Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education

Parenting & Family Articles & More
How teens today are different from past generations, a psychologist mines big data on teens and finds many ways this generation—the “igens"—is different from boomers, gen xers, and millennials..
Every generation of teens is shaped by the social, political, and economic events of the day. Today’s teenagers are no different—and they’re the first generation whose lives are saturated by mobile technology and social media.
In her new book, psychologist Jean Twenge uses large-scale surveys to draw a detailed portrait of ten qualities that make today’s teens unique and the cultural forces shaping them. Her findings are by turn alarming, informative, surprising, and insightful, making the book— iGen:Why Today’s Super-Connected Kids Are Growing Up Less Rebellious, More Tolerant, Less Happy—and Completely Unprepared for Adulthood—and What That Means for the Rest of Us —an important read for anyone interested in teens’ lives.
Who are the iGens?

Twenge names the generation born between 1995 and 2012 “iGens” for their ubiquitous use of the iPhone, their valuing of individualism, their economic context of income inequality, their inclusiveness, and more.
She identifies their unique qualities by analyzing four nationally representative surveys of 11 million teens since the 1960s. Those surveys, which have asked the same questions (and some new ones) of teens year after year, allow comparisons among Boomers, Gen Xers, Millennials, and iGens at exactly the same ages. In addition to identifying cross-generational trends in these surveys, Twenge tests her inferences against her own follow-up surveys, interviews with teens, and findings from smaller experimental studies. Here are just a few of her conclusions.
iGens have poorer emotional health thanks to new media. Twenge finds that new media is making teens more lonely, anxious, and depressed, and is undermining their social skills and even their sleep.
iGens “grew up with cell phones, had an Instagram page before they started high school, and do not remember a time before the Internet,” writes Twenge. They spend five to six hours a day texting, chatting, gaming, web surfing, streaming and sharing videos, and hanging out online. While other observers have equivocated about the impact, Twenge is clear: More than two hours a day raises the risk for serious mental health problems.
She draws these conclusions by showing how the national rise in teen mental health problems mirrors the market penetration of iPhones—both take an upswing around 2012. This is correlational data, but competing explanations like rising academic pressure or the Great Recession don’t seem to explain teens’ mental health issues. And experimental studies suggest that when teens give up Facebook for a period or spend time in nature without their phones, for example, they become happier.
The mental health consequences are especially acute for younger teens, she writes. This makes sense developmentally, since the onset of puberty triggers a cascade of changes in the brain that make teens more emotional and more sensitive to their social world.
Social media use, Twenge explains, means teens are spending less time with their friends in person. At the same time, online content creates unrealistic expectations (about happiness, body image, and more) and more opportunities for feeling left out—which scientists now know has similar effects as physical pain . Girls may be especially vulnerable, since they use social media more, report feeling left out more often than boys, and report twice the rate of cyberbullying as boys do.
Social media is creating an “epidemic of anguish,” Twenge says.
iGens grow up more slowly. iGens also appear more reluctant to grow up. They are more likely than previous generations to hang out with their parents, postpone sex, and decline driver’s licenses.
More on Teens
Discover five ways parents can help prevent teen depression .
Learn how the adolescent brain transforms relationships .
Understand the purpose of the teenage brain .
Explore how to help teens find purpose .
Twenge floats a fascinating hypothesis to explain this—one that is well-known in social science but seldom discussed outside academia. Life history theory argues that how fast teens grow up depends on their perceptions of their environment: When the environment is perceived as hostile and competitive, teens take a “fast life strategy,” growing up quickly, making larger families earlier, and focusing on survival. A “slow life strategy,” in contrast, occurs in safer environments and allows a greater investment in fewer children—more time for preschool soccer and kindergarten violin lessons.
“Youths of every racial group, region, and class are growing up more slowly,” says Twenge—a phenomenon she neither champions nor judges. However, employers and college administrators have complained about today’s teens’ lack of preparation for adulthood. In her popular book, How to Raise an Adult , Julie Lythcott-Haims writes that students entering college have been over-parented and as a result are timid about exploration, afraid to make mistakes, and unable to advocate for themselves.
Twenge suggests that the reality is more complicated. Today’s teens are legitimately closer to their parents than previous generations, but their life course has also been shaped by income inequality that demoralizes their hopes for the future. Compared to previous generations, iGens believe they have less control over how their lives turn out. Instead, they think that the system is already rigged against them—a dispiriting finding about a segment of the lifespan that is designed for creatively reimagining the future .
iGens exhibit more care for others. iGens, more than other generations, are respectful and inclusive of diversity of many kinds. Yet as a result, they reject offensive speech more than any earlier generation, and they are derided for their “fragility” and need for “ trigger warnings ” and “safe spaces.” (Trigger warnings are notifications that material to be covered may be distressing to some. A safe space is a zone that is absent of triggering rhetoric.)
Today’s colleges are tied in knots trying to reconcile their students’ increasing care for others with the importance of having open dialogue about difficult subjects. Dis-invitations to campus speakers are at an all-time high, more students believe the First Amendment is “outdated,” and some faculty have been fired for discussing race in their classrooms. Comedians are steering clear of college campuses, Twenge reports, afraid to offend.
The future of teen well-being
Social scientists will discuss Twenge’s data and conclusions for some time to come, and there is so much information—much of it correlational—there is bound to be a dropped stitch somewhere. For example, life history theory is a useful macro explanation for teens’ slow growth, but I wonder how income inequality or rising rates of insecure attachments among teens and their parents are contributing to this phenomenon. And Twenge claims that childhood has lengthened, but that runs counter to data showing earlier onset of puberty.
So what can we take away from Twenge’s thoughtful macro-analysis? The implicit lesson for parents is that we need more nuanced parenting. We can be close to our children and still foster self-reliance. We can allow some screen time for our teens and make sure the priority is still on in-person relationships. We can teach empathy and respect but also how to engage in hard discussions with people who disagree with us. We should not shirk from teaching skills for adulthood, or we risk raising unprepared children. And we can—and must—teach teens that marketing of new media is always to the benefit of the seller, not necessarily the buyer.
Yet it’s not all about parenting. The cross-generational analysis that Twenge offers is an important reminder that lives are shaped by historical shifts in culture, economy, and technology. Therefore, if we as a society truly care about human outcomes, we must carefully nurture the conditions in which the next generation can flourish.
We can’t market technologies that capture dopamine, hijack attention, and tether people to a screen, and then wonder why they are lonely and hurting. We can’t promote social movements that improve empathy, respect, and kindness toward others and then become frustrated that our kids are so sensitive. We can’t vote for politicians who stall upward mobility and then wonder why teens are not motivated. Society challenges teens and parents to improve; but can society take on the tough responsibility of making decisions with teens’ well-being in mind?
The good news is that iGens are less entitled, narcissistic, and over-confident than earlier generations, and they are ready to work hard. They are inclusive and concerned about social justice. And they are increasingly more diverse and less partisan, which means they may eventually insist on more cooperative, more just, and more egalitarian systems.
Social media will likely play a role in that revolution—if it doesn’t sink our kids with anxiety and depression first.
About the Author

Diana Divecha
Diana Divecha, Ph.D. , is a developmental psychologist, an assistant clinical professor at the Yale Child Study Center and Yale Center for Emotional Intelligence, and on the advisory board of the Greater Good Science Center. Her blog is developmentalscience.com .
You May Also Enjoy

This article — and everything on this site — is funded by readers like you.
Become a subscribing member today. Help us continue to bring “the science of a meaningful life” to you and to millions around the globe.
Find anything you save across the site in your account
It’s Time to Stop Talking About “Generations”
By Louis Menand
The discovery that you can make money marketing merchandise to teen-agers dates from the early nineteen-forties, which is also when the term “youth culture” first appeared in print. There was a reason that those things happened when they did: high school. Back in 1910, most young people worked; only fourteen per cent of fourteen- to seventeen-year-olds were still in school. In 1940, though, that proportion was seventy-three per cent. A social space had opened up between dependency and adulthood, and a new demographic was born: “youth.”
The rate of high-school attendance kept growing. By 1955, eighty-four per cent of high-school-age Americans were in school. (The figure for Western Europe was sixteen per cent.) Then, between 1956 and 1969, college enrollment in the United States more than doubled, and “youth” grew from a four-year demographic to an eight-year one. By 1969, it made sense that everyone was talking about the styles and values and tastes of young people: almost half the population was under twenty-five.
Today, a little less than a third of the population is under twenty-five, but youth remains a big consumer base for social-media platforms, streaming services, computer games, music, fashion, smartphones, apps, and all kinds of other goods, from motorized skateboards to eco-friendly water bottles. To keep this market churning, and to give the consulting industry something to sell to firms trying to understand (i.e., increase the productivity of) their younger workers, we have invented a concept that allows “youth culture” to be redefined periodically. This is the concept of the generation.
The term is borrowed from human reproductive biology. In a kinship structure, parents and their siblings constitute “the older generation”; offspring and their cousins are “the younger generation.” The time it takes, in our species, for the younger generation to become the older generation is traditionally said to be around thirty years. (For the fruit fly, it’s ten days.) That is how the term is used in the Hebrew Bible, and Herodotus said that a century could be thought of as the equivalent of three generations.
Around 1800, the term got transplanted from the family to society. The new idea was that people born within a given period, usually thirty years, belong to a single generation. There is no sound basis in biology or anything else for this claim, but it gave European scientists and intellectuals a way to make sense of something they were obsessed with, social and cultural change. What causes change? Can we predict it? Can we prevent it? Maybe the reason societies change is that people change, every thirty years.
Before 1945, most people who theorized about generations were talking about literary and artistic styles and intellectual trends—a shift from Romanticism to realism, for example, or from liberalism to conservatism. The sociologist Karl Mannheim, in an influential essay published in 1928, used the term “generation units” to refer to writers, artists, and political figures who self-consciously adopt new ways of doing things. Mannheim was not interested in trends within the broader population. He assumed that the culture of what he called “peasant communities” does not change.
Nineteenth-century generational theory took two forms. For some thinkers, generational change was the cause of social and historical change. New generations bring to the world new ways of thinking and doing, and weed out beliefs and practices that have grown obsolete. This keeps society rejuvenated. Generations are the pulse of history. Other writers thought that generations were different from one another because their members carried the imprint of the historical events they lived through. The reason we have generations is that we have change, not the other way around.
There are traces of both the pulse hypothesis and the imprint hypothesis in the way we talk about generations today. We tend to assume that there is a rhythm to social and cultural history that maps onto generational cohorts, such that each cohort is shaped by, or bears the imprint of, major historical events—Vietnam, 9/11, COVID . But we also think that young people develop their own culture, their own tastes and values, and that this new culture displaces the culture of the generation that preceded theirs.
Today, the time span of a generational cohort is usually taken to be around fifteen years (even though the median age of first-time mothers in the U.S. is now twenty-six and of first-time fathers thirty-one). People born within that period are supposed to carry a basket of characteristics that differentiate them from people born earlier or later.
This supposition requires leaps of faith. For one thing, there is no empirical basis for claiming that differences within a generation are smaller than differences between generations. (Do you have less in common with your parents than with people you have never met who happen to have been born a few years before or after you?) The theory also seems to require that a person born in 1965, the first year of Generation X, must have different values, tastes, and life experiences from a person born in 1964, the last year of the baby-boom generation (1946-64). And that someone born in the last birth year of Gen X, 1980, has more in common with someone born in 1965 or 1970 than with someone born in 1981 or 1990.
Everyone realizes that precision dating of this kind is silly, but although we know that chronological boundaries can blur a bit, we still imagine generational differences to be bright-line distinctions. People talk as though there were a unique DNA for Gen X—what in the nineteenth century was called a generational “entelechy”—even though the difference between a baby boomer and a Gen X-er is about as meaningful as the difference between a Leo and a Virgo.
You could say the same things about decades, of course. A year is, like a biological generation, a measurable thing, the time it takes the Earth to orbit the sun. But there is nothing in nature that corresponds to a decade—or a century, or a millennium. Those are terms of convenience, determined by the fact that we have ten fingers.
Yet we happily generalize about “the fifties” and “the sixties” as having dramatically distinct, well, entelechies. Decade-thinking is deeply embedded. For most of us, “She’s a seventies person” carries a lot more specific information than “She’s Gen X.” By this light, generations are just a novel way of slicing up the space-time continuum, no more arbitrary, and possibly a little less, than decades and centuries. The question, therefore, is not “Are generations real?” The question is “Are they a helpful way to understand anything?”
Bobby Duffy, the author of “The Generation Myth” (Basic), says yes, but they’re not as helpful as people think. Duffy is a social scientist at King’s College London. His argument is that generations are just one of three factors that explain changes in attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors. The others are historical events and “life-cycle effects,” that is, how people change as they age. His book illustrates, with a somewhat overwhelming array of graphs and statistics, how events and aging interact with birth cohort to explain differences in racial attitudes, happiness, suicide rates, political affiliations—you name it, for he thinks that his three factors explain everything.

Link copied
Duffy’s over-all finding is that people in different age groups are much more alike than all the talk about generations suggests, and one reason for all that talk, he thinks, is the consulting industry. He says that, in 2015, American firms spent some seventy million dollars on generational consulting (which doesn’t seem that much, actually). “What generational differences exist in the workplace?” he asks. His answer: “Virtually none.”
Duffy is good at using data to take apart many familiar generational characterizations. There is no evidence, he says, of a “loneliness epidemic” among young people, or of a rise in the rate of suicide. The falling off in sexual activity in the United States and the U.K. is population-wide, not just among the young.
He says that attitudes about gender in the United States correlate more closely with political party than with age, and that, in Europe, anyway, there are no big age divides in the recognition of climate change. There is “just about no evidence,” he says, that Generation Z (1997-2012, encompassing today’s college students) is more ethically motivated than other generations. When it comes to consumer boycotts and the like, “ ‘cancel culture’ seems to be more of a middle-age thing.” He worries that generational stereotypes—such as the characterization of Gen Z-ers as woke snowflakes—are promoted in order to fuel the culture wars.
The woke-snowflake stereotype is the target of “Gen Z, Explained” (Chicago), a heartfelt defense of the values and beliefs of contemporary college students. The book has four authors, Roberta Katz, Sarah Ogilvie, Jane Shaw, and Linda Woodhead—an anthropologist, a linguist, a historian, and a sociologist—and presents itself as a social-scientific study, including a “methodological appendix.” But it resembles what might be called journalistic ethnography: the portrayal of social types by means of interviews and anecdotes.
The authors adopt a key tenet of the pulse hypothesis. They see Gen Z-ers as agents of change, a generation that has created a youth culture that can transform society. (The fact that when they finished researching their book, in 2019, roughly half of Gen Z was under sixteen does not trouble them, just as the fact that at the time of Woodstock, in 1969, more than half the baby-boom generation was under thirteen doesn’t prevent people from making generalizations about the baby boomers.)
Their book is based on hour-long interviews with a hundred and twenty students at three colleges, two in California (Stanford and Foothill College, a well-regarded community college) and one in the U.K. (Lancaster, a selective research university). The authors inform us that the interviewees were chosen “by word of mouth and personal networking,” which sounds a lot like self-selection. It is, in any event (as they unapologetically acknowledge), hardly a randomized sample.
The authors tell us that the interviews were conducted entirely by student research assistants, which means that, unless the research assistants simply read questions off a list, there was no control over the depth or the direction of the interviews. There were also some focus groups, in which students talked about their lives with, mostly, their friends, an exercise performed in an echo chamber. Journalists, or popular ethnographers, would at least have met and observed their subjects. It’s mystifying why the authors felt a need to distance themselves in this way, given how selective their sample was to begin with. We are left with quotations detached from context. Self-reporting is taken at face value.
The authors supplemented the student interviews with a lexical glossary designed to pick out words and memes heavily used by young people, and with two surveys, designed by one of the authors (Woodhead) and conducted by YouGov, an Internet polling company, of eighteen- to twenty-five-year-olds in the United States and the U.K.
Where there is an awkward discrepancy between the survey results and what the college students say in the interviews, the authors attempt to explain it away. The YouGov surveys found that ninety-one per cent of all persons aged eighteen to twenty-five, American and British, identify as male or female, and only four per cent as gender fluid or nonbinary. (Five per cent declined to answer.) This does not match the impression created by the interviews, which suggest that there should be many more fluid and nonbinary young people out there, so the authors say that we don’t really know what the survey respondents meant by “male” and “female.” Well, then, maybe they should have been asked.
The authors attribute none of the characteristics they identify as Gen Z to the imprint of historical events—with a single exception: the rise of the World Wide Web. Gen Z is the first “born digital” generation. This fact has often been used to stereotype young people as screen-time addicts, captives of their smartphones, obsessed with how they appear on social media, and so on. The Internet is their “culture.” They are trapped in the Web. The authors of “Gen Z, Explained” emphatically reject this line of critique. They assure us that Gen Z-ers “understand both the potential and the downside of technology” and possess “critical awareness about the technology that shapes their lives.”
For the college students who were interviewed (although not, evidently, for the people who were surveyed), a big part of Gen Z culture revolves around identity. As the authors put it, “self-labeling has become an imperative that is impossible to escape.” This might seem to suggest a certain degree of self-absorption, but the authors assure us that these young people “are self-identified and self-reliant but markedly not self-centered, egotistical, or selfish.”
“Lily” is offered to illustrate the ethical richness of this new concern. It seems that Lily has a friend who is always late to meet with her: “She explained that while she of course wanted to honor and respect his unique identity, choices, and lifestyle—including his habitual tardiness—she was also frustrated by how that conflicted with her sense that he was then not respecting her identity and preference for timeliness.” The authors do not find this amusing.
The book’s big claim is that Gen Z-ers “may well be the heralds of new attitudes and expectations about how individuals and institutions can change for the better.” They have come up with new ways of working (collaborative), new forms of identity (fluid and intersectional), new concepts of community (diverse, inclusive, non-hierarchical).
Methodology aside, there is much that is refreshing here. There is no reason to assume that younger people are more likely to be passive victims of technology than older people (that assumption is classic old person’s bias), and it makes sense that, having grown up doing everything on a computer, Gen Z-ers have a fuller understanding of the digital universe than analog dinosaurs do. The dinosaurs can say, “You don’t know what you’re missing,” but Gen Z-ers can say, “You don’t understand what you’re getting.”
The claim that addiction to their devices is the cause of a rise in mental disorders among teen-agers is a lot like the old complaint that listening to rock and roll turns kids into animals. The authors cite a recent study (not their own) that concludes that the association between poor mental health and eating potatoes is greater than the association with technology use. We’re all in our own fishbowls. We should hesitate before we pass judgment on what life is like in the fishbowls of others.
The major problem with “Gen Z, Explained” is not so much the authors’ fawning tone, or their admiration for the students’ concerns—“environmental degradation, equality, violence, and injustice”—even though they are the same concerns that almost everyone in their social class has, regardless of age. The problem is the “heralds of a new dawn” stuff.
“A crisis looms for all unless we can find ways to change,” they warn. “Gen Zers have ideas of the type of world they would like to bring into being. By listening carefully to what they are saying, we can appreciate the lessons they have to teach us: be real, know who you are, be responsible for your own well-being, support your friends, open up institutions to the talents of the many, not the few, embrace diversity, make the world kinder, live by your values.”
I believe we have been here before, Captain. Fifty-one years ago, The New Yorker ran a thirty-nine-thousand-word piece that began:
There is a revolution under way . . . It is now spreading with amazing rapidity, and already our laws, institutions, and social structure are changing in consequence. Its ultimate creation could be a higher reason, a more human community, and a new and liberated individual. This is the revolution of the new generation.
The author was a forty-two-year-old Yale Law School professor named Charles Reich, and the piece was an excerpt from his book “The Greening of America,” which, when it came out, later that year, went to No. 1 on the Times best-seller list.
Reich had been in San Francisco in 1967, during the so-called Summer of Love, and was amazed and excited by the flower-power wing of the counterculture—the bell-bottom pants (about which he waxes ecstatic in the book), the marijuana and the psychedelic drugs, the music, the peace-and-love life style, everything.
He became convinced that the only way to cure the ills of American life was to follow the young people. “The new generation has shown the way to the one method of change that will work in today’s post-industrial society: revolution by consciousness,” he wrote. “This means a new way of living, almost a new man. This is what the new generation has been searching for, and what it has started to achieve.”
So how did that work out? The trouble, of course, was that Reich was basing his observations and predictions on, to use Mannheim’s term, a generation unit—a tiny number of people who were hyperconscious of their choices and values and saw themselves as being in revolt against the bad thinking and failed practices of previous generations. The folks who showed up for the Summer of Love were not a representative sample of sixties youth.
Most young people in the sixties did not practice free love, take drugs, or protest the war in Vietnam. In a poll taken in 1967, when people were asked whether couples should wait to have sex until they were married, sixty-three per cent of those in their twenties said yes, virtually the same as in the general population. In 1969, when people aged twenty-one to twenty-nine were asked whether they had ever used marijuana, eighty-eight per cent said no. When the same group was asked whether the United States should withdraw immediately from Vietnam, three-quarters said no, about the same as in the general population.
Most young people in the sixties were not even notably liberal. When people who attended college from 1966 to 1968 were asked which candidate they preferred in the 1968 Presidential election, fifty-three per cent said Richard Nixon or George Wallace. Among those who attended college from 1962 to 1965, fifty-seven per cent preferred Nixon or Wallace, which matched the results in the general election.
The authors of “Gen Z, Explained” are making the same erroneous extrapolation. They are generalizing on the basis of a very small group of privileged people, born within five or six years of one another, who inhabit insular communities of the like-minded. It’s fine to try to find out what these people think. Just don’t call them a generation.
Most of the millions of Gen Z-ers may be quite different from the scrupulously ethical, community-minded young people in the book. Duffy cites a survey, conducted in 2019 by a market-research firm, in which people were asked to name the characteristics of baby boomers, Gen X-ers, millennials (1981-96), and Gen Z-ers. The top five characteristics assigned to Gen Z were: tech-savvy, materialistic, selfish, lazy, and arrogant. The lowest-ranked characteristic was ethical. When Gen Z-ers were asked to describe their own generation, they came up with an almost identical list. Most people born after 1996 apparently don’t think quite as well of themselves as the college students in “Gen Z, Explained” do.
In any case, “explaining” people by asking them what they think and then repeating their answers is not sociology. Contemporary college students did not invent new ways of thinking about identity and community. Those were already rooted in the institutional culture of higher education. From Day One, college students are instructed about the importance of diversity, inclusion, honesty, collaboration—all the virtuous things that the authors of “Gen Z, Explained” attribute to the new generation. Students can say (and some do say) to their teachers and their institutions, “You’re not living up to those values.” But the values are shared values.
And they were in place long before Gen Z entered college. Take “intersectionality,” which the students in “Gen Z, Explained” use as a way of refining traditional categories of identity. That term has been around for more than thirty years. It was coined (as the authors note) in 1989, by the law professor Kimberlé Crenshaw. And Crenshaw was born in 1959. She’s a boomer.
“Diversity,” as an institutional priority, dates back even farther. It played a prominent role in the affirmative-action case of Regents of the University of California v. Bakke, in 1978, which opened the constitutional door to race-conscious admissions. That was three “generations” ago. Since then, almost every selective college has worked to achieve a diverse student body and boasts about it when it succeeds. College students think of themselves and their peers in terms of identity because of how the institution thinks of them.
People who went to college in an earlier era may find this emphasis a distraction from students’ education. Why should they be constantly forced to think about their own demographic profiles and their differences from other students? But look at American politics—look at world politics—over the past five years. Aren’t identity and difference kind of important things to understand?
And who creates “youth culture,” anyway? Older people. Youth has agency in the sense that it can choose to listen to the music or wear the clothing or march in the demonstrations or not. And there are certainly ground-up products (bell-bottoms, actually). Generally, though, youth has the same degree of agency that I have when buying a car. I can choose the model I want, but I do not make the cars.
Failure to recognize the way the fabric is woven leads to skewed social history. The so-called Silent Generation is a particularly outrageous example. That term has come to describe Americans who went to high school and college in the nineteen-fifties, partly because it sets up a convenient contrast to the baby-boom generation that followed. Those boomers, we think—they were not silent! In fact, they mostly were.
The term “Silent Generation” was coined in 1951, in an article in Time —and so was not intended to characterize the decade. “Today’s generation is ready to conform,” the article concluded. Time defined the Silent Generation as people aged eighteen to twenty-eight—that is, those who entered the workforce mostly in the nineteen-forties. Though the birth dates of Time’s Silent Generation were 1923 to 1933, the term somehow migrated to later dates, and it is now used for the generation born between 1928 and 1945.
So who were these silent conformists? Gloria Steinem, Muhammad Ali, Tom Hayden, Abbie Hoffman, Jerry Rubin, Nina Simone, Bob Dylan, Noam Chomsky, Philip Roth, Susan Sontag, Martin Luther King, Jr., Billie Jean King, Jesse Jackson, Joan Baez, Berry Gordy, Amiri Baraka, Ken Kesey, Huey Newton, Jerry Garcia, Janis Joplin, Jimi Hendrix, Andy Warhol . . . Sorry, am I boring you?
It was people like these, along with even older folks, like Timothy Leary, Allen Ginsberg, and Pauli Murray, who were active in the culture and the politics of the nineteen-sixties. Apart from a few musicians, it is hard to name a single major figure in that decade who was a baby boomer. But the boomers, most of whom were too young then even to know what was going on, get the credit (or, just as unfairly, the blame).
Mannheim thought that the great danger in generational analysis was the elision of class as a factor in determining beliefs, attitudes, and experiences. Today, we would add race, gender, immigration status, and any number of other “preconditions.” A woman born to an immigrant family in San Antonio in 1947 had very different life chances from a white man born in San Francisco that year. Yet the baby-boom prototype is a white male college student wearing striped bell-bottoms and a peace button, just as the Gen Z prototype is a female high-school student with spending money and an Instagram account.
For some reason, Duffy, too, adopts the conventional names and dates of the postwar generations (all of which originated in popular culture). He offers no rationale for this, and it slightly obscures one of his best points, which is that the most formative period for many people happens not in their school years but once they leave school and enter the workforce. That is when they confront life-determining economic and social circumstances, and where factors like their race, their gender, and their parents’ wealth make an especially pronounced difference to their chances.
Studies have consistently indicated that people do not become more conservative as they age. As Duffy shows, however, some people find entry into adulthood delayed by economic circumstances. This tends to differentiate their responses to survey questions about things like expectations. Eventually, he says, everyone catches up. In other words, if you are basing your characterization of a generation on what people say when they are young, you are doing astrology. You are ascribing to birth dates what is really the result of changing conditions.
Take the boomers: when those who were born between 1946 and 1952 entered the workforce, the economy was surging. When those who were born between 1953 and 1964 entered it, the economy was a dumpster fire. It took longer for younger boomers to start a career or buy a house. People in that kind of situation are therefore likely to register in surveys as “materialistic.” But it’s not the Zeitgeist that’s making them that way. It’s just the business cycle. ♦
New Yorker Favorites
- How we became infected by chain e-mail .
- Twelve classic movies to watch with your kids.
- The secret lives of fungi .
- The photographer who claimed to capture the ghost of Abraham Lincoln .
- Why are Americans still uncomfortable with atheism ?
- The enduring romance of the night train .
- Sign up for our daily newsletter to receive the best stories from The New Yorker .
Books & Fiction
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Amanda Petrusich

By David Remnick

By Dhruv Khullar

By Kyle Chayka

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Gen Z are not ‘coddled.’ They are highly collaborative, self-reliant and pragmatic, according to new Stanford-affiliated research
Generation Z, the first generation never to know the world without the internet, value diversity and finding their own unique identities, says Stanford scholar Roberta Katz.
Generation Z – also known as Gen Z, iGen or postmillennial – are a highly collaborative cohort that cares deeply about others and have a pragmatic attitude about how to address a set of inherited issues like climate change, according to research by Roberta Katz, a senior research scholar at Stanford’s Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences (CASBS) .

Roberta Katz (Image credit: Charles Katz)
Since 2017, Katz, along with her co-authors, Sarah Ogilvie, a linguist at the University of Oxford and formerly at Stanford; Jane Shaw, a historian who is the principal of Harris Manchester College at Oxford and was previously dean for Religious Life at Stanford; and Linda Woodhead, a sociologist at King’s College London, collaborated as part of a multi-year CASBS research project to better understand a generation who, born between the mid-1990s to around 2010, grew up with digital tools always at their fingertips.
Their findings are based on some 120 interviews gathered on three college campuses – Stanford University; Foothill College, a community college in Los Altos Hills, California; and Lancaster University, a research university in Lancaster, England. A set of focus groups and two surveys in the U.S. and the U.K. were administered to a representative sample of over 2,000 adults aged between 18 and 25 years old.
Contributing further to the scholar’s understanding of Gen Z was the creation of the “ iGen corpus ,” a 70 million item digital repository of spoken and written language of people aged 16 to 25 years that included transcripts from the researchers’ interviews and focus groups, as well as public data from the social media platforms Twitter, Reddit, Twitch, 4chan and YouTube, as well as memes and copypastas from Facebook and Instagram. Ogilvie, the principal investigator on the corpus research team, along with a team of Stanford student research assistants, applied machine learning algorithms to discover the many ways in which young people today express themselves.
Taken together, the scholars’ research offers a snapshot of who Gen Zers really are, what matters to them and why. Findings from Katz’s and her co-authors’ research are detailed in a new book, Gen Z, Explained: The Art of Living in a Digital Age (University of Chicago Press, 2021).
Here, Katz discusses some of what she and her colleagues learned from their extensive research into how Gen Zers, the most diverse generation yet , experience and understand the world.
Based on your research, can you briefly describe the typical Gen Zer?
In summary, a typical Gen Zer is a self-driver who deeply cares about others, strives for a diverse community, is highly collaborative and social, values flexibility, relevance, authenticity and non-hierarchical leadership, and, while dismayed about inherited issues like climate change, has a pragmatic attitude about the work that has to be done to address those issues.
How has growing up in an internet-connected society shaped how Gen Zers see and experience the world and everyday life?
Internet-related technologies have dramatically changed the speed, scale and scope of human communications, resulting in significant changes in how people work, play, shop, find friends and learn about other people. For Gen Zers living in the United States and Britain (the two places we studied), the “norm” they experienced as children was a world that operated at speed, scale and scope. They developed an early facility with powerful digital tools that allowed them to be self-reliant as well as collaborative. Similarly, because they could learn about people and cultures around the globe from an early age, they developed a greater appreciation for diversity and the importance of finding their own unique identities.
What do people most misunderstand or get wrong about Gen Zers?
For quite a while, people were critical of what they saw as a generation that was too coddled and “soft.” Gen Zers were called “snowflakes” and “unwilling to grow up.” But much of that negative judgment came from a misunderstanding of what it is like to grow up in today’s world when compared with how their elders grew up. As an example, Gen Zers have been criticized as lazy because they don’t have after-school or summer jobs. But many Gen Zers have been earning significant dollars online through a variety of activities, even including product placements on fashion-advice sites. Another example concerns drivers’ licenses: older people, for whom getting a driver’s license was a rite of passage toward adulthood, have criticized Gen Zers who do not rush to take their driver’s tests when they turn 16, but this criticism fails to consider that Gen Zers have no need to drive when they have ready access to ride services like Uber and Lyft.
Do you think Gen Zers get an undeserved bad rap?
Yes, but that is changing. Of late, many people are beginning to appreciate the strength and pragmatism of Gen Zers.
What were you most surprised to learn about Gen Zers?
Our biggest surprise came in response to this interview question: “What type of communication do you like best?” We expected the interviewees to respond with their favorite type of digital communication – e.g., text, email, chat group, DM, FaceTime, Skype, etc. – but instead nearly every single person said their favorite form of communication was “in person.”
As Gen Zers enter the workforce, what would be helpful for other generations to know about their post-millennial colleagues?
For those who are now experiencing Gen Zers in the workplace, my advice is to recognize that these new colleagues are used to working collaboratively and flexibly, with an eye to being efficient in getting the job done. They are pragmatic and value direct communication, authenticity and relevance. They also value self-care. They may be more likely than older people were when they were the age of the Gen Zers to question rules and authority because they are so used to finding what they need on their own. They are not always right; often they don’t know what they need, especially in a new setting, and this is where inter-generational dialogue can be so helpful. Both the older and the younger colleagues can learn from the other, in each case by listening with more respect, appreciation and trust. The older colleague can learn some helpful new ways of getting a job done, while the younger colleague may learn good reasons for why things have long been done in a certain way. Without that dialogue, we’ll have a wasteful tug of war between the past and the future. The goal is for older and younger generations to work together, with openness and trust, to ensure that the wisdom – but not what has become the excess baggage – of the past is not lost to the future.
How has studying Gen Zers changed your own interactions with this generation?
I came to understand that Gen Zers are, on the whole, much better adapted to life in a digital age than those of us who are older and that they can be very frustrated by what appear to them to be outdated and often irrelevant ways of doing things. As one simple example that we cite in the book, an older person would likely assume that any organization needs a set of officers, for that has been the norm in their experience, but a Gen Zer would say, from their lived experience, that there is no need to elect officers (or other leaders) if the group can accomplish its mission through online collaborations that take advantage of the participants’ diverse skills.
In my own interactions with Gen Zers, I am much more likely than I used to be to listen closely to what they say, and to refrain from making a judgment about their ideas, values and behaviors based on an assumption that they are wrong and I am right. They often do things differently, have some different values and have some different ideas about the future than I do, and I have come to appreciate and trust that they often have a new and better approach. Many of us who are older have a different understanding of how the world works, which is rooted in our own early experiences, so it’s easy for us to assume that the world will continue to operate in much the same way going forward and that the young people need to adapt to that older way of living. But the younger people are necessarily future-oriented, and as we all are increasingly coming to appreciate, the digital-age future is quite different from the industrial-age past.
For 13 years, Katz served under Stanford University Presidents John Hennessy and Marc Tessier-Lavigne as the associate vice president for strategic planning. She also served as President Tessier-Lavigne’s interim chief of staff until early 2017. Katz has been deeply involved in the facilitation of a variety of interdisciplinary research initiatives at Stanford, and she is a current member of the CASBS board of directors.
This research was funded by the Knight Foundation.

What do we owe future generations? And what can we do to make their world a better place?
Senior Lecturer in Psychology, Australian Catholic University
Disclosure statement
Michael Noetel receives funding from the Australian Research Council, National Health and Medical Research Council, the Centre for Effective Altruism, and Sport Australia. He is a Director of Effective Altruism Australia.
Australian Catholic University provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
Your great grandchildren are powerless in today’s society. As Oxford philosopher William MacAskill says:
They cannot vote or lobby or run for public office, so politicians have scant incentive to think about them. They can’t bargain or trade with us, so they have little representation in the market, And they can’t make their views heard directly: they can’t tweet, or write articles in newspapers, or march in the streets. They are utterly disenfranchised.
But the things we do now influence them: for better or worse. We make laws that govern them, build infrastructure for them and take out loans for them to pay back. So what happens when we consider future generations while we make decisions today?
Review: What We Owe the Future – William MacAskill (OneWorld)
This is the key question in What We Owe the Future . It argues for what MacAskill calls longtermism: “the idea that positively influencing the longterm future is a key moral priority of our time.” He describes it as an extension of civil rights and women’s suffrage; as humanity marches on, we strive to consider a wider circle of people when making decisions about how to structure our societies.
MacAskill makes a compelling case that we should consider how to ensure a good future not only for our children’s children, but also the children of their children. In short, MacAskill argues that “future people count, there could be a lot of them, and we can make their lives go better.”
Read more: Friday essay: 'I feel my heart breaking today' – a climate scientist's path through grief towards hope
Future people count
It’s hard to feel for future people. We are bad enough at feeling for our future selves. As The Simpsons puts it: “That’s a problem for future Homer. Man, I don’t envy that guy.”
We all know we should protect our health for our own future. In a similar vein, MacAskill argues that we all “know” future people count.
Concern for future generations is common sense across diverse intellectual traditions […] When we dispose of radioactive waste, we don’t say, “Who cares if this poisons people centuries from now?” Similarly, few of us who care about climate change or pollution do so solely for the sake of people alive today. We build museums and parks and bridges that we hope will last for generations; we invest in schools and longterm scientific projects; we preserve paintings, traditions, languages; we protect beautiful places.
There could be a lot of future people
Future people count, and MacAskill counts those people. The sheer number of future people might make their wellbeing a key moral priority. According to MacAskill and others, humanity’s future could be vast : much, much more than the 8 billion alive today.
While it’s hard to feel the gravitas, our actions may affect a dizzying number of people. Even if we last just 1 million years, as long as the average mammal – and even if the global population fell to 1 billion people – then there would be 9.1 trillion people in the future.
We might struggle to care, because these numbers can be hard to feel . Our emotions don’t track well against large numbers. If I said a nuclear war would kill 500 million people, you might see that as a “huge problem”. If I instead said that the number is actually closer to 5 billion , it still feels like a “huge problem”. It does not emotionally feel 10 times worse. If we risk the trillions of people who could live in the future, that could be 1,000 times worse – but it doesn’t feel 1,000 times worse.
MacAskill does not argue we should give those people 1,000 times more concern than people alive today. Likewise, MacAskill does not say we should morally weight a person living a million years from now exactly the same as someone alive 10 or 100 years from now. Those distinctions won’t change what we can feasibly achieve now, given how hard change can be.
Instead, he shows if we care about future people at all, even those 100 years hence, we should simply be doing more . Fortunately, there are concrete things humanity can do.
Read more: Labor's climate change bill is set to become law – but 3 important measures are missing
We can make the lives of future people better
Another reason we struggle to be motivated by big problems is that they feel insurmountable. This is a particular concern with future generations. Does anything I do make a difference, or is it a drop in the bucket? How do we know what to do when the long-run effects are so uncertain ?

Even present-day problems can feel hard to tackle. At least for those problems we can get fast, reliable feedback on progress. Even with that advantage, we struggle. For the second year in a row, we did not make progress toward our sustainable development goals, like reducing war, poverty, and increasing growth. Globally, 4.3% of children still die before the age of five. COVID-19 has killed about 23 million people . Can we – and should we – justify focusing on future generations when we face these problems now?
MacAskill argues we can. Because the number of people is so large, he also argues we should. He identifies some areas where we could do things that protect the future while also helping people who are alive now. Many solutions are win-win.
For example, the current pandemic has shown that unforeseen events can have a devastating effect. Yet, despite the recent pandemic, many governments have done little to set up more robust systems that could prevent the next pandemic. MacAskill outlines ways in which those future pandemics could be worse.
Most worrying are the threats from engineered pathogens, which
[…] could be much more destructive than natural pathogens because they can be modified to have dangerous new properties. Could someone design a pathogen with maximum destructive power—something with the lethality of Ebola and the contagiousness of measles?
He gives examples, like militaries and terrorist groups, that have tried to engineer pathogens in the past.
The risk of an engineered pandemic wiping us all out in the next 100 years is between 0.1% and 3%, according to estimates laid out in the book.
That might sound low, but MacAskill argues we would not step on a plane if you were told “it ‘only’ had a one-in-a-thousand chance of crashing and killing everyone on board”. These threaten not only future generations, but people reading this – and everyone they know.
MacAskill outlines ways in which we might be able to prevent engineered pandemics, like researching better personal protective equipment, cheaper and faster diagnostics, better infrastructure, or better governance of synthetic biology. Doing so would help save the lives of people alive today, reduce the risk of technological stagnation and protect humanity’s future.
The same win-wins might apply to decarbonisation , safe development of artificial intelligence , reducing risks from nuclear war , and other threats to humanity.
Read more: Even a 'limited' nuclear war would starve millions of people, new study reveals
Things you can do to protect future generations
Some “longtermist” issues, like climate change, are already firmly in the public consciousness. As a result, some may find MacAskill’s book “common sense”. Others may find the speculation about the far future pretty wild (like all possible views of the longterm future).
MacAskill strikes an accessible balance between anchoring the arguments to concrete examples, while making modest extrapolations into the future. He helps us see how “common sense” principles can lead to novel or neglected conclusions.
For example, if there is any moral weight on future people, then many common societal goals (like faster economic growth) are vastly less important than reducing risks of extinction (like nuclear non-proliferation). It makes humanity look like an “imprudent teenager”, with many years ahead, but more power than wisdom:
Even if you think [the risk of extinction] is only a one-in-a-thousand, the risk to humanity this century is still ten times higher than the risk of your dying this year in a car crash. If humanity is like a teenager, then she is one who speeds around blind corners, drunk, without wearing a seat belt.
Our biases toward present, local problems are strong, so connecting emotionally with the ideas can be hard. But MacAskill makes a compelling case for longtermism through clear stories and good metaphors. He answers many questions I had about safeguarding the future. Will the future be good or bad? Would it really matter if humanity ended? And, importantly, is there anything I can actually do?
The short answer is yes, there is. Things you might already do help, like minimising your carbon footprint – but MacAskill argues “other things you can do are radically more impactful”. For example, reducing your meat consumption would address climate change, but donating money to the world’s most effective climate charities might be far more effective.
Beyond donations, three other personal decisions seem particularly high impact to me: political activism, spreading good ideas, and having children […] But by far the most important decision you will make, in terms of your lifetime impact, is your choice of career.
MacAskill points to a range of resources – many of which he founded – that guide people in these areas. For those who might have flexibility in their career, MacAskill founded 80,000 Hours , which helps people find impactful, satisfying careers. For those trying to donate more impactfully, he founded Giving What We Can. And, for spreading good ideas, he started a social movement called Effective Altruism .
Longtermism is one of those good ideas. It helps us better place our present in humanity’s bigger story. It’s humbling and inspiring to see the role we can play in protecting the future. We can enjoy life now and safeguard the future for our great grandchildren. MasAskill clearly shows that we owe it to them.
- Climate change
- Generations
- Future generations
- Effective altruism
- longtermism

Senior Lecturer - Earth System Science

Operations Coordinator

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Deputy Social Media Producer

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy

Essay on Today’s Generation
Students are often asked to write an essay on Today’s Generation in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Today’s Generation
Understanding today’s generation.
Today’s generation, often called Generation Z, is a tech-savvy group born between 1997 and 2012. They are digital natives, growing up with the internet, smartphones, and social media.
Adapting to Change
This generation adapts to change quickly. They are used to fast-paced technological advancements and are comfortable learning new things. They value diversity and inclusivity.
Challenges Faced
Despite their adaptability, they face challenges like online bullying and mental health issues. The pressure to always be ‘connected’ can be overwhelming.
Understanding today’s generation helps us to nurture their talents and address their challenges effectively.
250 Words Essay on Today’s Generation
Introduction.
Today’s generation, often referred to as Generation Z or the iGeneration, is a demographic cohort following the millennials. Born between the mid-to-late 1990s and early 2010s, they are the first generation to be raised in the era of smartphones and social media, which has significantly impacted their communication styles, values, and worldviews.
Characteristics of Today’s Generation
One of the defining characteristics of today’s generation is their digital nativeness. They are comfortable with technology, having grown up with the internet, smartphones, and social media as integral parts of their lives. This has led to a generation that is highly connected, with global perspectives and a strong sense of social responsibility.
Challenges and Opportunities
However, this digital immersion also presents challenges. The over-reliance on technology can lead to issues like cyberbullying, privacy concerns, and mental health problems. Yet, it also presents opportunities. Today’s generation is adept at multitasking, quick to adapt to new technologies, and skilled at leveraging digital platforms for creative expression and social activism.
The unique characteristics and challenges of today’s generation are shaping the world in new ways. As digital natives, they are redefining communication, education, and work, and are poised to drive significant societal and technological advancements. Understanding and addressing their needs and aspirations is crucial for creating a future that leverages their strengths and mitigates their challenges.
500 Words Essay on Today’s Generation
The characteristics of today’s generation.
Today’s generation, often referred to as Generation Z or the iGeneration, is markedly different from its predecessors. Born between the mid-to-late 1990s and the early 2010s, this generation is the first to grow up in a world where the internet, social media, and advanced technology are the norm rather than the exception.
One of the defining characteristics of today’s generation is their digital nativity. Unlike previous generations who had to adapt to the digital world, today’s youth are born into it. They are comfortable navigating the digital landscape, be it for communication, education, or entertainment. This has enabled them to develop skills such as multitasking and information filtering at an early age.
Impact of Technology on Today’s Generation
The impact of technology on today’s generation is profound and multifaceted. On one hand, it has made information access unprecedentedly easy. The internet has become the primary source of knowledge, and with the advent of online learning platforms, the traditional boundaries of education have been expanded.
However, the ubiquity of technology also brings challenges. Cyberbullying, online privacy threats, and the potential for misinformation are significant concerns. Moreover, the overuse of technology can lead to issues like decreased physical activity and face-to-face social interaction. Balancing the benefits and drawbacks of technology is a unique challenge for today’s generation.
Societal and Environmental Consciousness
Today’s generation is remarkably conscious of societal and environmental issues. They are more likely to champion causes such as climate change, mental health, and social justice. This heightened awareness and activism are largely facilitated by social media, which provides a platform for sharing information, rallying support, and mobilizing action.
The Future and Today’s Generation
Despite the challenges they face, today’s generation is resilient and adaptable. They are problem solvers who are not afraid to challenge the status quo. As the most educated generation to date, they are poised to bring about significant changes in various fields.
However, it’s crucial to remember that today’s generation is not a monolith. Their experiences and perspectives are diverse, shaped by factors like race, gender, socioeconomic status, and geography. As such, it’s essential to avoid overgeneralizing and to appreciate the richness of their individual experiences.
In conclusion, today’s generation is a dynamic and complex group. They are digital natives, navigating a world interwoven with technology. They are socially and environmentally conscious, driven to make a positive impact on the world. And despite the challenges they face, they are resilient, adaptable, and poised to shape the future. Understanding them is not just an academic exercise, but a necessity for anyone looking to stay relevant in an ever-evolving world.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Generation Gap
- Essay on Gender Sensitization
- Essay on Gender Justice
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
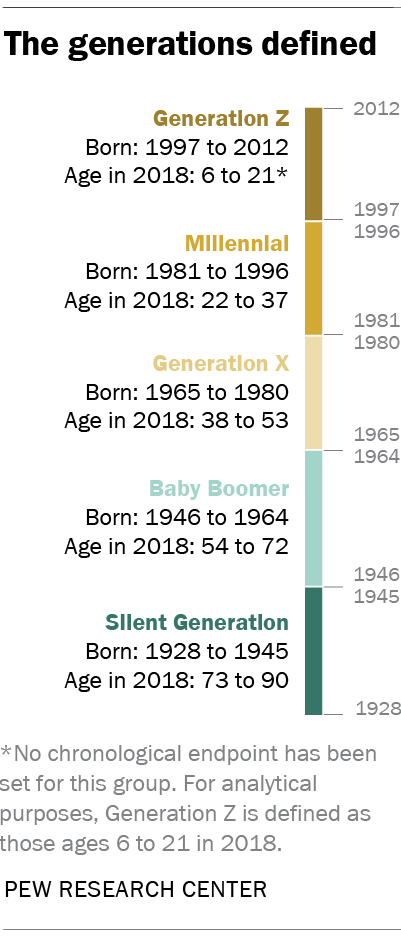
What is Gen Z?

Gen Z is currently the second-youngest generation, with millennials before and Generation Alpha after. Like every generation, Gen Z’s behaviors are shaped by how they grew up. Young people today have come of age in the shadow of climate doom, pandemic lockdowns, and fears of economic collapse. The first Gen Zers were born when the internet had just achieved widespread use. They’re called “ digital natives ”—the first generation to grow up with the internet as a part of daily life. The generation spans a wide range: the oldest Gen Zers have jobs and mortgages, while the youngest are still preteens. Globally, Gen Z is growing fast: Gen Zers will make up a quarter of the population of the Asia–Pacific region by 2025. Read on to understand what makes Gen Z tick.
Learn more about our Growth, Marketing & Sales Practice .
What is a generation?
Get to know and directly engage with senior mckinsey experts on gen z..
Anita Balchandani is a senior partner in McKinsey’s London office; Erica Coe is a partner in the Atlanta office; Kana Enomoto is a senior knowledge expert and associate partner in the Washington, DC, office; Tracy Francis is a senior partner in the São Paulo office; and Jennifer Schmidt is a senior partner in the Minneapolis office.
No doubt you’re already familiar with the concept of generation within families. Your grandparents, parents, children, and children’s children all make up a distinct generation in relation to you. But each of them also belongs to a diffuse category of their peers, grouped together based on when they were born and what they experience during their lives. Social scientists have studied generations—in theory and more practically—for millennia. More recently, thinkers like August Comte have argued that generational change is the engine behind social change. More specifically, each generation entering into a new life stage at more or less the same time is the pulse that creates the history of a society.
Specific major-scale events can also shape the outlook of a generation and are often reflected in how they’re named. The Lost Generation, for example, is named for the malaise and disillusionment experienced by people who lived through World War I. Later, the Greatest Generation was named for the heroic sacrifice many made during World War II. Their children, born soon after the war ended, are called baby boomers; their outlook, in turn, was colored by the Vietnam War and the social upheavals of the 1960s. More recently, millennials’ worldviews have been shaped by the September 11 attacks and the proliferation of the internet.
Of course, these are generalizations: every so-called generation comprises a multitude of unique individuals with their own opinions, values, behaviors, and plans for the future. Some social scientists even believe that the practice of studying generations can obfuscate what motivates people on an individual level. Generational theory should be understood with this caveat, and used only as a way of thinking about society, rather than the gospel truth.
What is unique about Gen Z?
While there are substantive differences within the cohort known as Gen Z, there are a few commonalities its members share .
As the first real digital natives, Gen Zers—speaking generally—are extremely online . Gen Zers are known for working, shopping, dating, and making friends online; in Asia, Gen Zers spend six or more hours per day on their phones .
Digital natives often turn to the internet when looking for any kind of information, including news and reviews prior to making a purchase . They flit between sites, apps, and social media feeds , each one forming a different part of their online ecosystem. Having grown up with social media, Gen Zers curate their online selves more carefully than those in prior generations have, and they are more likely to turn to trends of anonymity, more personalized feeds, and a smaller online presence, even as they voraciously consume media online .
Video-sharing social media sites have seen a meteoric rise as Gen Z comes of age. TikTok currently rules trends, feelings, and culture for Gen Zers, who make up 60 percent of the app’s one billion-plus users . Gen Zers flock to corners of the internet where they can discuss their passions and interests with those who share them—from gaming to K-pop —bonding with both people they know in real life and ones they’ve only met online.
Gen Z also faces an unprecedented behavioral health crisis: US Gen Zers surveyed by McKinsey report the least positive outlook and the highest prevalence of mental illness of any generation, and European respondents report struggling with self-stigma. This pessimism is fueled by growing global unrest , wars and disruptions , financial crises , and educational interruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic . Feelings of “climate anxiety” are also widely reported : many Gen Zers report that they think about the fate of the planet on a daily basis.
They are already seeing decreased economic opportunity and don’t assume a social safety net will be there to catch them as pensions shrink, saving for retirement gets more difficult , and the older population grows . Already, 58 percent of Gen Zers in a recent McKinsey survey reported not having a basic social need met —the largest percentage by far of any generation.
But Gen Zers also report a more nuanced perspective around the stigma of mental illness than other generations. European Gen Zers seem less inclined to discriminate against people with mental illness ( although they do stigmatize themselves ).

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
However, Gen Z is also generally known for its idealism —they’re part of a new wave of “ inclusive consumers ” and socially progressive dreamers. Generally speaking, Gen Zers believe in doing their part to help stop the intensification of climate change and to establish greater equity for all. More than any other generation, Gen Z collectively demands purpose and accountability , the creation of more opportunities for people of diverse and underrepresented backgrounds , and rigorous sustainable and green practices .
Learn more about McKinsey’s Retail , Healthcare , and Sustainability Practices, and check out our Diversity and Inclusion collection .
How are Gen Zers different from millennials?
Those on the cusp of Gen Z and millennial—people who were born shortly before the turn of the millennium—are sometimes referred to as “Zillennials” or “Zennials.” That includes older Gen Zers who’ve been in the workforce for a few years and young millennials who identify more with Gen Z.
However, Gen Z generally has its own formative experiences distinct from those of most millennials . Here are some ways American Gen Zers differ from their older counterparts :
- They are generally more pragmatic , with both complicated idealism and worries for the future. Gen Zers dream of personal career fulfillment but expect economic struggles.
- They have less positive life outlooks , with lower levels of emotional and social well-being than older generations.
- They are more interested in belonging to an inclusive, supportive community .
- They are more individualistic, with a stronger sense of personal expression.
- They are more politically and socially active , advocating for what they believe on social media.
What are Gen Z’s values?
Gen Zers generally have strong values related to racial justice and sustainability . Mobilizations like the Global Climate March, led by Gen Z activist Greta Thunberg, thrive on the activism of young people.
Climate change is one of the issues Gen Zers care about most. They frequently call for reform on personal, public, and global scales to prevent future catastrophe. Many Gen Zers describe themselves as environmentally conscious, and the majority of Gen Z expects to see sustainability commitments from companies and organizations.
Gen Z is also living in a time marked by rapidly rising inflation and financial woes. Rising student loan debt also plagues many members of this generation.
What are Gen Z fashion trends?
Gen Z loves expressive clothes, wants to stand out rather than fit in , and has an ever-changing style —what was in a month ago might already be out today. Their trend-chasing habits are supported by fast-fashion retailers supplying accessible ways to switch it up. One Gen Z staple shop, Chinese fast-fashion giant Shein, adds 6,000 new products to its website per day . This may seem at odds with the generation’s values of sustainability, but the speed at which Gen Z trends change and their desire for unique style can sometimes overcome their eco-scruples.
Gen Zers also love thrifting and vintage styles—which are much more in line with their calls for circular fashion . Both ’90s and y2k-style clothes have seen a major comeback, including fast-fashion dupes and clothes dug out of closets and thrift stores. Fashion resale has experienced massive growth thanks to Gen Z resellers and influencers, and it’s normal for a Gen Z wardrobe to be a mix of cheap fast fashion and treasured vintage pieces.
Learn more about McKinsey’s Retail Practice .

What do Gen Z shoppers want?
The internet has changed retail forever and shaped the tastes of digital natives. Here’s how:
- Consumption is about access rather than ownership —Gen Zers subscribe to streaming platforms instead of buying films or music. This trend extends even to services like car shares or luxury-clothing rentals.
- Gen Zers accept their tastes might change, and they are more likely to spend on experiences that enrich their day-to-day lives than millennials, who are more likely to splurge on luxury.
- Members of this generation care about ease of use: mobile pay, app-based services, and simple online transactions are important, and brands have found major success by restructuring to suit Gen Z tastes .
- Gen Zers like brick-and-mortar stores more than millennials do but still want a great online shopping experience . Some brands have even found success through online-first launches , often supported by Gen Z consumers.
- Ads are everywhere; Gen Zers experience brands “ at every moment ” as they move through their digital and physical worlds.
And as a generation committed to its values, Gen Z expects the same of its retailers—Gen Zers often choose brands that have a strong story or purpose , as well as those committed to green practices . In one McKinsey study, 73 percent of Gen Z reported trying to purchase from companies they consider ethical, and nine out of ten believe that companies have a responsibility to address environmental and social issues . However, they can tell when a brand is just paying lip service and isn’t backing up diversity or sustainability claims with real change.
Many Gen Zers throughout Asia see the internet as the first place to go when researching new products to purchase; in the United States, 40 percent of Gen Zers admit to being influenced online , often by the brands featured in the videos they watch. Members filter a lot of information, from influencers, family, and friends, to decide where and how they want to spend .
For more in-depth exploration of these topics, see McKinsey’s Generation Z collection . Learn more about Gen Z insights by subscribing to our newsletter —and check out entry-level job opportunities if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced include:
- “ The Gen Z Equation ,” June 26, 2023, McKinsey Quarterly Five Fifty
- “ Heat waves, the war in Ukraine, and stigma: Gen Z’s perspectives on mental health ,” September 27, 2022, Lea Arora, Erica Coe , Martin Dewhurst, and Kana Enomoto
- “ Addressing the unprecedented behavioral-health challenges facing Generation Z ,” January 14, 2022, Erica Coe , Jenny Cordina , Kana Enomoto , Raelyn Jacobson , Sharon Mei, and Nikhil Seshan
- “ Giving Gen Z customers what they want: A conversation with by.U ,” November 11, 2021, Edward Ying, Trio Lumbantoruan, and Andrew Roth
- “ Gen Z and the Latin American consumer today, ” December 10, 2020, Tracy Francis and Fernanda Hoefel
- “ How Gen Z and millennials are shaping the future of US retail ,” September 28, 2020, Bo Finneman and Emma Spagnuolo
- “ Meet Generation Z: Shaping the future of shopping ,” August 4, 2020, Bo Finneman and Emma Spagnuolo
- “ The young and the restless: Generation Z in America ,” March 20, 2020, Shruti Bhargava, Bo Finneman , Jennifer Schmidt , and Emma Spagnuolo
- “ Asia’s Generation Z comes of age ,” March 17, 2020, Thomas Rüdiger Smith and Naomi Yamakawa
- “ The influence of ‘woke’ consumers on fashion ,” February 12, 2019, Imran Amed, Anita Balchandani , Marco Beltrami, Achim Berg , Saskia Hedrich, and Felix Rölkens
- “‘ True Gen’: Generation Z and its implications for companies ,” November 12, 2018, Tracy Francis and Fernanda Hoefel

Want to know more about Gen Z?
Related articles.

How does Gen Z see its place in the working world? With trepidation

Addressing the unprecedented behavioral-health challenges facing Generation Z

Heat waves, the war in Ukraine, and stigma: Gen Z’s perspectives on mental health
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:

Millennial life: How young adulthood today compares with prior generations
Over the past 50 years – from the Silent Generation’s young adulthood to that of Millennials today – the United States has undergone large cultural and societal shifts. Now that the youngest Millennials are adults, how do they compare with those who were their age in the generations that came before them?
In general, they’re better educated – a factor tied to employment and financial well-being – but there is a sharp divide between the economic fortunes of those who have a college education and those who don’t.
Millennials have brought more racial and ethnic diversity to American society. And Millennial women, like Generation X women, are more likely to participate in the nation’s workforce than prior generations.
Compared with previous generations, Millennials – those ages 22 to 37 in 2018 – are delaying or foregoing marriage and have been somewhat slower in forming their own households. They are also more likely to be living at home with their parents, and for longer stretches.
And Millennials are now the second-largest generation in the U.S. electorate (after Baby Boomers), a fact that continues to shape the country’s politics given their Democratic leanings when compared with older generations.
Those are some of the broad strokes that have emerged from Pew Research Center’s work on Millennials over the past few years. Now that the youngest Millennials are in their 20s, we have done a comprehensive update of our prior demographic work on generations. Here are the details.
Today’s young adults are much better educated than their grandparents, as the share of young adults with a bachelor’s degree or higher has steadily climbed since 1968. Among Millennials, around four-in-ten (39%) of those ages 25 to 37 have a bachelor’s degree or higher, compared with just 15% of the Silent Generation, roughly a quarter of Baby Boomers and about three-in-ten Gen Xers (29%) when they were the same age.
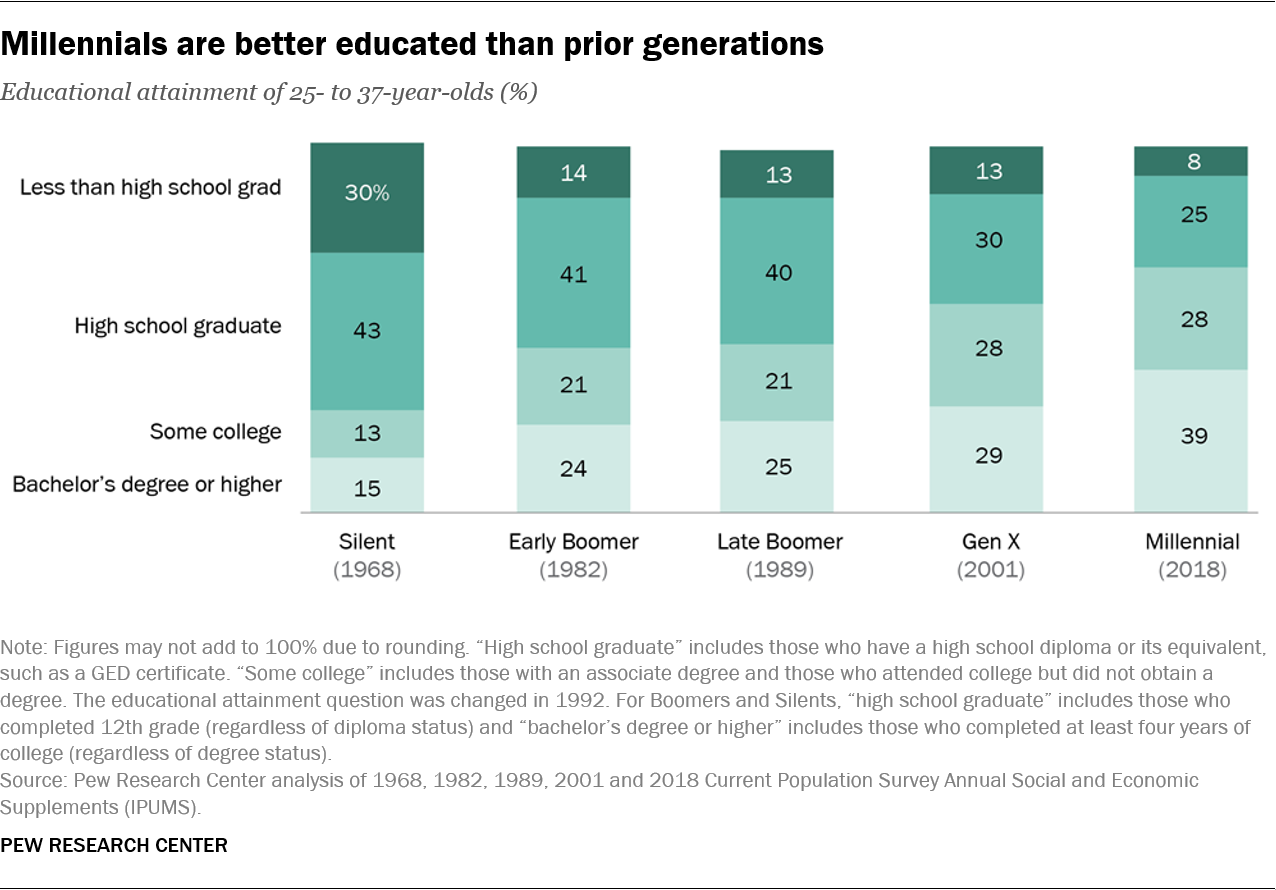
Gains in educational attainment have been especially steep for young women. Among women of the Silent Generation, only 11% had obtained at least a bachelor’s degree when they were young (ages 25 to 37 in 1968). Millennial women are about four times (43%) as likely as their Silent predecessors to have completed as much education at the same age. Millennial men are also better educated than their predecessors. About one-third of Millennial men (36%) have at least a bachelor’s degree, nearly double the share of Silent Generation men (19%) when they were ages 25 to 37.
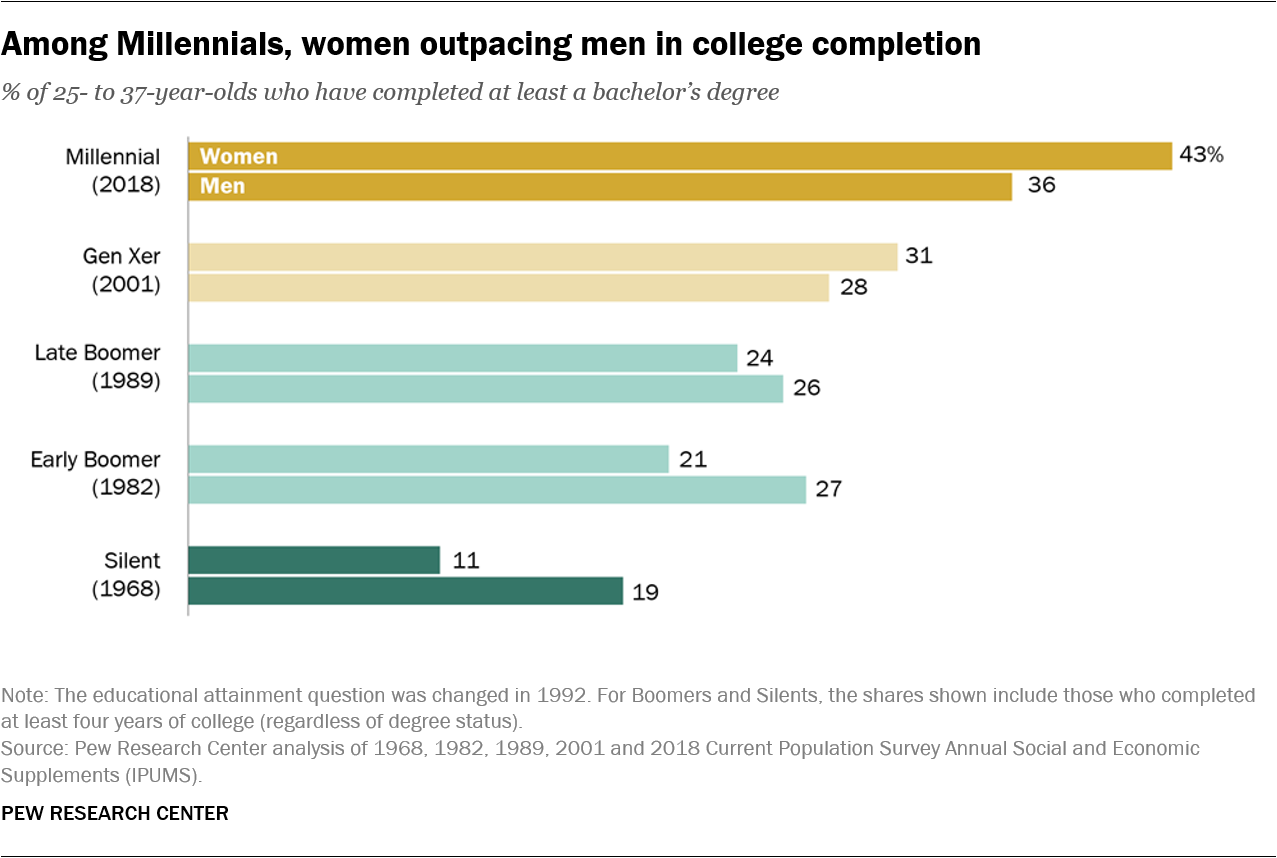
While educational attainment has steadily increased for men and women over the past five decades, the share of Millennial women with a bachelor’s degree is now higher than that of men – a reversal from the Silent Generation and Boomers. Gen X women were the first to outpace men in terms of education, with a 3-percentage-point advantage over Gen X men in 2001. Before that, late Boomer men in 1989 had a 2-point advantage over Boomer women.

Boomer women surged into the workforce as young adults, setting the stage for more Gen X and Millennial women to follow suit. In 1966, when Silent Generation women were ages 22 through 37, a majority (58%) were not participating in the labor force while 40% were employed. For Millennial women today, 72% are employed while just a quarter are not in the labor force. Boomer women were the turning point. As early as 1985, more young Boomer women were employed (66%) than were not in the labor force (28%).
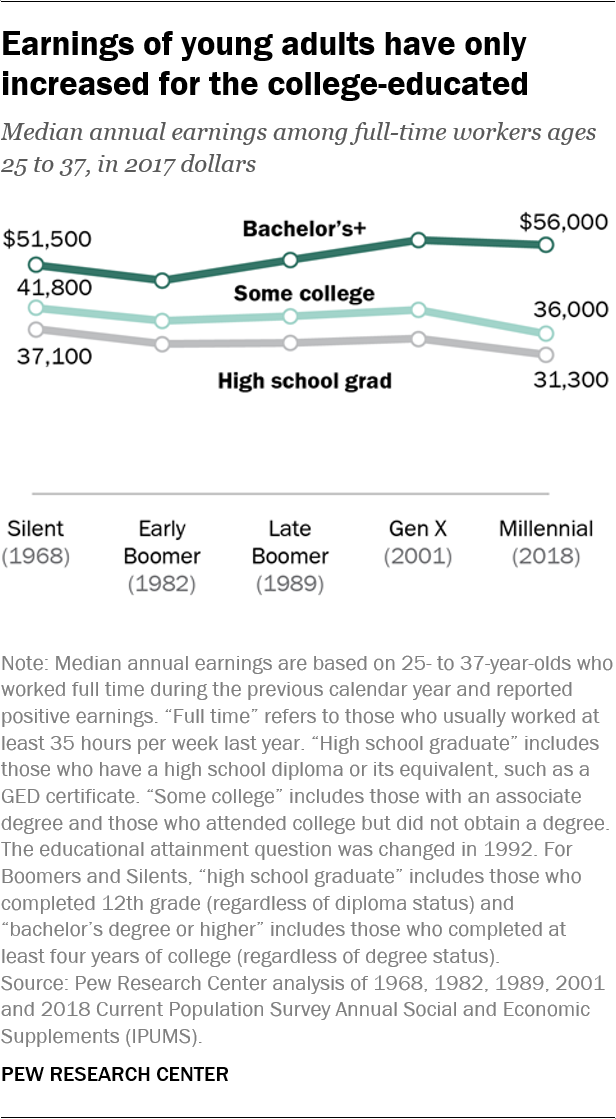
And despite a reputation for job hopping, Millennial workers are just as likely to stick with their employers as Gen X workers were when they were the same age. Roughly seven-in-ten each of Millennials ages 22 to 37 in 2018 (70%) and Gen Xers the same age in 2002 (69%) reported working for their current employer at least 13 months. About three-in-ten of both groups said they’d been with their employer for at least five years.
Of course, the economy varied for each generation. While the Great Recession affected Americans broadly, it created a particularly challenging job market for Millennials entering the workforce. The unemployment rate was especially high for America’s youngest adults in the years just after the recession, a reality that would impact Millennials’ future earnings and wealth.
Income and wealth
The financial well-being of Millennials is complicated. The individual earnings for young workers have remained mostly flat over the past 50 years. But this belies a notably large gap in earnings between Millennials who have a college education and those who don’t. Similarly, the household income trends for young adults markedly diverge by education. As far as household wealth, Millennials appear to have accumulated slightly less than older generations had at the same age.
Millennials with a bachelor’s degree or more and a full-time job had median annual earnings valued at $56,000 in 2018, roughly equal to those of college-educated Generation X workers in 2001. But for Millennials with some college or less, annual earnings were lower than their counterparts in prior generations. For example, Millennial workers with some college education reported making $36,000, lower than the $38,900 early Baby Boomer workers made at the same age in 1982. The pattern is similar for those young adults who never attended college.
Millennials in 2018 had a median household income of roughly $71,400, similar to that of Gen X young adults ($70,700) in 2001. (This analysis is in 2017 dollars and is adjusted for household size. Additionally, household income includes the earnings of the young adult, as well as the income of anyone else living in the household.)
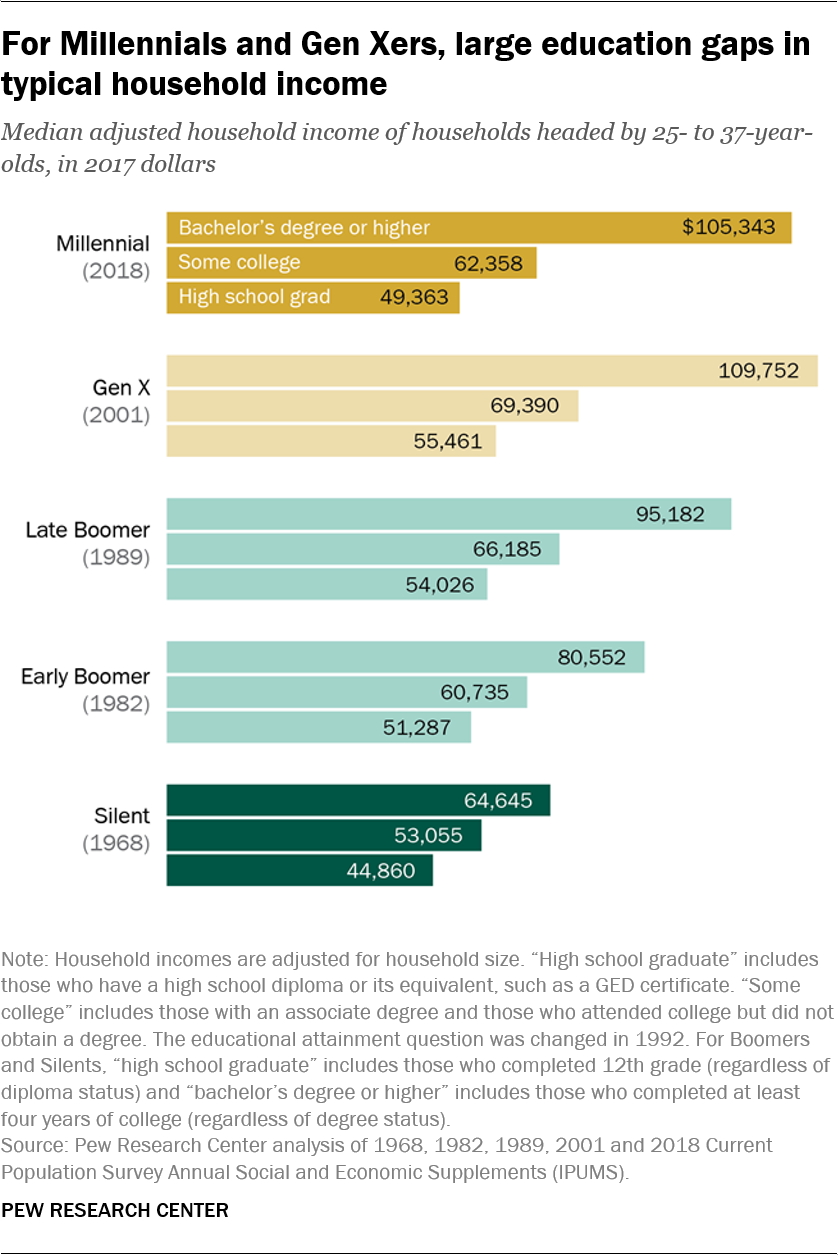
The growing gap by education is even more apparent when looking at annual household income. For households headed by Millennials ages 25 to 37 in 2018, the median adjusted household income was about $105,300 for those with a bachelor’s degree or higher, roughly $56,000 greater than that of households headed by high school graduates. The median household income difference by education for prior generations ranged from $41,200 for late Boomers to $19,700 for the Silent Generation when they were young.
While young adults in general do not have much accumulated wealth, Millennials have slightly less wealth than Boomers did at the same age. The median net worth of households headed by Millennials (ages 20 to 35 in 2016) was about $12,500 in 2016, compared with $20,700 for households headed by Boomers the same age in 1983. Median net worth of Gen X households at the same age was about $15,100.
This modest difference in wealth can be partly attributed to differences in debt by generation. Compared with earlier generations, more Millennials have outstanding student debt, and the amount of it they owe tends to be greater. The share of young adult households with any student debt doubled from 1998 (when Gen Xers were ages 20 to 35) to 2016 (when Millennials were that age). In addition, the median amount of debt was nearly 50% greater for Millennials with outstanding student debt ($19,000) than for Gen X debt holders when they were young ($12,800).
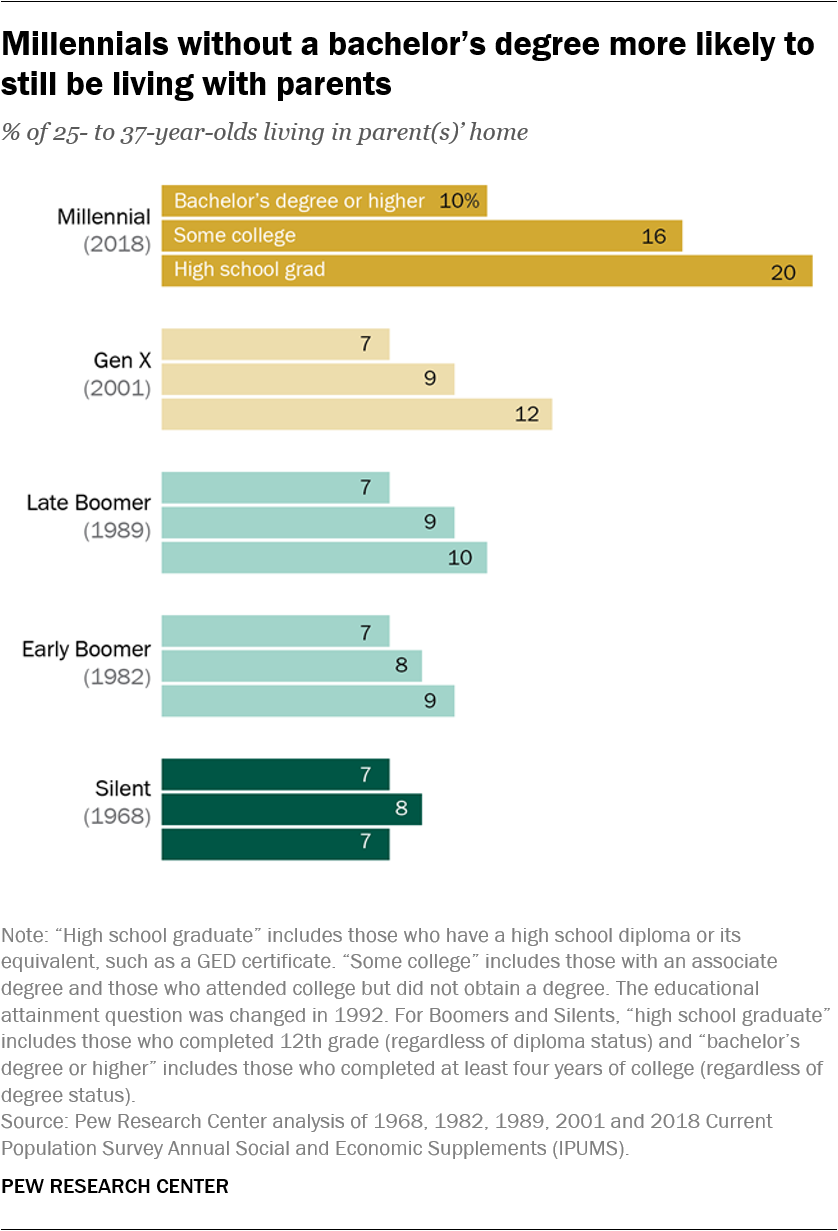
Millennials, hit hard by the Great Recession, have been somewhat slower in forming their own households than previous generations. They’re more likely to live in their parents’ home and also more likely to be at home for longer stretches . In 2018, 15% of Millennials (ages 25 to 37) were living in their parents’ home. This is nearly double the share of early Boomers and Silents (8% each) and 6 percentage points higher than Gen Xers who did so when they were the same age.
The rise in young adults living at home is especially prominent among those with lower education. Millennials who never attended college were twice as likely as those with a bachelor’s degree or more to live with their parents (20% vs. 10%). This gap was narrower or nonexistent in previous generations. Roughly equal shares of Silents (about 7% each) lived in their parents’ home when they were ages 25 to 37, regardless of educational attainment.
Millennials are also moving significantly less than earlier generations of young adults. About one-in-six Millennials ages 25 to 37 (16%) have moved in the past year. For previous generations at the same age, roughly a quarter had.

On the whole, Millennials are starting families later than their counterparts in prior generations. Just under half (46%) of Millennials ages 25 to 37 are married, a steep drop from the 83% of Silents who were married in 1968. The share of 25- to 37-year-olds who were married steadily dropped for each succeeding generation, from 67% of early Boomers to 57% of Gen Xers. This in part reflects broader societal shifts toward marrying later in life. In 1968, the typical American woman first married at age 21 and the typical American man first wed at 23. Today, those figures have climbed to 28 for women and 30 for men.
But it’s not all about delayed marriage. The share of adults who have never married is increasing with each successive generation. If current patterns continue, an estimated one-in-four of today’s young adults will have never married by the time they reach their mid-40s to early 50s – a record high share.
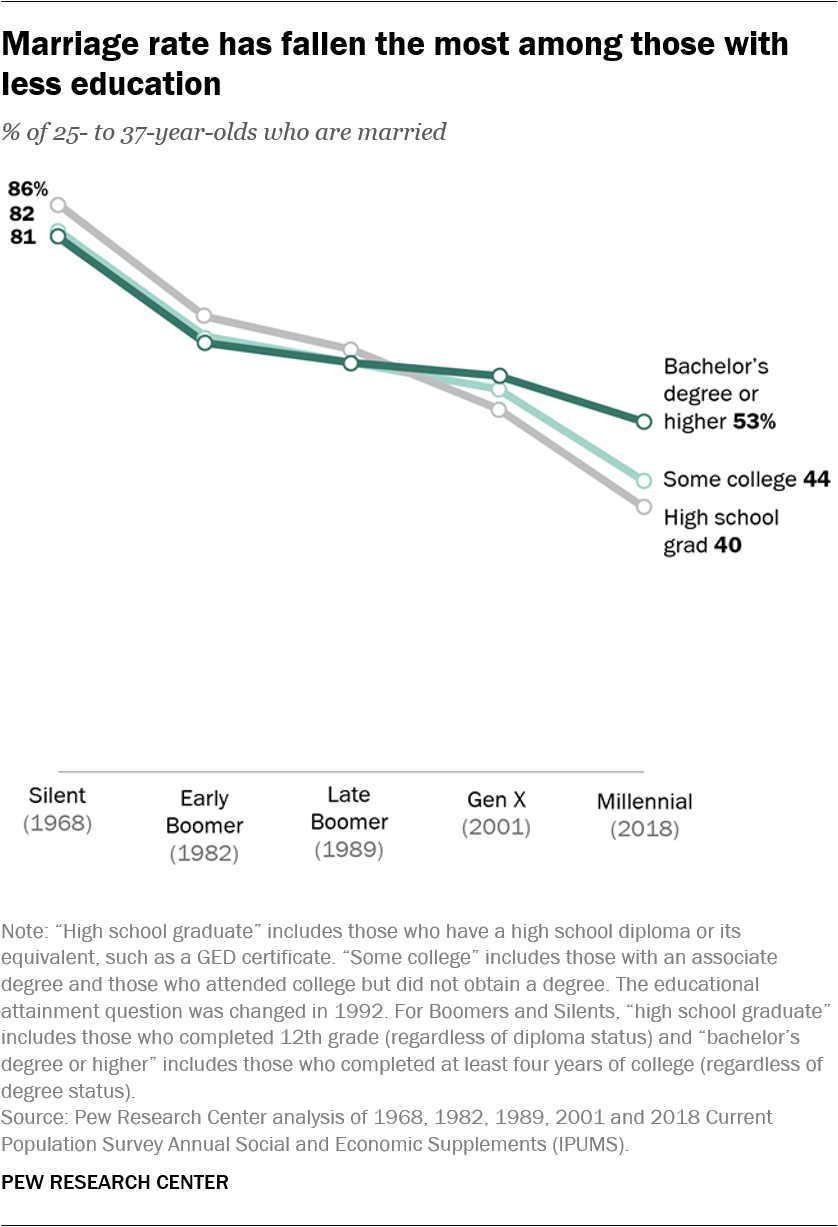
In prior generations, those ages 25 to 37 whose highest level of education was a high school diploma were more likely than those with a bachelor’s degree or higher to be married. Gen Xers reversed this trend, and the divide widened among Millennials. Four-in-ten Millennials with just a high school diploma (40%) are currently married, compared with 53% of Millennials with at least a bachelor’s degree. In comparison, 86% of Silent Generation high school graduates were married in 1968 versus 81% of Silents with a bachelor’s degree or more.
Millennial women are also waiting longer to become parents than prior generations did. In 2016, 48% of Millennial women (ages 20 to 35 at the time) were moms. When Generation X women were the same age in 2000, 57% were already mothers, similar to the share of Boomer women (58%) in 1984. Still, Millennial women now account for the vast majority of annual U.S. births, and more than 17 million Millennial women have become mothers.
Younger generations (Generation X, Millennials and Generation Z) now make up a clear majority of America’s voting-eligible population . As of November 2018, nearly six-in-ten adults eligible to vote (59%) were from one of these three generations, with Boomers and older generations making up the other 41%.
However, young adults have historically been less likely to vote than their older counterparts, and these younger generations have followed that same pattern, turning out to vote at lower rates than older generations in recent elections.
In the 2016 election, Millennials and Gen Xers cast more votes than Boomers and older generations, giving the younger generations a slight majority of total votes cast. However, higher shares of Silent/Greatest generation eligible voters (70%) and Boomers (69%) reported voting in the 2016 election compared with Gen X (63%) and Millennial (51%) eligible voters. Going forward, Millennial turnout may increase as this generation grows older.
Generational differences in political attitudes and partisan affiliation are as wide as they have been in decades. Among registered voters, 59% of Millennials affiliate with the Democratic Party or lean Democratic, compared with about half of Boomers and Gen Xers (48% each) and 43% of the Silent Generation. With this divide comes generational differences on specific issue areas , from views of racial discrimination and immigration to foreign policy and the scope of government.
Population change and the future
By 2019, Millennials are projected to number 73 million, overtaking Baby Boomers as the largest living adult generation . Although a greater number of births underlie the Baby Boom generation, Millennials will outnumber Boomers in part because immigration has been boosting their numbers.
Millennials are also bringing more racial and ethnic diversity. When the Silent Generation was young (ages 22 to 37), 84% were non-Hispanic white. For Millennials, the share is just 55%. This change is driven partly by the growing number of Hispanic and Asian immigrants , whose ranks have increased since the Boomer generation. The increased prevalence of interracial marriage and differences in fertility patterns have also contributed to the country’s shifting racial and ethnic makeup.
Looking ahead at the next generation, early benchmarks show Generation Z (those ages 6 to 21 in 2018) is on track to be the nation’s most diverse and best-educated generation yet. Nearly half (48%) are racial or ethnic minorities. And while most are still in K-12 schools, the oldest Gen Zers are enrolling in college at a higher rate than even Millennials were at their age. Early indications are that their opinions on issues are similar to those of Millennials .
Of course, Gen Z is still very young and may be shaped by future unknown events. But Pew Research Center looks forward to spending the next few years studying life for this new generation as it enters adulthood.
All photos via Getty Images
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
Reimagining Design with Nature: ecological urbanism in Moscow
- Reflective Essay
- Published: 10 September 2019
- Volume 1 , pages 233–247, ( 2019 )
Cite this article
- Brian Mark Evans ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1420-1682 1
977 Accesses
2 Citations
Explore all metrics
The twenty-first century is the era when populations of cities will exceed rural communities for the first time in human history. The population growth of cities in many countries, including those in transition from planned to market economies, is putting considerable strain on ecological and natural resources. This paper examines four central issues: (a) the challenges and opportunities presented through working in jurisdictions where there are no official or established methods in place to guide regional, ecological and landscape planning and design; (b) the experience of the author’s practice—Gillespies LLP—in addressing these challenges using techniques and methods inspired by McHarg in Design with Nature in the Russian Federation in the first decade of the twenty-first century; (c) the augmentation of methods derived from Design with Nature in reference to innovations in technology since its publication and the contribution that the art of landscape painters can make to landscape analysis and interpretation; and (d) the application of this experience to the international competition and colloquium for the expansion of Moscow. The text concludes with a comment on how the application of this learning and methodological development to landscape and ecological planning and design was judged to be a central tenant of the winning design. Finally, a concluding section reflects on lessons learned and conclusions drawn.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Principles for public space design, planning to do better
Matthew Carmona
What is a walkable place? The walkability debate in urban design
Ann Forsyth

Acknowledgements
The landscape team from Gillespies Glasgow Studio (Steve Nelson, Graeme Pert, Joanne Walker, Rory Wilson and Chris Swan) led by the author and all our collaborators in the Capital Cities Planning Group.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Mackintosh School of Architecture, The Glasgow School of Art, 167 Renfrew Street, Glasgow, G3 6BY, UK
Brian Mark Evans
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Brian Mark Evans .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Evans, B.M. Reimagining Design with Nature: ecological urbanism in Moscow. Socio Ecol Pract Res 1 , 233–247 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42532-019-00031-5
Download citation
Received : 17 March 2019
Accepted : 13 August 2019
Published : 10 September 2019
Issue Date : October 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s42532-019-00031-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Design With Nature
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Home — Essay Samples — Geography & Travel — Travel and Tourism Industry — The History of Moscow City
The History of Moscow City
- Categories: Russia Travel and Tourism Industry
About this sample

Words: 614 |
Published: Feb 12, 2019
Words: 614 | Page: 1 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Geography & Travel

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
13 pages / 6011 words
1 pages / 657 words
4 pages / 2143 words
6 pages / 3010 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Travel and Tourism Industry
The ethics in the hospitality industry play a pivotal role in shaping the reputation and success of businesses within this sector. Ethics encompass the principles and values that guide behavior, decision-making, and interactions [...]
Traveling is an enriching experience that allows individuals to explore new cultures, meet people from different backgrounds, and broaden their perspectives. In the summer of 2019, I had the opportunity to embark on an amazing [...]
Travelling is a topic that has been debated for centuries, with some arguing that it is a waste of time and money, while others believe that it is an essential part of life. In this essay, I will argue that travelling is not [...]
Traveling has always been a significant part of my life. From a young age, I have been fortunate enough to explore different cultures, experience new traditions, and immerse myself in the beauty of our world. My passion for [...]
When planning a business trip all aspects and decisions rely heavily on the budget set by the company for the trip. Once Sandfords have confirmed the location careful consideration should be used to choose the travel method and [...]
Tourism is an action of worldwide imperativeness and importance as it is a major force in the economy (Cooper et al. 2008). Tourism has undeniably developed as one of the most significant economic and social phenomena of the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
In Moscow’s Technological Advances, a ‘Double-Edged Sword’
The latest example is Face Pay, which replaces a Metro card with facial recognition. It may be advanced, but activists are sounding the alarm on privacy issues.

By Celestine Bohlen
The Moscow Metro — a world-class marvel of efficient mass transportation since it opened in 1935 — made headlines last month with a very 21st-century innovation: a payment system that doesn’t require passengers to produce a ticket, a transit card, a smartphone or a contactless bank card. All they have to do is show their face.
By Oct. 15, the facial recognition system, called Face Pay, was up and running at about 240 stations on the Moscow Metro, a sprawling and constantly expanding system famous for its on-time track record and its grandiose and ornate stations.
Moscow city officials were quick to tout the system’s latest technological innovation, one of several over the last decade. “There are no analogues of Face Pay in terms of quality and ease of use for a passenger anywhere in the world,” said Maksim Liksutov, deputy mayor for transport.
To activate Face Pay, passengers must connect their photo with a bank card and the Metro’s Troika, or transit card, via a special mobile app. Once connected, a camera at the turnstiles identifies their faces (even with masks on) and opens the gates. In theory, it should take two to three seconds for a passenger to clear the turnstile, easing the crush of people at peak rush hours.
It is one of the most visible — and controversial — of the city’s projects to modernize its services, one that takes full advantage of advancing biometric technology and the skills of a new generation of Russian computer engineers. “The technology is new and very complex, we will continue to work on improving it,’’ said Moscow’s mayor, Sergei Sobyanin, in a statement.
But digital privacy activists in Russia were quick to raise the alarm, noting that the new system is not just about improving service on the Moscow Metro. “It is a good pretext to put cameras at the turnstiles,’’ said Artyom Koslyuk, a director at Roskomsvoboda, a digital rights group based in Moscow. “This will allow them to perfect the algorithms used for the recognition of faces.’’
According to Mr. Koslyuk, Moscow ranks third in the world for the most surveillance on streets and public transport, with some 200,000 cameras placed around the city and on the Metro to help police identify criminals and prevent crime. Russian police have already used facial recognition to find and arrest demonstrators who participated in peaceful opposition protests.
The two other countries that have gone ahead with facial recognition payment systems are China and Belarus, where privacy rights are also of little concern to the government. (In Belarus, the facial recognition system on the Minsk metro is called Look and Go.) In contrast, the European Parliament voted last month in favor of a nonbinding resolution to ban use of facial recognition technology in public places for police purposes.
Moscow officials have tried to calm concerns about privacy invasion by insisting that the images and data collected are “securely encrypted.’’ Roskomsvoboda, though, said they have uncovered evidence that the system is porous, vulnerable to intruders who can use the data and images for criminal purposes.
Privacy advocates are pushing for a more transparent system of control for this and other advanced, and often intrusive, technologies. “We need to be sure that all these innovations are used to help the people, not harm them,’’ said Mr. Koslyuk.
Face Pay is part of a broader set of efforts in the city to institute technological solutions. Moscow is undoubtedly Russia’s “smartest” city, not least because it is the nation’s capital, and a focus of government attention. Its 12.5 million people make it the second most populous city in Europe — and it is growing. Between 2002 and 2010, while Russia’s population decreased by 1.2 percent, Moscow’s grew by 10.9 percent. And the average wage in the capital is almost double the national average.
The capital also gets royal treatment from the federal government. In 2019, Moscow’s urban renewal budget equaled that of the rest of the country.
“Moscow has the power in terms of finance and budgets,’’ said Sergei Kamolov, a professor at the prestigious Moscow State Institute of International Relations. “Moscow is in the avant-garde, a test case for all different kinds of systems.’’
Two years ago, Russia adopted its own system for ranking its “smart cities,” measuring what is called their “I.Q. level.” This provides benchmarks for cities to measure progress in putting modern techniques and digital services in place for their population. Mr. Kamolov said these are useful tools to pressure local officials to meet targets set in a national “Smart Cities” program.
Mr. Kamolov, who is member of a working group on the “Smart Cities” program, cautions that its ideas and technologies are not easily duplicated from city to city. Nor, he said, do fancy new technologies necessarily have an impact on the citizens’ quality of life. “It seems to me that ‘Smart Cities’ is a deep marketing concept,’’ he said in a telephone interview.
In recent years, Russia has put a major nationwide effort into its e-government services. Ahead of the 2018 World Cup, Russia developed a system of e-visas, allowing tourists to come into the country for a limited time and for limited purpose. And like many countries, it has developed a popular online government portal — known as Gosuslugi , a one-stop website where citizens can retrieve documents, pay fines and make appointments. In a 2020 United Nations e-government survey , Russia’s services ranked 36th out of 193 countries.
In this, as in other areas, Moscow leads the way. More Muscovites use Gosuslgi proportionately than any other region of Russia — not surprising given its concentration of young, educated and computer literate people. But other regions are stepping up efforts to catch up, by offering special courses for computer literacy , especially for the elderly.
Moscow and six other regions were also used as a test case for Russia’s experiment with online voting in last September’s parliamentary elections. The system was challenged by democracy protesters, who described it as a “black box” that allowed the government to fiddle with the vote. Setting aside the contested results — a huge caveat, to be sure — online voting did its job, at least on a technical level.
Moscow has introduced other digital services in health care, in schools and in the legal system, but transportation continues to receive a hefty share of the city’s modernization budget.
According to Mr. Kamolov, Moscow has the largest fleet of electronic buses in Europe while the Metro — which now moves about six million passengers on weekdays (down from more than eight million in the pre-Covid era) — still commands a large portion of public funds: $27 billion for expansion and improvement from 2011 to 2022 , most of it for expansion but some of it undoubtedly for the facial recognition system that is now expected to be introduced in other Russian cities.
At Roskomsvoboda, Mr. Koslyuk says the key to introducing advanced digital services that depend on personal data is trust. ‘‘We need to be sure there are controls,’’ he said. “These improvements can be a double-edged sword.”
- Contributors : About the Site
Newgeography.com
- Urban Issues
- Small Cities
- Demographics
Moscow, like other international urban areas , is decentralizing, despite considerable barriers. The expansion will lead to even more decentralization, which is likely to lead to less time "stuck in traffic" and more comfortable lifestyles. Let's hope that Russia's urban development policies, along with its plans to restore population growth, will lead to higher household incomes and much improved economic performance.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris and the author of “ War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life ”
Note 1: The 23 ward (ku) area of Tokyo is the geography of the former city of Tokyo, which was abolished in the 1940s. There is considerable confusion about the geography of Tokyo. For example, the 23 ward area is a part of the prefecture of Tokyo, which is also called the Tokyo Metropolis, which has led some analysts to think of it as the Tokyo metropolitan area (labor market area). In fact, the Tokyo metropolitan area, variously defined, includes, at a minimum the prefectures of Tokyo, Kanagawa, Chiba and Saitama with some municipalities in Gunma, Ibaraki and Tochigi. The metropolitan area contains nearly three times the population of the "Tokyo Metropolis."
Note 2: The expansion area (556 square miles or 1,440 square kilometers) has a current population of 250,000.
Note 3: Includes all residents in suburban districts with at least part of their population in the urban area.
Note 4: Urban area data not yet available.
Photo: St. Basil's Cathedral (all photos by author)
- Login to post comments
- Evolving Urban Form: Development Profiles of World Urban Areas
- Transportation
Comment viewing options
Road in city area.
The roads and ways of the city areas are very clumsy and many accidents are happening due to the short road. But you need to maintain the driving properly otherwise you may face accident. So now the government decided to expand the road which may put the positive effect on automobile sector. I think it is a helpful service for the society people. If you have a BMW car and you have faced any problem then better to repair it at BMW Repair Spring, TX for the best service.
Transit & transportation
Transit and transportation services are quite impressive in most of the urban cities; therefore people were getting better benefits from suitable transportation service. Urban cities like Moscow, Washington, New York and Tokyo; we have found high margin of transportation system that helps to build a better communication network in these cities. I hope through the help of modern transportation system we are able to bring revolutionary change in automobile industries; in this above article we have also found the same concepts to develop transportation system. Mercedes repair in Torrance
Moscow is bursting Noblesse
Moscow is bursting Noblesse at the seams. The core city covers more than 420 square miles (1,090 kilometers), and has a population of approximately 11.5 million people. With 27,300 residents per square mile (10,500 per square kilometer), Moscow is one percent more dense than the bleach anime watch city of New York, though Moscow covers 30 percent more land. The 23 ward area of Tokyo (see Note) is at least a third more dense, though Moscow's land area is at least half again as large as Tokyo. All three core areas rely
Belgravia Villas is a new
Belgravia Villas is a new and upcoming cluster housing located in the Ang Mo Kio area, nested right in the Ang Mo Kio landed area. It is within a short drive to Little India, Orchard and city area. With expected completion in mid 2016, it comprises of 118 units in total with 100 units of terrace and 18 units of Semi-D. belgravia villas
Russians seeing the light while Western elites are bickering?
What an extremely interesting analysis - well done, Wendell.
It is also extremely interesting that the Russian leadership is reasonably pragmatic about urban form, in contrast to the "planners" of the post-rational West.
An acquaintance recently sent me an article from "The New Yorker", re Moscow's traffic problems.
The article "abstract" is HERE (but access to the full article requires subscription)
http://www.newyorker.com/reporting/2010/08/02/100802fa_fact_gessen
One classic quote worth taking from it, is: "People will endure all manner of humiliation to keep driving".
I do find it odd that the "New Yorker" article author says nothing at all about the rail transit system Moscow had, on which everyone was obliged to travel, under Communism. It can't surely have vaporised into thin air?
Moscow is a classic illustration of just how outmoded rails are, and how important "automobility" is, when the auto supplants rails so rapidly than even when everybody did travel on rails up to a certain date, and the road network dates to that era, when nobody was allowed to own a car; an article written just 2 decades later does not even mention the rail transit system, other than to criticise the mayor for "failing to invest in a transit system".......!!!!!!!!
This is also a give-away of "The New Yorker's" inability to shake off the modern PC ideology on rails vs cars.
Subscribe to NG Articles
Get new posts by email:, connect with us:.

NewGeography.com is a joint venture of Joel Kotkin and Praxis Strategy Group
Featured Content

The Coming of Neo-Feudalism

Infinite Suburbia

Recent blog posts
- The Truth About Being Jewish and in College
- Feudal Future: The Impact of Third-Party Candidates in Tipping the Election Scale
- Multiple More Jobs Accessible by Automobile Than by Transit
- Large Majority of Minorities Live in Suburbs
- Feudal Future: Addressing the Housing Affordability Crisis & Protecting the Middle Class Dream
- Shift of Net Domestic Migration to Smaller MSAs and Outside CBSAs
- Feudal Future Podcast: Navigating the Global Politics That May Shape America's 2024 Elections
- YIMBY Can Populate Conference Halls (at Least)
- Feudal Future Podcast: Exploring the Impact of Catholic Schools on Underserved Communities
- Feudal Future Podcast: Exploring the Paradox of Peace and Economics in Taiwan-China Relations

Recent popular content
- Revisiting Toronto’s G20 Costs
- Engines of Opportunity
- Agressive Canadian Progressivism is Descending the Country into Crazy
- What Is a Global City?
- California Is the Homeland of Progressive Anti-Semitism
- Gavin Newsom's Futile Bid to Trump-Proof California
- "Jaw-Droppingly Shameless:" Mother Jones on California High Speed Rail Projection
- Are Chinese Ready to Rent?
More from this author
- Largest World Cities: 2014
- Largest Cities in the World: 2016
- World Urban Areas Population and Density: A 2012 Update
- Largest 1,000 Cities on Earth: World Urban Areas: 2015 Edition
- The Evolving Urban Form: Rio de Janeiro
Recommended Books
Blogroll and partner sites.
- Burgh Diaspora
- Center for Economic Research and Forecasting
- China Urban Development Blog
- Chris Bradford - Austin Contrarian
- Houston Strategies
- LA Observed
- Multiplier Effect: Levy Economics Institute
- The Rural Blog
- The Urbanophile
- Request new password
- © 2024 New Geography
- CONTRIBUTORS :
- PRIVACY POLICY
- Stay up to date:


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Every generation of teens is shaped by the social, political, and economic events of the day. Today's teenagers are no different—and they're the first generation whose lives are saturated by mobile technology and social media. In her new book, psychologist Jean Twenge uses large-scale surveys to draw a detailed portrait of ten qualities ...
The sociologist Karl Mannheim, in an influential essay published in 1928, used the term "generation units" to refer to writers, artists, and political figures who self-consciously adopt new ...
January 3, 2022. Gen Z are not 'coddled.'. They are highly collaborative, self-reliant and pragmatic, according to new Stanford-affiliated research. Generation Z, the first generation never to ...
Longtermism is one of those good ideas. It helps us better place our present in humanity's bigger story. It's humbling and inspiring to see the role we can play in protecting the future. We ...
In conclusion, today's generation is a dynamic and complex group. They are digital natives, navigating a world interwoven with technology. They are socially and environmentally conscious, driven to make a positive impact on the world. And despite the challenges they face, they are resilient, adaptable, and poised to shape the future.
The generation of people born between 1997 and 2012 is changing fashion, culture, politics, the workplace and more. A younger generation of crossword constructors is using an old form to reflect ...
Teenagers in the new generation spend most of their time chatting with their friends on their mobile phones or chatting online more than doing anything else. On the other hand, people from older generation are accustomed to writing letters to contact friends that are far away. Furthermore, they like to deal with other people face to face.
According to an August 2018 report from Bloomberg, Gen Z is set to outnumber millennials within a year: Gen Z will comprise 32 percent of the global population of 7.7 billion in 2019, nudging ...
Gen Z is currently the second-youngest generation, with millennials before and Generation Alpha after. Like every generation, Gen Z's behaviors are shaped by how they grew up. Young people today have come of age in the shadow of climate doom, pandemic lockdowns, and fears of economic collapse. The first Gen Zers were born when the internet ...
Generation Z represents the leading edge of the country's changing racial and ethnic makeup. A bare majority (52%) are non-Hispanic white - significantly smaller than the share of Millennials who were non-Hispanic white in 2002 (61%). One-in-four Gen Zers are Hispanic, 14% are black, 6% are Asian and 5% are some other race or two or more races.
Introduction Today's generation is very different from their parents' generation. Essay on the topic of the generation gap will shed light on these... read full [Essay Sample] for free. search. Essay Samples. ... the people from new generation in Burma need to adapt with different people and different lifestyle because they are living in ...
Four-in-ten Millennials with just a high school diploma (40%) are currently married, compared with 53% of Millennials with at least a bachelor's degree. In comparison, 86% of Silent Generation high school graduates were married in 1968 versus 81% of Silents with a bachelor's degree or more. Millennial women are also waiting longer to become ...
Then, on a pad of paper or a word processor, write continuously for two or three minutes. Don't stop, not even for a moment. Write down anything that comes to mind, no matter how nonsensical it seems, as long as it somehow relates to the topic you began with. If you need to, time yourself to make sure you write for a few minutes straight.
The EssayNew Generation Thinkers 2023. New Generation Thinker Dan Taylor's essay takes us to the site of the Dagenham Ford factory, and shares the insights he's gained about planning from ...
Better Essays. 1767 Words. 8 Pages. Open Document. The New Generation. Are the youth simply throwing their lives down a long and winding pipeline which leads to nothing but an empty space somewhere in this prodigious yet opportunistic world we live in? It's a question one must think about now that the new generation has decided to place their ...
generations come and go every generation owns it own particular values attitudes morals and goals that make them apart from the other generations. A generation gap has always been noticed between the past and the new generations. this barrier between generations has been created due to many different reasons such as - technological progress ...
717 Words2 Pages. Recommended: Technology and society. The older generation has taught the newer generation many lessons, ranging from basic education to social conduct. However, the newer generation also has many lessons to teach the older generation, such as open mindedness, freedom of thought, perseverance, and enjoying life.
In 2003, a UK landscape studio was offered the opportunity to become involved in the design of a new settlement in the Moscow Region to carry out landscape planning and design (Figs. 1, 2a, b—Moscow in context). Gillespies LLP is a long-established practice of landscape architects, urban designers and environmental planners established in Glasgow, UK, in 1962 (Gillespies web link 2019).
The History of Moscow City. Moscow is the capital and largest city of Russia as well as the. It is also the 4th largest city in the world, and is the first in size among all European cities. Moscow was founded in 1147 by Yuri Dolgoruki, a prince of the region. The town lay on important land and water trade routes, and it grew and prospered.
Face Pay is part of a broader set of efforts in the city to institute technological solutions. Moscow is undoubtedly Russia's "smartest" city, not least because it is the nation's capital ...
Moscow is bursting at the seams. The core city covers more than 420 square miles (1,090 kilometers), and has a population of approximately 11.5 million people. With 27,300 residents per square mile (10,500 per square kilometer), Moscow is one percent more dense than the city of New York, though Moscow covers 30 percent more land.