Persuasive Essay Guide
Persuasive Essay About Covid19

How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid19 | Examples & Tips
11 min read

People also read
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing an Effective Persuasive Essay
200+ Persuasive Essay Topics to Help You Out
Learn How to Create a Persuasive Essay Outline
30+ Free Persuasive Essay Examples To Get You Started
Read Excellent Examples of Persuasive Essay About Gun Control
Crafting a Convincing Persuasive Essay About Abortion
Learn to Write Persuasive Essay About Business With Examples and Tips
Check Out 12 Persuasive Essay About Online Education Examples
Persuasive Essay About Smoking - Making a Powerful Argument with Examples
Are you looking to write a persuasive essay about the Covid-19 pandemic?
Writing a compelling and informative essay about this global crisis can be challenging. It requires researching the latest information, understanding the facts, and presenting your argument persuasively.
But don’t worry! with some guidance from experts, you’ll be able to write an effective and persuasive essay about Covid-19.
In this blog post, we’ll outline the basics of writing a persuasive essay . We’ll provide clear examples, helpful tips, and essential information for crafting your own persuasive piece on Covid-19.
Read on to get started on your essay.
- 1. Steps to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
- 2. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid19
- 3. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Vaccine
- 4. Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Integration
- 5. Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid 19
- 6. Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
- 7. Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
- 8. Common Topics for a Persuasive Essay on COVID-19
Steps to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Here are the steps to help you write a persuasive essay on this topic, along with an example essay:
Step 1: Choose a Specific Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should clearly state your position on a specific aspect of COVID-19. It should be debatable and clear. For example:
Step 2: Research and Gather Information
Collect reliable and up-to-date information from reputable sources to support your thesis statement. This may include statistics, expert opinions, and scientific studies. For instance:
- COVID-19 vaccination effectiveness data
- Information on vaccine mandates in different countries
- Expert statements from health organizations like the WHO or CDC
Step 3: Outline Your Essay
Create a clear and organized outline to structure your essay. A persuasive essay typically follows this structure:
- Introduction
- Background Information
- Body Paragraphs (with supporting evidence)
- Counterarguments (addressing opposing views)
Step 4: Write the Introduction
In the introduction, grab your reader's attention and present your thesis statement. For example:
Step 5: Provide Background Information
Offer context and background information to help your readers understand the issue better. For instance:
Step 6: Develop Body Paragraphs
Each body paragraph should present a single point or piece of evidence that supports your thesis statement. Use clear topic sentences, evidence, and analysis. Here's an example:
Step 7: Address Counterarguments
Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and refute them with strong counterarguments. This demonstrates that you've considered different perspectives. For example:
Step 8: Write the Conclusion
Summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement in the conclusion. End with a strong call to action or thought-provoking statement. For instance:
Step 9: Revise and Proofread
Edit your essay for clarity, coherence, grammar, and spelling errors. Ensure that your argument flows logically.
Step 10: Cite Your Sources
Include proper citations and a bibliography page to give credit to your sources.
Remember to adjust your approach and arguments based on your target audience and the specific angle you want to take in your persuasive essay about COVID-19.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid19
When writing a persuasive essay about the Covid-19 pandemic, it’s important to consider how you want to present your argument. To help you get started, here are some example essays for you to read:
Check out some more PDF examples below:
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Pandemic
Sample Of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 In The Philippines - Example
If you're in search of a compelling persuasive essay on business, don't miss out on our “ persuasive essay about business ” blog!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Vaccine
Covid19 vaccines are one of the ways to prevent the spread of Covid-19, but they have been a source of controversy. Different sides argue about the benefits or dangers of the new vaccines. Whatever your point of view is, writing a persuasive essay about it is a good way of organizing your thoughts and persuading others.
A persuasive essay about the Covid-19 vaccine could consider the benefits of getting vaccinated as well as the potential side effects.
Below are some examples of persuasive essays on getting vaccinated for Covid-19.
Covid19 Vaccine Persuasive Essay
Persuasive Essay on Covid Vaccines
Interested in thought-provoking discussions on abortion? Read our persuasive essay about abortion blog to eplore arguments!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Integration
Covid19 has drastically changed the way people interact in schools, markets, and workplaces. In short, it has affected all aspects of life. However, people have started to learn to live with Covid19.
Writing a persuasive essay about it shouldn't be stressful. Read the sample essay below to get idea for your own essay about Covid19 integration.
Persuasive Essay About Working From Home During Covid19
Searching for the topic of Online Education? Our persuasive essay about online education is a must-read.
Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid 19
Covid-19 has been an ever-evolving issue, with new developments and discoveries being made on a daily basis.
Writing an argumentative essay about such an issue is both interesting and challenging. It allows you to evaluate different aspects of the pandemic, as well as consider potential solutions.
Here are some examples of argumentative essays on Covid19.
Argumentative Essay About Covid19 Sample
Argumentative Essay About Covid19 With Introduction Body and Conclusion
Looking for a persuasive take on the topic of smoking? You'll find it all related arguments in out Persuasive Essay About Smoking blog!
Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
Do you need to prepare a speech about Covid19 and need examples? We have them for you!
Persuasive speeches about Covid-19 can provide the audience with valuable insights on how to best handle the pandemic. They can be used to advocate for specific changes in policies or simply raise awareness about the virus.
Check out some examples of persuasive speeches on Covid-19:
Persuasive Speech About Covid-19 Example
Persuasive Speech About Vaccine For Covid-19
You can also read persuasive essay examples on other topics to master your persuasive techniques!
Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Writing a persuasive essay about COVID-19 requires a thoughtful approach to present your arguments effectively.
Here are some tips to help you craft a compelling persuasive essay on this topic:
Choose a Specific Angle
Start by narrowing down your focus. COVID-19 is a broad topic, so selecting a specific aspect or issue related to it will make your essay more persuasive and manageable. For example, you could focus on vaccination, public health measures, the economic impact, or misinformation.
Provide Credible Sources
Support your arguments with credible sources such as scientific studies, government reports, and reputable news outlets. Reliable sources enhance the credibility of your essay.
Use Persuasive Language
Employ persuasive techniques, such as ethos (establishing credibility), pathos (appealing to emotions), and logos (using logic and evidence). Use vivid examples and anecdotes to make your points relatable.
Organize Your Essay
Structure your essay involves creating a persuasive essay outline and establishing a logical flow from one point to the next. Each paragraph should focus on a single point, and transitions between paragraphs should be smooth and logical.
Emphasize Benefits
Highlight the benefits of your proposed actions or viewpoints. Explain how your suggestions can improve public health, safety, or well-being. Make it clear why your audience should support your position.
Use Visuals -H3
Incorporate graphs, charts, and statistics when applicable. Visual aids can reinforce your arguments and make complex data more accessible to your readers.
Call to Action
End your essay with a strong call to action. Encourage your readers to take a specific step or consider your viewpoint. Make it clear what you want them to do or think after reading your essay.
Revise and Edit
Proofread your essay for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Make sure your arguments are well-structured and that your writing flows smoothly.
Seek Feedback
Have someone else read your essay to get feedback. They may offer valuable insights and help you identify areas where your persuasive techniques can be improved.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Common Topics for a Persuasive Essay on COVID-19
Here are some persuasive essay topics on COVID-19:
- The Importance of Vaccination Mandates for COVID-19 Control
- Balancing Public Health and Personal Freedom During a Pandemic
- The Economic Impact of Lockdowns vs. Public Health Benefits
- The Role of Misinformation in Fueling Vaccine Hesitancy
- Remote Learning vs. In-Person Education: What's Best for Students?
- The Ethics of Vaccine Distribution: Prioritizing Vulnerable Populations
- The Mental Health Crisis Amidst the COVID-19 Pandemic
- The Long-Term Effects of COVID-19 on Healthcare Systems
- Global Cooperation vs. Vaccine Nationalism in Fighting the Pandemic
- The Future of Telemedicine: Expanding Healthcare Access Post-COVID-19
In search of more inspiring topics for your next persuasive essay? Our persuasive essay topics blog has plenty of ideas!
To sum it up,
You have read good sample essays and got some helpful tips. You now have the tools you needed to write a persuasive essay about Covid-19. So don't let the doubts stop you, start writing!
If you need professional writing help, don't worry! We've got that for you as well.
MyPerfectWords.com is a professional essay writing service that can help you craft an excellent persuasive essay on Covid-19. Our experienced essay writer will create a well-structured, insightful paper in no time!
So don't hesitate and get in touch with our persuasive essay writing service today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there any ethical considerations when writing a persuasive essay about covid-19.
Yes, there are ethical considerations when writing a persuasive essay about COVID-19. It's essential to ensure the information is accurate, not contribute to misinformation, and be sensitive to the pandemic's impact on individuals and communities. Additionally, respecting diverse viewpoints and emphasizing public health benefits can promote ethical communication.
What impact does COVID-19 have on society?
The impact of COVID-19 on society is far-reaching. It has led to job and economic losses, an increase in stress and mental health disorders, and changes in education systems. It has also had a negative effect on social interactions, as people have been asked to limit their contact with others.

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Should COVID-19 vaccines be mandatory? Two experts discuss
Senior Research Fellow, Oxford Uehiro Centre for Practical Ethics, University of Oxford
NIHR Academic Clinical Fellow in Public Health Medicine, UCL
Disclosure statement
Alberto Giubilini receives funding from the Arts and Humanities Research Council/UK Research and Innovation (AHRC/UKRI) and has previously received funding from the Wellcome Trust.
Vageesh Jain is affiliated with Public Health England under an honorary contract as a speciality registrar.
University College London provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation UK.
University of Oxford provides funding as a member of The Conversation UK.
View all partners

To be properly protective, COVID-19 vaccines need to be given to most people worldwide. Only through widespread vaccination will we reach herd immunity – where enough people are immune to stop the disease from spreading freely. To achieve this, some have suggested vaccines should be made compulsory , though the UK government has ruled this out . But with high rates of COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in the UK and elsewhere , is this the right call? Here, two experts to make the case for and against mandatory COVID-19 vaccines.
Alberto Giubilini, Senior Research Fellow, Oxford Uehiro Centre for Practical Ethics, University of Oxford
COVID-19 vaccination should be mandatory – at least for certain groups. This means there would be penalties for failure to vaccinate, such as fines or limitations on freedom of movement.
The less burdensome it is for an individual to do something that prevents harm to others, and the greater the harm prevented, the stronger the ethical reason for mandating it.
Being vaccinated dramatically reduces the risk of seriously harming or killing others. Vaccines such as the Pfizer , AstraZeneca or Moderna ones with 90-95% efficacy at preventing people from getting sick are also likely to be effective at stopping the virus from spreading, though possibly to a lower degree. Such benefits would come at a very minimal cost to individuals.
Lockdown is mandatory. Exactly like mandatory vaccination, it protects vulnerable people from COVID-19. But, as I have argued in detail elsewhere, unlike mandatory vaccination, lockdown entails very large individual and societal costs. It is inconsistent to accept mandatory lockdown but reject mandatory vaccination. The latter can achieve a much greater good at a much smaller cost.
Also, mandatory vaccination ensures that the risks and burdens of reaching herd immunity are distributed evenly across the population. Because herd immunity benefits society collectively, it’s only fair that the responsibility of reaching it is shared evenly among society’s individual members.
Of course, we might achieve herd immunity through less restrictive alternatives than making vaccination mandatory – such as information campaigns to encourage people to be vaccinated. But even if we reach herd immunity, the higher the uptake of vaccines, the lower the risk of falling below the herd immunity threshold at a later time. We should do everything we can to prevent that emergency from happening – especially when the cost of doing so is low.
Fostering trust and driving uptake by making people more informed is a nice narrative, but it’s risky. Merely giving people information on vaccines does not always result in increased willingness to vaccinate and might actually lower confidence in vaccines. On the other hand, we’ve seen mandatory vaccination policies in Italy recently successfully boost vaccine uptake for other diseases.
Mandatory seatbelt policies have proven very successful in reducing deaths from car accidents, and are now widely endorsed despite the (very small) risks that seatbelts entail. We should see vaccines as seatbelts against COVID-19. In fact, as very special seatbelts, which protect ourselves and protect others.

Vageesh Jain, NIHR Academic Clinical Fellow in Public Health Medicine, UCL
Mandatory vaccination does not automatically increase vaccine uptake. An EU-funded project on epidemics and pandemics, which took place several years before COVID-19, found no evidence to support this notion. Looking at Baltic and Scandinavian countries, the project’s report noted that countries “where a vaccination is mandatory do not usually reach better coverage than neighbour or similar countries where there is no legal obligation”.
According to the Nuffield Council of Bioethics, mandatory vaccination may be justified for highly contagious and serious diseases. But although contagious, Public Health England does not classify COVID-19 as a high-consequence infectious disease due to its relatively low case fatality rate.
COVID-19 severity is strongly linked with age, dividing individual perceptions of vulnerability within populations. The death rate is estimated at 7.8% in people aged over 80, but at just 0.0016% in children aged nine and under. In a liberal democracy, forcing the vaccination of millions of young and healthy citizens who perceive themselves to be at an acceptably low risk from COVID-19 will be ethically disputed and is politically risky.
Public apprehensions for a novel vaccine produced at breakneck speed are wholly legitimate. A UK survey of 70,000 people found 49% were “very likely” to get a COVID-19 vaccine once available. US surveys are similar . This is not because the majority are anti-vaxxers.
Despite promising headlines, the trials and pharmaceutical processes surrounding them have not yet been scrutinised. With the first trials only beginning in April , there is limited data on long-term safety and efficacy. We don’t know how long immunity lasts for. None of the trials were designed to tell us if the vaccine prevents serious disease or virus transmission.
To disregard these ubiquitous concerns would be counterproductive. As a tool for combating anti-vaxxers – estimated at around 58 million globally and making up a small minority of those not getting vaccinated – mandatory vaccines are also problematic. The forces driving scientific and political populism are the same . Anti-vaxxers do not trust experts, industry and especially not the government. A government mandate will not just be met with unshakeable defiance, but will also be weaponised to recruit others to the anti-vaxxer cause.
In the early 1990s, polio was endemic in India , with between 500 and 1,000 children getting paralysed daily. By 2011, the virus was eliminated. This was not achieved through legislation. It was down to a consolidated effort to involve communities, target high-need groups, understand concerns, inform, educate, remove barriers, invest in local delivery systems and link with political and religious leaders.
Mandatory vaccination is rarely justified. The successful roll-out of novel COVID-19 vaccines will require time, communication and trust. We have come too far, too fast, to lose our nerve now.
- Mandatory vaccination
- Coronavirus
- Vaccine hesitancy
- Coronavirus insights

School of Social Sciences – Public Policy and International Relations opportunities

Partner, Senior Talent Acquisition

Deputy Editor - Technology

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Deputy Vice-Chancellor (Academic and Student Life)
Get Email Updates from Ballotpedia
First Name *
Please complete the Captcha above
Ballotpedia on Facebook
Share this page
Follow Ballotpedia
Ballotpedia on Twitter
Arguments in the debate over responses to the coronavirus (covid-19) pandemic, 2020.
State and local government responses to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic have varied widely. Those responses have generated a similar variety of responses from pundits, policy makers, lawmakers, and more. This article highlights the arguments over government responses in several areas:
- Universal or mass testing
Mask requirements
School closures, travel restrictions, lockdown/stay-at-home orders.
- Expansion of absentee or mail-in voting
Religious service restrictions
This article is a hub for our coverage of arguments within each area of debate. It includes links to policy-specific pages that provide an overview of the arguments within each topic. It also includes links to state-specific pages that dive into the debate that's happening in each state about a variety of policies.
These arguments come from a variety of sources, including public officials, journalists, think tanks, economists, scientists, and other stakeholders. We encourage you to share the debates happening in your local community to [email protected] .
For an overview of federal, state, and local responses around the country, click here .
- 1.1 Testing
- 1.2 Mask requirements
- 1.3 School closures
- 1.4 Travel restrictions
- 1.5 Lockdown/stay-at-home orders
- 1.6 Expansion of absentee/mail-in voting
- 1.7 Religious service restrictions
- 2 General resources
- 4 External links
- 5 Footnotes
Topics and arguments
The main areas of disagreement about universal or mass testing for COVID-19 before the economy can reopen are:
- Universal testing is necessary
- Universal testing is effective
- Universal testing is possible
- Universal testing is not necessary
- Universal testing is not possible
- Universal testing would divert and waste resources
- Universal testing might be dangerous
- Massive testing is too expensive
- Universal testing results are unreliable
- Universal testing is too slow to protect public health
The main areas of disagreement about mask requirements during the coronavirus pandemic are:
- Masks reduce airborne spread of coronavirus
- Mask requirements are good for the economy
- Mask laws are justified to promote public health
- Mask mandates should apply statewide
- Masks reduce the intensity of COVID-19 infection and sickness
- Mask requirements are not necessary to stop the spread of coronavirus
- Mask requirements give a false sense of security
- Mask requirements restrict freedom
- Masks present other health risks
- Mask requirements have harmful social consequences
- Mask requirements are unenforceable
The main areas of disagreement about school closures during the coronavirus pandemic are:
- School closures are necessary to prevent the spread of the virus
- Evidence from past pandemics supports the efficacy of school closures
- Reopening Universities will increase COVID-19 spread
- Reopening schools puts people of color at higher risk
- Keep schools closed because COVID-19 outbreaks are inevitable
- School closures are ineffective in preventing the spread of the virus
- School closures pose significant unintended consequences
- School closures and reopening plans have disparate economic effects
- School closures and distance learning exacerbate digital divide
- Reopen schools to protect the economy
- School-aged children have reduced COVID-19 risk
The main areas of disagreement about travel restrictions are:
- Travel restrictions prevent the spread of the virus
- Travel restrictions promote the state's safety image
- Travel restrictions are constitutional
- Travel restrictions protect tourism workers
- Certain travel restrictions are unconstitutional
- Travel restrictions are unfair to tourism businesses
- Travel restrictions are difficult to enforce
- Travel restrictions are ineffective
- Travel restrictions damage local economies
The main areas of disagreement about lockdown/stay-at-home orders are:
- Lockdown/stay-at-home orders are necessary
- Lockdown/stay-at-home orders are better for the economy long-term
- Lockdown/stay-at-home orders are legal
- Lockdown/stay-at-home orders are limited
- Lockdown/stay-at-home orders are unnecessary
- Lockdown/stay-at-home orders are worse than the coronavirus pandemic itself
- Lockdown/stay-at-home orders are illegal
- Lockdown/stay-at-home orders are unpopular
- Lockdown/stay-at-home orders are unenforceable
- Lockdown/stay-at-home orders go too far
- Lockdown/stay-at-home orders create COVID-19 risks
Expansion of absentee/mail-in voting
The main areas of disagreement about the expansion of absentee/mail-in voting are:
- Absentee/mail-in voting reduces the spread of COVID-19
- Absentee/mail-in voting expansion is necessary to facilitate access to voting
- Expanding absentee/mail-in voting is unlikely to increase fraud
- Expanding vote-by-mail is fair to both major parties
- States have the capacity and experience to expand absentee/mail-in voting
- Absentee/mail-in voting is less reliable than in-person voting
- Absentee/mail-in voting systems can fail
- Absentee/mail-in voting poses a higher risk for fraud and manipulation
- It is unnecessary to change voting systems in response to COVID-19
- The expansion of absentee/mail-in voting systems open the door to flawed election policies
- Expansion of absentee/mail-in voting systems creates election controversies (“blue shift”)
The main areas of disagreement about religious service restrictions are:
- Public safety priorities take precedence over religious interests
- Religious services present a higher risk than other social and business activities
- Restrictions on physical gatherings do not preclude religious practices
- Limiting religious gatherings during a pandemic aligns with most religious values
- Skepticism of religious restrictions has harmed religious communities during COVID-19
- In-person religious gatherings are not essential services
- Religious gathering restrictions do not discriminate against faiths
- Religious service restrictions violate the First Amendment and religious freedom
- Religious services are essential
- Religious service restrictions put church viability at risk
- There is insufficient evidence that religious services pose a higher risk than other social and business activities
- COVID-19 religious restrictions unfair to some faiths
General resources
Click the links below to explore official resources related to the coronavirus outbreak.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
- National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor
- U.S. Department of Education
- World Health Organization
- Trends in Number of COVID-19 Cases and Deaths in the US Reported to CDC, by State/Territory
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccinations, Our World in Data (Number of vaccines administered)
- Coronavirus Vaccine Tracker, New York Times (Progress of vaccine trials)
- Ballotpedia: Political responses to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, 2020
- State government responses to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, 2020
- Government official, politician, and candidate deaths, diagnoses, and quarantines due to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, 2020-2021
- Changes to ballot measure campaigns, procedures, and policies in response to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, 2020-2022
- Ballotpedia's elections calendar
External links
The external resources listed below are related to the coronavirus pandemic.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
- National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
- Coronavirus arguments by topic
- One-off pages, evergreen
Ballotpedia features 451,939 encyclopedic articles written and curated by our professional staff of editors, writers, and researchers. Click here to contact our editorial staff or report an error . For media inquiries, contact us here . Please donate here to support our continued expansion.
Information about voting
- What's on my ballot?
- Where do I vote?
- How do I register to vote?
- How do I request a ballot?
- When do I vote?
- When are polls open?
- Who represents me?
2024 Elections
- Presidential election
- Presidential candidates
- Congressional elections
- Ballot measures
- State executive elections
- State legislative elections
- State judge elections
- Local elections
- School board elections
2025 Elections
- State executives
- State legislatures
- State judges
- Municipal officials
- School boards
- Election legislation tracking
- State trifectas
- State triplexes
- Redistricting
- Pivot counties
- State supreme court partisanship
- Polling indexes
Public Policy
- Administrative state
- Criminal justice policy
- Education policy
- Environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG)
- Unemployment insurance
- Work requirements
- Policy in the states
Information for candidates
- Ballotpedia's Candidate Survey
- How do I run for office?
- How do I update a page?
- Election results
- Send us candidate contact info
Get Engaged
- Donate to Ballotpedia
- Report an error
- Newsletters
- Ballotpedia podcast
- Ballotpedia Boutique
- Media inquiries
- Premium research services
- 2024 Elections calendar
- 2024 Presidential election
- Biden Administration
- Recall elections
- Ballotpedia News
SITE NAVIGATION
- Ballotpedia's Sample Ballot
- 2024 Congressional elections
- 2024 State executive elections
- 2024 State legislative elections
- 2024 State judge elections
- 2024 Local elections
- 2024 Ballot measures
- Upcoming elections
- 2025 Statewide primary dates
- 2025 State executive elections
- 2025 State legislative elections
- 2025 Local elections
- 2025 Ballot measures
- Party committee fundraising, 2023-2024
- State Executive Competitiveness Report, 2023
- State government trifectas in 2023
- State Legislative Competitiveness Report, 2023
- Endorsements in school board elections, 2023
- Partisanship in 2023 United States local elections
- Trends in 2023 ballot measures
- Cabinet officials
- Executive orders and actions
- Key legislation
- Judicial nominations
- White House senior staff
- U.S. President
- U.S. Congress
- U.S. Supreme Court
- Federal courts
- State government
- Municipal government
- Election policy
- Running for office
- Ballotpedia's weekly podcast
- About Ballotpedia
- Editorial independence
- Job opportunities
- News and events
- Privacy policy
- Disclaimers
How to Write About Coronavirus in a College Essay
Students can share how they navigated life during the coronavirus pandemic in a full-length essay or an optional supplement.
Writing About COVID-19 in College Essays

Getty Images
Experts say students should be honest and not limit themselves to merely their experiences with the pandemic.
The global impact of COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, means colleges and prospective students alike are in for an admissions cycle like no other. Both face unprecedented challenges and questions as they grapple with their respective futures amid the ongoing fallout of the pandemic.
Colleges must examine applicants without the aid of standardized test scores for many – a factor that prompted many schools to go test-optional for now . Even grades, a significant component of a college application, may be hard to interpret with some high schools adopting pass-fail classes last spring due to the pandemic. Major college admissions factors are suddenly skewed.
"I can't help but think other (admissions) factors are going to matter more," says Ethan Sawyer, founder of the College Essay Guy, a website that offers free and paid essay-writing resources.
College essays and letters of recommendation , Sawyer says, are likely to carry more weight than ever in this admissions cycle. And many essays will likely focus on how the pandemic shaped students' lives throughout an often tumultuous 2020.
But before writing a college essay focused on the coronavirus, students should explore whether it's the best topic for them.
Writing About COVID-19 for a College Application
Much of daily life has been colored by the coronavirus. Virtual learning is the norm at many colleges and high schools, many extracurriculars have vanished and social lives have stalled for students complying with measures to stop the spread of COVID-19.
"For some young people, the pandemic took away what they envisioned as their senior year," says Robert Alexander, dean of admissions, financial aid and enrollment management at the University of Rochester in New York. "Maybe that's a spot on a varsity athletic team or the lead role in the fall play. And it's OK for them to mourn what should have been and what they feel like they lost, but more important is how are they making the most of the opportunities they do have?"
That question, Alexander says, is what colleges want answered if students choose to address COVID-19 in their college essay.
But the question of whether a student should write about the coronavirus is tricky. The answer depends largely on the student.
"In general, I don't think students should write about COVID-19 in their main personal statement for their application," Robin Miller, master college admissions counselor at IvyWise, a college counseling company, wrote in an email.
"Certainly, there may be exceptions to this based on a student's individual experience, but since the personal essay is the main place in the application where the student can really allow their voice to be heard and share insight into who they are as an individual, there are likely many other topics they can choose to write about that are more distinctive and unique than COVID-19," Miller says.
Opinions among admissions experts vary on whether to write about the likely popular topic of the pandemic.
"If your essay communicates something positive, unique, and compelling about you in an interesting and eloquent way, go for it," Carolyn Pippen, principal college admissions counselor at IvyWise, wrote in an email. She adds that students shouldn't be dissuaded from writing about a topic merely because it's common, noting that "topics are bound to repeat, no matter how hard we try to avoid it."
Above all, she urges honesty.
"If your experience within the context of the pandemic has been truly unique, then write about that experience, and the standing out will take care of itself," Pippen says. "If your experience has been generally the same as most other students in your context, then trying to find a unique angle can easily cross the line into exploiting a tragedy, or at least appearing as though you have."
But focusing entirely on the pandemic can limit a student to a single story and narrow who they are in an application, Sawyer says. "There are so many wonderful possibilities for what you can say about yourself outside of your experience within the pandemic."
He notes that passions, strengths, career interests and personal identity are among the multitude of essay topic options available to applicants and encourages them to probe their values to help determine the topic that matters most to them – and write about it.
That doesn't mean the pandemic experience has to be ignored if applicants feel the need to write about it.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form.
To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App has added an optional section to address this topic. Applicants have 250 words to describe their pandemic experience and the personal and academic impact of COVID-19.
"That's not a trick question, and there's no right or wrong answer," Alexander says. Colleges want to know, he adds, how students navigated the pandemic, how they prioritized their time, what responsibilities they took on and what they learned along the way.
If students can distill all of the above information into 250 words, there's likely no need to write about it in a full-length college essay, experts say. And applicants whose lives were not heavily altered by the pandemic may even choose to skip the optional COVID-19 question.
"This space is best used to discuss hardship and/or significant challenges that the student and/or the student's family experienced as a result of COVID-19 and how they have responded to those difficulties," Miller notes. Using the section to acknowledge a lack of impact, she adds, "could be perceived as trite and lacking insight, despite the good intentions of the applicant."
To guard against this lack of awareness, Sawyer encourages students to tap someone they trust to review their writing , whether it's the 250-word Common App response or the full-length essay.
Experts tend to agree that the short-form approach to this as an essay topic works better, but there are exceptions. And if a student does have a coronavirus story that he or she feels must be told, Alexander encourages the writer to be authentic in the essay.
"My advice for an essay about COVID-19 is the same as my advice about an essay for any topic – and that is, don't write what you think we want to read or hear," Alexander says. "Write what really changed you and that story that now is yours and yours alone to tell."
Sawyer urges students to ask themselves, "What's the sentence that only I can write?" He also encourages students to remember that the pandemic is only a chapter of their lives and not the whole book.
Miller, who cautions against writing a full-length essay on the coronavirus, says that if students choose to do so they should have a conversation with their high school counselor about whether that's the right move. And if students choose to proceed with COVID-19 as a topic, she says they need to be clear, detailed and insightful about what they learned and how they adapted along the way.
"Approaching the essay in this manner will provide important balance while demonstrating personal growth and vulnerability," Miller says.
Pippen encourages students to remember that they are in an unprecedented time for college admissions.
"It is important to keep in mind with all of these (admission) factors that no colleges have ever had to consider them this way in the selection process, if at all," Pippen says. "They have had very little time to calibrate their evaluations of different application components within their offices, let alone across institutions. This means that colleges will all be handling the admissions process a little bit differently, and their approaches may even evolve over the course of the admissions cycle."
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
10 Ways to Discover College Essay Ideas

Tags: students , colleges , college admissions , college applications , college search , Coronavirus
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
Toward semiconductor gender equity.
Alexis McKittrick March 22, 2024

March Madness in the Classroom
Cole Claybourn March 21, 2024

20 Lower-Cost Online Private Colleges
Sarah Wood March 21, 2024

How to Choose a Microcredential
Sarah Wood March 20, 2024

Basic Components of an Online Course
Cole Claybourn March 19, 2024

Can You Double Minor in College?
Sarah Wood March 15, 2024

How to Avoid Scholarship Scams
Cole Claybourn March 15, 2024

Ways to Maximize Campus Life
Anayat Durrani March 14, 2024

8 People to Meet on Your College Campus
Sarah Wood March 12, 2024

Completing College Applications on Time
Cole Claybourn March 12, 2024

Persuasive Essay Writing
Persuasive Essay About Covid 19

Top Examples of Persuasive Essay about Covid-19
Published on: Jan 10, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 29, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide
Easy and Unique Persuasive Essay Topics with Tips
The Basics of Crafting an Outstanding Persuasive Essay Outline
Ace Your Next Essay With These Persuasive Essay Examples!
Persuasive Essay About Gun Control - Best Examples for Students
Learn How To Write An Impressive Persuasive Essay About Business
Learn How to Craft a Compelling Persuasive Essay About Abortion With Examples!
Make Your Point: Tips and Examples for Writing a Persuasive Essay About Online Education
Learn How To Craft a Powerful Persuasive Essay About Bullying
Craft an Engaging Persuasive Essay About Smoking: Examples & Tips
Learn How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Social Media With Examples
Craft an Effective Argument: Examples of Persuasive Essay About Death Penalty
Share this article
In these recent years, covid-19 has emerged as a major global challenge. It has caused immense global economic, social, and health problems.
Writing a persuasive essay on COVID-19 can be tricky with all the information and misinformation.
But don't worry! We have compiled a list of persuasive essay examples during this pandemic to help you get started.
Here are some examples and tips to help you create an effective persuasive essay about this pandemic.
On This Page On This Page -->
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
The coronavirus pandemic has everyone on edge. You can expect your teachers to give you an essay about covid-19. You might be overwhelmed about what to write in an essay.
Worry no more!
Here are a few examples to help get you started.
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Pandemic
Sample Of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 In The Philippines - Example
Check out some more persuasive essay examples to get more inspiration and guidance.
Examples of Persuasive Essay About the Covid-19 Vaccine
With so much uncertainty surrounding the Covid-19 vaccine, it can be challenging for students to write a persuasive essay about getting vaccinated.
Here are a few examples of persuasive essays about vaccination against covid-19.
Check these out to learn more.
Persuasive essay on the covid-19 vaccine
Tough Essay Due? Hire a Writer!

Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Integration
Writing a persuasive essay on Covid-19 integration doesn't have to be stressful or overwhelming.
With the right approach and preparation, you can write an essay that will get them top marks!
Here are a few samples of compelling persuasive essays. Give them a look and get inspiration for your next essay.
Integration of Covid-19 Persuasive essay
Integration of Covid-19 Persuasive essay sample
Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid-19
Writing an argumentative essay can be a daunting task, especially when the topic is as broad as the novel coronavirus pandemic.
Read the following examples of how to make a compelling argument on covid-19.
Argumentative essay on Covid-19
Argumentative Essay On Covid-19
Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
Writing a persuasive speech about anything can seem daunting. However, writing a persuasive speech about something as important as the Covid-19 pandemic doesnât have to be difficult.
So let's explore some examples of perfectly written persuasive essays.
Persuasive Speech About Covid-19 Example
Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay
Here are seven tips that can help you create a strong argument on the topic of covid-19.
Check out this informative video to learn more about effective tips and tricks for writing persuasive essays.
1. Start with an attention-grabbing hook:
Use a quote, statistic, or interesting fact related to your argument at the beginning of your essay to draw the reader in.
2. Make sure you have a clear thesis statement:
A thesis statement is one sentence that expresses the main idea of your essay. It should clearly state your stance on the topic and provide a strong foundation for the rest of your content.
3. Support each point with evidence:
To make an effective argument, you must back up each point with credible evidence from reputable sources. This will help build credibility and validate your claims throughout your paper.
4. Use emotional language and tone:
Emotional appeals are powerful tools to help make your argument more convincing. Use appropriate language for the audience and evokes emotion to draw them in and get them on board with your claims.
5. Anticipate counterarguments:
Use proper counterarguments to effectively address all point of views.
Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and address them directly by providing evidence or reasoning why they are wrong.
6. Stay focused:
Keep your main idea in mind throughout the essay, making sure all of your arguments support it. Donât stray off-topic or introduce unnecessary information that will distract from the purpose of your paper.
7. Conclude strongly:
Make sure you end on a strong note. Reemphasize your main points, restate your thesis statement, and challenge the reader to respond or take action in some way. This will leave a lasting impression in their minds and make them more likely to agree with you.
Writing an effective persuasive essay is a piece of cake with our guide and examples. Check them out to learn more!

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
We hope that you have found the inspiration to write your next persuasive essay about covid-19.
However, If you're overwhelmed by the task, don't worry - our professional essay writing service is here to help.
Our expert and experienced persuasive essay writer can help you write a persuasive essay on covid-19 that gets your readers' attention.
Our professional essay writer can provide you with all the resources and support you need to craft a well-written, well-researched essay. Our essay writing service offers top-notch quality and guaranteed results.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you begin a persuasive essay.
To begin a persuasive essay, you must choose a topic you feel strongly about and formulate an argument or position. Start by researching your topic thoroughly and then formulating your thesis statement.
What are good topics for persuasive essays?
Good topics for persuasive essays include healthcare reform, gender issues, racial inequalities, animal rights, environmental protection, and political change. Other popular topics are social media addiction, internet censorship, gun control legislation, and education reform.
What impact does COVID-19 have on society?
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a major impact on society worldwide. It has changed the way we interact with one another. The pandemic has also caused economic disruption, forcing many businesses to close or downsize their operations.
Cathy A. (Literature, Education)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, covid-19: scientific arguments, denialism, eugenics, and the construction of the antisocial distancing discourse in brazil.

- 1 Faculty of Public Health's Audioteca Collection, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
- 2 School of Arts Science and Humanities, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
Since March 11, the world has been experiencing a pandemic of Sars-Cov-2, the new coronavirus, which emerged in China in late December 2019 and causes the COVID-19 disease. Pandemics are characterized by pathogen's ability of emerging or re-emerging across geographical boundaries, simultaneously affecting a large number of people around the world, due to the sustained transmission in humans. In the case of the COVID-19 pandemic, we have witnessed in real time the dissemination of different types of information about it and strategies used to contain the rate of virus contamination. Our main goal in this study is to analyze the discursive production of the Brazilian journalistic media about vertical isolation as a supposed scientific strategy, and to demonstrate how that has been used in the denialist approach adopted by the Brazilian President Jair Bolsonaro. The research was carried out on the Google platform, using the following descriptors: coronavirus and herd immunity; coronavirus and the Imperial College herd immunity strategy; vertical isolation; Bolsonaro and vertical isolation. Thirty-six articles were selected for a qualitative analysis besides the original article by David L. Katz (published in The New York Times), where he claims the creation of the vertical confinement strategy. All documents of the analytical corpus are open and free of charge. The articles were submitted to discursive analysis and the main results shows that Brazilian media highlighted Bolsonaro's proposal of vertical isolation and amplified his pandemic denial and eugenics policies The mass media vehicles play a central role in the dissemination of information and should commit to the publication of reliable and trustworthy information, as well as to objectively situate the areas of knowledge of the specialists whose opinions are being published.
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic presents itself as concerning for the majority of people across the planet. This concern is guided by a number of characteristics of Sars-Cov-2 and by the contemporary lifestyle. The virus has a high potential for dissemination in the globalized world—by mid-August 2020, more than 20.7 million people had been contaminated; part of this contingent became seriously ill, requiring hospitalization, and nearly 780 thousand people had died 1 . There is still no treatment available for this disease, nor vaccines that might prevent infection. These factors, together with the lack of knowledge and the uncertainties on the evolution of the infection/disease, as well as the post-infection immunological responses, have led to great investments in scientific research in the several fields of science, while at the same time the population searches incessantly for information in order to make sense of their own experiences.
Within this context of a pandemic, mass media holds a key social role; as a source of information that is historically recognized and trustworthy, the media has been disseminating and modeling the ways in which ordinary people think about and deal with everyday events. It is important to remember that the conditions of truth and of social justification are the pillars that support the belief in journalistic discourse, which becomes trustworthy and credible as long as it manages to prove the veracity of its testimony, by means of the detailing of facts and the citation of specialized sources ( Lisboa and Benetti, 2015 ).
It is important to note, however, that this “proof of veracity” does not make news stories “mirrors” of reality, but instead, simply one of the possible narratives about social occurrences. Transformed into information, these occurrences are shared between members of society and journalists, who in turn claim a monopoly on this knowledge (defining what is news), meaning that, more than passive observers, they are active participants in the construction of reality ( Traquina, 2007 ). Although creative, journalistic activity is submitted to a number of “tyrannies”: of the deadlines and formats of journalistic production; of superior hierarchies (editors-in-chief, news editors, and, frequently, the owners of the platforms); the imperatives of journalism as a business; the extreme competition; and the action/pressure of different social actors searching to highlight their own matters ( Traquina, 2007 ). Thus, newsmaking results in journalism's capacity for producing social facts, in other words, for instituting realities, according to the repertories and contexts that the journalist chooses to use.
We have, in addition, used journalistic discursive practices within the perspective offered by Van Der Haak et al. (2012) , who state that journalism, as a public asset, should produce information and analyses that are useful for democratic societies, based on transparency, independence, the use of reliable sources, and the detailed analysis of events.
In this text we took the journalistic coverage of COVID-19 as a producer of meanings and social facts ( Spink, 2004 ). We also used the perspective of Thompson (2014) , for whom the process of news production, whichever it may be, always occurs within a socio-historical context that allows media outlets to capture and transform a certain number of everyday events into messages (symbolic forms) in detriment of an infinity of others.
We considered the context of exceptionality of the pandemic, where researchers and scientists are being obliged to accelerate their production to a rhythm never seen before, in order to provide clinical responses to the disease and guide public policies and State actions for managing public health around the world. This implies that most of the knowledge produced about Sars-CoV-2 and the disease it causes is being permanently revised, refuted, and discarded.
The problem is that, with this frenetic production, the refuted suppositions have often already reached a level of dissemination and absorption by common sense and even by public authorities which, due to a variety of interests, makes it impossible to revert their use, remaining as valid points of view. In other words, even when these suppositions have been invalidated by science, they continue as a social fact, affecting the lives of people and the manners in which they make their decisions when faced with the epidemic. Thus, it is important for journalists and mass media companies to be vigilant regarding the possible consequences of the content they relay.
We are referring, therefore, to the decisive role played by mass media in structuring the public space. This is a sensitive debate around the world, as it involves controlling the access to the production and circulation of the information that is transformed into messages (symbolic content) by a restricted number of actors, according to private interests or that of the groups that the media represents ( Thompson, 2014 ). This aspect is especially problematic in Brazil. The country has a historical asymmetry in the relationship between mass media and society, establishing what Kucinski (2006) call the “principle of exclusion,” violating the human right to information.
In Brazil, different from that which occurred for the most part in the liberal democracies of the global North, the mediatic market is marked by an ideological, economic, and political homogeneity that is usually pro-establishment. From the start, the media—and particularly the press—has historically reproduced with great fidelity the oligarchic model of land ownership, with a predominance in newspaper management of the “favoritism typical of the command culture of large rural properties” ( Kucinski, 2006 , p. 20).
The business model for national media is amplified by Brazil's complexity. Companies are configurated as oligopolies, with properties that are horizontal, vertical, and crisscrossed by different mediums (newspapers, magazines, AM and FM radio, open access and pay TV, internet provider) within the same market, whether local, regional, or national. This process was accentuated by the privatization of telecommunications during the 1990s ( de Lima, 2001 , 2011 ; Malinverni, 2016 ). Currently, according to the Brazilian section of the MOM (Media Ownership Monitor)/Reporters Sans Frontiéres, eight economic family groups control 26 of the 50 largest media vehicles in the country, according to audience and to scheduling capacity; in other words, in terms of potential to influence public opinion.
Divided into four large sectors (print, radio, TV, and online), the study, which resulted in the report “Who controls the media in Brazil,” released in late 2017, indicates a red alert for the Brazilian mediatic system due to the high concentration of audience and properties, the high geographic concentration, and the lack of transparency, besides economic, political, and religious interference in the production of information 2 . Seven of the twelve vehicles that published the news stories analyzed in this work integrate the control group describe above. The most paradigmatic of these is the Globo group, the largest oligopoly in this sector in Brazil and Latin America, and one of the largest in the world, with more than half of the audience among the first four (36.9%). The concentration of media outlets by a small number of private groups restricts competition and, consequently, the diversity to represent the distinct interests of society. Without the possibility of contradiction, there is a predominance in the mediatic market of what many studies and analysts call “penseé unique” ( de Lima, 2011 ).
Faced with such a complex dynamic—taken here in the sense proposed by Law and Mol (2002) , according to whom innumerable actors, materialities, and sociabilities perform the several facets of a phenomenon—and with the up-to-the-minute scope of the pandemic, which takes place in real time, journalistic coverage is up against enormous difficulties. These range from the immediacy of translating the technical-scientific knowledge of several fields to critical evaluations on what to publish and the possible effects.
Historically, at moments of public health emergency, the population and journalists wait to receive trustworthy information from governmental organizations and political leaderships, whose actions are based on the guidance of health authorities. In Brazil, however, besides this complexity that is inherent to the pandemic, mass media must deal with other challenges. The first, as we will see in the analyses, lies in reporting two distinct official discourses on controlling COVID-19: that of the president of the Republic and his supporters; and that of the scientists in the field of health, technicians from the Ministry of Health (in the first months), and governors and mayors who are favorable to social distancing. This resulted in a politicization of the actions for disease control.
Brazil has a Unified Health System (Sistema Único de Saúde—SUS) that guarantees universal health access to all within the national territory; the System is well-structured and organized in a decentralized manner. Since the promulgation of the 1988 Constitution, it is up to the federal government to establish guidelines and coordinate healthcare actions, allocating a budget for the states and municipalities, who manage resources and actions according to local/regional needs. This system counts on a structure of sanitary surveillance and consolidated data registration that allows the monitoring of healthcare actions throughout the country. The pandemic, however, hit Brazil at a point when SUS has been weakened, since, as stated by Menezes et al. (2019) , from 2016 a policy of defunding healthcare has been implemented, by means of the approval of a constitutional amendment that froze the federal budget in this sector for the next 20 years, with readjustment calculations based only on inflation. This policy of deconstructing SUS has intensified during the Bolsonaro government, with already-perceptible effects upon the population's health: “For example, the loss of 8.5 thousand Cuban doctors from the More Doctors Program, who were treating around 30 million Brazilians, in 2.9 thousand municipalities and indigenous villages” ( Menezes et al., 2019 , p. 67).
Despite this process of scrapping, from January to May the technical team of the Ministry of Health, responsible for managing SUS, carried out assertive actions relating to the pandemic, creating decrees, establishing benchmarks for action, and guiding the population. The president of the Republic, however, who refuses to acknowledge the severity of the pandemic, has been producing and divulging, from the start, counterinformation that contradicts the ministerial discourse. Within this context, on April 16, Bolsonaro dismissed the minister of Health, doctor and politician, and nominated a new leader for the department, an oncologist and business entrepreneur who works in the private sector. With a more technical profile, he remained only 28 days in office, and resigned due to disagreeing with the president's position regarding use of chloroquine to combat COVID-19. Therefore, since May 15, the position of minister of Health has been occupied in an interim manner by a general without any health background, who nominated other members of the military, equally without specialized training, to key roles in the Ministry of Health, furthering the dismantling of SUS 3 .
Brazilian journalism gave plenty of space for this polarization between the president and his supporters and the Ministry of Health, during the first months of the pandemic, as well as to the national and international scientific community on the subject of measures of social distancing. The analysis of articles indicated that the journalistic coverage often considered both discourses as equivalent, even knowing that the president and his supporters had no scientific backing—on the contrary, they often based themselves on false news and unfounded calculations.
For Gelbspan (1998 , p. 57–58), in discussing journalistic coverage of global warning:
The professional canon of journalistic fairness requires reporters who write about a controversy to present competing points of view. When the issue is of a political or social nature, fairness – presenting the most compelling arguments of both sides with equal weight – is a fundamental check on biased reporting. But this canon causes problems when it is applied to issues of science. It seems to demand that journalists present competing points of views on a scientific question as though they had equal scientific weight, when actually they do not.
In this sense, it is crucial that journalists covering themes that involve science know how to translate the concepts and recognize strong evidence so as not to fall into the mistake that Pitts (2018) designates “ both-sideism.” Rosen (2010) , discussing this journalistic strategy, states that it is often adopted in order to seek an “objectivity,” by means of which the journalist would speak from a supposed position of neutrality (a view from nowhere), and could not therefore be accused of favoring one position. For Sousa (2002) , this position is a tributary of two ideological forces that modulate news: that of objectivity and that of professionalism. The first explains the descriptive and factual orientation of news, with its mimetic ambition regarding reality that becomes explicit, and the systematic identification of sources of information in news statements; the second is based on the belief that the production routine and professional experience are sufficient tools for journalistic exemption. Supported by deontological codes constructed throughout history, the journalist acts as a “professional authority,” imbued with the right and the obligation to mediate and simplify information on daily happenings ( Traquina, 2007 ). In other words, under the jargon “interests of society,” the press acts within a discursive safe conduct that “authorizes” the prescription of standards and practices, while at the same time serving as an “argumentative shield” that protects and exempts journalists and owners of communication vehicles from the consequences of their discursive practices ( Malinverni et al., 2012 ). This strategy, however, impedes a deeper analysis and the production of precise information based on the truth.
Another challenge that journalists face is the increasingly precarious nature of work in newsrooms, and a lack of specialization in the area of health ( Malinverni and Cuenca, 2017 ), both of which have become more of an issue over the past decade with the financial crisis that has impacted media companies, especially print journalism, due to the rise of virtual media ( Castilho, 2015 ), affecting directly the quality of the news. Vukasovich and Vukasovich (2016) indicate, additionally, that globalization and the incessant pressures of newsmaking are two more elements that greatly impact the quality of journalistic coverage.
Methodology
In this work we carried out the discursive analysis of journalistic coverage following two key thematic lines: herd immunity and vertical isolation. Using Google search, we researched news articles on the Sars-CoV-2 epidemic in Brazil using four descriptors: 1—Herd immunity and coronavirus; 2—Herd immunity and Imperial College; 3—Vertical isolation; and 4—Bolsonaro and vertical isolation. Criteria for inclusion: the first three pages of results presented by Google; articles published by print media and mass news sites with high visitation numbers and open access links. Criteria for exclusion: blogs with no connection to mass media or governmental and non-governmental organizations; low repercussion media, videos and links that can be exclusively accessed by subscribers; texts reproduced ipsis litteris on other sites.
The time period set for article selection was March 16 to April 30, 2020, starting 5 days before the date on which the Ministry of Health confirmed community transmission of the disease in the country (March 20) and a public health emergency was declared by most state and municipal governments.
In the first phase of systemization, 101 texts were located; of these, after application of the above criteria, 36 were selected for analysis: 8 articles under descriptor 1; 8 under descriptor 2; 11 under descriptor 3; and 9 under descriptor 4. All texts were copied into Word to be later read in full and analyzed. The texts were published on 12 websites, linked to nine media groups: UOL, Folha de S.Paulo and Bol/UOL (Grupo Folha); O Globo (Organizações Globo); Saúde Estadão (Grupo Estado); Saúde Abril and Veja (Grupo Abril); Gazeta do Acre (independent); IstoÉ Dinheiro (Editora Três); BBC News Brasil (a subsidiary of BBC, controlled by the British government); El País Brasil (from the Spanish group PRISA); and CNN Brasil (a subsidiary of the American CNN). The four first, as already mentioned, are among the organizations that control almost 60% of the national audience. Historically, they operate under the establishment logic, with episodic demonstrations of divergences that lend an appearance of plurality. Rarely do they explicitly support a candidate or political party, although the journalistic coverage is always more favorable to agendas that adopt a center or right-wing positioning within the political spectrum. This perspective, shared by IstoÉ Dinheiro and CNN Brasil, has been in effect in the country since mid-March of 2020. The Gazeta do Acre is the only independent vehicle; in other words, that is not connected to a multimedia conglomerate. It was founded by two reporters who worked at an alternative newspaper which, in the 1970s, challenged the censorship imposed by the military regime and reported the daily violence committed by the large landowners against the small-scale rubber tree tappers—among them Acre environmentalist Chico Mendes, murdered by local ranchers in 1988. El País Brasil and BBC News Brasil follow the more liberal line of journalistic coverage set by their parent companies. These characteristics may explain why these three vehicles were the only ones to adopt a more critical approach to Bolsonaro's discourse, as will be discussed.
We adopted the theoretical perspective of discursive practices ( Spink, 2004 ), focusing on the language in use, a social practice analyzed in the intersection between performative aspects of language (when, in which conditions, with what intention, in which manner) and the conditions of production (understood in this case both as social and interactional context, and in the Foucauldian sense of historical constructions).
In this approach, the notion of interpretative repertories of Wetherell and Potter (1988 , p. 172) is central:
Repertoires could be seen as building blocks speakers use for constructing versions of actions, cognitive processes, and other phenomena. Any particular repertoire is constructed out of a restricted range of terms used in a specific stylistic and grammatical fashion. Commonly these terms are derived from one or more key metaphors and the presence of a repertoire will often be signaled by certain tropes or figures of speech.
The circulation dynamic of the interpretative repertories, within the flow of production of meanings, updates contents and processes present in the history of a society.
In this analysis we looked for these standards in the journalistic coverage of the two studied themes, making clear the content of the discussions and marking out the meanings they produce, as well as situating the contexts for production of the articles. Therefore, throughout the text, we introduce episodes and events that contextualize the analysis and help us to understand the scenario for news production, since, as stated by Rosen et al. (1997 , p.3), “[…] the journalism itself, the art of telling our collective story, is never independent of the country and culture in which the story is told.”
Strategies of Social Distancing and Herd Immunity in Brazil
The strategies of social distancing and of herd immunity were already circulating in Brazilian media before the official declaration of sustained transmission of Sars-CoV-2 in the country. We carried out this study associating the descriptor “Herd immunity” to coronavirus and to Imperial College. Next, we introduce the main results of the discursive analysis, discussing the meanings produced by the articles found with these descriptors.
The first article with the descriptor herd immunity (“What is ‘group immunity,' the polemical strategy of the United Kingdom to combat coronavirus” 4 ) dates from March 16, and was published by two large Brazilian news sites; its central theme is the debate surrounding the measures adopted by the United Kingdom. The article discusses the criticism suffered by the British government that, contrary to countries such as Italy, Spain, and France, had decided not to adopt a strategy of social suppression, betting on the free circulation of the virus in order to consequently lead the population toward herd immunity (a mitigation strategy). According to this text, the mitigation measure would help preserve the economy, since all activities would remain operational. The key criticism stemmed from the scientific community, for whom mitigation would lead to an uncontrolled growth in the number of people contaminated by Sars-CoV-2, with an inevitable rise in infections and the overburdening of the National Health Service (NHS) due to hospitalization demands for severe cases. This debate permeated the 16 articles analyzed under the descriptor “Herd immunity,” progressively incorporating references to reports from the Imperial College.
All the articles analyzed, when discussing herd immunity, made reference at some point to the United Kingdom and/or its prime minister and team. The United States and its president were also cited in six articles. Thus, we can say that the debate on social distancing, in Brazil, was closely connected to the measures and pronouncements of British and North American political authorities. Despite herd immunity having been considered and discussed in other cities/countries in Europe, the perspective that dominated the Brazilian news was that of the UK and the USA.
In addition to the positioning of political authorities, the scientific reports of the Imperial College were also widely commented on by the Brazilian media, and for this reason it was included as a descriptor. This institution appears often as being responsible for publishing studies that made the UK and the USA give up on the mitigation strategy. The majority of articles published between March 17 and April 24 refer directly to a specific report by the Imperial College, made public on March 16, which presents calculations regarding the lethality of the disease and the number of sick people according to each behavioral strategy adopted by the two countries. Only one article, from March 26, cites the report that makes estimates regarding the possible effects of the different non-pharmacological strategies in Brazil.
It is interesting to observe that, among the group of articles discussing herd immunity there are explanations on what this strategy entails. But most of these (5 articles) promote a simplification of this strategy, which can be explained by observing the authorship of the analyzed texts: only in three were the authors specialists. The first of these, mentioned above and produced by BBC News Brasil, is signed by a foreign journalist, a specialist in scientific communication. The second—““Coronavirus: must almost everyone catch it to end the pandemic?” 5 , from March 25, published in the health section of the website of Veja magazine—was written by two Brazilian researchers from the field of microbiology who acted as scientific disseminators. In this article there is a clear effort to translate expert knowledge for ordinary non-specialized readers, in a clear and simple manner, focusing on the reasons that herd immunity could not be legitimized by science to guide public policies against Sars-CoV-2. The third article—“Who is immune to coronavirus?” 6 , published on April 14 by the newspaper Folha de S.Paulo and available on the UOL website—was written by Marc Lipsitch, a professor of Epidemiology at Harvard University's School of Public Health. Published originally in the New York Times , it is a direct translation. In these three articles, there is a greater care in explaining herd immunity, based on scientific knowledge.
Another factor that could explain the simplifications and superficial approaches adopted by the Brazilian media for the theme of herd immunity relates to the sources consulted and used in the articles. Historically, the production of news articles in the field of health includes consultation with known specialists who can expound on the theme with authority, productivity, and credibility, conferring legitimacy and reliability to the information presented ( Tuchman, 1983 ; Traquina, 2007 ). However, with regard to the debate on herd immunity, the analyzed articles make little use of consulting epidemiologists, the most appropriate specialists when it comes to this theme. Among the medical sources, the articles prioritized the opinions of virologists, infectious disease specialists, and immunologists; only four epidemiologists were consulted—two Brazilians, one from North America, and one from India. This may have contributed toward the polarization of measures of social distancing, as the guidelines suggested by epidemiology would explain with more clarity the catastrophic effects of the epidemic on the healthcare system and, consequently, on people's lives, if natural herd immunity were to be adopted in the country.
The articles that cite the reports of the Imperial College approach the theme in a manner that presents, together with projections of mathematical models that favor suppression, the arguments contrary to this measure, as well as the “harmful” effects of broad and unrestricted social distancing on the economy.
The concept of herd immunity has a longstanding and legitimate scientific basis, which postulates that the infection of a percentage of the population is enough to block transmission of a virus, and therefore can contain or even eradicate it within a certain territory. Since this debate began, the World Health Organization (WHO) and scientists all over the world have explained that this concept applies to immunization by means of vaccinations, and that investing in natural herd immunity against COVID-19 would overburden the healthcare systems, causing hundreds of thousands of avoidable deaths.
The positioning of some government leaders in favor of this strategy appears to be oriented by Malthusian theories, according to which some populations, such as the elderly, can be considered as weak and surplus ( Mezzadra, 2020 ). In this manner, they could become “naturally” extinct by pandemics, such as the case of COVID-19. Hannah et al. (2020) observe that, by defending herd immunity, governors assume that the biopolitical interests of capital take precedence over the biopolitical interests of life. One of the articles of the corpus emphasizes that matters of economy were decisive in the debate on herd immunity. The text “Specialists recommend herd immunity for poor countries 7 ”—produced by Bloomberg, a news agency of the financial sector, and published in the finance section of UOL on April 22—, presents herd immunity as the only alternative for poor, young countries such as India. The journalist presents arguments from an Indian epidemiologist as well as researchers from the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy and Princeton University in defense of this strategy:
[…] allow the virus to circulate in a controlled manner throughout the next seven months would provide immunity to 60% of the country's population by November, and thus, contain the disease. Mortality could be limited while the virus propagates, in comparison to European countries, such as Italy, since 93.5% of the Indian population is under 65 years, it is said, although they have not divulged projections on the number of dead .
The article is overly brief, but points out that this is a risky strategy, concluding that at the moment not much was known regarding immunity to coronavirus.
The possibility of using the strategy of herd immunity to minimize the effects of the pandemic on the economy was discussed hypothetically in many of the articles analyzed, but not indicated as a viable solution. For instance, the texts that mention this discussion in the United Kingdom clarify that the British government refuted that they were seeking herd immunity. This proposal would be morally unacceptable, since the known lethality data indicates that this strategy would imply acceptance and recognition that at least 1% of the population could die, in addition to a high number of hospitalizations, leading to a collapse of the healthcare services.
In the 16 articles analyzed with descriptors 1 and 2, only one has a critical approach and presents the Imperial College projections for Brazil. The article is “Coronavirus pandemic: the best scenario is disastrous 8 ,” published on March 30 on the website of the Gazeta do Acre , a local newspaper of the state of Acre, at the extreme north of the country. The text presents the calculations for the newspaper's hometown, the state capital Rio Branco, informing the amount of people who would get sick and die if suppression were not adopted. The other articles touched generically upon the theme, without taking the trouble to inform about the effects of different measures within the local contexts of Brazilian cities with their inequalities.
Among the articles of this corpus , the only argument in favor of herd immunity that had no economic framing was that of a supposed prevention of a second wave of the disease, since in the countries that adopted restrictive measures only a small portion of the population would have had contact with the virus, and thus the virus would once again strike these populations.
Before we continue the discussion, it is important to present the facts for the Brazilian context. From March 11, some state governors and mayors began to declare non-pharmacological measures to deal with the pandemic, following recommendations from the Ministry of Health and creating scientific committees. Throughout that entire month, several states and municipalities suspended classes at all educational levels, prohibiting events and religious services, and closing commerce and non-essential services, maintaining only healthcare, pharmacies, and grocery stores, in addition to bars, restaurants, and bakeries, although these last could only serve customers by delivery. These measures met with strong resistance from entrepreneurs and politicians, especially the president of the Republic and his social and political support base.
In this manner, from mid-March and throughout the month of April, the media began to include in discussions of the pandemic the financial damage that social distancing measures could provoke, and the effects on people's daily lives. In this context, the news began to construct a narrative around the concept of “two sides”; one favorable to the strategy of seeking herd immunity, and the other, to social distancing. As previously discussed, his false equivalency between scientifically based arguments and fragile arguments supported by hypotheses is damaging to the coverage of scientific themes ( Gelbspan, 1998 ).
With regard to herd immunity, this approach was present in many of the articles analyzed, with only two of the news stories breaking this logic. The first, titled “Epidemiologist opposes Osmar Terra and sees Brazil as far from the end of the epidemic 9 ,” from April 14, published on the UOL website, the journalist presents the arguments of an epidemiologist to deconstruct the reasoning presented by congressman Osmar Terra 10 , an advisor to Bolsonaro and part of his support base. As the central character in the text, and in opposition to Osmar Terra, the epidemiologist, who is also the rector of a federal university, demonstrates with data and scientific evidence that the country was far from reaching herd immunity, and points out the political polarization of the debate on social distancing:
The discussion about social distancing in all the media is based on ideology and not science. There is a group of people who think we must relax and who voted on the same candidate [Bolsonaro], and the other people, who voted against, are in favor of distancing .
The epidemiologist's perception on the role of the media in this polarization is precise. Osmar Terra is a member of Congress who, despite a degree in medicine and an appointment as Health Secretary, is not a specialist in this theme. It is worth noting that, according to the evaluation carried out by the website Radar aos Fatos, which checks and verifies fake news , he was the parliamentary member who most divulged false news on COVID-19 11 . More than that, the fact that there was a link to the video in which the congressman reproduces false news signals that the news site UOL itself contributed toward disseminating an opinion that, based on antiscientific visions, not only encourages the political polarization of the epidemic scenario, but also confuses the population. This polarization indicates a narrative framing typical of political coverage, in which reality is taken as “[…] a field in conflict, a bipolar world of successive hostilities” ( Motta, 2007 , p. 10), feeding the confrontation with successive affirmations that belie the sources, in a dramatic game based on the notion of contradiction. In the case of this coverage, the narrative option for the “two opposite sides” of the phenomenon makes no sense, as by giving equal weight and space to the scientific evidence and positioning of the majority of national and international scientists, and the opinions of a small group of denialist politicians with an anti-science agenda, the media breaks their social commitment of informing the population correctly about phenomena and events that impact daily life, such as the case of the COVID-19 epidemic.
The second article for the descriptor “herd immunity”—the previously mentioned “Coronavirus pandemic: the best scenario is disastrous” of the Gazeta do Acre —was the only one among the 16 news stories analyzed to critically situate the attacks of Bolsonaro and his supporters upon suppression measures. The text, with authorship stated simply as “Newsroom,” classifies Bolsonaro's statements as unfounded and absurd:
At this moment, the majority of countries, the Ministry of Health of Brazil, governors and mayors from all around the country, based on directives given by the WHO, are trying to adopt the measure of suppression to control the epidemic in Brazil .
However, president Bolsonaro and a small group of his counselors and advisors (which includes his children) are the only dissonant voices and are actively advocating the adoption of the mitigation strategy to control dissemination of the virus in Brazil .
This is a noisy minority, incidentally. Thanks to the control that the president and his children have over their thousands of fanatic followers, the social networks are inundated with the most absurd campaigns in favor of this option of control .
From “Vertical Interdiction” to “Vertical Isolation,” The Use of Scientists' Opinions for Denialism
The analysis demonstrated that the use of the terminology “vertical isolation” was imposed by President Bolsonaro himself and naturalized by the media. On March 24, in a pronouncement on the radio and TV network 12 , he urged the population to abandon the social distancing measures that had been recommended by the Ministry of Health and which, as previously mentioned, had been adopted by several governors and mayors. His proposal: keep in confinement only the so-called risk groups. In Brazil, this would be the elderly population over 60 years of age and those with chronic diseases, besides symptomatic cases. In his speech, which shocked the national and international scientific community and those Brazilians who had adhered to social distancing—at least 50% of the population, in several regions, at the start of community transmission—, Bolsonaro stated that COVID-19 was just “a little flu,” a “little cold” that was inoffensive to the majority of the young and the healthy who, like him, had an “athletic history” 13 . The following morning (25), when asked by a reporter how the country would protect these vulnerable groups, he answered: “[…] there is horizontal isolation, that they're doing here, and there's the vertical. It's the vertical [for groups at risk]” 14 .
The term vertical isolation resonated intensely in newspapers and news sites, and, after March 25, it was in the title of the 20 articles analyzed for descriptors 3 and 4 (“Vertical” isolation” and “Bolsonaro and vertical isolation”). When explaining the concept proposed by Bolsonaro, three texts cited the hypotheses of David L. Katz, a doctor who specialized in diet and nutrition 15 , which were published in an article in The New York Times , on March 20, 2020, with one text also bringing up an article by epidemiologist John Ioannidis, statistician, and co-director of the Stanford Prevention Research Center, published on March 17, on the StatNews website. Both were critics of the social suppression measures proposed and adopted in some Asian and European countries.
The analysis also suggested that the terminology “vertical isolation” which circulated in the national media was a translation of the arguments proposed by Katz, which were in turn anchored on the debate about herd immunity and the initial mitigation strategies adopted by the UK and USA to deal with the pandemic. Although quickly rejected by the scientific community, “isolation” as a synonym to distancing continued to resonate in Brazilian newspapers and news sites and is still used today in this sense.
Katz's article (“Is our fight against coronavirus worse than the disease?”) was published 5 days before Bolsonaro's interview. In it, Katz employs classic concepts of epidemiology to make a misleading analysis, based on a still-fragile foundation of data about the pandemic, as we will see in the following analysis. Centered on repertories from epidemiology, he frames social distancing as a potentially harmful “war” strategy, with socioeconomic consequences and effects upon the healthcare systems that could be worse than the disease. From the very start, with the title, Katz makes use of militaristic metaphors—a longstanding and recurring discursive strategy in all dimensions of the dissemination of science and medicine ( Wenner, 2007 )—in order to build his thesis for reducing the costs of the “war” against the new coronavirus.
He supports his arguments by interpreting data from South Korea, which indicated that 99% of COVID-19 cases were light, while the lethality of the disease basically affected those who were more vulnerable. Still employing war metaphors, Katz concludes that the most advisable approach would be a “surgical strike,” naming this a “vertical interdiction,” which would consist in forbidding circulation only for those who are most vulnerable and exposing the majority of the population to the virus, thus attaining herd immunity. In the text, even though the social impact of distancing is mentioned, it is clear that the specialist is preoccupied with the financial aspect:
I am deeply concerned that the social, economic and public health consequences of this near total meltdown of normal life — schools and businesses closed, gatherings banned — will be long lasting and calamitous, possibly more severe than the direct toll of the virus itself. The stock market will bounce back in time, but many businesses never will. The unemployment, impoverishment and despair likely to result will be public health scourges of the first order ( Katz, 2020 ).
Likewise, the arguments made by Ioannidis—in the article “We know enough now to act decisively against COVID-19. Social distancing is a good place to start”—focused on the economic effects of distancing measures:
If that is the true rate, locking down the world with potentially tremendous social and financial consequences may be totally irrational. It's like an elephant being attacked by a house cat. Frustrated and trying to avoid the cat, the elephant accidentally jumps off a cliff and dies ( Ioannidis, 2020 ).
The hypotheses of Ioannidis and, mainly, Katz gather elements that are of great use to the interests of the denialists, in the sense used by Hoofnagle and Hoofnagle (2007) and referenced by Diethelm and McKee (2009) , for whom the denialist discourse is constructed around rhetorical arguments,
[…] to give the appearance of argument or legitimate debate, when in actuality there is none. These false arguments are used when one has few or no facts to support one's viewpoint against a scientific consensus or against overwhelming evidence to the contrary. They are effective in distracting from actual useful debate using emotionally appealing, but ultimately empty and illogical assertions ( Hoofnagle and Hoofnagle, 2007 ).
The denial is constructed with basis on five discursive tactics which, together or separately, produce pseudoscientific discourse ( Hoofnagle and Hoofnagle, 2007 ; Diethelm and McKee, 2009 ). Three of these bring to light the manner in which the arguments of the two American specialists help sustain the denialism of President Bolsonaro and his supporters: (1) selectivity in choosing out-of-context scientific data in order to suggest error; (2) the use of specialists whose opinions are inconsistent with the knowledge established by scientific canon; and (3) resorting to isolated articles that challenge the dominant consensus as a means of discrediting the entire field.
In Brazil, the hypotheses of Ioannidis and, above all, Katz were presented by the media as an explanation for the vertical isolation proposed by Bolsonaro. The news stories also included criticism of this strategy by Brazilian and international specialists. This is what can be surmised from the article “What is the vertical isolation that Bolsonaro wants and why do specialists fear it will cause more deaths 16 ” published on the BBC News Brasil website, on March 25. In this news piece, the arguments of the two American specialists are rejected by the scientific community, due to their hypothetical nature, based on fragile data and a partial analysis that does not include the response capacity of the healthcare system; in this case, American healthcare. One of the opposing sources presented in the article is Harry Crane, a statistics professor from Rutgers University, who considered that their mistake was:
[…] to allow themselves to be affected by the desire to negate a situation that can cause despair. “Under severe uncertainty, it's natural instinct and common sense to hope for the best, but prepare for the worst”, wrote Crane, in response to the article by Ioannidis. This is because the mortality rate does not depend only on the clinical picture that the virus itself can produce, but also the capacity for response of societies for treating the sick .
The text makes it clear that, while the hypotheses of the two specialists were refuted by their peers, they were rapidly embraced by neoliberal politicians and economists, becoming “[…] music for the ears of the governmental economy teams who were trying to finish public accounting in midst of the perspective of recession” (BBC News Brasil, 2020). The journalist who authored the text supports this statement by citing part of an editorial from The Wall Street Journal , published in the wake of the Ioannidis article:
“ America urgently needs a pandemic strategy that is more economically and socially sustainable than the current national lockdown”, summarized the editorial from The Wall Street Journal, known for expressing the thoughts of the American economic elite, a week ago .
In the same article, the journalist affirms that the conclusions of Katz and Ioannidis acquired a following in the team of the Brazilian minister of Economy, “[…] in search of a gentler solution for the public health crisis.”
But it was, above all, the political support base of denialist leaders that took on the hypotheses of the two specialists and began using them to contest social distancing measures. In the news piece “Why is vertical isolation seen with skepticism 17 ?” produced by the agency Conteúdo Estadão and published on five news sites, on March 30, there is a clear use of these specialist arguments in the discourse against distancing:
Defended by President Jair Bolsonaro, the so-called “vertical isolation” of the population is a minority theory among scientists and is viewed with skepticism by the medical community. It consists on separating those who are in the risk group from being exposed to the virus, such as those older than 60 and those with chronic diseases (UOL, March 30).
Although the title of the article points to skepticism, the body of text brings a plurality of opinions, under the dichotomy of pros-cons and advantages-disadvantages of this strategy, including the discussion on herd immunity as a strategy and the reasons it was discarded in the United Kingdom. The most interesting point brought up in the article is a comparison of the supporters of Bolsonaro and Donald Trump. After informing that the American president had recommended extreme distancing, following the publication of the Imperial College study on March 16, the article adds that Trump went back to defending a quick return to activities in the United States, projecting a flexibilization in 10 days, which did not end up taking place but still had repercussions among Bolsonaro supporters:
Excerpts of the video with this speech from the American [Trump] were disseminated by supporters of Bolsonaro in Brazil, as a supposed sign that the Americans would relax their measures. After being criticized, Trump pulled back and said that the date to reopen the country was just a suggestion, but that the end of social isolation would not take place without backing from scientists. The day before yesterday, Trump affirmed that he is thinking of establishing an official quarantine for states such as New York (which has the majority of cases), New Jersey and Connecticut .
This text makes it clear how the denialist discourse of Trump and Bolsonaro align and, at the same time, how the largely connected environments of the social networks serve as feedback for both of their support bases. However, by indicating a new retreat by Trump, the text also demonstrates that his denialism was more vulnerable to scientific and medical arguments in favor of social distancing. The impression that we get is that Trump oscillates, either denying the scientific reading of the severity of the pandemic in his discourse and actions, or accepting information from scientists, different in this way from Bolsonaro, who has been unwavering in his denialist positioning from the start of the epidemic in Brazil.
Media Adhesion and Naturalization of “Vertical Isolation”
In the 20 articles analyzed for descriptor 3 (Vertical isolation), vertical isolation appears as a specific type of social distancing, allowing us to infer the media's unrestricted adhesion to the terminology, central to the sum of information circulated in both corpora . Instrumental, 10 of the 11 titles for descriptor 3 were constructed around the notions of functioning/operation of this model, seeking to explain vertical isolation with its advantages, disadvantages, and risks 18 .
We raised several hypotheses on what may have contributed to this: the generalist nature and increasingly precarious state of Brazilian mass journalism and the absence of epidemiologists as sources for news stories, already discussed in this work; the didacticism employed in the framing of texts, announced even in the titles.
This pedagogic concern brings to light the efforts made by journalists to translate to readers, who are always assumed to be laypeople, the technical-scientific jargon employed in the news. This didacticism—which legitimizes journalists as “[…] the place of ‘being able to show', of ‘being able to say' and ‘being able to analyze' (…) as a place of mediation and of revelation of truth” ( Vizeu, 2009 , p. 77)—may have contributed in particular toward the production of the meaning of “vertical isolation” as a scientifically validated consensus strategy that “mirrors” a supposed epidemiological reality, aseptic and neutral.
It is necessary, therefore, to problematize the media's naturalization of “vertical isolation” to express measures of social distancing (quarantine, cordon sanitaire , lockdown). In first place, the terminology confuses two distinct models of attention to epidemics. In the field of health, including Brazil, the established scientific consensus uses the term isolation to designate the care given to an infected and symptomatic patient, and is therefore a model for individual attention, belonging to the field of clinical medicine; distancing, on the other hand, implies collective/populational care, affiliated to epidemiology.
The use of “social isolation” in the place of social distancing is also a sematic error as it is based on a false synonymy. In the Portuguese language, “isolate” means to separate, segregate, and confine a person from all others in their social circle—in Brazilian dictionaries, among examples of isolate, we find medical activity aimed at treating patients with contagious diseases. On the other hand, distancing is the act or effect of separating people/groups, centered on a notion of physical space and not segregation.
By using one term in place of another, naturalizing a theoretical hypothesis that is still under discussion and therefore not validated by the scientific community, the media legitimized the term social isolation as common sense. And this may have contributed to the construction of a derogatory meaning for the strategy of social distancing, amplifying the resistance of the Brazilian population toward this measure.
Vertical Isolation, Denialism, and Eugenics
The denialist discourse throughout the world is not just aligned to anti-science, but also resonates as a more or less homogeneous mark of eugenics. In Brazil, this is no different. The social and scientific movement for improving the human race that emerged at the end of the nineteenth century and was widely experimented with by the German Nazi regime during World War II (1939–1945), arrived in the country in 1918, with the creation of the Eugenics Society of São Paulo. Intellectuals from several areas notably from medicine and the public health services, gathered around this movement, and the triad of sanitation, hygiene, and eugenics supported a broad and generalized project for civilizational progress ( Maciel, 1999 ), with medical knowledge playing a central role.
Racial regeneration would occur by means of three types of eugenics: positive, negative, and preventive. This last, also called prophylactic hygiene by Brazilian eugenists, was mixed with principles of rural and urban sanitation, the suppression of social vices such as alcoholism, control of immigration and of matrimony, and the compulsory sterilization of “degenerates.” In the 1930s, the main activist in Brazilian eugenics, Renato Kehl, openly assumed his favorable position to some of the measures adopted by the German eugenics movement ( Kobayashi et al., 2009 ).
Thus, the world eugenics ideology met the Brazilian positivist-hygienist movement, forming a new and active field, of hygienist-physicians, the protagonists and disseminators of the eugenics elements that would mark the actions of Brazilian public health for the next decades, and which still linger today in many practices, especially in the field of social care. This scientific rationality led to the implementation of “[…] projects of eugenic nature that intended to eliminate disease, separate madness and poverty” ( Schwarcz, 1993 , p. 34), focusing mainly on immigrants, Black people, and the poor ( Diwan, 2007 ). Acting in an intensive manner, the hygienist doctors undertook “[…] what they imagined to be a national regenerative mission, exerting functions, carrying out tasks, occupying positions that were strange to medicine,” and disseminating the certainty “[…] of being able to end the blemishes of the nation, collaborating with Brazil's administrative and social entirety” ( Mota, 2003 , p. 21).
From the start of the community transmission of Sars-CoV-2 in Brazil it is possible to observe this memory of eugenics in Bolsonaro's denialism, especially in his defense of vertical isolation. As governors and mayors began to officially order social distancing, the president's position became more and more radical. This is what can be surmised from the article “Bolsonaro once again minimizes COVID-19 and says that Health is studying vertical isolation 19 ,” published on the financial news site IstoÉ Dinheiro on March 26. In this piece, the president once again says that “ some governors and mayors erred in the dose” of containment measures, demanding the reopening of all sectors of the economy:
“ And do a stay-at-home campaign. Don't let grandpa leave the house, leave him in a corner. When you get home have a shower, wash your hands, wipe your ears with sanitizer gel. That's it”, he declared .
In the excerpt, Bolsonaro dehumanizes the elderly, the main target for his strategy of vertical isolation, turning their existence into objects in face of the epidemic. In his ambition to maintain the capitalist order, the president treats this subject (the elderly) as objects without free will who must be segregated in a “corner,” removing “their individual, malleable, unique characteristics” and transforming them “into empty husks, representations of themselves who, apparently, are no longer covered by the State of right” ( Souza, 2017 , p. 70).
In the same article, when commenting on the critical situations in other countries and on the perspectives of how the disease would manifest in Brazil, Bolsonaro yet again invests in a rhetoric of dehumanization:
“ I don't think it's going to reach that point, even because Brazilians should be studied, they don't catch anything. You see the guy leaping into sewage, coming out, diving in and nothing happens” .
This speech speaks directly of the more vulnerable social classes in Brazil that, due to conditions of extreme poverty, are subject to extremely precarious production relations. In this manner, it is possible to identify in the president's discourse a correlation between men and rats, who are immune to sewers. This perspective, in turn, bears a resemblance to the metaphor of the crab man, created by doctor and geographer Josué de Castro to designate a new species of Brazilians: those excluded from the production processes and who took their subsistence from the mangrove swamps of Recife, mixing them up with the crabs they fed upon 20 . Later, in the 1990s, following on the heels of the crab men, the gabiru men emerged. This hyperbole was used to designate country folk who lost their lands to large-scale farming and ended up in urban shantytowns, carrying with them an old acquaintance, hunger ( Portella et al., 1992 ; de Melo Filho, 2003 ). From the Tupi wa'wiru , gabiru means that which devours supplies, lives off trash, begs for hand-outs, causes repugnance, attacks and steals ( Portella et al., 1992 ).
Besides touching upon this social imaginary of the excluded Brazilian, the speech is evidence of a reading in which the population can be left to their own luck, without needing the actions of a protective State since they are, by their animalistic nature, survivors.
In addition to the theoretical fragility of Bolsonaro's proposal, the news stories analyzed also demonstrate that the strategy was unfeasible due to Brazil's socioeconomic inequalities. In the article “Vertical isolation proposed by Bolsonaro may accelerate contagion by coronavirus and compromise health systems 21 ,” published on March 25 on the El País Brasil website, health specialists and medical authorities alert to the risks of accelerated contagion in Brazil and a rapidly compromised healthcare system:
“ The theoretical idea of vertical isolation is that you can allow young people to circulate. They would become infected and could become immune. But we don't know how this works with COVID-19 and we can't guarantee the exclusive isolation of a specific group”, alerts the doctor Valdes Bollela, professor at the School of Medicine of USP Ribeirão Preto [São Paulo University of Ribeiro Preto] . (…) You think you can separate all the people [in the risk groups] who are young from those who are over 60? (…) People with HIV, diabetes and the elderly who count on their families? I can't imagine that in real life. In a theoretical idea, it's possible. In practice, it's a trap (…) In Brazil, a lot of people depend exactly on the care of their children” .
On the isolation of the elderly, in an article published on March 25 on the CNN Brasil website, along with the previously mentioned press conference video, titled “Bolsonaro vai propor isolamento vertical para conter coronavírus 22 ,” other related opinions are mentioned:
[…] each family must be responsible for their relatives. “The people need to stop pushing things onto the public powers”, he stated. (…) He stressed that the president of the United States, Donald Trump, follows a “similar line” as to measures to contain the disease, referencing yesterday's speech by the North-American in which he intends to end quarantine in the USA “by Easter” .
In these excerpts, it is possible to observe Bolsonaro's contempt for the excluding social characteristics in Brazil, where extreme social inequality would make it impossible to completely isolate the elderly and those with comorbidities from their relatives. Additionally, this also indicates his positioning on two aspects: the first, in prioritizing the economy—what really matters is to keep people working and generating income and taxes; the second, in making the State exempt from the consequences of its omission regarding the risks that the elderly face, in other words, that their life or death is not a problem of the public powers but of their families. Bolsonaro also uses the reference to the president of the United States in order to legitimize and strengthen his arguments and transmit the idea that there is a consensus between them regarding the pandemic, reinforcing the thesis that vertical isolation would be a viable strategy, since it was adopted by a developed country.
The article is short and uses a neutral tone, but it refers to a number of links, informing us, among other things, that Bolsonaro was the target of protests by Brazilians who were maintaining social distancing and of criticism by politicians:
The speech [referring to the press conference video posted at the start of the article and already mentioned in this analysis] — during which there were records of pot-banging protests in several of the country's capitals — gave rise to criticism by health secretaries, authorities and politicians (CNN Brasil, March 25).
The website brings visibility to the president's speeches without the concern of reflecting upon them or of pointing out their damaging effects upon the population's health.
In the article “Bolsonaro defende isolamento vertical e sugere que país pode 'sair da normalidade democrática 23 ,”' produced by international news agency Ansa and published on the website of the O Globo newspaper (March 25), the president also makes what can be considered his first threat of democratic rupture, using the argument that measures of social distancing would provoke an economic crisis of enormous proportions, which could lead to social convulsions.
“ […] what happened in Chile [street movement that left its mark upon the Chilean scenario for months] will be small change next to what could happen in Brazil. We will all pay a price that will take years to pay, that is, if Brazil might not yet leave the democratic normality that you all defend so much, no one knows what can happen in Brazil” (…) “The chaos makes it so the left can seize the moment to come to power.”
By treating a scientifically legitimized event—the existence of an epidemic with planetary proportions—as an “excuse” of the Brazilian left to take his power, Bolsonaro brings up a fourth element that is characteristic of denialism: the identification of conspiracies among the consensuses of science. For conspiracy theorists, the validation of science is not a result of an evidence-based consensus among scientists, but of the involvement of these scientists in a complex and secret conspiracy ( Hoofnagle and Hoofnagle, 2007 ). In this sense, the process of peer revision “[…] is seen as a tool by which the conspirators suppress dissent, rather than as a means of weeding out papers and grant applications unsupported by evidence or lacking logical thought” ( Diethelm and McKee, 2009 ).
“So What?”: Considerations on a Eugenics Discourse
Denialism has different motivations—economic, political, personal, ideological, or religious—, but has as a common point the rejection of any thesis incompatible with the fundamental beliefs of those who hold them. As the analyses demonstrate, a first dimension of the denialism of Jair Bolsonaro on the Sars-Cov-2 epidemic is based on the idea that the effects of an economic crisis would be worse than the severe consequences of the disease itself on people's lives. As seen in this work, this discourse aligns with that of other denialist world leaders, such as President Donald Trump and Prime Minister Boris Johnson —although, different from the Brazilian president, these leaders have oscillated throughout the pandemic between accepting scientific arguments in favor of the population's health and prioritizing the economy.
In terms of the economic argument, however, a second dimension emerges in Bolsonaro's discourse: that of eugenics. Under the terminology of vertical isolation, naturalized and legitimized by the media, the Brazilian president turns the most vulnerable segment of the population into objects, establishing a moral compass according to which, faced with the needs of maintaining the relations of capitalist production, some lives are worth less than others, and that this would be enough to justify the sacrifice.
It is important to point out that this discursive posture is not casual or chaotic. There is a method here that, moreover, helped to elect Bolsonaro 24 , known for his racist, misogynistic, sexist, and xenophobic statements. In 2017, during the electoral campaign for presidency, the then parliamentary member promised to end all demarcation of land for Indigenous Peoples 25 : “You can be certain that, if I get there (…) There will not be a centimeter marked off for indigenous reservations or for quilombola 26 lands.”
At the same event, he made disparaging and fat-shaming comments: “I went to a quilombo. The lightest Afro-descendent there weighed seven arrobas (arroba is a measurement used to weigh cattle; one arroba is equivalent to 15 kg). They do nothing. I think he was of no use even to serve for breeding.” Ironically, this speech, which drew laughter from the audience, was given at Hebraica in Rio de Janeiro, one of the most traditional Jewish associations in the country.
In the wake of the rise of right-wing populism that, in the last years, has benefitted other leaders around the world, Bolsonaro was elected for his antisystem rhetoric, exploiting the fears and prejudices of ordinary voters, undermining the credibility of traditional political parties and democratic institutions, and normalizing discriminatory discourse, thanks to the reach of his social media, which he and his group manage with mastery, and with advisory help from Steve Bannon, former vice-president of Cambridge Analytica ( Ricard and Medeiros, 2020 ). When he took over the presidency of the Republic, in January 2019, he not only radicalized this rhetoric but also, in many cases, transformed it into State policy—in the first days of his government, he ended social and environmental protection structures and programs; under Bolsonaro, for example, the recognition of quilombos fell to the lowest levels in history 27 .
On March 18, in an interview to Fox News 28 during an official visit to the United States, Bolsonaro attacked immigrants by defending Trump's plans to build a wall on the border between the USA and Mexico: “The majority of immigrants do not have good intentions and do not want to do good for Americans.” It is worth remembering that there are over a million Brazilians living in the USA. In this manner, the alignment of Bolsonaro's migratory policies with those of the American president—who in December 2019 called Haiti, El Salvador, and African countries “shitholes”—indicates “a racist slant, since not by chance most immigrants are Black or Indigenous people, from countries with a non-white populational majority. There is a logic that is eugenic, racist, and ethnic in nature,” states Dennis Oliveira in the same article—a journalism professor from the University of São Paulo (USP) and an activist in the Rede Quilombação network.
As the Brazilian health crisis grew in severity, Bolsonaro's eugenics slant became more explicit, until it reached an emblematic declaration: “So what? I'm sorry. What do you want me to do? I'm a Messiah, but I don't do miracles 29 .” Spoken to a group of reporters and supporters in front of the Alvorada Palace, the presidential residence in Brasília, on the night of April 28, when Brazil hit 5,017 official deaths, the phrase was followed by a disturbing statement on the severity of COVID-19 among the elderly: “I regret the situation we are going through with the virus. We sympathize with the families who have lost their loved ones, who were mostly elderly. But such is life. Tomorrow it will be me [to die].”
The numbers for the epidemic in Brazil indicate that the eugenics project is succeeding, since on June 5, CNN informed that 40% more Black than white people die from COVID-19 in Brazil 30 . Although the country did not officially adopt the vertical isolation policy proposed by Bolsonaro, because the Supreme Court decreed that states and municipalities had the autonomy to adopt social distancing measures, Bolsonaro's government continued to boycott the actions of governors and mayors to contain dissemination of the virus. This boycott could be observed in the presidential decrees that increased the list of activities considered essential, in the delays and inefficiency in implementing financial aid to those who were left without income, in the absence of effective programs to subsidize small businesses, and, of course, in Bolsonaro's speeches, which resonated throughout the country both by means of mass media and social networks 31 .
Up until the conclusion of this article, the Ministry of Health was still under the interim command of a general who, like Bolsonaro, also adopted a denialist stance. On May 20, under this administration, the ministry published a protocol 32 with guidelines for prescribing chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for light, moderate, and severe cases of COVID-19. Although there is no strong scientific evidence on the effectiveness of this medication, the Bolsonaro administration maintains its use as a standard for care in SUS. Since the start of June 33 , the government has been changing the manner and time for divulging the epidemiological reports that update infection cases and deaths by the disease, while also announcing the adoption of a new methodology for sharing the data which will invalidate comparisons with the previous numbers and, consequently, affect monitoring of the evolution of COVID-19 in the country. One of the aims of this strategy is to reduce the visibility of the number of deaths and misinform the population. Following the same direction, the Department of Social Communication created a “life scoreboard,” a report disseminated exclusively on the presidency's social networks that highlights the number of recovery cases while omitting the deaths.
In addition to these actions, the president's denialist speeches that are spread both by mass media and social networks have a direct effect upon the behavior of the population regarding social distancing, as demonstrated by Ajzenman et al. (2020) .
In this scenario, our study demonstrates that the Brazilian mass media is still fixed upon the notion that it is necessary to present both sides of an event, giving each equal weight, even when one has assumed a denialist position toward the science. This positioning, justified normally by the pursuit of neutrality in news coverage, allows for the spreading of false premises posing as science and strengthens the denialist and eugenist project of Bolsonaro. This occurs because, as stated by Happer and Philo (2013) , the media holds a central role in spreading information and in the process of focusing attention on a specific subject, as well as in defining a public agenda.
Another aspect identified in the study relates to the characteristics of the method adopted by Bolsonaro since the elections, which have endured during this past year-and-a-half of his mandate: the discursive verbiage, often grotesque and always of populist appeal, which the Brazilian media appears to have become a hostage of. And, by amplifying the president's speeches, the media symbolically places him at the center of the coordination of control measures for the epidemic in Brazil, a role he has never undertaken. In this sense, we agree with Rosen (2020) and Smith (2020) , who identified the same phenomenon in the media coverage of coronavirus in the United States, pointing to the need of removing President Trump as a protagonist in news about the theme.
Under the guise of conclusion, it is important to highlight an action which indicates that the Brazilian press has gradually taken on a more critical posture. In June, faced with the proposal from the Ministry of Health for presenting incomplete data on COVID-19, the six largest newspapers and news sites in the country united in order to compile and systematize daily the data from the State Departments of Health 34 , ensuring a higher reliability and transparency of the numbers, thus acting as overseers for the public powers and guaranteeing the dissemination of correct information. However, in a health crisis with the magnitude of the present one, much more is necessary than merely making numbers visible. Newspapers and news sites have a key role, since the information they produce and circulate guide collective and individual behaviors ( Stevens and Hornik, 2014 ). Therefore, it is crucial that journalists take on a critical posture, knowing how to identify the multiple faces of denialism and making clear the damaging effects of eugenics policies upon the health of the population.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. All the articles/data used in the research are listed in the footnotes and are open access.
Author Contributions
CM and JB contributed to the design and implementation of the research, to the analysis of the results, and to the writing of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
1. ^ Daily map of Johns Hopkins University and Medicine. Available at https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html .
2. ^ Carried out in partnership between the RSF and the Intervozes collective, MOM-Brasil was the 11th study throughout the world and also the largest—up until 2017, the number of vehicles investigated had reached at the most 40. Available at: http://brazil.mom-rsf.org/br/ .
3. ^ Available at: https://brasil.elpais.com/brasil/2020-06-25/nem-o-pior-ministro-da-saude-fez-o-que-exercito-esta-fazendo-desmontando-a-engrenagem-do-sus.html .
4. ^ “What is ‘group immunity,' the polemical strategy of the United Kingdom to combat coronavirus.” Available at: https://noticias.uol.com.br/saude/ultimas-noticias/bbc/2020/03/16/o-que-e-a-imunidade-de-grupo-a-polemica-estrategia-do-reino-unido-para-combater-coronavirus.htm .
5. ^ “Coronavirus: must almost everyone catch it to end the pandemic?” Available at: https://saude.abril.com.br/blog/cientistas-explicam/coronavirus-quase-todo-mundo-tem-que-pegar-para-a-pandemia-passar/ .
6. ^ “Who is immune to coronavirus?” Available at: https://www1.folha.uol.com.br/equilibrioesaude/2020/04/quem-e-imune-ao-coronavirus.shtml .
7. ^ “Specialists recommend herd immunity for poor countries.” Available at: https://economia.uol.com.br/noticias/bloomberg/2020/04/22/especialistas-recomendam-imunidade-de-rebanho-para-paises-pobres.htm .
8. ^ “Coronavirus pandemic: the best scenario is disastrous.” Available at: https://agazetadoacre.com/2020/03/pandemia-de-coronavirus-o-melhor-cenario-e-desastroso/ .
9. ^ “Epidemiologist opposes Osmar Terra and sees Brazil as far from the end of the epidemic.” Available at: https://www.bol.uol.com.br/noticias/2020/04/14/brasil-esta-longe-do-final-da-epidemia-e-de-imunizacao-diz-epidemiologista.htm .
10. ^ Doctor, former Health Secretary of Rio Grande do Sul and former minister for presidents Michel Temer (who took over the presidency of the Republic in 2016, after the parliamentary coup against president Dilma Rousseff) and for Bolsonaro himself, Terra had participated, the day before, in a debate on the epidemic promoted by UOL, one of the largest news sites in the country. Available at: https://noticias.uol.com.br/politica/ultimas-noticias/2020/04/13/governistas-criticam-isolamento-e-minimizam-briga-bolsonaro-x-mandetta.htm .
11. ^ Available at: https://www1.folha.uol.com.br/poder/2020/05/deputados-divulgam-fake-news-sobre-coronavirus-para-ecoar-discurso-de-bolsonaro.shtml .
12. ^ Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fy9dqEsjkVk .
13. ^ Link to the pronouncement.
14. ^ After 7m14s. Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?reload=9&v=vp3A_8vywC0 .
15. ^ The president of the True Health Initiative and director-founder of the Yale-Griffin Prevention Research Center.
16. ^ “What is the vertical isolation that Bolsonaro wants and why do specialists fear it will cause more deaths?” Available at: https://www.bbc.com/portuguese/internacional-52043112 .
17. ^ “Why is vertical isolation seen with skepticism?” Available at: https://saude.estadao.com.br/noticias/geral,por-que-isolamento-vertical-e-visto-com-ceticismo,70003252797 .
18. ^ The titles of the articles (descriptor 3): What is vertical isolation against coronavirus; What is the vertical isolation that Bolsonaro wants and why do specialists fear it will cause more deaths?; Does vertical isolation work? Reality has already answered that question, says doctor; What is vertical isolation and why it may not work; What is vertical isolation [and why this may not be a good idea)?]; What is vertical isolation (and why this is not a good idea)? Horizontal vs. vertical isolation: know the pros and cons of the strategies to contain coronavirus; Health alerts to rash transition, but sees vertical isolation as possible in little-affected locations; and, What are the risks of adopting only vertical isolation, proposed by Bolsonaro; What is the vertical isolation that Bolsonaro wants and why do specialists fear it will cause more deaths?; Specialists: Brazil's characteristics do not permit vertical isolation; Health alerts to rash transition, but sees vertical isolation as possible in little-affected locations; Turkey endures drastic consequences of vertical isolation.
19. ^ Bolsonaro once again minimizes COVID-19 and says that Health is studying vertical isolation. Available at: https://www.istoedinheiro.com.br/bolsonaro-volta-a-minimizar-COVID-19-e-diz-que-saude-estuda-isolamento-vertical/ .
20. ^ The notion of the crab men emerged from the main works of Josué de Castro: Geografia da fome (1948), Geopol í tica da fome (1951), Documentário do Nordeste (1957), Fatores de localização da cidade do Recife (1957), and Homens e caranguejos (1967), the last an autobiographical romance.
21. ^ “Vertical isolation proposed by Bolsonaro may accelerate contagion by coronavirus and compromise health systems.” Available at: https://brasil.elpais.com/brasil/2020-03-25/isolamento-vertical-proposto-por-bolsonaro-pode-acelerar-contagios-por-coronavirus-e-comprometer-sistema-de-saude.html .
22. ^ “Bolsonaro will propose vertical isolation to contain coronavirus.” Available at: https://www.cnnbrasil.com.br/politica/2020/03/25/bolsonaro-nao-estou-preocupado-com-a-minha-popularidade .
23. ^ “Bolsonaro defends vertical isolation and suggests the country may ‘depart from democratic normality.”' Available at: https://oglobo.globo.com/brasil/bolsonaro-defende-isolamento-vertical-sugere-que-pais-pode-sair-da-normalidade-democratica-24327038 .
24. ^ After retiring as a captain of the Brazilian Army at the age of 33, Bolsonaro has been a professional politician for over 30 years. Before becoming president, he was on the Rio de Janeiro city council and, later, was a federal congressman for 27 years. During that period, he presented only two draft bills.
25. ^ Available at: https://veja.abril.com.br/brasil/bolsonaro-e-acusado-de-racismo-por-frase-em-palestra-na-hebraica/ .
26. ^ Quilombo are settlements first established by escaped slaves in Brazil. Quilombolas are the descendants of Afro-Brazilian slaves who escaped from slave plantations that existed in Brazil until abolition in 1888. Since 2003 the Decreto 4.887/2003,recognized Quilombo communities and their claims to the land they inhabited, but only 219 of the 2,926 Quilombos have land titles.
27. ^ Available at: https://www.bol.uol.com.br/noticias/2020/06/23/sob-bolsonaro-reconhecimento-de-quilombolas-cai-ao-menor-patamar-da-historia.htm .
28. ^ Available at: https://ponte.org/eugenia-2-0-a-politica-migratoria-de-bolsonaro/ .
29. ^ Available at: https://veja.abril.com.br/politica/e-dai-nao-faco-milagres-diz-bolsonaro-sobre-mortes-por-COVID-19/ .
30. ^ Available at: https://www.cnnbrasil.com.br/saude/2020/06/05/negros-morrem-40-mais-que-brancos-por-coronavirus-no-brasil .
31. ^ Available at: https://www.huffpostbrasil.com/entry/mortes-COVID-19-25-junho_br_5ef4b64cc5b66c3126832ef9 .
32. ^ Available at: https://www.saude.gov.br/images/pdf/2020/May/20/orientacoes-manuseio-medicamentoso-covid19.pdf .
33. ^ To read further, see: “ https://www.huffpostbrasil.com/entry/mortes-COVID-19-25-junho_br_5ef4b64cc5b66c3126832ef9 .
34. ^ Available at: https://www1.folha.uol.com.br/equilibrioesaude/2020/06/congressistas-e-entidades-elogiam-consorcio-de-imprensa-para-coletar-dados-da-COVID-19.shtml .
Ajzenman, N., Cavalcanti, T., and Da Mata, D. (2020). More Than Words: Leaders' Speech and Risky Behavior During a Pandemic . Available online at: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3582908 (accessed June 30, 2020).
Google Scholar
Castilho, C. (2015). Morrem os jornais, surgem as marcas jornalística. Observat da Imprensa, 29 set. Disponível . Available online at: http://observatoriodaimprensa.com.br/imprensa-em-questao/morrem-os-jornais-surgem-as-marcas-jornalisticas/ (accessed June 28, 2020).
de Lima, V. A. (2001). Mídia: teoria e política . São Paulo: Fundação Perseu Abramo.
de Lima, V. A. (2011). Regulação das comunicações: história, poder e direitos . São Paulo: Paulus.
de Melo Filho, D. A. (2003). Swamps, men and crabs in Josué de Castro: meanings and their unfolding. Hist. Cienc. Saude-Manguinhos 10, 505–524. doi: 10.1590/S0104-59702003000200002
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Diethelm, P., and McKee, M. (2009). Denialism: what is it and how should scientists respond? Eur. J. Public Health . 19, 2–4. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckn139
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Diwan, P. (2007). Raça pura. Uma história da eugenia no Brasil e no mundo . São Paulo: Contexto.
Gelbspan, R. (1998). The Heat Is on: The Climate Crisis, the Cover-Up, the Prescription . Cambridge, MA: Perseus Press.
Hannah, M. G., Hutta, J. S., and Schemann, C. (2020). Thinking Through COVID-19 Responses with Foucault – An Initial Overview. Antipode . Available online at: https://antipodeonline.org/2020/05/05/thinking-through-COVID-19-responses-with-foucault/ (accessed May 30, 2020).
Happer, C., and Philo, G. (2013). The role of the media in the construction of public belief and social change. J. Soc. Political Psychol . 321:336. doi: 10.5964/jspp.v1i1.96
Hoofnagle, M., and Hoofnagle, C. (2007). Hello And Welcome To Denialism Blog . Available online at: https://scienceblogs.com/denialism/about (accessed June 12, 2020).
Ioannidis, J. P. A. (2020, March 17). A fiasco in the making? As the coronavirus pandemic takes hold, we are making decisions without reliable data. StatNews . Available online at: https://www.statnews.com/2020/03/17/a-fiasco-in-the-making-as-the-coronavirus-pandemic-takes-hold-we-are-making-decisions-without-reliable-data/ (accessed May 12, 2020).
Katz, D. L. (2020, March 20). Is our fight against coronavirus worse than the disease? The News York Times . Available online at: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/03/20/opinion/coronavirus-pandemic-social-distancing.html (accessed May 12, 2020).
Kobayashi, E., Faria, L., and Costa, M. C. (2009). Eugenics and the rockefeller foundation in Brazil: health as an instrument of national regeneration. Sociologias 11, 314–51. doi: 10.1590/S1517-45222009000200012
Kucinski, B. (2006). Síndrome da antena parabólica:ética no jornalismo brasileiro . São Paulo: Fundação Perseu Abramo.
Law, J., and Mol, A. (2002). Complexities: Social Studies of Knowledge Practices. Durham: Duke University Press. doi: 10.1215/9780822383550
Lisboa, S., and Benetti, M. (2015). Journalism as justified true belief. Br. J. Res. 11, 10–29. doi: 10.25200/BJR.v11n2.2015.843
de Maciel, M. E. S. (1999). Eugenics in Brazil . Available online at: https://lume.ufrgs.br/bitstream/handle/10183/31532/000297021.pdf?sequence=1 ; https://www.vix.com/pt/ciencia/547185/o-que-foi-o-movimento-de-eugenia-no-brasil-tao-absurdo-que-e-dificil-acreditar (accessed May 13, 2020).
Malinverni, C. (2016). Epidemia midiática de febre amarela: desdobramentos e aprendizados de uma crise de comunicação na saúde pública brasileira Tese (Doutorado em Ciências) . Faculdade de Saúde Pública, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil.
Malinverni, C., and Cuenca, A. M. B. (2017). “Epidemias midiáticas, a doença como um produto jornalístico,” in Comunicação, mídia e saúde: novos agentes, novas agendas , ed C. d'Avila and U. Trigueiros (Rio de Janeiro: Luminatti Editora), 7.
Malinverni, C., Cuenca, A. M. B., and Brigagão, J. I. M. (2012). Media epidemics: sense production and social configuration of yellow fever in the journalistic coverage, 2007-2008. Phys. Revista de Saúde Coletiva 22, 853–872. doi: 10.1590/S0103-73312012000300002
Menezes, A. P. R., Moretti, B., and Reis, A. A. C. (2019). O futuro do SUS: impactos das reformas neoliberais na saúde pública – austeridade versus universalidade. Saúde Debate 43, 58–70. doi: 10.1590/0103-11042019s505
Mezzadra, S. (2020). Politics of struggles in the time of pandemic. Verso . Available online at: https://www.versobooks.com/blogs/4598-politics-of-struggles-in-the-time-of-pandemic (accessed June 26th, 2020).
Mota, A. (2003). Quem é bom já nasce feito: sanitarismo e eugenia no Brasil . Rio de Janeiro: DP&A.
Motta, L. G. (2007). Enquadramentos lúdicodramáticos no jornalismo: mapas culturais para organizar conflitos politicos . Available online at: https://pt.scribd.com/document/78063603/4134 (accessed March 14, 2020).
Pitts, L. (2018, September 15). “Both sides-ism” a big problem in journalism. The Post and Courier . Available online at: https://www.postandcourier.com/opinion/commentary/both-sides-ism-a-big-problem-in-journalism/article_9bab8232-b6bd-11e8-84ca-5784be02719c.html (accessed May 26, 2020).
Portella, T., Aamot, D., and Passavante, Z. (1992). Homem-gabiru: catalogação de uma espécie . São Paulo: Hucitec.
Ricard, J., and Medeiros, J. (2020). Using Misinformation as a Political Weapon: COVID-19 and Bolsonaro in Brazil . Boston, MA: The Harvard Kennedy School Misinformation Review, I:2. doi: 10.37016/mr-2020-013
Rosen, J. (2010, November 10). The view from nowhere: questions and answers. Press Think . Available online at: https://pressthink.org/2010/11/the-view-from-nowhere-questions-and-answers/ (accessed March 26, 2020).
Rosen, J. (2020, April 19). Five improvements in the design of coronavirus coverage. Press Think . available online at: https://pressthink.org/2020/04/five-improvements-in-the-design-of-coronavirus-coverage/ (accessed June 30, 2020).
Rosen, J., Merrit, D. B., and Austin, L. (1997). Theory and Practice: Lessons from Experience . Dayton, OH: Kettering Foudation. Available online at: https://www.kettering.org/sites/default/files/product-downloads/Public%20Journalism.pdf (accessed March 14, 2020).
Schwarcz, L. M. (1993). O espetáculo das raças: cientistas, instituições e questão racial no Brasil (1870-1930) . São Paulo: Companhia das Letras.
Smith, B. (2020, April 19). Trump has begun his corona campaign. We don't have to play along. The New York Times . Available online at: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/04/19/business/media/donald-trump-coronavirus-campaign-media.html (accessed March 31, 2020).
Sousa, J. P. (2002). Por que as notícias são como são? Construindo uma teoria da notícia. Biblioteca On-line de Ciências da Comunicação . Available online at: http://www.bocc.ubi.pt/pag/sousa-jorge-pedro-construindo-teoria-da-noticia.pdf (accessed April 29, 2020).
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Souza, H. B. (2017). The Medusa's sight: reification and politics reconfiguration trough art teaching and scenic practice. Moringa 8, 69–80. doi: 10.22478/ufpb.2177-8841.2017v8n2.37769
Spink, M. J. (ed.). (2004). Práticas Discursivas e Produção de Sentidos No Cotidiano . São Paulo: Cortez, 278.
Stevens, R., and Hornik, R. C. (2014). AIDS in black and white: the influence of newspaper coverage of HIV/AIDS on HIV/AIDS testing among african americans and white americans, 1993–2007. J. Health Commun . 19, 893–906. doi: 10.1080/10810730.2013.864730
Thompson, J. B. (2014). A mídia e a modernidade: uma teoria social da mídia . Rio de Janeiro: Editora Vozes.
Traquina, N. (2007). O que é jornalismo . Lisboa: Quimera.
Tuchman, G. (1983). La producción de la noticia: estudio sobre la construcción de la realidad . Barcelona: Gili.
Van Der Haak, B., Parks, M., and Castells, M. (2012). The future of journalism: networked journalism. Int. J. Commun . 6, 2923–2938.
Vizeu, A. (2009). O telejornalismo como lugar de referência e a função pedagógica. Revista Famecos 16:40. doi: 10.15448/1980-3729.2009.40.6321
Vukasovich, C., and Vukasovich, T. D. (2016). Humanitarian intervention, a predictable narrative? A comparative analysis of media narratives from Serbia to Syria. Glob. Med. Commun . 12, 311–331. doi: 10.1177/1742766516653163
Wenner, M. (2007, February 15). The war against war metaphors. The Scientist . Available online at: https://www.the-scientist.com/daily-news/the-war-against-war-metaphors-46786 (accessed July 13, 2020).
Wetherell, M., and Potter, J. (1988). “Discourse analysis and the identification of interpretive repertoires,” in Analysing Everyday Explanation: A Casebook of Methods , ed C. Antaki (Newbury Park, CA: Sage), 168–83.
Keywords: novel SARS-coronavirus-2/SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19, digital media, eugenics, denialism, public health communication, journalism
Citation: Malinverni C and Brigagão JIM (2020) COVID-19: Scientific Arguments, Denialism, Eugenics, and the Construction of the Antisocial Distancing Discourse in Brazil. Front. Commun. 5:582963. doi: 10.3389/fcomm.2020.582963
Received: 13 July 2020; Accepted: 30 September 2020; Published: 04 November 2020.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2020 Malinverni and Brigagão. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Claudia Malinverni, claudia.malinverni@usp.br ; Jacqueline Isaac Machado Brigagão, jac@usp.br
This article is part of the Research Topic
Strategic Narratives in Political and Crisis Communication: Responses to COVID-19
- Newsletters
Site search
- Israel-Hamas war
- 2024 election
- Kate Middleton
- TikTok’s fate
- Supreme Court
- All explainers
- Future Perfect
Filed under:
Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus
Artists, novelists, critics, and essayists are writing the first draft of history.
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Read these 12 moving essays about life during coronavirus
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/66606035/1207638131.jpg.0.jpg)
The world is grappling with an invisible, deadly enemy, trying to understand how to live with the threat posed by a virus . For some writers, the only way forward is to put pen to paper, trying to conceptualize and document what it feels like to continue living as countries are under lockdown and regular life seems to have ground to a halt.
So as the coronavirus pandemic has stretched around the world, it’s sparked a crop of diary entries and essays that describe how life has changed. Novelists, critics, artists, and journalists have put words to the feelings many are experiencing. The result is a first draft of how we’ll someday remember this time, filled with uncertainty and pain and fear as well as small moments of hope and humanity.
At the New York Review of Books, Ali Bhutto writes that in Karachi, Pakistan, the government-imposed curfew due to the virus is “eerily reminiscent of past military clampdowns”:
Beneath the quiet calm lies a sense that society has been unhinged and that the usual rules no longer apply. Small groups of pedestrians look on from the shadows, like an audience watching a spectacle slowly unfolding. People pause on street corners and in the shade of trees, under the watchful gaze of the paramilitary forces and the police.
His essay concludes with the sobering note that “in the minds of many, Covid-19 is just another life-threatening hazard in a city that stumbles from one crisis to another.”
Writing from Chattanooga, novelist Jamie Quatro documents the mixed ways her neighbors have been responding to the threat, and the frustration of conflicting direction, or no direction at all, from local, state, and federal leaders:
Whiplash, trying to keep up with who’s ordering what. We’re already experiencing enough chaos without this back-and-forth. Why didn’t the federal government issue a nationwide shelter-in-place at the get-go, the way other countries did? What happens when one state’s shelter-in-place ends, while others continue? Do states still under quarantine close their borders? We are still one nation, not fifty individual countries. Right?
Award-winning photojournalist Alessio Mamo, quarantined with his partner Marta in Sicily after she tested positive for the virus, accompanies his photographs in the Guardian of their confinement with a reflection on being confined :
The doctors asked me to take a second test, but again I tested negative. Perhaps I’m immune? The days dragged on in my apartment, in black and white, like my photos. Sometimes we tried to smile, imagining that I was asymptomatic, because I was the virus. Our smiles seemed to bring good news. My mother left hospital, but I won’t be able to see her for weeks. Marta started breathing well again, and so did I. I would have liked to photograph my country in the midst of this emergency, the battles that the doctors wage on the frontline, the hospitals pushed to their limits, Italy on its knees fighting an invisible enemy. That enemy, a day in March, knocked on my door instead.
In the New York Times Magazine, deputy editor Jessica Lustig writes with devastating clarity about her family’s life in Brooklyn while her husband battled the virus, weeks before most people began taking the threat seriously:
At the door of the clinic, we stand looking out at two older women chatting outside the doorway, oblivious. Do I wave them away? Call out that they should get far away, go home, wash their hands, stay inside? Instead we just stand there, awkwardly, until they move on. Only then do we step outside to begin the long three-block walk home. I point out the early magnolia, the forsythia. T says he is cold. The untrimmed hairs on his neck, under his beard, are white. The few people walking past us on the sidewalk don’t know that we are visitors from the future. A vision, a premonition, a walking visitation. This will be them: Either T, in the mask, or — if they’re lucky — me, tending to him.
Essayist Leslie Jamison writes in the New York Review of Books about being shut away alone in her New York City apartment with her 2-year-old daughter since she became sick:
The virus. Its sinewy, intimate name. What does it feel like in my body today? Shivering under blankets. A hot itch behind the eyes. Three sweatshirts in the middle of the day. My daughter trying to pull another blanket over my body with her tiny arms. An ache in the muscles that somehow makes it hard to lie still. This loss of taste has become a kind of sensory quarantine. It’s as if the quarantine keeps inching closer and closer to my insides. First I lost the touch of other bodies; then I lost the air; now I’ve lost the taste of bananas. Nothing about any of these losses is particularly unique. I’ve made a schedule so I won’t go insane with the toddler. Five days ago, I wrote Walk/Adventure! on it, next to a cut-out illustration of a tiger—as if we’d see tigers on our walks. It was good to keep possibility alive.
At Literary Hub, novelist Heidi Pitlor writes about the elastic nature of time during her family’s quarantine in Massachusetts:
During a shutdown, the things that mark our days—commuting to work, sending our kids to school, having a drink with friends—vanish and time takes on a flat, seamless quality. Without some self-imposed structure, it’s easy to feel a little untethered. A friend recently posted on Facebook: “For those who have lost track, today is Blursday the fortyteenth of Maprilay.” ... Giving shape to time is especially important now, when the future is so shapeless. We do not know whether the virus will continue to rage for weeks or months or, lord help us, on and off for years. We do not know when we will feel safe again. And so many of us, minus those who are gifted at compartmentalization or denial, remain largely captive to fear. We may stay this way if we do not create at least the illusion of movement in our lives, our long days spent with ourselves or partners or families.
Novelist Lauren Groff writes at the New York Review of Books about trying to escape the prison of her fears while sequestered at home in Gainesville, Florida:
Some people have imaginations sparked only by what they can see; I blame this blinkered empiricism for the parks overwhelmed with people, the bars, until a few nights ago, thickly thronged. My imagination is the opposite. I fear everything invisible to me. From the enclosure of my house, I am afraid of the suffering that isn’t present before me, the people running out of money and food or drowning in the fluid in their lungs, the deaths of health-care workers now growing ill while performing their duties. I fear the federal government, which the right wing has so—intentionally—weakened that not only is it insufficient to help its people, it is actively standing in help’s way. I fear we won’t sufficiently punish the right. I fear leaving the house and spreading the disease. I fear what this time of fear is doing to my children, their imaginations, and their souls.
At ArtForum , Berlin-based critic and writer Kristian Vistrup Madsen reflects on martinis, melancholia, and Finnish artist Jaakko Pallasvuo’s 2018 graphic novel Retreat , in which three young people exile themselves in the woods:
In melancholia, the shape of what is ending, and its temporality, is sprawling and incomprehensible. The ambivalence makes it hard to bear. The world of Retreat is rendered in lush pink and purple watercolors, which dissolve into wild and messy abstractions. In apocalypse, the divisions established in genesis bleed back out. My own Corona-retreat is similarly soft, color-field like, each day a blurred succession of quarantinis, YouTube–yoga, and televized press conferences. As restrictions mount, so does abstraction. For now, I’m still rooting for love to save the world.
At the Paris Review , Matt Levin writes about reading Virginia Woolf’s novel The Waves during quarantine:
A retreat, a quarantine, a sickness—they simultaneously distort and clarify, curtail and expand. It is an ideal state in which to read literature with a reputation for difficulty and inaccessibility, those hermetic books shorn of the handholds of conventional plot or characterization or description. A novel like Virginia Woolf’s The Waves is perfect for the state of interiority induced by quarantine—a story of three men and three women, meeting after the death of a mutual friend, told entirely in the overlapping internal monologues of the six, interspersed only with sections of pure, achingly beautiful descriptions of the natural world, a day’s procession and recession of light and waves. The novel is, in my mind’s eye, a perfectly spherical object. It is translucent and shimmering and infinitely fragile, prone to shatter at the slightest disturbance. It is not a book that can be read in snatches on the subway—it demands total absorption. Though it revels in a stark emotional nakedness, the book remains aloof, remote in its own deep self-absorption.
In an essay for the Financial Times, novelist Arundhati Roy writes with anger about Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s anemic response to the threat, but also offers a glimmer of hope for the future:
Historically, pandemics have forced humans to break with the past and imagine their world anew. This one is no different. It is a portal, a gateway between one world and the next. We can choose to walk through it, dragging the carcasses of our prejudice and hatred, our avarice, our data banks and dead ideas, our dead rivers and smoky skies behind us. Or we can walk through lightly, with little luggage, ready to imagine another world. And ready to fight for it.
From Boston, Nora Caplan-Bricker writes in The Point about the strange contraction of space under quarantine, in which a friend in Beirut is as close as the one around the corner in the same city:
It’s a nice illusion—nice to feel like we’re in it together, even if my real world has shrunk to one person, my husband, who sits with his laptop in the other room. It’s nice in the same way as reading those essays that reframe social distancing as solidarity. “We must begin to see the negative space as clearly as the positive, to know what we don’t do is also brilliant and full of love,” the poet Anne Boyer wrote on March 10th, the day that Massachusetts declared a state of emergency. If you squint, you could almost make sense of this quarantine as an effort to flatten, along with the curve, the distinctions we make between our bonds with others. Right now, I care for my neighbor in the same way I demonstrate love for my mother: in all instances, I stay away. And in moments this month, I have loved strangers with an intensity that is new to me. On March 14th, the Saturday night after the end of life as we knew it, I went out with my dog and found the street silent: no lines for restaurants, no children on bicycles, no couples strolling with little cups of ice cream. It had taken the combined will of thousands of people to deliver such a sudden and complete emptiness. I felt so grateful, and so bereft.
And on his own website, musician and artist David Byrne writes about rediscovering the value of working for collective good , saying that “what is happening now is an opportunity to learn how to change our behavior”:
In emergencies, citizens can suddenly cooperate and collaborate. Change can happen. We’re going to need to work together as the effects of climate change ramp up. In order for capitalism to survive in any form, we will have to be a little more socialist. Here is an opportunity for us to see things differently — to see that we really are all connected — and adjust our behavior accordingly. Are we willing to do this? Is this moment an opportunity to see how truly interdependent we all are? To live in a world that is different and better than the one we live in now? We might be too far down the road to test every asymptomatic person, but a change in our mindsets, in how we view our neighbors, could lay the groundwork for the collective action we’ll need to deal with other global crises. The time to see how connected we all are is now.
The portrait these writers paint of a world under quarantine is multifaceted. Our worlds have contracted to the confines of our homes, and yet in some ways we’re more connected than ever to one another. We feel fear and boredom, anger and gratitude, frustration and strange peace. Uncertainty drives us to find metaphors and images that will let us wrap our minds around what is happening.
Yet there’s no single “what” that is happening. Everyone is contending with the pandemic and its effects from different places and in different ways. Reading others’ experiences — even the most frightening ones — can help alleviate the loneliness and dread, a little, and remind us that what we’re going through is both unique and shared by all.
Will you help keep Vox free for all?
At Vox, we believe that clarity is power, and that power shouldn’t only be available to those who can afford to pay. That’s why we keep our work free. Millions rely on Vox’s clear, high-quality journalism to understand the forces shaping today’s world. Support our mission and help keep Vox free for all by making a financial contribution to Vox today.
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via

Next Up In Culture
Sign up for the newsletter today, explained.
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
Thanks for signing up!
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.

Congress can’t get anything done. Except on foreign aid.

The battle for blame over a deadly terror attack in Moscow

We’re long overdue for an Asian lead on The Bachelor franchise

The House GOP just gave Biden’s campaign a huge gift

Kate Middleton’s cancer diagnosis is part of a frightening global trend

The disappearance of Kate Middleton, explained
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Attitudes on voluntary and mandatory vaccination against COVID-19: Evidence from Germany
Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation DIW Berlin / SOEP, Berlin, Germany
* E-mail: [email protected] (CSP); [email protected] (CS)
Affiliation Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany
Affiliations DIW Berlin / SOEP, Berlin, Germany, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany
- Daniel Graeber,
- Christoph Schmidt-Petri,
- Carsten Schröder

- Published: May 10, 2021
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372
- Reader Comments
Several vaccines against COVID-19 have now been developed and are already being rolled out around the world. The decision whether or not to get vaccinated has so far been left to the individual citizens. However, there are good reasons, both in theory as well as in practice, to believe that the willingness to get vaccinated might not be sufficiently high to achieve herd immunity. A policy of mandatory vaccination could ensure high levels of vaccination coverage, but its legitimacy is doubtful. We investigate the willingness to get vaccinated and the reasons for an acceptance (or rejection) of a policy of mandatory vaccination against COVID-19 in June and July 2020 in Germany based on a representative real time survey, a random sub-sample (SOEP-CoV) of the German Socio-Economic Panel (SOEP). Our results show that about 70 percent of adults in Germany would voluntarily get vaccinated against the coronavirus if a vaccine without side effects was available. About half of residents of Germany are in favor, and half against, a policy of mandatory vaccination. The approval rate for mandatory vaccination is significantly higher among those who would get vaccinated voluntarily (around 60 percent) than among those who would not get vaccinated voluntarily (27 percent). The individual willingness to get vaccinated and acceptance of a policy of mandatory vaccination correlates systematically with socio-demographic and psychological characteristics of the respondents. We conclude that as far as people’s declared intentions are concerned, herd immunity could be reached without a policy of mandatory vaccination, but that such a policy might be found acceptable too, were it to become necessary.
Citation: Graeber D, Schmidt-Petri C, Schröder C (2021) Attitudes on voluntary and mandatory vaccination against COVID-19: Evidence from Germany. PLoS ONE 16(5): e0248372. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372
Editor: Valerio Capraro, Middlesex University, UNITED KINGDOM
Received: October 19, 2020; Accepted: February 25, 2021; Published: May 10, 2021
Copyright: © 2021 Graeber et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: Our analyses rely on the German Socio-Economic Panel (SOEP), an independent scientific data infrastructure established in 1984. We, as users, cannot send the data to the journal and make them publicly available, as this is against SOEP's statutes (and most likely against the statutes of all providers of micro data). However, this should not be a hurdle, as researchers from scientific institutions around the globe can access the data (free of costs) once they have signed a user contract. The scientific use file of the SOEP with anonymous microdata is made available free of charge to universities and research institutes for research and teaching purposes. The direct use of SOEP data is subject to the provisions of German data protection law. Therefore, signing a data distribution contract is the single precondition for working with SOEP data. The data distribution contract can be requested with a form which can be downloaded from: http://www.diw.de/documents/dokumentenarchiv/17/diw_01.c.88926.de/soep_application_contract.pdf .
Funding: The data collection of the SOEP-CoV Study was financially supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. We acknowledge support by the KIT-Publication Fund of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
Great efforts have been made worldwide to develop a vaccine against COVID-19. When we first drafted this article, in October 2020, 35 different potential vaccines were in clinical trials and 145 were still in the pre-clinical stage. In February 2021, several vaccines have been approved in many countries and are being rolled out, 74 are in clinical trials, and 182 are in the pre-clinical stage [ 1 ].
These developments are very encouraging, as a wide availability of vaccines is seen by many as a prerequisite for a return to a “normal” pre-COVID-19 type of social and economic life. With the growing availability of vaccines comes the hope that coercive measures such as restrictions on international trade, contact restrictions, and travel bans, etc., which cause enormous economic and social costs, may soon be removed and will not need to be reimplemented.
Of course, any vaccine is only an effective contribution to a return to normal life if a sufficiently high number of people are actually vaccinated, yielding herd immunity. If so, vaccination secures a public good: protection from COVID-19 for everyone. From a microeconomic perspective, this raises a well-known problem, free-riding: If the vaccination is freely available but not obligatory, then citizens’ individual decisions determine the extent to which this public good is made available. In order to make that decision, they will weigh their own costs and benefits. These costs include the time sacrificed, physical unpleasantness, possible side effects of a vaccination, etc. The benefits to a particular individual are primarily, but not necessarily exclusively, the reduction in risk to that person’s own health or material well-being. From a welfare perspective, if individuals do not take into account the positive externalities on third parties that their own vaccination triggers, there will be an undersupply of the public good. Following [ 2 , 3 ], individuals’ utility function may also include other-regarding preferences and hence yield a direct benefit from contributions to a public good. In our context, people could therefore benefit from a ‘warm glow of vaccinating’, because by vaccinating themselves they also reduce the risks of others. But even so there is certainly no guarantee that the social optimum will be reached [ 4 ] or that a sufficiently high number of people will freely choose to get vaccinated.
It is frequently argued that vaccination should be made mandatory because of the free-rider problem [ 5 ]: While vaccinated individuals have incurred private costs in terms of discomfort or money and receive the private benefit of a reduced risk of getting the disease, the major collective benefit, the reduced incidence of disease, is public. If enough other people produce the public benefit, and the circulation of the virus decreases accordingly, an individual might rationally decide to free-ride on others’ decisions. A policy of mandatory vaccination would prevent this.
[ 6 ] argue that such a policy would not be necessary: “If vaccinations are perfect, then if one is vaccinated he or she does not care whether others are vaccinated, so there is no longer any public good problem” ([ 6 ], p. 70). Hence there would not be a case in favor of mandatory vaccination, as under such a policy, individuals who would have favored not to be vaccinated are made worse off, while those who anyway would get vaccinated are not better off.
However, by definition, ‘perfect’ vaccination means that everyone vaccinated is perfectly immune [ 6 ]. In the current situation, it can neither be taken for granted that a perfect vaccination is being or will be provided soon, nor that everyone who wants to also will have the possibility to be vaccinated (both financially and in terms of health). If perfect vaccination is not feasible, however, mandatory vaccination is not dominated by a laissez faire solution [ 6 ].
Extensions of this theoretical public good analysis emphasize the relevance of behavioral aspects not typically considered in classical models. The empirical literature also highlights a number of factors that matter for vaccine uptake. For instance [ 7 ], show that social norms matter for an individual’s willingness to get a vaccination and that such norms can suppress vaccine uptake even in the presence of frequent disease outbreaks. Further [ 8 ], show that the design of public vaccination policies should also take intergroup interactions into account. Other-regarding preferences can explain voluntary vaccination uptake, as argued by [ 9 ]. For example [ 10 ], show that the presence of individuals who cannot get vaccinated, like babies and the elderly, increases the willingness to get vaccinated. The static model in [ 6 ] also does not reflect interactive processes [ 9 , 11 ]. show that vaccination is the individually best response until a certain vaccination rate is reached in the population and becomes a social dilemma only from this vaccination rate until herd immunity is maximized. Communicating the social benefits of vaccination can have positive effects, particularly when this protects vulnerable groups, but it can also invite free-riding [ 12 ]. Those people who cannot get vaccinated themselves for medical reasons are particularly vulnerable: they cannot protect themselves even if they wanted to and, hence, depend on their fellow citizens to protect them by preventing the spread of the virus through their vaccination. Children, too, need to be considered separately. Since they cannot give informed consent to a voluntary vaccination themselves, they might have to be protected from their parents (who might be unwilling to get them vaccinated) in case of particularly serious diseases (see [ 13 , 14 ]).
There is, in summary, hope that the public goods problem may be overcome, as social and behavioral science offers a wide array of potential policy options to influence people’s perceptions and reactions to the pandemic (for an extensive up-to-date overview, see [ 15 ]). It is not clear, however, how the research on well-established vaccines carries over to the current pandemic, and recent developments seem to indicate that the willingness to get vaccinated against the novel coronavirus is currently rather low. We therefore chose to investigate two fundamental questions at the opposite extremes of the spectrum of policy options: would a sufficient number of people voluntarily undergo vaccination to achieve herd immunity? Or would a mandatory vaccination against COVID-19 be acceptable to achieve herd immunity?
A legal duty to be vaccinated against COVID-19 could be an alternative to other coercive measures if one assumes that a high-risk, unregulated, laissez faire approach is not a realistic policy option: it seems irresponsible to lift all restrictions because the virus would soon spread through the entire population. Coercive measures of some kind therefore seem inevitable. Mandatory vaccination could be preferable to other coercive measures, provided the interference with bodily integrity would be considered less socially costly in the long run than the effects of prolonged lockdowns. Emotions run high where vaccination policies are concerned, but because mandatory vaccination might become a realistic scenario, it is worth investigating what the general population thinks about such a policy.
It is important to emphasize that a legal duty to vaccinate against COVID-19 would not imply a legal (or even moral) duty to vaccinate against other diseases. The novel coronavirus is a special case in many respects: In contrast to influenza, for example, the population does not have a background immunity from past infections. In addition, many infected people do not show symptoms (a recent meta-study estimates this to be one in six infected [ 16 ]) and, hence, cannot protect others from being infected through voluntary self-quarantining. Thus, people with COVID-19 represent a much higher risk of infection for others than, for example, people who come down with influenza, assuming that these would normally stay at home. Therefore, a vaccination against COVID-19 is much more important from the social perspective than e.g. a vaccination against influenza: not for self-protection, but to protect other people from unintentional infection. Although classic liberal positions (cf. [ 17 ]) would reject a paternalist legal obligation to protect oneself through vaccination, they plausibly would favor a policy of mandatory vaccination in the case of COVID-19 to protect others from being harmed. In modern philosophical discussions, even some libertarians are in favor of mandatory vaccination against serious diseases for similar reasons (see [ 18 ] and for an overview [ 19 ]).
Though there are philosophical reasons supporting a policy of mandatory vaccination, we want to emphasize that we are not advocating it as a concrete policy option for Germany at this moment. Our aim is to understand whether the general public would consider such a policy acceptable, or which sections of the population, and why. To this end, we study the willingness to get vaccinated and the acceptance of a policy of mandatory vaccination against COVID-19 in June and July 2020 in Germany. We use unique real time survey data from a sub-sample (SOEP-CoV) of the German Socio-Economic Panel (SOEP, see [ 20 ]). A set of questions about vaccination was part of the later stages of SOEP-CoV, an ongoing research project initiated in April 2020. This so-called ‘vaccination module’ included questions on the willingness to get vaccinated voluntarily and the acceptance of a policy of mandatory vaccination against COVID-19. In addition, individuals could indicate reasons for their preference regarding the second question. Using the rich data of the SOEP, pre-pandemic income, education, household context, personality, political preferences etc., which can be directly linked with SOEP-CoV, we are able to provide a detailed picture on who intends to get vaccinated and who does not.
The most important result of our study is that about 70 percent of adults in Germany would get vaccinated voluntarily against COVID-19 if a vaccine without significant side effects was available. Further, about half of adults in Germany are in favor, and half against, a policy of mandatory vaccination against COVID-19. The approval rate for mandatory vaccination is significantly higher among those who would get vaccinated voluntarily (around 60 percent) than among those who would not get vaccinated voluntarily (27 percent). However, 22 percent of the individuals would disapprove of both a voluntary and a mandatory vaccination and 8 percent can be characterized as ‘passengers’ (they are not willing to get vaccinated but do support a policy of mandatory vaccination, but they might not all be ‘free-riders’ in the standard sense). In this group, surprisingly, 86 percent state that, without a mandatory vaccination, too few individuals would get vaccinated and about 87 percent indicate that most people underestimate how dangerous COVID-19 is. In general, the willingness to get vaccinated is significantly lower for female, younger, and less educated respondents as well as those with lower income. A policy of mandatory vaccination is rejected with higher probability by women and favored by older people and those living in the eastern federal states.
Data, measures, and methods
Data: soep and soep-cov.
The German Socio-economic Panel (SOEP) is among the largest and longest-running representative panel surveys worldwide and is recognized for maintaining the highest standards of data quality and research ethics [ 20 ]. In 2020, the survey covers about 30,000 adults in 20,000 households. Since the same individuals and households participate in the study every year, life courses of the respondents can be tracked and intertemporal analyses can be carried out at the individual and at the household level. The data contain information on the respondents’ household situation, education, labor market outcomes, and health, among others (see [ 20 , 21 ]).
To better understand the effects of the corona pandemic, a special survey called SOEP-CoV was conducted within the framework of the SOEP, which consisted of a random sample of about 6,700 SOEP respondents, (see [ 21 , 22 ]). SOEP-CoV was surveyed in nine staggered tranches from early April to the end of July 2020 and collected data on the following topics: a) Prevalence, health behavior, and health inequality; b) Labor market and gainful employment; c) Social life, networks, and mobility; d) Mental health and well-being; and e) Social cohesion. Over time, some new question modules were introduced within these five thematic complexes. These included the ‘vaccination module’ (see questionnaires available under www.soep-cov.de/Methodik/ ).
Measures: Preferences toward vaccination against COVID-19
The ‘vaccination module’ went into the field with tranches 7 to 9, in June and July 2020, and covered a total of 851 persons aged 19 years and older. At that moment, major research efforts were being undertaken, but it was not clear whether any vaccine would actually be found. The module hence starts with a question on the hypothetical willingness to get vaccinated against COVID-19:
- “Let us assume that a vaccine against the novel coronavirus that is shown to have no significant side effects is found. Would you get vaccinated?” The response categories are ’Yes’, ’No’, and ‘no answer’. The module contains a further question about mandatory vaccination with the same response categories:
- “Would you be in favor of a policy of mandatory vaccination against the coronavirus?” In addition, the interviewees were asked about their reasons for or against a policy of mandatory vaccination. For this purpose, a filter was used to adapt the arguments according to the respondents’ answers to question (B). The arguments given were as follows:
Argument 1: Others’ willingness to get vaccinated without mandatory vaccination
- Against mandatory vaccination: “Enough people would get vaccinated even without a policy of mandatory vaccination.”
- In favor of mandatory vaccination: “Only with a policy of mandatory vaccination would enough people get vaccinated.”
Argument 2: Misperception of risks
- Against mandatory vaccination: “Most people overestimate the dangerousness of the virus.”
- In favor of mandatory vaccination: “Most people underestimate the dangerousness of the virus.”
Argument 3: Legitimacy of a policy of mandatory vaccinations in general
- Against mandatory vaccination: “A policy of mandatory vaccination is never permissible, even in the case of very dangerous diseases.”
- In favor of mandatory vaccination: “A policy of mandatory vaccinations would make sense also for less dangerous diseases.”
Argument 4: Other reasons (without listing these reasons explicitly)
The first three arguments are of particular relevance for political decision-making. Although there is quite a lot of research on the reasons people have not to get vaccinated themselves, there is much less research on what people think about policies of mandatory vaccinations, and up to present–at least to our knowledge–none on the application to the special case of the novel coronavirus. As the reasons for the individual decision need not carry over to the policy assessment, and given the previously discussed particularities of the coronavirus, we focused on factors that are both of theoretical importance and under discussion in the general public. It would be interesting, for instance, if many people did not have the intention to get vaccinated themselves, yet believed that enough other people would get vaccinated so that mandatory vaccination would not be required. Similarly, it would be surprising if people wanted to get vaccinated yet believed that others overestimated the dangerousness of the virus. Finally, we wanted to see whether people considered mandatory vaccinations potentially legitimate at all.
Sample selection, weighting, and item non-response
Since SOEP-CoV is a random sample from the SOEP population, the SOEP-CoV data 2020 can be linked with the regular SOEP data of previous years. Thus, attitudes toward vaccination against COVID-19 that were collected during the pandemic can be linked to the characteristics of the respondents before the outbreak of the pandemic (e.g., income or educational level). Since these characteristics were collected before the pandemic, they can be considered unaffected by the pandemic event and, hence, exogenous ( S1 File provides definitions of all dependent and independent variables used in the empirical analyses).
The response rate in the vaccination module was high. Altogether, only 4.58 percent of the 851 respondents did not answer the question about voluntary vaccination and 3.41 percent did not answer the question about mandatory vaccination. Of those who supported (objected to) mandatory vaccination, 0.26 (1.82) percent did not provide at least one motive in the follow-up question. Hence, bias from item non-response should be small and we did not correct for it. As the focal variables are coded dichotomously (yes = 1; no = 0), there was no need to remove outliers in them from the database.
To derive population-wide estimates, the SOEP-CoV data is equipped with frequency weights. The weighting of SOEP-CoV follows the standard weighting used in SOEP [ 23 , 24 ]. Based on the SOEP household weights, weights for all persons in the participating households were generated via a marginal adjustment step and corrected for selection effects. Furthermore, the data were corrected for the fact that some SOEP subsamples were excluded from the SOEP-CoV study from the outset. To address potential selection effects and adjust frequency weights accordingly, we followed the two-step procedure recommended in [ 25 ]:
- Step 1: Estimation of a logistic regression model where the dependent variable is a dummy variable indicating whether respondents belong to the working sample of tranches 7 to 9 (dummy is equal to one) or not (dummy is zero). All variables included in the following analyses serve as explanatory variables.
- Step 2: If at least one analysis variable shows a significant (i.e., p -value below 0.05) and at the same time meaningful effect (i.e., coefficient above 0.01) with respect to the assignment to the analysis population, a correction of the SOEP-CoV weights is performed by multiplying the frequency weights by the inverse estimated probability. In other words, multiplying the SOEP-CoV weights belonging to the analysis set by the inverse predicted probability yields the sought adjusted weight that can be used to calculate population statistics. In the present case, an adjustment using the following variables is indicated: Extraversion and whether respondents live in a household in which at least one household member was tested for COVID-19. Overall, selection on observables is very minor. Unless otherwise stated, our results are weighted with the adjusted probability weights.
Statistical framework
Since the vaccination questions are answered once by each respondent, our empirical strategy is between-person. Uni- and bivariate results for our focal variable, attitudes toward vaccination, are presented as weighted means or percentages. Assessments of differences in attitudes or characteristics between-groups rely on two-tailed t-tests, with statistical significance evaluated at p <0.01, p <0.05, and p <0.10 using the survey weights explained above. Our empirical strategy involves multiple between-group tests. This raises the question of whether a correction is necessary for multiple hypotheses testing. We do not implement such a correction because we seek to compare a certain attitude or characteristic between groups and not to draw, at the end of the test series, a concluding summary of all tests results.
Willingness to get vaccinated and attitudes toward a policy of mandatory vaccination
For the questions on voluntary vaccination (A) and mandatory vaccination (B), four groups in the population may be distinguished:
- Anti-vaccination: interviewees who would not get vaccinated voluntarily against the coronavirus and who also oppose a policy of mandatory vaccination.
- Anti-duty: interviewees who would get vaccinated voluntarily but oppose a policy of mandatory vaccination.
- Passengers: interviewees who would not get vaccinated voluntarily but are in favor of mandatory vaccination. We refer to this group as ‘passengers’ because they apparently want to see the public good of herd immunity provided by mandatory vaccination, yet would not voluntarily contribute to this good. Some of these passengers might be free-riders in the standard sense, trying to benefit from the decisions of others while not voluntarily contributing themselves, while others might not be able to get vaccinated for medical reasons. If mandatory vaccination were introduced, the first group, but not the second, would also get vaccinated, of course. Neither group would actually free-ride, but the first might initially have wanted to.
- Pro-vaccination: interviewees who would get vaccinated voluntarily and are also in favor of mandatory vaccination.
Overall, 70 percent of adults in Germany would voluntarily get vaccinated against the coronavirus, provided a vaccine without significant side effects was available ( Table 1 : groups 2 and 4). This value corresponds exactly to the results of [ 26 ]. From May till September 2020, the COVID-19 snapshot monitoring (COSMO) at the University of Erfurt showed relatively constant values of between 60 and 66 percent; it was only in April that it showed an exceptionally high value of 79 percent, and it has now decreased further (cf. [ 27 ], p. 76; an overview of previous studies on the willingness to get vaccinated in Germany is provided in S2 File .). Overall, these studies paint a consistent picture, with a slight decline in the willingness in the second half of 2020.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.t001
Approximately half of the interviewees are against, and half are in favor of, a policy of mandatory vaccination (against: 51%, groups 1 and 2, in favor: 49%, groups 3 and 4). These values, too, coincide almost exactly with those of the COSMO monitoring since May 2020 (cf. [ 27 ], p. 78), which in April showed an approval rate for mandatory vaccination of 73 percent, but later discontinued this question (till July 2020, and it has been decreasing since; see S2 File ). The agreement with a policy of mandatory vaccination is clearly higher, namely almost 60 percent (41/(41+29) = 0.59) among those who would get vaccinated voluntarily than with those who would not let themselves be vaccinated voluntarily, i.e. approximately 27 percent (8/(8+22) = 0.27).
Attitudes toward a policy of mandatory vaccination
The four groups differ noticeably in how they assess the arguments presented to them. This is shown in Table 2 , which gives the group-specific approval rate for each argument in combination with the p-values of t-tests in S3.1 Table in S3 File .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.t002
Argument 1.
The groups differ markedly in how likely they think it is that others will get vaccinated. Among the two groups that are against a policy of mandatory vaccination, 56 percent of the ‘anti-vaccination’ group (who would not get vaccinated voluntarily) think that their fellow citizens would get vaccinated sufficiently frequently such that mandatory vaccinations would not be necessary. Almost 80 percent of the ‘anti-duty’ group (the members of which would get vaccinated voluntarily) think the same. Among the two groups that are in favor of mandatory vaccination, 85 percent of the ‘passengers’ (who would not voluntarily get vaccinated) think that the others would not voluntarily get vaccinated either, as do slightly more than 90 percent of the ‘pro-vaccination’ group (who would also get vaccinated voluntarily).
Argument 2.
These results run in parallel with the assessment of the dangerousness of the virus. Even though the analysis is not causal, we can see that about 50 percent of the ‘anti-vaccination’ group and 30 percent of the ‘anti-duty’ group think that most people overestimate the dangerousness of SARS-CoV-2. Exactly the opposite, that most people underestimate the dangerousness, is believed by nearly 90 percent of the ‘passenger’ group and by slightly more than 80 percent of the ‘pro-vaccination’ group. Summarizing the numbers differently, one could say that groups 2 and 4, who would voluntarily get vaccinated, probably have similar opinions about whether their fellow citizens correctly assess the danger posed by the virus. About 80 percent of the members of the ‘pro-vaccination’ group think that most people underestimate the danger. Of the members of the ‘anti-duty’ group, we only know with certainty that 30 percent of them believe that most people overestimate the danger–we do not know, however, how the remaining 70 percent are divided between ’underestimate’ and ’correctly estimate’. The difference between the corresponding values for groups 1 and 3 is significantly higher.
Looking at arguments 1 and 2, we may conclude that there is a high level of disagreement among the population about the dangerousness of the virus. This disagreement probably explains why people have such different attitudes toward getting vaccinated and toward the necessity (or not) of a policy of mandatory vaccination.
The position of the group of the ‘passengers’ is hard to understand. On the one hand, they favor a policy of mandatory vaccination, presumably because, as they do believe, the dangerousness of the virus is often underestimated. On the other hand, they probably assume that they themselves do not underestimate that dangerousness, but nevertheless would not get vaccinated voluntarily. One reason for this could be their medical condition: they might be willing but unable to get vaccinated for medical reasons. If so, they would not be trying to free-ride. It is unclear, however, how much weight the appeal to such a hypothetical medical contraindication should have, given that at the time of the interviews, no vaccine was even available. Some, but not all, of the ‘passengers’ are probably free-riders in the standard sense.
Argument 3.
Approximately 40 percent of both the ‘anti-vaccination’ group and the ‘anti-duty’ group agree with the statement that a mandatory vaccination is never permissible, not even with very dangerous diseases. Since these two groups reject mandatory vaccination against COVID-19, this means that for the remaining 60 percent of the group, mandatory vaccination may well be permissible–but apparently only for diseases that they would have to consider as even more dangerous than COVID-19. Conversely, well over 60 percent of the ‘passenger’ group and just over 70 percent of the ‘pro-vaccination’ group agree with the statement that a policy of mandatory vaccination would also make sense for less dangerous diseases. In combination with the results for argument 2, these two groups could therefore believe that their fellow citizens also underestimate the danger of such other diseases. It is interesting to note that, overall, people in Germany estimate the probability that the novel coronavirus will cause a life-threatening disease within the next twelve months to be high (cf. [ 20 ]). This probability is around 25 percent across our four groups. In group 1 it is 20 percent, in group 2 around 27 percent, in group 3 it is 30 percent and in group 4 it is 25 percent (see Table 3 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.t003
Other reasons (which were not further broken down in the questionnaire for capacity reasons) are important primarily among those respondents who would not themselves get vaccinated and also oppose mandatory vaccination. Although questions (A) and (B) explicitly assume that a vaccine would not have any significant side effects, this could be due to a deeper skepticism about vaccination, which we hope to be able to explore in future research (on ’vaccine denialism’ see [ 28 ]).
Characteristics of the ‘anti-vaccination’, ‘anti-duty’, ‘passenger’, and ‘pro-vaccination’ groups
Description of the individual characteristics of the groups..
We would like to know in more detail who is in favor of a policy of mandatory vaccination against COVID-19 and who is opposing it, as well as what the socio-economic characteristics of those who would get vaccinated and of those who would not are. Table 3 shows how the four groups defined above differ across various socio-demographic characteristics (measured before the pandemic), personality (measured before the pandemic), health (before and during the pandemic), and political orientation (measured before the pandemic). Statistical t-tests for the significance of differences in characteristics between groups are shown in S3.2 Table in S3 File assuming equal variances across groups. S3.3 Table in S3 File provides supporting evidence: tests for equality of variance across groups provides support for this assumption in about 90% of the cases, and as S3.4 Table in S3 File . shows, relaxing the equality of variances assumption does not change our conclusions.
Socio-demographic characteristics . Almost 60 percent of the ‘anti-vaccination’ group are female, they are on average 48 years old, 12 percent of them have a university degree and their monthly net household income in 2019 averaged just under EUR 2,800. Around 27 percent have children under 16 and around 17 percent live in the eastern German states. ‘Passengers’ do not differ in their characteristics statistically significantly from this group. The members of the ‘anti-duty’ group, by contrast, are much more likely to be male and more often have a university degree. In comparison to the ‘anti-vaccination’ group, the members of the ‘pro-vaccination’ group are also more often male and older, and are also more likely to have a university degree. In particular, older interviewees are more likely to be in groups that favor mandatory vaccination and persons with a university education in groups comprising those who would get vaccinated voluntarily.
Personality traits . SOEP collects the personality traits of the respondents using a battery of questions that measure the five dimensions of the so-called ’Big Five’ [ 29 ]. The Big Five are the five most important groups of character traits in personality research: ’openness’, ’conscientiousness’, ’extraversion (sociability)’, ’tolerance’, and ’neuroticism’. Furthermore, risk attitude is surveyed. We see that members of the ‘anti-vaccination’ group tend to be more sociable but less open than the other groups. Their willingness to take risks is similar to that of the members of the ‘anti-duty’ and of the ‘pro-vaccination’ groups, but is significantly higher than that of ‘passengers’. Members of the ‘anti-duty’ group are particularly unsociable compared to the other groups, but open to new experiences. The ‘passengers’ are, like the members of the ‘pro-vaccination’ group, less neurotic. They are particularly tolerable and the least willing to take risks of the four groups.
Health . As far as the health of those surveyed is concerned, statistically significant differences are only evident in the number of illnesses: Members of the ‘anti-vaccination’ group have significantly fewer risk diseases than ‘passengers’ and members of the ‘pro-vaccination’ group. ‘Anti-duty’ members, on the other hand, have significantly fewer diseases than the ‘passengers’. Thus, overall, it may be said that those who refuse a policy of mandatory vaccination have fewer risk diseases at the time of the survey. There are no differences between the groups in terms of whether a member of the respondent’s household has already undergone a test for an infection with corona. It should be noted, however, that the number of cases of those tested for an infection is comparatively small.
Political orientation . As far as the political orientation of the respondents is concerned, no systematic significant differences between the four groups are identified. Only the members of the ‘anti-vaccination’ group seem to be positioned somewhat more to the right in the party spectrum than the members of the ‘anti-duty’ group.
Multivariate description of the characteristics of the four groups.
The differences and similarities with regard to group composition described above always refer to a single characteristic, i.e. they are univariate. Additionally, the relationships between individual characteristics of the respondents–after taking other characteristics into account–and their attitude toward mandatory or voluntary vaccination are explained below using a multivariate model (logistic estimation; see Eq ( 1 )). The dependent variable is either an indicator that describes the respondent’s own willingness to get vaccinated voluntarily (value 1 = yes; 0 = no; Table 4 ) or an indicator (value 1 = yes; 0 = no) that describes whether the respondents favors a policy of mandatory vaccination ( Table 5 ). As our interest is the explanation of data structures, we do not use survey weights in the multivariate analysis.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.t004
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.t005
With regard to the willingness to voluntarily get vaccinated ( Table 4 ), some significant differences in socio-demographic characteristics are observed. If all other characteristics are kept constant, the willingness to vaccinate is about 10 percentage points lower in women than in men. It is positively associated with age (0.4 percentage points per year of life), education (13 percentage points if respondents have a university degree compared to the other education categories), and household income (2.5 percentage points per 1,000 euros). The personality traits of the Big Five do not correlate with the respondents’ willingness to vaccinate; only openness is slightly positively associated with the willingness to vaccinate. In the health block, there is also only one significant variable that correlates with the willingness to get vaccinated: The higher the respondents estimate the probability that the virus could trigger a life-threatening disease in them, the more willing they are to be vaccinated.
A policy of mandatory vaccination ( Table 5 ) is also rejected with higher probability by women, but favored by older people and those living in the eastern federal states, ceteris paribus . Approval is negatively associated with neuroticism, i.e. emotional instability, and positively associated with the subjective probability of contracting life-threatening COVID-19.
The tables presenting the logit estimations include an initial model diagnostic: the Pseudo- R 2 . In S4 File , we present two additional model diagnostics: First, the linktest for both logit models does not find any evidence for model misspecifications. Second, a receiver operator characteristic (ROC) analysis provides evidence that the predictive power of our two models is acceptable. In addition, to assess multicollinearity, we have computed variance inflation factors (VIF) in S5 File . As a rule of thumb, a variable whose VIF values exceeds 10 may merit further investigation. In both regressions, the VIF of none of the explanatory variable exceeds 7.7 and the average VIF over all variables is below 2.1. It should also be noted that the two separate logit models do not model correlation and heteroscedasticity between the two outcomes (vaccinate voluntarily or obligatorily). Hence, in S6 File , as a robustness check, we have estimated a multivariate probit model using Stata’s mvprobit command that relies on simulated maximum likelihood [ 30 ]. S6.1-S6.6 Tables in S6 File compare the coefficients of the multivariate probit with the two separate models. Overall, there are some changes in the magnitude of the coefficients, but no changes in the signs of the regression coefficients or significance levels.
It is possible that respondents who did not give an answer about their vaccination preferences–for example, because they are still undecided–would decide to vaccinate or support mandatory vaccination after an adequate vaccination campaign. In a robustness check, we followed this argument by assigning respondents who refused to answer the question about voluntary or mandatory vaccination to the ‘yes’ category and repeated the logit estimation. This does not change our results (see S7.1 and S7.2 Tables in S7 File , S8 File provides our Stata code, which prepares the data and conducts all the statistical analyses, as well as the outputs of the multivariate estimations).
Finally, Table 6 provides a statistical comparison of the marginal effects from the model on willingness to get vaccinated ( Table 4 ) and attitudes toward mandatory vaccinations ( Table 5 ). We find no significant differences in marginal effects between the two models except for two variables: tertiary education and eastern federal states. The marginal effect for tertiary education is significantly larger for the willingness to get vaccinated model while the opposite is true for eastern federal states.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.t006
Politicians must make decisions which are based on incomplete information yet have far-reaching consequences for public health, personal freedom, and economic prosperity. It seems that many citizens are prepared to behave responsibly in the sense that they are prepared to endure a ‘little sting’ for the good of all: a vast majority of the German population (70 percent) state that they would get vaccinated as soon as a vaccine against COVID-19 was available. This means that under favorable conditions, a legal duty to get vaccinated to achieve herd immunity might not be necessary. It should, however, be noted that the question was asked in a stylized context: Potential side effects or ineffectiveness of the then hypothetical vaccine were assumed away. Though there is no reason to believe the vaccines currently being administered are more problematic in this respect than any other vaccines in use, neither can strictly be guaranteed in reality. In addition, the time required for a vaccination, the process of the vaccination itself (i.e. the injection), bureaucratic administration (e.g. making an appointment with the family doctor) or any necessary co-payment should de facto reduce the willingness to get vaccinated. Furthermore, at the time of writing, not only is it still unclear how quickly a vaccine can even be produced in the quantity required and administered to enough people, it is also unclear how long its effect will last. It is not even clear what percentage of the population would have to be vaccinated to achieve herd immunity, as this also depends on individual behavior and legal (or ethical) norms which are likely to continue to change (e.g. an explicit or implicit obligation to wear a mask of a specific variety in public transport or a testing obligation for people returning from trips abroad) [ 31 , 32 ]. Hence, a sufficiently high willingness to get vaccinated in the ‘best case’ scenario investigated here is an idealization and in any case only one relevant factor among many.
We observed there to be gender differences in the willingness to get vaccinated: women are less willing to get vaccinated, and also less willing to support a policy of mandatory vaccination. This is surprising, given that men are generally less likely to engage in preventive behavior [ 33 ] and women have been shown to be more willing to engage in preventive behavior in the pandemic, for instance by wearing face masks when recommended [ 34 ], and they also seem to be more compliant with other measures in general [ 35 ]. However, men are also more severely affected by the coronavirus [ 36 ] and women generally more skeptical about vaccinations, especially against COVID-19 [ 37 ]. We don’t know whether our interviewees frame their decision to get vaccinated or not as a situation of a social dilemma, but if so, previous results on gender differences in cooperation suggest men and women might have to be addressed differently to influence their decisions [ 38 , 39 ]. We also observed that income and education increase the willingness to get vaccinated voluntarily. It has also been shown recently that the willingness to pay for a vaccine against Covid-19 is positively impacted by, among other variables, income [ 40 ].
A mandatory vaccination would almost certainly achieve herd immunity against COVID-19, since all those for whom there is no medical contraindication would also get vaccinated. About half of the respondents approve and disapprove, respectively, of such a mandatory vaccination policy. In this context, the strong disagreement among the participants of the study regarding the dangerousness of the virus is particularly striking. Many of those who reject a policy of mandatory vaccination assume the dangerousness of the virus is being overestimated by others, while those who approve of a policy of mandatory vaccination seem to believe the exact opposite. This is highly problematic: at most one of the two groups can be right. Plausibly, the interviewees themselves differ in how dangerous they think the virus is. This yields a concrete and important policy recommendation (see also [ 40 , 41 ]): we need more reliable data on the dangerousness of SARS-CoV-2 and to communicate this data more clearly to the general public. Though the ‘knowledge-deficit’ explanation of low vaccine uptake might not work for well-established vaccines [ 42 ], we have found evidence that this might be different for COVID-19.
We are not recommending a policy of mandatory vaccination in this paper, but merely investigating the attitudes of people towards it. A policy of mandatory vaccination would be an extreme solution to solve the potential problem of low vaccine uptake, and a lot may be said in favor of less extreme policies (as outlined in [ 15 ], for instance). Vaccination could also be made mandatory only for certain groups of people (e.g. nurses, physicians, physiotherapists, people working in confined spaces, people travelling on public transport etc.), or only after time has conclusively shown that not enough people actually get vaccinated. It might also turn out that people are unwilling to take the second dose of a two-dose vaccine, or not accept refresher doses, which would further complicate the situation and might require subtle intertemporal strategy choice. Before making any vaccination mandatory, people could also be paid or incentivized in other ways to accept it [ 43 ]. If, as we hope, people take the external effects of their action into account, and a sufficiently high number of people get vaccinated as a result, mandatory vaccination won’t be necessary.
This article investigates the willingness to get vaccinated and the acceptance of a policy of mandatory vaccination against COVID-19 in June and July 2020 in Germany. Our first main result is that a large majority of about 70 percent of adults in Germany would voluntarily get vaccinated against the novel coronavirus if a vaccine without side effects was available. Our second result is that about half of this population is in favor of, and half against, a policy of mandatory vaccination. Our third main result is that the individual willingness to get vaccinated and acceptance of a policy of mandatory vaccination correlates systematically with several socio-demographics (gender, age, education, income) but, overall, not with psychological characteristics of the respondents.
When interpreting the results from our survey, it should be noted that preferences were elicited in an ideal-typical situation: a vaccine which is effective and free of side effects is immediately available for the entire population at zero cost. Future research will have to show how actual vaccination behavior differs in real-life situations that deviate from this ideal-typical situation.
Supporting information
S1 file. variable definitions..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.s001
S2 File. Comparison with further studies in Germany.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.s002
S3 File. Complementary estimation results.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.s003
S4 File. Additional diagnostics for the logit models.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.s004
S5 File. Multicollinearity across explanatory variables.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.s005
S6 File. Functional form assumptions and simultaneity.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.s006
S7 File. Imputation.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.s007
S8 File. Stata code.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0248372.s008
Acknowledgments
We thank Thomas Rieger for his outstanding research assistance.
- 1. WHO. Draft Landscape of COVID-19 candidate vaccines. 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-COVID-19-candidate-vaccines (accessed: March 2, 2021).
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 5. Stiglitz JE. Economics of the public sector. 2nd edn. W.W. Norton & Co.: New York. 1988.
- PubMed/NCBI
- 17. Mill JS. On Liberty. In: Collected Works of John Stuart Mill , ed. Robson J.M. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, London: Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1963–1991). 1859; 33. https://oll.libertyfund.org/titles/165 .
- 19. Giubilini A. The Ethics of Vaccination. Palgrave Studies in Ethics and Public Policy. Open Access. 2019. https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007%2F978-3-030-02068-2 .
- 21. Schröder C, Goebel J, Grabka MM, Graeber D, Kröger H, Kroh M, et al. Vor dem COVID-19-Virus sind nicht alle Erwerbstätigen gleich. DIW aktuell. 2020; 41.
- 23. Siegers R, Belcheva V, Silbermann T. SOEP-Core v35 Documentation of Sample Sizes and Panel Attrition in the German Socio-Economic Panel (SOEP) (1984 until 2018). SOEP Survey Papers. 2020; 826.
- 24. Kroh M, Siegers R, Kühne S. Gewichtung und Integration von Auffrischungsstichproben am Beispiel des Sozio-oekonomischen Panels (SOEP), in Nonresponse Bias: Qualitätssicherung Sozialwissenschaftlicher Umfragen. Eds.: Schupp J. und Wolf . Wiesbaden: Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden. 2015; C: 409–44.
- 25. Siegers S, Steinhauer HW, Zinn S. Gewichtung der SOEP-CoV-Studie 2020, SOEP Survey Papers, Series C–Data Documentation. 2020; 888.
- 28. Navin M. Values and Vaccine Refusal: Hard Questions in Epistemology, Ethics and Health Care, New York: Routledge. 2016.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 01 February 2022
Persuasive narrative during the COVID-19 pandemic: Norwegian Prime Minister Erna Solberg’s posts on Facebook
- Sanjana Arora ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0107-7061 1 ,
- Jonas Debesay 2 &
- Hande Eslen-Ziya ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7113-6771 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 9 , Article number: 35 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
7009 Accesses
4 Citations
5 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Cultural and media studies
- Politics and international relations
This article explores the Facebook posts of Norway’s Prime Minister Erna Solberg to highlight the key features of her crisis communication during the COVID-19 pandemic. It draws on data from Solberg’s Facebook posts from February 27, 2020 to February 9, 2021 (i.e., starting from the day when the first case of COVID-19 was recorded in Norway until the time of data collection for this study). Out of her 271 posts, 157 of them were about COVID-19 and were chosen for analysis. The analyses identified five major themes: (1) Promoting responsibility and togetherness (2) Coping (3) Being in control amidst uncertainty (4) Fostering hope and (5) Relating with the followers. Drawing inspiration from Boin, Stern and Sundelius’, work on persuasive narratives, this study shows the ways that Solberg’s posts about COVID-19 exhibit all five identified frame functions. In addition, the findings add contextual nuances to the frame functions through the theme of ‘Responsibilization and togetherness’, which are reflected through references to Norwegianness and the cultural concept and practice of dugnad . This study adds to our knowledge about how persuasive narratives are incorporated into the social media communication strategies of leaders and highlights the usefulness of this framework for studying ongoing and future crises.
Similar content being viewed by others
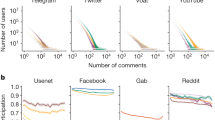
Persistent interaction patterns across social media platforms and over time
Michele Avalle, Niccolò Di Marco, … Walter Quattrociocchi
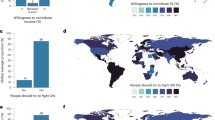
Globally representative evidence on the actual and perceived support for climate action
Peter Andre, Teodora Boneva, … Armin Falk
Participatory action research
Flora Cornish, Nancy Breton, … Darrin Hodgetts
Introduction
The economic and social disruption caused by the COVID-19 pandemic is having major impacts on people’s livelihoods and their health. As of 18 April 2021, there have been 140,322,903 confirmed cases of SARS-CoV-2 infections and 3,003,794 deaths (WHO, 2021 ), making the COVID-19 pandemic an unprecedented global health crisis of the century. As countries across the world grapple with mitigating the risks associated with the pandemic, communication—an essential component of planning, response, and recovery during crisis (Houston et al., 2014 )—has been one of the integral parts of the crisis management (Reddy and Gupta, 2020 ). Crisis communication highlights legitimation strategies, but also indicates how government institutions themselves make sense of crises (Brandt and Wörlein, 2020 ). Moreover, crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic can disrupt the socio-political order of societies, leaving a cognitive void in the minds of the public that can be filled with fear and uncertainty (Boin et al., 2016 ). In Norway, COVID-19 has been called a fear-driven pandemic that is based on alarming information of long-term illness and disability that is out of politicians control (Vogt and Pahle, 2020 ). Having control over the dramaturgy of political communication is thus central to effective leadership and crisis management (Boin et al., 2016 ). Effective communication can help societies handle uncertainty and promote adherence to behaviour change while fostering hope among the citizens (Finset et al., 2020 ).
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to rapidly evolve, and social media plays a pivotal role in meeting the communication needs of the public during such crisis (Van Dijck, 2013 ). As social media use increases during crises, leaders and public officials may utilise this platform to communicate, which in return helps reduce public panic and builds trust (Kavanaugh et al., 2012 ). As a result of the cultural and symbolic value of social media in contemporary times (Jenzen et al., 2021 ), the communication of public leaders in the midst of uncertainty and fear facilitates interpersonal and group interaction. Research has shown that, when compared to the traditional media platforms, social media platforms are used by leaders and elected officials to communicate, inform, and engage with their citizens (Golbeck et al., 2010 ). They use social media to spread messages farther and faster than it would be possible with traditional media (Sutton et al., 2013 ). What leaders post on social media can give insights into their communication and leadership strategies during crises. Understanding how leaders communicate with the public during crises will not only provide us with the knowledge about their governance styles but will also guide us to their meaning-making in times of uncertainty. Based on this assumption we will be studying the Facebook posts of Norwegian Prime Minister Erna Solberg, with the aim to highlight the key features of her communication. In doing so, we will take an exploratory rather than confirmatory perspective (Boudreau et al., 2001 ).
Solberg, member of the Conservative Party and in power since 2013, was defeated by the centre-left as this paper was being revised. Solberg has had a long career in politics, becoming a deputy representative to the Bergen City Council in 1979 when she was 18 years old. She was elected to the Parliament in 1989 where she was the youngest member of her party group (Notaker and Tvedt, 2021 ). Solberg’s tough stance on issues such as immigration earned her the nickname of ‘Jern-Erna’ [Iron Erna] (Reuters, 2013 ). However, upon her appointment as Prime Minister, Solberg displayed a ‘softer side’ by caring about voters’ jobs, health, and schools (Notaker and Tvedt, 2021 ).
The first Norwegian COVID-19 patient was diagnosed on February 26, 2020. While the initial spread of infection was relatively slow, cases increased quickly by March 12 th , after winter break for schools ended and many Norwegians returned from skiing holidays in Northern Italy (Dagsavisen, 2020 ). On March 12, the Norwegian Directorate of Health (NDH) adopted comprehensive measures to prevent the spread, which included closing day care centres, schools, and educational institutions. The measures also included a ban on cultural events, closed swimming gyms and pools, a halt to all service provisions that involved being less than one meter away from another person, and prohibiting visits to recreational cabins Footnote 1 , among others. Behavioural measures such as recommendations to keep physical distance, encourage handwashing, quarantine, stay home when ill, work from home, and avoid public transportation were also included. Following the lockdown, Norway became the first European country to announce that the situation was under control due to low levels of hospitalizations and mortalities (Christensen and Lægreid, 2020 ). In Norway, as of March 22, 2021, there have been over eighty thousand confirmed cases of coronavirus infection and more than six hundred deaths due to COVID-19. Norway has had far fewer COVID-19 cases, deaths, and hospitalizations per capita than most other countries in Western Europe or the United States (Christensen and Lægreid, 2020 ). Compared to its Scandinavian neighbours Denmark and Sweden, the proportion of cases of infections and deaths have been much lower (WHO, 2021 ), despite the three countries sharing similar social welfare and healthcare systems. Recently, a report submitted by the Corona Committee in Norway also concluded that the overall handling of the crisis by the government has been good. Not only has the number of infections and deaths in Norway been much lower than most countries in Europe, but the healthcare services have also remained stable, and society has remained relatively open (Lund, 2021 ). It is probable that good governance and responsible leadership demonstrated by the Norwegian cabinet and Prime Minister Erna Solberg contributed to this success.
In Norway, there is considerably less focus on individualization of candidates in political parties as compared to for instance the US, since the electoral system in Norway is based on proportional representation (Karlsen and Enjolras, 2016 ). Despite this, with the presence of digital and social media, there has been increasing focus on the individual candidates, leading to ‘decentralising personalisation’ (Karlsen and Enjolras, 2016 ; Balmas et al., 2014 ). Given this context, Erna Solberg’s Facebook account during the COVID-19 pandemic serves as an intermediary platform between the government’s role and her own personal profile as the Prime Minister who has been handling the COVID-19 crisis. Solberg has used Facebook more actively than other outlets like Twitter and has more followers on Facebook than any other platform. The proportion of Facebook users in Norway vis-a-vis other social media platform is also the highest (for example, 84% of people use Facebook compared to 22% who use Twitter who use Twitter) (Werliin and Kokholm, 2016 ). Facebook thus serves as an important platform for public leaders in Norway during crises, and therefore, by analysing Solberg’s Facebook posts, we aim to demonstrate the key features of her communication strategy during the COVID-19 crisis.
Background on crisis and crisis communication
Crisis is defined as a rare, and significant public situation creating undesirable consequences (Coombs, 2015 ; Gruber et al., 2015 ). In most cases it is ‘an unpredictable event that threatens important expectancies of stakeholders and can seriously impact an organization’s performance and generate negative outcomes’ (Coombs, 2015 : p. 3). Crisis communication on the other hand is referred as the strategies used to lessen the uncertainties during crisis via the dissemination and exchange of information (Collins et al., 2016 ). Effective crisis communication establishes reliability and maintains public trust. It should be frequent, consistent and involve compassionate messages conveyed in an inspired and transformational communication style. It is essential that public officials and leaders when communicating crisis relevant information be efficient and informative. Past research has shown the importance of repetition of the consistent interaction to help the message reach the recipients clearly and increase compliance behaviour in cases of crisis (Stephens et al., 2013 ). Inconsistent messages on the other hand were found to cause misperception and confusion, leading to a non-compliant behaviour by the recipients. The content of the message as well as its tone is also an important indicator of whether the recipients will comply or not (Sutton et al., 2013 ). Sources of crisis communication, such as leaders and public health officials, are perceived to be reliable and trustworthy when they exhibit concern and care (Heath and O’ Hair, 2010 ). In addition, they can be more effective in building relationship with the public, if they consider the cultural factors that play a role in their communicating about risks (Aldoory, 2010 ).
Boin et al. ( 2016 ) argue that crisis communication is one of the key challenges, which leaders face during a crisis situation. During crisis communication, leaders are required to frame ‘meaning’ of the crisis in order to shape how public perceives the risks, consequences and how they respond to the measures being taken. Developing a persuasive narrative in communication is thus integral to succesful framing of the crisis and for a strategic leadership. The construction of a successful persuasive narrative requires five frame functions: namely that the narrative will offer a credible explanation of what happened, it will provide guidance, instil hope, show empathy, and suggest that leaders are in control (Boin et al., 2016 ). In doing so, leaders aid the public’s understanding of the facts associated with crisis while sumltaneously acknolwedging and appealing to collective emotions. In incorporating these frame functions, leaders are posed with various choices and decision-making such as how they choose to or not choose to dramatise the situation, the language that they use and how they appeal to the colleactive emotions and stress.
As digital media technologies became popular resources for getting and spreading information, public officials and leaders also increasingly started using them as domains during the crises. In fact, for some scholars the use of social media while enabling mutual interaction between the leaders and recipients has altered the field of crisis communication altogether. For instance, it was found that as social media enables constant and effective communication, it was used more regularly than traditional media outlets during crisis (Kim and Liu, 2012 ). Similarly, Utz et al. ( 2013 ) discussed how for effective crisis communication strategy, the use of media channels, social media—Twitter, and Facebook—versus traditional— newspapers—was more critical than the type of the crisis. Moreover, Schultz et al. ( 2011 ) concluded that when compared to traditional media networks, crisis communication received less negative response when social media was used. Hence, it is not to our surprise that public officials nowadays are turning to social media platforms for communicating with the masses during crisis. They not only use these tools to communicate about crisis but also request information from the public. This was the case during the COVID-19 pandemic crisis where social media was employed by political leaders across the globe to mediate the communication of information about the pandemic as well as for reaching out to their citizens. This paper by focusing on the Norwegian case and more specifically on the Norwegian Prime Minister’s Facebook use during the time of COVID-19 pandemic aims to explore the use of social media platforms by political leaders during crisis. Our goal is to better understand how political leaders adapt social media technologies in their communication strategies during crises.
Our data that covers Erna Solberg’s Facebook posts between February 27, 2020, and February 10, 2021 (a total of 271 posts) were extracted from Footnote 2 into an Excel sheet. A total of 114 posts were removed as they were not related to COVID-19 leaving us 157 posts for further analysis. To aid the coding process, we noted the variables presented in Table 1 . These are: date, number of interactions, number, and type of reactions (e.g., angry, sad, like, etc.), URLs of links shared, and a description of the content of the posts that was later used in the qualitative analysis. We also noted if the posts were made during any particularly critical period (e.g., before, during or after new restrictive measures were introduced). The content of the posts and the number of likes and other reactions derived from this data should be considered a ‘snapshot’ of Solberg’s posts as they appeared at the time of data collection (Brügger, 2013 ), as it is possible that some posts have been subsequently removed, or that the numbers and types of reactions to the posts have changed by the publication date
The data was analysed through thematic analysis (Braun and Clarke, 2006 ): in the first step, we read all posts and generated the first set of codes. Next, we combined all the similar codes while labelling them in clusters and organised them into analytical themes/categories (see Fig. 1 ). The authors then discussed and reviewed these analytical themes and merged them into aggregate/conceptual themes. Lastly, we reviewed the aggregate themes through the lens of the five frame functions of persuasive narrative and identified commonalities and differences. We have included some posts under each theme to illustrate our analytical process and illuminate the themes (Sandelowski, 1994 ). All posts presented here were translated from Norwegian to English by the authors.

Schematic formulation of a theme from the categories captured in posts.
Our analysis resulted in five themes: (1) Promoting responsibility and togetherness (2) Coping (3) Being in control amidst uncertainty (4) Fostering hope and (5) Relating with the followers. In reviewing our findings from the framework of Boin et al. ( 2016 ), we found that all five frame functions of persuasive narrative were embedded in Solberg’s posts and aligned with our themes. Below we discuss our themes with reference to frame functions of Boin et al. ( 2016 ) for a persuasive narrative and in doing so, add contextual nuances to each theme.
Promoting responsibility and togetherness: we are in this together
Analysis of Solberg’s posts revealed a strong message of responsibility and togetherness. In almost all shares, she not only emphasized solidarity but also called for courage and responsibility. This Facebook post, shared soon after comprehensive shut-down measures were introduced, shows how important, for Solberg, was Norwegian solidarity expressed as ‘we’ (March 12, 2020):
Dear everyone. In times of crisis, we understand how dependent we are on each other. What unites us is more important than what separates us. This is not the time for ‘I’. This is the time for ‘we’.
Lunn et al. ( 2020 ) note that citizens are isolated during government induced or self-imposed quarantines: appeals to collective action and a spirit of ‘we-are-in-it-together’ are important ways to ensure compliance with quarantine and hence curb the rate of infection. Leaders in countries such New Zealand, UK, Brazil have also been found to have used a similar narrative emphasizing patriotic duty, love of country, and coming together as one, to mobilise community action (Dada et al., 2021 ).
Her posts were also imbued with appreciation and expression of gratitude towards healthcare workers and those who follow rules. For example, after introduction of the ban to travel to cabins and after the government’s decision to extend regulations until after Easter, Solberg posted the following on April 4, 2020, receiving a high number of likes:
I feel proud when I see how we handle this together. Many thanks to everyone who follows the advice from the health authorities. Many thanks to everyone in the health service who works hard and perseveres. Many thanks to all Norwegians for the patience, love and solidarity we now show each other
The use of the word ‘I’ and how it was being used in reference to ‘feel[ing] proud’, we argue, highlights the ‘positioning of self’ by Solberg. Davies and Harré ( 1990 ) claim that development of the notion of ‘positioning’ is a contribution to the understanding of personhood, and how speakers choose to position their personal identity vis-a-vis their discontinuous personal diversity (such as being the Prime Minister, politician, Norwegian citizen, etc.). In such posts, whether intentionally or unintentionally, we also see the discursive practices through which Solberg allocates meaning to her position as a Prime Minister by emphasising that she feels proud upon seeing those who follow advice. At the same time, her emphasis on ‘we’, as in how ‘ we handle this together’, places her as a member of the Norwegian masses.
Moreover, such references to togetherness and solidarity also reflect attempts to utilise the existing nationalistic cultural repertoire of the Norwegian concept of dugnad . For example, on New Year’s Day following the Gjerdrum community disaster (a sudden and unexpected mudslide that destroyed several residential houses) and rise in the number of infections during the holiday period (2125 reported cases on December 29, 2020), Solberg posted the following post:
[…] During the year we have put behind us, Norway has lined up for the big dugnad . People have put their interests and dreams on hold to protect the elderly and the risk groups. It has saved lives. I am deeply grateful, proud and touched, for the way the Norwegian people have handled the biggest challenge for our society since World War II. We lined up for each other when it mattered most…
Dugnad in Norwegian is voluntary work that is performed as a collective effort (Moss and Sandbakken, 2021 ). Nilsen and Skarpenes ( 2020 ) discuss how the concept of dugnad is embedded in a moral repertoire of the socially responsible citizen that is indicative of a specifically Norwegian welfare mentality and conclude that dugnad is imperative for the sustainability and resilience of the Norwegian welfare model. Before the pandemic, Simon and Mobekk ( 2019 ) argued that the concept of dugnad is central to Norwegian culture, inculcating prosocial and cooperative behaviour, and thereby plays a role in Norway being one of the most egalitarian democracies and having high levels of equality and reciprocity. In the context of COVID-19, social anthropologist Thomas Hylland Eriksen ( 2020 ) pointed out that one reason for the success of the Norwegian approach was the mobilisation of broader society to fight COVID-19, driven by the notion of dugnad . Similarly, Moss and Sandbakken ( 2021 ) analysed data from press conferences and interviews with members of the public and found that many participants mentioned liking how the government talked of ‘a spirit of dugnad ’ ( dugnadsånd ), appealing to shared voluntary work rather than strict rules. The authors posit that in a pandemic it is crucial to create and use meta-narratives that are a good fit with the context in order to aid meaning-making and increase compliance. The use of dugnad as a cultural repertoire has, however, met with criticism from some scholars, who argue that ‘a word associated with solidarity, unity, and voluntary work obscures the forced nature of the measures’ (Tjora, 2020 ) and shifts the onus for finding solutions onto individual citizens or groups (Nilsen and Skarpenes, 2020 ; Hungnes, 2016 ).
Despite the criticism of imbibing such cultural repertoire, the alignment of the key values of Norwegian society with the core message of encouraging collective action is essential for a crisis narrative to be politically effective (Boin et al., 2016 ). Furthermore, the theme of ‘Promoting responsibility and togetherness’ shows the context specific nature of crisis communication narrative in the case of COVID-19 in Norway and therefore adds to the components for a persuasive narrative.
Coping: everything will be fine
Solberg’s Footnote 3 posts also carried messages that address the consequences of coping with COVID-19, namely self-isolation, and loneliness. For instance, her posts guided followers in dealing with loneliness and maintaining general physical and mental health. The Norwegian government, like that of many other countries, had introduced measures such as mandatory quarantine and social distancing rules to manage the spread of the virus. Studies have shown that home confinement during COVID-19 has negatively affected the emotional state of individuals due to depression and anxiety and has led to or increased a sedentary lifestyle (Sang et al., 2020 ). Thus, emphasis on the well-being of the population during COVID-19 is important for effective crisis management (WHO, 2020a ) because increased well-being would reinforce its coping abilities during illness and hardships. As these are not the direct effects of the COVID-19 infection, but a result of the contagion containment measures imposed on citizens by the government, we observe Solberg taking responsibility and providing solutions to help. In doing so, she appears sensitive and caring towards the public.
Christensen and Lægreid ( 2020 ) attribute the ‘high-performing’ handling of the pandemic in Norway to the initial focus on suppression, followed by a control strategy. The authors further examine the ideas that having successful communication with the public, a collaborative and pragmatic decision-making style, the country’s resourcefulness, and high trust of government all contributed to the relative success in Norway. Adopting the correct and effective strategy indeed heavily influences the outcomes of crises. However, to fill the ‘cognitive void’ that the public might be experiencing, leaders need to manage the meaning-making process and ensure legitimacy of their actions (Boin et al., 2016 ). Solberg and the other ministers played an important role in communicating with citizens and the media through daily media briefings together with the NDH (Norwegian Directorate of Health) and NIPH (Norwegian Institute of Public Health) (Christensen and Lægreid, 2020 )
Solberg emphasized the impact of loneliness, for example, during one of the first holiday periods during the pandemic when comprehensive shut-down measures were introduced, she wrote:
Many people may feel lonely during holidays such as Easter, and the corona crisis exacerbates this. Therefore, I would like to encourage everyone to call someone you know is alone at Easter. The little things can mean a lot. Happy Easter!
A study by Blix et al. ( 2021 ) on the topic of mental health in the Norwegian population during the COVID-19 pandemic found that a substantial proportion of the population experienced significant psychological distress in the early phases. More than one out of four reported ongoing psychological distress over the threshold for clinically significant symptoms. Two other categories of individuals (those recently exposed to violence and those with pre-existing mental health problems) were found to be at special risk but worrying about the consequences of the pandemic was also found to contribute negatively to mental health. In this regard, Shah et al. ( 2020 ) argued that several nations have failed to address the mental health aspect among the public, as far more effort is being focused on understanding the epidemiology, clinical features, transmission patterns, and management of COVID-19. Solberg’s open discussion about mental health during the pandemic implies a situation-specific and data-driven strategy of managing the less visible effects of the pandemic and show insight in anticipating future needs (Han et al., 2020 ).
Moreover, Solberg’s posts also subtly utilised the Norwegian concept of friluftsliv , which translates as ‘free air life,’ a philosophy of outdoor living and connection with nature (Henderson and Vikander 2007 ). Friluftsliv is associated with grand narratives of Norwegian national identity depicting outdoor adventures, foraging, and a deep connection to nature (Jørgensen-Vittersø, 2021 ). For example, with the re-opening of DNT [Den Norske Turistforening] cabins in mid-2020, Solberg in her post on June 11 emphasized the importance of being outdoors in fresh air:
We need to use our bodies and get out into the light and fresh air. It is important for both physical and mental health! I hope many have a good and active Norwegian holiday this year!
In these posts, Solberg also shared pictures of herself being outdoors. In such ways, Solberg appeared to be offering not only guidance for coping with the challenges and consequences of living during the pandemic, but also emphasizing one characteristic of the Norwegian culture, which they are proud of—spending time in nature. Be it advice to spend time in nature, or to keep social distance or self-isolation, we consider that Solberg’s approach to coping aligns with the frame function of ‘offering guidance’. During a crisis, leaders have a window of opportunity during which they can communicate a frame to not only make sense of the crisis but also to provide guidance and to portray themselves as attentive and concerned about the challenging circumstances faced by the public (Boin et al., 2016 ). By depicting herself as attuned to the emotions experienced by her followers during the pandemic and by utilising the moment to suggest ways of coping, Solberg’s communication encapsulates the frame function of offering guidance for a persuasive narrative.
Being in control amidst uncertainty
In her posts, Solberg presented a narrative of being in control amidst uncertainty, which aligns with two of the frame functions of Boin et al. ( 2016 ), namely offering a credible explanation and suggesting that leaders are in control. In times of a crisis, it is important that leaders do not downplay the gravity of the situation or claim unrealistically optimistic scenarios (Boin et al., 2016 ). We see that Solberg maintained a balance by providing a detailed explanation of her actions and the reasons behind the restrictive measures taken. At the same time, she acknowledged the uncertainty inherent in the ever-changing crisis and demonstrated her concern. According to Lunn et al. ( 2020 ), in situations characterised by uncertainty and fear, responsible leaders need to signal that they are in control of the situation, which can be demonstrated by making decisions with confidence and honesty. Moreover, it is also essential that leaders do not make promises that are impossible or unrealistic, because doing that can impede the persuasiveness of their narrative by affecting their credibility later (Boin et al., 2016 ). In Solberg’s posts, we see that she displays confidence but also the reality of uncertainty and concern, which is a sign of effective leadership and shows ‘bounded optimism’ (Brassey and Kruyt, 2020 ). The following post where she writes about her worries and concerns followed by advice is a good example of credibility and control:
I am worried. Right now, we have ongoing outbreaks in Bergen, Oslo, Trondheim and Hammerfest… We know that vigorous work is being done intensively in these municipalities with infection detection and other measures. Although Norway has relatively low infection rates, we also register here at home that the number of hospital admissions and the number of infected have increased recently. We now have the highest number of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 since May… We also see that the infection has begun to spread to older age groups. And there is a significant risk that the numbers will continue to rise as we see in Europe. That is why we have today announced new national austerity measures next week. We can still reverse the trend here at home…
A demonstration of concern from role models has been shown to have a role in persuading the public to adhere to recommendations (Simon and Mobekk, 2019 ). Tannenbaum et al. ( 2015 ) note that fear is easier to handle when it is acknowledged, which relates to the idea of ‘citizens being anxious enough to take the advice from the authorities to heart and optimistic enough as to feel that their actions make a difference’ (Petersen, 2020 ). Inculcating ‘optimistic anxiety’ (Tannenbaum et al., 2015 ) is therefore an important feature of crisis communication narratives.
Another important nuance that emerges from Solberg’s posts is her comparisons to other countries to draw attention to the seriousness of the situation. For example, on November 5, 2020, Solberg made the following post announcing new national measures, which received over 5000 likes:
My message to the Norwegian people is: Stay at home as much as possible. Have the least possible social contact with others. It is absolutely necessary to avoid a new shutdown. Norway is at the beginning of the second wave of infection… The virus is spreading rapidly and all counties now have outbreaks. The government is therefore introducing new national infection control measures… If the current rate of infection continues, the number of inpatients in intensive care units will increase sharply in the coming weeks. This will lead to less intensive capacity for other seriously ill people. We are now where the Netherlands was at the beginning of September. A very rapid increase in infection in the Netherlands quickly led to more patients in the intensive care unit… Other European countries have similar experiences. There is therefore a heavy seriousness about the situation. And we must take responsibility together
By giving detailed reasoning behind measures being taken amidst uncertainty, Solberg exhibits both confidence and honesty in her narratives (Lunn et al., 2020 ). Another key feature that emerges from the post above is the emphasis on the risks of an increase in infection, and the possibility of a new lockdown and overburdening of intensive care capacity, thereby reflecting a more strongly persuasive intent. Such emphasis on the risks is different from other posts where Solberg exhibits control and optimism much more strongly. This adaption from a communicative stance to a more persuasive one could result from not only the perceived severity of the situation, but also the perceived risks of pandemic fatigue. Pandemic fatigue has been defined by the WHO as a lack of motivation to adhere to recommended protective behaviours (WHO, 2020b ). According to surveys conducted in different countries, most people have been shown to possess adequate knowledge of COVID-19 and the precautions required to keep safe, yet factors like emotions and context have been found to have greater impact on behaviours than knowledge (Gavi the Vaccine Alliance, 2020 ). A study of different ways of communicating healthcare messages suggested that believability of the messages and the recipients’ reactions to them can be influenced by the persuasive intent (Wang and Shen, 2019 ). Koh et al. ( 2020 ) also discuss the importance of devising effective and successful communications for a sustained period without message fatigue setting in, which includes concern for the way the communication is framed. Overall, we see that Solberg’s posts provide a rationale with portrayal of the government being in control of managing the crisis.
Fostering hope and return to normalcy
Solberg’s posts also emphasized the hopeful aspects of the crisis by appealing to followers to look forward to a return to everyday life, and new educational and economic prospects, despite the difficult current circumstances. This theme aligns with the frame of ‘instilling hope’ as per frame functions for a persuasive narrative by Boin et al. ( 2016 ). During a crisis, more than ever, effective leaders embody the hopes and fears of the society under threat, and therefore they should strive to inculcate optimism of a better future (Boin et al., 2016 ). Previous research has documented that in times of turmoil, followers especially look up to leadership that serves as a beacon of hope for and faith in a positive future, more than they do in times of prosperity (Stam et al., 2018 ; Shamir et al., 1993 ). According to Boin et al., leadership during crisis always has a moral dimension. On January 10, 2021, by which time Norway had witnessed over 50000 cases of infection and over 400 deaths as well as the Gjerdrum disaster, Solberg made the following post:
Dear everyone. This year I hope we can take our dreams back. After a year of pandemic and fear. Then I look forward to seeing creativity unleashed…
Another post that emphasized the optimism for educational prospects was made on April 15, 2020, and drew over 5000 likes:
Today is the last deadline to apply to a vocational school, college or university. I understand that it can feel strange to apply for an education this autumn while the educational institutions keep their campuses closed. Maybe someone also thinks the idea of moving from home to a new city seems extra scary these days. To you I want to say that everyday life will return. Therefore, my appeal to you who want to study: do not put your life on hold, but apply for education this year!
Lessons from previous crises tell us that leaders need to pay attention to the fear of the ongoing threat, as well as sadness and grief, and to provide hope to mitigate social disruption (Maak et al., 2021 ). Here, we see that Solberg’s is attempting to convey hope while also acknowledging the challenges and impact of COVID-19. In doing so, the messages also emphasise self-efficacy and trust in the government. Hope and resilience are closely aligned constructs, as they both include a tendency towards maintaining an optimistic outlook in the face of adversity (Duggal et al., 2016 ). Thus, fostering hope during crisis can help the community cope with the consequences of the crisis. Moreover, by using emotional appeals, leaders can influence attitudes and behaviours as well as induce compassion (Ghio et al., 2020 ).
The theme of fostering hope in Solberg’s posts was found to be particularly emphasized during and before national holidays or important events. Her posts often utilised humour to foster positivity, particularly during critical periods such as during or after implementation of stricter COVID-19 measures. For example, a day after it was announced that infection-reduction measures would continue throughout Christmas, Solberg shared a snipped of her response to a question asked in a press conference and posted:
Can Santa actually come to visit this year?
Creating human moments and hope is a sign of compassionate leadership and helps to establish the relational foundation for widespread support for pandemic control measures (Maak et al., 2021 ). Also, by utilising humour, Solberg adapts the tone of her messages, a tactic that has been found to significantly affect audiences’ attitudes and behaviours, help people manage their emotions, and strengthen support for pandemic measures (Lee and Basnyat, 2013 )
Relating with followers
The last theme is about the posts in which Solberg relates to the public by providing personal information, acknowledging, and relating with the difficult circumstances, and using humour or a private tone in her posts. For example, the post below was made just before Easter and it received more than 13000 likes, making it to be the third-most liked post of Solberg related to COVID-19 during this period.
It will be a different Easter this year. Let’s make the best of it. We can play fun board games with our loved ones, read the book we never have time to read, listen to an audiobook or explore the local area. The last few weeks have been challenging for all of us, but we want to get through this… Sindre and I have recharged with board games and wish you all a very happy Easter!
Empathy is an important component of the persuasive narrative, especially during crises when the decisions made by authorities to mitigate, and control can also have consequences for people’s lives. For crisis communication to be effective, the information provided to the public should not be too factual or portray leaders as distant from the citizens (Shen, 2010 ; Lunn et al., 2020 ). By demonstrating concern and acknowledging the impact of crises, leaders can empathise with the public (Shen, 2010 ; Lunn et al., 2020 ). We see Solberg personifying the challenges of COVID-19 by referring to how the times have been challenging for ‘all of us’. According to Boin et al. ( 2016 ), a leader’s personification of suffering is instrumental in showing empathy because the public is then able to relate to them.
Further, previously in a study by Larsson ( 2015 ) about Norwegian party leaders on Facebook during the 2013 ‘short campaign’, it was found that personal content referencing private life is increasingly employed by Norwegian party leaders. Enli and Rosenberg ( 2018 ) investigated voters’ evaluations of politicians as authentic or ‘real,’ and Solberg was found to be one of the most perceived authentic politicians. Enli ( 2014 ) had earlier suggested that Erna Solberg’s public profile as predictable, anti-elitist and imperfect constructs her authenticity.
A similar example of relatability with followers during the pandemic was the instance when she forgot the rule of not shaking hands during public meetups and press conferences. After the event, she wrote:
It is important that we can have some humour in a difficult time Even a prime minister can forget, but now it is important that we all remember to follow the advice of the health authorities…
She also used an engaging communicative style when interacting with her followers:
Then the holiday is over… a different summer, a little cold, weekly meetings in the Government’s Corona Committee on video, beautiful nature experiences from Norway and a lot of rain. Let me share a wonderful little meeting with a lynx on the lawn on Varaldsøy… Have you had a nice summer?
Thus, Solberg embeds references to her private life, which also helps to personify the messages in her posts and thus relate with the public. In addition, by relating with the public on an everyday basis and through the acknowledgment of shared challenges during crisis, Solberg’s narrative also appears empathetic. Our theme of ‘Relating to the public’ thus encapsulates frame function of ‘showing empathy’ for developing a persuasive narrative, as per Boin et al. ( 2016 ).
Concluding remarks
This paper was an attempt to explore the Facebook posts of Norway’s Prime Minister Erna Solberg to highlight the key features of her crisis communication during the COVID-19 pandemic. By drawing on data from Solberg’s Facebook posts during the pandemic our analyses identified five major themes, (1) Promoting responsibility and togetherness (2) Coping (3) Being in control amidst uncertainty (4) Fostering hope and (5) Relating with the followers, where we went in detail explanation by using frame functions of a persuasive narrative by Boin et al. ( 2016 ). We furthermore discussed the specific Norwegian contextual nuances to the frame functions. These were the theme ‘Responsibilization and togetherness’, presented via the references to Norwegianness and the cultural concept and practice of dugnad . Hence, our paper showed how during crisis persuasive narratives are incorporated into the social media communication strategies of political leaders.
The paper also showed how persuasive narratives are delivered through praising the public’s efforts, promoting togetherness, caring about the public’s well-being, displaying optimism and confidence in the government’s measures. It elaborated on how crisis management on social media was done via the use of humour and personal information. Humour was used as a tool to engage with the public and help them relate and comply to the COVID-19 restrictions. Hence, Solberg used Facebook to capitalise on a wide-reaching social medium (Hallahan, 2010 ). While the communication of leaders during crises helps to fill the cognitive void, the use of social media helps build societal resilience by improving awareness and encouraging preparedness (Boin et al., 2016 )
Even so, the success of a persuasive narrative is to a great extent dependant on the credibility of its proponents (Boin et al., 2016 ). The reputation of the leader and the organisation that they represent plays a key role in framing a successful persuasive narrative. In general, Norwegians have more trust in each other and their institutions than most other countries (Skirbekk and Grimen, 2012 ). A survey conducted by the Norwegian Citizen’s Panel [Norsk Medborgerpanel] in March 2020 found that trust in government, in the health authorities, in parliament, and in national and local politicians had increased, as did trust in the Prime Minister during the pandemic (Dahl, 2020 ). Clearly, Solberg seems to have benefitted from the trust capital in Norwegian society with her Facebook communications during a crisis. More recently, Erna Solberg has received heavy criticism for breach of COVID-19 restrictions during a family trip to Geilo for her 60th birthday (The Guardian, 2021a ). Following which, Erna Solberg, has been investigated by police and fined (The Guardian, 2021b ). Thus, while her Facebook posts exhibiting components of a persuasive narrative received popularity, her actions have nevertheless been subjected to scrutiny and criticisms in mainstream media (Larsen, 2021 ). According to Boin et al. ( 2016 : p. 72), the retainment of confidence of the public is essential for the communication strategies to be effective. Therefore, such media criticism might undermine the credibility of Solberg and her cabinet, leading to less credible and politically ineffective narratives. On the other hand, past performances, and reputation also play an important role in increasing leaders’ personal credibility in the face of crisis (Boin et al., 2016 ). Consequently, Solberg’s long career in politics and her reputation of caring about the citizens as previously discussed, could buffer the recent impact on her credibility. Moreover, communication during and after a crisis affects long-term impressions (Coombs, 2007 ). With the personification of politics in Norway or ‘decentralising personalization’ (Balmas et al., 2014 ), the criticisms paved at Erna, however, reflect more of a personal crisis than a national crisis. And while we do not analyse Solberg’s posts beyond 9 th Feb. 2021 i.e., after Solberg spoke about the Geilo trip incident on her Facebook account, we see that she follows similar strategy in handling this personal crisis as the national crisis of COVID-19, through use of a persuasive narrative. Future studies can therefore focus on how Solberg and other political leaders utilise the strategy of persuasive narrative in management of personal crisis in nexus with national crisis such as that of COVID-19.
Further, we concur with Christensen and Lægreid ( 2020 ) who write that the ‘political leadership has succeeded well in connecting governance capacity and legitimacy using the argument that Norway had sufficient resources to deal with the crisis. While the health resource capacity and preparedness of Norway inarguably contributes to the outcomes of the crisis, communicating a successful persuasive narrative with credibility is integral to gaining legitimacy and filling the cognitive void (Boin et al., 2016 ). Erna Solberg’s use of persuasive narrative in Facebook posts, seems therefore to have been effective in the management of the COVID-19 pandemic, but her latest unfortunate incident goes to show how politicians’ management of crises is tenuous and highly dependent on public trust.
Our study adds to the significance and knowledge of how persuasive narratives are incorporated into the communication strategy of leaders on a social media platform and highlights the usefulness of this framework for studies about ongoing and future crises. By using data from social media, our findings also add to the understanding of the increased personification of politics and how leaders utilise this personification to communicate government measures and engage with the public during a crisis. Future research can further explore how public leaders and health authorities’ frame crises situations, actions, issues, and responsibility to dramatise and reinforce key ideas (Hallahan, 1999 ). Such insights can pave way for understanding public’s shaping of risk perceptions and compliance to behavioural measures during crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
Data availability
The dataset analysed during the current study is available through the public profile of Erna Solberg on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ernasolberg/ . This dataset was derived from Crowd Tangle which can be accessed through request at https://www.crowdtangle.com/ .
Known as ‘hyttetur’, cabin trips are deeply rooted in Norwegian culture and way of life
Crowdtangle extracts both historical and current data of post contents and metadata such as the date the post was made, number of likes, other reactions and shares. Information about how to access raw material included in this study can be found in the data availability statement at the end of the article.
‘Everything will be fine’ [ Alt blir bra ] was one of the campaigns that spread because of the COVID-19 crisis in Norway depicting pictures of a rainbow.
Aldoory L (2010) The ecological perspective and other ways to (re)consider cultural factors in risk communication. In: Heath R, O’ Hair (eds) Handbook of risk and crisis communication. Routledge, New York, pp. 227–246
Google Scholar
Balmas M, Rahat G, Sheafer T, Shenhav SR (2014) Two routes to personalized politics: Centralized and decentralized personalization. Party Polit 20(1):37–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/1354068811436037
Article Google Scholar
Blix I, Birkeland MS, Thoresen S (2021) Worry and Mental Health in the COVID-19 Pandemic: Vulnerability Factors in the General Norwegian Population. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-192098/v1 . Accessed 10 Jun 2021
Boin A, Stern E, Sundelius B (2016) The politics of crisis management: Public leadership under pressure. Cambridge University Press
Boudreau MC, Gefen D, Straub DW (2001) Validation in information systems research: a state-of-the-art assessment. MIS Quart 25(1):1. https://doi.org/10.2307/3250956
Brandt P, Wörlein J (2020) Government crisis communication during the pandemic. https://www.sciencespo.fr/en/news/news/government-crisis-communications-during-the-pandemic/4862 . Accessed 20 May 2021
Braun V, Clarke V (2006) Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol 3(2):77–101. https://doi.org/10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Brassey J, Kruyt M (2020) How to demonstrate calm and optimism in a crisis. McKinsey & Company, April. 2020. https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/organization/our-insights/how-to-demonstrate-calm-and-optimism-in-a-crisis . Accessed 27 May 2021
Brügger N (2013) Historical network analysis of the web. Soc Sci Comput Review 31(3):306–21. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894439312454267
Christensen T, Lægreid P (2020) Balancing governance capacity and legitimacy: how the Norwegian government handled the COVID‐19 crisis as a high performer. Public Admin Rev 80(5):774–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/puar.13241
Collins M, Neville K, Hynes W, Madden M (2016) Communication in a disaster-the development of a crisis communication tool within the S-HELP project. J Decis Syst 25(1):160–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/12460125.2016.1187392
Coombs WT (2007) Protecting organization reputations during a crisis: the development and application of situational crisis communication theory. Corp Reput Rev 10(3):163–176. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.crr.1550049
Coombs WT (2015) Ongoing crisis communication: planning, managing and responding. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA
CrowdTangle (2021) CrowdTangle Team. Facebook, Menlo Park, California, United States. List ID: 1504404 2021
Dada S, Ashworth HC, Bewa MJ, Dhatt R (2021) Words matter: political and gender analysis of speeches made by heads of government during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMJ Global Health 6(1):e003910. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.10.20187427
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Dagsavisen (2020) FHI: Norge ble varslet om koronasmitte fra Østerrike allerede 4. mars 2020 (Norway was notified of corona infection from Austria as early as 4 March 2020). https://www.dagsavisen.no/nyheter/innenriks/2020/10/30/fhi-norge-ble-varslet-om-koronasmitte-fra-osterrike-allerede-4-mars/ . Accessed on 1 Apr 2021
Dahl T (2020) Stolar meir på Erna og mindre på naboen (Rely more on Erna and less on the neighbor). https://www.uib.no/aktuelt/135017/stolar-meir-p%C3%A5-erna-og-mindre-p%C3%A5-naboen . Accessed 3 Jul 2021
Davies B, Harré R (1990) Positioning: the discursive production of selves. J Theory Soc Behav 20(1):43–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-5914.1990.tb00174.x
Duggal D, Sacks-Zimmerman A, Liberta T (2016) The impact of hope and resilience on multiple factors in neurosurgical patients. Cureus 8(10). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.849
Enli G (2014) Mediated authenticity. Peter Lang Incorporated, New York
Enli G, Rosenberg LT (2018) Trust in the age of social media: Populist politicians seem more authentic. Soc Media Soc 4(1):2056305118764430. https://doi.org/10.1177/2056305118764430
Eriksen TH (2020) Norway’s response to Covid-19 and the Janus face of Nordic trust. https://www.coronatimes.net/norway-covid-19-nordic-trust/ . Accessed on 15 May 2021
Finset A, Bosworth H, Butow P, Gulbrandsen P, Hulsman RL, Pieterse AH et al. (2020) Effective health communication–a key factor in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. Patient Educ Couns 103(5):873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2020.03.027
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gavi the Vaccine Alliance (2020) 10 reasons why pandemic fatigue could threaten global health in 2021. https://www.gavi.org/vaccineswork/10-reasons-why-pandemic-fatigue-could-threaten-global-health-2021 . Accessed 15 Jun 2021
Ghio D, Lawes-Wickwar S, Tang M, Epton T, Howlett N, Jenkinson E (2020) What influences people’s responses to public health messages for managing risks and preventing infectious diseases? A rapid systematic review of the evidence and recommendations. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/nz7tr . Accessed 28 May 2021
Golbeck J, Grimes JM, Rogers A (2010) Twitter use by the US Congress. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 61(8):1612–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.21344
Gruber DA, Smerek RE, Thomas-Hunt MC, James EH (2015) The real-time power of Twitter: Crisis management and leadership in an age of social media. Bus Horizon 58(2):163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2014.10.006
Hallahan K (1999) Seven models of framing: implications for public relations. J Public Relat Res 11(3):205–242. https://doi.org/10.1207/s1532754xjprr1103_02
Hallahan K (2010) Crises and risk in cyberspace. In: Heath R, Hair O’ (ed) Handbook of risk and crisis communication. Routledge, New York, NY, pp. 412–445
Han RH, Schmidt MN, Waits WM, Bell AK, Miller TL (2020) Planning for mental health needs during COVID-19. Curr Psychiatry Rep 22(12):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-020-01189-6
Heath R, O’ Hair H (2010) The significance of crisis and risk communication. In: Heath R, Hair O’ (ed) Handbook of risk and crisis communication. Routledge, New York, pp. 5–30
Chapter Google Scholar
Henderson B, Vikander N (eds) (2007) Nature first: outdoor life the friluftsliv way. Dundurn
Houston JB et al. (2014) Social media and disasters: a functional framework for social media use in disaster planning, response, and research. Disasters 39(1):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/disa.12092
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Hungnes S (2016) Den norske dugnadskulturen (The Norwegian voluntary culture. https://agendamagasin.no/kommentarer/den-norske-dugnadskulturen/ . Accessed 25 May 2021
Jenzen O, Erhart I, Eslen-Ziya H, Korkut U, McGarry A (2021) The symbol of social media in contemporary protest: Twitter and the Gezi Park movement. Convergence 27(2):414–37. https://doi.org/10.1177/1354856520933747
Jørgensen-Vittersø KA (2021) From fresh air and sunbathing to wildlife and snow caves: ‘Friluftsliv’in norwegian primary schools, 1939–1980. In: Roos M, Berge KL, Edgren H (eds) Exploring textbooks and cultural change in nordic education 1536–2020. Brill, pp 245–259
Karlsen R, Enjolras B (2016) Styles of social media campaigning and influence in a hybrid political communication system: linking candidate survey data with Twitter data. Inte J Press/Politics 21(3):338–57. https://doi.org/10.1177/1940161216645335
Kavanaugh AL, Fox EA, Sheetz SD, Yang S, Li LT, Shoemaker DJ et al. (2012) Social media use by government: from the routine to the critical. Gov Inform Q 29(4):480–91. https://doi.org/10.1145/2037556.2037574
Kim S, Liu BF (2012) Are all crises opportunities? A comparison of how corporate and government organizations responded to the 2009 flu pandemic. J Public Relat Res 24(1):69–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/1062726x.2012.626136
Koh PK-K, Chan LL, Tan E-K (2020) Messaging fatigue and desensitisation to information during pandemic. Arch Med Res 51(7):716–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.06.014
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Larsen K (2021) Erna Solbergs popularitet stuper (Erna Solberg’s popularity plummets). https://www.dagbladet.no/nyheter/erna-solbergs-popularitet-stuper/73597485 . Accessed 15th Apr
Larsson AO (2015) Pandering, protesting, engaging. Norwegian party leaders on Facebook during the 2013 ‘Short campaign’. Inform Commun Soc 18(4):459–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/1369118x.2014.967269
Lee ST, Basnyat I (2013) From press release to news: mapping the framing of the 2009 H1N1 A influenza pandemic. Health Commun 28(2):119–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/10410236.2012.658550
Lund J (2021) Somling, rot og ulovligheter (Procrastination, clutter and illegalities). https://www.aftenposten.no/meninger/kommentar/i/BlPRjw/somling-rot-og-ulovligheter . Accessed on 25 May 2021
Lunn P, Belton C, Lavin C, McGowan F, Timmons S, Robertson D (2020) Using behavioural science to help fight the coronavirus. J Behav Public Administration, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.30636/jbpa.31.147
Maak T, Pless NM, Wohlgezogen F (2021) The fault lines of leadership: Lessons from the global Covid-19 crisis. J Change Manag 21(1):66–86. https://doi.org/10.1080/14697017.2021.1861724
Moss SM, Sandbakken EM (2021) “Everybody needs to do their part, so we can get this under control.” reactions to the norwegian government meta‐narratives on COVID‐19 measures. Polit Psychol 42(5):881–898. https://doi.org/10.1111/pops.12727
Notaker H, Tvedt KA (2021) Stor Norske Leksikon: Erna Solberg ( https://snl.no/Erna_Solberg . Accessed on 20 Apr 2021
Nilsen ACE, Skarpenes O (2020) Coping with COVID-19. Dugnad: a case of the moral premise of the Norwegian welfare state. International Journal of Sociology and Social Policy. (ahead-of-print). https://doi.org/10.1108/ijssp-07-2020-0263
Petersen MB (2020) The unpleasant truth is the best protection against coronavirus. Politiken. https://pure.au.dk/portal/files/181464339/The_unpleasant_truth_is_the_best_protection_against_coronavirus_Michael_Bang_Petersen.pdf . Accessed 11 Jun 2021
Reddy BV, Gupta A (2020) Importance of effective communication during COVID-19 infodemic. J Fam Med Prim Care 9(8):3793. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_719_20
Reuters (2013) Iron Erna’s softer side wins through in Norway election 2013. https://www.scmp.com/news/world/article/1307898/iron-ernas-softer-side-wins-through-norway-election . Accessed 27 Apr 2021
Sandelowski M (1994) Focus on qualitative methods. The use of quotes in qualitative research. Res Nurs Health 17(6):479–482. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.4770170611
Sang X, Menhas R, Saqib ZA, Mahmood S, Weng Y, Khurshid S, et al. (2020) The psychological impacts of CoViD-19 home confinement and physical activity: a structural equation model analysis. Front Psychol 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.614770
Schultz F, Utz S, Göritz A (2011) Is the medium the message? Perceptions of and reactions to crisis communication via twitter, blogs and traditional media. Public Relat Rev 37(1):20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2010.12.001
Shah K, Kamrai D, Mekala H, Mann B, Desai K, Patel RS (2020) Focus on mental health during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic: applying learnings from the past outbreaks. Cureus 12(3). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.7405
Shamir B, House RJ, Arthur MB (1993) The motivational effects of charismatic leadership: a self-concept based theory. Organ Sci 4(4):577–94. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.4.4.577
Shen L (2010) Mitigating psychological reactance: the role of message-induced empathy in persuasion. Hum Commun Res 36(3):397–422. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2958.2010.01381.x
Article ADS Google Scholar
Simon C, Mobekk H (2019) Dugnad: a fact and a narrative of Norwegian prosocial behavior. Perspect Behav Sci 42(4):815–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40614-019-00227-w
Skirbekk H, Grimen H (2012) Tillit i Norge (Trust in Norway). Res Publica, Oslo
Stam D, van Knippenberg D, Wisse B, Nederveen Pieterse A (2018) Motivation in words: promotion-and prevention-oriented leader communication in times of crisis. J Manag 44(7):2859–87. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206316654543
Stephens KK, Barrett AK, Mahometa MJ (2013) Organizational communication in emergencies: Using multiple channels and sources to combat noise and capture attention. Hum Commun Res 39(2):230–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/hcre.12002
Sutton J, Spiro E, Butts C, Fitzhugh S, Johnson B, Greczek M (2013) Tweeting the spill: Online informal communications, social networks, and conversational microstructures during the Deepwater Horizon oilspill. Int J Inform Syst Crisis Resp Manag 5(1):58–76. https://doi.org/10.4018/jiscrm.2013010104
Tannenbaum MB, Hepler J, Zimmerman RS, Saul L, Jacobs S, Wilson K et al. (2015) Appealing to fear: a meta-analysis of fear appeal effectiveness and theories. Psychol Bull 141(6):1178. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0039729
The Guardian (2021a) Norwegian PM Erna Solberg investigated for Covid rules breach. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/mar/19/norwegian-pm-erna-solberg-investigated-for-covid-rules-breach . Accessed 25th Mar 2021
The Guardian (2021b) Norwegian PM fined after breaking Covid rules with birthday party. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/apr/09/norway-prime-minister-erna-solberg-fined-breaking-covid-rules-birthday . Accessed 15th Mar 2021
Tjora A (2020) Tillitsfull dugnad eller instruert solidaritet (Trusting voluntary work or instructed solidarity) https://www.universitetsavisa.no/koronavirus-ytring/tillitsfull-dugnad-eller-instruert-solidaritet/111642 . Accessed on 21 May 2021
Utz S, Schultz F, Glocka S (2013) Crisis communication online: How medium, crisis type and emotions affected public reactions in the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster. Public Relat Rev 39(1):40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pubrev.2012.09.010
Van Dijck J (2013) Facebook and the engineering of connectivity: A multi-layered approach to social media platforms. Convergence 19(2):141–55. https://doi.org/10.1177/1354856512457548
Vogt H, Pahle A (2020) En fryktdrevet pandemi av varige helseproblemer (A fear-driven pandemic of lasting health problems) https://www.aftenposten.no/meninger/kronikk/i/opdB6a/en-fryktdrevet-pandemi-av-varige-helseproblemer . Accessed 20 May 2021
Wang W, Shen F (2019) The effects of health narratives: Examining the moderating role of persuasive intent. Health Market Q 36(2):120–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/07359683.2019.1575061
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Werliin R, Kokholm M (2016) Device study: Social media across the Nordics. https://www.audienceproject.com/wp-content/uploads/study_social_media_across_the_nordics.pdf . Accessed 18 Jun 2021
World Health Organization (2020a) Mental health and psychosocial considerations during the COVID-19 outbreak, 18 March 2020. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/mental-health-considerations.pdf . Accessed 10 Jun 2021
World Health Organization (2020b) Pandemic fatigue: reinvigorating the public to prevent COVID-19: policy framework for supporting pandemic prevention and management: revised version November 2020. World Health Organization. Regional Office for Europe. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/337574 . Accessed 17 Jun 2021
World Health Organization (2021) WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard 2021 https://covid19.who.int/?gclid=Cj0KCQjw9_mDBhCGARIsAN3PaFNVuA3kABELXjY66cXUIVcTNNBkPrX57w1OtZL1GYBomSnvTRflQTcaAoxkEALw_wcB . Accessed 18 Apr 2021
Download references
Acknowledgements
This article is published as part of the research project ‘Fighting Pandemics with Enhanced Risk Communication: Messages, Compliance and Vulnerability During the COVID-19 Outbreak (PAN-FIGHT)’, which is financed by the Norwegian Research Council (Project number: 312767).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway
Sanjana Arora & Hande Eslen-Ziya
Oslo Metropolitan University, Oslo, Norway
Jonas Debesay
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sanjana Arora .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Arora, S., Debesay, J. & Eslen-Ziya, H. Persuasive narrative during the COVID-19 pandemic: Norwegian Prime Minister Erna Solberg’s posts on Facebook. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 9 , 35 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01051-5
Download citation
Received : 12 October 2021
Accepted : 17 January 2022
Published : 01 February 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01051-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Norwegian “dugnad” as a rhetorical device in public health communication during the covid-19 pandemic. a qualitative study from immigrant’s perspectives.
- Raquel Herrero-Arias
- Irina Vladimirovna Halbostad
- Esperanza Diaz
Archives of Public Health (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection

An Ethical Anaylsis of the Arguments Both For and Against COVID-19 Vaccine Mandates for Healthcare Workers
Since the development of the first U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved vaccine for the prevention of serious disease and death associated with the SARS-CoV-2 virus, health care workers have been expected to comply with mandatory immunization requirements or face potential termination of employment and censure by their state medical boards. Although most accepted this mandate, there have been several who have felt this was an unnecessary intrusion and violation of their right to choose their own health care mitigation strategies, or an infringement on their autonomy and other civil liberties. Others have argued that being a health care professional places your duties above your own self-interests, so-called fiduciary duties. As a result of these duties, there is an expected obligation to do the best action to achieve the “most good” for society. A so-called “utilitarian argument.”
We explore arguments both for and against these mandatory vaccine requirements and conclude using duty- and consequence-based moral reasoning to weigh the merits of each.
Conclusions
Although arguments for and against vaccine mandates are compelling, it is the opinion of the Ethics Committee of the American Academy of Emergency Medicine that vaccine mandates for health care workers are ethically just and appropriate, and the benefit to society far outweighs the minor inconvenience to an individual's personal liberties.
Introduction
The introduction of COVID-19 vaccine mandates for health care workers has caused debate and disruption in hospitals across the world, as well as within the United States. Several arguments have been made for and against the mandates, although mostly in political and social media. As the Ethics Committee of the American Academy of Emergency Medicine (AAEM), we are entrusted to guide the Academy and its members, and hopefully the entire emergency medicine (EM) community, regarding ethical matters affecting all facets of emergency care. COVID-19 quickly became a polarizing public health crisis, affecting people of all educational, socioeconomic, political, religious, and demographic backgrounds. COVID-19 greatly impacted emergency departments (EDs), which are often front and center to issues related to not only disease and its manifestations, but to the effects of vaccine mandates on health care professionals. As an ethics committee, we focus our arguments solely on ethics and do not debate the safety or efficacy of vaccines. The Ethics Committee accepts that these vaccines were recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and are U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved, and proceed with the assumption that these vaccines meet safety requirements ( 1 ). We will also not debate the role of immunity from prior COVID-19 infection as being equivalent to the vaccine, as study on the equivalency is still ongoing at the time of writing this article. We will also avoid religious and legal arguments (except to mention one precedent case on public health law and vaccine mandates, which was based on a utilitarian ethical principle). Similarly, we will avoid discussion of religious or medical exemptions that may legitimately prevent receiving the vaccine. We present the arguments both for and against vaccine mandates and weigh the substantive arguments made by two panels of members, representing arguments “for” (M.M., B.W., A.U., E.S.) and “against” (L.D., R.B., D.F., A.G.) mandates. A.G. examined each of the arguments for their ethical soundness and, using principles of moral reasoning invoking deontology and consequentialism, concluded with the recommended moral position.
Of note, we use the term health care workers to include a physician-led team that may consist of any combination of residents, fellows, medical students, nurses, advanced practice providers, and health care assistants and technologists. It is not enough to focus on one out of this diverse group. As a physician-led group, it is the position of AAEM and most physician societies that medical care is best led by a board-certified physician, who also ensures the professional ethics guiding their practice are exhibited in each team member.
Arguments in Favor of Vaccine Mandates
Historically, vaccine mandates have been part of the protections under public health laws of many nations of the world. As far back as 1807, the German state of Bavaria introduced a mandate for vaccination of the public after development of the smallpox vaccine ( 2 ). In the 1905 Jacobson vs. Massachusetts decision, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that state vaccine mandates were legal and enforceable to protect public health ( 3 ). Although in recent years there have been controversies regarding mandatory vaccination for schoolchildren, in large part these vaccination mandates have continued yearly without public debate. Generally speaking, and using the principle of acceptability, most members of the public have long accepted the role vaccines play in protecting their health and the health of those around them. There are many definitions of acceptability in ethics, however, we find most illustrative the following: “Acceptability is a multi-faceted construct that reflects the extent to which people delivering or receiving a healthcare intervention consider it to be appropriate, based on anticipated or experienced cognitive and emotional responses to the intervention” ( 4 ).
The initial argument in support of the COVID-19 vaccine mandates for health care workers must start with the principle of justice and consistency and their related ethical concepts that support fair and equitable treatment of individuals. Although justice is typically viewed through a patient-centric lens, it is reasonable to expect that health care workers not only treat their patients justly, but be treated and act justly and consistent with their professional ethics. Justice is defined as “fair, equitable, and appropriate treatment of persons” ( 5 ). There is a further implied principle within justice, that is, consistency. It is impossible to be just yet inconsistent. Just policies, even with caveats and exceptions, must be reproducible and consistent, otherwise they will not withstand scrutiny by society and, as a result, will not be ethical. A policy is just if it is fair, and the policy to mandate that health care workers receive the COVID-19 vaccine is fair, equitable, and appropriate, as it seeks to provide a means to distribute a necessary treatment without discrimination or bias and its benefits far outweigh any risks.
For the last half century, health care workers had generally accepted, as part of the requirements for obtaining hospital privileges, the role of mandatory vaccines for their and society's good. It is reasonable and expected then to mandate additional vaccines, as diseases become prevalent and vaccines are discovered, with the same intent to provide protection to health care workers and their patients. Prior to March 2020, proof of certain mandatory vaccinations, such as hepatitis B, tetanus, measles, mumps and rubella, and other childhood vaccinations (or proof of immunity) was an accepted norm in the process of starting clinical work in most clinical settings in the United States ( 6 ). When the COVID-19 vaccination became available, given the similar public health protection that the vaccination provided for this disease, it is reasonable and not an unusual or unfair burden on health care workers to add one more vaccine to the multitude they are required to get in order to provide clinical care. As stated in the first principle of AAEM's Principles of Ethics, there is a fiduciary duty by physicians to place the patient's interests above their own ( 7 ). In keeping with this principle, it is hard to conceive that refusing to protect oneself from severe disease from COVID-19, as well as the reported decreased rate of viral transmission and hence disease in vaccinated persons compared with the unvaccinated, is consistent with placing the interests of patients above health care workers ( 8 ).
One of the core tenets of medical ethics is the principle of nonmaleficence. This is best described as our unique duty to “do no harm,” as described in the Hippocratic Oath, which states physicians must “act in a way which does no harm” ( 9 ). Given the data that suggest even with the most recent highly virulent and contagious mutations of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, there is a decreased risk of transmission from vaccinated individuals, hence vaccinated health care workers uphold their duty of nonmaleficence to their patients. In contrast, remaining unvaccinated potentially exposes highly vulnerable patients and coworkers to the virus and potentially COVID-19. In addition, a health care worker who is unavailable due to COVID-19 and who is unvaccinated unfairly shifts more work burden on to their vaccinated coworkers and reduces the pool of health care workers available to society, which is worse during a pandemic.
Given the trust that society has in the medical profession, and the resultant duty that health care workers owe to society, ensuring wellness both physically and emotionally is integral in providing ethically based care. Health care workers aim not just to avoid causing harm to patients, but to ensure good. Beneficence , another throwback to the Hippocratic Oath, is defined as “an act of charity, mercy, and kindness with a strong connotation of doing good to others including moral obligation. All professionals have the foundational moral imperative of doing right. In the context of the professional–client relationship, the professional is obligated to, always and without exception, favor the well-being and interest of the client” ( 10 ). This definition is especially helpful in reiterating the fiduciary responsibility health care workers have to their patients and the need to ensure they are willing and able to provide ethical care, which implies having not only the technical and experiential knowledge, but the appropriate state of mind and physical well-being. A sick health care worker diminishes the potency of the physician–patient relationship.
As alluded to earlier, public health ethics, policy, and law have generally been structured around the utilitarian principle of doing the best for the most ( 11 ). Its underlying theme is to maximize the good in society to the benefit of the most members of that society. It acknowledges that there are certain segments of the society in which individual liberties may be affected to protect the welfare of other members, but it is felt to be just and appropriate ethically for the greater good of society. Like all other vaccines mandated to attend school or for employment in a health care facility in the United States, once the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine was approved by the FDA, its role in risk-mitigating the serious sequela of COVID-19 was sufficient justification to mandate that all health care workers add this vaccine to the list of mandatory vaccines, thereby ensuring protection for the vulnerable who seek medical care ( 12 ). Serving as a mini-cosmos of society, vaccine mandates for health care workers ensure that the greatest utility (i.e., protection from COVID-19) is achieved.
Argument against Vaccine Mandates
Utilitarianism appeals to us during times of crisis. It offers an enticing solution: do the greatest good, to the greatest number of people. However, the pursuit of utilitarian ideals often challenges the rights of the individual. In the COVID-19 pandemic, the utilitarian argument has been applied to vaccine mandates.
Why is vaccination a moral issue? The decision to become vaccinated and the prevention of harm fulfills the first categorical imperative and it also has the appeal of prudence. Vaccine mandates risk treating individuals as a means to an end and risk running afoul of the second categorical imperative. Utilitarian advocates would argue for a vaccine mandate as it provides the greatest well-being for the most people possible. The utilitarian argument that vaccine mandates are doing the best for the most falls flat when taking into consideration that a vaccine for the seasonal influenza virus (flu), for example, is available and, although required by many health care facilities, it is not mandated, as there is a workaround for those who refuse it. Using the principle of consistency to ensure like circumstances are treated similarly: if utilitarianism was to be the underpinning of the COVID-19 vaccine mandate, one would expect that the flu vaccine would also be mandated, as its impact on the health care field is just as large as SARS-CoV-2, yet only four states require it ( 13 ). Furthermore, individuals who choose not to receive an influenza vaccine are not harassed, stigmatized, or threatened with termination of their job, but are allowed to seek exemptions or are required to mask for the entirety of the flu season. Consistency is key in ethical principles and consistency in this utilitarian argument seems to be lacking.
To the “pro” argument on acceptability, we must disagree. It requires very little formal research to establish that many things deemed absolutely correct 100 years ago may not be acceptable today. Society only questions the “status quo” when enough individuals refuse to follow it, or when advances in science or other studies elevate our collective knowledge. There are, and have been, many “accepted” practices that are not fair, equitable, just, or ethical, and hence acceptability as a criterion lacks merits. Likewise, we must question the “fiduciary” argument that blindly mandates physician wellness and interests below that of their patients. Moral injury, burnout, post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, for example, are all concepts permeating the medical (especially EM) literature, and are directly related to the work environment of medicine. Although it is important in general terms to hold the patient's medical interests over one's own, does this require self-sacrifice in order to uphold the Hippocratic Oath? Are we, as health care workers, now enslaved to the profession without any rights of our own? We are entrusted with great responsibility and trust by society and have access to the greatest bodies of knowledge, yet as subject matter experts we are not afforded the same “right to refuse” as any other autonomous agent in the free world. For that, we call foul.
It is our position that Kantian ethics provide a solution to this dilemma and address both the concerns of individual rights and society at large. Kant's moral theory describes individuals as having intrinsic worth as autonomous, rational agents. He describes a concept of “good will” in which people have the capacity to recognize a moral act and the duty to act on it. This is an ongoing, conscious process ( 14 ). In contrast, utilitarianism would view the intrinsic value of individual choice in its effects. In Jeremy Bentham's interpretation, this was hedonism: the degree of how much pleasure could be caused or pain avoided ( 15 , 16 ). Other philosophers view the ideal outcomes of personal decisions as well-being. For the utilitarian John Stuart Mill, decisions or rules were also viewed as moral to the degree in which they benefited the majority ( 17 ).
Central to Kant's work were his categorical imperatives, that is, moral laws applicable to all individuals ( 14 ). These are laws freely accessible to individuals using reason and intellect and apply to all equally. The first principle described the concept of universalizability; a moral actor considers the principle underlying their personal decisions and the effect if all other individuals acted in a similar manner. The second principle emphasizes that humanity should be an end in itself, and never a means to an end. As human beings are rational and autonomous, we can set our own goals; humans exist for themselves and are morally self-governed.
It is important to note that Kant thought that decisions could be divided into those that were prudent and those that were ethical ( 14 ). Often, these categories coincide. During the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a wide range of public health decisions made with the intent of limiting morbidity and mortality. Masking, travel restrictions, and quarantining after exposure fall into both categories. A prudent individual, concerned about their own health and considering their duty to preserve both their own health and that of their peers would reasonably adopt these measures to preserve their own health and longevity as well as that of their peers.
Kantian philosophers must argue against these mandates, as it is the individual's duty to identify the moral good offered by these vaccines and take the appropriate action. Compelling action and violating personal autonomy to reach the so-called, “herd immunity” would be a moral evil.
To this dilemma, we offer a solution. We have seen the public's trust in clinicians and the medical establishment erode throughout this pandemic, as people chafe against changing mandates and norms. The evidence we have of the benefit of the vaccines for our patients is clear; it is both a prudent and moral decision. But it is a personal decision based on moral duty. Physicians must continue to educate and guide to moral clarity. To do anything else is to treat our patients as a means to an end.
We have presented ethical arguments both for and against a mandate for health care workers to receive vaccination against COVID-19. A key argument for vaccine mandates rests on the ethical requirements for health care workers to place the well-being of the community as a whole above their own individual interests. Whereas, the key arguments against mandates state that an individual's autonomy must be primary, and that autonomy should not be overridden or ignored in the name of a “higher” good.
Both arguments being compelling, it is the opinion of the Ethics Committee of AAEM that vaccine mandates for health care workers are ethically just and appropriate, and the benefit to society far outweighs the minor inconvenience to an individual's personal liberties. This opinion rests on the following key conditions: the risks of the disease are significant to society as a whole, the vaccine has been FDA-approved (which implies thoroughly tested and deemed “safe”), and there are exceptions for those with legitimate medical or religious reasons. Vaccine mandates are consistent with professional ethics and fiduciary duties to patients. Society's interest should be held as primary over individual interests, especially as it concerns an action that is consistent and congruent with actions in our well established and accepted practice of medicine. That said, as we see a shift from pandemic to endemic status, and the research grows on natural vs. obtained immunity, there may be a shift in this opinion over time on mandatory COVID-19 vaccination.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the AAEM Ethics Committee for their assistance in providing critical feedback on this manuscript.
Students’ Essays on Infectious Disease Prevention, COVID-19 Published Nationwide
As part of the BIO 173: Global Change and Infectious Disease course, Professor Fred Cohan assigns students to write an essay persuading others to prevent future and mitigate present infectious diseases. If students submit their essay to a news outlet—and it’s published—Cohan awards them with extra credit.
As a result of this assignment, more than 25 students have had their work published in newspapers across the United States. Many of these essays cite and applaud the University’s Keep Wes Safe campaign and its COVID-19 testing protocols.
Cohan, professor of biology and Huffington Foundation Professor in the College of the Environment (COE), began teaching the Global Change and Infectious Disease course in 2009, when the COE was established. “I wanted very much to contribute a course to what I saw as a real game-changer in Wesleyan’s interest in the environment. The course is about all the ways that human demands on the environment have brought us infectious diseases, over past millennia and in the present, and why our environmental disturbances will continue to bring us infections into the future.”
Over the years, Cohan learned that he can sustainably teach about 170 students every year without running out of interested students. This fall, he had 207. Although he didn’t change the overall structure of his course to accommodate COVID-19 topics, he did add material on the current pandemic to various sections of the course.
“I wouldn’t say that the population of the class increased tremendously as a result of COVID-19, but I think the enthusiasm of the students for the material has increased substantially,” he said.
To accommodate online learning, Cohan shaved off 15 minutes from his normal 80-minute lectures to allow for discussion sections, led by Cohan and teaching assistants. “While the lectures mostly dealt with biology, the discussions focused on how changes in behavior and policy can solve the infectious disease problems brought by human disturbance of the environment,” he said.
Based on student responses to an introspective exam question, Cohan learned that many students enjoyed a new hope that we could each contribute to fighting infectious disease. “They discovered that the solution to infectious disease is not entirely a waiting game for the right technologies to come along,” he said. “Many enjoyed learning about fighting infectious disease from a moral and social perspective. And especially, the students enjoyed learning about the ‘socialism of the microbe,’ how preventing and curing others’ infections will prevent others’ infections from becoming our own. The students enjoyed seeing how this idea can drive both domestic and international health policies.”
A sampling of the published student essays are below:
Alexander Giummo ’22 and Mike Dunderdale’s ’23 op-ed titled “ A National Testing Proposal: Let’s Fight Back Against COVID-19 ” was published in the Journal Inquirer in Manchester, Conn.
They wrote: “With an expansive and increased testing plan for U.S. citizens, those who are COVID-positive could limit the number of contacts they have, and this would also help to enable more effective contact tracing. Testing could also allow for the return of some ‘normal’ events, such as small social gatherings, sports, and in-person class and work schedules.
“We propose a national testing strategy in line with the one that has kept Wesleyan students safe this year. The plan would require a strong push by the federal government to fund the initiative, but it is vital to successful containment of the virus.
“Twice a week, all people living in the U.S. should report to a local testing site staffed with professionals where the anterior nasal swab Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test, used by Wesleyan and supported by the Broad Institute, would be implemented.”
Kalyani Mohan ’22 and Kalli Jackson ’22 penned an essay titled “ Where Public Health Meets Politics: COVID-19 in the United States ,” which was published in Wesleyan’s Arcadia Political Review .
They wrote: “While the U.S. would certainly benefit from a strengthened pandemic response team and structural changes to public health systems, that alone isn’t enough, as American society is immensely stratified, socially and culturally. The politicization of the COVID-19 pandemic shows that individualism, libertarianism and capitalism are deeply ingrained in American culture, to the extent that Americans often blind to the fact community welfare can be equivalent to personal welfare. Pandemics are multifaceted, and preventing them requires not just a cultural shift but an emotional one amongst the American people, one guided by empathy—towards other people, different communities and the planet. Politics should be a tool, not a weapon against its people.”
Sydnee Goyer ’21 and Marcel Thompson’s ’22 essay “ This Flu Season Will Be Decisive in the Fight Against COVID-19 ” also was published in Arcadia Political Review .
“With winter approaching all around the Northern Hemisphere, people are preparing for what has already been named a “twindemic,” meaning the joint threat of the coronavirus and the seasonal flu,” they wrote. “While it is known that seasonal vaccinations reduce the risk of getting the flu by up to 60% and also reduce the severity of the illness after the contamination, additional research has been conducted in order to know whether or not flu shots could reduce the risk of people getting COVID-19. In addition to the flu shot, it is essential that people remain vigilant in maintaining proper social distancing, washing your hands thoroughly, and continuing to wear masks in public spaces.”
An op-ed titled “ The Pandemic Has Shown Us How Workplace Culture Needs to Change ,” written by Adam Hickey ’22 and George Fuss ’21, was published in Park City, Utah’s The Park Record .
They wrote: “One review of academic surveys (most of which were conducted in the United States) conducted in 2019 found that between 35% and 97% of respondents in those surveys reported having attended work while they were ill, often because of workplace culture or policy which generated pressure to do so. Choosing to ignore sickness and return to the workplace while one is ill puts colleagues at risk, regardless of the perceived severity of your own illness; COVID-19 is an overbearing reminder that a disease that may cause mild, even cold-like symptoms for some can still carry fatal consequences for others.
“A mandatory paid sick leave policy for every worker, ideally across the globe, would allow essential workers to return to work when necessary while still providing enough wiggle room for economically impoverished employees to take time off without going broke if they believe they’ve contracted an illness so as not to infect the rest of their workplace and the public at large.”

Women’s cross country team members and classmates Jane Hollander ’23 and Sara Greene ’23 wrote a sports-themed essay titled “ This Season, High School Winter Sports Aren’t Worth the Risk ,” which was published in Tap into Scotch Plains/Fanwood , based in Scotch Plains, N.J. Their essay focused on the risks high school sports pose on student-athletes, their families, and the greater community.
“We don’t propose cutting off sports entirely— rather, we need to be realistic about the levels at which athletes should be participating. There are ways to make practices safer,” they wrote. “At [Wesleyan], we began the season in ‘cohorts,’ so the amount of people exposed to one another would be smaller. For non-contact sports, social distancing can be easily implemented, and for others, teams can focus on drills, strength and conditioning workouts, and skill-building exercises. Racing sports such as swim and track can compete virtually, comparing times with other schools, and team sports can focus their competition on intra-team scrimmages. These changes can allow for the continuation of a sense of normalcy and team camaraderie without the exposure to students from different geographic areas in confined, indoor spaces.”
Brook Guiffre ’23 and Maddie Clarke’s ’22 op-ed titled “ On the Pandemic ” was published in Hometown Weekly, based in Medfield, Mass.
“The first case of COVID-19 in the United States was recorded on January 20th, 2020. For the next month and a half, the U.S. continued operating normally, while many other countries began their lockdown,” they wrote. “One month later, on February 29th, 2020, the federal government approved a national testing program, but it was too little too late. The U.S. was already in pandemic mode, and completely unprepared. Frontline workers lacked access to N-95 masks, infected patients struggled to get tested, and national leaders informed the public that COVID-19 was nothing more than the common flu. Ultimately, this unpreparedness led to thousands of avoidable deaths and long-term changes to daily life. With the risk of novel infectious diseases emerging in the future being high, it is imperative that the U.S. learn from its failure and better prepare for future pandemics now. By strengthening our public health response and re-establishing government organizations specialized in disease control, we have the ability to prevent more years spent masked and six feet apart.”
In addition, their other essay, “ On Mass Extinction ,” was also published by Hometown Weekly .
“The sixth mass extinction—which scientists have coined as the Holocene Extinction—is upon us. According to the United Nations, around one million plant and animal species are currently in danger of extinction, and many more within the next decade. While other extinctions have occurred in Earth’s history, none have occurred at such a rapid rate,” they wrote. “For the sake of both biodiversity and infectious diseases, it is in our best interest to stop pushing this Holocene Extinction further.”
An essay titled “ Learning from Our Mistakes: How to Protect Ourselves and Our Communities from Diseases ,” written by Nicole Veru ’21 and Zoe Darmon ’21, was published in My Hometown Bronxville, based in Bronxville, N.Y.
“We can protect ourselves and others from future infectious diseases by ensuring that we are vaccinated,” they wrote. “Vaccines have high levels of success if enough people get them. Due to vaccines, society is no longer ravaged by childhood diseases such as mumps, rubella, measles, and smallpox. We have been able to eradicate diseases through vaccines; smallpox, one of the world’s most consequential diseases, was eradicated from the world in the 1970s.
“In 2000, the U.S. was nearly free of measles, yet, due to hesitations by anti-vaxxers, there continues to be cases. From 2000–2015 there were over 18 measles outbreaks in the U.S. This is because unless a disease is completely eradicated, there will be a new generation susceptible.
“Although vaccines are not 100% effective at preventing infection, if we continue to get vaccinated, we protect ourselves and those around us. If enough people are vaccinated, societies can develop herd immunity. The amount of people vaccinated to obtain herd immunity depends on the disease, but if this fraction is obtained, the spread of disease is contained. Through herd immunity, we protect those who may not be able to get vaccinated, such as people who are immunocompromised and the tiny portion of people for whom the vaccine is not effective.”
Dhruvi Rana ’22 and Bryce Gillis ’22 co-authored an op-ed titled “ We Must Educate Those Who Remain Skeptical of the Dangers of COVID-19 ,” which was published in Rhode Island Central .
“As Rhode Island enters the winter season, temperatures are beginning to drop and many studies have demonstrated that colder weather and lower humidity are correlated with higher transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19,” they wrote. “By simply talking or breathing, we release respiratory droplets and aerosols (tiny fluid particles which could carry the coronavirus pathogen), which can remain in the air for minutes to hours.
“In order to establish herd immunity in the US, we must educate those who remain skeptical of the dangers of COVID-19. Whether community-driven or state-funded, educational campaigns are needed to ensure that everyone fully comprehends how severe COVID-19 is and the significance of airborne transmission. While we await a vaccine, it is necessary now more than ever that we social distance, avoid crowds, and wear masks, given that colder temperatures will likely yield increased transmission of the virus.”
Danielle Rinaldi ’21 and Verónica Matos Socorro ’21 published their op-ed titled “ Community Forum: How Mask-Wearing Demands a Cultural Reset ” in the Ewing Observer , based in Lawrence, N.J.
“In their own attempt to change personal behavior during the pandemic, Wesleyan University has mandated mask-wearing in almost every facet of campus life,” they wrote. “As members of our community, we must recognize that mask-wearing is something we are all responsible and accountable for, not only because it is a form of protection for us, but just as important for others as well. However, it seems as though both Covid fatigue and complacency are dominating the mindsets of Americans, leading to even more unwillingness to mask up. Ultimately, it is inevitable that this pandemic will not be the last in our lifespan due to global warming creating irreversible losses in biodiversity. As a result, it is imperative that we adopt the norm of mask-wearing now and undergo a culture shift of the abandonment of an individualistic mindset, and instead, create a society that prioritizes taking care of others for the benefit of all.”

Shayna Dollinger ’22 and Hayley Lipson ’21 wrote an essay titled “ My Pandemic Year in College Has Brought Pride and Purpose. ” Dollinger submitted the piece, rewritten in first person, to Jewish News of Northern California . Read more about Dollinger’s publication in this News @ Wesleyan article .
“I lay in the dead grass, a 6-by-6-foot square all to myself. I cheer for my best friend, who is on the stage constructed at the bottom of Foss hill, dancing with her Bollywood dance group. Masks cover their ordinarily smiling faces as their bodies move in sync. Looking around at friends and classmates, each in their own 6-by-6 world, I feel an overwhelming sense of normalcy.
“One of the ways in which Wesleyan has prevented outbreaks on campus is by holding safe, socially distanced events that students want to attend. By giving us places to be and things to do on the weekends, we are discouraged from breaking rules and causing outbreaks at ‘super-spreader’ events.”
An op-ed written by Luna Mac-Williams ’22 and Daëlle Coriolan ’24 titled “ Collectivist Practices to Combat COVID-19 ” was published in the Wesleyan Argus .
“We are embroiled in a global pandemic that disproportionately affects poor communities of color, and in the midst of a higher cultural consciousness of systemic inequities,” they wrote. “A cultural shift to center collectivist thought and action not only would prove helpful in disease prevention, but also belongs in conversation with the Black Lives Matter movement. Collectivist models of thinking effectively target the needs of vulnerable populations including the sick, the disenfranchised, the systematically marginalized. Collectivist systems provide care, decentering the capitalist, individualist system, and focusing on how communities can work to be self-sufficient and uplift our own neighbors.”
An essay written by Maria Noto ’21 , titled “ U.S. Individualism Has Deadly Consequences ,” is published in the Oneonta Daily Star , based in Oneonta, N.Y.
She wrote, “When analyzing the cultures of certain East Asian countries, several differences stand out. For instance, when people are sick and during the cold and flu season, many East Asian cultures, including South Korea, use mask-wearing. What is considered a threat to freedom by some Americans is a preventive action and community obligation in this example. This, along with many other cultural differences, is insightful in understanding their ability to contain the virus.
“These differences are deeply seeded in the values of a culture. However, there is hope for the U.S. and other individualistic cultures in recognizing and adopting these community-centered approaches. Our mindset needs to be revolutionized with the help of federal and local assistance: mandating masks, passing another stimulus package, contact tracing, etc… However, these measures will be unsuccessful unless everyone participates for the good of a community.”
A published op-ed by Madison Szabo ’23 , Caitlyn Ferrante ’23 ran in the Two Rivers Times . The piece is titled “ Anxiety and Aspiration: Analyzing the Politicization of the Pandemic .”
John Lee ’21 and Taylor Goodman-Leong ’21 have published their op-ed titled “ Reassessing the media’s approach to COVID-19 ” in Weekly Monday Cafe 24 (Page 2).
An essay by Eleanor Raab ’21 and Elizabeth Nefferdorf ’22 titled “ Preventing the Next Epidemic ” was published in The Almanac .
- Keep Wes Safe
- student publications
- Teaching during the pandemic
Related Articles
New Research Suggests Ocean May Increase in Oxygen During Warming
Wesleyan in the news: march 2024.
“You Just Have to Read This…”: Books by Wesleyan Authors Anbinder ’84, Hill ’93, and Olson ’97
Previous matesan's new book explores political violence, islamist mobilization in egypt and indonesia, next students launch fun, interactive virtual program for school-aged kids.
Special Issue: COVID-19
This essay was published as part of a Special Issue on Misinformation and COVID-19, guest-edited by Dr. Meghan McGinty (Director of Emergency Management, NYC Health + Hospitals) and Nat Gyenes (Director, Meedan Digital Health Lab).
Peer Reviewed
The causes and consequences of COVID-19 misperceptions: Understanding the role of news and social media
Article metrics.
CrossRef Citations
Altmetric Score
PDF Downloads
We investigate the relationship between media consumption, misinformation, and important attitudes and behaviours during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. We find that comparatively more misinformation circulates on Twitter, while news media tends to reinforce public health recommendations like social distancing. We find that exposure to social media is associated with misperceptions regarding basic facts about COVID-19 while the inverse is true for news media. These misperceptions are in turn associated with lower compliance with social distancing measures. We thus draw a clear link from misinformation circulating on social media, notably Twitter, to behaviours and attitudes that potentially magnify the scale and lethality of COVID-19.
Department of Political Science, McGill University, Canada
Munk School of Global Affairs and Public Policy, University of Toronto, Canada
Max Bell School of Public Policy, McGill University, Canada
School of Computer Science, McGill University, Canada
Department of Languages, Literatures, and Cultures, McGill University, Canada
Computer Science Program, McGill University, Canada

Research Questions
- How prevalent is misinformation surrounding COVID-19 on Twitter, and how does this compare to Canadian news media?
- Does the type of media one is exposed to influence social distancing behaviours and beliefs about COVID-19?
- Is there a link between COVID-19 misinformation and perceptions of the pandemic’s severity and compliance with social distancing recommendations?
Essay Summary
- We evaluate the presence of misinformation and public health recommendations regarding COVID-19 in a massive corpus of tweets as well as all articles published on nineteen Canadian news sites. Using these data, we show that preventative measures are more encouraged and covered on traditional news media, while misinformation appears more frequently on Twitter.
- To evaluate the impact of this greater level of misinformation, we conducted a nationally representative survey that included questions about common misperceptions regarding COVID-19, risk perceptions, social distancing compliance, and exposure to traditional news and social media. We find that being exposed to news media is associated with fewer misperceptions and more social distancing compliance while conversely, social media exposure is associated with more misperceptions and less social distancing compliance.
- Misperceptions regarding the virus are in turn associated with less compliance with social distancing measures, even when controlling for a broad range of other attitudes and characteristics.
- Association between social media exposure and social distancing non-compliance is eliminated when accounting for effect of misperceptions, providing evidence that social media is associated with non-compliance through increasing misperceptions about the virus.
Implications
The COVID-19 pandemic has been accompanied by a so-called “infodemic”—a global spread of misinformation that poses a serious problem for public health. Infodemics are concerning because the spread of false or misleading information has the capacity to change transmission patterns (Kim et al., 2019) and consequently the scale and lethality of a pandemic. This information can be shared by any media, but there is reason to be particularly concerned about the role that social media, such as Facebook and Twitter, play in incidentally boosting misperceptions. These platforms are increasingly relied upon as primary sources of news (Mitchell et al., 2016) and misinformation has been heavily documented on them (Garrett, 2019; Vicario et al., 2016). Scholars have found medical and health misinformation on the platforms, including that related to vaccines (Radzikowski et al., 2016) and other virus epidemics such as Ebola (Fung et al., 2016) and Zika (Sharma et al., 2017).
However, misinformation content typically makes up a low percentage of overall discussion of a topic (e.g. Fung et al., 2016) and mere exposure to misinformation does not guarantee belief in that misinformation. More research is thus needed to understand the extent and consequences of misinformation surrounding COVID-19 on social media. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Twitter, Facebook and other platforms have engaged in efforts to combat misinformation but they have continued to receive widespread criticism that misinformation is still appearing on prominent pages and groups (Kouzy et al., 2020; NewsGuard, 2020). The extent to which misinformation continues to circulate on these platforms and influence people’s attitudes and behaviours is still very much an open question.
Here, we draw on three data sets and a sequential mixed method approach to better understand the consequences of online misinformation for important behaviours and attitudes. First, we collected nearly 2.5 million tweets explicitly referring to COVID-19 in the Canadian context. Second, we collected just over 9 thousand articles from nineteen Canadian English-language news sites from the same time period. We coded both of these media sets for misinformation and public health recommendations. Third, we conducted a nationally representative survey that included questions related to media consumption habits, COVID-19 perceptions and misperceptions, and social distancing compliance. As our outcome variables are continuous, we use Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression to identify relationships between news and social media exposure, misperceptions, compliance with social distancing measures, and risk perceptions. We use these data to illustrate: 1) the relative prevalence of misinformation on Twitter; and 2) a powerful association between social media usage and misperceptions, on the one hand, and social distancing non-compliance on the other.
Misinformation and compliance with social distancing
We first compare the presence of misinformation on Twitter with that on news media and find, consistent with the other country cases (Chadwick & Vaccari, 2019; Vicario et al., 2016), comparatively higher levels of misinformation circulating on the social media platform. We also found that recommendations for safe practices during the pandemic (e.g. washing hands, social distancing) appeared much more frequently in the Canadian news media. These findings are in line with literature examining fake news which finds a large difference in information quality across media (Al-Rawi, 2019; Guess & Nyhan, 2018).
Spending time in a media environment that contains misinformation is likely to change attitudes and behaviours. Even if users are not nested in networks that propagate misinformation, they are likely to be incidentally exposed to information from a variety of perspectives (Feezell, 2018; Fletcher & Nielsen, 2018; Weeks et al., 2017). Even a highly curated social media feed is thus still likely to contain misinformation. As cumulative exposure to misinformation increases, users are likely to experience a reinforcement effect whereby familiarity leads to stronger belief (Dechêne et al., 2010).
To evaluate this empirically, we conducted a national survey that included questions on information consumption habits and a battery of COVID-19 misperceptions that could be the result of exposure to misinformation. We find that those who self-report exposure to the misinformation-rich social media environment do tend to have more misperceptions regarding COVID-19. These findings are consistent with others that link exposure to misinformation and misperceptions (Garrett et al., 2016; Jamieson & Albarracín, 2020). Social media users also self-report less compliance with social distancing.
Misperceptions are most meaningful when they impact behaviors in dangerous ways. During a pandemic, misperceptions can be fatal. In this case, we find that misperceptions are associated with reduced COVID-19 risk perceptions and with lower compliance with social distancing measures. We continue to find strong effects after controlling for socio-economic characteristics as well as scientific literacy. After accounting for the effect of misperceptions on social distancing non-compliance, social media usage no longer has a significant association with non-compliance, providing evidence that social media may lead to less social distancing compliance through its effect on COVID-19 misperceptions.
While some social media companies have made efforts to suppress misinformation on their platforms, there continues to be a high level of misinformation relative to news media. Highly polarized political environments and media ecosystems can lead to the spread of misinformation, such as in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic (Allcott et al., 2020; Motta et al., 2020). But even in healthy media ecosystems with less partisan news (Owen et al., 2020), social media can continue to facilitate the spread of misinformation. There is a real danger that without concerted efforts to reduce the amount of misinformation shared on social media, the large-scale social efforts required to combat COVID-19 will be undermined.
We contribute to a growing base of evidence that misinformation circulating on social media poses public health risks and join others in calling for social media companies to put greater focus on flattening the curve of misinformation (Donovan, 2020). These findings also provide governments with stronger evidence that the misinformation circulating on social media can be directly linked to misperceptions and public health risks. Such evidence is essential for them to chart an effective policy course. Finally, the methods and approach developed in this paper can be fruitfully applied to study other waves of misinformation and the research community can build upon the link clearly drawn between misinformation exposure, misperceptions, and downstream attitudes and behaviours.
We found use of social media platforms broadly contributes to misperceptions but were unable to precise the overall level of misinformation circulating on non-Twitter social media. Data access for researchers to platforms such as Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram is limited and virtually non-existent for SnapChat, WhatsApp, and WeChat. Cross-platform content comparisons are an important ingredient for a rich understand of the social media environment and these social media companies must better open their platforms to research in the public interest.
Finding 1: Misinformation about COVID-19 is circulated more on Twitter as compared to traditional media.
We find large differences between the quality of information shared about COVID-19 on traditional news and Twitter. Figure 1 shows the percentage of COVID-19 related content that contains information linked to a particular theme. The plot reports the prevalence of information on both social and news media for: 1) three specific pieces of misinformation; 2) a general set of content that describes the pandemic itself as a conspiracy or a hoax; and 3) advice about hygiene and social distancing during the pandemic. We differentiate content that shared misinformation (red in the plot) from content that debunked misinformation (green in the plot).
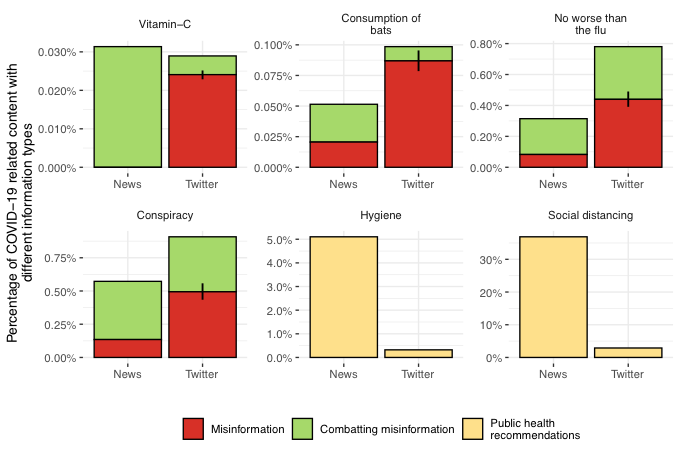
There are large differences between the levels of misinformation on Twitter and news media. Misinformation was comparatively more common on Twitter across all four categories, while debunking was relatively more common in traditional news. Meanwhile, advice on hygiene and social distancing appeared much more frequently in news media. Note that higher percentages are to be expected for longer format news articles since we rely on keyword searches for identification. This makes the misinformation findings even starker – despite much higher average word counts, far fewer news articles propagate misinformation.
Finding 2: There is a strong association between social media exposure and misperceptions about COVID-19. The inverse is true for exposure to traditional news.
Among our survey respondents we find a corresponding strong association between social media exposure and misperceptions about COVID-19. These results are plotted in Figure 2, with controls included for both socioeconomic characteristics and demographics. Moving from no social media exposure to its maximum is expected to increase one’s misperceptions of COVID-19 by 0.22 on the 0-1 scale and decreased self-reported social distancing compliance by 0.12 on that same scale.
This result stands in stark contrast with the observed relationship between traditional news exposure and our outcome measures. Traditional news exposure is positively associated with correct perceptions regarding COVID-19. Moving from no news exposure to its highest level is expected to reduce misperceptions by 0.12 on the 0-1 scale and to increase social distancing compliance by 0.28 on that same scale. The effects are plotted in Figure 2. Social media usage appears to be correlated with COVID-19 misperceptions, suggesting these misperceptions are partially a result of misinformation on social media. The same cannot be said of traditional news exposure.
Finding 3: Misperceptions about the pandemic are associated with lower levels of risk perceptions and social distancing compliance.
COVID-19 misperceptions are also powerfully associated with lower levels of social distancing compliance. Moving from the lowest level of COVID-19 misperceptions to its maximum is associated with a reduction of one’s social distancing by 0.39 on the 0-1 scale. The previously observed relationship between social media exposure and misperceptions disappears, suggestive of a mediated relationship. That is, social media exposure increases misperceptions, which in turn reduces social distancing compliance. Misperceptions is also weakly associated with lower COVID-19 risk perceptions. Estimates from our models using COVID-19 concern as the outcome can be found in the left panel of Figure 3, while social distancing can be found in the right panel.
Finally, we also see that the relationship between misinformation and both social distancing compliance and COVID-19 concern hold when including controls for science literacy and a number of fundamental predispositions that are likely associated with both misperceptions and following the advice of scientific experts, such as anti-intellectualism, pseudoscientific beliefs, and left-right ideology. These estimates can similarly be found in Figure 3.
Canadian Twitter and news data were collected from March 26 th to April 6 th , 2020. We collected all English-language tweets from a set of 620,000 users that have been determined to be likely Canadians. For inclusion, a given user must self-identify as Canadian-based, follow a large number of Canadian political elite accounts, or frequently use Canadian-specific hashtags. News media was collected from nineteen prominent Canadian news sites with active RSS feeds. These tweets and news articles were searched for “covid” or “coronavirus”, leaving a sample of 2.25 million tweets and 8,857 news articles.
Of the COVID-19 related content, we searched for terms associated with four instances of misinformation that circulated during the COVID-19 pandemic: that COVID-19 was no more serious than the flu, that vitamin C or other supplements will prevent contraction of the virus, that the initial animal-to-human transfer of the virus was the direct result of eating bats, or that COVID-19 was a hoax or conspiracy. Given that we used keyword searches to identify content, we manually reviewed a random sample of 500 tweets from each instance of misinformation. Each tweet was coded as one of four categories: propagating misinformation, combatting misinformation, content with the relevant keywords but unrelated to misinformation, or content that refers to the misinformation but does not offer comment.
We then calculated the overall level of misinformation for that instance on Twitter by multiplying the overall volume of tweets by the proportion of hand-coded content where misinformation was identified. Each news article that included relevant keywords was similarly coded. The volume of the news mentioning these terms was sufficiently low that all news articles were hand coded. To identify health recommendations, we used a similar keyword search for terms associated with particular recommendations: 1) social distancing including staying at home, staying at least 6 feet or 2 meters away and avoiding gatherings; and 2) washing hands and not touching any part of your face. 1 Further details on the media collection strategy and hand-coding schema are available in the supporting materials.
For survey data, we used a sample of nearly 2,500 Canadian citizens 18 years or older drawn from a probability-based online national panel fielded from April 2-6, 2020. Quotas we set on age, gender, region, and language to ensure sample representativeness, and data was further weighted within region by gender and age based on the 2016 Canadian census.
We measure levels of COVID-19 misperceptions by asking respondents to rate the truthfulness of a series of nine false claims, such as the coronavirus being no worse than the seasonal flu or that it can be warded off with Vitamin C. Each was asked on a scale from definitely false (0) to definitely true (5). We use Cronbach’s Alpha as an indicator of scale reliability. Cronbach’s Alpha ranges from 0-1, with scores above 0.8 indicating the reliability is “good.” These items score 0.88, so we can safely construct a 0-1 scale of misperceptions from them.
We evaluate COVID-19 risk perceptions with a pair of questions asking respondents how serious of a threat they believe the pandemic to be for themselves and for Canadians, respectively. Each question was asked on a scale from not at all (0) to very (4). We construct a continuous index with these items.
We quantify social distancing by asking respondents to indicate which of a series of behaviours they had undertaken in response to the pandemic, such as working from home or avoiding in-person contact with friends, family, and acquaintances. We use principal component analysis (PCA) to reduce the number of dimensions in these data while minimizing information loss. The analysis revealed 2 distinct dimensions in our questions. One dimension includes factors strongly determined by occupation, such as working from home and switching to online meetings. The other dimension contains more inclusive behaviours such as avoiding contact, travel, and crowded places. We generate predictions from the PCA for this latter dimension to use in our analyses. The factor loadings can be found in Table A1 of the supporting materials.
We gauge news and social media consumption by asking respondents to identify news outlets and social media platforms they have used over the past week for political news. The list of news outlets included 17 organizations such as mainstream sources like CBC and Global, and partisan outlets like Rebel Media and National Observer. The list of social media platforms included 10 options such as Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and Instagram. We sum the total number of outlets/platforms respondents report using and take the log to adjust for extreme values. We measure offline political discussion with an index based on questions asking how often respondents have discussed politics with family, friends, and acquaintances over the past week. Descriptions of our primary variables can be found in Table A2 of the supporting materials.
We evaluate our hypotheses using a standard design that evaluates the association between our explanatory and outcome variables controlling for other observable factors we measured. In practice, randomly assigning social media exposure is impractical, while randomly assigning misinformation is unethical. This approach allows us to describe these relationships, though we cannot make definite claims to causality.
We hypothesize that social media exposure is associated with misinformation on COVID-19. Figure 2 presents the coefficients of models predicting the effects of news exposure, social media exposure, and political discussion on COVID-19 misinformation, risk perceptions, and social distancing. Socio-economic and demographic control estimates are not displayed. Full estimation results can be found in the Table A3 of the supporting materials.
We further hypothesize that COVID-19 misinformation is associated with lower COVID-19 risk perceptions and less social distancing compliance. Figure 3 presents the coefficients for models predicting the effects of misinformation, news exposure, and social media exposure on severity perceptions and social distancing. We show models with and without controls for science literacy and other predispositions. Full estimation results can be found in the Table A4 of the supporting materials.
Limitations and robustness
A study such as this comes with clear limitations. First, we have evaluated information coming from only a section of the overall media ecosystem and during a specific time-period. The level of misinformation differs across platforms and online news sites and a more granular investigation into these dynamics would be valuable. Our analysis suggests that similar dynamics exist across social media platforms, however. In the supplementary materials we show that associations between misperceptions and social media usage are even higher for other social media platforms, suggesting that our analysis of Twitter content may underrepresent the prevalence of misinformation on social media writ large. As noted above, existing limitations on data access make such cross-platform research difficult.
Second, our data is drawn from a single country and language case study and other countries may have different media environments and levels of misinformation circulating on social media. We anticipate the underlying dynamics found in this paper to hold across these contexts, however. Those who consume information from platforms where misinformation is more prevalent will have greater misperceptions and that these misperceptions will be linked to lower compliance with social distancing and lower risk perceptions. Third, an ecological problem is present wherein we do not link survey respondents directly to their social media consumption (and evaluation of the misinformation they are exposed to) and lack the ability to randomly assign social media exposure to make a strong causal argument. We cannot and do not make a causal argument here but argue instead that there is strong evidence for a misinformation to misperceptions to lower social distancing compliance link.
- / Fake News
- / Mainstream Media
- / Public Health
- / Social Media
Cite this Essay
Bridgman, A., Merkley, E., Loewen, P. J., Owen, T., Ruths, D., Teichmann, L., & Zhilin, O. (2020). The causes and consequences of COVID-19 misperceptions: Understanding the role of news and social media. Harvard Kennedy School (HKS) Misinformation Review . https://doi.org/10.37016/mr-2020-028
Bibliography
Allcott, H., Boxell, L., Conway, J. C., Gentzkow, M., Thaler, M., & Yang, D. Y. (2020). Polarization and Public Health: Partisan Differences in Social Distancing during the Coronavirus Pandemic (Working Paper No. 26946; Working Paper Series). National Bureau of Economic Research. https://doi.org/10.3386/w26946
Al-Rawi, A. (2019). Gatekeeping Fake News Discourses on Mainstream Media Versus Social Media. Social Science Computer Review , 37 (6), 687–704. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894439318795849
Chadwick, A., & Vaccari, C. (2019). News sharing on UK social media: Misinformation, disinformation, and correction [Report]. Loughborough University. https://repository.lboro.ac.uk/articles/News_sharing_on_UK_social_media_misinformation_disinformation_and_correction/9471269
Dechêne, A., Stahl, C., Hansen, J., & Wänke, M. (2010). The Truth About the Truth: A Meta-Analytic Review of the Truth Effect. Personality and Social Psychology Review , 14 (2), 238–257. https://doi.org/10.1177/1088868309352251
Donovan, J. (2020). Social-media companies must flatten the curve of misinformation. Nature . https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-01107-z
Feezell, J. T. (2018). Agenda Setting through Social Media: The Importance of Incidental News Exposure and Social Filtering in the Digital Era. Political Research Quarterly , 71 (2), 482–494. https://doi.org/10.1177/1065912917744895
Fletcher, R., & Nielsen, R. K. (2018). Are people incidentally exposed to news on social media? A comparative analysis. New Media & Society , 20 (7), 2450–2468. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444817724170
Fung, I. C.-H., Fu, K.-W., Chan, C.-H., Chan, B. S. B., Cheung, C.-N., Abraham, T., & Tse, Z. T. H. (2016). Social Media’s Initial Reaction to Information and Misinformation on Ebola, August 2014: Facts and Rumors. Public Health Reports , 131 (3), 461–473. https://doi.org/10.1177/003335491613100312
Garrett, R. K. (2019). Social media’s contribution to political misperceptions in U.S. Presidential elections. PLoS ONE , 14 (3). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213500
Garrett, R. K., Weeks, B. E., & Neo, R. L. (2016). Driving a Wedge Between Evidence and Beliefs: How Online Ideological News Exposure Promotes Political Misperceptions. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication , 21 (5), 331–348. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcc4.12164
Guess, A., & Nyhan, B. (2018). Selective Exposure to Misinformation: Evidence from the consumption of fake news during the 2016 U.S. presidential campaign. European Research Council , 49.
Jamieson, K. H., & Albarracín, D. (2020). The Relation between Media Consumption and Misinformation at the Outset of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic in the US. Harvard Kennedy School Misinformation Review , 2 . https://doi.org/10.37016/mr-2020-012
Kim, L., Fast, S. M., & Markuzon, N. (2019). Incorporating media data into a model of infectious disease transmission. PLOS ONE , 14 (2), e0197646. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197646
Kouzy, R., Abi Jaoude, J., Kraitem, A., El Alam, M. B., Karam, B., Adib, E., Zarka, J., Traboulsi, C., Akl, E. W., & Baddour, K. (2020). Coronavirus Goes Viral: Quantifying the COVID-19 Misinformation Epidemic on Twitter. Cureus , 12 (3). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.7255
Mitchell, A., Gottfried, J., Barthel, M., & Shearer, E. (2016, July 7). The Modern News Consumer. Pew Research Center’s Journalism Project . https://www.journalism.org/2016/07/07/the-modern-news-consumer/
Motta, M., Stecula, D., & Farhart, C. E. (2020). How Right-Leaning Media Coverage of COVID-19 Facilitated the Spread of Misinformation in the Early Stages of the Pandemic [Preprint]. SocArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/a8r3p
NewsGuard. (2020). Superspreaders . https://www.newsguardtech.com/superspreaders/
Owen, T., Loewen, P., Ruths, D., Bridgman, A., Gorwa, R., MacLellan, S., Merkley, E., & Zhilin, O. (2020). Lessons in Resilience: Canada’s Digital Media Ecosystem and the 2019 Election . Public Policy Forum. https://ppforum.ca/articles/lessons-in-resilience-canadas-digital-media-ecosystem-and-the-2019-election/
Radzikowski, J., Stefanidis, A., Jacobsen, K. H., Croitoru, A., Crooks, A., & Delamater, P. L. (2016). The Measles Vaccination Narrative in Twitter: A Quantitative Analysis. JMIR Public Health and Surveillance , 2 (1), e1. https://doi.org/10.2196/publichealth.5059
Sharma, M., Yadav, K., Yadav, N., & Ferdinand, K. C. (2017). Zika virus pandemic—Analysis of Facebook as a social media health information platform. American Journal of Infection Control , 45 (3), 301–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2016.08.022
Shin, J., Jian, L., Driscoll, K., & Bar, F. (2018). The diffusion of misinformation on social media: Temporal pattern, message, and source. Computers in Human Behavior , 83 , 278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.02.008
Vicario, M. D., Bessi, A., Zollo, F., Petroni, F., Scala, A., Caldarelli, G., Stanley, H. E., & Quattrociocchi, W. (2016). The spreading of misinformation online. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 113 (3), 554–559. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1517441113
Weeks, B. E., Lane, D. S., Kim, D. H., Lee, S. S., & Kwak, N. (2017). Incidental Exposure, Selective Exposure, and Political Information Sharing: Integrating Online Exposure Patterns and Expression on Social Media. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication , 22 (6), 363–379. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcc4.12199
The project was funded through the Department of Canadian Heritage’s Digital Citizens Initiative.
Competing Interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The research protocol was approved by the institutional review board at University of Toronto. Human subjects gave informed consent before participating and were debriefed at the end of the study.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original author and source are properly credited.
Data Availability
All materials needed to replicate this study are available via the Harvard Dataverse: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/5QS2XP .
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
An Overview of the Vaccine Debate
Looking at Both Sides of the Argument
There is a wealth of research demonstrating the efficacy and safety of vaccines —including how some have virtually eradicated infectious diseases that once killed millions. However, this has done little to sway those who believe that untold harms are being hidden from the American public.
The vaccine debate—including the argument as to whether vaccines are safe, effective, or could cause conditions like autism —has received a lot of attention from the media in recent years. With so much conflicting information being publicized, it can be a challenge to discern what is true and what is not. Therefore, it is important to learn the facts before making health decisions.
Claims and Controversy
Those who are part of the anti-vaccination movement include not only non-medical professionals but several scientists and healthcare providers who hold alternative views about vaccines and vaccination in general.
Some notable examples include:
- British healthcare provider Andrew Wakefield, who in 1998 published research linking the MMR vaccine and autism . That study has since been retracted, and he was later removed from the medical registry in the United Kingdom for falsifying scientific data.
- Pediatrician Bob Sears, who wrote the bestseller "The Vaccine Book: Making the Right Decision for your Child ," which suggested that many essential childhood vaccines were "optional." However, he was subsequently put on probation by the Medical Review Board of California in 2018 for alleged medical negligence and the inappropriate writing of medical exemptions for vaccinations.
- Dr. Jane M. Orient, director of the Association of American Healthcare Providers and Surgeons, who was among the leading opponents of the COVID-19 vaccine and one of the leading proponents of using hydroxychloroquine to treat COVID-19 during the pandemic.
These opposing views and claims, along with other information promoted by the news and social media, have led some people to question whether they know everything they need to know about vaccines.
Common Concerns Regarding Vaccines
The arguments made against vaccines are not new and have been made well before the first vaccine was developed for smallpox back in the 18th century.
The following are some of the common arguments against vaccines:
- Vaccines contain "toxic" ingredients that can lead to an assortment of chronic health conditions such as autism.
- Vaccines are a tool of "Big Pharma," in which manufacturers are willing to profit off of harm to children.
- Governments are "pharma shills," meaning they are bought off by pharmaceutical companies to hide cures or approve drugs that are not safe.
- A child’s immune system is too immature to handle vaccines , leading the immune system to become overwhelmed and trigger an array of abnormal health conditions.
- Natural immunity is best , suggesting that a natural infection that causes disease is "better" than receiving a vaccine that may cause mild side effects.
- Vaccines are not tested properly , suggesting a (highly unethical) approach in which one group of people is given a vaccine, another group is not, and both are intentionally inoculated with the same virus or bacteria.
- Infectious diseases have declined due in part to improved hygiene and sanitation , suggesting that hand-washing and other sanitary interventions are all that are needed to prevent epidemics.
- Vaccines cause the body to "shed" virus , a claim that is medically true, although the amount of shed virus is rarely enough to cause infection.
The impact of anti-vaccination claims has been profound. For example, it has led to a resurgence of measles in the United States and Europe, despite the fact that the disease was declared eliminated in the U.S. back in 2000.
Studies have suggested that the anti-vaccination movement has cast doubt on the importance of childhood vaccinations among large sectors of the population. The added burden of the COVID-19 pandemic has led to further declines in vaccination rates.
There is also concern that the same repercussions may affect COVID-19 vaccination rates—both domestically and abroad. Ultimately, vaccine rates must be high for herd immunity to be effective.
According to a study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the rate of complete recommended vaccination among babies age 5 months has declined from 66.6% in 2016 to 49.7% by May 2020. Declines in vaccination coverage were seen in other age groups as well.
Benefits of Vaccination
Of the vaccines recommended by the CDC, the benefits of immunization are seen to overwhelmingly outweigh the potential risks. While there are some people who may need to avoid certain vaccines due to underlying health conditions, the vast majority can do so safely.
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, there are five important reasons why your child should get the recommended vaccines:
- Immunizations can save your child’s life . Consider that polio once killed up to 30% of those who developed paralytic symptoms. Due to polio vaccination, the disease is no longer a public health concern in the United States.
- Vaccination is very safe and effective . Injection site pain and mild, flu-like symptoms may occur with vaccine shots. However, serious side effects , such as a severe allergic reaction, are very rare.
- Immunization protects others . Because respiratory viruses can spread easily among children, getting your child vaccinated not only protects your child but prevents the further spread of disease.
- Immunizations can save you time and money . According to the non-profit Borgen Project, the average cost of a measles vaccination around the world is roughly $1.76, whereas the average cost of treating measles is $307. In the end, the cost of prevention is invariably smaller than the cost of treatment.
- Immunization protects future generations . Smallpox vaccinations have led to the eradication of smallpox . Rubella (German measles) vaccinations have helped eliminate birth defects caused by infection of pregnant mothers in the developed world. With persistence and increased community uptake, measles could one day be declared eliminated (again) as well.
A Word From Verywell
If you have any questions or concerns about vaccinations, do not hesitate to speak with your healthcare provider or your child's pediatrician.
If a vaccine on the immunization schedule has been missed, speak to a healthcare provider before seeking the vaccination on your own (such as at a pharmacy or clinic). In some cases, additional doses may be needed.
Vaccines Healthcare Provider Discussion Guide
Get our printable guide for your next healthcare provider's appointment to help you ask the right questions.
Sign up for our Health Tip of the Day newsletter, and receive daily tips that will help you live your healthiest life.
Thank you, {{form.email}}, for signing up.
There was an error. Please try again.
Eggerton L. Lancet retracts 12-year-old article linking autism to MMR vaccines . CMAJ . 2010 Mar 9; 182(4):e199-200. doi:10.1503/cmaj.109-3179
Park A. Doctor behind vaccine-autism link loses license . Time .
Offit PA, Moser CA. The problem with Dr Bob's alternative vaccine schedule . Pediatrics. 2009 Jan;123 (1):e164-e169. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-2189
Before the Medical Board of California, Department of Consumer Affairs, State of California. In the Matter of the Accusation Against Robert William Sears, M.D., Case No. 800-2015-012268 .
Stolberg SG. Anti-vaccine doctor has been invited to testify before Senate committee . The New York Times.
Wolfe RM, Sharp LK. Anti-vaccinationists past and present . BMJ. 2002;325(7361):430-2. doi:10.1136/bmj.325.7361.430
Agley J, Xiao Y. Misinformation about COVID-19: Evidence for differential latent profiles and a strong association with trust in science . BMC Public Health. 2021;21:89. doi:10.1186/s12889-020-10103-x
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles history .
Hussain A, Ali S, Ahmed M, Hussain S. The anti-vaccination movement: a regression in modern medicine . Cureus . 2018;10(7): e2919. doi:10.7759/cureus.2919
Bramer CA, Kimmins LM, Swanson R, et al. Decline in child vaccination coverage during the COVID-19 pandemic — Michigan Care Improvement Registry, May 2016–May 2020 . MMWR. 2020 May;69(20):630-1. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6920e1
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Why vaccinate .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Poliomyelitis .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Making the vaccine decision .
Borgen Project. What is the cost of measles in the developed world? .
By Vincent Iannelli, MD Vincent Iannelli, MD, is a board-certified pediatrician and fellow of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Dr. Iannelli has cared for children for more than 20 years.
Librarians/Admins
- EBSCOhost Collection Manager
- EBSCO Experience Manager
- EBSCO Connect
- Start your research
- EBSCO Mobile App
Clinical Decisions Users
- DynaMed Decisions
- Dynamic Health
- Waiting Rooms
- NoveList Blog
The Argument for Open Research in the Time of COVID-19

Most research disciplines, regardless of whether in STEM or social sciences, consist of a common approach — taking a specific methodology or approach, applying some computation to analyze whatever data are collected to gain insights into a new topic and draw conclusions. How these approaches and analyses are recorded and made available is critical to assess, reproduce, and fully understand the research, any resulting data and insights.
When research is publicly funded, there is a solid argument for what’s produced to be openly available and the need for open research suddenly gains clarity and focus during a global public health crisis. Health professionals around the world need, and absolutely should have, access to any new scientific diagnostic approaches, as quickly as possible. Emerging or trusted computational tools for modeling disease epidemiology, or approaches for machine learning prognosis using clinical characteristics, should be made available for immediate reuse by others.
A global scientific collaboration has been lauded as scientists come together to perform research during the pandemic. The New York Times piece, “ Covid-19 Changed How the World Does Science, Together ” noted:
“While political leaders have locked their borders, scientists have been shattering theirs, creating a global collaboration unlike any in history. Never before, researchers say, have so many experts in so many countries focused simultaneously on a single topic and with such urgency. Nearly all other research has ground to a halt.”
Many funders and health organizations are demanding that research approaches and results be made open. Preprints have offered one solution, and their value during this challenging time has been evident in the huge volume of COVID-19 related content appearing online. For example, this collection of COVID-19 SARS-CoV-2 preprints on medRxiv and bioRxiv has more than 1900 manuscripts.
Now, protocols.io and Code Ocean are working to ensure that those research approaches remain open. These open access online tools are ideal repositories for all protocol and methodological approaches as well as computational pipelines and code. Online collaborative research tools are helpful to researchers who are restricted in how they can work and collaborate. For those at the frontline conducting scientific research, these tools serve as an ideal way to share their insights and approaches. Here’s how protocols.io and Code Ocean are supporting the research community during this unprecedented time:
protocols.io
A dedicated open methods community in protocols.io.
When methods and protocols relating to the SARS-CoV2 virus and COVID-19 started to appear on protocols.io earlier this year, the protocols.io team quickly realized the value of creating the “ Coronavirus Method Development Community ”, a shared workspace for new protocols relevant to the virus. An incredibly fast-growing community on protocols.io, this Open Community already has more than 300 members and is growing daily.
On the Coronavirus Method Development Community, many members are active, adding comments to already posted protocols or starting their own discussion threads. The protocols are many and varied, from COVID-19 clinical diagnostic PCR approaches, viral plaque assays, methods to culture SARS-CoV-2, and Coronavirus sequencing protocols (some of which were adapted as new ‘forked’ versions of Ebola sequencing protocols that were already available on protocols.io). Other protocols include mask building ideas, how to 3D print personal protective equipment and the World Health Organization’s recommended hand-rub formulations.
When asked about using protocols.io during the current crisis, Public Health Virologist Ian MacKay, a member of the protocols.io open community noted the following:
“ protocols.io makes it possible to rapidly put our tested methods onto an open-access platform. It permitted ongoing curation of the protocol, and it provided us a platform for further discussion with the ability to really drill down into the nitty-gritty about the protocol with other users, if needed. We used protocols.io for our SARS-CoV-2 PCR methods as soon as we could. We wanted those who might not have access to expertise in assay design, optimization and validation so they could benefit from our work. protocols.io provides a global collegiality that is in dire need at times like these.”
Interested in protocols.io and Code Ocean?

protocols.io Editorial Support
Alongside, and in support of, this motivated community, protocols.io has been working behind the scenes to grow and mobilize their team of editors to support researchers offering to import and check coronavirus-related protocols into the open community, then assigning the protocol back to the appropriate contact person.
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, the team at Code Ocean has announced unlimited cloud compute and storage for COVID-19-related projects. Code Ocean’s goal has always been to help accelerate the pace of research by providing researchers with a better way to develop, collaborate and share code and data. Science builds on transparency, replication and collaboration. Code Ocean is currently supporting researchers working on COVID-19 in the following two areas:
Rapid dissemination of interactive and open research results
Code Ocean provides in-browser access to compute capsules, permanent records of pre-built computational environments containing all software, code, data, and results for a project. Compute capsules allow researchers to instantly inspect and interact with published work, as well as dynamically update new code or datasets to explore new possibilities based on existing research.
One recent compute capsule accompanying a medRxiv preprint from the Global Policy Lab at The University of California, Berkeley is an example of the rapid and open research response to COVID-19. Hsiang et al . evaluated the effect of large-scale anti-contagion policies on the COVID-19 pandemic. The analysis includes 49 packages and code in Python, R and Stata, and public epidemiological datasets from 6 countries, all of which is open access and fully reproducible. The study finds:
“We estimate that, to date, current policies have already prevented or delayed on the order of eighty-million infections. These findings may help inform whether or when ongoing policies should be lifted or intensified, and they can support decision-making in the over 150 countries where COVID-19 has been detected but not yet achieved high infection rates.”
As the authors state in the capsule:
“The easiest way to interact with our code and data is via this Code Ocean capsule, because all of the relevant setup described below has been done for you.”
When a research project is published in a compute capsule, researchers interested in the work can directly re-run the analysis interactively in a built-in computational workbench, including a command line interface, JupyterLab/Notebook, RStudio, and Shiny on cloud instances with a few clicks on Code Ocean. Alternatively, researchers can also export the entire capsule and rebuild the project (using a Docker image) on their own devices without a Code Ocean account.
All capsules preserve the data used in the analysis even if this data is removed from the original public location in the future. Some capsules, including the example from Hsiang et al. above, also allow users to dynamically update the analysis with new data as they are being released.
Whether in-browser or rebuilt locally, interactive compute capsules can lower the barrier to examine and extend new research findings, potentially shortening decision-making cycles and helping with time-sensitive policies.
Convenient access to preconfigured cloud compute environments
In countries, campuses or labs experiencing disruptions or without access to research compute infrastructure, Code Ocean provides a web-based solution that can be accessed with only a laptop and the internet. Algorithms, simulations, and analyses in different programming languages can be easily shared and multiple collaborators added, enabling teams to continue research activities at a distance.
One difficulty with internal and external collaborations is onboarding collaborators. With Code Ocean, teams do not have to spend time setting up computational environments. Instead, new team members with different levels of technical experience can get started in the same computational environment right away.
For a complex disease like COVID-19, it takes time to gather the various pieces of the puzzle from researchers around the globe. Unfortunately, we’re in a race against time to better understand the pathology, the genetics that underpin the disease, and how best to control and treat, or vaccinate against COVID-19. Researchers need to avail themselves of tools that already exist to support and accelerate their ability to make progress in these vital efforts.
The combination of Code Ocean and protocols.io, along with other open tools, could significantly shorten the cycle to disseminate each advance and make the resulting efforts and insights reproducible. These tools reduce the iterations needed to confirm and build on results, whether formally published or preprinted, and they reduce the effort required to validate existing or emerging methods. Making the most of the combined power offered by research infrastructure tools that support and capture the development and dissemination of computational and/or experimental research processes, and facilitate research being built upon, will accelerate the overall pace of scientific discovery.
Supreme Court Wary of States’ Bid to Limit Federal Contact With Social Media Companies
A majority of the justices appeared convinced that government officials should be able to try to persuade private companies, whether news organizations or tech platforms, not to publish information so long as the requests are not backed by coercive threats.
- Share full article

Adam Liptak
Reporting from Washington
Here’s the latest on the First Amendment case.
A majority of the Supreme Court seemed wary on Monday of a bid by two Republican-led states to limit the Biden administration’s interactions with social media companies, with several justices questioning the states’ legal theories and factual assertions.
Most of the justices appeared convinced that government officials should be able to try to persuade private companies, whether news organizations or tech platforms, not to publish information so long as the requests are not backed by coercive threats.
The dispute was the latest in an extraordinary series of cases this term requiring the justices to assess the meaning of free speech in the internet era.
Justices Brett M. Kavanaugh and Elena Kagan, both former White House lawyers, said interactions between administration officials and news outlets provided a valuable analogy. Efforts by officials to influence coverage are, they said, part of a valuable dialogue that is not prohibited by the First Amendment.
Members of the court also raised questions about whether the plaintiffs — Missouri and Louisiana, along with five individuals — had suffered the kind of injury that gave them standing to sue. They also suggested that a broad injunction prohibiting contacts between many officials and the platforms was not a proper remedy in any event.
“I don’t see a single item in your briefs that would satisfy our normal tests,” Justice Kagan told J. Benjamin Aguiñaga, Louisiana’s solicitor general.
Justice Sonia Sotomayor accused the states of distorting the record in the case. “I have such a problem with your brief,” she told Mr. Aguiñaga. “You omit information that changes the context of some of your claims. You attribute things to people who it didn’t happen to.”
Mr. Aguiñaga apologized “if any aspect of our brief was not as forthcoming as it should have been.”
The justices peppered Mr. Aguiñaga with hypothetical questions about national security, doxxing of public officials and contests that could endanger teenagers, all suggesting that there is a role for vigorous efforts by the government to combat harmful speech.
Justice Samuel A. Alito Jr., the member of the court who appeared most sympathetic to the states’ position, urged his colleagues to remain focused on the case before them.
“Whatever coercion means,” he said, “whatever happened here is sufficient.”
The case arose from a barrage of communications from administration officials urging platforms to take down posts on topics like the coronavirus vaccines and claims of election fraud. Last year, a federal appeals court severely limited such interactions .
The Supreme Court put that injunction on hold last year while it considered the administration’s appeal. If it were to go into effect, said Brian H. Fletcher, a lawyer for the government, it would prohibit all sorts of speech, including public comments from the press secretary or other senior officials seeking to discourage posts harmful to children or conveying antisemitic or Islamophobic messages.
He added that the social media companies had been moderating content on their platforms long before they were contacted by officials, had powerful business incentives to do so and were following their own policies. The companies acted independently of the government, he said, and often rejected requests to take down postings.
“These were sophisticated parties,” he said. “They routinely said no to the government. They weren’t open about it. They didn’t hesitate to do it. And when they said no to the government, the government never engaged in any sort of retaliation.”
Justice Alito said the volume and intensity of the contacts were troubling, as was the suggestion in some of them that the government and the platforms were partners in an effort to combat misinformation about the pandemic.
Mr. Fletcher responded that the messages had to be understood “in the context of an effort to get Americans vaccinated during a once-in-a-lifetime pandemic” at “a time when thousands of Americans were still dying every week.” The platforms, he added, acknowledged “a responsibility to give people accurate information.”
Mr. Aguiñaga presented a different picture of the relationship between the government and the platforms.
“Behind closed doors, the government badgers the platforms 24/7,” he said. “It abuses them with profanity. It warns that the highest levels of the White House are concerned. It ominously says that the White House is considering its options.”
“Under this onslaught,” he added, “the platforms routinely cave.”
The court this term has repeatedly grappled with fundamental questions about the scope of the government’s authority over major technology platforms. On Friday, the court set rules for when government officials can block users from their private social media accounts. Last month, the court considered the constitutionality of laws in Florida and Texas that limit large social media companies from making editorial judgments about which messages to allow.
Those four cases, along with the one on Monday, will collectively rebalance the power of the government and powerful technology platforms in the realm of free speech.
A second argument on Monday posed a related constitutional question about government power and free speech, though not in the context of social media sites. It concerns whether a state official in New York violated the First Amendment by encouraging companies to stop doing business with the National Rifle Association. The justices appeared to be favoring the gun rights group.
The states in Monday’s first case, Murthy v. Missouri, No. 23-411, did not dispute that the platforms were entitled to make independent decisions about what to feature on their sites. But they said the conduct of government officials in urging them to take down what they say is misinformation amounted to censorship that violated the First Amendment.
A unanimous three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit agreed, saying that officials from the White House, the surgeon general’s office, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the F.B.I. had most likely crossed constitutional lines in their bid to persuade platforms to take down posts about what they had flagged as misinformation.
The panel, in an unsigned opinion , said the officials had become excessively entangled with the platforms or used threats to spur them to act. The panel entered an injunction forbidding many officials to coerce or significantly encourage social media companies to remove content protected by the First Amendment.
The Biden administration filed an emergency application in September asking the Supreme Court to pause the injunction, saying that the government was entitled to express its views and to try to persuade others to take action.
The court granted the administration’s application , put the Fifth Circuit’s ruling on hold and agreed to hear the case.
Three justices dissented. “Government censorship of private speech is antithetical to our democratic form of government, and therefore today’s decision is highly disturbing,” Justice Alito wrote, joined by Justices Clarence Thomas and Neil M. Gorsuch.
Those same three justices voiced the most skepticism of the Biden administration’s position at Monday’s argument.
Other justices asked about government interactions with the press. Justice Kavanaugh, who served in the White House in the administration of President George W. Bush, said that it was “probably not uncommon for government officials to protest an upcoming story on surveillance or detention policy and say, you know, if you run that it’s going to harm the war effort and put Americans at risk.”
That was perfectly proper, he suggested, adding that it would be a different matter if the request were backed by a threat of an antitrust action.
Justice Kavanaugh said he understood, based on his earlier government service, that there are “experienced government press people throughout the federal government who regularly call up the media and berate them.”
Justice Kagan echoed the point.
“Like Justice Kavanaugh,” she said, “I’ve had some experience encouraging the press to suppress their own speech.”
She sketched out some of those conversations: “You just wrote a bad editorial. Here are the five reasons you shouldn’t write another one. You just wrote a story that’s filled with factual errors. Here are the 10 reasons why you shouldn’t do that again.”
“I mean,” she said, “this happens literally thousands of times a day in the federal government.”
Chief Justice John G. Roberts Jr., another former White House lawyer, registered a lighthearted dissent, to laughter. “I have no experience coercing anybody,” he said.
But he added that the government is not monolithic and that different parts of it may hold and press competing views.
Justice Alito, who has been the subject of critical news coverage, seemed taken by the idea of pushing back against it, wondering aloud whether the court’s public information officer was in the courtroom.
“Maybe she should take a note about this,” he said. “So whenever they write something that we don’t like, she can call them up and curse them out and say ‘Why don’t we be partners? We’re on the same team.’”
What happens next? The court will probably not issue a decision until June.
Now that the arguments in the case are complete, the justices will cast tentative votes at a private conference in the coming days. The senior justice in the majority will then assign the majority opinion to a colleague — or keep it. Draft opinions, most likely including concurrences and dissents, will be prepared and exchanged.
On average, it takes the Supreme Court about three months after an argument to issue a decision. But rulings in a term’s more important cases — and this one qualifies — tend not to arrive until near the end of the term in June, no matter how early they were argued.
There are other reasons to think the decision will not arrive until late June. The case was argued in the court’s next-to-last two-week sitting, and the court will be busy this month and next with arguments on abortion and former President Donald J. Trump’s claim that he is immune from prosecution on charges that he plotted to overturn the 2020 election.
The decision must also be harmonized with rulings in related cases, including ones on whether states may prohibit technology platforms from deleting posts based on the viewpoints they express and whether a state official in New York violated the First Amendment by encouraging companies to stop doing business with the National Rifle Association.
Scholars have given varied explanations for why the biggest cases tend to land in June, no matter when they were argued. One is that justices keep polishing the opinions that will define their legacies until the last possible moment.
A 2015 study in The Duke Law Journal suggested a more personal reason: “The justices, most of whom have busy social schedules in Washington, may want to avoid tensions at their social functions by clustering the most controversial cases in the last week or two of the term — that is, just before they leave Washington for their summer recess.”
Advertisement
The court is hearing a related case on the N.R.A.
The question in the social media case is in one sense about government power over the internet. But at bottom it is about something more fundamental: striking the right balance between government advocacy for its policies, which is permissible, and coercion backed by threats of punishment, which is not.
The justices will return to that tension in Monday’s second argument, over whether a state official in New York violated the First Amendment by encouraging companies to stop doing business with the National Rifle Association after the 2018 school shooting in Parkland, Fla.
That question is at a general level the same as the one in the social media case, and its answer will also involve finding the constitutional line between persuasion and coercion.
The second case, National Rifle Association v. Vullo, No. 22-842, concerns the activities of Maria Vullo, a former superintendent of the New York State Department of Financial Services. In the aftermath of the school shooting in Parkland, Ms. Vullo said banks and insurance companies should consider whether they wanted to provide services to the group.
The N.R.A. sued, saying Ms. Vullo’s efforts leveraged government power in a way that violated the First Amendment.
A unanimous three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit, in New York, ruled against the N.R.A. Judge Denny Chin , writing for the panel, acknowledged that government officials may not “use their regulatory powers to coerce individuals or entities into refraining from protected speech.
“At the same time, however,” he wrote, “government officials have a right — indeed, a duty — to address issues of public concern.”
Ms. Vullo’s actions were on the right side of the constitutional line, Judge Chin wrote. Key documents, he said, “were written in an evenhanded, nonthreatening tone and employed words intended to persuade rather than intimidate.”
In its petition seeking Supreme Court review , the N.R.A. said the appeals court’s ruling could have sweeping consequences.
“The Second Circuit’s opinion below gives state officials free rein to financially blacklist their political opponents — from gun-rights groups to abortion-rights groups to environmentalist groups and beyond,” the petition said.
One sign that the N.R.A. has a plausible First Amendment argument: It is represented by the American Civil Liberties Union . David Cole, the A.C.L.U.’s national legal director, will argue the case on behalf of the gun rights group.
“In this hyper-polarized environment, where few are willing to cross the aisle on anything,” Mr. Cole said, “the fact that the A.C.L.U. is defending the N.R.A. here only underscores the importance of the free-speech principle at stake.”
Charlie Savage
Oral arguments in the case are over.
Fletcher, the Justice Department lawyer, is now back for rebuttal.
Jim Rutenberg
Justice Jackson asks Aguiñaga whether government can’t move against harm, like posts that might lead teens to commit suicide, and can’t tell the platforms to move to reduce the posts. Aguiñaga says the government can call platforms to say there’s a problem, but can’t apply pressure to remove that content.
“Is it your view that the government authorities could not declare those circumstances a public emergency and encourage social media platforms to take down the information that is instigating this problem?” “Your honor, the government absolutely can use the pulpit to say publicly, here’s what we recognize to be a public health issue, emergency. We this is obviously extremely terrible and the public shouldn’t tolerate this. Platforms — we see it’s going on on the platforms — but they can’t call the platforms and say, listen, we really think you should be taking this down because look at the problems that it’s causing.” “If it’s protected speech, your honor, then I think we get closer. But like, look, if you think that that’s if that’s clearly the way you’re asking the question, I understand that the instinct that that may, you know, may not be a First Amendment issue. I guess what I fall back on, your honor, is that at least where the government itself — there is no emergency like this. There’s nothing —” “No, my hypothetical is there is an emergency. My hypothetical is that there is an emergency, and I guess I’m asking you in that circumstance, can the government call the platforms and say this information that you are putting up on your platform is creating a serious public health emergency? We are encouraging you to take it down.” “I was with you right until that last comment, your honor. I think they absolutely can call and say this is a problem. It’s going rampant on your platforms. But the moment that the government tries to use its ability as the government and its stature as the government to pressure them to take it down, that is when you’re interfering with the third-party speech rights.”

Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson asks if the government could actually tell platforms they needed to take down leaked classified information. Aguiñaga, the Louisiana lawyer, says the government could do that. “I think that would be a great example where strict scrutiny would be in the government’s favor.”
“Part of the reason why you might be running into all of these difficulties with respect to the different factual circumstances is because you’re not focusing on the fact that there are times in which the government can, depending on the circumstances, encourage, perhaps even coerce, because they have a compelling interest in doing so. And so that’s why I keep coming back to the actual underlying First Amendment issue, which we can isolate in this case and just talk about about coercion. But I think that you have to admit that there are certain circumstances in which the government can provide information, encourage the platforms to take it down, tell them to take it down. I mean, what about what about the hypo of someone posting classified information? They say it’s my free speech right. I believe that, you know, I got access to this information and I want to post it. Are you suggesting that the government couldn’t say to the platforms, we need to take that down?” “No, your honor, because I think that would be a great example where strict scrutiny would cut in the government’s favor.”

Heightening the problem of the flawed factual record undergirding the litigation, Justice Sotomayor starkly accuses Aguiñaga himself of distorting facts of what happened: “I have such a problem with your brief, counselor. You omit information that changes the context of some of your claims. You attribute things to people who it didn’t happen to — at least in one of the defendants, it was her brother that something happened to, not her. I don’t know what to make of all this because I am not sure how we get to prove direct injury in any way.”

Aguiñaga apologizes if any of the brief is not “as forthcoming” as it should have been.
This exchange between Justice Kagan and Aguiñaga, in which the Louisiana lawyer concedes that it can be OK for the government to provide information to the platforms under some circumstances, shows the problem with having an unreliable factual record compiled by Judge Doughty about what actually happened. Fletcher is citing the district court’s findings to say the government crossed the line into official censorship, but are the specifics accurate?
Aguiñaga goes at a key issue in the government content moderation efforts of the past few years — what began as attempts to address foreign meddling and disinformation moved to cover speech from Americans in 2020, over an election and a pandemic.
In an exchange with Justice Kagan, Aguiñaga, the Louisiana lawyer, identifies a difference from the hypothetical Justice Kavanaugh brought up about government officials raising concerns with a newspaper about publishing an article: That is the government going directly to the speaker. What is “so pernicious” here is that the government is going to a third party — the platforms — and people may never learn about it.
Steven Lee Myers
Aguiñaga describes the communications between officials and the platforms as “unrelenting government pressure” going on outside of the public eye. “Pressuring platforms in back rooms, shielded from public view, is not using a bully pulpit. That’s just being a bully.”
The justices and Fletcher keep referencing a 1963 precedent, Bantam Books, Inc. v. Sullivan . It centered on a state commission in Rhode Island that was empowered to notify distributors of certain books and magazines it considered to be obscene that it had decided the materials were objectionable, request its “cooperation,” and to advise them that the commission had a duty to recommend prosecution of purveyors of obscenity. The Supreme Court ruled that these notices intimidated businesses and resulted in the suppression of the sale of the books and magazines --- an unconstitutional system of informal censorship.
Aguiñaga disputes the Biden administration’s standard for the case: “We don’t need coercion as a theory,” he said. He said the government “cannot induce, encourage or promote” to get private actors to do what government cannot: censor Americans’ speech.
Benjamin Aguiñaga, the solicitor general of Louisiana, is now arguing. Louisiana is one of the Republican-controlled states that brought the lawsuit arguing that the government was coercing social media platforms into taking down posts, amounting to government censorship.
Justice Kavanaugh, a former lawyer in George W. Bush's White House, raises a national-security analogy. He notes that it’s “not uncommon” for government officials to protest to a newspaper an upcoming story on surveillance or detention policy and say, “If you run that, it is going to harm the war effort and put Americans at risk.” The implication is under the lower-court rulings, the government would not be allowed to express such concerns.
Fletcher, the government lawyer, agrees with Justice Kavanaugh that that is an example of a valuable interchange as long as it stays on the persuasion side of the line. “Platforms — newspapers — want to know if their publishing a story might put lives at risk. And they don’t have to listen to the government, but that’s information that they can consider when exercising their editorial judgment.”
Justice Kavanaugh adds that it would become problematic coercion if the government tacked on that “And if you publish the story we’re going to pursue antitrust action against you.” Fletcher agrees again with him: “Huge problem, yeah.”
Fletcher argues that the social media platforms are large companies with sufficient clout to rebuff government efforts to influence them. In fact, when university researchers working with the government flagged misinformation about the 2020 election, the platforms refused to do anything two-thirds of the time .
Justice Kavanaugh pivots back to the Biden “killing people” line and notes that in a national security context there is some history of the government warning media outlets that their stories threaten to endanger Americans’ lives.
Justice Kagan floated the idea of resolving the case by saying the plaintiffs were not entitled to an injunction because they could not show they faced an imminent threat of future harm at the time of litigation, without getting into past content moderation disputes. Fletcher, the government lawyer, agrees that would be the narrowest and easiest way to resolve the matter.
Fletcher, the government lawyer, argues that government officials can persuade a private party to do something the private party is lawfully allowed to do, even when the government could not do that thing itself. He gives various examples: when government officials called on colleges to do more about antisemitic speech on campuses after the Oct. 7 attacks in Israel, encouraging parents to monitor their children’s cell phone usages, or internet companies to watch out for child sexual abuse on their platforms, even if the Fourth Amendment would prevent the government from doing that directly. Telling social media companies that the government thinks their algorithms or posting of certain things are causing harm is the same, he said.

Here’s the moment Justice Gorsuch was referring to regarding the president’s “killing people” line.
Justice Gorsuch asks if President Biden’s statement that the platforms were “killing people” by allowing misinformation to flow in the middle of the pandemic would amount to coercion. Fletcher says the president made clear afterward it was “exhortation, not threat.”
Alito is saying he can’t imagine the federal government cajoling and threatening print media. Fletcher notes that there is that sort of back and forth with the press, but Alito is getting at the central unsettled element in all of these cases. The platforms are something different, they provide pipelines, but through their algorithms and rules they are also applying their own version of editorial standards.

Justice Alito just demonstrated that he has bought into the misinformation in the lower court’s work, citing an example where a White House official said in an email to Facebook. “I want an answer on what happened here and I want it today.” In reality that (inappropriate) language was about getting a technical problem fixed with the presidential Instagram account, not about content moderation.
When Fletcher, the government lawyer, points out that the example Alito cited as happening repeatedly actually only happened once and had nothing to do with content moderation, Alito blows past the demonstration of his misunderstanding. “OK, well, put that aside. There’s all the rest.”
Fletcher raised an issue that some experts and research organizations involved in the case have: that many of communications cited in the lower courts included disputed facts, including quotations taken out of context.
Terry A. Doughty, the Trump-appointed district court judge who set the case off (after the Republican plaintiffs filed it in a place that would ensure he got the case) issued a ruling that has itself been criticized as being riddled with misinformation and conspiracy theories about what happened, setting up an unreliable factual record for the constitutional issues at play.
Here’s a recent item on the Just Security website that catalogs many ways Doughty torqued the facts to play into right-wing culture war notions — for example, falsely editing a quote in an email to Dr. Anthony Fauci to remove the word “published” before the words “take down” in a way that made it look like a scientist was urging steps to remove misinformation about vaccines, as opposed to publishing a rebuttal to it.
That goes to another major question in the case — did government action directly cause platforms to remove speech? The government has argued that it left it to platforms to make their own decisions as it flagged and even cajoled the companies about content.
Justice Samuel Alito and Fletcher, the government lawyer, are sparring over whether there are sufficient facts to show that the plaintiffs’ injuries — having their posts taken down to having accounts suspended by social media companies — were caused by government actions, giving them standing to seek an injunction. This is a major problem with this case, according to many legal observers.

The question, as the rhetoric in the case has gone so far, is whether the White House used its classic “bully pulpit” or used its “pulpit to bully.”
Brian Fletcher, the principal deputy solicitor general for the Biden administration, argues that the government has a right to speak to social media companies in an attempt to persuade them to choose to remove or reduce certain matters, so long as it does not coerce them. He said the test should be whether the government makes threats; bully-pulpit exhortations are protected by the First Amendment, he argued.
Michael D. Shear and David McCabe
Here’s how a Trump-appointed judge saw the Biden administration pressuring companies to censor speech.
This First Amendment case is a flashpoint in a broader effort by conservatives to document what they contend is a liberal conspiracy by Democrats and tech company executives to silence their views, and it taps into fury on the right about how social media companies have treated stories about the origins of Covid, the 2020 election and Hunter Biden, the president’s son.
The final outcome could shape the future of First Amendment law in a rapidly changing media environment and alter how far the government can go in trying to prevent the spread of potentially dangerous claims, particularly in an election or during emergencies like a pandemic.
The government’s actions at the heart of the case were intended largely as public health measures during the coronavirus pandemic. But a federal judge in Louisiana framed his ruling back in July through the filter of partisan culture wars — asking whether the government violated the First Amendment by unlawfully threatening the social media companies to censor speech that the Biden administration found distasteful and potentially harmful to the public.
In his ruling, Judge Terry A. Doughty described dozens of interactions between the administration and social media companies, including how two months after President Biden took office, his top digital adviser had emailed officials at Facebook urging them to do more to limit the spread of “vaccine hesitancy” on the social media platform.
Judge Doughty also outlined how officials at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention had held “weekly sync” meetings with Facebook, once emailing the company 16 “misinformation” posts. And in the summer of 2021, he wrote, the surgeon general’s top aide had repeatedly urged Google, Facebook and Twitter to do more to combat disinformation.
The case sets up a showdown between the justices and a conservative appeals court.
The appeals court that partly upheld limits on the Biden administration’s communications with social media companies has a reputation for issuing decisions too conservative for the Supreme Court, which is itself tilted to the right by a six-justice supermajority of Republican appointees.
Of the appeals court’s 17 active judges, only five were appointed by Democratic presidents. Six members of the court were appointed by President Donald J. Trump.
The court, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit, in New Orleans, hears appeals from federal trial courts in Louisiana, Mississippi and Texas. Those forums often attract ambitious lawsuits from conservative litigants correctly anticipating a favorable reception, and rulings from trial judges in those states are often affirmed by the Fifth Circuit.
But when those cases reach the Supreme Court, they sometimes fizzle out. An attack on the constitutionality of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, endorsed by three Trump appointees on the Fifth Circuit, did not seem to fare well before the justices when it was argued in October. Another, in which the Fifth Circuit struck down a federal law barring domestic abusers from carrying guns, was also met with skepticism .
Other rulings from the Fifth Circuit, on issues like immigration , abortion pills and so-called ghost guns , have also met with at least tentative disapproval from the Supreme Court, suggesting that the appeals court is out of step with the justices.
At a news briefing in September, Irv Gornstein, the executive director of Georgetown’s Supreme Court Institute, said the Fifth Circuit had staked out positions that “at least some of the center bloc of conservatives aren’t going to be able to stomach.”
He added that some of the rulings by the Fifth Circuit were “delivered from Crazy Town” and that “it would be shocking if at least some of those decisions are not reversed.”
The case is one of several about the intersection of free speech and technology on the court’s docket.
The Supreme Court hears First Amendment cases fairly often. But it has never before considered as many cases on what the Constitution has to say about free speech in the internet era as it will in its current term, set to end in June.
Monday’s argument will be the fifth one since October considering the fundamental question of the scope of government power over social media platforms. The decision in that case and the four others will collectively mark the boundaries of free expression in the digital age.
Last month, the Supreme Court considered two cases on whether Florida and Texas could limit prominent social media companies from moderating content on their platforms, appearing skeptical of the breadth of laws that had been enacted in an effort to shield conservative voices on technology sites.
On Friday, the court, in two unanimous rulings, set requirements for when elected officials could block people from their social media accounts.
The court’s decisions in the five cases will have broad political and economic implications. A ruling that tech platforms have no editorial discretion to decide which posts to allow, for instance, would expose users to a greater variety of viewpoints, but it would almost certainly amplify the ugliest aspects of the digital age, including hate speech and disinformation.
- Newsletters
- Account Activating this button will toggle the display of additional content Account Sign out
Even the Supreme Court’s Conservatives Are Fed Up With the Garbage Coming Out of the 5th Circuit
What happens when a lawless judge and a terrible appeals court embrace the dopiest First Amendment claim you’ve ever heard out of pure spite toward a Democratic president? That would be Murthy v. Missouri , a brain-meltingly dumb case that the Supreme Court was unfortunate enough to hear oral arguments in on Monday. Murthy poses a question so asinine that to ask it is to answer it: Can government officials encourage social media companies to moderate certain content that they deem harmful—most importantly, disinformation about COVID-19 in the middle of the pandemic?
Yes, of course they can: The First Amendment does not gag public officials from urging Facebook or the Washington Post or anyone else to publish or not publish certain information, especially when it contains dangerous lies about a once-in-a-century pandemic that could exacerbate the crisis. The First Amendment bars government censorship, not government persuasion, and the Biden administration planted itself on the latter side of that bright line. At least six justices grasped this basic constitutional principle on Monday. Several of them used arguments to highlight how this inane case illustrates so much of what’s wrong with the judiciary today, and hinted at the dangers it could pose to American democracy in the future. That we should pay attention to. The rest was an unfortunate sideshow.
Like so many Supreme Court cases these days, Murthy is built atop a heap of fake facts. The case began when Missouri and Louisiana sued agencies and officials across the Biden administration, falsely accusing them of coercing social media companies into censoring their residents’ free speech. (These states later added a handful of fringe anti-vaxxers to the suit.) They filed their complaint in the Monroe Division of the Western District of Louisiana, where—surprise!—they were guaranteed to draw a Trump appointee, Terry Doughty, the one judge hearing cases in that division. Judge Doughty has a record of issuing nationwide injunctions against the Biden administration on the basis of dubious legal and factual analysis. Most notably, he issued a nationwide bar against Biden’s vaccine mandate for health care workers in an opinion riddled with anti-vax nonsense (which the Supreme Court reversed ).
Doughty, in other words, was certain to rule against Biden in the social media case. Even still, the opinion he handed down on July 4, 2023, was a humiliating mess of contradictions, fabrications , and (ironically) misinformation . Doughty adopted the plaintiffs’ theory that the administration “coerced” social media companies into removing “conservative” speech about COVID, including posts promoting hydroxychloroquine and rejecting the efficacy of vaccines. He accused government officials of launching a “coordinated campaign” to silence conservatives by forcing private companies to take down anti-vax content, as well as false claims about election fraud. And he issued one of the most sweeping injunctions in the history of the American legal system, prohibiting any employee—including Homeland Security, the State Department, the Department of Justice, and the FBI—from “engaging in any communication of any kind with social-media companies” encouraging content moderation.
Doughty, it turns out, grievously butchered the record to reach his conclusion. An exhaustive analysis by Mike Masnick proves that Doughty consistently misrepresented testimony and other evidence in the record to construct a conspiracy theory with zero basis in reality. He distorted emails and other exchanges to make them look coercive when they were nothing of the sort, cherry-picking and rearranging quotations to put them in a censorious light. Yet the hard-right U.S. Court of Appeals for the 5 th Circuit, where law goes to die , affirmed Doughty’s conclusions and upheld much of his injunction (while narrowing it in part). That move sent the administration racing to the Supreme Court for an emergency stay, which it granted in October, over the dissents of Justices Samuel Alito, Neil Gorsuch, and Clarence Thomas. Monday’s arguments confirmed that a majority is prepared to side with Biden on the merits.
The justices did not sound happy to have the case before them. Justice Sonia Sotomayor scolded Louisiana Solicitor General Benjamin Aguiñaga (a former Alito clerk) for his lack of candor. “I have such a problem with your brief,” she told him. “You omit information that changes the context of some of your claims. You attribute things to people who it didn’t happen to.” Aguiñaga was unable to defend Doughty’s more extreme deceptions. So he had to fall back on what Justice Elena Kagan called an “extremely expansive” argument: the notion that “encouraging people to suppress their own speech” violates the First Amendment, even if it isn’t coercive. Kagan drew upon her past work in the executive branch to explain that, actually, government officials do this all the time . “I’ve had some experience encouraging press to suppress their own speech,” Kagan told Aguiñaga. Example: “You just wrote a bad editorial. Here are the five reasons you shouldn’t write another one.” Is that really unconstitutional?
Justice Brett Kavanaugh, a former White House staff secretary, also provided a real-world perspective after Alito fumed that officials had been too mean to the platforms and would never treat the traditional press so sharply. Kavanaugh gave Alito a reality check: “I’d assumed, thought, [and] experienced government press people throughout the federal government who regularly call up the media and berate them,” he told Deputy Solicitor General Brian Fletcher, who defended the administration. “You said the anger was unusual. I wasn’t entirely clear on that from my own experience.” Translation: Government employees yell at members of the media all the time. The media can accept or reject their requests. That is how it works .
But did Biden officials berate social media employees? Only on a few rare occasions. Here’s what really happened: The platforms in question, most prominently Facebook and Twitter, invited the government to help them identify and remove the most toxic disinformation. At the time, as Fletcher explained, these companies were eager to present themselves as “partners” with the administration in its push for COVID vaccination. Officials could “flag” questionable content, but the platforms made their own judgment calls, without any demonstrable fear of retaliation. Everyone agrees that the government violates free speech when it explicitly coerces companies into censoring expression under the threat of punishment. But, Fletcher persuasively argued, no such thing happened here.
That left Aguiñaga to lean on the theory that the government contravenes the First Amendment when it merely “encourages” specific content moderation. Justice Amy Coney Barrett, a stickler for legible rules, sounded borderline aghast at this baggy, boundless standard; she lobbed a series of hypotheticals at Aguiñaga that showed he was pushing a meaningless and impracticable test. Chief Justice John Roberts tried to help Aguiñaga understand that multiple agencies with competing agendas may pressure platforms in contradictory directions; doesn’t that “dilute the concept of coercion significantly?” (Aguiñaga just sounded confused.) Kavanaugh pointed out that the plaintiffs’ position could prevent officials from urging the press to safeguard national security by, for instance, asserting that a forthcoming article might imperil the troops.
Even Gorsuch, who started out sympathetic to Aguiñaga, was exasperated by the end, complaining that Doughty’s “universal injunction” was part of the “epidemic” that had to be stopped. Only Alito and Thomas sounded like surefire votes for the plaintiffs after nearly two hours of arguments, and Thomas’ heart was not fully in it. Alito stood alone in his increasingly uncontrolled and seething aggrievement .
The pandemic may be over, but Murthy remains a hugely relevant case. Perhaps most obviously, it is a cautionary tale about the extremism of Trump judges like Doughty, who keep issuing these lawless injunctions at the behest of red-state politicians, and the 5 th Circuit, which keeps upholding them. A disproportionate number of the Supreme Court’s cases this term emerge from the 5 th Circuit, which keeps appeasing the Trump-appointed zealots attempting to seize unimaginable amounts of power from the democratic branches. The chief justice is attempting to crack down on the kind of judge-shopping that occurred here, but the fight is just beginning. The evident frustration of Roberts, Kavanaugh, Barrett, and even Gorsuch on Monday suggests that a majority of the court is fed up with this political manipulation of the judiciary by rogue judges with undisguised partisan loyalties.
So, yes, SCOTUS is likely to reach the right result in Murthy . Alarmingly, though, so much damage has already been done. In light of Doughty’s injunction, the federal government shut down all of its efforts to combat disinformation, fearful of judicial sanctions. Bad actors have exploited this development to flood the internet with lies about the upcoming 2024 election. If foreign entities attempt to interfere with the election via social media, the Biden administration will have few tools left to fight them. It is just too late to revive the various task forces that worked with platforms before Doughty disbanded them last year. For the Murthy plaintiffs, then, a Supreme Court defeat may not matter much. They have already done immense damage to truth and transparency on the internet. And at this late date, the worst of it cannot be undone.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Vaccine. Covid19 vaccines are one of the ways to prevent the spread of Covid-19, but they have been a source of controversy. Different sides argue about the benefits or dangers of the new vaccines. Whatever your point of view is, writing a persuasive essay about it is a good way of organizing your ...
These discourses, from both practical and ethical perspectives, are used to evaluate the use of coercive jabs to combat COVID-19, which has caused more than 4.3 million deaths worldwide, among 210 million confirmed cases in the first 20 months [17], and remains ongoing. Justice is manifested through fairly sharing the benefits, risks and costs ...
While efficacious vaccines have been developed to inoculate against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2; also known as COVID-19), public vaccine hesitancy could still ...
Argumentative Essay about Covid 19. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. COVID-19 is an emerging public health problem, which started in China at the end of 2019 and gradually affected the majority of countries including India (1).
COVID-19 severity is strongly linked with age, dividing individual perceptions of vulnerability within populations. The death rate is estimated at 7.8% in people aged over 80, but at just 0.0016% ...
The main areas of disagreement about school closures during the coronavirus pandemic are: In favor of school closures. School closures are necessary to prevent the spread of the virus. Evidence from past pandemics supports the efficacy of school closures. Reopening Universities will increase COVID-19 spread.
This essay is part of "Reimagining the global economy: Building back better in a post-COVID-19 world," a collection of 12 essays presenting new ideas to guide policies and shape debates in a ...
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays. Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form. To help ...
Examples of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Integration. Writing a persuasive essay on Covid-19 integration doesn't have to be stressful or overwhelming. With the right approach and preparation, you can write an essay that will get them top marks! Here are a few samples of compelling persuasive essays.
Since March 11, the world has been experiencing a pandemic of Sars-Cov-2, the new coronavirus, which emerged in China in late December 2019 and causes the COVID-19 disease. Pandemics are characterized by pathogen's ability of emerging or re-emerging across geographical boundaries, simultaneously affecting a large number of people around the world, due to the sustained transmission in humans ...
The days dragged on in my apartment, in black and white, like my photos. Sometimes we tried to smile, imagining that I was asymptomatic, because I was the virus. Our smiles seemed to bring good ...
Here we use two survey experiments to study how persuasive messaging affects COVID-19 vaccine uptake intentions. In the first experiment, we test a large number of treatment messages. One subgroup of messages draws on the idea that mass vaccination is a collective action problem and highlighting the prosocial benefit of vaccination or the ...
Several vaccines against COVID-19 have now been developed and are already being rolled out around the world. The decision whether or not to get vaccinated has so far been left to the individual citizens. However, there are good reasons, both in theory as well as in practice, to believe that the willingness to get vaccinated might not be sufficiently high to achieve herd immunity. A policy of ...
Drawing inspiration from Boin, Stern and Sundelius', work on persuasive narratives, this study shows the ways that Solberg's posts about COVID-19 exhibit all five identified frame functions.
The initial argument in support of the COVID-19 vaccine mandates for health care workers must start with the principle of justice and consistency and their related ethical concepts that support fair and equitable treatment of individuals. Although justice is typically viewed through a patient-centric lens, it is reasonable to expect that health ...
Kalyani Mohan '22 and Kalli Jackson '22 penned an essay titled " Where Public Health Meets Politics: COVID-19 in the United States ," which was published in Wesleyan's Arcadia Political Review. They wrote: "While the U.S. would certainly benefit from a strengthened pandemic response team and structural changes to public health ...
Special Issue: COVID-19. This essay was published as part of a Special Issue on Misinformation and COVID-19, guest-edited by Dr. Meghan McGinty (Director of Emergency Management, NYC Health + Hospitals) and Nat Gyenes (Director, Meedan Digital Health Lab). ... We cannot and do not make a causal argument here but argue instead that there is ...
Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay, paper or report: APA. Moore, Sarah. (2022, January 17). The Importance of Global COVID-19 Vaccination.
The vaccine debate—including the argument as to whether vaccines are safe, effective, ... the leading opponents of the COVID-19 vaccine and one of the leading proponents of using hydroxychloroquine to treat COVID-19 during the pandemic. These opposing views and claims, along with other information promoted by the news and social media, have ...
One recent compute capsule accompanying a medRxiv preprint from the Global Policy Lab at The University of California, Berkeley is an example of the rapid and open research response to COVID-19. Hsiang et al. evaluated the effect of large-scale anti-contagion policies on the COVID-19 pandemic. The analysis includes 49 packages and code in ...
Chronic infections with the coronavirus are rare, even among immunocompromised people. But the Alpha variant of late 2020, the Omicron variant in late 2021 and BA.2.86, first detected last summer ...
Coronavirus Vaccination Vaccines. Essay Type: Argumentative. Words: 872. Pages: 2. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples.
Having recognized this, the Common App added a new optional 250-word essay that will give universities a chance to understand the atypical high school experience students have had. The prompt will ...
The subsequent paragraphs are going to provide detailed explanations of the reasons why it is necessary for the COVID-19 vaccine to be taken. Firstly, the COVID-19 vaccine is necessary because it helps build protection against the virus. COVID-19 is a terrifying and dangerous communicable disease. The virus affects the respiratory organ of the ...
Those changes continued well past Covid-19's peak, suggesting a widespread belief that standardized tests hold little value. ... Essays and interviews clearly are, but so are grades and GPAs ...
A second argument on Monday posed a related constitutional question about government power and free speech, though not in the context of social media sites. It concerns whether a state official in ...
On the face of it, that presents an ironclad case for blocking the steel merger. Take a step back, though, and the argument is less clear. The costs are greater than the deal-blockers imagine and ...
The rest was an unfortunate sideshow. Like so many Supreme Court cases these days, Murthy is built atop a heap of fake facts. The case began when Missouri and Louisiana sued agencies and officials ...