US South Carolina

Recently viewed courses
Recently viewed.
Find Your Dream School
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., 5 sat essay tips for a great score.
Thinking about tackling the SAT Essay? Here's what you need to know: you'll be asked to read a text (typically a speech or editorial of some sort) and discuss how the author effectively builds an argument. This might be a familiar task if you’ve done it in school, but if not, don’t worry. The format is straightforward, and with some practice, you can learn how to write a great SAT essay.
What is the SAT essay?
The SAT essay is optional and costs an additional fee of $17.00. Currently, only 25 colleges and universities require the SAT essay. You can find a searchable list of school requirements for the essay here . If there is any chance that you might apply to one of those schools, you should sign up for the essay. If you are not sure where you will apply, you should strongly consider signing up for the essay. Your essay score will appear on every score report you send to colleges, regardless of whether or not the school requires an essay.
Here are 5 tips for writing a killer SAT essay, should you decide to add on that section:

1. Stay Objective
The thing to remember here is that ETS (the company that writes the test) is not asking you for your opinion on a topic or a text. So be sure to maintain formal style and an objective tone. Tip: Avoid “I” and “you.
2. Keep It Tidy
Handwriting is becoming a lost art. Unfortunately, this is one occasion where your skill with a pencil matters. Graders read tons of essays each day. If they cannot decipher your script, they will lower your score. Do yourself a favor and write legibly.
3. (Indented) Paragraphs Are Your Friend
Remember the basic essay structure you learned in school: introductory paragraph, body paragraphs and a conclusion? The SAT essay graders love it! Your introduction should describe the text and paraphrase the argument being made, as well as introduce the specific elements of the passage and argument that you will discuss in the essay. Your conclusion should restate the goal of the passage/argument and sum up the points you made.
Read More: SAT Tips and Strategies
4. For Example…
Use your body paragraphs to back up your thesis statement by citing specific examples. Use short, relevant quotes from the text to support your points.
5. Don't Worry About the Exact Terms for Things
Blanking on terminology? When describing how the author builds his or her argument, “appeal to the emotions” is fine instead of specifically referencing “pathos.” And “comparison of two things” can be used instead of referring to a metaphor. If you do know the official terms, though, feel free to use them!
Build the right SAT prep plan for you
Our private tutors will help you build a prep plan that's customized to your score goals, study habits, and schedule.
Find a Tutor

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
Free MCAT Practice Test
Thank you! Look for the MCAT Review Guide in your inbox.
I already know my score.
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- Local Offices
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
Absolutely Essential SAT Writing Strategies
tl;dr: The SAT essay is graded on three metrics — Reading, Analysis, and Writing — each on a scale from 1-4. To score an 8/8/8 on the SAT essay, you need to understand the rubric and keep in mind the three important parts of the essay: analyzing the prompt, outlining, and writing. Analyzing the prompt requires you to identify the author’s claim, purpose, tone, and persuasive elements that help build the argument. Outlining helps you answer the three questions for each device—why, how, and affect—to ensure you have strong analysis. Finally, when writing the essay, make sure to include an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. With these tips, you can write a great SAT essay and get the top score!
❓ What are the SAT Sections?
In the SAT, you will have 4-5 sections on the test (depending on whether you choose to take the essay section or not)! The sections are:
- Check out this video with an overview of the reading section of the SAT .
- Writing and Language (aka the Grammar section)
- Make sure to watch this video with tips and tricks for the grammar section of the SAT .
- Math (No-Calculator)
- Review the important aspects of the math section with this SAT math review part 1 and part 2 .
- Math (Calculator Allowed)
- Writing/Essay (⚠️OPTIONAL ⚠️)
If you signed up for the essay portion of the SAT, you have a relaxing 2-minute break after the math calculator section. You're going to need it, as you have 50 minutes to write a rhetorical analysis essay. ⏲️
If you are taking AP Lang or have already taken the exam, you should be pretty familiar with this format of essay. It is very similar to FRQ 2, or the rhetorical analysis essay. 📰
✍️ Mastering the Rubric
Your essay is graded on these three metrics on a scale from 1-4:
Two readers will score your essay , so the highest score you can receive is an 8 on each of the three sections. Unlike the other SAT sections, there is no percentile for the SAT essay nor a composite score (the three categories aren't "added"). 💯 Let's break down each of these three scoring categories and how you can score an 8 in all three.

This scoring category covers comprehension! Essentially, the scorers want to see if you understand the relationship between the main idea(s) and important details. To get an 8 in this scoring category, you cannot misstate facts from the passage, nor make an interpretation about facts not in the passage.
One of the main things that SAT Essay scorers will check is to ensure you have textual evidence (quotations and/or paraphrases) throughout the essay to ensure that you have a true understanding of the text. 📚
What separates an 8 from a lower score in this category is whether you have thorough (as opposed to effective) comprehension of the text and whether you are making skillful (as opposed to appropriate) use of textual evidence. The line between thorough and skillful is drawn at your consistency; if you make a misrepresentation of text in just one place, that may lower you to a 6.
To earn a 8 in the analysis category, you should be accomplishing the following:
- Offering an insightful analysis of source text.
- Evaluating the author's choice of evidence, reasoning, stylistic & persuasive elements, and/or other features that you noticed.
- Using relevant, sufficient, and strategically chosen support for your claims or points.
- Consistently focusing on features that are most relevant to addressing the task.

What separates an 8 in analysis from a lower score is whether you have strategically chosen support for claims and whether your essay is consistent in its analysis and its focus on "features most relevant to addressing the task."
The writing rubric category is exactly what it sounds like—checking your ability to write an essay! There are a number of guidelines that SAT essay scorers will be looking at, and here are a few of them that will help you earn an 8:
- A cohesive essay that effectively uses and commands language
- A precise central claim
- Skillful introduction and conclusion
- Progression of ideas that is highly effective both within paragraphs and throughout the essay
- Wide variety in sentence structures
- Consistent use of precise word choice
- Formal style and objective tone
- Strong command of English conventions, an essay free of errors

Consistency is also key to getting a high score in this category. Having a mostly cohesive essay or including a few errors could bump your score down to a 6 or below!
📖 Analyzing Prompt and Passage
On test day, you're not going to see the rubric or even the three scoring categories. All you will get is the prompt and passage. It's important you analyze and annotate the prompt and passage to ensure you can write an effective essay.
On test day, you'll see this at the beginning of the essay.

The most important thing to do before you even start reading the passage is to read the given context. In this example, we know that the article is from the Huffington Post and the author Peter Goodman is writing about crisis and foreign policy. 🔥
Then, you'll read a passage about an argument written for a broad audience. In that passage, the author will make a claim, and use different techniques to persuade the audience of that claim.
Since you will be writing about how the author uses different techniques in the passage to make their argument more persuasive, that is exactly what you should look out for while writing your essay. 🔍
When reading the passage, you'll want to look at the three bullet points given in the prompt: specific factual evidence or examples, reasoning that connects evidence and claims, and other stylistic or persuasive elements that helps the author build the argument. 🚧
Here's a short bullet list of stylistic or persuasive elements that you can look out for:
- Shifts of any kind (in diction 🗣️, tone 😤, imagery 🖼️, etc.)
- Appeals to emotion 💕, logic 🧠, or credibility 👩🏽🎓
- Syntax (organization of paragraphs 📑, length of sentences ↔️)
- Unique diction or imagery (make sure to describe diction/imagery with an adjective )
After you find the rhetorical devices you want to analyze, you'll need to answer three important questions:
- Why does the author use this device or strategy?
- How does this device or strategy help them achieve their purpose?
- How does the device or strategy affect or change the audience?
You can strengthen your analysis and answer these three questions for each of your devices by outlining.
🗒️ Outlining
There are a few components to an outline that will help you secure an 8/8/8 on the SAT essay:
- Identifying audience & author's purpose
- Writing a thesis
- Identifying rhetorical devices
- Answering the three important "analysis" questions for each rhetorical device
On test day, find some white space under the article (or on the next page) to write your outline. Knowing and writing down these elements will make the writing process go a lot smoother!
📝 Writing the Essay
Let's break down how to write each section of the SAT essay portion: the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
Introduction
There are a few elements that you should explicitly include in your introduction:
- Author's claim in the passage
- Author's tone & purpose
- Audience of passage
- Specific rhetorical choices or persuasive elements in the passage that "enhance logic/persuasiveness" of the argument
One example template for an introduction is:

Here's an example:
Writer Marcus Stern in his article, "How to Prevent an Oil Train Disaster," asserts that new Obama-era regulations in 2015 were insufficient in protecting the public's safety and needed to be expanded. Stern adopts a critical tone to persuade his audience, the general public, of his purpose of supporting stricter, comprehensive regulations that reduce oil volatility. To achieve his purpose, Stern utilizes a variety of rhetorical techniques, including but not limited to specific credible evidence, appeals to the general public's fear of disaster, and emotional word choice that enhances the logic and persuasiveness of his argument.
Body Paragraphs
Your body paragraphs should create a line of reasoning , which is just a fancy of way of saying that it should follow the structure you outline in the essay. For instance, from the introduction paragraph above, I would make my first body paragraph about the "specific credible evidence," my second body paragraph about the appeals to the general public, and so on. 🤩
⚠️ Note: There is no minimum or maximum number of body paragraphs that you should include —focus on developing solid body paragraphs rather than including as many as possible!
You should include the following in a body paragraph to earn high scores on reading, analysis, and writing:
- A strong introduction sentence tied to the thesis
- Embedded quote or paraphrase with context
- Why the author uses this rhetorical strategy or persuasive element
- How it affects the audience and/or how it helps the author achieve their purpose
- Link back to thesis
Let's see these five elements in an example!
- Stern furthers his argument by appealing to the general public’s fear of disaster.
- He invokes specific visual imagery when asserting that an oil tanker rupture would send a “mushroom-shaped fireball” into the sky. In fact, Stern further builds his argument by citing the “nine other places in North America” in which oil tanker explosions materialized.
- Stern uses these appeals to logic and emotion primarily because they highlight a somber reality of the impacts of continued inaction.
- Because Stern includes multiple instances of oil explosions, the audience feels logically impacted. This sense of urgency communicated by the visual imagery makes the audience more convinced that action must be taken, specifically because it could harm them very soon.
- Ultimately, Stern successfully leaves the audience convinced that lax oil restriction could lead to devastating consequences that could harm the audience, which strengthens the persuasion of his argument that we should enact strict regulation that decreases volatility.

You may hear sometimes from your teacher that the conclusion is not that important, or that it can simply be one sentence. This is not true for the SAT; in fact, you could get points taken off the writing section with an oversimplified or non-existent conclusion.
However, you can score highly with a slightly reworded introduction! Here's what you should include in your conclusion:
- Author's central claim (reworded from intro)
- Persuasive elements/rhetorical choices
- Audience & author's purpose
Here's an example conclusion paragraph that includes those elements (and you can see its parallel to the intro):
Author Olmer Stern communicates to the general public that there is a necessity for stricter safety regulations that decrease oil volatility. To convince the audience of his purpose, Stern effectively invokes fearful emotion of the general public, cites specific evidence from the oil industry, and communicates powerful diction about the imminent oil threat to strengthen the logic and persuasiveness of his argument.
📂 Resources and Example Essays
There are some fantastic ways to practice for the SAT essay! Here are some useful resources and example essays :
- Two sample SAT Essay prompts from College Board's website
- 50 CrackSAT Practice Essays and Prompts
Guide Outline
Related content, sat math: guide to quadratic equations & radicals, sat math: guide to linear equations, sat math: how to use your calculator, sat reading: guide to the social science passage, how to study for the sat/psat english sections, sat language: guide to word choice & passive flow.
.png)
Stay Connected
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
What is the SAT? A Complete Guide to the Exam

Is your SAT score enough to get you into your dream school?
Our free chancing engine takes into consideration your SAT score, in addition to other profile factors, such as GPA and extracurriculars. Create a free account to discover your chances at hundreds of different schools.
Virtually every college’s admissions committee uses the SAT as a way to compare students from different educational backgrounds. It is managed and published by the College Board, which makes sure that the test covers skills relevant to colleges.
The SAT has changed a lot over its history, including what it measures, who uses the exam, and even what the letters stand for. We’re going to focus on what you need to know about the SAT as it exists today.
Why Should I Take the SAT?
The SAT demonstrates your academic ability to colleges, especially in language arts and math. Colleges use these scores to gauge if you are ready for college classes. Based on your score, they may even award merit scholarships or admission to their honors programs, and sometimes place you in higher-level courses.
The SAT is not the only test that colleges look at—there is also the ACT, an exam used in the same ways the SAT is used. Most colleges require either an official SAT or ACT score.
While used in similar ways, the SAT and ACT have different test structures, and most students prefer one style of test over the other. For example, the ACT has a science section, a different format for the essay portion, and tighter time constraints than the SAT. For more information on the two exams and how the SAT can help you earn scholarships, check out these posts:
- Should You Take Both the SAT and ACT?
- Which is Easier, the SAT or the ACT?
- Which Colleges Award Automatic Scholarships Based on SAT Scores?
- How Your SAT Scores can Help You Earn Scholarships
What is the SAT like?
How the sat is structured.
The SAT is structured into three tests with an optional fourth test: Reading, Writing and Language, Math, and an optional Essay.
The Reading Test measures your reading comprehension and analysis skills using excerpts from literary fiction or academic texts. You have:
- 65 minutes to answer 52 questions.
- 4 single passages in prose, social studies, and sciences.
- 1 pair of passages in either social studies or science.
- 10 to 11 questions for each single or paired passage.
- All multiple choice questions.
The Writing and Language Test measures your proofreading and editing skills using unfinished drafts. You have:
- 35 minutes to answer 44 questions
- 4 passages in narrative nonfiction, social studies, science, and career/industry
- 11 questions per passage.
- All multiple choice questions
Note that the questions may be in an unfamiliar format. Many questions refer to an underlined portion within the passage as a point of reference, and you will be asked to choose the answer that best improves the passage. These questions will also include a “NO CHANGE” option, which means that the way it appears in the passage is the best choice.
The Math Test measures your logic and problem-solving skills using math concepts. You have:
- Two sections, a no-calculator and a calculator section
- 15 multiple choice questions
- 5 gridded-response questions
- 30 multiple choice questions
- 8 gridded-response questions
The SAT Essay is optional and allows you to demonstrate your reading, analysis, and writing skills. You have:
- 50 minutes to respond to 1 essay question.
- The question involves analyzing a provided argument and explaining how the author develops the argument to persuade the reader.
- The 50 minutes includes time for reading the argument, analyzing it, planning your essay, and ultimately writing it.
The SAT was significantly modified in 2016, both in structure and scoring. For more information about the new SAT, check out these posts:
- Ultimate Guide to the New SAT Reading Test
- Ultimate Guide to the New SAT Writing and Language Test
- Ultimate Guide to the New SAT Math Test
What to Expect when Taking the SAT
The SAT is offered a handful of times throughout the school year, usually on Saturdays. Some high schools participate in SAT Day, where you take the SAT in school instead of having to go on your own time.
You will probably need to sign up for the SAT on your own at least once, and we’ve compiled a list of the SAT dates for 2018-2019 to get you started.
On test day, you’ll need to bring the following:
- Your admission ticket
- Two no. 2 pencils with erasers
- An approved calculator
- Recommended: a watch without an audible alarm (not a smartwatch), extra batteries for your calculator or extra pencils, water and snacks
For a complete list of which items you are allowed to bring, check out College Board’s Test Day Checklist .
No matter where you take the test, the testing center doors open at 7:45 a.m. and testing starts between 8:30 and 9:00 a.m. You will be assigned a seat and the testing coordinator will read you the testing instructions.
You will work on the Reading, then Writing and Language, then Math, then Essay portions of the test in that order. If you have extra time, you can check your answers in the current section, but you can’t move onto the next section or go back to a previous one.
Most students have one 10 minute break and one 5 minute break. You may use the restroom or eat a snack during the break, but you may not charge electronic devices, such as a phone, or else your scores will be canceled.
For students who don’t take the essay, they usually finish the test around 12:00pm. For students who do take the essay, they usually finish around 1:00pm.
How the SAT is Scored
Although the SAT has a whole suite of score assessments, the most common ways that people report scores is with the total score and section scores . There are two section scores on the SAT: Evidence-Based Reading and Writing, and Math. Each section is scored from 200 to 800 points.
The total score is the sum of the section scores, so it ranges from 400 to 1600.

Discover how your SAT score affects your chances
As part of our free guidance platform, our Admissions Assessment tells you what schools you need to improve your SAT score for and by how much. Sign up to get started today.
Tips for Doing Well on the SAT
To do well on the SAT, you should do your best to simulate a real test using one of College Board’s free practice tests . This will give you the best idea of what taking the official SAT will be like as well as the types of questions you can expect to see.
Analyze your score and reflect on what the test was like for you. Did you second-guess yourself? Rush through the test? Develop strategies to prevent negative test habits from happening and brush up on any academic skills you may need.
Depending on how much you want to improve your score, you’ll want to give yourself enough time to practice and study before taking the official SAT. Create a consistent study schedule and stick to it, using practice tests to measure the effectiveness of your strategies.
Need more tips? Check out our free guide with our top 8 tips for mastering the SAT.
For more information about the SAT and improving your score, check out these posts:
- How to Get a Perfect 1600 Score on the SAT
- What to Do if You’re Not Improving on the SAT
- How to Set a Realistic Target SAT Score
Want to know how your SAT score/ACT score impacts your chances of acceptance to your dream schools? Our free Chancing Engine will not only help you predict your odds, but also let you know how you stack up against other applicants, and which aspects of your profile to improve. Sign up for your free CollegeVine account today to gain access to our Chancing Engine and get a jumpstart on your college strategy!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


SAT Essay Scores Explained
On january 19th, 2021, college board announced that they will no longer administer the sat subject tests in the u.s. and that the essay would be retired. read our blog post to understand what this means in the near term and what the college board has in store for students down the road., our articles on subject tests and the sat essay will remain on our site for reference purposes as colleges and students transition to a revised testing landscape..

Why are there no percentiles for the essay on an SAT score report?
No percentiles or norms are provided in student reports. Even colleges do not receive any summary statistics. Given Compass’ concerns about the inaccuracy of essay scoring and the notable failures of the ACT on that front, the de-emphasis of norms would seem to be a good thing. The problem is that 10% of colleges are sticking with the SAT Essay as an admission requirement . While those colleges will not receive score distribution reports from the College Board, it is not difficult for them to construct their own statistics—officially or unofficially—based on thousands of applicants. Colleges can determine a “good score,” but students cannot. This asymmetry of information is harmful to students, as they are left to speculate how well they have performed and how their scores will be interpreted. Through our analysis, Compass hopes to provide students and parents more context for evaluating SAT Essay scores.
How has scoring changed? Is it still part of a student’s Total Score?
On the old SAT, the essay was a required component of the Writing section and made up approximately one-third of a student’s 200–800 score. The essay score itself was simply the sum (2–12) of two readers’ 1–6 scores. Readers were expected to grade holistically and not to focus on individual components of the writing. The SAT essay came under a great deal of criticism for being too loosely structured. Factual accuracy was not required; it was not that difficult to make pre-fabricated material fit the prompt; many colleges found the 2–12 essay scores of little use; and the conflation of the essay and “Writing” was, in some cases, blocking the use of the SAT Writing score—which included grammar and usage—entirely.
With the 2016 overhaul of the SAT came an attempt to make the essay more academically defensible while also making it optional (as the ACT essay had long been). The essay score is not a part of the 400–1600 score. Instead, a student opting to take the SAT Essay receives 2–8 scores in three dimensions: reading, analysis, and writing. No equating or fancy lookup table is involved. The scores are simply the sum of two readers’ 1–4 ratings in each dimension. There is no official totaling or averaging of scores, although colleges may choose to do so.
Readers avoid extremes
What is almost universally true about grading of standardized test essays is that readers gravitate to the middle of the scale. The default instinct is to nudge a score above or below a perceived cutoff or midpoint rather than to evenly distribute scores. When the only options are 1, 2, 3, or 4, the consequence is predictable—readers give out a lot of 2s and 3s and very few 1s and 4s. In fact, our analysis shows that 80% of all reader scores are 2s or 3s. This, in turn, means that most of the dimension scores (the sum of the two readers) range from 4 to 6. Analysis scores are outliers. A third of readers give essays a 1 in Analysis. Below is the distribution of reader scores across all dimensions.
What is a good SAT Essay score?
By combining multiple data sources—including extensive College Board scoring information—Compass has estimated the mean and mode (most common) essay scores for students at various score levels. We also found that the reading and writing dimensions were similar, while analysis scores lagged by a point across all sub-groups. These figures should not be viewed as cutoffs for “good” scores. The loose correlation of essay score to Total Score and the high standard deviation of essay scores means that students at all levels see wide variation of scores. The average essay-taking student scores a 1,080 on the SAT and receives just under a 5/4/5.
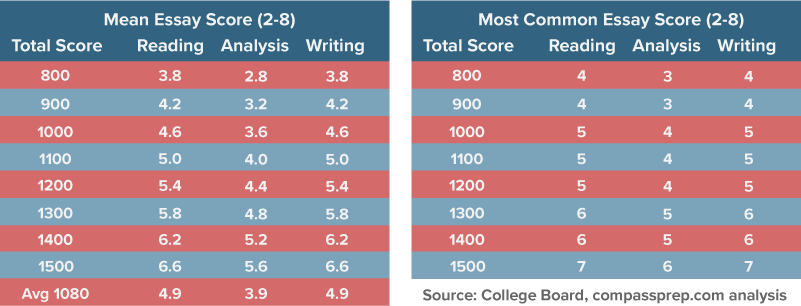
College Board recently released essay results for the class of 2017, so score distributions are now available. From these, percentiles can also be calculated. We provide these figures with mixed feelings. On the one hand, percentile scores on such an imperfect measure can be highly misleading. On the other hand, we feel that students should understand the full workings of essay scores.
The role of luck
What is frustrating to many students on the SAT and ACT is that they can score 98th percentile in most areas and then get a “middling” score on the essay. This result is actually quite predictable. Whereas math and verbal scores are the result of dozens of objective questions, the essay is a single question graded subjectively. To replace statistical concepts with a colloquial one—far more “luck” is involved than on the multiple-choice sections. What text is used in the essay stimulus? How well will the student respond to the style and subject matter? Which of the hundreds of readers were assigned to grade the student’s essay? What other essays has the reader recently scored?
Even good writers run into the unpredictability involved and the fact that essay readers give so few high scores. A 5 means that the Readers A and B gave the essay a 2 and a 3, respectively. Which reader was “right?” If the essay had encountered two readers like Reader A, it would have received a 4. If the essay had been given two readers like Reader B, it would have received a 6. That swing makes a large difference if we judge scores exclusively by percentiles, but essay scores are simply too blurry to make such cut-and-dry distinctions. More than 80% of students receive one of three scores—4, 5, or 6 on the reading and writing dimensions and 3, 4, or 5 on analysis.
What do colleges expect?
It’s unlikely that many colleges will release a breakdown of essay scores for admitted students—especially since so few are requiring it. What we know from experience with the ACT , though, is that even at the most competitive schools in the country, the 25th–75th percentile scores of admitted students were 8–10 on the ACT’s old 2–12 score range. We expect that things will play out similarly for the SAT and that most students admitted to highly selective colleges will have domain scores in the 5–7 range (possibly closer to 4–6 for analysis). It’s even less likely for students to average a high score across all three areas than it is to obtain a single high mark. We estimate that only a fraction of a percent of students will average an 8—for example [8/8/8, 7/8/8, 8/7/8, or 8,8,7].
Update as of October 2017. The University of California system has published the 25th–75th percentile ranges for enrolled students. It has chosen to work with total scores. The highest ranges—including those at UCLA and Berkeley—are 17–20. Those scores are inline with our estimates above.
How will colleges use the domain scores?
Colleges have been given no guidance by College Board on how to use essay scores for admission. Will they sum the scores? Will they average them? Will they value certain areas over others? Chances are that if you are worrying too much about those questions, then you are likely losing sight of the bigger picture. We know of no cases where admission committees will make formulaic use of essay scores. The scores are a very small, very error-prone part of a student’s testing portfolio.
How low is too low?
Are 3s and 4s, then, low enough that an otherwise high-scoring student should retest? There is no one-size-fits-all answer to that question. In general, it is a mistake to retest solely to improve an essay score unless a student is confident that the SAT Total Score can be maintained or improved. A student with a 1340 PSAT and 1280 SAT may feel that it is worthwhile to bring up low essay scores because she has previously shown that she can do better on the Evidence-based Reading and Writing and Math, as well. A student with a 1400 PSAT and 1540 SAT should think long and hard before committing to a retest. Admission results from the class of 2017 may give us some added insight into the use of SAT Essay scores.
Will colleges continue to require the SAT Essay?
For the class of 2017, Compass has prepared a list of the SAT Essay and ACT Writing policies for 360 of the top colleges . Several of the largest and most prestigious public university systems—California, Michigan, and Texas, for example, still require the essay, and a number of highly competitive private colleges do the same—for example, Dartmouth, Harvard, Princeton, and Stanford.
The number of excellent colleges not requiring the SAT Essay, though, is long and getting longer. Compass expects even more colleges to drop the essay requirement for the classes of 2018 and 2019. Policies are typically finalized in late spring or during the summer.
Should I skip the essay entirely?
A common question regarding SAT scores is whether the whole mess can be avoided by skipping the essay. After all, if only about 10% of colleges are requiring the section, is it really that important? Despite serious misgivings about the test and the ways scores are interpreted, Compass still recommends that most students take the essay unless they are certain that they will not be applying to any of the colleges requiring or recommending it. Nationally, about 70% of students choose to take the essay on at least one SAT administration. When looking at higher scoring segments, that quickly rises to 85–90%. Almost all Compass students take the SAT Essay at least once to insure that they do not miss out on educational opportunities.
Should I prepare for the SAT Essay?
Most Compass students decide to do some preparation for the essay, because taking any part of a test “cold” can be an unpleasant experience, and students want to avoid feeling like a retake is necessary. In addition to practicing exercises and tests, most students can perform well enough on the SAT Essay after 1–2 hours of tutoring. Students taking a Compass practice SAT will also receive a scored essay. Students interested in essay writing tips for the SAT can refer to Compass blog posts on the difference between the ACT and SAT tasks and the use of first person on the essays .
Will I be able to see my essay?
Yes. ACT makes it difficult to obtain a copy of your Writing essay, but College Board includes it as part of your online report.
Will colleges have access to my essay? Even if they don’t require it?
Yes, colleges are provided with student essays. We know of very few circumstances where SAT Essay reading is regularly conducted. Colleges that do not require the SAT Essay fall into the “consider” and “do not consider” camps. Schools do not always list this policy on their website or in their application materials, so it is hard to have a comprehensive list. We recommend contacting colleges for more information. In general, the essay will have little to no impact at colleges that do not require or recommend it.
Is the SAT Essay a reason to take the ACT instead?
Almost all colleges that require the SAT Essay require Writing for ACT-takers. The essays are very different on the two tests, but neither can be said to be universally “easier” or “harder.” Compass recommends that the primary sections of the tests determine your planning. Compass’ content experts have also written a piece on how to attack the ACT essay .
Key links in this post:
ACT and SAT essay requirements ACT Writing scores explained Comparing ACT and SAT essay tasks The use of first person in ACT and SAT essays Understanding the “audience and purpose” of the ACT essay Compass proctored practice testing for the ACT, SAT, and Subject Tests
About Art Sawyer
Art graduated magna cum laude from Harvard University, where he was the top-ranked liberal arts student in his class. Art pioneered the one-on-one approach to test prep in California in 1989 and co-founded Compass Education Group in 2004 in order to bring the best ideas and tutors into students' homes and computers. Although he has attained perfect scores on all flavors of the SAT and ACT, he is routinely beaten in backgammon.
SIGN UP FOR OUR NEWSLETTER
Role: --- Student Parent/Guardian Counselor Other
Class Year: --- 2024 2025 2026 2027 2028 2029 Other N/A
Popular Posts
- National Merit Semifinalist Cutoffs Class of 2025 April 8, 2024
- SAT and ACT Policies and Score Ranges for Popular Colleges and Universities April 11, 2024
- Colleges that Allow Self-Reporting of SAT and ACT Scores November 20, 2023
- National Merit Scholarship Program Explained October 4, 2023
- Using digital PSAT Scores to Compare SAT and ACT October 23, 2023
Recent Posts
- Testing Policies in the Spotlight April 11, 2024
- Superscoring and Score Choice Policies April 8, 2024
- You Received Your March SAT Scores, Now What? March 21, 2024
Previous Post SAT Subject Tests FAQ
Next post test prep in 10th grade: when does it make sense, 222 comments.
Hi! I’m a high school junior who took the October and November SATs. I got a 1500 on October and then retook it to get a 1590 in November. I’m very happy with my score, but my essays are troubling me. I got a 6-4-6 in October and thought I would improve in November, but I got a 6-3-6. I really cannot improve my actual SAT score, but I don’t understand the essay. I’ve always been a good writer and have consistently been praised for it in English class and outside of class. Is this essay score indicative of my writing skill? And will this essay hurt my chances at Ivy League and other top tier schools? None of the schools I plan on applying to require it, but, since I have to submit it, will it hurt my chances? Thank you so much.
Maya, The essay is becoming increasingly irrelevant. Honestly, a 6-4-6 is a fine score and will not hurt your chances for admission. It’s something of an odd writing task, so I wouldn’t worry that it doesn’t match your writing skills elsewhere.
By using this website, you agree to our Privacy Policy .
© 2024 Compass Education Group. SAT, PSAT, NMSC, National Merit, Merit Scholar, ACT, ISEE, SSAT, HSPT and AP are registered trademarks not owned by Compass Education Group. The trademark holders were not involved in the production of, and do not endorse, this website.
- OUR APPROACH
- DIGITAL SAT / PSAT
- ACADEMIC / STUDY SKILLS
- COLLEGE WRITING PREP
- HSPT / ISEE / SSAT / SHSAT
- ACT/SAT FUNDAMENTALS
- SAT, ACT, & PSAT
- TEST PREP ESSENTIALS
- MATH SUMMER BRIDGE
- PROCTORED (In-Person or Live Online)
- INTERACTIVE (Online, On-Demand)
- DIGITAL ADAPTIVE (New for Class of ’25 & Beyond)
- SELF-ADMINISTERED
- RESOURCE CENTER
- COMPASS GUIDE
- PRIVACY POLICY
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
The Optional SAT Essay: What to Know
Tackling this section of the SAT requires preparation and can boost some students' college applications.

Getty Images
Even though an increasing number of colleges are dropping standardized test requirements, students who must write the SAT essay can still stand to gain from doing so.
Although the essay portion of the SAT became optional in 2016, many students still chose to write it to demonstrate strong or improved writing skills to prospective colleges.
In June 2021, the College Board opted to discontinue the SAT essay. Now, only students in a few states and school districts still have access to — and must complete — the SAT essay. This requirement applies to some students in the SAT School Day program, for instance, among other groups.
How Colleges Use SAT, ACT Results
Tiffany Sorensen Sept. 14, 2020

Whether or not to write the SAT essay is not the biggest decision you will have to make in high school, but it is certainly one that requires thought on your part. Here are three things you should know about the 50-minute SAT essay as you decide whether to complete it:
- To excel on the SAT essay, you must be a trained reader.
- The SAT essay begs background knowledge of rhetoric and persuasive writing.
- A growing number of colleges are dropping standardized test requirements.
To Excel on the SAT Essay, You Must Be a Trained Reader
The SAT essay prompt never comes unaccompanied. On the contrary, it follows a text that is about 700 words long or approximately one page. Before test-takers can even plan their response, they must carefully read and – ideally – annotate the passage.
The multifaceted nature of the SAT essay prompt can be distressing to students who struggle with reading comprehension. But the good news is that this prompt is highly predictable: It always asks students to explain how the author builds his or her argument. In this case, "how” means which rhetorical devices are used, such as deductive reasoning, metaphors, etc.
Luckily, the author’s argument is usually spelled out in the prompt itself. For instance, consider this past SAT prompt : “Write an essay in which you explain how Paul Bogard builds an argument to persuade his audience that natural darkness should be preserved.”
Due to the essay prompt’s straightforward nature, students should read the passage with an eye toward specific devices used by the author rather than poring over “big ideas.” In tour SAT essay, aim to analyze at least two devices, with three being even better.
The SAT Essay Begs Background Knowledge of Rhetoric and Persuasive Writing
Since your SAT essay response must point to specific rhetorical devices that the author employs to convince the reader, you should make it a point to intimately know 10-15 common ones. The more familiar you are with rhetorical devices, the faster you will become at picking them out as you read texts.
Once you have read the passage and identified a handful of noteworthy rhetorical devices, you should apply many of the same essay-writing techniques you already use in your high school English classes.
For instance, you should start by brainstorming to see which devices you have the most to say about. After that, develop a concise thesis statement, incorporate quotes from the text, avoid wordiness and other infelicities of writing, close with an intriguing conclusion, and do everything else you could imagine your English teacher advising you to do.
Remember to always provide evidence from the text to support your claims. Finally, leave a few minutes at the end to review your essay for mistakes.
A Growing Number of Colleges Are Dropping Standardized Test Requirements
In recent years, some of America’s most prominent colleges and universities – including Ivy League institutions like Harvard University in Massachusetts, Princeton University in New Jersey and Yale University in Connecticut – have made submission of ACT and SAT scores optional.
While this trend began as early as 2018, the upheaval caused by COVID-19 has prompted many other schools to adopt a more lenient testing policy, as well.
Advocates for educational fairness have long expressed concerns that standardized admissions tests put underprivileged students at a disadvantage. In light of the coronavirus pandemic , which restricted exam access for almost all high school students, colleges have gotten on board with this idea by placing more emphasis on other factors in a student’s application.
To assess writing ability in alternative ways, colleges now place more emphasis on students’ grades in language-oriented subjects, as well as college application documents like the personal statement .
The fact that more colleges are lifting their ACT/SAT requirement does not imply that either test or any component of it is now obsolete. Students who must write the SAT essay can still stand to gain from doing so, especially those who wish to major in a writing-intensive field. The essay can also demonstrate a progression or upward trajectory in writing skills.
The SAT essay can give a boost to the college applications of the few students to whom it is still available. If the requirement applies to you, be sure to learn more about the SAT essay and practice it often as you prepare for your upcoming SAT.
13 Test Prep Tips for SAT and ACT Takers

Tags: SAT , standardized tests , students , education
About College Admissions Playbook
Stressed about getting into college? College Admissions Playbook, authored by Varsity Tutors , offers prospective college students advice on Advanced Placement and International Baccalaureate courses, SAT and ACT exams and the college application process. Varsity Tutors, an advertiser with U.S. News & World Report, is a live learning platform that connects students with personalized instruction to accelerate academic achievement. The company's end-to-end offerings also include mobile learning apps, online learning environments and other tutoring and test prep-focused technologies. Got a question? Email [email protected] .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
Supporting low-income college applicants.
Shavar Jeffries April 16, 2024

Supporting Black Women in Higher Ed
Zainab Okolo April 15, 2024

Law Schools With the Highest LSATs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 11, 2024

Today NAIA, Tomorrow Title IX?
Lauren Camera April 9, 2024


Grad School Housing Options
Anayat Durrani April 9, 2024

How to Decide if an MBA Is Worth it
Sarah Wood March 27, 2024

What to Wear to a Graduation
LaMont Jones, Jr. March 27, 2024

FAFSA Delays Alarm Families, Colleges
Sarah Wood March 25, 2024

Help Your Teen With the College Decision
Anayat Durrani March 25, 2024

Toward Semiconductor Gender Equity
Alexis McKittrick March 22, 2024


An NPR editor who wrote a critical essay on the company has resigned after being suspended
N EW YORK (AP) — A National Public Radio editor who wrote an essay criticizing his employer for promoting liberal views resigned on Wednesday, attacking NPR's new CEO on the way out.
Uri Berliner, a senior editor on NPR's business desk, posted his resignation letter on X, formerly Twitter, a day after it was revealed that he had been suspended for five days for violating company rules about outside work done without permission.
“I cannot work in a newsroom where I am disparaged by a new CEO whose divisive views confirm the very problems” written about in his essay, Berliner said in his resignation letter.
Katherine Maher, a former tech executive appointed in January as NPR’s chief executive, has been criticized by conservative activists for social media messages that disparaged former President Donald Trump. The messages predated her hiring at NPR.
NPR’s public relations chief said the organization does not comment on individual personnel matters.
The suspension and subsequent resignation highlight the delicate balance that many U.S. news organizations and their editorial employees face. On one hand, as journalists striving to produce unbiased news, they're not supposed to comment on contentious public issues; on the other, many journalists consider it their duty to critique their own organizations' approaches to journalism when needed.
In his essay , written for the online Free Press site, Berliner said NPR is dominated by liberals and no longer has an open-minded spirit. He traced the change to coverage of Trump's presidency.
“There's an unspoken consensus about the stories we should pursue and how they should be framed,” he wrote. “It's frictionless — one story after another about instances of supposed racism, transphobia, signs of the climate apocalypse, Israel doing something bad and the dire threat of Republican policies. It's almost like an assembly line.”
He said he'd brought up his concerns internally and no changes had been made, making him “a visible wrong-thinker at a place I love.”
In the essay's wake, NPR top editorial executive, Edith Chapin, said leadership strongly disagreed with Berliner's assessment of the outlet's journalism and the way it went about its work.
It's not clear what Berliner was referring to when he talked about disparagement by Maher. In a lengthy memo to staff members last week, she wrote: “Asking a question about whether we're living up to our mission should always be fair game: after all, journalism is nothing if not hard questions. Questioning whether our people are serving their mission with integrity, based on little more than the recognition of their identity, is profoundly disrespectful, hurtful and demeaning.”
Conservative activist Christopher Rufo revealed some of Maher's past tweets after the essay was published. In one tweet, dated January 2018, Maher wrote that “Donald Trump is a racist.” A post just before the 2020 election pictured her in a Biden campaign hat.
In response, an NPR spokeswoman said Maher, years before she joined the radio network, was exercising her right to express herself. She is not involved in editorial decisions at NPR, the network said.
The issue is an example of what can happen when business executives, instead of journalists, are appointed to roles overseeing news organizations: they find themselves scrutinized for signs of bias in ways they hadn’t been before. Recently, NBC Universal News Group Chairman Cesar Conde has been criticized for service on paid corporate boards.
Maher is the former head of the Wikimedia Foundation. NPR's own story about the 40-year-old executive's appointment in January noted that she “has never worked directly in journalism or at a news organization.”
In his resignation letter, Berliner said that he did not support any efforts to strip NPR of public funding. “I respect the integrity of my colleagues and wish for NPR to thrive and do important journalism,” he wrote.
David Bauder writes about media for The Associated Press. Follow him at http://twitter.com/dbauder


Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 4 sat sections: what they test and how to do well.
SAT General Info
Whether you're actively preparing for the SAT or simply want to learn more about the ubiquitous college entrance exam, it’s important you start with the basics: how many sections are on the SAT? W hat are the names of the SAT sections? And what kinds of skills does each section measure?
In this article, we answer all of your burning questions about the SAT sections . We'll begin by discussing how many sections are on the SAT as well as how these sections differ from one another. Then, we’ll go over the different skills on which you'll be tested, giving you our expert tips for combating each of the SAT test sections with confidence. Finally, we'll take a look at whether certain sections of the SAT are more important than others and what this means for you and your college applications.
UPDATE: SAT Essay No Longer Offered
In January 2021, the College Board announced that after June 2021, it would no longer offer the Essay portion of the SAT (except at schools who opt in during School Day Testing). It is now no longer possible to take the SAT Essay, unless your school is one of the small number who choose to offer it during SAT School Day Testing.
What does the end of the SAT Essay mean for your college applications? Check out our article on the College Board's SAT Essay decision for everything you need to know.
What Are the SAT Sections?
The SAT (which was redesigned in 2016 ) consists of four sections:
- Writing and Language
- Math (which consists of two subsections, No Calculator and Calculator)
- Essay (only offered during select SAT School Days)
As the College Board (the creator of the SAT) puts it, all sections of the SAT work together to test “what you learn in high school” and “what you need to succeed in college.” In other words, the goal of the SAT is to ensure you possess the appropriate reading, writing, and math skills deemed necessary for success as a college student.
Each of the SAT test sections appears only once on the exam and varies in the number of questions it contains as well as in how much time it allocates. The following table showcases some of the major features of the SAT test sections:
According to this table, the longest section (in terms of both time and number of questions) is the Math section . This is because the Math section is composed of two subsections: a No Calculator section (which always comes first) and a Calculator section. While the No Calculator section is fairly brief at only 25 minutes and 20 questions long, the Calculator section lasts for 55 minutes and contains a total of 38 questions.
You may also notice a few key similarities between the Reading and Writing and Language sections. These two sections were specifically designed to test a couple of the same skills — namely Command of Evidence and Words in Context — in different ways. The two sections also combine for an overall Evidence-Based Reading and Writing (EBRW) score out of 800 points, so they clearly have a lot in common with each other!
Lastly, the above table highlights how all sections of the SAT (excluding the Essay) are predominantly multiple choice . Most questions on the SAT contain four answer choices from which you must select one answer. On the Math section, however, you will also face a handful of grid-in questions for which you must come up with your own answers and bubble them in using the numbers provided.
Now that we've covered all of the fundamentals, let’s take a closer look at each of the four sections of the SAT.

The SAT Reading Section
The Reading section focuses on reading comprehension and understanding vocabulary in context . Each of the 52 questions in this section will be based on a passage. You'll be given five passages in total:
- 1 passage on U.S. or world literature
- 2 passages on history/social studies
- 2 passages on science (which may include graphs and/or charts)
On some areas of the Reading section, you may be given a pair of related passages instead of a single passage. You may also encounter graphs, charts, or other forms of data representation. (Note that you will not have to use any math for these questions, though you will be expected to know how to interpret the data provided.)
As illuminated in the table above, the Reading section test two primary skills:
- Command of Evidence: your ability to find concrete evidence within the passage to support the author’s claims or answers to specific questions
- Words in Context: your ability to decipher the meanings of vocabulary words within the context of the passage, and your ability to understand how word choice influences the style and tone of a text
Big Picture
Little Picture/Function
- Vocabulary in Context
- Author Technique
- Evidence Support
- Data Interpretation
Below, I describe each of these question types and then provide you with our best tips for doing well on the SAT Reading section.
SAT Reading Question Types
Here are the different types of questions you'll encounter on the SAT Reading section.
#1: Big Picture and Little Picture / Function
These two Reading question types are opposites: Big Picture questions focus on the main point of a passage , whereas Little Picture (or Function) questions focus on the function of specific lines or sentences within a passage . Your job, then, is to use contextual evidence to decipher either the author’s overall message or the function of a selected area of the text.

#2: Inference
For this Reading question type, you must correctly interpret the meaning of a sentence, a group of sentences, or the entire passage.

#3: Vocabulary in Context
These Reading questions ask you about the meaning of a specific word or phrase within the passage . These words and phrases may not always appear to be difficult but will usually take on lesser-known alternative meanings.

#4: Author Technique
This type of Reading question requires you to analyze the author’s stylistic choices in regards to tone, voice, perspective, etc.

#5: Evidence Support
For Evidence Support questions, you must locate contextual evidence for an answer to a previous question . (In other words, these questions are directly related to the questions that precede them.) To answer these questions, you must identify a particular line or group of lines from which you found the answer to a question.

#6: Data Interpretation
A Data Interpretation question requires you to interpret data (usually in the form of a table, chart, or graph) and understand how it relates to the passage.
Top 3 SAT Reading Tips
Once you've familiarized yourself with all of the Reading question types, it's time for you to employ our top three tips for the SAT Reading section!
#1: Practice Reading Passages
Because the Reading section revolves solely around passages, it's critical you dedicate the bulk of your SAT Reading prep to working with SAT-esque passages.
The best resources for passages similar to those you’ll encounter on the SAT are official SAT practice tests . These mock SAT tests created by the College Board offer a plethora of realistic Reading passages that closely mimic the style and form of the passages you'll be given on test day.
In addition to official practice tests, you can also use unofficial SAT Reading materials — as long as they contain high-quality Reading passages similar to those on the SAT.
Finally, it's a smart idea to read real-life texts, such as The New York Times , The Atlantic , and Psychology Today , from which SAT passages are often borrowed. This way you can familiarize yourself with the type of materials you'll see on test day.

#2: Use Process of Elimination
Process of elimination is an excellent strategy (and even one recommended by a perfect scorer !) that will aid you significantly on the Reading section.
As we already know, each Reading question offers four possible answer choices of which just one is correct. This means that the other three choices must contain clear signs indicating they’re incorrect . Some of the most common reasons answer choices are eliminated are that they're:
- Too specific
- Too loosely connected to the overall purpose or message of the passage
Remember, even a single word in an answer choice can make it incorrect , so look closely for any reason to eliminate a choice before deciding on the correct one. Be sure you avoid getting caught up in answer choices that sort of sound correct — if a choice doesn’t 100-percent answer the question or is ambiguous in any way, chances are it's wrong!
#3: Study Vocabulary Sparingly
Unlike the old (pre-2016) SAT, which often tested obscure vocabulary words in complete isolation, the new SAT only tests vocabulary knowledge within the context of passages . Additionally, current SAT vocabulary is only about medium difficulty , meaning many of the words tested are ones you've likely seen and may have even used before. (Woo hoo!)
The challenging part of SAT vocabulary, however, is being able to identify lesser-known tertiary meanings of common words . What this means is, while you no longer need to dedicate hours upon hours to memorizing thousands of vocabulary words, you do need to familiarize yourself with some of the rarer meanings of common words. Likewise, you should also know how to decipher a vocabulary word's meaning based on how it's being used in a passage.
These days, many SAT vocabulary words are similar to those on the ACT; thus, we recommend studying vocabulary for either test with both our list of SAT vocabulary words and our ACT list of 150 medium-level vocabulary words .

The SAT Writing and Language Section
The Writing and Language section (often referred to as simply the “Writing section”) may look similar to the Reading section, but instead of measuring your reading comprehension skills, this section measures your ability to identify and correct grammatical errors and stylistic weaknesses within passages . In other words, the Writing section is all about your proofreading and editing skills!
Like the Reading section, the Writing section revolves entirely around passages . These passages cover a wide array of topics, including careers, history/social studies, science, and the humanities. Unlike Reading passages, however, all Writing passages are nonfiction , taking the form of narratives, arguments, and explanatory texts.
Your primary mission on the Writing section is to correct (or leave as is, if no errors are present) words and sentences within these passages. For science-based passages containing charts or graphs, you may be asked to replace an incorrect sentence with a new sentence that more accurately reflects the data provided.
The Writing and Language section measures the following skills:
- Command of Evidence
- Words in Context
- Expression of Ideas
- Standard English Conventions
Below, I discuss each of these four question types and what they measure on the SAT Writing section. I then provide you with our top three tips for getting a great score on SAT Writing.
SAT Writing and Language Question Types
In this section, we examine the SAT Writing question types and look at examples of how they'll appear on the SAT.
#1: Command of Evidence
These types of Writing questions focus primarily on the big picture of a passage and usually ask you to provide evidence for why you are making a particular change .

#2: Words in Context
For these questions, you must replace a word or phrase with a more logical choice , or select “NO CHANGE” if the highlighted area is appropriate as is.

#3: Expression of Ideas
These questions require you to think about the various ways ideas can be expressed in words. More specifically, you must rearrange, add, combine, or delete sentences to improve the overall flow of a passage.

#4: Standard English Conventions
For Standard English Conventions questions, you must correct incorrect words or phrases, so that they adhere to the basic rules of English grammar, punctuation, spelling, and capitalization . If the highlighted word or phrase is grammatically sound, select “NO CHANGE.”

Top 3 SAT Writing and Language Tips
Here are our top tips for getting the score you want on the SAT Writing section!
#1: Master Common SAT Grammar and Punctuation Rules
Nearly half of all SAT Writing questions focus on standard English conventions, so naturally you can’t expect to do well on SAT Writing if you haven’t mastered the basic rules of English grammar and usage!
This doesn't mean you must review every single grammar rule in existence — just the ones most commonly tested on the SAT . For more details on what these rules are and how you can master them, check out our in-depth guides to SAT grammar and SAT punctuation .

#2: Read Articles and Essays
Because none of the Writing section's passages are works of fiction, your best bet is to read real-life newspaper and magazine articles, persuasive texts, and essays . As you study, you'll use these texts to hone your editorial eye, identifying transitional words and connections in thought.
You'll also want to examine how the author builds his or her argument or main point throughout the text . What evidence does he or she provide? Is it ultimately effective? Why or why not?
There will be a wide array of topics for Writing passages, so feel free to dig into a variety of texts. I recommend starting with major publications such as The New Yorker , The New York Times , The Atlantic , Wired , and Psychology Today .
#3: Hone Your Writing Skills
To be a sharp editor, you must understand how to write well. And to write well, you must learn from the feedback on your own writing .
Begin by noting any red marks on essays you turn in at school, making yourself aware of any errors you continuously make on your writing. If you’re confused about a mistake you've made, ask your teacher to explain the mistake and give you tips on how you can avoid making it again.
As you write essays for school, make sure you're also paying attention to the structure of your arguments . Consider the simple "hamburger" structure of essays: you've got your introduction (top bun), your evidence and supporting details (lettuce, tomato, and meat), and your conclusion (bottom bun). Knowing how to effectively structure your own essays should over time allow you to develop a keener understanding of how SAT passages are organized.
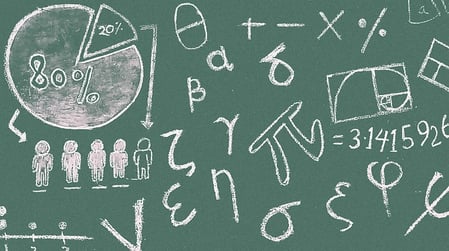
The SAT Math Section
Onto the world of numbers! Unlike the English-centered Reading and Writing sections, the SAT Math section consists of practical, real-world math and measures the problem-solving abilities most useful for college-level coursework and future employment.
The Math section comprises two subsections:
- Math No Calculator , for which you are not permitted to use a calculator
- Math Calculator , for which you may (but aren't required to) use a calculator
The Math section is the only section on the SAT (excluding the Essay) to contain a non-multiple-choice question format called the grid-in . 22 percent of Math questions are grid-ins , so although it’s not the main question format on SAT Math, it’s crucial you understand how it works.
The Math section tests you on the following concepts:
- Heart of Algebra
- Problem Solving and Data Analysis
- Passport to Advanced Math
- Additional Topics in Math
Below, I describe each of these Math question types and give you expert tips for securing an excellent SAT Math score.
SAT Math Question Types
Here are the four types of Math questions you'll see on the SAT.
#1: Heart of Algebra
This content area constitutes the largest focus of the SAT Math section , accounting for approximately one-third of all Math questions. Heart of Algebra questions focus on (you guessed it!) algebra — primarily linear equations, systems of equations, inequalities, and absolute values.

#2: Problem Solving and Data Analysis
There are 17 Problem Solving and Data Analysis questions on the SAT. All of these questions are on the Math Calculator subsection (meaning you'll see none of these on the No Calculator subsection). These questions focus on data interpretation (i.e., how to read charts, graphs, tables, etc.) as well as rates, ratios, percentages, linear and exponential relationships, and probability.
#3: Passport to Advanced Math
There are 16 Passport to Advanced Math questions on the SAT. These advanced questions test your understanding of the structure of equations and expressions , including your ability to rearrange and rewrite them. For these questions, you may be asked to solve a quadratic equation, create an exponential function, or manipulate polynomials.

#4: Additional Topics in Math
While 90 percent of the Math section deals with the three topics listed above, the last 10 percent targets what the College Board calls "Additional Topics in Math." This question type is basically a catch-all for any math concept that doesn’t fit neatly into the other three categories. Such topics predominantly deal with geometry , trigonometry , and complex numbers.
Top 3 SAT Math Tips
Use our top tips below to get your best score ever on SAT Math!
#1: Review Basic Math Concepts
You can’t expect to score highly on the Math section if you’re not familiar with most or all of the basic math concepts being tested on the SAT.
To get started, take a look at our giant stockpile of SAT Math resources you can use (for free!). This guide contains links to several Math guides offering a solid overview of critical math concepts you should know for the SAT, including algebra, numbers, coordinate geometry, and plane and solid geometry.
You can also check out our guide to the best SAT Math prep books and browse your options for high-quality Math content review and practice.
#2: Memorize Common Formulas
Another tip is to memorize all critical SAT Math formulas you’ll need for test day. Doing this will allow you to solve many math problems that you can't solve without knowledge of a particular formula.
But what about the reference diagram on the test? Do you really need to memorize formulas if you'll be given a list of them on the SAT? Although you may think memorizing these formulas is a waste of time, in reality memorizing them will actually save you time on test day . Here are the formulas exactly as you'll see them on the SAT:
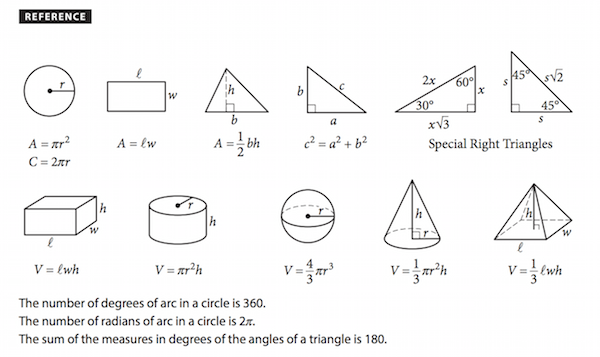
By memorizing the formulas above, you won't need to constantly flip back to the diagram and will therefore be able to solve math problems more quickly. This will effectively give you more time to put toward other math problems that are more challenging .
However, there is one caveat: the 12 formulas on this reference diagram deal specifically with geometry, a topic which makes up a significantly small portion of the new SAT. So while it’s crucial you memorize these formulas, it’ll be far more advantageous for you to prioritize other major laws and formulas that will not be given to you on test day and are more likely to come up on the SAT.
#3: Plug In Answers and Numbers
Our final tip for SAT Math is a popular test-taking strategy: plugging in answers and numbers . In this strategy, if you’re faced with a math problem you’re unsure how to solve, you can attempt to solve it by either plugging in random numbers or plugging in answer choices one by one. Doing this will reveal which answer choice yields the correct result.
Use the plug-in answer strategy for multiple-choice math questions that ask you to solve for a specific value. Always start with answer choice B or C , so you can determine whether to work your way up or down to get a higher or lower answer.
For multiple-choice and grid-in questions you don’t understand, try plugging in your own numbers (or sets of numbers) to see whether equations and inequalities hold true for various values.
Note that these strategies, though helpful, should generally only be used if you’re unsure how to solve a math problem using other methods, such as simplification and algebra. Ultimately, though, the SAT doesn’t care how you get an answer — just that it’s the correct one! So if you don't know what to do, get in there and plug away.

The SAT Essay (Optional)
NOTE: As we mentioned above, now that the Essay is only offered during select SAT School Days , very few students will take it. Additionally, no colleges still require the Essay, so even if you do take it, your score will not impact your college applications.
The SAT Essay is an entirely writing-based section for which you must read a 650-750-word passage and then write an essay analyzing how the author constructs his or her argument as well as how persuasive the argument is .
Note that you are not being asked whether you agree or disagree with the argument. You are also not expected to write about your personal experiences (like how test takers were prompted to do on the old SAT).
The Essay also uses a unique scoring system compared to those of the other SAT test sections. There are three components to the SAT Essay grade :
For each of these components, two graders will assign you a score on a scale of 1-4. These two scores are then added together to give you total scores for each component (on a scale of 2-8). Thus, a perfect SAT Essay grade would be 8|8|8 (4s from both graders for each of the three rubrics).
But what exactly do these three components measure? Below, I describe each of the SAT Essay grades and introduce to you our top three tips for ensuring a high Essay score on test day.
Skills Tested on the SAT Essay
The three components of the SAT Essay grading rubric each measure a different skill in regards to your writing ability.
The Reading score highlights your overall understanding of the passage and how well you use appropriate textual evidence from the passage to construct your essay.
The Analysis score shows how well you understand the construction of the author's argument in terms of reasoning, style, and evidence. It also measures your ability to choose the most effective evidence from the passage to support your evaluation.
The Writing score revolves entirely around your ability to write . You will be given a grade based on the strength of your thesis and on your essay's organization, focus, tone, style, and adherence to standard written English conventions.

Top 3 SAT Essay Tips
And now here are our expert SAT Essay tips to help you get the high score you deserve!
#1: Learn the Types of Examples to Look for in Passages
Before you take the exam, make sure you know all of the major types of examples you can look for in passages to use as support in your essay. The six types of evidence to be aware of are:
- Facts and statistics
- Counterarguments and counterclaims
- Explanation of evidence
- Vivid language
- Direct appeals to the reader
For more information, check out our detailed guide on how to look for and use these pieces of evidence . As you write, be sure you’re using the most relevant and effective support; you don’t need to use every example you find!
#2: Read the Prompt First
Although you'll likely be tempted to get through the passage before attacking the prompt, reading the prompt first can lend you a big hand as it directly states what the author’s central claim is . Once you know what kind of argument you'll be dealing with, you can then read the entire passage, keeping an eye out for any evidence that supports this central claim and thinking of ways you can effectively incorporate these pieces of evidence into your essay.
As a reminder, your essay should focus on what techniques and evidence the authors uses to set up his or her argument as well as how effective these techniques are.
#3: Write More Than 1 Page
Though not explicitly stated on the SAT Essay rubric, your essay must be of a reasonable length (1+ pages) in order to merit a high score . This means anything less than a page is bound to guarantee you a low essay score, as the essay will very likely lack sufficient detail, evidence, and analysis.
On test day, you’ll get four pages for writing (and one additional piece of scratch paper for planning and outlining your essay). Aim to use at least two pages for your essay. Anything longer is perfectly fine; however, just remember it's ultimately better to produce a succinct and focused essay instead of a verbose or tangential one.
Ready to go beyond just reading about the SAT? Then you'll love the free five-day trial for our SAT Complete Prep program . Designed and written by PrepScholar SAT experts , our SAT program customizes to your skill level in over 40 subskills so that you can focus your studying on what will get you the biggest score gains.
Click on the button below to try it out!

Are Certain SAT Sections More Important Than Others?
Because the SAT has several sections, you may be wondering which (if any) are the most important in regards to scores.
To start, the essay is, by far, the least important of all SAT sections . With the College Board no longer offering the essay during regular SAT administrations, nearly no students will now take it, and no colleges require essay scores. Basically, if you're one of the few people who do still take the essay (because your school required it for an SAT School Day), your score won't impact your college applications, although your high school might use the essay score for its own purposes.
But what about the SAT Reading, Writing, and Math sections? Which of these is the most important? Or are they all equally important?
Generally speaking, the SAT Reading, Writing, and Math sections are all of fairly equal importance . Most schools report SAT scores using the total score (a combination of the EBRW and Math scores), implying there is equal consideration of the Reading, Writing, and Math sections. Furthermore, any school requiring the SAT will always require scores from the Reading, Writing, and Math sections, so all three of these sections are evidently essential for college admission (unlike the optional Essay).
In spite of these trends, there may be cases in which one of the two scores (EBRW or Math) will hold slightly more weight than the other . For example, if you are applying to an engineering school like MIT, admissions committees may pay a little extra attention to your SAT Math score — the more relevant score to your program — and less to your EBRW score.
In the end, it's best to think of both your EBRW and Math scores as being equally important, and your Essay score (if you took the essay) as being the least important.
Key Takeaways for the SAT Sections
The SAT is composed of four sections: Reading, Writing and Language, Math, and Essay (optional). These sections target an array of academic skills deemed necessary for college, from reading comprehension to proofreading to problem solving.
To ultimately do well on the SAT, you must understand what each of the SAT sections measures, what each sections tests you on, and what approaches you can use to get the scores you want.
Although the Essay isn’t a requirement for any colleges anymore, those requiring SAT scores will often prefer applicants who have a strong set of EBRW (Reading and Writing) and Math scores, so always try to aim for a high total score !
What’s Next?
Want to learn more about the SAT? Take a look at our complete guide to what the SAT is and get tips on when to start studying and what resources you can use to get the scores you need for college!
Thinking of taking the ACT, too? Start with our introduction to the ACT sections and then check out our guide to what a good ACT score is to learn how you can get a great ACT score.
Disappointed with your scores? Want to improve your SAT score by 160 points? We've written a guide about the top 5 strategies you must be using to have a shot at improving your score. Download it for free now:

Hannah received her MA in Japanese Studies from the University of Michigan and holds a bachelor's degree from the University of Southern California. From 2013 to 2015, she taught English in Japan via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
NPR defends its journalism after senior editor says it has lost the public's trust

David Folkenflik

NPR is defending its journalism and integrity after a senior editor wrote an essay accusing it of losing the public's trust. Saul Loeb/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
NPR is defending its journalism and integrity after a senior editor wrote an essay accusing it of losing the public's trust.
NPR's top news executive defended its journalism and its commitment to reflecting a diverse array of views on Tuesday after a senior NPR editor wrote a broad critique of how the network has covered some of the most important stories of the age.
"An open-minded spirit no longer exists within NPR, and now, predictably, we don't have an audience that reflects America," writes Uri Berliner.
A strategic emphasis on diversity and inclusion on the basis of race, ethnicity and sexual orientation, promoted by NPR's former CEO, John Lansing, has fed "the absence of viewpoint diversity," Berliner writes.
NPR's chief news executive, Edith Chapin, wrote in a memo to staff Tuesday afternoon that she and the news leadership team strongly reject Berliner's assessment.
"We're proud to stand behind the exceptional work that our desks and shows do to cover a wide range of challenging stories," she wrote. "We believe that inclusion — among our staff, with our sourcing, and in our overall coverage — is critical to telling the nuanced stories of this country and our world."

NPR names tech executive Katherine Maher to lead in turbulent era
She added, "None of our work is above scrutiny or critique. We must have vigorous discussions in the newsroom about how we serve the public as a whole."
A spokesperson for NPR said Chapin, who also serves as the network's chief content officer, would have no further comment.
Praised by NPR's critics
Berliner is a senior editor on NPR's Business Desk. (Disclosure: I, too, am part of the Business Desk, and Berliner has edited many of my past stories. He did not see any version of this article or participate in its preparation before it was posted publicly.)
Berliner's essay , titled "I've Been at NPR for 25 years. Here's How We Lost America's Trust," was published by The Free Press, a website that has welcomed journalists who have concluded that mainstream news outlets have become reflexively liberal.
Berliner writes that as a Subaru-driving, Sarah Lawrence College graduate who "was raised by a lesbian peace activist mother ," he fits the mold of a loyal NPR fan.
Yet Berliner says NPR's news coverage has fallen short on some of the most controversial stories of recent years, from the question of whether former President Donald Trump colluded with Russia in the 2016 election, to the origins of the virus that causes COVID-19, to the significance and provenance of emails leaked from a laptop owned by Hunter Biden weeks before the 2020 election. In addition, he blasted NPR's coverage of the Israel-Hamas conflict.
On each of these stories, Berliner asserts, NPR has suffered from groupthink due to too little diversity of viewpoints in the newsroom.
The essay ricocheted Tuesday around conservative media , with some labeling Berliner a whistleblower . Others picked it up on social media, including Elon Musk, who has lambasted NPR for leaving his social media site, X. (Musk emailed another NPR reporter a link to Berliner's article with a gibe that the reporter was a "quisling" — a World War II reference to someone who collaborates with the enemy.)
When asked for further comment late Tuesday, Berliner declined, saying the essay spoke for itself.
The arguments he raises — and counters — have percolated across U.S. newsrooms in recent years. The #MeToo sexual harassment scandals of 2016 and 2017 forced newsrooms to listen to and heed more junior colleagues. The social justice movement prompted by the killing of George Floyd in 2020 inspired a reckoning in many places. Newsroom leaders often appeared to stand on shaky ground.
Leaders at many newsrooms, including top editors at The New York Times and the Los Angeles Times , lost their jobs. Legendary Washington Post Executive Editor Martin Baron wrote in his memoir that he feared his bonds with the staff were "frayed beyond repair," especially over the degree of self-expression his journalists expected to exert on social media, before he decided to step down in early 2021.
Since then, Baron and others — including leaders of some of these newsrooms — have suggested that the pendulum has swung too far.

Author Interviews
Legendary editor marty baron describes his 'collision of power' with trump and bezos.
New York Times publisher A.G. Sulzberger warned last year against journalists embracing a stance of what he calls "one-side-ism": "where journalists are demonstrating that they're on the side of the righteous."
"I really think that that can create blind spots and echo chambers," he said.
Internal arguments at The Times over the strength of its reporting on accusations that Hamas engaged in sexual assaults as part of a strategy for its Oct. 7 attack on Israel erupted publicly . The paper conducted an investigation to determine the source of a leak over a planned episode of the paper's podcast The Daily on the subject, which months later has not been released. The newsroom guild accused the paper of "targeted interrogation" of journalists of Middle Eastern descent.
Heated pushback in NPR's newsroom
Given Berliner's account of private conversations, several NPR journalists question whether they can now trust him with unguarded assessments about stories in real time. Others express frustration that he had not sought out comment in advance of publication. Berliner acknowledged to me that for this story, he did not seek NPR's approval to publish the piece, nor did he give the network advance notice.
Some of Berliner's NPR colleagues are responding heatedly. Fernando Alfonso, a senior supervising editor for digital news, wrote that he wholeheartedly rejected Berliner's critique of the coverage of the Israel-Hamas conflict, for which NPR's journalists, like their peers, periodically put themselves at risk.
Alfonso also took issue with Berliner's concern over the focus on diversity at NPR.
"As a person of color who has often worked in newsrooms with little to no people who look like me, the efforts NPR has made to diversify its workforce and its sources are unique and appropriate given the news industry's long-standing lack of diversity," Alfonso says. "These efforts should be celebrated and not denigrated as Uri has done."
After this story was first published, Berliner contested Alfonso's characterization, saying his criticism of NPR is about the lack of diversity of viewpoints, not its diversity itself.
"I never criticized NPR's priority of achieving a more diverse workforce in terms of race, ethnicity and sexual orientation. I have not 'denigrated' NPR's newsroom diversity goals," Berliner said. "That's wrong."
Questions of diversity
Under former CEO John Lansing, NPR made increasing diversity, both of its staff and its audience, its "North Star" mission. Berliner says in the essay that NPR failed to consider broader diversity of viewpoint, noting, "In D.C., where NPR is headquartered and many of us live, I found 87 registered Democrats working in editorial positions and zero Republicans."
Berliner cited audience estimates that suggested a concurrent falloff in listening by Republicans. (The number of people listening to NPR broadcasts and terrestrial radio broadly has declined since the start of the pandemic.)
Former NPR vice president for news and ombudsman Jeffrey Dvorkin tweeted , "I know Uri. He's not wrong."
Others questioned Berliner's logic. "This probably gets causality somewhat backward," tweeted Semafor Washington editor Jordan Weissmann . "I'd guess that a lot of NPR listeners who voted for [Mitt] Romney have changed how they identify politically."
Similarly, Nieman Lab founder Joshua Benton suggested the rise of Trump alienated many NPR-appreciating Republicans from the GOP.
In recent years, NPR has greatly enhanced the percentage of people of color in its workforce and its executive ranks. Four out of 10 staffers are people of color; nearly half of NPR's leadership team identifies as Black, Asian or Latino.
"The philosophy is: Do you want to serve all of America and make sure it sounds like all of America, or not?" Lansing, who stepped down last month, says in response to Berliner's piece. "I'd welcome the argument against that."
"On radio, we were really lagging in our representation of an audience that makes us look like what America looks like today," Lansing says. The U.S. looks and sounds a lot different than it did in 1971, when NPR's first show was broadcast, Lansing says.
A network spokesperson says new NPR CEO Katherine Maher supports Chapin and her response to Berliner's critique.
The spokesperson says that Maher "believes that it's a healthy thing for a public service newsroom to engage in rigorous consideration of the needs of our audiences, including where we serve our mission well and where we can serve it better."
Disclosure: This story was reported and written by NPR Media Correspondent David Folkenflik and edited by Deputy Business Editor Emily Kopp and Managing Editor Gerry Holmes. Under NPR's protocol for reporting on itself, no NPR corporate official or news executive reviewed this story before it was posted publicly.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
February 28, 2024. The SAT Essay section is a lot like a typical writing assignment in which you're asked to read and analyze a passage and then produce an essay in response to a single prompt about that passage. It gives you the opportunity to demonstrate your reading, analysis, and writing skills—which are critical to readiness for ...
Responses to the optional SAT Essay are scored using a carefully designed process. Two different people will read and score your essay. Each scorer awards 1-4 points for each dimension: reading, analysis, and writing. The two scores for each dimension are added. You'll receive three scores for the SAT Essay—one for each dimension—ranging ...
This guide gets deep into every aspect of the SAT essay, from the rubric to prompts to the nuts and bolts of how to write a high-scoring essay. You'll learn the best tips and strategies to use to maximize the value of your SAT essay practice as well as how much time to devote to prepping for the essay. If you're looking for a comprehensive ...
This is the argument you need to deconstruct in your essay. Writing an SAT essay consists of four major stages: Reading: 5-10 minutes. Analyzing & Planning: 7-12 minutes. Writing: 25-35 minutes. Revising: 2-3 minutes. There's a wide time range for a few of these stages, since people work at different rates.
For example, with this practice essay, it could look like this: Intro: Braun argues that continuing to invest in space tech and research keeps us competitive in the world economy. Devices: logos, imagery, allusion. Body 1: Logos (logic): paragraph 3, 5, 7. Body 2: Imagery: paragraph 4, 6. Body 3: Allusion: paragraph 8.
Here are 5 tips for writing a killer SAT essay, should you decide to add on that section: 1. Stay Objective. The thing to remember here is that ETS (the company that writes the test) is not asking you for your opinion on a topic or a text. So be sure to maintain formal style and an objective tone.
The new SAT Essay is a lot like a typical college or upper-level high school writing assignment in which you're asked to analyze a text. You'll be provided a passage between 650 and 750 words, and you will be asked to explain how the author builds an argument to persuade his or her audience.
The SAT essay rubric is the next best thing to an answer key for the essay - use it as a lens through which to view and assess your essay. Of course, you don't have the time to become an expert SAT essay grader - that's not your job. You just have to apply the rubric as best as you can to your essays and work on fixing your weak areas. For ...
Absolutely Essential SAT Writing Strategies. November 15, 2022. •. 10.8 min read. tl;dr: The SAT essay is graded on three metrics — Reading, Analysis, and Writing — each on a scale from 1-4. To score an 8/8/8 on the SAT essay, you need to understand the rubric and keep in mind the three important parts of the essay: analyzing the prompt ...
In the SAT essay section, you are given one passage of about 650 - 750 words. You have 50 minutes to read through the passage and analyze it. Analyzing the passage does not mean simply stating what the passage is about. It's also not about agreeing, disagreeing, or sharing your personal opinion about the content.
You have 50 minutes to read the passage and write an essay in response to the prompt provided inside this booklet. CD . 0 . REMINDERS • Do not write your essay in this booklet. Only what you write on the lined pages of your answer sheet will be evaluated. • An off-topic essay will not be evaluated. STANDARD TIME . Essay: 50 . minutes . This ...
The SAT is structured into three tests with an optional fourth test: Reading, Writing and Language, Math, and an optional Essay. The Reading Test measures your reading comprehension and analysis skills using excerpts from literary fiction or academic texts. You have: 65 minutes to answer 52 questions.
The essay score is not a part of the 400-1600 score. Instead, a student opting to take the SAT Essay receives 2-8 scores in three dimensions: reading, analysis, and writing. No equating or fancy lookup table is involved. The scores are simply the sum of two readers' 1-4 ratings in each dimension. There is no official totaling or ...
How the SAT Is Structured. The digital SAT is composed of two sections: Reading and Writing and Math. Students have 64 minutes to complete the Reading and Writing section and 70 minutes to complete the Math section for a total of 2 hours and 14 minutes. Each section is divided into 2 equal length modules, and there is a 10-minute break between ...
Your total score is your overall score and is a combination of your section scores (see below). The highest composite score for the SAT is 800+800, or 1600. The average score is 1000. Your section scores are the individual scores for the two main sections of the SAT: Reading and Writing and Math. Each of these sections is scored out of 800, and ...
The SAT was revised in March 2016. The aspect of the exam that is most changed is the essay. Instead of writing a 25-minute opinion piece, you will have 50 minutes to analyze how the author of a given passage constructs his or her argument. Additionally, instead of having the exam integrated into your composite score, you will receive a ...
The SAT puts your achievements into context. That means it shows off your qualifications to colleges and helps you stand out. Most colleges—including those that are test optional—still accept SAT scores. Together with high school grades, the SAT can show your potential to succeed in college or career. Learn more about why you should take ...
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
This is your SAT score, also referred to as your total score. Next to your score are the numbers 400-1600, indicating that the range of possible scores on the SAT is 400-1600. To the right of your total score is your score percentile, telling you what percentage of students who took the test did better or worse than you.
Here are three things you should know about the 50-minute SAT essay as you decide whether to complete it: To excel on the SAT essay, you must be a trained reader. The SAT essay begs background ...
What Does the SAT Cover? The SAT has four sections, as well an optional essay. The first section will be Reading, followed by Writing and Language, then the no calculator section of Math, followed by the Math section you're allowed a calculator on. If you decide to take the SAT essay, it'll be the final section of the exam.
In his essay, written for the online Free Press site, Berliner said NPR is dominated by liberals and no longer has an open-minded spirit.He traced the change to coverage of Trump's presidency ...
Almost all the ballistic missiles and drones Iran launched at Israel in an unprecedented attack late Saturday were intercepted and failed to meet their mark, according to Israel and the United ...
Key Takeaways for the SAT Sections. The SAT is composed of four sections: Reading, Writing and Language, Math, and Essay (optional). These sections target an array of academic skills deemed necessary for college, from reading comprehension to proofreading to problem solving.
When asked for further comment late Tuesday, Berliner declined, saying the essay spoke for itself. The arguments he raises — and counters — have percolated across U.S. newsrooms in recent years.
SAT Essay Scoring. Find information on how the SAT Essay, available through some of our state partnerships, is scored. Learn more about SAT scores and the other information in your score report.