Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods

Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read
Case Study-Based Learning
Enhancing learning through immediate application.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

If you've ever tried to learn a new concept, you probably appreciate that "knowing" is different from "doing." When you have an opportunity to apply your knowledge, the lesson typically becomes much more real.
Adults often learn differently from children, and we have different motivations for learning. Typically, we learn new skills because we want to. We recognize the need to learn and grow, and we usually need – or want – to apply our newfound knowledge soon after we've learned it.
A popular theory of adult learning is andragogy (the art and science of leading man, or adults), as opposed to the better-known pedagogy (the art and science of leading children). Malcolm Knowles , a professor of adult education, was considered the father of andragogy, which is based on four key observations of adult learners:
- Adults learn best if they know why they're learning something.
- Adults often learn best through experience.
- Adults tend to view learning as an opportunity to solve problems.
- Adults learn best when the topic is relevant to them and immediately applicable.
This means that you'll get the best results with adults when they're fully involved in the learning experience. Give an adult an opportunity to practice and work with a new skill, and you have a solid foundation for high-quality learning that the person will likely retain over time.
So, how can you best use these adult learning principles in your training and development efforts? Case studies provide an excellent way of practicing and applying new concepts. As such, they're very useful tools in adult learning, and it's important to understand how to get the maximum value from them.
What Is a Case Study?
Case studies are a form of problem-based learning, where you present a situation that needs a resolution. A typical business case study is a detailed account, or story, of what happened in a particular company, industry, or project over a set period of time.
The learner is given details about the situation, often in a historical context. The key players are introduced. Objectives and challenges are outlined. This is followed by specific examples and data, which the learner then uses to analyze the situation, determine what happened, and make recommendations.
The depth of a case depends on the lesson being taught. A case study can be two pages, 20 pages, or more. A good case study makes the reader think critically about the information presented, and then develop a thorough assessment of the situation, leading to a well-thought-out solution or recommendation.
Why Use a Case Study?
Case studies are a great way to improve a learning experience, because they get the learner involved, and encourage immediate use of newly acquired skills.
They differ from lectures or assigned readings because they require participation and deliberate application of a broad range of skills. For example, if you study financial analysis through straightforward learning methods, you may have to calculate and understand a long list of financial ratios (don't worry if you don't know what these are). Likewise, you may be given a set of financial statements to complete a ratio analysis. But until you put the exercise into context, you may not really know why you're doing the analysis.
With a case study, however, you might explore whether a bank should provide financing to a borrower, or whether a company is about to make a good acquisition. Suddenly, the act of calculating ratios becomes secondary – it's more important to understand what the ratios tell you. This is how case studies can make the difference between knowing what to do, and knowing how, when, and why to do it.
Then, what really separates case studies from other practical forms of learning – like scenarios and simulations – is the ability to compare the learner's recommendations with what actually happened. When you know what really happened, it's much easier to evaluate the "correctness" of the answers given.
When to Use a Case Study
As you can see, case studies are powerful and effective training tools. They also work best with practical, applied training, so make sure you use them appropriately.
Remember these tips:
- Case studies tend to focus on why and how to apply a skill or concept, not on remembering facts and details. Use case studies when understanding the concept is more important than memorizing correct responses.
- Case studies are great team-building opportunities. When a team gets together to solve a case, they'll have to work through different opinions, methods, and perspectives.
- Use case studies to build problem-solving skills, particularly those that are valuable when applied, but are likely to be used infrequently. This helps people get practice with these skills that they might not otherwise get.
- Case studies can be used to evaluate past problem solving. People can be asked what they'd do in that situation, and think about what could have been done differently.
Ensuring Maximum Value From Case Studies
The first thing to remember is that you already need to have enough theoretical knowledge to handle the questions and challenges in the case study. Otherwise, it can be like trying to solve a puzzle with some of the pieces missing.
Here are some additional tips for how to approach a case study. Depending on the exact nature of the case, some tips will be more relevant than others.
- Read the case at least three times before you start any analysis. Case studies usually have lots of details, and it's easy to miss something in your first, or even second, reading.
- Once you're thoroughly familiar with the case, note the facts. Identify which are relevant to the tasks you've been assigned. In a good case study, there are often many more facts than you need for your analysis.
- If the case contains large amounts of data, analyze this data for relevant trends. For example, have sales dropped steadily, or was there an unexpected high or low point?
- If the case involves a description of a company's history, find the key events, and consider how they may have impacted the current situation.
- Consider using techniques like SWOT analysis and Porter's Five Forces Analysis to understand the organization's strategic position.
- Stay with the facts when you draw conclusions. These include facts given in the case as well as established facts about the environmental context. Don't rely on personal opinions when you put together your answers.
Writing a Case Study
You may have to write a case study yourself. These are complex documents that take a while to research and compile. The quality of the case study influences the quality of the analysis. Here are some tips if you want to write your own:
- Write your case study as a structured story. The goal is to capture an interesting situation or challenge and then bring it to life with words and information. You want the reader to feel a part of what's happening.
- Present information so that a "right" answer isn't obvious. The goal is to develop the learner's ability to analyze and assess, not necessarily to make the same decision as the people in the actual case.
- Do background research to fully understand what happened and why. You may need to talk to key stakeholders to get their perspectives as well.
- Determine the key challenge. What needs to be resolved? The case study should focus on one main question or issue.
- Define the context. Talk about significant events leading up to the situation. What organizational factors are important for understanding the problem and assessing what should be done? Include cultural factors where possible.
- Identify key decision makers and stakeholders. Describe their roles and perspectives, as well as their motivations and interests.
- Make sure that you provide the right data to allow people to reach appropriate conclusions.
- Make sure that you have permission to use any information you include.
A typical case study structure includes these elements:
- Executive summary. Define the objective, and state the key challenge.
- Opening paragraph. Capture the reader's interest.
- Scope. Describe the background, context, approach, and issues involved.
- Presentation of facts. Develop an objective picture of what's happening.
- Description of key issues. Present viewpoints, decisions, and interests of key parties.
Because case studies have proved to be such effective teaching tools, many are already written. Some excellent sources of free cases are The Times 100 , CasePlace.org , and Schroeder & Schroeder Inc . You can often search for cases by topic or industry. These cases are expertly prepared, based mostly on real situations, and used extensively in business schools to teach management concepts.
Case studies are a great way to improve learning and training. They provide learners with an opportunity to solve a problem by applying what they know.
There are no unpleasant consequences for getting it "wrong," and cases give learners a much better understanding of what they really know and what they need to practice.
Case studies can be used in many ways, as team-building tools, and for skill development. You can write your own case study, but a large number are already prepared. Given the enormous benefits of practical learning applications like this, case studies are definitely something to consider adding to your next training session.
Knowles, M. (1973). 'The Adult Learner: A Neglected Species [online].' Available here .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
What is leadership video.
An Introduction to Leadership
An Introduction to Planning
An Overview of Planning and How the Different Types of Plans Relate to Each Other
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Try Mind Tools for FREE
Get unlimited access to all our career-boosting content and member benefits with our 7-day free trial.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Team Briefings

Onboarding With STEPS
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
New pain points podcast - perfectionism.
Why Am I Such a Perfectionist?
Pain Points Podcast - Building Trust
Developing and Strengthening Trust at Work
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Seeing the big picture with mind maps.
Exploring ideas from all angles
Animated Video
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What the Case Study Method Really Teaches
- Nitin Nohria

Seven meta-skills that stick even if the cases fade from memory.
It’s been 100 years since Harvard Business School began using the case study method. Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment, bias recognition, judgement, collaboration, curiosity, and self-confidence.
During my decade as dean of Harvard Business School, I spent hundreds of hours talking with our alumni. To enliven these conversations, I relied on a favorite question: “What was the most important thing you learned from your time in our MBA program?”
- Nitin Nohria is the George F. Baker Professor of Business Administration, Distinguished University Service Professor, and former dean of Harvard Business School.
Partner Center
- First Online: 27 October 2022
Cite this chapter

- R. M. Channaveer 4 &
- Rajendra Baikady 5
2410 Accesses
1 Citations
This chapter reviews the strengths and limitations of case study as a research method in social sciences. It provides an account of an evidence base to justify why a case study is best suitable for some research questions and why not for some other research questions. Case study designing around the research context, defining the structure and modality, conducting the study, collecting the data through triangulation mode, analysing the data, and interpreting the data and theory building at the end give a holistic view of it. In addition, the chapter also focuses on the types of case study and when and where to use case study as a research method in social science research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Ang, C. S., Lee, K. F., & Dipolog-Ubanan, G. F. (2019). Determinants of first-year student identity and satisfaction in higher education: A quantitative case study. SAGE Open, 9 (2), 215824401984668. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244019846689
Baxter, P., & Jack, S. (2015). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report . Published. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/2008.1573
Bhatta, T. P. (2018). Case study research, philosophical position and theory building: A methodological discussion. Dhaulagiri Journal of Sociology and Anthropology, 12 , 72–79. https://doi.org/10.3126/dsaj.v12i0.22182
Article Google Scholar
Bromley, P. D. (1990). Academic contributions to psychological counselling. A philosophy of science for the study of individual cases. Counselling Psychology Quarterly , 3 (3), 299–307.
Google Scholar
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A., Huby, G., Avery, A., & Sheikh, A. (2011). The case study approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 11 (1), 1–9.
Grässel, E., & Schirmer, B. (2006). The use of volunteers to support family carers of dementia patients: Results of a prospective longitudinal study investigating expectations towards and experience with training and professional support. Zeitschrift Fur Gerontologie Und Geriatrie, 39 (3), 217–226.
Greenwood, D., & Lowenthal, D. (2005). Case study as a means of researching social work and improving practitioner education. Journal of Social Work Practice, 19 (2), 181–193. https://doi.org/10.1080/02650530500144782
Gülseçen, S., & Kubat, A. (2006). Teaching ICT to teacher candidates using PBL: A qualitative and quantitative evaluation. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 9 (2), 96–106.
Gomm, R., Hammersley, M., & Foster, P. (2000). Case study and generalization. Case study method , 98–115.
Hamera, J., Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2011). Performance ethnography . SAGE.
Hayes, N. (2000). Doing psychological research (p. 133). Open University Press.
Harrison, H., Birks, M., Franklin, R., & Mills, J. (2017). Case study research: Foundations and methodological orientations. In Forum qualitative sozialforschung/forum: Qualitative social research (Vol. 18, No. 1).
Iwakabe, S., & Gazzola, N. (2009). From single-case studies to practice-based knowledge: Aggregating and synthesizing case studies. Psychotherapy Research, 19 (4–5), 601–611. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503300802688494
Johnson, M. P. (2006). Decision models for the location of community corrections centers. Environment and Planning b: Planning and Design, 33 (3), 393–412. https://doi.org/10.1068/b3125
Kaarbo, J., & Beasley, R. K. (1999). A practical guide to the comparative case study method in political psychology. Political Psychology, 20 (2), 369–391. https://doi.org/10.1111/0162-895x.00149
Lovell, G. I. (2006). Justice excused: The deployment of law in everyday political encounters. Law Society Review, 40 (2), 283–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5893.2006.00265.x
McDonough, S., & McDonough, S. (1997). Research methods as part of English language teacher education. English Language Teacher Education and Development, 3 (1), 84–96.
Meredith, J. (1998). Building operations management theory through case and field research. Journal of Operations Management, 16 (4), 441–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-6963(98)00023-0
Mills, A. J., Durepos, G., & Wiebe, E. (Eds.). (2009). Encyclopedia of case study research . Sage Publications.
Ochieng, P. A. (2009). An analysis of the strengths and limitation of qualitative and quantitative research paradigms. Problems of Education in the 21st Century , 13 , 13.
Page, E. B., Webb, E. J., Campell, D. T., Schwart, R. D., & Sechrest, L. (1966). Unobtrusive measures: Nonreactive research in the social sciences. American Educational Research Journal, 3 (4), 317. https://doi.org/10.2307/1162043
Rashid, Y., Rashid, A., Warraich, M. A., Sabir, S. S., & Waseem, A. (2019). Case study method: A step-by-step guide for business researchers. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 18 , 160940691986242. https://doi.org/10.1177/1609406919862424
Ridder, H. G. (2017). The theory contribution of case study research designs. Business Research, 10 (2), 281–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40685-017-0045-z
Sadeghi Moghadam, M. R., Ghasemnia Arabi, N., & Khoshsima, G. (2021). A Review of case study method in operations management research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 20 , 160940692110100. https://doi.org/10.1177/16094069211010088
Sommer, B. B., & Sommer, R. (1997). A practical guide to behavioral research: Tools and techniques . Oxford University Press.
Stake, R. E. (2010). Qualitative research: Studying how things work .
Stake, R. E. (1995). The Art of Case Study Research . Sage Publications.
Stoecker, R. (1991). Evaluating and rethinking the case study. The Sociological Review, 39 (1), 88–112.
Suryani, A. (2013). Comparing case study and ethnography as qualitative research approaches .
Taylor, S., & Berridge, V. (2006). Medicinal plants and malaria: An historical case study of research at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in the twentieth century. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 100 (8), 707–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.11.017
Tellis, W. (1997). Introduction to case study. The Qualitative Report . Published. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/1997.2024
Towne, L., & Shavelson, R. J. (2002). Scientific research in education . National Academy Press Publications Sales Office.
Widdowson, M. D. J. (2011). Case study research methodology. International Journal of Transactional Analysis Research, 2 (1), 25–34.
Yin, R. K. (2004). The case study anthology . Sage.
Yin, R. K. (2003). Design and methods. Case Study Research , 3 (9.2).
Yin, R. K. (1994). Case study research: Design and methods (2nd ed.). Sage Publishing.
Yin, R. (1984). Case study research: Design and methods . Sage Publications Beverly Hills.
Yin, R. (1993). Applications of case study research . Sage Publishing.
Zainal, Z. (2003). An investigation into the effects of discipline-specific knowledge, proficiency and genre on reading comprehension and strategies of Malaysia ESP Students. Unpublished Ph. D. Thesis. University of Reading , 1 (1).
Zeisel, J. (1984). Inquiry by design: Tools for environment-behaviour research (No. 5). CUP archive.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Social Work, Central University of Karnataka, Kadaganchi, India
R. M. Channaveer
Department of Social Work, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Rajendra Baikady
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to R. M. Channaveer .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Centre for Family and Child Studies, Research Institute of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates
M. Rezaul Islam
Department of Development Studies, University of Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Niaz Ahmed Khan
Department of Social Work, School of Humanities, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Channaveer, R.M., Baikady, R. (2022). Case Study. In: Islam, M.R., Khan, N.A., Baikady, R. (eds) Principles of Social Research Methodology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5441-2_21
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5441-2_21
Published : 27 October 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-5219-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-5441-2
eBook Packages : Social Sciences
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 21, Issue 1
- What is a case study?
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Roberta Heale 1 ,
- Alison Twycross 2
- 1 School of Nursing , Laurentian University , Sudbury , Ontario , Canada
- 2 School of Health and Social Care , London South Bank University , London , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Roberta Heale, School of Nursing, Laurentian University, Sudbury, ON P3E2C6, Canada; rheale{at}laurentian.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2017-102845
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
What is it?
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research. 1 However, very simply… ‘a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units’. 1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a single individual, group, community or some other unit in which the researcher examines in-depth data relating to several variables. 2
Often there are several similar cases to consider such as educational or social service programmes that are delivered from a number of locations. Although similar, they are complex and have unique features. In these circumstances, the evaluation of several, similar cases will provide a better answer to a research question than if only one case is examined, hence the multiple-case study. Stake asserts that the cases are grouped and viewed as one entity, called the quintain . 6 ‘We study what is similar and different about the cases to understand the quintain better’. 6
The steps when using case study methodology are the same as for other types of research. 6 The first step is defining the single case or identifying a group of similar cases that can then be incorporated into a multiple-case study. A search to determine what is known about the case(s) is typically conducted. This may include a review of the literature, grey literature, media, reports and more, which serves to establish a basic understanding of the cases and informs the development of research questions. Data in case studies are often, but not exclusively, qualitative in nature. In multiple-case studies, analysis within cases and across cases is conducted. Themes arise from the analyses and assertions about the cases as a whole, or the quintain, emerge. 6
Benefits and limitations of case studies
If a researcher wants to study a specific phenomenon arising from a particular entity, then a single-case study is warranted and will allow for a in-depth understanding of the single phenomenon and, as discussed above, would involve collecting several different types of data. This is illustrated in example 1 below.
Using a multiple-case research study allows for a more in-depth understanding of the cases as a unit, through comparison of similarities and differences of the individual cases embedded within the quintain. Evidence arising from multiple-case studies is often stronger and more reliable than from single-case research. Multiple-case studies allow for more comprehensive exploration of research questions and theory development. 6
Despite the advantages of case studies, there are limitations. The sheer volume of data is difficult to organise and data analysis and integration strategies need to be carefully thought through. There is also sometimes a temptation to veer away from the research focus. 2 Reporting of findings from multiple-case research studies is also challenging at times, 1 particularly in relation to the word limits for some journal papers.
Examples of case studies
Example 1: nurses’ paediatric pain management practices.
One of the authors of this paper (AT) has used a case study approach to explore nurses’ paediatric pain management practices. This involved collecting several datasets:
Observational data to gain a picture about actual pain management practices.
Questionnaire data about nurses’ knowledge about paediatric pain management practices and how well they felt they managed pain in children.
Questionnaire data about how critical nurses perceived pain management tasks to be.
These datasets were analysed separately and then compared 7–9 and demonstrated that nurses’ level of theoretical did not impact on the quality of their pain management practices. 7 Nor did individual nurse’s perceptions of how critical a task was effect the likelihood of them carrying out this task in practice. 8 There was also a difference in self-reported and observed practices 9 ; actual (observed) practices did not confirm to best practice guidelines, whereas self-reported practices tended to.
Example 2: quality of care for complex patients at Nurse Practitioner-Led Clinics (NPLCs)
The other author of this paper (RH) has conducted a multiple-case study to determine the quality of care for patients with complex clinical presentations in NPLCs in Ontario, Canada. 10 Five NPLCs served as individual cases that, together, represented the quatrain. Three types of data were collected including:
Review of documentation related to the NPLC model (media, annual reports, research articles, grey literature and regulatory legislation).
Interviews with nurse practitioners (NPs) practising at the five NPLCs to determine their perceptions of the impact of the NPLC model on the quality of care provided to patients with multimorbidity.
Chart audits conducted at the five NPLCs to determine the extent to which evidence-based guidelines were followed for patients with diabetes and at least one other chronic condition.
The three sources of data collected from the five NPLCs were analysed and themes arose related to the quality of care for complex patients at NPLCs. The multiple-case study confirmed that nurse practitioners are the primary care providers at the NPLCs, and this positively impacts the quality of care for patients with multimorbidity. Healthcare policy, such as lack of an increase in salary for NPs for 10 years, has resulted in issues in recruitment and retention of NPs at NPLCs. This, along with insufficient resources in the communities where NPLCs are located and high patient vulnerability at NPLCs, have a negative impact on the quality of care. 10
These examples illustrate how collecting data about a single case or multiple cases helps us to better understand the phenomenon in question. Case study methodology serves to provide a framework for evaluation and analysis of complex issues. It shines a light on the holistic nature of nursing practice and offers a perspective that informs improved patient care.
- Gustafsson J
- Calanzaro M
- Sandelowski M
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
5 Benefits of Learning Through the Case Study Method

- 28 Nov 2023
While several factors make HBS Online unique —including a global Community and real-world outcomes —active learning through the case study method rises to the top.
In a 2023 City Square Associates survey, 74 percent of HBS Online learners who also took a course from another provider said HBS Online’s case method and real-world examples were better by comparison.
Here’s a primer on the case method, five benefits you could gain, and how to experience it for yourself.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is the Harvard Business School Case Study Method?
The case study method , or case method , is a learning technique in which you’re presented with a real-world business challenge and asked how you’d solve it. After working through it yourself and with peers, you’re told how the scenario played out.
HBS pioneered the case method in 1922. Shortly before, in 1921, the first case was written.
“How do you go into an ambiguous situation and get to the bottom of it?” says HBS Professor Jan Rivkin, former senior associate dean and chair of HBS's master of business administration (MBA) program, in a video about the case method . “That skill—the skill of figuring out a course of inquiry to choose a course of action—that skill is as relevant today as it was in 1921.”
Originally developed for the in-person MBA classroom, HBS Online adapted the case method into an engaging, interactive online learning experience in 2014.
In HBS Online courses , you learn about each case from the business professional who experienced it. After reviewing their videos, you’re prompted to take their perspective and explain how you’d handle their situation.
You then get to read peers’ responses, “star” them, and comment to further the discussion. Afterward, you learn how the professional handled it and their key takeaways.
HBS Online’s adaptation of the case method incorporates the famed HBS “cold call,” in which you’re called on at random to make a decision without time to prepare.
“Learning came to life!” said Sheneka Balogun , chief administration officer and chief of staff at LeMoyne-Owen College, of her experience taking the Credential of Readiness (CORe) program . “The videos from the professors, the interactive cold calls where you were randomly selected to participate, and the case studies that enhanced and often captured the essence of objectives and learning goals were all embedded in each module. This made learning fun, engaging, and student-friendly.”
If you’re considering taking a course that leverages the case study method, here are five benefits you could experience.
5 Benefits of Learning Through Case Studies
1. take new perspectives.
The case method prompts you to consider a scenario from another person’s perspective. To work through the situation and come up with a solution, you must consider their circumstances, limitations, risk tolerance, stakeholders, resources, and potential consequences to assess how to respond.
Taking on new perspectives not only can help you navigate your own challenges but also others’. Putting yourself in someone else’s situation to understand their motivations and needs can go a long way when collaborating with stakeholders.
2. Hone Your Decision-Making Skills
Another skill you can build is the ability to make decisions effectively . The case study method forces you to use limited information to decide how to handle a problem—just like in the real world.
Throughout your career, you’ll need to make difficult decisions with incomplete or imperfect information—and sometimes, you won’t feel qualified to do so. Learning through the case method allows you to practice this skill in a low-stakes environment. When facing a real challenge, you’ll be better prepared to think quickly, collaborate with others, and present and defend your solution.
3. Become More Open-Minded
As you collaborate with peers on responses, it becomes clear that not everyone solves problems the same way. Exposing yourself to various approaches and perspectives can help you become a more open-minded professional.
When you’re part of a diverse group of learners from around the world, your experiences, cultures, and backgrounds contribute to a range of opinions on each case.
On the HBS Online course platform, you’re prompted to view and comment on others’ responses, and discussion is encouraged. This practice of considering others’ perspectives can make you more receptive in your career.
“You’d be surprised at how much you can learn from your peers,” said Ratnaditya Jonnalagadda , a software engineer who took CORe.
In addition to interacting with peers in the course platform, Jonnalagadda was part of the HBS Online Community , where he networked with other professionals and continued discussions sparked by course content.
“You get to understand your peers better, and students share examples of businesses implementing a concept from a module you just learned,” Jonnalagadda said. “It’s a very good way to cement the concepts in one's mind.”
4. Enhance Your Curiosity
One byproduct of taking on different perspectives is that it enables you to picture yourself in various roles, industries, and business functions.
“Each case offers an opportunity for students to see what resonates with them, what excites them, what bores them, which role they could imagine inhabiting in their careers,” says former HBS Dean Nitin Nohria in the Harvard Business Review . “Cases stimulate curiosity about the range of opportunities in the world and the many ways that students can make a difference as leaders.”
Through the case method, you can “try on” roles you may not have considered and feel more prepared to change or advance your career .
5. Build Your Self-Confidence
Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader’s perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and defend your opinions and decisions to peers, you prepare to do the same in your career.
According to a 2022 City Square Associates survey , 84 percent of HBS Online learners report feeling more confident making business decisions after taking a course.
“Self-confidence is difficult to teach or coach, but the case study method seems to instill it in people,” Nohria says in the Harvard Business Review . “There may well be other ways of learning these meta-skills, such as the repeated experience gained through practice or guidance from a gifted coach. However, under the direction of a masterful teacher, the case method can engage students and help them develop powerful meta-skills like no other form of teaching.”

How to Experience the Case Study Method
If the case method seems like a good fit for your learning style, experience it for yourself by taking an HBS Online course. Offerings span seven subject areas, including:
- Business essentials
- Leadership and management
- Entrepreneurship and innovation
- Finance and accounting
- Business in society
No matter which course or credential program you choose, you’ll examine case studies from real business professionals, work through their challenges alongside peers, and gain valuable insights to apply to your career.
Are you interested in discovering how HBS Online can help advance your career? Explore our course catalog and download our free guide —complete with interactive workbook sections—to determine if online learning is right for you and which course to take.

About the Author
- Columbia University in the City of New York
- Office of Teaching, Learning, and Innovation
- University Policies
- Columbia Online
- Academic Calendar
- Resources and Technology
- Resources and Guides
Case Method Teaching and Learning
What is the case method? How can the case method be used to engage learners? What are some strategies for getting started? This guide helps instructors answer these questions by providing an overview of the case method while highlighting learner-centered and digitally-enhanced approaches to teaching with the case method. The guide also offers tips to instructors as they get started with the case method and additional references and resources.
On this page:
What is case method teaching.
- Case Method at Columbia
Why use the Case Method?
Case method teaching approaches, how do i get started.
- Additional Resources
The CTL is here to help!
For support with implementing a case method approach in your course, email [email protected] to schedule your 1-1 consultation .
Cite this resource: Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning (2019). Case Method Teaching and Learning. Columbia University. Retrieved from [today’s date] from https://ctl.columbia.edu/resources-and-technology/resources/case-method/
Case method 1 teaching is an active form of instruction that focuses on a case and involves students learning by doing 2 3 . Cases are real or invented stories 4 that include “an educational message” or recount events, problems, dilemmas, theoretical or conceptual issue that requires analysis and/or decision-making.
Case-based teaching simulates real world situations and asks students to actively grapple with complex problems 5 6 This method of instruction is used across disciplines to promote learning, and is common in law, business, medicine, among other fields. See Table 1 below for a few types of cases and the learning they promote.
Table 1: Types of cases and the learning they promote.
For a more complete list, see Case Types & Teaching Methods: A Classification Scheme from the National Center for Case Study Teaching in Science.
Back to Top
Case Method Teaching and Learning at Columbia
The case method is actively used in classrooms across Columbia, at the Morningside campus in the School of International and Public Affairs (SIPA), the School of Business, Arts and Sciences, among others, and at Columbia University Irving Medical campus.
Faculty Spotlight:
Professor Mary Ann Price on Using Case Study Method to Place Pre-Med Students in Real-Life Scenarios
Read more
Professor De Pinho on Using the Case Method in the Mailman Core
Case method teaching has been found to improve student learning, to increase students’ perception of learning gains, and to meet learning objectives 8 9 . Faculty have noted the instructional benefits of cases including greater student engagement in their learning 10 , deeper student understanding of concepts, stronger critical thinking skills, and an ability to make connections across content areas and view an issue from multiple perspectives 11 .
Through case-based learning, students are the ones asking questions about the case, doing the problem-solving, interacting with and learning from their peers, “unpacking” the case, analyzing the case, and summarizing the case. They learn how to work with limited information and ambiguity, think in professional or disciplinary ways, and ask themselves “what would I do if I were in this specific situation?”
The case method bridges theory to practice, and promotes the development of skills including: communication, active listening, critical thinking, decision-making, and metacognitive skills 12 , as students apply course content knowledge, reflect on what they know and their approach to analyzing, and make sense of a case.
Though the case method has historical roots as an instructor-centered approach that uses the Socratic dialogue and cold-calling, it is possible to take a more learner-centered approach in which students take on roles and tasks traditionally left to the instructor.
Cases are often used as “vehicles for classroom discussion” 13 . Students should be encouraged to take ownership of their learning from a case. Discussion-based approaches engage students in thinking and communicating about a case. Instructors can set up a case activity in which students are the ones doing the work of “asking questions, summarizing content, generating hypotheses, proposing theories, or offering critical analyses” 14 .
The role of the instructor is to share a case or ask students to share or create a case to use in class, set expectations, provide instructions, and assign students roles in the discussion. Student roles in a case discussion can include:
- discussion “starters” get the conversation started with a question or posing the questions that their peers came up with;
- facilitators listen actively, validate the contributions of peers, ask follow-up questions, draw connections, refocus the conversation as needed;
- recorders take-notes of the main points of the discussion, record on the board, upload to CourseWorks, or type and project on the screen; and
- discussion “wrappers” lead a summary of the main points of the discussion.
Prior to the case discussion, instructors can model case analysis and the types of questions students should ask, co-create discussion guidelines with students, and ask for students to submit discussion questions. During the discussion, the instructor can keep time, intervene as necessary (however the students should be doing the talking), and pause the discussion for a debrief and to ask students to reflect on what and how they learned from the case activity.
Note: case discussions can be enhanced using technology. Live discussions can occur via video-conferencing (e.g., using Zoom ) or asynchronous discussions can occur using the Discussions tool in CourseWorks (Canvas) .
Table 2 includes a few interactive case method approaches. Regardless of the approach selected, it is important to create a learning environment in which students feel comfortable participating in a case activity and learning from one another. See below for tips on supporting student in how to learn from a case in the “getting started” section and how to create a supportive learning environment in the Guide for Inclusive Teaching at Columbia .
Table 2. Strategies for Engaging Students in Case-Based Learning
Approaches to case teaching should be informed by course learning objectives, and can be adapted for small, large, hybrid, and online classes. Instructional technology can be used in various ways to deliver, facilitate, and assess the case method. For instance, an online module can be created in CourseWorks (Canvas) to structure the delivery of the case, allow students to work at their own pace, engage all learners, even those reluctant to speak up in class, and assess understanding of a case and student learning. Modules can include text, embedded media (e.g., using Panopto or Mediathread ) curated by the instructor, online discussion, and assessments. Students can be asked to read a case and/or watch a short video, respond to quiz questions and receive immediate feedback, post questions to a discussion, and share resources.
For more information about options for incorporating educational technology to your course, please contact your Learning Designer .
To ensure that students are learning from the case approach, ask them to pause and reflect on what and how they learned from the case. Time to reflect builds your students’ metacognition, and when these reflections are collected they provides you with insights about the effectiveness of your approach in promoting student learning.
Well designed case-based learning experiences: 1) motivate student involvement, 2) have students doing the work, 3) help students develop knowledge and skills, and 4) have students learning from each other.
Designing a case-based learning experience should center around the learning objectives for a course. The following points focus on intentional design.
Identify learning objectives, determine scope, and anticipate challenges.
- Why use the case method in your course? How will it promote student learning differently than other approaches?
- What are the learning objectives that need to be met by the case method? What knowledge should students apply and skills should they practice?
- What is the scope of the case? (a brief activity in a single class session to a semester-long case-based course; if new to case method, start small with a single case).
- What challenges do you anticipate (e.g., student preparation and prior experiences with case learning, discomfort with discussion, peer-to-peer learning, managing discussion) and how will you plan for these in your design?
- If you are asking students to use transferable skills for the case method (e.g., teamwork, digital literacy) make them explicit.
Determine how you will know if the learning objectives were met and develop a plan for evaluating the effectiveness of the case method to inform future case teaching.
- What assessments and criteria will you use to evaluate student work or participation in case discussion?
- How will you evaluate the effectiveness of the case method? What feedback will you collect from students?
- How might you leverage technology for assessment purposes? For example, could you quiz students about the case online before class, accept assignment submissions online, use audience response systems (e.g., PollEverywhere) for formative assessment during class?
Select an existing case, create your own, or encourage students to bring course-relevant cases, and prepare for its delivery
- Where will the case method fit into the course learning sequence?
- Is the case at the appropriate level of complexity? Is it inclusive, culturally relevant, and relatable to students?
- What materials and preparation will be needed to present the case to students? (e.g., readings, audiovisual materials, set up a module in CourseWorks).
Plan for the case discussion and an active role for students
- What will your role be in facilitating case-based learning? How will you model case analysis for your students? (e.g., present a short case and demo your approach and the process of case learning) (Davis, 2009).
- What discussion guidelines will you use that include your students’ input?
- How will you encourage students to ask and answer questions, summarize their work, take notes, and debrief the case?
- If students will be working in groups, how will groups form? What size will the groups be? What instructions will they be given? How will you ensure that everyone participates? What will they need to submit? Can technology be leveraged for any of these areas?
- Have you considered students of varied cognitive and physical abilities and how they might participate in the activities/discussions, including those that involve technology?
Student preparation and expectations
- How will you communicate about the case method approach to your students? When will you articulate the purpose of case-based learning and expectations of student engagement? What information about case-based learning and expectations will be included in the syllabus?
- What preparation and/or assignment(s) will students complete in order to learn from the case? (e.g., read the case prior to class, watch a case video prior to class, post to a CourseWorks discussion, submit a brief memo, complete a short writing assignment to check students’ understanding of a case, take on a specific role, prepare to present a critique during in-class discussion).
Andersen, E. and Schiano, B. (2014). Teaching with Cases: A Practical Guide . Harvard Business Press.
Bonney, K. M. (2015). Case Study Teaching Method Improves Student Performance and Perceptions of Learning Gains†. Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education , 16 (1), 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v16i1.846
Davis, B.G. (2009). Chapter 24: Case Studies. In Tools for Teaching. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass.
Garvin, D.A. (2003). Making the Case: Professional Education for the world of practice. Harvard Magazine. September-October 2003, Volume 106, Number 1, 56-107.
Golich, V.L. (2000). The ABCs of Case Teaching. International Studies Perspectives. 1, 11-29.
Golich, V.L.; Boyer, M; Franko, P.; and Lamy, S. (2000). The ABCs of Case Teaching. Pew Case Studies in International Affairs. Institute for the Study of Diplomacy.
Heath, J. (2015). Teaching & Writing Cases: A Practical Guide. The Case Center, UK.
Herreid, C.F. (2011). Case Study Teaching. New Directions for Teaching and Learning. No. 128, Winder 2011, 31 – 40.
Herreid, C.F. (2007). Start with a Story: The Case Study Method of Teaching College Science . National Science Teachers Association. Available as an ebook through Columbia Libraries.
Herreid, C.F. (2006). “Clicker” Cases: Introducing Case Study Teaching Into Large Classrooms. Journal of College Science Teaching. Oct 2006, 36(2). https://search.proquest.com/docview/200323718?pq-origsite=gscholar
Krain, M. (2016). Putting the Learning in Case Learning? The Effects of Case-Based Approaches on Student Knowledge, Attitudes, and Engagement. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching. 27(2), 131-153.
Lundberg, K.O. (Ed.). (2011). Our Digital Future: Boardrooms and Newsrooms. Knight Case Studies Initiative.
Popil, I. (2011). Promotion of critical thinking by using case studies as teaching method. Nurse Education Today, 31(2), 204–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2010.06.002
Schiano, B. and Andersen, E. (2017). Teaching with Cases Online . Harvard Business Publishing.
Thistlethwaite, JE; Davies, D.; Ekeocha, S.; Kidd, J.M.; MacDougall, C.; Matthews, P.; Purkis, J.; Clay D. (2012). The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education: A BEME systematic review . Medical Teacher. 2012; 34(6): e421-44.
Yadav, A.; Lundeberg, M.; DeSchryver, M.; Dirkin, K.; Schiller, N.A.; Maier, K. and Herreid, C.F. (2007). Teaching Science with Case Studies: A National Survey of Faculty Perceptions of the Benefits and Challenges of Using Cases. Journal of College Science Teaching; Sept/Oct 2007; 37(1).
Weimer, M. (2013). Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass.
Additional resources
Teaching with Cases , Harvard Kennedy School of Government.
Features “what is a teaching case?” video that defines a teaching case, and provides documents to help students prepare for case learning, Common case teaching challenges and solutions, tips for teaching with cases.
Promoting excellence and innovation in case method teaching: Teaching by the Case Method , Christensen Center for Teaching & Learning. Harvard Business School.
National Center for Case Study Teaching in Science . University of Buffalo.
A collection of peer-reviewed STEM cases to teach scientific concepts and content, promote process skills and critical thinking. The Center welcomes case submissions. Case classification scheme of case types and teaching methods:
- Different types of cases: analysis case, dilemma/decision case, directed case, interrupted case, clicker case, a flipped case, a laboratory case.
- Different types of teaching methods: problem-based learning, discussion, debate, intimate debate, public hearing, trial, jigsaw, role-play.
Columbia Resources
Resources available to support your use of case method: The University hosts a number of case collections including: the Case Consortium (a collection of free cases in the fields of journalism, public policy, public health, and other disciplines that include teaching and learning resources; SIPA’s Picker Case Collection (audiovisual case studies on public sector innovation, filmed around the world and involving SIPA student teams in producing the cases); and Columbia Business School CaseWorks , which develops teaching cases and materials for use in Columbia Business School classrooms.
Center for Teaching and Learning
The Center for Teaching and Learning (CTL) offers a variety of programs and services for instructors at Columbia. The CTL can provide customized support as you plan to use the case method approach through implementation. Schedule a one-on-one consultation.
Office of the Provost
The Hybrid Learning Course Redesign grant program from the Office of the Provost provides support for faculty who are developing innovative and technology-enhanced pedagogy and learning strategies in the classroom. In addition to funding, faculty awardees receive support from CTL staff as they redesign, deliver, and evaluate their hybrid courses.
The Start Small! Mini-Grant provides support to faculty who are interested in experimenting with one new pedagogical strategy or tool. Faculty awardees receive funds and CTL support for a one-semester period.
Explore our teaching resources.
- Blended Learning
- Contemplative Pedagogy
- Inclusive Teaching Guide
- FAQ for Teaching Assistants
- Metacognition
CTL resources and technology for you.
- Overview of all CTL Resources and Technology
- The origins of this method can be traced to Harvard University where in 1870 the Law School began using cases to teach students how to think like lawyers using real court decisions. This was followed by the Business School in 1920 (Garvin, 2003). These professional schools recognized that lecture mode of instruction was insufficient to teach critical professional skills, and that active learning would better prepare learners for their professional lives. ↩
- Golich, V.L. (2000). The ABCs of Case Teaching. International Studies Perspectives. 1, 11-29. ↩
- Herreid, C.F. (2007). Start with a Story: The Case Study Method of Teaching College Science . National Science Teachers Association. Available as an ebook through Columbia Libraries. ↩
- Davis, B.G. (2009). Chapter 24: Case Studies. In Tools for Teaching. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass. ↩
- Andersen, E. and Schiano, B. (2014). Teaching with Cases: A Practical Guide . Harvard Business Press. ↩
- Lundberg, K.O. (Ed.). (2011). Our Digital Future: Boardrooms and Newsrooms. Knight Case Studies Initiative. ↩
- Heath, J. (2015). Teaching & Writing Cases: A Practical Guide. The Case Center, UK. ↩
- Bonney, K. M. (2015). Case Study Teaching Method Improves Student Performance and Perceptions of Learning Gains†. Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education , 16 (1), 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v16i1.846 ↩
- Krain, M. (2016). Putting the Learning in Case Learning? The Effects of Case-Based Approaches on Student Knowledge, Attitudes, and Engagement. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching. 27(2), 131-153. ↩
- Thistlethwaite, JE; Davies, D.; Ekeocha, S.; Kidd, J.M.; MacDougall, C.; Matthews, P.; Purkis, J.; Clay D. (2012). The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education: A BEME systematic review . Medical Teacher. 2012; 34(6): e421-44. ↩
- Yadav, A.; Lundeberg, M.; DeSchryver, M.; Dirkin, K.; Schiller, N.A.; Maier, K. and Herreid, C.F. (2007). Teaching Science with Case Studies: A National Survey of Faculty Perceptions of the Benefits and Challenges of Using Cases. Journal of College Science Teaching; Sept/Oct 2007; 37(1). ↩
- Popil, I. (2011). Promotion of critical thinking by using case studies as teaching method. Nurse Education Today, 31(2), 204–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2010.06.002 ↩
- Weimer, M. (2013). Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice. Second Edition. Jossey-Bass. ↩
- Herreid, C.F. (2006). “Clicker” Cases: Introducing Case Study Teaching Into Large Classrooms. Journal of College Science Teaching. Oct 2006, 36(2). https://search.proquest.com/docview/200323718?pq-origsite=gscholar ↩
This website uses cookies to identify users, improve the user experience and requires cookies to work. By continuing to use this website, you consent to Columbia University's use of cookies and similar technologies, in accordance with the Columbia University Website Cookie Notice .
7-day free trial | No credit card required
Deliver Faster Support Right From Gmail

Table of contents
10 best knowledge base article templates for every business.
Startups, small businesses, or large enterprises – irrespective of the size of your business, a knowledge base is essential to provide efficient customer support and for managing business information.
A knowledge base acts as a central repository for crucial information, FAQs, and solutions, ensuring that both customers and employees have easy access to the knowledge they need.
In this article, we’ll delve into the top 10 Knowledge Base Article Templates for businesses to streamline information delivery and enhance customer support.
Table of Contents
10 best knowledge base article templates.
Here are ten knowledge base article templates that can help you structure your content effectively. Feel free to play around with and customize these templates to suit your specific organizational and customer needs:
Template 1: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Knowledge Base Article
This is a foundational template that helps businesses address common queries and provide quick solutions to customers. This template organizes information in a question-and-answer format, making it easy for customers to find the answers they need efficiently. Here’s how it benefits businesses –
Template Structure:
Title: [Topic-specific, clear, and concise]
Introduction (Optional): Briefly introduce the topic and its importance.
[Continue listing questions and answers as needed]
Conclusion (Optional): Summarize key takeaways or direct users to related articles or resources.
Feedback Section (Optional): Encourage users to provide feedback or suggest additional questions.
Title: How to Track Your Order Questions: How can I track my order? Answer: To track your order, log in to your account and go to the “Order History” section. There, you’ll find detailed tracking information for your recent purchases. Example: Let’s say you’re eagerly waiting for your package. Use this guide to monitor its journey from our warehouse to your doorstep. What should I do if my tracking information is not updating? Answer: If tracking information hasn’t changed for a while, don’t worry. It can take some time to update. However, if you have concerns, contact our support team at [email protected] for assistance. Example: Patience is key when tracking shipments. If you ever have doubts, our team is ready to help. [Continue with additional FAQs]
Template 2: Troubleshooting Guide Knowledge Base Article
The Troubleshooting Guide Knowledge Base Article is designed to assist customers in diagnosing and resolving common issues with a product or service. It provides a step-by-step approach to problem-solving. Here’s how it benefits your business –
Title: [Clear and concise]
Introduction (Optional): Briefly set the context and importance of the troubleshooting guide.
Troubleshooting Steps:
Conclusion (Optional): Summarize the key steps and emphasize successful resolution.
Feedback Section (Optional): Encourage users to provide feedback on the troubleshooting guide’s effectiveness.
Title: Wi-Fi Connection Troubleshooting Guide Introduction: Having trouble with your Wi-Fi? Follow these steps to identify and resolve common connection issues. Troubleshooting Steps: Identify the Problem Symptoms: Slow internet, frequent disconnections Possible Causes: Router issues, interference, outdated firmware Isolate the Issue Step 1: Check if other devices are connected to the same network and experiencing similar problems. Step 2: Test your connection on different devices to confirm the issue is not device-specific. Resolve the Problem Step 1: Restart your router by unplugging it for 30 seconds and plugging it back in. Wait for the lights to stabilize. Step 2: Check for firmware updates on your router’s admin page and install any available updates. Conclusion: By following these steps, you can quickly address Wi-Fi connectivity issues and enjoy a stable internet connection. Feedback Section: Did this troubleshooting guide help you resolve your Wi-Fi issues? Let us know in the comments below.
Recommended Read: Tips on Creating Great Knowledge Base Articles
Template 3: Product Documentation Knowledge Base Article
The Product Documentation Knowledge Base Article template is essential for businesses to provide comprehensive information about their products or services. It serves as a user manual and reference guide. Here’s how it benefits businesses –
Conclusion (Optional): Summarize key points and encourage users to explore further.
Feedback Section (Optional): Encourage users to provide feedback on the product documentation’s helpfulness.
Title: Quick Start Guide for ABC Smartphone Sections: Product Overview Description: The ABC Smartphone is a versatile device designed for everyday use, with a focus on performance and ease of use. Getting Started Installation: Insert the SIM card and power on the phone. It will guide you through the initial setup. Configuration: Customize your settings in just a few taps. Using the Product Basic Functions: Make calls, send messages, and take photos with these straightforward instructions. Troubleshooting: If you encounter issues, consult our troubleshooting section for quick solutions. Conclusion: This quick start guide helps you begin using your ABC Smartphone. For more in-depth information, explore our other articles. Feedback Section: Did this quick start guide assist you in setting up your ABC Smartphone? Share your thoughts or questions in the comments below.
Template 4: Step-by-Step Tutorial Knowledge Base Article
The Step-by-Step Tutorial Knowledge Base Article template is designed to guide users through a specific process or task, breaking it down into easy-to-follow steps. This template is particularly useful for businesses looking to educate their customers or employees. It benefits businesses in the following ways –
Tutorial Steps:
[Continue with additional steps]
Conclusion (Optional): Summarize the tutorial and its importance.
Feedback Section (Optional): Encourage users to provide feedback or ask questions related to the tutorial.
Title: How to Set Up Email Filters Tutorial Steps: Step 1: Access Email Settings Objective: Learn how to access your email settings to set up filters. Instructions: -Log in to your email account. -Click on “Settings” or the gear icon. -Select “Email Filters” or a similar option. Step 2: Create a Filter Objective: Set up a filter to organize or categorize incoming emails. Instructions: -Click “Add Filter” or a similar button. -Define filter criteria (e.g., sender’s address, subject, keywords). -Specify the action (e.g., move to folder, mark as read). Step 3: Save and Activate the Filter Objective: Ensure your filter is active and ready to process incoming emails. Instructions: -Name your filter for easy reference. -Click “Save” or an equivalent option. -Confirm that the filter is enabled. Conclusion: By following these steps, you can efficiently manage your email inbox by setting up filters to organize incoming messages. Feedback Section: Did this tutorial help you set up email filters? Share your thoughts or questions in the comments below.
Recommended Read: 10 Best Knowledge Base Software for Your Business [2024]
Template 5: Troubleshooting Flowchart Knowledge Base Article
The Troubleshooting Flowchart Knowledge Base Article presents complex problem-solving processes in a visual and user-friendly format. It’s ideal for businesses aiming to guide users through intricate troubleshooting procedures. Here’s how it can be of value to businesses –
Introduction (Optional): Provide context for the troubleshooting process and explain why it’s important.
Troubleshooting Flowchart:
Explanation of Steps:
Conclusion (Optional): Summarize the troubleshooting process and highlight its effectiveness.
Feedback Section (Optional): Encourage users to provide feedback or ask questions related to the troubleshooting process.
Title: Wi-Fi Connection Issues Troubleshooting Flowchart Introduction: If you’re experiencing Wi-Fi connection problems, this flowchart will help you identify and resolve the issue step by step. Troubleshooting Flowchart: [Insert a visual flowchart showing decision points and steps] Explanation of Steps: Step 1: Check Device Connectivity Objective: Ensure your device is properly connected to Wi-Fi. Instructions: -Check if your device is connected to the correct Wi-Fi network. -Verify that other devices are connected successfully. Step 2: Reboot Your Router Objective: Restart your router to resolve common issues. Instructions: -Unplug the router for 30 seconds and plug it back in. -Wait for the router to fully restart. Conclusion: By following the steps in this flowchart, you can troubleshoot and resolve Wi-Fi connection issues effectively. Feedback Section: Did this troubleshooting flowchart help you resolve your Wi-Fi issues? Share your feedback or questions in the comments below.
Template 6: Product Comparison Knowledge Base Article
The Product Comparison Knowledge Base Article is a valuable tool for businesses to help customers make informed purchasing decisions. It presents a detailed comparison between two or more products or services. Here’s how it benefits businesses –
Title: [Clear and descriptive]
Introduction (Optional): Briefly introduce the comparison and explain its significance.
Comparison Sections:
Conclusion (Optional): Summarize the comparison and provide recommendations or considerations.
Feedback Section (Optional): Encourage users to provide feedback or ask questions related to the product comparison.
Title: Laptop Model X vs. Laptop Model Y Comparison Comparison Sections: Laptop Model X vs. Laptop Model Y Feature Comparison: Model X: -Display Size: 14 inches -CPU: Intel Core i5 -Storage: 256GB SSD Model Y: -Display Size: 15.6 inches -CPU: AMD Ryzen 7 -Storage: 512GB SSD Pros and Cons: Model X: -Pros: Compact, lightweight -Cons: Slightly smaller display Model Y: -Pros: Larger screen, powerful CPU -Cons: Slightly heavier Conclusion: Consider your priorities. Model X is a portable option, while Model Y offers a larger display and more processing power. Feedback Section: Did this comparison help you decide between Laptop Model X and Model Y? Share your feedback or questions in the comments below.
Template 7: Case Study Knowledge Base Article
The Case Study Knowledge Base Article template delves into real-life scenarios or examples related to a product, service, or business operation. It showcases practical applications and outcomes. Here’s how it benefits businesses:
Introduction: Briefly introduce the case study and its relevance. Set the context for readers.
Case Study Sections:
Conclusion (Optional): Summarize the case study’s significance and relevance.
Feedback Section (Optional): Encourage users to provide feedback or share their thoughts on the case study.
Title: Enhancing Customer Support with AI Chatbots: A Case Study Introduction: Explore how Company XYZ improved customer support efficiency by implementing AI chatbots in this real-world case study. Case Study Sections: Background Description: Company XYZ, a growing e-commerce business, faced challenges in managing a high volume of customer inquiries, leading to delayed responses and customer frustration. Challenges Description: The challenges included overwhelming customer inquiries, long response times, and the need to scale support operations rapidly. Solution Description: Company XYZ implemented AI-powered chatbots that could handle routine inquiries, provide instant responses, and escalate complex issues to human agents. Results Description: -Response times reduced by 80%, leading to higher customer satisfaction. -Human agents could focus on more complex issues, improving the overall quality of support. -Operating costs decreased significantly due to reduced staffing needs. Key Takeaways Description: -AI chatbots can effectively handle routine inquiries, providing quick solutions. -Combining automation with human support can lead to efficient and high-quality customer service. -AI-driven solutions can help businesses scale operations while managing costs. Conclusion: This case study demonstrates how AI chatbots transformed customer support for Company XYZ, resulting in improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction. Feedback Section: Did this case study inspire ideas for improving your customer support? Share your thoughts or questions in the comments below.
Template 8: Tips and Tricks Knowledge Base Article
The Tips and Tricks Knowledge Base Article offers users valuable insights, advice, and expert tips related to a product, service, or skill. It aims to enhance user knowledge and proficiency. Here’s how it benefits businesses –
Title: [Clear and engaging]
Introduction (Optional): Briefly introduce the topic and explain why these tips and tricks are valuable.
Tips and Tricks Sections:
[Continue with additional tips and tricks]
Conclusion (Optional): Summarize the collection of tips and encourage users to explore further resources.
Feedback Section (Optional): Encourage users to provide feedback or share their experiences with the tips.
Title: 4 Email Productivity Hacks Introduction: Want to boost your email productivity? Check out these 4 quick email hacks to streamline your inbox. Tips and Tricks Sections: Tip 1: Use Keyboard Shortcuts Description: Learn essential keyboard shortcuts like “Ctrl + C” for copying text or “Ctrl + S” for saving drafts to save time while composing emails. Tip 2: Create Email Filters Description: Set up filters to automatically categorize and organize incoming emails into folders, keeping your inbox clutter-free. Tip 3: Schedule Email Sending Description: Compose emails in advance and schedule them to be sent at the most convenient times for your recipients. Tip 4: Unsubscribe from Unwanted Emails Description: Regularly unsubscribe from newsletters and promotional emails to declutter your inbox and reduce distractions. Conclusion: Implement these 4 email productivity hacks to streamline your email management and boost your efficiency. Feedback Section: Which email hack did you find most useful? Share your thoughts or suggest other email productivity tips in the comments below.
Template 9: Glossary Knowledge Base Article
The Glossary Knowledge Base Article serves as a comprehensive reference for users by defining key terms, acronyms, or jargon related to a specific industry, product, or field of knowledge. Here’s how it helps businesses –
Introduction (Optional): Briefly introduce the glossary and its purpose.
Glossary Sections:
[Continue with additional terms and definitions]
Conclusion (Optional): Summarize the glossary and encourage users to explore other related resources.
Feedback Section (Optional): Encourage users to provide feedback, suggest additional terms, or ask questions related to the glossary.
Title: Social Media Marketing Glossary Introduction: New to social media marketing? Our glossary provides definitions for commonly used terms in the world of digital marketing and social media. Glossary Sections: Term 1: Engagement Rate Definition: Engagement rate measures the level of interaction and involvement your audience has with your social media content, often calculated as likes, shares, comments, and clicks divided by the total reach. Term 2: Hashtag Definition: A hashtag is a word or phrase preceded by the “#” symbol, used on social media platforms to categorize and make content discoverable by others interested in the same topic. Term 3: ROI (Return on Investment) Definition: ROI is a metric used to assess the profitability of social media marketing campaigns by comparing the gained benefits (such as revenue or customer acquisition) to the costs involved. Conclusion: Our social media marketing glossary aims to provide clarity on key terms used in the field. Understanding these terms will help you navigate the world of digital marketing effectively. Feedback Section: Did our glossary help you clarify any social media marketing terms? Share your feedback or suggest additional terms for inclusion in the comments below.
Template 10: Installation Guide Knowledge Base Article
The Installation Guide Knowledge Base Article provides users with detailed instructions on how to properly install and set up a product or software. It aims to ensure a smooth installation process. Here’s how it benefits businesses:
Title: [Clear and straightforward]
Introduction (Optional): Briefly introduce the installation guide.
Installation Guide Sections:
Conclusion (Optional): Summarize the installation guide’s importance.
Feedback Section (Optional): Encourage user feedback or questions.
Title: Smartphone App Installation Guide Introduction: Installing a new app on your smartphone? Our guide will walk you through the process. Installation Guide Sections:
System Requirements Description: Ensure your smartphone is running a compatible operating system (e.g., Android 8.0+ or iOS 13+). Installation Process Step 1: Open your device’s app store (e.g., Google Play or Apple App Store) and search for the app. Step 2: Tap “Install” to download and install the app on your device. Troubleshooting Issue 1: If the installation is stuck, check your internet connection and try again. Issue 2: For “App Crashes,” try restarting your device or updating the app. Conclusion: You’ve successfully installed the app. Enjoy using it for your daily tasks! Feedback Section: Did our smartphone app installation guide help you? Share your feedback or ask questions in the comments below.
Wrapping Up
Incorporating these knowledge base article templates will transform the way you offer customer support and your information-sharing processes. These templates not only provide a structured approach but also unlock several benefits.
They streamline customer inquiries, reduce support workload, and empower users with self-help resources. By utilizing them effectively, you’ll enhance customer experiences and empower your team with the tools they need to excel.
Try Hiver for Free
Try Hiver, the simplest shared inbox solution loved by 8000+ teams

Troubleshooting Common Google Groups Issues
Google Groups is widely used by many businesses for team collaboration. And it has its benefits. It’s free, it’s part of the Google Workspace and hardly takes 5 minutes to...

Top 11 DragApp Alternatives for Businesses
DragApp is a productivity software designed to simplify email and task management for teams that use Gmail. It does this by transforming your Gmail into a centralized workspace....

27 Google Chrome Extensions for Managing Emails
Want to get more out of Gmail? In this article, we have hand-picked some of the best Google Chrome extensions for managing...

Hiver has come along as a trustworthy, discerning, and dependable sidekick that has helped us manage our emails better and faster.

Hiver is extremely easy to use. We were able to hit the ground running right from day one. Plus, their customer service is fantastic!

We're 100% Gmail. Working on customer queries from Gmail was exactly what we needed. Moreover, moving to Hiver was a painless affair.

Search form
- About Faculty Development and Support
- Programs and Funding Opportunities
Consultations, Observations, and Services
- Strategic Resources & Digital Publications
- Canvas @ Yale Support
- Learning Environments @ Yale
- Teaching Workshops
- Teaching Consultations and Classroom Observations
- Teaching Programs
- Spring Teaching Forum
- Written and Oral Communication Workshops and Panels
- Writing Resources & Tutorials
- About the Graduate Writing Laboratory
- Writing and Public Speaking Consultations
- Writing Workshops and Panels
- Writing Peer-Review Groups
- Writing Retreats and All Writes
- Online Writing Resources for Graduate Students
- About Teaching Development for Graduate and Professional School Students
- Teaching Programs and Grants
- Teaching Forums
- Resources for Graduate Student Teachers
- About Undergraduate Writing and Tutoring
- Academic Strategies Program
- The Writing Center
- STEM Tutoring & Programs
- Humanities & Social Sciences
- Center for Language Study
- Online Course Catalog
- Antiracist Pedagogy
- NECQL 2019: NorthEast Consortium for Quantitative Literacy XXII Meeting
- STEMinar Series
- Teaching in Context: Troubling Times
- Helmsley Postdoctoral Teaching Scholars
- Pedagogical Partners
- Instructional Materials
- Evaluation & Research
- STEM Education Job Opportunities
- Yale Connect
- Online Education Legal Statements
You are here
Case-based learning.
Case-based learning (CBL) is an established approach used across disciplines where students apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios, promoting higher levels of cognition (see Bloom’s Taxonomy ). In CBL classrooms, students typically work in groups on case studies, stories involving one or more characters and/or scenarios. The cases present a disciplinary problem or problems for which students devise solutions under the guidance of the instructor. CBL has a strong history of successful implementation in medical, law, and business schools, and is increasingly used within undergraduate education, particularly within pre-professional majors and the sciences (Herreid, 1994). This method involves guided inquiry and is grounded in constructivism whereby students form new meanings by interacting with their knowledge and the environment (Lee, 2012).
There are a number of benefits to using CBL in the classroom. In a review of the literature, Williams (2005) describes how CBL: utilizes collaborative learning, facilitates the integration of learning, develops students’ intrinsic and extrinsic motivation to learn, encourages learner self-reflection and critical reflection, allows for scientific inquiry, integrates knowledge and practice, and supports the development of a variety of learning skills.
CBL has several defining characteristics, including versatility, storytelling power, and efficient self-guided learning. In a systematic analysis of 104 articles in health professions education, CBL was found to be utilized in courses with less than 50 to over 1000 students (Thistlethwaite et al., 2012). In these classrooms, group sizes ranged from 1 to 30, with most consisting of 2 to 15 students. Instructors varied in the proportion of time they implemented CBL in the classroom, ranging from one case spanning two hours of classroom time, to year-long case-based courses. These findings demonstrate that instructors use CBL in a variety of ways in their classrooms.
The stories that comprise the framework of case studies are also a key component to CBL’s effectiveness. Jonassen and Hernandez-Serrano (2002, p.66) describe how storytelling:
Is a method of negotiating and renegotiating meanings that allows us to enter into other’s realms of meaning through messages they utter in their stories,
Helps us find our place in a culture,
Allows us to explicate and to interpret, and
Facilitates the attainment of vicarious experience by helping us to distinguish the positive models to emulate from the negative model.
Neurochemically, listening to stories can activate oxytocin, a hormone that increases one’s sensitivity to social cues, resulting in more empathy, generosity, compassion and trustworthiness (Zak, 2013; Kosfeld et al., 2005). The stories within case studies serve as a means by which learners form new understandings through characters and/or scenarios.
CBL is often described in conjunction or in comparison with problem-based learning (PBL). While the lines are often confusingly blurred within the literature, in the most conservative of definitions, the features distinguishing the two approaches include that PBL involves open rather than guided inquiry, is less structured, and the instructor plays a more passive role. In PBL multiple solutions to the problem may exit, but the problem is often initially not well-defined. PBL also has a stronger emphasis on developing self-directed learning. The choice between implementing CBL versus PBL is highly dependent on the goals and context of the instruction. For example, in a comparison of PBL and CBL approaches during a curricular shift at two medical schools, students and faculty preferred CBL to PBL (Srinivasan et al., 2007). Students perceived CBL to be a more efficient process and more clinically applicable. However, in another context, PBL might be the favored approach.
In a review of the effectiveness of CBL in health profession education, Thistlethwaite et al. (2012), found several benefits:
Students enjoyed the method and thought it enhanced their learning,
Instructors liked how CBL engaged students in learning,
CBL seemed to facilitate small group learning, but the authors could not distinguish between whether it was the case itself or the small group learning that occurred as facilitated by the case.
Other studies have also reported on the effectiveness of CBL in achieving learning outcomes (Bonney, 2015; Breslin, 2008; Herreid, 2013; Krain, 2016). These findings suggest that CBL is a vehicle of engagement for instruction, and facilitates an environment whereby students can construct knowledge.
Science – Students are given a scenario to which they apply their basic science knowledge and problem-solving skills to help them solve the case. One example within the biological sciences is two brothers who have a family history of a genetic illness. They each have mutations within a particular sequence in their DNA. Students work through the case and draw conclusions about the biological impacts of these mutations using basic science. Sample cases: You are Not the Mother of Your Children ; Organic Chemisty and Your Cellphone: Organic Light-Emitting Diodes ; A Light on Physics: F-Number and Exposure Time
Medicine – Medical or pre-health students read about a patient presenting with specific symptoms. Students decide which questions are important to ask the patient in their medical history, how long they have experienced such symptoms, etc. The case unfolds and students use clinical reasoning, propose relevant tests, develop a differential diagnoses and a plan of treatment. Sample cases: The Case of the Crying Baby: Surgical vs. Medical Management ; The Plan: Ethics and Physician Assisted Suicide ; The Haemophilus Vaccine: A Victory for Immunologic Engineering
Public Health – A case study describes a pandemic of a deadly infectious disease. Students work through the case to identify Patient Zero, the person who was the first to spread the disease, and how that individual became infected. Sample cases: The Protective Parent ; The Elusive Tuberculosis Case: The CDC and Andrew Speaker ; Credible Voice: WHO-Beijing and the SARS Crisis
Law – A case study presents a legal dilemma for which students use problem solving to decide the best way to advise and defend a client. Students are presented information that changes during the case. Sample cases: Mortgage Crisis Call (abstract) ; The Case of the Unpaid Interns (abstract) ; Police-Community Dialogue (abstract)
Business – Students work on a case study that presents the history of a business success or failure. They apply business principles learned in the classroom and assess why the venture was successful or not. Sample cases: SELCO-Determining a path forward ; Project Masiluleke: Texting and Testing to Fight HIV/AIDS in South Africa ; Mayo Clinic: Design Thinking in Healthcare
Humanities - Students consider a case that presents a theater facing financial and management difficulties. They apply business and theater principles learned in the classroom to the case, working together to create solutions for the theater. Sample cases: David Geffen School of Drama
Recommendations
Finding and Writing Cases
Consider utilizing or adapting open access cases - The availability of open resources and databases containing cases that instructors can download makes this approach even more accessible in the classroom. Two examples of open databases are the Case Center on Public Leadership and Harvard Kennedy School (HKS) Case Program , which focus on government, leadership and public policy case studies.
- Consider writing original cases - In the event that an instructor is unable to find open access cases relevant to their course learning objectives, they may choose to write their own. See the following resources on case writing: Cooking with Betty Crocker: A Recipe for Case Writing ; The Way of Flesch: The Art of Writing Readable Cases ; Twixt Fact and Fiction: A Case Writer’s Dilemma ; And All That Jazz: An Essay Extolling the Virtues of Writing Case Teaching Notes .
Implementing Cases
Take baby steps if new to CBL - While entire courses and curricula may involve case-based learning, instructors who desire to implement on a smaller-scale can integrate a single case into their class, and increase the number of cases utilized over time as desired.
Use cases in classes that are small, medium or large - Cases can be scaled to any course size. In large classes with stadium seating, students can work with peers nearby, while in small classes with more flexible seating arrangements, teams can move their chairs closer together. CBL can introduce more noise (and energy) in the classroom to which an instructor often quickly becomes accustomed. Further, students can be asked to work on cases outside of class, and wrap up discussion during the next class meeting.
Encourage collaborative work - Cases present an opportunity for students to work together to solve cases which the historical literature supports as beneficial to student learning (Bruffee, 1993). Allow students to work in groups to answer case questions.
Form diverse teams as feasible - When students work within diverse teams they can be exposed to a variety of perspectives that can help them solve the case. Depending on the context of the course, priorities, and the background information gathered about the students enrolled in the class, instructors may choose to organize student groups to allow for diversity in factors such as current course grades, gender, race/ethnicity, personality, among other items.
Use stable teams as appropriate - If CBL is a large component of the course, a research-supported practice is to keep teams together long enough to go through the stages of group development: forming, storming, norming, performing and adjourning (Tuckman, 1965).
Walk around to guide groups - In CBL instructors serve as facilitators of student learning. Walking around allows the instructor to monitor student progress as well as identify and support any groups that may be struggling. Teaching assistants can also play a valuable role in supporting groups.
Interrupt strategically - Only every so often, for conversation in large group discussion of the case, especially when students appear confused on key concepts. An effective practice to help students meet case learning goals is to guide them as a whole group when the class is ready. This may include selecting a few student groups to present answers to discussion questions to the entire class, asking the class a question relevant to the case using polling software, and/or performing a mini-lesson on an area that appears to be confusing among students.
Assess student learning in multiple ways - Students can be assessed informally by asking groups to report back answers to various case questions. This practice also helps students stay on task, and keeps them accountable. Cases can also be included on exams using related scenarios where students are asked to apply their knowledge.
Barrows HS. (1996). Problem-based learning in medicine and beyond: a brief overview. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 68, 3-12.
Bonney KM. (2015). Case Study Teaching Method Improves Student Performance and Perceptions of Learning Gains. Journal of Microbiology and Biology Education, 16(1): 21-28.
Breslin M, Buchanan, R. (2008) On the Case Study Method of Research and Teaching in Design. Design Issues, 24(1), 36-40.
Bruffee KS. (1993). Collaborative learning: Higher education, interdependence, and authority of knowledge. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, MD.
Herreid CF. (2013). Start with a Story: The Case Study Method of Teaching College Science, edited by Clyde Freeman Herreid. Originally published in 2006 by the National Science Teachers Association (NSTA); reprinted by the National Center for Case Study Teaching in Science (NCCSTS) in 2013.
Herreid CH. (1994). Case studies in science: A novel method of science education. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 23(4), 221–229.
Jonassen DH and Hernandez-Serrano J. (2002). Case-based reasoning and instructional design: Using stories to support problem solving. Educational Technology, Research and Development, 50(2), 65-77.
Kosfeld M, Heinrichs M, Zak PJ, Fischbacher U, Fehr E. (2005). Oxytocin increases trust in humans. Nature, 435, 673-676.
Krain M. (2016) Putting the learning in case learning? The effects of case-based approaches on student knowledge, attitudes, and engagement. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching, 27(2), 131-153.
Lee V. (2012). What is Inquiry-Guided Learning? New Directions for Learning, 129:5-14.
Nkhoma M, Sriratanaviriyakul N. (2017). Using case method to enrich students’ learning outcomes. Active Learning in Higher Education, 18(1):37-50.
Srinivasan et al. (2007). Comparing problem-based learning with case-based learning: Effects of a major curricular shift at two institutions. Academic Medicine, 82(1): 74-82.
Thistlethwaite JE et al. (2012). The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education. A BEME systematic review: BEME Guide No. 23. Medical Teacher, 34, e421-e444.
Tuckman B. (1965). Development sequence in small groups. Psychological Bulletin, 63(6), 384-99.
Williams B. (2005). Case-based learning - a review of the literature: is there scope for this educational paradigm in prehospital education? Emerg Med, 22, 577-581.
Zak, PJ (2013). How Stories Change the Brain. Retrieved from: https://greatergood.berkeley.edu/article/item/how_stories_change_brain

YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN

Reserve a Room
The Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning partners with departments and groups on-campus throughout the year to share its space. Please review the reservation form and submit a request.

Instructional Enhancement Fund
The Instructional Enhancement Fund (IEF) awards grants of up to $500 to support the timely integration of new learning activities into an existing undergraduate or graduate course. All Yale instructors of record, including tenured and tenure-track faculty, clinical instructional faculty, lecturers, lectors, and part-time acting instructors (PTAIs), are eligible to apply. Award decisions are typically provided within two weeks to help instructors implement ideas for the current semester.

The Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning routinely supports members of the Yale community with individual instructional consultations and classroom observations.
- The Experience
- The Programs
- Faculty & Research
The Library will be closed Dec. 21, 2023, through Jan. 3, 2024. Online resources remain available.
- GSB Library
Knowledge Base
- GSB Library Knowledge Base
- 2 Analyst Reports
- 6 Books/eBooks/audiobooks
- 40 Company Info & Financials
- 20 Company Lists
- 7 Consumers & Demographics
- 8 Countries & International Markets
- 42 Database Access Help
- 9 Deals (M&A, IPO)
- 4 Economic Indicators
- 11 ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)
- 20 Financial Markets & Securities
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions
- 13 Industries & Markets
- 11 Journal Articles
- 49 Large Datasets
- 6 Library Use/Policies
- 13 News/Magazine Articles
- 1 Research Impact
- 103 Research Tips
- 18 Statistics
- 8 VC/PE/Startups
Harvard Business School Case Studies
Unfortunately, libraries are unable to purchase Harvard Business School cases.
Harvard Business School cases are typically used in the classroom. Harvard Business Review is a magazine.
Stanford GSB Faculty and Faculty Assistants
Contact GSB Course Support for access to cases to support teaching.
Search for Harvard Business School cases .
Other Instructors
Request an educator's account to purchase educator's copies for a discounted price. You can also create Coursepacks for students to purchase at a discount.
Students, Alumni, and Others
Find and purchase cases at the Harvard Business Publishing website .
Links & Files
- Alternative places to find case studies
- Harvard Business Review Access
Related Library Tips
Related topics.
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resource Use
Most resources are only available to current Stanford students, faculty, and staff.
Researchers are responsible for using these resources appropriately. See the eResources Usage policy .
Accessibility Support
Ask Us for accessibility support with library resources.
Case Study - Description
- Available Topics
- Top Documents
- Recently Updated
- Internal KB

Description
This discussion type aims to engage students with the content seriously. This discussion type can be the heart of the content knowledge activities, relying on activities that direct students to read, analyze, and investigate content material. New content knowledge builds on the student’s understanding and expands the knowledge base needed to apply and use the knowledge (Boettcher, 2019).
Expand All | Collapse All
Use it when you want...
- Students to work with the ideas, researching possibilities and relationships and connecting the dots.
- Students to build on their current understanding and expand their knowledge base to apply and use that knowledge.
- Identify a case study or develop a new one that aligns with your course outcomes or unit objectives. The case can be real or hypothetical.
- Develop a case study with questions to guide students’ analysis. Distribute the case to students by using a page as a course assignment or discussion in Canvas.
- Identify your expectations for students to work on the case. For example, the timeframe or the point(s) of view for students. Also, consider how you expect to monitor or assess the group process and the format of the end product.
- Consider your interest in assessing the group's process and how that impacts technology needs. For example, you may want to establish separate assignments for students to submit in-progress reports or reflections on their group experience.
- Form student groups and communicate the case and expectations. Allow a forum for students to ask questions.
- Direct students to sort out factual data, apply analytical tools, articulate issues, and reflect on relevant experiences. Have them recommend actions that resolve the problem in the case.
- You may wish to set up student groups in Canvas and guide students in using campus tools available through Canvas to have their group discussions.
- Have students prepare a statement describing their assessment of the case, the options they see, and their recommendations for a decision.
- Guide discussion of the cases with the entire class. Students will want to know what happened if the case is a real-world example. Share this with them after they have reported on it.
- Have students turn in their final product.
- Review the students’ statements on the case study.
- Provide feedback/grades to group participants.
- Debrief the activity with the class. Some ways this may be done include class announcements or a class-wide discussion forum.
- Investigation and Research Discussions
- Case Study - Example
- Case Study - Rubric
- Affordances of Online Discussions
- Steps for Building an Online Asynchronous Discussion
- Using Online Discussions to Increase Student Engagement
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Becoming a Better You: A Guide to Self-Learning While Working Full-Time
Concept of national innovation systems, case study: henry ford’s contributions to organizational behavior and leadership, de bono’s six thinking hats: a creative and critical thinking model, what is a contact center and its role in the customer journey.

Working almost any full-time job can be taxing. Finding time to learn a new skill or get a degree while maintaining productivity often seems like a near-impossible goal for those trying to pursue it. And yet, millions of people do it every day – and so can you. Imagine holding down that job while pursuing an AACSB online MBA – not easy, right? Even if you’re engaging in self-directed learning, you’re going to need that same level of discipline and commitment to get the results you’re after. But with determination, good time management, and a vision for what you want, anything is possible. … Read the rest
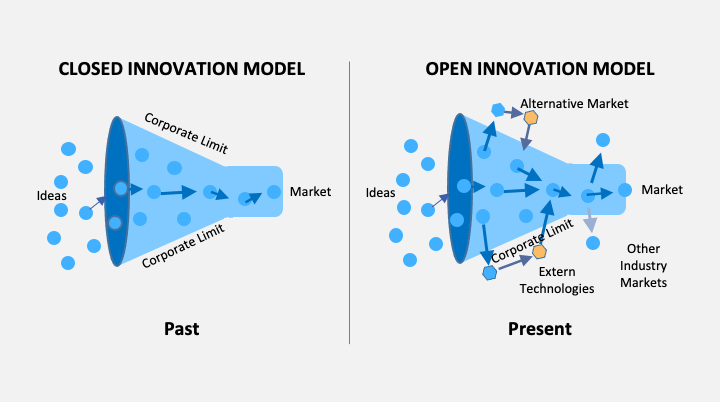
There is no widely agreed definition of national innovation systems. National innovation systems are built on the assumption that understanding the interconnectedness of the actors engaged in innovation is crucial to enhancing technical performance. Innovation and technological advancement are the outcomes of a multifaceted network of connections between actors who produce, transmit, and consume various types of knowledge. The manners in which these actors interrelate with one another as components of a social system of knowledge consumption and generation, and also the technology they employ, have a significant influence on a country’s creative performance. The most prevalent actors are public research institutions, universities, and commercial enterprises, as well as the individuals who work for them.… Read the rest

Henry Ford, born in 1863 with his innovative ideas in producing motor vehicles and excellent engineering works went on to become the hero of people in the industry. His primary goal was always to produce petrol propelled motor vehicle and in 1896 he developed his first self propelled vehicle which he called the quadricycle. After a lot of struggles and legal battles, he founded the Ford Motor Company in 1903 with only $28000. He dreamed of making efficient affordable cars and in 1908 produced the popular model T. Henry Ford changed the world with his revolutionary ideas and transformed the motor industry with his leadership.… Read the rest
Creative thinking has always been one of the main aspects in the successful implementation of any business strategy. In the prospect of business growth and development, it is necessary to establish an effective decision-making approach, which will help to outline the company’s strengths and decrease the negative impact of weaknesses. The Six Thinking Hats technique is a framework for thinking and decision making introduced by a famous expert in the sphere of creative thinking, invented in the early 1980s – Dr. Edward de Bono, and is licensed by Advanced Practical Thinking (APTT), of Des Moines, Iowa. Organizations such as Prudential Insurance, IBM, Federal Express, British Airways, Polaroid, Pepsico, DuPont, and Nippon Telephone and Telegraph use the Six Thinking Hats method.… Read the rest

The customer service landscape is rapidly evolving, with contact centers at the heart of this transformation. These hubs of communication are critical for engaging with customers across platforms, offering support, and delivering on customer expectations. Understanding what is a Contact Center and its function is vital for any business looking to improve its customer service. In this article, we will delve into the essentials of a contact center’s role in the modern customer journey, and how it can be the key to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
A contact center is more than just a modern call center; it’s a central point from where all customer contacts are managed.… Read the rest
What Is Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)?

While some companies aim to grow their customer base, the successful ones recognize the importance of increasing customer lifetime value. Loyal customers offer more value to your business‐generating over 10x more revenue. Customer lifetime value is an important concept to understand from a marketing standpoint. The cost of obtaining a customer and gaining that first sale is often much higher than the costs of maintaining the relationship with the customer.
Customer lifetime value (CLV) is a critical metric used to estimate the value of each customer you acquire. It validates whether you’re actually producing a profit. Several companies strive to increase customer lifetime value because they believe it’s a good indicator of business performance.… Read the rest
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
KnowledgeManagement →
No results found in working knowledge.
- Were any results found in one of the other content buckets on the left?
- Try removing some search filters.
- Use different search filters.
Learn to get the most on how to set up & utilize a knowledge base, save emails and 'wow' your customers.
Our knowledge management e-books.
Expand your understanding of knowledge bases with our collection of free ebooks.

Knowledge Management a Theoretical & Practical Guide (200+ pages)
Unlike our other two books, this is not a quick read. This is the ULTIMATE guide to understanding everything about knowledge management.
It's normally $9.99 on Amazon , but we are giving it away totally free (no email opt-in or anything) to our customers.
- An in-depth look at what knowledge management is , and the different models of it.
- Implementing a knowledge management strategy , and the implications it can have on your organization
- Organization-wide knowledge management implementation from capturing knowledge to sharing and re-using it.

Scaling Support with a Knowledge Base
A quick read that teaches you how to turn your knowledge base into an ultimate support machine.
A culmination of a lot of the ideas we've presented to customers when they faced the 3 common problems with knowledge bases.
- How to customize effectively so your knowledge base suits the needs of your most valuable customers
- How to generate and increase traffic to your knowledge base easily
- How to write the perfect content that helps your customers while you rest

Using An Internal Knowledge Base To Super-Power Your Organization
Would your organization benefit from having a better eco-system for sharing knowledge? Do you feel as if employee onboarding could be improved? If Yes, this e-book might be a good fit for you.
- How to effectively onboard employees using a knowledge base
- Documenting & Systemizing Training employees , via a knowledge bases
- Using a knowledge base to reduce employee churn rate
Looking to improve your EXISTING knowledge base? Let Helpjuice help you – Try our lastest free tool!

Free Knowledge Base Analyzer & Grader
Ever wondered how good your knowledge base is? Type in your current KB URL and our analyzer will dig through it, grade it, and tell you how to improve it!
Knowledge Base Case Studies
World's Best Knowledge Bases, Let our Customers From Industries Teach You How They Did it

(50 - 100 people)
Collage.com Team uses Helpjuice Seven days a week To Deliver Amazing Support.

Real Estate
(100 - 500 people)
RMS Cloud Resolves 50-75% of day to day support requests with Helpjuice Knowledge Base

Web Hosting
(11 - 50 people)
Fast-Growing Web Hosting Company Instantly Sees Positive ROI With Using Helpjuice

IT Services
IT Services Firm Leverages Knowledge Base For Collaboration (instead of Google Drive/Sharepoint)
Integrations.
Helpjuice's Integrations help bring you and your team instant knowledge when you need it with our easy-to-use and powerful Chrome & Ticketing and Bot Integrations.
Slack Integration
Instantly access, create, and share your team’s Helpjuice articles straight from Slack, with the Helpjuice Slack bot.
Microsoft Teams Integration
Instantly search, share and create articles directly from the Microsoft Teams. Configure an Microsoft Teams Channel to Receive Automated Notifications when new Knowledge Base Articles are Created.
Salesforce Cases Integration
Help ignite your customer support team's performance, with Helpjuice's AI-powered KB suggestions.
Zendesk Ticketing Integration
Pull relevant KB Articles from your Helpjuice knowledge base straight into your Zendesk tickets.
Google Chrome Integration
Help teams work more efficiently by giving them instant access to information, wherever they are with our google Chrome Integration.
Olark Integration
Helpjuice provides an Olark plugin will analyze when users start chatting with you and smartly find Knowledge Base articles that match what the user is talking about and suggest them to you so you can use as a response.
Zapier Integration
With the Helpjuice Zapier integration you can connect your Helpjuice knowledge base to over 1,000+ Integrations.
Freshdesk Integration
Instantly search and share your Helpjuice Knowledge Base Articles from within Freshdesk tickets.
Ready to try our knowledge base software?
Start scaling your customer support, and, collaborate better with your team..

Case Studies - Knowledge Management System Examples
To find out more about how KPS’ Knowledge Management software has helped our clients to increase service delivery quality and efficiency, and how it could help you, download one of our knowledge management case studies below:
- Contact Centre
- Employee Knowledge Sharing Solutions
- Service Desk
- Web Self-Service

Baldwin County Commission Customer Service Advisors provide expert advice and guidance to citizens with KPS Universal Knowledge
Baldwin County, Alabama, located along the shores of the Gulf of Mexico and Mobile Bay, has a population of over 200,000 residents as of the 2020 Cens...

KPS provides LBBD a single unified platform to capture and quickly access information from a variety of sources
The London Borough of Barking and Dagenham council (LBBD), based in East London, serves a population of approximately 230,000 citizens on a wide range...

KPS product ensures IU Health representatives provide patients with quality and timely information
Service knowledge management helps service agents and self service interactions become effective, timely and conclusive. Knowledge management plays a ...

Helping Universities to Save Money and Improve Student Services
Together with student fees and rising expectations of students, this is prompting the need for universities and further education institutions to deli...

SRO Solutions Improve Business in Offshore and Marine Sectors using Knowledge Management
SRO Solutions deliver leading asset management solutions, focusing on the three main sectors of Transportation, Offshore Oil & Gas and Manufacturing &...

When Outdated Systems no Longer Meet Requirements in Online Retail Contact Centre
What happens when legacy systems used for documenting key processes no longer meet the requirements of a fast evolving contact centre environment? Th...

Customer Service – Which Channels are Trending?
What are the key trends when customers choose service channel? Working with ContactBabel the contract centre research specialist we have collected inf...

Knowledge Management Software for Accessing Multiple Content Formats
A common need in contact centre operations that focus on providing detailed information and advice is READY ACCESS to the organisations knowledge base...

Knowledge Management delivers efficiencies in Public Health Contact Centres
KPS Knowledge Management tool helps Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) operator Serco manage and deliver multiple health related information services ...

Knowledge Management Software on G-Cloud
By joining G-Cloud KPS offers enhanced value for UK Central and Local Government service delivery. The KPS G-Cloud Knowledge Management Software can b...

Inner Circle Guide – Self Service in Multi Channel Customer Service Delivery
The multichannel revolution in customer service is not just about costs savings. There are real improvement opportunities in service delivery quality....

IT Service Desk Challenges and Solutions
When that employee is working in front-line services such as an IT service desk environment, an inability to provide the right information at first co...

24 Hour IT Support at Reduced Costs – Is this Possible?
Like many organisations requiring 24 hour IT support, police forces across the UK are faced with pressure to reduce cost and at the same time concentr...

University of Ottawa Knowledge Management Software
University of Ottawa (uOttawa) has over 42,000 students, 5,000 employees and 180,000 alumni and has a 97% employment rate for graduates. uOttawa uses ...

Service Knowledge Management Interactions in Health & Education?
Service knowledge management helps service agents and self service interactions become effective, timely and conclusive, which in turn reduces optiona...

Web Self Service
An Abundance of Information vs. What you need When you need It Information is everywhere, on demand 24/7 but the only information you want at any one ...

What do Local Councils and Financial Institutions have in Common?
Unfortunately the Lack of Trust and Poor Customers Services experiences can often link these two different sectors. Lack of Trust & Poor C...
What Problems Are Faced by the IT Help Desk?
Urged to do more with less whilst becoming increasingly accountable for the results is forcing IT help desks to reduce costs whilst still putting the ...
Sunrise Software
Sunrise Software Knowledge Management Solution for Help-desk and Customer Service Centres Sunrise is the UK‘s leading independent developer and solu...

United Health Care Knowledge Management Software
United Health Care Knowledge Management Software Solution ITSM United Healthcare is an operating division of United Health Group, the largest single h...

Stroma Knowledge Management Software
Stroma Service Consulting IT Service Management Solutions Stroma Service Consulting is an established IT consulting company that supports clients with...

Sheffield City Council Knowledge Management Software
Sheffield City Council Knowledge Management Software Solution for their Contact Centre Sheffield City Council uses Knowledge Powered Solution’s Know...

Quintica Knowledge Management Software
Quintica Knowledge Management Software for Enhancing Service Management Formed in 2001, Quintica is an ICT Technology and Professional Services system...

Contact 121 Knowledge Management Software
Contact 1-2-1 Australia Knowledge Management Software for Business Process Outsourcing Contact 1-2-1 is a flexible and affordable provider of full-ser...

NCC Group Escrow Management Solution We are working with NCC Group, a leading provider of Escrow Solutions, to offer our customers the peace of mind o...

Canterbury Christ Church University Knowledge Management Software
Canterbury Christ Church University Knowledge Management Software for Dynamic FAQs and Web Self Service Canterbury Christchurch University in Kent is...

Silah Gulf Knowledge Management Software
Silah Gulf Knowledge Management Software for Web Self Service Silah Gulf use KPS’s Universal Knowledge as part of their E Government Portal Ser...
Managing Organisational Data & Information Effectively
The lack of physical evidence of how big the issue may be can also be an issue. The challenge is to monitor your information mountain effectively! The...

How can you Access Public Sector Information, Easily?
These are some of the questions that I will explore in this blog series around Local Authorities, the information that they provide and some solutions...
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn more
How Indigenous expertise is empowering climate action: A case study from Oceania

Indigenous Peoples are the world's foremost experts on preserving the climate and biodiversity — listening to them is the key to protecting our planet. Image: REUTERS/Dylan Martinez
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Amanda Young
Ginelle greene-dewasmes.

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved .chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
- Industrial-scale capitalism and mass urbanization have accelerated environmental degradation, necessitating a reconnection with nature and Indigenous expertise.
- Indigenous knowledge systems offer holistic approaches to environmental sustainability and are increasingly recognized for their value in climate action.
- Examples like traditional fire management and innovative applications of Indigenous knowledge demonstrate the potential for collaboration and cross-pollination between Indigenous and other practices to address climate and ecological challenges.
On Monday 15 April 2024 , the largest global annual gathering of Indigenous Peoples kicked off at the United Nations Headquarters in New York, with participants calling for greater efforts to close financial gaps for Indigenous Peoples. Next month, Sydney Climate Action Week during May 13-19 will take place in Australia, a series of community-led events across Sydney from all aspects of the climate action ecosystem.
Such a coming together of stakeholders presents a prime opportunity to explore how traditional regional innovation models can contribute global solutions under a more inclusive climate agenda.
Have you read?
Renewables projects must respect indigenous peoples and local communities. here's how, indigenous leaders bringing their knowledge to davos 2024, 5 ways indigenous people are protecting the planet, disconnection from nature is exacerbating climate change.
Industrial-scale capitalism has accelerated the erosion of climate and ecological systems. Mass urbanization has driven economic growth and extractive industries on scales previously unimaginable. Sadly, these trends are increasing. Around 2007, the United Nations estimated , we had reached a tipping point in the world: more people were living in urban than rural areas. By 2022, 57% of all humans became urban based. In developed nations, a whopping 80% of citizens are urban. Both of these trends are predicted to increase .
This is reflected in how we are responding to the climate emergency. We are rapidly losing our connection to nature, with scarce nature feedback loops in citified life. This skews our perceptions and worldviews. Our academies are urban, our scientists are trained and our businesspeople, financiers, teachers, politicians are upskilled in mostly urban landscapes. Atrophied natural knowledge leaves us unequipped for dealing with the complexity of ecosystems. We need to humbly acknowledge the true experts in nature, Indigenous people, and ask for their guidance, meeting with our resources to activate this expertise.
Indigenous knowledge in climate action
“The planet’s ill health has largely come about because humans have forgotten their relationship and responsibility to country. Imagine if we could tap into the way First Nations cultures focus on deep, holistic connections to the environment to help us rethink environmental and health policies.”
Although Indigenous knowledge systems have been built on millennia of lived experience, iteration and adaptation, they have too often been ignored.
Today, however, there is growing interest in the value of Indigenous knowledge systems in the wake of environmental and climate challenges. In contrast to non-indigenous value systems, indigenous value systems focus on environmental sustainability as an end in itself that is required for cultural, social and economic well-being. The knowledge we have lost is still very much alive in Indigenous worlds, built through millennia of observation and ecological management.
The world needs to reframe both the role and deep knowledge of Indigenous people as experts. Signs of this shift are already emerging. In carbon and emerging biodiversity markets , any project involving, run by or partnered with Indigenous people attracts a premium carbon credit price in recognition of the deeper integrity, provenance and permanence Indigenous people bring that mitigate greenwashing claims.
Harnessing Indigenous expertise for modern global impact
An example of superior Indigenous technology is found in traditional fire management . Western fuel reduction strategies have triggered catastrophic fires when containment lines are broken, but Indigenous people have practiced for millennia “cool burning” that allows time for biodiversity to move to safety. This knowledge is needed across Europe and North America, both of which have experienced staggering brush fires. According to Firesticks , the not-for-profit Indigenous network, “aboriginal fire management has become a priority for community, cultural, social and environmental wellbeing”. This awareness showcases an example of the acknowledged inter-relatedness of knowledge, land, culture and identity — and the prioritization of environmental wellbeing alongside the community and culture.
Alongside ancient practices sit novel applications of Indigenous knowledge. Rainstick, a novel biotech company that was inspired by the traditions of the Maiawali People of central west Queensland, Australia, has built on a 10,000-year-old practice that acknowledges the influence of lightning on how plants grow. The resulting approach combines ancient expertise with modern technology to show that indigenous knowledge is ever-changing and can be applied in new and novel ways for climate action. Another example can be found in Savimbo fair trade credits , which is Indigenous at its core — removing intermediaries to ensure Indigenous experts can attract capital to resist further incursion into precious Indigenous-managed lands by developers.
Indigenous people are also sharing their profound knowledge with each other to manage and fix the problem of climate change. In the Ampliseed network, Indigenous people managing lands as diverse as the snow-covered Boreal Forest in Canada, World Heritage Listed Coral Reefs, tropical rainforest in the Peruvian Amazon, Mediterranean habitat in Chile and Australia’s 10 vast central deserts are cross-pollinating their knowledge, navigating the climate disaster and creating global impact at the Climate and Biodiversity CoPs .
Next steps for applying Indigenous expertise
Given that 80% of remaining biodiversity is on Indigenous lands and in Indigenous hands, it is clear with the emerging biodiversity markets that Indigenous people are the primary market actors. Therefore, financing models need to evolve in order to safeguard and invest in the role of Indigenous people as stewards and equity owners of the conservation of the precious remaining biodiversity. Similarly, financing all other opportunities to cross-pollinate Western and Indigenous knowledge systems is essential.
The growing body of evidence reveals a simple truth: Indigenous people hold a key to our collective response to climate and ecological challenges.
Indigenous-led organizations are thriving by sharing this knowledge, and people and the planet are benefiting in turn.
With contributions from Harry Guinness, Head of Net Zero Strategy, Greenhouse.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
The Agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} Weekly
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Climate Action .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Climate finance: What are debt-for-nature swaps and how can they help countries?
Kate Whiting
April 26, 2024

Beyond greenwashing: 5 key strategies for genuine sustainability in agriculture
Santiago Gowland
April 24, 2024

What is desertification and why is it important to understand?
Andrea Willige
April 23, 2024

Global forest restoration goals can be achieved with youth-led ecopreneurship
Agustin Rosello, Anali Bustos, Fernando Morales de Rueda, Jennifer Hong and Paula Sarigumba

The planet’s outlook is in our hands. Which future will we incentivize?
Carlos Correa
April 22, 2024

This Earth Day we consider the impact of climate change on human health
Shyam Bishen and Annika Green
- (855) 776-7763
Training Maker
Survey Maker
Webinar Ninja
All Products
ProProfs.com
- Get Started Free
Trusted By Over 15 Million Users Globally

Knowledge Base Software Customer Success Case
Manufacturing

Testimonials

Bill Wisell
Health Licensing Coordinator, Nebraska Department of Human and Health Services
ProProfs support is one of the best I have experienced. They truly care about their customers and deliver resolutions fast.

Trever Ehrlich
Creative Solutions Manager, Kenco Logistics
With ProProfs, we've had an explosion in data available to our team; in just a few months, our knowledge base has exploded to over 200 useful articles full of relevant data, documentation, images and video.

Bob Bednarz
Learning & Development Manager, Smokeball
The client-facing knowledge base we created using ProProfs Knowledge Base software was of significant help in increasing page views and improving engagement rate.

Professor Daniel Stein
Director of Technology Initiatives, Touro College.
I love ProProfs user experience. The interface is easy to use yet packed with powerful settings.

Judy Hutchison
Systems Director, RightAnswer.com
The software empowered us to implement, update, and maintain user documentation with ease and now we are sorted.

Tom Michael Dela Cruz
Training Specialist, The Studio Technologies Inc.
We significantly reduced errors in every order, thanks to the centralized source of information we created using ProProfs Knowledge Base Software.

Erik Uhlich
Product Manager, Descartes Systems (Germany) GmbH
The result of using ProProfs Knowledge Base software as our "new" tool for end-user documentation is that even other departments participate in writing articles. The process of user management contributes significantly to producing good quality content. Being a Product Manager, I can review articles and make changes before finally publishing it. Changes that are requested can be done quickly and effortlessly. Thanks to ProProfs, our end-user documentation is constantly growing, and now even other products of the company will find their way into ProProfs. We are happy.
We Believe Software Should Make You Happy
We are building a 100-year company with a mission to DELIGHT customers. People think we’re crazy to offer phone, chat , and email support . We still do it. When it comes to awesome support & building delightful software, we go the distance - try it, and you will love it.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case ...
Some famous books about case study methodology (Merriam, 2002; Stake, 1995; Yin, 2011) provide useful details on case study research but they emphasize more on theory as compared to practice, and most of them do not provide the basic knowledge of case study conduct for beginners (Hancock & Algozzine, 2016). This article is an attempt to bridge ...
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples. Now that you understand what a case study is, let's look at real-life case study examples. In this section, we'll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
Case studies are a form of problem-based learning, where you present a situation that needs a resolution. A typical business case study is a detailed account, or story, of what happened in a particular company, industry, or project over a set period of time. The learner is given details about the situation, often in a historical context.
Beyond teaching specific subject matter, the case study method excels in instilling meta-skills in students. This article explains the importance of seven such skills: preparation, discernment ...
The definitions of case study evolved over a period of time. Case study is defined as "a systematic inquiry into an event or a set of related events which aims to describe and explain the phenomenon of interest" (Bromley, 1990).Stoecker defined a case study as an "intensive research in which interpretations are given based on observable concrete interconnections between actual properties ...
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply… 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units'.1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a ...
Through the case method, you can "try on" roles you may not have considered and feel more prepared to change or advance your career. 5. Build Your Self-Confidence. Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader's perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and ...
A case study can also refer to a specific research methodology used to study phenomena in-depth, often qualitatively, by focusing on one or a few examples, rather than a large-scale quantitative study. ProQuest One Business - includes business-related journals and reports. After doing a search, to the left of the results expand the Document ...
The Effects of Case-Based Approaches on Student Knowledge, Attitudes, and Engagement. Journal on Excellence in College Teaching. 27(2), 131-153. Lundberg, K.O. (Ed.). (2011). Our Digital Future: Boardrooms and Newsrooms. Knight Case Studies Initiative. Popil, I. (2011). Promotion of critical thinking by using case studies as teaching method.
The Case Study Knowledge Base Article template delves into real-life scenarios or examples related to a product, service, or business operation. It showcases practical applications and outcomes. Here's how it benefits businesses: Highlights the practical use of products or services in real-world situations.
Knowledge Base Case Studies World's Best Knowledge Bases, Let our Customers From Industries Teach You How They Did it. Virgin Mobile Delivering 40% More Self-Service Support To Customers With Helpjuice. Check Out What Some of Our Customers Are Saying! Telecommunications (1,000 - 5,000 people)
Case-Based Learning. Case-based learning (CBL) is an established approach used across disciplines where students apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios, promoting higher levels of cognition (see Bloom's Taxonomy ). In CBL classrooms, students typically work in groups on case studies, stories involving one or more characters and/or ...
Students, Alumni, and Others. Find and purchase cases at the Harvard Business Publishing website. Links & Files. Alternative places to find case studies. Harvard Business Review Access. Answered By: Alice Kalinowski. Nov 03, 2020.
New content knowledge builds on the student's understanding and expands the knowledge base needed to apply and use the knowledge (Boettcher, 2019). Expand All | Collapse All. ... Identify a case study or develop a new one that aligns with your course outcomes or unit objectives. The case can be real or hypothetical.
Study Materials, Lecture Notes, Seminars, Solved Assignments, Business Case Studies, Research Papers, Theses and Dissertations for Master of Business Administration (MBA) Programs in B-Schools and Universities like London Business School, Harvard Business School, INSEAD, Stanford University, MIT etc. and Universities across the globe.
An organization's captured (and codified) knowledge--white papers, case studies, documented processes--should help project teams perform better, but does it? Existing research has not answered the question, even as U.S. companies alone spend billions annually on knowledge management programs. Looking at large-scale, objective data from Indian ...
Knowledge Base Case Studies. World's Best Knowledge Bases, Let our Customers From Industries Teach You How They Did it. E-Commerce (50 - 100 people) Collage.com Team uses Helpjuice Seven days a week To Deliver Amazing Support. Read Case Study. Real Estate (100 - 500 people)
To find out more about how KPS' Knowledge Management software has helped our clients to increase service delivery quality and efficiency, and how it could help you, download one of our knowledge management case studies below: Request a demo. All. Contact Centre. Employee Knowledge Sharing Solutions. Service Desk. Web Self-Service.
Knowledge of these differing levels was built into the first workshop where, after unpacking the four dimensions of the PISA framework, the teachers were asked what their implementation might look like at beginning, developing, embedding and leading stages of schools' and educators' global competence journey. ... An Australian Case Study ...
How Indigenous expertise is empowering climate action: A case study from Oceania Apr 23, 2024. ... This knowledge is needed across Europe and North America, both of which have experienced staggering brush fires. According to Firesticks, the not-for-profit Indigenous network, "aboriginal fire management has become a priority for community ...
Our knowledge base has exploded to over 200 useful articles full of relevant data, documentation, images and video Trever Ehrlich Creative Solutions Manager, Kenco Logistics. Read Full Story. The support has been solid. Issues are always resolved within 24-48 hours.
As a case study, the automated machine learning method was applied to predict the spatial distribution of soil subgroups in Heshan farm. A total of 110 soil samples and 10 terrain variables were utilized in the designed experiments. ... Consequently, many studies began to leverage knowledge from prior datasets to initialize the search space to ...
In the case study, we developed four typical rule sets as examples based on the constructed rule system to group rock discontinuities and subsume the fractured rock discontinuities. ... We converted the semantic-based geologic knowledge base into formalized language that can be enforced by the rule engine based on DROOLS. DROOLS is a JBOSS ...