Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation

How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
Published on September 7, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 21, 2023.
The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation , appearing right after the table of contents . Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant topic .
Your introduction should include:
- Your topic, in context: what does your reader need to know to understand your thesis dissertation?
- Your focus and scope: what specific aspect of the topic will you address?
- The relevance of your research: how does your work fit into existing studies on your topic?
- Your questions and objectives: what does your research aim to find out, and how?
- An overview of your structure: what does each section contribute to the overall aim?
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to start your introduction, topic and context, focus and scope, relevance and importance, questions and objectives, overview of the structure, thesis introduction example, introduction checklist, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about introductions.
Although your introduction kicks off your dissertation, it doesn’t have to be the first thing you write — in fact, it’s often one of the very last parts to be completed (just before your abstract ).
It’s a good idea to write a rough draft of your introduction as you begin your research, to help guide you. If you wrote a research proposal , consider using this as a template, as it contains many of the same elements. However, be sure to revise your introduction throughout the writing process, making sure it matches the content of your ensuing sections.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Begin by introducing your dissertation topic and giving any necessary background information. It’s important to contextualize your research and generate interest. Aim to show why your topic is timely or important. You may want to mention a relevant news item, academic debate, or practical problem.
After a brief introduction to your general area of interest, narrow your focus and define the scope of your research.
You can narrow this down in many ways, such as by:
- Geographical area
- Time period
- Demographics or communities
- Themes or aspects of the topic
It’s essential to share your motivation for doing this research, as well as how it relates to existing work on your topic. Further, you should also mention what new insights you expect it will contribute.
Start by giving a brief overview of the current state of research. You should definitely cite the most relevant literature, but remember that you will conduct a more in-depth survey of relevant sources in the literature review section, so there’s no need to go too in-depth in the introduction.
Depending on your field, the importance of your research might focus on its practical application (e.g., in policy or management) or on advancing scholarly understanding of the topic (e.g., by developing theories or adding new empirical data). In many cases, it will do both.
Ultimately, your introduction should explain how your thesis or dissertation:
- Helps solve a practical or theoretical problem
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Builds on existing research
- Proposes a new understanding of your topic
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Perhaps the most important part of your introduction is your questions and objectives, as it sets up the expectations for the rest of your thesis or dissertation. How you formulate your research questions and research objectives will depend on your discipline, topic, and focus, but you should always clearly state the central aim of your research.
If your research aims to test hypotheses , you can formulate them here. Your introduction is also a good place for a conceptual framework that suggests relationships between variables .
- Conduct surveys to collect data on students’ levels of knowledge, understanding, and positive/negative perceptions of government policy.
- Determine whether attitudes to climate policy are associated with variables such as age, gender, region, and social class.
- Conduct interviews to gain qualitative insights into students’ perspectives and actions in relation to climate policy.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
I. Introduction
Human language consists of a set of vowels and consonants which are combined to form words. During the speech production process, thoughts are converted into spoken utterances to convey a message. The appropriate words and their meanings are selected in the mental lexicon (Dell & Burger, 1997). This pre-verbal message is then grammatically coded, during which a syntactic representation of the utterance is built.
Speech, language, and voice disorders affect the vocal cords, nerves, muscles, and brain structures, which result in a distorted language reception or speech production (Sataloff & Hawkshaw, 2014). The symptoms vary from adding superfluous words and taking pauses to hoarseness of the voice, depending on the type of disorder (Dodd, 2005). However, distortions of the speech may also occur as a result of a disease that seems unrelated to speech, such as multiple sclerosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
This study aims to determine which acoustic parameters are suitable for the automatic detection of exacerbations in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by investigating which aspects of speech differ between COPD patients and healthy speakers and which aspects differ between COPD patients in exacerbation and stable COPD patients.
Checklist: Introduction
I have introduced my research topic in an engaging way.
I have provided necessary context to help the reader understand my topic.
I have clearly specified the focus of my research.
I have shown the relevance and importance of the dissertation topic .
I have clearly stated the problem or question that my research addresses.
I have outlined the specific objectives of the research .
I have provided an overview of the dissertation’s structure .
You've written a strong introduction for your thesis or dissertation. Use the other checklists to continue improving your dissertation.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Scope of research is determined at the beginning of your research process , prior to the data collection stage. Sometimes called “scope of study,” your scope delineates what will and will not be covered in your project. It helps you focus your work and your time, ensuring that you’ll be able to achieve your goals and outcomes.
Defining a scope can be very useful in any research project, from a research proposal to a thesis or dissertation . A scope is needed for all types of research: quantitative , qualitative , and mixed methods .
To define your scope of research, consider the following:
- Budget constraints or any specifics of grant funding
- Your proposed timeline and duration
- Specifics about your population of study, your proposed sample size , and the research methodology you’ll pursue
- Any inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Any anticipated control , extraneous , or confounding variables that could bias your research if not accounted for properly.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/introduction-structure/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
How to write a fantastic thesis introduction (+15 examples)
The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write a powerful thesis introduction.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission if you make a purchase using the links below at no additional cost to you . I only recommend products or services that I truly believe can benefit my audience. As always, my opinions are my own.
Elements of a fantastic thesis introduction
Open with a (personal) story, begin with a problem, define a clear research gap, describe the scientific relevance of the thesis, describe the societal relevance of the thesis, write down the thesis’ core claim in 1-2 sentences, support your argument with sufficient evidence, consider possible objections, address the empirical research context, give a taste of the thesis’ empirical analysis, hint at the practical implications of the research, provide a reading guide, briefly summarise all chapters to come, design a figure illustrating the thesis structure.
An introductory chapter plays an integral part in every thesis. The first chapter has to include quite a lot of information to contextualise the research. At the same time, a good thesis introduction is not too long, but clear and to the point.
A powerful thesis introduction does the following:
- It captures the reader’s attention.
- It presents a clear research gap and emphasises the thesis’ relevance.
- It provides a compelling argument.
- It previews the research findings.
- It explains the structure of the thesis.
In addition, a powerful thesis introduction is well-written, logically structured, and free of grammar and spelling errors. Reputable thesis editors can elevate the quality of your introduction to the next level. If you are in search of a trustworthy thesis or dissertation editor who upholds high-quality standards and offers efficient turnaround times, I recommend the professional thesis and dissertation editing service provided by Editage .
This list can feel quite overwhelming. However, with some easy tips and tricks, you can accomplish all these goals in your thesis introduction. (And if you struggle with finding the right wording, have a look at academic key phrases for introductions .)
Ways to capture the reader’s attention
A powerful thesis introduction should spark the reader’s interest on the first pages. A reader should be enticed to continue reading! There are three common ways to capture the reader’s attention.
An established way to capture the reader’s attention in a thesis introduction is by starting with a story. Regardless of how abstract and ‘scientific’ the actual thesis content is, it can be useful to ease the reader into the topic with a short story.
This story can be, for instance, based on one of your study participants. It can also be a very personal account of one of your own experiences, which drew you to study the thesis topic in the first place.
Start by providing data or statistics
Data and statistics are another established way to immediately draw in your reader. Especially surprising or shocking numbers can highlight the importance of a thesis topic in the first few sentences!
So if your thesis topic lends itself to being kick-started with data or statistics, you are in for a quick and easy way to write a memorable thesis introduction.
The third established way to capture the reader’s attention is by starting with the problem that underlies your thesis. It is advisable to keep the problem simple. A few sentences at the start of the chapter should suffice.
Usually, at a later stage in the introductory chapter, it is common to go more in-depth, describing the research problem (and its scientific and societal relevance) in more detail.
You may also like: Minimalist writing for a better thesis
Emphasising the thesis’ relevance
A good thesis is a relevant thesis. No one wants to read about a concept that has already been explored hundreds of times, or that no one cares about.
Of course, a thesis heavily relies on the work of other scholars. However, each thesis is – and should be – unique. If you want to write a fantastic thesis introduction, your job is to point out this uniqueness!
In academic research, a research gap signifies a research area or research question that has not been explored yet, that has been insufficiently explored, or whose insights and findings are outdated.
Every thesis needs a crystal-clear research gap. Spell it out instead of letting your reader figure out why your thesis is relevant.
* This example has been taken from an actual academic paper on toxic behaviour in online games: Liu, J. and Agur, C. (2022). “After All, They Don’t Know Me” Exploring the Psychological Mechanisms of Toxic Behavior in Online Games. Games and Culture 1–24, DOI: 10.1177/15554120221115397
The scientific relevance of a thesis highlights the importance of your work in terms of advancing theoretical insights on a topic. You can think of this part as your contribution to the (international) academic literature.
Scientific relevance comes in different forms. For instance, you can critically assess a prominent theory explaining a specific phenomenon. Maybe something is missing? Or you can develop a novel framework that combines different frameworks used by other scholars. Or you can draw attention to the context-specific nature of a phenomenon that is discussed in the international literature.
The societal relevance of a thesis highlights the importance of your research in more practical terms. You can think of this part as your contribution beyond theoretical insights and academic publications.
Why are your insights useful? Who can benefit from your insights? How can your insights improve existing practices?

Formulating a compelling argument
Arguments are sets of reasons supporting an idea, which – in academia – often integrate theoretical and empirical insights. Think of an argument as an umbrella statement, or core claim. It should be no longer than one or two sentences.
Including an argument in the introduction of your thesis may seem counterintuitive. After all, the reader will be introduced to your core claim before reading all the chapters of your thesis that led you to this claim in the first place.
But rest assured: A clear argument at the start of your thesis introduction is a sign of a good thesis. It works like a movie teaser to generate interest. And it helps the reader to follow your subsequent line of argumentation.
The core claim of your thesis should be accompanied by sufficient evidence. This does not mean that you have to write 10 pages about your results at this point.
However, you do need to show the reader that your claim is credible and legitimate because of the work you have done.
A good argument already anticipates possible objections. Not everyone will agree with your core claim. Therefore, it is smart to think ahead. What criticism can you expect?
Think about reasons or opposing positions that people can come up with to disagree with your claim. Then, try to address them head-on.
Providing a captivating preview of findings
Similar to presenting a compelling argument, a fantastic thesis introduction also previews some of the findings. When reading an introduction, the reader wants to learn a bit more about the research context. Furthermore, a reader should get a taste of the type of analysis that will be conducted. And lastly, a hint at the practical implications of the findings encourages the reader to read until the end.
If you focus on a specific empirical context, make sure to provide some information about it. The empirical context could be, for instance, a country, an island, a school or city. Make sure the reader understands why you chose this context for your research, and why it fits to your research objective.
If you did all your research in a lab, this section is obviously irrelevant. However, in that case you should explain the setup of your experiment, etcetera.
The empirical part of your thesis centers around the collection and analysis of information. What information, and what evidence, did you generate? And what are some of the key findings?
For instance, you can provide a short summary of the different research methods that you used to collect data. Followed by a short overview of how you analysed this data, and some of the key findings. The reader needs to understand why your empirical analysis is worth reading.
You already highlighted the practical relevance of your thesis in the introductory chapter. However, you should also provide a preview of some of the practical implications that you will develop in your thesis based on your findings.
Presenting a crystal clear thesis structure
A fantastic thesis introduction helps the reader to understand the structure and logic of your whole thesis. This is probably the easiest part to write in a thesis introduction. However, this part can be best written at the very end, once everything else is ready.
A reading guide is an essential part in a thesis introduction! Usually, the reading guide can be found toward the end of the introductory chapter.
The reading guide basically tells the reader what to expect in the chapters to come.
In a longer thesis, such as a PhD thesis, it can be smart to provide a summary of each chapter to come. Think of a paragraph for each chapter, almost in the form of an abstract.
For shorter theses, which also have a shorter introduction, this step is not necessary.
Especially for longer theses, it tends to be a good idea to design a simple figure that illustrates the structure of your thesis. It helps the reader to better grasp the logic of your thesis.
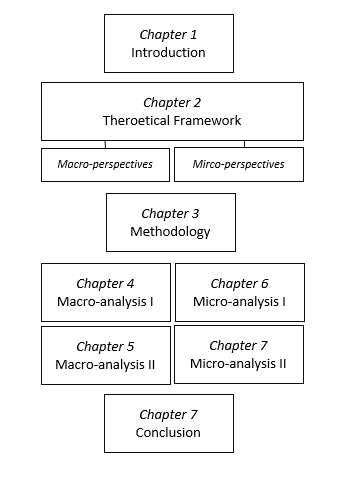
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox!
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
The most useful academic social networking sites for PhD students
10 reasons not to do a master's degree, related articles.

5 inspiring PhD thesis acknowledgement examples

The top 10 thesis defense questions (+ how to prepare strong answers)

Left your dissertation too late? Ways to take action now

Theoretical vs. conceptual frameworks: Simple definitions and an overview of key differences
- How it works
How to Write the Thesis Or Dissertation Introduction – Guide
Published by Carmen Troy at August 31st, 2021 , Revised On January 24, 2024
Introducing your Dissertation Topic
What would you tell someone if they asked you to introduce yourself? You’d probably start with your name, what you do for a living…etc., etc., etc. Think of your dissertation. How would you go about it if you had to introduce it to the world for the first time?
Keep this forefront in your mind for the remainder of this guide: you are introducing your research to the world that doesn’t even know it exists. Every word, phrase and line you write in your introduction will stand for the strength of your dissertation’s character.
This is not very different from how, in real life, if someone fails to introduce themselves properly (such as leaving out what they do for a living, where they live, etc.) to a stranger, it leaves a lasting impression on the stranger.
Don’t leave your dissertation a stranger among other strangers. Let’s review the little, basic concepts we already have at the back of our minds, perhaps, to piece them together in one body: an introduction.
What Goes Inside an Introduction
The exact ingredients of a dissertation or thesis introduction chapter vary depending on your chosen research topic, your university’s guidelines, and your academic subject – but they are generally mixed in one sequence or another to introduce an academic argument.
The critical elements of an excellent dissertation introduction include a definition of the selected research topic , a reference to previous studies on the subject, a statement of the value of the subject for academic and scientific communities, a clear aim/purpose of the study, a list of your objectives, a reference to viewpoints of other researchers and a justification for the research.
Topic Discussion versus Topic Introduction
Discussing and introducing a topic are two highly different aspects of dissertation introduction writing. You might find it easy to discuss a topic, but introducing it is much trickier.
The introduction is the first thing a reader reads; thus, it must be to the point, informative, engaging, and enjoyable. Even if one of these elements is missing, the reader will not be motivated to continue reading the paper and will move on to something different.
So, it’s critical to fully understand how to write the introduction of a dissertation before starting the actual write-up.
When writing a dissertation introduction, one has to explain the title, discuss the topic and present a background so that readers understand what your research is about and what results you expect to achieve at the end of the research work.
As a standard practice, you might work on your dissertation introduction chapter several times. Once when you’re working on your proposal and the second time when writing your actual dissertation.
“ Want to keep up with the progress of the work done by your writer? ResearchProspect can deliver your dissertation order in three parts; outline, first half, and final dissertation delivery. Here is the link to our online order form .
Many academics argue that the Introduction chapter should be the last section of the dissertation paper you should complete, but by no means is it the last part you would think of because this is where your research starts from.
Write the draft introduction as early as possible. You should write it at the same time as the proposal submission, although you must revise and edit it many times before it takes the final shape.
Considering its importance, many students remain unsure of how to write the introduction of a dissertation. Here are some of the essential elements of how to write the introduction of a dissertation that’ll provide much-needed dissertation introduction writing help.
Below are some guidelines for you to learn to write a flawless first-class dissertation paper.
Steps of Writing a Dissertation Introduction
1. research background – writing a dissertation introduction.
This is the very first section of your introduction. Building a background of your chosen topic will help you understand more about the topic and help readers know why the general research area is problematic, interesting, central, important, etc.
Your research background should include significant concepts related to your dissertation topic. This will give your supervisor and markers an idea that you’ve investigated the research problem thoroughly and know the various aspects of your topic.
The introduction to a dissertation shouldn’t talk only about other research work in the same area, as this will be discussed in the literature review section. Moreover, this section should not include the research design and data collection method(s) .
All about research strategy should be covered in the methodology chapter . Research background only helps to build up your research in general.
For instance, if your research is based on job satisfaction measures of a specific country, the content of the introduction chapter will generally be about job satisfaction and its impact.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Plagiarism free
- Never resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements

2. Significance of the Research
As a researcher, you must demonstrate how your research will provide value to the scientific and academic communities. If your dissertation is based on a specific company or industry, you need to explain why that industry and company were chosen.
If you’re comparing, explain why you’re doing so and what this research will yield. Regardless of your chosen research topic, explain thoroughly in this section why this research is being conducted and what benefits it will serve.
The idea here is to convince your supervisor and readers that the concept should be researched to find a solution to a problem.
3. Research Problem
Once you’ve described the main research problem and the importance of your research, the next step would be to present your problem statement , i.e., why this research is being conducted and its purpose.
This is one of the essential aspects of writing a dissertation’s introduction. Doing so will help your readers understand what you intend to do in this research and what they should expect from this study.
Presenting the research problem competently is crucial in persuading your readers to read other parts of the dissertation paper . This research problem is the crux of your dissertation, i.e., it gives a direction as to why this research is being carried out, and what issues the study will consider.
For example, if your dissertation is based on measuring the job satisfaction of a specific organisation, your research problem should talk about the problem the company is facing and how your research will help the company to solve that.
If your dissertation is not based on any specific organisation, you can explain the common issues that companies face when they do not consider job satisfaction as a pillar of business growth and elaborate on how your research will help them realise its importance.
Citing too many references in the introduction chapter isn’t recommended because here, you must explain why you chose to study a specific area and what your research will accomplish. Any citations only set the context, and you should leave the bulk of the literature for a later section.
4. Research Question(s)
The central part of your introduction is the research question , which should be based on your research problem and the dissertation title. Combining these two aspects will help you formulate an exciting yet manageable research question.
Your research question is what your research aims to answer and around which your dissertation will revolve. The research question should be specific and concise.
It should be a one- or two-line question you’ve set out to answer through your dissertation. For the job satisfaction example, a sample research question could be, how does job satisfaction positively impact employee performance?
Look up dissertation introduction examples online or ask your friends to get an idea of how an ideal research question is formed. Or you can review our dissertation introduction example here and research question examples here .
Once you’ve formed your research question, pick out vital elements from it, based on which you will then prepare your theoretical framework and literature review. You will come back to your research question again when concluding your dissertation .
Sometimes, you might have to formulate a hypothesis in place of a research question. The hypothesis is a simple statement you prove with your results , discussion and analysis .
A sample hypothesis could be job satisfaction is positively linked to employee job performance . The results of your dissertation could be in favour of this dissertation or against it.
Tip: Read up about what alternative, null, one-tailed and two-tailed hypotheses are so you can better formulate the hypothesis for your dissertation. Following are the definitions for each term, as retrieved from Trochim et al.’s Research Methods: The Essential Knowledge Base (2016):
- Alternative hypothesis (H 1 ): “A specific statement of prediction that usually states what you expect will happen in your study.”
- Null hypothesis (H 0 ): “The hypothesis that describes the possible outcomes other than the alternative hypothesis. Usually, the null hypothesis predicts there will be no effect of a program or treatment you are studying.”
- One-tailed hypothesis: “A hypothesis that specifies a direction; for example, when your hypothesis predicts that your program will increase the outcome.”
- Two-tailed hypothesis: “A hypothesis that does not specify a direction. For example, if you hypothesise that your program or intervention will affect an outcome, but you are unwilling to specify whether that effect will be positive or negative, you are using a two-tailed hypothesis.”
Get Help with Any Part of Your Dissertation!
UK’s best academic support services. How would you know until you try?
Interesting read: 10 ways to write a practical introduction fast .
Get Help With Any Part of Your Dissertation!
Uk’s best academic support services. how would you know until you try, 5. research aims and objectives.
Next, the research aims and objectives. Aims and objectives are broad statements of desired results of your dissertation . They reflect the expectations of the topic and research and address the long-term project outcomes.
These statements should use the concepts accurately, must be focused, should be able to convey your research intentions and serve as steps that communicate how your research question will be answered.
You should formulate your aims and objectives based on your topic, research question, or hypothesis. These are simple statements and are an extension of your research question.
Through the aims and objectives, you communicate to your readers what aspects of research you’ve considered and how you intend to answer your research question.
Usually, these statements initiate with words like ‘to explore’, ‘to study’, ‘to assess’, ‘to critically assess’, ‘to understand’, ‘to evaluate’ etc.
You could ask your supervisor to provide some thesis introduction examples to help you understand better how aims and objectives are formulated. More examples are here .
Your aims and objectives should be interrelated and connect to your research question and problem. If they do not, they’ll be considered vague and too broad in scope.
Always ensure your research aims and objectives are concise, brief, and relevant.
Once you conclude your dissertation , you will have to revert back to address whether your research aims and objectives have been met.
You will have to reflect on how your dissertation’s findings , analysis, and discussion related to your aims and objectives and how your research has helped in achieving them.
6. Research Limitations
This section is sometimes a part of the dissertation methodology section ; however, it is usually included in the introduction of a dissertation.
Every research has some limitations. Thus, it is normal for you to experience certain limitations when conducting your study.
You could experience research design limitations, data limitations or even financial limitations. Regardless of which type of limitation you may experience, your dissertation would be impacted. Thus, it would be best if you mentioned them without any hesitation.
When including this section in the introduction, make sure that you clearly state the type of constraint you experienced. This will help your supervisor understand what problems you went through while working on your dissertation.
However, one aspect that you should take care of is that your results, in no way, should be influenced by these restrictions. The results should not be compromised, or your dissertation will not be deemed authentic and reliable.
After you’ve mentioned your research limitations, discuss how you overcame them to produce a perfect dissertation .
Also, mention that your limitations do not adversely impact your results and that you’ve produced research with accurate results the academic community can rely on.
Also read: How to Write Dissertation Methodology .
7. Outline of the Dissertation
Even though this isn’t a mandatory sub-section of the introduction chapter, good introductory chapters in dissertations outline what’s to follow in the preceding chapters.
It is also usual to set out an outline of the rest of the dissertation . Depending on your university and academic subject, you might also be asked to include it in your research proposal .
Because your tutor might want to glance over it to see how you plan your dissertation and what sections you’d include; based on what sections you include and how you intend to research and cover them, they’d provide feedback for you to improve.
Usually, this section discusses what sections you plan to include and what concepts and aspects each section entails. A standard dissertation consists of five sections : chapters, introduction, literature review , methodology , results and discussion , and conclusion .
Some dissertation assignments do not use the same chapter for results and discussion. Instead, they split it into two different chapters, making six chapters. Check with your supervisor regarding which format you should follow.
When discussing the outline of your dissertation , remember that you’d have to mention what each section involves. Discuss all the significant aspects of each section to give a brief overview of what your dissertation contains, and this is precisely what our dissertation outline service provides.
Writing a dissertation introduction might seem complicated, but it is not if you understand what is expected of you. To understand the required elements and make sure that you focus on all of them.
Include all the aspects to ensure your supervisor and other readers can easily understand how you intend to undertake your research.
“If you find yourself stuck at any stage of your dissertation introduction, get introduction writing help from our writers! At ResearchProspect, we offer a dissertation writing service , and our qualified team of writers will also assist you in conducting in-depth research for your dissertation.
Dissertation Introduction Samples & Examples
Check out some basic samples of dissertation introduction chapters to get started.
FAQs about Dissertation Introduction
What is the purpose of an introduction chapter.
It’s used to introduce key constructs, ideas, models and/or theories etc. relating to the topic; things that you will be basing the remainder of your dissertation on.
How do you start an introduction in a dissertation?
There is more than one way of starting a dissertation’s introductory chapter. You can begin by stating a problem in your area of interest, review relevant literature, identify the gap, and introduce your topic. Or, you can go the opposite way, too. It’s all entirely up to your discretion. However, be consistent in the format you choose to write in.
How long can an introduction get?
It can range from 1000 to 2000 words for a master’s dissertation , but for a higher-level dissertation, it mostly ranges from 8,000 to 10,000 words ’ introduction chapter. In the end, though, it depends on the guidelines provided to you by your department.
Steps to Writing a Dissertation Introduction
You may also like.
Dissertation Methodology is the crux of dissertation project. In this article, we will provide tips for you to write an amazing dissertation methodology.
This brief introductory section aims to deal with the definitions of two paradigms, positivism and post-positivism, as well as their importance in research.
Wish that you had more time to write your dissertation paper? Here are some practical tips for you to learn “How to get dissertation deadline extension”.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Think of yourself as a member of a jury, listening to a lawyer who is presenting an opening argument. You'll want to know very soon whether the lawyer believes the accused to be guilty or not guilty, and how the lawyer plans to convince you. Readers of academic essays are like jury members: before they have read too far, they want to know what the essay argues as well as how the writer plans to make the argument. After reading your thesis statement, the reader should think, "This essay is going to try to convince me of something. I'm not convinced yet, but I'm interested to see how I might be."
An effective thesis cannot be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." A thesis is not a topic; nor is it a fact; nor is it an opinion. "Reasons for the fall of communism" is a topic. "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" is a fact known by educated people. "The fall of communism is the best thing that ever happened in Europe" is an opinion. (Superlatives like "the best" almost always lead to trouble. It's impossible to weigh every "thing" that ever happened in Europe. And what about the fall of Hitler? Couldn't that be "the best thing"?)
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay.
Steps in Constructing a Thesis
First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication. Does the author contradict himself or herself? Is a point made and later reversed? What are the deeper implications of the author's argument? Figuring out the why to one or more of these questions, or to related questions, will put you on the path to developing a working thesis. (Without the why, you probably have only come up with an observation—that there are, for instance, many different metaphors in such-and-such a poem—which is not a thesis.)
Once you have a working thesis, write it down. There is nothing as frustrating as hitting on a great idea for a thesis, then forgetting it when you lose concentration. And by writing down your thesis you will be forced to think of it clearly, logically, and concisely. You probably will not be able to write out a final-draft version of your thesis the first time you try, but you'll get yourself on the right track by writing down what you have.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction. Although this is not required in all academic essays, it is a good rule of thumb.
Anticipate the counterarguments. Once you have a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This will help you to refine your thesis, and it will also make you think of the arguments that you'll need to refute later on in your essay. (Every argument has a counterargument. If yours doesn't, then it's not an argument—it may be a fact, or an opinion, but it is not an argument.)
This statement is on its way to being a thesis. However, it is too easy to imagine possible counterarguments. For example, a political observer might believe that Dukakis lost because he suffered from a "soft-on-crime" image. If you complicate your thesis by anticipating the counterargument, you'll strengthen your argument, as shown in the sentence below.
Some Caveats and Some Examples
A thesis is never a question. Readers of academic essays expect to have questions discussed, explored, or even answered. A question ("Why did communism collapse in Eastern Europe?") is not an argument, and without an argument, a thesis is dead in the water.
A thesis is never a list. "For political, economic, social and cultural reasons, communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" does a good job of "telegraphing" the reader what to expect in the essay—a section about political reasons, a section about economic reasons, a section about social reasons, and a section about cultural reasons. However, political, economic, social and cultural reasons are pretty much the only possible reasons why communism could collapse. This sentence lacks tension and doesn't advance an argument. Everyone knows that politics, economics, and culture are important.
A thesis should never be vague, combative or confrontational. An ineffective thesis would be, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because communism is evil." This is hard to argue (evil from whose perspective? what does evil mean?) and it is likely to mark you as moralistic and judgmental rather than rational and thorough. It also may spark a defensive reaction from readers sympathetic to communism. If readers strongly disagree with you right off the bat, they may stop reading.
An effective thesis has a definable, arguable claim. "While cultural forces contributed to the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe, the disintegration of economies played the key role in driving its decline" is an effective thesis sentence that "telegraphs," so that the reader expects the essay to have a section about cultural forces and another about the disintegration of economies. This thesis makes a definite, arguable claim: that the disintegration of economies played a more important role than cultural forces in defeating communism in Eastern Europe. The reader would react to this statement by thinking, "Perhaps what the author says is true, but I am not convinced. I want to read further to see how the author argues this claim."
A thesis should be as clear and specific as possible. Avoid overused, general terms and abstractions. For example, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because of the ruling elite's inability to address the economic concerns of the people" is more powerful than "Communism collapsed due to societal discontent."
Copyright 1999, Maxine Rodburg and The Tutors of the Writing Center at Harvard University

How To Write A Thesis Introduction Chapter
Crafting the introductory chapter of a thesis can be confusing. If you are feeling the same, you are the at right place.
This post will explore how you can write a thesis introduction chapter, by outlining the essential components of a thesis introduction. We will look at the process, one section at a time, and explain them to help you get a hang of how to craft your thesis introduction.
How To Write A Good Thesis Introduction?
The opening section of a thesis introduction sets the stage for what’s to come, acting as a crucial hook to capture the reader’s attention.
Unlike the broader strokes found in the table of contents, this initial foray into your research is where you must distill the essence of your thesis into a potent, digestible form.
A skillful introduction begins with a concise preview of the chapter’s terrain, delineating the structure of the thesis with a clarity that avoids overwhelming the reader.
This is not the stage for exhaustive details; rather, it’s where you prime the reader with a snapshot of the intellectual journey ahead.
In crafting this segment, insiders advise adhering to a quartet of foundational sentences that offer an academic handshake to the reader.
First Section: I ntroduces the broad field of research, such as the significance of organisational skills development in business growth.
Second Section: Narrows the focus, pinpointing a specific research problem or gap — perhaps the debate on managing skill development in fast-paced industries like web development.
Third Section: Clearly state the research aims and objectives, guiding the reader to the ‘why’ behind your study. Finally, a sentence should outline the roadmap of the introduction chapter itself, forecasting the background context, research questions, significance, and limitations that will follow.
Such a calibrated approach ensures that every element from the research objective to the hypothesis is presented with precision.
This method, a well-guarded secret amongst seasoned researchers, transforms a mundane introduction into a compelling entrée into your dissertation or thesis.
Background To The Study
This section sets the tone for the research journey ahead. The goal here is to capture the reader’s attention by threading relevant background information into a coherent narrative that aligns with the research objectives of the thesis.
To write a good thesis introduction, one must carefully describe the background to highlight the context in which the research is grounded.
This involves not just a literature review but a strategic presentation of the current state of research, pinpointing where your work will wedge itself into the existing body of knowledge.
For instance, if the research project focuses on qualitative changes in urban planning, the introduction should spotlight key developmental milestones and policy shifts that foreground the study’s aims and objectives.
When writing this section, articulate the focus and scope of the research, ensuring the reader grasps the importance of the research questions and hypothesis.
This section must not only be informative but also engaging. By the end of the introductory chapter, the reader should be compelled to continue reading, having grasped a clear and easy-to-understand summary of each chapter that will follow.
It’s a good idea to address frequently asked questions and to clearly state any industry-specific terminology, assuming no prior expertise on the reader’s part.
This approach establishes a solid foundation for the rest of the thesis or dissertation, ensuring the reader is well-prepared to dive into the nuances of your research project.
Research Problem
Crafting the nucleus of your thesis or dissertation hinges on pinpointing a compelling research problem. This step is crucial; it is the keystone of a good thesis introduction chapter, drawing the reader’s attention and setting the stage for the rest of your thesis.

A well-defined research problem addresses a gap in the existing literature, underscored by a qualitative or quantitative body of research that lacks consensus or is outdated, especially in rapidly evolving fields.
Consider the dynamic sphere of organizational skills development. Established research might agree on strategies for industries where skills change at a snail’s pace.
However, if the landscape shifts more quickly—take web development for example, where new languages and platforms emerge incessantly—the literature gap becomes evident.
Herein lies the research problem: existing strategies may not suffice in industries characterized by a swift knowledge turnover.
When writing your introduction, your goal is to clearly state this gap. A great thesis introduction delineates what is known, what remains unknown, and why bridging this chasm is significant.
It should illuminate the research objectives and questions, laying out a roadmap for the reader in a language that’s clear and easy to understand, regardless of their familiarity with the topic.
You’ll be able to capture and maintain the reader’s interest by effectively communicating why your research matters—setting the scene for your hypothesis and subsequent investigation.
Remember, a good thesis introduction should not only provide background information but also articulate the focus and scope of the study, offering a preview of the structure of your thesis.
Research Aims, Objectives And Questions
This pivotal section lays out the foundation by providing relevant background information, but it is the articulation of research aims, objectives, and questions that clarifies the focus and scope of your study.
The research aim is the lighthouse of your thesis, illuminating the overarching purpose of your investigation.
For instance, a thesis exploring skills development in fast-paced industries might present an aim to evaluate the effectiveness of various strategies within UK web development companies. This broad goal sets the direction for more detailed planning.
Research objectives drill down into specifics, acting as stepping stones toward achieving your aim. They are the tangible checkpoints of your research project, often action-oriented, outlining what you will do.
Examples might include identifying common skills development strategies or evaluating their effectiveness. These objectives segment the monumental task into manageable portions, offering a clear and easy way to write a structured pathway for the research.

Equally critical are the research questions, which translate your objectives into inquiries that your thesis will answer. They narrow the focus even further, dictating the structure of the thesis.
For instance:
- “What are the prevalent skills development strategies employed by UK web development firms?”
- “How effective are these strategies?”
Such questions demand concrete responses and guide the reader through the rest of the thesis.
Significance Of The Study
The “Significance of the Study” section within the introduction chapter of your thesis or dissertation holds considerable weight in laying out the importance of your research.

This segment answers the pivotal question: “Why does this research matter?” It is strategically placed after the background information and literature review to underscore the contribution your study makes to the existing body of research.
In writing this section, you’ll be able to capture the reader’s attention by clearly stating the impact and added value your research project offers.
Whether it’s a qualitative or quantitative study, the significance must be articulated in terms of:
- Theoretical
- Academic, and
- Societal contributions.
For instance, it may fill gaps identified in the literature review, propose innovative solutions to pressing problems, or advance our understanding in a certain field.
A good thesis introduction will succinctly convey three main things: the research objective, the hypothesis or research questions, and the importance of your research.
It’s a good idea to provide your reader with a roadmap, foreshadowing the structure of the thesis and offering a summary of each chapter, thus enticing the reader to continue reading.
When you write the introduction section, it should also serve as a concise synopsis of the focus and scope of your research.
It’s often beneficial to include examples of introductions that clearly state the research objectives and questions, offering a snapshot of the whole thesis, and setting the stage for the rest of your thesis.
Limitations Of The Study
A thorough thesis introduction lays out specific research objectives and questions, yet it also sheds light on the study’s inherent boundaries. This is the purpose of the Limitation of The Study section.
The limitations section is not a confession of failure; instead, it’s a good idea to see it as demonstrating academic maturity.
Here, you clearly state the parameters within which the research was conducted.
For instance, a qualitative study might face scrutiny for subjectivity, or a quantitative one for potentially oversimplifying complexities. Other common constraints include the scope—perhaps focusing on a narrow aspect without considering variable interplay—resources, and generalizability.
For example, a study concentrated on a specific industry in Florida may not hold water in a different context, for example in Tokyo, Japan.
It’s essential to write this section with transparency. A good thesis introduction doesn’t shy away from limitations. Instead, it captures the reader’s attention by laying them out systematically, often in a dedicated paragraph for each chapter.
This honesty allows the reader to understand the research’s focus and scope while providing a clear and easy-to-follow structure of the thesis.
This approach also serves to manage the reader’s expectations. By preempting frequently asked questions about the scope of your research, the introductory chapter establishes a trust that encourages the reader to continue reading, aware of the contours shaping the body of research.
Thus, a well-articulated limitations section is not just part of the thesis; it is an integral piece of a responsibly woven research narrative.
Structural Outline Of Thesis, Thesis Statement
Within the thesis or dissertation, the structural outline section is akin to a compass, orienting the reader’s journey through the academic landscape laid out within the pages.
Crafting this section is a strategic exercise, one that requires an understanding of the work’s skeleton.
In essence, it’s the blueprint for the construction of a scholarly argument, and writing a good thesis necessitates a clear and easy-to-follow outline.
When you write a thesis outline, it’s not only about catching the reader’s attention; it’s also about holding it throughout the rest of the thesis.
This is where the structural outline comes into play, often beginning with an introduction chapter that presents the thesis statement, research objectives, and the importance of your research.
Following the introduction, a typical outline might proceed with Chapter 2, offering a literature review to acquaint the reader with existing literature and how this piece of research fits within it.
Subsequent chapters, each with a paragraph in the outline, detail the methodological approach—whether it’s qualitative or quantitative—and the research’s focus and scope.
A well-thought-out outline should also preview the structure of the thesis, succinctly:
- Summarizing the main aim and objectives of each chapter, and
- Indicating the type of data and analysis that will be presented.
This roadmap reassures the reader that the dissertation or thesis will cover the necessary ground in a logical progression, continuing from where the introduction first captivated their interest.
The structural outline is not only part of the thesis—it’s a strategic framework that informs the reader what to expect in each subsequent chapter.
Done correctly, this section allows the reader to understand the whole thesis in a nutshell and can often serve as a checklist for both the reader and the writer.
This ensures that the key stages of the research project are clearly stated and that the reader is provided with a roadmap to guide them through the detailed landscape of your scholarly work.
Write An Introduction Chapter With Ease
Mastering the thesis introduction chapter is a critical step towards a successful dissertation. It’s about striking a balance between engagement and information, presenting a snapshot of your research with clarity and intrigue.
Remember to start with a hook, establish the context, clarify your aims, and highlight the significance, all while being mindful of the study’s scope and limitations.
By adhering to these principles, your introduction will not only guide but also inspire your readers, laying a strong foundation for the in-depth exploration that follows in your thesis or dissertation.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

How to Write a Compelling Thesis Introduction

The introduction to your thesis is like a first impression: you want it to be great. It is the first chapter and appears before the literature review and after the table of contents. You want the introduction to set the stage for your reader: tell them what you’re writing about, why, and what comes next. So how can you write a compelling thesis introduction?
Structure and elements of a thesis introduction
Before you write a compelling thesis introduction, you need to know what elements belong in this section and how it should be structured. A typical thesis introduction includes:
- A clear thesis statement
- An explanation of the context (brief background) for the study
- The focus and scope of the paper
- An explanation of the relevance and importance of your research
- A description of the objectives of your research and how your methodology achieves them
- A guide to the structure of the rest of the thesis (roadmap)
A thesis introduction is typically about 10% of the total length of your paper. If your introduction includes diagrams or figures, the length may be longer. It is critical to include all of the points above when writing a clear and compelling introduction. You may include additional elements if you feel they are essential in introducing your topic to the audience.
Thesis introduction: Getting started
If you do decide to write your introduction first, you can draw on the information in your thesis/dissertation proposal to help construct your draft.
How should you draft your thesis introduction, and when should you do it?
Despite the fact that your introduction comes first in the structure of your thesis, there is absolutely no need to write it first. Starting your thesis is often difficult and overwhelming, and many writers suffer from blank page syndrome —the paralysis of not knowing where to start. For this reason, some people advocate writing a kind of placeholder introduction when you begin, just to get something written down. You are free to write the introduction section at the beginning, middle, or end of the thesis drafting process . I personally find it preferable to write the introduction to a paper after I have already drafted a significant portion of the remainder of the paper. This is because I can draw on what I have written already to make sure that I cover all of the important points above.
However, if you do decide to write your introduction first, you can draw on the information in your thesis/dissertation proposal to help construct your draft. Just keep in mind that you will need to revisit your introduction after you have written the rest of your thesis to make sure it still provides an accurate roadmap and summary of the paper for your readers.
Topic and background information
When you introduce your topic, you want to draw your reader in.
Your thesis introduction should begin by informing the reader what your topic is and providing them with some relevant background information. The amount of background information you provide in this step will actually depend on what type of thesis/dissertation you are writing.
If you are writing a paper in the natural sciences or some social sciences, then it will have a separate background section after the introduction. Not a lot of background information is needed here. You can just state the larger context of the research. However, if your paper is structured such that there is no separate background chapter, then this portion of your thesis will be a bit longer and that is okay.
When you introduce your topic, you want to draw your reader in. Provide them with the reasons your research is interesting and important so that they will want to keep reading. Don’t be afraid to offer up some surprising facts or an interesting anecdote. You don’t need to be sensationalist, but your writing does not have to be dry and boring also! It is encouraged that you try to connect to your reader by offering them a relevant fact or story about your topic.
Example (topic) Weaknesses in financial regulatory systems in the United States
Example (context): Highlight some news stories about banks allowing money laundering on a massive scale, which financed gangs and led to more street drugs in major American cities. You could include a story about someone personally impacted by drugs in their neighborhood and then connect the presence of drugs to the gangs who were allowed to launder their money through big banks.
Focus and scope of your thesis
Once you have introduced your reader to the broader topic and provided some background information, you might want to explain the specific focus and scope of your thesis.
Once you have introduced your reader to the broader topic and provided some background information, you might want to explain the specific focus and scope of your thesis. What aspect of your topic will you research in particular? Why? What will your research not cover, and why? While this second part is optional, it is often helpful to be very specific about the aims of your research.
Example : Regulatory capture in the Federal Reserve and how it contributes to lax enforcement of anti-money laundering regulations.
You might write about this by explaining that your study focuses on regulatory capture in the Federal Reserve because they are one of the primary regulatory bodies monitoring the financial institutions, which were caught allowing money laundering. You could further specify that you will be focusing specifically on the role the Federal Reserve plays in monitoring banks for compliance with anti-money laundering laws; however, you will not be talking about the role they play in monitoring for compliance in other areas such as loans or mergers. This prepares your reader for what they are going to read and sets their expectations for what will come next.
Explaining the relevance and importance of your research
You must explain to the reader why your research matters, and by implication, why your reader should continue reading!
This is one of the most critical parts of your introduction. You must explain to the reader why your research matters, and by implication, why your reader should continue reading! Your research does not have to be completely revolutionary or groundbreaking to have value. You don’t need to inflate the importance of the thesis/dissertation you are writing when explaining why the research you have done is worthwhile.
Example: Corruption is an increasingly important issue in the maintenance and promotion of democratic norms and good governance. Without the ability to enforce effective penalties against institutions that turn a blind eye to money laundering, democratic governments like the United States will be threatened by the increasing power of bad actors flouting regulations. With the dollar being the global reserve currency, the US must enforce anti-money laundering legislation at home to have any hopes of shutting down global networks of corrupt operators that rely on its financial institutions. Identifying the presence of regulatory capture in the Federal Reserve sounds the alarm bell for lawmakers and regulators and suggests important interventions for policymakers are needed.
The above example clearly explains the wider impact of the issue without making overly broad statements such as “this research will revolutionize financial regulation in the United States as we know it” or “this research provides a roadmap for ending corrupt financial flows.” Just focus on what made the issue important and interesting to you and clearly state it within the broader context you provided earlier on.
Giving your reader a roadmap
At the end of your thesis introduction, you will want to provide your reader with a roadmap to the rest of the thesis.
At the end of your thesis introduction, you will want to provide your reader with a roadmap to the rest of the thesis. This differs from your table of contents in that it provides more context and details for how and why you have structured your thesis the way you have. The format of “first, next, finally” is a clear and easy way to structure this section of your introduction.
Example: First , this study reviews the existing literature on regulatory capture and how it impacts enforcement actions, with a specific focus on financial institutions and the history of the Federal Reserve. Next , it discusses the materials used for this research and how analysis was performed. Finally , it explains the results of the data analysis and investigates what the results mean and implications for future policymaking.
Now your reader knows exactly what to expect and how this fits into your overall aims and objectives. They are primed with the knowledge of your topic, its background, its relevance, and your specific focus in this study.
One common problem people have when writing an introduction to a thesis is actually writing too much . Many students and young researchers fear they won’t have enough to say and then will find themselves with a super long introduction that they somehow need to cut in half. You don’t have to give too much detail in the introduction of your thesis! Remember, the substance of your paper is located in the chapters that follow. If you are struggling with how to cut down (or add to) your introduction, you might benefit from the help of a professional editor who can see your paper with fresh eyes and quickly help you revise it. The introduction is the first part of your thesis/dissertation that people will read, so use these tips to make sure you write a great one! Check out our site for more tips on how to write a good thesis/dissertation, where to find the best thesis editing services , and more about thesis editing and proofreading services .
Editor’s pick
Get free updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights from the research and publishing industry!
Checklist: Tips for writing a compelling thesis introduction
Remember the below points when you are writing a thesis introduction:
Know your audience
Refer to your thesis/dissertation proposal or notes
Make sure you clearly state your topic, aims, and objectives
Explain why your research matters
Try to offer interesting facts or statistics that may surprise your reader and draw their interest
Draw a roadmap of what your paper will discuss
Don’t try to write too much detail about your topic
Remember to revise your introduction as you revise other sections of your thesis
What are the typical elements in an introduction section? +
The typical elements in an introduction section are as follows:
- Thesis statement
- Brief background of the study
- The focus and scope of the article
- The relevance and importance of your research
Do I have to write my introduction first? +
You can write your introduction section whenever you feel ready. Many writers save the introduction section for last to make sure they provide a clear summary and roadmap of the content of the rest of the paper.
How long should my introduction be? +
Most introductions are about 10% of the total paper, but can be longer if they include figures or diagrams.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to structure a thesis
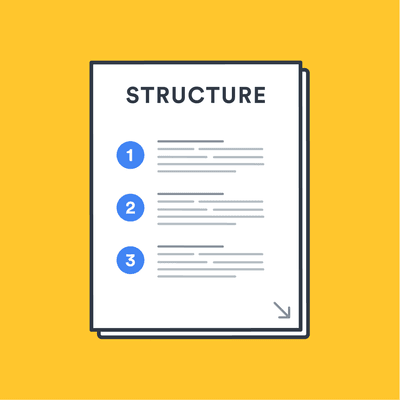
A typical thesis structure
1. abstract, 2. introduction, 3. literature review, 6. discussion, 7. conclusion, 8. reference list, frequently asked questions about structuring a thesis, related articles.
Starting a thesis can be daunting. There are so many questions in the beginning:
- How do you actually start your thesis?
- How do you structure it?
- What information should the individual chapters contain?
Each educational program has different demands on your thesis structure, which is why asking directly for the requirements of your program should be a first step. However, there is not much flexibility when it comes to structuring your thesis.
Abstract : a brief overview of your entire thesis.
Literature review : an evaluation of previous research on your topic that includes a discussion of gaps in the research and how your work may fill them.
Methods : outlines the methodology that you are using in your research.
Thesis : a large paper, or multi-chapter work, based on a topic relating to your field of study.
The abstract is the overview of your thesis and generally very short. This section should highlight the main contents of your thesis “at a glance” so that someone who is curious about your work can get the gist quickly. Take a look at our guide on how to write an abstract for more info.
Tip: Consider writing your abstract last, after you’ve written everything else.
The introduction to your thesis gives an overview of its basics or main points. It should answer the following questions:
- Why is the topic being studied?
- How is the topic being studied?
- What is being studied?
In answering the first question, you should know what your personal interest in this topic is and why it is relevant. Why does it matter?
To answer the "how", you should briefly explain how you are going to reach your research goal. Some prefer to answer that question in the methods chapter, but you can give a quick overview here.
And finally, you should explain "what" you are studying. You can also give background information here.
You should rewrite the introduction one last time when the writing is done to make sure it connects with your conclusion. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our thesis introduction guide .
A literature review is often part of the introduction, but it can be a separate section. It is an evaluation of previous research on the topic showing that there are gaps that your research will attempt to fill. A few tips for your literature review:
- Use a wide array of sources
- Show both sides of the coin
- Make sure to cover the classics in your field
- Present everything in a clear and structured manner
For more insights on lit reviews, take a look at our guide on how to write a literature review .
The methodology chapter outlines which methods you choose to gather data, how the data is analyzed and justifies why you chose that methodology . It shows how your choice of design and research methods is suited to answering your research question.
Make sure to also explain what the pitfalls of your approach are and how you have tried to mitigate them. Discussing where your study might come up short can give you more credibility, since it shows the reader that you are aware of its limitations.
Tip: Use graphs and tables, where appropriate, to visualize your results.
The results chapter outlines what you found out in relation to your research questions or hypotheses. It generally contains the facts of your research and does not include a lot of analysis, because that happens mostly in the discussion chapter.
Clearly visualize your results, using tables and graphs, especially when summarizing, and be consistent in your way of reporting. This means sticking to one format to help the reader evaluate and compare the data.
The discussion chapter includes your own analysis and interpretation of the data you gathered , comments on your results and explains what they mean. This is your opportunity to show that you have understood your findings and their significance.
Point out the limitations of your study, provide explanations for unexpected results, and note any questions that remain unanswered.
This is probably your most important chapter. This is where you highlight that your research objectives have been achieved. You can also reiterate any limitations to your study and make suggestions for future research.
Remember to check if you have really answered all your research questions and hypotheses in this chapter. Your thesis should be tied up nicely in the conclusion and show clearly what you did, what results you got, and what you learned. Discover how to write a good conclusion in our thesis conclusion guide .
At the end of your thesis, you’ll have to compile a list of references for everything you’ve cited above. Ideally, you should keep track of everything from the beginning. Otherwise, this could be a mammoth and pretty laborious task to do.
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to format and organize your citations. Paperpile allows you to organize and save your citations for later use and cite them in thousands of citation styles directly in Google Docs, Microsoft Word, or LaTeX:
🔲 Introduction
🔲 Literature review
🔲 Discussion
🔲 Conclusion
🔲 Reference list
The basic elements of a thesis are: Abstract, Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, Conclusion, and Reference List.
It's recommended to start a thesis by writing the literature review first. This way you learn more about the sources, before jumping to the discussion or any other element.
It's recommended to write the abstract of a thesis last, once everything else is done. This way you will be able to provide a complete overview of your work.
Usually, the discussion is the longest part of a thesis. In this part you are supposed to point out the limitations of your study, provide explanations for unexpected results, and note any questions that remain unanswered.
The order of the basic elements of a thesis are: 1. Abstract, 2. Introduction, 3. Literature Review, 4. Methods, 5. Results, 6. Discussion, 7. Conclusion, and 8. Reference List.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
Published on 9 September 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes.
The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation , appearing right after the table of contents . Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction.
Your introduction should include:
- Your topic, in context: what does your reader need to know to understand your thesis dissertation?
- Your focus and scope: what specific aspect of the topic will you address?
- The relevance of your research: how does your work fit into existing studies on your topic?
- Your questions and objectives: what does your research aim to find out, and how?
- An overview of your structure: what does each section contribute to the overall aim?
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to start your introduction, topic and context, focus and scope, relevance and importance, questions and objectives, overview of the structure, thesis introduction example, introduction checklist, frequently asked questions about introductions.
Although your introduction kicks off your dissertation, it doesn’t have to be the first thing you write – in fact, it’s often one of the very last parts to be completed (just before your abstract ).
It’s a good idea to write a rough draft of your introduction as you begin your research, to help guide you. If you wrote a research proposal , consider using this as a template, as it contains many of the same elements. However, be sure to revise your introduction throughout the writing process, making sure it matches the content of your ensuing sections.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Begin by introducing your research topic and giving any necessary background information. It’s important to contextualise your research and generate interest. Aim to show why your topic is timely or important. You may want to mention a relevant news item, academic debate, or practical problem.
After a brief introduction to your general area of interest, narrow your focus and define the scope of your research.
You can narrow this down in many ways, such as by:
- Geographical area
- Time period
- Demographics or communities
- Themes or aspects of the topic
It’s essential to share your motivation for doing this research, as well as how it relates to existing work on your topic. Further, you should also mention what new insights you expect it will contribute.
Start by giving a brief overview of the current state of research. You should definitely cite the most relevant literature, but remember that you will conduct a more in-depth survey of relevant sources in the literature review section, so there’s no need to go too in-depth in the introduction.
Depending on your field, the importance of your research might focus on its practical application (e.g., in policy or management) or on advancing scholarly understanding of the topic (e.g., by developing theories or adding new empirical data). In many cases, it will do both.
Ultimately, your introduction should explain how your thesis or dissertation:
- Helps solve a practical or theoretical problem
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Builds on existing research
- Proposes a new understanding of your topic
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Perhaps the most important part of your introduction is your questions and objectives, as it sets up the expectations for the rest of your thesis or dissertation. How you formulate your research questions and research objectives will depend on your discipline, topic, and focus, but you should always clearly state the central aim of your research.
If your research aims to test hypotheses , you can formulate them here. Your introduction is also a good place for a conceptual framework that suggests relationships between variables .
- Conduct surveys to collect data on students’ levels of knowledge, understanding, and positive/negative perceptions of government policy.
- Determine whether attitudes to climate policy are associated with variables such as age, gender, region, and social class.
- Conduct interviews to gain qualitative insights into students’ perspectives and actions in relation to climate policy.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
I. Introduction
Human language consists of a set of vowels and consonants which are combined to form words. During the speech production process, thoughts are converted into spoken utterances to convey a message. The appropriate words and their meanings are selected in the mental lexicon (Dell & Burger, 1997). This pre-verbal message is then grammatically coded, during which a syntactic representation of the utterance is built.
Speech, language, and voice disorders affect the vocal cords, nerves, muscles, and brain structures, which result in a distorted language reception or speech production (Sataloff & Hawkshaw, 2014). The symptoms vary from adding superfluous words and taking pauses to hoarseness of the voice, depending on the type of disorder (Dodd, 2005). However, distortions of the speech may also occur as a result of a disease that seems unrelated to speech, such as multiple sclerosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
This study aims to determine which acoustic parameters are suitable for the automatic detection of exacerbations in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by investigating which aspects of speech differ between COPD patients and healthy speakers and which aspects differ between COPD patients in exacerbation and stable COPD patients.
Checklist: Introduction
I have introduced my research topic in an engaging way.
I have provided necessary context to help the reader understand my topic.
I have clearly specified the focus of my research.
I have shown the relevance and importance of the dissertation topic .
I have clearly stated the problem or question that my research addresses.
I have outlined the specific objectives of the research .
I have provided an overview of the dissertation’s structure .
You've written a strong introduction for your thesis or dissertation. Use the other checklists to continue improving your dissertation.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an outline of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarise the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .

Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2022, September 09). How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Scribbr. Retrieved 15 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/introduction/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is a dissertation | 5 essential questions to get started, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion.

Easily understand how to write a PhD thesis introduction
Feb 26, 2019

Have you checked out the rest of The PhD Knowledge Base ? It’s home to hundreds more free resources and guides, written especially for PhD students.
Get the introduction right and the rest of your dissertation will follow.

What is the purpose of a PhD thesis introduction?
1. establish your research territory (by situating your research in a broader context), 2. establish and justify your niche (by describing why your research is needed) , 3. explain the significance of your research (by describing how you conducted the research).
- What your thesis is about
- Why it is important
- How it was conducted
- How it is laid out
The introduction as a whole should outline the significance and relevance of the thesis. The main criteria for a PhD is its role as an original contribution to knowledge, so the introduction is the space in which you very clearly outline that contribution.
How to structure an PhD thesis introduction
A typical PhD thesis introduction follows the following format:
- Introduction to the introduction: a short version (of only a few paragraphs) of the thesis’ aims, research questions, contribution, objectives and findings.
- State the overarching topic and aims of the thesis in more detail Provide a brief review of the literature related to the topic (this will be very brief if you have a separate literature review chapter)
- Define the terms and scope of the topic
- Critically evaluate the current state of the literature on that topic and identify your gap
- Outline why the research is important and the contribution that it makes
- Outline your epistemological and ontological position
- Clearly outline the research questions and problem(s) you seek to address
- State the hypotheses (if you are using any)
- Detail the most important concepts and variables
- Briefly describe your methodology
- Discuss the main findings
- Discuss the layout of the thesis
Much like the abstract, the reader shouldn’t have to wait long before they understand the contribution, what you are doing and how you are doing it. So, you’ll start by presenting your research in a clear, concise way in the opening few paragraphs. These opening paragraphs should briefly summarise the aims, objectives, research questions, main argument and contribution.
The reader shouldn’t have to wait long before they understand the contribution, what you are doing and how you are doing it.
A useful exercise here is to try and write the core elements of an introduction on a Post-it note. Keep trying until they fit. When they do, use that as the basis for these first few paragraphs. This is the same technique you use when filling out the PhD Writing Template .
As you go through the chapter, you will dial down into more and more detail. That means that the next stage, after the first few paragraphs, is to provide some context (steps 2-10 above).
Here you provide all the detail necessary to situate the study and make sense of the opening few paragraphs.
But, there are two things to bear in mind.
You will need to ease into the detail gently. Don’t launch straight from your opening paragraphs into huge amounts of detail. Follow the order of the 13 steps above and you will gradually ease into your discussion.
The danger of presenting too much information too soon is that you will confuse the reader. They will struggle to understand how the information you present is relevant and will struggle to understand how it relates to your thesis aims and objectives.
Simply follow the steps above.
You need to bear in mind that the level of detail you will go into (and therefore the length of the introduction) depends on the structure of your thesis.
If you have a standalone literature review, you will go into less detail about the current state of the literature and the gaps within it.
Similarly, if you have a dedicated theory chapter, you will not need to spend too much time on developing your theory framework.
The same is true for your methods.
The goal in any case is to present enough context to situate and make sense of your research questions but not overburden the reader with information that is superfluous to the goal of situating the research and which you will repeat at a later juncture anyhow.

Your PhD thesis. All on one page.
Use our free PhD structure template to quickly visualise every element of your thesis.
Common problems when writing your introduction
When we proofread PhDs , we see the same mistakes again and again.
Providing too much detail
There is a tendency to provide too much background information in the introduction. As we saw above, quite how much information you present in your thesis will depend on whether you have a standalone literature review or methods chapter. What you want to avoid is any unnecessary repetition.
Sometimes there is necessary repetition though. You need to present just enough information to contextualise your study and to be able to situate your aims, research questions an argument, but not too much that you end up confusing and bombarding the reader. Keep things simple here; it’s fine to overlook some of the more technical detail at this stage. Think of a newspaper article: the first couple of paragraphs provide a brief overview of the story. The detail comes later.
Not providing enough detail
On the flip side, some students don’t provide enough detail. The danger here is that the reader is left asking questions at the end of the introduction. Remember: they should be able to understand what your thesis is about, how it was conducted and why it is important just from reading the introduction. If you present too little detail then they won’t be able to. Read through your own introduction; is it clear what your contribution is and why it is important? If not, you haven’t got enough detail.
Launching into too much detail
Make sure you introduce gently. Don’t suddenly rush into lots of detail. Instead, you should make the aims, questions and contribution clear in the opening lines and then gradually layer on more detail. That way, the reader can keep up. Present too much detail too soon and the reader will become confused. The last place you want confusion is in the introduction; if the reader can’t follow your introduction, they won’t understand the thesis.
Not following a coherent structure so that the reader is left confused
Some students don’t follow a coherent logic when they write their introductions, which means that the reader is left confused.
For example, if you present too much background information and literature review before you outline the aim and purpose of the research, the reader will struggle to follow, because they won’t know why the background information is important.
The same is true if you discuss the methods before your research questions.
What we see often is important information being spread throughout the introduction in such a way that the reader has to hunt for it. Follow our layout guide above so that each piece of vital information is contained in its own mini section. Make your reader’s job as easy as possible.
Using too much technical language not properly defined
It’s more than likely that your research relies upon lots of technical terms, concepts and techniques. If you must talk about any of these in the introduction, be sure to offer clear and concise definitions. A failure to do so means that the reader is left confused.
Conducting a literature review
Unless you are explicitly avoiding a standalone literature review chapter, the introduction is not the place to review the literature. Sure, you will need to situate your study in a body of literature, but the introduction isn’t the place to critically discuss it or justify its inclusion in that literature. It’s enough to say that you will contribute to X body of literature and briefly discuss its core features and shortcomings. The literature review is the place to justify that decision and elaborate upon its features. Read our guide to writing literature reviews and our guide to being critical when you do so.
Finalising your thesis introduction
Once you have finished your thesis, ask yourself the following questions:
- Does the first line of the introduction discuss the problem that your thesis is addressing and the contribution that it is making?
- Does the introduction provide an overview of the thesis and end with a brief discussion on the content of each chapter?
- Does the introduction make a case for the research?
- Have the research questions/problems/hypotheses been clearly outlined (preferably early on)?
Now you know how to present your research as clearly and concisely as possible. Your reader (and examiner) will thank you, because they’ll be able to understand exactly what your study is about just from reading the introductory pages. Keep this guide to hand, whatever stage of the writing process you are at.
Have you downloaded our free one page PhD Writing Template ? It’s a really effective way to visualise your entire thesis on one page.
If you’re still struggling to structure your introduction, or you need any other support as you write your thesis, check out our one-on-one PhD coaching . It’s like having a personal trainer, but for your PhD.
Share this:
12 comments.
I was struggling with writing the introduction chapter. Really had no idea on how to organise my ideas. Completely lost and desolate. I have no one to encourage or support me. I prayed to God to give me knowledge and wisdom and guide me. After a while I found this site. Praise the Lord. I can’t thank u enough for addressing exactly what’s in my mind. Thank you. Glory be to God for directing me to this site.
All we aim to do here is to make life a little bit easier for PhD students. I know how hard I found it when I was completing mine, so I want to give something back to the community. I’m so pleased you found it useful. Good luck with writing up. If you need any support or if you have any questions at all, email me: [email protected]
Thank you very very much for your information it is resourceful. I was having a problem how to start my introduction.
It’s great to hear you found it useful. Thanks!
Hey, this is so useful thankyou! I’m wondering does this apply broadly to all PhD’s including humanities?
Yep – it sure does.
I found this piece of information helpful. I am preparing for my proposal defense in two weeks and needed to refine my introduction. Thank you very much. God bless you richly. I wish we can have a skype conversation.
Thank you again.
thank you, learned from this
Your advice and guidance has become my constant companion in what has been a very stressful time. You write with empathy and understanding. What a wonderful job you are doing for those of us who are too proud to seek advice and support from supervisors or colleagues. Sincerest thanks for taking the loneliness out of writing.
Such nice words. Thank you so much.
this is really useful!!!
Thanks Nora! I’m glad you found it useful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Your PhD and Covid
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Table of contents.

Definition:
Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student’s original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
History of Thesis
The concept of a thesis can be traced back to ancient Greece, where it was used as a way for students to demonstrate their knowledge of a particular subject. However, the modern form of the thesis as a scholarly document used to earn a degree is a relatively recent development.
The origin of the modern thesis can be traced back to medieval universities in Europe. During this time, students were required to present a “disputation” in which they would defend a particular thesis in front of their peers and faculty members. These disputations served as a way to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and were often the final requirement for earning a degree.
In the 17th century, the concept of the thesis was formalized further with the creation of the modern research university. Students were now required to complete a research project and present their findings in a written document, which would serve as the basis for their degree.
The modern thesis as we know it today has evolved over time, with different disciplines and institutions adopting their own standards and formats. However, the basic elements of a thesis – original research, a clear research question, a thorough review of the literature, and a well-argued conclusion – remain the same.
Structure of Thesis
The structure of a thesis may vary slightly depending on the specific requirements of the institution, department, or field of study, but generally, it follows a specific format.
Here’s a breakdown of the structure of a thesis:
This is the first page of the thesis that includes the title of the thesis, the name of the author, the name of the institution, the department, the date, and any other relevant information required by the institution.
This is a brief summary of the thesis that provides an overview of the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
This page provides a list of all the chapters and sections in the thesis and their page numbers.
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the research question, the context of the research, and the purpose of the study. The introduction should also outline the methodology and the scope of the research.
Literature Review
This chapter provides a critical analysis of the relevant literature on the research topic. It should demonstrate the gap in the existing knowledge and justify the need for the research.
Methodology
This chapter provides a detailed description of the research methods used to gather and analyze data. It should explain the research design, the sampling method, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures.
This chapter presents the findings of the research. It should include tables, graphs, and charts to illustrate the results.
This chapter interprets the results and relates them to the research question. It should explain the significance of the findings and their implications for the research topic.
This chapter summarizes the key findings and the main conclusions of the research. It should also provide recommendations for future research.
This section provides a list of all the sources cited in the thesis. The citation style may vary depending on the requirements of the institution or the field of study.
This section includes any additional material that supports the research, such as raw data, survey questionnaires, or other relevant documents.
How to write Thesis
Here are some steps to help you write a thesis:
- Choose a Topic: The first step in writing a thesis is to choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. You should also consider the scope of the topic and the availability of resources for research.
- Develop a Research Question: Once you have chosen a topic, you need to develop a research question that you will answer in your thesis. The research question should be specific, clear, and feasible.
- Conduct a Literature Review: Before you start your research, you need to conduct a literature review to identify the existing knowledge and gaps in the field. This will help you refine your research question and develop a research methodology.
- Develop a Research Methodology: Once you have refined your research question, you need to develop a research methodology that includes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis procedures.
- Collect and Analyze Data: After developing your research methodology, you need to collect and analyze data. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, experiments, or analyzing existing data.
- Write the Thesis: Once you have analyzed the data, you need to write the thesis. The thesis should follow a specific structure that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- Edit and Proofread: After completing the thesis, you need to edit and proofread it carefully. You should also have someone else review it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Submit the Thesis: Finally, you need to submit the thesis to your academic advisor or committee for review and evaluation.
Example of Thesis
Example of Thesis template for Students:
Title of Thesis
Table of Contents:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Literature Review
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
Chapter 4: Results
Chapter 5: Discussion
Chapter 6: Conclusion
References:
Appendices:
Note: That’s just a basic template, but it should give you an idea of the structure and content that a typical thesis might include. Be sure to consult with your department or supervisor for any specific formatting requirements they may have. Good luck with your thesis!
Application of Thesis
Thesis is an important academic document that serves several purposes. Here are some of the applications of thesis:
- Academic Requirement: A thesis is a requirement for many academic programs, especially at the graduate level. It is an essential component of the evaluation process and demonstrates the student’s ability to conduct original research and contribute to the knowledge in their field.
- Career Advancement: A thesis can also help in career advancement. Employers often value candidates who have completed a thesis as it demonstrates their research skills, critical thinking abilities, and their dedication to their field of study.
- Publication : A thesis can serve as a basis for future publications in academic journals, books, or conference proceedings. It provides the researcher with an opportunity to present their research to a wider audience and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.
- Personal Development: Writing a thesis is a challenging task that requires time, dedication, and perseverance. It provides the student with an opportunity to develop critical thinking, research, and writing skills that are essential for their personal and professional development.
- Impact on Society: The findings of a thesis can have an impact on society by addressing important issues, providing insights into complex problems, and contributing to the development of policies and practices.
Purpose of Thesis
The purpose of a thesis is to present original research findings in a clear and organized manner. It is a formal document that demonstrates a student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. The primary purposes of a thesis are:
- To Contribute to Knowledge: The main purpose of a thesis is to contribute to the knowledge in a particular field of study. By conducting original research and presenting their findings, the student adds new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- To Demonstrate Research Skills: A thesis is an opportunity for the student to demonstrate their research skills. This includes the ability to formulate a research question, design a research methodology, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- To Develop Critical Thinking: Writing a thesis requires critical thinking and analysis. The student must evaluate existing literature and identify gaps in the field, as well as develop and defend their own ideas.
- To Provide Evidence of Competence : A thesis provides evidence of the student’s competence in their field of study. It demonstrates their ability to apply theoretical concepts to real-world problems, and their ability to communicate their ideas effectively.
- To Facilitate Career Advancement : Completing a thesis can help the student advance their career by demonstrating their research skills and dedication to their field of study. It can also provide a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
When to Write Thesis
The timing for writing a thesis depends on the specific requirements of the academic program or institution. In most cases, the opportunity to write a thesis is typically offered at the graduate level, but there may be exceptions.
Generally, students should plan to write their thesis during the final year of their graduate program. This allows sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis. It is important to start planning the thesis early and to identify a research topic and research advisor as soon as possible.
In some cases, students may be able to write a thesis as part of an undergraduate program or as an independent research project outside of an academic program. In such cases, it is important to consult with faculty advisors or mentors to ensure that the research is appropriately designed and executed.
It is important to note that the process of writing a thesis can be time-consuming and requires a significant amount of effort and dedication. It is important to plan accordingly and to allocate sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis.
Characteristics of Thesis
The characteristics of a thesis vary depending on the specific academic program or institution. However, some general characteristics of a thesis include:
- Originality : A thesis should present original research findings or insights. It should demonstrate the student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study.
- Clarity : A thesis should be clear and concise. It should present the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions in a logical and organized manner. It should also be well-written, with proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Research-Based: A thesis should be based on rigorous research, which involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources. The research should be well-designed, with appropriate research methods and techniques.
- Evidence-Based : A thesis should be based on evidence, which means that all claims made in the thesis should be supported by data or literature. The evidence should be properly cited using appropriate citation styles.
- Critical Thinking: A thesis should demonstrate the student’s ability to critically analyze and evaluate information. It should present the student’s own ideas and arguments, and engage with existing literature in the field.
- Academic Style : A thesis should adhere to the conventions of academic writing. It should be well-structured, with clear headings and subheadings, and should use appropriate academic language.
Advantages of Thesis
There are several advantages to writing a thesis, including:
- Development of Research Skills: Writing a thesis requires extensive research and analytical skills. It helps to develop the student’s research skills, including the ability to formulate research questions, design and execute research methodologies, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Contribution to Knowledge: Writing a thesis provides an opportunity for the student to contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. By conducting original research, they can add new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- Preparation for Future Research: Completing a thesis prepares the student for future research projects. It provides them with the necessary skills to design and execute research methodologies, analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Career Advancement: Writing a thesis can help to advance the student’s career. It demonstrates their research skills and dedication to their field of study, and provides a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
- Personal Growth: Completing a thesis can be a challenging and rewarding experience. It requires dedication, hard work, and perseverance. It can help the student to develop self-confidence, independence, and a sense of accomplishment.
Limitations of Thesis
There are also some limitations to writing a thesis, including:
- Time and Resources: Writing a thesis requires a significant amount of time and resources. It can be a time-consuming and expensive process, as it may involve conducting original research, analyzing data, and producing a lengthy document.
- Narrow Focus: A thesis is typically focused on a specific research question or topic, which may limit the student’s exposure to other areas within their field of study.
- Limited Audience: A thesis is usually only read by a small number of people, such as the student’s thesis advisor and committee members. This limits the potential impact of the research findings.
- Lack of Real-World Application : Some thesis topics may be highly theoretical or academic in nature, which may limit their practical application in the real world.
- Pressure and Stress : Writing a thesis can be a stressful and pressure-filled experience, as it may involve meeting strict deadlines, conducting original research, and producing a high-quality document.
- Potential for Isolation: Writing a thesis can be a solitary experience, as the student may spend a significant amount of time working independently on their research and writing.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

Structuring a Thesis Introduction
A few weeks ago, I had a post on writing introductions , in which I discussed the standard three moves of an introduction. This model works very naturally in a short space such as a research proposal or article but can be harder to realize on the bigger canvas of a thesis introduction. Many thesis writers struggle with the need to provide adequate contextualizing detail before being able to give a satisfying account of their problem. Truth be told, this inclination—the feeling that our problem is so complex that any explanation will require extensive background—can be a bit of a graduate student weakness. Understanding that your thesis can be explained in a compressed fashion is often a step forward, if for no other reason than it can give you the wherewithal to answer the inevitable questions about your thesis topic without the stammering and the false starts and the over-reliance on the word ‘complicated’. I suggest that thesis writers take every possible opportunity to articulate their topic under severe space or time constraints. One possibility: look to see if your campus is having a Three Minute Thesis competition.
When I approach a thesis introduction, I start from the assumption that the reader shouldn’t have to wait to hear your guiding problem until they have the full context to that problem. You have to find a way of giving them the big picture before the deep context. Let’s take an imaginary example. You are writing your thesis on the reappearance of thestrals in the 1980s in Mirkwood Forest in the remote country of Archenland after a devastating forest fire caused by mineral extraction in the 1950s.* How are you going to structure an introduction in such a way that your reader doesn’t have to read 10 pages of bewildering and seemingly unconnected background? When a thesis writer attempts to give the full context before elaborating the problem, two things will happen. First, the reader will labour to see the significance of all that they are being told. Second, the reader will, in all likelihood, struggle to find connections between the various aspects of the context. Once you have explained what we need to know about thestrals, you will need to discuss the topography of Mirkwood, the endangered species policy framework in Archenland, the mineral extraction practices commonly used in the 1950s, and the way forest fires affect animal populations. If you haven’t started with your problem—the thing that brings these disparate areas into a meaningful conversation with each other—your introduction will begin with a baffling array of potentially disconnected bits of information.
The simplest solution to this problem is to provide a quick trip through the whole project in the first few paragraphs, before beginning to contextualize in earnest. I am picturing a thesis introduction that looks something like this:
- Introduction to the introduction: The first step will be a short version of the three moves, often in as little as three paragraphs, ending with some sort of transition to the next section where the full context will be provided.
- Context: Here the writer can give the full context in a way that flows from what has been said in the opening. The extent of the context given here will depend on what follows the introduction; if there will be a full lit review or a full context chapter to come, the detail provided here will, of course, be less extensive. If, on the other hand, the next step after the introduction will be a discussion of method, the work of contextualizing will have to be completed in its entirely here.
- Restatement of the problem: With this more fulsome treatment of context in mind, the reader is ready to hear a restatement of the problem and significance; this statement will echo what was said in the opening, but will have much more resonance for the reader who now has a deeper understanding of the research context.
- Restatement of the response: Similarly, the response can be restated in more meaningful detail for the reader who now has a better understanding of the problem.
- Roadmap: Brief indication of how the thesis will proceed.
What do you think about this as a possible structure for a thesis introduction? While I realize that it may sound a little rigid, I think such an approach is warranted here. Using this type of structure can give thesis writers an opportunity to come to a much better understanding of what they are trying to say. In other words, in my experience, thesis writers tend to feel better after reconstructing their introductions along these lines. For some, it may prove a useful way to present their introduction in their final draft; for other, it may just be a useful scaffold, something that they can improve upon once everything is on a surer footing.
Using this structure can help the writer craft an introduction that responds to the needs of the reader , rather than the demands of the material. Typically, the thesis introductions that I see provide an introduction to the topic but not necessarily to the piece of writing. Writers—especially writers in the throes of trying to conceptualize a book length research project—often forget that the audience’s ability to engage with the topic is mediated by the text. Introducing your introduction is one way to meet your key responsibility to guide the reader through the text . The thesis reader’s journey is a long one—why not do what you can to ensure that your reader sets off with the maximal understanding of their destination?
* With apologies to J.K. Rowling, J.R.R. Tolkien, and C.S. Lewis.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
34 responses to “ Structuring a Thesis Introduction ”
Pingback: Structuring a Thesis Introduction | University Life, Reviews and Study | Scoop.it
Pingback: Explorations of Style | the postmodern novel & beyond
The resurfacing of this post is so timely. I am currently drafting my introduction and am startled to find myself struggling to articulate my research question after just under a year working on it….! Thanks for another very helpful post.
Thank you for this post! I was hesitating about writing what you call “the introduction to the introduction” because it seemed a bit prim to me, but now that you gave this nifty example, I feel it is a great idea!
Thanks. I really like the word ‘prim’ to describe our trepidation about being more explicit about the moves we are making in our writing. I think it’s very possible to feel slightly embarrassed about spelling things out or about repeating ourselves in our writing. I wonder if we feel that we ought to be able to convey what we are doing in our writing without having to tell the reader what is going on, but I think this sets the bar pretty high! What I try to do in my own writing is to go ahead and make my intentions as explicit as possible, with the understanding that I may wish to go back and polish it later. Even if we don’t end up liking the first version very much, we always benefit from the exercise of making our intentions plain.
Yes, the best is that we will just going on and try to pursue our intentions. Editing or polishing it afterwards will help us refine anything what we wished to happen. Just like “thesis making”, it needs critiques to reach “our intentions” as you said.
Yes Tabea, writing “introduction” is the most difficult part of thesis making. It seems I was in the abyss looking for a single streak of light to guide me to the right path for my younger sisters’ thesis proposal as her prerequisites for graduation, 2 decades ago. Actually, writing “introduction” will not just happened once, but you keep editing your “introduction” especially when you are about to finish your chapter 3. The tips I can share at you is just try to make your “introduction” and make some edits afterwards . . . http://gabrinezgemina0.wordpress.com/2014/02/24/helping-guiding-and-coaching-you-on-your-thesis/
I’ve been royally struggling with the entire format of my thesis, despite being what I would consider a competent writer. Thank you for de-mystifying things 🙂
I would love to know what to call the introduction to the Introduction. Mine needs a heading of some description!
If the introduction chapter has a name other than “Introduction”, then you could just call the opening bit “Introduction”. If, on the other hand, your introductory chapter is going to be called “Introduction,” I guess you have two options. You could just leave it unnamed. That is, your first section would have no heading; once the intro-to-the-intro is complete, you would provide your first heading. Or you could give it a name that is either generic (“Overview” or “Setting the Stage”) or specific (something broad that plays on your thesis topic).
Thanks Rachael. My introduction is called just that but has several sub-headings. I was also thinking along the lines of ‘overview’.
thanks that helped me alot
WOW this helps me a lot. Thanks!!!
Thanks for your insight into writing a thesis introduction. I was just wondering if you could expand slightly on the “roadmap”. Where I’m going with my thesis sounds like what I would be writing in my response. Thank you again!
Thanks, Haley. By roadmap, I just mean the elaboration of what is to come in the thesis. “In the next chapter, I will …” and “The following chapters will be devoted to …”. That sort of thing. Since different theses can have such different introductions and then such different structures, the reader will usually benefit from an explicit elaboration of the overall plan. In my experience, writing a roadmap can also be quite instructive because it pushes us to lay out the relationships among the various parts.
Thanks. This is quite helpful. Quick question though. Under Introduction to the introduction, you mention that ”The first step will be a short version of the three moves…..
”What are the ”three moves” that you talk about here?
That is explained in the previous post, which I link to in the first sentence. Or you can follow this link .
As what I have said earlier that doing an introduction is the most difficult part of thesis making but everything in introduction is your intentions about the problem you want to study and that is the title of your thesis, actually as coach, I will let my clients to follow 8 steps to make their introduction complete because the first part of thesis is called Chapter 1 and others preferred to call it as “Introduction”. Either of these two has all the same purpose. It is always refers to “The Problem”. To know those 8 steps to follow and to make your introduction complete please click this link https://gabrinezgemina0.wordpress.com/2014/03/13/how-to-make-chapter-1-or-introduction-on-thesis/
Pingback: beginners in writing | About Resarch
Pingback: Online resources about research | Bits of HCI Design
Pingback: Facing the Challenges of Academic Writing – Academic Writing Center
Reblogged this on mydiaryspeaksblog .
This is absolutely brilliant exposition. You have confirmed everything my experience has taught me about what an introduction should be. Thank you!
Pingback: How to Write a Good PhD Introduction: Collected Resources | Turbulent London
This is exactly what I’ve needed. I’ve been taught the basics so many times that I feel it unraveled any ability I had to formulate a thesis. I appreciate this deconstruction so much. You have no idea.
I found this reassuring, as this was exactly what I was instinctively doing in my introduction. Thank you so much!
By “this” I mean writing an intro to the introduction chapter 🙂
Pingback: The Semester Finish Line – #ResNetSem
What a gem of a post! I’m currently working on my thesis and it can seem so overwhelming but this advice has definitely helped. thank you so much 🙂
Pingback: Thesis writing resources – Emma McIntosh
Pingback: Thesis introduction – Research Pointers
Pingback: Beginnings, Notes to a Client – LA BUHARDILLA WRITING COLLECTIVE
I came here after writing quite a good introduction in a search for an answer whether to do subheadings in there or not (of which I’m still not convinced).
I was happy to see that my introduction does most of what you recommend, except for the intro to the intro. For my project, I can’t really get behind it, partly because it would slightly break the flow of what I’ve written, but also because it seems slightly formulaic.
I think it makes sense only when your introduction is of a certain length. Mine is not yet a PhD thesis, only a Masters project, and as it is slightly less than a page, I feel it can probably be left out. If someone reads the whole thing back-to-back they would have came by the abstract already anyway.
Thanks, Petr. You are right–an intro to the intro would be redundant in a short introduction. As a separate point, while most people will come to your introduction having already read the abstract, it’s good practice to make sure the introduction stands alone.
I would say that subheadings aren’t going to be helpful in a short introduction. The goal of subheadings is to help a reader understand the linkages in your work; when they are deployed in a short text, they tend instead to undermine linkages and make things feel choppy.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Three key principles.
1. Using writing to clarify your own thinking 2. Committing to extensive revision 3. Understanding the needs of your reader
Looking for something?
Table of contents.
If you’d like an overview of all my past posts, please visit the Archives page.
Recent Posts
- Thriving as a Graduate Writer
- Looking Productive
- Breaking Points
- Conservatism of Expectations
- Nobody’s First Language
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address:
Recent Twitter Activity

Five Key Strategies
1. Reverse Outlines : Exposing the internal structure of a piece of writing by creating a reverse outline 2. Paragraphs : Treating paragraphs as important units in your writing 3. Transitions : Making effective transitions between sentences, paragraphs, and sections 4. Sentences : Crafting better sentences with three central strategies 5. Metadiscourse : Shaping the reader’s experience of your writing
- Nigel Caplan
- Writing For Research
- The Scholarly Kitchen
- Stroppy Editor
- Sentence First
- Scientist Sees Squirrel
- The Thesis Whisperer
- Research Degree Insider
- Raul Pacheco-Vega, PhD
- Literature Reviews: A Blog for the Exasperated
- Supervising PhDs
- Doctoral Writing SIG
- Cecile Badenhorst
- LSE Impact Blog
- The Professor Is In
Older Posts
- June 2023 (1)
- May 2023 (2)
- April 2023 (2)
- March 2023 (2)
- February 2023 (2)
- January 2023 (1)
- April 2022 (1)
- March 2022 (1)
- January 2022 (2)
- July 2021 (1)
- December 2020 (1)
- August 2020 (1)
- July 2020 (1)
- April 2020 (1)
- March 2020 (1)
- February 2020 (1)
- December 2019 (1)
- November 2019 (1)
- February 2018 (1)
- August 2017 (1)
- April 2017 (1)
- March 2017 (1)
- January 2017 (1)
- October 2016 (1)
- August 2016 (1)
- March 2016 (1)
- January 2016 (2)
- November 2015 (1)
- October 2015 (1)
- September 2015 (1)
- June 2015 (1)
- May 2015 (1)
- April 2015 (1)
- February 2015 (1)
- January 2015 (1)
- December 2014 (1)
- October 2014 (2)
- September 2014 (1)
- August 2014 (1)
- May 2014 (1)
- April 2014 (2)
- March 2014 (2)
- February 2014 (1)
- January 2014 (2)
- December 2013 (2)
- November 2013 (2)
- October 2013 (2)
- September 2013 (2)
- August 2013 (2)
- June 2013 (2)
- May 2013 (4)
- April 2013 (4)
- March 2013 (4)
- February 2013 (3)
- January 2013 (3)
- December 2012 (3)
- November 2012 (5)
- October 2012 (4)
- September 2012 (4)
- August 2012 (2)
- June 2012 (1)
- May 2012 (1)
- April 2012 (1)
- March 2012 (2)
- February 2012 (4)
- January 2012 (4)
- December 2011 (1)
- November 2011 (3)
- October 2011 (4)
- September 2011 (5)
- August 2011 (3)
- July 2011 (2)
- June 2011 (6)
- May 2011 (5)
- April 2011 (8)
- March 2011 (8)
- February 2011 (8)
- January 2011 (6)

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
What’s Included: Introduction Template
This template covers all the core components required in the introduction chapter/section of a typical dissertation or thesis, including:
- The opening section
- Background of the research topic
- Statement of the problem
- Rationale (including the research aims, objectives, and questions)
- Scope of the study
- Significance of the study
- Structure of the document
The purpose of each section is clearly explained, followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover. We’ve also included practical examples to help you understand exactly what’s required, along with links to additional free resources (articles, videos, etc.) to help you along your research journey.
The cleanly formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX.
PS – if you’d like a high-level template for the entire thesis, you can we’ve got that too .
Thesis Introduction FAQS
What types of dissertations/theses can this template be used for.
The template follows the standard format for academic research projects, which means it will be suitable for the vast majority of dissertations and theses (especially those within the sciences), whether they are qualitative or quantitative in terms of design.
Keep in mind that the exact requirements for the introduction chapter/section will vary between universities and degree programs. These are typically minor, but it’s always a good idea to double-check your university’s requirements before you finalize your structure.
Is this template for an undergrad, Master or PhD-level thesis?
This template can be used for a dissertation, thesis or research project at any level of study. Doctoral-level projects typically require the introduction chapter to be more extensive/comprehensive, but the structure will typically remain the same.
Can I share this template with my friends/colleagues?
Yes, you’re welcome to share this template in its original format (no editing allowed). If you want to post about it on your blog or social media, we kindly request that you reference this page as your source.
What format is the template (DOC, PDF, PPT, etc.)?
The dissertation introduction chapter template is provided as a Google Doc. You can download it in MS Word format or make a copy to your Google Drive. You’re also welcome to convert it to whatever format works best for you, such as LaTeX or PDF.
What is the core purpose of this chapter?
The introduction chapter of a dissertation or thesis serves to introduce the research topic, clearly state the research problem, and outline the main research questions. It justifies the significance of the study, delineates its scope, and provides a roadmap of the dissertation’s structure.
In a nutshell, the introduction chapter sets the academic tone and context, laying the foundation for the subsequent analysis and discussion.
How long should the introduction chapter be?
This depends on the level of study (undergrad, Master or Doctoral), as well as your university’s specific requirements, so it’s best to check with them. As a general ballpark, introduction chapters for Masters-level projects are usually 1,500 – 2,000 words in length, while Doctoral-level projects can reach multiples of this.
How specific should the research objectives be in the introduction chapter?
In this chapter, your research objectives should be specific enough to clearly define the scope and direction of your study, but broad enough to encompass its overall aims.
Make sure that each objective can be realistically accomplished within the scope of your study and that each objective is directly related to and supports your research question(s).
As a rule of thumb, you should leave in-depth explanations for later chapters; the introduction should just provide a concise overview.
Can I mention the research results in the introduction?
How do i link the introduction to the literature review.
To transition smoothly from the introduction chapter to the literature review chapter in a thesis, it’s a good idea to:
- Conclude the introduction by summarising the main points, such as the research problem, objectives, and significance of your study.
- Explicitly state that the following chapter (literature review) will explore existing research and theoretical frameworks related to your topic.
- Emphasise how the literature review will address gaps or issues identified in the introduction, setting the stage for your research question or hypothesis.
- Use a sentence that acts as a bridge between the two chapters. For example, “To further understand this issue, the next chapter will critically examine the existing literature on [your topic].”
This approach will help form a logical flow and prepare the reader for the depth and context provided in the literature review.
Do you have templates for the other chapters?
Yes, we do. We are constantly developing our collection of free resources to help students complete their dissertations and theses. You can view all of our template resources here .
Can Grad Coach help me with my dissertation/thesis?
Yes, you’re welcome to get in touch with us to discuss our private coaching services .

- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Thesis Structure: Writing Guide For Your Success

If you are about to start writing your thesis, then it is extremely important to know as much as possible about the thesis structure. Learning the main thesis chapters should enable you to quickly structure your academic paper. Keep in mind that not structuring the paper correctly usually leads to severe penalties. We know some of you are probably having questions about numbering dissertation chapters. Basically, you just need to give all the major sections consecutive numbers. Use Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, and so on). Check out the most frequently asked questions and them move on to the 7 parts of the thesis or dissertation structure.
Thesis Structure Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a basic good structure for a thesis? A: The best structure is the one listed below. It contains the 7 important parts any thesis should have.
- What does “the structure of this dissertation is in manuscript style” mean? A: It means that the thesis includes one or more manuscripts that have been written in a way that facilitates publication. The thesis can, in this case, be a collection of papers that have been written or co-authored by the student.
- Which chapters of dissertation are mandatory? A: All the 7 chapters below are necessary, if you want to get a top score on your paper.
- Where can I get a thesis structure template? A: You can quickly get a thesis structure example from one of our seasoned academic writers. Don’t base your thesis on mediocre samples you find online.
- What is the preferred thesis sentence structure? A: There is no set sentence structure that you have to follow. Just make sure your writing is organized in a logical manner and that all complex terms are explained the first time you use them.
Thesis Abstract
The first part of the thesis structure is the abstract. It is basically an overview of the entire paper. There is no set dissertation abstract structure. It is just a summary of your thesis and it should be just 200 to 300 words long.
Thesis Introduction
The introduction is one of the most important dissertation chapters. It should contain all of the following information:
A bit of background about the topic. Some information about the current knowledge. The aim of your research (the gap in knowledge that prompted you to write the thesis).
Remember that the introduction must present the thesis statement. It is very important to learn more about the thesis statement structure. A great thesis statement will pique the interest of the evaluation committee.
Thesis Literature Review
Many students who are looking to learn how to structure a thesis don’t know about the Literature Review section. Why? Because many people prefer to include it into the introduction. However, by separating the literature review from the intro, you can focus more on why your research is important. You can evaluate the most important research on your topic and clearly show the gap in knowledge.
Thesis Methods
In most cases, the Methods section is the easiest part of the structure of a thesis. All you have to do is present the method or methods you chose for the research. Don’t forget to also explain why you chose that specific research method. Your audience needs to understand that the chosen method is the best for the task.
Thesis Results
This is one of the most important chapters of a dissertation. In the Results chapter, you need to present your findings. Remember that written text is not enough. You need figures, stats, graphs, and other forms of data. This section contains all the facts of your research and should be written in an objective, neutral manner. It would be unusual for your to discuss your findings in this section.
Thesis Discussion
The Discussion chapter is very important in the dissertation chapters structure. It is the reason why you didn’t discuss your findings in the Results section. This is the section you can use to talk about your findings and provide your own opinions about the results. Here is what you can do in the discussion section:
Explain to the audience what your results mean for the scientific community. Comment on each of the results and discuss how your findings support your thesis. Explain any unexpected results so the evaluation committee can see that you know what you’re doing. Interpret the results and tie them with other research on the subject. How does your research help the academic community?
Thesis Conclusion
While not the most important chapter, the conclusion is one of the important chapters in a dissertation. It is the part where you can show your readers that you have achieved your research objectives. You can talk a bit about what you’ve learned in the process and even make some suggestions regarding the need for future research. In most cases, students also reiterate the thesis statement at the beginning of the conclusion, followed by a short summary of the paper’s most important chapters.
Still Not Sure How to Structure Thesis?
In case you are still struggling to find the best history dissertation structure, you should get some help as fast as possible. Remember that writing a thesis takes weeks, if not months. Don’t spend too much time trying to find the best structure. Instead, get in touch with a reliable academic company and get some quick assistance. For examples, one of our writers can create a thesis outline for you. You can just follow the outline and everything will be just fine.
Of course, you can also get some help with the thesis formatting. Citations and references can be difficult to master. Each academic writing style (MLA, Chicago, APA, etc.) has its own requirements. The way you format your academic paper is very important. Bolding and italicizing can emphasize certain ideas. A professional editor can help you make the thesis stand out from the rest. After all, a pleasantly-formatted dissertation that impresses the evaluation committee with its structure and quality of content has a very high chance of getting a top score.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write
2. Hook the reader and grab their attention. 3. Provide relevant background. 4. Give the reader a sense of what the paper is about. 5. Preview key points and lead into your thesis statement. Frequently Asked Questions about writing a good thesis introduction.
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
1. Research Background - Writing a Dissertation Introduction. This is the very first section of your introduction. Building a background of your chosen topic will help you understand more about the topic and help readers know why the general research area is problematic, interesting, central, important, etc.
Stages in a thesis introduction. state the general topic and give some background. provide a review of the literature related to the topic. define the terms and scope of the topic. outline the current situation. evaluate the current situation (advantages/ disadvantages) and identify the gap. identify the importance of the proposed research.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction.
A good thesis introduction doesn't shy away from limitations. Instead, it captures the reader's attention by laying them out systematically, often in a dedicated paragraph for each chapter. This honesty allows the reader to understand the research's focus and scope while providing a clear and easy-to-follow structure of the thesis.
Before you write a compelling thesis introduction, you need to know what elements belong in this section and how it should be structured. A typical thesis introduction includes: A clear thesis statement. An explanation of the context (brief background) for the study. The focus and scope of the paper.
1 - Start with a presentation of the general topic and provide some background information. 2 - Continue with a short overview of the actual literature related to the topic. (briefly! keep the extension for your literature review). 3 - Introduce the principal idea and name the scope of the topic.
A typical thesis structure. 1. Abstract. The abstract is the overview of your thesis and generally very short. This section should highlight the main contents of your thesis "at a glance" so that someone who is curious about your work can get the gist quickly. Take a look at our guide on how to write an abstract for more info.
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
How to structure an PhD thesis introduction. A typical PhD thesis introduction follows the following format: Introduction to the introduction: a short version (of only a few paragraphs) of the thesis' aims, research questions, contribution, objectives and findings. State the overarching topic and aims of the thesis in more detail.
Chapter 1: Introduction [The introduction sets the stage for your thesis, providing background information on the topic, explaining the research problem or question, and outlining the scope and objectives of your research. It should also include a brief overview of the structure of your thesis, indicating what will be covered in each chapter.]
Introduction to the introduction: The first step will be a short version of the three moves, often in as little as three paragraphs, ending with some sort of transition to the next section where the full context will be provided. Context: Here the writer can give the full context in a way that flows from what has been said in the opening.
Every good introduction needs a thesis statement, a sentence that plainly and concisely explains the main topic. Thesis statements are often just a brief summary of your entire paper, including your argument or point of view for personal essays. For example, if your paper is about whether viewing violent cartoons impacts real-life violence ...
The introduction chapter of a dissertation or thesis serves to introduce the research topic, clearly state the research problem, and outline the main research questions. It justifies the significance of the study, delineates its scope, and provides a roadmap of the dissertation's structure.
Remember that the introduction must present the thesis statement. It is very important to learn more about the thesis statement structure. A great thesis statement will pique the interest of the evaluation committee. Thesis Literature Review. Many students who are looking to learn how to structure a thesis don't know about the Literature ...