concrete technology Recently Published Documents
Total documents.
- Latest Documents
- Most Cited Documents
- Contributed Authors
- Related Sources
- Related Keywords

Use of Prefabrication, Construction and Demolition Wastes as an Aggregate in Vibropressed Precast Concrete Blocks Production
The aim of current study was to determine the recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) applicability in the production of concrete mixture for vibropressed concrete blocks. The experiments were focused especially on the crushed waste material from the same concrete elements producing plant. For this type of precast elements only some finer fractions can be implemented and the “earth-moist” consistency of fresh mixture is required. The series of samples was prepared in which the mixture of natural aggregates was partially or totally substituted by recycled concrete aggregate. The 0/4 RCA fraction, which is usually rejected in ready mix concrete technology, plays a role of 0/2 sand. The substitution of sand fraction was from 20% to 100% respectively. The substitution of the coarser aggregate fractions by 4/16 RCA was also done. The standard properties of vibropressed elements, such as the degree of densification, the density of material, the compressive and splitting tensile strength and the water absorption capacity according to the relevant standards were determined. The parameters of materials with the natural aggregate substitution by RCA are affected by the ratio of recycled concrete aggregate. In most cases the results do not decline specially from those for reference samples, when only the natural sand (0/2) fraction is substituted by the 0/4 recycled aggregate. As one could expect, as lower the substitution, as better the test results. The partial substitution of natural aggregate by coarser fractions requires experimental verification; over 20% substitution of natural aggregate by 4/8, 8/16 or 0/16 RCA should be excluded.
The properties of preplaced aggregate concrete technology contain the industrial waste-material and the various shapes and sizes of coarse aggregate
Abstract The success of preplaced aggregate concrete technology depends on two main factors which are potential grout and coarse aggregate. This research was conducted experimentally to determine the effect of using two different fly ash sources as an alternative for the partial replacement of cement and several size and shapes of coarse aggregate on the compressive and tensile strength of PAC specimens. This involved the use of seven concrete mixes with a low water-cement ratio of 0.4 and cement to sand ratio of 1:0.75 to produce standard cylinder specimens of concrete containing rounded and crush aggregate. Moreover, fly ash was added at a dosage of 5% and 10% of cement weight while three shapes and sizes of a rounded and crushed aggregate at 20 mm, 30 mm, and a mixture of the two were also applied. The results showed the compressive strength of specimens with different sizes or a mix of rounded aggregate in PAC exhibited a similar performance with 30 mm of crushed coarse aggregate. Furthermore, the specimen with a higher content of calcium fly ash demonstrated a more rapid strength at an early age of seven days than those with lower content. Therefore, the partial replacement of cement with industrial waste material in the form of fly ash in preplaced aggregate concrete has the ability to save up to 10% of cement and also produce certain environmental benefits.
3D printing-A Review of Materials, Applications, and Challenges
Abstract: Now a days 3-Dimensional Printing (3DP) technology is used world widely and it can actually print each and every thing with the desired computer program. In Construction engineering the challenges are like availability of skilled man power, time constraint, cost effectiveness and complicated shapes etc. But with the help of an automated machine, the 3D printing technology, has huge potential to have faster and more accurate construction of complex and more laborious works. This technology can build three-dimensional (3D) objects by connecting layers of materials and can be applied to convert waste and by-products into new materials. The 3DP in concrete construction is increasing thanks to its freedom in geometry, rapidness, formwork-less printing, low waste generation, eco-friendliness, cost-saving nature and safety. This paper attempts to review the digital printing technology introduced in the construction industry and the also highlights the impact on concrete technology. It also discusses about the materials used in 3DP, mix design, various applications and challenges in the construction industry. Keywords: 3D printing, Concrete, 3DCP, Mix design.
Novel Fuzzy-Based Optimization Approaches for the Prediction of Ultimate Axial Load of Circular Concrete-Filled Steel Tubes
An accurate estimation of the axial compression capacity of the concrete-filled steel tubular (CFST) column is crucial for ensuring the safety of structures containing them and preventing related failures. In this article, two novel hybrid fuzzy systems (FS) were used to create a new framework for estimating the axial compression capacity of circular CCFST columns. In the hybrid models, differential evolution (DE) and firefly algorithm (FFA) techniques are employed in order to obtain the optimal membership functions of the base FS model. To train the models with the new hybrid techniques, i.e., FS-DE and FS-FFA, a substantial library of 410 experimental tests was compiled from openly available literature sources. The new model’s robustness and accuracy was assessed using a variety of statistical criteria both for model development and for model validation. The novel FS-FFA and FS-DE models were able to improve the prediction capacity of the base model by 9.68% and 6.58%, respectively. Furthermore, the proposed models exhibited considerably improved performance compared to existing design code methodologies. These models can be utilized for solving similar problems in structural engineering and concrete technology with an enhanced level of accuracy.
Design of Cold-Mixed High-Toughness Ultra-Thin Asphalt Layer towards Sustainable Pavement Construction
Ultra-thin asphalt overlay has become the mainstream measure of road preventive maintenance due to its good economic benefits and road performance. However, hot mix asphalt concrete technology is widely used at present, which is not the most ideal way to promote energy saving and emission reduction in the field of road maintenance. At the same time, the ultra-thin friction course based on cold mix technology, such as slurry seal layer, micro-surface, and other technologies, are still far behind the hot mix friction course in terms of crack resistance. In this research, by establishing an integrated design of materials and structures, a cold paving technology called “high-toughness cold-mixed ultra-thin pavement (HCUP)” is proposed. The high-viscosity emulsified bitumen prepared by using high-viscosity and high-elasticity modified bitumen is used as the binder and sticky layer of HCUP. The thickness of HCUP is 0.8–2.0 cm, the typical thickness is 1.2 cm, and the nominal maximum size of the coarse aggregate is 8 mm. Indoor tests show that HCUP-8 has water stability, anti-skid performance, high temperature performance, peeling resistance, and crack resistance that are not weaker than traditional hot-mixed ultra-thin wear layers such as AC-10, Novachip, and GT-8. At the same time, the test road paving further proved that HCUP-8 has excellent road performance with a view to providing new ideas for low-carbon and environmentally friendly road materials.
Unspoken Modernity: Bamboo-Reinforced Concrete, China 1901-40
Abstract Engineering science in the China of 1901-40 had unique characteristics that disrupt the idea of a universal approach to its history.1 The following case study describes the ideas and trials of introducing bamboo into the seemingly globalised technology of reinforced concrete—an innovation developed across the borders of mechanical, naval, civil, and aeronautical engineering. The article showcases a way of knowing and working by twentieth century engineers that has not been fully acknowledged, and is not only a phenomenon of China. While bamboo was a complicated and somewhat marginal object for engineering, it did make the European concrete technology more viable in the construction sites of China, and stimulate engineers’ experimental and resourceful spirit in mobilising both craft and scientific knowledge. It also opened up a challenge to engineering science of the time.
Evaluation of Rapid Repair of Concrete Pavements Using Precast Concrete Technology: A Sustainable and Cost-Effective Solution
Abstract Concrete and asphalt are the two competitive materials for a highway. In Sweden, the predominant material for the highway system is asphalt. But under certain conditions, concrete pavements are competitive alternatives. For example, concrete pavements are suitable for high-traffic volume roads, roads in tunnels, concentrated loads (e.g., bus stops and industrial pavement). Besides the load-carrying capacity, the concrete pavement has many advantages such as durability (wear resistance), resistance against frost heave, environment (pollution, recycling, and low rolling resistance leading to fuel savings), fire resistance, noise limitations, brightness, evenness and aesthetics. Concrete pavements are long-lasting but need final repair. Single slabs may crack in the jointed concrete pavement due to various structural and non-structural factors. Repair and maintenance operations are, therefore, necessary to increase the service life of the structures. To avoid extended lane closures, prevent traffic congestions, and expedite the pavement construction process, precast concrete technology is a recent innovative construction method that can meet the requirement of rapid construction and rehabilitation of the pavement. This paper evaluates rapid repair techniques of concrete pavement using precast concrete technology by analysing three case studies on jointed precast concrete pavements. The study showed that the required amount of time to re-open the pavement to traffic is dramatically reduced with jointed precast concrete panels.
Water Absorption of Incorporating Sustainable Quarry Dust in Self-Compacting Concrete
Abstract In construction industry nowadays, self-compacting concrete (SCC) is a concrete technology innovation which gives more benefits over conventional concrete. SCC was invented to improve concrete durability without using any vibrator while placing it into formwork. In order to conserve natural sand, quarry dust (QD) as a waste and sustainable material has been incorporated to replace fine aggregate in SCC. In this study, conventional concrete and quarry dust in self-compacting concrete (QDSCC) mixes consist of 0%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40% and 50% QD were prepared. The workability test was conducted to determine the performance of fresh concrete and ensuring all the QDSCC properties follow the acceptance criteria for SCC. Meanwhile, the hardened concrete specimens were water cured for 7, 28 and 60 days to conduct water absorption test. This research aim is to determine water absorption of incorporating sustainable QDSCC. Thus, it resulted that 50% of QDSCC has achieved the lowest water absorption of QDSCC as compared to other dosages. Finally, sustainability in concrete technology can be promoted by incorporating QDSCC.
Application of electro-hydraulic shock in concrete technology
Abstract The aspects, related to the influence of the electrohydraulic shock method use in a water-cement slurry passing in a closed chamber (activation reactor) with a pre-applied pressure to the system under various processing modes are highlighted in the article. In order to test the effect of this method on water-cement slurry, an installation was developed, consisting of: a high-voltage source, a high-voltage diode, capacitor banks, a closing element and an activation reactor. The necessary experiments were carried out on the completed installation. The procedure for conducting experiments is described in the work, shows a schematic diagram of the installation for performing activation, a diagram of the reactor, and the processing modes. Several activation modes were considered, depending on: the number of pulses (1-4), pulse energy (0.5-8 kJ), water-cement ratio (0.2-0.35), time intervals for starting treatment from the moment the cement was mixed with water (0 -120 minutes), volume and shape of the container (activation reactor), holding temperature (20-60°C), etc. According to the results of the data obtained, it was experimentally established that the use of electric pulse treatment of water-cement suspension has a positive effect on strength (cup compressive strength) indicators, obtained as a result of processing cement stone samples at different times of hardening (1-3 days). The compressive strength of the treated specimens’ increases in comparison with the untreated specimens, increase in strength reaches up to 45%, depending on the activation mode. The resulting effect was achieved due to many factors (high pressure, magnetic, temperature, energy, ultrasonic and other influences), which were applied in the most optimal period of time (stage) of the cement grain hydration process.
Built Infrastructure Renewal and Climate Change Mitigation Can Both Find Solutions in CO2
From technology to policy, the US is thinking about construction differently. The federal government is motivated to address the aging infrastructure across the country, and policy proposals are surfacing that seek green methods of performing this construction. This paper reviews the current status of concrete technology and policy to provide insight into the current state of the art. The scale of CO2 emissions from concrete production and use is elucidated. Current embodied emissions reduction methods show that action can be taken today in small and large projects alike. Additionally, developing concrete technologies offers pathways to reuse and rely on concrete for longer service lifetimes and reduce their lifetime embodied emissions. These concrete technologies must be implemented, and public procurement proves a unique tool to develop a nationwide demand signal for low embodied carbon building materials. Local governments closely interact with concrete producers, state governments oversee large infrastructure projects, and the federal government invests massively in construction. All three levels of government must coordinate for the effective rollout of low embodied carbon construction practices. Disparate policy approaches show successes and pitfalls to developing an effective construction policy that is aligned with climate. Importantly, approaches to addressing the twin challenge of climate change and crumbling infrastructure must consider the whole lifetime of the concrete. Throughout this paper, we examine the sector to highlight current practices and provide a vision for effective implementation.
Export Citation Format
Share document.

Concrete Technology
- Fellowship Proposal Format
- MIT Concrete Sustainability Hub
- Library Help
- PCA Cement and Concrete Thesaurus
- Masonry Products and Properties
- Aluminum Frames in Masonry Walls
- Geothermal Heating and Cooling Systems
- Joint Types and Weather Resistance
- Masonry Walls and the Importance of Mockups
- Segmental Retaining Walls
- Verifying Compressive Strength of Masonry
- White and Colored Masonry Mortars
- Cold Weather Masonry Construction
- Code Win for Balanced Design
- Creating a Virtual Laboratory
- Design-Build and Masonry Construction
- The Masonry Society Becomes Sole Sponsor of Code and Specification
- Quality Assurance and Inspection
- Retempering
- Special Inspection in the Codes and Standards
- Earthquakes
- Fire Safety
- Fire Safe Buildings and Masonry Codes
- Fire Resistant Walls
- HIgh Wind Events
- Performance of Roof Materials
- Stucco Frequently Asked Questions
- Stucco Color and Texture
- Stucco Installation Standards
- Materials for Stucco
- Performance of Stucco
- Stucco Repair
- White Cement Frequently Asked Questions
- White Self-Consolidating Concrete
- Building Tips for Trouble-Free Slabs
- Cold Weather Concreting
- Placing Joints in Concrete Flatwork: Why, How, and When
- Role of Concrete Curing
- The Difference Between Curing and Drying Concrete
- Finishing Air-Entrained Concrete
- Hot Weather Concrete Construction
- Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures
- Recycled Aggregates
- Ultra-High Performance Concrete

In its simplest form, concrete is a mixture of paste and aggregates (rocks). The paste, composed essentially of portland cement and water, coats the surface of the fine (small) and coarse (larger) aggregates. Through a series of chemical reactions called hydration, the paste hardens and gains strength to form the rock-like mass known as concrete.
Within this process lies the key to a remarkable trait of concrete: it's plastic and malleable when newly mixed, strong and durable when hardened. These qualities explain why one material, concrete, can build skyscrapers, bridges, sidewalks and superhighways, houses and dams.
The Portland Cement Association has sponsored research directed at extending the boundaries of technical knowledge in the field since 1916.
PCA information reflects the latest on standards, specifications, test methods and guides of ASTM International (ASTM), the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO), the American Concrete Institute (ACI), and the National Ready Mixed Concrete Association (NRMCA).
It addresses the properties of concrete needed in construction applications, including strength and durability, and provides guidance on all aspects of concrete from mix design to batching, mixing, transporting, placing, consolidating, finishing, and curing.
Cement Manufacturing Transparency Reporting
As an early industry sector responder to evolving green building requirements, PCA and its members were among contributors to the creation of 2014 Product Category Rules (PCR) on North American cements published by ASTM, Product Category Rules For Preparing an Environmental Product Declaration for Portland, Blended Hydraulic, Masonry, Mortar, and Plastic (Stucco) Cements. To see or download the PCR, click here .
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
- Department of Structural Engineering and Building Materials
- Research clusters
- Research themes
Concrete technology
The performance of cement-based materials is highly dependent on the microstructure which is formed by hydration. The concrete technology group of prof. dr. ir. Geert De Schutter is focussing on advanced cement based materials with specific properties, such as for example self-compacting concrete. Other research topics include hydration, microstructure, transport properties, durability, rheology and mechanical properties of (self-compacting) concrete. Alternative mixing procedures and pumping techniques are investigated.
An overview of some current and recent research topics is given hereafter.
- Self-Compacting Concrete (SCC)
Since many years, Self-Compacting Concrete (SCC) is one of the major research topics within the Magnel Laboratory for Concrete Research. Initially, the mix design was studied, linked to hydration studies. Based on microstructural studies, mechanical and durability properties have been fundamentally studied. Now, focus is mainly on rheological studies, in view of the development of new casting procedures. One of the projects is focussing on the fundamental control of concrete rheology by optimising mixing energy and superplasticizer design, based on FBRM as a fundamental experimental technique. Some other important projects linked to rheology of fresh cementitious materials are mentioned in the following bullets.
- Smart Casting of Concrete Structures by means of active rheology and stiffening control (“SmartCast”) (2016-2021)
Recently, Prof. G. De Schutter was awarded an ERC Advanced Grant for the project “SmartCast”. This project is aiming for Active Rheology Control (ARC) and Active Stiffening Control (ASC) during casting of concrete, in view of more automated production of concrete structures. Some more information can be found on the general website of Ghent University: Geert De Schutter – SmartCast . Also watch our short video introduction to the SmartCast project!
- 3D-Printing and Digital Fabrication of Concrete (2018-2023)
Prof. G. De Schutter is the principal investigator of the Ghent University Concerted Research Action “Generic materials study towards high quality advanced medical, food and engineering 3D structures”. The project also includes research groups from Materials Science and Engineering (Prof. L. Cardon), Food Technology and Engineering (Prof. K. Dewettinck), and the Department of Morphology of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine (Prof. P. Cornillie). The aim of the project is to provide a fundamental understanding of extrusion based additive manufacturing and 3D casting of multicomponent materials toward high quality end products. Thanks to a generic research methodology, covering common challenges on rheology and solidification, the 3D product quality of a wide pallet of materials will be realised, including thermoplastic/thermoset polymers, self-compacting concrete, and fat-based food dispersions.
- Alternative binders for cement based materials
The use of alternative materials as addition and/or replacement of cement, leads to new binary and ternary cement based materials with modified microstructure development. The resulting transport properties are modelled in two different research projects, with special attention to microstructure development and the influence of the interfacial transition zone between matrix and aggregate. Besides that, the influence on the durability is being analysed, and this with respect to the developed interface zone as well as with respect to the general microstructure. In parallel, the application of artificial porous pozzolanic materials for mitigation of the autogenous shrinkage cracking of high performance concrete is studied.’ Furthermore, the hydration of cementitious materials under the influence of physical fields is also one of the current research topics.
- Radioactivity
The influence of chemically detrimental processes such as radioactive radiation on the transport properties of self-compacting concrete are studied as well (in cooperation with SCK-CEN ). In this regard, the modelling of the influence of these processes on the microstructure are of major importance.
- Creep and shrinkage of hardened concrete
For high rise buildings, creep of hardened concrete is an important factor in determining the final deformations. An accurate modelling for this is indispensable. In cooperation with Tongji University (China) this problem is being focussed on.
Often, small cracks in the concrete are being formed in an early stage, e.g. due to shrinkage or thermal effects. These cracks, although often limited in crack width and depth, can have an important effect on the durability of the concrete due to the accelerated penetration of aggressive substances. Fundamental studies also focus on the penetration of chlorides in concrete, and their interaction with the electric double layer (in cooperation with Hunan University). Furthermore, in-depth studies are ongoing concerning the damage mechanism in case of alkali silica reaction, and concerning the carbonation of cementitious materials containing fly ash. In a joint research project with the Department of Engineering Geology of the Faculty of Sciences, the frost damage in concrete and natural building stones is fundamentally studies at the microstructural level, involving advanced techniques like micro-tomography while freezing.

A vacuum mixing installation for cement based materials is available in the Magnel Lab for Concrete Research. This equipment, obtained through a Hercules financing project, is currently unique in the world with respect to research on concrete. By means of this high-tech installation, new steps can be made in the development of advanced cementitious materials.
Prof. Geert De Schutter
Prof. Veerle Boel
Research projects
Research Projects Concrete Technology
List of Civil Engineering Project Topics on Concrete

If you are a research student looking to write a thesis or project on concrete for civil engineering students we have compiled a list of some relevant project research topics/ideas on concrete .
Concrete, a term in civil engineering or construction , is a structural material consisting of hard, chemically inert substance known as aggregate (usually sand and gravel) that is held together by water and cement.
As a key component of civil or construction engineering some of your research may be related or in some way have something to do with concrete. So hopefully you find this compilation useful.
If you want to dive in straight away and browse our entire database for civil engineering project topics on concrete projects as well as thesis, dissertations and research papers on concrete, see the below link
- Projects on Concrete for Civil Engineering Students
Some Civil Engineering Research Topics on Concrete
Mechanical Properties of Concrete
The main aim of the research is to study the mechanical properties of concrete and heir effects in concrete stability and failure. He fractures mechanical properties in particular uniaxial tensile strength Ft, young’s modules Eo and fractures energy Gf as sell as the shape of the stress strain and the stress- deformation relation were investigated for high strength and normal strength concrete. | Project | 125 Pages | See Full Document
Effect of Crude Oil Contaminated Sand on the Engineering Properties of Concrete
A considerable fraction of sand in Niger Delta Area of Nigeria is contaminated with crude oil. The contaminated sand is largely utilised by local contractors for the production of concrete. However, there is need to establish its suitability in concreting. Previous works have centered on hardened uncontaminated concrete in crude oil environment but not on concrete made with Crude Oil Contaminated Sand (COCS). This research was designed to evaluate the effect of COCS on some engineering properties of fresh and hardened COCS concrete. | 160 Pages | Thesis | See Full Material
Strength And Microstructure Of Lateritic Concrete Containing Palm Kernel Shell (Pks) As Partial Replacement For Coarse Aggregates
This research work reports the investigation carried out to determine the strength and microstructure of lateritic concrete containing palm kernel shell (PKS) as partial replacement of coarse aggregates. The study employed different mix proportions, which resulted in casting and testing 148 cubes at 7, 14, 21, 28, 60, and 90-days of curing, to determine the best and economic proportion that will give compressive strength. | 72 Pages | Thesis | See Full Material
Comparative Study On The Strength Of Lightweight Foamed Concrete Using Different Reagents (Lithofoam & Sodium Lauryl Sulphate)
This project presents the results of the investigation conducted on a lightweight foamed concrete using different reagents; Sodium Lauryl Sulphate (SLS) and Lithofoam, with a view to determining its potential as a construction material in Nigeria. The properties investigated on the foamed concrete having target density of 1800kg/m3 were: workability, bulk density and compressive strength. | 66 Pages | Project | See Full Material
Enhancing Concrete Properties with the Use of Coconut (coir) Fibers and Admixture
In countries where industrialization is on the rise there is a corresponding increase in waste production resulting from industries which eventually upsets the environment and community for which they provide. While most of these waste generated are hazardous and should be managed, others could be put to appropriate use either directly or after been recycled. | 76 Pages | Project | See Full Material
Use Of Recycled Concrete As Coarse Aggregate For High Strength Concrete
This study is concerned with the production of high strength concrete using recycled concrete aggregates as alternative to natural aggregates. The study includes also the determination of the proportions, characteristics and components of concrete mixes required for production and use in multiple applications at suitable prices. | 116 Pages | Thesis | See Full Material
Comparative Study of Strength of Truss Reinforced Concrete Beam and Conventional Reinforced Concrete Beam
This work presents comparative study of strength of truss reinforced concrete beam and conventional reinforced concrete beam. Two sets of 0.15 x 0.15 x 1m beams were cast. One set was cast using truss as a system of reinforcement at spacing of 100mm, 150mm and 200mm. The other set was cast using longitudinal bars and links at spacing of 100mm, 150mm, and 200mm as the conventional reinforcement. In all 27 truss and 27 conventional reinforcement beams were cast. | 170 pages | Thesis | See Full Material
Some Later Days Structural Properties Of Concrete Containing Palm Oil Empty Bunch Ash (Poeba) As Partial Replacement Of Cement In Concrete
In an attempt to reduced non-renewable material usage, reduce green-house substances and at the same time be relevant to our environment, this research presents the progress of investigation going on to evaluate some properties of POEBA as partial replacement of cement in the production of structural concrete. This research work is carried out to determine the properties of Palm Oil Empty Bunch Ash (POEBA) when used as partial replacement for Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) in concrete | 70 pages | Project | See Full Material
Investigation Of The Structural Characteristics Of Lime-cement Concrete
This work investigated the structural characteristics of lime cement concrete using 30 selected mix ratios. The properties studied include, compressive strength, flexural strength, splitting tensile strength, shear strength, poisson ratio, modulus of elasticity, and modulus of rigidity. A total of 360 concrete cube specimen, 360 concrete prototype beam specimen, and 360 concrete cylinder specimen were cast and cured in open water tanks. 3 specimen were cast for each mix proportion. | 282 pages | Thesis | See Full Material
Strength Assessment of No-Fines Concrete Pavement
The purpose of this project work is to assess the strength of No-fines concrete pavement. No-Fines concrete is use in low traffic volume, pathways, sidewalk and parking lots. No-fines concrete is produced by using ordinary Portland cement, coarse aggregates, and water. In this study, Two (2) batches of no-fines concrete each with two different water – cement ratio 0.36 and 0.45 and cement – coarse aggregate 1:4 and 1:6 were prepared to find the mix that generated high compressive strength and splitting tensile strength | 79 Pages | Project | See Full Materials
Effect Of Using Basalt And Limestone As Coarse Aggregate In Concrete Mixtures
In this study, concrete mixtures were tested to effect of basalt and limestone as coarse aggregate and evaluate their efficiency on fresh and hardened concrete to achieve the design compressive strengths of [25N/mm2]. By using different proportions is 25%, 50%, 75% and100 %from the weight of coarse aggregate. The study was carried out for 6 types of concrete mixes designed by British Standard, compressive strength of concrete and workability were measured in the reconstruction of maturing for ( 7, 28 and 56) days. | 85 pages | Thesis | See Full Material
Rice Husk Ash And Grinded Rice Husk Effect On The Compressive Strength And Workability Of Concrete
The importance of concrete in modem society cannot be underestimated. There is no escaping from the impact of concrete on everyday life. Concrete is a composite material which is made of filler and a binder. Typical concrete is a mixture of fine aggregate (sand), coarse aggregate (rock), cement, and water. Nowadays the usage of concrete is increasing from time to time due to the rapid development of construction industry. | 71 Pages | Project | See Full Material
The Effect of Silica Fume (S.F) on the Properties of Fresh and Hardened Concrete
Concrete is a composite material consisting of aggregates enclosed in a matrix of cement paste including possible pozzolans, has two major components, cement paste and aggregates. The strength of concrete depends upon the strength of these components, their deformation properties, and the adhesion between the paste and aggregate surface [ 1 ]. In recent years, the construction industry has shown significant interest in the use of high strength concrete (HSC), in applications such as dams, bridges and high rise buildings. | 84 pages | Thesis | See Full Material
Structural Performance Of Lateritic Concrete Containing Palm Kernel Shell (PKS) As A Partial Replacement Of Coarse Aggregate
Sand has traditionally been used as fine aggregate in structural concrete. It is usually imported from relatively distant places at high costs, and this increases the overall cost of making concrete and of providing housing in various Nigerian communities. This study investigates the performance of 409/o of laterite as fine aggregate in place of sand, and specifically seeks to determine whether lateritic concrete containing pies would satisfy the minimum compressive strength requirement of BS 8110 (1997) for use in reinforced concrete works, which is 25 N/mm. | 75 Pages | Project | See Full Material
More Research Resources on Concrete in Civil Engineering
- Thesis, Dissertations & Projects on Concrete in Civil Engineering
- Seminars, Papers, Articles on Concrete in Civil Engineering
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
share this!
April 17, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
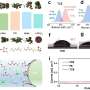
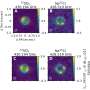
Research proposes virtual-dimension increase of EMG signals for prosthetic hands gesture recognition
by Beijing Institute of Technology Press Co., Ltd
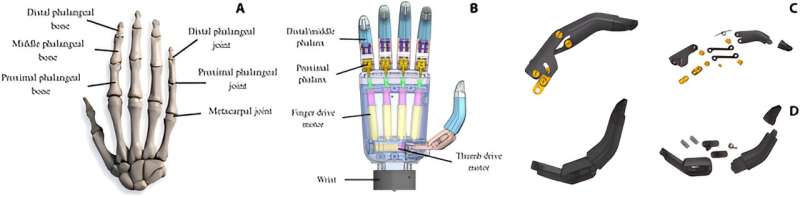
The electromyographic (EMG) signal is the bioelectrical current generated during muscle contraction. It can be transmitted as an input signal to an intelligent bionic prosthetic hand to control hand movements. By increasing the number of signal acquisition channels, richer information about the intention of the action can be captured, thus improving the success rate of the recognition of the intention of the action. However, it is not better to have more acquisition channels.
As the number of channels increases, the hardware system becomes more complex, and the effect of improving the accuracy of gesture recognition gradually decreases, resulting in the control effect reaching a bottleneck.
To address these issues, a team of researchers from Beijing Institute of Technology proposed a method to improve gesture recognition accuracy by virtually increasing the number of EMG signal channels.
The team published their findings in Cyborg and Bionic Systems .
This method extracts amplitude features from EMG signals to represent the contraction intensity of a muscle over time. The absolute values of the intensity differences between channels are then calculated. These difference values are merged with the original data to form new samples with more columns, simulating an actual increase in the dimensionality of the data. This makes use of the implicit coordination information between muscles during movement.
Even if the number of physical acquisition channels is limited, this approach improves recognition accuracy because it does not rely solely on the amount of data directly acquired by the sensor.
To validate their method, the authors compared the accuracy of gesture intent recognition before and after adding virtual dimensions. The accuracy of gesture recognition using EMG signals after the addition of virtual dimensions was improved compared to unprocessed EMG signals. In addition, the greater the number of EMG signal acquisition channels and the richer the EMG signals obtained, the higher the success rate of gesture recognition.
In addition, based on the filtered feature selection approach, the research team introduced a separability metric derived from the dispersion and correlation of the feature set (separability of feature vectors SFV). The SFV value can predict the classification effect before classification is performed and validate the effectiveness of the virtual dimensionality increase strategy in terms of the change in the separability of the feature set.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Microsoft's AI app VASA-1 makes photographs talk and sing with believable facial expressions
31 minutes ago
To build a better AI helper, start by modeling the irrational behavior of humans
34 minutes ago

Versatile fibers offer improved energy storage capacity for wearable devices
Harnessing solar energy for high-efficiency NH₃ production

A dexterous four-legged robot that can walk and handle objects simultaneously
3 hours ago

Climate change will increase value of residential rooftop solar panels across US, study finds
5 hours ago

Bitcoin's next 'halving' is right around the corner. Here's what you need to know
6 hours ago
Team develops a way to teach a computer to type like a human
17 hours ago
Universal 'cocktail electrolyte' developed for 4.6 V ultra-stable fast charging of commercial lithium-ion batteries

Garbage could replace a quarter of petroleum-based jet fuel every year
18 hours ago
Related Stories

Optimizing gesture recognition system design
Aug 30, 2023
A photonic feature extractor for broadband radio-frequency signals
Apr 2, 2024

WaveGlove: A glove with five inertial sensors for hand gesture recognition
Jun 15, 2021

Simple, accurate, and efficient: Improving the way computers recognize hand gestures
Dec 28, 2021

Fingerprinting with machine vision
Jan 29, 2024

Hybrid machine-learning approach gives a hand to prosthetic-limb gesture accuracy
Feb 7, 2022
Recommended for you

Floating solar's potential to support sustainable development
21 hours ago

An ink for 3D-printing flexible devices without mechanical joints

Octopus inspires new suction mechanism for robots
Apr 18, 2024

Using sim-to-real reinforcement learning to train robots to do simple tasks in broad environments
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Tech Xplore in any form.
Your Privacy
This site uses cookies to assist with navigation, analyse your use of our services, collect data for ads personalisation and provide content from third parties. By using our site, you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
E-mail newsletter
- Frontiers in Materials
- Structural Materials
- Research Topics
Advanced Concretes and Their Structural Applications-Volume III
Total Downloads
Total Views and Downloads
About this Research Topic
This Research Topic is Volume III of a series. The previous volume can be found here: Advanced Concretes and Their Structural Applications Construction materials play ...
Keywords : Concrete, High Performance, Reinforcement, Functionality, Mechanical Properties, Structural Performance.
Important Note : All contributions to this Research Topic must be within the scope of the section and journal to which they are submitted, as defined in their mission statements. Frontiers reserves the right to guide an out-of-scope manuscript to a more suitable section or journal at any stage of peer review.
Topic Editors
Topic coordinators, recent articles, submission deadlines, participating journals.
Manuscripts can be submitted to this Research Topic via the following journals:
total views
- Demographics
No records found
total views article views downloads topic views
Top countries
Top referring sites, about frontiers research topics.
With their unique mixes of varied contributions from Original Research to Review Articles, Research Topics unify the most influential researchers, the latest key findings and historical advances in a hot research area! Find out more on how to host your own Frontiers Research Topic or contribute to one as an author.
Researchers create new AI pipeline for identifying molecular interactions
Understanding how proteins interact with each other is crucial for developing new treatments and understanding diseases. Thanks to computational advances, a team of researchers led by Assistant Professor of Chemistry Alberto Perez has developed a groundbreaking algorithm to identify these molecular interactions.
Perez's research team included two graduate students from UF, Arup Mondal and Bhumika Singh, and a handful of researchers from Rutgers University and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. The team published their findings in Angewandte Chemie , a leading chemistry journal based in Germany.
Named the AF-CBA Pipeline, this innovative tool offers unparalleled accuracy and speed in pinpointing the strongest peptide binders to a specific protein. It does this by using AI to simulate molecular interactions, sorting through thousands of candidate molecules to identify the molecule that interacts best with the protein of interest.
The AI-driven approach allows the pipeline to perform these actions in a fraction of the time it would take humans or traditional physics based-approaches to accomplish the same task.
"Think of it like a grocery store," Perez explained. "When you want to buy the best possible fruit, you have to compare sizes and aspects. There are too many fruits to try them all of course, so you compare a few before making a selection. This AI method, however, can not only try them all, but can also reliably pick out the best one."
Typically, the proteins of interest are the ones that cause the most damage to our bodies when they misbehave. By finding what molecules interact with these problematic proteins, the pipeline opens avenues for targeted therapies to combat ailments such as inflammation, immune dysregulation, and cancer.
"Knowing the structure of the strongest peptide binder in turn helps us in the rational designing of new drug therapeutics," Perez said.
The groundbreaking nature of the pipeline is enhanced by its foundation on pre-existing technology: a program called AlphaFold. Developed by Google Deepmind, AlphaFold uses deep learning to predict protein structures. This reliance on familiar technology will be a boon for the pipeline's accessibility to researchers and will help ensure its future adoption.
Moving forward, Perez and his team aim to expand their pipeline to gain further biological insights and inhibit disease agents. They have two viruses in their sights: murine leukemia virus and Kaposi's sarcoma virus. Both viruses can cause serious health issues, especially tumors, and interact with as-of-now unknown proteins.
"We want to design novel libraries of peptides," Perez said. "AF-CBA will allow us to identify those designed peptides that bind stronger than the viral peptides."
- Pharmacology
- Human Biology
- Educational Technology
- Computational Biology
- Information Technology
- Mathematical Modeling
- Stem cell treatments
- Infectious disease
- Biological tissue
- Molecular biology
- Antioxidant
- Adult stem cell
Story Source:
Materials provided by University of Florida . Original written by Brian Smith. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Arup Mondal, Bhumika Singh, Roland Felkner, Anna De Falco, GVT Swapna, gaetano montelione, Monica Roth, Alberto Perez. A Computational Pipeline for Accurate Prioritization of Protein‐Protein Binding Candidates in High‐Throughput Protein Libraries . Angewandte Chemie International Edition , 2024; DOI: 10.1002/anie.202405767
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- How 3D Printers Can Give Robots a Soft Touch
- Combo of Multiple Health Stressors Harming Bees
- Methane Emission On a Cold Brown Dwarf
- Remarkable Memories of Mountain Chickadees
- Predicting Future Marine Extinctions
- Drain On Economy Due to Climate Change
- 'Tube Map' Around Planets and Moons
- 'Bizarre' Evolutionary Pattern: Homo Lineage
- Largest Known Marine Reptile
- Neolithic Humans Lived in Lava Tube Caves
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
Suggestions or feedback?

MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Advancing technology for aquaculture
Press contact :.
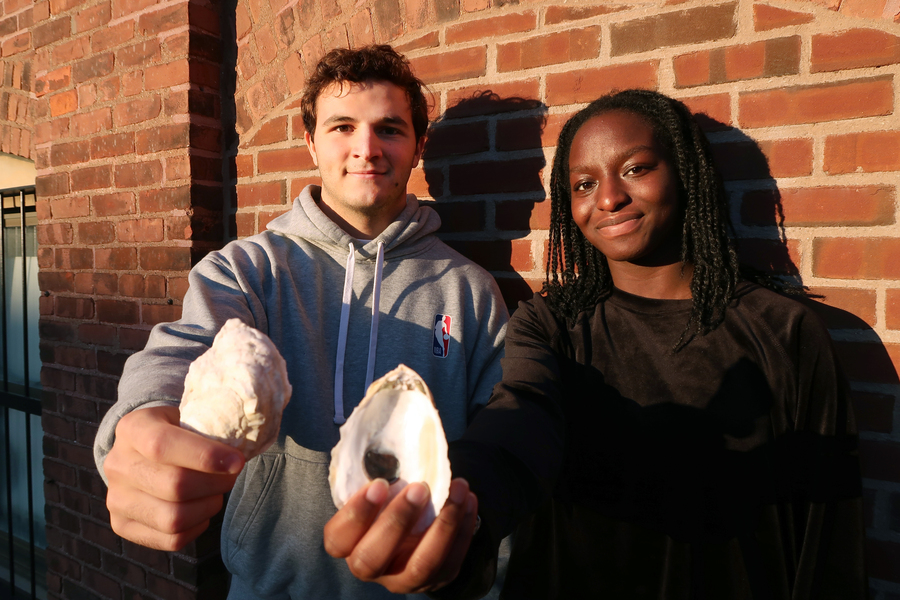

Previous image Next image
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, aquaculture in the United States represents a $1.5 billion industry annually. Like land-based farming, shellfish aquaculture requires healthy seed production in order to maintain a sustainable industry. Aquaculture hatchery production of shellfish larvae — seeds — requires close monitoring to track mortality rates and assess health from the earliest stages of life.
Careful observation is necessary to inform production scheduling, determine effects of naturally occurring harmful bacteria, and ensure sustainable seed production. This is an essential step for shellfish hatcheries but is currently a time-consuming manual process prone to human error.
With funding from MIT’s Abdul Latif Jameel Water and Food Systems Lab (J-WAFS), MIT Sea Grant is working with Associate Professor Otto Cordero of the MIT Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Professor Taskin Padir and Research Scientist Mark Zolotas at the Northeastern University Institute for Experiential Robotics, and others at the Aquaculture Research Corporation (ARC), and the Cape Cod Commercial Fishermen’s Alliance, to advance technology for the aquaculture industry. Located on Cape Cod, ARC is a leading shellfish hatchery, farm, and wholesaler that plays a vital role in providing high-quality shellfish seed to local and regional growers.
Two MIT students have joined the effort this semester, working with Robert Vincent, MIT Sea Grant’s assistant director of advisory services, through the Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program (UROP).
First-year student Unyime Usua and sophomore Santiago Borrego are using microscopy images of shellfish seed from ARC to train machine learning algorithms that will help automate the identification and counting process. The resulting user-friendly image recognition tool aims to aid aquaculturists in differentiating and counting healthy, unhealthy, and dead shellfish larvae, improving accuracy and reducing time and effort.
Vincent explains that AI is a powerful tool for environmental science that enables researchers, industry, and resource managers to address challenges that have long been pinch points for accurate data collection, analysis, predictions, and streamlining processes. “Funding support from programs like J-WAFS enable us to tackle these problems head-on,” he says.
ARC faces challenges with manually quantifying larvae classes, an important step in their seed production process. "When larvae are in their growing stages they are constantly being sized and counted,” explains Cheryl James, ARC larval/juvenile production manager. “This process is critical to encourage optimal growth and strengthen the population."
Developing an automated identification and counting system will help to improve this step in the production process with time and cost benefits. “This is not an easy task,” says Vincent, “but with the guidance of Dr. Zolotas at the Northeastern University Institute for Experiential Robotics and the work of the UROP students, we have made solid progress.”
The UROP program benefits both researchers and students. Involving MIT UROP students in developing these types of systems provides insights into AI applications that they might not have considered, providing opportunities to explore, learn, and apply themselves while contributing to solving real challenges.
Borrego saw this project as an opportunity to apply what he’d learned in class 6.390 (Introduction to Machine Learning) to a real-world issue. “I was starting to form an idea of how computers can see images and extract information from them,” he says. “I wanted to keep exploring that.”
Usua decided to pursue the project because of the direct industry impacts it could have. “I’m pretty interested in seeing how we can utilize machine learning to make people’s lives easier. We are using AI to help biologists make this counting and identification process easier.” While Usua wasn’t familiar with aquaculture before starting this project, she explains, “Just hearing about the hatcheries that Dr. Vincent was telling us about, it was unfortunate that not a lot of people know what’s going on and the problems that they’re facing.”
On Cape Cod alone, aquaculture is an $18 million per year industry. But the Massachusetts Division of Marine Fisheries estimates that hatcheries are only able to meet 70–80 percent of seed demand annually, which impacts local growers and economies. Through this project, the partners aim to develop technology that will increase seed production, advance industry capabilities, and help understand and improve the hatchery microbiome.
Borrego explains the initial challenge of having limited data to work with. “Starting out, we had to go through and label all of the data, but going through that process helped me learn a lot.” In true MIT fashion, he shares his takeaway from the project: “Try to get the best out of what you’re given with the data you have to work with. You’re going to have to adapt and change your strategies depending on what you have.”
Usua describes her experience going through the research process, communicating in a team, and deciding what approaches to take. “Research is a difficult and long process, but there is a lot to gain from it because it teaches you to look for things on your own and find your own solutions to problems.”
In addition to increasing seed production and reducing the human labor required in the hatchery process, the collaborators expect this project to contribute to cost savings and technology integration to support one of the most underserved industries in the United States.
Borrego and Usua both plan to continue their work for a second semester with MIT Sea Grant. Borrego is interested in learning more about how technology can be used to protect the environment and wildlife. Usua says she hopes to explore more projects related to aquaculture. “It seems like there’s an infinite amount of ways to tackle these issues.”
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Research project webpage
- MIT Sea Grant
- Abdul Latif Jameel Water and Food Systems Lab (J-WAFS)
- Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
- Aquacultural Research Corporation
- Cape Cod Commercial Fishermen's Alliance
- Northeastern University Institute for Experiential Robotics
Related Topics
- Civil and environmental engineering
- Mechanical engineering
- Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program (UROP)
- Agriculture
- Environment
- Sustainability
- Supply chains
- Artificial intelligence
- Computer vision
- Undergraduate
- Collaboration
Related Articles

J-WAFS announces 2023 seed grant recipients

Meet the Oystamaran

More than a meal
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

Researching extreme environments
Read full story →

To build a better AI helper, start by modeling the irrational behavior of humans

Using deep learning to image the Earth’s planetary boundary layer

New flight procedures to reduce noise from aircraft departing and arriving at Boston Logan Airport

New major crosses disciplines to address climate change

Four MIT faculty named 2023 AAAS Fellows
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
share this!
April 17, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
Research group runs simulations capable of describing South America's climate with unprecedented accuracy
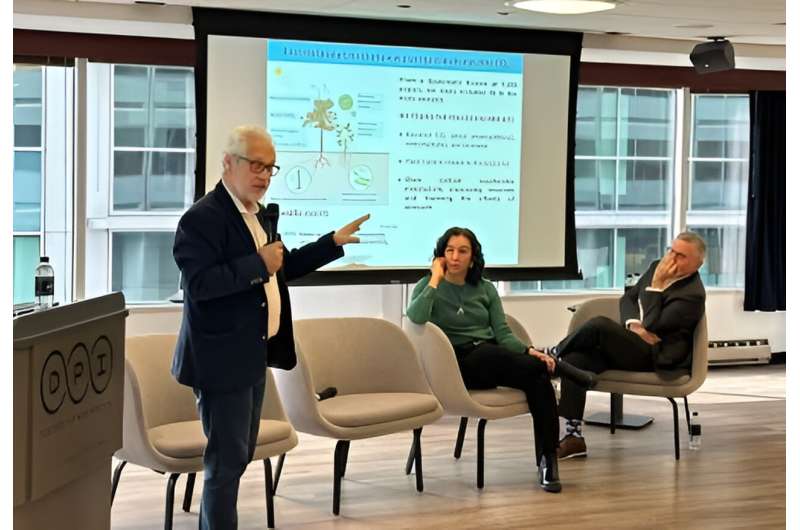

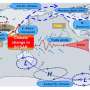
A consortium made up of researchers from more than ten countries, including Brazil, the United States and some European nations, is running simulations of the past and future climate in South America with unprecedented resolution. The aim is to create a computer visualization model that more accurately represents the hydroclimatic processes that occur in the region to help decision makers implement more effective measures to adapt to the impacts of climate change.
The work was presented at a panel discussion on climate on April 10, during FAPESP Week Illinois , in Chicago (United States).
"We're now beginning to be able to correctly represent the hydroclimate of South America at the scales needed," said Francina Dominguez, a researcher at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois in Urbana-Champaign and coordinator of the project.
According to Dominguez, the climate in South America, like in all regions of the world, is changing. Increased droughts have been recorded in the southern Amazon, the Cerrado region, northern Brazil, and Chile. This scenario has affected agricultural yields, water supplies for reservoirs, hydroelectric power generation, and tens of millions of people in major metropolitan areas such as São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Santiago de Chile.
The Andean glaciers, which are an important source of water, have lost 30% of their area in the tropics and up to 60% in the southern Andes, the highest rates of glacier mass loss in the world. On the other hand, southeastern South America has experienced an increase in annual rainfall and an intensification of heavy precipitation since the beginning of the 20th century.
"South America is facing two gigantic forces, which are climate change and land-use change, which have occurred not only in the Amazon rainforest but also in other areas of the region, such as the Chaco in Argentina. We also have very big changes in both the global and regional climate. As a result of these processes, we've observed that climate extremes are changing across the continent, putting the water and food security of millions of people at risk," said Dominguez.
Future climate projections are based on global climate models (GCMs). Despite having improved greatly in recent decades, these conceptual representations of the global climate are unable to capture the details of South America's hydroclimate and exhibit significant distortions, the researcher noted.
Part of this problem is related to the coarse spatial resolution of these models, whose horizontal grid spacing, which represents the land and oceans, is on the order of tens of kilometers (km). As a result, they are unable to correctly represent processes that occur at smaller scales and in mountainous regions, such as relief rain—which occurs when clouds encounter obstacles such as hills and mountains—and snowfall that accumulates on mountains and glaciers.
"With current GCMs, it isn't possible to see complex topographies, and that's a problem in South America, where there are the Andes and other areas with that characteristic," Dominguez said.
GCMs also fail to realistically represent cyclones, low-level jets—the narrow zone of maximum winds that occurs in the first few kilometers of the atmosphere—and storms from organized connective systems.
"In regions of the River Plate basin, as well as in São Paulo and other large urban and agricultural areas in South America, organized convection is one of the most important precipitation mechanisms and is not correctly represented in global climate models ," said Dominguez.
Based on this finding, the researchers, through a research consortium called the South America Affinity Group, have run two computer simulations of a weather research and forecasting (WRF) model with unprecedented high resolution and a grid spacing of 4 km, representing the continent's historical and future climate.
The aim is to use the historical simulation to validate the model and better understand the hydroclimatic characteristics of the continent in greater detail, and to use the future climate simulation to assess the changes that are likely to occur in South America under a warmer climate.
"This is a major effort involving more than 100 scientists, many of them from Brazil, and most of them from São Paulo," Dominguez said.
Low computational performance
According to Kelvin Droegemeier, professor of atmospheric sciences at the University of Illinois in Urbana-Champaign, incredibly sophisticated models of the Earth system have been developed in recent years, representing the atmosphere, ice, oceans, and biogeochemical cycles, among other elements.
These models require very powerful computers for long-term integration. The problem, however, is that they can only reach a small fraction of the maximum capacity of today's machines.
"Current models only reach between 2% and 3% of an exascale machine [a type of high-performance computer with a capacity around a thousand times faster than the most powerful supercomputers in use]. It's as if these models were a Ferrari or a Formula 1 racing car and could only be driven at a speed of 25 kilometers per hour," the researcher compared.
In addition, the models have resolution and physics problems and are unable to capture details such as processes that take place in regions such as South America. "These models have many problems, but the fault isn't with them, but with the systems they're being run on," Droegemeier explained.
In order to advance the computational capacity to run Earth system models, the US university will hold an international meeting between late September and early October this year aimed at developing a computational system for frontier Earth system science in climate simulation and projection.
"The aim will be to discuss where the computing systems are that will allow us to run these models at very high global resolution. We have interested parties, such as chip manufacturers like NVIDIA and Intel, interested in joining the discussion," the researcher said.
The US university is also developing a blueprint to create a national center for predicting extreme events caused by climate change and another on the science of prediction and its applications, Droegemeier announced.
Marcos Buckeridge, a professor at the University of São Paulo (USP), also participated in the panel discussion on climate studies.
Provided by FAPESP
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Development of organic semiconductors featuring ultrafast electrons
6 minutes ago
Uncovering key players in gene silencing: Insights into plant growth and human diseases
23 minutes ago

Many prisoners go years without touching a smartphone—it means they struggle to navigate life on the outside
31 minutes ago

Mycoheterotrophic plants as a key to the 'Wood Wide Web'
Technical trials for easing the (cosmological) tension
A hydrocarbon molecule as supplier and energy storage solution for solar energy

Comprehensive model unravels quantum-mechanical effects behind photoluminescence in thin gold films

Cosmic rays streamed through Earth's atmosphere 41,000 years ago: New findings on the Laschamps excursion
Study suggests Io's volcanoes have been active for 4.5 billion years
2 hours ago

Ghost particle on the scales: Research offers more precise determination of neutrino mass
5 hours ago
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
Unlocking the secrets of prof. verschure's rosetta stones, iceland warming up again - quakes swarming.
20 hours ago
Tidal friction and global warming
Apr 18, 2024
Large eruption at Ruang volcano, Indonesia
Apr 17, 2024
M 4.8 - Whitehouse Station, New Jersey, US
Apr 6, 2024
Major Earthquakes - 7.4 (7.2) Mag and 6.4 Mag near Hualien, Taiwan
Apr 5, 2024
More from Earth Sciences
Related Stories

Snow-capped mountains at risk from climate change
Jan 17, 2024
Climate change in the South China Sea found to have global impacts on weather patterns
Jan 16, 2024

Study shows cloud clustering causes more extreme rain
Feb 23, 2024

Reflecting real-world precipitation extremes in climate simulations
Nov 21, 2023

Climate change main culprit for hot South American winter
Oct 10, 2023

Climate change may lead to more landfalling tropical cyclones in China
Jun 21, 2021
Recommended for you

Warming of Antarctic deep-sea waters contribute to sea level rise in North Atlantic, study finds

Unraveling the mysteries of consecutive atmospheric river events
17 hours ago

Scientists reveal hydroclimatic changes on multiple timescales in Central Asia over the past 7,800 years
18 hours ago

Toxic fireproof chemicals can be absorbed through touch, 3D-printed skin model shows
19 hours ago

A third of China's urban population at risk of city sinking, new satellite data shows

'Human-induced' climate change behind deadly Sahel heat wave: Study
23 hours ago
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The American Concrete Institute. Founded in 1904 and headquartered in Farmington Hills, Michigan, USA, the American Concrete Institute is a leading authority and resource worldwide for the development, dissemination, and adoption of its consensus-based standards, technical resources, educational programs, and proven expertise for individuals and organizations involved in concrete design ...
Digital transformation of concrete technology is one of the current "hot topics" tackled by both academia and industry. The final goal is to fully integrate the already existing advanced concrete technologies with novel sensors, virtual reality, or Internet of things to create self-learning and highly automated platforms controlling design, production, and long-term usage and maintenance ...
Abstract. Concrete technology is developing fast over the past several decades, and increasingly more high-performance concretes are now available in the market. Among others, ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) is best known for its high mechanical strength and material durability. In this chapter, historical development of UHPC is briefly ...
1. Introduction. Concrete is a sustainable and versatile construction material which can produce structures that last for thousands of years. Due to the many areas of application, concrete is the second most consumed material on Earth, only after water, with a global production of around 4.1 billion tons of cement in 2021 (Statista, 2023), and an annual concrete consumption about 7 times ...
Recent Innovations in Concrete Technology and Its Structural Applications ... we encourage comprehensive review articles and innovative experimental research contributions to cover the following topics: Development of novel concrete materials with high mechanical performance or special functionality ... and will be listed together on the ...
The construction industry seeks to utilize self-healing concrete due to its sustainability benefits and long-term performance (Park and Choi, 2019; Reddy and Ravitheja, 2019).The study by Ackermann examines the self-healing properties of structural and early age cracks (Ackermann, 2018).This experiment utilizes crystalline admixture (CA) as an improvisation tool.
This paper reviews the current status of concrete technology and policy to provide insight into the current state of the art. The scale of CO2 emissions from concrete production and use is elucidated. Current embodied emissions reduction methods show that action can be taken today in small and large projects alike.
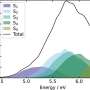
It is interesting to know which research hotspots in the field of advance concrete technology in AI techniques have received more attention from researchers during the last decade. Therefore, by scrutinizing the topics of the collected articles, the top five topics by number and percentage of participation are shown in Figure 18 .
Concrete Technologies - Science topic. One of the most crucial ways to reach the sustainability and development of the world in the future is to work and research on Concrete Technology. The ...
Elsa Olivetti, the Esther and Harold E. Edgerton Associate Professor in the MIT Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Jie Chen, MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab research scientist and manager, think artificial intelligence can help meet this need by designing and formulating new, more sustainable concrete mixtures, with lower costs and ...
Intelligent concrete also contributes to the resilience of infrastructures, with its ability to react upon an external stimulus, such as stress, deformation, humidity, and temperature. These published research studies on this research topic aim to cover original or review articles exploring the innovation in intelligent concrete.
Enhancement of concrete performance requires a deep understanding of the nature of hydration products. In concrete engineering, structural design is used to create buildings and infrastructures. Integrated materials and structural design is one type of design philosophy that takes an interdisciplinary and holistic approach.
Concrete's role in reducing building and pavement emissions. MIT researchers find emissions of U.S. buildings and pavements can be reduced by around 50 percent even as concrete use increases. September 16, 2021. Read full story.
In the last decade, the two major trends in concrete technology are to develop concrete materials with superior mechanical performance and better sustainability. For advanced concrete structures, designing and developing concrete materials with superior mechanical performances are beneficial to improving structural reliability and safety. On the other hand, large quantities of wastes/by ...
Concrete Technology. In its simplest form, concrete is a mixture of paste and aggregates (rocks). The paste, composed essentially of portland cement and water, coats the surface of the fine (small) and coarse (larger) aggregates. Through a series of chemical reactions called hydration, the paste hardens and gains strength to form the rock-like ...
Ritsumeikan University. Please have a look to the following research works available on researchgate: 1. Article Sustainable Concrete Technology. 2. Article Thirty Years Researches on Development ...
The concrete technology group of prof. dr. ir. Geert De Schutter is focussing on advanced cement based materials with specific properties, such as for example self-compacting concrete. Other research topics include hydration, microstructure, transport properties, durability, rheology and mechanical properties of (self-compacting) concrete.
25.3.1 Theory on the compressive strength of cement-based concrete. In concrete technology and industry, it is known that the ingredients for a bad concrete are exactly the same as for a good concrete. It is the relative proportions that matter. Furthermore, since Feret, Bolomey or Abrams, it has been established that the compressive strength ...
Some Civil Engineering Research Topics on Concrete. Mechanical Properties of Concrete. The main aim of the research is to study the mechanical properties of concrete and heir effects in concrete stability and failure. He fractures mechanical properties in particular uniaxial tensile strength Ft, young's modules Eo and fractures energy Gf as ...
A diagram shows an efficient way to synthesize lithium (Li) from sodium (Na) and back again. In the new Nature Materials paper, the Liu Lab demonstrated the synthesis of pure phase sodium cobalt ...
This could pave the way for entirely new organic solar modules. The fundamentals for conversion and storage using the molecule have now been published in the journal Nature Chemistry.. Hopes ...
Keywords: Nano science and technology, Concrete Composites, Cement, Asphalt, Polymer, Geopolymer, Alkali-activated, Fundamentals, Design, Fabrication, Test, Characterization, Simulation, Microstructures, Performances of fresh concrete, Mechanical performances, (Mul . Important Note: All contributions to this Research Topic must be within the scope of the section and journal to which they are ...
These sessions feature presentations of original, unpublished results from ongoing research projects and leading-edge concrete technology and research throughout the world. The sessions discuss recent techniques, research methods, and describe emerging ideas in concrete research. ... providing on-demand access to a wide range of topics on ...
The electromyographic (EMG) signal is the bioelectrical current generated during muscle contraction. It can be transmitted as an input signal to an intelligent bionic prosthetic hand to control hand movements. By increasing the number of signal acquisition channels, richer information about the intention of the action can be captured, thus improving the success rate of the recognition of the ...
A figure from the UC Davis coal train pollution study showing the study area with estimated PM2.5 concentrations associated with a 2.1 μg/m 3 increase in the annual PM2.5 average. Credit: UC Davis
This Research Topic is Volume III of a series. The previous volume can be found here: Advanced Concretes and Their Structural Applications Construction materials play a critical role in building modern infrastructures that stand the test of time. In recent decades, novel advanced construction materials have emerged, such as high performance/smart concrete, fiber-reinforced concrete, high ...
Perez's research team included two graduate students from UF, Arup Mondal and Bhumika Singh, and a handful of researchers from Rutgers University and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
NEWS ON CONCRETE TECHNOLOGY. Connecting with the Middle East and North Africa. Big 5 Global returns for its 44th edition in Dubai bringing together 2,200+ exhibitors and 68,000+ attendees to capitalize on opportunities worth $7 trillion in MEASA. ACI Announces Michael Thomas Concrete Durability Award.
Topics View All →. Explore: Machine learning ... (ARC), and the Cape Cod Commercial Fishermen's Alliance, to advance technology for the aquaculture industry. Located on Cape Cod, ARC is a leading shellfish hatchery, farm, and wholesaler that plays a vital role in providing high-quality shellfish seed to local and regional growers ...
Based on this finding, the researchers, through a research consortium called the South America Affinity Group, have run two computer simulations of a weather research and forecasting (WRF) model ...