CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free

Class 9 Mathematics Number System Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 9 Mathematics Number System Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 9 Mathematics Number System . These Assignments for Grade 9 Mathematics Number System cover all important topics which can come in your standard 9 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Number System , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 9 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Mathematics Number System Class 9 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Mathematics Number System Class 9. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Mathematics Number System class 9 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 9 Mathematics Number System Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Mathematics Number System Class 9 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics Number System . Students and teachers can download and save all free Mathematics Number System assignments in Pdf for grade 9th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 9 important questions and answers for Mathematics Number System as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 9 Mathematics Number System and CBSE Assignments for Mathematics Number System Class 9 will be really helpful for standard 9th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 9th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics Number System Download in Pdf

Advantages of Class 9 Mathematics Number System Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Mathematics Number System assignments for Grade 9, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Mathematics Number System textbooks for Class 9 .
- All Mathematics Number System assignments for Class 9 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 9 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Mathematics Number System chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 9 Mathematics Number System question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 9 Mathematics Number System students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Mathematics Number System Class 9 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 9 Mathematics Number System chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Mathematics Number System in Grade 9, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Mathematics Number System Grade 9 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 9 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 9 Social Science Assignments

Class 9 Mathematics Surface areas and Volumes Assignments

Class 9 Sanskrit Assignments
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 - Number Systems
- NCERT Solutions

NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number System - Free PDF
Class 9 Chapter 1 delves into the principles covered under the topic of the number system. Vedantu offers an expert-curated NCERT answer for CBSE Class 9 Chapter 1. To ace your preparations, get the NCERT solution supplied by our professionals. The freely available pdf offers step-by-step solutions to the NCERT practice problems. The NCERT solutions pdf contains the answers to all of the Class 9 syllabus questions.
If you are a student who is looking for an easy way to summarise the complete chapter, look no further! Start your preparation with the solutions provided by the experts of Vedantu and ace your studies.

Exercises under NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number Systems
Ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 1, "number systems", consists of six exercises, each covering a specific set of questions. below is a detailed explanation of each exercise: exercise 1.1: this exercise covers basic concepts of the number system, such as natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, etc. the questions in this exercise aim to familiarise students with these concepts and their properties. exercise 1.2: this exercise covers the representation of numbers in decimal form. the questions in this exercise require students to convert fractions into decimals, decimals into fractions, and perform basic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division on decimals. exercise 1.3: this exercise deals with the representation of rational numbers on a number line. the questions in this exercise require students to mark the position of given rational numbers on a number line and identify the rational number represented by a given point on the number line. exercise 1.4: this exercise covers the representation of irrational numbers on a number line. the questions in this exercise require students to mark the position of given irrational numbers on a number line and identify the irrational number represented by a given point on the number line. exercise 1.5: this exercise deals with the conversion of recurring decimals into fractions. the questions in this exercise require students to write recurring decimals as fractions and vice versa. exercise 1.6: this exercise covers the comparison of rational numbers. the questions in this exercise require students to compare given rational numbers using the concept of inequality, find rational numbers between two given rational numbers, and represent rational numbers on a number line., ncert solutions class 9 maths chapter 1 number system - free pdf download, exercise (1.1).
1. Is zero a rational number? Can you write it in the form $\dfrac{ {p}}{ {q}}$, where $ {p}$ and $ {q}$ are integers and $ {q}\ne {0}$? Describe it.
Ans: Remember that, according to the definition of rational number,
a rational number is a number that can be expressed in the form of $\dfrac{p}{q}$, where $p$ and $q$ are integers and $q\ne \text{0}$.
Now, notice that zero can be represented as $\dfrac{0}{1},\dfrac{0}{2},\dfrac{0}{3},\dfrac{0}{4},\dfrac{0}{5}.....$
Also, it can be expressed as $\dfrac{0}{-1},\dfrac{0}{-2},\dfrac{0}{-3},\dfrac{0}{-4}.....$
Therefore, it is concluded from here that $0$ can be expressed in the form of $\dfrac{p}{q}$, where $p$ and $q$ are integers.
Hence, zero must be a rational number.
2. Find any six rational numbers between $ {3}$ and $ {4}$.
Ans: It is known that there are infinitely many rational numbers between any two numbers. Since we need to find $6$ rational numbers between $3$ and $4$, so multiply and divide the numbers by $7$ (or by any number greater than $6$)
Then it gives,
$ 3=3\times \dfrac{7}{7}=\dfrac{21}{7} $
$ 4=4\times \dfrac{7}{7}=\dfrac{28}{7} $
Hence, $6$ rational numbers found between $3$ and $4$ are $\dfrac{22}{7},\dfrac{23}{7},\dfrac{24}{7},\dfrac{25}{7},\dfrac{26}{7},\dfrac{27}{7}$.
3. Find any five rational numbers between $\dfrac{ {3}}{ {5}}$ and $\dfrac{ {4}}{ {5}}$.
Ans: It is known that there are infinitely many rational numbers between any two numbers.
Since here we need to find five rational numbers between $\dfrac{3}{5}$ and $\dfrac{4}{5}$, so multiply and divide by $6$ (or by any number greater than $5$).
Then it gives,
$\dfrac{3}{5}=\dfrac{3}{5}\times \dfrac{6}{6}=\dfrac{18}{30}$,
$\dfrac{4}{5}=\dfrac{4}{5}\times \dfrac{6}{6}=\dfrac{24}{30}$.
Hence, $5$ rational numbers found between $\dfrac{3}{5}$ and $\dfrac{4}{5}$ are
$\dfrac{19}{30},\dfrac{20}{30},\dfrac{21}{30},\dfrac{22}{30},\dfrac{23}{30}$.
4. State whether the following statements are true or false. Give reasons for your answers.
(i) Every natural number is a whole number.
Ans: Write the whole numbers and natural numbers in a separate manner.
It is known that the whole number series is $0,1,2,3,4,5.....$. and
the natural number series is $1,2,3,4,5.....$.
Therefore, it is concluded that all the natural numbers lie in the whole number series as represented in the diagram given below.
Thus, it is concluded that every natural number is a whole number.
Hence, the given statement is true.
(ii) Every integer is a whole number.
Ans: Write the integers and whole numbers in a separate manner.
It is known that integers are those rational numbers that can be expressed in the form of $\dfrac{p}{q}$, where $q=1$.
Now, the series of integers is like $0,\,\pm 1,\,\pm 2,\,\pm 3,\,\pm 4,\,...$.
But the whole numbers are $0,1,2,3,4,...$.
Therefore, it is seen that all the whole numbers lie within the integer numbers, but the negative integers are not included in the whole number series.
Thus, it can be concluded from here that every integer is not a whole number.
Hence, the given statement is false.
(iii) Every rational number is a whole number.
Ans: Write the rational numbers and whole numbers in a separate manner.
It is known that rational numbers are the numbers that can be expressed in the form $\dfrac{p}{q}$, where $q\ne 0$ and the whole numbers are represented as $0,\,1,\,2,\,3,\,4,\,5,...$
Now, notice that every whole number can be expressed in the form of $\dfrac{p}{q}$
as \[\dfrac{0}{1},\text{ }\dfrac{1}{1},\text{ }\dfrac{2}{1},\text{ }\dfrac{3}{1},\text{ }\dfrac{4}{1},\text{ }\dfrac{5}{1}\],…
Thus, every whole number is a rational number, but all the rational numbers are not whole numbers. For example,
$\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{1}{3},\dfrac{1}{4},\dfrac{1}{5},...$ are not whole numbers.
Therefore, it is concluded from here that every rational number is not a whole number.
Exercise (1.2)
1. State whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answers.
(i) Every irrational number is a real number.
Ans: Write the irrational numbers and the real numbers in a separate manner.
The irrational numbers are the numbers that cannot be represented in the form $\dfrac{p}{q},$ where $p$ and $q$ are integers and $q\ne 0.$
For example, $\sqrt{2},3\pi ,\text{ }.011011011...$ are all irrational numbers.
The real number is the collection of both rational numbers and irrational numbers.
For example, $0,\,\pm \dfrac{1}{2},\,\pm \sqrt{2}\,,\pm \pi ,...$ are all real numbers.
Thus, it is concluded that every irrational number is a real number.
(ii) Every point on the number line is of the form $\sqrt{m}$, where m is a natural number.
Ans: Consider points on a number line to represent negative as well as positive numbers.
Observe that, positive numbers on the number line can be expressed as $\sqrt{1,}\sqrt{1.1,}\sqrt{1.2},\sqrt{1.3},\,...$, but any negative number on the number line cannot be expressed as $\sqrt{-1},\sqrt{-1.1},\sqrt{-1.2},\sqrt{-1.3},...$, because these are not real numbers.
Therefore, it is concluded from here that every number point on the number line is not of the form $\sqrt{m}$, where $m$ is a natural number.
(iii) Every real number is an irrational number.
Real numbers are the collection of rational numbers (Ex: $\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{2}{3},\dfrac{3}{5},\dfrac{5}{7},$……) and the irrational numbers (Ex: $\sqrt{2},3\pi ,\text{ }.011011011...$).
Therefore, it can be concluded that every irrational number is a real number, but
every real number cannot be an irrational number.
Hence, the given statement is false.
2. Are the square roots of all positive integer numbers irrational? If not, provide an example of the square root of a number that is not an irrational number.
Ans: Square root of every positive integer does not give an integer.
For example: $\sqrt{2},\sqrt{3,}\sqrt{5},\sqrt{6},...$ are not integers, and hence these are irrational numbers. But $\sqrt{4}$ gives $\pm 2$ , these are integers and so, $\sqrt{4}$ is not an irrational number.
Therefore, it is concluded that the square root of every positive integer is not an irrational number.
3. Represent $\sqrt{5}$ on the number line.
Ans: Follow the procedures to get $\sqrt{5}$ on the number line.
Firstly, Draw a line segment $AB$ of $2$ unit on the number line.
Secondly, draw a perpendicular line segment $BC$ at $B$ of $1$ units.
Thirdly, join the points $C$ and $A$, to form a line segment $AC$.
Fourthly, apply the Pythagoras Theorem as
$ A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} $
$ A{{C}^{2}}={{2}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}} $
$ A{{C}^{2}}=4+1=5 $
$ AC=\sqrt{5} $
Finally, draw the arc $ACD$, to find the number $\sqrt{5}$ on the number line as given in the diagram below.
Exercise (1.3)
1. Write the following in decimal form and say what kind of decimal expansion each has:
(i) $\mathbf{\dfrac{ {36}}{ {100}}}$
Ans: Divide $36$ by $100$.
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, {0.36}$
$100 {\overline{)\;36\quad}}$
$\underline{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-0\quad}$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,360$
$\underline{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-300\quad}$
$\;\;\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,600$
$\underline{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-600}$
$\underline{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\quad 0 \,\,\,\,\,}$
So, $\dfrac{36}{100}=0.36$ and it is a terminating decimal number.
(ii) $\mathbf{\dfrac{ {1}}{ {11}}}$
Ans: Divide $1$ by $11$.
${\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,0.0909..}$
$11 \, {\overline{)\;1\quad}}$
$\underline{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-0\quad}$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,10$
$\underline{\,\;\;\,\,-0\quad}$
$\;\;\,\,\,\,100$
$\underline{\,\,\,\,\;-99}$
$\,\,\,\,\,\, \quad 10$
$\quad\underline{\;\;-0\quad}$
$\;\;\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,100$
$\underline{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\;-99}$
$\quad\,\,\,\,\,\,\,1\quad$
It is noticed that while dividing $1$ by $11$, in the quotient $09$ is repeated.
So, $\dfrac{1}{11}=0.0909.....$ or
$\dfrac{1}{11}=0.\overline{09}$
and it is a non-terminating and recurring decimal number.
(iii) $ \mathbf{{4}\dfrac{ {1}}{ {8}}}$
Ans: $4\dfrac{1}{8}=4+\dfrac{1}{8}=\dfrac{32+1}{8}=\dfrac{33}{8}$
Divide $33$ by $8$.
$\,\,\,\,\,{4.125}$
$8 {\overline{)\;33\quad}}$
$\underline{\,\,\,\,-32\quad}$
$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,10$
$\underline{\;\;\,\,\,\,-8\quad}$
$\;\;\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,20$
$\underline{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-16}$
$\;\quad\quad\,\,\,\,40$
$\quad\underline{\quad\,\,-40\quad}$
$\quad\underline{\quad\,\, \,\,\,\,0\quad}$
Notice that, after dividing $33$ by $8$, the remainder is found as $0$.
So, $4\dfrac{1}{8}=4.125$ and it is a terminating decimal number.
(iv) $\mathbf{\dfrac{ {3}}{ {13}}}$
Ans: Divide $3$ by $13$.
$\quad \,\,{0.230769}$
$13 {\overline{)\;3\quad}}$
$\underline{\quad-0\quad}$
$\quad\quad 30$
$\underline{\;\,\quad-26\quad}$
$\;\quad\quad\,\,\,40$
$\underline{\quad\quad\,\,-39\quad}$
$\;\quad\quad\quad\;10$
$\quad\underline{\quad\quad -0\quad}$
$\quad{\quad\quad \quad 100}$
$\quad\quad\underline{\quad \,\, -91\quad}$
$\quad\quad \quad \,\,\,\quad90$
$\quad\quad\underline{\quad\,\,\,\,\,-78\quad}$
$\quad\quad\quad\quad \quad 120$
$\quad \quad\underline{\quad\quad\,\,-117\quad}$
$\quad\quad\underline{\quad \quad\quad\,\, 3\quad}$
It is observed that while dividing $3$ by $13$, the remainder is found as $3$ and that is repeated after each $6$ continuous divisions.
So, $\dfrac{3}{13}=0.230769.......$ or
$\dfrac{3}{13}=0.\overline{230769}$
(v) $\mathbf{\dfrac{ {2}}{ {11}}}$
Ans: Divide $2$ by $11$.
$\quad \,\,{0.1818}$
$11 {\overline{)\;2\quad}}$
$\quad\quad20$
$\underline{\quad\;-11\quad}$
$\quad\quad \;\,90$
$\underline{\quad\,\,\,\, -88\;}$
$\;\quad\quad\;20$
$\quad\underline{\quad-11\quad}$
$\quad{\quad\quad 90}$
$\quad\underline{\,\,\quad -88}$
$\quad\quad\quad\,\,2\quad$
It can be noticed that while dividing $2$ by $11$, the remainder is obtained as $2$ and then $9$, and these two numbers are repeated infinitely as remainders.
So, $\dfrac{2}{11}=0.1818.....$ or
$\dfrac{2}{11}=0.\overline{18}$
(vi) $\mathbf{\dfrac{ {329}}{ {400}}}$
Ans: Divide $329$ by $400$.
$\quad \quad{0.8225}$
$400 {\overline{)\;329\quad}}$
$\underline{\quad\,\,-0\quad}$
$\quad\quad3290$
$\underline{\quad\;-3200\quad}$
$\quad\quad\quad\;900$
$\underline{\quad\quad\quad-800\;}$
$\quad\quad\quad\quad\;1000$
$\quad\underline{\quad\quad\quad-800\quad}$
$\quad{\quad\quad\quad\quad\,\,2000}$
$\quad\underline{\quad\quad\quad\quad-2000\quad}$
$\quad\underline{\quad\quad\quad\quad\,\,\,\,\,\, 0 \quad}$
It can be seen that while dividing $329$ by $400$, the remainder is obtained as $0$.
So, $\dfrac{329}{400}=0.8225$ and is a terminating decimal number.
2. You know that $\dfrac{ {1}}{ {7}} {=0} {.142857}...$. Can you predict what the decimal expansions of $\dfrac{ {2}}{ {7}} {,}\dfrac{ {3}}{ {7}} {,}\dfrac{ {4}}{ {7}} {,}\dfrac{ {5}}{ {7}} {,}\dfrac{ {6}}{ {7}}$ are, without actually doing the long division? If so, how?
$\text{[}$Hint: Study the remainders while finding the value of $\dfrac{ {1}}{ {7}}$ carefully.$\text{]}$
Ans: Note that, $\dfrac{2}{7},\dfrac{3}{7},\dfrac{4}{7},\dfrac{5}{7}$ and $\dfrac{6}{7}$ can be rewritten as $2\times \dfrac{1}{7},\text{ 3}\times \dfrac{1}{7},\text{ 4}\times \dfrac{1}{7},\text{ 5}\times \dfrac{1}{7},$ and $6\times \dfrac{1}{7}$
Substituting the value of $\dfrac{1}{7}=0.142857$ , gives
$2 \times \dfrac{1}{7} = 2\times 0.142857...=0.285714...$
$ 3\times \dfrac{1}{7} = 3\times .428571…= .428571...$
\[4\times \dfrac{1}{7}=4\times 0.142857...\]\[\text{=}\,\text{0}\text{.571428}...\]
$5\times \dfrac{1}{7}=5\times 0.71425...$ \[\text{=}\,\text{0}\text{.714285}...\]
$6\times \dfrac{1}{7}=6\times 0.142857...$\[\text{=}\,\text{0}\text{.857142}...\]
So, the values of $\dfrac{2}{7},\text{ }\dfrac{3}{7},\text{ }\dfrac{4}{7},\text{ }\dfrac{5}{7}$ and $\dfrac{6}{7}$ obtained without performing long division are
\[\dfrac{2}{7}=0.\overline{285714}\]
$\dfrac{3}{7}=0.\overline{428571}$
$\dfrac{4}{7}=0.\overline{571428}$
\[\dfrac{5}{7}=0.\overline{714285}\]
$\dfrac{6}{7}=0.\overline{857142}$
3. Express the following in the form \[\dfrac{ {p}}{ {q}}\], where $ {p}$ and $ {q}$ are integers and $ {q}\ne {0}$.
(i) $\mathbf{ {0} {.}\overline{ {6}}}$
Ans: Let $x=0.\overline{6}$
$\Rightarrow x=0.6666$ ….… (1)
Multiplying both sides of the equation (1) by $10$, gives
$10x=0.6666\times 10$
$10x=6.6666$….. …… (2)
Subtracting the equation $\left( 1 \right)$ from $\left( 2 \right)$, gives
$ 10x=6.6666..... $
$ \underline{-x=0.6666.....} $
$ 9x=6 $
$ 9x=6 $
$ x=\dfrac{6}{9}=\dfrac{2}{3} $
So, the decimal number becomes
$0.\overline{6}=\dfrac{2}{3}$ and it is in the required $\dfrac{p}{q}$ form.
(ii) $\mathbf{ {0} {.}\overline{ {47}}}$
Ans: Let $x=0.\overline{47}$
$\text{ }\Rightarrow x=0.47777.....$ ……(a)
Multiplying both sides of the equation (a) by $10$, gives
$10x=4.7777.....$ ……(b)
Subtracting the equation $\left( a \right)$ from $\left( b \right)$, gives
$ 10x=4.7777..... $
$ \underline{-x=0.4777.....} $
$ 9x=4.3 $
$x=\dfrac{4.3}{9}\times \dfrac{10}{10} $
$ \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{43}{90} $
So, the decimal number becomes
$0.\overline{47}=\dfrac{43}{90}$ and it is in the required $\dfrac{p}{q}$ form.
(iii) $ \mathbf{{0} {.}\overline{ {001}}}$
Ans: Let $x=0.\overline{001} $ …… (1)
Since the number of recurring decimal number is $3$, so multiplying both sides of the equation (1) by $1000$, gives
$1000\times x=1000\times 0.001001.....$ …… (2)
Subtracting the equation (1) from (2) gives
$ 1000x=1.001001..... $
$ \underline{\text{ }-x=0.001001.....} $
$ 999x=1 $
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{999}$
Hence, the decimal number becomes
$0.\overline{001}=\dfrac{1}{999}$ and it is in the $\dfrac{p}{q}$ form.
4. Express $ {0} {.99999}.....$ in the form of $\dfrac{ {p}}{ {q}}$ . Are you surprised by your answer? With your teacher and classmates, discuss why the answer makes sense.
Let $x=0.99999.....$ ....... (a)
Multiplying by $10$ both sides of the equation (a), gives
$10x=9.9999.....$ …… (b)
Now, subtracting the equation (a) from (b), gives
$ 10x=9.99999..... $
$ \underline{\,-x=0.99999.....} $
$ 9x=9 $
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{9}{9}$
$\Rightarrow x=1$.
$0.99999...=\dfrac{1}{1}$ which is in the $\dfrac{p}{q}$ form.
Yes, for a moment we are amazed by our answer, but when we observe that $0.9999.........$ is extending infinitely, then the answer makes sense.
Therefore, there is no difference between $1$ and $0.9999.........$ and hence these two numbers are equal.
5. What can the maximum number of digits be in the repeating block of digits in the decimal expansion of $\dfrac{ {1}}{ {17}}$ ? Perform the division to check your answer.
Ans: Here the number of digits in the recurring block of $\dfrac{1}{17}$ is to be determined. So, let us calculate the long division to obtain the recurring block of $\dfrac{1}{17}$. Dividing $1$ by $17$ gives
$\quad\quad {0.0588235294117646}$
$17{\overline{)\quad1\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad}}$
$\underline{\quad\,\,\,\,-0\quad}\qquad\qquad\qquad$
$\quad \quad \,\,\,10\qquad\qquad\quad\quad$
$\underline{\quad \quad -0\quad}\qquad\qquad\quad$
$\quad \quad \,\,\,\,\,\;100\qquad\qquad\qquad$
$\underline{\quad \quad \,\,-85\;}\qquad\qquad\quad$
$\quad\qquad\,\,\;150\qquad\qquad\quad$
$\quad\underline{\qquad-136\;}\qquad\qquad\quad$
$\quad{\quad\quad\quad 140}\qquad\qquad\;\;$
$\quad\underline{\qquad-136\quad}\qquad\quad$
${\quad \qquad \,\,\quad 40 \quad}\quad$
$\underline{\qquad \,\,\,\quad -34\;\;}\quad$
$\;\qquad \qquad\,\,60$
$\underline{\qquad \qquad-51}$
$\quad\quad \qquad \quad 90$
$\quad\;\;\underline{\quad \qquad-85}$
$\qquad\quad\;\quad\,\,\,\, 50$
$\quad\quad\;\;\underline{\,\,\quad\,\, -34}$
$\quad\quad\qquad \quad 160$
$\qquad\quad\;\underline{\quad-153}$
$\qquad\qquad\quad\;70$
$\qquad\quad\quad\;\;\underline{-68}$
$\quad\,\,\qquad\qquad 20$
$\qquad\qquad\quad\underline{-17}$
$\qquad\qquad\quad\quad\; 130$
$\qquad\qquad\quad\;\;\underline{-119}$
$\qquad\qquad\qquad\quad 110$
$\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\underline{-102}$
$\qquad\qquad\qquad\quad\quad\quad 80$
$\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\underline{-68}$
$\qquad\qquad\qquad\quad\quad\quad\; 120$
$\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\underline{-119}$
$\qquad\qquad\qquad\quad\quad\quad\; 1$
Thus, it is noticed that while dividing $1$ by $17$, we found $16$ number of digits in the
repeating block of decimal expansion that will continue to be $1$ after going through $16$ continuous divisions.
Hence, it is concluded that $\dfrac{1}{17}=0.0588235294117647.....$ or
$\dfrac{1}{17}=0.\overline{0588235294117647}$ and it is a recurring and non-terminating decimal number.
6. Look at several examples of rational numbers in the form $\dfrac{ {p}}{ {q}}\left( {q}\ne {0} \right)$, where $ {p}$ and $ {q}$ are integers with no common factors other than $ {1}$ and having terminating decimal representations (expansions). Can you guess what property $ {q}$ must satisfy?
Ans: Let us consider the examples of such rational numbers $\dfrac{5}{2},\dfrac{5}{4},\dfrac{2}{5},\dfrac{2}{10},\dfrac{5}{16}$ of the form $\dfrac{p}{q}$ which have terminating decimal representations.
$ \dfrac{5}{2}=2.5 $
$ \dfrac{5}{4}=1.25 $
$ \dfrac{2}{5}=0.4 $
$ \dfrac{2}{10}=0.2 $
$ \dfrac{5}{16}=0.3125 $
In each of the above examples, it can be noticed that the denominators of the rational numbers have powers of $2,5$ or both.
So, $q$ must satisfy the form either ${{2}^{m}}$, or ${{5}^{n}}$, or both ${{2}^{m}}\times {{5}^{n}}$ (where $m=0,1,2,3.....$ and $n=0,1,2,3.....$) in the form of $\dfrac{p}{q}$.
7. Write three numbers whose decimal expansions are non-terminating non-recurring.
Ans: All the irrational numbers are non-terminating and non-recurring, because irrational numbers do not have any representations of the form of $\dfrac{p}{q}$ $\left( q\ne 0 \right)$, where $p$ and $q$are integers. For example:
$\sqrt{2}=1.41421.....$,
$\sqrt{3}=1.73205...$
$\sqrt{7}=2.645751....$
are the numbers whose decimal representations are non-terminating and non-recurring.
8. Find any three irrational numbers between the rational numbers $\dfrac{ {5}}{ {7}}$ and $\dfrac{ {9}}{ {11}}$.
Ans: Converting $\dfrac{5}{7}$and $\dfrac{9}{11}$ into the decimal form gives
$\dfrac{5}{7}=0.714285.....$ and
$\dfrac{9}{11}=0.818181.....$
Therefore, $3$ irrational numbers that are contained between $0.714285......$ and $0.818181.....$
$ 0.73073007300073...... $
$ 0.74074007400074...... $
$ 0.76076007600076...... $
Hence, three irrational numbers between the rational numbers $\dfrac{5}{7}$ and $\dfrac{9}{11}$ are
9. Classify the following numbers as rational or irrational:
(i) $\mathbf{\sqrt{ {23}}}$
Ans: The following diagram reminds us of the distinctions among the types of rational and irrational numbers.
After evaluating the square root gives
$\sqrt{23}=4.795831.....$ , which is an irrational number.
(ii) $\mathbf{\sqrt{ {225}}}$
Ans: After evaluating the square root gives
$\sqrt{225}=15$, which is a rational number.
That is, $\sqrt{225}$ is a rational number.
(iii) $ \mathbf{{0} {.3796}}$
Ans: The given number is $0.3796$. It is terminating decimal.
So, $0.3796$ is a rational number.
(iv) $ \mathbf{{7} {.478478}}$
Ans: The given number is \[7.478478\ldots .\]
It is a non-terminating and recurring decimal that can be written in the $\dfrac{p}{q}$ form.
Let $x=7.478478\ldots .$ ……(a)
Multiplying the equation (a) both sides by $100$ gives
$\Rightarrow 1000x=7478.478478.....$ ……(b)
Subtracting the equation (a) from (b), gives
$ 1000x=7478.478478.... $
$ \underline{\text{ }-x=\text{ }7.478478\ldots .} $
$ 999x=7471 $
$ \text{ }x=\dfrac{7471}{999} $
Therefore, $7.478478.....=\dfrac{7471}{999}$, which is in the form of $\dfrac{p}{q}$
So, $7.478478...$ is a rational number.
(v) $ \mathbf{{1} {.101001000100001}.....}$
Ans: The given number is \[1.101001000100001....\]
It can be clearly seen that the number \[1.101001000100001....\] is a non-terminating and non-recurring decimal and it is known that non-terminating non-recurring decimals cannot be written in the form of $\dfrac{p}{q}$.
Hence, the number \[1.101001000100001....\] is an irrational number.
Exercise (1.4)
1. Visualize \[ {3} {.765}\] on the number line, using successive magnification.
It is clear that the value \[3.765\] lies between the numbers $3$ and $4$.
Also, the number $3.7$ and $3.8$ lie between the numbers $3$ and $4$.
The number $3.76$ and $3.77$ lie between the numbers $3$ and $4$.
Again, the numbers $3.764$ and $3.766$ lie between the numbers $3.76$ and $3.77$.
Thus, the number $3.765$ lies between the numbers $3.764$ and $3.766$.
So, first locate the numbers $3$ and $4$ on the number line, then use the successive magnification as shown in the diagrams below.
Locate the numbers 3 and 4
Apply Magnification Between 3 and 4
Apply Magnification Between 3.7 and 3.8
Apply Magnification Between 3.76 and 3.77
Apply Magnification Between 3.764 and 3.766 and Find 3.765
2. Visualize $ {4} {.}\overline{ {26}}$ on the number line, up to $ {4}$ decimal places.
Ans: The number $4.\overline{26}$ can be represented as $4.262.....$.
Apply successive magnification, after locating the numbers $4$ and $5$ on the number line and visualize the number up to $4$ decimal places as given in the following diagrams.
The number $4.2$ is located between $4$ and $5$ .
The number $4.26$ is located between $4.2$ and $4.3$.
The number $4.262$ is located between $4.26$ and \[4.27\].
The number \[4.2626\] is located between \[4.262\] and \[4.263\].
Exercise (1.5)
1. Classify the following numbers as rational or irrational:
(i) $ \mathbf{{2-}\sqrt{ {5}}}$
Ans: The given number is $2-\sqrt{5}$.
Here, $\sqrt{5}=2.236.....$ and it is a non-repeating and non-terminating irrational number.
Therefore, substituting the value of $\sqrt{5}$ gives
$2-\sqrt{5}=2-2.236.....$
$=-0.236.....$, which is an irrational number.
So, $2-\sqrt{5}$ is an irrational number.
(ii) $\mathbf{\left( {3+}\sqrt{ {23}} \right) {-}\left( \sqrt{ {23}} \right)}$
Ans: The given number is $\left( 3+\sqrt{23} \right)-\left( \sqrt{23} \right)$.
The number can be written as
$\left( 3+\sqrt{23} \right)-\sqrt{23}=3+\sqrt{23}-\sqrt{23} $
$ =3 $
$=\dfrac{3}{1}$, which is in the $\dfrac{p}{q}$ form and so, it is a rational number.
Hence, the number $\left( 3+\sqrt{23} \right)-\sqrt{23}$ is a rational number.
(iii) $\mathbf{\dfrac{ {2}\sqrt{ {7}}}{ {7}\sqrt{ {7}}}}$
Ans: The given number is $\dfrac{2\sqrt{7}}{7\sqrt{7}}$.
$\dfrac{2\sqrt{7}}{7\sqrt{7}}=\dfrac{2}{7}$, which is in the $\dfrac{p}{q}$ form and so, it is a rational number.
Hence, the number $\dfrac{2\sqrt{7}}{7\sqrt{7}}$ is a rational number.
(iv) $\mathbf{\dfrac{ {1}}{\sqrt{ {2}}}}$
Ans: The given number is $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$.
It is known that, $\sqrt{2}=1.414.....$ and it is a non-repeating and non-terminating irrational number.
Hence, the number $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ is an irrational number.
(v) $ \mathbf{{2\pi }}$
Ans: The given number is $2\pi $.
It is known that, $\pi =3.1415$ and it is an irrational number.
Now remember that, Rational $\times $ Irrational = Irrational.
Hence, $2\pi $ is also an irrational number.
2. Simplify each of the of the following expressions:
(i) $\mathbf{\left( {3+}\sqrt{ {3}} \right)\left( {2+}\sqrt{ {2}} \right)}$
Ans: The given number is $\left( 3+\sqrt{3} \right)\left( 2+\sqrt{2} \right)$.
By calculating the multiplication, it can be written as
$\left( 3+\sqrt{3} \right)\left( 2+\sqrt{2} \right)=3\left( 2+\sqrt{2} \right)+\sqrt{3}\left( 2+\sqrt{2} \right)$.
\[= 6 + 4 \sqrt{2} + 2 \sqrt{3}+ \sqrt{6}\]
(ii) $\mathbf{\left( {3+}\sqrt{ {3}} \right)\left( {3-}\sqrt{ {3}} \right)}$
Ans: The given number is $\left( 3+\sqrt{3} \right)\left( 3-\sqrt{3} \right)$.
By applying the formula $\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}$, the number can be written as
$\left( 3+\sqrt{3} \right)\left( 3-\sqrt{3} \right)={{3}^{2}}-{{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}}=9-3=6$.
(iii) $\mathbf{{{\left( \sqrt{ {5}} {+}\sqrt{ {2}} \right)}^{ {2}}}}$
Ans: The given number is ${{\left( \sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}$.
Applying the formula ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2+}}2ab+{{b}^{2}}$, the number can be written as
${{\left( \sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}+2\sqrt{5}\sqrt{2}+{{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}$
$=5+2\sqrt{10}+2$
$=7+2\sqrt{10}$.
(iv) $\mathbf{\left( \sqrt{ {5}}-\sqrt{ {2}} \right)\left( \sqrt{ {5}} {+}\sqrt{ {2}} \right)}$
Ans: The given number is $\left( \sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2} \right)\left( \sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2} \right)$.
Applying the formula $\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}$, the number can be expressed as
$\left( \sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2} \right)\left( \sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2} \right)={{\left( \sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}$
$ =3. $
3. Recall that, $ {\pi }$ is defined as the ratio of the circumference (say $ {c}$) of a circle to its diameter (say $ {d}$). That is, $ {\pi =}\dfrac{ {c}}{ {d}}$ .This seems to contradict the fact that $ {\pi }$ is irrational. How will you resolve this contradiction?
Ans: It is known that, $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$, which is a rational number. But, note that this value of $\pi $ is an approximation.
On dividing $22$ by $7$, the quotient $3.14...$ is a non-recurring and non-terminating number. Therefore, it is an irrational number.
In order of increasing accuracy, approximate fractions are
$\dfrac{22}{7}$, $\dfrac{333}{106}$, $\dfrac{355}{113}$, $\dfrac{52163}{16604}$, $\dfrac{103993}{33102}$, and \[\dfrac{245850922}{78256779}\].
Each of the above quotients has the value $3.14...$, which is a non-recurring and non-terminating number.
Thus, $\pi $ is irrational.
So, either circumference $\left( c \right)$ or diameter $\left( d \right)$ or both should be irrational numbers.
Hence, it is concluded that there is no contradiction regarding the value of $\pi $ and it is made out that the value of $\pi $ is irrational.
4. Represent $\sqrt{ {9} {.3}}$ on the number line.
Ans: Follow the procedure given below to represent the number $\sqrt{9.3}$.
First, mark the distance $9.3$ units from a fixed-point $A$ on the number line to get a point $B$. Then $AB=9.3$ units.
Secondly, from the point $B$ mark a distance of $1$ unit and denote the ending point as $C$.
Thirdly, locate the midpoint of $AC$ and denote it as $O$.
Fourthly, draw a semi-circle to the centre $O$ with the radius $OC=5.15$ units. Then
$ AC=AB+BC $
$ =9.3+1 $
$ =10.3 $
So, $OC=\dfrac{AC}{2}=\dfrac{10.3}{2}=5.15$.
Finally, draw a perpendicular line at $B$ and draw an arc to the centre $B$ and then let it meet at the semicircle $AC$ at $D$ as given in the diagram below.
5. Rationalize the denominators of the following:
(i) $\mathbf{\dfrac{ {1}}{\sqrt{ {7}}}}$
Ans: The given number is $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{7}}$.
Multiplying and dividing by $\sqrt{7}$ to the number gives
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{7}}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{\sqrt{7}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{7}$.
(ii) $\mathbf{\dfrac{ {1}}{\sqrt{ {7}} {-}\sqrt{ {6}}}}$
Ans: The given number is $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{7}-\sqrt{6}}$.
Multiplying and dividing by $\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{6}$ to the number gives
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{7}-\sqrt{6}}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{6}}{\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{6}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{6}}{\left( \sqrt{7}-\sqrt{6} \right)\left( \sqrt{7}+\sqrt{6} \right)}$
Now, applying the formula $\left( a-b \right)\left( a+b \right)={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}$ to the denominator gives
$ \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{7}-\sqrt{6}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{6}}{{{\left( \sqrt{7} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}}} $
$ =\dfrac{\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{6}}{7-6} $
$ =\dfrac{\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{6}}{1}. $
(iii) $\mathbf{\dfrac{ {1}}{\sqrt{ {5}} {+}\sqrt{ {2}}}}$
Ans: The given number is $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}}$.
Multiplying and dividing by $\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2}$ to the number gives
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2}}{\left( \sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2} \right)\left( \sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2} \right)}$
Now, applying the formula $\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}$ to the denominator gives
$ \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2}}{{{\left( \sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}} $
$ =\dfrac{\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2}}{5-2} $
$ =\dfrac{\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2}}{3}. $
(iv) $\mathbf{\dfrac{ {1}}{\sqrt{ {7}} {-2}}}$
Ans: The given number is $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{7}-2}$.
Multiplying and dividing by $\sqrt{7}+2$ to the number gives
$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{7}-2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}+2}{\left( \sqrt{7}-2 \right)\left( \sqrt{7}+2 \right)}\\$.
Now, applying the formula $\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}$ to the denominator gives
$ \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{7}-2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}+2}{{{\left( \sqrt{7} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}} $
$ =\dfrac{\sqrt{7}+2}{7-4} $
$ =\dfrac{\sqrt{7}+2}{3}. $
Exercise (1.6)
1. Compute the value of each of the following expressions:
(i) $\mathbf{ {6}{{ {4}}^{\dfrac{ {1}}{ {2}}}}}$
Ans: The given number is \[{{64}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\].
By the laws of indices,
${{a}^{\dfrac{m}{n}}}=\sqrt[n]{{{a}^{m}}}$, where$a>0$.
$ {{64}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}=\sqrt[2]{64} $
$ =\sqrt[2]{8\times \text{8}} $
$ =8. $
Hence, the value of ${{64}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}$ is $8$.
(ii) $ \mathbf{{3}{{ {2}}^{\dfrac{ {1}}{ {5}}}}}$
Ans: The given number is ${{32}^{\dfrac{1}{5}}}$.
${{a}^{\dfrac{m}{n}}}=\sqrt[m]{{{a}^{m}}}$, where $a>0$
$ {{32}^{\dfrac{1}{5}}}=\sqrt[5]{32}$
$ =\sqrt[5]{2\times 2\times 2\times 2\times 2} $
$ =\sqrt[5]{{{2}^{5}}} $
Alternative Method:
By the law of indices ${{\left( {{a}^{m}} \right)}^{n}}={{a}^{mn}}$, then it gives
$ {{32}^{\dfrac{1}{5}}}={{(2\times 2\times 2\times 2\times 2)}^{\dfrac{1}{5}}}$
$ ={{\left( {{2}^{5}} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{5}}} $
$ ={{2}^{\dfrac{5}{5}}} $
Hence, the value of the expression ${{32}^{\dfrac{1}{5}}}$ is $2$.
(iii) $\mathbf{{12}{{ {5}}^{\dfrac{ {1}}{ {5}}}}}$
Ans: The given number is ${{125}^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}$.
By the laws of indices
${{a}^{\dfrac{m}{n}}}=\sqrt[n]{{{a}^{m}}}$ where$a>0$.
$ {{125}^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}=\sqrt[3]{125} $
$ =\sqrt[3]{5\times 5\times 5} $
$ =5. $
Hence, the value of the expression ${{125}^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}$ is $5$.
2. Compute the value of each of the following expressions:
(i) $\mathbf{{{ {9}}^{\dfrac{ {3}}{ {2}}}}}$
Ans: The given number is ${{9}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}$.
${{a}^{\dfrac{m}{n}}}=\sqrt[n]{{{a}^{m}}}$ where $a>0$.
$ {{9}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}=\sqrt[2]{{{\left( 9 \right)}^{3}}} $
$ =\sqrt[2]{9\times 9\times 9} $
$ =\sqrt[2]{3\times 3\times 3\times 3\times 3\times 3} $
$=3\times 3\times 3 $
By the laws of indices, ${{\left( {{a}^{m}} \right)}^{n}}={{a}^{mn}}$, then it gives
$ {{9}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}={{\left( 3\times 3 \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}$
$ ={{\left( {{3}^{2}} \right)}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}} $
$ ={{3}^{2\times \dfrac{3}{2}}} $
$ ={{3}^{3}} $
${{9}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}=27.$
Hence, the value of the expression ${{9}^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}$ is $27$.
(ii) $\mathbf{{3}{{ {2}}^{\dfrac{ {2}}{ {5}}}}}$
Ans: We know that ${{a}^{\dfrac{m}{n}}}=\sqrt[n]{{{a}^{m}}}$ where $a>0$.
We conclude that ${{32}^{\dfrac{2}{5}}}$ can also be written as
$ \sqrt[5]{{{\left( 32 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt[5]{\left( 2\times 2\times 2\times 2\times 2 \right)\times \left( 2\times 2\times 2\times 2\times 2 \right)} $
$ =2\times 2 $
$ =4 $
Therefore, the value of ${{32}^{\dfrac{2}{5}}}$ is $4$.
(iii) $\mathbf{{1}{{ {6}}^{\dfrac{ {3}}{ {4}}}}}$
Ans: The given number is ${{16}^{\dfrac{3}{4}}}$.
By the laws of indices,
${{a}^{\dfrac{m}{n}}}=\sqrt[n]{{{a}^{m}}}$, where $a>0$.
$ {{16}^{\dfrac{3}{4}}}=\sqrt[4]{{{\left( 16 \right)}^{3}}} $
$ =\sqrt[4]{\left( 2\times 2\times 2\times 2 \right)\times \left( 2\times 2\times 2\times 2 \right)\times \left( 2\times 2\times 2\times 2 \right)} $
$ =2\times 2\times 2 $
Hence, the value of the expression ${{16}^{\dfrac{3}{4}}}$ is $8$.
${{({{a}^{m}})}^{n}}={{a}^{mn}}$, where $a>0$.
$ {{16}^{\dfrac{3}{4}}}={{(4\times 4)}^{\dfrac{3}{4}}} $
$ ={{({{4}^{2}})}^{\dfrac{3}{4}}} $
$ ={{(4)}^{2\times \dfrac{3}{4}}} $
$ ={{({{2}^{2}})}^{2\times \dfrac{3}{4}}} $
$ ={{2}^{2\times 2\times \dfrac{3}{4}}} $
$ ={{2}^{3}} $
Hence, the value of the expression is ${{16}^{\dfrac{3}{4}}}=8$.
(iv) $\mathbf{{12}{{ {5}}^{ {-}\dfrac{ {1}}{ {3}}}}}$
Ans: The given number is ${{125}^{-\dfrac{1}{3}}}$.
By the laws of indices, it is known that
${{a}^{-n}}=\dfrac{1}{{{a}^{^{n}}}}$, where $a>0$.
Therefore,
$ {{125}^{-\dfrac{1}{3}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{125}^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}} $
$ ={{\left( \dfrac{1}{125} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} $
$ =\sqrt[3]{\left( \dfrac{1}{125} \right)} $
$ =\sqrt[3]{\left( \dfrac{1}{5}\times \dfrac{1}{5}\times \dfrac{1}{5} \right)} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{5}. $
Hence, the value of the expression ${{125}^{-\dfrac{1}{3}}}$ is $\dfrac{1}{5}$.
3. Simplify and evaluate each of the expressions:
(i)$\mathbf{{{ {2}}^{\dfrac{ {2}}{ {3}}}} {.}{{ {2}}^{\dfrac{ {1}}{ {5}}}}}$
Ans: The given expression is ${{2}^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}{{.2}^{\dfrac{1}{5}}}$.
By the laws of indices, it is known that
${{a}^{m}}\cdot {{a}^{n}}={{a}^{m+n}}$, where $a>0$.
${{2}^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}{{.2}^{\dfrac{1}{5}}}={{(2)}^{\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{1}{5}}}$
$ ={{(2)}^{\dfrac{10+3}{15}}} $
$ ={{2}^{\dfrac{13}{15}}}. $
Hence, the value of the expression ${{2}^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}{{.2}^{\dfrac{1}{5}}}$ is ${{2}^{\dfrac{13}{15}}}$.
(ii) $\mathbf{{{\left( {{ {3}}^{\dfrac{ {1}}{ {3}}}} \right)}^{ {7}}}}$
Ans: The given expression is ${{\left( {{3}^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \right)}^{7}}$.
It is known by the laws of indices that,
${{({{a}^{m}})}^{n}}={{a}^{mn}}$, where $a>0$.
${{\left( {{3}^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \right)}^{7}}={{3}^{\dfrac{7}{3}}}.$
Hence, the value of the expression ${{\left( {{3}^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \right)}^{7}}$is ${{3}^{\dfrac{7}{3}}}$.
(iii) $\dfrac{ {1}{{ {1}}^{\dfrac{ {1}}{ {2}}}}}{ {1}{{ {1}}^{\dfrac{ {1}}{ {4}}}}}$
Ans: The given number is $\dfrac{{{11}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}{{{11}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}}$.
It is known by the Laws of Indices that
$\dfrac{{{a}^{m}}}{{{a}^{n}}}={{a}^{m-n}}$, where $a>0$.
$\dfrac{{{11}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}{{{11}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}}={{11}^{\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4}}} $
$ ={{11}^{\dfrac{2-1}{4}}} $
$ ={{11}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}. $
Hence, the value of the expression $\dfrac{{{11}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}}{{{11}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}}$ is ${{11}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}$.
(iv) $\mathbf{{{ {7}}^{\dfrac{ {1}}{ {2}}}} {.}{{ {8}}^{\dfrac{ {1}}{ {2}}}}}$
Ans: The given expression is ${{7}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\cdot {{8}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}$.
${{a}^{m}}\cdot {{b}^{m}}={{(a\cdot b)}^{m}}$, where $a>0$.
$ {{7}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\cdot {{8}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}={{(7\times 8)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} $ $={{(56)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}. $
Hence, the value of the expression ${{7}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\cdot {{8}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}$ is ${{(56)}^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}$.
You can opt for Chapter 1 - Number System NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths PDF for Upcoming Exams and also You can Find the Solutions of All the Maths Chapters below.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths
Chapter 1 - Number System
Chapter 2 - Polynomials
Chapter 3 - Coordinate Geometry
Chapter 4 - Linear Equations in Two Variables
Chapter 5 - Introductions to Euclids Geometry
Chapter 6 - Lines and Angles
Chapter 7 - Triangles
Chapter 8 - Quadrilaterals
Chapter 9 - Areas of Parallelogram and Triangles
Chapter 10 - Circles
Chapter 11 - Constructions
Chapter 12 - Herons formula
Chapter 13 - Surface area and Volumes
Chapter 14 - Statistics
Chapter 15 - Probability
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 All Exercise
Class 9 maths chapter 1 solutions - free pdf download.
Now that we have given you an idea about how important it is to get a base in maths early on, we shall also acknowledge that math is not the easiest subject in the world for everyone. Sometimes, it can be a thing of nightmares, quite literally when you need to stay up all night trying to understand some or another concept for a maths exam the next day. Here’s where the NCERT solutions for class 9 maths ch 1 come in - they can help you out in such situations where you aren’t being able to understand. These NCERT solutions for class 9 maths (chapter 1 especially) are magical for students who dislike or are weak in maths. They provide all the answers to the questions in the back of every chapter in the book so that a student need not incessantly struggle with the same.
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 - Weightage
Maths comes for a total of 100 marks, out of which 20 marks go from the internal assessment and the rest of the 80 marks come from the written final exam. The following is the breakdown of the syllabus and marks weightage of NCERT class 9 maths.
Maths Class 9
The Following is a Breakdown of the Weightage Marks for the Internal Assessment:
The Following is the Weightage Breakdown for the Final Written Exam:
As mentioned in the table, maths class 9 chapter 1, Number Systems, counts for 8 marks out of the total 80 marks for the written exam.
Benefits of NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1
The NCERT answers for class 9 mathematics chapter 1 are extremely beneficial to students for a variety of reasons. At Vedantu, we strive to make the answers we develop for all students as exact and precise as possible, so that they are usable and beneficial to students. The following are some of the reasons why students should use the class 9 mathematics NCERT answers for chapter 1.
The NCERT solutions by Vedantu are completely free to access - there’s no need to pay for the materials that you need for your studies, and we understand this.
These maths NCERT solutions of class 9 chapter 1 not only help with studying for exams, but they’re also helpful for when students are trying to finish difficult homework questions.
Vedantu’s class 9 maths chapter 1 NCERT solutions are in a PDF format which can be downloaded. This prevents students from unnecessarily wasting time on the internet when the solutions are right there in your files on your PC or even mobile phone or tablet.
The solutions can be printed, and this ensures that screen time for students is reduced.
The solutions have been written by maths teachers who are experienced in the field and, thus, the accuracy of the solutions is ensured.
Key Topics at a Glance
The number system is one of the most important chapters in the Class 9 Mathematics syllabus. The following is a summary of some of the key topics that must be addressed under the number system. We propose that students go through each of these concepts in order to acquire a solid understanding of the entire number system.
The number line
Whole numbers
Natural numbers
Rational numbers
Irrational numbers
Properties of numbers
Divisibility
H.C.F. and L.C.M.
Progressions
Multiplication tables
Squares and square roots
Cubes and cube roots
This concluded the discussion of the NCERT answers for Class 9 Chapter 1. We've seen the answers to every question in Chapter 1's exercises. To ace your exams, download the NCERT answers PDF. We hope we were able to answer your questions.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 - Number Systems
1. What all Comes Under the Purview of NCERT Maths Class 9 Chapter 1 Number Systems?
The subjects covered in NCERT mathematics class 9 chapter 1 Number Systems include a brief introduction to number systems using number lines, defining rational and irrational numbers using fractions, defining real numbers and declaring their decimal expansions. The chapter then returns to the number line to teach pupils how to express real numbers on it. In addition, the chapter teaches pupils how to add, subtract, multiply, and divide real numbers, or how to perform operations on real numbers. The rules of exponents for real numbers are a part of operations and are the final topic in class 9 mathematics chapter 1.
2. What are the Weightage Marks for Mathematics in Class 9?
The total mathematics paper in class 9 is 100 marks, like any other subject. Out of these 100 marks, 20 marks goes from internal assessments (pen and paper tests, multiple assessments, portfolios/project work and lab practicals for 5 marks each), and the remaining 80 marks are from the written test at the end of the school year. Out of these 80 marks, the chapter Number Systems comes for 8 marks, Algebra for 17 marks, Coordinate Geometry for 4 marks, Geometry for 28 marks, Mensuration for 13 marks, and Statistics and Probability for 10 marks. All of these chapters’ respective marks total up to a cumulative 80 marks for the written paper.
3. How many sums are there in the NCERT Class 9 Chapter 1 Number System?
There are six exercises in the NCERT Class 9 Chapter 1 Number System. In the first exercise, Ex-1.1, there are 4 sums and in the second exercise, Ex-1.2, there are 3 sums. These first two exercises deal with the basic concepts of the number system, such as identifying the features of a rational number or an irrational number and locating them on the number line. In the third exercise, Ex-1.3, there are 9 sums, and most of them have sub-questions. The fourth exercise, Ex-1.4, comprises 2 sums, that deal with successive magnification for locating a decimal number on the number line. The fifth exercise, Ex-1.5, consists of 5 sums, on the concept of rationalization. The sixth exercise, Ex-1.6, consists of 3 sums, that have sub-questions. The sums in this exercise will require you to find the various roots of numbers.
4. Why should we download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1?
Students should download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 from Vedantu (vedantu.com) to understand and learn the concepts of the Number System easily. These solutions are available free of cost on Vedantu (vedantu.com). Students must have a solid base of all concepts of Class 9 Maths if they want to score well in their exams. They can download the NCERT Solutions and other study materials such as important questions and revision notes for all subjects of Class 9. You can download these from Vedantu mobile app also.
5. Why are Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 important?
Some students find it difficult to study and score good marks in their Maths exam. They get nervous while preparing for it and goof up in their exams. However, if they utilise the best resources for studying, they can do well. This is why the Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 is important. The answers to all the questions from the back of each chapter are provided for the reference of students.
6. Give an overview of concepts present in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1?
The concepts in the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 include the introduction of number systems, rational and irrational numbers using fractions, defining real numbers, decimal expansions of real numbers, number line, representing real numbers on a number line, addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of real numbers and laws of exponents for real numbers. Chapter 1 of Class 9 Maths has a weightage of 8 marks in the final exam.
7. Do I Need to Practice all Questions Provided in NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Number Systems?
Yes. Students should practice all the questions provided in the NCERT Solutions of the Number Systems chapter of Class 9 Maths, as they have been created with precision and accuracy, by expert faculty, for the students. Students can access them for free and also download them for offline use to reduce their screen time. The solutions are beneficial not only for exams but also for school homework.
8. Where can I get the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1?
Students can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 from NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1. These are available free of cost on Vedantu (vedantu.com). These can be downloaded from the Vedantu app as well. The answers to all the questions from the 6 exercises of Chapter 1 Number Systems are provided in the NCERT Solutions. Students would also learn how to solve one question with different techniques if available. This will help them learn how to structure their answers in their Class 9 Maths exam.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9

- Number System
NCERT curriculum (for CBSE/ICSE) Class 9 - Number System
Unlimited worksheets.
Every time you click the New Worksheet button, you will get a brand new printable PDF worksheet on Number System . You can choose to include answers and step-by-step solutions.
Unlimited Online Practice
Unlimited adaptive online practice on Number System . Practice that feels like play! Get shields, trophies, certificates and scores. Master Number System as you play.

Unlimited Online Tests
Take unlimited online tests on Number System . Get instant scores and step-by-step solutions on submission. Make sure you always get your answers right in Number System .
Contents: Number System
Number System - Questions on Number System
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Bseb 10th result.
- Bihar Board Result 2024
- UP Board Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 - Number System
Here you can find the ncert solutions for cbse class 9maths chapter 1- number system. it includes a detailed explanation of the answers and covers the easiest methods for solving the questions given in the chapter..

In this article, we are providing the NCERT solutions to Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 - Number System. All these solutions are available in PDF format which you may access totally free of cost. Our subject experts have reviewed these NCERT solutions to provide you the error-free content which will make it easy for you to make an effective preparation for the annual exams.
Why you should solve NCERT exercise questions?
Solving the NCERT exercise problems will help you
→ clear all the concepts and formulae you learned in a chapter
→ familiarise with different types of questions that can be asked in exams
→ get enough practice which is the key to success in the Mathematics exam
→ improve your accuracy and speed
So, to get the desired result in exams, it’s very necessary for students to thoroughly solve the questions given at the end of each chapter of the Class 9 Maths NCERT book.
Some of the questions and solutions are as follows:

Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- BSEB Bihar Board 10th Result 2024
- Bihar Board 10th Result 2024
- Bihar Board Matric Result 2024
- biharboardonline.bihar.gov.in Result 2024
- Bihar Board Matric 10th Result 2024
- Bihar Board Result 2024 Class 10
- Bihar Board Result 2024 by Jagran Josh
- Class 10th Result 2024 Bihar Board
- Bihar Board 10th Topper List 2024
Trending Categories
- CBSE Class 9 Subjects
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics
- CBSE Class 9 Study Material
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9
- CBSE Class 9
Latest Education News
IFSCA Assistant Manager Recruitment 2024: Apply Online For Grade A Posts at ifsca.gov.in, Check Eligibility
(Updated) MI vs RR Head to Head in IPL: Check Stats, Records and Results
Doctors protest in South Korea: What could be the reason?
Who Won Yesterday IPL Match: CSK vs DC, Match 13, Check All Details and Latest Points Table
[Current] Orange Cap and Purple Cap Holders in IPL 2024
[Today] IPL 2024 Points Table: Team Rankings and Net Run Rate
RESULT LINK - BSEB 10th Matric Result 2024 OUT: बिहार बोर्ड 10वीं का रिजल्ट bsebmatric.org पर जारी, लड़कियों ने मारी बाजी, देखें Topper List
DDU Result 2024 OUT at ddugu.ac.in; Download UG and PG Semester Marksheet PDF
Instagram Tests New Feature for Co-Watching Videos with Friends
You have incredible observation skills if you can spot 3 differences between the car in garage pictures within 15 seconds.
MSDSU Result 2024 OUT on msdsu.ac.in, Direct Link to Download UG Odd Semester Marksheet
VBSPU Result 2024 OUT on vbspu.ac.in, Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Use Your Hawk Eyes To Spot A Needle In 12 Seconds!
ssc.gov.in Answer Key 2024: यहाँ से डाउनलोड करें एसएससी जीडी कांस्टेबल उत्तर कुंजी पीडीएफ
bsebmatric.org Result 2024 OUT: जारी हुआ बिहार बोर्ड मेट्रिक के नतीजे, अब तक का सबसे बेहतर रहा परिणाम, टॉप-10 में 51 छात्रों ने बनाई जगह
BSEB 10th Result 2024: 10वीं का परिणाम जारी होते ही ये मीम हो रहे वायरल
BSEB 10th Toppers List 2024: शिवांकर कुमार 97.8 फीसदी अंकों के साथ बने टॉपर, देखें टॉप पांच की लिस्ट
Seek and Find Puzzle: Where's the Crescent Moon Hiding in this Easter Extravaganza?
Bihar Board Matric 10th Result 2024 Analysis: जानें कैसा रहा बिहार बोर्ड दसवीं में छात्रों का प्रदर्शन, यहां देखें सभी सटीक आंकड़ें
Bihar Board Result 2024 Class 10 OUT: When, Where, and How to Check BSEB 10th Result Online
Assignment - Number System, Class 9 Math PDF Download
TRUE / FALSE TYPE QUESTION 1. The sum of two rational numbers in rational 2. The sum of two irrational numbers is irrational. 3. The product of two rational numbers is rational. 4. The product of two irrational numbers is irrational. 5. The sum of a rational number and an irrational number is irrational. 6. The product of a non zero rational number and an irrational number is a rational number. 7. Every real number is rational. 8. π is irrational and 22/7 is rational. 9. Every rational number must be a whole number. 10. The number zero is both positive and negative. 11. The sum of two prime numbers is always even. 12. The product of two odd numbers is always odd.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
22. Express the following in the form of p/q.
23. Examine, whether the following numbers are rational or an irrational :
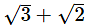
24. Write two irrational numbers between 0.2 and 0.21. 25. Write three irrational numbers between 0.202002000200002.... and 0.203003000300003.... . 26. (i) Write two irrational numbers between 0.21 and 0.2222.... (ii) Find three different irrational numbers between the rational numbers 5/7 and 5/9 27. Write three irrational numbers between √3 and √5 . 28. Find two irrational numbers between 0.5 and 0.55.
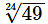
Express as a pure surd :-
Express each of the following as a mixed surd :-
45. Simplify :-
50. Find the rationalising factor of
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
TRUE & FALSE TYPE QUESTIONS 1. True
FILL IN THE BALANKS
13. Real, Rational number, irrational number
14. Terminating, recurring
16. Rational
20. 718/1665
21. Rational, irrational
VERY SHORT ANSWERS
22. (i) 1/3 (ii) 37/99 (iii) 6/11 (iv) 5/99 (v) 4/3 (vi) 23/37 (vii) 311/99 (viii) 9/55 (ix) 49/37 (x)295/9
23. (i) Irrational (ii) Rational (iii) Irrational (iv)Irrational (v) Irrational (vi)Irrational (vii) Rational (viii) Irrational (ix) Irrational (x) Irrational (xi) Irrational
24. 0.2010010001...., 0.2020020002.... 25. 0.20201001000100001...., 0.202020020002..., 0.202030030003.... 26. (i) 0.21010010001.... , 0.21020020002..... (ii) 0.2010010001 ............., 0.2020020002 ..........., 27. 1.8010010001....., 1.9010010001..., 2.010010001...
28. 0.501001.001..., 0.5020020002..... 29. 0.101001000100001, 0.1020020002....
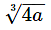
47. 33
Top Courses for Class 9
Faqs on assignment - number system, class 9 math, assignment - number system, semester notes, mock tests for examination, previous year questions with solutions, important questions, practice quizzes, shortcuts and tricks, viva questions, study material, objective type questions, sample paper, class 9 math, past year papers, extra questions, video lectures.

Assignment - Number System, Class 9 Math Free PDF Download
Importance of assignment - number system, class 9 math, assignment - number system, class 9 math notes, assignment - number system, class 9 math class 9 questions, study assignment - number system, class 9 math on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.
Search This Blog
Cbse mathematics.
Basic concepts, definitions and formulas of mathematics, mathematics assignments for 9th standard to 10+2 standard, maths study material for 8th, 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th classes, Mathematics lesson plan for classes 8th,10th and 12th standard, Interesting maths riddles and maths magic, Class-wise mathematics study material for students from 8th to 12. A complete resource centre of mathematics for students and teachers
Featured Posts
Maths assignment class viii | quadrilateral, math assignment class ix ch -1| number system, maths assignment class 9th chapter 1.

MATHEMATICS ASSIGNMENT CLASS IX NUMBER SYSTEM
(a) 1⁸ × 3⁰ × 5³ × 2² Ans; 500,
(b) 4 -3 × 4⁸ ÷ 4² Ans; 64
(d) 3 -4 × 3 -5 ÷ 3¹⁰ Ans; 3 -19
Download complete pdf file

Plese send us solution today is our test
Need solutions toooo
Post a Comment
Breaking news, popular post on this blog, lesson plan maths class 10 | for mathematics teacher.

Lesson Plan Math Class 10 (Ch-1) | Real Numbers

Lesson Plan Maths Class XII | For Maths Teacher

- Assignment 10 15
- Assignment 11 12
- Assignment 12 14
- Assignment 8 8
- Assignment 9 5
- Lesson plan 10 15
- Lesson Plan 12 13
- Lesson Plan 8 10
- Maths 10 20
- Maths 11 21
- Maths 12 17
SUBSCRIBE FOR NEW POSTS
Get new posts by email:.
AssignmentsBag.com
Assignments For Class 9 Mathematics Number System
Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics Number System have been developed for Standard 9 students based on the latest syllabus and textbooks applicable in CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools. Parents and students can download the full collection of class assignments for class 9 Mathematics Number System from our website as we have provided all topic wise assignments free in PDF format which can be downloaded easily. Students are recommended to do these assignments daily by taking printouts and going through the questions and answers for Grade 9 Mathematics Number System. You should try to do these test assignments on a daily basis so that you are able to understand the concepts and details of each chapter in your Mathematics Number System book and get good marks in class 9 exams.
Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics Number System as per CBSE NCERT pattern
All students studying in Grade 9 Mathematics Number System should download the assignments provided here and use them for their daily routine practice. This will help them to get better grades in Mathematics Number System exam for standard 9. We have made sure that all topics given in your textbook for Mathematics Number System which is suggested in Class 9 have been covered ad we have made assignments and test papers for all topics which your teacher has been teaching in your class. All chapter wise assignments have been made by our teachers after full research of each important topic in the textbooks so that you have enough questions and their solutions to help them practice so that they are able to get full practice and understanding of all important topics. Our teachers at https://www.assignmentsbag.com have made sure that all test papers have been designed as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and examination pattern. These question banks have been recommended in various schools and have supported many students to practice and further enhance their scores in school and have also assisted them to appear in other school level tests and examinations. Its easy to take print of thee assignments as all are available in PDF format.
Some advantages of Free Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics Number System
- Solving Assignments for Mathematics Number System Class 9 helps to further enhance understanding of the topics given in your text book which will help you to get better marks
- By solving one assignment given in your class by Mathematics Number System teacher for class 9 will help you to keep in touch with the topic thus reducing dependence on last minute studies
- You will be able to understand the type of questions which are expected in your Mathematics Number System class test
- You will be able to revise all topics given in the ebook for Class 9 Mathematics Number System as all questions have been provided in the question banks
- NCERT Class 9 Mathematics Number System Workbooks will surely help you to make your concepts stronger and better than anyone else in your class.
- Parents will be able to take print out of the assignments and give to their child easily.
All free Printable practice assignments are in PDF single lick download format and have been prepared by Class 9 Mathematics Number System teachers after full study of all topics which have been given in each chapter so that the students are able to take complete benefit from the worksheets. The Chapter wise question bank and revision assignments can be accessed free and anywhere. Go ahead and click on the links above to download free CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Number System Assignments PDF.
Free PDF download of Maths Assignment for Class 9 Number System created by master educators from the latest syllabus of CBSE Boards. By practicing these Maths Assignment for Class 9 Number System pdf will help you to score more marks in your CBSE Board Examinations. We also give free NCERT Solutions and other study materials for students to make their preparation better.
Students who are searching for better solutions can download the Maths Assignment for Class 9 Number System with answers to assist you with revising the whole syllabus and score higher marks in your exam.
Maths Assignment for Class 9 Number System shows up with an answer key with step-by-step answers for students to comprehend the problem at each level and not retain it.
Since you are given all the essential data with respect to CBSE Class 8 Science Worksheet and we trust this definite article is useful. So Students who are planning for the Exam should have to have better-solving skills. What’s more, to have these skills, one should rehearse enough of the science assignment for class 8 pdf. Also, most importantly, students should have to finish the assignments after completing their syllabus. Dealing with the CBSE Science assignment for class 8 pdf will be more helpful to get good marks in the exam. So begin your preparation on Assignment for Class 8 Science to score higher marks

You can download free assignments for class 9 Mathematics Number System from https://www.assignmentsbag.com
You can get free PDF downloadable assignments for Grade 9 Mathematics Number System from our website which has been developed by teachers after doing extensive research in each topic.
On our website we have provided assignments for all subjects in Grade 9, all topic wise test sheets have been provided in a logical manner so that you can scroll through the topics and download the worksheet that you want.
You can easily get question banks, topic wise notes and questions and other useful study material from https://www.assignmentsbag.com without any charge
Yes all test papers for Mathematics Number System Class 9 are available for free, no charge has been put so that the students can benefit from it. And offcourse all is available for download in PDF format and with a single click you can download all assignments.
https://www.assignmentsbag.com is the best portal to download all assignments for all classes without any charges.
Related Posts

Assignments For Class 8 Mathematics Exponents and Powers

Assignments For Class 3 Marathi
Work and energy chapter 11 class 9 science assignments.
- NCERT Exemplar
- Maths Exemplar Class 9
- Number Systems
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 - Number Systems
Ncert exemplar solutions class 9 maths chapter 1 – free pdf download.
NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number System is provided here for students to prepare well for exams. These exemplar problems and solutions are designed by experts in accordance with the CBSE Syllabus for Class 9, which covers the following topics of the Number System:
- Rational numbers and irrational numbers
- Finding rational numbers between two given numbers
- Locating irrational numbers in a number line
- Real numbers and their decimal expansions are terminating or non-terminating, recurring or non-recurring.
- Finding irrational numbers between two given numbers
- Operations performed on real numbers
- Rationalising the denominator
- Laws of exponents for real numbers
To facilitate easy learning and help students understand the concepts discussed in Chapter 1, free NCERT Exemplars are provided here, which can be downloaded in the form of a PDF. Students can use these materials as a reference tool for studying as well as practising sums. The exemplars also contain solved questions relevant to the exercise problems present in the NCERT textbook .
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 – Number Systems

Access Answers to NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number Systems
Exercise 1.1 Page No: 2
Write the correct answer in each of the following:
1. Every rational number is
(A) a natural number
(B) an integer
(C) a real number
(D) a whole number
Explanation:
We know that rational and irrational numbers taken together are known as real numbers. Therefore, every real number is either a rational number or an irrational number. Hence, every rational number is a real number.
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
2. Between two rational numbers
(A) there is no rational number
(B) there is exactly one rational number
(C) there are infinitely many rational numbers
(D) there are only rational numbers and no irrational numbers
Between two rational numbers, there is infinitely many rational numbers.
3. Decimal representation of a rational number cannot be
(A) terminating
(B) non-terminating
(C) non-terminating repeating
(D) non-terminating non-repeating
The decimal representation of a rational number cannot be non-terminating and non-repeating.
Hence, (D) is the correct option.
4. The product of any two irrational numbers is
(A) always an irrational number
(B) always a rational number
(C) always an integer
(D) sometimes rational, sometimes irrational
The product of any two irrational numbers is sometimes rational and sometimes irrational.
5. The decimal expansion of the number √2 is
(A) a finite decimal
(B) 1.41421
(C) non-terminating recurring
(D) non-terminating non-recurring
The decimal expansion of the number √2 = 1.41421356237…
6. Which of the following is irrational?
(A) √4/√9 = 2/3
(B) √12/√3 = 2√3/√3 = 2
(C) √7 = 2.64575131106
(D) √81 = 9
Here, (C) √7 = 2.64575131106 is a non-terminating decimal expansion.
7. Which of the following is irrational?

(D) 0.4014001400014…
A number is irrational if and only if its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-recurring.
(A) is a terminating decimal and, therefore, cannot be an irrational number.
(B) is a non-terminating and recurring decimal and, therefore, cannot be irrational.
(C) is a non-terminating and recurring decimal and, therefore, cannot be irrational.
(D) is a non-terminating and non-recurring decimal and therefore is an irrational number.
8. A rational number between √2 and √3 is
(A) (√2+√3)/2
(B) (√2. √3)/2
√2 =1.4142135…. and √3 =1.732050807….
(A) (√2+√3)/2 = 1.57313218497… is a non-terminating and non-recurring decimal and, therefore, is an irrational number.
(B) (√2. √3)/2 = 1.22474487139… is a non-terminating and non-recurring decimal and, therefore, is an irrational number.
(C) 1.5 is a terminating decimal and, therefore, is a rational number.
(D) 1.8 is a terminating decimal and, therefore, is a rational number.
Here both 1.5 and 1.8 are rational numbers. But, 1.8 does not lie in between √2 =1.4142135…. and √3 =1.732050807…. Whereas 1.5 lies in between √2 =1.4142135…. and √3 =1.732050807….
9. The value of 1.999… in the form p/q , where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0, is
(B) 1999/1000
(A) 19/10 = 1.9
(B) 1999/1000= 1.999
(D) 1/9 = 0.111….
Let x = 1.9999….. — (1)
Multiply equation (1) with 10
10x = 19.9999….. — (2)
Subtract equation (1) from equation(2),
x = 1.9999… = 2
10. 2√3 + √3 is equal to
Taking √3 common,
√3(2+1) = √3(3) = 3√3
Exercise 1.2 Page No: 6
1. Let x and y be rational and irrational numbers, respectively. Is x + y necessarily an irrational number? Give an example in support of your answer.
Yes, if x and y are rational and irrational numbers, respectively, then x+ y is an irrational number.
For example,
Let x = 5 and y = √2.
Then, x+y = 5 + √2 = 5 + 1.414… = 6.414…
Here, 6.414 is a non-terminating and non-recurring decimal and therefore is an irrational number.
Hence, x + y is an irrational number.
2. Let x be rational and y be irrational. Is xy necessarily irrational? Justify your answer with an example.
No, if x is a rational number and y is an irrational number, then xy is not necessarily an irrational number. It can be rational if x = 0, which is a rational number.
For example:
Let y = √2, which is irrational.
Consider x = 2, which is rational.
Then, x × y = 2 × √2 = 2√2, which is irrational.
Consider x = 0, which is rational.
Then xy = 0 × √2 = 0, which is rational.
Therefore, we can conclude that the product of a rational and an irrational number is always irrational, only if the rational number is not zero.
Exercise 1.3 Page No: 9
1. Find which of the variables x, y, z and u represent rational numbers and which irrational numbers:
(i) x 2 = 5
(ii) y 2 = 9 (iii) z 2 = .04
(iv) 𝑢 2 = 17/4
(i) x 2 = 5
On solving, we get
Hence, x is an irrational number.
(ii) y 2 = 9
Hence, y is a rational number.
(iii) z 2 = .04
⇒ z = ± 0.2
Hence, z is a rational number.
(iv) u 2 = 17/4
⇒ u = ± √17/2
√17 is irrational.
Hence, u is an irrational number
2. Find three rational numbers between
(i) –1 and –2
(ii) 0.1 and 0.11 (iii) 5/7 and 6/7
(iv) 1/4 and 1/5
Three rational numbers between –1 and –2 are –1.1, –1.2 and –1.3.
(ii) 0.1 and 0.11
Three rational numbers between 0.1 and 0.11 are 0.101, 0.102 and 0.103.
(iii) 5/7 and 6/7
5/7 can be written as (5 × 10)/(7 × 10) = 50/70
6/7 can be written as (6 × 10)/(7 × 10) = 60/70
Three rational numbers between 5/7 and 6/7 = three rational numbers between 50/70 and 60/70.
Three rational numbers between 5/7 and 6/7 are 51/70, 52/70, 53/70.
Here, according to the question,
LCM of 4 and 5 is 20.
Let us make the denominators common, 80.
(4 × 20) = 80 and (5 × 16) = 80
1/4 can be written as (1 × 20)/(4 × 20) = 20/80
1/5 can be written as (1 × 16)/(5 × 16) = 16/80
Three rational numbers between 1/4 and 1/5 = three rational numbers between 16/80 and 20/80.
Therefore, the three rational numbers are 17/80, 18/80 and 19/80.
3. Insert a rational number and an irrational number between the following:
(i) 2 and 3
(ii) 0 and 0.1 (iii) 1/3 and 1/2
(iv) –2/5 and 1/2 (v) 0.15 and 0.16
(vi) √2 and √3 (vii) 2.357 and 3.121 (viii) .0001 and .001 (ix) 3.623623 and 0.484848 (x) 6.375289 and 6.375738.
So, the rational number between 2 and 3 = 2.5
And, the irrational number between 2 and 3 = 2.040040004…
(ii) 0 and 0.1
So, the rational number between 0 and 0.1 = 0.05
And, irrational number between 0 and 0.1 = 0.007000700007…
(iii) 1/3 and 1/2
LCM of 3 and 2 is 6.
1/3 can be written as (1 × 20)/(3 × 20) = 20/60
1/2 can be written as (1 × 30)/(2 × 30) = 30/60
So, the rational number between 1/3 and 1/2 = 25/60
And, irrational number between 1/3 and 1/2 = irrational number between 0.33 and 0.5 = 0.414114111…
(iv) – 2/5 and 1/2
LCM of 5 and 2 is 10.
-2/5 = -0.4
-2/5 can be written as (-2 × 2)/(5 × 2) = -4/10
1/2 can be written as (1 × 5)/(2 × 5) = 5/10
So, rational number between -2/5 and 1/2 = rational number between -4/10 and 5/10 = 1/10
And, irrational number between -2/5 and 1/2 = irrational number between -0.4 and 0.5 = 0.414114111…
(v) 0.15 and 0.16
The rational number between 0.15 and 0.16 = 0.151
The irrational number between 0.15 and 0.16 = 0.151551555…
(vi) √2 and √3
√2 = 1.41 and √3 = 1.732
Rational number between √2 and √3 = rational number between 1.41 and 1.732 = 1.5
The irrational number between √2 and √3 = irrational number between 1.41 and 1.732 = 1.585585558…
(vii) 2.357 and 3.121
The rational number between 2.357 and 3.121 = 3
The irrational number between 2.357 and 3.121 = 3.101101110…
(viii) .0001 and .001
Rational number between .0001 and .001 = 0.00011
The irrational number between .0001 and .001 = 0.0001131331333…
(ix) 3.623623 and 0.484848
The rational number between 3.623623 and 0.484848 = 1
The irrational number between 3.623623 and 0.484848 = 1.909009000…
(x) 6.375289 and 6.375738.
The rational number between 6.375289 and 6.375738 = 6.3753
The irrational number between 6.375289 and 6.375738 = 6.375414114111…
4. Represent the following numbers on the number line:
7, 7.2, −3/2, −12/5

5. Locate √5, √10 and √17 on the number line.
√5 on the number line:
5 can be written as the sum of the square of two natural numbers:
i.e., 5 =1+ 4 =1 2 + 2 2
On the number line,
Take OA = 2 units.
Perpendicular to OA, draw BA = 1 unit.
Using the Pythagoras theorem,
We have, OB= √5
Draw an arc with centre O and radius OB using a compass such that it intersects the number line at point C.
Then, we get, C corresponds to √5. Or we can say that OC = √5

√10 on the number line:
10 can be written as the sum of the square of two natural numbers:
i.e., 10 =1+ 9 =1 2 + 3 2
Take OA = 3 units.
We have, OB= √10
Then, point C corresponds to √10. Or we can say that OC = √10

√17 on the number line:
17 can be written as the sum of the square of two natural numbers:
i.e., 17 =1+ 16 =1 2 + 4 2
Take OA = 4 units.
We have, OB= √17
Then, point C corresponds to √17. Or, we can say that OC = √17

6. Represent geometrically the following numbers on the number line:
Draw a line segment such that AB = 4.5 units.
Mark C at a distance of 1 unit from B.
Mark O is the mid-point of AC.
Draw a semicircle with centre O and radius OC.
Draw a line perpendicular to AC, passing through B and intersecting the semicircle at D.
Now, BD = √4.5.
Draw an arc with centre B and radius BD, meeting AC produced at E.
Then, BE = BD = √4.5 units.

Draw a line segment such that AB = 5.6 units.
Now, BD = √5.6
Then BE = BD = √5.6 units.

Draw a line segment such that AB = 8.1 units.
Mark O, is the mid-point of AC.
Now, BD = √8.1.
Then BE = BD = √8.1 units.

Draw a line segment such that AB = 2.3 units.
Now, BD = √2.3.
Then BE = BD = √2.3 units.

7. Express the following in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0 :
(ii) 0.888…

(v) 0.2555…

(vii) .00323232…
(viii) .404040…
We know that,
0/2 can be written as,
0.2 = 2/10 = 1/5
Assume that 𝑥 = 0.888 …
⇒ 𝑥 = 0.8 ……………. Eq.(1)
Multiply L.H.S and R.H.S by 10,
10 𝑥 = 8.8 ……………. Eq.(2)
Subtracting equation (1) from (2),
10 𝑥 − 𝑥 = 8.8 − 0.8

Assume that 𝑥 = 5.2 ……………. Eq.(1)
10 𝑥 = 52.2 …………… Eq. (2)
10 𝑥 − 𝑥 = 52.2 − 5.2

Assume that 𝑥 = 0.001 ……………. Eq. (1)
Multiply L.H.S and R.H.S by 1000,
1000 𝑥 = 1.001 …………… Eq. (2)
1000𝑥 − 𝑥 = 1.001 − 0.001
⇒ 𝑥 = 1/999
Assume that 𝑥 = 0.2555 …
⇒ x = 0.25 ……………. Eq. (1)
10 x = 2.5 ……………. Eq. (2)
Multiply L.H.S and R.H.S by 100,
100 x = 25.5 …………. Eq. (3)
Subtracting equation (2) from (3),
100 x-10x = 25.5 – 2.5
⇒ 𝑥 = 23/90

Let 𝑥 = 0.134 ………….…. Eq. (1)
10 𝑥 = 1.34 ………………. Eq. (2)
1000 𝑥 = 134.34 …………. Eq. (3)
1000 𝑥 − 10𝑥 = 134.34 − 1.34
⇒ 990𝑥 = 133
⇒ 𝑥 = 133/990
Let 𝑥 = 0.00323232 …
⇒ x = 0.0032 ………….…. Eq. (1)
100x = 0.32 ……………. Eq. (2)
Multiply L.H.S and R.H.S by 10000,
10000 x = 32.32 …………. Eq. (3)
10000 x-100x = 32.32 – 0.32
⇒ 9900𝑥 = 32
⇒ 𝑥 = 32/9900 = 8/2475
Let 𝑥 = 0.404040 …
⇒ 𝑥 = 0. 40 ………..….…. (1)
100 𝑥 = 40.40 ……….…. (2)
100 𝑥 − 𝑥 = 40.40 − 0.40
⇒ 𝑥 = 40/99
Exercise 1.4 Page No: 12

Let x = 0.6
Multiply by 10 on L.H.S and R.H.S,
So, the p/q form of 0.6 = 3/5
Let y = 0.77777…
10y = 7.7777…
10y – y = 7.7777777……. – 0.7777777…………..
So the p/q form of 0.7777… = 7/9
Let z = 0.47777…
10z = 4.7777…
10z – z = 4.7777777… – 0.47777777…
9z = 4.2999
So the p/q form of 0.4777… = 43/90

x+y+z = 3/5 + 7/9 + 43/90
= (54 + 70 + 43)/90
2. Simplify:

Let us first make the denominators the same,
To make the denominators the same, cross-multiply the first and second terms of the equation.

Now, again make the denominators the same by cross-multiplying the obtained term and the third term of the given equation in the question.

3. If √2 =1.414, √3 =1.732, then find the value of

Let us first make the denominators the same by cross multiplication method

Observing the denominator, we can say that,
Denominators are of the form,
(a + b) × (a – b) = (a 2 – b 2 )
Here a = 3√3
a 2 = (3√3) 2 = 27
b 2 = (2√2) 2 = 8

BYJU’S also provides study resources, such as notes, exemplar books, NCERT Solutions and question papers for students to prepare well and score good marks in their exams. Also, it is recommended to solve sample papers and previous years’ question papers which gives an idea of question types asked in the annual exam from Chapter 1, Number System. Solving the NCERT Exemplar questions will help students to understand the chapter and to practise higher-level questions related to the Number System .
Download BYJU’S – The Learning App and get personalised videos, explaining different types of Maths topics, such as number systems and different types of numbers, etc., and experience a new way of learning to understand the concepts easily.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1
What are the topics covered in chapter 1 of ncert exemplar solutions for class 9 maths, what are rational numbers according to ncert exemplar solutions for class 9 maths chapter 1, how to rationalise the denominator discussed in chapter 1 of ncert exemplar solutions for class 9 maths, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Good work for byjus
very useful solutions
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
We have provided below free printable Class 9 Mathematics Number System Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 9 Mathematics Number System.These Assignments for Grade 9 Mathematics Number System cover all important topics which can come in your standard 9 tests and examinations.Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 9 ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 - Number Systems. As the Number System is one of the important topics in Maths, it has a weightage of 8 marks in Class 9 Maths CBSE exams. On an average three questions are asked from this unit. One out of three questions in part A (1 marks).
The Maths assignment for Class 9 Number System list of questions and answers provide thorough insights on the topic's resources and offers easy tricks to identify quicker ways to solve the questions faster while also being more aware and making sure students don't go wrong or commit any silly mistakes in their solutions.
Below given important Number system questions for 9th class students will help them to get acquainted with a wide variation of questions and thus, develop problem-solving skills. Q.1: Find five rational numbers between 1 and 2. Solution: We have to find five rational numbers between 1 and 2. So, let us write the numbers with denominator 5 + 1 = 6.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1, "Number Systems", consists of six exercises, each covering a specific set of questions. Below is a detailed explanation of each exercise: Exercise 1.1: This exercise covers basic concepts of the number system, such as natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, etc.
Class 9. 12 units · 41 skills. Unit 1. Number systems. Unit 2. Polynomials. Unit 3. ... Math; Class 9; Unit 1: Number systems. 500 possible mastery points. Mastered. Proficient. Familiar. ... Learn. Intro to rational & irrational numbers (Opens a modal) Practice. Number systems 1.1 Get 7 of 10 questions to level up! Number systems 1.2. Learn ...
NCERT Solution for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1: The first chapter of NCERT Class 9th talks about the basic number system segregated into Whole numbers, Rational numbers, Irrational number s and Integers. Various theorems and concepts contributed by eminent mathematicians have been explained in the chapter to describe the theorems' origin.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number Systems Ex 1.5. Ex 1.5 Class 9 Maths Question 1. Classify the following numbers as rational or irrational. Solution: (i) Since, it is a difference of a rational and an irrational number. ∴ 2 - √5 is an irrational number. (ii) 3 + 23−−√ - 23−−√ = 3 + 23−−√ - 23−− ...
Class 9 - Number System problems, online practice, tests, worksheets, quizzes, and teacher assignments. ... Maths; Class 9; Number System; NCERT curriculum (for CBSE/ICSE) Class 9 - Number System. Unlimited Worksheets .
On subtracting equation (1) from (2), we get. ⇒ 99x = 103.2. ⇒ x = 103.2/99 = 1032/990. Which is the required rational number. Step 4: Reduce the obtained rational number to its simplest form. Thus, x = 172/165. Also Access: Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 polynomials Notes. NECRT Solution for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number System.
In this article, we are providing the NCERT solutions to Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 - Number System. All these solutions are available in PDF format which you may access totally free of cost.
Number system for class 9 which is the first chapter has been given here for students to get a reference for the same. Here you will learn about the Number System with its definition and types of numbers. ... Important Questions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number System; Introduction to number system class 9. The collection of numbers is called the ...
The "Assignment - Number System, Class 9 Math Class 9 Questions" guide is a valuable resource for all aspiring students preparing for the Class 9 exam. It focuses on providing a wide range of practice questions to help students gauge their understanding of the exam topics. These questions cover the entire syllabus, ensuring comprehensive ...
Basic concepts, definitions and formulas of mathematics, mathematics assignments for 9th standard to 10+2 standard, maths study material for 8th, 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th classes, Mathematics lesson plan for classes 8th,10th and 12th standard, Interesting maths riddles and maths magic, Class-wise mathematics study material for students from 8th to 12.
Maths Assignment Class 9th Chapter 1. Math Assignment for Class IX Ch -1, Number System strictly according to the CBSE syllabus. Extra questions based on the topic Number System. MATHEMATICS ASSIGNMENT CLASS IX. NUMBER SYSTEM. Q1- Insert 5 rational and 5 irrational numbers between. (a) 7 & 8, (b) 2 & 3.2, (c) 2.7 & 6.32,
Maths Assignment for Class 9 Number System shows up with an answer key with step-by-step answers for students to comprehend the problem at each level and not retain it. Since you are given all the essential data with respect to CBSE Class 8 Science Worksheet and we trust this definite article is useful. So Students who are planning for the Exam ...
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 - Free PDF Download. NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number System is provided here for students to prepare well for exams. These exemplar problems and solutions are designed by experts in accordance with the CBSE Syllabus for Class 9, which covers the following topics of the Number System: