Most Popular
English and social studies teachers pioneer ai usage in schools, study finds, best summarising strategies for students.
13 days ago

TeachMeforFree Review
How to cite page numbers in apa, what is accidental plagiarism, the origins of film essay sample, example.

By Ion Martea
There are multiple debates concerning the origins of film. Photographers in the nineteenth century were anxious to find a way to capture movement, almost from the moment they discovered the art of photography. It took less than half a century, and by the 1870s, Edward Muybridge has already made significant advances, managing with the use of the zoopraxiscope to exhibit successfully a series of moving images. Muybridge was a scientist, so for him the experiments did not serve an artistic purpose. That is why, despite their historical importance in the development of technology, his pieces are rather foreign to film as we understand it.
The birth of film as an artform can be pinpointed conveniently to 1895, with the first public exhibition of a number of one-minute single shots directed by the Lumière brothers. L’arrivée d’un train à La Ciotat [Arrival of a Train at La Ciotat] (1896) has all the attributes to earn it the accolade of being the first film, particularly as it was shown originally to a large audience. However, as the popularity of television and home video has proven, film spectatorship can also be solitary. The acceptance of film as a solitary experience, not only a collective one, has allowed the earlier mavericks (who only managed to offer screenings of their output to one spectator at a time) to claim the invention of the medium.
The recently discovered Roundhay Garden Scene (1888) is probably the earliest film, followed swiftly by works by two other Englishmen: William Friese-Greene working in the UK (1889), and William K.L. Dickson, the celebrated employee at Edison Manufacturing Company, in the USA (1890). These are all raw pieces, running several seconds, yet they all share two elements lacking in Muybridge’s work, namely a continuous rather than cyclical sequence, and most importantly the occurrence of certain emotional experiences to images that are potentially ideological in essence.
Pinpointing the true birth of film, as opposed to the conception of it, is therefore a more difficult task than one would expect. What is the first production that is both technically and ideologically essential for this early period?
A case can be made for a little known and less celebrated production by William K.L. Dickson and his fellow cinematographer William Heise, Dickson Greeting. In a dark background, a man in his early thirties, Dickson himself, with a hat in his right hand, smiles and greets all of us. It is a simple greeting, yet it is impossible to resist taking the gesture as a symbolic welcome into the world of film.
William K.L. Dickson’s inventions of both the kinetograph and the kinetoscope stand as two of the most important developments in the industry. The convention that film should be 35mm wide is another of his essential decisions. Even the Lumière’s cinematograph is a slight improvement on Dickson’s work. Therefore, the solitary greeting, coming from the inventor himself, is all the more intriguing.
As opposed to the Lumière technique of recording social events as historical documents, from the very beginning, Dickson saw the potential of using the moving image to tell a story, primarily through performance. In Dickson Greeting, judging from the body language, he is clearly performing for the camera, aware of the effect this might have over the spectator. It is then to assume that the greeting into the world of motion pictures was fully intended by the filmmaker.
A contemporary journalist from the New York Sun covering the first presentation of the kinetograph to a group of 147 members of the convention of women’s club in America in May 1891 remarked: ‘As they looked through this hole, they saw the picture of a man. It was a most marvellous picture. It bowed and smiled and waved its hands and took off its hat with the most perfect naturalness and grace. Every motion was perfect. There was not a hitch or a jerk.’
Film’s ability to reproduce naturalness seemed to have been noted at the dawn of the industry. However, Dickson was the one to develop this potential by consistently staging events to be filmed. The point was not to show the magic of motion pictures through visual effects, as pursued throughout the 1890s by Émile Reynaud and Georges Méliès, but to create sequences that looked like snippets of reality. The staging is less apparent in Dickson Greeting, although it is implied by the mere process of posing for the camera, but the directorial technique is evident in less successful pieces such as Men Boxing (1891), in which two men seem to do anything but box.
One other important element introduced in Dickson Greeting is the tradition of constructing a narrative through a single/leading performer, in clear opposition to the contemporary European shorts, primarily concerned with establishing a social context. Hollywood, throughout most of the 20th century, rarely questioned the idea that individualism is intrinsic to American culture. Instead, it got hold of the concept and used it scrupulously, ultimately leading to severe criticism of single-mindedness and over-simplification of film narrative.
Of course, such generalisations bring with them exceptions to the rule. However, the persistence of leading characters in early American film did create a certain cultural expectation in the audience that they should be able to identify with the emotions of a single individual, and through him or her to access universal ideas. Yet, this tradition was not necessarily the expression of a national trait, but was arguably a result of the technical limitations of the kinetograph, which did not make it easy to work with a large cast.
The sheer rawness of early film is often off-putting and can make the films seem uninteresting to modern audiences. However, it is precisely this crudeness that helps us identify the essential elements of film. Dickson Greeting is neither the first film, nor the most celebrated one, yet its symbolic magnetism of establishing film as a technical invention capable of developing a meta-linguistic artistic narrative, makes it as one of the most intriguing productions in the history of the medium. Dickson welcomed us; we could not resist the temptation to come in. We believed in his performance and allowed ourselves to be charmed by the illusion of motion pictures. In that, the film is unique.
——–
This was written under a Creative Commons License, with edits: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from Expository Essay Examples and Samples

Nov 23 2023
Why Is Of Mice And Men Banned

Nov 07 2023
Pride and Prejudice Themes

May 10 2023
Remote Collaboration and Evidence Based Care Essay Sample, Example
Related writing guides, writing an expository essay.
Remember Me
Is English your native language ? Yes No
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
Javascript is disabled
- We are changing
- Pictureville Presents
- Accessible screenings
- Sound and Vision
- Objects and stories
- Researchers
- Access to our collection
- Research help
- Research directory
- Donate an object
- Science Museum Group Journal
- Press office
- Support the museum
- Volunteering
- Corporate sponsorship
National Science and Media Museum Bradford BD1 1NQ
The museum, IMAX and Pictureville are temporarily closed. Find out about our major transformation .
A very short history of cinema
Published: 18 June 2020
Learn about the history and development of cinema, from the Kinetoscope in 1891 to today’s 3D revival.
Cinematography is the illusion of movement by the recording and subsequent rapid projection of many still photographic pictures on a screen. Originally a product of 19th-century scientific endeavour, cinema has become a medium of mass entertainment and communication, and today it is a multi-billion-pound industry.
Who invented cinema?

No one person invented cinema. However, in 1891 the Edison Company successfully demonstrated a prototype of the Kinetoscope , which enabled one person at a time to view moving pictures.
The first public Kinetoscope demonstration took place in 1893. By 1894 the Kinetoscope was a commercial success, with public parlours established around the world.
The first to present projected moving pictures to a paying audience were the Lumière brothers in December 1895 in Paris, France. They used a device of their own making, the Cinématographe, which was a camera, a projector and a film printer all in one.
What were early films like?
At first, films were very short, sometimes only a few minutes or less. They were shown at fairgrounds, music halls, or anywhere a screen could be set up and a room darkened. Subjects included local scenes and activities, views of foreign lands, short comedies and newsworthy events.
The films were accompanied by lectures, music and a lot of audience participation. Although they did not have synchronised dialogue, they were not ‘silent’ as they are sometimes described.
The rise of the film industry
By 1914, several national film industries were established. At this time, Europe, Russia and Scandinavia were the dominant industries; America was much less important. Films became longer and storytelling, or narrative, became the dominant form.
As more people paid to see movies, the industry which grew around them was prepared to invest more money in their production, distribution and exhibition, so large studios were established and dedicated cinemas built. The First World War greatly affected the film industry in Europe, and the American industry grew in relative importance.
The first 30 years of cinema were characterised by the growth and consolidation of an industrial base, the establishment of the narrative form, and refinement of technology.
Adding colour
Colour was first added to black-and-white movies through hand colouring, tinting, toning and stencilling.
By 1906, the principles of colour separation were used to produce so-called ‘natural colour’ moving images with the British Kinemacolor process, first presented to the public in 1909.
Kinemacolor was primarily used for documentary (or ‘actuality’) films, such as the epic With Our King and Queen Through India (also known as The Delhi Durbar ) of 1912, which ran for over 2 hours in total.
The early Technicolor processes from 1915 onwards were cumbersome and expensive, and colour was not used more widely until the introduction of its three‑colour process in 1932. It was used for films such as Gone With the Wind and The Wizard of Oz (both 1939) in Hollywood and A Matter of Life and Death (1946) in the UK.

Frames of stencil colour film

Advertisement for With Our King and Queen Through India , 1912

Adding sound

The first attempts to add synchronised sound to projected pictures used phonographic cylinders or discs.
The first feature-length movie incorporating synchronised dialogue, The Jazz Singer (USA, 1927), used the Warner Brothers’ Vitaphone system, which employed a separate record disc with each reel of film for the sound.
This system proved unreliable and was soon replaced by an optical, variable density soundtrack recorded photographically along the edge of the film, developed originally for newsreels such as Movietone.
Cinema’s Golden Age
By the early 1930s, nearly all feature-length movies were presented with synchronised sound and, by the mid-1930s, some were in full colour too. The advent of sound secured the dominant role of the American industry and gave rise to the so-called ‘Golden Age of Hollywood’.
During the 1930s and 1940s, cinema was the principal form of popular entertainment, with people often attending cinemas twice a week. Ornate ’super’ cinemas or ‘picture palaces’, offering extra facilities such as cafés and ballrooms, came to towns and cities; many of them could hold over 3,000 people in a single auditorium.
In Britain, the highest attendances occurred in 1946, with over 31 million visits to the cinema each week.

What is the aspect ratio?
Thomas Edison had used perforated 35mm film in the Kinetoscope, and in 1909 this was adopted as the worldwide industry standard. The picture had a width-to-height relationship—known as the aspect ratio—of 4:3 or 1.33:1. The first number refers to the width of the screen, and the second to the height. So for example, for every 4 centimetres in width, there will be 3 in height.
With the advent of optical sound, the aspect ratio was adjusted to 1.37:1. This is known as the ‘Academy ratio’, as it was officially approved by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (the Oscars people) in 1932.
Although there were many experiments with other formats, there were no major changes in screen ratios until the 1950s.
How did cinema compete with television?

The introduction of television in America prompted a number of technical experiments designed to maintain public interest in cinema.
In 1952, the Cinerama process, using three projectors and a wide, deeply curved screen together with multi-track surround sound, was premiered. It had a very large aspect ratio of 2.59:1, giving audiences a greater sense of immersion, and proved extremely popular.
However, Cinerama was technically complex and therefore expensive to produce and show. Widescreen cinema was not widely adopted by the industry until the invention of CinemaScope in 1953 and Todd‑AO in 1955. Both processes used single projectors in their presentation.

CinemaScope ‘squeezed’ images on 35mm film; when projected, they were expanded laterally by the projector lens to fit the screen. Todd-AO used film with a width of 70mm. By the end of the 1950s, these innovations had effectively changed the shape of the cinema screen, with aspect ratios of either 2.35:1 or 1.66:1 becoming standard. Stereo sound, which had been experimented with in the 1940s, also became part of the new widescreen experience.
Specialist large-screen systems using 70mm film were also developed. The most successful of these has been IMAX, which as of 2020 has over 1,500 screens around the world. For many years IMAX cinemas have shown films specially made in its unique 2D or 3D formats but more recently they have shown popular mainstream feature films which have been digitally re-mastered in the IMAX format, often with additional scenes or 3D effects.

How have cinema attendance figures changed?
While cinemas had some success in fighting the competition of television, they never regained the position and influence they held in the 1930s and 40s, and over the next 30 years audiences dwindled. By 1984 cinema attendances in Britain had declined to one million a week.

By the late 2000s, however, that number had trebled. The first British multiplex was built in Milton Keynes in 1985, sparking a boom in out-of-town multiplex cinemas.
Today, most people see films on television, whether terrestrial, satellite or subscription video on demand (SVOD) services. Streaming film content on computers, tablets and mobile phones is becoming more common as it proves to be more convenient for modern audiences and lifestyles.
Although America still appears to be the most influential film industry, the reality is more complex. Many films are produced internationally—either made in various countries or financed by multinational companies that have interests across a range of media.
What’s next?
In the past 20 years, film production has been profoundly altered by the impact of rapidly improving digital technology. Most mainstream productions are now shot on digital formats with subsequent processes, such as editing and special effects, undertaken on computers.
Cinemas have invested in digital projection facilities capable of producing screen images that rival the sharpness, detail and brightness of traditional film projection. Only a small number of more specialist cinemas have retained film projection equipment.
In the past few years there has been a revival of interest in 3D features, sparked by the availability of digital technology. Whether this will be more than a short-term phenomenon (as previous attempts at 3D in the 1950s and 1980s had been) remains to be seen, though the trend towards 3D production has seen greater investment and industry commitment than before.
Further reading
- Cinematography in the Science Museum Group collection
- The Lumière Brothers: Pioneers of cinema and colour photography , National Science and Media Museum blog
- Cinerama in the UK: The history of 3-strip cinema in Pictureville Cinema , National Science and Media Museum blog
- BFI Filmography—a complete history of UK feature film
- BFI National Archive
- Imperial War Museums film archive

Pictureville Cinema
Pictureville is the home of cinema at the National Science and Media Museum, showing everything from blockbusters to indie gems.

Robert Paul and the race to invent cinema
Discover the story of Robert Paul, the forgotten pioneer whose innovations earned him the title of ‘father of the British film industry’.

Cinema technology
Discover objects from our collection which illuminate the technological development of moving pictures.
- Part of the Science Museum Group
- Terms and conditions
- Privacy and cookies
- Modern Slavery Statement
- Web accessibility
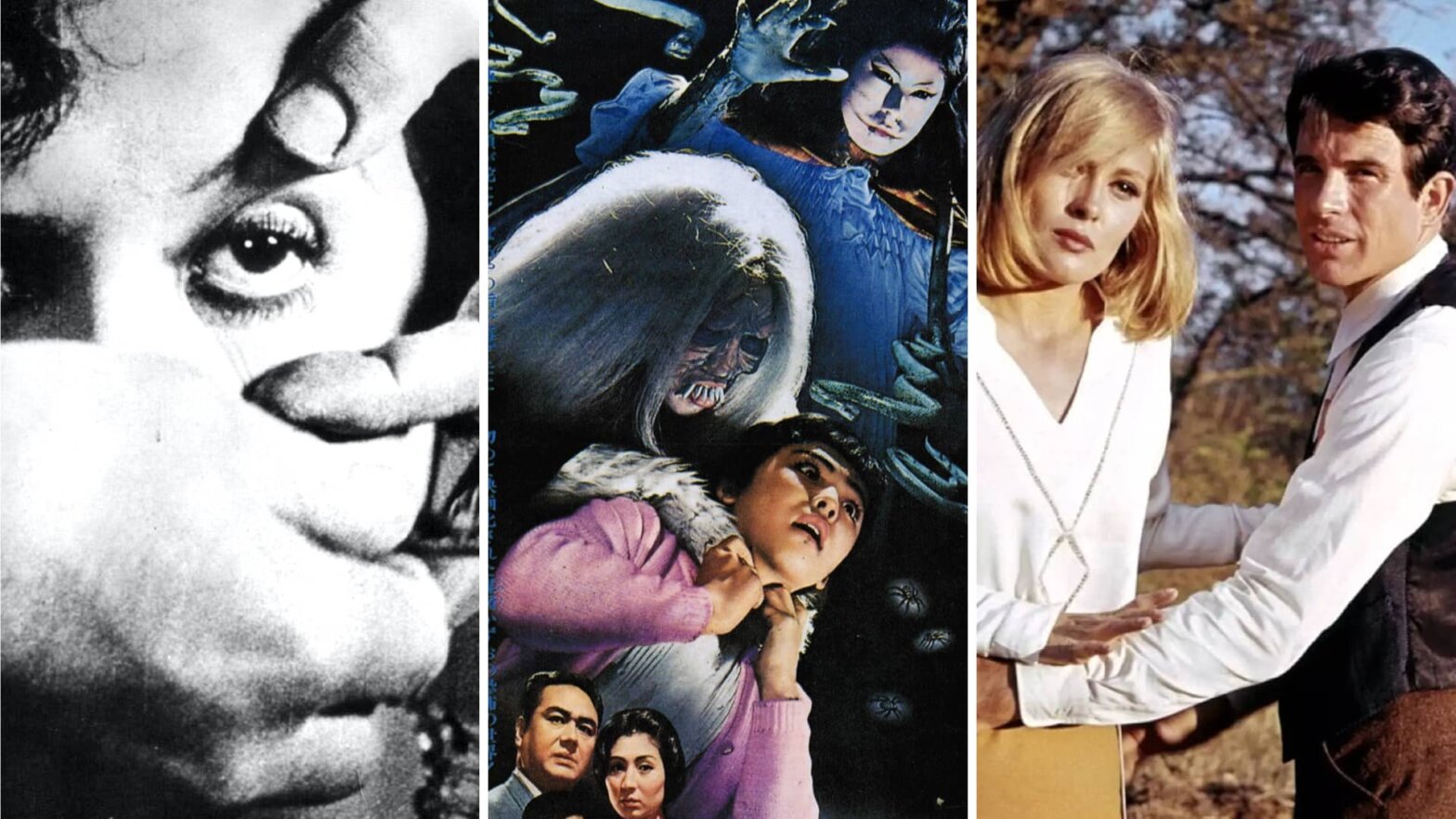

The History of Film Timeline — All Eras of Film History Explained
M otion pictures have enticed and inspired artists, audiences, and critics for more than a century. Today, we’re going to explore the history of film by looking at the major movements that have defined cinema worldwide. We’re also going to explore the technical craft of filmmaking from the persistence of vision to colorization to synchronous sound. By the end, you’ll know all the broad strokes in the history of film.
Note: this article doesn’t cover every piece of film history. Some minor movements and technical breakthroughs have been left out – check out the StudioBinder blog for more content.
- Pre-Film: Photographic Techniques and Motion Picture Theory
- The Nascent Film Era (1870s-1910): The First Motion Pictures
- The First Film Movements: Dadaism, German Expressionism, and Soviet Montage Theory
- Manifest Destiny and the End of the Silent Era
- Hollywood Epics and the Pre-Code Era
- The Early Golden Age and the Introduction of Color
- Wartime Film and Cinematic Propaganda
- Post-War Film Movements: French New Wave, Italian Neorealism, Scandinavian Revival, and Bengali Cinema
- The Golden Age of Hollywood: The Studio System and Censorship
- New Hollywood: The Emergence of Global Blockbuster Cinema
- Dogme 95 and the Independent Movement
- New Methods of Cinematic Distribution and the Current State of Film
When Were Movies Invented?
Pre-film techniques and theory.
Movies refer to moving pictures and moving pictures can be traced all the way back to prehistoric times. Have you ever made a shadow puppet show? If you have, then you’ve made a moving picture.
To create a moving picture with your hands is one thing, to utilize a device is another. The camera obscura (believed to have been circulated in the fifth century BCE) is perhaps the oldest photographic device in existence. The camera obscura is a device that’s used to reproduce images by reflecting light through a small peephole.
Here’s a picture of one from Gemma Frisius’ 1545 book De Radio Astronomica et Geometrica :
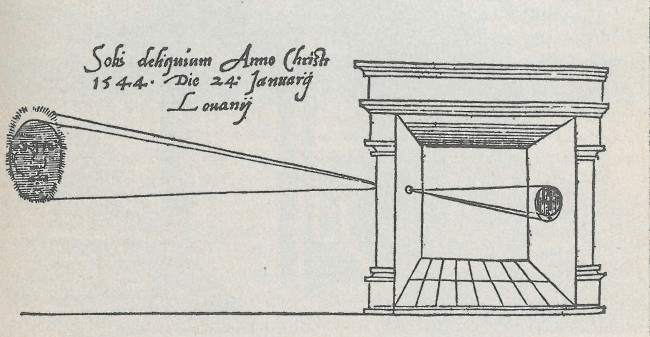
When Did Movies Start? • Camera Obscura in ‘De Radio Astronomica et Geometrica’
Through the camera obscura, we can trace the principles of filmmaking back thousands of years. But despite the technical achievement of the camera obscura, it took many of those years to develop the technology needed to capture moving images then later display them.
When Was Film Invented?
The first motion pictures.
When were movies invented ? The first motion pictures were incredibly simple – usually just a few frames of people or animals. Eadweard Muybridge’s The Horse in Motion is perhaps the most famous of these early motion pictures. In 1878, Muybridge set up a racing track with 24 cameras to photograph whether horses gallop with all four hooves off the ground at any time
The result was sensational. Muybridge’s pictures set the stage for all coming films; check out a short video on Muybridge and his work below.
When Did the First Movie Come Out? • Eadweard Muybridge’s ‘The Horse in Motion’ by San Francisco Museum of Modern Art
Muybridge’s job wasn’t done after taking the photographs though; he still had to produce a projection machine to display them. So, Muybridge built a device called the zoopraxiscope, which was regarded as a breakthrough device for motion picture projecting.
Muybridge’s films (and tech) inspired Thomas Edison to study motion picture theory and develop his own camera equipment.
Films as we know them today emerged globally around the turn of the century, circa 1900. Much of that development can be attributed to the works of the Lumière Brothers, who together pioneered the technical craft of moviemaking with their cinematograph projection machine. The Lumière Brothers’ 1895 shorts are regarded as the first commercial films of all-time; though not technically true (remember Muybridge’s work).
French actor and illusionist Georges Méliès attempted to buy a cinematograph from the Lumière Brothers in 1895, but was denied. So, Méliès ventured elsewhere; eventually finding a partner in Englishman Robert W. Paul.
Over the following years, Méliès learned just about everything there was to know about movies and projection machines. Here’s a video on Méliès’ master of film and the illusory arts from Crash Course Film History.
When Were Movies Invented? • Georges Méliès – Master of Illusion by Crash Course
Méliès’ shorts The One Man Band (1900) and A Trip to the Moon (1902) are considered two of the most trailblazing films in all of film history. Over the course of his career, Méliès produced over 500 films. His contemporary mastery of visual effects , multiple exposure , and cinematography made him one of the greatest filmmakers of all-time .
Movie History
The first film movements.
War and cinema go together like two peas in a pod. As we continue on through our analysis of the history of film, you’ll start to notice that just about every major movement sprouted in the wake of war. First, the movements that sprouted in response to World War I:
DADAISM AND SURREALISM
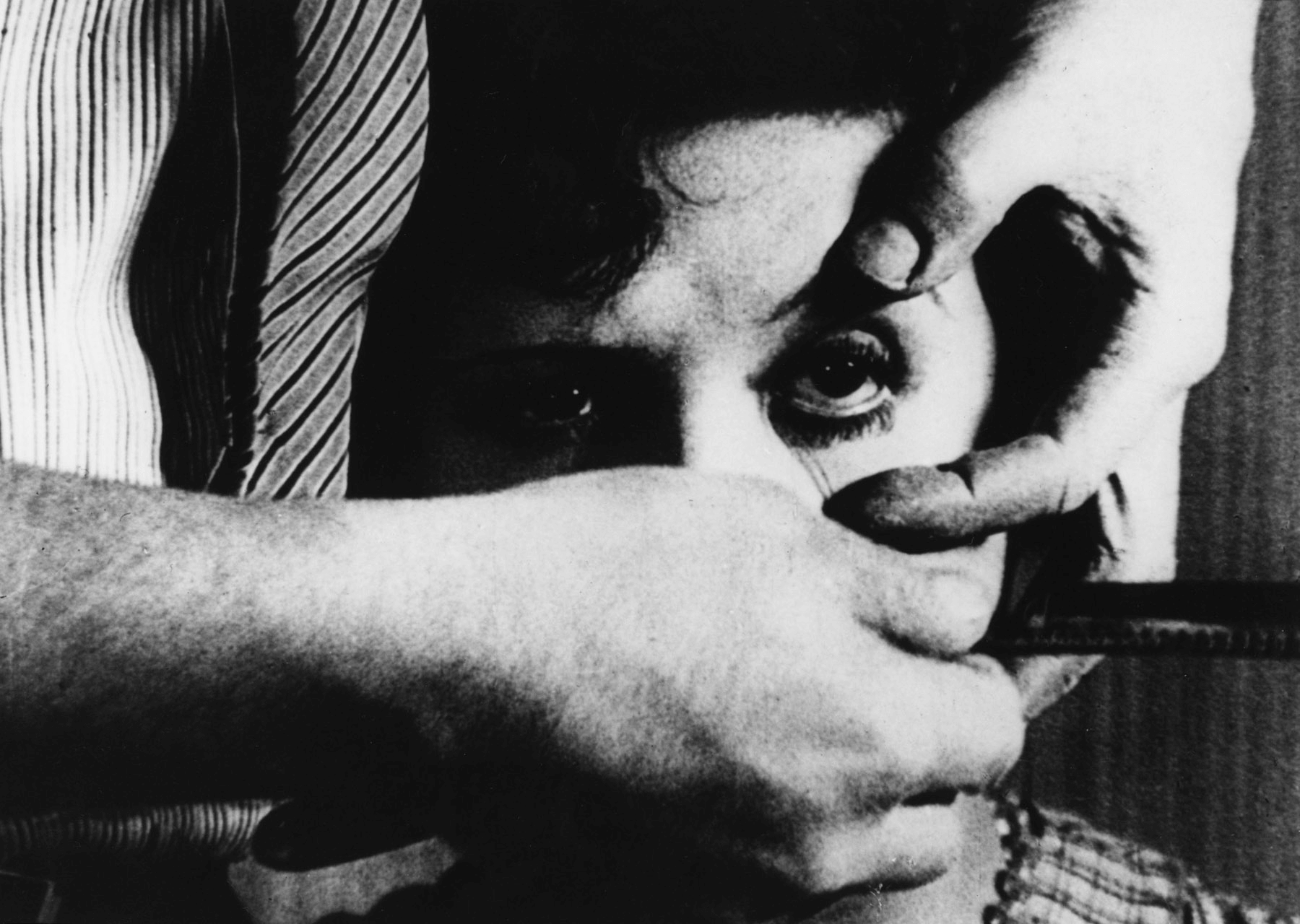
History of Motion Pictures • Still From ‘Un Chien Andalou’ by Luis Buñuel and Salvador Dalí
Major Dadaist filmmakers: Luis Buñuel, Salvador Dalí, Germaine Dulac.
Major Dadaist films: Return to Reason (1923), The Seashell and the Clergyman (1928), U n Chien Andalou (1929).
Dadaism – an art movement that began in Zurich, Switzerland during World War I (1915) – rejected authority; effectively laying the groundwork for surrealist cinema .
Dadaism may have begun in Zurich circa 1915, but it didn’t take off until years later in Paris, France. By 1920, the people of France had expressed a growing disillusionment with the country’s government and economy. Sound familiar?
That’s because they’re the same points of conflict that incited the French Revolution. But this time around, the French people revolted in a different way: with art. And not just any art: bonkers, crazy, absurd, anti-this, anti-that art.
It’s important to note that Paris wasn’t the only place where dadaist art was being created. But it was the place where most of the dadaist, surrealist film was being created. We’ll get to dadaist film in a short bit, but first, let’s review a quick video on Dada art from Curious Muse.
Where Did Film Originate? • Dadaism in 8 Minutes by Curious Muse
Salvador Dalí, Germaine Dulac, and Luis Buñuel were some of the forefront faces of the surrealist film movement of the 1920s. French filmmakers, such as Jean Epstein and Jean Renoir experimented with surrealist films during this era as well.
Dalí and Buñuel’s 1929 film Un Chien Andalou is undoubtedly one of the most influential surrealist/dadaist films. Let’s check out a clip:
History of Movies • ‘Un Chien Andalou’ Clip
The influence of Un Chien Andalou on surrealist cinema can’t be quantified; key similarities can be seen between the film and the works of Walt Disney, David Lynch , Terry Gilliam , and other surrealist directors.
Learn more about surrealism in film →
GERMAN EXPRESSIONISM

The Creation of Film and German Expressionism • Still From ‘The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari’ by Robert Wiene
- German Expressionism – an art movement defined by monumentalist structures and ideas – began before World War I but didn’t take off in popularity until after the war, much like the Dadaist movement.
- Major German Expressionist filmmakers: Fritz Lang, F.W. Murnau, Robert Wiene
- Major German Expressionist films: The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari (1920), Nosferatu (1922), and Metropolis (1927).
German Expressionism changed everything for the “look” and “feel” of cinema. When you think of German Expressionism, think contrast, gothic, dark, brooding imagery and colored filters. Here’s a quick video on the German Expressionist movement from Crash Course:
History of Film Timeline • German Expressionism Explained
The great works of the German Expressionist movement are some of the earliest movies I consider accessible to modern audiences. Perhaps no German Expressionist film proves this point better than Fritz Lang’s M ; which was the ultimate culmination of the movement’s stylistic tenets. Check out the trailer for M below.
Most Important Film in History of German Expressionism • ‘M’ (1931) Trailer, Restored by BFI
M not only epitomized the “monster” tone of the German Expressionist era, it set the stage for all future psychological thrillers. The film also pioneered sound engineering in film through the clever use of diegetic and non-diegetic sound . Fun fact: it was also one of the first movies to incorporate a leitmotif as part of its soundtrack.
Over time, the stylistic flourishes of the German Expressionist movement gave way to new voices – but its influence lived on in monster-horror and chiaroscuro lighting techniques.
Learn more about German Expressionism →
SOVIET MONTAGE THEORY
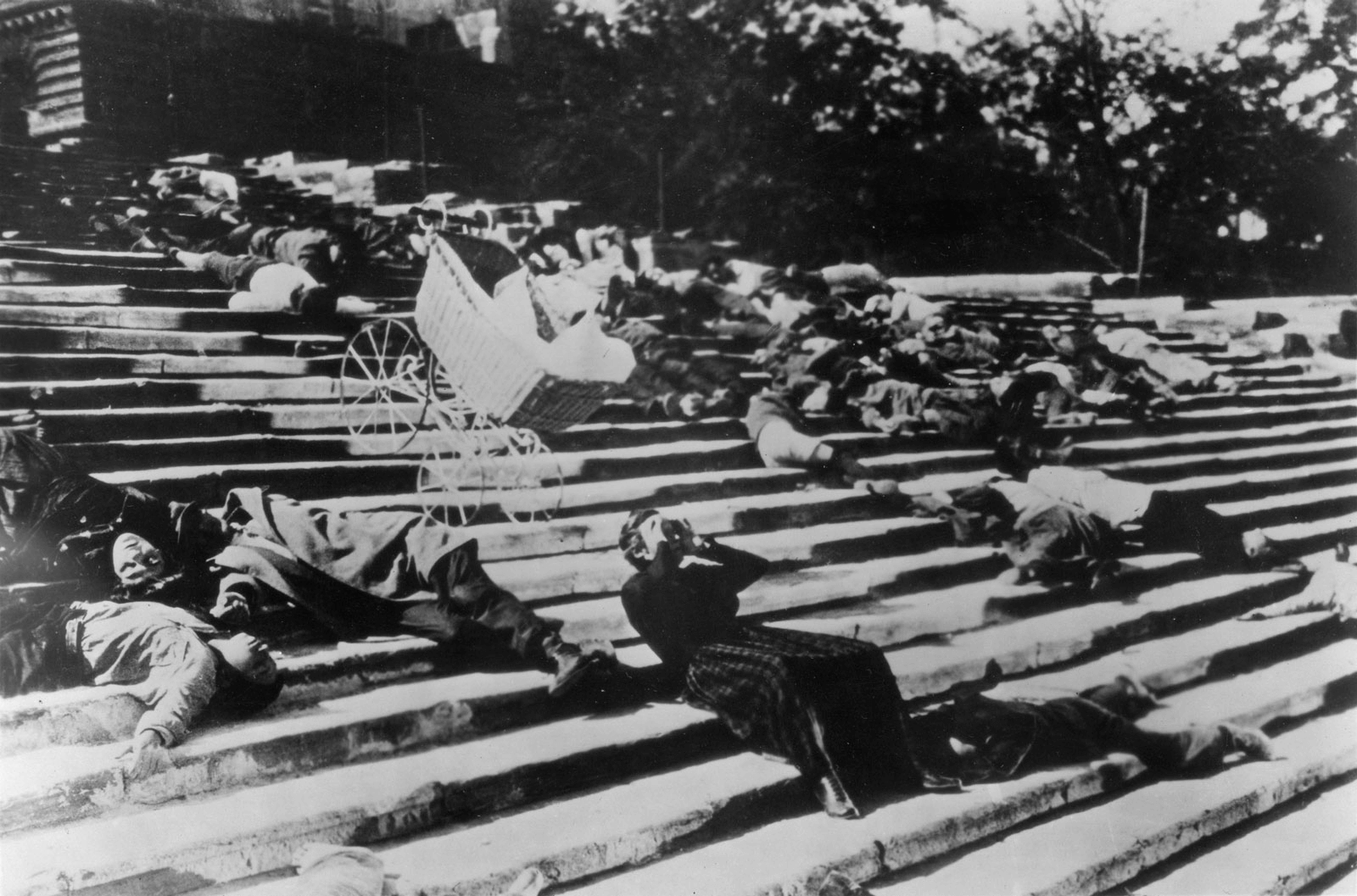
Film History 101 • The Odessa Steps in ‘Battleship Potemkin’
- Soviet Montage Theory – a Soviet Russian film movement that helped establish the principles of film editing – took place from the 1910s to the 1930s.
- Major Soviet Montage Theory filmmakers: Lev Kuleshov, Sergei Eisenstein , Dziga Vertov.
- Major Soviet Montage Theory films: Kino-Eye (1924), Battleship Potemkin (1925), Man With a Movie Camera (1929).
Soviet Montage Theory was a deconstructionist film movement, so as to say it wasn’t as interested in making movies as it was taking movies apart… or seeing how they worked. That being said, Soviet Montage Theory did produce some classics.
Here’s a video on Soviet Montage Theory from Filmmaker IQ:
Eras of Movies • The History of Cutting in Soviet Montage Theory by Filmmaker IQ
The Bolshevik government set-up a film school called VGIK (the Gerasimov Institute of Cinematography) after the Russian Revolution. The practitioners of Soviet Montage Theory were the OG members of the “film school generation;” Kuleshov and Eisenstein were their teachers.
Battleship Potemkin was the most noteworthy film to come out of the Soviet Montage Theory movement. Check out an awesome analysis from One Hundred Years of Cinema below.
History of Film Summary • How Sergei Eisenstein Used Montage to Film the Unfilmable by One Hundred Years of Cinema
Soviet Montage Theory begged filmmakers to arrange, deconstruct, and rearrange film clips to better communicate emotional associations to audiences. The legacy of Soviet Montage Theory lives on in the form of the Kuleshov effect and contemporary montages .
Learn more about Soviet Montage Theory →
When Did Movies Become Popular?
The end of the silent era.
There was no Hollywood in the early years of American cinema – there was only Thomas Edison’s Motion Picture Patents Company in New Jersey.
Ever wonder why Europe seemed to dominate the early years of film? Well it was because Thomas Edison sued American filmmakers into oblivion. Edison owned a litany of U.S. patents on camera tech – and he wielded his stamps of ownership with righteous fury. The Edison Manufacturing Company did produce some noteworthy early films – such as 1903’s The Great Train Robbery – but their gaps were few and far between.
To escape Edison’s legal monopoly, filmmakers ventured west, all the way to Southern California.
Fortunate for the nomads: the arid temperature and mountainous terrain of Southern California proved perfect for making movies. By the early 1910s, Hollywood emerged as the working capital of the United States’s movie industry.
Director/actors like Charlie Chaplin , Harold Lloyd and Buster Keaton became stars – but remember, movies were silent, and people knew there would be an acoustic revolution in cinema. Before we move on from the Silent Era, check out this great video from Crash Course.
When Did Movies Become Popular? • The Silent Era by Crash Course
The Silent Era holds an important place in film history – but it was mostly ushered out in 1927 with The Jazz Singer . Al Jolson singing in The Jazz Singer is considered the first time sound ever synchronized with a feature film . Over the next few years, Hollywood cinema exploded in popularity. This short period from 1927-1934 is known as pre-Code Hollywood.
When Did Hollywood Start?
Pre-code hollywood.
In our previous section, we touched on the rise of Hollywood, but not the Hollywood epic. The Hollywood epic, which we regard as longer in duration and wider in scope than the average movie, set the stage for blockbuster cinema. So, let’s quickly touch on the history of Hollywood epics before jumping into pre-code Hollywood.
It’s impossible to talk about Hollywood epics without bringing up D.W. Griffith. Griffith was an American film director who created a lot of what we consider “the structure” of feature films. His 1915 epic The Birth of a Nation brought the technique of cinematic storytelling into the future, while consequently keeping its subject matter in the objectionable past.
For more on Griffith’s The Birth of a Nation (and its complicated legacy), check out this poignant interview clip with Spike Lee .
History of Filmmaking • Spike Lee on ‘The Birth of a Nation’
As Lee suggests, it’s important to acknowledge the technical achievement of films like The Birth of a Nation and Gone With the Wind without condoning their horrid subject matter.
As another great director once said: “tomorrow’s democracy discriminates against discrimination. Its charter won’t include the freedom to end freedom.” – Orson Welles.
Griffith made more than a few Hollywood epics in his time, but none were more famous than The Birth of a Nation .
Okay, now that we reviewed the foundations of the Hollywood epic, let’s move on to pre-code Hollywood.
PRE-CODE HOLLYWOOD
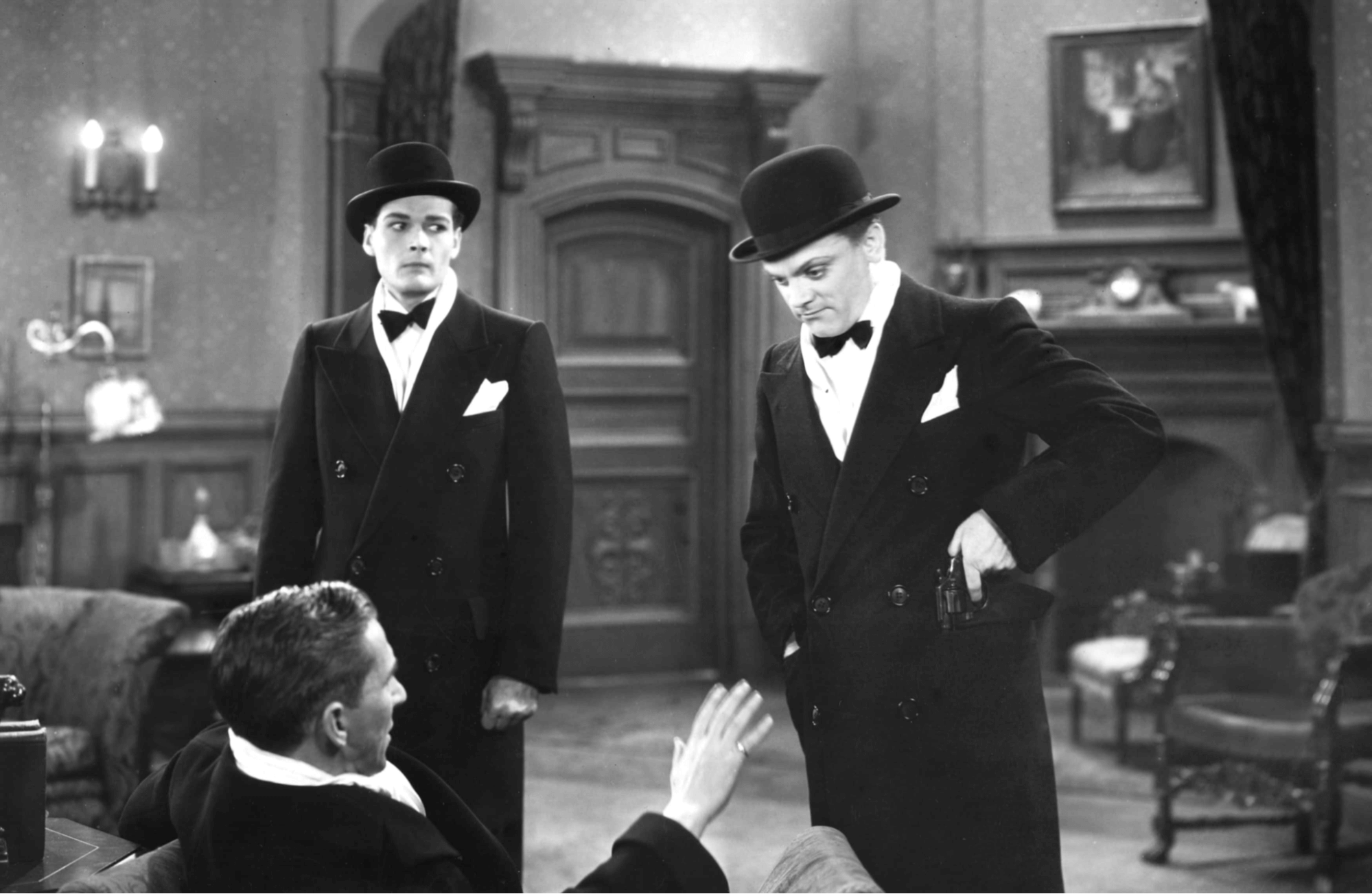

A History of Film • James Cagney in ‘The Public Enemy’
- Pre-Code Hollywood – a period in Hollywood history after the advent of sound but before the institution of the Hays Code – circa ~1927-1934.
- Major Pre-Code stars: Ruth Chatterton, Warren William, James Cagney.
- Major Pre-Code films: Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde (1931), The Public Enemy (1931), Baby Face (1933).
Pre-Code Hollywood was wild. Not just wild in an uninhibited sense, but in a thematic sense too. Films produced during the pre-Code era often focused on illicit subject matter, like bootlegging, prostitution, and murder – that wasn't the status quo for Hollywood – and it wouldn’t be again until 1968.
We’ll get to why that year is important for film history in a bit, but first let’s review pre-Code Hollywood with a couple of selected scenes from Kevin Wentink on YouTube.
Movie Film History • Pre-Code Classic Clips
Pre-Code movies were jubilant in their creativity; largely because they were uncensored . But alas, their period was short-lived. In 1934, MPPDA Chairman William Hays instituted the Motion Picture Production Code banning explicit depictions of sex, violence, and other “sinful” deeds in movies.
Learn more about Pre-Code Hollywood →
Development of Movies
The early golden age and color in film.
The 1930s and early 1940s produced some of the greatest movies of all-time – but they also changed everything about the movie-making process. By the end of the Pre-Code era, the free independent spirit of filmmaking had all but evaporated; Hollywood studios had vertically integrated their business operations, which meant they conceptualized, produced, and distributed everything “in-house.”
That doesn’t mean movies made during these years were bad though. Quite the contrary – perhaps the two greatest American films ever made, Citizen Kane and Casablanca , were made between 1934 and 1944.
But despite their enormous influence, neither Citizen Kane nor Casablanca could hold a candle to the influence of another film from this decade: The Wizard of Oz .
The Wizard of Oz wasn’t the first film to use Technicolor , but it was credited with bringing color to the masses. For more on the industry-altering introduction of color, check out this video on The Wizard of Oz from Vox.
When Was Color Movies Invented? • How Technicolor Changed Movies
Technicolor was groundbreaking for cinema, but the dye-transfer process of its colorization was hard… and cost prohibitive for studios. So, camera manufacturers experimented with new processes to streamline color photography. Overtime, they were rewarded with new technologies and techniques.
Learn more about Technicolor →
Cinema Eras
Wartime and propaganda films.
In 1937, Benito Mussolini founded Cinecittà , a massive studio that operated under the slogan “Il cinema è l'arma più forte,” which translates to “the cinema is the strongest weapon.” During this time, countries all around the world used cinema as a weapon to influence the minds and hearts of their citizens.
This was especially true in the United States – prolific directors like Frank Capra, John Ford, John Huston, George Stevens, and William Wyler enlisted in the U.S. Armed Forces to make movies to support the U.S. war cause.
Documentarian Laurent Bouzereau made a three-part series about the war films of Capra, Ford, Huston, Stevens, and Wyler. Check out the trailer for Five Came Back below.
A History of Film • Five Came Back Trailer
Wartime film is important to explore because it teaches us about how people interpret propaganda. For posterity’s sake, let’s define propaganda as biased information that’s used to promote political points.
Propaganda films are often regarded with a negative connotation because they sh0w a one-sided perspective. Films of this era – such as those commissioned for the US Department of War’s Why We Fight series – were one-sided because they were made to counter the enemy’s rhetoric. It’s important to note that “one-sided” doesn’t mean “wrong” – in the case of the Why We Fight series, I think most people would agree that the one-sidedness was appropriate.
Over time, wartime film became more nuanced – a point proven by the 1966 masterwork The Battle of Algiers .
History of Movies
Post-war film movements.
Global cinema underwent a renaissance after World War II; technically, creatively, and conceptually. We’re going to cover a few of the most prominent post-war film movements, starting with Italian Neorealism.
ITALIAN NEOREALISM

Movie Film History • Still from Vittorio De Sica’s ‘Umberto D.’
- Italian Neorealism (1944-1960) – an Italian film movement that brought filmmaking to the streets; defined by depictions of the Italian state after World War II.
- Major Italian Neorealist film-makers: Vittorio De Sica, Roberto Rossellini, Michelangelo Antonioni, Luchino Visconti, Federico Fellini .
- Major Italian Neorealist films: Rome, Open City (1945), Bicycle Thieves (1948), La Strada (1954), Il Posto (1961).
Martin Scorcese called Italian Neorealism “the rehabilitation of an entire culture and people through cinema.” World War II devastated the Italian state: socially, economically, and culturally.
It took people’s lives and jobs, but perhaps more importantly, it took their humanity. After the War, the people needed an outlet of expression, and a place to reconstruct a new national identity. Here’s a quick video on Italian Neorealism.
Movie History • How Italian Neorealism Brought the Grit of the Streets to the Big Screen by No Film School
Italian Neorealism produced some of the greatest films ever made. There’s some debate as to when the movement started and ended – some say 1943-1954, others say 1945-1955 – but I say it started with Rome, Open City and ended with Il Posto . Why? Because those movies perfectly encompass the defining arc of Italian Neorealism, from street-life after World War II to the rise of bureaucracy. Rome, Open City shows Italy in the thick of chaos, and Il Posto shows Italy on the precipice of a new era.
The legacy of Italian Neorealism lives on in the independent filmmaking of directors like Richard Linklater, Steven Soderbergh, and Sean Baker.
Learn more about Italian Neorealism →
FRENCH NEW WAVE
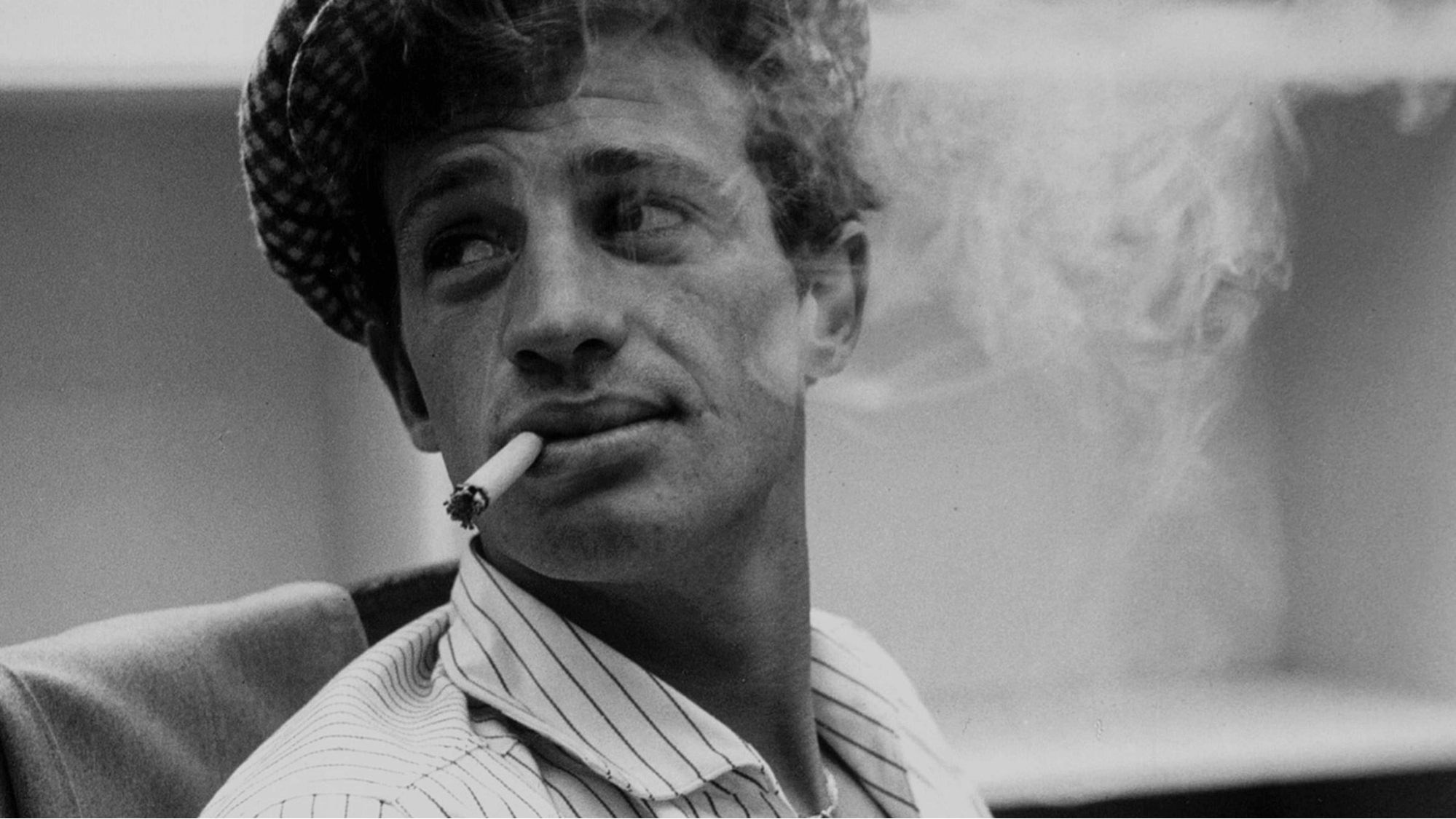

Development of Movies • Still From Jean-Luc Godard’s Breathless
- French New Wave (1950s onwards) – or La Nouvelle Rogue, a French art movement popularized by critics, defined by experimental ideas – inspired by old-Hollywood and progressive editing techniques from Orson Welles and Alfred Hitchcock.
- Major French New Wave filmmakers: Jean-Luc Godard , François Truffaut , Agnes Varda.
- Major French New Wave films: The 400 Blows (1959), Breathless (1960), Cleo from 5 to 7 (1962).
The French New Wave proliferated the auteur theory , which suggests the director is the author of a movie; which makes sense considering a lot of the best French New Wave films featured minimalist narratives. Take Jean-Luc Godard’s Breathless for example: the story is secondary to audio and visuals. The French New Wave was about independent filmmaking – taking a camera into the streets and making a movie by any means necessary.
Here’s a quick video on The French New Wave by The Cinema Cartography.
History of Filmmaking • Breaking the Rules With the French New Wave by The Cinema Cartography
It’s important to note that the pioneers of the French New Wave weren’t amateurs – most (but not all) were critics at Cahiers du cinéma , a respected French film magazine. Writers like Godard, Rivette, and Chabrol knew what they were doing long before they released their great works.
Other directors, like Agnes Varda and Alain Resnais, were members of the Left Bank, a somewhat more traditionalist art group. Left Bank directors tended to put more emphasis on their narratives as opposed to their Cahiers du cinéma counterparts.
The French New popularized (but did not invent) innovative filmmaking techniques like jump cuts and tracking shots . The influence of the French New Wave can be seen in music videos, existentialist cinema, and French film noir .
Learn more about the French New Wave →
Learn more about the Best French New Wave Films →
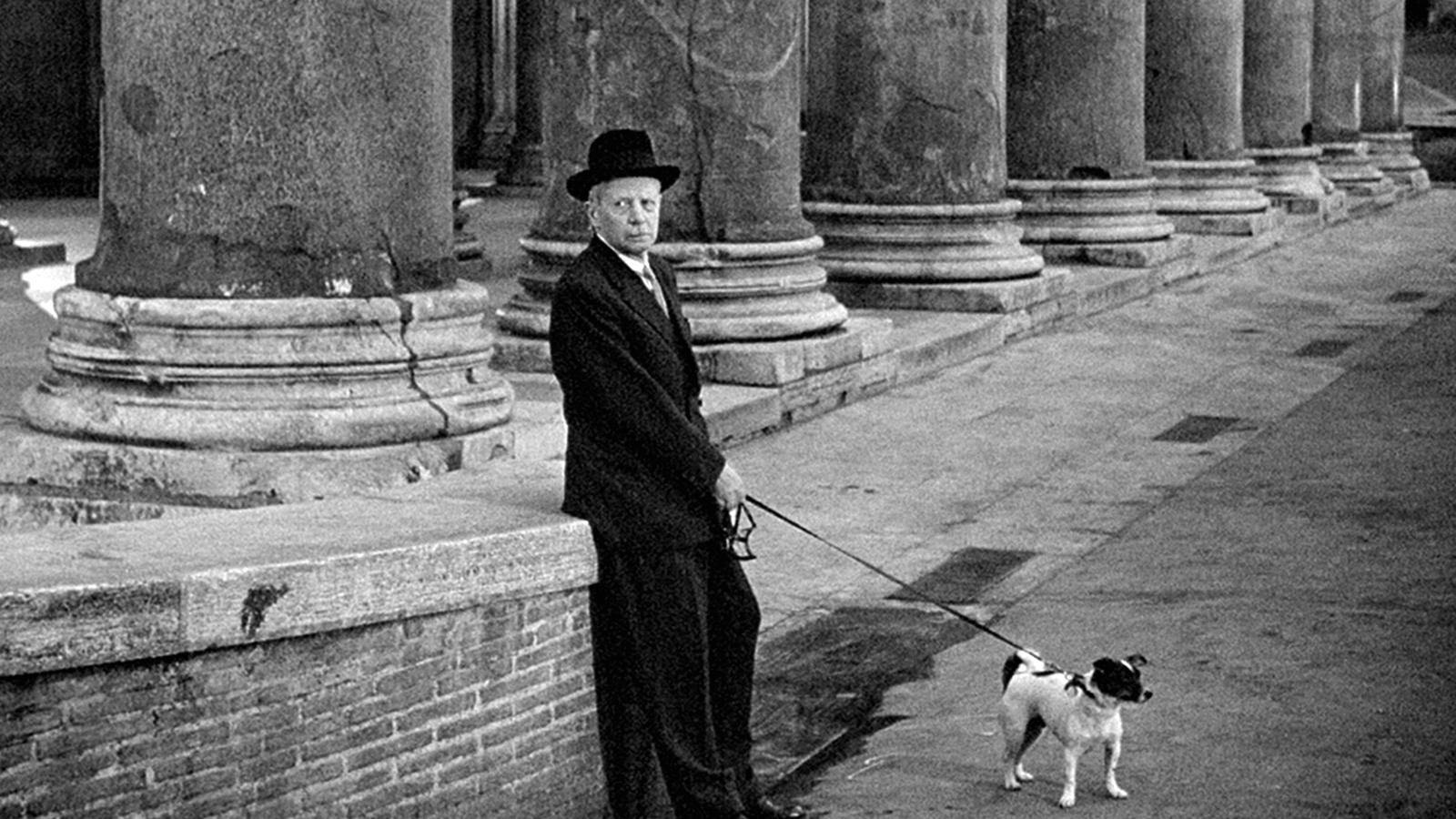
SCANDINAVIAN REVIVAL
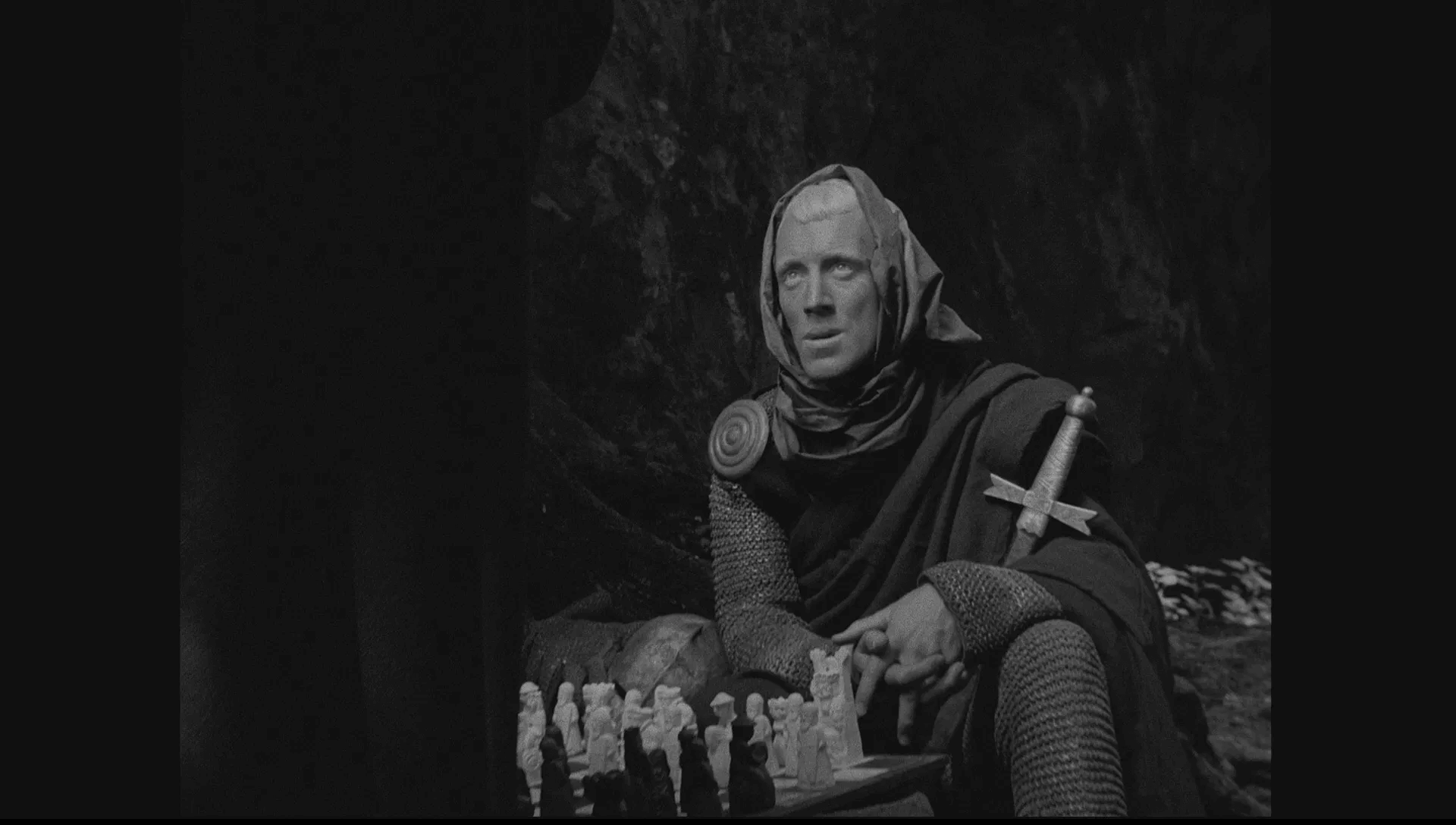

A History of Film • Still from Ingmar Bergman’s ‘The Seventh Seal’
- Scandinavian Revival (1940s-1950s) – a filmmaking movement in Scandinavia, particularly Denmark and Sweden, defined by monochrome visuals, philosophical quandaries, and reinterpretations of religious ideals.
- Major Scandinavian Revival filmmakers: Carl Theodor Dreyer and Ingmar Bergman.
- Major Scandinavian Revival films: Day of Wrath (1943), The Seventh Seal (1957), Wild Strawberries (1957).
Swedish, Danish, and Finnish films have played an important role in cinema for more than 100 years. The Scandinavian Revival – or renaissance of Scandinavian-centric films from the 1940s-1950s – put the films of Sweden, Denmark, and Finland in front of the world stage.
Here’s a quick video on the works of the most famous Scandinavian director of all-time: Ingmar Bergman .
History of Cinema • Ingmar Bergman’s Cinema by The Criterion Collection
The influence of Scandinavian Revival can be seen in the works of Danish directors like Thomas Vinterberg and Lars von Trier , as well as countless other filmmakers around the world.
BENGALI CINEMA
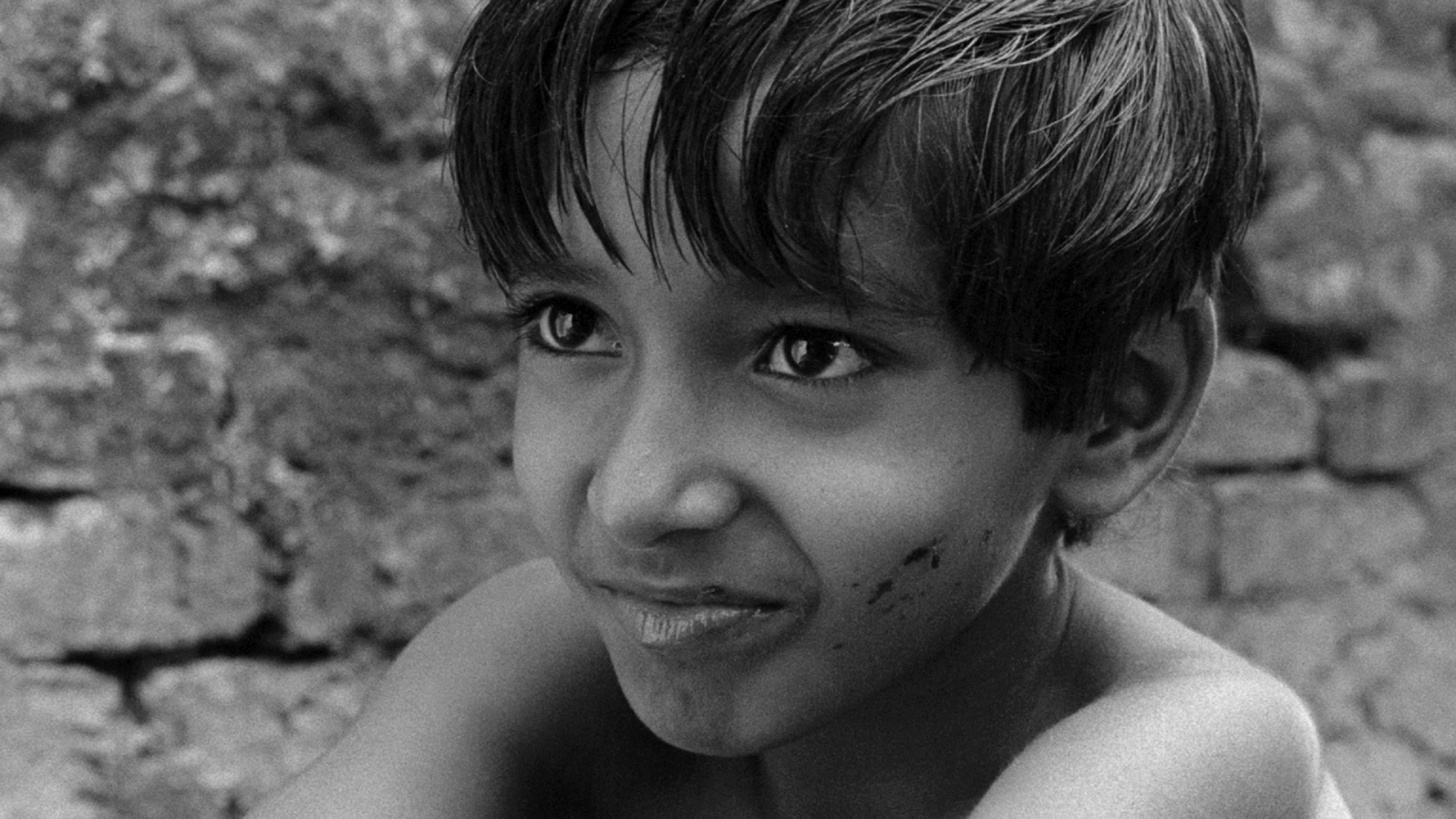
History of Motion Pictures • Still from Satyajit Ray’s ‘Pather Panchali’
- Bengali Cinema – or the cinema of West Bengal; also known as Tollywood, helped develop arthouse films parallel to the mainstream Indian cinema.
- Major Bengali filmmakers: Satyajit Ray and Mrinal Sen.
- Major Bengali films: Pather Panchali (1955) and Bhuvan Shome (1969).
The Indian film industry is the biggest film industry in the world. Each year, India produces more than a thousand feature-films. When most people think of Indian cinema, they think of Bollywood “song and dance” masalas – but did you know the country underwent a New Wave (similar to France, Italy, and Scandinavia) after World War II? The influence of the Indian New Wave, or classic Bengali cinema, is hard to quantify; perhaps it’s better expressed by the efforts of the Academy Film Archive, Criterion Collection, and L'Immagine Ritrovata film restoration artists. Here's an introduction to one of India's greatest directors, Satyajit Ray.
Evolution of Cinema • How Satyajit Ray Directs a Movie
In 2020, Martin Scorsese said, “In the relatively short history of cinema, Satyajit Ray is one of the names that we all need to know, whose films we all need to see.” Ray is undoubtedly one of the preeminent masters of international cinema – and his name belongs in the conversation with Hitchcock, Renoir, Kurosawa, Welles, and all the other trailblazing filmmakers of the mid-20th century.
Learn more about Indian Cinema →
OTHER POST-WAR & NEW WAVE MOVEMENTS
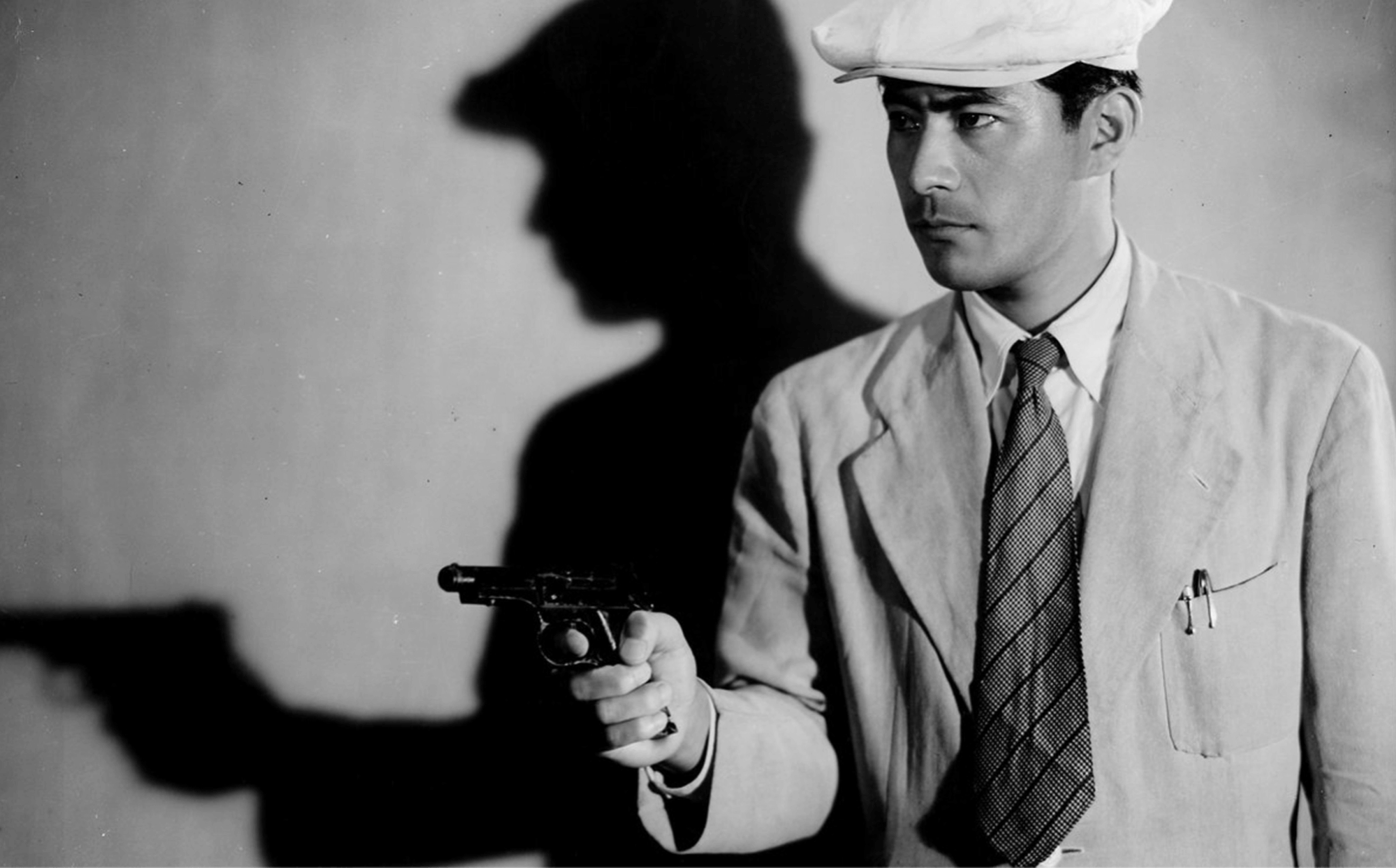

How Has Film Changed Over Time? • Still from Akira Kurosawa’s ‘Stray Dog’
Italy, France, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, and India weren’t the only countries that underwent “New Waves” after World War II; Japan, Iran, Great Britain, and Russia had minor film revolutions as well.
In Japan, directors like Akira Kurosawa and Yasujirō Ozu introduced new filmmaking techniques to the masses; their 1940s-1950s films were great, but some filmmakers, like Hiroshi Teshigahara and Nagisa Ōshima felt they were better suited to make films about “modern” Japan.
Here’s a quick video on the Japanese New Wave from Film Studies for YouTube.
Cinema Eras • Japanese New Wave Video Essay by Film Studies for YouTube
Some cinema historians combine the Japanese New Wave with the post-war era. For simplicity’s sake, we’ll do the same: the major films of this era (1940s-1960s) include Rashomon (1950), Tokyo Story (1953), and Seven Samurai (1954).
The Iranian New Wave began about fifteen years after the end of World War II, circa 1960-onwards. Iranian cinema is an important part of Iranian culture. Here’s a quick video on Iranian cinema from BBC News.
Important Dates in Film History • Spotlight on Iran’s Film Industry via BBC News
Cinema historians widely consider Dariush Mehrjui’s The Cow (1969) to be a foundational film for the movement. Abbas Kiarostami is perhaps the most famous Iranian filmmaker of all-time. His film Close-Up (1990) is regarded as one of the greatest films ever produced in Iran.
The British New Wave was a minor film movement that was defined by kitchen-sink realism – or depictions of ordinary life. Many filmmakers of the British New Wave were critics before they were directors; and they wanted to depict the average life of Britain through a filmic eye.
Here’s a lecture on the British New Wave from Professor Ian Christie at Gresham College.
History of Filmmaking • Street-Life and New Wave British Cinema by Gresham College
The British New Wave became synonymous with Cinéma vérité (cinema of truth) over the course of its brief existence. Some of the major pictures of the movement include: Look Back in Anger (1959) and Saturday Night and Sunday Morning (1960).
Russian cinema is complex… probably just as complex as American cinema. We could spend 100 pages talking about Russian cinema – but that’s not the focus of this article. We already talked about Soviet Montage Theory, so let’s skip ahead to post World War II Soviet cinema.
When I think of post-war Soviet cinema, I think of one name: Andrei Tarkovsky . Tarkovsky directed internationally-renowned films like Andrei Rublev (1969), Solaris (1972), and Stalker (1979) in his brief career as the Soviet Union’s pre-eminent maestro.
Here’s a deep dive into the works of Tarkovsky by “Like Stories of Old.”
Film Industry Timeline • Praying Through Cinema – Understanding Andrei Tarkovsky by Like Stories of Old
Tarkovsky wasn’t the only great filmmaker in the post-war Soviet Union – but he was probably the best. I’d be remiss if I didn’t use this section to focus on him.
History of Film Timeline
The golden age of hollywood.
The Hollywood Golden Age began with the fall of pre-Code Hollywood (1934) and lasted until the birth of New Hollywood (1968).
- Major stars of the Hollywood Golden Age: Humphrey Bogart, Cary Grant, Katharine Hepburn, Audrey Hepburn, Elizabeth Taylor, Clark Gable, Ingrid Bergman, Henry Fonda, Kirk Douglas, Gregory Peck, Lauren Bacall, Grace Kelly, James Dean, Marlon Brando.
- Major filmmakers of the Hollywood Golden Age: Cecil B. DeMille , Orson Welles , Billy Wilder , Frank Capra , John Huston , Alfred Hitchcock , John Ford , Elia Kazan , David Lean , Joseph Manckiewicz.
Notice how many names we included? It’s ridiculous – it would be wrong to omit any of them; and still, there are probably dozens of iconic figures missing. The Hollywood Golden Age was all about stars. Stars sold pictures and the studios knew it. “Hepburn” could sell a movie every time; it didn’t matter which Hepburn – or what the movie was about.
Here’s a breakdown of the Hollywood Golden Age from Crash Course.
History of Movies • The Golden Age of Hollywood by Crash Course
There are a few sub-eras within the Hollywood Golden Age era; let’s break them down in detail.

Important Dates in Film History • Photo of MPPDA Chairman William Hays
In 1934, Chairman William Hays of the Motion Picture Producers and Distributors of America instituted a production code that banned graphic cinematic depictions of sex, violence, and other illicit deeds.
The “Production Code” or “ Hays Code ” was responsible for the censorship of Hollywood films for 34 years.
For more on the history of Hollywood censorship and movie ratings, check out the video from Filmmaker IQ below.
How Has Film Changed Over Time? • History of Hollywood Censorship by Filmmaker IQ
The Hays Code kept cinema tame, which led to Hollywood romanticism. But it also made cinema unrealistic, which made the American public yearn for improbable outcomes. Not to mention that it set race relations back an indeterminable amount of years. The Hays Code specifically forbade miscegenation, or “the breeding of people of different races.”
Ultimately, the censorship of Hollywood films was about keeping power in the hands of people with power. It had some positive unintended outcomes – but it wasn’t worth the cost of suppression.
Learn more about the Hays Code →
Learn more about the history of movie censorship →

Film Industry Timeline • Still from Nicholas Ray’s ‘In a Lonely Place’
Film noir is a style of film that’s defined by moralistic themes, high contrast lighting, and mysterious plots. Oftentimes, film noirs feature hardboiled protagonists . It’s important to note that film noir is a style, not a film movement. As such, we won’t list “film noir directors,” but we will list some iconic examples of film noir.
Major Hollywood film noirs: The Maltese Falcon (1941), Double Indemnity (1944), Sunset Boulevard (1950).
Hollywood film noirs were inspired by classic detective fiction stories, like those of Arthur Conan Doyle and Edgar Allan Poe. Over time, film noir was adopted as a style around the world – most famously in Great Britain with Carol Reed’s The Third Man .
Here’s a video on defining film noir from Jack’s Movie Reviews.
Eras of Movies • Defining Film Noir by Jack’s Movie Reviews
We could spend another 50 pages on film noir (like many other topics in this compendium) – but instead, let’s continue on.
Learn more about film noir →

How Movies Have Changed Over Time • Still from John Ford’s ‘The Searchers’
Hollywood westerns were incredibly popular during the Golden Age. Why? Because the American people loved stories of lawlessness and expansion, dating all the way back to Erastus Beadle’s dime novels – making the western the perfect subgenre for vicarious cinema.
Major Hollywood westerns: Stagecoach (1939), High Noon (1952), The Searchers (1956).
Westerns, much like film noirs, allowed repressed audiences to feel alive at the movie theater. Remember: Hollywood films were censored during the Golden Age, which meant you couldn’t find graphic violence or pornography at the theaters. So, audiences took what they could get – which was usually film noirs and Westerns.
Here’s a video on the history of Westerns in Hollywood cinema.
Evolution of Film • Western Movies History by Ministry of Cinema
Hollywood westerns inspired a global fascination with cowboys, mercenaries, and gunslingers, directly leading to samurai cinema, spaghetti westerns, zapata westerns, and neo-westerns.
Learn more about Spaghetti Westerns →
Learn more about Neo-Westerns →
McCARTHYISM & THE BLACKLIST

How Movies Have Changed Over Time • Bryan Cranston as Blacklisted Screenwriter Dalton Trumbo
In 1947, the state of Wisconsin elected notorious fear-monger Joseph McCarthy as senator of their state. McCarthy hated free-speech – that’s not a one-sided perspective, that’s the truth. McCarthy spent his entire career demagoguing, and his legacy shows that.
In 1950, ten Hollywood screenwriters were summoned to appear before the United States Congress House of Un-American Activities, largely because of McCarthy's divisive rhetoric against communist sympathizers. The screenwriters were cited for contempt of congress and fired from their jobs, and thus, the blacklist was born.
For more on McCarthyism and the Hollywood blacklist , check out the video from Ted-Ed below.
The History of Film • McCarthyism and the Blacklist by Ted-Ed
The Hollywood blacklist derailed the careers of hundreds of writers, directors, and producers from 1950-1960. The blacklist ended when Kirk Douglas credited Dalton Trumbo – one of the most famous blacklisted screenwriters – as the screenwriter of Stanley Kubrick’s Spartacus , effectively taking back control of Hollywood.
Learn more about the Hollywood Blacklist →
THE PARAMOUNT CASE

The History of Film • Paramount Studios Classic Style Logo
In 1948, the Supreme Court of the United States ruled that the five major motion picture studios: Paramount, Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer (MGM), Warner Bros., 20th Century Fox, and RKO violated the U.S. Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890.
As a result of the decision, movie studios could no longer solely create and distribute movies to their own theaters.
It may not sound important, but the Paramount Case changed everything for American cinema. Here’s a quick video on the Case and its lasting impact on Hollywood.
The History of Filmmaking • Film History 101: The Paramount Decree by Omar Rivera
The Paramount Case opened the door for international films and independent theaters. It also gave businesses more freedom to show movies outside of the MPPDA ratings system.
Evolution of Cinema
New hollywood.
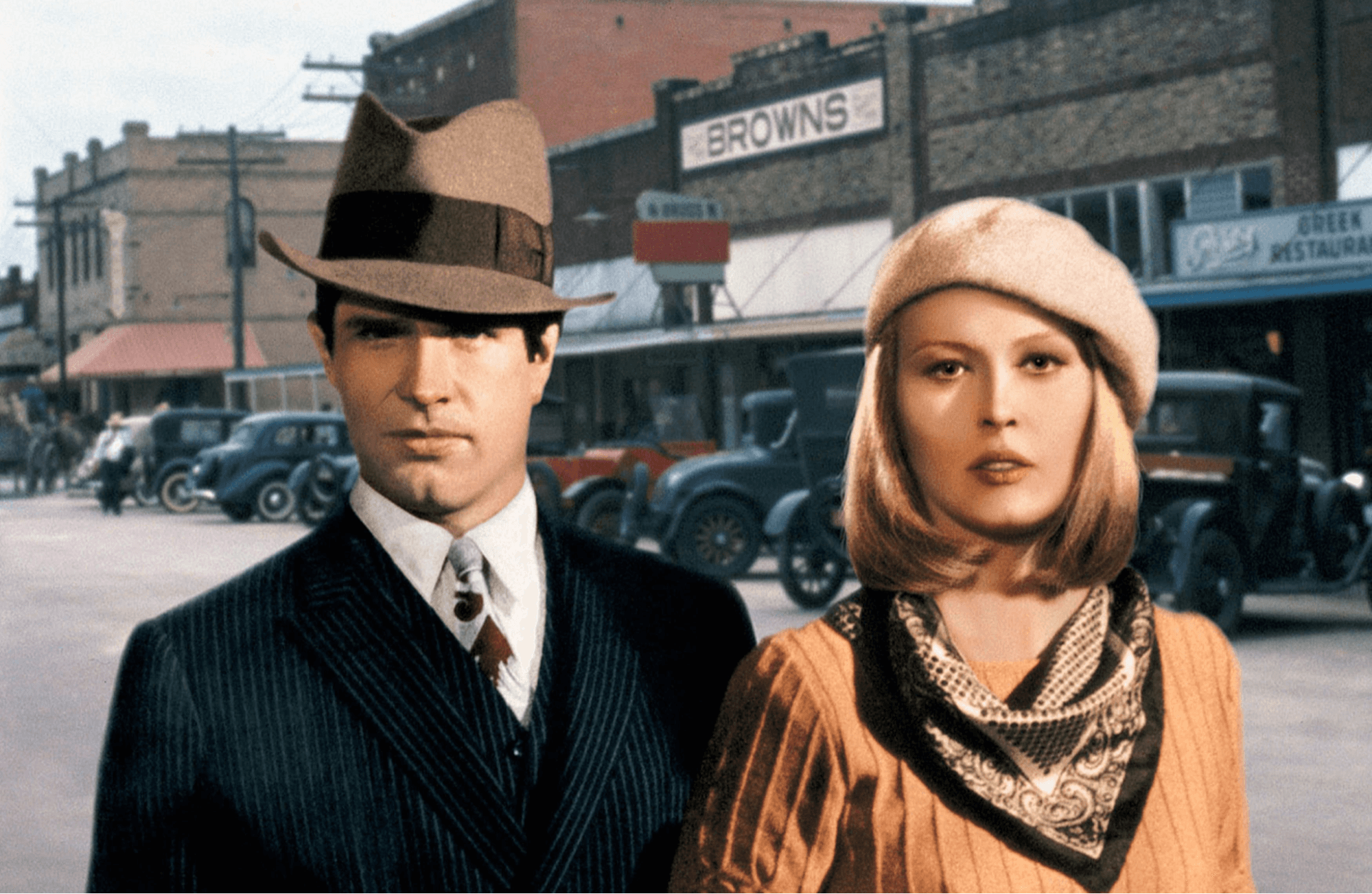

Movie History • Still from Arthur Penn’s’ Bonnie and Clyde’
- New Hollywood, otherwise known as the Hollywood New Wave, introduced “the film school generation” to Hollywood. New Hollywood films are defined as larger in scope, darker in subject matter, and overtly more graphic than their Golden Age predecessors.
- Major New Hollywood filmmakers: George Lucas , Steven Spielberg , Martin Scorsese , Brian De Palma , Peter Bogdanovich, Woody Allen , Francis Ford Coppola , James Cameron .
- Major New Hollywood films: Bonnie and Clyde (1967), The Graduate (1967), Easy Rider (1969), Midnight Cowboy (1969), The Godfather (1972), American Graffiti (1973).
New Hollywood ushered American filmmaking into a new era by returning to the popular genres of the pre-Code era, such as gangster films and sex-centric films. It also marked the emergence of “film-school” directors like George Lucas, Steven Spielberg, and Martin Scorsese. It’s clear from watching New Hollywood films that the writers and directors who produced them were acutely aware of cinema history.
During this era, writers like Woody Allen employed themes of existentialist cinema found in the French New Wave and Italian Neorealism (among other movements). Directors like Martin Scorsese utilized advanced framing techniques pioneered by masters of the pre-war era.
For more on New Hollywood, check out this feature documentary based Peter Biskind's seminal book "Easy Riders, Raging Bulls."
Movie History • How New Hollywood Was Born
New Hollywood (and its immediate aftermath) produced some of the greatest films of all-time: such as The Godfather (1972), The Godfather Part II (1974), Chinatown (1974), Taxi Driver (1976), Network (1976), and Annie Hall (1977).
Somewhat tragically, New Hollywood ended with the emergence of blockbuster films – such as Jaws (1975) and Star Wars (1977) – in the mid to late 1970s.
Learn more about New Hollywood →
Eras of Movies
Dogme 95 and independent movements.
Big-budget movies dominated the movie-scene after New Hollywood ended. Suddenly, cinema became more of a spectacle than an art-form. That’s not to say movies produced during this era (1975-1995) were bad – some big-budget films, like Back to the Future (1985) and Jurassic Park (1993) were financially successful and critically acclaimed; and writer/directors like John Hughes found enormous success making studio films about seemingly mundane life.
But despite the financial prospect of making contrived studio films, some filmmakers decided to go back to their roots and make films independently, much in the vein of the artists of the French New Wave. This spirit inspired the Danish Dogme 95 movement and the American Independent movement.
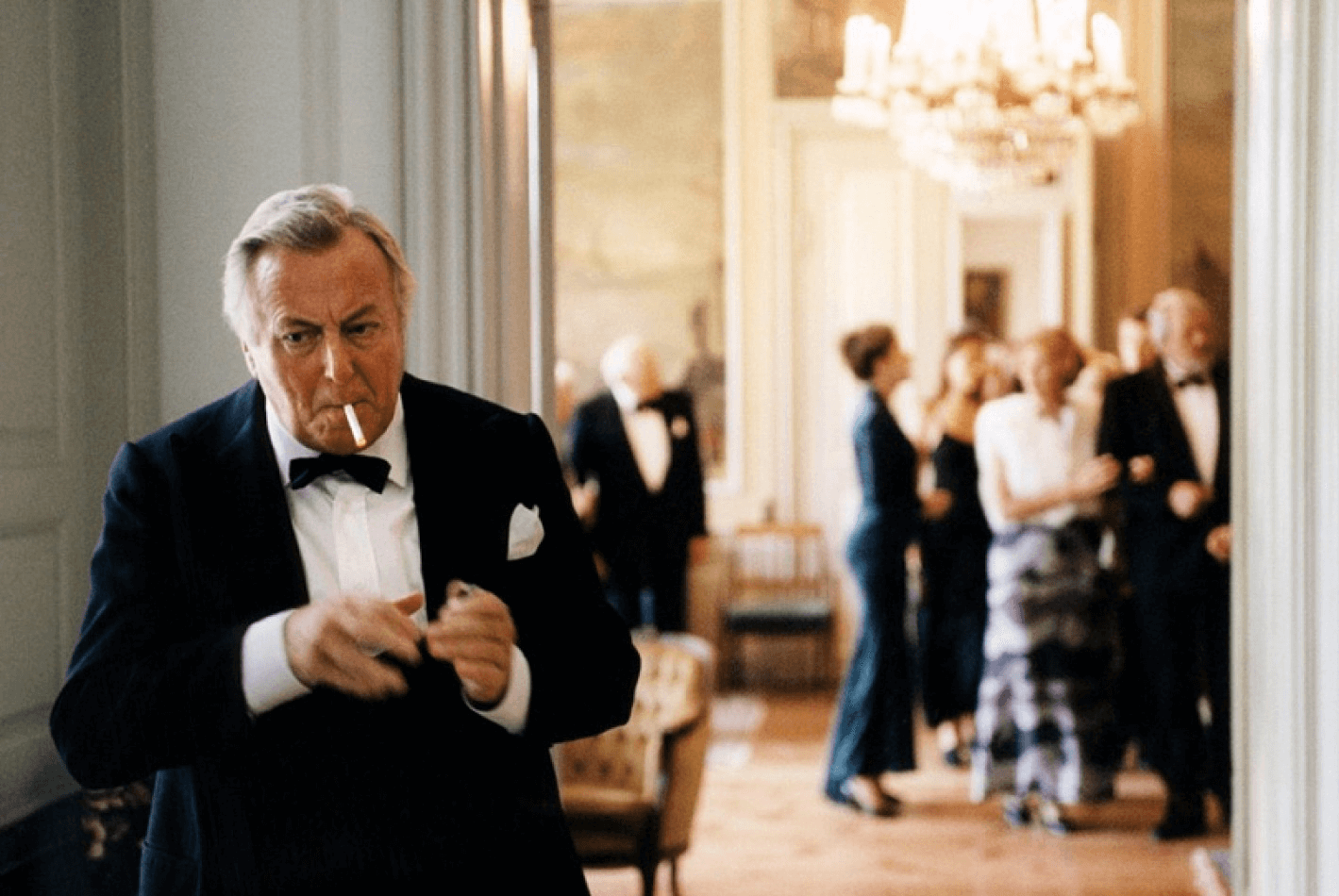

Evolution of Film • Photo Still from ‘Festen’ by Thomas Vinterberg
D0gme 95 – a Danish film movement that brought filmmaking back to its primal roots: no non-diegetic sound, no superficial action, and no director credit.
Major Dogme 95 filmmakers: Thomas Vinterberg and Lars von Trier
Major Dogme 95 films: Dogme #1 – Festen (1998), Dogme #2 – The Idiots (1998), Dogme #12 – Italian for Beginners (2000).
It’s ironic that Dogme 95 , which states the director must not be credited, is perhaps best known for the fame of two of its founders: Thomas Vinterberg and Lars von Trier. Dogme 95 sought to rid cinema of extravagant special effects and challenging productions by making the filmmaking process as simple as possible. To do this, its founders created the Vows of Chastity: a ten-part manifesto for Dogme 95 filmmaking.
Check out a video on the Vows of Chastity and Dogme 95 below.
History of Cinema • Vows of Chastity – Films of Dogme 95 by FilmStruck
Ultimately, the Vows of Chastity proved too limiting for filmmakers – but their influence lives on in New Danish cinema and independent films all over the world.
Learn more about Dogme 95 →
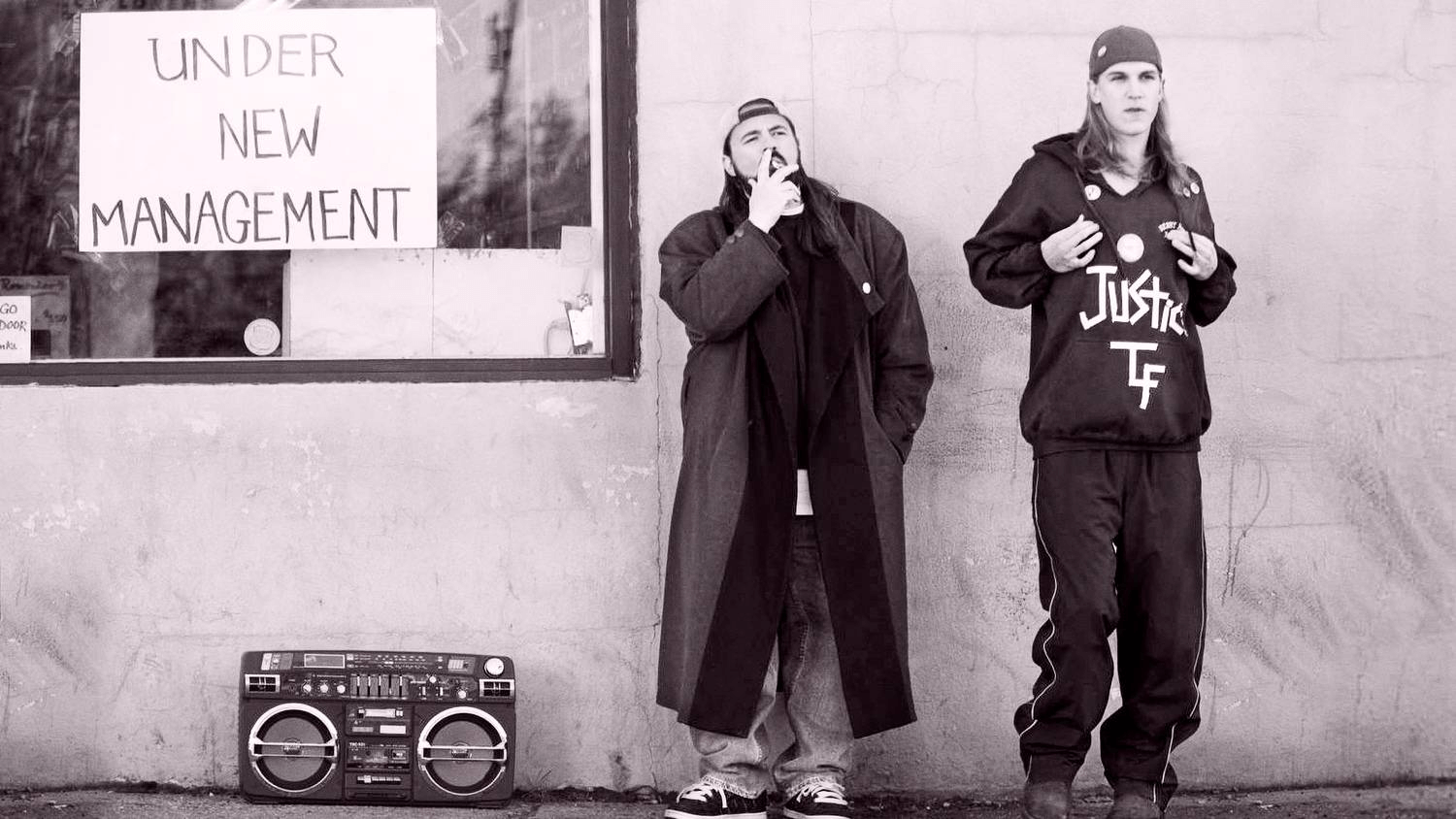

History of Cinema • Still from Kevin Smith’s ‘Clerks’
Indie film – or late 80s, early 90s cinema produced outside of the major motion picture system – was about experimenting with new cinematic forms, pushing the Generation Next agenda, and making art by any means necessary.
Major indie filmmakers: Richard Linklater , Wes Anderson , Steven Soderbergh , Jim Jarmusch .
Major indie films: Sex, Lies, and Videotape (1989), Slacker (1990), and Bottle Rocket (1994).
The American indie movement launched the careers of a myriad of great directors. It also marked the beginning of a major decline for film. The advent of digital cameras and DVDs meant film was becoming a luxury. Conversely, it meant procuring the necessary equipment needed to make movies was easier than ever.
Indie-films introduced the idea that anybody could make movies. For better or worse, the point proved to be true. The '90s and early 2000s were littered with independently produced, scarcely funded movies. It was unrestrained, but it was also liberating.
Check out this video on no-budget filmmaking from The Royal Ocean Film Society to learn more about the indie movement.
Evolution of Cinema • Lessons for the No-Budget Feature by The Royal Ocean Film Society
The indie movement (as it was known then) ended when the major studios (like Disney and Turner) bought the independent studios (like Miramax and New Line). Today, we often refer to minimalist, low-budget movies as independent, but the truth is just about every production studio is owned by a conglomerate.
How Has the Film Industry Changed?
New distribution methods.
The current state of cinema is in flux due to a wide array of issues, including (but not limited to) the economic impact of the Covid-19 pandemic, the wide-adoption of new streaming services from first-party producers, i.e. Netflix, Disney, Paramount, etc., and the growth of new media forms.
Over the last few years, big-budget epics like Marvel’s The Avengers and Star Wars have performed well at the U.S. and Chinese box-office, but their success has often come at the expense of medium-budget movies; the result being a deeper lining of the pockets of exorbitantly wealthy corporations.
Still, there’s a lot of money to be made – a point perhaps best proven by the rise of the Chinese film industry. In 2020, China overtook North America as the world’s biggest box-office market, per THR. Check out a video on Hengdian, China’s largest film studio from South China Morning Report.

Movie History • Inside China’s Largest Film Studio by South China Morning Report
Movies seem to get bigger and bigger every year but the development of computer-generated-imagery and compositing techniques has given filmmakers the technology to create vast worlds in limited spaces.
So: what’s next for film? Who’s to say for certain? The future of the industry looks cloudy – but there’s definite promise on the horizon. More people have cinema-capable cameras in their pocket today than ever before. Perhaps the next great movement will take off soon.
Related Posts
- What is CinemaScope →
- When Was the Camera Invented →
- What Was the First Movie Ever Made →
100 Years of Cinematography
The history of film includes a lot more than what we went over here. In 2019, the American Society of Cinematographers celebrated 100 years of great cinematography with a list of legendary works. In our next article, we break down some of the ASC’s choices with video examples. Follow along as we look at the work of Conrad Hall, Vittorio Storaro, and more.
Up Next: Best Cinematography of All-Time →
Showcase your vision with elegant shot lists and storyboards..
Create robust and customizable shot lists. Upload images to make storyboards and slideshows.
Learn More ➜
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- What are the 12 Principles of Animation — Ultimate Guide
- What is Pacing in Writing — And Why It’s So Important
- What Does O.S. Mean in a Script & How to Use It
- What Does a Leadman Do in Film — Job Description Explained
- What is a Unit Production Manager — Job and Role Explained
- 1 Pinterest

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8.2 The History of Movies
Learning objectives.
- Identify key points in the development of the motion picture industry.
- Identify key developments of the motion picture industry and technology.
- Identify influential films in movie history.
The movie industry as we know it today originated in the early 19th century through a series of technological developments: the creation of photography, the discovery of the illusion of motion by combining individual still images, and the study of human and animal locomotion. The history presented here begins at the culmination of these technological developments, where the idea of the motion picture as an entertainment industry first emerged. Since then, the industry has seen extraordinary transformations, some driven by the artistic visions of individual participants, some by commercial necessity, and still others by accident. The history of the cinema is complex, and for every important innovator and movement listed here, others have been left out. Nonetheless, after reading this section you will understand the broad arc of the development of a medium that has captured the imaginations of audiences worldwide for over a century.
The Beginnings: Motion Picture Technology of the Late 19th Century
While the experience of watching movies on smartphones may seem like a drastic departure from the communal nature of film viewing as we think of it today, in some ways the small-format, single-viewer display is a return to film’s early roots. In 1891, the inventor Thomas Edison, together with William Dickson, a young laboratory assistant, came out with what they called the kinetoscope , a device that would become the predecessor to the motion picture projector. The kinetoscope was a cabinet with a window through which individual viewers could experience the illusion of a moving image (Gale Virtual Reference Library) (British Movie Classics). A perforated celluloid film strip with a sequence of images on it was rapidly spooled between a light bulb and a lens, creating the illusion of motion (Britannica). The images viewers could see in the kinetoscope captured events and performances that had been staged at Edison’s film studio in East Orange, New Jersey, especially for the Edison kinetograph (the camera that produced kinetoscope film sequences): circus performances, dancing women, cockfights, boxing matches, and even a tooth extraction by a dentist (Robinson, 1994).
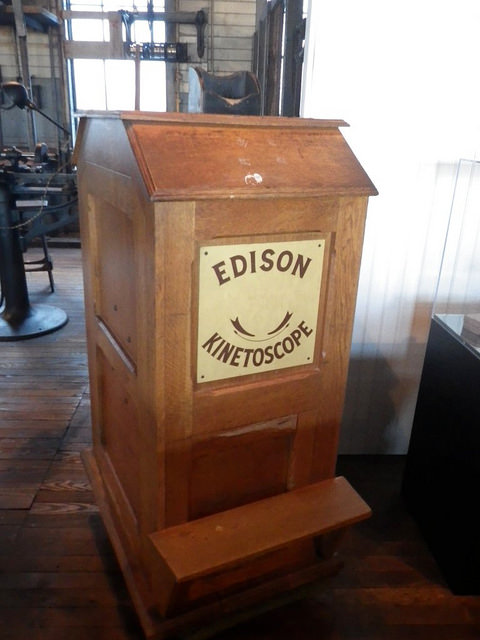

The Edison kinetoscope.
todd.vision – Kinetoscope – CC BY 2.0.
As the kinetoscope gained popularity, the Edison Company began installing machines in hotel lobbies, amusement parks, and penny arcades, and soon kinetoscope parlors—where customers could pay around 25 cents for admission to a bank of machines—had opened around the country. However, when friends and collaborators suggested that Edison find a way to project his kinetoscope images for audience viewing, he apparently refused, claiming that such an invention would be a less profitable venture (Britannica).
Because Edison hadn’t secured an international patent for his invention, variations of the kinetoscope were soon being copied and distributed throughout Europe. This new form of entertainment was an instant success, and a number of mechanics and inventors, seeing an opportunity, began toying with methods of projecting the moving images onto a larger screen. However, it was the invention of two brothers, Auguste and Louis Lumière—photographic goods manufacturers in Lyon, France—that saw the most commercial success. In 1895, the brothers patented the cinématographe (from which we get the term cinema ), a lightweight film projector that also functioned as a camera and printer. Unlike the Edison kinetograph, the cinématographe was lightweight enough for easy outdoor filming, and over the years the brothers used the camera to take well over 1,000 short films, most of which depicted scenes from everyday life. In December 1895, in the basement lounge of the Grand Café, Rue des Capucines in Paris, the Lumières held the world’s first ever commercial film screening, a sequence of about 10 short scenes, including the brother’s first film, Workers Leaving the Lumière Factory , a segment lasting less than a minute and depicting workers leaving the family’s photographic instrument factory at the end of the day, as shown in the still frame here in Figure 8.3 (Encyclopedia of the Age of Industry and Empire).
Believing that audiences would get bored watching scenes that they could just as easily observe on a casual walk around the city, Louis Lumière claimed that the cinema was “an invention without a future (Menand, 2005),” but a demand for motion pictures grew at such a rapid rate that soon representatives of the Lumière company were traveling throughout Europe and the world, showing half-hour screenings of the company’s films. While cinema initially competed with other popular forms of entertainment—circuses, vaudeville acts, theater troupes, magic shows, and many others—eventually it would supplant these various entertainments as the main commercial attraction (Menand, 2005). Within a year of the Lumières’ first commercial screening, competing film companies were offering moving-picture acts in music halls and vaudeville theaters across Great Britain. In the United States, the Edison Company, having purchased the rights to an improved projector that they called the Vitascope , held their first film screening in April 1896 at Koster and Bial’s Music Hall in Herald Square, New York City.
Film’s profound impact on its earliest viewers is difficult to imagine today, inundated as many are by video images. However, the sheer volume of reports about the early audience’s disbelief, delight, and even fear at what they were seeing suggests that viewing a film was an overwhelming experience for many. Spectators gasped at the realistic details in films such as Robert Paul’s Rough Sea at Dover , and at times people panicked and tried to flee the theater during films in which trains or moving carriages sped toward the audience (Robinson). Even the public’s perception of film as a medium was considerably different from the contemporary understanding; the moving image was an improvement upon the photograph—a medium with which viewers were already familiar—and this is perhaps why the earliest films documented events in brief segments but didn’t tell stories. During this “novelty period” of cinema, audiences were more interested by the phenomenon of the film projector itself, so vaudeville halls advertised the kind of projector they were using (for example “The Vitascope—Edison’s Latest Marvel”) (Balcanasu, et. al.), rather than the names of the films (Britannica Online).

Workers Leaving the Lumière Factory: One of the first films viewed by an audience.
Craig Duffy – Workers Leaving The Lumiere Factory – CC BY-NC 2.0.
By the close of the 19th century, as public excitement over the moving picture’s novelty gradually wore off, filmmakers were also beginning to experiment with film’s possibilities as a medium in itself (not simply, as it had been regarded up until then, as a tool for documentation, analogous to the camera or the phonograph). Technical innovations allowed filmmakers like Parisian cinema owner Georges Méliès to experiment with special effects that produced seemingly magical transformations on screen: flowers turned into women, people disappeared with puffs of smoke, a man appeared where a woman had just been standing, and other similar tricks (Robinson).
Not only did Méliès, a former magician, invent the “ trick film ,” which producers in England and the United States began to imitate, but he was also the one to transform cinema into the narrative medium it is today. Whereas before, filmmakers had only ever created single-shot films that lasted a minute or less, Méliès began joining these short films together to create stories. His 30-scene Trip to the Moon (1902), a film based on a Jules Verne novel, may have been the most widely seen production in cinema’s first decade (Robinson). However, Méliès never developed his technique beyond treating the narrative film as a staged theatrical performance; his camera, representing the vantage point of an audience facing a stage, never moved during the filming of a scene. In 1912, Méliès released his last commercially successful production, The Conquest of the Pole , and from then on, he lost audiences to filmmakers who were experimenting with more sophisticated techniques (Encyclopedia of Communication and Information).

Georges Méliès’s Trip to the Moon was one of the first films to incorporate fantasy elements and to use “trick” filming techniques, both of which heavily influenced future filmmakers.
The Nickelodeon Craze (1904–1908)
One of these innovative filmmakers was Edwin S. Porter, a projectionist and engineer for the Edison Company. Porter’s 12-minute film, The Great Train Robbery (1903), broke with the stagelike compositions of Méliès-style films through its use of editing, camera pans, rear projections, and diagonally composed shots that produced a continuity of action. Not only did The Great Train Robbery establish the realistic narrative as a standard in cinema, it was also the first major box-office hit. Its success paved the way for the growth of the film industry, as investors, recognizing the motion picture’s great moneymaking potential, began opening the first permanent film theaters around the country.
Known as nickelodeons because of their 5 cent admission charge, these early motion picture theaters, often housed in converted storefronts, were especially popular among the working class of the time, who couldn’t afford live theater. Between 1904 and 1908, around 9,000 nickelodeons appeared in the United States. It was the nickelodeon’s popularity that established film as a mass entertainment medium (Dictionary of American History).
The “Biz”: The Motion Picture Industry Emerges
As the demand for motion pictures grew, production companies were created to meet it. At the peak of nickelodeon popularity in 1910 (Britannica Online), there were 20 or so major motion picture companies in the United States. However, heated disputes often broke out among these companies over patent rights and industry control, leading even the most powerful among them to fear fragmentation that would loosen their hold on the market (Fielding, 1967). Because of these concerns, the 10 leading companies—including Edison, Biograph, Vitagraph, and others—formed the Motion Picture Patents Company (MPPC) in 1908. The MPPC was a trade group that pooled the most significant motion picture patents and established an exclusive contract between these companies and the Eastman Kodak Company as a supplier of film stock. Also known as the Trust , the MPPC’s goal was to standardize the industry and shut out competition through monopolistic control. Under the Trust’s licensing system, only certain licensed companies could participate in the exchange, distribution, and production of film at different levels of the industry—a shut-out tactic that eventually backfired, leading the excluded, independent distributors to organize in opposition to the Trust (Britannica Online).
The Rise of the Feature
In these early years, theaters were still running single-reel films, which came at a standard length of 1,000 feet, allowing for about 16 minutes of playing time. However, companies began to import multiple-reel films from European producers around 1907, and the format gained popular acceptance in the United States in 1912 with Louis Mercanton’s highly successful Queen Elizabeth , a three-and-a-half reel “feature,” starring the French actress Sarah Bernhardt. As exhibitors began to show more features—as the multiple-reel film came to be called—they discovered a number of advantages over the single-reel short. For one thing, audiences saw these longer films as special events and were willing to pay more for admission, and because of the popularity of the feature narratives , features generally experienced longer runs in theaters than their single-reel predecessors (Motion Pictures). Additionally, the feature film gained popularity among the middle classes, who saw its length as analogous to the more “respectable” entertainment of live theater (Motion Pictures). Following the example of the French film d’art , U.S. feature producers often took their material from sources that would appeal to a wealthier and better educated audience, such as histories, literature, and stage productions (Robinson).
As it turns out, the feature film was one factor that brought about the eventual downfall of the MPPC. The inflexible structuring of the Trust’s exhibition and distribution system made the organization resistant to change. When movie studio, and Trust member, Vitagraph began to release features like A Tale of Two Cities (1911) and Uncle Tom’s Cabin (1910), the Trust forced it to exhibit the films serially in single-reel showings to keep with industry standards. The MPPC also underestimated the appeal of the star system, a trend that began when producers chose famous stage actors like Mary Pickford and James O’Neill to play the leading roles in their productions and to grace their advertising posters (Robinson). Because of the MPPC’s inflexibility, independent companies were the only ones able to capitalize on two important trends that were to become film’s future: single-reel features and star power. Today, few people would recognize names like Vitagraph or Biograph, but the independents that outlasted them—Universal, Goldwyn (which would later merge with Metro and Mayer), Fox (later 20th Century Fox), and Paramount (the later version of the Lasky Corporation)—have become household names.
As moviegoing increased in popularity among the middle class, and as the feature films began keeping audiences in their seats for longer periods of time, exhibitors found a need to create more comfortable and richly decorated theater spaces to attract their audiences. These “dream palaces,” so called because of their often lavish embellishments of marble, brass, guilding, and cut glass, not only came to replace the nickelodeon theater, but also created the demand that would lead to the Hollywood studio system. Some producers realized that the growing demand for new work could only be met if the films were produced on a regular, year-round system. However, this was impractical with the current system that often relied on outdoor filming and was predominately based in Chicago and New York—two cities whose weather conditions prevented outdoor filming for a significant portion of the year. Different companies attempted filming in warmer locations such as Florida, Texas, and Cuba, but the place where producers eventually found the most success was a small, industrial suburb of Los Angeles called Hollywood.
Hollywood proved to be an ideal location for a number of reasons. Not only was the climate temperate and sunny year-round, but land was plentiful and cheap, and the location allowed close access to a number of diverse topographies: mountains, lakes, desert, coasts, and forests. By 1915, more than 60 percent of U.S. film production was centered in Hollywood (Britannica Online).
The Art of Silent Film
While the development of narrative film was largely driven by commercial factors, it is also important to acknowledge the role of individual artists who turned it into a medium of personal expression. The motion picture of the silent era was generally simplistic in nature; acted in overly animated movements to engage the eye; and accompanied by live music, played by musicians in the theater, and written titles to create a mood and to narrate a story. Within the confines of this medium, one filmmaker in particular emerged to transform the silent film into an art and to unlock its potential as a medium of serious expression and persuasion. D. W. Griffith, who entered the film industry as an actor in 1907, quickly moved to a directing role in which he worked closely with his camera crew to experiment with shots, angles, and editing techniques that could heighten the emotional intensity of his scenes. He found that by practicing parallel editing , in which a film alternates between two or more scenes of action, he could create an illusion of simultaneity. He could then heighten the tension of the film’s drama by alternating between cuts more and more rapidly until the scenes of action converged. Griffith used this technique to great effect in his controversial film The Birth of a Nation , which will be discussed in greater detail later on in this chapter. Other techniques that Griffith employed to new effect included panning shots , through which he was able to establish a sense of scene and to engage his audience more fully in the experience of the film, and tracking shots , or shots that traveled with the movement of a scene (Motion Pictures), which allowed the audience—through the eye of the camera—to participate in the film’s action.
MPAA: Combating Censorship
As film became an increasingly lucrative U.S. industry, prominent industry figures like D. W. Griffith, slapstick comedian/director Charlie Chaplin, and actors Mary Pickford and Douglas Fairbanks grew extremely wealthy and influential. Public attitudes toward stars and toward some stars’ extravagant lifestyles were divided, much as they are today: On the one hand, these celebrities were idolized and imitated in popular culture, yet at the same time, they were criticized for representing a threat, on and off screen, to traditional morals and social order. And much as it does today, the news media liked to sensationalize the lives of celebrities to sell stories. Comedian Roscoe “Fatty” Arbuckle, who worked alongside future icons Charlie Chaplin and Buster Keaton, was at the center of one of the biggest scandals of the silent era. When Arbuckle hosted a marathon party over Labor Day weekend in 1921, one of his guests, model Virginia Rapp, was rushed to the hospital, where she later died. Reports of a drunken orgy, rape, and murder surfaced. Following World War I, the United States was in the middle of significant social reforms, such as Prohibition. Many feared that movies and their stars could threaten the moral order of the country. Because of the nature of the crime and the celebrity involved, these fears became inexplicably tied to the Artbuckle case (Motion Pictures). Even though autopsy reports ruled that Rapp had died from causes for which Arbuckle could not be blamed, the comedian was tried (and acquitted) for manslaughter, and his career was ruined.
The Arbuckle affair and a series of other scandals only increased public fears about Hollywood’s impact. In response to this perceived threat, state and local governments increasingly tried to censor the content of films that depicted crime, violence, and sexually explicit material. Deciding that they needed to protect themselves from government censorship and to foster a more favorable public image, the major Hollywood studios organized in 1922 to form an association they called the Motion Picture Producers and Distributers of America (later renamed the Motion Picture Association of America, or MPAA ). Among other things, the MPAA instituted a code of self-censorship for the motion picture industry. Today, the MPAA operates by a voluntary rating system, which means producers can voluntarily submit a film for review, which is designed to alert viewers to the age-appropriateness of a film, while still protecting the filmmakers’ artistic freedom (Motion Picture Association of America).
Silent Film’s Demise
In 1925, Warner Bros. was just a small Hollywood studio looking for opportunities to expand. When representatives from Western Electric offered to sell the studio the rights to a new technology they called Vitaphone, a sound-on-disc system that had failed to capture the interest of any of the industry giants, Warner Bros. executives took a chance, predicting that the novelty of talking films might be a way to make a quick, short-term profit. Little did they anticipate that their gamble would not only establish them as a major Hollywood presence but also change the industry forever.
The pairing of sound with motion pictures was nothing new in itself. Edison, after all, had commissioned the kinetoscope to create a visual accompaniment to the phonograph, and many early theaters had orchestra pits to provide musical accompaniment to their films. Even the smaller picture houses with lower budgets almost always had an organ or piano. When Warner Bros. purchased Vitaphone technology, it planned to use it to provide prerecorded orchestral accompaniment for its films, thereby increasing their marketability to the smaller theaters that didn’t have their own orchestra pits (Gochenour, 2000). In 1926, Warner debuted the system with the release of Don Juan , a costume drama accompanied by a recording of the New York Philharmonic Orchestra; the public responded enthusiastically (Motion Pictures). By 1927, after a $3 million campaign, Warner Bros. had wired more than 150 theaters in the United States, and it released its second sound film, The Jazz Singer , in which the actor Al Jolson improvised a few lines of synchronized dialogue and sang six songs. The film was a major breakthrough. Audiences, hearing an actor speak on screen for the first time, were enchanted (Gochenour). While radio, a new and popular entertainment, had been drawing audiences away from the picture houses for some time, with the birth of the “ talkie ,” or talking film, audiences once again returned to the cinema in large numbers, lured by the promise of seeing and hearing their idols perform (Higham, 1973). By 1929, three-fourths of Hollywood films had some form of sound accompaniment, and by 1930, the silent film was a thing of the past (Gochenour).
“I Don’t Think We’re in Kansas Anymore”: Film Goes Technicolor
Although the techniques of tinting and hand painting had been available methods for adding color to films for some time (Georges Méliès, for instance, employed a crew to hand-paint many of his films), neither method ever caught on. The hand-painting technique became impractical with the advent of mass-produced film, and the tinting process, which filmmakers discovered would create an interference with the transmission of sound in films, was abandoned with the rise of the talkie. However, in 1922, Herbert Kalmus’s Technicolor company introduced a dye-transfer technique that allowed it to produce a full-length film, The Toll of the Sea , in two primary colors (Gale Virtual Reference Library). However, because only two colors were used, the appearance of The Toll of the Sea (1922), The Ten Commandments (1923), and other early Technicolor films was not very lifelike. By 1932, Technicolor had designed a three-color system with more realistic results, and for the next 25 years, all color films were produced with this improved system. Disney’s Three Little Pigs (1933) and Snow White and the Seven Dwarves (1936) and films with live actors, like MGM’s The Wizard of Oz (1939) and Gone With the Wind (1939), experienced early success using Technicolor’s three-color method.
Despite the success of certain color films in the 1930s, Hollywood, like the rest of the United States, was feeling the impact of the Great Depression, and the expenses of special cameras, crews, and Technicolor lab processing made color films impractical for studios trying to cut costs. Therefore, it wasn’t until the end of the 1940s that Technicolor would largely displace the black-and-white film (Motion Pictures in Color).
Rise and Fall of the Hollywood Studio
The spike in theater attendance that followed the introduction of talking films changed the economic structure of the motion picture industry, bringing about some of the largest mergers in industry history. By 1930, eight studios produced 95 percent of all American films, and they continued to experience growth even during the Depression. The five most influential of these studios—Warner Bros., Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer, RKO, 20th Century Fox, and Paramount—were vertically integrated ; that is, they controlled every part of the system as it related to their films, from the production to release, distribution, and even viewing. Because they owned theater chains worldwide, these studios controlled which movies exhibitors ran, and because they “owned” a stock of directors, actors, writers, and technical assistants by contract, each studio produced films of a particular character.
The late 1930s and early 1940s are sometimes known as the “ Golden Age ” of cinema, a time of unparalleled success for the movie industry; by 1939, film was the 11th-largest industry in the United States, and during World War II, when the U.S. economy was once again flourishing, two-thirds of Americans were attending the theater at least once a week (Britannica Online). Some of the most acclaimed movies in history were released during this period, including Citizen Kane and The Grapes of Wrath . However, postwar inflation, a temporary loss of key foreign markets, the advent of the television, and other factors combined to bring that rapid growth to an end. In 1948, the case of the United States v. Paramount Pictures —mandating competition and forcing the studios to relinquish control over theater chains—dealt the final devastating blow from which the studio system would never recover. Control of the major studios reverted to Wall Street, where the studios were eventually absorbed by multinational corporations, and the powerful studio heads lost the influence they had held for nearly 30 years (Baers, 2000).
Rise and Decline of Movie Viewing During Hollywood’s “Golden Age”
Graph from Pautz, Michelle C. 2002. The Decline in Average Weekly Cinema Attendance: 1930–2000. Issues in Political Economy, 11 (Summer): 54–65.
Post–World War II: Television Presents a Threat
While economic factors and antitrust legislation played key roles in the decline of the studio system, perhaps the most important factor in that decline was the advent of the television. Given the opportunity to watch “movies” from the comfort of their own homes, the millions of Americans who owned a television by the early 1950s were attending the cinema far less regularly than they had only several years earlier (Motion Pictures). In an attempt to win back diminishing audiences, studios did their best to exploit the greatest advantages film held over television. For one thing, television broadcasting in the 1950s was all in black and white, whereas the film industry had the advantage of color. While producing a color film was still an expensive undertaking in the late 1940s, a couple of changes occurred in the industry in the early 1950s to make color not only more affordable, but more realistic in its appearance. In 1950, as the result of antitrust legislation, Technicolor lost its monopoly on the color film industry, allowing other providers to offer more competitive pricing on filming and processing services. At the same time, Kodak came out with a multilayer film stock that made it possible to use more affordable cameras and to produce a higher quality image. Kodak’s Eastmancolor option was an integral component in converting the industry to color. In the late 1940s, only 12 percent of features were in color; however, by 1954 (after the release of Kodak Eastmancolor) more than 50 percent of movies were in color (Britannica Online).
Another clear advantage on which filmmakers tried to capitalize was the sheer size of the cinema experience. With the release of the epic biblical film The Robe in 1953, 20th Century Fox introduced the method that would soon be adopted by nearly every studio in Hollywood: a technology that allowed filmmakers to squeeze a wide-angle image onto conventional 35-mm film stock, thereby increasing the aspect ratio (the ratio of a screen’s width to its height) of their images. This wide-screen format increased the immersive quality of the theater experience. Nonetheless, even with these advancements, movie attendance never again reached the record numbers it experienced in 1946, at the peak of the Golden Age of Hollywood (Britannica Online).
Mass Entertainment, Mass Paranoia: HUAC and the Hollywood Blacklist
The Cold War with the Soviet Union began in 1947, and with it came the widespread fear of communism, not only from the outside, but equally from within. To undermine this perceived threat, the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) commenced investigations to locate communist sympathizers in America who were suspected of conducting espionage for the Soviet Union. In the highly conservative and paranoid atmosphere of the time, Hollywood, the source of a mass-cultural medium, came under fire in response to fears that subversive, communist messages were being embedded in films. In November 1947, more than 100 people in the movie business were called to testify before the HUAC about their and their colleagues’ involvement with communist affairs. Of those investigated, 10 in particular refused to cooperate with the committee’s questions. These 10, later known as the Hollywood Ten, were fired from their jobs and sentenced to serve up to a year in prison. The studios, already slipping in influence and profit, were eager to cooperate in order to save themselves, and a number of producers signed an agreement stating that no communists would work in Hollywood.
The hearings, which recommenced in 1951 with the rise of Senator Joseph McCarthy’s influence, turned into a kind of witch hunt as witnesses were asked to testify against their associates, and a blacklist of suspected communists evolved. Over 324 individuals lost their jobs in the film industry as a result of blacklisting (the denial of work in a certain field or industry) and HUAC investigations (Georgakas, 2004; Mills, 2007; Dressler, et. al., 2005).
Down With the Establishment: Youth Culture of the 1960s and 1970s
Movies of the late 1960s began attracting a younger demographic, as a growing number of young people were drawn in by films like Sam Peckinpah’s The Wild Bunch (1969), Stanley Kubrick’s 2001: A Space Odyssey (1968), Arthur Penn’s Bonnie and Clyde (1967), and Dennis Hopper’s Easy Rider (1969)—all revolutionary in their genres—that displayed a sentiment of unrest toward conventional social orders and included some of the earliest instances of realistic and brutal violence in film. These four films in particular grossed so much money at the box offices that producers began churning out low-budget copycats to draw in a new, profitable market (Motion Pictures). While this led to a rise in youth-culture films, few of them saw great success. However, the new liberal attitudes toward depictions of sex and violence in these films represented a sea of change in the movie industry that manifested in many movies of the 1970s, including Francis Ford Coppola’s The Godfather (1972), William Friedkin’s The Exorcist (1973), and Steven Spielberg’s Jaws (1975), all three of which saw great financial success (Britannica Online; Belton, 1994).
Blockbusters, Knockoffs, and Sequels
In the 1970s, with the rise of work by Coppola, Spielberg, George Lucas, Martin Scorsese, and others, a new breed of director emerged. These directors were young and film-school educated, and they contributed a sense of professionalism, sophistication, and technical mastery to their work, leading to a wave of blockbuster productions, including Close Encounters of the Third Kind (1977), Star Wars (1977), Raiders of the Lost Ark (1981), and E.T.: The Extra-Terrestrial (1982). The computer-generated special effects that were available at this time also contributed to the success of a number of large-budget productions. In response to these and several earlier blockbusters, movie production and marketing techniques also began to shift, with studios investing more money in fewer films in the hopes of producing more big successes. For the first time, the hefty sums producers and distributers invested didn’t go to production costs alone; distributers were discovering the benefits of TV and radio advertising and finding that doubling their advertising costs could increase profits as much as three or four times over. With the opening of Jaws , one of the five top-grossing films of the decade (and the highest grossing film of all time until the release of Star Wars in 1977), Hollywood embraced the wide-release method of movie distribution, abandoning the release methods of earlier decades, in which a film would debut in only a handful of select theaters in major cities before it became gradually available to mass audiences. Jaws was released in 600 theaters simultaneously, and the big-budget films that followed came out in anywhere from 800 to 2,000 theaters nationwide on their opening weekends (Belton; Hanson & Garcia-Myers, 2000).
The major Hollywood studios of the late 1970s and early 1980s, now run by international corporations, tended to favor the conservative gamble of the tried and true, and as a result, the period saw an unprecedented number of high-budget sequels—as in the Star Wars , Indiana Jones , and Godfather films—as well as imitations and adaptations of earlier successful material, such as the plethora of “slasher” films that followed the success of the 1979 thriller Halloween . Additionally, corporations sought revenue sources beyond the movie theater, looking to the video and cable releases of their films. Introduced in 1975, the VCR became nearly ubiquitous in American homes by 1998 with 88.9 million households owning the appliance (Rosen & Meier, 2000). Cable television’s growth was slower, but ownership of VCRs gave people a new reason to subscribe, and cable subsequently expanded as well (Rogers). And the newly introduced concept of film-based merchandise (toys, games, books, etc.) allowed companies to increase profits even more.
The 1990s and Beyond
The 1990s saw the rise of two divergent strands of cinema: the technically spectacular blockbuster with special, computer-generated effects and the independent, low-budget film. The capabilities of special effects were enhanced when studios began manipulating film digitally. Early examples of this technology can be seen in Terminator 2: Judgment Day (1991) and Jurassic Park (1993). Films with an epic scope— Independence Day (1996), Titanic (1997), and The Matrix (1999)—also employed a range of computer-animation techniques and special effects to wow audiences and to draw more viewers to the big screen. Toy Story (1995), the first fully computer-animated film, and those that came after it, such as Antz (1998), A Bug’s Life (1998), and Toy Story 2 (1999), displayed the improved capabilities of computer-generated animation (Sedman, 2000). At the same time, independent directors and producers, such as the Coen brothers and Spike Jonze, experienced an increased popularity, often for lower-budget films that audiences were more likely to watch on video at home (Britannica Online). A prime example of this is the 1996 Academy Awards program, when independent films dominated the Best Picture category. Only one movie from a big film studio was nominated— Jerry Maguire —while the rest were independent films. The growth of both independent movies and special-effects-laden blockbusters continues to the present day. You will read more about current issues and trends and the future of the movie industry later on in this chapter.
Key Takeaways
- The concept of the motion picture was first introduced to a mass audience through Thomas Edison’s kinetoscope in 1891. However, it wasn’t until the Lumière brothers released the cinématographe in 1895 that motion pictures were projected for audience viewing. In the United States, film established itself as a popular form of entertainment with the nickelodeon theater in the 1910s.
- The release of The Jazz Singer in 1927 marked the birth of the talking film, and by 1930 silent film was a thing of the past. Technicolor emerged for film around the same time and found early success with movies like The Wizard of Oz and Gone With the Wind . However, people would continue to make films in black and white until the late 1950s.
- By 1915 most of the major film studios had moved to Hollywood. During the Golden Age of Hollywood, these major studios controlled every aspect of the movie industry, and the films they produced drew crowds to theaters in numbers that have still not been surpassed. After World War II, the studio system declined as a result of antitrust legislation that took power away from studios and of the invention of the television.
- During the 1960s and 1970s, there was a rise in films—including Bonnie and Clyde , The Wild Bunch , 2001: A Space Odyssey , and Easy Rider —that celebrated the emerging youth culture and a rejection of the conservatism of the previous decades. This also led to looser attitudes toward depictions of sexuality and violence in film. The 1970s and 1980s saw the rise of the blockbuster, with films like Jaws , Star Wars , Raiders of the Lost Ark , and The Godfather .
- The adoption of the VCR by most households in the 1980s reduced audiences at movie theaters but opened a new mass market of home movie viewers. Improvements in computer animation led to more special effects in film during the 1990s with movies like The Matrix , Jurassic Park , and the first fully computer-animated film, Toy Story .
Identify four films that you would consider to be representative of major developments in the industry and in film as a medium that were outlined in this section. Imagine you are using these films to explain movie history to a friend. Provide a detailed explanation of why each of these films represents significant changes in attitudes, technology, or trends and situate each in the overall context of film’s development. Consider the following questions:
- How did this movie influence the film industry?
- What has been the lasting impact of this movie on the film industry?
- How was the film industry and technology different before this film?
Baers, Michael. “Studio System,” in St. James Encyclopedia of Popular Culture , ed. Sara Pendergast and Tom Pendergast (Detroit: St. James Press, 2000), vol. 4, 565.
Balcanasu, Andrei Ionut, Sergey V. Smagin, and Stephanie K. Thrift, “Edison and the Lumiere Brothers,” Cartoons and Cinema of the 20th Century , http://library.thinkquest.org/C0118600/index.phtml?menu=en%3B1%3Bci1001.html .
Belton, American Cinema/American Culture , 305.
Belton, John. American Cinema/American Culture . (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1994), 284 –2 90.
Britannica Online, s.v. “History of the Motion Picture”.
Britannica Online, s.v. “Kinetoscope,” http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/318211/Kinetoscope/318211main/Article .
Britannica Online, s.v. “nickelodeon.”
Britannica Online. s.v. “History of the Motion Picture.” http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/394161/history-of-the-motion picture ; Robinson, From Peep Show to Palace , 45, 53.
British Movie Classics, “The Kinetoscope,” British Movie Classics, http://www.britishmovieclassics.com/thekinetoscope.php .
Dictionary of American History, 3rd ed., s.v. “Nickelodeon,” by Ryan F. Holznagel, Gale Virtual Reference Library.
Dresler, Kathleen, Kari Lewis, Tiffany Schoser and Cathy Nordine, “The Hollywood Ten,” Dalton Trumbo, 2005, http://www.mcpld.org/trumbo/WebPages/hollywoodten.htm .
Encyclopedia of Communication and Information (New York: MacMillan Reference USA, 2002), s.v. “Méliès, Georges,” by Ted C. Jones, Gale Virtual Reference Library.
Encyclopedia of the Age of Industry and Empire, s.v. “Cinema.”
Fielding, Raymond A Technological History of Motion Pictures and Television (Berkeley: California Univ. Press, 1967) 21.
Gale Virtual Reference Library, “Motion Pictures in Color,” in American Decades , ed. Judith S. Baughman and others, vol. 3, Gale Virtual Reference Library.
Gale Virtual Reference Library, Europe 1789–1914: Encyclopedia of the Age of Industry and Empire, vol. 1, s.v. “Cinema,” by Alan Williams, Gale Virtual Reference Library.
Georgakas, Dan. “Hollywood Blacklist,” in Encyclopedia of the American Left , ed. Mari Jo Buhle, Paul Buhle, and Dan Georgakas, 2004, http://writing.upenn.edu/~afilreis/50s/blacklist.html .
Gochenour, “Birth of the ‘Talkies,’” 578.
Gochenour, Phil. “Birth of the ‘Talkies’: The Development of Synchronized Sound for Motion Pictures,” in Science and Its Times , vol. 6, 1900–1950 , ed. Neil Schlager and Josh Lauer (Detroit: Gale, 2000), 577.
Hanson, Steve and Sandra Garcia-Myers, “Blockbusters,” in St. James Encyclopedia of Popular Culture , ed. Sara Pendergast and Tom Pendergast (Detroit: St. James Press, 2000), vol. 1, 282.
Higham, Charles. The Art of the American Film: 1900–1971 . (Garden City: Doubleday & Company, 1973), 85.
Menand, Louis “Gross Points,” New Yorker , February 7, 2005, http://www.newyorker.com/archive/2005/02/07/050207crat_atlarge .
Mills, Michael. “Blacklist: A Different Look at the 1947 HUAC Hearings,” Modern Times, 2007, http://www.moderntimes.com/blacklist/ .
Motion Picture Association of America, “History of the MPAA,” http://www.mpaa.org/about/history .
Motion Pictures in Color, “Motion Pictures in Color.”
Motion Pictures, “Griffith,” Motion Pictures , http://www.uv.es/EBRIT/macro/macro_5004_39_6.html#0011 .
Motion Pictures, “Post World War I US Cinema,” Motion Pictures , http://www.uv.es/EBRIT/macro/macro_5004_39_10.html#0015 .
Motion Pictures, “Pre World War II Sound Era: Introduction of Sound,” Motion Pictures , http://www.uv.es/EBRIT/macro/macro_5004_39_11.html#0017 . Motion Pictures, “Pre World-War I US Cinema,” Motion Pictures: The Silent Feature: 1910-27 , http://www.uv.es/EBRIT/macro/macro_5004_39_4.html#0009 .
Motion Pictures, “Recent Trends in US Cinema,” Motion Pictures , http://www.uv.es/EBRIT/macro/macro_5004_39_37.html#0045 .
Motion Pictures, “The War Years and Post World War II Trends: Decline of the Hollywood Studios,” Motion Pictures , http://www.uv.es/EBRIT/macro/macro_5004_39_24.html#0030 .
Robinson, From Peep Show to Palace , 135, 144.
Robinson, From Peep Show to Palace , 63.
Robinson, From Peep Show to Palace , 74–75; Encyclopedia of the Age of Industry and Empire , s.v. “Cinema.”
Robinson, David. From Peep Show to Palace: The Birth of American Film (New York: Columbia University Press, 1994), 43 – 44.
Rogers, Everett. “Video is Here to Stay,” Center for Media Literacy , http://www.medialit.org/reading-room/video-here-stay .
Rosen, Karen and Alan Meier, “Power Measurements and National Energy Consumption of Televisions and Video Cassette Recorders in the USA,” Energy , 25, no. 3 (2000), 220.
Sedman, David. “Film Industry, Technology of,” in Encyclopedia of Communication and Information , ed. Jorge Reina Schement (New York: MacMillan Reference, 2000), vol. 1, 340.
Understanding Media and Culture Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Al Razutis – Visual Essays: Origins of Film (1973-1984)

A six-part film by Al Razutis (1973-1984)
56 min. color, sound
These six essays on film/image history reconstruct cinema history by ‘re-imagining’ its origins, and its poetries, and use historical films themselves (as ‘text’) to provide the meanings of their creations. Together, these film essays comprise a critical/structural investigation of silent cinema ending with Segei Eisenstein’s works (for Stalin) – from Lumiere and Melies through surrealism and horros, to montage and propaganda, we ‘re-invent’ epochs in cinema that became its language and culture.
“Both the visual artist and the educator make their appearances throughout Origins of Film, but it looks to be the poet who has the final say. Informing the overall shape of the project is an argument that is presented at a number of levels. Each film is structured around a distinct set of optical printing and collage techniques [and] … embodies a `look’ which becomes the film’s central strategy and metaphor.” (Peter Chapman, Independent Eye)
LUMIÈRE’S TRAIN (ARRIVING AT THE STATION 9 min. sound b/w 1979 The subject of the first essay is cinema itself: an apparatus of representation wherein fact and fiction are recreated. As such, the pro-filmic facts are necessarily drawn from two of cinema’s “pioneers”: Louis and Auguste Lumière and Abel Gance ( La Roue, ), with additional material provided from a Warner Brothers featurette, Spills for Thrills.
The film breaks down into four distinct sections and is loosely centred around Lumière’s classic one-shot film of a train pulling into a station Arrivée d’un train à la Ciotat, L’ (1895).
The exposition and form of the film is closely tied to the tradition of cine-structural poems which foreground the materials of the medium (light, dark, form as shadow-projection of the cinematic apparatus). Using alternations between positive and negative, the film chronicles the “coming to life” (of the apparatus) and the resulting action/movement and documentation of events – encompassing incidents (the near mishaps), human expectations (the arrival at the station), and human spectacle(the destruction of the trains, the station in chaos). Towards this purpose, I have used an expanding narrative, a play on the title itself, and the shifting conditions of synchronous and asynchronous sound/image (and image-to-image). (A.R.)
MÉLIÈS CATALOGUE 8 min. color silent 1973 The first essay created in 1973 and inspired by the origins of cinema and the works (1896-1912) of magician-illusionist Georges Méliès. This burning celluloid montage film presents the mythic iconography of the films of Georges Méliès — a dreamlike terrain, a grab-bag of magician’s surprises, a cornucopia of players that proceed from the imagination of that “magician” of cinema – announced by the opening motif, “the magic box”.
These incidents are presented/framed within the graphic form of burning frames, each image-shot erupting and being displaced by the following shot. This is an essay featuring discontinuity and surprise. Images in this piece were compiled from approximately 30 films by Georges Méliès, most notably ‘A Trip to the Moon (1902)’ — (A.R.)
SEQUELS IN TRANSFIGURED TIME 14 min. SEPIA-color sound 1974 Sequels in Transfigured Time returns to Georges Méliès and notably portions of A Trip to the Moon (1902) and other early Méliès films (including a hand-colored early film, and uses techniques of ‘frozen stills becoming movement’, still which are initially ‘abstractions’ through the absence of movement and denial of depth (via graphic solarization). The stills are meditations on the “becoming of motion-picture reality” through movement and seamless editing (the “invisible”cut), mechanisms in the ‘creation of narrative’ (which Méliès thought to be secondary to a ‘dreamland’ for the eye).
This essay is also an elegy for Georges Méliès, his “Eden lost and found,” his cine-world becoming obsolete and “ghostlike.” This is a ‘sound film’ with the ‘Elegy for Méliès’ occuring at the end (as voice-over ). — (A.R.)
GHOST: IMAGE 12 min. B&W sound 1976-79 Thematically proceeding from the previous (Méliès) fantasy films, GHOST: IMAGE encompasses that tradition of “fantastic” films that includes Dada, Cubism, Surrealism, Expressionism, Poetic Realism, Symbolism, and eventually the horror genre (and of course Fritz Lang’s Metropolis ).
Its formal design, the mirror image, creates a denial of axis and screen direction,with the result that the viewer must read “through the images.” At times, the mirror images are reduced to their Rorschach component, and complemented by the presence of fragmented poetry (after T.S. Eliot and automatic writing), a metonymic realm suggesting “automatic disclosures” and unconscious correspondences in the developing discourse. The familiar myths of woman as ‘madonna’ / ‘victim’ / ‘temptress’, and ‘redemption through knowledge and science,’ ‘fear of the undead,” and ‘fear of the irrational,’ form the signposts of this historical and cultural terrain.
Contains excerpts from aproximately 20 surrealist, dada, horror, films. (A.R.)
FOR ARTAUD 10 min. color sound 1982 Re-imagining Antonin Artaud’s Theater of Cruelty within a context of Dryer’s (Passion of Joan of Arc) and spectacle, we reach into a ‘terror’ as evoked in this films of sparkling fragmented images and cacophonies of chant. The film tears and re-combines, as the film expressionism of Dryer meets the tradition of Gothic horror and beyond that, Artaud. It brings to mind a humanity caught between absolutes, the good and the evils of monstrous proportions, of classicism, and of questions of individuation. Artaud, though a figure indirectly associated with film history, is suggested in this essay as prime provocateur in the collision between classicism (the “Greek chorus”) and romantic expressionism. Dreyer’s Passion of Joan of Arc – in which Artaud himself appears (as the monk) – serves to set the stage for this “inquisition.” (A.R.)
STORMING THE WINTER PALACE 16 min. color sound 1984 14 min. SEPIA-color sound 1974 This last visual essay focuses on montage and the dialectics of Sergei Eisenstein’s films, indicating their influence as cornerstones of silent cinema and as major contributions to the evolution of later cinema. Eisenstein’s work in the areas of ‘methods of montage’, non-verbal signification and allegorical subjects constructed by juxtaposition (the collision, the dialectics) of meanings, is subjected in this film by Razutis to three “framing” processes: inversion of chronological narrative, fragmentation and repetition of selected montage passages, and the interrogation of selected Oktober sequences by the application of ‘saccadic eye movement’ (animated) techniques.
The end of the visual essays cycle brings on the ‘textual’ (to be read) cinema, the cinema of constructed meanings, and persuasions, where a new ‘winter palace’ (center of power) is sure to arise. The film contains sequences from ‘Battleship Potempkin’ and ‘Oktober’ by Sergei Eisenstein, now in the service of the Party.

http://nitroflare.com/view/8E485CA06306F05/VISUAL_ESSAYS.part1.rar http://nitroflare.com/view/0105B71371C172F/VISUAL_ESSAYS.part2.rar http://nitroflare.com/view/767EC5A53331C81/VISUAL_ESSAYS.part3.rar
Language:English Subtitles:English
Ryûsuke Hamaguchi - Netemo sametemo AKA Asako I & II (2018)
Bailu feng - bai yi zhan shi aka soldier in white (1949), leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Melika Bass – Creature Companion (2018) July 5, 2018
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Essay Film
Introduction, anthologies.
- Bibliographies
- Spectator Engagement
- Personal Documentary
- 1940s Watershed Years
- Chris Marker
- Alain Resnais
- Jean-Luc Godard
- Harun Farocki
- Latin American Cinema
- Installation and Exhibition
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Documentary Film
- Dziga Vertov
- Trinh T. Minh-ha
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Jacques Tati
- Media Materiality
- The Golden Girls
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Essay Film by Yelizaveta Moss LAST REVIEWED: 24 March 2021 LAST MODIFIED: 24 March 2021 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199791286-0216
The term “essay film” has become increasingly used in film criticism to describe a self-reflective and self-referential documentary cinema that blurs the lines between fiction and nonfiction. Scholars unanimously agree that the first published use of the term was by Richter in 1940. Also uncontested is that Andre Bazin, in 1958, was the first to analyze a film, which was Marker’s Letter from Siberia (1958), according to the essay form. The French New Wave created a popularization of short essay films, and German New Cinema saw a resurgence in essay films due to a broad interest in examining German history. But beyond these origins of the term, scholars deviate on what exactly constitutes an essay film and how to categorize essay films. Generally, scholars fall into two camps: those who find a literary genealogy to the essay film and those who find a documentary genealogy to the essay film. The most commonly cited essay filmmakers are French and German: Marker, Resnais, Godard, and Farocki. These filmmakers are singled out for their breadth of essay film projects, as opposed to filmmakers who have made an essay film but who specialize in other genres. Though essay films have been and are being produced outside of the West, scholarship specifically addressing essay films focuses largely on France and Germany, although Solanas and Getino’s theory of “Third Cinema” and approval of certain French essay films has produced some essay film scholarship on Latin America. But the gap in scholarship on global essay film remains, with hope of being bridged by some forthcoming work. Since the term “essay film” is used so sparingly for specific films and filmmakers, the scholarship on essay film tends to take the form of single articles or chapters in either film theory or documentary anthologies and journals. Some recent scholarship has pointed out the evolutionary quality of essay films, emphasizing their ability to change form and style as a response to conventional filmmaking practices. The most recent scholarship and conference papers on essay film have shifted from an emphasis on literary essay to an emphasis on technology, arguing that essay film has the potential in the 21st century to present technology as self-conscious and self-reflexive of its role in art.
Both anthologies dedicated entirely to essay film have been published in order to fill gaps in essay film scholarship. Biemann 2003 brings the discussion of essay film into the digital age by explicitly resisting traditional German and French film and literary theory. Papazian and Eades 2016 also resists European theory by explicitly showcasing work on postcolonial and transnational essay film.
Biemann, Ursula, ed. Stuff It: The Video Essay in the Digital Age . New York: Springer, 2003.
This anthology positions Marker’s Sans Soleil (1983) as the originator of the post-structuralist essay film. In opposition to German and French film and literary theory, Biemann discusses video essays with respect to non-linear and non-logical movement of thought and a range of new media in Internet, digital imaging, and art installation. In its resistance to the French/German theory influence on essay film, this anthology makes a concerted effort to include other theoretical influences, such as transnationalism, postcolonialism, and globalization.
Papazian, Elizabeth, and Caroline Eades, eds. The Essay Film: Dialogue, Politics, Utopia . London: Wallflower, 2016.
This forthcoming anthology bridges several gaps in 21st-century essay film scholarship: non-Western cinemas, popular cinema, and digital media.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Cinema and Media Studies »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- 2001: A Space Odyssey
- Accounting, Motion Picture
- Action Cinema
- Advertising and Promotion
- African American Cinema
- African American Stars
- African Cinema
- AIDS in Film and Television
- Akerman, Chantal
- Allen, Woody
- Almodóvar, Pedro
- Altman, Robert
- American Cinema, 1895-1915
- American Cinema, 1939-1975
- American Cinema, 1976 to Present
- American Independent Cinema
- American Independent Cinema, Producers
- American Public Broadcasting
- Anderson, Wes
- Animals in Film and Media
- Animation and the Animated Film
- Arbuckle, Roscoe
- Architecture and Cinema
- Argentine Cinema
- Aronofsky, Darren
- Arzner, Dorothy
- Asian American Cinema
- Asian Television
- Astaire, Fred and Rogers, Ginger
- Audiences and Moviegoing Cultures
- Australian Cinema
- Authorship, Television
- Avant-Garde and Experimental Film
- Bachchan, Amitabh
- Battle of Algiers, The
- Battleship Potemkin, The
- Bazin, André
- Bergman, Ingmar
- Bernstein, Elmer
- Bertolucci, Bernardo
- Bigelow, Kathryn
- Birth of a Nation, The
- Blade Runner
- Blockbusters
- Bong, Joon Ho
- Brakhage, Stan
- Brando, Marlon
- Brazilian Cinema
- Breaking Bad
- Bresson, Robert
- British Cinema
- Broadcasting, Australian
- Buffy the Vampire Slayer
- Burnett, Charles
- Buñuel, Luis
- Cameron, James
- Campion, Jane
- Canadian Cinema
- Capra, Frank
- Carpenter, John
- Cassavetes, John
- Cavell, Stanley
- Chahine, Youssef
- Chan, Jackie
- Chaplin, Charles
- Children in Film
- Chinese Cinema
- Cinecittà Studios
- Cinema and Media Industries, Creative Labor in
- Cinema and the Visual Arts
- Cinematography and Cinematographers
- Citizen Kane
- City in Film, The
- Cocteau, Jean
- Coen Brothers, The
- Colonial Educational Film
- Comedy, Film
- Comedy, Television
- Comics, Film, and Media
- Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI)
- Copland, Aaron
- Coppola, Francis Ford
- Copyright and Piracy
- Corman, Roger
- Costume and Fashion
- Cronenberg, David
- Cuban Cinema
- Cult Cinema
- Dance and Film
- de Oliveira, Manoel
- Dean, James
- Deleuze, Gilles
- Denis, Claire
- Deren, Maya
- Design, Art, Set, and Production
- Detective Films
- Dietrich, Marlene
- Digital Media and Convergence Culture
- Disney, Walt
- Downton Abbey
- Dr. Strangelove
- Dreyer, Carl Theodor
- Eastern European Television
- Eastwood, Clint
- Eisenstein, Sergei
- Elfman, Danny
- Ethnographic Film
- European Television
- Exhibition and Distribution
- Exploitation Film
- Fairbanks, Douglas
- Fan Studies
- Fellini, Federico
- Film Aesthetics
- Film and Literature
- Film Guilds and Unions
- Film, Historical
- Film Preservation and Restoration
- Film Theory and Criticism, Science Fiction
- Film Theory Before 1945
- Film Theory, Psychoanalytic
- Finance Film, The
- French Cinema
- Game of Thrones
- Gance, Abel
- Gangster Films
- Garbo, Greta
- Garland, Judy
- German Cinema
- Gilliam, Terry
- Global Television Industry
- Godard, Jean-Luc
- Godfather Trilogy, The
- Greek Cinema
- Griffith, D.W.
- Hammett, Dashiell
- Haneke, Michael
- Hawks, Howard
- Haynes, Todd
- Hepburn, Katharine
- Herrmann, Bernard
- Herzog, Werner
- Hindi Cinema, Popular
- Hitchcock, Alfred
- Hollywood Studios
- Holocaust Cinema
- Hong Kong Cinema
- Horror-Comedy
- Hsiao-Hsien, Hou
- Hungarian Cinema
- Icelandic Cinema
- Immigration and Cinema
- Indigenous Media
- Industrial, Educational, and Instructional Television and ...
- Invasion of the Body Snatchers
- Iranian Cinema
- Irish Cinema
- Israeli Cinema
- It Happened One Night
- Italian Americans in Cinema and Media
- Italian Cinema
- Japanese Cinema
- Jazz Singer, The
- Jews in American Cinema and Media
- Keaton, Buster
- Kitano, Takeshi
- Korean Cinema
- Kracauer, Siegfried
- Kubrick, Stanley
- Lang, Fritz
- Latina/o Americans in Film and Television
- Lee, Chang-dong
- Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Queer (LGBTQ) Cin...
- Lord of the Rings Trilogy, The
- Los Angeles and Cinema
- Lubitsch, Ernst
- Lumet, Sidney
- Lupino, Ida
- Lynch, David
- Marker, Chris
- Martel, Lucrecia
- Masculinity in Film
- Media, Community
- Media Ecology
- Memory and the Flashback in Cinema
- Metz, Christian
- Mexican Film
- Micheaux, Oscar
- Ming-liang, Tsai
- Minnelli, Vincente
- Miyazaki, Hayao
- Méliès, Georges
- Modernism and Film
- Monroe, Marilyn
- Mészáros, Márta
- Music and Cinema, Classical Hollywood
- Music and Cinema, Global Practices
- Music, Television
- Music Video
- Musicals on Television
- Native Americans
- New Media Art
- New Media Policy
- New Media Theory
- New York City and Cinema
- New Zealand Cinema
- Opera and Film
- Ophuls, Max
- Orphan Films
- Oshima, Nagisa
- Ozu, Yasujiro
- Panh, Rithy
- Pasolini, Pier Paolo
- Passion of Joan of Arc, The
- Peckinpah, Sam
- Philosophy and Film
- Photography and Cinema
- Pickford, Mary
- Planet of the Apes
- Poems, Novels, and Plays About Film
- Poitier, Sidney
- Polanski, Roman
- Polish Cinema
- Politics, Hollywood and
- Pop, Blues, and Jazz in Film
- Pornography
- Postcolonial Theory in Film
- Potter, Sally
- Prime Time Drama
- Queer Television
- Queer Theory
- Race and Cinema
- Radio and Sound Studies
- Ray, Nicholas
- Ray, Satyajit
- Reality Television
- Reenactment in Cinema and Media
- Regulation, Television
- Religion and Film
- Remakes, Sequels and Prequels
- Renoir, Jean
- Resnais, Alain
- Romanian Cinema
- Romantic Comedy, American
- Rossellini, Roberto
- Russian Cinema
- Saturday Night Live
- Scandinavian Cinema
- Scorsese, Martin
- Scott, Ridley
- Searchers, The
- Sennett, Mack
- Sesame Street
- Shakespeare on Film
- Silent Film
- Simpsons, The
- Singin' in the Rain
- Sirk, Douglas
- Soap Operas
- Social Class
- Social Media
- Social Problem Films
- Soderbergh, Steven
- Sound Design, Film
- Sound, Film
- Spanish Cinema
- Spanish-Language Television
- Spielberg, Steven
- Sports and Media
- Sports in Film
- Stand-Up Comedians
- Stop-Motion Animation
- Streaming Television
- Sturges, Preston
- Surrealism and Film
- Taiwanese Cinema
- Tarantino, Quentin
- Tarkovsky, Andrei
- Television Audiences
- Television Celebrity
- Television, History of
- Television Industry, American
- Theater and Film
- Theory, Cognitive Film
- Theory, Critical Media
- Theory, Feminist Film
- Theory, Film
- Theory, Trauma
- Touch of Evil
- Transnational and Diasporic Cinema
- Trinh, T. Minh-ha
- Truffaut, François
- Turkish Cinema
- Twilight Zone, The
- Varda, Agnès
- Vertov, Dziga
- Video and Computer Games
- Video Installation
- Violence and Cinema
- Virtual Reality
- Visconti, Luchino
- Von Sternberg, Josef
- Von Stroheim, Erich
- von Trier, Lars
- Warhol, The Films of Andy
- Waters, John
- Wayne, John
- Weerasethakul, Apichatpong
- Weir, Peter
- Welles, Orson
- Whedon, Joss
- Wilder, Billy
- Williams, John
- Wiseman, Frederick
- Wizard of Oz, The
- Women and Film
- Women and the Silent Screen
- Wong, Anna May
- Wong, Kar-wai
- Wood, Natalie
- Yang, Edward
- Yimou, Zhang
- Yugoslav and Post-Yugoslav Cinema
- Zinnemann, Fred
- Zombies in Cinema and Media
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|185.80.151.41]
- 185.80.151.41

The secret history of the essay film
Charting the resurgence of ‘sort of documentaries’ to celebrate chris marker, king of the essay film.
“Essay films are arguably the most innovative and popular form of filmmaking since the 1990s,” wrote Timothy Corrigan in his notable 2011 book, The Essay Film . True, perhaps, but mention of the genre to your average joe won’t spark the instant recognition of today’s romcoms, sci-fis and period dramas. The thing is, essay films have been around since the dawn of cinema: they emerged not long after the Lumière brothers recorded the first ever motion pictures of Lyonnaise factory workers in 1894, yet their definition is still ambiguous.
They are similar to documentary and non-fiction film in that they are often based in reality, using words, images and sounds to convey a message. But according to Chris Darke – co-curator of the Whitechapel Gallery’s current retrospective of the great essay filmmaker Chris Marker – it is “the personal aspect and style of address” that makes the essay film distinct. It is this flexibility that has appealed to contemporary filmmakers, permitting a fresh, nuanced viewing experience.
Geoff Andrew, a senior programmer at the BFI who helped curate last year’s landmark essay film season, explained, “they are sort of documentaries, sort of non-fiction films.” The issue is that some filmmakers try to provide an objective point of view when it is just not possible. “There’s always somebody manipulating footage and manipulating reality to present some sort of message.” Andrew continued, “So, in a way, all documentaries are essay films.”
But the essay film is particularly resurgent these days, with filmmakers like Michael Moore , Werner Herzog , and Nick Broomfield molding the genre in their own ways. Their popularity isn’t just due to incendiary topics like men getting eaten by bears as in Herzog’s Grizzly Man and high school massacres as in Moore’s Bowling for Columbine ; essay films are capable of compelling beauty. Now, with the Whitechapel Gallery ’s retrospective of the late Frenchman, Chris Marker , arguably the greatest essay filmmaker there’s ever been, we take a look at the essay film’s secret history.

1909 - D. W. Griffith ’s A Corner in Wheat
Considered by some to be the first essay film ever, A Corner in Wheat is a little subversive thorn in the side of the man. Lasting only 14 minutes, it tells the tale of a ruthless crop gambler who amasses riches by monopolising the wheat market, exploits the agricultural poor, and is promptly killed under a pile of his own grain. Think twice, greedy capitalists.
1929 - Dziga Vertov’s Man with a Movie Camera
“The film drama is the opium of the people,” proclaimed Soviet film pioneer Dziga Vertov , “down with Bourgeois fairy-tale scenarios.” He was the most radical of his fellow Soviet filmmaker compatriots, and Man with a Movie Camera was his masterpiece. In it, he tried to create an “international language of cinema” through a beguiling mix of jump cuts, split screens and superimpositions. Vertov’s idea was to uncover the artifice of filmmaking, with one scene of the film depicting a cameraman inside a giant beer.
1940 - Hans Richter’s The Film Essay
The term “essay film” was originally coined by German artist Hans Richter, who wrote in his 1940 paper, The Film Essay : “The film essay enables the filmmaker to make the ‘invisible’ world of thoughts and ideas visible on the screen... The essay film produces complex thought – reflections that are not necessarily bound to reality, but can also be contradictory, irrational, and fantastic.” So while World War II was blazing away, a new cinema was born.
1982 - Chris Marker’s Sans Soleil
You know that this brilliant, freewheeling travelogue is something special when it suggests that Pac-Man is “a perfect graphic metaphor for the human condition.” It takes in anti-colonial struggles, sumo wrestling, a volcanic eruption in Iceland, the antiquities of the Vatican, Marker’s love of cats and more. An unnamed female narrates a circuitous journey from Africa to Japan, in an engaging style never seen before. Some might say he laid down a marker.
1993 - Derek Jarman’s Blue
Diagnosed with HIV and beginning to lose his eyesight, Jarman decided to turn his illness into his art. Although the premise of nothing but a dim, blue background accompanied by voiceovers for 79 minutes might not seem enthralling, it really is. Jarman recalls memories of his past lovers, and his current life of endless pill-popping, with a poignant score by Brian Eno and Simon Fisher Turner .
1998 - Jean -Luc Godard’s Histoire(s) du cinema
Comprised of hundreds of clips of films, music and poetry, this eight part series – that took over a decade to make – remained a secret seen only at a precious few film festivals thanks to the gargantuan amount of rights needed to be cleared. Histoire(s) du cinema is an epic of free association whose central theme is voyeurism, since Godard believes that cinema consists of a man looking at a woman. Harriet Andersson , topless and alluring on a beach in Ingmar Bergman ’s Monika , is one of many examples.
2004 - Michael Moore’s Fahrenheit 9/11
The most successful documentary at the US box office ever, Fahrenheit 9/11 is a prime example of the essay film’s wild popularisation (it also won the Palme d’Or at Cannes). Michael Moore ’s swipe at the Republican jugular was a classic example of the essay filmmaker’s prominence, outrightly mocking President George W. Bush and questioning the fairness of his election. Disney refused to distribute the film, and the rest is history.
2010 - Errol Morris’ Tabloid
Tabloid is the outrageous story of a former Miss Wyoming, Joyce McKinney, who was alleged to have kidnapped an American mormon missionary living in England, handcuffed him to a bed in a Devonshire cottage and made him a sex slave. The woman claimed she was saving the man from a cult, but then fleed to Canada wearing a red wig, where she posed as part of a mime troupe. As ever, Errol Morris deftly offers alternate explanations, which led to McKinney suing him after the release of the film.
2014 - Hito Steyerl’s How Not To Be Seen: A Fucking Didactic Educationa l
After touring galleries of the world and a recent stint at the ICA, Hito Steyerl ’s How Not To Be Seen made waves as “an art for our times”. It is a disembowelling satire that mocks the idea that it we can become invisible and have genuine privacy, in this digital age. If we want to disappear, it suggests, we should become poor, or hide in plain sight, or get “disappeared” by the authorities.
Chris Marker: A Grin Without a Cat is on until 22 June at Whitechapel Gallery
Download the app 📱
- Build your network and meet other creatives
- Be the first to hear about exclusive Dazed events and offers
- Share your work with our community


Site Content
Essays on the essay film.
Edited by Nora M. Alter and Timothy Corrigan
Columbia University Press

Pub Date: March 2017
ISBN: 9780231172677
Format: Paperback
List Price: $37.00 £30.00
Shipping Options
Purchasing options are not available in this country.
ISBN: 9780231172660
Format: Hardcover
List Price: $120.00 £100.00
ISBN: 9780231543996
Format: E-book
List Price: $36.99 £30.00
- EPUB via the Columbia UP App
- PDF via the Columbia UP App
Creatively and capaciously, this rich volume gets at the essay film not only by including key critics and practitioners of the form but, importantly, by going beyond the genre itself to broader contributions to essay theorization from philosophy and belles lettres. An exciting, inventive volume with great delights at every turn. Dana Polan, New York University
Alter and Corrigan's masterful new volume on the essay film is rigorous, comprehensive, and refreshingly surprising. Their invaluable collection probes theoretical reflections on the essay as a mode of expression and a way of thinking in light of the creative and political investments of filmmakers around the globe; it also chronicles the essay film's changing countenances, from its prehistory and early signs of life to novel permutations in the present. Featuring a very distinguished cast of players, this collection is a production of the highest order. Eric Rentschler, Harvard University
Nora Alter and Tim Corrigan bring their seasoned literary experience to herd but never tame the unruly essay film. Its prestige soaring, this mode is tethered to a long history of experimental writing that will keep it from disappearing into the bog of blogs and YouTube mashups whose best examples it is already inspiring. The proof is in the Table of Contents: a brilliant litany of sensitive, reliable writers, who dare to take on the most daring forms of image-thought the cinema has produced. Dudley Andrew, Yale University
Recent years have witnessed a rapid growth in interest in the history, concept and diverse manifestations of the essay film. In this essential collection, Nora Alter and Timothy Corrigan have brought together a superb selection of foundational texts with a range of key recent writings by leading scholars and essay filmmakers. The result is an enormously rich resource for anyone interested in the past, present, and future of this most vital of audiovisual forms. Michael Witt, University of Roehampton
About the Author
- Film and Media Studies
- Film History, Theory, and Criticism
- Photography
- Film and Culture Series
Search form

You are here
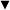
- Archive Blog
Essays on the Essay Film
About the author.

In addition to his long career in film archiving and curating, Jan-Christopher Horak has taught at universities around the world. His recent book, Saul Bass: Anatomy of Film Design (2014) was published by University Press of Kentucky.
"Archival Spaces" Blog - Ithaca College

Sans soleil (1983)
For decades, I’ve been interested in the essay film, ever since I fell in love with Jean-Luc Godard’s work from the 1960s, like Pierrot le fou (1965), Two or Three Things I Know About Her (1967), but especially since the 1990s, when I wrote about Godard’s colleague Chris Marker, whose Sans soleil (1983) is a masterpiece of the genre. Recently, I discussed Saul Bass’ Why Man Creates (1968) as an essay film. But is it a genre? Straddling documentary and fiction, the subjectivity of the author and the objectivity of the filmed image, vacillating between image and sound, visuality and the word, essay films in many ways defy definition. Jean-Pierre Gorin, himself a film essayist, writes in Essays on the Essay Film (ed. Nora M. Alter and Timothy Corrigan, Columbia University Press, 2017): “They come in all sizes, shapes, and hues – and they will continue to do so... How can one even attempt to draw its floor plan, sketch its history and catalog the idiosyncratic products that appear in its inventory?” (p. 270).
Such semantic nebulousness already held true for the literary essay, as this anthology documents. Max Bense notes that essays always imply a level of experimentation, because they are exploring various forms of subjectivity. Similarly, the essays in this volume experiment with possible definitions of film essays. Essays on the Essay Film is accordingly divided into four sections: 1. Theoretical essays on the essay as a literary form by Georg Lukács, Robert Musil, Max Bense, Theodor W. Adorno and Aldous Huxley. 2. Previously published essays on the essay film by Hans Richter, Alexandre Astruc and André Bazin. 3. Analytical essays by Phillip Lopate, Paul Arthur, Michael Renov, Timothy Corrigan and Raymond Bellour. 4. Essays by filmmakers of the form, including Gorin, Hito Steyerl, Ross McElwee, Laura Mulvey and Isaac Julien.

Pierrot le fou (1965)
The editors make a wise decision to include writings on the literary essay, since many of its characteristics can be applied to essay films. Georg Lukács, for example, supposes that the essay is not an act of creating the new, but rather only of reconfiguring previously known information. Max Bense defines essays as a form of experimental writing that eschews absolute statements in the interest of exploring parameters and possibilities. Theodor Adorno takes Bense a step further by connecting the essay to anti-Platonic values, such as the ephemeral, the transitory, and the fragmentary. Given the ambiguity of the image, the push and pull between the filmmaker’s subjectivity and the objectivity of the image, are not such values integral to the cinema experience?
The earliest theoretical statements about the essay film come from experimental filmmaker and artist Hans Richter, who in his 1939 tract, Struggle for the Film: Towards a Socially Responsible Cinema , foresees a new form of documentary that has the ability to visualize thought. Alexander Astruc, an early member of the French New Wave , theorized the future of cinema in neither documentary nor fiction films, but rather in filmmakers who use the camera as a pen— le camera au stylo— for the expression of authorial subjectivity. Phillip Lopate, on the other hand, defines five characteristics for the essay film: 1. It has to communicate through language, whether spoken or written. 2. It must be the work of a single author. 3. It must set itself the task of solving a specific problem or problems. 4. It must be a wholly personal point of view. 5. It must be eloquent and interesting. Like Lopate, the late film critic and essayist Paul Arthur focuses on the film auteur, insisting that the essay film must give evidence a critical, self-reflexive author who is able to communicate through word and image.
Timothy Corrigan contributes a historical analysis of the essay film, from Dziga Vertov to Agnès Varda, agreeing with Lukács’ thesis that the essay film indeed creates no new forms, but remixes and recontextualizes ideas that are already in circulation. The final part of his essay focuses on a close reading of Varda’s The Gleaners and I (2000).
Again and again the authors of the volume emphasize the essay film’s openness of form and always-tentative contours that defy any absolute definitions. Thus, the authors of Essays , as well as the even more subjective contributions of the filmmakers, discuss definitions and characteristics of a genre that isn’t one, unable or unwilling to draw definite conclusions. They are consciously circling around an indefinable object. The pleasure here is not to be found in the end goal, but rather in the intellectual journey. Nevertheless, it would have been nice if there had at least been agreement about when the essay film first appeared in film history, whether with Dziga Vertov’s Man with a Movie Camera (1929), Georges Franju’s Le sang des bêtes (1949) or Chris Marker’s Lettre de Sibérie (1958). A filmography of the essay film would have helped readers visualize the parameters of what films are considered essay films, a common ground for further discussion. Personally, I would have also liked to have read more about the aesthetics of the essay film, its visual and emotional appeal, not just intellectual pull. In retrospect, I remember the tactile sensuality of images in many of the films discussed, scenes that evoke emotion. I also question whether the essay or essay film is mainly a remix, and not in some way an independent creation of aesthetic value. Despite these slight reservations, this volume is eminently readable and a contribution to understanding a form of cinema that continues to morph and grow.
< Back to Archival Spaces blog
To report problems, broken links, or comment on the website, please contact support
Copyright © 2024 UCLA Film & Television Archive. All Rights Reserved

- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Historical Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Browse content in Art
- History of Art
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical Literature
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- History by Period
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Intellectual History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- Political History
- Regional and National History
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Language Teaching and Learning
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Acquisition
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Christianity
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Browse content in Law
- Company and Commercial Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Criminal Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Legal System and Practice
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Browse content in Economics
- Economic History
- Browse content in Education
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Browse content in Politics
- Asian Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- European Union
- Human Rights and Politics
- International Relations
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Theory
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Public Policy
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Sociology of Religion
- Reviews and Awards
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

- < Previous
- Next chapter >
Introduction
- Published: July 2019
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
In this introductory chapter readers are made familiar with the expanding research field of essayistic filmmaking in world cinema-contexts around the globe. Brenda Hollweg and Igor Krstíc argue that the essay film is a privileged political and ethical tool by means of which filmmakers around the world approach historically specific and locally, geographically concrete issues against larger global issues and universal concerns. The chapter also includes a genealogical overview of important moments in the development of essay filmmaking, particularly during the 1920s and 1960s, and provides readers with short abstracts on the individual chapters and their specific transnationally inflected case studies on essay film practitioners from around the world.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
- Google Scholar Indexing
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Text size: A A A
About the BFI
Strategy and policy
Press releases and media enquiries
Jobs and opportunities
Join and support
Become a Member
Become a Patron
Using your BFI Membership
Corporate support
Trusts and foundations
Make a donation
Watch films on BFI Player
BFI Southbank tickets

- Follow @bfi
Watch and discover
In this section
Watch at home on BFI Player
What’s on at BFI Southbank
What’s on at BFI IMAX
BFI National Archive
Explore our festivals
BFI film releases
Read features and reviews
Read film comment from Sight & Sound
I want to…
Watch films online
Browse BFI Southbank seasons
Book a film for my cinema
Find out about international touring programmes
Learning and training
BFI Film Academy: opportunities for young creatives
Get funding to progress my creative career
Find resources and events for teachers
Join events and activities for families
BFI Reuben Library
Search the BFI National Archive collections
Browse our education events
Use film and TV in my classroom
Read research data and market intelligence
Funding and industry
Get funding and support
Search for projects funded by National Lottery
Apply for British certification and tax relief
Industry data and insights
Inclusion in the film industry
Find projects backed by the BFI
Get help as a new filmmaker and find out about NETWORK
Read industry research and statistics
Find out about booking film programmes internationally
You are here

The essay film
In recent years the essay film has attained widespread recognition as a particular category of film practice, with its own history and canonical figures and texts. In tandem with a major season throughout August at London’s BFI Southbank, Sight & Sound explores the characteristics that have come to define this most elastic of forms and looks in detail at a dozen influential milestone essay films.
Andrew Tracy , Katy McGahan , Olaf Möller , Sergio Wolf , Nina Power Updated: 7 May 2019

from our August 2013 issue
Le camera stylo? Dziga Vertov’s Man with a Movie Camera (1929)
I recently had a heated argument with a cinephile filmmaking friend about Chris Marker’s Sans soleil (1983). Having recently completed her first feature, and with such matters on her mind, my friend contended that the film’s power lay in its combinations of image and sound, irrespective of Marker’s inimitable voiceover narration. “Do you think that people who can’t understand English or French will get nothing out of the film?” she said; to which I – hot under the collar – replied that they might very well get something, but that something would not be the complete work.

The Sight & Sound Deep Focus season Thought in Action: The Art of the Essay Film runs at BFI Southbank 1-28 August 2013, with a keynote lecture by Kodwo Eshun on 1 August, a talk by writer and academic Laura Rascaroli on 27 August and a closing panel debate on 28 August.
To take this film-lovers’ tiff to a more elevated plane, what it suggests is that the essentialist conception of cinema is still present in cinephilic and critical culture, as are the difficulties of containing within it works that disrupt its very fabric. Ever since Vachel Lindsay published The Art of the Moving Picture in 1915 the quest to secure the autonomy of film as both medium and art – that ever-elusive ‘pure cinema’ – has been a preoccupation of film scholars, critics, cinephiles and filmmakers alike. My friend’s implicit derogation of the irreducible literary element of Sans soleil and her neo- Godard ian invocation of ‘image and sound’ touch on that strain of this phenomenon which finds, in the technical-functional combination of those two elements, an alchemical, if not transubstantiational, result.
Mechanically created, cinema defies mechanism: it is poetic, transportive and, if not irrational, then a-rational. This mystically-minded view has a long and illustrious tradition in film history, stretching from the sense-deranging surrealists – who famously found accidental poetry in the juxtapositions created by randomly walking into and out of films; to the surrealist-influenced, scientifically trained and ontologically minded André Bazin , whose realist veneration of the long take centred on the very preternaturalness of nature as revealed by the unblinking gaze of the camera; to the trash-bin idolatry of the American underground, weaving new cinematic mythologies from Hollywood detritus; and to auteurism itself, which (in its more simplistic iterations) sees the essence of the filmmaker inscribed even upon the most compromised of works.
It isn’t going too far to claim that this tradition has constituted the foundation of cinephilic culture and helped to shape the cinematic canon itself. If Marker has now been welcomed into that canon and – thanks to the far greater availability of his work – into the mainstream of (primarily DVD-educated) cinephilia, it is rarely acknowledged how much of that work cheerfully undercuts many of the long-held assumptions and pieties upon which it is built.
In his review of Letter from Siberia (1957), Bazin placed Marker at right angles to cinema proper, describing the film’s “primary material” as intelligence – specifically a “verbal intelligence” – rather than image. He dubbed Marker’s method a “horizontal” montage, “as opposed to traditional montage that plays with the sense of duration through the relationship of shot to shot”.
Here, claimed Bazin, “a given image doesn’t refer to the one that preceded it or the one that will follow, but rather it refers laterally, in some way, to what is said.” Thus the very thing which makes Letter “extraordinary”, in Bazin’s estimation, is also what makes it not-cinema. Looking for a term to describe it, Bazin hit upon a prophetic turn of phrase, writing that Marker’s film is, “to borrow Jean Vigo’s formulation of À propos de Nice (‘a documentary point of view’), an essay documented by film. The important word is ‘essay’, understood in the same sense that it has in literature – an essay at once historical and political, written by a poet as well.”
Marker’s canonisation has proceeded apace with that of the form of which he has become the exemplar. Whether used as critical/curatorial shorthand in reviews and programme notes, employed as a model by filmmakers or examined in theoretical depth in major retrospectives (this summer’s BFI Southbank programme, for instance, follows upon Andréa Picard’s two-part series ‘The Way of the Termite’ at TIFF Cinémathèque in 2009-2010, which drew inspiration from Jean-Pierre Gorin ’s groundbreaking programme of the same title at Vienna Filmmuseum in 2007), the ‘essay film’ has attained in recent years widespread recognition as a particular, if perennially porous, mode of film practice. An appealingly simple formulation, the term has proved both taxonomically useful and remarkably elastic, allowing one to define a field of previously unassimilable objects while ranging far and wide throughout film history to claim other previously identified objects for this invented tradition.

Las Hurdes (1933)
It is crucial to note that the ‘essay film’ is not only a post-facto appellation for a kind of film practice that had not bothered to mark itself with a moniker, but also an invention and an intervention. While it has acquired its own set of canonical ‘texts’ that include the collected works of Marker, much of Godard – from the missive (the 52-minute Letter to Jane , 1972) to the massive ( Histoire(s) de cinéma , 1988-98) – Welles’s F for Fake (1973) and Thom Andersen’s Los Angeles Plays Itself (2003), it has also poached on the territory of other, ‘sovereign’ forms, expanding its purview in accordance with the whims of its missionaries.
From documentary especially, Vigo’s aforementioned À propos de Nice, Ivens’s Rain (1929), Buñuel’s sardonic Las Hurdes (1933), Resnais’s Night and Fog (1955), Rouch and Morin’s Chronicle of a Summer (1961); from the avant garde, Akerman’s Je, Tu, Il, Elle (1974), Straub/Huillet’s Trop tôt, trop tard (1982); from agitprop, Getino and Solanas’s The Hour of the Furnaces (1968), Portabella’s Informe general… (1976); and even from ‘pure’ fiction, for example Gorin’s provocative selection of Griffith’s A Corner in Wheat (1909).
Just as within itself the essay film presents, in the words of Gorin, “the meandering of an intelligence that tries to multiply the entries and the exits into the material it has elected (or by which it has been elected),” so, without, its scope expands exponentially through the industrious activity of its adherents, blithely cutting across definitional borders and – as per the Manny Farber ian concept which gave Gorin’s ‘Termite’ series its name – creating meaning precisely by eating away at its own boundaries. In the scope of its application and its association more with an (amorphous) sensibility as opposed to fixed rules, the essay film bears similarities to the most famous of all fabricated genres: film noir, which has been located both in its natural habitat of the crime thriller as well as in such disparate climates as melodramas, westerns and science fiction.
The essay film, however, has proved even more peripatetic: where noir was formulated from the films of a determinate historical period (no matter that the temporal goalposts are continually shifted), the essay film is resolutely unfixed in time; it has its choice of forebears. And while noir, despite its occasional shadings over into semi-documentary during the 1940s, remains bound to fictional narratives, the essay film moves blithely between the realms of fiction and non-fiction, complicating the terms of both.
“Here is a form that seems to accommodate the two sides of that divide at the same time, that can navigate from documentary to fiction and back, creating other polarities in the process between which it can operate,” writes Gorin. When Orson Welles , in the closing moments of his masterful meditation on authenticity and illusion F for Fake, chortles, “I did promise that for one hour, I’d tell you only the truth. For the past 17 minutes, I’ve been lying my head off,” he is expressing both the conjuror’s pleasure in a trick well played and the artist’s delight in a self-defined mode that is cheerfully impure in both form and, perhaps, intention.
Nevertheless, as the essay film merrily traipses through celluloid history it intersects with ‘pure cinema’ at many turns and its form as such owes much to one particularly prominent variety thereof.
The montage tradition
If the mystical strain described above represents the Dionysian side of pure cinema, Soviet montage was its Apollonian opposite: randomness, revelation and sensuous response countered by construction, forceful argumentation and didactic instruction.
No less than the mystics, however, the montagists were after essences. Eisenstein , Dziga Vertov and Pudovkin , along with their transnational associates and acolytes, sought to crystallise abstract concepts in the direct and purposeful juxtaposition of forceful, hard-edged images – the general made powerfully, viscerally immediate in the particular. Here, says Eisenstein, in the umbrella-wielding harpies who set upon the revolutionaries in October (1928), is bourgeois Reaction made manifest; here, in the serried ranks of soldiers proceeding as one down the Odessa Steps in Battleship Potemkin (1925), is Oppression undisguised; here, in the condemned Potemkin sailor who wins over his imminent executioners with a cry of “Brothers!” – a moment powerfully invoked by Marker at the beginning of his magnum opus A Grin Without a Cat (1977) – is Solidarity emergent and, from it, the seeds of Revolution.
The relentlessly unidirectional focus of classical Soviet montage puts it methodologically and temperamentally at odds with the ruminative, digressive and playful qualities we associate with the essay film. So, too, the former’s fierce ideological certainty and cadre spirit contrast with that free play of the mind, the Montaigne -inspired meanderings of individual intelligence, that so characterise our image of the latter.
Beyond Marker’s personal interest in and inheritance from the Soviet masters, classical montage laid the foundations of the essay film most pertinently in its foregrounding of the presence, within the fabric of the film, of a directing intelligence. Conducting their experiments in film not through ‘pure’ abstraction but through narrative, the montagists made manifest at least two operative levels within the film: the narrative itself and the arrangement of that narrative by which the deeper structures that move it are made legible. Against the seamless, immersive illusionism of commercial cinema, montage was a key for decrypting those social forces, both overt and hidden, that govern human society.
And as such it was method rather than material that was the pathway to truth. Fidelity to the authentic – whether the accurate representation of historical events or the documentary flavouring of Eisensteinian typage – was important only insomuch as it provided the filmmaker with another tool to reach a considerably higher plane of reality.

Dziga Vertov’s Enthusiasm (1931)
Midway on their Marxian mission to change the world rather than interpret it, the montagists actively made the world even as they revealed it. In doing so they powerfully expressed the dialectic between control and chaos that would come to be not only one of the chief motors of the essay film but the crux of modernity itself.
Vertov’s Man with a Movie Camera (1929), now claimed as the most venerable and venerated ancestor of the essay film (and this despite its prototypically purist claim to realise a ‘universal’ cinematic language “based on its complete separation from the language of literature and the theatre”) is the archetypal model of this high-modernist agon. While it is the turning of the movie projector itself and the penetrating gaze of Vertov’s kino-eye that sets the whirling dynamo of the city into motion, the recorder creating that which it records, that motion is also outside its control.
At the dawn of the cinematic century, the American writer Henry Adams saw in the dynamo both the expression of human mastery over nature and a conduit to mysterious, elemental powers beyond our comprehension. So, too, the modernist ambition expressed in literature, painting, architecture and cinema to capture a subject from all angles – to exhaust its wealth of surfaces, meanings, implications, resonances – collides with awe (or fear) before a plenitude that can never be encompassed.
Remove the high-modernist sense of mission and we can see this same dynamic as animating the essay film – recall that last, parenthetical term in Gorin’s formulation of the essay film, “multiply[ing] the entries and the exits into the material it has elected (or by which it has been elected)”. The nimble movements and multi-angled perspectives of the essay film are founded on this negotiation between active choice and passive possession; on the recognition that even the keenest insight pales in the face of an ultimate unknowability.
The other key inheritance the essay film received from the classical montage tradition, perhaps inevitably, was a progressive spirit, however variously defined. While Leni Riefenstahl’s Triumph of the Will (1935) and Olympia (1938) amply and chillingly demonstrated that montage, like any instrumental apparatus, has no inherent ideological nature, hers were more the exceptions that proved the rule. (Though why, apart from ideological repulsiveness, should Riefenstahl’s plentifully fabricated ‘documentaries’ not be considered as essay films in their own right?)
The overwhelming fact remains that the great majority of those who drew upon the Soviet montagists for explicitly ideological ends (as opposed to Hollywood’s opportunistic swipings) resided on the left of the spectrum – and, in the montagists’ most notable successor in the period immediately following, retained their alignment with and inextricability from the state.
Progressive vs radical
The Grierson ian documentary movement in Britain neutered the political and aesthetic radicalism of its more dynamic model in favour of paternalistic progressivism founded on conformity, class complacency and snobbery towards its own medium. But if it offered a far paler antecedent to the essay film than the Soviet montage tradition, it nevertheless represents an important stage in the evolution of the essay-film form, for reasons not unrelated to some of those rather staid qualities.
The Soviet montagists had created a vision of modernity racing into the future at pace with the social and spiritual liberation of its proletarian pilot-passenger, an aggressively public ideology of group solidarity. The Grierson school, by contrast, offered a domesticated image of an efficient, rational and productive modern industrial society based on interconnected but separate public and private spheres, as per the ideological values of middle-class liberal individualism.
The Soviet montagists had looked to forge a universal, ‘pure’ cinematic language, at least before the oppressive dictates of Stalinist socialist realism shackled them. The Grierson school, evincing a middle-class disdain for the popular and ‘low’ arts, sought instead to purify the sullied medium of cinema by importing extra-cinematic prestige: most notably Night Mail (1936), with its Auden -penned, Britten -scored ode to the magic of the mail, or Humphrey Jennings’s salute to wartime solidarity A Diary for Timothy (1945), with its mildly sententious E.M. Forster narration.

Night Mail (1936)
What this domesticated dynamism and retrograde pursuit of high-cultural bona fides achieved, however, was to mingle a newfound cinematic language (montage) with a traditionally literary one (narration); and, despite the salutes to state-oriented communality, to re-introduce the individual, idiosyncratic voice as the vehicle of meaning – as the mediating intelligence that connects the viewer to the images viewed.
In Night Mail especially there is, in the whimsy of the Auden text and the film’s synchronisation of private time and public history, an intimation of the essay film’s musing, reflective voice as the chugging rhythm of the narration timed to the speeding wheels of the train gives way to a nocturnal vision of solitary dreamers bedevilled by spectral monsters, awakening in expectation of the postman’s knock with a “quickening of the heart/for who can bear to be forgot?”
It’s a curiously disquieting conclusion: this unsettling, anxious vision of disappearance that takes on an even darker shade with the looming spectre of war – one that rhymes, five decades on, with the wistful search of Marker’s narrator in Sans soleil, seeking those fleeting images which “quicken the heart” in a world where wars both past and present have been forgotten, subsumed in a modern society built upon the systematic banishment of memory.
It is, of course, with the seminal post-war collaborations between Marker and Alain Resnais that the essay film proper emerges. In contrast to the striving culture-snobbery of the Griersonian documentary, the Resnais-Marker collaborations (and the Resnais solo documentary shorts that preceded them) inaugurate a blithe, seemingly effortless dialogue between cinema and the other arts in both their subjects (painting, sculpture) and their assorted creative personnel (writers Paul Éluard , Jean Cayrol , Raymond Queneau , composers Darius Milhaud and Hanns Eisler ). This also marks the point where the revolutionary line of the Soviets and the soft, statist liberalism of the British documentarians give way to a more free-floating but staunchly oppositional leftism, one derived as much from a spirit of humanistic inquiry as from ideological affiliation.
Related to this was the form’s problems with official patronage. Originally conceived as commissions by various French government or government-affiliated bodies, the Resnais-Marker films famously ran into trouble from French censors: Les statues meurent aussi (1953) for its condemnation of French colonialism, Night and Fog for its shots of Vichy policemen guarding deportation camps; the former film would have its second half lopped off before being cleared for screening, the latter its offending shots removed.
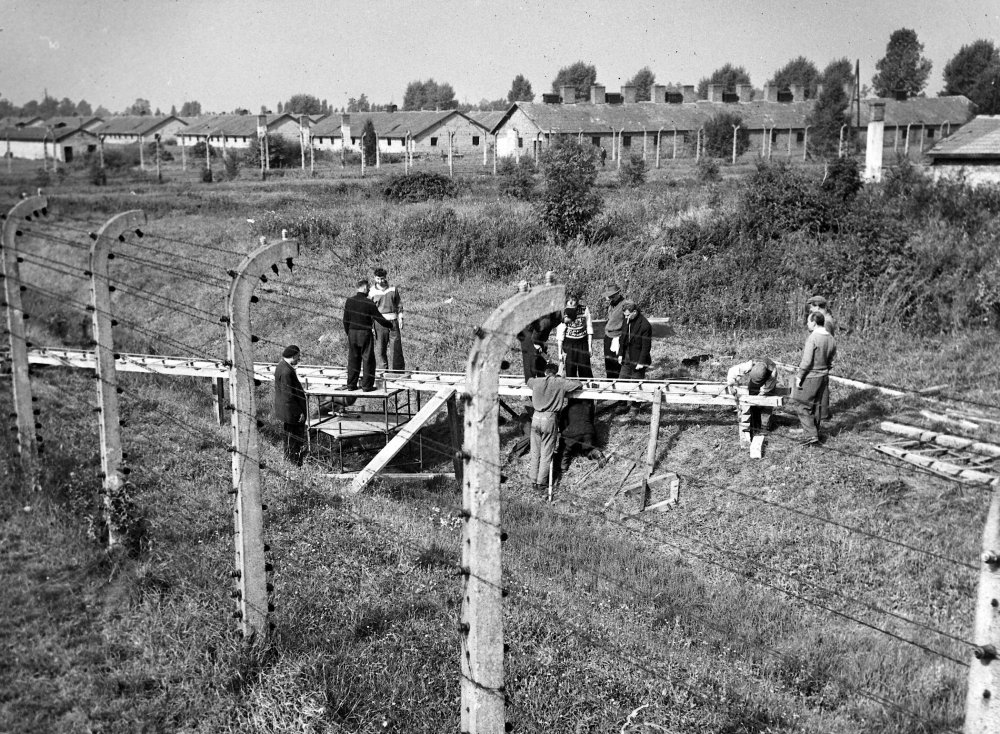

Night and Fog (1955)
Appropriately, it is at this moment that the emphasis of the essay film begins to shift away from tactile presence – the whirl of the city, the rhythm of the rain, the workings of industry – to felt absence. The montagists had marvelled at the workings of human creations which raced ahead irrespective of human efforts; here, the systems created by humanity to master the world write, in their very functioning, an epitaph for those things extinguished in the act of mastering them. The African masks preserved in the Musée de l’Homme in Les statues meurent aussi speak of a bloody legacy of vanquished and conquered civilisations; the labyrinthine archival complex of the Bibliothèque Nationale in the sardonically titled Toute la mémoire du monde (1956) sparks a disquisition on all that is forgotten in the act of cataloguing knowledge; the miracle of modern plastics saluted in the witty, industrially commissioned Le Chant du styrène (1958) regresses backwards to its homely beginnings; in Night and Fog an unprecedentedly enormous effort of human organisation marshals itself to actively produce a dreadful, previously unimaginable nullity.
To overstate the case, loss is the primary motor of the modern essay film: loss of belief in the image’s ability to faithfully reflect reality; loss of faith in the cinema’s ability to capture life as it is lived; loss of illusions about cinema’s ‘purity’, its autonomy from the other arts or, for that matter, the world.
“You never know what you may be filming,” notes one of Marker’s narrating surrogates in A Grin Without a Cat, as footage of the Chilean equestrian team at the 1952 Helsinki Olympics offers a glimpse of a future member of the Pinochet junta. The image and sound captured at the time of filming offer one facet of reality; it is only with this lateral move outside that reality that the future reality it conceals can speak.
What will distinguish the essay film, as Bazin noted, is not only its ability to make the image but also its ability to interrogate it, to dispel the illusion of its sovereignty and see it as part of a matrix of meaning that extends beyond the screen. No less than were the montagists, the film-essayists seek the motive forces of modern society not by crystallising eternal verities in powerful images but by investigating that ever-shifting, kaleidoscopic relationship between our regime of images and the realities it both reveals and occludes.
— Andrew Tracy
1. À propos de Nice
Jean Vigo, 1930
Few documentaries have achieved the cult status of the 22-minute A propos de Nice, co-directed by Jean Vigo and cameraman Boris Kaufman at the beginning of their careers. The film retains a spontaneous, apparently haphazard, quality yet its careful montage combines a strong realist drive, lyrical dashes – helped by Marc Perrone’s accordion music – and a clear political agenda.
In today’s era, in which the Côte d’Azur has become a byword for hedonistic consumption, it’s refreshing to see a film that systematically undermines its glossy surface. Using images sometimes ‘stolen’ with hidden cameras, A propos de Nice moves between the city’s main sites of pleasure: the Casino, the Promenade des Anglais, the Hotel Negresco and the carnival. Occasionally the filmmakers remind us of the sea, the birds, the wind in the trees but mostly they contrast people: the rich play tennis, the poor boules; the rich have tea, the poor gamble in the (then) squalid streets of the Old Town.
As often, women bear the brunt of any critique of bourgeois consumption: a rich old woman’s head is compared to an ostrich, others grin as they gaze up at phallic factory chimneys; young women dance frenetically, their crotch to the camera. In the film’s most famous image, an elegant woman is ‘stripped’ by the camera to reveal her naked body – not quite matched by a man’s shoes vanishing to display his naked feet to the shoe-shine.
An essay film avant la lettre , A propos de Nice ends on Soviet-style workers’ faces and burning furnaces. The message is clear, even if it has not been heeded by history.
— Ginette Vincendeau
2. A Diary for Timothy
Humphrey Jennings, 1945
A Diary for Timothy takes the form of a journal addressed to the eponymous Timothy James Jenkins, born on 3 September 1944, exactly five years after Britain’s entry into World War II. The narrator, Michael Redgrave , a benevolent offscreen presence, informs young Timothy about the momentous events since his birth and later advises that, even when the war is over, there will be “everyday danger”.
The subjectivity and speculative approach maintained throughout are more akin to the essay tradition than traditional propaganda in their rejection of mere glib conveyance of information or thunderous hectoring. Instead Jennings invites us quietly to observe the nuances of everyday life as Britain enters the final chapter of the war. Against the momentous political backdrop, otherwise routine, everyday activities are ascribed new profundity as the Welsh miner Geronwy, Alan the farmer, Bill the railway engineer and Peter the convalescent fighter pilot go about their daily business.
Within the confines of the Ministry of Information’s remit – to lift the spirits of a battle-weary nation – and the loose narrative framework of Timothy’s first six months, Jennings finds ample expression for the kind of formal experiment that sets his work apart from that of other contemporary documentarians. He worked across film, painting, photography, theatrical design, journalism and poetry; in Diary his protean spirit finds expression in a manner that transgresses the conventional parameters of wartime propaganda, stretching into film poem, philosophical reflection, social document, surrealistic ethnographic observation and impressionistic symphony. Managing to keep to the right side of sentimentality, it still makes for potent viewing.
— Catherine McGahan
3. Toute la mémoire du monde
Alain Resnais, 1956
In the opening credits of Toute la mémoire du monde, alongside the director’s name and that of producer Pierre Braunberger , one reads the mysterious designation “Groupe des XXX”. This Group of Thirty was an assembly of filmmakers who mobilised in the early 1950s to defend the “style, quality and ambitious subject matter” of short films in post-war France; the signatories of its 1953 ‘Declaration’ included Resnais , Chris Marker and Agnès Varda. The success of the campaign contributed to a golden age of short filmmaking that would last a decade and form the crucible of the French essay film.
A 22-minute poetic documentary about the old French Bibliothèque Nationale, Toute la mémoire du monde is a key work in this strand of filmmaking and one which can also be seen as part of a loose ‘trilogy of memory’ in Resnais’s early documentaries. Les statues meurent aussi (co-directed with Chris Marker) explored cultural memory as embodied in African art and the depredations of colonialism; Night and Fog was a seminal reckoning with the historical memory of the Nazi death camps. While less politically controversial than these earlier works, Toute la mémoire du monde’s depiction of the Bibliothèque Nationale is still oddly suggestive of a prison, with its uniformed guards and endless corridors. In W.G. Sebald ’s 2001 novel Austerlitz, directly after a passage dedicated to Resnais’s film, the protagonist describes his uncertainty over whether, when using the library, he “was on the Islands of the Blest, or, on the contrary, in a penal colony”.
Resnais explores the workings of the library through the effective device of following a book from arrival and cataloguing to its delivery to a reader (the book itself being something of an in-joke: a mocked-up travel guide to Mars in the Petite Planète series Marker was then editing for Editions du Seuil). With Resnais’s probing, mobile camerawork and a commentary by French writer Remo Forlani, Toute la mémoire du monde transforms the library into a mysterious labyrinth, something between an edifice and an organism: part brain and part tomb.
— Chris Darke
4. The House is Black
(Khaneh siah ast) Forough Farrokhzad, 1963
Before the House of Makhmalbaf there was The House is Black. Called “the greatest of all Iranian films” by critic Jonathan Rosenbaum, who helped translate the subtitles from Farsi into English, this 20-minute black-and-white essay film by feminist poet Farrokhzad was shot in a leper colony near Tabriz in northern Iran and has been heralded as the touchstone of the Iranian New Wave.
The buildings of the Baba Baghi colony are brick and peeling whitewash but a student asked to write a sentence using the word ‘house’ offers Khaneh siah ast : the house is black. His hand, seen in close-up, is one of many in the film; rather than objects of medical curiosity, these hands – some fingerless, many distorted by the disease – are agents, always in movement, doing, making, exercising, praying. In putting white words on the blackboard, the student makes part of the film; in the next shots, the film’s credits appear, similarly handwritten on the same blackboard.
As they negotiate the camera’s gaze and provide the soundtrack by singing, stamping and wheeling a barrow, the lepers are co-authors of the film. Farrokhzad echoes their prayers, heard and seen on screen, with her voiceover, which collages religious texts, beginning with the passage from Psalm 55 famously set to music by Mendelssohn (“O for the wings of a dove”).
In the conjunctions between Farrokhzad’s poetic narration and diegetic sound, including tanbur-playing, an intense assonance arises. Its beat is provided by uniquely lyrical associative editing that would influence Abbas Kiarostami , who quotes Farrokhzad’s poem ‘The Wind Will Carry Us’ in his eponymous film . Repeated shots of familiar bodily movement, made musical, move the film insistently into the viewer’s body: it is infectious. Posing a question of aesthetics, The House Is Black uses the contagious gaze of cinema to dissolve the screen between Us and Them.
— Sophie Mayer
5. Letter to Jane: An Investigation About a Still
Jean-Luc Godard & Jean-Pierre Gorin, 1972
With its invocation of Brecht (“Uncle Bertolt”), rejection of visual pleasure (for 52 minutes we’re mostly looking at a single black-and-white still) and discussion of the role of intellectuals in “the revolution”, Letter to Jane is so much of its time as to appear untranslatable to the present except as a curio from a distant era of radical cinema. Between 1969 and 1971, Godard and Gorin made films collectively as part of the Dziga Vertov Group before they returned, in 1972, to the mainstream with Tout va bien , a big-budget film about the aftermath of May 1968 featuring leftist stars Yves Montand and Jane Fonda . It was to the latter that Godard and Gorin directed their Letter after seeing a news photograph of her on a solidarity visit to North Vietnam in August 1972.
Intended to accompany the US release of Tout va bien, Letter to Jane is ‘a letter’ only in as much as it is fairly conversational in tone, with Godard and Gorin delivering their voiceovers in English. It’s stylistically more akin to the ‘blackboard films’ of the time, with their combination of pedagogical instruction and stern auto-critique.
It’s also an inspired semiological reading of a media image and a reckoning with the contradictions of celebrity activism. Godard and Gorin examine the image’s framing and camera angle and ask why Fonda is the ‘star’ of the photograph while the Vietnamese themselves remain faceless or out of focus? And what of her expression of compassionate concern? This “expression of an expression” they trace back, via an elaboration of the Kuleshov effect , through other famous faces – Henry Fonda , John Wayne , Lillian Gish and Falconetti – concluding that it allows for “no reverse shot” and serves only to bolster Western “good conscience”.
Letter to Jane is ultimately concerned with the same question that troubled philosophers such as Levinas and Derrida : what’s at stake ethically when one claims to speak “in place of the other”? Any contemporary critique of celebrity activism – from Bono and Geldof to Angelina Jolie – should start here, with a pair of gauchiste trolls muttering darkly beneath a press shot of ‘Hanoi Jane’.
6. F for Fake
Orson Welles, 1973
Those who insist it was all downhill for Orson Welles after Citizen Kane would do well to take a close look at this film made more than three decades later, in its own idiosyncratic way a masterpiece just as innovative as his better-known feature debut.
Perhaps the film’s comparative and undeserved critical neglect is due to its predominantly playful tone, or perhaps it’s because it is a low-budget, hard-to-categorise, deeply personal work that mixes original material with plenty of footage filmed by others – most extensively taken from a documentary by François Reichenbach about Clifford Irving and his bogus biography of his friend Elmyr de Hory , an art forger who claimed to have painted pictures attributed to famous names and hung in the world’s most prestigious galleries.
If the film had simply offered an account of the hoaxes perpetrated by that disreputable duo, it would have been entertaining enough but, by means of some extremely inventive, innovative and inspired editing, Welles broadens his study of fakery to take in his own history as a ‘charlatan’ – not merely his lifelong penchant for magician’s tricks but also the 1938 radio broadcast of his news-report adaptation of H.G. Wells’ The War of the Worlds – as well as observations on Howard Hughes , Pablo Picasso and the anonymous builders of Chartres cathedral. So it is that Welles contrives to conjure up, behind a colourful cloak of consistently entertaining mischief, a rueful meditation on truth and falsehood, art and authorship – a subject presumably dear to his heart following Pauline Kael ’s then recent attempts to persuade the world that Herman J. Mankiewicz had been the real creative force behind Kane.
As a riposte to that thesis (albeit never framed as such), F for Fake is subtle, robust, supremely erudite and never once bitter; the darkest moment – as Welles contemplates the serene magnificence of Chartres – is at once an uncharacteristic but touchingly heartfelt display of humility and a poignant memento mori. And it is in this delicate balancing of the autobiographical with the universal, as well as in the dazzling deployment of cinematic form to illustrate and mirror content, that the film works its once unique, now highly influential magic.
— Geoff Andrew
7. How to Live in the German Federal Republic
(Leben – BRD) Harun Farocki, 1990
Harun Farocki ’s portrait of West Germany in 32 simulations from training sessions has no commentary, just the actions themselves in all their surreal beauty, one after the other. The Bundesrepublik Deutschland is shown as a nation of people who can deal with everything because they have been prepared – taught how to react properly in every possible situation.
We know how birth works; how to behave in kindergarten; how to chat up girls, boys or whatever we fancy (for we’re liberal-minded, if only in principle); how to look for a job and maybe live without finding one; how to wiggle our arses in the hottest way possible when we pole-dance, or manage a hostage crisis without things getting (too) bloody. Whatever job we do, we know it by heart; we also know how to manage whatever kind of psychological breakdown we experience; and we are also prepared for the end, and even have an idea about how our burial will go. This is the nation: one of fearful people in dire need of control over their one chance of getting it right.
Viewed from the present, How to Live in the German Federal Republic is revealed as the archetype of many a Farocki film in the decades to follow, for example Die Umschulung (1994), Der Auftritt (1996) or Nicht ohne Risiko (2004), all of which document as dispassionately as possible different – not necessarily simulated – scenarios of social interactions related to labour and capital. For all their enlightening beauty, none of these ever came close to How to Live in the German Federal Republic which, depending on one’s mood, can play like an absurd comedy or the most gut-wrenching drama. Yet one disquieting thing is certain: How to Live in the German Federal Republic didn’t age – our lives still look the same.
— Olaf Möller
8. One Man’s War
(La Guerre d’un seul homme) Edgardo Cozarinsky , 1982

One Man’s War proves that an auteur film can be made without writing a line, recording a sound or shooting a single frame. It’s easy to point to the ‘extraordinary’ character of the film, given its combination of materials that were not made to cohabit; there couldn’t be a less plausible dialogue than the one Cozarinsky establishes between the newsreels shot during the Nazi occupation of Paris and the Parisian diaries of novelist and Nazi officer Ernst Jünger . There’s some truth to Pascal Bonitzer’s assertion in Cahiers du cinéma in 1982 that the principle of the documentary was inverted here, since it is the images that provide a commentary for the voice.
But that observation still doesn’t pin down the uniqueness of a work that forces history through a series of registers, styles and dimensions, wiping out the distance between reality and subjectivity, propaganda and literature, cinema and journalism, daily life and dream, and establishing the idea not so much of communicating vessels as of contaminating vessels.
To enquire about the essayistic dimension of One Man’s War is to submit it to a test of purity against which the film itself is rebelling. This is no ars combinatoria but systems of collision and harmony; organic in their temporal development and experimental in their procedural eagerness. It’s like a machine created to die instantly; neither Cozarinsky nor anyone else could repeat the trick, as is the case with all great avant-garde works.
By blurring the genre of his literary essays, his fictional films, his archival documentaries, his literary fictions, Cozarinsky showed he knew how to reinvent the erasure of borders. One Man’s War is not a film about the Occupation but a meditation on the different forms in which that Occupation can be represented.
—Sergio Wolf. Translated by Mar Diestro-Dópido
9. Sans soleil
Chris Marker, 1982
There are many moments to quicken the heart in Sans soleil but one in particular demonstrates the method at work in Marker’s peerless film. An unseen female narrator reads from letters sent to her by a globetrotting cameraman named Sandor Krasna (Marker’s nom de voyage), one of which muses on the 11th-century Japanese writer Sei Shōnagon .
As we hear of Shōnagon’s “list of elegant things, distressing things, even of things not worth doing”, we watch images of a missile being launched and a hovering bomber. What’s the connection? There is none. Nothing here fixes word and image in illustrative lockstep; it’s in the space between them that Sans soleil makes room for the spectator to drift, dream and think – to inimitable effect.
Sans soleil was Marker’s return to a personal mode of filmmaking after more than a decade in militant cinema. His reprise of the epistolary form looks back to earlier films such as Letter from Siberia (1958) but the ‘voice’ here is both intimate and removed. The narrator’s reading of Krasna’s letters flips the first person to the third, using ‘he’ instead of ‘I’. Distance and proximity in the words mirror, multiply and magnify both the distances travelled and the time spanned in the images, especially those of the 1960s and its lost dreams of revolutionary social change.
While it’s handy to define Sans soleil as an ‘essay film’, there’s something about the dry term that doesn’t do justice to the experience of watching it. After Marker’s death last year, when writing programme notes on the film, I came up with a line that captures something of what it’s like to watch Sans soleil: “a mesmerising, lucid and lovely river of film, which, like the river of the ancients, is never the same when one steps into it a second time”.
10. Handsworth Songs
Black Audio Film Collective, 1986
Made at the time of civil unrest in Birmingham, this key example of the essay film at its most complex remains relevant both formally and thematically. Handsworth Songs is no straightforward attempt to provide answers as to why the riots happened; instead, using archive film spliced with made and found footage of the events and the media and popular reaction to them, it creates a poetic sense of context.
The film is an example of counter-media in that it slows down the demand for either immediate explanation or blanket condemnation. Its stillness allows the history of immigration and the subsequent hostility of the media and the police to the black and Asian population to be told in careful detail.
One repeated scene shows a young black man running through a group of white policemen who surround him on all sides. He manages to break free several times before being wrestled to the ground; if only for one brief, utopian moment, an entirely different history of race in the UK is opened up.
The waves of post-war immigration are charted in the stories told both by a dominant (and frequently repressive) televisual narrative and, importantly, by migrants themselves. Interviews mingle with voiceover, music accompanies the machines that the Windrush generation work at. But there are no definitive answers here, only, as the Black Audio Film Collective memorably suggests, “the ghosts of songs”.
— Nina Power
11. Los Angeles Plays Itself
Thom Andersen, 2003
One of the attractions that drew early film pioneers out west, besides the sunlight and the industrial freedom, was the versatility of the southern Californian landscape: with sea, snowy mountains, desert, fruit groves, Spanish missions, an urban downtown and suburban boulevards all within a 100-mile radius, the Los Angeles basin quickly and famously became a kind of giant open-air film studio, available and pliant.
Of course, some people actually live there too. “Sometimes I think that gives me the right to criticise,” growls native Angeleno Andersen in his forensic three-hour prosecution of moving images of the movie city, whose mounting litany of complaints – couched in Encke King’s gravelly, near-parodically irritated voiceover, and sometimes organised, as Stuart Klawans wrote in The Nation, “in the manner of a saloon orator” – belies a sly humour leavening a radically serious intent.
Inspired in part by Mark Rappaport’s factual essay appropriations of screen fictions (Rock Hudson’s Home Movies, 1993; From the Journals of Jean Seberg , 1995), as well as Godard’s Histoire(s) de cinéma, this “city symphony in reverse” asserts public rights to our screen discourse through its magpie method as well as its argument. (Today you could rebrand it ‘Occupy Hollywood’.) Tinseltown malfeasance is evidenced across some 200 different film clips, from offences against geography and slurs against architecture to the overt historical mythologies of Chinatown (1974), Who Framed Roger Rabbit (1988) and L.A. Confidential (1997), in which the city’s class and cultural fault-lines are repainted “in crocodile tears” as doleful tragedies of conspiracy, promoting hopelessness in the face of injustice.
Andersen’s film by contrast spurs us to independent activism, starting with the reclamation of our gaze: “What if we watch with our voluntary attention, instead of letting the movies direct us?” he asks, peering beyond the foregrounding of character and story. And what if more movies were better and more useful, helping us see our world for what it is? Los Angeles Plays Itself grows most moving – and useful – extolling the Los Angeles neorealism Andersen has in mind: stories of “so many men unneeded, unwanted”, as he says over a scene from Billy Woodberry’s Bless Their Little Hearts (1983), “in a world in which there is so much to be done”.
— Nick Bradshaw
12. La Morte Rouge
Víctor Erice, 2006
The famously unprolific Spanish director Víctor Erice may remain best known for his full-length fiction feature The Spirit of the Beehive (1973), but his other films are no less rewarding. Having made a brilliant foray into the fertile territory located somewhere between ‘documentary’ and ‘fiction’ with The Quince Tree Sun (1992), in this half-hour film made for the ‘Correspondences’ exhibition exploring resemblances in the oeuvres of Erice and Kiarostami , the relationship between reality and artifice becomes his very subject.
A ‘small’ work, it comprises stills, archive footage, clips from an old Sherlock Holmes movie, a few brief new scenes – mostly without actors – and music by Mompou and (for once, superbly used) Arvo Pärt . If its tone – it’s introduced as a “soliloquy” – and scale are modest, its thematic range and philosophical sophistication are considerable.
The title is the name of the Québécois village that is the setting for The Scarlet Claw (1944), a wartime Holmes mystery starring Basil Rathbone and Nigel Bruce which was the first movie Erice ever saw, taken by his sister to the Kursaal cinema in San Sebastian.
For the five-year-old, the experience was a revelation: unable to distinguish the ‘reality’ of the newsreel from that of the nightmare world of Roy William Neill’s film, he not only learned that death and murder existed but noted that the adults in the audience, presumably privy to some secret knowledge denied him, were unaffected by the corpses on screen. Had this something to do with war? Why was La Morte Rouge not on any map? And what did it signify that postman Potts was not, in fact, Potts but the killer – and an actor (whatever that was) to boot?
From such personal reminiscences – evoked with wondrous intimacy in the immaculate Castillian of the writer-director’s own wry narration – Erice fashions a lyrical meditation on themes that have underpinned his work from Beehive to Broken Windows (2012): time and change, memory and identity, innocence and experience, war and death. And because he understands, intellectually and emotionally, that the time-based medium he himself works in can reveal unforgettably vivid realities that belong wholly to the realm of the imaginary, La Morte Rouge is a great film not only about the power of cinema but about life itself.
Sight & Sound: the August 2013 issue

In this issue: Frances Ha’s Greta Gerwig – the most exciting actress in America? Plus Ryan Gosling in Only God Forgives, Wadjda, The Wall,...
More from this issue
DVDs and Blu Ray

Buy The Complete Humphrey Jennings Collection Volume Three: A Diary for Timothy on DVD and Blu Ray
Humphrey Jennings’s transition from wartime to peacetime filmmaking.

Buy Chronicle of a Summer on DVD and Blu Ray
Jean Rouch’s hugely influential and ground-breaking documentary.
Further reading

Video essay: The essay film – some thoughts of discontent
Kevin B. Lee

The land still lies: Handsworth Songs and the English riots

The world at sea: The Forgotten Space

What I owe to Chris Marker
Patricio Guzmán

His and her ghosts: reworking La Jetée
Melissa Bradshaw

At home (and away) with Agnès Varda
Daniel Trilling

Pere Portabella looks back

John Akomfrah’s Hauntologies
Laura Allsop

The roots of neorealism
Back to the top
Commercial and licensing
BFI distribution
Archive content sales and licensing
BFI book releases and trade sales
Selling to the BFI
Terms of use
BFI Southbank purchases
Online community guidelines
Cookies and privacy
©2024 British Film Institute. All rights reserved. Registered charity 287780.

See something different
Subscribe now for exclusive offers and the best of cinema. Hand-picked.
- Festival Reports
- Book Reviews
- Great Directors
- Great Actors
- Special Dossiers
- Past Issues
- Support us on Patreon
Subscribe to Senses of Cinema to receive news of our latest cinema journal. Enter your email address below:

- Thank you to our Patrons
- Style Guide
- Advertisers
- Call for Contributions

Defining the Cinematic Essay: The Essay Film by Elizabeth A. Papazian & Caroline Eades, and Essays on the Essay Film by Nora M. Alter & Timothy Corrigan

When it came time for the students to create their own documentaries, one of my policies was for them to “throw objectivity out the window”. To quote John Grierson, documentaries are the “creative treatment of actuality.” Capturing the truth, whatever it may be, is quite nearly impossible if not utterly futile. Often, filmmakers deliberately manipulate their footage in order to achieve educational, informative and persuasive objectives. To illustrate, I screened Robert Flaherty’s 1922 film Nanook of the North and always marveled at the students’ reactions when, after the screening, I informed them that the film’s depiction of traditional Inuit life was entirely a reenactment. While many students were shocked and disappointed when they learned this, others accepted Flaherty’s defence of the film as true to the spirit, if not the letter, of the Inuit’s vanishing way of life. Another example that I screened was a clip from controversial filmmaker Michael Moore’s Bowling for Columbine (2002) which demonstrated how Moore shrewdly used editing to villainise then-NRA president Charlton Heston. Though a majority of the class agreed with Moore’s anti-gun violence agenda, many were infuriated about being “lied to” and “misled” by the editing tactics. Naturally these examples also raise questions about the role of ethics in documentary filmmaking, but even films that are not deliberately manipulative are still “the product of individuals, [and] will always display bias and be in some manner didactic.” (Alter/Corrigan, p. 193.)
To further my point on the elusive nature of objectivity, I screened Alain Resnais’s Nuit et brouillard ( Night and Fog , 1956), Chris Marker’s Sans Soleil (1983) and Ari Folman’s Waltz with Bashir (2008.) Yet at this point I began to wonder if I was still teaching documentary or if I had ventured into some other territory. I was aware that Koyaanisqatsi had also been classified as an experimental film by notable scholars such as David Bordwell. On the other hand, Nuit et brouillard is labeled a documentary film but poses more questions than answers, since it is “unable to adequately document the reality it seeks.” (Alter/Corrigan p. 210.) Resnais’s short film interweaves black and white archival footage with colour film of Auschwitz and other camps. The colour sequences were shot in 1955, when the camps had already been deserted for ten years. Nuit et brouillard scrutinises the brutality of the Holocaust while contemplating the social, political and ethical responsibilities of the Nazis. Yet it also questions the more abstract role of knowledge and memory, both individual and communal, within the context of such horrific circumstances. The students did not challenge Night and Fog’s classification as a documentary, but they wondered if Waltz with Bashir and especially Sans Soleil had entirely different objectives since they seemed to do more than present factual information. The students also noted that these films seemed to merge with other genres, and wondered if there was a different classification for them aside from poetic, observational, participatory, et al. Although it is animated, Waltz with Bashir is classified as a documentary since it is based on Folman’s own experiences during the 1982 Lebanon War. Also, as Roger Ebert notes, animation is “the best way to reconstruct memories, fantasies, hallucinations, possibilities, past and present.” 2 However, it is not solely a document of Folman’s experiences or of the war itself. It is also a subjective meditation on the nature of human perception. As Folman attempts to reconstruct past events through the memories of his fellow soldiers, Waltz with Bashir investigates the very nature of truth itself. These films definitely challenged the idea of documentary as a strict genre, but the students noticed that they each had interesting similarities. Aside from educating, informing and persuading, they also used non-fiction sounds and images to visualise abstract concepts and ideas.
Sans Soleil (Marker, 1983)
Sans Soleil has been described as “a meditation on place […] where spatial availability confuses the sense of time and memory.” (Alter/Corrigan, p. 117.) Some of my students felt that Marker’s film, which is composed of images from Japan and elsewhere, was more like a “filmed travelogue”. Others described it as a “film journal” since Marker used images and narration to describe certain experiences, thoughts and memories. Yet my students’ understanding of Sans Soleil was problematised when they discovered that the narration was delivered by “a fictional, nameless woman […] reading aloud from, or else paraphrasing, letters sent to her by a fictional, globe-trotting cameraman.” 3 Upon learning this, several students wondered if Sans Soleil was actually a narrative and not a documentary at all. I briefly explained that, since it was also an attempt to visualise abstract concepts, Sans Soleil was known as an essay film. Yet this only complicated things further! The students wondered if other films we saw in the class were essayistic as well. Was Koyaanisqatsi an essay on humanity’s impact on the world? Was Jesus Camp (Heidi Ewing and Rachel Grady, 2006) an essay on the place of religion in society and politics? Where was the line between documentary and the essay film? Between essay and narrative? Or was the essay just another type of documentary? Rather than immerse myself in the difficulties of describing the essay film, I quickly changed the topic to the students’ own projects, and encouraged them to shape their documentaries through related processes of investigation and exploration.
If I had been able to read “Essays on the Essay Film” by Nora M. Alter & Timothy Corrigan and “The Essay Film: Dialogue, Politics, Utopia” by Elizabeth A. Papazian & Caroline Eades before teaching this class, I still may not have been able to provide definitive answers to my students’ questions. But this is not to say that either of these books are vague and inconclusive! Each one is an insightful collection of articles that explores the complexities of the essay film. In her essay “The Essay Film: Problems, Definitions, Textual Commitments” featured in Alter and Corrigan’s “Essays on the Essay Film” Laura Rascaroli wisely notes that “we must resist the temptation to overtheorise the form or, even worse, to crystallise it into a genre…” since the essay film is a “matrix of all generic possibilities.” (Alter/Corrigan, p. 190) Fabienne Costa goes so far as saying that “The ‘cinematographic essay’ is neither a category of films nor a genre. It is more a type of image, which achieves essay quality.” (Alter/Corrigan, p. 190) It is true that filmmakers, critics, and scholars (myself included) have attempted to understand the essay film better by grouping it with genres that bear many similarities, such as documentary and experimental cinema. Yet despite these similarities, the authors suggest that the essay film needs to be differentiated from both documentary and avant-garde practices of filmmaking. Both “Essays on the Essay Film” and “The Essay Film: Dialogue, Politics, Utopia” illustrate that this mutable form should not be understood as a specific genre, but rather recognised for its profoundly reflective and reflexive capabilities. The essay film can even defy established formulas. As stated by filmmaker Jean-Pierre Gorin in his essay “Proposal for a Tussle” the essay film “can navigate from documentary to fiction and back, creating other polarities in the process between which it can operate.” (Alter/Corrigan, p. 270.)
Nora M. Alter and Timothy Corrigan’s “Essays on the Essay Film” consists of writings by distinguished scholars such as Andre Bazin, Theodore Adorno, Hans Richter and Laura Mulvey, but also includes more recent work by Thomas Elsaesser, Laura Rascaroli and others. Although each carefully selected text spans different time periods and cultural backgrounds, Alter and Corrigan weave together a comprehensive, yet pliable description of the cinematic essay.
“Essays on the Essay Film” begins by including articles that investigate the form and function of the written essay. This first chapter, appropriately titled “Foundations” provides a solid groundwork for many of the concepts discussed in the following chapters. Although the written essay is obviously different from the work created by filmmakers such as Chris Marker and Trinh T. Minh-ha, Alter and Corrigan note that these texts “have been influential to both critics and practitioners of the contemporary film essay.” (p. 7) The articles in this chapter range from Georg Lukacs’s 1910 “On the Nature and Form of the Essay” to “Preface to the Collected Essays of Aldous Huxley” which was published in 1960. Over a span of fifty years, the authors illustrate how the very concept of the essay was affected by changing practices of art, history, philosophy, culture, economics, politics, as well as through modernist and postmodernist lenses. However, these articles are still surprisingly relevant for contemporary scholars and practitioners. For example, in an excerpt from The Man Without Qualities , Robert Musil writes that, “A man who wants the truth becomes a scholar; a man who wants to give free play to his subjectivity may become a writer; but what should a man do who wants something in between?” (p. 45.) Naturally, this reminded me of my class’s discussion on Sans Soleil and Waltz with Bashir. It concisely encapsulates the difficulties that arise when the essay film crosses boundaries of fiction and non-fiction. However, in his 1948 essay “On the Essay and its Prose”, Max Bense believes that the essay lies within the realm of experimentation, since “there is a strange border area that develops between poetry and prose, between the aesthetic stage of creation and the ethical stage of persuasion.” (p. 52.) Bense also notes that the word “essay” itself means “to attempt” or to “experiment” and believes that the essay firmly belongs in the realm of experimental and avant-garde. This is appropriate enough, given that writers, and more recently filmmakers and video artists have pushed the boundaries of their mediums in order to explore their deepest thoughts and emotions.
Alter and Corrigan follow this chapter with “The Essay Film Through History” which details the evolution of the essay film. Writing in 1940, Hans Richter considers the essay film a new type of documentary and praises its abilities to break beyond the purportedly objective goals of documentaries in an attempt to “visualize thoughts on screen.” (p. 91) Eighteen years later, Andre Bazin celebrates Chris Marker’s thought-provoking voice-over narration as well as his method of “not restricting himself to using documentary images filmed on the spot, but [using] any and all filmic material that might help his case.” (p. 104) Bazin even compares Marker’s style to the work of animator Norman McLaren, supporting the idea of the essay film’s use of unfettered creativity. By the time the reader gets to the third chapter, “Contemporary Positions”, he or she is well aware of the capricious and malleable nature of the essay film. As Corrigan remarks:
As it develops in and out of those documentary and avant-garde traditions, the history of the essay film underlines a central critical point: that the essayistic should not necessarily be seen simply as an alternative to either of these practices (or to narrative cinema); rather it rhymes with and retimes them as counterpoints within and to them. Situated between the categories of realism and formal experimentation and geared to the possibilities of “public expression,” the essay film suggests an appropriation of certain avant-garde and documentary practices in a way different from the early historical practices of both, just as it tends to invert and restructure the relations between the essayistic and narrative to subsume narrative within that public expression. The essayistic play between fact and fiction, between the documentary and the experimental, or between non-narrative and narrative becomes a place where the essay film inhabits other forms and practices. (p. 198)
Alter and Corrigan’s volume implies that the essay can inhabit many forms, styles or genres. More importantly is the idea that it should be recognised for its intentions and capabilities. Whatever form it takes, the essay is an attempt to seek, explore, understand, visualise and question, without necessarily providing clearly defined answers. The essay film also places considerable value on the intellect and opinion of the viewer, since it is an invitation to reflect on the thoughts, experiences, emotions and perceptions that are being conveyed. “Essays on the Essay Film” sensibly concludes with the chapter entitled “Filmmakers on the Essayistic”. Notable filmmakers, such as Lynn Sachs and Ross McElwee provide valuable insight into their own practices. The featured filmmakers, documentarians and video artists in this chapter do not focus specifically on what form their work takes, but what they are trying to achieve. For instance, in her article “On Writing the Film Essay,” Lynn Sachs proclaims that “My job is not to educate but rather to spark a curiosity in my viewer that moves from the inside out.” (p. 287.) Admittedly, Sachs’s statement contradicts the idea that documentary films seek to educate, inform and persuade, which I taught in my own classes. Yet Sachs’s insights, as well as those of the many other filmmakers in “Essays on the Essay Film” demonstrate how the camera is as versatile as the pen when communicating thoughts, emotions and ideas.
Tree of Life (Malick, 2011)
Elizabeth A. Papazian and Caroline Eades have also compiled several surprising, challenging and thoroughly captivating articles that exemplify the many forms that the essay film can take. The Essay Film: Dialogue, Politics, Utopia includes articles by several prominent scholars that explore the essay film’s place throughout history as well as within various cultural settings. Like Alter and Corrigan, they also present a convincing argument that the essay film is distinct from both documentary, avant-garde and narrative filmmaking, since it is “characterized by a loose, fragmentary, playful, even ironic approach […] and raises new questions about the construction of the subject, the relationship of the subject to the world and the aesthetic possibilities of cinema.” (Papazian/Eades, p. 1) Papazian and Eades explore how essayistic tendencies can manifest in narrative, documentary, avant-garde, and even video art through careful analyses of specific films and videos. The book opens with Timothy Corrigan’s “Essayism and Contemporary Film Narrative” which explores how the essayistic can inhabit narrative film, specifically through Terrence Malick’s The Tree of Life and Lech Majewski’s The Mill and the Cross , both released in 2011. Corrigan observes that The Tree of Life “continually seems to resist its own narrative logic” (p. 18) by presenting a highly fragmented and non-linear plot. Instead of placing it into the hybrid realm of experimental-narrative, however, Corrigan argues that:
Rather than locate a linear connection between past, present and future, the narrative flashbacks in The Tree of Life become a search for genesis – or more accurately many geneses – which might be better described as disruptive recollections that never adequately collect and circulate, as fractured and drifting images and moments producing not evolutionary lines, but the spreading reflective branches of essayism. (p. 19-20.)
The Essay Film: Dialogue, Politics, Utopia continues with essays by other acclaimed, yet indefinable filmmakers such as Jean Luc-Godard and Claire Denis. Essays by Rick Warner and Martine Beugnet explore how these filmmakers defy closure and continuity, even while appearing to work within established forms and genres. Ann Eaken Moss explores the essayistic approach that Chantal Akerman imbues within her experimental “home movies.” News from Home (1977) is a meditation on Akerman’s own sense of dislocation from her home in Belgium while she adapts to life in New York City. In “Inside/Outside: Nicolasito Guillen Landrian’s Subversive Strategy in Coffea Arabiga” Ernesto Livon-Grosman investigates Landrian’s means of furtively including his own political agenda within a government-sanctioned documentary. What was meant to be a propagandistic documentary about the benefits of Cuban coffee plantations becomes an essayistic critique on the power structure of Fidel Castro’s government. (Livon-Grosman.) Papazian and Eades conclude their volume with an afterward by Laura Rascaroli, affirming that “it is with the potentiality of all essay films to question and challenge their own form”. (p. 300) The essay film may be distinct from narrative, documentary and the avant-garde, but it itself has no discernable style or formula. The Essay Film: Dialogue, Politics, Utopia clearly illustrates how the essay film, although bordering on established genres “must create the conditions of its own form.” (pp. 301-302.) Every filmmaker’s unique thoughts, experiences, meditations, questions and perceptions cannot neatly fit into a strict set of generic guidelines. However, this does not make the essay film more difficult to understand, but further implies that it is a unique practice rather than a specific form.
News from Home (Akerman, 1977)
Even with the insight provided by these two volumes, I do not regret introducing the essay film to my documentary students, despite their questions and confusion. As illustrated throughout Essays on the Essay Film and The Essay Film: Dialogue, Politics, Utopia it has typically been an esoteric and transgressive form, and perhaps including it with better known genres such as documentary and experimental films could be an effective way of introducing it to beginning filmmakers and scholars. Then again, perhaps it should be taught as a form separate from documentary, narrative and the avant-garde. I do wish that I was able to speak more about it at length during that particular instance, since the essay film deserves a considerable amount of thought and attention. Whether or not there is a correct pedagogical approach to teaching the essay film, both of these volumes are tremendously illuminating, but also open the door to further discussion about this compelling form of cinema.
- Bill Nichols, Introduction to Documentary , 2nd ed. (Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press, 2010). ↩
- Roger Ebert, “Waltz with Bashir”, rogerebert.com , January 21, 2009, https://www.rogerebert.com/reviews/waltz-with-bashir-2009 ↩
- Jonathan Rosenbaum, “Personal Effects: The Guarded Intimacy of Sans Soleil”, The Criterion Collection , June 25, 2017, https://www.criterion.com/current/posts/484-personal-effects-the-guarded-intimacy-of-sans-soleil ↩

On The Site
- performing arts
Godard and the Essay Film

A Form That Thinks
by Rick Warner
Imprint: Northwestern University Press
288 Pages , 6.00 x 9.00 in , 49 b-w images
- 9780810137370
- Published: July 2018
- 9780810137387
- 9780810137394
- Description
RICK WARNER is an assistant professor of film in the Department of English and Comparative Literature at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill.
“ Godard and the Essay Film is a first-rate piece of scholarship that makes substantial contributions on a variety of topics, including the essay as literary and cinematic form, film and philosophy, and the study of the indispensable oeuvre of Jean-Luc Godard.” —Michael Renov, author of The Subject of Documentary ". . . a superb piece of work, reaffirming cinema as a (potentially) philosophical machine that can lead us to think (that we have not yet begun thinking)." — Studies in European Cinema
“ Godard and the Essay Film is an exceptionally innovative and fresh study that manages to rethink one of the most important and challenging filmmakers in cinema history. In the process, Warner has also engaged one of the most important and prominent waves in modern filmmaking, the essay film. While there is a growing body of scholarship on this subject, Warner’s more focused engagement offers keen new insights that extend beyond Godard’s work.” —Timothy Corrigan, author of The Essay Film: From Montaigne, After Marker
"It is made clear in Godard and the Essay Film, through meticulous close readings of scenes and techniques, that Godard's primary goal in his essay films is to establish a conversation with the viewer. Such a dialogue, where the viewer is asked to decode montaged connections, identify references and provide answers to posed scenarios, is understandably difficult and ultimately always unfinished . . . Also unique to this book is the emphasis on co-filmmaking . . ." —Yelizaveta Goldfarb Moss, Screen "There is no shortage of books on provocative French-Swiss director Jean-Luc Godard, but this one serves the additional function of intervening in discussion of a difficult-to-define type of move: the essay film . . . The book's strongest discussions are those in which Warner opens up Godard's work to its contexts, and a particular highlight is the chapter on couples and coupling, which deals with Godard's collaborations with Anne-Marie Miéville." —K. M. Flanagan, George Mason University, CHOICE
Related Books

Learn more about upcoming publications, events, and news from Northwestern University Press.
- Architecture and Design
- Asian and Pacific Studies
- Business and Economics
- Classical and Ancient Near Eastern Studies
- Computer Sciences
- Cultural Studies
- Engineering
- General Interest
- Geosciences
- Industrial Chemistry
- Islamic and Middle Eastern Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Library and Information Science, Book Studies
- Life Sciences
- Linguistics and Semiotics
- Literary Studies
- Materials Sciences
- Mathematics
- Social Sciences
- Sports and Recreation
- Theology and Religion
- Publish your article
- The role of authors
- Promoting your article
- Abstracting & indexing
- Publishing Ethics
- Why publish with De Gruyter
- How to publish with De Gruyter
- Our book series
- Our subject areas
- Your digital product at De Gruyter
- Contribute to our reference works
- Product information
- Tools & resources
- Product Information
- Promotional Materials
- Orders and Inquiries
- FAQ for Library Suppliers and Book Sellers
- Repository Policy
- Free access policy
- Open Access agreements
- Database portals
- For Authors
- Customer service
- People + Culture
- Journal Management
- How to join us
- Working at De Gruyter
- Mission & Vision
- De Gruyter Foundation
- De Gruyter Ebound
- Our Responsibility
- Partner publishers

Your purchase has been completed. Your documents are now available to view.
14. Of The History of The Essay Film: Vertov to Varda (2011)
From the book essays on the essay film.
- Timothy Corrigan
- X / Twitter
Supplementary Materials
Please login or register with De Gruyter to order this product.
Chapters in this book (33)

The origin of all things: Kyotographie 2024 – a photo essay
The 12 th annual Kyotographie photography festival features 13 exhibitions staged in striking locations across the Japanese city of Kyoto. Photographers from around the world submitted pictures on the theme of ‘source’
- The Kyotographie international photography festival runs until 12 May
S pring in Kyoto ushers in cherry blossom season, but it also marks the return of one of the biggest photo festivals in Asia. Kyotographie, now in its 12th year, fuses the past and present with its striking images and unique locations. The 13 exhibitions are staged in temples, galleries and traditional private homes across the Japanese city, showcasing the work of national and international photographers.
The festival is loosely centred on a theme – and this year the directors, Lucille Reyboz and Yusuke Nakanishi, asked participants to focus on the word “source” by delving into the essence of beginnings and the nexus of creation and discovery.

The Yamomami struggle. Photograph by Claudia Andujar
The source is the initiator, the origin of all things. It is the creation of life, a place where conflict arises or freedom is obtained; it is the space in which something is found, born or created. It is a struggle Claudia Andujar and the Yanomami shaman and leader Davi Kopenawa know too well. The Yanomami Struggle is the first retrospective exhibition in Japan by the Brazilian artist and activist Andujar with the Yanomami people of Brazil.
It is more than 50 years since she began photographing the Yanomami, the people of the Amazon rainforest near Brazil’s border with Venezuela, an initial encounter that changed their lives. Andujar’s work is not just a showcase of her photographic talent but, with Kopenawa accompanying the exhibition to Japan for the first time, it is a platform to bring the Yanomami’s message to a wider Asian audience.

The Yanomami Struggle. Photograph by Claudia Andujar
The first part of the exhibition features photographs taken by Andjuar in the 1970s, alongside artwork by the Yanomami people and words by Kopenawa. The second part narrates the continuing violence inflicted by non-Indigenous society on the Yanomami. The project is a platform for the Yamomani people to be seen and protected from ongoing threats. The exhibition, curated by Thyago Nogueira from São Paulo’s Instituto Moreira Salles, is a smaller version of one that has been touring the world since 2018.

The Yanomami Struggle, by Claudia Andujar, and artwork by the Yanomami people.
The Moroccan artist Yassine Alaoui Ismaili (Yoriyas) is showing new work made during his Kyotographie artist-in-residence programme for young Africans. The images from the Japanese city feature alongside his project Casablanca Not the Movie.

Children Transform the Sheep for Eid al-Adha into a Playground in Casablanca. Photograph by Yassine Alaoui Ismaili (Yoriyas)

Yoriyas gave up his career as a breakdancer and took up photography as a means of self-expression. His project Casablanca Not the Movie documents the streets of the city where he lives with candid shots and complex compositions. His work, which combines performance and photography, encourages us to focus on how we inhabit urban spaces. The exhibition’s clever use of display and Yoriyas’s experience with choreography force the viewer to see the work at unconventional angles. He says: “The camera frame is like a theatre stage. The people in the frame are my dancers. By moving the camera, I am choreographing my subjects without even knowing it. When an interesting movement catches my eye, I press the shutter. My training has taught me to immediately understand space, movement, connection and story. I photograph in the same way that I choreograph.”

The contrasts in Casablanca take many forms, including social, political, religious and chromatic. Photograph by Yoriyas
From Our Windows is a collaboration bringing together two important Japanese female photographers, both of whom shares aspects of their lives through photography, in a dialogue about different generations. The exhibition is supported by Women in Motion, which throws a spotlight on the talent of women in the arts in an attempt to reach gender equality in the field. Rinko Kawauchi, an internationally acclaimed photographer, chose to exhibit with Tokuko Ushioda who, at 83, continues to create vibrant new works. Kawauchi says of Ushioda: “I respect the fact that she has been active as a photographer since a time when it was difficult for women to advance in society, and that she is sincerely committed to engaging with the life that unfolds in front of her.” This exhibition features photographs taken by each of them of their families.

Photograph by Rinko Kawauchi.
Kawauchi’s two bodies of work, Cui Cui and As It Is, focus on family life. The first series is a family album relating to the death of her grandfather and the second showcases the three years after the birth of her child. Family, birth, death and daily life are threads through both bodies of work that help to create an emotional experience that transcends the generations.

Rinko Kawauchi and Tokuko Ushioda at the Kyoto City Kyocera Museum of Art
Kawauchi says: “My works will be exhibited alongside Ushioda. Each of the works from the two series are in a space that is the same size, located side by side. The works show the accumulation of time that we have spent. They are a record of the days we spent with our families, and they are also the result of facing ourselves. We hope to share with visitors what we have seen through the act of photography, which we have continued to do even though our generations are different, and to enjoy the fact that we are now living in the same era.”
Ushioda’s first solo exhibition features two series: the intimate My Husband and also Ice Box, a fixed-point observation of her own and friends’ refrigerators. Ushioda says: “I worked on that series [Ice Box] for around 20 years or so. Like collecting insects, I took photographs of refrigerators in houses here and there and in my own home, which eventually culminated in this body of work.”

Entries from Tokuko Ushida’s series Ice Box.
James Mollison’s ongoing project Where Children Sleep is on display at the Kyoto Art Centre with a clever display that turns each photograph into its own bedroom.

A child portrayed in Where Children Sleep, Nemis, Canada.
Featuring 35 children from 28 countries, the project encourages viewers to think about poverty, wealth, the climate emergency, gun violence, education, gender issues and refugee crises. Mollison says: “From the start, I didn’t want to think about needy children in the developing world, but rather something more inclusive, about children from all types of situations.” Featuring everything from a trailer in Kentucky during an opioid crisis and a football fan’s bedroom in Yokohama, Japan, to a tipi in Mongolia, the project offers an engrossing look at disparate lives.

From Where Children Sleep, Nirto, Somalia

Joshim, India. Photographs by James Mollison
Phosphor, Art & Fashion (1990-2023) is the first big retrospective exhibition devoted to the Dutch artist Viviane Sassen . It covers 30 years of works, including previously unseen photographs, and combines them with video installations, paintings and collages that showcase her taste for ambiguity and drama in a distinctive language of her own.

Eudocimus Ruber, from the series Of Mud and Lotus, 2017. Photograph by Viviane Sassen and Stevenson
The exhibition opens with self-portraits taken during Sassen’s time as a model. “I wanted to regain power over my own body. With a man behind the camera, a sort of tension always develops, which is often about eroticism, but usually about power,” she says. Sassen lived in Kenya as a child, and the series produced there and in South Africa are dreamlike, bold and enigmatic. She describes this period as her “years of magical thinking”. The staging of the exhibition in an old newspaper printing press contrasts with the light, shadows and bold, clashing colours of her work. The lack of natural light intensifies the flamboyant tones of the elaborately composed fashion work.

Dior Magazine (2021), and Milk, from the series Lexicon, 2006. Photographs by Viviane Sassen and Stevenson

Viviane Sassen’s immersive video installation at the Kyoto Shimbun B1F print plant. Photograph by Joanna Ruck
The source of and inspiration for Kyotographie can be traced to Lucien Clergue, the founder of Les Rencontres d’Arles, the first international photography festival, which took place in 1969. Arles, where Clergue grew up and lived all his life, was a canvas for his photography work in the 1950s. Shortly after the second world war, many Roma were freed from internment camps and came to Arles, where Clergue forged a close relationship with the community. Gypsy Tempo reveals the daily life of these families – their nomadic lifestyle, the role of religion and how music and dance are used to tell stories.

Draga in Polka-Dot Dress, Saintes-Maries-de-la-Mer, 1957. Photographs by Lucien Clergue

Little Gypsy Girl in the Chapel, Cannet 1958
During this time, Clergue discovered, and then helped propel to fame, the Gypsy guitarist Manitas de Plata and his friend José Reyes. Manitas went on to become a famous musician in the 1960s who, together with Clergue, toured the world, including Japan.
Kyotographie 2024 was launched alongside its sister festival, Kyotophonie , an international music event, with performances by Los Graciosos, a band from Catalonia who play contemporary Gypsy music. Meanwhile, the sounds of De Plata can be heard by viewers of Clergue’s exhibition.

The Magic Circle, Saintes-Maries-de-la-Mer, 1958, by Lucien Clergue.
Kyotographie 2024 runs until 12 May at venues across Kyoto, Japan.
- The Guardian picture essay
- Photography
- Exhibitions
- Asia Pacific
Most viewed
The movie that will make you question everything about American racism
Share this article
Reminder, this is a Premium article and requires a subscription to read.
"Superb": Aunjanue Ellis-Taylor as Isabel Wilkerson and Jon Bernthal, who plays devoted husband Brett Hamilton. Photo / supplied
Origin is an extraordinary film which is part-biopic, part-love story, but mostly a socio-political essay. It recounts the academic and personal journey of African-American author Isabel Wilkerson to a fascinating and courageous hypothesis that argues for the reframing of critical race theory in America.
A Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist, Wilkerson (a luminous Aunjanue Ellis-Taylor) is the brain behind the 2020 anthropological bestseller Caste: The Origins of Our Discontents . Prompted by the 2012 murder of black teenager Trayvon Martin, Wilkerson argued that race issues in the US were not down to “racism” as we consider it, but that in fact several places around the world have historically oppressed peoples on the basis of social stratification, specifically caste.
Director Ava DuVernay has confronted American racism before in her civil rights-era film Selma and the documentary series When They See Us . Here, she dramatises not just the principles unearthed by Wilkerson’s study but the author’s literal voyage of discovery, as she visits Germany and India and finds parallels with the way the Nazis in the 1930s and 40s, and Indian society to this day, enforce a tyranny of exclusion and oppression over certain groups of its people.
It’s an eye-opening thesis, one that DuVernay nicely articulates through employing an enthralling mix of genres: beautifully acted drama between Ellis-Taylor and Jon Bernthal as her devoted husband; archive footage neatly glued into recreations of true-life historical stories; and the depiction of current day horrors which is hybrid-documentary – specifically the Delhi street scenes, in which members of the lowest-ranking Dalit caste, the so-called “untouchables”, are lowered into sewers which they clean by hand.
Ellis-Taylor is superb as Wilkerson guides the audience through her examination of ideas, using a whiteboard to spell out various points, and having earnest discussions with her non-academic relatives at family barbecues. Crucially, we never feel lectured to, but instead, brought along on a frequently absorbing expedition.
While some may feel that mixing Wilkerson’s personal tragedies with her sociological investigations muddles the film’s tone or lessens the impact of its thesis, these unanticipated details delivered the most moving and heartbreaking screen moments I’ve experienced in years. By fleshing out Wilkerson as a whole, real woman, Ellis-Taylor avoids the caricature of the blinkered, unemotional, intellectual workaholic.
Granted, DuVernay does lean heavily on the music to lead her audience through emotions of devastation and exhilaration. Composer Kris Bowers’ score is unsubtle yet enjoyable – and arguably helps propel us through a two-hour, 20-minute running time, a length necessary to tell Wilkerson’s story but potentially an endeavour for the viewer.
DuVernay, who made the 2018 fantasy film A Wrinkle in Time in New Zealand , asked our own Stan Walker to write for the soundtrack, and his song I Am , with its te reo chorus, feels fitting as an apt provocation to the NZ viewer, and surprising, given there’s no explicit mention of the Pacific in DuVernay’s film.
As a glorious piece of cinema and an insightful and well-articulated idea, Origin is a must-see for those curious to learn something new, and to view the state of our world through a fresh lens.
Rating out of 5: ★★★★★
Origin, directed by Ava DuVernay, is in cinemas now.

Latest from The Listener

Happy tears and dancing in the aisles: How the 2024 Taite Prize went down
Russell Baillie on the Taite Prize ceremony at Auckland’s Q Theatre.

Mad About the Boy: A flawed but fascinating look at one of the world’s greatest showmen

Anthony Ellison’s take on today’s shock Cabinet reshuffle

D-Day link, fake scarlet fever, and a rat dinner: One woman’s secret war in France

Six questions you’ll need answers to if you’re bidding farewell to Xtra Mail
Advertisement
Supported by
How the Movie ‘Civil War’ Echoes Real Political Anxieties
“Civil War” has tapped into a dark set of national angst. In polls and in interviews, a segment of voters say they fear the country’s divides may lead to actual, not just rhetorical, battles.
- Share full article

By Lisa Lerer
One subject seems to be unifying the right and the left today: Disunion.
From the multiplex to social media, the prospect of America collapsing into armed conflict has moved from being an idea on the tinfoil-hat fringes to an active undercurrent of the country’s political conversation.
Voters at campaign events bring up their worries that political division could lead to large-scale political violence. Pollsters regularly ask about the idea in opinion surveys. A cottage industry has arisen for speculative fiction, serious assessments and forums about whether the country could be on the verge of a modern-day version of the bloodiest war in American history.
And “Civil War,” a dystopian action film about an alternative America plunged into a bloody domestic conflict, has topped box office sales for two consecutive weekends. The movie has outperformed expectations at theaters from Brownsville, Texas, to Boston, tapping into a dark set of national anxieties that took hold after the Jan. 6, 2021, storming of the Capitol.
Of course, the notion of a future civil war remains a mere notion. But, as another presidential election approaches, it has suddenly become a hotly debated one, reflecting the bipartisan sense of unease that has permeated American politics. In polls and in interviews , a segment of voters have said they fear that the country’s divides have grown so deep that they may lead not just to rhetorical battles but actual ones.
“I personally do not believe we will descend into a formal armed civil war,” said Maya Wiley, who ran for mayor of New York City in 2021 and now serves as the president of the Leadership Conference on Civil and Human Rights, a civil rights group that has fielded several polls on the topic. “But it’s in the air. It doesn’t surprise me at all that we’re seeing a very explicit fear of where things could go.”
Such fear has been stirred by the violence and chaos that subtly and overtly pervades American politics. Violent threats against members of Congress have reached record levels, as have reports of hate crimes in the country’s largest cities. The husband of Nancy Pelosi, the former House speaker, was beaten with a hammer in his home. The criminal trial of a former president unfolded in a courthouse while a man nearby doused himself with an accelerant and set his body on fire.
In his first campaign speech of the year, President Biden warned of threats to the country’s democracy and suggested that former President Donald J. Trump could stoke future political violence.
“I make this sacred pledge to you: The defense, protection and preservation of American democracy will remain, as it has been, the central cause of my presidency,” he said in an address near Valley Forge, Pa., the site of one of the darkest periods of the American Revolution.
Mr. Trump has glorified the Jan. 6 rioters as patriots and maintained his false claims that the 2020 election was stolen from him. When the former president was asked last August by Tucker Carlson whether the country was headed to open conflict, he declined to directly answer.
“I don’t know,” Mr. Trump said. “There’s a level of passion that I’ve never seen. There’s a level of hatred that I’ve never seen, and that’s probably a bad combination.”
The film has no grounding in such partisan politics. The sides are unclear and the ideology — a “Western Alliance” of secessionists from California and Texas — is impossible to imagine given the stark partisan divides between the states. No details are given about the cause of the conflict or the different visions each side has for the future of the country. There’s no mention of Congress, the courts or other civic institutions other than the presidency and references to the F.B.I.
That political vagueness was an intentional choice by the British writer and director, Alex Garland, who began working on the film in 2020 before the Jan. 6 riot at the Capitol. “I’d say this film is about checks and balances: polarization, division, the way populist politics leads toward extremism, where extremism itself will end up and where the press is in all of that,” Mr. Garland told The New York Times .
His goal was to create a movie that could illustrate the risks of polarization — not just in the United States but globally — and reach the widest audience possible, said Eric Schultz, a Democratic strategist who met with Mr. Garland in the fall of 2021 and worked as a consultant for the film.
The opaque politics have helped the movie attract an audience that bridges political divides. Exit interviews conducted for A24, the studio that produced the movie, found that half of moviegoers identified as “liberal” and half as “conservative,” according to a person with knowledge of the film’s performance in various markets.
The film outperformed expectations in traditionally conservative markets like Oklahoma City and Colorado Springs, as well as more liberal ones like Portland, Ore. In Phoenix and Dallas, a majority of filmgoers identified as moderate or conservative. The top reason viewers cited for seeing the movie was not an interest in independent cinema or action films but the “political dystopian story line.”
The interest in political chaos tracks with a growing body of research showing a dramatic uptick in public fears of violence.
The polling by Ms. Wiley’s organization found that 53 percent of likely voters believed the country was on the path to a second Civil War.
Other surveys show related concerns. Forty-nine percent of adults said they expected violence from the losing side in future elections, in a poll conducted by CBS/YouGov this year. And a survey by The Associated Press/NORC Center for Public Affairs Research found that majorities of both Democratic and Republican adults said American democracy could be at risk depending on who won the next election.
Jess Morales Rocketto, a leader of Equis Research, which studies Latino voters , said discussion of a civil war could stem from more of a feeling of insecurity than a reality for voters.
“I think that people believe we are on the brink of civil war,” she said. “When people say stuff like civil war, World War III, what they mean is volatility and instability. They are saying, ‘I feel unsafe.’”
But Barbara F. Walter, a political scientist at the University of California, San Diego, who studies civil wars, says the prospect of such a conflict isn’t just metaphorical. She believes the country is facing a decade or two of political instability and violence that could include assassinations of politicians or judges and the rise of militia groups.
The movie’s realistic portrayal of such violence taking place in deeply American settings — a golf course, a roadside gas station, the Lincoln Memorial — put the scenes of violence Americans associate more with foreign conflicts into sharper relief, she said.
“This notion that America could never have a civil war; we’ve already had a really, really big one,” said Ms. Walter, the author of “How Civil Wars Start.” “There’s a sense of naiveté, of innocence, that we’re too good for that sort of stuff. We’re not.”
David Mandel, a producer and writer on the television show “Veep,” said the most successful movies and shows about American political life had a “reciprocal relationship” with public opinion about politics. His show, a comedy about a bumbling vice president that began during the Obama administration, was based on the idea that politicians behaved differently in private, and that a miscalculated public remark could lead to their political destruction. As president, Mr. Trump routinely defied that norm, and “Veep” ended before he left the White House.
“By a couple of weeks into the Trump administration, there was no ‘behind closed doors’ and there was no such thing as comeuppance,” Mr. Mandel said. “The show became impossible to do.”
David W. Blight, a historian at Yale University who specializes in the Civil War period, said he did not believe the country stood on the precipice of another one. But if the country were to reach that point, he said, the conflict could share more with the movie version than the historical one.
The Civil War was a regional and ideological crisis that featured some of the largest armies ever formed, he said. A second one would most likely be far more local and vigilante, and stirred by increasing polarization and institutional mistrust.
“For the last couple of years, there’s been all this chatter and a few books out about whether the U.S. is on the brink of a new civil war, and you have to keep telling people, ‘Well no, not in the way you may think about it,’” he said. “Our real Civil War blinds us in that sense.”
Lisa Lerer is a national political reporter for The Times, based in New York. She has covered American politics for nearly two decades. More about Lisa Lerer
Our Coverage of the 2024 Election
Presidential Race
Donald Trump has put forth a law-and-order candidacy while also criticizing the legal system when it comes to himself and making exceptions for his supporters. Here’s a look at his complicated relationship with law enforcement.
Kamala Harris, campaigning in Wisconsin, took sharp swipes at Trump for his actions on abortion , a hot topic across the country . But she stayed silent on the war in Gaza, another issue erupting elsewhere among the critical bloc of young voters she has been courting.
President Biden announced $7 billion in grants for solar power projects and tried to draw a contrast with Republicans who want to roll back his policies on climate change.
Other Key Races
David McCormick, the G.O.P. senate candidate, has often spoken about his modest upbringing on a farm in Pennsylvania . A close look at his past tells a different story.
Summer Lee’s race in Pennsylvania once seemed primed to become a major test of Democratic attitudes about the Middle East . But in much of the district, an expected ideological battle has not arrived.
A high-energy crowd rallied in Pittsburgh to support Representative Summer Lee, a left-leaning congresswoman whose primary is a high-profile test of whether she can stave off a challenge aimed in part at her stance over the war in Gaza.
After Hamas’s Oct. 7 attack on Israel, pro-Israel political groups put the Democratic Party’s most outspoken critics on notice. The groups have raised millions to challenge candidates they see as not sufficiently pro-Israel, but have spent little as public opinion shifts.
Trump’s long, strange history with the tabloids
The new york city papers gave him the headlines he craved; the national enquirer buried the ones he didn’t.

When Marla Maples was about to give birth to Donald Trump ’s fourth child, Tiffany, in 1993, then-New York Daily News gossip columnist Linda Stasi had her editor’s orders: Get in the room to see the baby.
Maples objected, but Trump invited Stasi to the hospital, where she walked into the private room after the birth, conducted a quick interview, then asked if her photographer could snap a photo. Maples shooed her out, Stasi said in an interview. Trump soon followed, holding an empty blanket. “Here, take my picture. Just pretend there’s a baby in here,” Stasi recalled Trump saying. The camera flashed.
Subscribe to The Trump Trials, our weekly email newsletter on Donald Trump's four criminal cases
The photo was never published, but the incident highlights the lengths Trump was willing to go to accommodate the tabloid press, which in turn accommodated him in his insatiable, years-long pursuit of headlines long before he ran for office.
Yet when it came to his 2016 campaign for president, he needed to bury stories about his personal exploits, not promote them. That called for what former National Enquirer CEO David Pecker, during testimony Monday in the first trial of a former president, described as the “checkbook journalism” of a supermarket tabloid. Stories Pecker’s tabloid bought and buried are now at the heart of Trump’s trial, playing out in a federal courtroom in Lower Manhattan. Pecker was the first witness for the prosecution, with testimony continuing Tuesday following an abbreviated start on Monday.
While the New York City tabloids had greased Trump’s rise as a business executive with a constant churn of publicity, when he turned politician, aiming for the highest office in the land with no stops in between, he found a ready partner in the National Enquirer, according to former employees, court filings and people familiar with the dynamic who spoke on the condition of anonymity to preserve relationships in the industry. The Manhattan tabloids catered to a wide swath of New York society — and did not pay for stories — while the Enquirer and its ilk have always occupied a down-market position on newsstands and reached deep into the country through their prominent placement in grocery store checkout aisles. The story that resulted in Trump’s trial never made it to those aisles.
The prosecution’s case centers on the argument that Trump intended to help his campaign when he covered up a $130,000 payment to adult-film star Stormy Daniels. The money allegedly kept her from speaking out during the campaign about an extramarital sexual encounter she says she’d had with Trump years earlier. Trump faces 34 felony counts of falsifying business records to hide his reimbursement payments to his former longtime personal lawyer Michael Cohen for the money paid to Daniels. Prosecutors say the coverup involved altering business records to conceal the crimes of violating federal campaign finance contribution limits and New York tax and election laws.
The trial promises to spotlight lurid details of Trump’s sex life and look closely at granular bookkeeping statutes, but prosecutors will also delve into Trump’s long-standing ties with the tabloid press, using aspects of them against him.
Years before he entered politics, a young Trump ventured onto the real estate scene in Manhattan as a small player, busting out of his developer father’s Queens and Brooklyn stomping grounds. Propelled by his father’s money, the lawyer and fixer Roy Cohn’s ruthless tactics and his own self-promotion skills, he made his name in Manhattan power circles by making his life a fixture in the city’s vibrant tabloids. Trump deployed juicy bits of gossip and bombastic quotes to craft his image as a billionaire playboy for the consumption of millions of daily commuting readers. He impersonated his own PR representative to plant stories and used the cutthroat competition between columnists to his advantage, according to tabloid reporters who spoke to him regularly.
During Trump’s rise as a real estate figure, he nurtured relationships with individual tabloid writers. They gleefully chronicled Trump’s escapades in his business and tumultuous love life. Two tabloid doyennes captivated New York with the breakdown of his first marriage, to Ivana Trump. She had the ear of the late Liz Smith, the former star Daily News columnist; he had that of the New York Post’s Cindy Adams. The two columnists squared off, dishing out dueling narratives fed by their respective sources. Trump reportedly supplied the Post with the famous headline “Best Sex I’ve Ever Had,” ascribed to Marla Maples, to retaliate against a Daily News item about Ivana Trump that had angered him. But countless other stories found their way into the tabloids with his help, burnishing his image and settling scores with his foes.
People magazine’s Sue Carswell described Trump’s introducing himself on the phone as John Miller, Trump’s PR person. Trump used other aliases, including John Barron, according to former columnists who received such calls, some of whom spoke on the condition of anonymity to talk about their sourcing.
“Donald has always been in love with publicity and the front page of the New York Post and the New York Daily News,” said R. Couri Hay, a mainstay of New York gossip circles who wrote for the Enquirer, Interview magazine and others over many decades.
The relationships paid mutual dividends. After weeks of nonstop Trump stories in February 1990, an irate Staten Island reader wrote in a letter to the Daily News: “I have suffered through your tacky journalism revolving around the Trumps’ every move. There’s enough garbage tabloids floating around without lowering your standards to that level.” An in-house newsletter that month in which the paper congratulated itself on its coverage acknowledged that many readers had expressed similar sentiments, “but circulation was up 30-40,000 a day,” the newsletter said, “so it’s safe to assume far more readers enjoyed the coverage than were turned off by it.”
Such a staple of the tabloid diet was Trump that he often featured in the annual Inner Circle parody show staged by City Hall reporters, who take on the mayor and other powerful New York newsmakers. The mayor routinely produces a rebuttal sketch — which is how an infamous video of Rudy Giuliani in drag, with Trump nuzzling his bosom, came to be in 2000.
Trump and the tabloids were “a love affair with multiple divorces,” recalled Hay. It’s an image of Trump that many New Yorkers, possibly including some of those who found their way into the jury box of his current trial, remember well.
Last week before jury selection, prosecutors received New York Supreme Court Justice Juan Merchan’s permission to discuss before the jury a 2015 meeting at Trump Tower with Trump, Cohen and Pecker, then the top executive at National Enquirer parent company American Media Inc. — and the first witness called by the prosecution. At that meeting, the government alleges the three men discussed publishing positive stories about Trump and negative pieces about his political opponents.
“The entire point of the Trump Tower meeting was to control the flow of information that reached the electorate to accentuate the positive, hide the negative and exaggerate information that would be harmful to Trump’s opponents,” Assistant District Attorney Joshua Steinglass argued before Merchan last week. The defense team countered that such meetings with media representatives are common for candidates, and said that the meeting was not part of any charged criminal conduct.
In addition to the meeting, the judge said he would allow into evidence a series of National Enquirer stories attacking Trump’s opponents. Those stories, one by one, skewered Trump’s Republican primary rivals.
Some of those stories were shared before publication with Cohen, who acted as a key intermediary between the Enquirer and Trump, The Washington Post has previously reported. At trial, the prosecution argued that “many of these headlines and the stories behind them were shown to Mr. Trump before they were published so he could approve, reject or suggest changes.”
Pecker did not respond to requests for comment. Nor did Dylan Howard, who has since left the Enquirer but at the time was chief content officer of AMI. Howard denied to The Post at the time that the Enquirer shared articles before publication with Trump or his intermediaries. Howard told The Post that the Enquirer published positive stories about Trump because they performed above average on the newsstand, as did negative stories about his 2016 rival, Hillary Clinton. The Enquirer covered them accordingly, Howard said.
Before Trump faced off against Clinton, he bested a wide field of Republican primary candidates. The Enquirer weighed in on nearly all of them.
“Bungling Surgeon Ben Carson Left Sponge In Patient’s Brain!” read the headline in October 2015, describing the renowned former brain surgeon Carson, just as he was surging in polls. After the story ran, Carson told an interviewer that “the people who oppose me have been crawling through every ditch,” and pushed the story to the Enquirer, which found five or six disgruntled patients out of the 15,000 operations he conducted.
“Pervy Ted Cruz Caught Cheating — With 5 Secret Mistresses!” read a headline in March 2016 about the Texas senator. Cruz called the story “garbage” and accused Trump of enlisting his “friends” at the Enquirer to “do his bidding.” At the time, Howard denied to The Post that the story had come from Trump’s camp, instead accusing the Marco Rubio campaign of planting the story, an allegation Rubio’s former campaign manager denied.
During the general election, the Enquirer turned its attention to Clinton, alleging in several stories that she suffered from an array of serious health concerns. The publication doctored photographs to make her appear sickly, according to former Enquirer staffers who requested anonymity to describe internal Enquirer business. One piece predicted that she would be “dead in six months!” She turned 76 in October.
Coverage of Trump had a different flavor. In early 2016, the Enquirer published a glowing, two-part interview with Trump, and the publication endorsed him in March of that year, declaring that “nobody understands the economy better than this self-made billionaire, and only he is willing and able to fix it.” Other headlines included, “Trump’s Plan For World Peace!” and “Proof! FBI Plot to Impeach Trump!”
Trump’s connection to AMI may have been unlike his connection to the city tabloids, but it was just as binding. A former executive of Trump’s casino business was a member of AMI’s four-member board of directors. Trump and Pecker have been friends for years, after meeting at Mar-a-Lago in the late 1980s, Pecker testified on Tuesday. In July 2013, Trump tweeted that Pecker should become CEO of Time magazine. “He’d make it exciting and win awards!” Trump wrote at the time.
The two overlapped in their professional lives. Pecker testified Tuesday that he persuaded Trump to launch a magazine called Trump Style, which Pecker oversaw when he was CEO of publisher Hachette Filipacchi’s U.S. division. Trump introduced Pecker at Pace University in 1998 when Pecker received an honorary doctorate.
Pecker testified that he had “a lot of dealings with Mr. Trump because as a celebrity in his own right at that time, he was very helpful in introducing me to other executives, other people in New York.”
Trump had maintained a good relationship with the Enquirer, according to Iain Calder, who edited the paper for 20 years, into the 1990s, and described Trump in his memoir as someone who “loves publicity — but only if he controls it.” Calder added that “sometimes we let him influence an angle or delete something that really infuriated him.”
But the relationship deepened when Pecker moved to AMI in 1999. Quickly, Pecker discouraged reporters from writing negative stories about Trump, according to former employees who requested anonymity to discuss sensitive internal discussions. Trump was known as a “Friend of Pecker,” these people said, which protected him from negative stories in the publication.
The Enquirer accumulated tips, articles and documents on a wide array of story subjects, but only some of that material was deployed, they said. Some Trump material, such as old stories about a rape allegation against Donald Trump from his first wife, Ivana, (an allegation arising from their divorce proceedings that he denied and she retracted) were kept secure. But files on Bill and Hillary Clinton were regularly mined for stories, they added.
What many of the staff didn’t realize, however, was that there was a different batch of stories that the Enquirer’s parent company had contractually agreed to keep out of circulation. The details of those arrangements were closely held by a small number of executives at the top of the company, including Pecker.
Despite Trump’s long-standing close relationship with Pecker, his relationship with AMI shifted when the company signed a non-prosecution agreement with authorities in 2018 and admitted to paying $150,000 in hush money to Playboy model Karen McDougal, who alleged a 10-month affair with Trump. AMI agreed that it had paid McDougal to “suppress the model’s story” and “prevent it from influencing the election,” the non-prosecution agreement states. As part of that agreement, AMI said it would cooperate with prosecutors.
Though the trial will focus on the Daniels’s reimbursement, the prosecution plans to present to the jury other examples of Trump-related stories the Enquirer paid for but never ran. McDougal’s is one. A Trump-related story that the Enquirer purchased in late 2015 involved a $30,000 payment to a onetime Trump Tower doorman who was offering an embarrassing story about a “love child” fathered by then-candidate Trump. The Enquirer said in a statement it never published the claim because of questions about its credibility.
Merchan has ruled that McDougal and the doorman, Dino Sajudin, can be questioned about the payments they received from AMI to keep their stories quiet.
As for Daily News and New York Post coverage of Trump, it could seem transactional, but it could be hard-hitting, too, delivering scoops that managed to cut through the thicket of fictions Trump spun up, even if the winking, punning headlines gave the tabs — and Trump — cover either way.
“It was great because if you had a story, you knew you could get him on the phone,” Richard Johnson, former editor of the New York Post’s Page Six, said in an interview. The one drawback? “He’s not the most trustworthy source.”
Alice Crites contributed to this report.
Trump New York hush money case
Former president Donald Trump’s criminal hush money trial is underway in New York. Follow live updates from the trial .
Jury selection: A full jury of 12 jurors and six alternates has been seated. Here’s what we know about the jurors .
The case: The investigation involves a $130,000 payment made to Stormy Daniels, an adult-film actress , during the 2016 presidential campaign. It’s one of many ongoing investigations involving Trump . Here are some of the key people in the case .
The charges: Trump is charged with 34 felony counts of falsifying business records. Falsifying business records is a felony in New York when there is an “intent to defraud” that includes an intent to “commit another crime or to aid or conceal” another crime. He has pleaded not guilty . Here’s what to know about the charges — and any potential sentence .
Can Trump still run for president? The short answer, legal experts said, is yes. The U.S. Constitution does not forbid Trump, or anyone else, from serving as president if convicted of a felony.

Screen Rant
Star wars' upcoming jedi origin movie can reveal the ancient history of starkiller base.
Starkiller Base has an extensive history that links to the Jedi Order, meaning Star Wars’ upcoming Jedi origin film can detail its past.
- Star Wars' Dawn of the Jedi movie will explore the beginnings of the Order, the latter of which has been confirmed to be tied to Ilum.
- After the release of The Force Awakens, it was confirmed that Starkiller Base was built into Ilum's core.
- The Dawn of the Jedi movie could include origin stories for several Jedi-related aspects, including lightsaber construction via the exploration of Ilum and thus, Starkiller Base.
The upcoming Jedi origin film, tentatively titled Star Wars: Dawn of the Jedi , could detail the ancient history of Starkiller Base. Starkiller Base was introduced in Star Wars: The Force Awakens as a major weapon in the early timeline of Star Wars' First Order . Despite being a major part of the first sequel movie, Starkiller Base received little in the way of proper exploration, contributing to complaints that the sequel trilogy is among Star Wars' worst .
That said, while the sequel films did not explore much about Starkiller, the opportunity remains for upcoming Star Wars movies to do so. One such film was announced alongside Dave Filoni's New Republic film and Rey's New Jedi Order story. Through this project, Star Wars' Dawn of the Jedi story , the ancient history of Starkiller Base can finally be explored in a way that ties several sections of the Star Wars franchise together.
Starkiller Base Was Actually The Sacred Jedi Planet Ilum
A planet integral to the jedi order, ilum, is starkiller base..
In Star Wars: The Force Awakens , Starkiller Base was shown as a barren, cold, and icy planet. The film failed to divulge where the planet was in the galaxy, though the novelization of Episode VII revealed a massive fact about the superweapon. The novelization confirmed that Starkiller Base was built into the core of the planet Ilum, a planet vital to the Jedi Order for generations.
In Star Wars: The Clone Wars , among other projects, Ilum was shown as an icy planet where Jedi younglings would find Kyber crystals to construct their first lightsaber . After Starkiller Base was revealed as Ilum, it was similarly revealed that the Kyber foundations of the planet were being used to partially power the superweapon used by the First Order to destroy the New Republic. However, these details were left out of Star Wars: The Force Awakens , meaning future Star Wars movies have the opportunity to explore the base's history.
Will James Mangold's Dawn Of The Jedi Show The Discovery Of Ilum?
In the wider areas of Star Wars canon, it has been confirmed that Ilum was discovered in the earliest days of the Jedi Order. Star Wars: Dawn of the Jedi is set to focus on exactly this: the beginning of the Jedi Order and their connection with the Force. As such, it could be the case that the discovery of Ilum and its Kyber-based properties are included in James Mangold's upcoming movie .
It would be equally logical for Ilum - a place confirmed as synonymous with first lightsabers - to be included in some capacity.
This would certainly make sense, as a story about Star Wars' first Jedi will likely include the origin of many aspects audiences have come to associate with the Order. For instance, the origins of Jedi lightsabers would certainly be a logical inclusion of Mangold's movie. If this is the case, it would be equally logical for Ilum - a place confirmed as synonymous with first lightsabers - to be included in some capacity. Through this, Star Wars: Dawn of the Jedi can provide the backstory and history of Starkiller Base via the founding of Ilum, something the sequels failed to adequately explore.
Star Wars: Dawn of the Jedi
Announced at Star Wars Celebration in 2023, Star Wars: Dawn of the Jedi is a prequel focusing on the first-ever Jedi. Taking place 25,000 before Star Wars: Episode I - The Phantom Menace, Dawn of the Jedi will explore the events set prior to the Old Republic and the Disney+ series, The Acolyte.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
history of film, history of cinema, a popular form of mass media, from the 19th century to the present. (Read Martin Scorsese's Britannica essay on film preservation.) Early years, 1830-1910 Origins. The illusion of films is based on the optical phenomena known as persistence of vision and the phi phenomenon.The first of these causes the brain to retain images cast upon the retina of the ...
The Origins of Film Essay Sample, Example. There are multiple debates concerning the origins of film. Photographers in the nineteenth century were anxious to find a way to capture movement, almost from the moment they discovered the art of photography. It took less than half a century, and by the 1870s, Edward Muybridge has already made ...
The first to present projected moving pictures to a paying audience were the Lumière brothers in December 1895 in Paris, France. They used a device of their own making, the Cinématographe, which was a camera, a projector and a film printer all in one. Detail of Kinetoscope, made by Thomas Edison in 1894.
Méliès' shorts The One Man Band (1900) and A Trip to the Moon (1902) are considered two of the most trailblazing films in all of film history. Over the course of his career, Méliès produced over 500 films. His contemporary mastery of visual effects, multiple exposure, and cinematography made him one of the greatest filmmakers of all-time.. Movie History
The movie industry as we know it today originated in the early 19th century through a series of technological developments: the creation of photography, the discovery of the illusion of motion by combining individual still images, and the study of human and animal locomotion. The history presented here begins at the culmination of these ...
Movie poster for The Passion of Joan of Arc (1928; English-language version of La Passion de Jeanne d'Arc), directed by Carl Theodor Dreyer. history of film, also called history of the motion picture, History of cinema from the 19th century to the present. Following the invention of photography in the 1820s, attempts began to capture motion on ...
A six-part film by Al Razutis (1973-1984) 56 min. color, sound. These six essays on film/image history reconstruct cinema history by 're-imagining' its origins, and its poetries, and use historical films themselves (as 'text') to provide the meanings of their creations. Together, these film essays comprise a critical/structural ...
1286 Words. 6 Pages. Open Document. A major change that has occurred in the development of film is the linearity of narrative. The history of film spans over one hundred years ago, with classical narrative emerging in Hollywood around the nineteen thirties. The classical narrative period had a strong emphasis on linearity and coherence, where ...
The history of the movie industry dates from the early 19th century. Motion pictures or what is commonly referred to as movies developed gradually from the carnival innovation to what has developed to be among the most noteworthy forms of communication and entertainment in the modern world (Parkison, 1995). The first machine for the production ...
The first essay created in 1973 and inspired by the origins of cinema and the works (18961912) of magician- -illusionist Georges Méliès. This burning celluloid
The French New Wave created a popularization of short essay films, and German New Cinema saw a resurgence in essay films due to a broad interest in examining German history. But beyond these origins of the term, scholars deviate on what exactly constitutes an essay film and how to categorize essay films.
1940 - Hans Richter's The Film Essay. The term "essay film" was originally coined by German artist Hans Richter, who wrote in his 1940 paper, The Film Essay: "The film essay enables the filmmaker to make the 'invisible' world of thoughts and ideas visible on the screen...The essay film produces complex thought - reflections that are not necessarily bound to reality, but can also ...
Abstract: These six essays on film/image histo ry reconstruct cinema history by ' re- imagining' its origins, and its p oetries, and use historical fil ms themselves (as 'text') to provide the ...
Nora M. Alter is professor of film and media studies in the School of Theater, Film and Media Arts at Temple University. She is author of Vietnam Protest Theatre: The Television War on Stage (1996), Projecting History: German Nonfiction Cinema, 1967-2000 (2002), and Chris Marker (2006), and co-editor (with Lutz Koepnick) of Sound Matters: Essays on the Acoustics of Modern German Culture (2004).
The Essay Film Through History 6. "The Film Essay: A New Type of Documentary Film," by Hans Richter 7. "The Future of Cinema," by Alexandre Astruc 8. "Bazin on Marker," by André Bazin Part III. Contemporary Positions 9. "In Search of the Centaur: The Essay-Film," by Phillip Lopate
Transformation of Film length and story telling. Movies have greatly evolved since the 19th century, with movies now becoming longer and narrative form or story telling becoming the dominant form of movies. The evolution of movies from the cinema or motion pictures of the 19 th century to the movies of present day is such tremendous, especially ...
Nevertheless, it would have been nice if there had at least been agreement about when the essay film first appeared in film history, whether with Dziga Vertov's Man with a Movie Camera (1929), Georges Franju's Le sang des bêtes (1949) or Chris Marker's Lettre de Sibérie (1958). A filmography of the essay film would have helped readers ...
The chapter also includes a genealogical overview of important moments in the development of essay filmmaking, particularly during the 1920s and 1960s, and provides readers with short abstracts on the individual chapters and their specific transnationally inflected case studies on essay film practitioners from around the world.
The Sight & Sound Deep Focus season Thought in Action: The Art of the Essay Film runs at BFI Southbank 1-28 August 2013, with a keynote lecture by Kodwo Eshun on 1 August, a talk by writer and academic Laura Rascaroli on 27 August and a closing panel debate on 28 August. To take this film-lovers' tiff to a more elevated plane, what it ...
The Essay Film: Dialogue, Politics, Utopia includes articles by several prominent scholars that explore the essay film's place throughout history as well as within various cultural settings. Like Alter and Corrigan, they also present a convincing argument that the essay film is distinct from both documentary, avant-garde and narrative ...
Remaining in Asia, the colonial origins of the Hong Kong International Film Festival are explored in Ruby Cheung's essay. Countering established accounts of the festival's genesis and later corporatization, Cheung singles out the political forces that gave rise to it, and stresses the direct and indirect implications of the colonial ...
Godard and the Essay Film offers a history and analysis of the essay film, one of the most significant forms of intellectual filmmaking since the end of Worl... Skip to content. Search titles or authors. Books. ... Godard and the Essay Film A Form That Thinks. by Rick Warner. Imprint: Northwestern University Press. 288 Pages, 6.00 x 9.00 in, 49 ...
Of The History of The Essay Film: Vertov to Varda (2011)". Essays on the Essay Film , edited by Nora M. Alter and Timothy Corrigan, New York Chichester, West Sussex: Columbia University Press, 2017, pp. 197-226.
The Yamomami struggle. Photograph by Claudia Andujar. The source is the initiator, the origin of all things. It is the creation of life, a place where conflict arises or freedom is obtained; it is ...
Origin is an extraordinary film which is part-biopic, part-love story, but mostly a socio-political essay. It recounts the academic and personal journey of African-American author Isabel Wilkerson ...
The movie has outperformed expectations at theaters from Brownsville, Texas, to Boston, tapping into a dark set of national anxieties that took hold after the Jan. 6, 2021, storming of the Capitol.
The prosecution's case centers on the argument that Trump intended to help his campaign when he covered up a $130,000 payment to adult-film star Stormy Daniels.
The upcoming Jedi origin film, tentatively titled Star Wars: Dawn of the Jedi, could detail the ancient history of Starkiller Base.Starkiller Base was introduced in Star Wars: The Force Awakens as a major weapon in the early timeline of Star Wars' First Order.Despite being a major part of the first sequel movie, Starkiller Base received little in the way of proper exploration, contributing to ...
War films often try to overwhelm you with authenticity. Movies like "Saving Private Ryan," (1998), "Dunkirk," (2017) or this year's "Civil War" saturate viewers with the realism of ...
A year's worth of rain unleashed immense flash flooding in Dubai Tuesday as roads turned into rivers and rushing water inundated homes and businesses. Shocking video showed the tarmac of Dubai ...