How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated April 17, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by

Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Laundromat Business Plan + Example Templates

13 Min. Read
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan

6 Min. Read
How to Do a SWOT Analysis for Better Strategic Planning

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
10 Step Process for Effective Business Problem Solving
Posted august 3, 2021 by harriet genever.

When you start a small business or launch a startup, the one thing you can count on is the unexpected. No matter how thoroughly you plan, forecast , and test, problems are bound to arise. This is why as an entrepreneur, you need to know how to solve business problems effectively.
What is problem solving in business?
Problem solving in business relates to establishing processes that mitigate or remove obstacles currently preventing you from reaching strategic goals . These are typically complex issues that create a gap between actual results and your desired outcome. They may be present in a single team, operational process, or throughout your entire organization, typically without an immediate or obvious solution.
To approach problem solving successfully, you need to establish consistent processes that help you evaluate, explore solutions, prioritize execution, and measure success. In many ways, it should be similar to how you review business performance through a monthly plan review . You work through the same documentation, look for gaps, dig deeper to identify the root cause, and hash out options. Without this process, you simply cannot expect to solve problems efficiently or effectively.
Why problem solving is important for your business
While some would say problem-solving comes naturally, it’s actually a skill you can grow and refine over time. Problem solving skills will help you and your team tackle critical issues and conflicts as they arise. It starts from the top. You as the business owner or CEO needing to display the type of level-headed problem solving that you expect to see from your employees.
Doing so will help you and your staff quickly deal with issues, establish and refine a problem solving process, turn challenges into opportunities, and generally keep a level head. Now, the best business leaders didn’t just find a magic solution to solve their problems, they built processes and leveraged tools to find success. And you can do the same.
By following this 10-step process, you can develop your problem-solving skills and approach any issue that arises with confidence.
1. Define the problem
When a problem arises, it can be very easy to jump right into creating a solution. However, if you don’t thoroughly examine what led to the problem in the first place, you may create a strategy that doesn’t actually solve it. You may just be treating the symptoms.
For instance, if you realize that your sales from new customers are dropping, your first inclination might be to rush into putting together a marketing plan to increase exposure. But what if decreasing sales are just a symptom of the real problem?
When you define the problem, you want to be sure you’re not missing the forest for the trees. If you have a large issue on your hands, you’ll want to look at it from several different angles:
Competition
Is a competitor’s promotion or pricing affecting your sales? Are there new entrants in your market? How are they marketing their product or business?
Business model
Is your business model sustainable? Is it realistic for how fast you want to grow? Should you explore different pricing or cost strategies?
Market factors
How are world events and the nation’s economy affecting your customers and your sales?
Are there any issues affecting your team? Do they have the tools and resources they need to succeed?
Goal alignment
Is everyone on your team working toward the same goal ? Have you communicated your short-term and long-term business goals clearly and often?
There are a lot of ways to approach the issue when you’re facing a serious business problem. The key is to make sure you’re getting a full snapshot of what’s going on so you don’t waste money and resources on band-aid solutions.
Going back to our example, by looking at every facet of your business, you may discover that you’re spending more on advertising than your competitors already. And instead, there’s a communication gap within your team that’s leading to the mishandling of new customers and therefore lost sales.
If you jumped into fixing the exposure of your brand, you would have been dumping more money into an area you’re already winning. Potentially leading to greater losses as more and more new customers are dropped due to poor internal communication.
This is why it’s so vital that you explore your blind spots and track the problem to its source.
2. Conduct a SWOT analysis
All good businesses solve some sort of problem for customers. What if your particular business problem is actually an opportunity, or even a strength if considered from a different angle? This is when you’d want to conduct a SWOT analysis to determine if that is in fact the case.
SWOT is a great tool for strategic planning and bringing multiple viewpoints to the table when you’re looking at investing resources to solve a problem. This may even be incorporated in your attempts to identify the source of your problem, as it can quickly outline specific strengths and weaknesses of your business. And then by identifying any potential opportunities or threats, you can utilize your findings to kickstart a solution.
3. Identify multiple solutions with design thinking
As you approach solving your problem, you may want to consider using the design thinking approach . It’s often used by organizations looking to solve big, community-based problems. One of its strengths is that it requires involving a wide range of people in the problem-solving process. Which leads to multiple perspectives and solutions arising.
This approach—applying your company’s skills and expertise to a problem in the market—is the basis for design thinking.
It’s not about finding the most complex problems to solve, but about finding common needs within the organization and in the real world and coming up with solutions that fit those needs. When you’re solving business problems, this applies in the sense that you’re looking for solutions that address underlying issues—you’re looking at the big picture.
4. Conduct market research and customer outreach
Market research and customer outreach aren’t the sorts of things small business owners and startups can do once and then cross off the list. When you’re facing a roadblock, think back to the last time you did some solid market research or took a deep dive into understanding the competitive landscape .
Market research and the insights you get from customer outreach aren’t a silver bullet. Many companies struggle with what they should do with conflicting data points. But it’s worth struggling through and gathering information that can help you better understand your target market . Plus, your customers can be one of the best sources of criticism. It’s actually a gift if you can avoid taking the negatives personally .
The worst thing you can do when you’re facing challenges is isolating yourself from your customers and ignore your competition. So survey your customers. Put together a competitive matrix .
5. Seek input from your team and your mentors
Don’t do your SWOT analysis or design thinking work by yourself. The freedom to express concerns, opinions, and ideas will allow people in an organization to speak up. Their feedback is going to help you move faster and more efficiently. If you have a team in place, bring them into the discussion. You hired them to be experts in their area; use their expertise to navigate and dig deeper into underlying causes of problems and potential solutions.
If you’re running your business solo, at least bring in a trusted mentor. SCORE offers a free business mentorship program if you don’t already have one. It can also be helpful to connect with a strategic business advisor , especially if business financials aren’t your strongest suit.
Quoting Stephen Covey, who said that “strength lies in differences, not in similarities,” speaking to the importance of diversity when it comes to problem-solving in business. The more diverse a team is , the more often innovative solutions to the problems faced by the organization appear.
In fact, it has been found that groups that show greater diversity were better at solving problems than groups made up specifically of highly skilled problem solvers. So whoever you bring in to help you problem-solve, resist the urge to surround yourself with people who already agree with you about everything.
6. Apply lean planning for nimble execution
So you do your SWOT analysis and your design thinking exercise. You come up with a set of strong, data-driven ideas. But implementing them requires you to adjust your budget, or your strategic plan, or even your understanding of your target market.
Are you willing to change course? Can you quickly make adjustments? Well in order to grow, you can’t be afraid to be nimble .
By adopting the lean business planning method —the process of revising your business strategy regularly—you’ll be able to shift your strategies more fluidly. You don’t want to change course every week, and you don’t want to fall victim to shiny object thinking. But you can strike a balance that allows you to reduce your business’s risk while keeping your team heading in the right direction.
Along the way, you’ll make strategic decisions that don’t pan out the way you hoped. The best thing you can do is test your ideas and iterate often so you’re not wasting money and resources on things that don’t work. That’s Lean Planning .
7. Model different financial scenarios
When you’re trying to solve a serious business problem, one of the best things you can do is build a few different financial forecasts so you can model different scenarios. You might find that the idea that seemed the strongest will take longer than you thought to reverse a negative financial trend. At the very least you’ll have better insight into the financial impact of moving in a different direction.
The real benefit here is looking at different tactical approaches to the same problem. Maybe instead of increasing sales right now, you’re better off in the long run if you adopt a strategy to reduce churn and retain your best customers. You won’t know unless you model a few different scenarios. You can do this by using spreadsheets, and a tool like LivePlan can make it easier and quicker.
8. Watch your cash flow
While you’re working to solve a challenging business problem, pay particular attention to your cash flow and your cash flow forecast . Understanding when your company is at risk of running out of cash in the bank can help you be proactive. It’s a lot easier to get a line of credit while your financials still look good and healthy, than when you’re one pay period away from ruin.
If you’re dealing with a serious issue, it’s easy to start to get tunnel vision. You’ll benefit from maintaining a little breathing room for your business as you figure out what to do next.
9. Use a decision-making framework
Once you’ve gathered all the information you need, generated a number of ideas, and done some financial modeling, you might still feel uncertain. It’s natural—you’re not a fortune-teller. You’re trying to make the best decision you can with the information you have.
This article offers a really useful approach to making decisions. It starts with putting your options into a matrix like this one:

Use this sort of framework to put everything you’ve learned out on the table. If you’re working with a bigger team, this sort of exercise can also bring the rest of your team to the table so they feel some ownership over the outcome.
10. Identify key metrics to track
How will you know your problem is solved? And not just the symptom—how will you know when you’ve addressed the underlying issues? Before you dive into enacting the solution, make sure you know what success looks like.
Decide on a few key performance indicators . Take a baseline measurement, and set a goal and a timeframe. You’re essentially translating your solution into a plan, complete with milestones and goals. Without these, you’ve simply made a blind decision with no way to track success. You need those goals and milestones to make your plan real .
Problem solving skills to improve
As you and your team work through this process, it’s worth keeping in mind specific problem solving skills you should continue to develop. Bolstering your ability, as well as your team, to solve problems effectively will only make this process more useful and efficient. Here are a few key skills to work on.
Emotional intelligence
It can be very easy to make quick, emotional responses in a time of crisis or when discussing something you’re passionate about. To avoid making assumptions and letting your emotions get the best of you, you need to focus on empathizing with others. This involves understanding your own emotional state, reactions and listening carefully to the responses of your team. The more you’re able to listen carefully, the better you’ll be at asking for and taking advice that actually leads to effective problem solving.
Jumping right into a solution can immediately kill the possibility of solving your problem. Just like when you start a business , you need to do the research into what the problem you’re solving actually is. Luckily, you can embed research into your problem solving by holding active reviews of financial performance and team processes. Simply asking “What? Where? When? How?” can lead to more in-depth explorations of potential issues.
The best thing you can do to grow your research abilities is to encourage and practice curiosity. Look at every problem as an opportunity. Something that may be trouble now, but is worth exploring and finding the right solution. You’ll pick up best practices, useful tools and fine-tune your own research process the more you’re willing to explore.
Brainstorming
Creatively brainstorming with your team is somewhat of an art form. There needs to be a willingness to throw everything at the wall and act as if nothing is a bad idea at the start. This style of collaboration encourages participation without fear of rejection. It also helps outline potential solutions outside of your current scope, that you can refine and turn into realistic action.
Work on breaking down problems and try to give everyone in the room a voice. The more input you allow, the greater potential you have for finding the best solution.
Decisiveness
One thing that can drag out acting upon a potential solution, is being indecisive. If you aren’t willing to state when the final cutoff for deliberation is, you simply won’t take steps quickly enough. This is when having a process for problem solving comes in handy, as it purposefully outlines when you should start taking action.
Work on choosing decision-makers, identify necessary results and be prepared to analyze and adjust if necessary. You don’t have to get it right every time, but taking action at the right time, even if it fails, is almost more vital than never taking a step.
Stemming off failure, you need to learn to be resilient. Again, no one gets it perfect every single time. There are so many factors in play to consider and sometimes even the most well-thought-out solution doesn’t stick. Instead of being down on yourself or your team, look to separate yourself from the problem and continue to think of it as a puzzle worth solving. Every failure is a learning opportunity and it only helps you further refine and eliminate issues in your strategy.
Problem solving is a process
The key to effective problem-solving in business is the ability to adapt. You can waste a lot of resources on staying the wrong course for too long. So make a plan to reduce your risk now. Think about what you’d do if you were faced with a problem large enough to sink your business. Be as proactive as you can.
Editor’s note: This article was originally published in 2016. It was updated in 2021.
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Harriet Genever
Posted in management, join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Mastering the Art of Business Problem Statements: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples
Why is the business problem statement is important.
The business problem statement provides the impetus for a business initiative in practical business related terms. It is a description of an issue currently existing and the context for how it will be addressed.
In a business setting, anyone who is involved in problem-solving or decision-making should be involved in developing a business problem statement. This could include managers, executives, analysts, project managers, or subject matter experts.
Typically, the responsibility for developing a problem statement falls on the person or team that is leading the effort to address the problem. This may be a project manager, a cross-functional team, or an individual responsible for a specific area of the business – including the Business Analyst!
In some cases, it may be appropriate to involve external consultants or experts in developing a problem statement. This can bring fresh perspectives and specialised knowledge to the problem-solving process.
Ultimately, the goal is to involve all relevant stakeholders in developing a problem statement to ensure that the problem is fully understood and the proposed solutions are feasible and effective.
Developing a business problem statement is important for several reasons:
- Clarify the problem: Developing a problem statement helps you to clarify and define the problem you are trying to solve. This can help you to focus your efforts on the key issues and avoid wasting time and resources on non-essential tasks.
- Identify the root causes: A well-crafted problem statement can help you to identify the root causes of the problem. This is important because it allows you to develop effective solutions that address the underlying issues rather than just treating the symptoms.
- Communicate with stakeholders: A problem statement provides a clear and concise summary of the problem and its impact. This can help you to communicate effectively with stakeholders and get their buy-in for your proposed solutions.
- Measure progress: A problem statement provides a baseline for measuring progress. By defining the problem and its impact, you can track your progress over time and determine whether your solutions are effective.
- Prioritise resources: A problem statement can help you to prioritise your resources and focus on the most critical problems. This is especially important in situations where resources are limited, and you need to make strategic decisions about where to allocate your time and money.
Developing a business problem statement is essential for effective problem-solving. It helps to clarify the problem, identify the root causes, communicate with stakeholders, measure progress, and prioritise resources.
When to Develop Problem Statements
You can develop a problem statement whenever you need to identify and analyse a problem, and develop solutions to address it. Some specific situations where this can occur include:
- Project initiation: When starting a new project, a problem statement template can be used to define the scope and objectives of the project, and identify potential risks and issues that may impact the project’s success.
- Process improvement: When looking to improve a business process, product, or service, a problem statement template can be used to identify and analyse the root causes of the problem, and develop solutions to address them.
- Research projects: When developing a research project, a problem statement template can be used to formulate research questions, and identify the gaps and limitations in existing literature or data.
- Policy development: When developing policies and programs to address social, economic, or environmental issues, a problem statement template can be used to identify and analyse the policy issue, and develop evidence-based solutions.
- Strategic planning: When developing a strategic plan for an organisation, a problem statement template can be used to identify and analyse the challenges and opportunities facing the organisation, and develop a roadmap for achieving its goals.
Overall, you can use a problem statement template whenever you need to identify and analyse a problem, and develop solutions to address it. Categorisation will help you develop a structured, consistent, and efficient approach to problem-solving.
Categorisation of Business Problem Statements
There are several ways to categorise business problem statements, and the specific categories may vary depending on the organisation or industry. Here are some common ways to categorise business problem statements:
- Functional area: Categorise the problem statement based on the functional area of the business that is affected. For example, problems related to marketing, finance, operations, human resources, or information technology.
- Customer impact: Categorise the problem statement based on the impact on customers or clients. For example, problems related to customer satisfaction, retention, acquisition, or loyalty.
- Business process: Categorise the problem statement based on the business process that is affected. For example, problems related to supply chain management, product development, sales, or customer service.
- Strategic priority: Categorise the problem statement based on the strategic priority of the organisation. For example, problems related to growth, innovation, cost reduction, or risk management.
- Industry or market: Categorise the problem statement based on the industry or market in which the business operates. For example, problems related to competition, changing customer needs, or regulatory compliance.
- Business architecture. Categorise the problem statement based on capabilities to help you understand business capability maturity, the impacts on change, and opportunities for improvement. See below for categories.
By categorising business problem statements, you can better understand the scope and nature of the problems and develop targeted solutions that address the root causes of the problems. This can help to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your problem-solving efforts.
Business Architecture Categories
Problem statements can be described in a single statement followed by a real example to emphasise the issue. When developing an understanding of the problems to be resolved think across the seven broad areas shown below and ask questions accordingly. Examples are given for each category using the architectural approach with the capability subsets of: strategy; service/products, people; processes; applications; information, and infrastructure.
1. Strategy
- Poor alignment with business objectives.
- Initiatives are currently not aligned to an overall vision.
- Siloed implementation of projects.
2. Service / Products
- Impediment to service delivery due to untimely retrieval of information.
- Slow responsiveness in engaging sales leads due to untimely retrieval of information.
- High level of product returns due to errors made on sales orders.
- Inadequate training of staff and/or lack of capacity for staff to support areas of the business experiencing bottlenecks.
- Poorly defined roles and responsibilities creates confusion and poor responsiveness to operational demands.
- Poor service delivery due to staff capacity and training issues.
4. Processes
- Myriad of duplicated business processes and applications.
- Intensive manual processing due to physical handling of paperwork, mail outs and manual coordination of events.
- Double data entry and manual maintenance of data in spread sheets or personal databases.
5. Applications
- Poorly developed functionality due to inadequate definition of business and functional requirements.
- Out of date functionality caused by a constantly evolving business climate.
- Little or no application support due to proprietary or redundant software.
6. Information
- Unstructured information and content stored on various devices making search and retrieval very difficult.
- No metadata attached to information making search and retrieval difficult.
- Disparate methods of coding the same types of datasets in disparate repositories.
7. Infrastructure
- Not a lot known about all systems making the strategic coordination of maintenance difficult.
- Multiple applications are supported on multiple systems creating unnecessary maintenance overheads by supporting duplicate systems.
When you have understood problems, describe the risks associated with each to fully emphasise the potential impacts on the business (e.g. costs, inefficiencies, and lost opportunities).
A Problem Statement Example in Business
Below is an example describing a problem statement, description and associated risk for a highly manual business process that can easily be resolved with technology.
Problem Statement: Intensive manual processing due to physical handling of paperwork. Description : Annual leave forms are typically filled out by the Employee, printed, sent to the Manager/Delegate for approval, sent to Human Resources for verification and data entry, scanned and uploaded to the EDRMS, and then sent to Payroll for (re) data entry. Risk : This highly manual scenario leads to ‘bottlenecks’ in service delivery and promotes the risk of poor organisational response to business and lost time that should be spent carrying out core business.
Tools for Developing Problem Statements
To develop the problem statement and associated risks of a project, engage with managers and subject matter experts within the relevant business areas. Ask them questions specific to your categorisation approach to bring out the details of where the problems lie. This approach can be implemented in the project’s initial set up and analysis phases irrespective of the methodology (i.e., Agile or Waterfall) being utilised. It is useful for developing project mandates and business cases.
There are several tools you can use to write a business problem statement, including:
- Brainstorming: Gather a group of stakeholders or team members and brainstorm all of the potential problems facing the business. Narrow down the list to the most pressing issues and identify the root cause of each problem.
- SWOT analysis: Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) to identify the internal and external factors impacting the business. Use this analysis to pinpoint the key problem areas.
- Fishbone diagram: Use a fishbone diagram (also known as an Ishikawa diagram) to identify the potential causes of a problem. This tool can help you visualise the different factors contributing to the problem and narrow down the root cause.
- 5 Whys: Ask “why” five times to get to the root cause of a problem. This technique can help you dig deeper into the underlying issues and identify the root cause of a problem. The Five Whys is an excellent technique to support your questioning approach.
- Problem Statement Template: Use a template to guide you through the process of writing a problem statement. A good problem statement template will prompt you to identify the problem, the impact it’s having on the business, the root cause, and potential solutions.
- Consult an expert: If you’re struggling to identify the problem or need help framing it in a concise and clear manner, consider consulting an expert in business analysis or strategy. They can provide valuable insights and guidance.
Specific Steps in Developing Problem Statements
Here are some steps to help you develop a problem statement:
- Identify the problem: Start by identifying the problem you want to solve. The problem should be specific, measurable, and relevant to your goals or objectives.
- Understand the context: Gather information about the problem and its impact. This could include data, research studies, reports, or input from stakeholders.
- Define the problem: Clearly define the problem by breaking it down into its key components. Use one of the tools mentioned above to get a comprehensive understanding of the problem.
- Analyse the problem: Analyse the problem by identifying the root causes, the impact on stakeholders, and the potential consequences of not addressing the problem.
- Create a problem statement: Use the information gathered in the previous steps to create a problem statement that summarises the problem, its impact, and its root causes. The problem statement should be concise, clear, and focused on the key issues.
- Refine the problem statement: Review and refine the problem statement to ensure that it accurately and clearly describes the problem and its impact. Refine the language, structure and categorisation as needed.
- Validate the problem statement: Validate the problem statement by testing it with stakeholders and subject matter experts. Get feedback on the clarity, accuracy, and relevance of the problem statement.
By following these steps, you can develop a problem statement that provides a clear and concise overview of the problem and its impact. This will help you to focus your efforts on developing effective solutions that address the root causes of the problem.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

The Right Way to Solve Complex Business Problems
Corey Phelps, a strategy professor at McGill University, says great problem solvers are hard to find. Even seasoned professionals at the highest levels of organizations regularly...
- Apple Podcasts
Corey Phelps, a strategy professor at McGill University, says great problem solvers are hard to find. Even seasoned professionals at the highest levels of organizations regularly fail to identify the real problem and instead jump to exploring solutions. Phelps identifies the common traps and outlines a research-proven method to solve problems effectively. He’s the coauthor of the book, Cracked it! How to solve big problems and sell solutions like top strategy consultants.
Download this podcast
Welcome to the IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Curt Nickisch.
Problem-solving is in demand. It’s considered the top skill for success at management consulting firms. And it’s increasingly desired for everyone, not just new MBA’s.
A report from the World Economic Forum predicts that more than one-third of all jobs across all industries will require complex problem-solving as one of their core skills by 2020.
The problem is, we’re often really bad at problem-solving. Our guest today says even the most educated and experienced of senior leaders go about it the wrong way.
COREY PHELPS: I think this is one of the misnomers about problem-solving. There’s this belief that because we do it so frequently – and especially for senior leaders, they have a lot of experience, they solve problems for a living – and as such we would expect them to be quite good at it. And I think what we find is that they’re not. They don’t solve problems well because they fall prey to basically the foibles of being a human being – they fall prey to the cognitive biases and the pitfalls of problem-solving.
CURT NICKISCH: That’s Corey Phelps. He says fixing these foibles is possible and almost straightforward. You can improve your problem-solving skills by following a disciplined method.
Corey Phelps is a strategy professor at McGill University. He’s also the co-author of the book “Cracked It: How to Solve Big Problems and Sell Solutions like Top Strategy C onsultants.” Corey thanks for coming on the show.
COREY PHELPS: Thank you for the opportunity to talk.
CURT NICKISCH: Another probably many, many biases that prevent people from solving big problems well.
COREY PHELPS: Absolutely.
CURT NICKISCH: What are some of the most common, or your favorite stumbling blocks?
COREY PHELPS: Well, one of my favorites is essentially the problem of jumping to solutions or the challenge of jumping to solutions.
CURT NICKISCH: Oh, come on Corey. That’s so much fun.
COREY PHELPS: It is, and it’s very much a result of how our brains have evolved to process information, but it’s my favorite because we all do it. And especially I would say it happens in organizations because in organizations when you layer on these time pressures and you layer on these concerns about efficiency and productivity, it creates enormous, I would say incentive to say “I don’t have time to carefully define and analyze the problem. I got to get a solution. I got to implement it as quick as possible.” And the fundamental bias I think is, is illustrated beautifully by Danny Kahneman in his book “Thinking, Fast and Slow,” is that our minds are essentially hardwired to think fast.
We are able to pay attention to a tiny little bit of information. We can then weave a very coherent story that makes sense to us. And then we can use that story to jump very quickly to a solution that we just know will work. And if we just were able to move from that approach of what Kahneman and cognitive psychologists called “System 1 thinking” to “System 2 thinking” – that is to slow down, be more deliberative, be more structured – we would be able to better understand the problem that we’re trying to solve and be more effective and exhaustive with the tools that we want to use to understand the problem before we actually go into solution-generation mode.
CURT NICKISCH: Complex problems demand different areas of expertise and often as individuals we’re coming to those problems with one of them. And I wonder if that’s often the problem of problem-solving, which is that a manager is approaching it from their own expertise and because of that, they see the problem through a certain way. Is that one of the cognitive biases that stop people from being effective problem solvers?
COREY PHELPS: Yeah. That’s often referred to as the expertise trap. It basically colors and influences what we pay attention to with respect to a particular problem. And it limits us with respect to the tools that we can bring to bear to solve that problem. In the world of psychology, there’s famous psychologist, Abraham Maslow, who is famous for the hierarchy of needs. He’s also famous for something that was a also known as MaSlow’s axiom, Maslow’s law. It’s also called the law of the instrument, and to paraphrase Maslow, he basically said, “Look, I suppose if the only tool that you have in your toolkit is a hammer, everything looks like a nail.”
His point is that if you’re, for example, a finance expert and your toolkit is the toolkit of let’s say, discounted cash flow analysis for valuation, then you’re going to see problems through that very narrow lens. Now, one of the ways out of this, I think to your point is collaboration becomes fundamentally important. And collaboration starts with the recognition that I don’t have all of the tools, all of the knowledge in me to effectively solve this. So I need to recruit people that can actually help me.
CURT NICKISCH: That’s really interesting. I wonder how much the fact that you have solved a problem before it makes you have a bias for that same solution for future problems?
COREY PHELPS: Yeah, that’s a great question. What you’re alluding to is analogical reasoning, and we know that human beings, one of the things that allows us to operate in novel settings is that we can draw on our past experience. And we do so when it comes to problem solving, often times without being conscious or mentally aware of it. We reach into our memory and we ask ourselves a very simple question: “Have I seen a problem like this before?”
And if it looks familiar to me, the tendency then is to say, “Okay, well what worked in solving that problem that I faced before?” And then to say, “Well, if it worked in that setting, then it should work in this setting.” So that’s reasoning by analogy.
Reasoning by analogy has a great upside. It allows human beings to not become overwhelmed by the tremendous novelty that they face in their daily lives. The downside is that if we don’t truly understand it at sort of a deep level, whether or not the two problems are similar or different, then we can make what cognitive psychologists called surface-level analogies.
And we can then say, “Oh, this looks a lot like the problem I faced before, that solution that worked there is going to easily work here.” And we try that solution and it fails and it fails largely because if we dug a little bit deeper, the two problems actually aren’t much alike at all in terms of their underlying causes.
CURT NICKISCH: The starkest example of this, I think, in your book is Ron Johnson who left Apple to become CEO of JC Penney. Can you talk about that a little bit and what that episode for the company says about this?
COREY PHELPS: So yes, its – Ron Johnson had been hired away from Target in the United States to, by Steve Jobs to help create Apple stores. Apple stores are as many people know the most successful physical retailer on the planet measured by, for example, sales per square foot or per square meter. He’s got the golden touch. He’s created this tremendously successful retail format for Apple.
So the day that it was announced that Ron Johnson was going to step into the CEO role at JC Penney, the stock price of JC Penney went up by almost 18 percent. So clearly he was viewed as the savior. Johnson moves very, very quickly. Within a few months, he announces that he has a strategic plan and it basically comes in three parts.
Part number one is he’s going to eliminate discount pricing. JC Penney had been a very aggressive sales promoter. The second piece of it is he’s going to completely change how they organize merchandise. It’s no longer going to be organized by function – so menswear, housewares, those sorts of things. It’s going to be organized by boutique, so there’s going to be a Levi’s boutique, a Martha Stewart Boutique, a Joe Fresh Boutique and so on.
And it would drop the JC P enney name, they would call it JCP. And he rolls this out over the course of about 12 months across the entire chain of over 1100 stores. What this tells us, he’s so confident in his solution, his strategic transformation, that he doesn’t think it’s worth it to test this out on one or two pilot stores.
CURT NICKISCH: Yeah, he was quoted as saying: “At Apple, we didn’t test anything.”
COREY PHELPS: We didn’t test. Yes. What worked at Apple, he assumed would work at JC Penney. And the critical thing that I think he missed is that JC Penney customers are very different from Apple store customers. In fact, JC Penney customers love the discount. They love the thrill of hunting for a deal.
CURT NICKISCH: Which seems so fundamental to business, right? Understanding your customer. It’s just kind of shocking, I guess, to hear the story.
COREY PHELPS: It is shocking and especially when you consider that Ron Johnson had spent his entire career in retail, so this is someone that had faced, had seen, problems in retailers for decades – for over three decades by the time that he got to JC Penney. So you would expect someone with that degree of experience in that industry wouldn’t make that leap of, well, what worked at Apple stores is going to work at JC Penney stores, but in fact that’s exactly what happened.
CURT NICKISCH: In your book, you essentially suggest four steps that you recommend people use. Tell us about the four steps then.
COREY PHELPS: So in the book we describe what we call the “Four S method,” so four stages, each of which starts with the letter “s”. So the first stage is “state the problem.” Stating the problem is fundamentally about defining what the problem is that you are attempting to solve.
CURT NICKISCH: And you probably would say don’t hurry over that first step or the other three are going to be kind of pointless.
COREY PHELPS: Yeah, that’s exactly the point of of laying out the four s’s. There’s a tremendous amount of desire even amongst senior executives to want to get in and fix the problem. In other words, what’s the trouble? What are the symptoms? What would define success? What are the constraints that we would be operating under? Who owns the problem? And then who are the key stakeholders?
Oftentimes that step is skipped over and we go right into, “I’ve got a hypothesis about what I think the solution is and I’m so obsessed with getting this thing fixed quickly, I’m not going to bother to analyze it particularly well or test the validity of my assumptions. I’m going to go right into implementation mode.”
The second step, what we call “structure the problem” is once you have defined the problem, you need to then start to identify what are the potential causes of that problem. So there are different tools that we talked about in the book that you can structure a problem for analysis. Once you’ve structured the problem for analysis and you’ve conducted the analysis that helps you identify what are the underlying causes that are contributing to it, which will then inform the third stage which is generating solutions for the problem and then testing and evaluating those solutions.
CURT NICKISCH: Is the danger that that third step – generating solutions – is the step that people spend the most time on or have the most fun with?
COREY PHELPS: Yeah. The danger is, is that what that’s naturally what people gravitate towards. So we want to skip over the first two, state and structure.
CURT NICKISCH: As soon as you said it, I was like, “let’s talk about that more.”
COREY PHELPS: Yeah. And we want to jump right into solutioning because people love to talk about their ideas that are going to fix the problem. And that’s actually a useful way to frame a discussion about solutions – we could, or we might do this – because it opens up possibilities for experimentation.
And the problem is that when we often talk about what we could do, we have very little understanding of what the problem is that we’re trying to solve and what are the underlying causes of that problem. Because as you said, solution generation is fun. Look, the classic example is brainstorming. Let’s get a bunch of people in a room and let’s talk about the ideas on how to fix this thing. And again, be deliberate, be disciplined. Do those first stages, the first two stages – state and structure – before you get into the solution generation phase.
CURT NICKISCH: Yeah. The other thing that often happens there is just the lack of awareness of just the cost of the different solutions – how much time, or what they would actually take to do.
COREY PHELPS: Yeah, and again, I’ll go back to that example I used of brainstorming where it’s fun to get a group of people together and talk about our ideas and how to fix the problem. There’s a couple challenges of that. One is what often happens when we do that is we tend to censor the solutions that we come up with. In other words, we ask ourselves, “if I say this idea, people are gonna, think I’m crazy, or people going to say: that’s stupid, that’ll never work, we can’t do that in our organization. It’s going to be too expensive, it’s going to take too much time. We don’t have the resources to do it.”
So brainstorming downside is we we self-sensor, so that’s where you need to have deep insight into your organization in terms of A. what’s going to be feasible, B. what’s going to be desirable on the part of the people that actually have the problem, who you’re trying to solve the problem for and C. from a business standpoint, is it going to be financially attractive for us?
So applying again a set of disciplined criteria that help you choose amongst those ideas for potential solutions. Then the last stage of the process which is selling – because it’s rare in any organization that someone or the group of people that come up with the solution actually have the power and the resources to implement it, so that means they’re going to have to persuade other people to buy into it and want to help.
CURT NICKISCH: Design thinking is another really different method essentially for solving problems or coming up with solutions that just aren’t arrived at through usual problem-solving or usual decision-making processes. I’m just wondering how design thinking comes to play when you’re also outlining these, you know, disciplined methods for stating and solving problems.
COREY PHELPS: For us it’s about choosing the right approach. You know what the potential causes of a problem are. You just don’t know which ones are operating in the particular problem you’re trying to solve. And what that means is that you’ve got a theory – and this is largely the world of strategy consultants – strategy consultants have theories. They have, if you hear them speak, deep understanding of different types of organizational problems, and what they bring is an analytic tool kit that says, “first we’re going to identify all the possible problems, all the possible causes I should say, of this problem. We’re going to figure out which ones are operating and we’re going to use that to come up with a solution.” Then you’ve got problems that you have no idea what the causes are. You’re in a world of unknown unknowns or unk-unks as the operations management people call them.
CURT NICKISCH: That’s terrible.
COREY PHELPS: In other words, you don’t have a theory. So the question is, how do you begin? Well, this is where design thinking can be quite valuable. Design thinking says: first off, let’s find out who are the human beings, the people that are actually experiencing this problem, and let’s go out and let’s talk to them. Let’s observe them. Let’s immerse ourselves in their experience and let’s start to develop an understanding of the causes of the problem from their perspective.
So rather than go into it and say, “I have a theory,” let’s go the design thinking route and let’s actually based upon interactions with users or customers, let’s actually develop a theory. And then we’ll use our new understanding or new insight into the causes of the problem to move into the solution generation phase.
CURT NICKISCH: Problem-solving – we know that that’s something that employers look for when they’re recruiting people. It is one of those phrases that, you know, I’m sure somebody out there has, has the title at a company Chief Problem Solver instead of CEO, right? So, it’s almost one of those phrases that so over used it can lose its meaning.
And if you are being hired or you’re trying to make a case for being on a team that’s tackling a problem, how do you make a compelling case that you are a good problem solver? How can you actually show it?
COREY PHELPS: It’s a great question and then I have two answers to this question. So one is, look at the end of the day, the proof is in the pudding. In other words, can you point to successful solutions that you’ve come up with – solutions that have actually been effective in solving a problem? So that’s one.
The second thing is can you actually articulate how you approach problem-solving? In other words, do you follow a method or are you reinventing the wheel every time you solve a problem? Is it an ad hoc approach? And I think this issue really comes to a head when it comes to the world of strategy consulting firms when they recruit. For example, Mckinsey, you’ve got the Mckinsey problem-solving test, which is again, a test that’s actually trying to elicit the extent to which people are good applicants are good at solving problems
And then you’ve got the case interview. And in the case interview, what they’re looking at is do you have a mastery over certain tools. But what they’re really looking at is, are you actually following a logical process to solve this problem? Because again, what they’re interested in is finding- to your point – people that are going to be good at solving complex organizational problems. So they’re trying to get some evidence that they can demonstrate that they’re good at it and some evidence that they follow a deliberate process.
CURT NICKISCH: So even if you’re not interviewing at a consulting firm, that’s a good approach, to show your thinking, show your process, show the questions you ask?
COREY PHELPS: Yeah, and to your point earlier, at least if we look at what recruiters of MBA students are saying these days, they’re saying, for example, according to the FT’s recent survey, they’re saying that we want people with really good problem solving skills, and by the same token, we find that that’s a skill that’s difficult for us to recruit for. And that reinforces our interest in this area because the fundamental idea for the book is to give people a method. We’re trying to equip not just MBA students but everybody that’s going to face complex problems with a toolkit to solve them better.
CURT NICKISCH: Corey, this has been really great. Thank you.
COREY PHELPS: Thanks for the opportunity. I appreciate it.
CURT NICKISCH: That’s Corey Phelps. He teaches strategy at McGill University, and he co-wrote the book “Cracked It: How to Solve Big Problems and Sell Solutions Like Top Strategy Consultants.”
This episode was produced by Mary Dooe. We got technical help from Rob Eckhardt. Adam Buchholz is our audio product manager.
Thanks for listening to the HBR IdeaCast. I’m Curt Nickisch.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about decision making and problem solving, partner center.
Six problem-solving mindsets for very uncertain times
Great problem solvers are made, not born. That’s what we’ve found after decades of problem solving with leaders across business, nonprofit, and policy sectors. These leaders learn to adopt a particularly open and curious mindset, and adhere to a systematic process for cracking even the most inscrutable problems. They’re terrific problem solvers under any conditions. And when conditions of uncertainty are at their peak, they’re at their brilliant best.
Six mutually reinforcing approaches underly their success: (1) being ever-curious about every element of a problem; (2) being imperfectionists , with a high tolerance for ambiguity; (3) having a “dragonfly eye” view of the world, to see through multiple lenses; (4) pursuing occurrent behavior and experimenting relentlessly; (5) tapping into the collective intelligence , acknowledging that the smartest people are not in the room; and (6) practicing “show and tell” because storytelling begets action (exhibit).
Here’s how they do it.
1. Be ever-curious
As any parent knows, four-year-olds are unceasing askers. Think of the never-ending “whys” that make little children so delightful—and relentless. For the very young, everything is new and wildly uncertain. But they’re on a mission of discovery, and they’re determined to figure things out. And they’re good at it! That high-energy inquisitiveness is why we have high shelves and childproof bottles.
When you face radical uncertainty, remember your four-year-old or channel the four-year-old within you. Relentlessly ask, “Why is this so?” Unfortunately, somewhere between preschool and the boardroom, we tend to stop asking. Our brains make sense of massive numbers of data points by imposing patterns that have worked for us and other humans in the past. That’s why a simple technique, worth employing at the beginning of problem solving, is simply to pause and ask why conditions or assumptions are so until you arrive at the root of the problem. 1 This approach was originally developed by Sakichi Toyoda, the founder of Toyota.
Natural human biases in decision making, including confirmation, availability, and anchoring biases, often cause us to shut down the range of solutions too early. 2 Daniel Kahneman, Thinking, Fast and Slow , New York, NY: Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2011. Better—and more creative—solutions come from being curious about the broader range of potential answers.
One simple suggestion from author and economist Caroline Webb to generate more curiosity in team problem solving is to put a question mark behind your initial hypotheses or first-cut answers. This small artifice is surprisingly powerful: it tends to encourage multiple solution paths and puts the focus, correctly, on assembling evidence. We also like thesis/antithesis, or red team/blue team, sessions, in which you divide a group into opposing teams that argue against the early answers—typically, more traditional conclusions that are more likely to come from a conventional pattern. Why is this solution better? Why not that one? We’ve found that better results come from embracing uncertainty. Curiosity is the engine of creativity.
We have to be comfortable with estimating probabilities to make good decisions, even when these guesses are imperfect. Unfortunately, we have truckloads of evidence showing that human beings aren’t good intuitive statisticians.
2. Tolerate ambiguity—and stay humble!
When we think of problem solvers, many of us tend to picture a poised and brilliant engineer. We may imagine a mastermind who knows what she’s doing and approaches a problem with purpose. The reality, though, is that most good problem solving has a lot of trial and error; it’s more like the apparent randomness of rugby than the precision of linear programming. We form hypotheses, porpoise into the data, and then surface and refine (or throw out) our initial guess at the answer. This above all requires an embrace of imperfection and a tolerance for ambiguity—and a gambler’s sense of probabilities.
The real world is highly uncertain. Reality unfolds as the complex product of stochastic events and human reactions. The impact of COVID-19 is but one example: we address the health and economic effects of the disease, and their complex interactions, with almost no prior knowledge. We have to be comfortable with estimating probabilities to make good decisions, even when these guesses are imperfect. Unfortunately, we have truckloads of evidence showing that human beings aren’t good intuitive statisticians. Guesses based on gut instinct can be wildly wrong. That’s why one of the keys to operating in uncertain environments is epistemic humility, which Erik Angner defines as “the realization that our knowledge is always provisional and incomplete—and that it might require revision in light of new evidence.” 3 Erik Angner, “Epistemic humility—knowing your limits in a pandemic,” Behavioral Scientist , April 13, 2020, behavioralscientist.org.
Recent research shows that we are better at solving problems when we think in terms of odds rather than certainties. 4 Annie Duke, Thinking in Terms of Bets: Making Smarter Decisions When You Don’t Have All the Facts , New York, NY: Portfolio/Penguin, 2018. For example, when the Australian research body Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), which owned a core patent on the wireless internet protocol, sought royalties from major companies, it was initially rebuffed. The CSIRO bet that it could go to court to protect its intellectual property because it estimated that it needed only 10 percent odds of success for this to be a good wager, given the legal costs and likely payoff. It improved its odds by picking the weakest of the IP violators and selecting a legal jurisdiction that favored plaintiffs. This probabilistic thinking paid off and eventually led to settlements to CSIRO exceeding $500 million. 5 CSIRO briefing to US Government, December 5, 2006. A tolerance for ambiguity and a willingness to play the odds helped the organization feel its way to a good solution path.
To embrace imperfectionism with epistemic humility, start by challenging solutions that imply certainty. You can do that in the nicest way by asking questions such as “What would we have to believe for this to be true?” This brings to the surface implicit assumptions about probabilities and makes it easier to assess alternatives. When uncertainty is high, see if you can make small moves or acquire information at a reasonable cost to edge out into a solution set. Perfect knowledge is in short supply, particularly for complex business and societal problems. Embracing imperfection can lead to more effective problem solving. It’s practically a must in situations of high uncertainty, such as the beginning of a problem-solving process or during an emergency.
Good problem solving typically involves designing experiments to reduce key uncertainties. Each move provides additional information and builds capabilities.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
3. take a dragonfly-eye view.
Dragonfly-eye perception is common to great problem solvers. Dragonflies have large, compound eyes, with thousands of lenses and photoreceptors sensitive to different wavelengths of light. Although we don’t know exactly how their insect brains process all this visual information, by analogy they see multiple perspectives not available to humans. The idea of a dragonfly eye taking in 360 degrees of perception 6 Philip Tetlock and Dan Gardner, Superforecasting: The Art and Science of Prediction , New York, NY: Crown, 2015. is an attribute of “superforecasters”—people, often without domain expertise, who are the best at forecasting events.
Think of this as widening the aperture on a problem or viewing it through multiple lenses. The object is to see beyond the familiar tropes into which our pattern-recognizing brains want to assemble perceptions. By widening the aperture, we can identify threats or opportunities beyond the periphery of vision.
Consider the outbreak of HIV in India in the early 1990s—a major public-health threat. Ashok Alexander, director of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation’s India Aids Initiative, provided a brilliant example of not just vision but also dragonfly vision. Facing a complex social map with a rapidly increasing infection rate, he widened the problem’s definition, from a traditional epidemiological HIV transmission model at known “hot spots,” to one in which sex workers facing violence were made the centerpiece.
This approach led to the “Avahan solution,” which addressed a broader set of leverage points by including the sociocultural context of sex work. The solution was rolled out to more than 600 communities and eventually credited with preventing 600,000 infections. The narrow medical perspective was sensible and expected, but it didn’t tap into the related issue of violence against sex workers, which yielded a richer solution set. Often, a secret unlocks itself only when one looks at a problem from multiple perspectives, including some that initially seem orthogonal.
The secret to developing a dragonfly-eye view is to “anchor outside” rather than inside when faced with problems of uncertainty and opportunity. Take the broader ecosystem as a starting point. That will encourage you to talk with customers, suppliers, or, better yet, players in a different but related industry or space. Going through the customer journey with design-thinking in mind is another powerful way to get a 360-degree view of a problem. But take note: when decision makers face highly constrained time frames or resources, they may have to narrow the aperture and deliver a tight, conventional answer.

Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
4. pursue occurrent behavior.
Occurrent behavior is what actually happens in a time and place, not what was potential or predicted behavior. Complex problems don’t give up their secrets easily. But that shouldn’t deter problem solvers from exploring whether evidence on the facets of a solution can be observed, or running experiments to test hypotheses. You can think of this approach as creating data rather than just looking for what has been collected already. It’s critical for new market entry—or new market creation. It also comes in handy should you find that crunching old data is leading to stale solutions.
Most of the problem-solving teams we are involved with have twin dilemmas of uncertainty and complexity, at times combined as truly “wicked problems.” 7 A term coined in a now famous 1973 article: Horst W. J. Rittel and Melvin Webber, “Dilemmas in a general theory of planning,” Policy Sciences , 1973, Number 4, pp. 155–69. For companies ambitious to win in the great unknown in an emerging segment—such as electric cars or autonomous vehicles, where the market isn’t fully established—good problem solving typically involves designing experiments to reduce key uncertainties, not just relying on existing data. Each move (such as buying IP or acquiring a component supplier) and each experiment (including on-road closed tests) not only provides additional information to make decisions but also builds capabilities and assets that support further steps. Over time, their experiments, including alliances and acquisitions, come to resemble staircases that lead to either the goal or to abandonment of the goal. Problem-solving organizations can “bootstrap” themselves into highly uncertain new spaces, building information, foundational assets, and confidence as they take steps forward.
Risk-embracing problem solvers find a solution path by constantly experimenting. Statisticians use the abbreviation EVPI—the expected value of perfect information—to show the value of gaining additional information that typically comes from samples and experiments, such as responses to price changes in particular markets. A/B testing is a powerful tool for experimenting with prices, promotions, and other features and is particularly useful for digital marketplaces and consumer goods. Online marketplaces make A/B testing easy. Yet most conventional markets also offer opportunities to mimic the market’s segmentation and use it to test different approaches.
The mindset required to be a restless experimenter is consistent with the notion in start-ups of “failing fast.” It means that you get product and customer affirmation or rejection quickly through beta tests and trial offerings. Don’t take a lack of external data as an impediment—it may actually be a gift, since purchasable data is almost always from a conventional way of meeting needs, and is available to your competitors too. Your own experiments allow you to generate your own data; this gives you insights that others don’t have. If it is difficult (or unethical) to experiment, look for the “natural experiments” provided by different policies in similar locations. An example would be to compare outcomes in twin cities, such as Minneapolis–St. Paul.
It’s a mistake to think that your team has the smartest people in the room. They aren’t there. They’re invariably somewhere else. Nor do they need to be there if you can access their intelligence via other means.
5. Tap into collective intelligence and the wisdom of the crowd
Chris Bradley, a coauthor of Strategy Beyond the Hockey Stick , 8 Chris Bradley, Marin Hirt, and Sven Smit, Strategy Beyond the Hockey Stick: People, Probabilities, and Big Moves to Beat the Odds , Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2018. observed that “it’s a mistake to think that on your team you have the smartest people in the room. They aren’t there. They’re invariably somewhere else.” 9 For more from Chris Bradley, in a conversation with Rob McLean, see “ Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver ,” August 2019. Nor do they need to be there if you can access their intelligence via other means. In an ever-changing world where conditions can evolve unpredictably, crowdsourcing invites the smartest people in the world to work with you. For example, in seeking a machine-learning algorithm to identify fish catch species and quantities on fishing boats, the Nature Conservancy (TNC) turned to Kaggle and offered a $150,000 prize for the best algorithm. This offer attracted 2,293 teams from all over the world. TNC now uses the winning algorithm to identify fish types and sizes caught on fishing boats in Asia to protect endangered Pacific tuna and other species.
Crowdsourced problem solving is familiar in another guise: benchmarking. When Sir Rod Carnegie was CEO of Conzinc Riotinto Australia (CRA), he was concerned about the costs of unscheduled downtime with heavy trucks, particularly those requiring tire changes. He asked his management team who was best in the world at changing tires; their answer was Formula One, the auto racing competition. A team traveled to the United Kingdom to learn best practice for tire changes in racetrack pits and then implemented what it learned thousands of miles away, in the Pilbara region of Western Australia. The smartest team for this problem wasn’t in the mining industry at all.
Of course, while crowdsourcing can be useful when conventional thinking yields solutions that are too expensive or incomplete for the challenge at hand, it has its limitations. Good crowdsourcing takes time to set up, can be expensive, and may signal to your competitors what you are up to. Beware of hidden costs, such as inadvertently divulging information and having to sieve through huge volumes of irrelevant, inferior suggestions to find the rare gem of a solution.
Accept that it’s OK to draw on diverse experiences and expertise other than your own. Start with brainstorming sessions that engage people from outside your team. Try broader crowdsourcing competitions to generate ideas. Or bring in deep-learning talent to see what insights exist in your data that conventional approaches haven’t brought to light. The broader the circles of information you access, the more likely it is that your solutions will be novel and creative.
Rookie problem solvers show you their analytic process and math to convince you they are clever. Seasoned problem solvers show you differently.
6. Show and tell to drive action
We started our list of mindsets with a reference to children, and we return to children now, with “show and tell.” As you no doubt remember—back when you were more curious!—show and tell is an elementary-school activity. It’s not usually associated with problem solving, but it probably piqued your interest. In fact, this approach is critical to problem solving. Show and tell is how you connect your audience with the problem and then use combinations of logic and persuasion to get action.
The show-and-tell mindset aims to bring decision makers into a problem-solving domain you have created. A team from the Nature Conservancy, for instance, was presenting a proposal asking a philanthropic foundation to support the restoration of oyster reefs. Before the presentation, the team brought 17 plastic buckets of water into the boardroom and placed them around the perimeter. When the foundation’s staff members entered the room, they immediately wanted to know what the buckets were for. The team explained that oyster-reef restoration massively improves water quality because each oyster filters 17 buckets of water per day. Fish stocks improve, and oysters can also be harvested to help make the economics work. The decision makers were brought into the problem-solving domain through show and tell. They approved the funding requested and loved the physical dimension of the problem they were part of solving.
Rookie problem solvers show you their analytic process and mathematics to convince you that they are clever. That’s sometimes called APK, the anxious parade of knowledge. But seasoned problem solvers show you differently. The most elegant problem solving is that which makes the solution obvious. The late economist Herb Simon put it this way: “Solving a problem simply means representing it so as to make the solution transparent.” 10 Herbert Simon, The Sciences of the Artificial , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1969.
To get better at show and tell, start by being clear about the action that should flow from your problem solving and findings: the governing idea for change. Then find a way to present your logic visually so that the path to answers can be debated and embraced. Present the argument emotionally as well as logically, and show why the preferred action offers an attractive balance between risks and rewards. But don’t stop there. Spell out the risks of inaction, which often have a higher cost than imperfect actions have.
The mindsets of great problem solvers are just as important as the methods they employ. A mindset that encourages curiosity, embraces imperfection, rewards a dragonfly-eye view of the problem, creates new data from experiments and collective intelligence, and drives action through compelling show-and-tell storytelling creates radical new possibilities under high levels of unpredictability. Of course, these approaches can be helpful in a broad range of circumstances, but in times of massive uncertainty, they are essential.
Charles Conn is an alumnus of McKinsey’s Sydney office and is a board member of Patagonia and former CEO of the Rhodes Trust. Robert McLean is an alumnus of the Sydney office and is the advisory-board chair of the Nature Conservancy Australia. They are the authors of Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything (Wiley, 2018).
This article was edited by David Schwartz, an executive editor in the Tel Aviv office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategy to beat the odds

Dwight Eisenhower: Lessons from the ‘balancer in chief’
Limited time: Try B12 $1/mo for 3 months.
Launch an online presence that makes it simple to attract, win, and serve clients
B12 uses AI and experts to quickly set up your website, scheduling, payments, email marketing, and more.

How to solve the most common small business problems

It can be exciting and intimidating to start and grow a small business . The challenges small businesses face can greatly impact their growth and success. Small business owners face so many obstacles, from managing cash flow to finding and retaining talent. It's easy to solve these common problems with the right strategy.
In this blog post, we'll talk about the most common problems small businesses face and how to solve them. Entrepreneurs can navigate the ups and downs of entrepreneurship by understanding these challenges and implementing effective strategies.
The life cycle of a small business
Exploring the five stages of business growth.
Many small businesses go through a predictable life cycle as they grow and develop. Understanding these stages can help entrepreneurs navigate the challenges and opportunities that arise at each phase. Business owners can take proactive steps toward sustainable growth by knowing where their business stands and what lies ahead. Here are the five stages:
Stage 1: seed stage
During the seed stage, the business is just an idea or a concept. An entrepreneur focuses on market research, refining their business plan, and getting funding or investment. Future growth depends on this stage.
Here's when you validate your business concept, identify your customers, and develop your value proposition. Start-ups in the seed stage often face challenges such as limited resources, uncertainty, and the need for market validation.
Stage 2: start-up stage
The start-up stage is when the business is officially launched. An entrepreneur works to build a brand, get customers, and refine their product or service. This stage often involves high levels of uncertainty and requires continuous adaptation and learning.
Entrepreneurs take concrete steps to make their ideas a reality during this phase. They get funding, set up operations, and register as a legal entity. At this stage, startups have to manage cash flow, build a customer base, and set up efficient processes.
Stage 3: growth stage
In the growth stage, the business begins to experience increased demand and revenue. The focus shifts to scalability and expanding operations to meet customer needs. Managing rapid growth can bring challenges, like hiring and retaining skilled employees, and optimizing operations to accommodate the growing customer base. This stage requires careful financial management, effective marketing strategies, and the implementation of scalable systems.
Stage 4: expansion stage
During the expansion stage, the business seeks to penetrate new markets or diversify its product/service offering. This may involve expanding geographically, acquiring competitors , or launching new product lines.
Expansion can bring opportunities, but it also comes with challenges, such as market saturation, increased competition, and strategic planning. This stage involves significant investment, strategic partnerships, and careful planning to ensure sustainable growth and profitability.
Stage 5: maturity stage
The maturity stage is characterized by a stable and profitable business. At this point, it's all about maintaining market share, optimizing operations, and exploring new ideas. Businesses need to adapt constantly to changing market conditions to stay successful.
In the mature stage, companies may face market obsolescence, declining growth rates, and the need to constantly innovate to stay relevant.
Small business owners can learn a lot from the stages of business growth. Entrepreneurs can take proactive steps toward long-term success by recognizing challenges and opportunities at every stage. Let’s dig deeper into the challenges small businesses face at each stage and provide practical solutions.
Common problems that small businesses face
Problem 1: lack of proper planning and strategy.
Small businesses often have problems with planning and strategy. It's hard for small businesses to navigate growth challenges without a roadmap and a plan. A small business owner needs a strategic vision that outlines their goals, objectives, and the steps to get there. A solid plan can help small businesses allocate resources, identify risks, and make informed decisions.
Problem 2: insufficient financial management
Small businesses often face issues related to financial management. You need to know your finances to grow your business. Cash flow problems, investment difficulties, and even failure can be caused by poor financial management. Keeping accurate financial records, monitoring cash flow, and forecasting properly are all things small business owners should focus on. Making informed financial decisions, securing funding when needed, and managing expenses can be done by small businesses who stay on top of their finances.
Problem 3: ineffective marketing and branding
It's hard for small businesses to stand out in today's market. Small businesses struggle with creating and implementing marketing strategies. The result can be low customer awareness, low sales, and difficulty reaching your target market.
Small business owners need to understand their target market, identify their unique selling proposition, and craft a compelling brand message. Marketing tactics like social media, content marketing, and targeted advertising can help small businesses grow.

Problem 4: difficulty in scaling operations
It's hard for small businesses to scale . Small businesses may find it hard to meet increased demand, deliver products or services efficiently, and keep customers happy as they grow. It's up to small business owners to develop scalable systems and processes to overcome this challenge. This can involve investing in technology and automation, streamlining operations, and strategically expanding their workforce. With scalable solutions, small businesses can manage growth, stay agile, and consistently deliver quality products and services.
Solutions to the common problems faced by small businesses
Solution 1: creating a comprehensive business plan.
To grow and succeed, small businesses need a good business plan. The plan outlines the company's goals, target market, and strategies for achieving profitability. Analyzing competitors and conducting market research can help business owners identify challenges and opportunities. The plan should also have a detailed budget and resource allocation. Ultimately, a comprehensive business plan helps you overcome potential roadblocks and gives your company a clear direction for growth.
Solution 2: implementing proper financial management practices
Mismanagement of finances is a big problem for small businesses. Insufficient cash flow, poor budgeting, and insufficient financial records can hurt growth. Business owners can gain better visibility into their financial health by implementing good financial management practices. A good cash flow management strategy includes minimizing expenses and maximizing revenue. Making informed decisions, seizing opportunities, and overcoming financial challenges are all possible with sound financial practices.
Solution 3: developing an effective marketing strategy
Branding and marketing are crucial for small businesses. Businesses can't reach their target audience and make sales without an effective marketing strategy. Develop a marketing plan for your small business by identifying your target market and understanding your customers. For maximum reach and influence, consider leveraging social media, email marketing, content marketing, and paid advertising. Implementing a well-planned marketing strategy can help businesses build brand awareness, attract new customers, and grow.
Solution 4: applying scalable systems and processes
Small businesses need scalable systems and processes to grow. Scalable systems can help businesses avoid operational inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and inconsistent processes. Business owners can handle increased demand more effectively if they implement scalable processes, such as automated workflows, standardized procedures, and efficient supply chain management.
Scalable systems also allow businesses to adapt to changes and expand without sacrificing quality. Sustainable growth can be achieved by focusing on scalability.
Key takeaways and actionable steps for business growth
It's important to understand the challenges at each stage of the business life cycle to solve the most common problems facing small businesses . You can better prepare yourself for the hurdles ahead by recognizing the five stages of growth - seed stage, start-up stage, growth stage, expansion stage, and maturity stage.
The importance of addressing issues in small business for overall economic growth
The backbone of any economy is small businesses, which create jobs and innovate. Many of these businesses face challenges that limit their growth. Small businesses need support, resources, and mentorship programs from governments, institutions, and stakeholders to succeed.
Adopting a comprehensive approach to overcoming business challenges
It's crucial to adopt a comprehensive approach to running a successful small business to solve the most common problems. Creating a detailed business plan, implementing sound financial management practices, developing effective marketing strategies, implementing scalable systems and processes, and building a reliable team are all part of this process.
Grow your business’s visibility with B12
Equip your small business for future growth using a powerful platform like B12. With B12, you can generate a professional and eye-catching website, which can help you attract more visitors and get more conversions. B12’s DIY website editor makes it easy for you to make changes anytime and upload your branding elements for brand cohesion.
B12’s suite of powerful solutions also helps you scale as you grow. Leverage tools like online payments , email automation, scheduling , and more to attract and engage your client base. Use B12 to establish your small business online and get everything you need to sell services. Get started today for free in 60 seconds.
Attract, win, and serve more clients
Receive helpful resources directly to your inbox to help you succeed online.
Related posts

Spend less time on your website and more time growing your business
Let B12 set up your professional online presence with everything you need to attract, win, and serve clients.
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools
4 Proven Techniques For Effective Business Problem Solving

Free Business Problem Statement Templates
Aayushi Mistry
- December 18, 2023
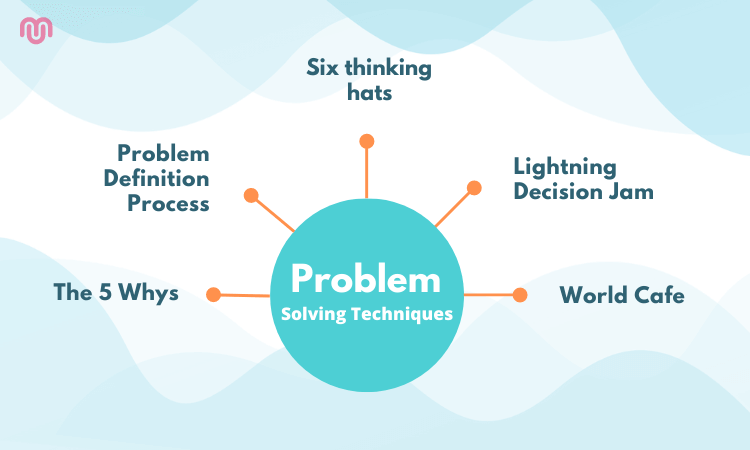
There are several fundamentals on which your business stands, remains stable, and soars at the heights for you. These fundamentals are Research and Development of your product and services, Marketing along with market analysis and implementations, sales, accounts, customer support, and human resources. These fundamentals remain the same regardless of the size of your company.
Ideally, for your company to run smoothly, all the fundamentals must remain in balance. However, more often than not, the real scenario is far away from the ideal. As problems arise every day, your business needs new optimizations every day. And it is within these problems that you will actually find the job of having a business.
In any way, it is very important for you to look at your operations and make them as error-free as possible. But, how to do that? Well, this is what this blog post is all about-Actionable steps to business problem-solving .
So Firstly, You Have to Determine What Is the Actual Problem?
Running a company is not easy. Hundreds of things come at you from all different directions. In that case, a lot of time, you might not even realize that there is any problem. So when you see that everything is not the way it is supposed to be. Find out the actual problem.
There could be a problem in any of the fundamental aspects that we discussed above. Moreover, A lot of times, it is possible to have problems in multiple areas of business. And knowing the area of the problem is the first and most important step toward solving the problem.
And then, understand the seriousness of the problem?
At times, the problem at hand requires a solution. But you might not need to act on it immediately. It is so much like a dent in your ship. But other times, the problems might thrash right under your ship. And it becomes so severe that you need to work on it immediately. If not, the problem might just sink your entire business.
Some of such severe problems include not having adequate funds, improper marketing, and sales strategy, not enough human resources, shortage of technology, improper leadership, and more.
However, at the end of the day, you get to decide on the severity of the problem.
Apply proper damage control
Once you figure out the seriousness of the problem, think about what you can do immediately. A few problems may not have an instant solution. But they can definitely have instant damage control. So, by the time you reach the root of your problem and bring the solution, apply the appropriate damage control.
And solve problems from the very root
A lot of time, a problem is not just the bits that appear on the surface. In fact, it has a deeper end than we could think of. So, every time you find a problem, give it an analytical approach. Give it a helicopter view and find out the factors contributing to your problem. Doing so will help you solve the problem from its deepest point. And along with that, will also help you streamline other operations affecting it.
To Identify The Problem, Here Are a Few Techniques You Can Implement.

Apply SWOT analysis
SWOT analysis stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. A lot of times, companies use this model for competitive analysis . But it can also give you insights into the operations and management of your company. It helps you figure out the strong points and weak points of every operation of all the departments.
Similarly, it always helps you pinpoint your weakness and threats. And most often, the problem in your company is underlined with weakness and probable threats. And to identify it and look deeply at it, SWOT analysis could be your best tool.
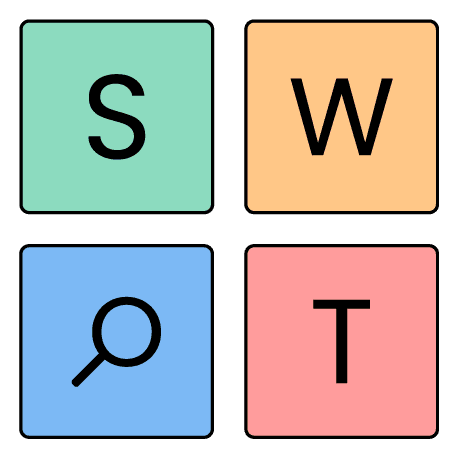
Want to create a SWOT Analysis for your Business?
Craft a powerful SWOT Analysis in just minutes using our user-friendly and free online SWOT Analysis Generator Tool!
Conduct Market Research
You surely pay a lot of your time and effort to make your operations smooth. But a lot of the time, your problem is outside your office. That’s because the market keeps changing all the time. The reason for the change could be anything including competitors, the change in demand and supply, recession or economic boom, or anything!
The market is unpredictable and it can change at any moment. Sometimes the change is obvious and sometimes it is out of the blue. But even the most minute change can shake the very fundamentals of your business.
In that case, you need to keep conducting market research and analysis. So you can steer the growth of your company strategically. And along with that, it will also help you to identify the problem and solve it.
Refer Case Studies
A lot of companies like to document their previous problems and their solutions. And it is not a bad idea. But it can also be overwhelming and hence, most companies do not prefer to do it. But there are a lot of business journals online and offline that document some of the most challenging problems and breakthroughs.
In fact, there are different journals and magazines for different areas of business. And being a business person, it is always a good idea to catch up with those journals and magazines.
It gives you a different perspective on the problems that you have at hand. Moreover, it might even encourage you to do things differently to avoid certain problems. Furthermore, it is always good to be informed about the business world in general.
Discuss with your team and mentors
While it is true that a team of like-minded people helps you smooth your office operations. But sometimes, it takes the differences that make you look for your solutions differently. And that’s how your teammates can help you out. And usually, mentors are more experienced.
They have generally seen the more perplexing scenario in the business and in the market. And you could surely rely on their judgment to solve problems. The goal is to solve your problems quickly and efficiently.
And if taking advice from your teammates, peers, and mentors can accelerate the process then you must always consider it.
Be creative
No matter the problem or situation, it is always a good idea to think out of the box. It not only forces you to have unique solutions. But also, puts you in distinct positions which you can leverage to take your business to new heights. Along with that, you also find ways to optimize your finances and resources, like using employee templates to improve your workflow. After all, problem-solving in business is all about creativity and implementation.
And while you make a point to look at the solutions creatively, make sure you have more than one approach to it. This way will have multiple backs up plans if you get stuck.
Track the progress
All your thoughtful, well-discussed, creative solutions won’t be enough if you do not analyze and optimize them. So, when you come up with solutions, make sustainable plans to analyze them.
While following the above-mentioned steps,
4 Effective Problem-Solving Techniques:
Six thinking hats.

Six Thinking Hats focuses on identifying the problems and their solutions from different perspectives. It involves consulting with team members from different departments and ranks. And that’s how you get a complete overview of the situations and their solutions. It involves data research and analysis as well as creative brainstorming.
This problem-solving technique opens space for different ideas and removes roadblocks from a solution.
Lightning Decision Jam
Lightning Decision Jam is one of the most important problem-solving strategies. The problem-solving process requires more of a creative upfront. It does not only set things right but allows you to have fun along the way.
In this problem-solving technique, you invite a few qualified people from your team and discuss a certain problem. These people put their problems and their probable solutions on a sheet of paper without any discussion. One by one, they present it to the host and discuss it collectively.
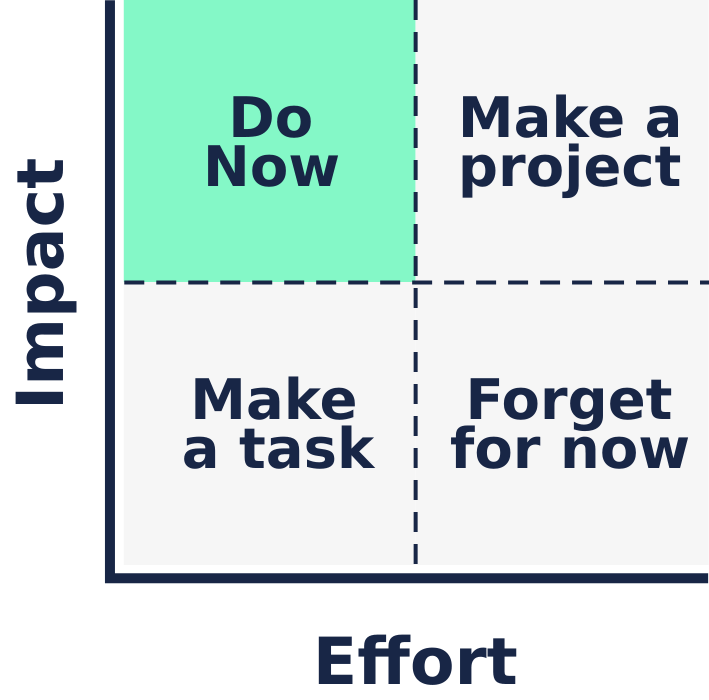
After which the priority of the solution is then decided by a collective vote and the solution is put into execution accordingly. The best advantages of this technique are:
- Your entire team is in alignment with the problem, the solution, and the implementation.
- Everyone on the team has a divided responsibility.
- Everyone on the team takes accountability for each other.
Hence, the result of the implied solution is seen clearly.
The 5 Why’s
This problem-solving technique not only goes as deep as the problem but is at the heart of the organization. It aligns with your vision, mission, and your practices to achieve it. It is highly effective in helping a group to find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct root cause analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it into a root cause problem statement, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to guide a group through a root cause analysis with ease.
World Cafe is a powerful problem-solving technique that directs your team’s attention to solving complex problems. This problem-solving technique enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere. The participants self-organize and explore relevant topics for problem-solving purposes.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
About the Author

Since childhood, I was in awe of the magic that words bring. But while studying computer science in college, my world turned upside down. I found my calling in being a copywriter and I plunged into a world of words. Since then, there is no looking back. Even today, nothing excites me to find out the wonders the words can bring!
Related Articles

Business Problem Statement Explained with Examples
What is SWOT Analysis & How to Conduct it

Writing a Business Plan Confidentiality Statement
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates
How to Write a Business Project Solution Plan
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Write a Business Plan
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">

Examples of Training Agendas
The purpose of contingency planning, communication plans & strategies for it projects.
- How to Temporarily Disable Your Logitech Webcam
- How to Write an Organizational Development Intervention Proposal
Business case documents and project plans can be used to identify and propose solutions for a variety of business problems. The difference is that while a business case document presents a number of possible solutions to a business problem, a project plan proposes a single solution. Because there’s typically more than one way to solve a business problem, a business case document can be a good starting point. Once the business owner selects the best solution, project plans that define action steps for solving the problem can then be developed.
Problem Identification and Analysis
Identify the root cause and contributing factors to a problem by conducting a cause-and-effect analysis. Start with a clear, written description of the problem. State the exact problem, including details such as who is involved and when and where it occurs or occurred. Clarity is essential in order to develop a comprehensive understanding of the problem. Next, identify and describe how tangible and intangible factors such as equipment, business processes or attitudes may be contributing to the problem. For example, a problem such as high employee turnover might be related to a general failure to hire the right type of person for the job. Insufficient HR training, ineffective skills testing, and communications bottlenecks between department managers and HR might all be contributing factors.
Brainstorm Possible Solutions
Most business problems have numerous solution options. In this phase of developing a project solution plan you should identify and explore them all. Start by brainstorming to create a list of possible solution options, each addressing an identified contributing factor. Describe each option in as much detail as possible. For example, possible solutions for reducing high employee turnover might include establishing a formal HR department or additional training to bolster the business owner or other employees currently responsible for interviewing and hiring new employees. Implementing computerized skills testing procedures or developing a communications protocol for HR and department managers are additional alternative solutions.
Analyze and Prioritize
Conduct a cost-benefit analysis for each possible solution and then prioritize each solution according to how successfully it solves the problem in the most cost-effective way. The cost-benefit analysis for each solution should include a full cost estimate, financial and intangible benefit projections, and an estimate or time frame for when the solution can be expected to pay off. Although unlikely, it’s possible that the most cost-effective solution may be to take no action at the current time. This depends on the severity of the problem and its potential long-term effect on business efficiency and profitability.
Create a Project Plan
The final step in writing a business project solution plan is to choose a solution and create a project plan. A thorough solution plan includes project goals, a list of deliverables required to meet project goals, and a schedule or timeline for completing the project. Supporting documentation such as personnel and resource requirements, a project communications strategy, and a risk identification and management plan should also be created and incorporated into the project plan.
- TechTarget: How to Write a Business Case Document
- ProjectSmart: Project Planning a Step by Step Guide
- Mind Tools: Cause and Effect Analysis
Based in Green Bay, Wisc., Jackie Lohrey has been writing professionally since 2009. In addition to writing web content and training manuals for small business clients and nonprofit organizations, including ERA Realtors and the Bay Area Humane Society, Lohrey also works as a finance data analyst for a global business outsourcing company.
Related Articles
How to evaluate problem solving in a business, how to conduct strategic planning for a project, how to develop a skill gap analysis, what are the steps that make up a workable plan, how to make prioritization decisions, what is the difference between strategic planning & strategic implementation, critical path planning and scheduling, examples of project rationale, what is capital expenditure planning, most popular.
- 1 How to Evaluate Problem Solving in a Business
- 2 How to Conduct Strategic Planning for a Project
- 3 How to Develop a Skill Gap Analysis
- 4 What Are the Steps That Make Up a Workable Plan?
We've launched Scorpion Connect and Chat AI . Learn More
Effective Problem Statement Examples in Business

Every great company started by solving an important problem. The more effectively you articulate a problem, the more valuable your solution will be. This is why your business plan needs to have a problem statement.
A common mistake businesses make is that they do not give the problem as much importance as the solution. Instead, most business owners get excited about the solution — but in doing so, they tend to forget to explain why the problem is important.
A well-articulated problem gives your solution more value. It makes your entire plan 10x more effective.
This article takes a look at what a problem statement is. It also includes problem statement examples, how to write an effective problem statement for your business, and more.
Get help with your marketing
What is a problem statement .
Ultimately, most business owners want their company’s products or services to solve a problem for their core customers.
That means your problem statement is the heart of your concept. It is the very thing that gets people interested in you and your business. Eventually, it becomes the focal point.
Put simply, a problem statement defines a problem and identifies what a solution would look like. But to build a good case for the problem is to not just state the problem. You should also build an engaging story around that problem — one that people can relate to.
Purpose of a problem statement
Problem statements are important to businesses, individuals, and other entities because they help keep the entire team focused on solutions. Problem statements are also important for these reasons:
- First, they allows you to identify and explain the problem in a concise but detailed way. This gives the reader a comprehensive view of what's going on. You can identify who the problem impacts, what the impacts are, where the problem occurs, and why and when it needs to be fixed.
- They clarify what the expected outcomes are. When you establish what the desired situation looks like, it helps give an overarching idea about the entire project. The proposed solution, scope, and goals of the solution are all made clear through the problem statement.
- They act as a guide, helping you navigate your business and can help your team remain focused. You'll find that you'll come back to your problem statement from time to time to ensure the solution has been implemented and that it does indeed solve the initial problem.
A great problem statement will help to ensure that all objectives of your business are being met.
Examples of problem statements in business
There are tons of successful examples of problem statements from various companies. Let's take Netflix for example. They solved the problem of having to go to the video store to rent movies.
Netflix originally eliminated the need to go to the video store by delivering movies in an envelope to your mailbox. This allowed people to keep the movies for as long as they'd like.
At that time, the use case for Netflix was something like this:
"Going to the video store is a pain. People don't like traveling back and forth just to rent a movie and they hate paying late fees even more."
A simple interpretation of Netflix's problem statement would be:
Problem: "Going to the video store requires fighting traffic, wandering the aisles,, and waiting in long lines just to get a single movie."
Solution: "Netflix allows anyone to enjoy thousands of titles streamed directly to their home or delivered to their mailbox."
As you can see in just two sentences, you have given a potential investor an easy problem/solution statement. This example of what Netflix's problem statement would have looked like is simple, yet it gets straight to the point.
A good problem statement will solely focus on the problem. This allows the audience to build a powerful case for the problem and accept the solution you are trying to provide.
Another example problem statement is from Facebook . Harvard had its very own version of Facebook when Mark Zuckerberg was a student. Zuckerberg's frustration was that "he could only search and look at people's information on the university's version of Facebook and not perform any sort of social interactions like liking, commenting, etc."
This was when he came up with the idea to create a new platform. He hoped to create something new that allowed users to search for people according to their interests. Users would also be able to create an online network of friends and study groups.
Facebook’s problem statement would have probably said something like:
“A lack of social interaction among a group of people who share common interests/attributes is a waste of time. People cannot create strong connections without interacting with each other.”
A simple interpretation of Facebook’s problem statement would be:
Problem: Connecting with others and being able to comment or like their posts, etc., can have an adverse effect on making strong connections with like-minded people.
Solution: Facebook allows you to connect, create strong connections and interact with people with similar interests.
Key elements of a good problem statement
There are certain key elements to a good problem statement. These include:
Ideal situation
Your problem statement should outline what the ideal situation would be if there wasn't a problem that needed your attention. This is where you will identify the goals and the scope of the project. This section needs to give a clear understanding of what the ideal scenario will be once the issue is resolved and what your business can do to solve the issue.
Moving on, your problem statement should concisely describe what the current reality is for your business. Here, you will identify the problem, state why it's a problem, and identify who the problem is affecting. Moreover, this section will also describe when and where the problem was identified. All in all, this section is basically a scenario analysis.
Consequences
At this stage, your problem statement needs to identify the consequences of the problem. It should outline how people affected by the problem are being impacted and quantify how much the problem is impacting them. Some common consequences may include the loss of time, money, resources, competitive advantage, productivity, and efficiency.
This section of your problem statement may include a few possible solutions to the problem. It is important to not identify a specific solution. The purpose of this section is to guide the business team on how to research, investigate and resolve the problem.
How to write a problem statement
When writing a great problem statement, there are a few things to keep in mind. Here are some tips to follow when writing a problem statement for your business:
Describe the ideal situation you aim to achieve
To get started, try to provide some context that will make it easier to understand the problem. Begin by explaining how the particular process should work. Before mentioning the problem, try to describe how the process would function if the current problem didn't exist. Be sure to keep the end-user in mind.
Let's say you have an idea of how to increase efficiency in a process to maximize the best use of resources. You can start describing a theoretical situation whereby the system is far more efficient and work towards your proposal from there. Just keep in mind who, what, where, and why so that you can stay on point.
Choose the biggest problem to solve
Oftentimes, you may find that your products or services can solve multiple problems. However, when defining your problem statement, focus on the biggest problem you can solve.
If you are going to be pitching to investors, keep in mind that they won't be able to remember all of the problems. They're most likely to remember your products/services that can solve their biggest problem.
Consider audience's needs
Be sure to review reports and talk to your employees to fully understand the scope of the problem. Their problem-solving skills can come in handy.
Take into consideration the needs and experiences of your audience when writing problem statements. People will relate to you and your problem statement if they have experienced something similar.
Furthermore, the vision for your product or service should be the same as well. The more your target audience relates to your story, the better they'll understand and connect with it.
Provide facts about the problem
Most business problem statements are backed by surveys or statistics. Your business's problem statement can include references to internal or external reports, staffing reports, statistics, customer demographics, national trends, etc. Of course, what you include depends on the problem you're solving.
Try to avoid adding excess numbers and irrelevant information. Ensure that you only include key statistics and solid data that highlight the severity of the problem.
Explain the benefits of your proposed solution
At this point in your problem statement, you've described the ideal situation where the problem doesn't exist. You've also pointed out the problem, explained what the consequences are if they're not fixed, and proposed solutions.
It is now time to explain the benefits of your solution. Focus on the efficiency and the financial impact of your solutions. Talk about the financial costs your solution will decrease and how your solution can free up revenue streams. You can also address the intangible benefits of your solution like increased client satisfaction.
If you need help solving business problems of your own, or you want to step up your marketing efforts, contact the team at Scorpion. We have helped thousands of home services , legal , franchise , and other small business professionals grow their businesses.
If you liked this, you might also like these.
We partner with you to create a digital marketing strategy that works for your business, not anyone else’s. Your customers find and choose you, again and again. And you get more of what you want out of your business. Every day.

5 Key Elements of a Successful Ad

7 Memorable Marketing Moments from 2022

Locally Grown Episode 11: How Small Businesses Can Survive When Inflation Hits
You don't have time to waste on marketing. Subscribe to our newsletter

50 Business Problem Statement Examples [+Tips To Write]
Editorial Team

Whether you are a budding entrepreneur or a seasoned one, you need to have insights into what a problem statement for a business is, its examples, how to write it, and any other information about it.
When workplace staff members and departmental teams express initiative in solving problems, they demonstrate competence in handling complex and unanticipated challenges at work. Businesses rely on individuals and teams that can effectively analyze challenges and propose working solutions.
In this article, we offer tips on how to generate problem statements, with 50 comprehensive business examples you can use for reference.
What’s The Meaning Of A Problem Statement?
A problem statement summarizes a challenge that needs timely intervention to help improve a situation. It summarizes the problem in business, why it is a problem and how to address it. Businesses thrive when they can solve potential and existing customers’ issues.
Pointers On How To Write A Problem Statement
A problem statement must be accurate and precise. There are vital components to consider when crafting a problem statement that can positively impact a project’s outcome. These include:
1. A Description Of How Things Should Work
First, provide some context that will make it easier to understand the problem by explaining how this process is supposed to function and work. Mention the problem while keeping the end-user in mind.
2. An Overview Of What The Problem Is And Explaining Its Impact
A practical problem statement should address a problem stating what it is, why it is a problem, and the benefits of solving it. It reveals who the problem affects and why it needs fixing. You could indicate any attempts you have undertaken to fix the problem and why those attempts did not work. Explain in detail your understanding of the problem at hand. Usually, fixing a problem in a business setup will help improve efficiency in the workflow processes, save time, minimize the wastage of resources, and impact the cost.
3. An Explanation Of The Cost Implications
When you explain the problem to critical stakeholders, mention the cost implications of not addressing the issue. Entrepreneurs understand the money language better, so framing the problem and projected solution regarding financial consequences is easier. Try to be specific by pinpointing exact figures of how much the business will lose if the issue remains unresolved and how much the business will save by implementing a workable solution. The problem of wasting resources or preventing the company from maximizing profits should reflect in the problem statement.
4. Evidence To Support Your Theory
After stating the financial implications, you need to support your claims with evidence if the stakeholders are to take you seriously. You must conduct comprehensive research, cite your sources, and give practical examples. You must have relevant data to present if the need arises.
5. Suggestions For The Solutions
A problem statement should propose a detailed solution to the problem. At this juncture, you need to have a firm grasp of where the challenges are arising from and offer practical approaches to mitigate them. You must outline your objectives by suggesting an ingenious strategy for addressing challenges.
6. Benefits Of Your Suggested Solutions
After pinpointing the problem:
- Explain the ramifications of not fixing these setbacks and propose appropriate solutions.
- Demonstrate this by focusing on efficiency and the financial impact the solution will have helps convince stakeholders of the viability of the problem statement.
- Comprehensively outline how the solution will impact finances by increasing revenue streams, reducing expenses, improving productivity, saving time, and increasing profit margins.
7. A Summary Of The Problem And The Expected Solution
In conclusion, you must summarize the problem, explain why it needs fixing, and provide an overview of why your solution is the best.
50 Business Problem Statement Examples
1. social media channel.
While Mark Zuckerberg was studying, Harvard had its version of Facebook. Though it was possible to search other students’ profiles on the university wall, it was not possible to interact and perform any social interaction by liking, commenting, or networking.
Problem: The logistics of trying to connect, network, and interact with like-minded friends without physically having to travel.
“Human beings are social beings. They would love to interact and network with people in faraway places without physically traveling. People love to socialize but hate having to spend to do it.”
Solution: Facebook allows its audience to search and network with like-minded individuals.
2. Manufacturing
Problem: An inefficient manual assembly process that consumes plenty of time affects productivity as employees have to spend hours manually installing machine parts. The long delays negatively impact production goals as you could spend that time developing products is spent fixing faulty machines.
Solution: Automating assembly processes and installing conveyor belts to optimize manufacturing workflows.
Problem Statement: Rigorous labor-intensive processing due to manual paperwork management.
3. Streaming Entertainment Service Company
Netflix, Hulu, and other streaming services came to solve the problem of people having to go to video stores to rent movies. They did this by trying to eliminate video stores and delivering movies to customers allowing them to keep those movies for as long as they needed. For this, their problem statement would be similar to this one:
“Clients detest going to a video store. They don’t like traveling back and forth and they hate paying late fees even more.” An interpretation of the problem statement is:
Problem: Going to the store entails fighting through traffic and waiting in queues for your turn to get the movies you want.
Solution: The streaming service allows customers to enjoy numerous movies streamed directly to their mailbox. In this short statement, you have given an investor a simplified view of the problem and its solution. Grand problem statements focus on issues so the audience can identify with that problem and appreciate the solution the business is trying to come up with.
4. Software Company
Problem: Manual auditing delays processes in the finance department due to the cumbersome process of verifying and counterchecking financial statements, searching for documents for reference, and manually collaborating with different teams is negatively affecting productivity. The lengthy auditing process leads to many errors where documents get misplaced or lost, and it takes a lot of time to locate and retrieve them.
Solution: An online database with search filters that simplifies the process of searching for documents.
5. Busy Office
Process: Forms for different functions like annual, sick or emergency leave need to be filled by employees for review and management approval. Human resource teams must scrutinize the forms, verify, scan, and upload them to the system. After that, the papers move to the finance department for manual re-entry, and payroll preparation begins.
Problem: Overdependence on the manual system leads to irregularities, delays, omissions, and mistakes in service delivery to employees and vendors. This promotes a poor organizational response to arising issues and wastes precious time trying to identify and correct errors.
Solution: Automating repetitive processes to help teams concentrate on the core business.
6. Engineering
Problem: Manual transportation of machine parts from one assembly line to the next, leading to inefficiencies making it impossible to meet the yearly production goals despite hiring additional staff.
Solution: To minimize manual transportation of machine parts and increase reliance on mechanical robot arms and conveyor belts that appear between assembly lines. Such a move will prevent employees from walking back and forth across the assembly lines.
Problem Statement: Employee Efficiency to Improve Productivity
7. Healthcare Center
A medical facility operates 24/7 as patients need care round the clock.
Problem: There’s an insufficiency of medical personnel, especially on the night shift, which presents challenges during emergencies. Unfortunately, patients must wait hours for medical assistance, leading to inefficiencies.
Solution: The hospital must always have a medic on call to handle each department to prevent patients from being stranded during emergencies. Hiring part-time staff for the night shift will help alleviate the problem.
8. Cosmetics
Problem Statement: Customer dissatisfaction with skin care products for Caucasian skin
Problem: Customers complain about the harshness of the sunblock cream.
Impact: Mistrust and suspicion about the quality of the products.
Solution: Product recall as it needs more analysis and tests.
9. Ecommerce Business
Problem Statement : Sales Quote Output
The quote generation display is critical as sales teams must swiftly generate quotes for customers to make their payments on time.
Problem : The quote generation display in the sales app is faulty, with sales teams complaining that the screen is prone to errors and consumes plenty of time to make it function. These issues have led to lost productivity in the sales department.
Solution : The department needs app improvements by replacing or upgrading existing software.
10. Business Startup
Problem Statement : Inefficient customer data security
Problem : storing customer data in separate data stores with questionable encryption security practices presents operational risks and substantial reputational challenges.
Solution : Enlist the services of an IT expert to help improve the process of storing customer data.
11. Consultancy Firm
Problem Statement: Sales Software Outage
Problem: Collapsing of the manual and automatic communication software for an extended period causes a communication breakdown. One section of the app experienced an outage that the mechanical system failed to pick up. Technicians tried the manual option but experienced error notifications a couple of times. The manual and automatic processes could not redirect calls to the API in a timely process leading to miscommunication and a loss in productivity. The setback arose during core business hours which had a massive negative impact on sales.
Solution : The outage could have been managed if the problem had been detected with API calls being redirected to a different location.
12. SaaS Company
Problem : Users of our software have challenges using it as they have to manually transfer information into the CRM after sending proposals. They need the CRM to track emails, phone calls, and other conversations that involve customer interactions. Without CRM integration, the software causes a frustrating experience for software users.
Solution : Send segmented surveys to determine the most effective CRMs to integrate and customize these integrations to improve user experience.
Problem Statement : Saas platform with an AI assistant for recruiters.
13. Recruitment Firms
Hiring teams experience numerous repetitive hiring tasks, including vetting applications, scheduling or rescheduling interviews, handling cancellations, responding to concerns, and shortlisting applicants at various application stages.
Problem: Plenty of tedious, monotonous manual work takes away the joy of meeting and assessing applicants that perfectly fit job descriptions.
Solution : Utilizing artificial intelligence technology or software applications that automate these processes.
14. Employee Management
Problem: Our organization needs a more secure way of onboarding and offboarding employees because the current system is cumbersome. Hiring managers have to depend on security teams to perform the same tasks.
Solution: automating repetitive onboarding and offboarding processes.
15. Learning Institutions
Problem Statement: Motivation for resolving tech issues Our school needs a work-from-home policy that allows staff to operate remotely.
Problem: Our inexperience is causing us anxiety as we may lose competent staff to our more organized competitors.
Solution: provide our teams with adequate tools and devices to protect the security of our data when staff operate remotely. We must provide secure access to cloud computing software and communication channels like Zoom or Microsoft Teams. Learning to use collaboration software will be a mandatory skill for staff.
16. Real Estate
Problem: Despite our real estate company’s decision to benchmark for free trial sign-ups that have remained steady, our paid subscriptions declined in the last few weeks. This means our business isn’t experiencing a traffic setback but a conversion challenge caused by a rise in mortgage interest rates, widespread economic challenges, pricing, and workflow processes.
Solution: Restructure the free trial to offer less value because users gain too much from the free plan, which prevents them from signing up for a paid plan. Currently, users must sign up for a paid plan to access leads of real estate deals. We should also upgrade our software to include additional features that will retain investors on our platform.
17. Software Application
Problem: Users of our newspaper app avoid sharing content through the app and instead export the content from the app. This poses a challenge in our marketing strategy because potential customers need to be made aware that the content shared originates from our app leading to lower conversion rates. It also poses a challenge for app users as exporting range is time-consuming and could decrease app usage.
18. Sales Strategies
Problem: Sales reps conduct manual planning using Excel spreadsheets and typed printout lists. They need more time which leads to difficulty in meeting targets. It also causes challenges in knowing which targets to visit, which affects sales and the inability to meet set goals.
19. Customer Care
Problem: customers call the contact center seeking updates on their applications. Due to the vast volume, many applicants wait long hours to speak to an agent because the call center is understaffed. Employees are ill-equipped and lack adequate access to applicants’ track records, further compounding the backlog. The outcome leads to a frustrating experience for both applicants and staff.
Problem Statement: Using project management software for collaboration improves efficiency and productivity.
20. Problem: Communication breakdown caused by overreliance on an inefficient manual system.
Solution: Introducing technology by integrating a reliable project management system.
21. Problem Statement: Stay-at-home-mums need an avenue to feel connected to a support group as they spend long periods alone.
Solution: An app or social media channel where these mums can interact and network while attending to their babies.
22. Digital Transformation
Problem Statement: Customers need a solution to help them create websites without overreliance on IT experts.
Problem: People detest contacting IT specialists as the process is cumbersome.
Solution: Apps that offer guidance to web users in creating simple websites.
23. Agricultural Firm
Problem Statement: Preserving perishables to minimize wastage.
Problem: Though Jack& Jill Farms provides products to many supermarkets across the country, they consistently experience a loss due to their limited storage capacity and the fact that most of their products are highly perishable.
Solution: Maintain an efficient supply chain to guarantee a ready market once the product leaves the farms. The firm must invest in modern storage facilities to improve preservation and shipping.
24. Waste Management
Problem Statement : Conduct a study on the proper waste management system.
Problem: Manufacturing firms in my area are releasing industrial chemicals into the river leading to environmental degradation.
Solution: Present a research proposal to the city authorities requesting permission to conduct a proper waste management system analysis and devise a viable solution.
25. Virtual Assistant
Problem: Challenges onboarding new clients, which lead to prolonged periods of idleness and a struggle to meet basic needs
Solution: Integrating new technology in marketing and creating awareness for the business.
Other examples of problem statement ideas include:
26. Problem: Fierce competition
Solution: Market the business online and offline using technology and modern strategies.
27. Problem: Unrealistic expectations
Solution: Manage expectations by setting realistic goals.
28. Problem: Challenges in hiring suitable candidates
Solution: Shortlist suitable applicants and review each application noting an applicant’s experience level and skills.
29. Problem: Cyber security threats that lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Solution: Engaging the services of an IT expert.
30. Problem: challenges in gaining client trust
Solution: Develop healthy relationships to improve trust.
31. Problem: Financial setbacks
Solution: Engage the services of a financial expert who can help streamline cash flows and budgetary allocations and share helpful insights.
32. Problem: Uncertainty about the future and not being able to predict customer and market trends
Solution: Consulting the services of an expert who can predict essential trends.
33. Problem: Resisting change.
Solution: Know when to embrace change by firing and hiring new staff or overhauling processes to improve efficiency.
34. Problem: Employee retention
Solution: Addressing employee challenges and offering incentives, and rewarding job performance
35. Problem : Lack of startup capital
Solution: Use locally available material, start small, and consistently plow profits into the business.
36. Problem: Fluctuating prices due to inflation
Problem Statement: Diversify and Optimize
Solution: Altering business models to suit the current prevailing situation.
37. Problem: Administrative Workload
Solution: Outsourcing or hiring temporary staff to handle bookkeeping, repetitive tasks or automating workflows.
38. Problem: Time Management Challenges
Solution: Proper planning and organization by prioritizing and delegating tasks, especially those with short turnaround periods.
39. Problem: Marketing And Advertising Challenges
Solution: Defining what strategies would work best by researching the market and identifying the ideal target market. From there, develop a plan that targets that group.
40. Problem: Low Business Leads To Client Over-Dependence
Solution: Diversify your client base to prevent closing the shop once a major client closes their account with you.
41. Problem: Indiscipline In Money Management
Solution: Learning good financial habits and disciplining oneself to stick to set rules. A business should have a diversified client base to cushion the company when a single client quits or defaults payments.
42. Problem: Work-Related Pressure Leading To Fatigue
Solution: Most successful business owners fall into the habit of overworking, leading to burnout and fatigue. Success doesn’t mean slavery but the ability to integrate balance into one’s activities.
43. Problem: Founder Dependence
Solution: A business that stagnates without its founder is a business with a time limit.
44. Problem Statement: Balancing Growth And Quality
Problem: sometimes, a business must sacrifice to scale up. This means that you may only be able to manage some client relationships personally.
Solution: Navigate the process to allow growth without interfering with the brand.
45. Problem: Meeting Customer Demand
Solution: Awareness of what the customer wants and prioritizing their needs
46. Problem: Maintaining quality customer relations
Solution: Consistency, patience, and nurturing healthy relationships
47. Problem: Preserving a good reputation
The speed of information makes tracking your business’s public image challenging.
Solution: Utilize software or companies that track social media for mentions of your company. With technology, you can get notifications about an arising issue and be able to address it immediately.
48. Problem: Marketing in a saturated marketplace
Solution: Market strategically using unique and compelling messages to attract potential clients
49. Problem: Choosing the right tools
Solution: Identify the need and look for tools that help meet that specific need.
50. Problem: Globalization
Understanding foreign cultures are crucial to penetrating new markets with existing products or services.
Solution: Altering designs to accommodate new markets
Conclusion
Every successful company starts by creating a solution to a need, an important reason your business needs to have a problem statement. The better you articulate the problem, the more treasured your solution will be. Most companies make the mistake of not giving the problem as much importance as the solution. Instead, many entrepreneurs concentrate on the solution and completely forget to explain why the problem is essential. Before your business markets a solution to a problem, make sure your clientele is aware of the problem your business is solving, which is made clear through your problem statement. Comprehensively articulating a problem statement help in improving the effectiveness of your business.
- Why It’s Important to Hire an InventHelp Patent Attorney?
- Choose the Right Company for Business Satellite Imaging
- Why You Should Still Be Excited About Becoming an Entrepreneur
- How to Run an Effective and Safe Machine Shop
most recent

Top 33 SeaWorld Parks Entertainment Interview Questions and Answers 2024

Top 33 Senior Financial Analyst Interview Questions and Answers 2024

Top 33 Time Series Analysis Interview Questions and Answers 2024
© 2024 Copyright ProjectPractical.com
Diagramming Build diagrams of all kinds from flowcharts to floor plans with intuitive tools and templates.
Whiteboarding collaborate with your team on a seamless workspace no matter where they are., data generate diagrams from data and add data to shapes to enhance your existing visuals., enterprise friendly easy to administer and license your entire organization., security see how we keep your data safe., apps & integrations connect to all the tools you use from microsoft, google workspace, atlassian, and more..
- What's New Read about new features and updates.
Product Management Roadmap features, brainstorm, and report on development, so your team can ship features that users love.
Software engineering design and maintain complex systems collaboratively., information technology visualize system architecture, document processes, and communicate internal policies., sales close bigger deals with reproducible processes that lead to successful onboarding and training..
- Getting Started Learn how to make any type of visual with SmartDraw. Familiarize yourself with the UI, choosing templates, managing documents, and more.
- Templates get inspired by browsing examples and templates available in SmartDraw.
Diagrams Learn about all the types of diagrams you can create with SmartDraw.
Whiteboard learn how to combine free-form brainstorming with diagram blueprints all while collaborating with your team., data visualizers learn how to generate visuals like org charts and class diagrams from data., development platform browse built-in data visualizers and see how you can build your own custom visualization., open api the smartdraw api allows you to skip the drawing process and generate diagrams from data automatically., shape data add data to shapes, import data, export manifests, and create data rules to change dashboards that update..
- Explore SmartDraw Check out useful features that will make your life easier.
- Blog Read articles about best practices, find tips on collaborating, learn to give better presentations and more.
Support Search through SmartDraw's knowledge base, view frequently asked questions, or contact our support team.
Site license site licenses start as low as $2,995 for your entire organization..
- Team License The SmartDraw team License puts you in control with powerful administrative features.
Apps & Integrations Connect to all the tools you use.
- Contact Sales
What's New?
Solutions By Team
Save money, reduce hassle, and get more.
Unleash your team's productivity by combining enterprise-class diagramming, whiteboarding, and data while saving 10x over Visio and Lucidchart!
Getting Started Learn to make visuals, familiarize yourself with the UI, choosing templates, managing documents, and more.
Templates get inspired by browsing examples and templates available in smartdraw., developer resources, additional resources.
Team License The SmartDraw Team License puts you in control with powerful administrative features.
Solutions for your team.
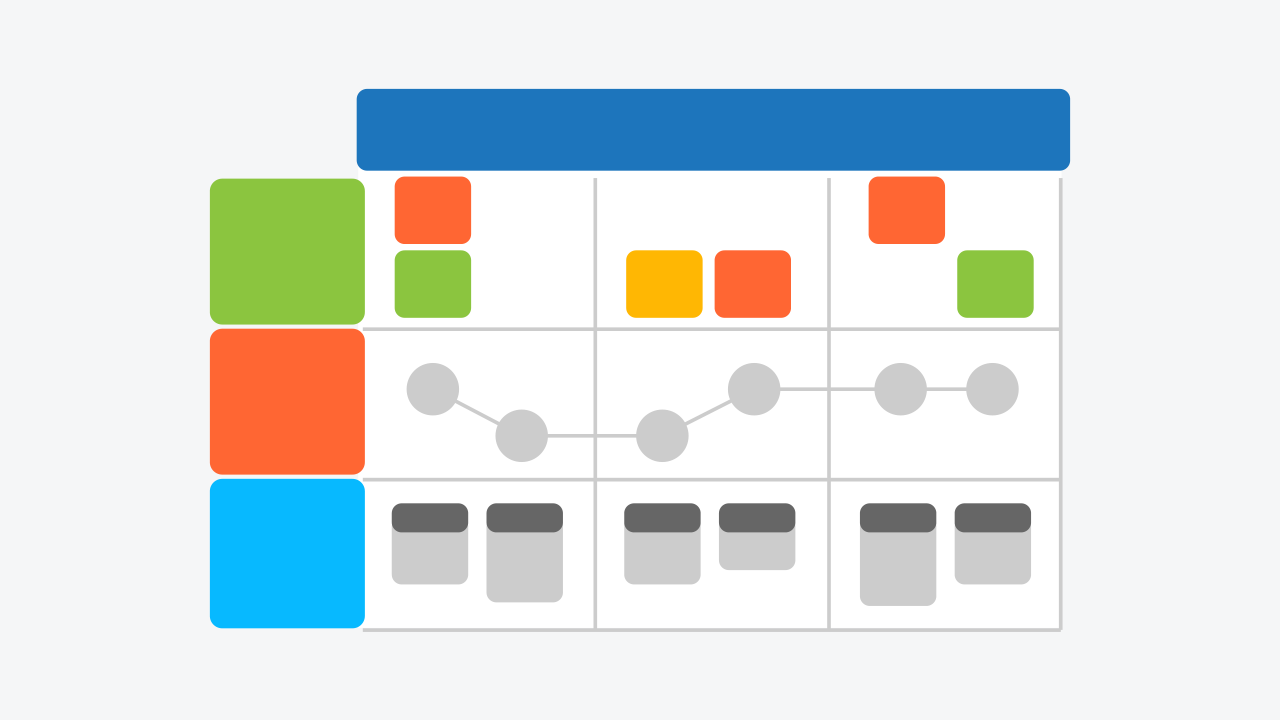
5 Small Business Problems and Solutions
There's nothing quite like the excitement of owning your own business. But it also involves plenty of challenges you need to understand and be prepared to handle.
Here are five common small business problems and suggestions for how to deal with them.
1. Insufficient Capital or Cash Flow
By far the biggest hurdle faced by start-ups and other small enterprises is money. Too many times, entrepreneurs don't start out with enough capital. Start-up costs often exceed budget. When starting out, get multiple bids for large-ticket items and always set up a contingency reserve for possible cost overruns.
The other factor is cash flow. It's easy to be overly optimistic when projecting a break-even point. Be careful about forecasting unrealistic sales figures, or cutting your operating budget too thin. Many experts suggest having enough cash on hand to sustain the business for two years, at a minimum.
2. Failure to Plan
All too often entrepreneurs "fly by the seat of their pants." Unfortunately, many of these businesses become casualties before they get very far off the ground.
If you want to succeed, you're going to have to treat your small business in much the same way that larger, successful companies treat theirs. Have a strategic plan with your vision, goals, and some market analysis. Develop a business plan with a detailed budget, cash flow and break-even analyses. These don't have to be long, narrative documents. In fact, you can create most of what you need with a few flowcharts, mind maps, project charts, and other business strategy diagrams.
But don't cut corners in your research and analysis. It's easy to get anxious about your new venture and overlook the difficulties you will face. Take your time and create well thought-out plans. Dealing with and planning for tough issues in advance will be a huge step toward your ultimate success.
3. Not Getting Expert Advice
You will pay a little more for a lawyer and a CPA to get your business established than if you do it yourself. But this isn't replanting the flower bed in the front yard. Mistakes can be extremely costly. Good professionals will more than pay for themselves over time and you'll sleep better knowing that you have things set up properly.
4. Time Management
A plan is only good if you stick to it. That requires managing time well. Now, managing time well doesn't mean packing so much into your calendar that you can't possibly get it done. Pick and choose what's important, focus on the critical stuff, and get it done. Little things will fall through the cracks. Let them. If they're really important, they'll come back up.
Use tools to help you, such as Gantt charts or Kanban boards. The visual displays make it easy to quickly decide on important tasks and follow them through to completion.
5. Resistance to Change
Whether your company is a start-up or has been around for 100 years, innovation can be a frightening thing. But change is real. Don't get stuck in archaic ways of doing things. Embrace a culture of forward thinking. Be open with your staff about changes taking place in your organization, as well.
More Articles
- SmartDraw Blog
- Productivity
- Collaboration

Five Reasons Why Great Companies Have Happy Workers

Create a Visual Business Plan

There's No Such Thing as a Bad Idea
Smartdraw makes diagramming easy.

Most Common Business Problems and How to Solve Them

In the ever-evolving world of business, challenges are an inevitable part of the journey. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting out, you’re likely to encounter a variety of hurdles along the way. This article explores some of the most common business problems and offers practical solutions to help you navigate them successfully.
1. Cash Flow Issues
Problem: One of the most prevalent issues that businesses face is cash flow problems. This occurs when a company has more expenses than revenue, leading to financial instability.
Solution: To combat cash flow issues, consider the following strategies:
- Create a detailed cash flow forecast to anticipate and plan for future financial needs.
- Negotiate favourable payment terms with suppliers to improve working capital.
- Explore alternative funding sources, such as loans or investors, to inject cash into the business when needed.
2. Lack of Market Differentiation
Problem: In a competitive marketplace, it can be challenging to stand out from the crowd. Many businesses struggle with differentiating themselves from their competitors.
Solution: To set your business apart, focus on:
- Identifying your unique selling proposition (USP) and communicating it clearly to your target audience.
- Conducting thorough market research to understand your customers’ needs and preferences.
- Continuously innovating and adapting your products or services to meet changing market demands.
3. Ineffective Marketing
Problem: Without effective marketing, even the best products or services may go unnoticed. Many businesses struggle with marketing their offerings effectively.
Solution: To enhance your marketing efforts :
- Develop a comprehensive marketing strategy that includes digital marketing, social media, and traditional advertising channels.
- Invest in content marketing to establish your business as an industry authority.
- Utilise data analytics to track and optimise your marketing campaigns for better results.
4. Employee Productivity and Retention
Problem: Maintaining a motivated and productive workforce is essential for business success. High turnover rates and unmotivated employees can be detrimental.
Solution: To improve employee productivity and retention:
- Offer competitive compensation and benefits packages.
- Provide ongoing training and opportunities for skill development.
- Foster a positive company culture that values teamwork, communication, and work-life balance.
5. Scaling Challenges
Problem: Expanding a business can be both exciting and daunting. Many businesses struggle with scaling operations effectively.
Solution: To navigate the challenges of scaling:
- Develop a scalable business plan that outlines growth strategies and resource allocation.
- Invest in technology and infrastructure to support expansion.
- Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to ensure growth remains sustainable.
6. Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Problem: Navigating the complex landscape of regulations and compliance requirements can be a significant challenge for businesses, especially in highly regulated industries.
Solution: To stay compliant and avoid legal issues :
- Stay updated on industry-specific regulations and compliance standards.
- Consult with legal and regulatory experts to ensure adherence to all requirements.
- Implement robust internal controls and documentation processes.
7. Customer Acquisition and Retention
Problem: Acquiring new customers and retaining existing ones is an ongoing struggle for many businesses, especially in competitive markets.
Solution: To boost customer acquisition and retention:
- Develop a customer-centric approach that focuses on providing exceptional experiences.
- Implement loyalty programs and incentives to reward loyal customers.
- Utilise customer feedback to continuously improve products and services.
In the dynamic world of business, challenges are par for the course. However, with the right strategies and a proactive mindset, these common problems can be effectively addressed and overcome. By focusing on financial management, differentiation, marketing, employee engagement, scalability, compliance, and customer relationships, you can navigate the business landscape with confidence. Remember, every challenge presents an opportunity for growth and improvement, making your business more resilient and successful in the long run.
You might also like

Leave a Reply
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
About Advisory Excellence
Advisory Excellence profiles the best advisers around the globe, enabling users to quickly and easily find the expert they need in their location. All applicants are subjected to a stringent vetting process prior to acceptance.
Join Advisory Excellence
If you would like to apply for membership, simply fill out your details on our application form . If you have not heard back from us within 2 weeks of submitting the application, we are afraid that means your application has not been successful.
- The Power of Consolidation for Financial Wellness: An Overview
- Road Rage Incidents: How Aggressive Driving Leads to Accidents
- 9 Key Strategies For A Profitable Online Fashion Business

Plan Projections
ideas to numbers .. simple financial projections
Home > Business Plan > The Solution in a Business Plan

The Solution in a Business Plan
…our solution to the customers problem is…
The Solution is about the Customer
The solution is all about the customer not the product. Consequently this is not the place to put all the technical detail about your product. It is important to realize that this section is about what you do and how you can solve the problem the customer has.
There is no set style for the solutions statement of the business plan, a few paragraphs together with bullet points should be sufficient to explain what it is you do, the solution you provide, and why it solves the customer problem.
Keep the description simple, if possible tell a story as to how a customer solved their problem using your solution. Remember a good story will help people remain engaged with your business plan. Avoid technical jargon and highlight the customer benefits not the technical benefits of your solution.
Additional Information
This post is part of a series of posts under the heading the Contents of a Business Plan Guide . The aim of the guide is to explain what each section of a simple business plan should include and how each of those sections relates to each other. The next post in this series is presenting the product and technology .
About the Author
Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Plan Projections. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
You May Also Like
1-800-488-6040
- My Career or Business
- My Health & Vitality
- My Mental Health
- My Finances & Building Wealth
- My Relationship
- My Leadership Skills
- My Productivity
- Growth Solutions
- About Tony Robbins
- The Science of Tony Robbins
- Contribution
- Company Culture
- Get Involved
- Success Stories
- Case Studies
- Events Calendar
- The Unshakeable Business
- Unleash the Power Within
- Business Mastery
- Date With Destiny
- Life Mastery Virtual
- Wealth Mastery Virtual
- Life & Wealth Mastery Fiji
- Leadership Academy
- Inner Circle Community
- Pinnacle Enterprise
- Platinum Partnership
- Unleash Her Power Within
- Business Coaching
- Results Coaching
- Business Results Training
- Life Coaching
- Health Coaching
- Meet Tony’s Coaches
- All Products
- Nutraceuticals
- Life Force Book
- Tony Robbins Books
- Training Systems
- Breakthrough App
- Netflix Documentary
- Free Tools & Quizzes
Home » Business Cycle » Common business problems
Overcome your business problems
Your business is chugging along delivering its products and services and then BAM! You hit a brick wall. Whether it’s an employee matter, a delivery problem, or a logistics issue, the impact spreads across the rest of your business. Sound familiar? You’re not alone. If you’re running a small company or startup, you’ve probably faced a range of common business problems – and if you haven’t, you most likely will soon. Solving business challenges requires preparation, early identification and a plan to address any issues.
Discover your strengths as a business owner – and crush your problems
Identifying common business problems
Determining your company’s issues helps to break your business challenges into two sections: surface-level business problems (easy fixes) and core business problems (more intensive solutions).
Surface-level business problems
Surface-level problems in business typically affect day-to-day business management and manifest as employee or customer dissatisfaction. These issues can also occur naturally in the market. Examples of common business problems in this category include:
High employee turnover rate
Increase in competition
Falling sales or lack of growth
Supply chain issues
Poor financial management
Low customer loyalty
Core business problems
These arise when we dig deeper into the reasons behind surface-level issues, which – at first glance – seem easier to fix. However, they’re both related, and to fix surface-level problems permanently, you must get to the core of what’s really holding your company back.
Tony tells us, “Success is 80% psychology and 20% mechanics,” which means failure is also about your psychology . Overcoming common business problems will take more than putting up an ad or increasing your marketing budget – dig deeper, take action, and amazing things will happen.
The 9 most common business problems
Every business experiences problems, regardless of your industry, business size or the phase of your business cycle. If your business is stagnant, you feel stuck, or you’re not experiencing the growth you desire, determine if you’re experiencing one of these common business problems.
1. Finding your purpose
Does your company feel adrift? Do you change your mission statement constantly? If so, you’re experiencing a lack of purpose, one of the most common problems in business. After all, how can you expect to create raving fan employees if you don’t wake up every morning excited for the day ahead? In addition, a lack of purpose can create employee retention problems .
Being a strong leader is synonymous with having a sense of purpose , and a genuine belief in personal success will help your business thrive. Your purpose gives you passion, drive, certainty, and the ability to overcome towering obstacles. A business is only as strong as the psychology of its leader – it’s up to you to do the work and bring purpose to your company.
2. Developing your brand identity
Developing your brand identity is vital to marketing and sales success, and struggling to establish an identity is one of the biggest business problems you’ll experience during the growth stage. Your identity epitomizes your company’s core values , mission and goals and profoundly affects company culture, impacting your ability to hire and retain the best employees.
Your brand identity drives the emotional connection with your consumer and ultimately creates customer loyalty . With a strong brand identity, you know who you are and your direction. Without it, you’ll be lost in the dark and struggle to inspire raving fan customers .
3. Providing value
Shrinking profits is a common business problem that can sometimes lead to bankruptcy. It’s easy to blame the market, but there’s always a reason for significant market shifts. If customers are flocking to competitors, then take note – you probably lack specific services or features they deem valuable.
To be successful in business, you must practice constant strategic innovation . Determine your X-factor – what sets you apart from the competition? How do you bring more value to your customers? What makes your company different ? If you don’t know the answers to these questions, it’s time to sit down and think about them.
4. Planning ahead
Purpose and identity are crucial to your success, but also remember to make a massive action plan (MAP), which allows you to stay agile in response to business challenges while keeping your eye on the prize. For example, most business owners aren’t prepared for a recession even though the economy is in recession 60% of the time. It’s easy to feel confident during good times, but it’s the hardships that matter.
A MAP outlines how your business will survive an income downturn, irrespective of whether it’s caused by a recession or the shifting valuation of your product or service. If your business isn’t built to weather the storms, it’ll be dead in the water. Get prepared for a recession and other adverse economic possibilities before they happen.
5. Creating an exit strategy
No one wants to think about the collapse of their business, which is why so few owners bother with developing an exit strategy . However, in many cases, leaving the business at some point is the ultimate goal, whether through a leveraged buyout , passing the business onto your children, or selling to key employees. Knowing your preferred endgame will help you develop the best path to get there.
Forty-five percent of business owners spend over 40 hours weekly in the office and never find a way to extricate themselves. Does that sound like you? If so, it’s time to start working on your exit strategy.

6. Controlling your fear
New business owners often allow the fear of uncertainty to affect how they run their organizations. Fear of failure, not being a good enough leader, and fear of the economy’s future can create a scarcity mindset and negatively affect decisions and behaviors. Hyper-focusing on these things will set your business up for failure and reduce the chances of achieving success.
If you have these limiting beliefs , it’s time to change them to empowering beliefs that can help you thrive as a leader. Use fear to push your business to greater heights . Decide that success will happen no matter what, and many business problems will resolve themselves along the way.
7. Harnessing the power of technology
New entrepreneurs often have an old-school mindset and make the mistake of thinking they don’t need technology. Others believe they’re in a business that doesn’t need technology to succeed. In today’s economy, it’s essential to harness the power of technology to avoid being disrupted by competitors.
From artificial intelligence to automation, emerging tech has a place in every business. Address these common business problems with strategic innovation team meetings to discuss incorporating new technology into your business to beat your competition .
8. Developing your skills
While it’s crucial to shift your mindset, control your emotions and be decisive in business, it’s also important to take a realistic look at your strengths and weaknesses. To be successful, business owners need skills like reading financial statements , hiring the right employees and scaling mindfully .
Your psychology and skillset are the foundation you’ll build for the rest of your business. You can’t build a sturdy structure without sealing the cracks and strengthening the base. You can personally develop these skills or outsource them to focus on other aspects of the business. Being honest about current and future challenges allows you to scale your business sustainably.
9. Asking for help
When entrepreneurs lack specific skills, the inability to reach out to available resources is one of their biggest problems in business. Being a great leader means using everything at your disposal to get the job done. Resourcefulness is one of a leader’s top traits . When it comes to business, the best leaders leverage what they have to fill in the gaps.
Stop convincing yourself that “strong leaders don’t ask for support,” and you’ll find that business help is out there. Sign up for a free CEO Strategy Session and discover new strategies to supercharge your success. You’ll find resources to solve your current business problems and create a blueprint for lasting organizational change .
Examples of companies experiencing problems
Even the most prominent businesses were scrappy startups at the beginning. Irrespective of industry, you’ll experience the same universal challenges businesses worldwide face. How you view these business problems is critical: Are they obstacles or opportunities for growth ?
Apple overcame numerous business challenges – and near bankruptcy – before becoming a force of nature, and they didn’t do it by thinking small. When sales were down, Apple turned to marketing and innovation to solve problems, which led to the creation of the society-changing iPhone.
Starbucks is another household name that triumphed over business problems. During the 2008 recession, the earnings of this billion-dollar coffee chain dropped by more than 50%. In response, the company brought back CEO Howard Schultz, who showed exemplary crisis leadership . Schultz examined Starbucks’ practices and concluded they were in the customer business, not the coffee business. He put the focus back on customers and dragged the company back from the brink of failure.
Remember, business problems are just opportunities in disguise. It’s time to stop living in fear and start building the skills and mindset you need to overcome any challenge .
Ready to crush your business problems?
Discover how to defeat common business problems with Tony Robbins’ free 7 Forces of Business Mastery content series.
© 2024 Robbins Research International, Inc. All rights reserved.
French supermarket chain Casino to axe jobs in overhaul
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Olivier Sorgho; Editing by Sudip Kar-Gupta, Dominique Vidalon and Alexander Smith
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

China Q1 industrial profits' growth pace stirs doubts about economic recovery
China's industrial profits fell in March and slowed gains for the quarter compared to the first two months, official data showed on Saturday, raising doubts about the strength of a recovery for the world's second-biggest economy.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. Keep the team on the same page. A clearly defined problem serves as a guidepost for you and your team. It ensures that everyone knows what the goal is and stays aligned. Whenever there's a question about what the business should focus on, you can always circle back to that original problem statement. 5.
They include: 1. Define the problem. Defining the problem is the primary aspect of a business problem statement. Summarize your problem in simple and layman terms. It is highly recommended to avoid industrial lingo and buzzwords. Write a 3-5 sentences long summary, avoid writing more than it. 2.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Your business plan needs a problem statement, because every great company starts by solving an important problem. The more accurately you articulate the problem, the more valuable the solution will be. A common founder faux pas is overlooking the importance of giving the problem more weight than the solution.
Here are 11 common business problems with potential solutions to help you develop plans and strategies for your own organization: 1. Uncertain purpose. Some companies experience a loss of purpose or uncertainty. This can happen if an organization participates in multiple different industries or frequently changes its mission statement.
And you can do the same. By following this 10-step process, you can develop your problem-solving skills and approach any issue that arises with confidence. 1. Define the problem. When a problem arises, it can be very easy to jump right into creating a solution. However, if you don't thoroughly examine what led to the problem in the first ...
For example, problems related to growth, innovation, cost reduction, or risk management. Industry or market: Categorise the problem statement based on the industry or market in which the business operates. For example, problems related to competition, changing customer needs, or regulatory compliance. Business architecture.
All episodes. Details. Transcript. December 04, 2018. Corey Phelps, a strategy professor at McGill University, says great problem solvers are hard to find. Even seasoned professionals at the ...
Here are the key elements of a successful project statement: Below, we provide a step-by-step problem statement example. Read on to learn how a business owner might go about summarizing a problem, defining that problem's impact, and developing potential solutions for that problem. 1. Summary of the Problem.
It also comes in handy should you find that crunching old data is leading to stale solutions. Most of the problem-solving teams we are involved with have twin dilemmas of uncertainty and complexity, at times combined as truly "wicked problems." 7 A term coined in a now famous 1973 article: Horst W. J. Rittel and Melvin Webber, "Dilemmas ...
Solution 1: creating a comprehensive business plan. To grow and succeed, small businesses need a good business plan. The plan outlines the company's goals, target market, and strategies for achieving profitability. Analyzing competitors and conducting market research can help business owners identify challenges and opportunities.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
4 Proven Techniques For Effective Business Problem Solving. There are several fundamentals on which your business stands, remains stable, and soars at the heights for you. These fundamentals are Research and Development of your product and services, Marketing along with market analysis and implementations, sales, accounts, customer support, and ...
Create a Project Plan. The final step in writing a business project solution plan is to choose a solution and create a project plan. A thorough solution plan includes project goals, a list of ...
A common mistake businesses make is that they do not give the problem as much importance as the solution. Instead, most business owners get excited about the solution — but in doing so, they tend to forget to explain why the problem is important. A well-articulated problem gives your solution more value. It makes your entire plan 10x more ...
And fortunately for me, I have a solution to that problem. So as you're articulating your business's problem and how you solve it, make sure it's a clear and compelling statement for your customer.
Problem Statement: Rigorous labor-intensive processing due to manual paperwork management. 3. Streaming Entertainment Service Company. Netflix, Hulu, and other streaming services came to solve the problem of people having to go to video stores to rent movies.
The process and the results are the same - starting with creative questions to find the real opportunity. 2. Adopt a more effective problem-solving mindset. Analyze your habitual approach to ...
Here are five common small business problems and suggestions for how to deal with them. 1. Insufficient Capital or Cash Flow. By far the biggest hurdle faced by start-ups and other small enterprises is money. Too many times, entrepreneurs don't start out with enough capital. Start-up costs often exceed budget.
4. Employee Productivity and Retention. Problem: Maintaining a motivated and productive workforce is essential for business success. High turnover rates and unmotivated employees can be detrimental. Solution: To improve employee productivity and retention: Offer competitive compensation and benefits packages.
Use The 'Five Whys' Method. One of our favorite techniques here at ROK is the simple yet effective "Five Whys" method. It involves gathering a team and repeatedly asking "why ...
The Solution is about the Customer. The solution section of the business plan can only come after the customer problem has been defined. Trying to present a solution in search of a problem is a mistake and is a tough sell to present to an investor. The solution has to match the customer problem.
Surface-level problems in business typically affect day-to-day business management and manifest as employee or customer dissatisfaction. These issues can also occur naturally in the market. Examples of common business problems in this category include: High employee turnover rate. Increase in competition. Falling sales or lack of growth.
Develop a plan. Follow through with your project. Review results and produce insights. Your business case development provides the core elements required to solve a problem, including metrics and ...
Step 6: Tie it all together. End your proposal with a conclusion that briefly summarizes the problem, solution, and benefits. Emphasize the significant parts, and make your proposal stand out by ...
Unlimited small business plans for all your devices. Connect seamlessly on every device. All unlimited business plans on our 5G network are packed with incredible benefits and value—with no annual contracts. During congestion, heavy data users (>50GB/mo. for most plans) and customers choosing lower-prioritized plans may notice lower speeds ...
The N.C. Office of Recovery Resiliency (NCORR) today announced the launch of a new Heat Action Plan Toolkit that aims to reduce heat-related health impacts to North Carolina residents and workers. The toolkit launch coincides with Earth Day, a global event focused on environmental protection, which is critical to reducing climate impacts such ...
Supermarket group Casino said on Wednesday it would cut up to 3,267 jobs to tackle its financial problems, while refocusing its business with the aim of becoming France's leading convenience ...
Ely, a local attorney and former state lawmaker, has been working as a volunteer with the city to come up with a comprehensive plan to deal with the homeless crisis. "I called in various locales ...
Get a $40 monthly discount on an eligible tablet line when bundled with a qualifying voice plan. 2. 1 With $20 monthly bill credit and AutoPay using eligible payment method. Business Unlimited Ultimate: Activate up to 4K UHD streaming on capable device, or video typically streams in SD. With AutoPay & eligible payment method.