Size of Government and Intervention in the Economy Essay
Introduction, size of government, intervention in the economy, reference list.
The size of the government has become a sensitive issue in the last couple of years. The debate stems from the high cost of running the government. There have been concerns that a big government adds to the wage bill and does not help in service provision (Messmore, 2007). This paper will analyze the issue of government intervention in the economy while at the same time review the essence of the big government.
The emergence of an administrative state and the question of a big government reflects the phases, which countries go through. For example, the principle of administrative states was positive for managing the economy and, at the same time, offering direction to the nation (Gregg, 2004).
On the other hand, there have been different opinions on the state of a big government and how the latter could be an obstacle towards meaningful growth. It is necessary to note that government intervention is real and should not be underestimated. The economy requires a great deal of intervention in order for various elements to function properly.
The role of government in terms of intervening in the economy cannot be underestimated. There are many issues that surround the economy and, consequently, require urgent intervention by the government. For example, the question of social security is an important aspect that should be incorporated into any economy (Russell, 1935).
Social security means that citizens would be in a position of being cushioned against hard economic times during their working years and after retirement. Thus, the government is much needed in terms of developing a comprehensive social security mechanism that addresses the needs of citizens. This shows that, at some point, the government has to intervene in running the economy.
The second merit of a legislation such as the one mentioned above is that the population develops a savings culture. For example, social security requires that every citizen contributes to a fund upon which the funds are utilized at a later date. When most people embark on such a culture, the idea of saving becomes realistic.
From an economic point of view, a nation with a savings culture makes considerable progress in the long run as compared to regions where such funds do not exist. Social security can be described from the perspective of a fund that caters for the wellbeing of citizens.
Social security programs have been described as major drivers of progressivism. For example, when social security programs are unveiled, the government is able to initiate a considerable amount of economic development (Dreier & Flacks, 2003).
Progressivism entails making the right transition in relation to economic and social reforms. In this regard, the social security fund can be viewed as a social and economic tool that bolsters aspirations of any country (Halpin & Williams, 2010). In addition, these kinds of programs are important for estimating short- and long-term outlook of the country.
Economists believe that minimal government intervention is required for raising the economic prospects. However, little as well as no government intervention is not good and would lead to disastrous consequences.
In summary, it can be mentioned that social security programs are vital in terms of enhancing economic and social development of any country. As long as social security programs are firmly in place, there is every need to believe that the welfare of the people has been taken to account. Nothing beats a strong welfare system in any country.
Dreier, P., & Flacks, D. (2003). Patriotism and progressivism. Peace Review , 15 (4), 397-404.
Gregg, S. (2004). Markets, morality, and civil society. The Intercollegiate Review , 23-30.
Halpin, J., & Williams, C.P. (2010). Progressive traditions: The progressive intellectual tradition in America . Web.
Messmore, R. (2007). A moral case against big government: How government shapes the character, vision, and virtue of citizens. Web.
Russell, B. (1935). The case for socialism . Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 20). Size of Government and Intervention in the Economy. https://ivypanda.com/essays/size-of-government-and-intervention-in-the-economy/
"Size of Government and Intervention in the Economy." IvyPanda , 20 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/size-of-government-and-intervention-in-the-economy/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Size of Government and Intervention in the Economy'. 20 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Size of Government and Intervention in the Economy." February 20, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/size-of-government-and-intervention-in-the-economy/.
1. IvyPanda . "Size of Government and Intervention in the Economy." February 20, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/size-of-government-and-intervention-in-the-economy/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Size of Government and Intervention in the Economy." February 20, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/size-of-government-and-intervention-in-the-economy/.
- Progressivism in the American Reform Period
- American Progressivism and Woodrow Wilson
- Administrative Progressivism in Relation to Online Learning
- Progressivism: Causes and Effects
- The History of Education and Progressivism
- Progressivism in American History
- The Progressive Era Significance
- Theodore Roosevelt and Contradictions of Imperialism
- Impact of philosopher to the educational process and purpose
- Progressive Ideology by President Roosevelt
- The Risks and Benefits of Outsourcing in Indonesia
- Hong Kong Economic Modernization
- India and Singapore’s Hard and Soft Infrastructure
- RMB's Depreciation Effect on the US MNCs
- Analyzing the Health Care System of Cuba
- Search Search Please fill out this field.

Why Do Governments Intervene?
- How Do Governments Respond?
The Federal Reserve System
- Achieving Financial Stability
- Government Policy FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Government & Policy
What Impact Does Economics Have on Government Policy?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Group1805-3b9f749674f0434184ef75020339bd35.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
Economic conditions often inform the policy changes that governments elect to enact. Specifically in the United States, government policy has always had a large amount of influence on economic growth, the creation of new business entities, and the success of financial markets.
In the broadest sense, a country's economic activity reflects what people, businesses, and governments want to buy and what they want to sell. Because the U.S. has a capitalist economy that relies on the principles of a free market, theoretically, it is primarily the decisions of consumers and producers that mold the economy.
Key Takeaways
- Economic conditions often inform the policy changes that governments elect to enact.
- In the U.S., government policy has always had a large amount of influence on economic growth and the creation of new business entities.
- For those in political power, having a track record of economic growth is often an important consideration (especially if they are in a position of seeking re-election).
- To ensure strong economic growth, there are two main ways that the federal government may respond to economic activity: fiscal policy and monetary policy.
- In the U.S., the Federal Reserve System directs the country's monetary policy.
The government may decide to regulate some aspects of economic activity in order to engineer economic growth or prevent negative economic conditions in the future. In general, a government's active role in responding to and influencing the economic circumstances of a country is for the purpose of preserving and furthering the economic interests of the general public.
For those in political power, having a track record of economic growth is often an important consideration (especially if they are in a position of seeking re-election). In the U.S., many studies have shown that the economy is a major factor that affects how people vote (specifically in the U.S. presidential election). Strong economic growth typically translates to high job creation, stronger wage growth, better financial market performance, and higher corporate profits.
How Do Governments Respond to Economic Activity?
To ensure strong economic growth, there are two main ways that the federal government may respond to economic activity: fiscal policy and monetary policy .
Monetary Policy
One of the most common ways that a government may attempt to influence a country's economic activities is by adjusting the cost of borrowing money. This is most often done by lowering or raising the federal funds rate , a target interest rate that impacts short-term rates on debt such as consumer loans and credit cards. The Federal Reserve increases the federal funds rate to constrict economic growth and decreases the federal funds rate to encourage economic growth.
Another form of monetary policy is the act of the Federal Reserve buying and selling government securities. When the Fed buys a security from a bank, it increases the money supply by injecting funds into that bank. Alternatively, it can sell securities to remove cash and decrease the money supply.
Monetary Policy Example
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Federal Reserve quickly reduced the federal funds rate to 0%. By setting prevailing interest rates very low, the Federal Reserve attempted to support economic activity, maximize employment, and meet price stability goals.
Fiscal Policy
The government may also enact policies that adjust spending, change tax rates, or introduce tax incentives. In regard to government budgets, the government identifies whether or not it wants to spend more money than it anticipates collecting. This process of evaluating public spending aims to promote economic prosperity or cool an overheated economy.
Instead of focusing on how the government spends money, common fiscal policy revolves around how the government collects money. Offering tax incentives, additional tax credits, or lowering tax rates decreases the economic burden on citizens and promotes economic growth. Striking down favorable tax laws or increasing taxes slows economic activity.
Fiscal Policy Example
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Federal government awarded economic impact payments (i.e. stimulus checks) to qualifying Americans. The government directly sent eligible individuals money to promote economic activity and encourage household spending.
Fiscal and monetary policies are both intended to either slow down or ramp up the speed of the economy's rate of growth. This, in turn, can impact the level of prices and the employment rate in the country. However, there are subtle differences between these two types of government action.
Differences Between Government Policies
Change in the money supply or how easy credit is to obtain
Adjustment in federal funds interest rates or money supply
Set by Central Bank
Heavily independent of the political process
Impacts debt industries like housing market
Change in how the existing monetary supply is utilized
Adjustments in government spending and tax rates
Set by Federal Government
Heavily integrated with political process
Impacts government budgets/net deficits
In the U.S., the Federal Reserve System directs the country's monetary policy. The Federal Reserve System—also called "the Fed"—is the central bank of the United States. Established in 1913 by Congress, the Fed controls the money supply and actively uses policy to respond to and influence economic conditions.
The Fed adjusts the interest rate that banks charge to borrow from one another. (This cost is then passed onto consumers.) The Fed may lower the interest rate to keep borrowing cheap, ensure that credit is widely available, and boost consumer (and business) confidence. Conversely, the Fed may decide to raise interest rates in a strong economy, or in response to inflation concerns—the increase in prices that occurs when people have more to spend than what's available to buy.
In the two ways governments can intervene in the economy, you'll note that monetary policy is set by the Federal Reserve, an independent entity technically not part of the Federal government. On the other hand, fiscal policy requires political intervention and majority approval (for items not issued by executive order by the President).
Achieving Financial Stability in the U.S. Economy
Prior to the creation of the Fed in 1913, the U.S. had experienced several severe economic disruptions as a result of massive bank failures and business bankruptcies. As an institution, the Fed was tasked with ensuring financial stability in the U.S. economy.
After the Great Depression , the greatest threat to the stability of the U.S. economy was recessionary periods: periods of slow economic growth and high unemployment rates. In combination, these two factors created a sustained period of decline in the gross domestic product (GDP). In response to this, the government increased its own spending, cut taxes (in order to encourage consumers to spend more), and increased the money supply (which also encouraged more spending).
Beginning in the 1970s, a different economic reality emerged. This expansionary economy with substantial money supply growth led to a sustained period of a high level of inflation. In response to these economic factors, the U.S. government started focusing less on combating recession and more on controlling inflation. Thus, the government enacted policies that limited government spending, reduced tax cuts, and limited growth in the money supply.
At this time, the government also shifted away from its reliance on fiscal policy—the manipulation of government revenues to influence the economy. The fiscal policy did not prove effective at addressing high levels of inflation, high levels of unemployment , and vast government deficits. Instead, the government turned to monetary policy—controlling the nation's money supply through such devices as interest rates—in order to regulate the overall pace of economic activity.
Since the 1970s, the two main goals of the Fed have been to achieve maximum employment in the U.S. and to maintain a stable inflation rate. This dual mandate is difficult to achieve; by combating one of the goals, it becomes more difficult to fight the other.
While outside events may influence economic activity, governments use economic means to enact changes as they see fit. This may include changes to tax policy, adjustments to the federal funds rate, fluctuations in the money supply, or alternations to government spending.
Should the Government Intervene in the Economy?
Whether or not the government should intervene in the economy is a deeply-rooted philosophical question. Some believe it is the government's responsibility to protect its citizens from economic hardship. Others believe the natural course of free markets and free trade will self-regulate as it is supposed to.
Why Might the Government Intervene in the Economy?
The government has an inherent interest in protecting the well-being of its citizens. Due to prevailing conditions in the world, the government might see fit to enact certain legislation to preserve the quality of life for its citizens. The government might also enact legislation to promote economic well-being and equity across different socioeconomic classes.
What Are Some Ways the Government Intervenes in the Economy?
The government has two primary ways of interacting with the economy. Through monetary policy, the government controls prevailing interest rates and makes obtaining debt easier or harder. Through fiscal policy, the government controls spending levels and how to allocate resources.
Keynesian economic theory holds that governments should hold their citizens out of a recession. Governments do this by enacting monetary and fiscal policies. By having a central bank (i.e. the Federal Reserve), the United States has the ability to manipulate economic policy in an attempt to intervene when appropriate.
U.S. Department of State. " U.S. 2022 Midterm Elections: Role of the Economy in Elections ."
Sage Publications. " Economic Perceptions and Voting Behavior in US Presidential Elections ."
Federal Reserve Board. " Monetary Policy Principles and Practice ."
Federal Reserve Board. " Federal Reserve issues FOMC statement, March 15, 2020 ."
Internal Revenue Service. " Economic Impact Payments: What You Need to Know ."
Federal Reserve Board. " What Is the Purpose of the Federal Reserve System? "
Federal Reserve History. " The Great Inflation ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-168701692-0bca0d25eb564072815026f1b2ebc2e9.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Pros and cons of government intervention
A key economic debate is the extent to which should governments intervene in the economy?
- At one extreme, free-market economists/libertarians, argue that government intervention should be limited to all but the most basic services, such as the protection of private property and the maintenance of law and order.
- At the other extreme, Marxist economists argue that the government should intervene in all areas of the economy to ensure the most efficient and equitable distribution of resources.
In between, most economists believe it is a question of balance, with the government intervening in areas where the market fails to provide a desirable outcome. Main areas of government intervention include:
- Provide public goods (e.g. national defense) from general taxation
- Provide basic health care and education standards.
- Environmental regulation and protection.
- Limit the power of monopolies.
- Regulation on worker rights.
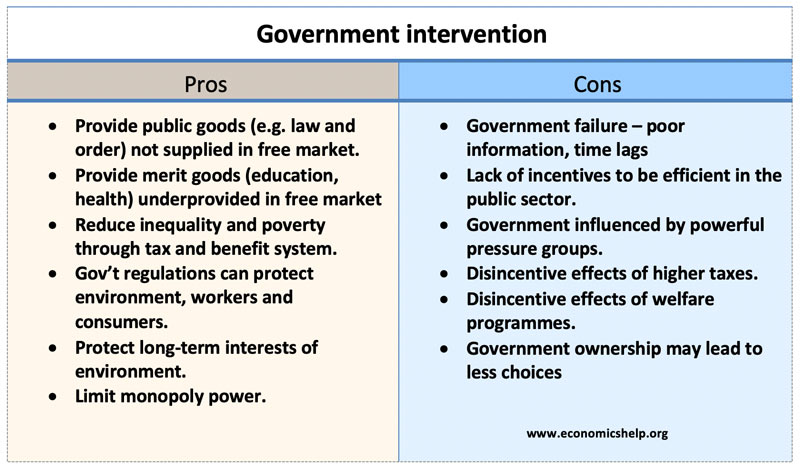
Reasons for Government intervention
- Equality . In a free market, there is likely to be significant inequality and poverty. This is not due to a meritocracy, but it could be due to unfair advantages of circumstances (inherited wealth, superior education). Governments can intervene to provide a basic security net – unemployment benefit, minimum income for those who are sick and disabled. This increases net economic welfare and enables individuals to escape the worst poverty. This government intervention can also prevent social unrest from extremes of inequality.
- Public goods . Public goods tend not to be provided in a free market because there is no financial incentive for firms to provide goods that people can enjoy for free. Governments can provide national defence, law and order and pay for it out of general taxation. Looking after the environment is also a public good, there are an increasing number of areas, where a government is needed to deal with issues such as forest fires, rising sea levels and pressure on water supplies.
- Education . Merit goods are under-consumed in free-market because people underestimate the personal benefits and/or ignore the external benefits. This leads to an underprovision of health care and education. Government intervention to provide free education can lead to a significant improvement in the quality of life for people who are educated. There are also many positive externalities to the rest of society. A well-educated society can improve labour productivity and economic growth.
- Shift consumer behaviour . The consumption of demerit goods like alcohol, tobacco and opiates can cause personal costs and significant social costs (e.g. crime). If the government identifies damaging goods, they can slowly change consumer behaviour – such as using higher tax, advertising campaigns and behavioural economics , e.g. making cigarettes difficult to buy with unappealing packets. Long-term government campaigns to reduce smoking in the UK and US have been effective in reducing smoking rates – something that has helped to increase life-expectancy.
- Environment . The environment is an area with a significant need of government intervention. The free market ignores external costs of business on the environment. It also fails to consider long-term considerations. For example, market forces may lead to the burning of fossil fuels, which cause increasing environmental problems around the world – which will get worse in the future. Given the potential costs to future generations, there needs to be government action to shift behaviour to renewable energy which doesn’t cause these environmental costs. Also, the environment involves many issues where private ownership does not apply. If pollution causes a worsening air quality, then this affects everyone on the planet, but market mechanisms do not provide an opportunity to deal with the issue. (If someone pollutes your back-garden, you can sue them. But, if air quality deteriorates, who takes action?
- Monopoly power. In a free market, firms can gain monopoly power to charge high prices to consumers and monopsony power to pay lower wages to workers. This increases inequality and deadweight welfare loss . Government intervention to limit mergers and monopoly power can lead to increased economic welfare.
- Strategic planning on infrastructure . Another limitation of the free market is to underinvest in quasi-public goods like roads and railways. This can lead to transport bottlenecks. Governments can plan for future transport trends and invest in the roads and railways which are needed for the future.
Disadvantages of government intervention
- Government failure . Government failure is a term to describe how government intervention can cause its own problems. For example, the government may take decisions for short-term political consideration which lead to an inefficient outcome. For example, government tariffs to protect domestic industry spark off a trade war, where the economy contracts.
- Lack of incentives . In the free market, individuals have a profit incentive to innovate and cut costs, but in the public sector, this incentive is not there. Therefore, it can lead to inefficient production. For example, state-owned industries have frequently been inefficient, overstaffed and produce goods not demanded by consumers.
- Political pressure groups . Milton Friedman once quipped ‘There is nothing as permanent as a temporary government bailout.’ He was referring to farming subsidies. Introduced in the 1930s during the Great Depression to alleviate a farming recession. After the Second World War, no government dared to remove subsidies because farmers were a powerful pressure group who wanted to keep the subsidies.
- Less choice . Often government intervention in the economy (e.g. nationalisation of industries) has been associated with less choice. Government produced services have a monopoly. Command economies, often had very little choice as government decided what to produce. Choice is an important element of economic freedom and being able to maximise individual welfare. (Not all government intervention leads to less choice.
- Impact of personal freedom. An increasing aspect of government intervention is through efforts to shift consumer behaviour – e.g. reduce congestion, improve health through reducing smoking rates and a healthier lifestyle. This includes taxes, behavioural influences and regulations. Sometimes people can feel this is overbearing on their individual choice.
Example of government intervention in health care
Pros of intervention.
- The government can provide universal health care so no-one dies due to lack of affordability.
- Universal government health care is fair.
- Health care is considered a human right and intrinsic to good quality of life
- Better health care can improve long-term labour productivity as workers with better health can work for longer and take less time off due to sickness.
- Government health care can prevent the stress and costs of going bankrupt from medical bills. In the US where the private sector has large role, unexpected medical bills cause bankruptcy. (66% of bankruptcy-related to health costs – CNBC )
- Economies of scale in government provision. The government can bulk buy medicines, supplies and also offer specialised services.
- The government can provide medicines at cost rather than for the inflated prices of the private sector.
- The government can ration health care to where it is actually needed and helpful. Under a system of private insurance where someone else is paying, millions may be spent on treatments with only very marginal improvements on the quality of life. Government health care has to use resources where it is needed. The private sector may push treatments like plastic surgery which are of doubtful value.
- It is argued the private sector have a profit incentive to cut costs and be more efficient. However, in health care, this is not the case. Doctors and nurses are not motivated like profit as in other sectors. Cutting costs may involve cutting the quality of care.
- If firms don’t have to provide private health care costs, it will reduce the costs of employing workers.
Cons of intervention
- Government provision may reduce the choice of individuals who prefer to choose their private insurers and doctor.
- The private sector may have profit incentives to cut costs and offer innovative new treatments that would be desired.
- With government provision, services may be limited by tax revenue. It is more likely that services will be rationed leading to longer waiting lists and some treatments not available.
- Government health care will require higher tax. Higher income tax may lead to lower incentives to work (though whilst taxes will rise, health insurance costs will be lower.)
- Government Intervention in Markets
- Market Failure
11 thoughts on “Pros and cons of government intervention”
Can I get the possible effects of a government intervening in the labour Market by imposing a minimum wage
thank you very much🙏🏽🙏🏽
Thank you I appreciate🙏🙏🙏🙏
Really helpful with my Foundations economic studies. Recommend for my other colleague to use it too.
Thank you Gurame
Very helpful. Thank you for providing me with this useful information that I needed for my economics class. Much appreciated.
Thank you so much, this article was well put together, and I appreciate the step by step, easy to understand format. Have a good one.
“GOVERNMENT” Should not get invoked with the poor! Governments requires numerous hundred thousand dollar a year employees and pension and health benefits forever, for people working w/ an gov-Agency! Give it to the Salvation Army & charity groups!!
Comments are closed.
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Emotions
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Culture
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Law and Politics
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Oncology
- Medical Toxicology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Games
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business History
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Methodology
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Theory
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >
9 Government Intervention in the Economy
Author Webpage
- Published: September 1998
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Discusses the attitudes of Western European publics towards economic liberalism and economic interventionism during the past few decades. While beliefs about the desirability of state intervention in the economy, and of state ownership of public assets are central to modern political ideologies, there is scant evidence that interventionism and liberalism constitute opposite positions in the public mind. Questions of whether governments should practice economic interventionism, or whether assets should be removed into government ownership, tend to be answered not in terms of philosophical principle, but in terms of whether the government is felt to be worthy of the powers entrusted to it. Interventionism tends to be supported by those who lose out under laissez‐faire economies, by women, by young people, and by old people. These tendencies can be explained by the fact that, on the whole, it is middle‐aged men who tend to profit most from the liberal capitalist system.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
- Google Scholar Indexing
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
Better Knowledge. Your Insight Is Sharper
Government Intervention: Examples, Reasons, and Impacts
Updated on April 10, 2022 by Ahmad Nasrudin

What’s it : Government intervention refers to the government’s deliberate actions to influence resource allocation and market mechanisms. It can take many forms, from regulations, taxes, subsidies, to monetary and fiscal policy. In some cases, the government also sets maximum and minimum price limits on the market.
Government intervention and the economic system
Broadly speaking, the significance of the intervention depends on the economic system adopted by a country.
Under a command economy system , government intervention is highly significant. The government determines what is best for the economy and society. It allocates resources and determines the production and distribution of goods.
The private sector’s role is minimal or even zero. Under a command economy system, the market mechanism does not work.
In contrast, a free-market economy operates in reverse compared to a command economy. The free market system emphasizes the minimization of intervention. The private sector plays a significant in the allocation of economic resources.
The market operates freely through a supply and demand mechanism. This mechanism directs the allocation of resources more efficiently than the command economy system. Under this system, the government’s role is usually limited to enforcing rules to recognize and protect private property ownership.
Furthermore, under a mixed economy system , interventions are more diverse than in a market economy, but not as extreme as a command economy. The government has a role, and so does the private sector.
The significance of the roles of the government and the private sector also varies between countries. Some countries, such as China and Cuba, are more inclined towards a command economy. The government plays a significant role. Meanwhile, in countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom, the private sector plays a more dominant role in managing economic resources.
Reasons for government intervention in the economy
The government intervenes in the economy with several objectives, such as:
Redistributing income and wealth. For example, the government launched various welfare programs such as unemployment insurance, health, and free education. It sustains the quality of life of those who are economically disadvantaged. Taxation is also another avenue for redistribution of income.
Providing public goods . Examples of public goods are public parks, infrastructure, and national defense. The private sector often does not want to provide it because it is unprofitable. Hence, the government took a role.
Promoting fair competition . Through antimonopoly regulations, the government prevents unfair competition practices such as collusion and predatory pricing.
Securing and spurring the domestic economy. For example, the government set trade barriers to protect domestic industries from competing imported products. So, they continue to grow and create more jobs.
Protecting people . For example, the government launched a consumer protection policy, quality requirements, occupational safety, and the environment.
Changing consumer behavior . Intervention is one way to reduce the impact of negative externalities. For example, the government could increase taxes on products such as alcoholic beverages and tobacco.
Preserving the environment . Without government regulations and policies, companies are more likely to ignore external costs to the environment. They overexploit natural resources or allow waste to flow into the environment without further treatment. Such practices certainly jeopardize the long-term sustainability of the economy.
Achieving macroeconomic goals. The four macroeconomic goals are sustainable economic growth, full employment, low inflation, and balance of payments equilibrium.
Ways of government intervention
Government intervention takes many forms, from the micro to the macro level. In this article, I try to group them into the following categories:
Economic policy
Regulations, price controls.
The economic policy falls into two main categories:
Supply-side policy
- Demand-side policy
The government designs supply-side policies to influence aggregate supply in the economy. Typically, these policies focus on increasing production efficiency, either in product markets or factor markets (e.g., labor market).
In the product market, the government promotes competition by launching antimonopoly, deregulation , and privatization policies. Competition forces producers to be more efficient and innovative to stay in the market and make a profit.
Furthermore, in the labor market, the government is trying to improve labor mobility and quality. That is through various programs such as education, training, and reduction of union power.
Demand-side policies
Demand-side policies consist of fiscal policy and monetary policy. The government is responsible for the fiscal policy through changes in its spending and taxes. Meanwhile, monetary policy is under the responsibility of the central bank or monetary authority. It seeks to influence the money supply in the economy. Both affect the economy through their effect on aggregate demand.
To stimulate economic growth, the government and the central bank adopted expansionary policies. That is usually during a weak economy, such as an economic recession. The options are to:
- Increase government spending
- Lower taxes
- Cut policy rates
- Open market operations through central bank purchases of government securities
- Lower the reserve requirement ratio
Meanwhile, to avoid high inflationary pressure, both implement a contractionary policy. High inflation endangers economic stability and can lead to hyperinflation. Among the options for implementing a contractionary policy are:
- Reducing government spending
- Lifting taxes
- Raising the policy rate
- Open market operations by selling government securities
- Raising the reserve requirement ratio
The government ensures that economic activities run healthily. Several regulations aim to encourage business activity. While others, to control business activities and avoid unwanted results or negative externalities.
There are many variations of government regulations, and each affects economic activity in different ways. The following are several categories of government regulations:
Employment . The government issues rules, regulations, and laws regarding wages, fair recruitment, and workforce health and safety.
Environment . For example, the government launches various regulations regarding the environmental impact of company operations on the surrounding environment, such as environmental safety standards and waste management.
Consumer protection . The focus is to protect consumers from unfair practices related to price rules, health and safety standards, and product descriptions.
Competition . It is in the government’s interest to promote fair competition. These types of rules and regulations include antitrust and merger and takeover regulations. This category includes deregulation, namely eliminating regulations or restrictions such as limits on foreign investors’ share ownership.
Information and reporting . An example of these rules and regulations are accounting standards and the security of consumers’ personal information.
Taxes are the main source of government revenue. The government uses it to finance several programs and to pay off debts. In addition to government operations, the government uses taxes to increase economic capital by providing public goods such as roads, bridges, trains, public parks, and national defense. This economic capital is vital for increasing the production capacity of the economy in the long run.
The government collects taxes from taxpayers, which come from the household and business sectors. The government can impose it directly on taxpayers, such as through income tax and profit tax. Or, it is indirectly as in sales tax and value-added tax.
Tax is a means of redistribution of income. Also, taxes affect the financial behavior of businesses and households. For example, an increase in taxes reduces household disposable income . Therefore, households tend to spend less on goods and services.
Under a price control policy, the government sets price limits for certain goods and services. The two forms of price control are:
Price ceiling
Price floor.
Price ceilings limit the maximum prices for goods and services. Suppliers cannot charge a price higher than that price. The purpose of a price ceiling is to protect consumers by ensuring it is affordable to as many consumers as possible. An example is the rental price of residential property.
To be effective, the government sets a price ceiling below the free-market equilibrium price.
Setting a price ceiling has the following implications:
Bringing up the shortage . Due to lower prices, more consumers are asking for it. Conversely, lower prices make fewer producers willing to supply. Therefore, the market will experience excess demand (shortage), where the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied.
Less efficient and decreasing economic surplus. Economic surplus is the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus. Due to lower prices, the producer surplus will decrease. They get less profit. Meanwhile, even though consumers get lower prices, however, they face a shortage. Supply decreases because producers supply fewer goods.
Rationing . Because of the shortage, consumers have a more challenging time finding goods. Suppose it goes on for a long time. In that case, the government may need to ration goods to ensure their availability for as many consumers as possible.
Raising a black market. The black market thrives on shortages. The producer may sell at a higher than the ceiling on the black market. Likewise, some consumers who already own goods will sell back to other consumers at a higher price to profit.
It is the minimum price that can be charged for a good or service. Its purpose is to protect suppliers of goods or services.
The most quoted example of a price floor is the minimum wage. In this case, individuals act as suppliers of labor services, while companies are buyers. With the minimum wage, workers make enough money from their jobs to meet their basic needs.
To be effective, the government sets the price floor above the equilibrium price. Because prices are higher, more and more suppliers are willing to supply goods and services. On the other hand, the quantity demanded is less because the price becomes more expensive for consumers. As a result, the market will experience an excess supply, where the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded.
The government also provides subsidies to households or companies. Examples include fuel oil, public health care, education, research and development, fertilizers, and raw materials subsidies. Soft loans also fall into this category.
The provision of subsidies reduces the burden on households. They spend less money on these goods and services, enabling a better standard of living.
For companies, subsidies reduce production costs. It stimulates them to produce more. Also, they can sell at a lower price, making the product more competitive in the market.
Disagreements among economists
Some economists view government intervention as necessary. However, they are still arguing about how much the government should intervene and how they should intervene. In macroeconomics, both gave rise to schools of thought: Keynesian economics and Neoclassical economics.
Keynesian views that the government should intervene. When there is a disequilibrium, the economy will not move towards the new equilibrium by itself.
Take the case when the economy is depressed. Among the solutions to getting out of the economic depression is stimulating government spending, which is a part of aggregate demand.
As we know, aggregate demand consists of household consumption, business investment , government spending, and net exports. Net exports are beyond the control of the domestic economy because they depend on global economic conditions. Thus, the main options for stimulating aggregate demand are through consumption, investment, and government spending.
But, during the economic depression, business profits worsen as demand falls. Likewise, household income drops due to high levels of unemployment. Therefore, it is almost impossible to increase consumption and investment during the depression.
Thus, a more sensible option would be to increase government spending. The budget depends more on discretionary government policies than on economic conditions.
In contrast, Neoclassical economists view government intervention should be minimal. The market mechanism will work and direct the economy towards equilibrium. According to Neoclassical economists, supply and demand are the main factors that determine goods, output, and income in an economy. So, government intervention will only make the economy no better.
Negative effects of government intervention
Although the aim is positive to build the economy and society’s prosperity, interventions often result in unintended consequences. The following are the opposing sides of government intervention in the economy:
Government failure . It happens when the intervention doesn’t produce better results. The market becomes inefficient in allocating resources. The government may also consider short-term effects rather than the long-term. For example, trade barriers protect domestic industries. But, it also disincentives producers to be more innovative and more efficient. Likewise, in the case of production subsidies.
Increased costs . For example, companies have to spend more money to meet product safety and health standards. They also bear the cost of further processing the production waste.
Fewer options . In an extreme case is the command economy. The government decides what to produce and how to distribute it.
Discrimination policy. Intervention may be beneficial for some, but detrimental for others. Take competition policy, for example. The government may favor state-owned companies over private companies. Likewise, in a bailout, the government used tax revenues to save the big banks instead of all the banks.
5 NEW ARTICLES

Private Savings: Formula and Explanation
What's it: Private savings equal to the sum of household and business savings. And savings

How to Handle and Resolve Stakeholder Conflicts
Stakeholders have different interests and goals, which are often contradictory. Stakeholder

Where Do Comparative Advantages Come From?
The comparative advantage stems from the ability to produce goods and services at low opportunity

What are the Benefits of International Trade?
Increased access to cheaper and more varied goods and services is key benefits of international

What is the Capital Budgeting Process?
In simple terms, the capital budgeting process involves generating ideas, making proposals about
5 TRENDING ARTICLES
- Small Business: Characteristics, Importance, Disadvantages
- Why is the Business Environment Important? What are the Factors?
- Business Size: Definition, Measurement, Classification
- What Are the Effects of Industrialization? [Positive and Negative Impacts]
- Shamrock Organization: How it Works, Advantages and Disadvantages
EXPLORE MORE

Thursday, May 10, 2007
Government intervention in the macro economy..
- Supply Side Policies.
- Interventionist . Government intervention to overcome market failure. For example, spending on education and training to reduce occupational immobilities.
- Market Oriented supply side polices : This occurs when the government reduces regulations and enables market to work more freely. For example, reducing the power of trades unions and minimum wages can reduce labour market inflexibility's.
- They will take a long time, e.g. increasing education standards.
- May be subject to government failure. e.g. spending on education misplaced.
- Promoting free markets may increase inequality. E.g. removing trades unions may lead to worker exploitation.
- Supply side policies UK
- Fiscal Policy - changing the level of government spending and taxation in the economy. It will effect the government's budget and fiscal position.
- Monetary Policy - Influencing the supply and demand for money. In the UK monetary policy revolves around changing interest rates, which are set by the MPC (Bank of England).
- The government could pursue deflationary fiscal policy. This involves increasing tax rate and / or cutting spending.
- The MPC could increase interest rates. This is known as a tightening of monetary policy. Note, in the UK the government no longer sets monetary policy, the Bof E is independent.
- Government can introduce Expansionary Fiscal Policy. This involves cutting taxes and / or increasing spending, AD should increase.
- The MPC can cut interest rates.
- It is difficult to control predict future economic trends, therefore, it can be difficult to know how much to change tax rates / interest rates.
- Time Lags, Interest rates can take upto 18 months to have an effects.
- Crowding out. Expansionary fiscal policy may increase government spending, but, reduce private sector spending.
- Depends on Confidence. For example, a cut in income tax may not increase AD, if confidence is low.
Post a Comment
Final dates! Join the tutor2u subject teams in London for a day of exam technique and revision at the cinema. Learn more →
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Economics news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Economics Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
Government Intervention
Government intervention is regulatory action taken by government that seek to change the decisions made by individuals, groups and organisations about social and economic matters.
Government intervention is any action carried out by the government that affects the market with the objective of changing the free market equilibrium / outcome.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
Edexcel A-Level Economics (A) Theme 1 Knowledge Organiser
Exam Support

In the News Teaching Activity – growing obesity and its health costs (Mar 2024)
7th March 2024
In the News Teaching Activity – will the government’s latest dental policies get to the root of the NHS dentist shortage problem? (Feb 2024)
15th February 2024
In the News Teaching Activity – Lack of competition in the baby milk formula market is adding to the cost-of-living crisis (Dec 2023)
4th December 2023

Government Intervention - Australia Bans Imported Disposable Vapes
28th November 2023
Is the sugar tax cutting teeth extractions among the young?
17th November 2023
Government Intervention - Price paid for UK offshore power to rise by 66%
16th November 2023
4.1.8.9 Government Intervention - Maximum Prices (AQA A-Level Economics Teaching PowerPoint)
Teaching PowerPoints
4.1.8.9 Government Intervention - Minimum Prices (AQA A-Level Economics Teaching PowerPoint)
Market failure and government failure: could a tax curb meat’s health and environmental problems.
Study Notes
1.4.1 Maximum Prices (Edexcel A-Level Economics Teaching PowerPoint)
1.4.1 minimum prices (edexcel a-level economics teaching powerpoint), 1.4.1 government intervention in markets (edexcel), 1.1.6 free market economies, mixed economy and command economy, 1.3.2 externalities and government intervention (edexcel a-level economics teaching powerpoint), in the news teaching activity: vaping and negative externalities (sept 2023).
11th September 2023

Government Intervention - Is it Time for a Meat Tax?
France to spend €200m on destroying excess wine as demand falls.
27th August 2023
What are unintended consequences in economics?
What are economic incentives and why are they important, government intervention - evaluating uk steel subsidies.
Topic Videos
Revision Session on Government Intervention
3rd May 2023
De-Merit Goods - Australia to ban recreational vaping
Norway's salmon tax - a leap towards sustainability.
4th April 2023
De-merit goods - should the government toughen gambling laws?
29th March 2023
Economic Development - Do Buffer Stocks Work?
Market failure and government intervention - the row over london’s ultra-low emission zone.
7th March 2023
Can buffer stock schemes help to promote economic growth and development in low income countries?
Should home insulation in the uk be subsidised.
16th February 2023
Government Intervention - What is a Pigouvian Tax?
Significance of ped with indirect taxes, uk bus price cap scheme is extended.
19th December 2022
New Zealand legislates to ban cigarettes for future generations
15th December 2022
Bus fares in England to be capped at £2 per journey for 3 months
3rd September 2022

Shifts in Demand and Supply - Fish and Chip Shops Facing Closure
24th August 2022
Energy Price Crisis - Is there a case for government subsidy of energy intensive industries?
14th August 2022
Plastic packaging disposal tops 100 billion pieces a year in the UK
13th July 2022
Unintended Consequences - The Impact of a Minimum Price on Alcohol
10th June 2022

Plans to raise the minimum legal age for smoking to 21 years
8th June 2022
2022 Exams - Policies to Reduce Negative Production Externalities
Evaluating government intervention, government intervention - economics of carbon taxes, key diagrams - producer subsidies (supply and demand analysis), key diagrams - producer subsidies (cost and revenue analysis), government intervention - analysis diagram for a specific tax, evaluating government intervention.
18th April 2018
Government intervention - Paris announces car ban for central districts
23rd February 2022
Plastic Packaging Tax (Revision Essay Plan)
Welfare loss from indirect taxes, sugar tax (student essay).
Practice Exam Questions
UK government offers consumer subsidy for heat pumps
19th October 2021
Free Markets
Teaching activity: introduction to economics (gcse).
Teaching Activities
Maximum prices - Why rent control isn’t working in Sweden
27th August 2021
Pigouvian Taxes - Beyond Meat boss backs tax on meat consumption
3rd August 2021
Education economics - should government intervene to mandate lower tuition fees for local students?
22nd July 2021
Vodafone fined for breaches of consumer protection rules
26th October 2016
Smog and the Clean Air Act
27th November 2016
Ban on online junk food ads for kids
8th December 2016
Finland aims to be tobacco free by 2040
28th January 2017
State Intervention – Growth and Development
Market failure & government intervention (revision presentation), privatisation, stakeholders (government intervention), fiscal policy - government intervention, government intervention - maximum prices, government intervention - indirect taxes, government intervention - buffer stock schemes, government failure (revision presentation), as micro multiple choice: subsidies for social housing, revision presentation on government failure, producer subsidies, pollution taxes and negative externalities, minimum wages - analysis of impact (labour markets), maximum prices - analysis, evaluating government intervention in markets, maximum prices - 2021 revision update, government intervention: could new legislation change uk betting firms for good.
1st February 2021
Minimum Prices - 2021 Revision Update
Indirect taxes and producer surplus, subsidies - 2021 revision update, regulating emissions: should ads for large polluting vehicles be banned.
6th August 2020
Changes in Demand - Match Up Activity
Quizzes & Activities
Competition policy - an investigation into government intervention to promote competition in markets [Year 12]
17th June 2020
Gambling and Behavioural Economics [Head Start in A-Level Economics]
Government failure (online lesson).
Online Lessons
Government Failure: Would a junk food tax cause government failure
Introduction to supply side policies (online lesson), sugar (soda) taxes (government intervention).

Should the sugar tax be scrapped?
16th July 2019
Paper 1 Micro: Top Revision Videos on Market Failure and Government Intervention
Us imposes ban on flavoured e-cigarettes.
3rd January 2020
Market Failure and Government Intervention - Clear The Deck Key Term Knowledge Activity
Chinese government rations pork and sets maximum prices.
12th November 2019
Scottish minimum alcohol price reduces demand
26th September 2019
Spare ribs? China to tap pork reserves as swine fever hits industry
19th September 2019
Scottish alcohol sales drop after minimum price intervention
21st June 2019
Market for Electric Vehicles (Revision Essay Plan)
Key micro diagrams (government intervention), test 3 - edge in economics revision mc - government intervention, indirect taxes (government intervention), producer subsidies (government intervention), synoptic economics revision - solar energy policy, energy price cap - analysis and evaluation arguments, economics of a latte levy - kaa and evaluation paragraphs, rent controls - analysis and evaluation points, producer support in markets, plastic bottle tax (chain of analysis), should the uk rail industry be nationalised, edexcel theme 3 micro knowledge book - government intervention, uk plastic bag charge set to be doubled to 10p.
27th December 2018
Chief Medical Officer calls for extended sugar and salt bans
21st December 2018
Minimum Alcohol Pricing (Revision Essay Plan)
Micro and macro effects of an executive pay cap (labour markets), government intervention in markets (quizlet activity), government floats ban on energy drinks for under-18s.
30th August 2018
What is the most convenient way to provide the public loo?
15th August 2018
Government Intervention - Subsidies
Buffer stock schemes (government intervention), minimum wage and living wage (government intervention), maximum prices (government intervention), government intervention - minimum prices, regulations (government intervention), government failure, negative externalities and government intervention, analysing and evaluating government intervention in markets, building confidence in writing synoptic 25 mark essays (edexcel), department of awesome evaluation (updated: june 2018), edge revision webinar: market failure and government intervention, test 18: a level economics: mcq revision on indirect taxes and subsidies, policies to improve food affordability (revision essay plan), misguided sugar tax unlikely to be effective in tackling obesity.
12th April 2018
Minimum Alcohol Prices (Government Intervention)
Test 1: a level economics: mcq revision on market failure and government intervention, taxing de-merit goods (chain of analysis), economics of health care funding, congestion in uk cities - 'ranking activity'.
6th February 2018
Privatisation and Regulation - FT series of articles
24th January 2018
Credit card surcharge bans and government failure
18th January 2018
UK bans microbeads
9th January 2018
Using the negative externalities of plastic as practice of exam technique
10th December 2017
Pay-per-mile scheme considered for non-British lorries
30th December 2017
Elasticity of Demand in Action: Sugary Drink Demand and Higher Prices
17th October 2017
Evaluating the pub smoking ban
1st October 2017
France makes childhood vaccinations compulsory
9th August 2017
10 Years on from the Smoking Ban
2nd July 2017
Microeconomics diagram in your pocket
4th June 2017
Indirect Taxes and Economic Welfare (MCQ Revision Questions)
Positive externalities from breakfast clubs.
10th April 2017
Further intervention suggested in Fixed Odds Betting Terminal market
31st January 2017
Intervention in Markets - Will the legal highs ban work?
31st May 2016
Growth and Governments
26th May 2016
New cigarette packaging regulations comes in to force today
20th May 2016
Bacon sandwich with sugar, anyone?
27th October 2015
Jamie Oliver calls for Sugar Tax on Soft Drinks
20th October 2015
US sugar tax effectiveness questioned
27th August 2015
Resources on the Sugar Tax
20th March 2016
Economics for the Breaking Bad Generation
16th March 2016
The Bots Are Taking Over!
24th February 2016
Market Failure and Behavioural Policies - Research Assignment
7th February 2016
HS2 to arrive early - in Crewe?
30th November 2015
IPencil and the Rise of Activist Laizzez-Faire
25th November 2015
Scotland introduces a minimum charge for plastic bags
21st October 2014
Plain packaging for cigarettes
17th February 2015
CMA targets pay day lenders and comparison websites
24th February 2015
The Invisible Hand of the Ticket Tout
1st March 2015
Building the Entrepreneurial State
2nd April 2015
Climate Change Coal and Intervention
30th May 2015
Climate Change, coal, and Government and Business Intervention
Wearable tech - the new 'merit good'.
19th August 2015
Scottish Minimum Price for Alcohol Faces Delay
3rd September 2015

The Irish potato famine - classic demand and supply
22nd September 2015
UK Steelmakers seek government help
24th September 2015
Tobacco tax increase is urged
12th October 2015
Our subjects
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.
- How It Works
- Topic Generator
- United States
- View all categories

Essay Sample on Government Intervention in the Economy
Introduction.
Government intervention in the economy is essential as it determines and improves the outcomes in the free market to prevent unsustainable growth. Government intervention helps address issues such as environmental preservation, reallocation of resources, distribution and redistribution of income, and stabilization of the economy. The government also intervenes to resolve social problems such as unemployment and maintain an acceptable standard of living. While some proponents insist on the ideologies of communism and government intervention, others think that the government should limit its role and power in the economy as it presents unnecessary infringement of freedom. This essay, therefore, seeks to give an in-depth analysis of the proponents and opponents' argument for government intervention in the economy.
Is your time best spent reading someone else’s essay? Get a 100% original essay FROM A CERTIFIED WRITER!
Proponents of Government Intervention in the Economy
The clayton antitrust act.
The first proponent of government intervention in the economy is the Clayton Antitrust Act, an amendment that was passed by the United States Congress in 1914. The Clayton Antitrust Act focuses on various topics such as price fixing, price discrimination, and unfair business practices. The Act was enacted to regulate the big corporations that used price fixing tactics and anti-competitive mergers to dominate the markets, and section 2 of the Act provides "That it shall be unlawful for any person engaged in commerce, in the course of such commerce, either directly or indirectly to discriminate in price between different purchasers of commodities...."
The Act further declared actions such as boycotts, peaceful strikes, agricultural cooperatives, picketing and labor unions as legal according to the federal law. The Act prohibited local price cutting and exclusive sales. Section 4 of the Act gives the right to any individual who institutes a private lawsuit claiming that he is injured by an act that is against the antitrust laws. Section 7 of the Act provides for adequate guidelines for mergers and acquisitions of companies.
President Franklin D. Roosevelt Says Government Must Act, 1933
The second proponent of government intervention in the economy is President Franklin D. Roosevelt. President Franklin Roosevelt in his inaugural speech tried to assess the damage caused to the economy and proposed changes to improve the economy of the country. The President in his statement noted that "Values have shrunken to fantastic levels; taxes have risen; our ability to pay has fallen; government of all kinds is faced by serious curtailment of income; the means of exchange are frozen in the currents of trade..."
President Roosevelt proposed a New Deal that would reshape the economy's structure of the country by employing and giving financial security to the citizens. President Roosevelt was determined to end the great depression that had caused the collapse of stock markets. His speech gave people a sense of optimism and hopes to fight for his program the New Deal, and in part states that "The only thing we have to fear is fear itself." The New Deal was to introduce reforms in the social and economic spheres. The speech emphasized the need for regulations aimed at resolving the country's economic and social problems. President Roosevelt believed that the federal government had the power to get the country out of its depression by implementing work relief programs, emergency relief programs, banking reform programs, and agricultural programs. His speech also emphasized the need for the Social Security Act, union protection programs and programs that would help the migrant workers and farmers.
Opponents of Government Intervention in the Economy
President herbert hoover applauds limited government, 1931.
President Herbert Hoover believed in Limited Government intervention in the economy, and his limited response did not help the Americans during the struggle of the great depression. The Americans needed government intervention, but President Herbert Hoover's philosophy denied the Americans government aid. He instead appealed for the spirit of volunteerism, asking the Americans to try and believe in individualism and begged the businesses entities to retain their workers. This philosophy of limited government only drove the economy into economic turmoil. President Hoover believed in individualism citing that hard work pays and that the citizens could overcome hardships, and therefore refused to give government handouts to the people.
President Hoover thought that government aid destroys character and initiative of the American people. The president refrained from implementing regulations economic activities such as the stock markets. President Hoover initiated charity events urging wealthy people to donate to the poor and helped the state and private relief agencies alienate poverty, but his efforts were not sufficient to eradicate the widespread poverty and the economic turmoil. According to President Hoover, economic struggles were meant to test their character and courage, and the Americans were supposed to maintain the ideals of the American system and come out stronger in character, faith, and courage.
The Supreme Court Accepts Limits on Working Women's Hours: Muller v. Oregon, 1908
The Supreme Court verdict in the case of Muller v. Oregon can be quoted as the other opponent of intervention in the economy because the case upheld a law that limits the workday for the female wage to only ten hours. The case expanded the state's involvement in the sector of protective labor legislation. This case emphasized its decision basing its logic on the medical and social explanations that there is need to protect the female gender because overworking them is harmful to their health. The court agreed and claimed that females are the mothers of society, and this gave the government access to implement laws that regulate the workplace by gender. This intervention by the government denied women the same privileges and rights as other fellow citizens to bargain in the market and contract without restrictions. The Supreme Court decision laid disability on women by applauding the limits on working women's hours.
This essay has identified some of the proponents and opponents of government intervention and the importance of intervention that enhances sustainable growth. From the proponent's view such as the Clayton Antitrust Act, government intervention helps regulate price fixing, price discrimination, and unfair business practices. The Act was enacted to impose regulations on big corporations that used price fixing tactics and anti-competitive mergers to dominate the markets. Another proponent is President Franklin Roosevelt, and in his inaugural speech, he tried to assess the damage caused to the economy and proposed changes to improve the economy of the country. On the other hand, there are those who oppose Government intervention such as President Herbert Hoover who believed in limited government, and appealed for individualism and in return led to the widespread poverty and economic turmoil. Other opponents include the Supreme Court decision in the case of Muller v. Oregon that denied women the same privileges and rights as other fellow citizens to bargain in the market and contract without restrictions. From the above arguments, it is safe to conclude that government intervention is essential in the economy.
Bibliography
Norton, Mary Beth, Jane Kamensky, Carol Sheriff, David W. Blight, and Howard Chudacoff. A People and a Nation, Volume II: Since 1865. Boston: Cengage Learning, 2014.
Cite this page
Essay Sample on Government Intervention in the Economy. (2022, Dec 14). Retrieved from https://proessays.net/essays/essay-sample-on-government-intervention-in-the-economy
so we do not vouch for their quality
If you are the original author of this essay and no longer wish to have it published on the ProEssays website, please click below to request its removal:
- Paper Sample on Global Financial System
- Research Paper on Age Discrimination in Employment
- Gifted Education in Australia Essay
- Paper Example on Intelligence Community
- Essay Sample on The Role of U.S Government on Economy in Employment
- Essay Example on Ronald Reagan's 1966 Campaign: Innovative Politics of the Future
- Employee Benefits: Job Satisfaction & Employee Loyalty - Essay Sample
Liked this essay sample but need an original one?
Hire a professional with VAST experience and 25% off!
24/7 online support
NO plagiarism
Submit your request
Sorry, but it's not possible to copy the text due to security reasons.
Would you like to get this essay by email?
Interested in this essay?
Get it now!
Unfortunately, you can’t copy samples. Solve your problem differently! Provide your email for sample delivery
You agree to receive our emails and consent to our Terms & Conditions
Sample is in your inbox
Avoid editing or writing from scratch! Order original essay online with 25% off. Delivery in 6+ hours!
Hungary to consider fuel price intervention, says economy minister
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Anita Komuves and Gergely Szakacs Editing by David Goodman
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

China Q1 industrial profits' growth pace stirs doubts about economic recovery
China's industrial profits fell in March and slowed gains for the quarter compared to the first two months, official data showed on Saturday, raising doubts about the strength of a recovery for the world's second-biggest economy.

We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Government intervention on the economic outcome. In my opinion, government interventions have an overall positive effect. First, it allows for redistribution of wealth, leading to greater equality. The free market systems are inherently unequal in terms of income and opportunity since privilege largely determines the possibility of creating value.
This thesis is a collection of three essays on economic growth, and development. The theme of our inquiry is the role of government intervention in defining the pace, and character of economic growth in the distant future. The analysis in the entire volume is undertaken at purely theoretical level. We proceed with a general summary of the three
The main purpose of this paper is to address the government intervention in the economy. It is considered the founder of modern economics. Adam Smith stated that the free market is guided by an ...
The role of government in terms of intervening in the economy cannot be underestimated. There are many issues that surround the economy and, consequently, require urgent intervention by the government. For example, the question of social security is an important aspect that should be incorporated into any economy (Russell, 1935).
Differences Between Government Policies. Monetary Policy. Change in the money supply or how easy credit is to obtain. Adjustment in federal funds interest rates or money supply. Set by Central ...
This leads to an underprovision of health care and education. Government intervention to provide free education can lead to a significant improvement in the quality of life for people who are educated. There are also many positive externalities to the rest of society. A well-educated society can improve labour productivity and economic growth.
Support for government management of the economy increased between 1979 and 1981, when the energy crisis threatened living standards in most Western countries (Figure 9.5 ). This accords with our working hypothesis, as it suggests that demands for government intervention thrive on failures of the capitalist economy.
The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted a vast spectrum of unprecedented government interventions. This column discusses the impact of various interventions on COVID-19 transmission dynamics and the associated economic consequences. Examining the variation in government policies, it finds that policies such as lockdown, school closure, centralised quarantine and mask wearing are effective in ...
The governments' intervention in the economy impacts technological performance and sustainability. This role has become even more critical due to the COVID-19 situation and in the context of the continuous increase in resource consumption, which requires finding alternative solutions. We provide a comprehensive literature review about the state's economic functions, redistribution of ...
Learn about government intervention in the economy. Discover reasons, types, and examples of government intervention, and consider the positive and negative impacts. Updated: 11/21/2023 ...
Under a command economy system, government intervention is highly significant. The government determines what is best for the economy and society. It allocates resources and determines the production and distribution of goods. The private sector's role is minimal or even zero. Under a command economy system, the market mechanism does not work.
The government intervenes in the macro economy in various ways including demand and supply side policies. Macro Economics Objectives of the government include: 1. Low Unemployment. 2. High but sustainable economic growth. 3. Low Inflation (inflation target in UK CPI = 2%) 4.
special circumstances under which such intervention is not needed. It then looks briefly at the numerous ways that intervention might be justified, and how. All this is done first in the context of a closed economy. Section III then opens the economy up to international trade, asking how the closed-economy reasoning can be extended and what to ...
Government Intervention in Economic Welfare Essay. In pure market economy, price has been set by price mechanism where it coordinates the interaction between demand and supply resulting in a price changes. According to an economist Adam Smith (1776), in his book "The Wealth of Nations", price mechanism is likened to be an "invisible hand ...
12th October 2015. Government intervention is regulatory action taken by government that seek to change the decisions made by individuals, groups and organisations about social and economic matters.Government intervention is any action carried out by the government that affects the market with the objective of changing the free market ...
Most reasons for government to intervene in the economy can be categorized in three ways - correction of market failure; non-economic objectives; and redistribution of income. First, we will look at how government intervention to correct market failure. Market failure occurs when the allocation of goods and services in a free market do not ...
The Role of Government Intervention in the Economy The economy is a complex system that requires careful management in order to function efficiently. While the market forces of supply and demand are essential to the functioning of the economy, there are situations where government intervention is necessary to ensure that the economy operates in ...
Essay On Government Intervention In Economy. Economics is one field of social science that examines and analyzes the economic activities of people. Economic activities include production of goods and services, consumption expenditure of household and distribution of goods and services. It is a study of how people make choice with the limited ...
Essay Writing Service. There are many advantages of government intervention such as even income distribution, no social injustice, secured public goods and services, property rights and welfare opportunities for those who cannot afford. Whereas, according to some economists the government intervention may also result in few disadvantages.
This essay has identified some of the proponents and opponents of government intervention and the importance of intervention that enhances sustainable growth. From the proponent's view such as the Clayton Antitrust Act, government intervention helps regulate price fixing, price discrimination, and unfair business practices.
Essay On Government Intervention. 912 Words4 Pages. For many countries, it is vital that the government is successful at meeting the citizen's needs. Each nation will need different forms of government depending on their requirements of the community. Examples of different types of government include communism, which consists of a lot of ...
A government's intervention in the economy of a country, especially in the United States has fueled debates and criticisms, market failures, disruptions in the free-flow of market economic transactions between producers and consumers. However, its benefits far outweigh the dangers of failure in the economic affairs of the country.
Hungary's government will consider whether to enforce lower fuel prices after a review by the Central Statistics Office (KSH) of regional average price levels, Economy Minister Marton Nagy told ...
Essay Writing Service. There are many advantages of government intervention such as even income distribution, no social injustice, secured public goods and services, property rights and welfare opportunities for those who cannot afford. Whereas, according to some economists the government intervention may also result in few disadvantages.
Japanese officials rolled out further warnings on the yen after the currency slumped through the 155 mark against the dollar, leaving market players on edge ahead of a central bank meeting and US ...