysis
Unlike a simple column chart, which represents a single variable, clustered column charts display multiple data variables, making them suitable for comparative analysis.

This chart compares different types of expenses (rent, utilities, marketing) over four quarters (q1, q2, q3, q4).
Each group of bars represents a quarter, with individual bars showing the expenses for each category within that quarter.
This layout allows for an easy comparison of how each type of expense changes from quarter to quarter.
#3 Consistent units of measurement
Use a clustered column chart when the data series you want to compare has the same unit of measurement.
So, avoid using column charts that compare data series with different units of measurement.
For example, in the chart below, ‘Sales’ and ‘ROI’ have different units of measurement.
The data series ‘Sales’ is of type number. Whereas the data series ‘ROI’ is of type percentage:
#4 Comparable data sizes
Use a clustered column chart when the data series you want to compare are of comparable sizes.
So, if the values of one data series dwarf the values of the other data series, then do not use the column chart.
For example, in the chart below, the values of the data series ‘Website Traffic’ completely dwarf the values of the data series named ‘Transactions’:
#5 Displaying extremes
Use a clustered column chart when you want to show the maximum and minimum values of each data series you want to compare.
For example, if you have monthly sales data for several products, a clustered column chart can clearly display each product’s highest and lowest sales figures side by side.
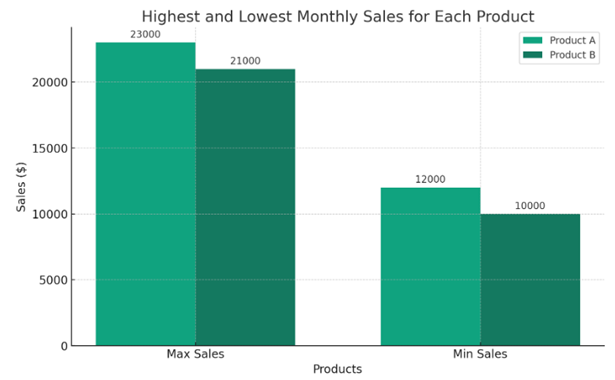
This visual comparison can quickly convey which products have the most variation in sales and the overall range of sales figures for each product.
#6 Focus on short-term trends
Use a clustered column chart to focus on short-term trends, particularly when comparing multiple data series over a short period, like days or weeks.
For example, if you’re analyzing weekly sales data across different store locations, a clustered column chart can visually represent each store’s weekly sales.
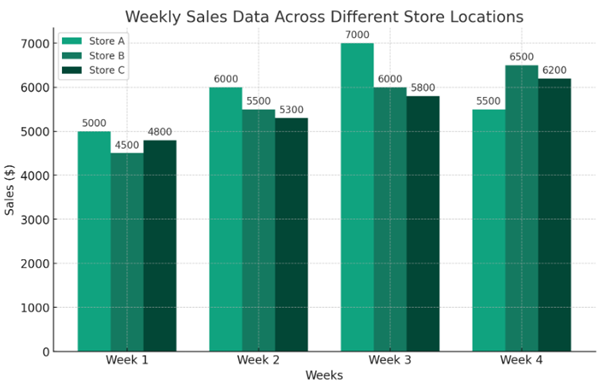
This setup makes it easy to identify any short-term trends or anomalies, such as a sudden spike or drop in sales at a particular location.
#7 The order of categories is not important.
Use a clustered column chart when the order of categories is not important to the interpretation of the data.
This chart type emphasizes comparing different categories or groups rather than the sequence or progression of data points.
For example, suppose you’re comparing the performance of different departments within a company, such as sales, marketing, and finance.

In that case, the order in which these departments are listed on the chart doesn’t affect the interpretation of the data.
Each department’s performance is displayed independently of the others, allowing for easy comparison without implying any sequential relationship.
#8 Comparing subcategories within a main category
If you have data broken down into subcategories within a larger category, a clustered column chart can effectively compare these subgroups side by side.
A clustered column chart is particularly useful for comparing data broken down into subcategories within a larger category.
This type of chart allows you to display each subgroup side by side within the larger category, making it easy to compare the subgroups.
For example, imagine you have sales data for a clothing store categorized by seasons (Spring, Summer, Fall, Winter).
Within each season, you have subcategories like Men’s Wear, Women’s Wear, and Children’s Wear.
A clustered column chart can effectively display this data, showing each clothing type’s sales side by side for each season.

This layout helps quickly compare how different types of clothing perform in each season.
#9 Visualizing part-to-whole relationships
When you want to show how different parts contribute to the whole in multiple categories, clustered column charts can display this effectively, especially if each category has the same parts or subcategories.

The clustered column chart above shows how different parts (Engine, Wheels, and Body) contribute to the total sales in various car categories (Sedan, SUV, Hatchback).
Each group of bars represents a car type, with individual bars showing the sales of each component for that type of car.
This layout allows for an easy comparison of how different components contribute to the sales of each car type.
For example, you can quickly see which components are more popular in Sedans versus SUVs or Hatchbacks.
This type of chart is particularly useful in manufacturing and sales analysis, providing insights into which parts drive sales in different market segments.
#10 Evaluating performance across different groups
Clustered column charts are excellent for comparing performance metrics across different groups or segments, like comparing sales across different regions or customer segments.
#11 Presenting survey results
Clustered column charts are good for presenting survey data, especially where respondents are divided into different demographic groups and you want to compare responses to the same questions across these groups.

The clustered column chart above presents survey responses across different demographic age groups (18-24, 25-34, 35-44, 45+).
Each group of bars represents an age group, with individual bars showing the percentage of responses to three different survey questions.
This chart format makes it easy to compare the responses to each question across the various age groups.
For example, you can quickly see how the responses to Question 1 vary between the youngest and oldest age groups or how the opinions on Questions 2 and 3 differ across all groups.
This type of visualization is particularly useful in survey analysis, where comparing responses across different demographic segments can provide valuable insights into the preferences and opinions of different age groups.
Breaking a clustered column chart
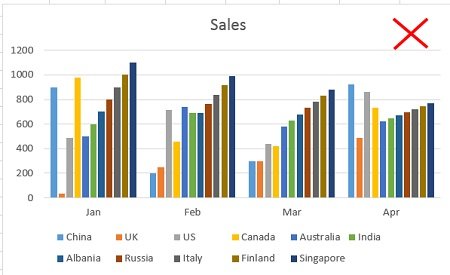
One method of making this chart easier to read and understand is breaking it into several smaller clustered column charts.
For example, you can create one column chart that compares the sales performance of various countries in January.
Create another column chart which just compares the sales performance of various countries in Feb and so on:

The rule of thumb is to avoid presenting too much data in one chart, regardless of the chart type.
A combination chart is simply a combination of two or more charts.
For example, the combination of a column chart with a line chart.
I use combination charts a lot, and I think you must know how to create them as they are very useful.
#1 Use a combination chart when you want to compare two or more data series that have different units of measurement:
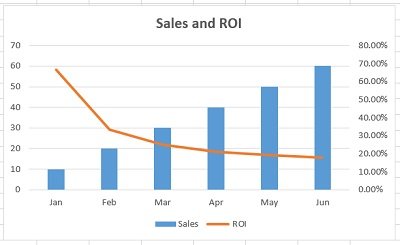
#2 Use a combination chart when you want to compare two or more data series that are not of comparable sizes:
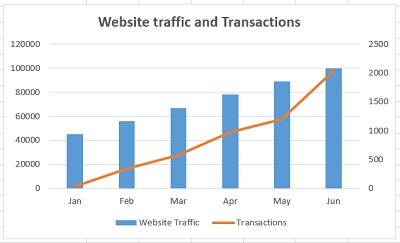
#3 Use a combination chart when you want to display different types of data in different ways that can be represented in the same chart. For example, line, bar and column charts can be used on the same chart.
Use a stacked column chart when you want to compare data series along with their composition, and the overall size of each data series is important:
Use a 100% stacked column chart when you want to compare data series along with their composition but the overall size of each data series is not important:
This chart is used to show the percentage of multiple data series in stacked columns.
Use a stacked area chart when you want to show the trend of composition and emphasize the magnitude of change over time.
For example, the following stacked area chart shows the breakdown of website traffic:
Use a bar chart whenever the axis labels are too long to fit in a column chart:
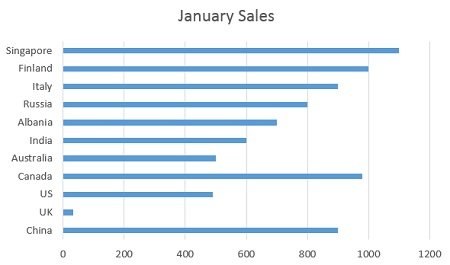
What are the different types of bar charts?
Horizontal bar charts – Represent the data horizontally. The data categories are shown on the vertical axis, and data values are shown on the horizontal axis.
Vertical bar charts – Also called a column chart. It represents the numerical values represented in the vertical bars. These are used mainly to display age ranges and salary ranges.
Grouped bar charts – Grouped bar charts represent the different time period numbers that belong to a single category.
Stacked bar charts – It is a bar chart that represents the comparisons between categories of data but with the ability to compare and break down the data.
#1 Use a pie chart to show a 100% composition of data. In other words, the various pie slices you use must add up to 100%.
This means do not create a pie chart where the various pie slices do not represent parts of the whole pie.
For example, the following pie chart is not a good representation of data composition as the two pie slices add up to 82% and not 100%:
#2 Use a pie chart to show the composition of data only when you have got one data series and less than five categories to plot.
For example, the following pie chart shows the breakdown of website traffic sources in the last month:
Here I have got only four categories (search traffic, referral traffic, direct traffic , and campaigns) to plot.
So a pie chart is ideal for showing the breakdown.
However, if there were more than four categories to plot, like eight or ten categories, the pie chart would have become cluttered and hard to read.
For example, the following pie chart looks cluttered because it has got too many categories:
#3 Pie charts generally express the part to the whole relationship in your data. When your data is represented in ‘percentage’ or ‘part of’, then a pie chart best meets your needs.
#4 Use a pie chart to show data composition only when the pie slices are of comparable sizes.
In other words, do not use a pie chart if the size of one pie slice completely dwarfs the size of the other pie slice(s):
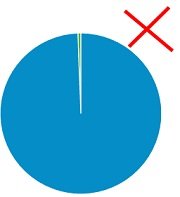
#5 Order your pie slices so that as you look clockwise from top to bottom, the biggest pie slice comes first, followed by the second biggest pie slice and so on. This makes the pie chart easy to read:
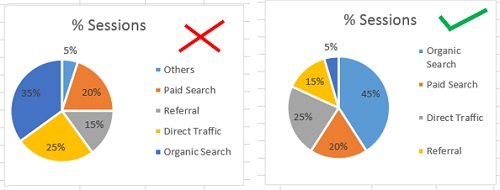
These pie charts are made from the following data:
To create a pie chart where the biggest pie slice comes first, followed by the second biggest pie slice and so on.
I have sorted the data in decreasing order (from largest to smallest).
Best practices for using pie charts
Limit the number of pie slices
Always make sure to use a minimal number of slices when creating a pie chart. It is really difficult to read a large number of slices.
If you have more than five categories, it is recommended to use a different chart type.
Make sure all data adds up to 100%
Verify that the pie slices are valued at 100% when added up.
Include annotations : Include percentages and labels for your pie chart to make it easy to read.
Pie charts work best for 25%, 50%, 75% and 100%.
Don’t compare multiple pie charts.
Do not use multiple pie charts for comparison as the slice sizes are really difficult to compare side by side.
If you want to visualize just one type of data and it contains a numeric value that does not fall in any range/interval, then use the number chart:

If you want to visualize just one type of data and it contains a numeric value that falls in a range/interval, then use the gauge chart (also known as the speedometer chart):
A gauge chart should be used when you want to validate if your data falls in the acceptable range or not.
A gauge chart would generally have the maximum value as default and thresholds as low, medium and high, which indicates if the data is falling within the acceptable range.
Thresholds would be displayed in red, green and yellow for specified values.
#1 Consider using a scatter chart when you want to analyze and report the relationship/correlation between two variables:
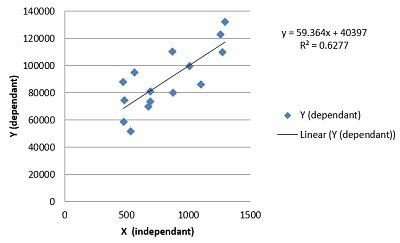
This chart shows that the relationship between the two variables (‘x’ and ‘y’) is linear. As the value of the variable ‘x’ increases, there is a corresponding increase in the value of the variable ‘y’.
#2 Create a scatter chart only when ten or more data points are on the horizontal axis. The more data points, the better it is for a scatter chart. Conversely, just a few data points (like five or six) are not good enough for creating a scatter chart.
#3 Use a scatter chart when you want to show ‘why’. For example: why revenue is correlated with average order value or why conversion rate is correlated with the number of transactions.
Use a histogram to show frequency distribution for quantitative data.
A histogram represents the visual representation of numerical data that falls within a specified range of values called ‘bins’. It looks exactly like a vertical graph.
Note: You would need to install the ‘ Analysis ToolPak ’ to create a histogram in Excel.
The ‘Actual vs target’ chart is a combination chart that requires some formatting.
You can’t insert this chart straightaway into your Excel spreadsheet.
Use this chart when you have got multiple goals, and you want to show progress towards each goal.
The chart below shows whether target sales were achieved in each quarter:
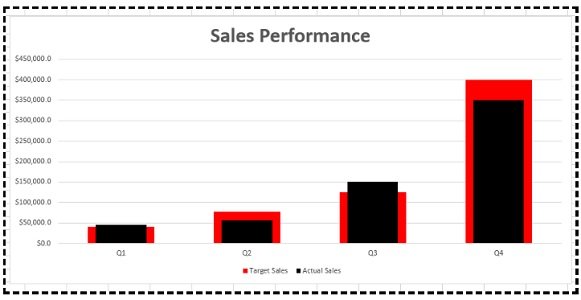
This chart is based on the following data table:
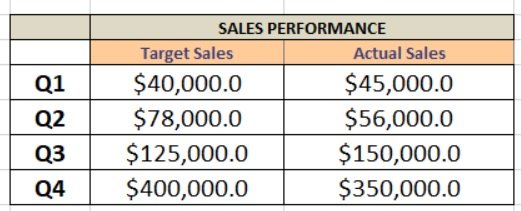
A Bullet chart is a combination chart (though it looks like a single bar chart) which is used to show progress towards a single goal using a range of predefined qualitative and quantitative parameters.
You can’t insert this chart straightaway into your Excel spreadsheet and it is also quite tricky to create.
If you have multiple goals and you want to show progress towards each goal then use the ‘Actual vs. target’ chart.
But if you have only one goal and you want to show progress towards this goal (by using both qualitative and quantitative data) then use the bullet chart.
A bullet chart can be a vertical bar chart or horizontal bar chart. The choice of vertical or horizontal alignment depends on the space available to use for data visualization.
The chart below shows the performance of sales in Quarter 4:
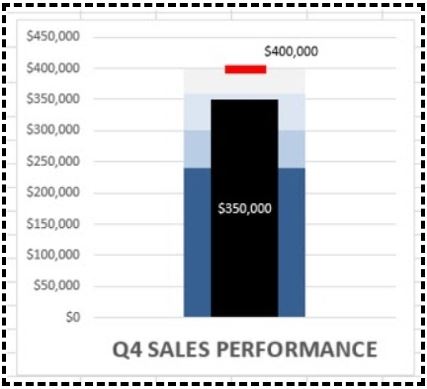
If the actual sales are between $0 to $240,000 then sales performance is considered ‘Poor’.
If the actual sales are between $240,000 to $300,000 ($240,000 + $60,000) then it is considered ‘Fair’.
If the actual sales are between $300,000 to $360,000 ($240,000 + $60,000 + $60,000) then it is considered ‘Good’.
If the actual sales are between $360,000 to $400,000 ($240,000 + $60,000 + $60,000 + $40,000) then it is considered ‘Excellent’.
As the name suggests the funnel chart is used for funnel visualization. It is perfect for showing lead funnel and sales funnels.
Funnel charts visually represent the progressive reduction of data from one phase to another phase.
The first stage is usually referred to as the intake stage.
This chart is available in MS Excel (2016 and above). You just need to select your data table and then insert the ‘Funnel’ chart.
The chart below shows different stages of the purchase funnel and how user moved from one stage to the next:
This chart is based on the following data table:

For example, let us take an example of an ecommerce business.
Funnel charts can be used to understand how many users have added the products to the cart, provided shipping details and completed the purchase.
It also provides us with information about users who have abandoned the cart.
Funnel charts are mostly used for the sales process and to identify potential problems.
A funnel consists of a higher value, called the head, and the lower part, which is referred to as the neck.
Use a Venn diagram to show the overlapping of data.
The multi-channel conversion visualizer chart used in Google Analytics to visualize multi-channel attribution is a Venn diagram:
In web analytics, we can use a Venn diagram to determine whether or not a website has got attribution problems.
If there is little to no overlap between two or more marketing channels, the website doesn’t have attribution issues.
If there is a good amount of overlap, the website has attribution issues. You should seriously consider taking multi-channel attribution into account while analyzing and interpreting the performance of marketing campaigns.
To learn more about attribution modelling read this article: Beginners Guide to Google Analytics Attribution Modelling
Another great use of Venn diagrams is in visualizing the backlinks overlaps between websites:
The tool I have used to create this Venn diagram is Venny .
Note : You can create a Venn diagram in Excel. Check out this tutorial on the Microsoft Office website: Create a Venn diagram .
What are the different types of Venn diagrams?
Two set diagrams – Two circles with overlapping properties. This is the most common and simplest form of the Venn diagram used to compare two metrics or variables.
Three set diagrams – This lets you visualize the relationship between three subjects rather than two variables.
Four set diagram – This comprises four circles with overlapping properties. It is a bit more complex than the normal Venn diagram, and each circle represents the different aspect of the data and their comparison to other variables.
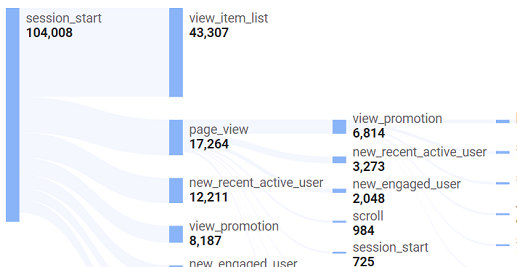
A Sankey diagram visualizes the flow of data between different stages, groups or categories of a process through a series of connected nodes or paths.
Each node represents a stage, group, or category in the process, and each path represents the flow of data between those stages, groups, or categories.
The width of each path is proportional to the amount of flow it represents.
So you can easily see which stages or categories are the most important or have the greatest impact on the overall process.
By visualizing the flow of data in this way, Sankey diagrams can help you understand the structure of a process and identify areas where improvements can be made to increase efficiency or effectiveness.
In the following cases, you can use a Sankey diagram:
#1 You want to show the flow of website visitors through different pages or sections of a website.
#2 You want to visualize the customers’ purchase journey.
#3 You want to identify patterns, trends, and areas of opportunity or concern in your customers’ purchase journey.
For example, you might notice that many customers drop out of the consideration stage, indicating that you need to improve your marketing or product messaging to engage potential customers better.
In Excel, you can create Sankey diagrams using third-party add-ins or manually using Excel’s built-in charting tools.
Creating Sankey diagrams manually in Excel can be time-consuming and may not produce the most aesthetically pleasing or informative charts.
Using third-party add-ins can often provide more advanced features and flexibility in creating Sankey diagrams.
Some popular add-ins for creating Sankey diagrams in Excel include NodeXL and Tableau.
Which charts to avoid for reporting purposes?
Throughout this article, I have talked about the charts that should be used.
However, there are some charts that should be avoided for reporting purposes unless your target audience is as data-savvy as you.
Following are those charts:
#1 Charts to avoid > Treemap
#2 Charts to avoid > Waterfall chart
#3 Charts to avoid > Radar chart
#4 Charts to avoid > Bubble chart
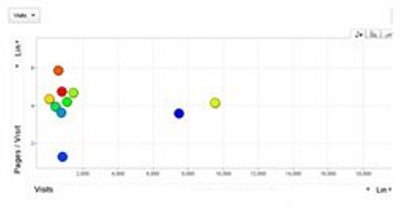
The reason you should avoid reporting data via these charts to your clients is simple.
Most people have no idea what you are trying to communicate via these charts.
Use these charts only when your target audience is as data-savvy as you.
How to change the chart type in Excel ?
MS Excel allows you to change the chart type.
For example, you can convert a clustered column chart into a stacked column chart. Or you can convert a column chart into a bar chart.
For example, let’s convert the following column chart into a bar chart:
Follow the steps below to change the chart type in excel:
Step-1 : Open MS Excel and navigate to the spreadsheet which contains the chart you want to edit
Step-2 : Select the chart, and then from the ”Design’ tab, click on the ‘Change Chart Type’ button:
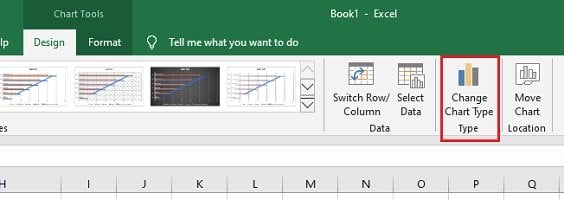
You will now see the ‘Change Chart Type’ dialog box like the one below:
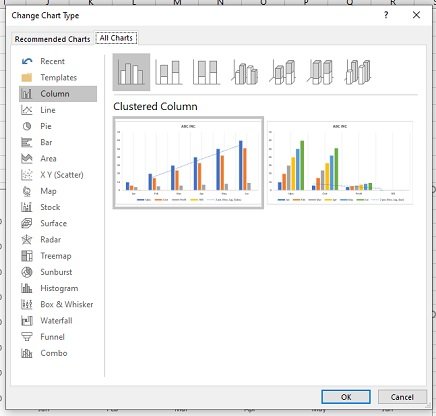
Step-3 : Click on ‘Bar’ (from the left-hand navigation) and then click on the ‘OK’ button:
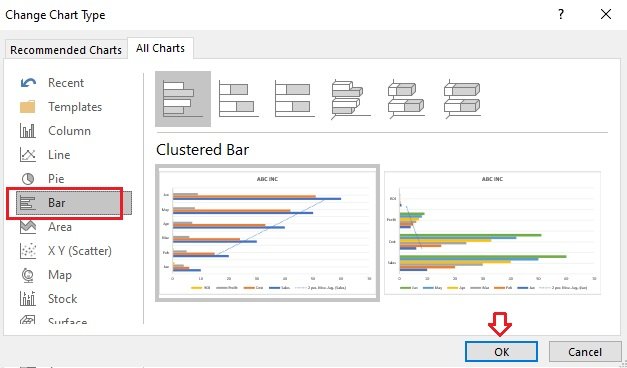
Excel will now change your column chart into a bar chart:
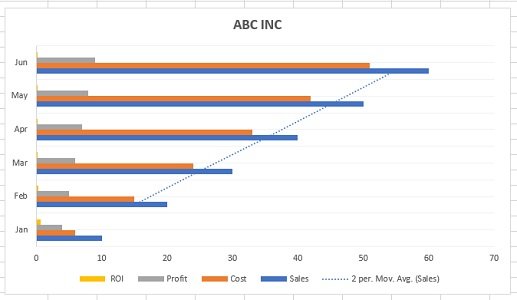
What is data visualization in Excel?
Data visualization is the presentation of data (both qualitative and quantitative data) in graphical format.
In Excel, charts and graphs are used to make a visual representation of data.
What are the benefits of data visualization
Through data visualization you can easily:
- Visualize data (make sense of data, especially big data)
- Classify and categorize data
- Find a relationship among data
- Understand the composition of data
- Understand the distribution of data
- Understand the overlapping of data
- Determine patterns and trends
- Detect outliers and other anomalies in data
- Predict future trends
Data presentation is a very important skill for an optimizer (marketer, analyst). In fact, it is so valuable that LinkedIn lists it as one of the top skills that can get you hired.
Excel charts are commonly used for data visualization and presentation. But selecting the right Excel chart is always a challenge.
If you use an incorrect Excel chart for your analysis, you may misinterpret data and make the wrong business and marketing decisions.
If you use an incorrect Excel chart for your presentation, stakeholders may misinterpret your charts and take wrong decisions.
Therefore selecting the right Excel chart is critically important.
What are the most common data types that can be visualized?
Following are the most common data types that can be visualized:
#1 Quantitative data (also known as interval/ratio data) is the data that can be measured. For example, ten customers, sales, ROI, weight, etc.
#2 Qualitative data can be classified/categorized but cannot be measured. For example, colors, satisfaction, rankings, etc.
#3 Discrete data – quantitative data with a finite number of values/observations. For example, five customers, 17 points, 12 steps, etc.
#4 Continuous data – quantitative data with value / observation within a range/interval. For example sales in the last year.
#5 Nominal data – qualitative data that cannot be put into a meaningful order (i.e. ranked). For example {Blue, Yellow, Green, Red, Black}
#6 Ordinal data – qualitative data that can be put into a meaningful order (i.e. ranked). For example, {very satisfied, satisfied, unsatisfied, very unsatisfied} or {strong dislike, dislike, neutral, like, strong like}.
The anatomy of an Excel chart
To read an Excel chart, you must understand the various components of the chart.
Consider the following data table in Excel:
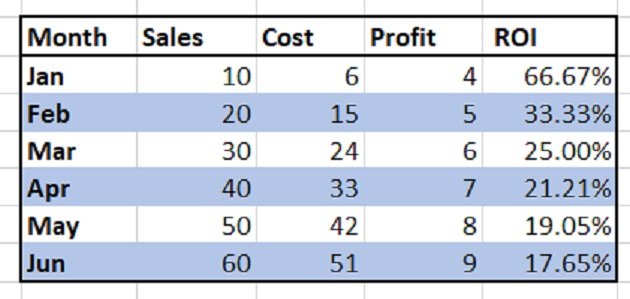
This data table has got five variables : ‘Month’, ‘Sales’, ‘Cost’, ‘Profit’, and ‘ROI’:
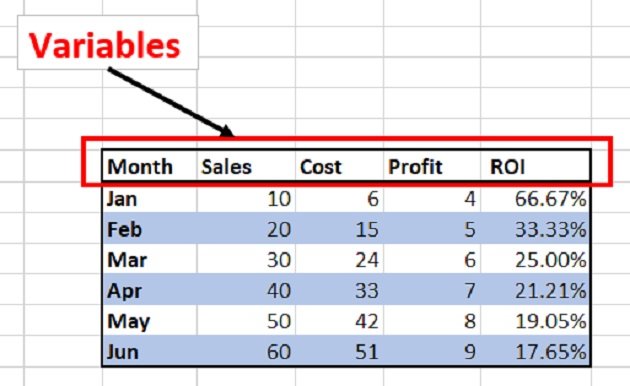
This data table is made up of categories and data series :
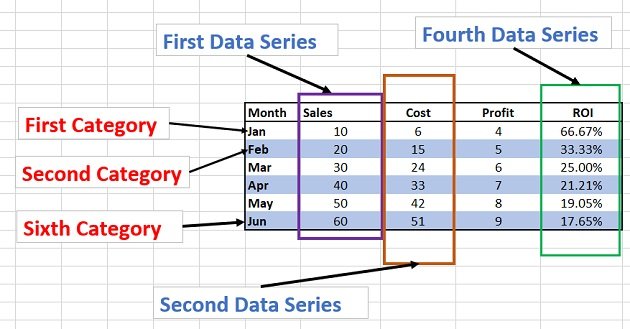
Categories – Here, the first category is ‘Jan’, the second category is ‘Feb’, the third category is ‘Mar’, etc.
Data series – A data series is a set of related data points.
Data points – A data point represents an individual unit of data. 10, 20, 30, 40, etc., are examples of data points. In the context of charts, a data point represents a mark on a chart:
Consider the following Excel chart, which is made from the data table mentioned earlier:
This chart is made up of the following chart elements:

- Primary Horizontal Axis:
- Primary Vertical Axis
- Secondary Vertical Axis
- Primary Horizontal Axis Title
- Primary Vertical Axis Title
- Secondary Vertical Axis Title
- Chart Title
- Data Labels
In Excel, categories are plotted on the horizontal axis and data series are plotted on the vertical axis:
From the chart above, we can conclude the following:
- Months are plotted on the primary horizontal axis.
- Sales, cost, and profit are plotted on the primary vertical axis.
- ROI is plotted on the secondary vertical axis.
Following are examples of other Excel chart elements:
- Data Table with legend keys
- Data Table with no legend keys
- Error bars (Standard Error)
- Error bars (Percentage)
- Error bars (Standard Deviation)
- Primary Major Horizontal Gridlines
- Primary Major Vertical Gridlines
- Primary Minor Horizontal Gridlines
- Primary Minor Vertical Gridlines
- Linear Trendline
- Exponential Trendline
- Linear Forecast Trendline
- Moving Average Trendline
#1 Data table with legend keys
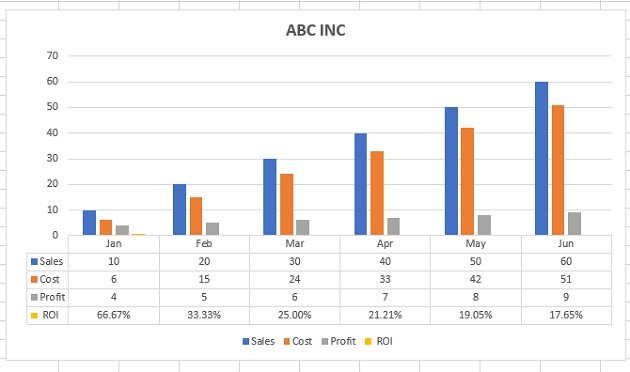
#2 Data table with no legend keys
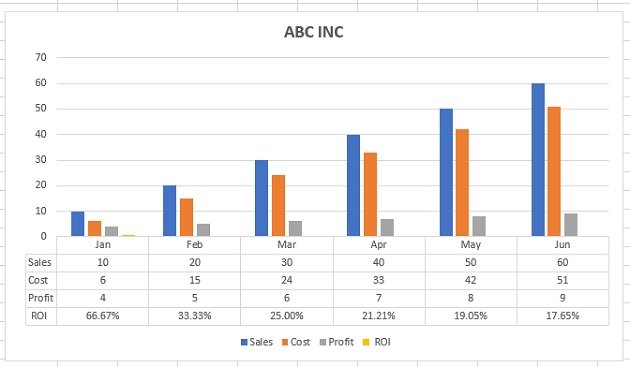
#3 Error bars (standard error)
If you want to see the margin of error as a standard error amount, then use the standard error bar.
About Error Bar An error bar is a line through a point on a graph, parallel to one of the axes, which can help you see margins of error at a glance.
#4 Error bars (percentage)
If you want to see the margin of error as a percentage, use the percentage error bar.
#5 Error bars (standard deviation)
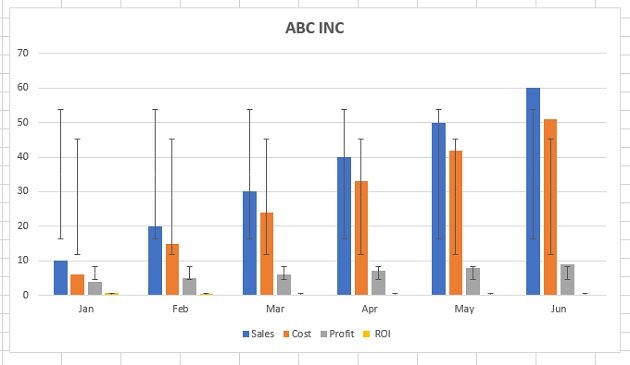
If you want to see the margin of error as a standard deviation, then use the standard deviation error bar.
#6 Primary major horizontal gridlines
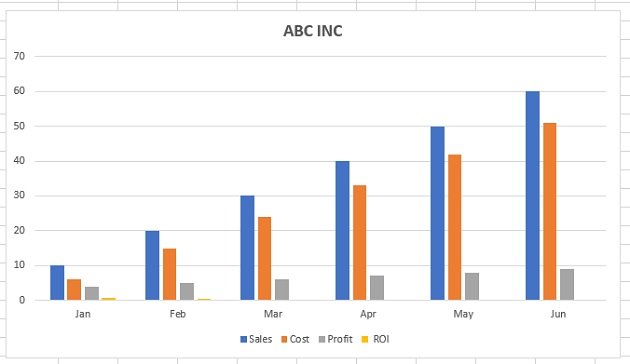
About Chart Gridlines Chart gridlines are the faint lines that appear on the plot area of a chart. They are used to make the data in a chart that displays axes easier to read. They can appear both horizontal and vertical.
#7 Primary major vertical gridlines
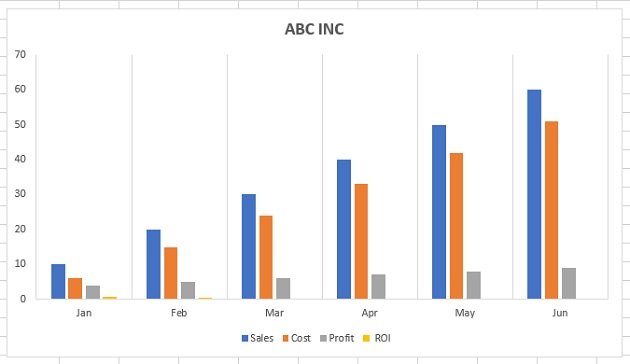
#8 Primary minor horizontal gridlines
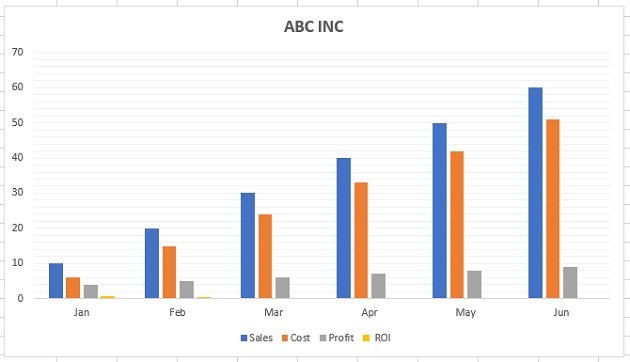
#9 Primary minor vertical gridlines
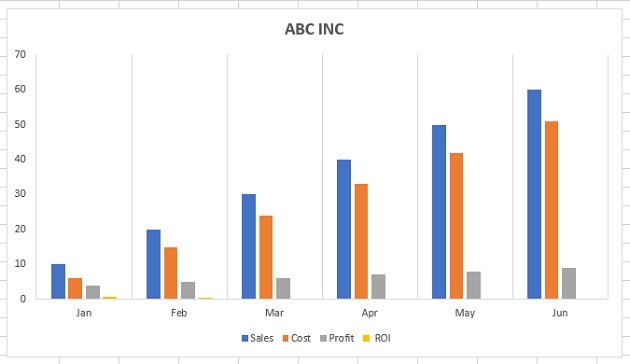
#10 Linear trendline
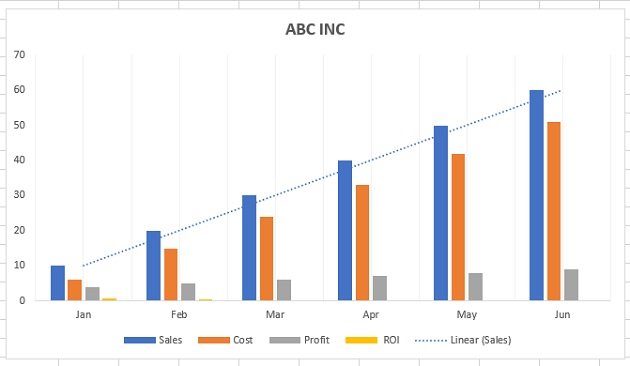
Use the Linear trendline if your data set is linear (resembles a straight line) and the data values are increasing or decreasing at a steady rate.
About Trendlines The trendlines are used to graphically display trends in data. A trend is a movement in a particular direction. A trend can be short (or seasonal), intermediate, or long term. Longer the trend more significant it is. For example, a 3 months trend is not as significant as 3 years trend.
#11 Exponential trendline
Use the exponential trendline if data values increase or decrease at increasingly higher rates.
#12 Linear forecast trendline
Use the Linear forecast trendline if your data set is linear (resembles a straight line), the data values are increasing or decreasing at a steady rate, and you want to forecast the data.
#13 Moving average trendline
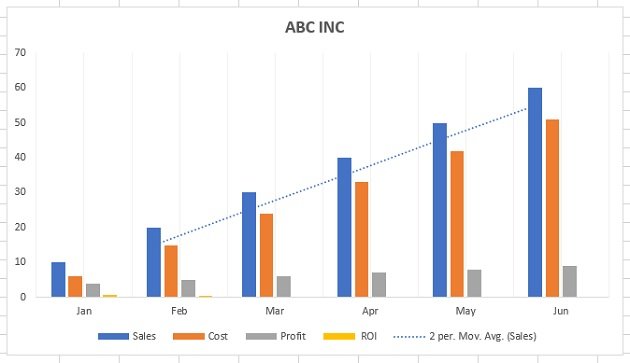
Use the moving average trendline if there is a lot of fluctuation in your data.
How to add a chart to an Excel spreadsheet?
To add a chart to an Excel spreadsheet, follow the steps below:
Step-1 : Open MS Excel and navigate to the spreadsheet, which contains the data table you want to use for creating a chart.
Step-2 : Select data for the chart:
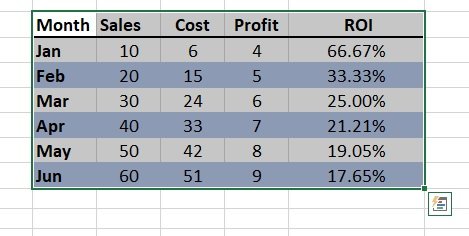
Step-3 : Click on the ‘Insert’ tab:
Step-4 : Click on the ‘Recommended Charts’ button:
Step-5 : Select the chart you want to use from the ‘Insert chart’ dialog box and then click on the ‘ok’ button:
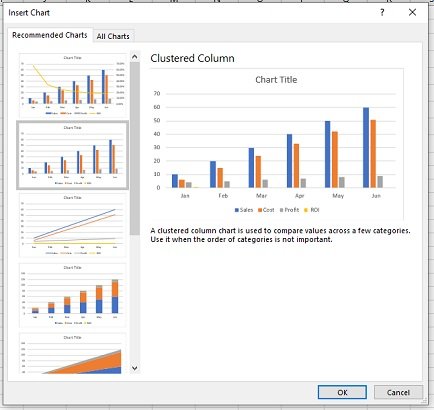
You should now be able to see the chosen chart inserted in your spreadsheet:
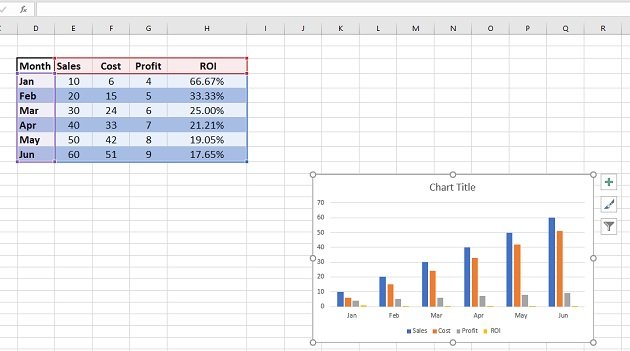
How to add, change, or remove a chart element in Excel?
To add, change or remove a chart element in Excel (2013 or above), follow the steps below:
Step-1 : Open MS Excel and navigate to the spreadsheet which contains the chart you want to edit.
Step-2 : Select the chart, and then from the ”Design’ tab, click on the ‘ Add Chart Element ‘ drop-down menu:
Step-3 : Select the chart element you want to add, change or remove from one of the drop-down menus.
For example, if you want to add a data table to your chart, then click on ‘ Data Table ‘ > ‘ With legend Keys ‘:
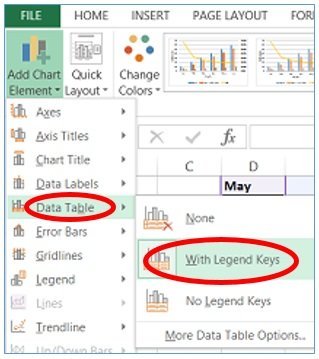
You can now see your chart along with the data table:
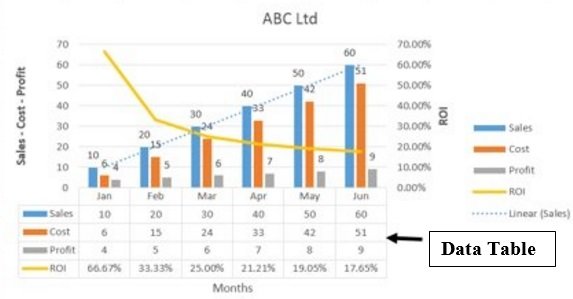
How to add a trendline to a chart in excel?
Follow the steps below:
Step-2 : Select the chart, and then from the ”Design’ tab, click on the ‘ Add Chart Element ‘ drop-down menu.
Step-3 : Click on the ‘Trendline’ drop-down menu and select the type of trendline you want to add to your chart.
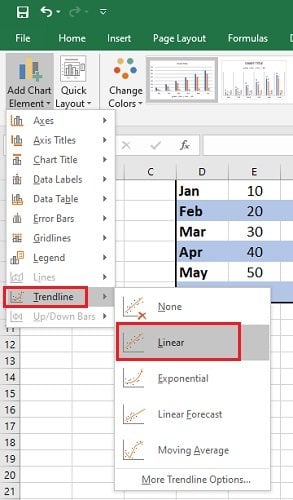
How to change the color or style of a chart ?
Step-2 : Select the chart, and then from the ”Design’ tab, click on the ‘ Change Colors ‘ drop-down menu to change the colours used in your chart:
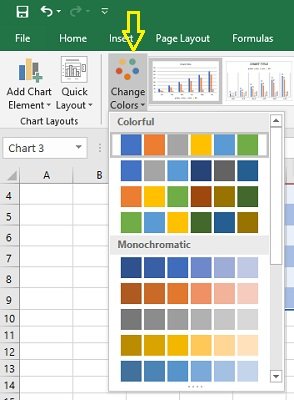
If you want to change the style/design of the chart, then click on one of the styles under the ‘Design’ tab:
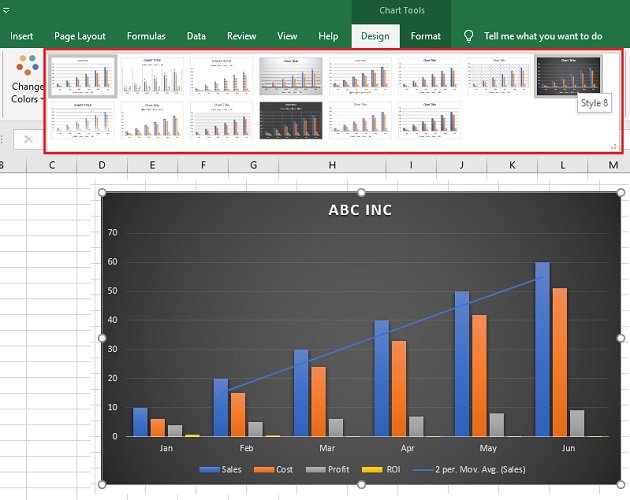
How to build data visualizations in Excel?
You can build a data visualization in excel through the following charts and graphs:
Other articles on Excel charts
- Which Chart Type Works Best for Summarizing Time-Based Data in Excel
- Five Advanced Excel Charts and Graphs
- Data Visualization in Excel Tutorial
- What type of chart to use to compare data in Excel
Articles on data analysis and reporting
- Top 20 reasons why people misinterpret data and reports
- Making Good Marketing Decisions Despite Faulty Analytics Data
- Ten tips to analyse data trends in Google Analytics
- 21 Secrets to Becoming a Champion in Data Reporting
- How to become a champion in data reporting via Storytelling
- Google Analytics Dashboard Tutorial
Frequently asked questions about types of charts in Excel
What is data visualization.
Data visualization is the presentation of data (both qualitative and quantitative data) in graphical format. Through data visualization you can easily: make sense of data (especially big data), classify and categorize data, find relationships among data, understand the composition of data, understand the distribution of data, understand the overlapping of data, determine patterns and trends, detect outliers and other anomalies in data, predict future trends and tell meaningful and engaging stories to decision-makers.
Why is it important to use the correct Excel chart?
If you use an incorrect Excel chart for your analysis, you may misinterpret data and make the wrong business and marketing decisions. If you use an incorrect Excel chart for your presentation, stakeholders may misinterpret your charts and take wrong decisions. Therefore selecting the right Excel chart is critically important.
What is a data series?
A data series is a set of related data points.
What is a data point?
A data point represents an individual unit of data. 10, 20, 30, 40, etc., are examples of data points. In the context of charts, a data point represents a mark on a chart.
What should be the criteria for selecting an Excel chart?
The type of Excel chart you select for your analysis and reporting should depend upon the type of data you want to analyse and report and what you want to do with the data. Do you want to classify and categorize data or find relationships among data or understand the composition, distribution or overlapping of data?
What is quantitative data?
Quantitative data (also known as interval/ratio data) is the data that can be measured. For example, ten customers, sales, ROI, weight etc.
What is qualitative data?
Qualitative data can be classified/categorized but cannot be measured, for example, colours, satisfaction, rankings, etc.
What is discrete data?
It is quantitative data with a finite number of values/observations. For example, five customers, 17 points, 12 steps etc.
What is continuous data?
It is quantitative data with value/observation within a range/interval. For example, sales in the last year.
What is nominal data?
Nominal data is qualitative data that can not be put into a meaningful order (i.e. ranked). For example {Blue, Yellow, Green, Red, Black}
My best selling books on Digital Analytics and Conversion Optimization

Maths and Stats for Web Analytics and Conversion Optimization This expert guide will teach you how to leverage the knowledge of maths and statistics in order to accurately interpret data and take actions, which can quickly improve the bottom-line of your online business.
Master the Essentials of Email Marketing Analytics This book focuses solely on the ‘analytics’ that power your email marketing optimization program and will help you dramatically reduce your cost per acquisition and increase marketing ROI by tracking the performance of the various KPIs and metrics used for email marketing.
Attribution Modelling in Google Analytics and Beyond SECOND EDITION OUT NOW! Attribution modelling is the process of determining the most effective marketing channels for investment. This book has been written to help you implement attribution modelling. It will teach you how to leverage the knowledge of attribution modelling in order to allocate marketing budget and understand buying behaviour.
Attribution Modelling in Google Ads and Facebook This book has been written to help you implement attribution modelling in Google Ads (Google AdWords) and Facebook. It will teach you, how to leverage the knowledge of attribution modelling in order to understand the customer purchasing journey and determine the most effective marketing channels for investment.
About the Author
Himanshu sharma.

- Founder, OptimizeSmart.com
- Over 15 years of experience in digital analytics and marketing
- Author of four best-selling books on digital analytics and conversion optimization
- Nominated for Digital Analytics Association Awards for Excellence
- Runs one of the most popular blogs in the world on digital analytics
- Consultant to countless small and big businesses over the decade
- Privacy Policy and Terms of Use
Privacy Overview
Excel Charts: A Complete Overview
Charts in Excel are used to represent data graphically. There are many types of charts in Excel that you can use based on the data.
In this Excel tutorial, you will learn everything about charts in Excel. You can learn to create a chart, format, move, copy or filter it.
The image below shows a 2-D column chart in Excel. It represents the year-wise sales of the first six months of ABC company.
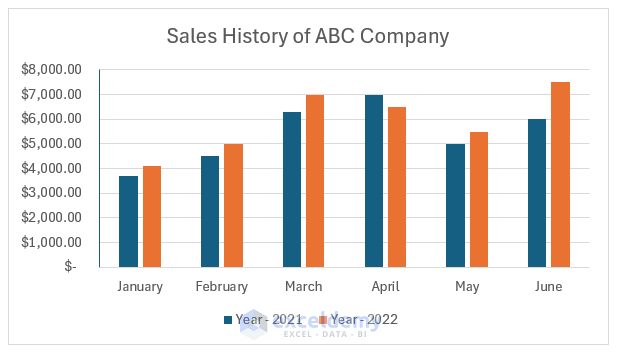
What Is a Chart in Excel?
A chart is a graphical and visual representation of data. In Excel, there are different kinds of charts. You can insert the data in a worksheet and Excel can provide you with beautiful and meaningful charts.
A chart can help viewers to understand the data, trends of the data, and future values easily. Column chart, pie chart, line chart, and bar chart are the most commonly used charts.
Types of Charts in Excel
1. column chart.
The chart that contains the categories on the horizontal axis and values on the vertical axis is called a column chart. It is also called a vertical bar chart. It helps to get an easy comparison between different categories and values.
2. Line Chart
The chart where category data is evenly distributed on the horizontal or X-axis and values are evenly distributed on the vertical axis or Y-axis is called a line chart . A line chart is basically used to show the trend over time.
3. Pie Chart
A pie chart displays one series of data through slices of a pie to understand the proportion or percentage of each item compared to the sum of all items. It is useful when you have only one data series and none of them are zero or less than zero.
4. Bar Chart
A chart where categories are plotted along a vertical axis and values are plotted along the horizontal axis is called a Bar chart . The Bar chart allows users to understand the comparison between individual items. It is available in 2-D and 3-D format in Excel.
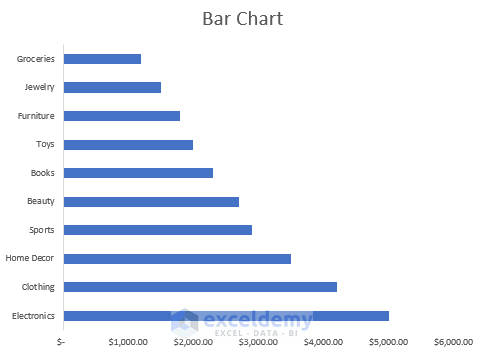
5. Area Chart
An area chart is basically a combination of a bar chart and a line chart. It illustrates the trends over time and total values across a trend. It allows us to compare the connection between parts of a whole. The 3-D format is also available for an area chart in Excel.
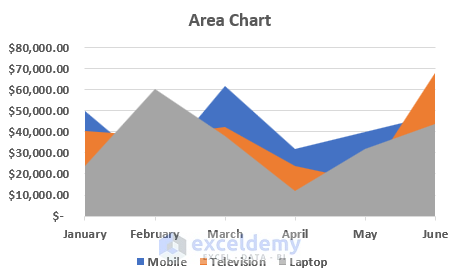
6. Scatter Chart
A scatter chart displays the data point for two variables in a two-dimensional plane. One variable is plotted along a horizontal axis and another is along a vertical axis. The data points are represented by dots in a scattered manner. You need to add more data to your scatter chart to get a better comparison.
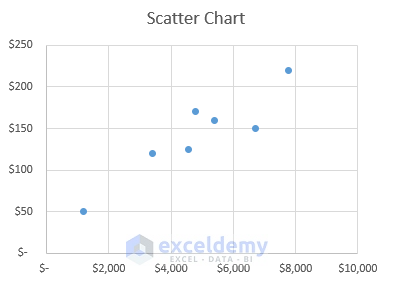
7. Map Chart
A map chart represents the values and categories across geographical regions. But there must be regions/countries/states or postal codes in your data.
8. Stock Chart
A stock chart displays the data of stock price like opening price, closing price, high price, low price, and volume. It helps to understand the fluctuations in stock prices.
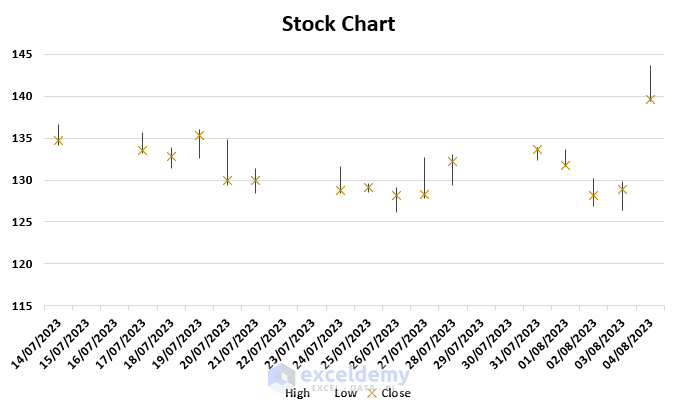
9. Surface Chart
A surface chart is a three-dimensional chart that represents the relations among three sets of data. It uses a topographic map, colors, and patterns to highlight areas for the same range of values.
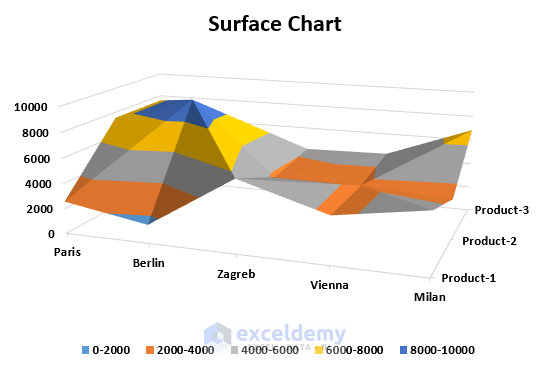
10. Radar Chart
A radar chart is used to compare multiple series of data. It uses several axes to highlight data originating from a central point. And connects data points for each variable using lines and areas.
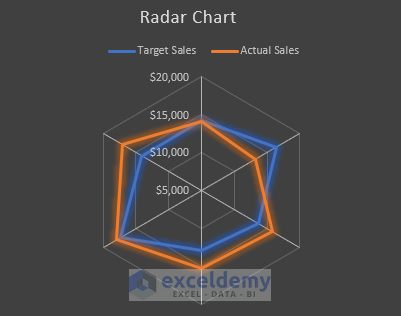
11. Treemap Chart
A treemap chart gives a hierarchical view of your data to compare different levels of category. It uses different colors for categories and is helpful for lots of data that is difficult to highlight in other charts.
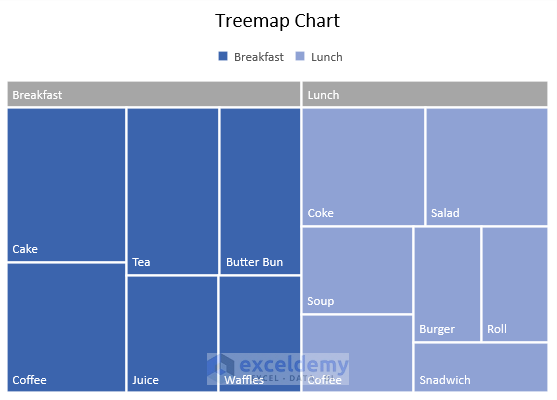
Note: Available on the newer versions since Office 2016.
12. Sunburst Chart
The sunburst chart is also used for displaying hierarchical data. A ring or circle represents each level of the hierarchy and the innermost circle is considered as the top level of the hierarchy. For one level a sunburst chart will look like a doughnut chart.
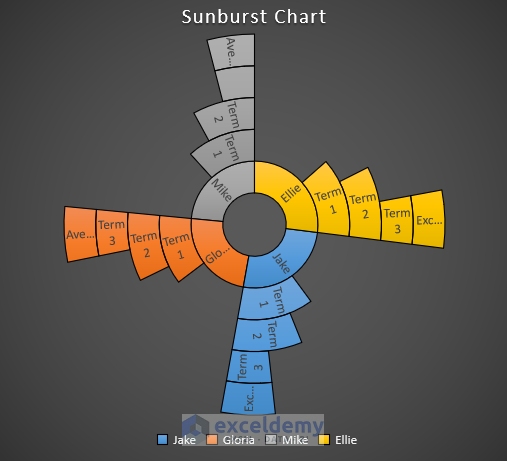
13. Histogram Chart
A chart where data is plotted to show frequencies within a distribution is called a histogram chart . Each column of a histogram chart is called a bin.
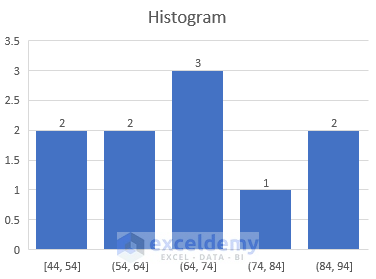
14. Box & Whisker Chart
A box and whisker chart is used to display the distribution of data into quartiles and highlight the mean. The vertical lines through boxes are called “whiskers”. The variability of quartiles is represented by the size of the lower or upper portion of the lines.
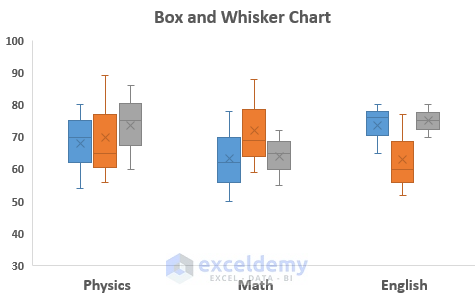
15. Waterfall Chart
A waterfall chart displays the running total of financial data. It helps to understand the effect of any addition or subtraction of data in the total. To differentiate between positive and negative data, color codes are used.
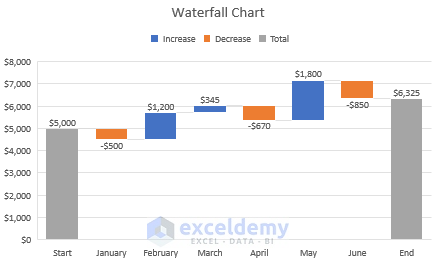
16. Funnel Chart
A chart that displays the values of multiple levels in a process is called a funnel chart . As the values are represented in descending order that’s why the shape of this chart looks like a funnel.
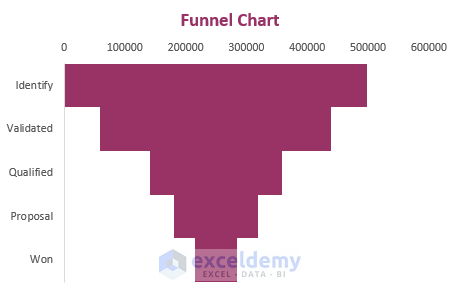
17. Combo Chart
When a chart combines different charts for a wide range of data for better understanding then it is called a combo chart . It includes a secondary axis.
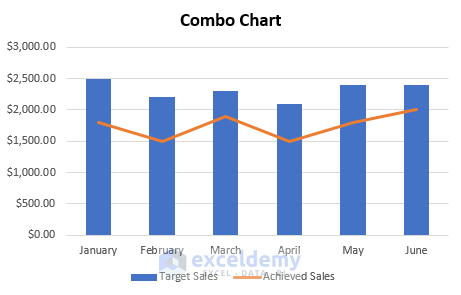
Note: Available on the newer versions since Office 2013.
How to Create a Chart in Excel
We can create a chart in Excel by following some easy steps. Suppose, we have a dataset in the range B4:D10 that contains the yearly sales history of a company.
Let’s follow the steps below to create a chart in Excel:
- Now, click on the Insert Column icon. A drop-down will appear.
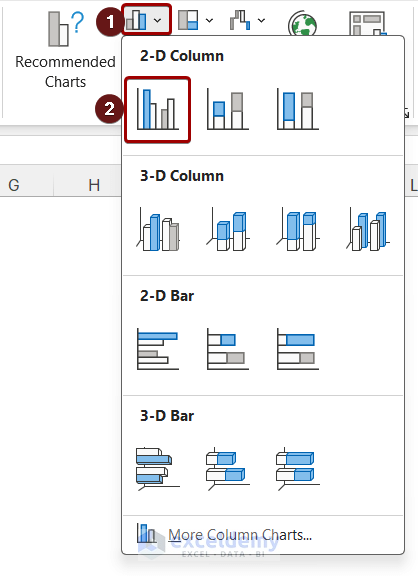
As a result, a Clustered Column will appear on the worksheet.
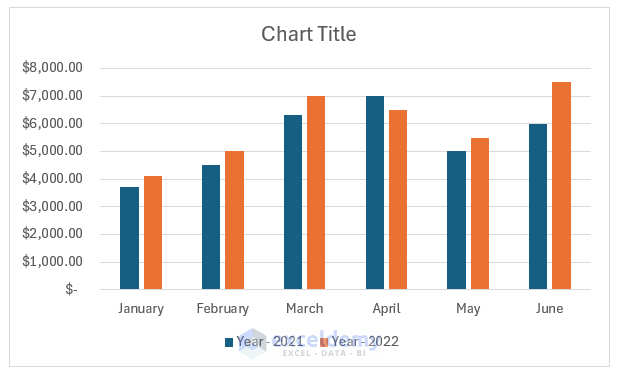
Create a chart using Recommended Charts option:
The ‘Recommended Charts’ option gives different types of charts based on your data. To create a chart using the Recommended Charts, you can follow the steps below:
How to Change Chart Layout and Style in Excel
Changing the chart layout will change the arrangement of different chart elements. To change the layout, follow the steps below:
- Select the chart to get the Chart Design tab on the ribbon.
- After that, click on the Quick Layout option. A drop-down menu will appear.
After selecting the desired layout, the chart will automatically change.
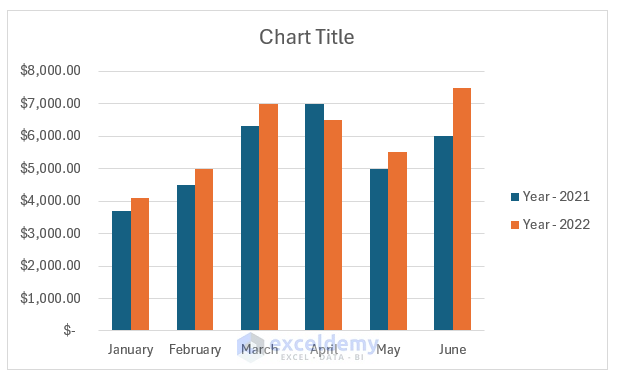
To change the chart style in Excel , you need to follow the steps below:
- Select a style from the Chart Styles group.
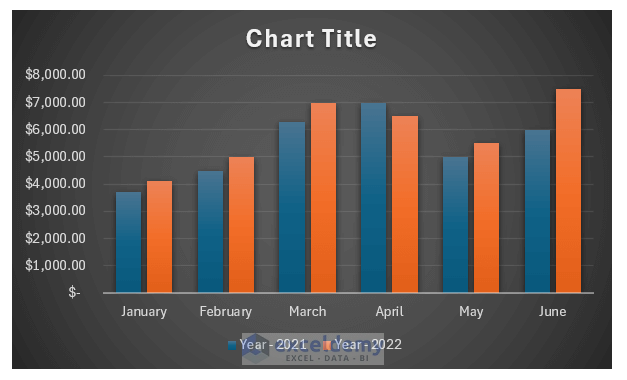
How to Add, Change or Remove Chart Elements in Excel
There are different kinds of elements in a chart in Excel. A chart in Excel contains Axes, Axis Titles, Chart Title, Data Table, Data Labels, Error Bars, Gridlines, Legend, Lines, Trendline, and Up/Down Bars. You can easily add, change, or remove these elements in Excel.
To add a chart element, you can follow the steps below:
- Click on the chart to get the Chart Design tab.
After that, you can see the chart with a data table.
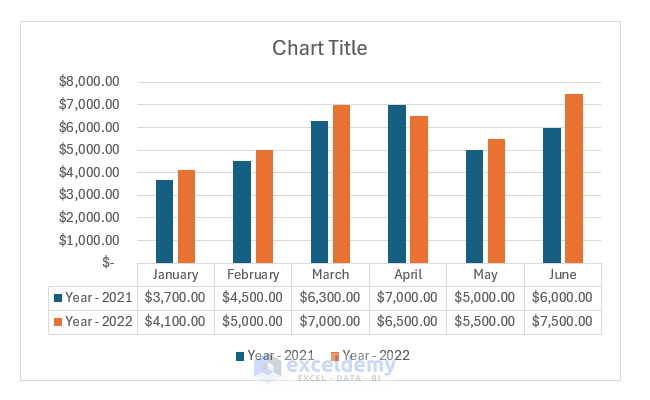
When you select a chart, a plus icon appears on the top-right side. If you click on the plus icon, you will see the chart elements. You can select or deselect the elements to add or remove them.
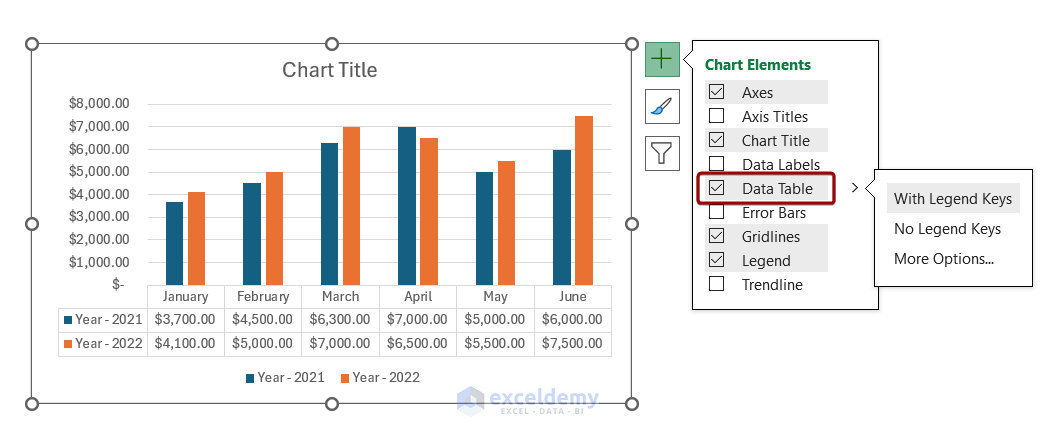
If you double-click on the Data Table, you will get a Format Data Table pane on the right side of the worksheet. You can select different options from there and format the data table.
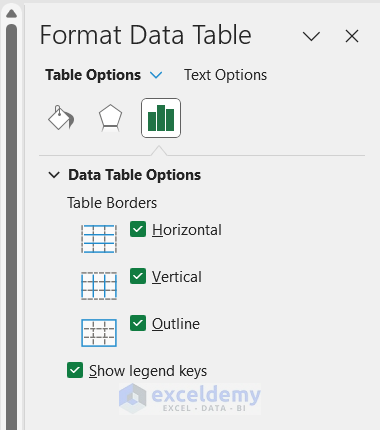
To remove a chart element, select the element and press the Delete key from your keyboard.
How to Switch Row and Column Data in Excel Chart
Sometimes, you may need to change the way a chart groups the data. In that case, you can use the Switch Row/Column option. For example, our chart shows year-wise sales data. To see month-wise data in a year, you can switch row/column.
To switch row/column, you can follow the steps below:
- Select the chart and go to the Chart Design tab.
After selecting the Switch Row/Column option, the chart will look like the image below.
How to Change Chart Type in Excel
After creating a chart, you may need to change the chart type based on the requirement. To change the chart type follow the steps below:
How to Format Charts in Excel
After creating a chart, you need to format it to make it visually attractive. You can format different chart elements to give it a better look. Here are some basic chart formatting in Excel :
1. Format Chart Axis
A chart generally has two axes: X and Y. You can format the axes by following the steps below:
As a result, you will see the changes on the Y-axis. You can follow the same steps to format the X-axis.
You can also change the position of the labels and number system of the axis from the Format Axis pane.
2. Format Chart Title
Chart title is an important element as it gives an overview of the chart. To add or edit a chart title, you can follow the steps below:
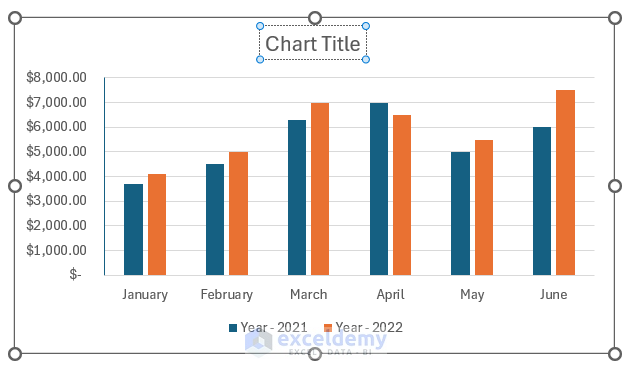
To format the chart title, you can double-click on it. It will open the Format Chart Title pane. Here, we have added a solid fill color to the chart title box. You can also explore different types of Title and Text options from here.
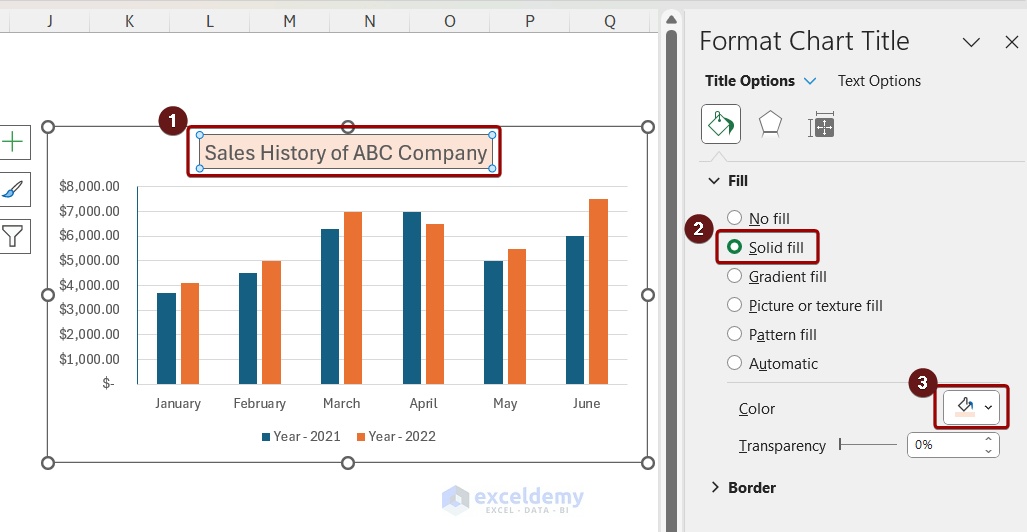
3. Format Legend
To format the legends, double-click on the legend. It will open the Format Legend pane. You can select different options from there.
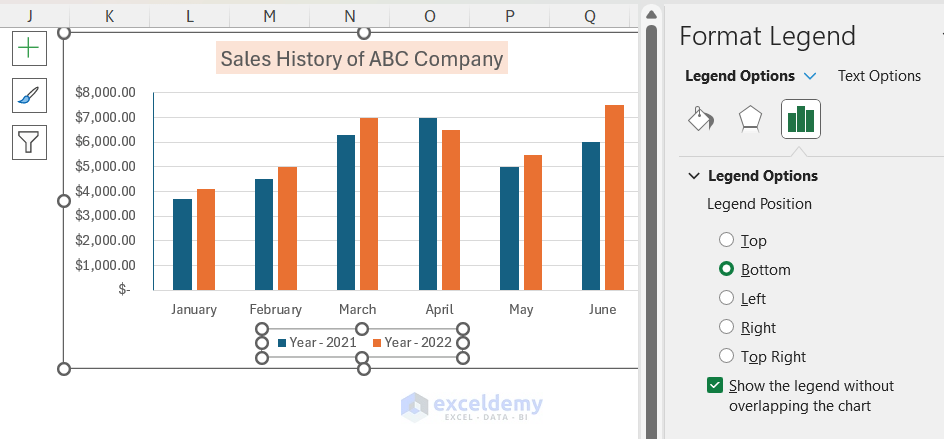
For example, if you select the Legend Position as Right , you will see legends like the image below.
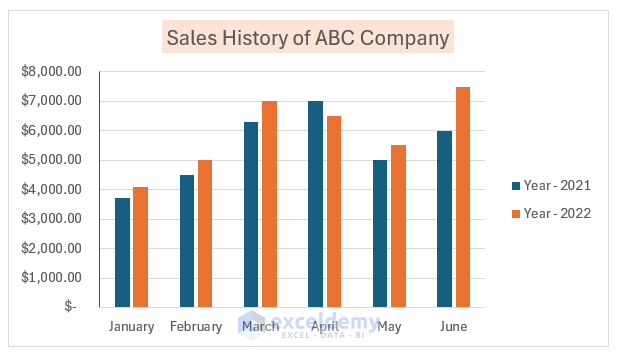
4. Format Data Label
Before formatting the data label, you need to add them to the chart. To add data labels, you can follow the steps below:
- Select the chart > click on the plus icon.
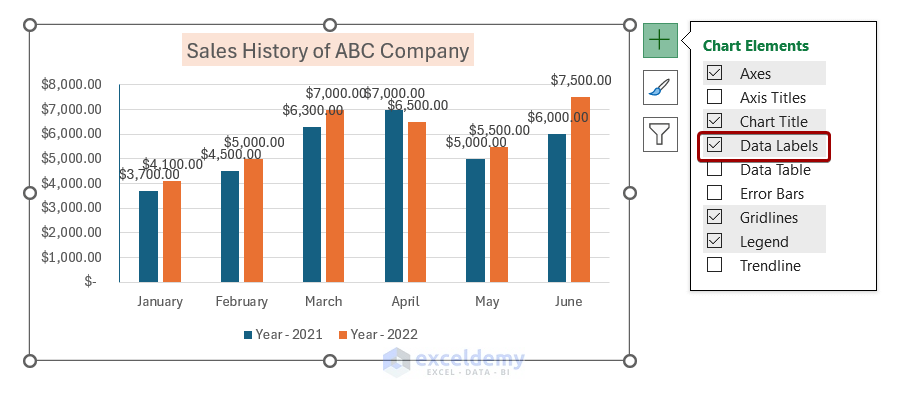
After adding data labels, you can format them using the following steps:
- Double-click on the data labels to open the Format Data Labels pane. You can select different options for different purposes. Here, we will change the number formatting of the data labels.
- To change the number formatting, go to the Number section.
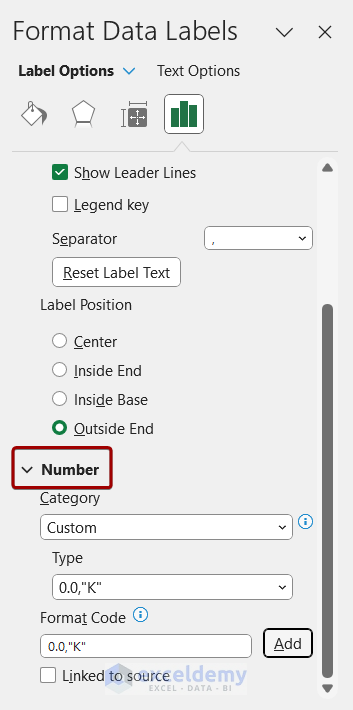
5. Format Data Series
We can format the data series to make the charts look more attractive. To do so, you can follow the steps below:
- Double-click on the data series to open the Format Data Series pane.
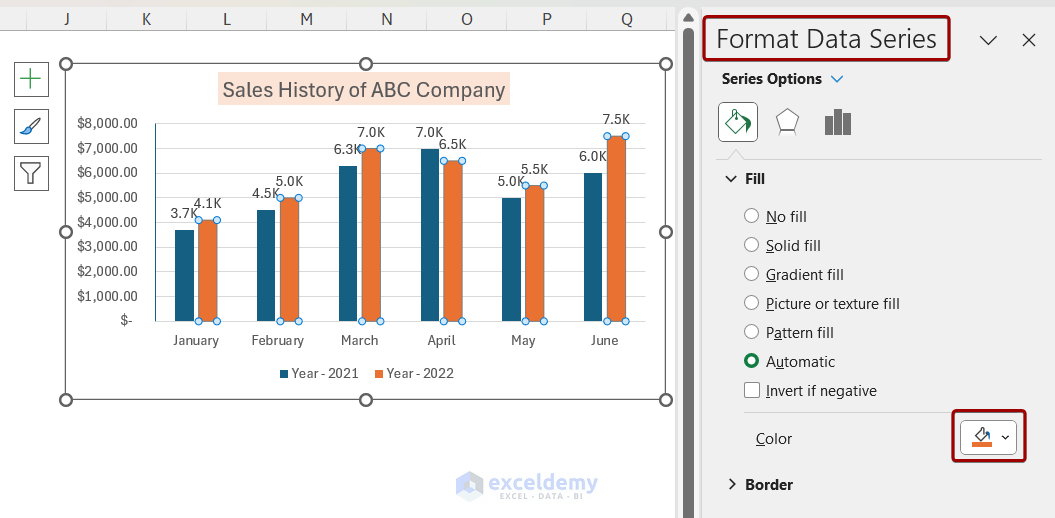
6. Format Chart Area
You can format the chart area and change its color to make the chart report-friendly. To format the chart area, follow the steps below:
- Double-click on the chart area to open the Format Chart Area pane.
As a result, you will see the color of the chart area has been changed.
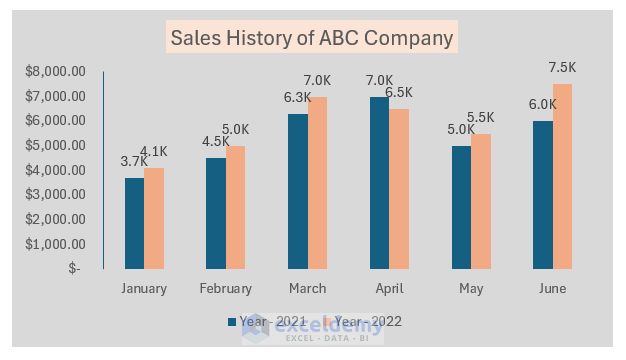
How to Move a Chart in Excel
In Excel, there are times when you need to move the chart to a different sheet. You can do that using the Move Chart option easily. Follow the steps below to move a chart in Excel:
- Select the chart to get the Chart Design option.
As a result, the chart will be moved into a new sheet.
You can also move the chart as an object on a different sheet. You need to select the second option from the Move Chart box and choose the desired worksheet.
How to Copy a Chart in Excel
While creating dashboards or reports, you need to copy a chart . You can copy a chart and paste it on any location. Follow the steps below to copy a chart:
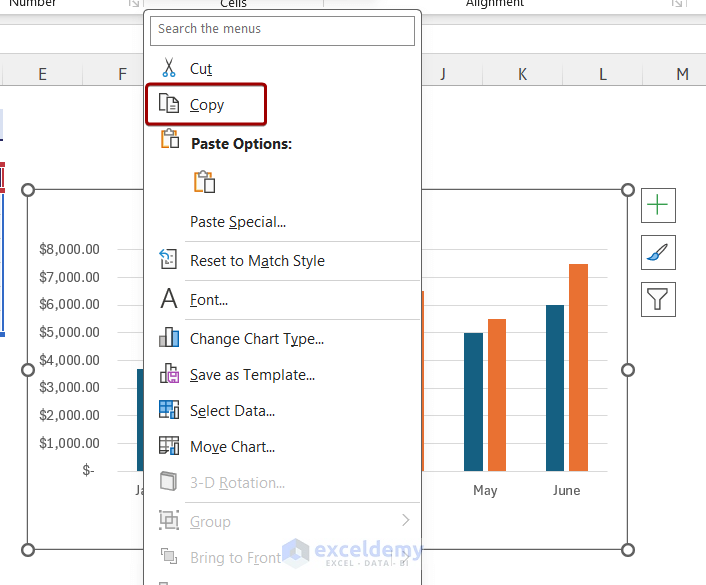
How to Resize a Chart in Excel
Resizing a chart is often necessary when you are working with a lot of data. You can resize the chart using the double-headed arrow. To resize a chart, follow the steps below:
- Select the chart and place the cursor on the small circle of the chart. The cursor will change into a double-headed arrow.
You can also resize the chart using the Format tab. Click on the chart and the Format tab will appear. You can resize the chart from the Size group.
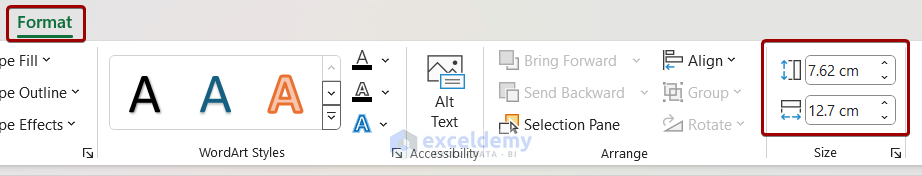
How to Filter Chart in Excel
Filtering a chart can help you visualize a specific amount of data in Excel. To filter a chart, you can follow the steps below:
- You can check/uncheck Series and Categories from the filter options. Here, we unchecked April and May from the Categories section.
After applying the filter, the chart will show the selected data.
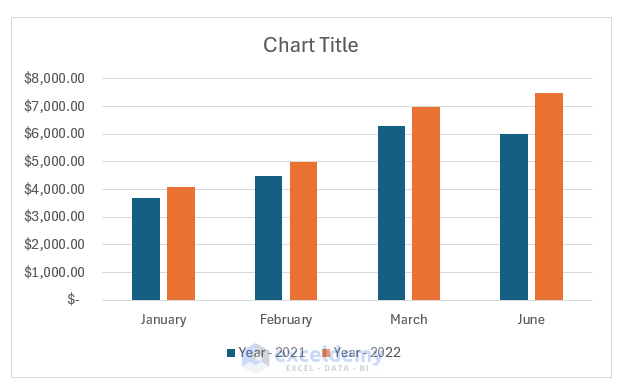
How to Keep Charts Up to Date in Excel
Sometimes, after creating a chart, we need to add new data to the chart. In that case, the chart doesn’t update the data automatically. For example, if we add the data for July to the chart, the chart doesn’t update the data.
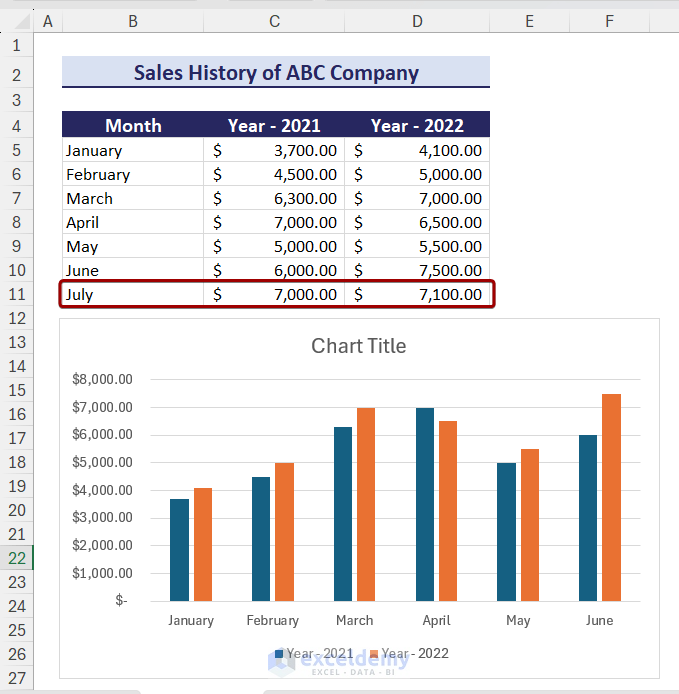
To keep charts up to date, you can follow the steps below:
- Select the chart area and the chart data will be selected automatically.
As a result, the chart will also show the new data.
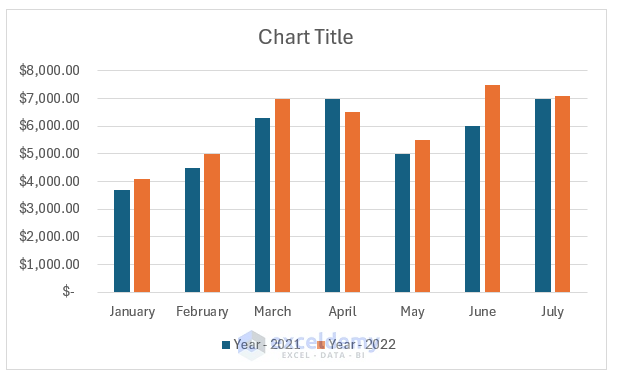
Tips: Before creating a chart, you can convert the chart data range into a table and then, create a chart using the data. In this way, the new data will automatically be updated on the chart.
How to Select the Best Chart in Excel
There are many types of charts in Excel. To select the best type of chart, you need to understand what type of data you are working with. You need to keep the following things in mind while selecting the chart:
- Understand the data
- What you need to show through your chart
- Identify the chart type
- Determine patterns and trends
- Different charts for different data
Download Practice Workbook
In this article, we have described everything related to charts in Excel. You can create, format, and customize using different steps in Excel. You can also learn to move, copy, and resize charts from this article. In Excel, there are many types of charts and each one has different uses. This article will help you to learn everything. If you have any queries or suggestions, let us know in the comment section.
Excel Charts: Knowledge Hub
- Create Embedded Chart in Excel
- Refresh Chart in Excel
- Use Chart Elements in Excel
- Add a Trendline in Excel
- Customize Excel Charts
- Excel Axis Scale
- Data for Excel Chart
- Add Data Series in Excel Chart
- Add a Data Table with Legend Keys
- Create Dot Plot in Excel
- Create Thermometer Chart in Excel
- Bubble Chart in Excel
- Excel Doughnut Chart
- Excel Pareto Chart
- Burndown Chart in Excel
- Excel Distribution Chart
- Make a Comparison Chart in Excel
- Progress Chart in Excel
- Excel Control Chart
- How to Plot an Equation in Excel
- Excel Chart Not Working
- Excel Advanced Charting
- Find Intersection of Two Curves in Excel
- Show Intersection Point in Excel Graph
- Create a Weight Loss Graph in Excel
- Make a Budget Constraint Graph on Excel
- Create Mekko/Marimekko Chart in Excel
- Create Activity Relationship Chart in Excel
- Secondary Axis in Excel
- Markers in Excel
- Dynamic Excel Charts
- Matrix Chart in Excel
- Meter Chart in Excel
- Excel Standard Curve
- Gantt Chart in Excel
<< Go Back To Learn Excel
What is ExcelDemy?
Tags: Learn Excel

Mursalin Ibne Salehin holds a BSc in Electrical and Electronics Engineering from Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology. Over the past 2 years, he has actively contributed to the ExcelDemy project, where he authored over 150 articles. He has also led a team with content development works. Currently, he is working as a Reviewer in the ExcelDemy Project. He likes using and learning about Microsoft Office, especially Excel. He is interested in data analysis with Excel, machine learning,... Read Full Bio
Leave a reply Cancel reply
ExcelDemy is a place where you can learn Excel, and get solutions to your Excel & Excel VBA-related problems, Data Analysis with Excel, etc. We provide tips, how to guide, provide online training, and also provide Excel solutions to your business problems.
Contact | Privacy Policy | TOS
- User Reviews
- List of Services
- Service Pricing

- Create Basic Excel Pivot Tables
- Excel Formulas and Functions
- Excel Charts and SmartArt Graphics
- Advanced Excel Training
- Data Analysis Excel for Beginners

Advanced Excel Exercises with Solutions PDF

- Courses Business Charts in Excel Master Excel Power Query – Beginner to Pro Fast Track to Power BI View all Courses
- For Business
- Power Excel
- Dashboards, Charts & Features
- VBA & Scripts
Business Charts in Excel course is NOW AVAILABLE! Discover more

Create Business charts that grab attention AND auto-update. Wow your coworkers and managers with smart time-saving techniques.

Power Query is essential for Excel users who work with lots of data. This course teaches you how to use Excel in Power Mode and create meaningful reports with far less effort.

Stay ahead of the game in 2024. Get access to our best-selling Power BI course now and become a highly sought-after Power BI professional. This course gets you started in Power BI – Fast!

How to Best Present Charts in PowerPoint
Have you ever been tasked with presenting a chart or a graph in a meeting?
If you are using PowerPoint during the presentation, the way you setup the PowerPoint slide matters.
Let’s look and a normal (otherwise known as “boring and confusing”) slide and compare it to an engaging and much more understandable slide, both of which tell the same story, but one performs the task to a greater degree of professionalism.

Watch video tutorial
In this tutorial:
- The Scenario
- Pros and Cons of Both Presentations
- Why is Animation so Discouraged in the Business World?
- Let’s Use Animation EFFECTIVELY!
- Finding the Three Largest Values
- Add the New Series to the Chart
- Let’s Calculate Change to Budget
- Transferring the Charts to a PowerPoint Slide
- Time to Start Animating
- Testing the Dynamic Nature of the Chart
You are the manager and an associate is presenting data from an Excel workbook in a PowerPoint presentation.
Presentation #1 – No Animation

Here are the main points being conveyed by the associate:
- The countries with the highest sales are USA, Germany, and India.
- Although USA has the greatest sales in absolute terms, there is a large negative deviation to budget due to an unplanned shutdown. Germany is also behind budget, though not to as great a degree as USA.
- India is ahead of budget by more than 20% due to a successful product Launch
Presentation #2 – with Animation
The same information is conveyed, but by bringing in the objects one at a time, and in time when they are discussed, the information is not only easier to understand, but each additional block of information has greater impact. But why does animating the chart(s) add so much to the conversation.
Let’s look at the pros and cons.
Presentation #1
- All the information is presented the moment the slide appears. The audience does not know where to apply their attention regarding what you are discussing; they lose focus.
- The audience will begin examining data that is not being discussed and attempt to infer what the information about.
- The audience is no longer listening to the presenter and key points being discussed are missed due to the lack of audience focus.
- It’s difficult to identify individual characteristics of the data when all data points are the same color.
- The slide was easy to make.
- More time to surf the Web for exciting XelPlus videos. 😊
Presentation #2
- Takes more time to craft the story.
- Need to invest some time learning a few animation skills in PowerPoint.
- Not as much time to surf the web for exciting XelPlus videos.
- The information appears on the screen as the story points are made by the presenter.
- Audience focus is maintained resulting in no missed information, reduced confusion, and increased comprehension.
- Story points are easily seen due to color changes.
- Audience doesn’t have to play “Match the Visual with the Speaker’s Message”.
As with any tool, misuse of the tool can bring about a negative reputation.
Too many business presentations use visually jarring, distracting, or confusing animation. Animation that serves no purpose, other than to showcase the PowerPoint skills of the presenter, is a BIG problem with most animated slideshows.
Animation should serve a purpose; it should help tell the story. If you can point to a piece of animation and ask, “How does this help make the message easier to understand?”, and the answer is, “It doesn’t”, GET RID of the ANIMATION!!!
As with every element in a story, if it doesn’t help push the story in a positive direction, it shouldn’t be part of your story.
This will require a tag-team effort between Excel and PowerPoint. Our data and charts will be created in Excel but animated in PowerPoint.
Begin with Excel
Below is our data set.

Start by creating a chart for the Country vs. Actual information. We’ll select cells A3 through B10 and then select Insert (tab) -> Charts (group) -> 2D Clustered Column ( top left ).

Apply the following modifications to the chart:
- Right-click on a bar and select “Add Data Labels”
- Delete the vertical axis
- Remove the horizontal gridlines
- Delete the title (we’ll have our own title in the PowerPoint presentation)
- Right-click on a bar and select “Format Data Series”. Under “Series Options” (bar chart icon), set the Gap Width to 80% to bring the bars closer together.
- Select the “Fill & Line” icon (tilted paint bucket) and set the fill color to a solid gray.
The result should appear as follows.

We now need to create a second series of data that will highlight the bars of the top three countries in a different color. Because Conditional Formatting doesn’t work with charts, we must use a bit of chart trickery to get the look we a striving for. The best part about the second data series is that PowerPoint will allow us to display them in sequence, giving us the illusion of changing the color of the bars.
- Select cell D3 and add the title “ 3 Largest Sales ”.
- Select cell D4 and enter the following formula:
This formula answers two questions:
- (using LARGE ) – Is the value of B4 greater than or equal to the 3 rd largest value in range B4:B10 ?
- (using IF ) – If so, display the value in cell B4 ; otherwise, display nothing ( two double-quotes ).
Fill the formula down from cell D4 through cell D10 and observe the results.

We will add the new column of “3 Largest Sales” values to the existing chart.
Right-click the chart and click “ Select Data… ”.

In the Select Data Source dialog box, click the “ Add ” button on the left under “ Legend Entries (Series) ”.

In the Edit Series dialog box, set the “ Series name ” to =Start!$D$3 and the “ Series values ” to =Start!$D$4:$D$10 .
NOTE: In your spreadsheets, replace the word “Start” with the name of the sheet that contains the data.

Our updated chart should appear as follows.

ANOTHER NOTE: A super cool way to add the new data series to the chart is to highlight the data and it’s heading (cells D3:D10 ) and click COPY (or CTRL-C ). Next, click in the corner of the chart and click PASTE (or CTRL-V ). Like magic, the new data appears.
The chart needs a small amount of tweaking to be perfect, so select the second data series and perform the following actions:
- Set the Fill color to light green
- Set the Series Overlap to 100%
As an added touch, set the chart’s border ( Shape Outline ) to No Outline . The result should appear as follows.

Our second chart will calculate the variance from Actual to Budget. The formula is quite simple.
Select cell E3 and add a heading, such as “ Change ”, and select cell E4 and enter the following formula.
Fill the formula down from cell E4 to cell E10 .

To create the second chart for variance, select cells A3:A10 , press and hold the CTRL key and select cells E3:E10 . Add the second chart the same way you created the first chart: Insert (tab) -> Charts (group) -> 2D Clustered Column ( top left ).

The second chart is not easy to understand…

… so, we’ll perform the following modifications:
- Remove the Chart Area fill color ( No fill ). This will make it easier to see the two chart’s data when placed close to one another.
- Delete the vertical axis.
- Delete the horizontal gridlines.
- Add data labels to the bars.
- Set the Gap Width to 500%.
- Remove the title.
- Position the chart below the first chart and set them to as close to the same width as you can.
- Set the chart’s border (Shape Outline) to No Outline.

A modification that is not as straightforward as the previous is the removal of the horizontal axis labels ( country names ).
You would think it would be as simple as selecting a country and pressing the Delete key on the keyboard. It can be that simple, but that technique is too destructive. We want to remove the country names but not the horizontal line that represents the axis.
To remove the country names without affecting the line, select a country name. In the Format Axis panel select Axis Options -> Labels -> Label Position and set the dropdown to None .

A nice touch would be to have the negative value bars formatted in a different color. To achieve this, select a bar in the lower chart. Next, in the Fill options, check the box labeled “ Invert if negative ” and set the color to the same light green as the first chart.
Once the first ( positive ) color is set ( the same light green as in the first chart ), a second color picker will appear allowing you to select the negative value color. We’ll set ours to light orange .

The result is as follows.

If we were to leave the charts in Excel, a common strategy would be to group the charts together as a single object. This makes moving and resizing easier.
Because we wish to send these charts to a PowerPoint slide, we can’t group them together. Grouped object are rendered as pictures in the destination application, thus losing much of the chart functionality.
Our strategy will be as follows.
- Select a corner of the first chart and click COPY ( or CTRL-C ).
- Switch to PowerPoint and select the destination slide.
- Click the bottom part of the PASTE button and select “ Keep Source Formatting & Ling Data (F) ”.
- Perform steps 1-3 on the second chart.
- Position and resize the charts as you see fit.

Because we retained full chart functionality in our pasted charts, you can feel free to change chart colors, font sizes, or add/remove features without affecting the original charts in Excel. Because we are likely to show this to a group of people, we can do things like make the data labels larger. This makes the values easier to read for those farther back in the room.

What IS connected between the Excel charts and the PowerPoint charts is the data. If the data changes in Excel, the Excel charts will automatically update. This update will carry over to the PowerPoint charts to display the same information.
As the charts stands ( see previous image ), it has a lot of information to impart.
We need to bring portions of the chart to the attention of the audience in small doses. This way, we maintain audience focus and improve comprehension.

Animating the Top Chart
Select the first chart ( top ) and switch to the Animations tab.
Although you can select any animation you wish, I find that when working with column charts, the Wipe effect is visually effective.
The Wipe effect gives the chart the illusion that the bars are “growing” out of the horizontal axis.
The default effect is to bring in the entire chart as a single object. We will change that setting by clicking Animations (tab) -> Animation (group) -> Effect Options -> Sequence -> By Series .

Remember that the first series in our chart are the gray bars and the second series are the green bars.
Animating the Bottom Chart
Select the second chart ( bottom ) and apply the Appear animation to the chart.

As with the Wipe effect used earlier, the entire chart appears in a single instance. We want each data point to appear one after the other. Select a bar in the lower chart and set the Effect Options to animate By Category .

This setting gives us the flexibility to bring each data point onto the screen in time with the telling of our story.
Since many of the data points contain little change, we want to focus on the countries with the most change ( i.e. USA and India. )
We have two main adjustments to apply:
- modify the data points for USA and India to have a Wipe effect, leaving the remaining countries as Appear
- make the data points with little change appear at once. We will make an adjustment to the animation sequence of the countries Canada, Germany, China, and Brazil so they appear as a singe block of data points.
Activate the Animation Pane by selecting Animation (tab) -> Advanced Animation (group) -> Animation Pane .

Expand the animation list for the second chart ( double down arrows ) to reveal the individual animations.

NOTE: There is limited room to display the names of the chart elements. If you are unsure as to which object in the animation list applies to which object in the chart, you can hover over a list item to see the complete name of the associated chart object.

We will use the animation sequence numbers when reference items in the list ( ex: 5 = USA and 10 = India. )

Select USA ( sequence number 5 ) and set the animation effect to Wipe .
Next, change the direction of the Wipe effect for USA ( sequence number 5 ) by changing the Effect Option from From Bottom to From Top . This adjustment is useful because USA has a large negative variance.

For the next four countries, because there is little difference between them, and their amounts are small, we want them to appear simultaneously.
Select sequence numbers 7 , 8 , and 9 ( Germany, China, and Brazil ) and set the Start option to With Previous . This will cause those 3 bars to appear when Canada’s data point ( sequence number 6 ) appears.

Select sequence number 10 ( India ) and set the animation effect to Wipe . The default wipe direction is From Bottom which will work well for positive values.
The result should appear as follows:
To test the chart’s updating feature, we will return to the Excel file and change the Actual value for India to 9,200 . This will produce a different “Top 3” color set.

If we return to PowerPoint, we can see the data has already updated.

If for some reason your chart does not update automatically, you can force an update by selecting Chart Design (tab) -> Data (group) -> Refresh Data .

Practice Workbook
Feel free to Download the Workbook HERE.
Feel free to Download the Slidedeck HERE.
Leila Gharani
I'm a 6x Microsoft MVP with over 15 years of experience implementing and professionals on Management Information Systems of different sizes and nature.
My background is Masters in Economics, Economist, Consultant, Oracle HFM Accounting Systems Expert, SAP BW Project Manager. My passion is teaching, experimenting and sharing. I am also addicted to learning and enjoy taking online courses on a variety of topics.
Need help deciding?
Find your ideal course with this quick quiz. Takes one minute.

Featured Course
Business Charts in Excel

Excel Essentials for the Real World

Visually Effective Excel Dashboards
Master excel power query – beginner to pro, featured tutorials.
Black Belt Excel Package

You might also like...

How to Use SUMIF Function in Excel
How to Insert a Check Mark in Excel

CAGR Formula in Excel

EXCLUSIVE FREE NEWSLETTER
Join between the sheets.
Kickstart your week with our free newsletter covering Excel hacks, Power BI tips, and the latest in AI. You get to stay updated and get all the insights you need, delivered straight to your inbox.
You can unsubscribe anytime of course.
Stay Ahead with Weekly Insights!
Dive into Excel, AI and other essential tech news:
carefully crafted for the modern professional.
Success! Now check your email to confirm your subscription.
There was an error submitting your subscription. Please try again.
#1 Excel tutorial on the net
Create a Chart | Change Chart Type | Switch Row/Column | Legend Position | Data Labels
A simple chart in Excel can say more than a sheet full of numbers. As you'll see, creating charts is very easy.
Create a Chart
To create a line chart, execute the following steps.
1. Select the range A1:D7.

2. On the Insert tab, in the Charts group, click the Line symbol.

3. Click Line with Markers.

Note: enter a title by clicking on Chart Title. For example, Wildlife Population.
Change Chart Type
You can easily change to a different type of chart at any time.
1. Select the chart.
2. On the Chart Design tab, in the Type group, click Change Chart Type.

3. On the left side, click Column.

4. Click OK.

Switch Row/Column
If you want to display the animals (instead of the months) on the horizontal axis, execute the following steps.
2. On the Chart Design tab, in the Data group, click Switch Row/Column.

Legend Position
To move the legend to the right side of the chart, execute the following steps.
2. Click the + button on the right side of the chart, click the arrow next to Legend and click Right.

Data Labels
You can use data labels to focus your readers' attention on a single data series or data point.
2. Click a green bar to select the Jun data series.
3. Hold down CTRL and use your arrow keys to select the population of Dolphins in June (tiny green bar).
4. Click the + button on the right side of the chart and click the check box next to Data Labels.

1/17 Completed! Learn much more about charts > Go to Next Chapter: Pivot Tables
Learn more, it's easy
- Column Chart
- Scatter Plot
- Data Series
- Combination Chart
- Gauge Chart
- Thermometer Chart
- Gantt Chart
- Pareto Chart
Download Excel File
- charts.xlsx
Next Chapter
- Pivot Tables
Follow Excel Easy
Most Popular
- Formulas and Functions
- Conditional Formatting
- Find Duplicates
- Drop-down List
- Index and Match
Become an Excel Pro
- 300 Examples
Charts • © 2010-2024 Popular Excel Topics: Pivot Tables • Vlookup • Formulas • Charts • Conditional Formatting
Charts and graphs in excel
this ppt is about charts in ms excel.there are many types of chart used in ms excel but in this ppt some common types are defined,as line chart,bar,column,area ,scatter chart etc... Read less

Recommended
More related content, what's hot, what's hot ( 20 ), similar to charts and graphs in excel, similar to charts and graphs in excel ( 20 ), recently uploaded, recently uploaded ( 20 ).
- 1. CHARTS AND GRAPHS IN EXCEL PRESENTED BY: ASIYA SALEEM IQRA NEHAL SANISH MEMON MARYAM SAEED SANIA RAHEEM
- 2. CONTENTS : • Introduction to charts. • Types of charts. • How to create/insert charts in EXCEL. • Importance of charts/graphs… • References..
- 3. A ‘chart’: “Any data which is represented graphically” OR “Diagram or graph that organizes and represents a set of numerical or qualitative data.”
- 4. TYPES OF CHART: • Scatter chart • Stock • Surface • Doughnut • Bubble • Radar • histogram
- 5. Common TYPES OF CHARTS • PIE CHART: • BAR CHART: • COLUMN CHART: • AREA CHART: • LINE CHART:
- 6. COLUMN CHART; • Shows the comparison between one or more series of data point. • STACKED: two comparisons of data points for time periods are stacked. • CLUSTERED: comparison of three data series for each time period.
- 7. PIE CHART; • Another frequently used chart is the pie chart. • A pie chart represents the distribution or proportion of each data item over a total value(represented by the overall pie).
- 8. BAR CHART; • A bar chart or bar graph is a chart that represent categorical data with rectangular or vertical bars.
- 9. AREA CHART; • Area charts are like line charts except that the area below the plot line is solid. • And like line charts ,area charts are used primarily to show trends over time or other category.
- 11. LINE CHART: • It is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points called “markers” connected by a straight line segments. • It is often used to visualize a trend in data over Intervals of time.
- 12. HOW TO INSERT A CHART:
- 13. IMPORTANCE OF CHARTS/GRAPHS:
- 14. 1. https://www.keynotesupport.com/exc el-basics/excel-chart-types.shtml 2. https://www.google.com.pk/search?q =charts+and+graphs+in+excel&rlz
- 15. THANK YOU!!
Free Excel Flowchart Templates
By Kate Eby | April 25, 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this guide, we’ve gathered the most useful flowchart templates in Excel. You’ll also learn how to create a flowchart using a template and how to create a flowchart in Excel from scratch. On this page, you’ll find a cross-functional flowchart template , a swimlane flowchart template , a decision flowchart template , a yes/no flowchart template , and more.
Excel Basic Flowchart Template
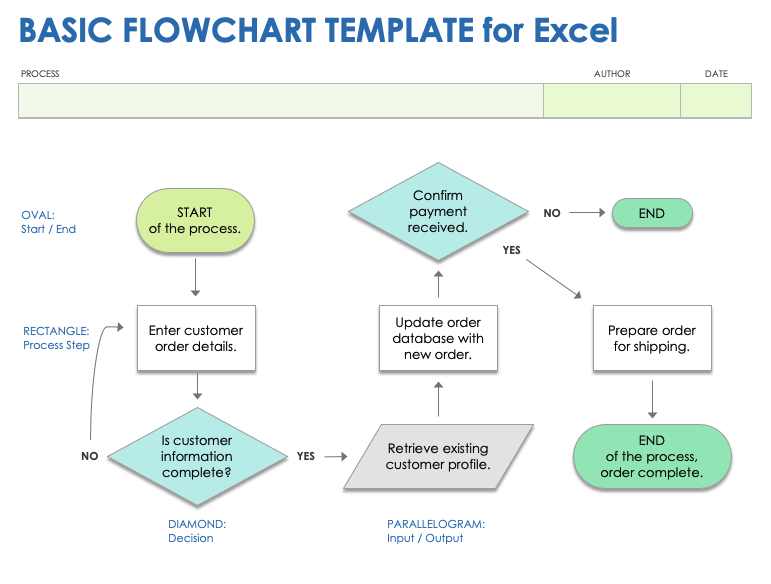
Download the Basic Flowchart Template for Excel
When to Use This Template: This basic flowchart template for Excel is good for documenting or planning a process using straightforward, linear steps. It's perfect for tasks that require clear and simple workflow visualization without complex branching. Notable Template Features: This template highlights each step of a process, big or small, making it easier to identify areas of improvement. Its simple design provides experts and beginners a clear picture of how work flows.
Check out these free flowchart templates in different formats to effortlessly map out your processes, making complex tasks simpler and more understandable.
Excel Cross-Functional Flowchart Template
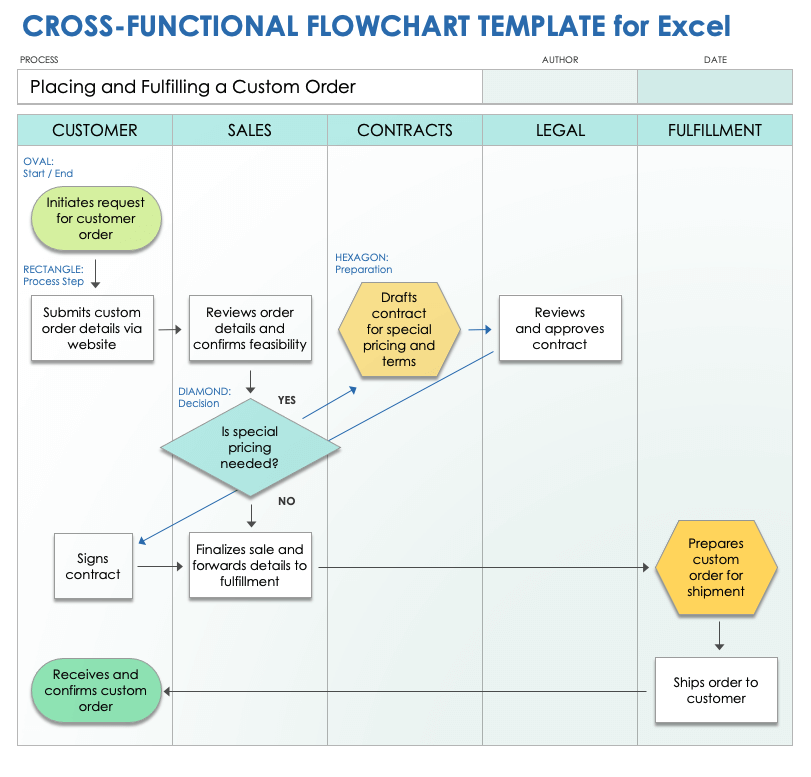
Download the Cross-Functional Flowchart Template for Excel
When to Use This Template: This cross-functional flowchart template shows how different teams or departments are working on a project and how they fit into the big picture. Notable Template Features: This template uses defined columns to easily identify which team is responsible for work. The clear layout stops confusion about who's responsible for each part of a project.
Excel Swimlane Flowchart Template

Download the Swimlane Flowchart Template for Excel
When to Use This Template: This swimlane flowchart template is your top choice for quickly identifying who's doing what at each phase of a big project. Notable Template Features: This template sorts tasks into lanes for different team members or departments.
Excel Decision Flowchart Template
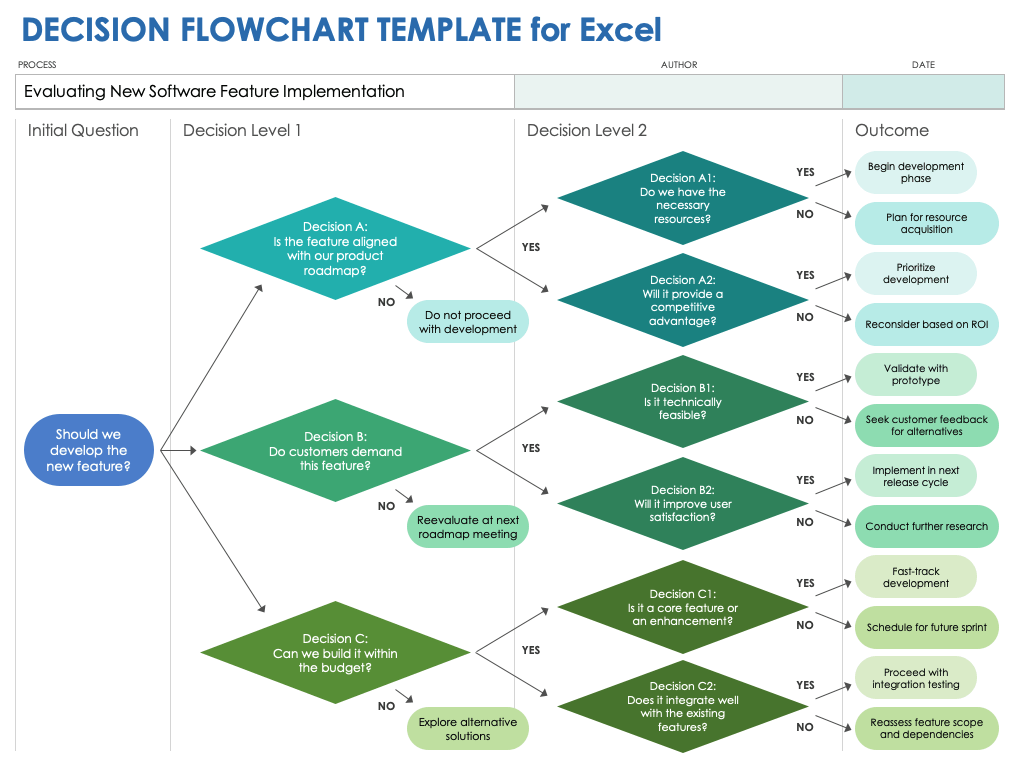
Download the Decision Flowchart Template for Excel
When to Use This Template: Turn to this flowchart template to map out the potential results for a decision you’re trying to make. Notable Template Features: This template simplifies complex decision-making processes by dividing them into straightforward yes or no options divided by decision level, so you can see how your choices at one point affect all those that follow. You can see the potential results of various decisions at every level of the process, clearly illustrating the outcomes of each choice.
Excel Yes/No Flowchart Template
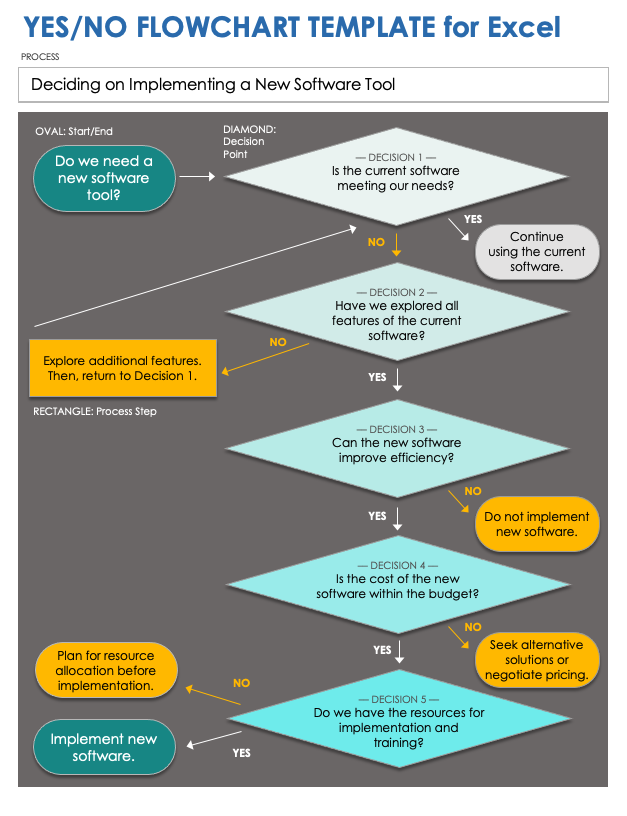
Download the Yes/No Flowchart Template for Excel
When to Use This Template: Use this yes/no flowchart template to make clear-cut decisions fast. It breaks down complex questions into manageable yes or no choices. Notable Template Features: The decision path on this template starts with a yes or no question and guides you to the right outcome. It also plots how different answers lead to different results.
Excel Data Flowchart Template
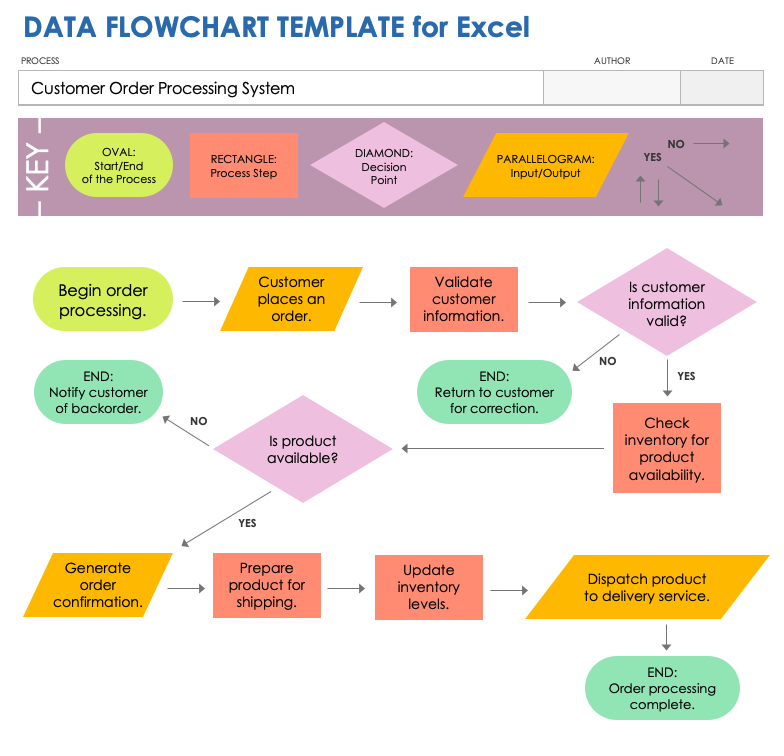
Download the Data Flowchart Template for Excel
When to Use This Template: Pick this data flowchart template to track how data moves and changes across a system or process. Use the template when setting up new systems or trying to improve existing ones. Notable Template Features: This template is designed specifically for data flow mapping, using distinct symbols to represent the collection, processing, storage, and sharing of data. It highlights each step of data interaction, making it easier to identify potential inefficiencies or security risks.
How to Create a Flowchart in Excel Using a Template
By creating a flowchart in Excel using a template, you streamline laying out processes or decisions. The elements you would use in a flowchart are already formatted and placed in the spreadsheet, making it easier to complete. Follow these steps to use a template for efficient and clear flowchart creation:
- Define Objectives Identify what to map out with your flowchart. You could use a flowchart to visualize a new project workflow, improve an existing process, or understand the steps involved in a task.
- Identify Key Steps Outline the main actions, decisions, and outcomes involved in your process. Consider the start point, the end point, and what happens in between in order to break down the process into manageable pieces.
- Gather Necessary Information Collect any details (understanding responsibilities, timeframes, or decision criteria, etc.) that need to be included in each step of the flowchart.
Use an Existing Flowchart Template Download a basic flowchart template for Excel , then rename and save the document.
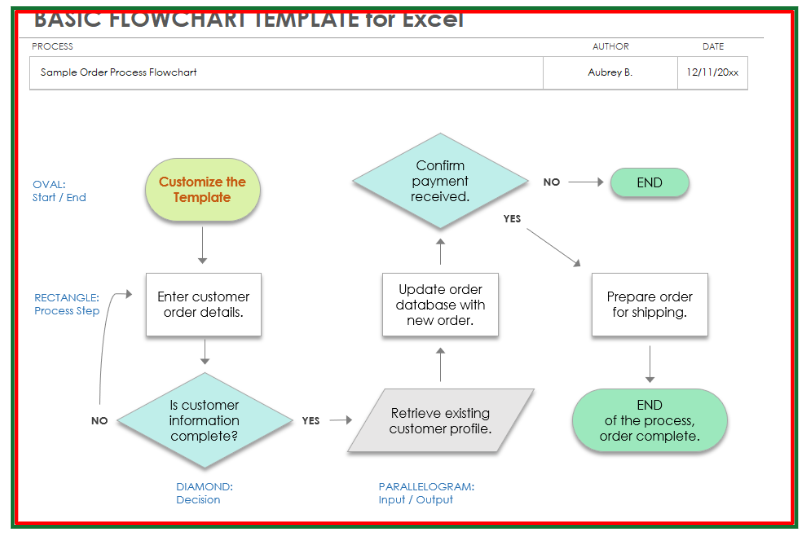
Name the Process Flow Open the template and click on the BLANK - Basic Flowchart tab. In the template’s header fields, enter the name of the process you want to chart, the flowchart’s author, and the creation date.
- Map Out the Process Mark the start of your process with the beginning shape (usually an oval). Click the START oval, select and highlight the existing text, and type the first step in your flowchart process. Repeat the same steps to change the content of each existing element in the flowchart. Use rectangles for actions or tasks, diamonds for decision points, and arrows to show the flow from one step to the next. Pro Tip: Access flowchart shapes in your Excel file by clicking on the Insert menu and clicking Shapes .

- Select the Shape: Click the flowchart shape containing the text you want to modify.
Change Shape Format and Size: Right-click the selected shape, and choose Format Shape . Click the Text Options tab in the formatting pane, and click the Text Box icon. Adjust the font, size, and color by selecting your preferences from the drop-down menus.

Change Shape Size: Click a shape. Click and drag the sizing handles on the corners or sides of the selected shape to resize.
- Review and Refine Once your flowchart is complete, review it for accuracy and clarity. Make sure it correctly reflects the process and is easy to understand. Adjust the layout or text as needed.
- Share Your Flowchart Save your completed Excel flowchart and share it with team members or stakeholders. You can export it as a PDF for easy sharing or print it for discussions and presentations.
How to Manually Create a Flowchart in Excel
You can create a flowchart in Excel by using the shapes feature to draw boxes and arrows to map your process. Making a flowchart in Excel is like drawing a guide to each step. It's helpful for understanding different tasks. Follow these steps to make a flowchart in Excel:
Open a Blank Excel Document Open Excel and click Blank Workbook . Name the workbook, choose a place to save it, and click the Save button.
Start with Shapes In the Excel workbook, click the Insert tab, click the Shapes drop-down arrow, and scroll to Flowchart options. Click on a shape, then click in your Excel spreadsheet to add the shape. Repeat for each shape you want to add to the flowchart.

Tip: Pick shapes, such as the square (for processes), diamond (for decisions), and circle (for start/end points) for your flowchart.
Make Shapes Bigger To provide enough room to write inside the selected shapes, you’ll need to make them bigger. Click a shape, and click Ctrl + A (on a PC and Command + A on a Mac) to select all the shapes. Click a corner on one of the shapes, and drag it to resize all the shapes together.
Personalize the Shapes After enlarging the shapes, double-click a shape to label it (e.g., Start , Task 1 , Process , etc.).
Adjust Font Size as Needed Highlight the text in the shape, and click the Home tab. Change the text size and color using the font collection and font size drop-down menus, respectively.
Connect the Dots Add arrows to the flowchart to draw connections between the shapes. Click the Insert tab, click the Shapes drop-down arrow, and scroll to the Arrow options. Click an arrow, then click the Excel workbook. Resize and re-orient the arrow, and drag it to where it should go in the flowchart.
Title the Flowchart Click the Insert tab, and click Text Box in the toolbar. Click where you want the title to appear on the flowchart and enter a title.
Save and Share the Flowchart Once you've completed your flowchart, save and share it with others.
Related Flowchart Templates
These templates offer extra functionality for creating flowcharts and additional formats. Use any of these templates to improve organization, make decisions, or identify how processes and teams work together.
Free Workflow Templates for PowerPoint
Dive into our selection of PowerPoint workflow templates to show how your workflows boost productivity and enhance team collaboration.
Free Process Mapping Templates
These process mapping templates can help you outline every phase of your business operations clearly for better insight and refinement.
Free Workflow Templates
Explore our workflow templates and use them to improve task ordering and the overall flow of business activities.
Free Business Organizational Chart Templates
Check out these organizational chart templates for small businesses, designed to depict company structure, roles, and reporting lines with clarity.
Free Decision Matrix Templates
Complete one of these unique decision matrix templates to make informed decisions by evaluating various options and their possible outcomes.
Free SIPOC Template

See this suppliers, inputs, process, outputs, customers (SIPOC) diagram template to capture a high-level overview of business processes, from suppliers to customers, in a concise format.
Free Gantt Chart Templates

These Gantt chart templates are ideal for visually organizing project schedules, tasks, and deadlines in a clear, concise format.
Free Project Timeline Templates

Use one of these project timeline templates to present the key phases and milestones of your project from start to finish in an easy-to-understand format .
Get the Most Out of Your Flowcharts with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Improve your marketing efforts and deliver best-in-class campaigns.
How-To Geek
Forget premium tools, here's how i use excel for project management.
Don't pay over the odds for something you can easily do on a spreadsheet.
Quick Links
Use drop-downs, create gantt charts to track progress, create a progress tracker, display due dates and time remaining.
You might be tempted to browse the web for top-of-the-range programs to help you with your project management. But stop—I'm going to talk you through some of Excel's tools that you can use and reuse to efficiently manage your project without having to fork out for expensive software.
Drop-downs are a great way to speed up your work processes, and make your project management system more professional. First, create the options to appear when you click a drop-down cell. Click the "+" at the bottom of your workbook, and double-click the new tab to rename it Options .
I need employee names and task status as drop-down options in my workbook, so I'll create the lists for these here.
Now, create another sheet where the tasks will be managed and rename it Tasks .
After creating a table with the task names on the left and an appropriate header at the top, select the cells that will contain the first drop-down with the options you just created on your Options sheet.
Next, in the Data tab on the ribbon, click "Data Validation."
In the Allow field of the Data Validation dialog box, choose "List." Then, click the Source field arrow, head to your Options sheet, and select the appropriate values for this drop-down. In my case, it's the values underneath the Employee Names heading, and their cell references will then show in the dialog box field. Even though the list of names runs from A2 to A10 on our Options sheet, I've selected A2 to A100 for our data validation, as this means any new names I add to the list will also be picked. Finally, click "OK."
You will then see the list of names appear when you click any cell in the Assignee column.
Now, repeat the process for the Status column, and anytime you want to add a drop-down list to your workbook, you can use and hide your Options sheet to create the choices.
A Gantt chart is a simple but effective table that shows you what task needs to be done in a project and when they need to be completed.
Excel has tools for creating simple Gantt charts , but they are less adaptable than those created from scratch. Keep reading to see how to create a more dynamic Gantt chart.
Step 1: Mark Your Timings Manually
Click "+" at the bottom of your workbook to create a new sheet, and call it Timing . On this new sheet type the tasks' names on the left and the months at the top. Next, map out your proposed timings using manual color fill. It doesn't matter what color you use, as this will be covered up later when we add more settings. Select the first cell you want to color, hold Ctrl, and then select the remaining cells. Then, go to the "Fill Color" drop-down in the Home tab on the ribbon and choose a color.
Step 2: Color the Cells According to Progress
I now want to color the cells according to their status. I'll do this by referring to the status I set for each task on the Tasks sheet set up in the section above. In the first colored cell of your Gantt chart, use the VLOOKUP formula :
=VLOOKUP( x , y , z )
where x is the cell reference in the chart you're looking up, y is where Excel should look to find the corresponding value, and z is the column number within the array.
So, here's what I'll type into my first Gantt chart cell:
=VLOOKUP($A2,Tasks!$A$1:$C$1000,3)
Because I have used mixed and absolute references (using the $ symbol) within our formulas , I can copy (Ctrl+C) and paste (Ctrl+V) this formula into the other colored cells.
If you use a black color fill, use white font so that you can see the values against the black backgrounds.
Finally, use Conditional Formatting to color the cells based on the values they contain.
Select all the cells in the Gantt chart, and in the Home tab on the ribbon, click Conditional Formatting > Manage Rules.
Click "New Rule" in the dialog box that appears, and create the following conditions (after you have set each one, click "OK" to set the next):
- For each rule, set the Rule Type to "Format Only Cells That Contain."
- Select "Specific Text" and "Containing" in the first two drop-down boxes.
- In the text box, type Done , In progress , Not started , or Changes required for each rule you create (as these are the options in the VLOOKUP for these cells that we created in the previous step).
- For each rule, format both the fill color and the text color to be the same—green for Done, yellow for In progress, and so on.
You will then see the relevant Gantt chart cells change color based on their status in the Tasks sheet.
Step 3: Highlight the Current Month
Start by typing the first date of each month in short form where you originally typed the name of the month. So, for example, replace the text in the cell containing January with 01/01/2024 . Then, do the same for February, before using AutoFill to complete the remaining months . Doing this tells Excel that these are dates, and not just text. Next, change the font color of these dates to gray.
To turn these back into the names of the months, select all the dates, click the Number Formatting drop-down option in the Home tab on the ribbon, and click "More Number Formats."
In the Format Cells dialog box, open the "Number" tab, and click "Custom" in the Category list. Then, in the Type field, type MMMM .
Then, click "OK" to see the result. To now make the current month stand out, select all the months in your Gantt chart, and click Conditional Formatting > New Rule. In the dialog box, click "Format Only Cells That Contain," select "Dates Occurring" in the first drop-down menu, and "This Month" in the second. Next, choose the formatting you want to use to make the current month stand out, such as black and bold text. Finally, click "OK."
You now have your completed and dynamic Gantt chart with the progress displayed and the current month emphasized.
Using the Gantt chart created in the steps outlined above, you can now create a progress tracker. You can either do this on the same sheet as where your Gantt chart is located or on a new tab. In my case, I want to show how many squares in our Gantt chart are marked as Done, In progress, Not started, and Changes required, and then calculate an overall progress percentage.
To do this, I'll need to use the COUNTIF function , which follows this syntax:
=COUNTIF( x , y )
where x is the array to evaluate and y is the criterion to count.
So, for the Done count, we will type
=COUNTIF($B$2:$I$10,"Done")
- $B$2:$I$10 —This references the cells in the Gantt chart using an absolute reference (notice the $ symbols).
- "Done" —Use the quotation marks to tell Excel you're looking to count the number of times this text string appears in the array.
Then, copy and paste this formula for the remaining details in your progress tracker, changing value y to match the value you're looking to count.
Next, calculate the overall progress using the following formula:
=SUM( a /( a + b + c + d ))
Where a is the number of cells in your Gantt chart containing the word Done, and b , c , and d are the number of cells containing the other status markers. Remember to change the number format of this cell to a percentage.
With the cell containing the newly calculated percentage selected, in the Insert tab on the ribbon, click the Chart button highlighted below, and select a 2-D bar chart.
Then, format your chart to remove any details you do not require, resulting in a progress bar showing your overall progress.
Remove the gridlines to make your progress bar easier to read and look more professional.
As well as tracking your project's progress, you can also track the time elapsed and time remaining.
1. First, type the start and due date manually using a date format that suits your region. Excel will automatically convert this to a date format, and you can amend the date format if required.
2. Next, add today's date by typing
and pressing enter.
3. Third, calculate the days elapsed so far using the following formula:
=SUM( x - y )
where x is the cell containing today's date, and y is the cell containing the start date. Then, calculate the weeks elapsed by dividing the days elapsed by seven.
4. You can also calculate the days remaining with the following formula:
=SUM( a - b )
where a is the cell containing the due date, and b is the cell containing today's date. Again, calculate the weeks remaining by dividing the days remaining by seven.
5. Then, create a percentage of the time passed with the following formula:
=SUM( c /( c + d ))
Where c is the total number of days elapsed and d is the total number of days remaining.
6. Finally, create a 2-D bar chart using the method described in the previous section.
Now you've created the perfect spreadsheet for project management, consider using Excel to help you monitor your budgets !

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To create a simple chart from scratch in PowerPoint, click Insert > Chart and pick the chart you want. Click Insert > Chart. Click the chart type and then double-click the chart you want. Tip: For help deciding which chart is best for your data, see Available chart types. In the worksheet that appears, replace the placeholder data with your own ...
To create a pie chart in Excel: Select the data you want to visualize. From the " Insert " tab, choose " Pie " from the chart options. You can customize your chart by changing the colors, adding labels, and adjusting other settings in the " Format Chart Area " pane. Here's a video guide on how to create a donut chart:
In this tutorial, we will explore the basics of creating graphical presentations in Excel. A. Exploring the different types of graphs and charts available in Excel. Excel offers a wide range of graph and chart types, each suited for different data sets and presentation purposes. Some of the most commonly used graph and chart types in Excel include:
To paste a chart into PowerPoint, there are some steps to take. Start by opening your Excel file. Select the chart you want to add then press Ctrl + C or right-click and choose "Copy". Switch to PowerPoint and go to the slide where you want to paste the chart. Press Ctrl + V or right-click and select "Paste".
Select Home and select the Paste down arrow. Or, right-click the slide. The different options for pasting a chart display. Choose Use Destination Theme & Embed Workbook to paste your chart into PowerPoint with the ability to edit it in PowerPoint and match your presentation's color scheme. Choose Keep Source Formatting & Embed Workbook to be ...
If you decide or can figure out which data comparison you want to make, choosing the right chart type is very easy: Pie, doughnut, or area: Use for part-to-whole data comparison. Bar, cylinder, cone, or pyramid: Use for a whole-to-whole data comparison. Line or column: Use for a time-series data comparison. Scatter or bubble: Use for a correlation data comparison in Excel.
6. Add an image. Whether it's a photograph, an artistic sketch or your logo, images go a long way in making your spreadsheet better. Images make your presentation look official and possess the professional feel in many of the beautiful presentations you have seen. Pictures speak a thousand words.
When used in PowerPoint presentations, Excel charts can enhance the overall impact of the presentation and convey the information more clearly. Here are six key features of using Excel charts in PowerPoint: Excel charts are easily customizable in PowerPoint. Users have access to a range of chart styles and formatting options that can be ...
Sure, the numbers themselves show impressive growth, and she could simply spit out those digits during her presentation. But, she really wants to make an impact—so, she's going to use an Excel chart to display the subscriber growth she's worked so hard for. How to build an Excel chart: A step-by-step Excel chart tutorial 1. Get your data ...
Step 3: Copy the selected data by pressing Ctrl+C or right-clicking and selecting "Copy". Step 4: Open PowerPoint and navigate to the slide where you want to insert the chart. Step 5: Paste the copied data into PowerPoint by pressing Ctrl+V or right-clicking and selecting "Paste".
Go to the Excel spreadsheet and select the chart by clicking on it. Then copy the chart using Ctrl+C on your keyboard. Now go to the PowerPoint slide where you want to paste the chart and press Ctrl+V. That is all it takes to insert an Excel chart into a PowerPoint presentation through copying and pasting.
Just double-click on the chart to open the associated Excel spreadsheet. Here, you can add, delete, or edit data. If you want to do it like a pro, ... The most important types of charts in PPT and which one is best for you. We have checked out why adding visuals is a game-changer for your presentations.
Creating effective Excel charts for PowerPoint presentations involves selecting and organizing data in Excel, choosing the most suitable chart type, and customizing chart format options to enhance visual appeal and clarity. When inserting charts into PowerPoint, it is important to select the appropriate slide, use the "Paste Special ...
To add a chart to an Excel spreadsheet, follow the steps below: Step-1: Open MS Excel and navigate to the spreadsheet, which contains the data table you want to use for creating a chart. Step-2: Select data for the chart: Step-3: Click on the 'Insert' tab: Step-4: Click on the 'Recommended Charts' button:
Step 3: Add Chart Elements. Adding chart elements to your chart or graph will enhance it by clarifying data or providing additional context. You can select a chart element by clicking on the Add Chart Element dropdown menu in the top left-hand corner (beneath the Home tab). To Display or Hide Axes: Select Axes.
Let's follow the steps below to create a chart in Excel: Select the range B4:D10. Then, go to the Insert tab. In the Insert tab, you need to go to the Charts group. You can find different types of charts in the Charts group. Now, click on the Insert Column icon.
Select a corner of the first chart and click COPY ( or CTRL-C ). Switch to PowerPoint and select the destination slide. Click the bottom part of the PASTE button and select " Keep Source Formatting & Ling Data (F) ". Perform steps 1-3 on the second chart. Position and resize the charts as you see fit.
1. Select the chart. 2. On the Chart Design tab, in the Data group, click Switch Row/Column. Result: Legend Position. To move the legend to the right side of the chart, execute the following steps. 1. Select the chart. 2. Click the + button on the right side of the chart, click the arrow next to Legend and click Right. Result: Data Labels
Type the data in EXCEL in 2 columns as shown - hair color in column 1, corresponding student count in column 2. To create a chart, you must first Select / Highlight the data. Second, Click INSERT from the menu bar and Select CHART. Alternately, you can select the Chart Button in the Standard Toolbar.
13. Adding Titles for Chart and Axes: continued Commonly Used Categories: • Chart Title and Axis Title: these categories will allow you to type in your title and label your dependent (y-axis) and independent variables (x- axis). • Axes: this option allows you to add, change or remove values on the x- or y-axis. • Gridlines: allows you to adjust gridlines on graph • Legend: opening this ...
I. Iqra Nehal. this ppt is about charts in ms excel.there are many types of chart used in ms excel but in this ppt some common types are defined,as line chart,bar,column,area ,scatter chart etc... Read more. Education. Slideshow view. Download now.
Open Excel and click Blank Workbook. Name the workbook, choose a place to save it, and click the Save button. Start with Shapes. In the Excel workbook, click the Insert tab, click the Shapes drop-down arrow, and scroll to Flowchart options. Click on a shape, then click in your Excel spreadsheet to add the shape.
Step 1: Mark Your Timings Manually. Click "+" at the bottom of your workbook to create a new sheet, and call it Timing. On this new sheet type the tasks' names on the left and the months at the top. Next, map out your proposed timings using manual color fill.
PowerPoint Presentation. Updated 4/26/24. Division of Developmental Services. Assistant Commissioner. Heather Norton. Administrative Assistant. Carla Clayton. Director Health & Safety Network Supports. Susan Moon.
May 10, 2024 10:11 AM ET TeamViewer SE (TMVWF) Stock, TMVWY Stock. SA Transcripts. 146.64K Follower s. The following slide deck was published by TeamViewer SE in conjunction with their 2024 Q1 ...
International Petroleum Corporation 2024 Q1 - Results - Earnings Call Presentation May 10, 2024 11:51 AM ET International Petroleum Corporation (IPCFF) Stock , IPCO:CA Stock SA Transcripts
The following slide deck was published by Técnicas Reunidas, S.A.