
List of 107 Classroom Teaching Strategies (With Examples)

Use this list of 107 classroom teaching strategies for your lesson plan or teaching portfolio. This can help demonstrate pedagogical knowledge and the ability to apply theory to practice.
Or, try some of these strategies out when you’re low on ideas and looking for a fresh way to teach in the classroom. Note that these are just some examples of teaching strategies – I’m sure there are even more out there!
Tip: Bookmark this page so you can come back to it every time you need some new teaching strategies!
Teaching Strategies Examples (List)
1. flipped instruction.
Description
Flipped classrooms involve asking students to complete the reading, preparation and introductory work at home. Then, during class time, the students do practice questions that they would traditionally do for homework.
- Flipped instruction enables the teacher to offload the direct instruction elements of education like Introductions to homework. This enables teachers to spend more time on student-centered differentiated support .
- Students may not complete their assigned pre-class homework, which will undermine the lesson.
Theoretical Link
Social Constructivism / Socio-Cultural Theory : The teacher can spend more time supporting students in a student-centered environment.
- Assign a video introducing a concept for homework.
- Spend the first 10 minutes of the lesson assessing students’ comprehension of the video
- Jump straight into student-centered practice tasks
- Walk around the class helping students who need additional support for the rest of the lesson
See my full article on Flipped Classrooms Pros and Cons.
Related Article: 25 Teaching Styles Examples
2. Play-based learning
Students learn cognitive, social, and physical skills during play tasks. Tasks can be teacher-led with specific goals (e.g. volume transfer in a sandpit) or unstructured student-led play.
- Engagement: students may be more engaged during active play-based learning compared to teacher-centered instruction.
- Cognition : students get the opportunity to learn through discovery and trial-and-error, helping to build neural pathways
- Social: students play together, developing communication, groupwork, and negotiation skills.
- Physical: play engages fine and gross motor functions , helping to improve physical abilities.
- Many traditionalist, including many parents and potentially your head teacher, may consider play to have no educational or academic benefit.
- Parents may frown upon this method for older students, despite its benefits across age groups.
- Many people consider that the risks of injury during play-based learning are too high.
( Read More: Pros and Cons of Play Based Learning )
Social Constructivism. Students learn through social interaction and building knowledge in their minds through trial and error.
Play is also encouraged in all 5 Contemporary Early Childhood Perspectives (Froebel, Reggio Emilia, Forest Schools , Steiner-Waldorf Schools, and Montessori).
- Use modelled instruction to show students how to play with developmentally appropriate resource-rich toys and puzzles. Consider puzzles that require mathematical skills that link to current curriculum outcomes.
- Provide students with the puzzles and allow free unstructured play time
- Mingle with the students, helping them with prompting and guiding questions
- End the lesson with a whole group discussion of what they learned during the lesson.
See my full article on Play Based Learning Pros and Cons .
3. Project-based learning (PBL)
Project-based learning requires students to spend an extended period of time (e.g. a week or more) on a single project to gain in-depth knowledge about the task. The projects should be personally meaningful and give students freedom to go in-depth on areas of interest.
- Students have the opportunity to become ‘experts’ on topics. By going deep on a topic, students may become very knowledgeable and feel empowered.
- A balance is struck between ensuring students focus on curriculum-linked projects and giving students the freedom to explore the details of a topic that are of personal interest.
- Students tend to have increased freedom using this approach. So, students need to learn self-regulation skills before beginning the task.
Constructivism in the Classroom : Students work independently using their own intellect and resources to learn. By doing personal research, students ‘construct’ knowledge in their minds and apply that knowledge to the project to demonstrate their knowledge.
- Teacher assigns students a research question, such as “What are the key characteristics of mammals?”
- Students work in small groups to come up with an idea for a poster, diagram, or presentation project on the topic.
- Teacher approves or asks for amendments of students’ proposed projects.
- Students are provided a series of lessons over a 2-week period in computer labs and in resource-rich classrooms to complete their project.
- Teacher checks-in intermittently to ensure standards are upheld and to stimulate students to improve upon their projects.
- The project concludes with students presenting their project to their parents.
4. Authentic Learning
Authentic learning involves having students learn about concepts in real-life (or near real-life) environments. Similarly, authentic assessment refers to assessments in real-life (or near real-life) environments
- By learning a task within its context, a student will understand its value for them outside of the classroom.
- Engagement: students may be more engaged in a task if they understand its practical application rather than just its theoretical purpose.
- Cognition and Memory: Students may find it easier to recall information if they can reflect on an instance in which they applied the knowledge to a real-life task.
- Authentic learning tasks are difficult to set-up from within a classroom.
- It is debatable whether so-called ‘authentic’ environments are genuinely authentic. A mock supermarket experience for practicing counting money, for example, lacks the potential for environmental distractions of a real-life situation.
- Some information is by its very nature academic and theoretical rather than practical, and this information is still of value to students.
Constructivism: Authentic learning environments are designed for students to be active learners who ‘construct’ knowledge through personal experience.
- An ESL teacher provides students with a set of conversational tasks to complete during a day’s field trip to the city.
- Students complete the tasks in the ‘real world’ by walking around the city asking for directions, buying lunch, etc.
- Class comes together at the end of the day to discuss and reflect on their experiences of applying their knowledge in the ‘real world’.
5. Discovery Learning
Discovery learning involves allowing students maximum freedom within a resource-rich environment to ‘discover’ answers to challenges. It requires students to build upon prior knowledge and use resources available in the environment to increase their own knowledge.
Discovery learning is often held in contrast to teacher-centered approaches, as students are not ‘told’ information; instead, they must discover knowledge for themselves..
- Students generate knowledge for themselves rather than being told what is right and wrong.
- By discovering truths, students will have a firmer understanding for the reasoning behind why something is true.
- Too much student freedom may distract students from the learning outcomes.
- This can be a time-consuming technique as students discover information at their own pace. It can therefore be difficult to implement in education systems that are packed with curriculum outcomes that must be met.
Construcitivism: Students generate their own knowledge through engagement with their environment rather than having truths ‘told’ to them by an authority figure.
- Teacher places the appropriate resources in the classroom to allow students to discover truths themselves. These resources may include science experiment stations, newspaper articles, etc.
- Teacher transparently presents the lesson objectives to the students, i.e. “What is heavier – sand or water?”
- Students are given minimal guidance, but sent to the learning stations to try to answer the prompt themselves.
- Teacher provides minimal guidance, recognizing that making mistakes and trying the ‘wrong thing’ is also a part of the discovery experience.
- Students get together at the end of the class to discuss what they ‘discovered’.
6. High Expectations
Setting high expectation involves requiring students to put in maximum effort during their lessons. HIgh expectations does not mean expecting all students to meet a certain standard. Rather, it means expecting each student to try to beat their own personal best.
- High expectations are necessary to ensure students continue to strive for improvement. Without high expectations in the classroom, students can become lazy and lose respect for education.
- Teachers need to be aware that sometimes students have ‘off days’ where they cannot succeed at their normal level. This may be due to health, hunger, or environmental factors .
- Teachers need to balance high expectations with compassion for their students. Try not to let burnout occur due to strenuous demands.
- Measure students’ prior knowledge to ascertain their current developmental level.
- Have students aim to achieve at or above their current ability in a given task.
- If students underperform, provide formative feedback and insist they readdress their work to make edits and improvements.
- Allow students to progress to subsequent tasks only when their work has met or exceeded the minimum standard you set for that individual.
See my full article on High Expectations in the Classroom .
7. Parent and Community Engagement
Parent and community engagement involves bringing students together with their community. It can involve bringing parents and community members into the classroom, or bringing students out into the community on field trips.
- By engaging with the community, students come to see themselves as a member of their community.
- It can help students to get to know important members of their community to give them a sense of belonging, and help them see (and, in the future, seek) support networks.
- By bringing role models into the classroom (especially minority and female role models), students can come to see that they could potentially become female firefighters, politicians of color, etc.
- Students can learn from more than just one teacher to get a variety of perspectives.
- Safety concerns often require teachers and community members to fill-in forms and complete background checks before community engagement can occur.
- Finding members of the community willing to work with teachers can be difficult.
Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory: Students learn within family and community contexts (children’s ‘first teachers’) in order to respect and carry-on culturally engaged learning.
- Teacher does networking to find community members willing to come into the classroom.
- Teacher finds relevant curriculum links that community members can help them teach about.
- Teacher and community members meet to discuss a lesson idea.
- Community members and teachers team-teach in the classroom.
- Students are given the opportunity for one-on-one time with community members.
- Students present the results of their lesson to community members before community members leave.
8. Unconditional Positive Regard
Unconditional positive regard involves teachers consistently and unconditionally viewing students as capable and competent. When students make mistakes, fail, or misbehave, it is the teacher’s role to continue to let students know that they believe in the student and their abilities.
- Empowering: when students are given unconditional positive regard, they know that their teacher believes in their ability to constantly do better.
- Shows Empathy and builds Trust: children come to learn to respect and trust their teacher when they know their teacher is always on ‘their side’.
- Teachers need to ensure that they still let students know that inappropriate behavior or lack of effort is unacceptable. The teacher should follow-up their discipline with comments about positive regard.
Humanist theory of Education : Humanist Carl Rogers invented this approach. He believed unconditional positive regard was necessary for building students’ self-confidence.
- “Even though you did not do well today, I expect that you will come to school doing better tomorrow.”
- “The quality of your work does not match your potential. Let’s talk about some strategies for improvement before you go away and do it again.”
See my full post on the Humanist approach to Education .
9. Modeled Teaching
Modeled teaching is an instructional strategy that involves the teacher ‘showing’ students how to do a task. The teacher shows the task while also breaking it down into small steps. This helps students to see how to complete the task.
- A very effective way to introduce new topics.
- The teacher maintains control when introducing a new idea to ensure students have appropriate understanding and safety knowledge before trying for themselves.
- Shows that learning can occur passively – students can learn simply by watching.
- Not appropriate as a standalone strategy. Students need to eventually try things alone to show competency. Therefore, consider matching modeled teaching up with the I Do, We Do, You Do method
Bandura’s Behaviorism: Bandura blends behaviorism with constructivism by showing that learning can occur through observation only.
See my full post on Behaviorism in Education , which has a segment on Bandura’s modelled instruction approach.
10. I Do We Do You Do Method
The I Do, We Do, You Do method is a scaffolding strategy that provides gradual release of responsibility from the teacher to the student. It involves three steps: (1) I Do: Teacher models the task; (2) We Do: Student and teacher do the task together; (3) You Do: Student attempts to complete the task alone.
- Students are provided an appropriate balance of support and freedom.
- Teacher has ample time to assess students’ abilities to make adjustments to their pedagogy as they move through the 3 steps (particularly in step 2)
- In large groups, students may fall behind at Steps 2 and 3.
Sociocultural Theory: Students learn through social interaction with a more knowledgeable other (see: Lev Vygotsky).
- Teacher asks all students to sit on a mat at the front of the class.
- Teacher models the steps required to complete the day’s task (I Do).
- Teacher re-does the task. This time, instead of telling the students the steps, the teacher asks students to raise their hand and tell the teacher what to do next (We Do)
- Teacher asks students to complete the task in small groups. Teacher walks around providing support (We Do)
- Students complete the lesson by doing the task alone. Teacher only intervenes for the few students who are still struggling (You Do)
See my full guide on implementing the I Do, We Do, You Do method .
11. Guided Practice / Cognitive Apprenticeship
Students follow along with their teacher as an ‘apprentice’. By working side-by-side, they learn the subtle little things (‘ tacit knowledge ’) required to know in order to master a skill.
- Students get very close one-to-one interaction with an expert, helping them learn.
- By learning-by-doing, the student learns not only the theory but also the skills required to complete tasks.
- An approach predominantly used for young children in Indigenous communities, which is not applicable on a wide scale in Western mass education systems.
- Requires one-to-one support, which is not often available.
Socio-Cultural Theory: Rogoff studied Guatemalan Indigenous teaching methods to come up with this approach. It fits under the socio-cultural theory because its emphasis is on social interaction between master and apprentice.
Common in trade schools for students studying to be mechanics, engineers, etc.
See my full guides on the Guided Practice teaching strategy and cognitive fexibility .
12. Scaffolding
Scaffolding involves providing support to students while they cannot complete a task alone. Then, when the student can complete the task alone, the teacher withdraws their support.
- Students feel supported while learning tasks that are just outside of their grasp at the present time.
- A clear way of guiding students towards new skills.
- May require a lot of one-to-one support, which can be difficult to provide in a classroom environment.
Socio-Cultural Theory: Scaffolding was invented by Jerome Bruner ( not Vygotsky).
- The teacher models a task before students try it themselves.
- The teacher provides the student with a visual aid (the scaffold, in this instance) that breaks the task down into small parts.
- After 15 minutes of practice with the visual aid, the aid is withdrawn and the students try the task alone.
13. Direct Instruction (a.k.a Explicit Teaching)
Direct instruction (also known as explicit teaching) is a teacher-centered approach that involves the teacher using simple straightforward language to explain concepts to students.
- Provides clear and direct knowledge to students
- Is sometimes the only way to teach something, particularly when introducing a new idea.
- Students cannot consolidate their knowledge with direct instruction alone. Explicit teaching should be followed-up with other teaching strategies that involve more active learning so students can practice and demonstrate their knowledge.
Behaviorism: Traditionally, direct instruction was embraced by behaviorists who believed in teacher-centered teaching. Today, it is used in most teaching approaches.
14. Repetition (Rote Learning)
Repetition involves giving students time to retry tasks over and over again until it is consolidated in their minds. The information should be safely in a student’s long-term memory before moving on.
- Repetition commits information to memory, and is often one of the only ways to ensure something is truly remembered long-term.
- Repetitive rote learning that lacks contextual background is hard to remember. Sometimes, giving context through doing tasks through real-life scenarios can be better for memory long-term.
- Repetition can disengage students and demotivate them.
- Doesn’t account for social and cognitive aspects of learning.
Behaviorism: Repetition is central to a behaviorist approach. Pavlov, a famous behaviorist found that he could teach his dog through repetitively associating a bell with food. The dog came to learn through repetition that the bell meant ‘food’.
See my full post on Behaviorism in Education.
15. Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition builds on simple repetition. Spaced repetition involves gradually increasing the space between times you repeat something. Repetition of a task should be very common. Over time, the task should be re-examined less and less often.
The idea behind spaced repetition is that the concept being learned is re-engaged with just before it is forgotten so that it is consistently recalled into memory and gradually sedimented into long-term memory.
- Provides long-term support to ensure students remember information over a sustained period of time.
- Perfect for revision and standardized test preparation.
- Can be disengaging and boring for students who tend to prefer active learning.
Behaviorism: Spaced repetition was invented by behaviorist theorist Ebbinghaus in 1885.
- Provide students with a sprinkle of review tasks as a part of their weekly homework.
- Start lessons (or set aside some time each week) with revision of tasks from months previously to jog students’ memory.
16. Prompting
Prompting involves providing students with nudges, guides and questions that will help them to move closer towards an answer. A prompt is a suggestion to a student that they pay attention to a particular aspect of a task that will help them get closer to the answer.
- Prompts are used regularly by teachers to get beyond blocks in student learning. Without prompts, students may never develop or improve.
- It is hard to know exactly how much prompting to give and at what stage. Students need time to think things through and make mistakes. Too much prompting too soon can prevent students from thinking for themselves.
Social Constructivism: Social constructivists believe teachers have a role in helping students to build knowledge in their minds. Teachers’ interventions can help spur knowledge development.
- A teacher might ask a question to get the student to look at the task from a different perspective.
- A teacher may point at a section of a diagram and ask them about that section.
- A teacher might start a sentence and ask a student to finish it.
17. Differentiation
Differentiation is a teaching strategy that requires teachers to change their teaching styles and educational materials to meet the diverse needs of students within a classroom. It generally involves grouping students into several sub-groups in the classroom based on ability, skillset or learning preferences.
- Enables the teacher to more effectively address the diverse needs of students in a large classroom.
- Ensures learning is more personalized in the hope that no child will be left behind in a lesson.
- Differentiation is often used as an excuse to dumb down a task – differentiated instruction should be paired with high expectations to ensure all students are working to their maximum potential.
Socio-cultural Theory: This approach acknowledges that all students have different social and cultural backgrounds. Therefore, each student requires a personalized learning approach. It realizes that one size fits all will not work because all students are different.
- Separate students into three ability groups: Advanced, Middle, and Lower. The advanced students can be provided with project-based learning tasks to complete while the teacher works with the middle and lower groups to provide additional support.
- Provide students with a range of tasks that addresses the same learning outcome. Students can choose between different tasks depending on their learning preferences.
18. Manipulatives
Manipulatives are physical educational toys (or: ‘tools’) which are used to support learning. Providing students with physical manipulatives during learning enables them to visualize their learning in a 3D space.
- Students can learn more actively when they have manipulatives than when learning through teacher-centered direct instruction methods.
- Helps students who need to visualize information to learn.
- Creation of physical models helps students to form mental models (‘ cognitive schemata ’).
- It can be expensive to gather enough materials for all students in a classroom.
- Providing students with toys can distract them from the task. Strong classroom management skills are required.
Constructivism: Constructivists including Freidrich Froebel and Maria Montessori have advocated for the use of educational toys to help students to explore and discover in student-led active learning contexts.
- Base Tens ‘Dienes Cubes’ are cubes that can be bunched into singles, groups of ten, groups of 100, and groups of 1000 to help students visualize the decimal system of counting.
- Colored beads can be used to help students in early childhood learn to recognize patterns.
- Froebel’s Gifts are 9 manipulative toys that students can use to solve developmentally appropriate puzzles.
19. Prior Knowledge Assessment
Prior knowledge assessment entails assessing students’ knowledge at the beginning of a unit of work in order to teach students at an appropriate level. If prior knowledge does not take place, teachers may teach content at a level that is either above or below a class’s optimal learning level.
- Ensures the content being taught is at an appropriate level.
- Respects the fact that students come into the classroom with pre-existing knowledge.
- Identifies misconceptions students may have about a topic.
- Enables teachers to take into account students’ cultural knowledge when preparing a unit of work.
- Ensure you assess prior knowledge well in advance so you can plan lessons based on prior knowledge. I’ve assessed prior knowledge at the start of a class before and realized the lesson I planned was completely useless!
20. Student-Teacher Conference
A student-teacher conference is a one-on-one discussion between a student and a teacher to take stock of a student’s needs. The conference usually involves a discussion of both strengths as well as areas for improvement. The conference should conclude with a list of goals for the teacher and student to mutually strive toward.
- An opportunity for both the teacher and student to express concerns and anxieties
- Helps students to feel ‘seen’, valued and cared for by the teacher
- Hard to achieve in every lesson. Teachers could consider systematically conferring with one or two students per lesson until all students are met with.
- There is a power imbalance in the student-teacher relationship which may prevent students from speaking candidly.
Socio-Cultural Theory: Interactions between teachers and students are important to learning within the socio-cultural approach.
- Print a list of your students with a column for ‘achievements’, ‘goals’ and ‘struggles’. Over the course of a week, meet up with your students and discuss with them what they’ve achieved in the current unit of work, what their goals are, and what the barriers are to achieving those goals.
21. Fill-In the Gaps (Cloze Passages)
A simple teaching strategy that involves asking students to fill-in an incomplete piece of text. This can happen verbally (starting a paragraph and asking students to complete it) and in writing (a traditional cloze passage).
- Helps students to jog their own memories by prompting them slightly.
- Enables teachers to quickly assess students’ knowledge (just-in-time assessment).
- Cannot be a consistently used strategy as students also need to learn through more challenging approaches such as discovery learning and project-based learning.
- Paper cloze passages involving a story in which the key phrases are removed.
- Prompting questions like: “Can you finish this sentence? The first king of England was …”
22. Peer Assisted Learning (PAL)
Has the teacher step aside and allows students to take charge of the learning environment.
- Students can often explain concepts to one another in a clear way because they’re on the same level and closer in their learning journey than the teacher, who probably learned the content years ago!
- Peer assisted learning is not the same as the students doing the teaching. Students should continue to view each others as partners in learning.
Socio-Cultural Theory: students learning through collaborative discussion fits firmly into the sociocultural theory of education .
- Invite students from a grade level above to come into the classroom and act as moderators of discussions on topics of interest.
- Pair stronger students with weaker students. Have the stronger students demonstrate their knowledge by supporting the weaker students. I find this works really well because children can often explain things in a clear language that other children can understand.
23. Poster Presentations
A poster presentation is a great way to demonstrate knowledge at the end of a lesson or unit of work. Provide the students with posters, pens, and printing materials if required.
- A fast, effective way of presenting knowledge to the class.
- Allows students to practice demonstration skills.
- Ends up with a physical product that can be photographed and added to the student’s portfolio to prove that outcomes have been met.
- Can be a lazy way to achieve presentation of knowledge. Ensure the focus remains on the content and not the coloring-in or drawing pretty pictures.
- Not useful for all lessons: when students can create a working model, diagram, etc. this would be preferred.
- Have students work in groups to write up their knowledge in a visually engaging way.
- Then, have each group verbally present their poster to the class.
24. Two-Minute Presentation
Two Minute verbal presentations, like posters, are an effective way of having students demonstrate their knowledge at the end of a lesson or unit of work. Each student gets two minutes to present their knowledge on a topic to the rest of the class.
- An effective, fast way of doing summative assessment.
- It is an inefficient use of other students’ time having them listen to 20 other two-minute presentations when they could be engaging in higher-order learning during that time. Students find it very boring and frustrating to sit through the assessment of other students.
- Use the two-minute presentation method for the final lesson in a series of lessons on one topic.
- Have students read over their notes from previous classes and write a summary of the top 10 points.
- Have students prepare their two-minute presentations by adding the notes to palm cards. With 10 points, students have about 12 second per point!
- Ensure students have time to practice with one another and instruct them on how to take additional notes on their palm cards for points they forgot during practice.
- If each student has a different topic or angle to present engagement may be enhanced during the class presentations.
25. De Bono’s 6 Thinking Hats
De Bono’s 6 thinking hats strategy asks students to look at an issue from multiple perspectives. It can be used for groups or individuals. Depending on the hat a student is provided, they have to think from a different perspective.
The Six Hats
- White hat: Provide the facts.
- Yellow hat: Explore the positives.
- Black hat: Explore the negatives (devil’s advocate).
- Red hat: Express your feelings and intuitions . Include concerns, dislikes and likes.
- Green hat: Be creative. Come up with new ideas and alternatives.
- Blue hat: The manager who ensures all the hats are sticking to their lane.
- Helps students to think outside of their own perspectives.
- Encourages students to attack an issue from many different angles.
- Teachers group work skills if used in a group.
- I often find it’s hard to get groups of 6, so sometimes one student has to use two hats.
- Introduce a contentious topic with a video or reading.
- Distribute hats to the students.
- Have students spend some time brainstorming what they would say on the issue from their perspective. If you have a large class, group all the white hats together, red hats together, etc. to work in groups for this part.
- Then rearrange students into groups where there is one colored hat per group (groups of 6 is ideal, or 5 with one person taking the role of blue hat as well).
- At the end of the class, have a whole group discussion summing up our points and list the details of the topic on the white board. Hopefully students will see that the issue is a very complex one!
26. Pop Quiz
A pop quiz is a short test that takes place with no prior warning. The quiz can be formative or summative. Link the quiz to rewards to keep students motivated to do well and be prepared at any moment.
- Can be motivating for students who enjoy the challenge of competing with themselves or others.
- Keeps students on their toes which encourages ongoing review and homework on the part of the students.
- May worry some students who are unprepared.
27. Democratic Vote
Taking a democratic vote is a progressive education strategy that attempts to empower students in the classroom. Have students vote on what or how they will learn within the classroom. This can be done at a small scale in a lesson plan by asking students to vote on how a lesson will progress, for example.
- Can empower students, giving them a sense of ownership over the classroom.
- Can build trust and rapport between the students and the teacher.
- Helps the teacher take the pulse of the class and understand what they want and need.
- Teachers may lose their power and control over the class if they overuse this approach.
- Just because the majority supports something, it doesn’t mean it’s best. A small group of students may fall behind and have their voices drowned out by the majority.
Progressive Education: Progressive educators such as Alfie Kohn advocate for empowering students through increased democracy in the classroom.
See my full post on Citizenship Education .
28. Non-Verbal Gestures
Using non-verbal gestures are powerful ways to help students learn, as well as to manage the classroom. Educators can explicitly teach signs or use gestures common in society.
- Teachers can give individual students instant feedback that is subtle and does not disrupt the rest of the class.
- Students feel acknowledged when small gestures are used just for them.
- It is a non-intrusive way of prompting students.
- Cultural sensitivity required. Different cultures ascribe different meanings to non-verbal gestures.
- Nods of approval can let a student know you have recognized their good work without disrupting the flow of the lesson.
- Pointing can be used to direct students’ attention toward prompts around the room or on worksheets that may help stimulate thinking.
- Tapping a watch can remind students to pay attention to time limitations of a lesson.
29. Environmental Manipulation
Environments have a strong impact on learning. Temperature, lighting, seating plans , colors and posters on the walls can all affect learning.
- A non-intrusive way of supporting learning.
- Helps students feel more comfortable in the classroom.
- Your classroom has limitations which may prevent the ideal environmental settings.
- Different students may work better in different environments (e.g. heat settings)
Humanism: Teachers pay attention to the conditions required for creating an optimal learning environment.
Classical Conditioning (Behaviorism): Students are ‘conditioned’ by cause-and-effect mechanisms that are subtle and that they aren’t even aware of.
For more, see my full post on behaviorism in education.
- When a class is too loud, try subtly turning off the fan. It’s amazing how often this small environmental manipulation can quiet down a class.
- Ensure the classroom is not too dark. A dark classroom can impede reading, especially for students who do not have perfect eyesight.
- Heat and noise can both prevent learning.
- Calm colors on the walls can help students relax into the learning environment.
30. Associative Learning
Associative learning takes place when several ideas are introduced to a student that are mutually reinforcing. In the classroom, this means presenting students with several stimulus materials that help a student to recall a fact.
- Is very effective during revision for an exam.
- Has questionable long-term benefits as at this stage the concept is not yet solidly consolidated in long-term memory. The recall of information is dependant on other associated information.
Behaviorism (Pavlov’s Dog): Most famously, Pavlov managed to get a dog to associate the ringing of a bell with food. The dog would salivate whenever the bell rang, whether or not there was food around.
Cognitive Constructivism: while associative learning is most commonly associated with Pavlov, constructivists also have an explanation. The more associations someone has with a topic, the more neural pathways are created connecting ideas. This helps improve memory recall.
See Also: Non-Associative Learning
- The teacher presents students with rhyming pairs to help a student associate one word with another. This can be effective in teaching vocabulary.
- When attempting to recall a fact, you can try to reflect on where you were and what else you were talking about when that fact was first introduced to you.
31. Cooperative Learning (Group Work)
Cooperative learning is a teaching strategy that involves having students work together rather than in competition. Usually, this takes place in small groups where the success of the group is dependant on the students working together to achieve a common goal (also known as positive interdependence). See more: Cooperative learning examples .
- Minimizes destructive competitiveness in the classroom which may undermine a collaborative and collegial atmosphere.
- Requires students to talk to one another which can help them learn from each other’s perspectives.
- Students need to be explicitly taught group work skills before participating.
- Some students may become lazy and let others do the work for the whole group.
Sociocultural Theory: Learning is stimulated when students converse with one another. They get to see others’ viewpoints which may help each student build upon or challenge their existing views.
32. Agenda Setting
The teacher presents the students with the agenda at the start of the day. The use of visual aids may be helpful here, allowing students to see a timeline of the day’s events on the board at the front of the classroom.
- Very effective for students with autism who often feel calmed knowing there is some structure to their day.
- Helps relax students into a day or even a lesson by giving them certainty about what’s to come.
- Any benefits that may arise lack scientific backing.
- Download a card set of images that represent different lesson types and activities. Use this card set to lay out a visual timeline for the students every morning.
33. Team Teaching
Instead of one teacher delivering a lesson to a group of students, several teachers get their classes together to teach one lesson to a larger group.
- Teachers can be more flexible. One teacher may take the role of presenter while the other acts as a support with students falling behind.
- Teachers can share the workload, particularly for preparation.
- Large groups may lead to some students falling behind without the teachers realizing.
- There is the potential for more noise distractions and subversive behavior in large groups.
- Teachers need to have the same work ethic for this to be effective.
- Large class sizes required.
- Consider having one teacher take the lead on all mathematics lessons and the other take the lead on all literature lessons. This enables each teacher to become more expert on their topic.
34. Directing Attention
Directing attention involves diverting students away from negative non-learning behaviors and towards positive behaviors by presenting them with engaging learning materials or ideas.
- Prevents negative behaviors without confrontation.
- Focuses on creating engaging lessons.
- Can be done multiple times in one lesson whenever a teacher sees a student is distracted.
- Tends to be more effective with younger children than older children.
- Use visual aids, worksheets and manipulatives to help direct and maintain students’ attention on something physical. With adults, I use flipchart paper (also known as butcher’s paper) as the prop to direct attention.
34. Visual Aids
Visual aids are any objects used in the classroom to attract students’ eyes and therefore immerse them more into a lesson. Visual aids can have both cognitive benefits (see: cognitive tools) and engagement benefits.
- Engagement: students are more likely to pay attention if they have something to look at.
- Cognition: some students may benefit from visualizing a concept to help them order ideas in their minds.
- Visual learning : some learners prefer learning visually than aurally (see: learning styles).
- A visual aid needs an educational purpose. Consider why you are using the visual aid before deciding to use it.
- Graphic Organizers
- Educational toys (see: Manipulatives)
35. Flexible Seating
Allowing students to sit where they choose, rather than having assigned seating, has had a resurgence in popularity in the past decade. A flexible seating classroom often has a range of differently organized workstations, allowing students to select a spot to sit that’s most comfortable for them and which best suits the style of learning that will be occuring in that lesson.
- Can reduce sedentary periods of time by allowing students to move around more during a lesson.
- Enables students to sit at a table that best suits their learning (computer table, group table, individual table, on a bean bag, etc.)
- There is often not enough space at workstations, meaning students end up not actually sitting where they choose.
- Often students like to have a spot they can call their own. It helps give students a sense of place and belonging.
- This approach is very common in the Agile Learning Spaces and Flexible Classrooms movement.
See my full post on the Common Classroom Seating Arrangements .
36. Formative Assessment (a.k.a Assessment for Learning)
Formative assessment involves assessing students’ learning throughout the learning process, not just at the end. Formative assessments can take place at one point in a unit of work or regularly throughout a lesson.
- Allows teachers to adjust their teaching if students are not quite up to where you expected, or if they are exceeding your expectations.
- Students get feedback on their progress before the summative assessment, allowing them to adjust.
- Gives the teacher a better understanding of their students. If a student fails a summative assessment but the teacher knows the student could do the task at the formative stage, more investigation can take place to see why there is a discrepancy.
- Can be time consuming to constantly assess students’ abilities.
- Formative assessments often lack the authority of summative assessment pieces.
- Formative assessments can be simple stops to get feedback and ongoing questioning of students.
- They can also take the form of pop quizzes or student-teacher conferences.
37. Summative Assessment
Summative assessments take place at the end of a unit of work and are often the formal final / overall grading of a student’s knowledge.
- Summative assessments are necessary for providing a final grade for a student and are often required by school boards.
- Summative assessments give students something to strive toward which may keep them motivated and encourage them to study.
- They are seen as too high-stakes and can cause stress for students.
- If a student does poorly, the assessment is right at the end, so the teacher and student often don’t have any more time address the problems and help progress the student’s learning.
- Standardized tests.
- Assessments for student portfolios.
- End-of-year exams.
- Entry exams.
38. Gamification
Gamification involves implementing elements of gameplay in your lessons. This can be as simple as creating a competition out of a mathematics quiz.
Recently, computer software such as excel and programming languages have been used in the classroom as elements of ‘digital’ gamification.
Don’t confuse gamification with game-based learning, which is discussed next.
- Gamification can make boring lessons fun , thereby increasing the engagement and motivation of students.
- Teachers must not lose focus on the learning outcomes that must be met. ‘Fun’ is not the goal, it is the means for achieving the goal, which is always learning .
- Get your students into two groups and have them compete in a trivia contest based on your lesson content.
- Give students table groups and reward tables with points depending oh how well they do.
See my full article on the pros and cons of digital play.
39. Game-Based Learning
Not to be confused with gamification, game-based learning involves the use of actual games (board games, computer games, sports games, etc.) into a lesson.
While gamification involves using elements of gameplay into lessons (points, competitions), game-based learning involves using actual games in a lesson.
- Students often love video games at home, so they get excited that they can play them in school as well.
- Games can also support cognition by prompting students to complete and practice tasks to win games. See also: cognitive tools.
- Parents may feel playing games in the classroom is not acceptable. Make sure parents know your reasoning behind using games.
- Ensure the focus remains on the learning outcomes, not just on ‘having fun’.
- Minecraft is a very popular computer game that is used in classrooms.
- Sim City is a popular game for city design courses.
- Use card games to teach counting. I teach ESL students counting using the game UNO.
See my full article on game-based learning as well as my explanations about how to use minecraft and sandbox games in the classroom .
40. Coaching
A coach does not stand in front of players and simply tell them what the ‘facts’ are. A coach stands behind a player. He watches the player and gives feedback on their performance. His job is to encourage, suggest adjustments and be the support network for the player.
Coaching is one of the great metaphors for teaching . A teacher who uses coaching as a strategy tried to emulate the role of the coach: observing and offering support and suggestions for adjustments.
- Student-centered : the student is the focus and the teacher is the supporter.
- Personalized: each student will get unique feedback based on their performance.
- Sometimes the teacher needs to introduce new ideas, meaning coaching may not be as useful as another approach such as modeling or direct instruction.
Sociocultural Theory: In sociocultural theory, teachers tend to encourage active learning and provide social support.
41. Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-based learning involves the teacher presenting a problem for the students to solve by making their own inquiries. It is similar to discovery learning, but is different in that inquiry based learning generally involves the teacher setting out a puzzling problem to solve at the start of the lesson.
- Students ‘find’ the answers rather than being given them by teachers.
- Answers emerge out of exploration, problem solving and discovery, meaning students learn why something is true, not simply what is true.
- Significant support is required to help guide students through their inquiry. Students need to be taught how to inquire and given the right inquiry tools (such as books, appropriate websites, etc.)
Constructivism: Students learn through constructing ideas in their heads rather than being told the facts.
42. Reciprocal Teaching
Reciprocal teaching involves having students facilitate their own small group lessons. It is usually used in reading lessons.
The teacher first models how to guide group discussions before sending students off to facilitate their own lesson. In groups of four, students usually take the roles of: questioner, clarifier, summarizer and predictor. Students read stimulus materials then self-facilitate a group discussion about the text.
- Students learn self-regulation learning skills which are essential for later in their lives.
- When students are trained up, the classes work very effectively and the teacher can fade into the background.
- Students learn group work, communication and negotiation skills. They also learn how to speak up in a group.
- Students learn to be mature even when the teacher isn’t looking. By taking on responsibility as ‘teachers’, students should rise to the challenge.
- Requires a lot of pre-teaching so students have the required skills for these sorts of lessons to work.
Sociocultural theory: working in groups, communicating and sharing ideas help stimulate thinking and encourages students to challenge their own ideas in order to improve them.
Example (Modelled off the I Do, We Do, You Do approach)
- The teacher should model the four roles required in front of the whole class, with several volunteers to act as the demonstration group.
- The teacher assigns groups and the four group roles: questioner, clarifier, summarizer and predictor.
- When students do the activity in small groups for the first time, explicitly walk the students through the steps. Use a bell or similar audible cue to cycle students through the group work steps.
- Allow the students to work in independent groups – walk around and help groups who are struggling.
43. Blended Learning
Blended learning involves a mix of online instruction and face-to-face learning. This strategy can be employed by giving students part of their instruction as homework online and part of it in class. It differs from flipped learning because a flipped classroom involves at-home instruction and in-class practice. Blended learning can have both practice and instruction occuring at home and/or in class
- Gives the teacher flexibility to teach partially during homework time and partially in class.
- Students need access to technology at home unless the at-home parts are only reading and printouts.
- Usually only suitable for university students who are short on time. Blended learning allows them to do some of the learning in their own time.
- Used regularly for distance learning students and rural and remote students.
- Used regularly at university level.
- If using this method, I recommend taking a look at the flipped learning model for some ideas of how to split your distance and in-class segments efficiently.
See my List of 10 Pros and Cons of teaching Online .
44. Growth Mindsets
A growth mindset focuses on teaching students that they have the power to improve and succeed if they put their effort into it. The opposite would be students refusing to try because they don’t think they have the power in their own hands to succeed.
Teaching growth mindsets is all about modelling positive behaviors. Include growth mindset in your lesson plans by finding points in the lesson to discuss specific strategies to move toward success, strategies for studying, and positive thinking.
- Focuses on helping students see that they have ‘ agency ’ (in other words, they are capable of improving their lives)
- Motivates students to improve their own lives
- Many students have many barriers to success. If you ignore those barriers and simply say ‘you can work harder’, this will make students feel disempowered. Teachers need to show students the pathways to success.
- Ensure the content is actually achievable for your students.
- Break down tasks into manageable chunks so that students know the steps toward success. Then, use encouragement to motivate students to put in their effort.
- Celebrate success to show students that they are competent and capable.
45. Culturally Responsive Teaching
Culturally responsive teaching is an instructional strategy that involves ensuring students’ cultures are integrated into lessons. This includes celebrating students’ cultural backgrounds when relevant and using learning styles that are dominant within your students’ cultures.
- Includes children from cultures that have been traditionally marginalized within the classroom.
- Minimizes the impact of Westernization of education.
- May make new students from cultures that are different to the majority in the class to feel a sense of inclusion and belonging in the classroom.
- Helps all students see the world from a variety of perspectives and learn to respect pluralism.
- Teachers need to be sensitive to cultures different to their own.
- Teachers should consult parents and community members about best strategies for the cultural needs of the students in the class.
Sociocultural theory: sociocultural theory believes
- Have role models from minority backgrounds come into the classroom to share their backgrounds.
- Consult with parents about ideal teaching methods within their culture.
- Avoid nonverbal gestures that have different meanings in different cultures.
- Another example: eye contact is considered respectful in Western cultures but acts of defiance in Indigenous Austealian culture.
46. Teaching to Mastery
Mastery learning and teaching is a strategy for ensuring all students meet a certain standard of understanding or ability before moving on.
Teachers set a benchmark of knowledge 9r ability for students to meet. Then, all assessment in this method is formative, where students are given feedback and as much time as possible to improve before progressing.
- Students are not left behind and gaps in their knowledge are not overlooked.
- Students may feel less stressed or rushed with this approach.
- There is no talk of inability or failure in this method as teachers and students keep working away at the task until success is achieved.
- There is not enough time in traditional school systems for this approach.
- The difference in abilities between students means some students will get a long way ahead while others remain a long way behind.
Humanism: there are elements of unconditional positive regard in this approach (see Carl Rogers).
- An example.may be that all students must get 80% on a test to progress to the next unit of work.
- This approach is common for getting a “handwriting license” in primary / elementary school.
47. Stimulus Materials and Props
Stimulus materials are tools that a teacher provides during lessons to spur students into engaging with the lesson or thinking more deeply about the content provided. They include videos, educational toys (manipulatives), worksheets, visual prompts, objects from outside the classroom, and so on.
Without stimulus materials, the classroom feels empty and detached from real life. Bring stimulus materials into the classroom to help students make stronger connections to things going on outside.
- Provides something for students to focus on which can focus students’ minds.
- Helps students to learn actively if they have the opportunity to touch and manipulate the props.
- Can inspire and draw-in students at the start of the lesson.
- Stimulus materials can be very expensive.
- Students can get distracted playing with the materials rather than listening to their peers or the teacher.
- Students need to learn to share materials.
Constructivism: constructivists encourage the use of props so that students can ‘learn by doing’ and be ‘hands on’ in their learning.
- Place several props into a bag. Have the students put their hands in the bag and see whether they can guess what the props are.
- Place an unusual prop related to your lesson in the middle of the classroom. Get the students to guess what it is before beginning the lesson.
48. Service Learning
Service learning involves having students meet learning outcomes while contributing to and ‘giving back to’ their community. This often involves volunteer work, internships and placements within the community where assistance is needed.
- Students can increase their sense of belonging within the community.
- Connections between learning and life are made explicit in this sort of learning.
- Learning moves from the theoretical to the practical.
- Students can come to see how they are connected to a wider ecosystem, and that they have an important part to play in serving that ecosystem for the good of all.
- It can be hard to place all your students in a service learning placement if there are many students to allocate.
- It may be impractical given safety and security requirements.
Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory: EST highlights that people are situated within community from whom they get their values and beliefs. By being more connected to the community, students learn who they are and how they’re connected to a society and culture that surrounds them.
- Prepare your students in the classroom. Consider having organizers or community members come into the classroom to tell the students what to expect.
- Have students write preparatory notes about what the intend to learn, who they intend to speak to, and what their day-by-day goals will be whilst doing the service learning.
- Have students complete their service learning / voluntary work in groups or individually.
- Meet with the students intermittently during the service learning and have student-teacher conferences on how it is progressing. Intervene where needed.
- Have students come together at the end of the project to reflect on what was learnt and how their understanding of their place in the community has evolved. Discuss possible future involvement and engagement in the community to emphasize that community involvement is an ongoing project.
49. Situated Learning
Invented by Lave and Wegner, situated learning involves learning by being embedded within a professional environment and slowly picking up the ways of doing and speaking within that context.
It has similarities to other instructional strategies outlined in this article such as service learning and cognitive apprenticeships. However, its defining feature is the slow absorption of knowledge through prolonged exposure to an authentic professional setting.
- Students learn the most important practical information required for a job.
- Students learn the ways of speaking and behaving that are required within a professional situation.
- Not practical as a teaching strategy in classrooms. It works best as an apprenticeship model for new graduates from university.
Sociocultural theory: the situated learning approach emphasizes the importance of learning from ‘more knowledgeable others’.
50. Sixty-Second Strategy
The sixty second strategy involves having students review one another’s work in three steps which take 60 seconds each. The steps are: respond, reflect and review. This usually takes place after a student presentation where the students give a cumulative 3 minutes of feedback and reflection on the presentation.
The goal is not just to give feedback to the presenter, but for the listeners to also think about how they would have done the presentation and what their own thoughts on the topic are.
- Students learn how to give feedback to others in positive and constructive ways.
- It is a great way for students to actively engage with other students’ presentations.
- Students need to know how to be positive in feedback and not be hurtful.
- Have the student who is presenting their work give their presentation.
- The students who watched the presentation have 60 seconds to write their thoughts on the topic that was presented.
- Next, the students have 60 seconds to write down feedback on the presenter’s work.
- Then the students have 60 seconds to provide positive affirmation and praise.
- At the end, have the students share their feedback with the presenter in small groups so that the environment is not so intimidating for the presenter.
51. Thumbs Down, Thumbs Up
Thumbs down, thumbs up is a simple strategy for getting immediate feedback from students. During a lesson, pause after each step to get instant thumbs down, thumbs up feedback on whether students understand the previous step.
If there are thumbs down, the teacher should ask those students if they have direct questions or whether they might want that section to be covered again in different language or more slowly.
- Enables the teacher to gauge students’ reactions in real time.
- Gives the students an opportunity to give the teacher feedback immediately so that they don’t fall behind or become frustrated.
- If the majority of students give thumbs up but only one or two give thumbs down, this is not endorsement to move on. Rather, the teacher should make sure no students fall behind.
52. Summarizing and Paraphrasing
For this teaching strategy, either the teacher or student summarizes something someone previously said in their own words in order to ensure they understanding each other without any misconceptions.
- In having a student repeat the teacher’s statement in their own words, the teacher can see whether students actually understand something.
- In repeating a student’s statement in different language, the teacher can see whether they truly understand what the student means.
- The biggest risk here is in the teacher ‘putting words in the student’s mouth’. This may give the student a free pass.
- The teacher explains a concept, then asks the student to repeat it without using the same words. A pause of a few minutes between the teacher’s explanation and the student’s response can be helpful in preventing the student from directly copying the teacher’s language. As time passes, the meaning should stay but the exact words should be forgotten.
- Alternatively, the student makes a statement, and the teacher translates it in their own words and finishes with “Is that what you meant?”
53. Demonstration
Demonstration involves showing the students a practical example of something that is being learned in class.
The difference between demonstration and modeling is that a demonstration usually:
- does not involve explicit explanation of all the steps, and
- is usually not followed by students having a go themselves.
Demonstration (rather than modelling) may be necessary when the concept being demonstrated is dangerous or requires expertise.
- Having something complex or theoretical demonstrated can be exciting to link theory to practice.
- Demonstrations may require expensive field trips or inviting experts and expert equipment into the classroom.
- A demonstration could be as complex as going to watch a space rocket launch or as simple as a ranger demonstrating how to use bear spray.
54. Role Modelling
Role modelling involves demonstrating the requisite behaviors or ideal way of acting within a learning environment. Role modelling has the intention of positively influencing students into copying the teacher’s positive learning behaviors.
- Students are socialized into behaving and learning in socially appropriate ways.
- A teacher who sets personal high expectations for their own learning will have those high expectations flow on toward the students.
- A teacher needs to be aware that all of their behaviors rub off on students. This means they need to ‘put on their happy face’ despite what’s going on in their private lives.
Bandura (Social learning theory): Albert Bandura believed that observation was important in influencing how people will behave and learn. See his famous Bobo doll experiment where children were more aggressive toward a doll when they observed an adult being aggressive toward it.
- Male teachers may role model positive masculinity, such as politeness and respect to all people regardless of gender.
- A teacher can be a role model my demonstrating engagement and volunteering within the community, insisting on respectfully welcoming guests when they enter the classroom, or having high regard and respect for reading, learning, and apologizing.
55. Predicting
Predicting involves asking students to make predictions or ‘guestimates’ before a study is undertaken. The teacher may make a prediction for the students to respond to, or ask students to make predictions themselves.
- It stimulates students to think about the logical flow-on effects of the things they are learning about (such as in science: gravity, momentum, etc.)
- Students are asked to think forward rather than simply react in the learning environment.
- At the start of a lesson (before introducing too much information), ask students what they think will happen during the lesson.
- Show the students a diagram or comic strip demonstrating sequence of events with the last few events missing. Have students fill-in the gaps.
56. Intentional Mistakes
The teacher inserts intentional mistakes into their teaching materials (such as misspellings in their presentations) or their speech in order to:
- Check students’ depth of knowledge,
- Make memorable teaching moments, or
- Keep students critically engaged.
- It keeps students on their toes throughout the lesson, particularly during the boring parts.
- It can make learning into a game if you let the students know to look out for the mistakes in advance. You could also offer a reward for the person who identifies the mistake.
- It can lead to critical discussion about common mistakes that students make in a topic.
- You may risk having students believe you had made the mistakes intentionally.
- Students may believe the mistakes are truths and end up believing things that are untrue.
- Create intentional spelling errors in your worksheets and powerpoint presentations.
- Mispronounce a word and see if students realize.
- Flip two words in a sentence and see if anyone realizes.
57. Reflection-in-Practice / Immediate Feedback
Immediate feedback is any feedback that takes place during a lesson rather than after a lesson or exam has been completed.
There are two primary types of immediate feedback: feedback from students to teachers, and feedback from teachers to students.
The feedback’s purpose should be to make impromptu changes during the lesson before it is too late.
- Teachers can adjust their teaching methods in the moment to ensure the lesson is a success.
- Students can adjust the ways they are going about completing a task to ensure it is successful.
- In large groups, one-to-one feedback can be difficult.
- Teachers need to be able to think on their feet to make immediate adjustments.
David Schon’s ‘Reflection in Practice’: According to Schon, successful practitioners reflect in practice rather than just on practice. Reflection in practice requires practitioners to reflect on what they’re doing while they’re doing it.
- Asking for a thumbs up / thumbs down from students to see if they understand something.
- Looking over the shoulder at children’s work to see how they’re coming to their conclusions.
- Accepting ‘hands up’ questions at any point during an explanation or lecture.
58. Whole Group Class Discussion (a.k.a Circle Time)
A whole group class discussion gets all students in the class talking to one another in one group. When I use this strategy, I try to get students sitting in a conversation circle. The benefits of students sitting in a circle include:
- There is a neutral power structure with no one at the head of the discussion.
- All students can see one another.
- Whole class discussions encourage all students to develop the confidence to share their own views publicly.
- If the whole class gets into it, there can be a lot of great back-and-forth.
- Often, the loudest and most confident students dominate the discussion.
- Some students are too shy to speak up.
- It is easy to embarrass a student, so be careful to be sensitive.
- Use a speaking stick so only one person speaks at a time. The only person who can speak is the person with the speaking stick.
- Use discussion circles so that all students can see each other when talking.
- If conversation is slow to start, consider asking individual students direct questions.
- Use open-ended questioning to force students to answer in full sentences.
59. Concentric Circles
Concentric circles is a method that builds on the whole group circle time discussion. Students sit in two concentric circles with the inner circle facing the outer circle. The students in the inner circle should be paired one-to-one with a student in the outer circle (like speed dating).
The teacher poses a question and the pairs are given 60 seconds to discuss the problem. Then, the students from the inner circle rotate one person to the right so they are facing a new partner for the next question.
- Disagreements about pairing and students working with their friends are resolved because each student gets a turn working with another student.
- Students get to learn and communicate with other students they don’t usually spend time with.
- Discussion can help students see perspectives that they did not come up with on their own.
- There needs to be an even number of students in the class so each student has a partner to work with.
Sociocultural theory: students learn by interacting with others to help them test, challenge and extend their own ideas.
60. Hot Seat
One student takes the role of a character from a book, history, etc. They dit in front of the class and get interviewed by their classmates. The student must stay in character and answer the questions from the perspective of that character.
- Students explore topics from perspectives other than their own, helping them to develop lateral thinking skills .
- Students need time to research their character and brainstorm their character’s perspectives on various topics before being put in the hot seat.
- Shy students or students who are not confident with the material may be intimidated by this instructional strategy.
- This strategy can be linked up with strategies like De Bono’s thinking hats where students would answer questions from a particular perspective.
61. Graphic Organizers
Graphic organizers are visual aids in the classroom designed to help students visualize and conceptualize ideas and their relationships with other ideas. Examples of graphic organizers include flowcharts, mind maps and venn diagrams. Use them to help students think more deeply about topics.
- Very useful for students who are visual learners.
- Provides a framework for deeper and critical thinking.
- Provides structure to help students who are unsure of how to proceed with critical thinking.
- Don’t stick to just one framework as the frameworks narrow the scope of thinking in exchange for depth. Mix up your graphic organizers.
Cognitive Constructivism: cognitive constructivists such as David Jonassen believe graphic organizers help students to share their cognitive load with the organizer, helping them to organize and sort ideas in their heads more effective.y
- Flow charts
- Venn diagrams
- Concept maps
- Network or family tree
- Spider diagram
- Compare-contrast matrix
- Series of events chain
- Character charts
62. Think Pair Share
This is one of the simplest, most frequently used, but also most effective classroom teaching strategies. Students think about a topic on their own. Then, they pair up with a partner and discuss, compare and contrast their thoughts together. Thirdly, the pair share what they discussed with the whole class.
- Moves students from individual thinking to social thinking in a clear process.
- Helps students to vocalize their own thoughts in small and large groups.
- Helps students to see other people’s perspectives by encouraging communication, compare and contrast.
- Students need the confidence to speak up in front of the whole class. I have found some students like to have the comfort of flip chart (butcher’s) paper as a prop when presenting their discussions to the class.
Sociocultural theory: learning through conversation allows students to see diverse perspectives and therefore improve on their own perspectives.
- Step 1: Think. Students are given 2 minutes to think about the topic on their own and take 5 bullet points on their own.
- Step 2: Pair. Students get together in pairs (or groups of 3 if appropriate) to compare and contrast their own ideas. Students discuss the ideas and come up with a collective group of ideas.
- Step 3: Share. Each group shares their own thoughts with the whole class. As each group presents, other classmates can challenge ideas or take additional notes to add to their own group’s thoughts.
63. Group Roles
Assigning group roles for students who are doing small group work is another simple instructional strategy to try. There are many group role types to be found online. I tend to use the roles of: timekeeper, moderator, notekeeper, and collector. All students should be equal discussion contributors, and this is managed by the moderator.
- Helps to structure the activity, give students certainty in what they are doing, and reduce the uncertainty from group work.
- Encourages communication to get students hearing other students’ ideas and perspectives
- Students must be explicitly taught the group roles and need time to practice them.
Sociocultural Theory: By communicating with peers, students widen their perspectives and (with more knowledgeable peers) have their knowledge scaffolded.
- Ensure you model the group roles before beginning the activity. Consider using a fishbowl method by having a sample group sit in the middle of a circle modeling the roles to the rest of the class.
- For the class’s first attempt at group roles, structure it very clearly by getting the students to follow a clear step-by-step guide. Slowly release responsibility to students when they are ready.
64. Barometer
The barometer method gets a measure of students’ opinions by asking them to stand on a line from 0 to 10 (1 = strongly disagree, 5 = unsure or conflicted, 10= strongly agree).
- Students tend to find this a non-intimidating way of sharing their opinions.
- Can be a good way of getting students talking. Once they stand on the line, you can ask them to explain why they stood where they did.
- It may be beneficial to prevent students from taking a neutral “I don’t know” stance without sufficient defence of this position.
Critical theory : The barometer could be paired with critical theory if students critique assumptions in society with a focus on the perspectives of marginalized groups.
- Introduce a complex or controversial issue through a book, video or class discussion.
- Ask students to stand on an imaginary line from 0 to 10 representing their opinion.
- Place students into three groups based on their position in the line: agree, unsure and disagree. Have the three groups present their 5 best arguments to the class.
65. Cognitive Tools
Cognitive tools are educational technologies designed to promote thinking beyond what a student can do without the technology. This might include using wearable technologies to help students map out their own movements to then test their knowledge of geography, use of excel sheets to create financial estimations, etc.
- Educational technologies can help us do things we couldn’t do without them.
- Can engage students who love computers and technology in learning tasks.
- Teachers must ensure technology use is focused on helping students learn more or at a higher level of critical thinking than if they didn’t have technology.
Cognitive Constructivism: this approach, invented by david Jonassen, emphasizes that computer technologies should be used to extend and promote higher-order cognition.
See my full article: Examples of Congitive Tools in Education .
66. Anticipation / Guestimation
Anticipation and guestimation is an instructional strategy designed to get students thinking about the consequences or flow-on effects of actions. Teachers ask students to make predictions based on limited knowledge about a topic
- Students often have to use mathematics and logical reasoning to succeed in this task.
- Students are required to be resourceful and seek clues that will show them the possible consequences of action.
- It is important to strike a balance between giving enough information to make informed guesses and not too much information that the students can deduce the full answer.
67. Silent Conversation
A silent conversation is a way of getting students to communicate without having them speak up in front of the class. Students write their responses to a prompt on sheets of paper but cannot speak while doing so. They should then also write responses to one another’s points so that they are ‘conversing’ through writing.
- Students who are shy to speak up my be more willing to participate, especially if their written response can stay anonymous.
- It can often be easier to respond in writing than speaking because students have time to reflect and think about the wording of their response before writing it.
- Only one student at a time can write their response. Consider what other students will be doing during this time.
- Students must be competent writers.
Sociocultural theory: we learn and extend our knowledge through social interaction. By seeing others’ points, we can improve or amend our own.
- One way to do this is to have a flip chart paper sheet (butcher’s paper) on a wall with a discussion prompt written above. Have students walk up to the paper intermittently thought a lesson to write responses to the prompt. After the first few students write their responses, the rest of the students must respond not to the prompt but to the answers written by previous students – how can they add to or challenge what someone else has already said?
- The second common way of having a silent conversation is to pass a piece of paper around the class and have students write their responses to conversation chains on the piece of paper.
68. Devil’s Advocate
A devil’s advocate is someone who argues for an opposing point of view in order to stir up an argument and poke holes in other points of view. The devil’s advocate does not necessarily need to believe the points they are arguing. Either the teacher or students can be the devil’s advocate I’m this teaching strategy.
- Encourages students to see their own blind spots or misunderstandings.
- Helps students to see a diversity of points of view.
- Improves students’ debating skills.
- Students and parents may interpret you devil’s advocate position as an attempt to teach unsavory views in the classroom.
Critical theory: A devil’s advocate can help students with skills desirable within critical theory, like seeing views of people who are not commonly heard in society and the capacity to critique dominant narratives in society.
- The teacher can note in their lesson plan moments when they believe there are opportunities to play devil’s advocate role promote debate.
- The teacher can give students debating points where one person acts as devil’s advocate and another as the person defending the dominant perspective.
69. Strategic Pauses
Strategic pauses are one of the most important tools in a teacher’s toolbox of teaching strategies. A strategic pause is a gap between statements to let a point sink in or linger, or to give students a moment to think about an answer before the teacher moves on.
- An excellent classroom management strategy
- Encourages students to think and not rely on teacher prompting
- Emphasizes important points
- Can leave students confused
- Requires follow-up and knowledge testing
Cognitive load theory: Too much information at one time can cause a student to lose track. Time is required for the mind to interpret, sort, stack, save and withdraw information in their mind (‘create cognitive schemata’).
- Pause after a question for 10 seconds before discussing the answer.
- If the class has started getting unsettled, often a pause in the teacher’s speaking is enough to settle them again and remind them to re-engage with the learning materials.
- Slow speech with sufficient pauses between ‘chunks’ of information (seeL ‘chunking’ strategy) can help students arrange information in their minds appropriately.
70. Chunking
Chunking involves presenting information in manageable ‘chunks’ to allow students to sufficiently process information before moving on to the next section of a lesson or task.
Teachers should present only a manageable amount of information to students before giving them a chance to consolidate the information and practice their new knowledge.
Without giving sufficient time to consolidate information before giving new information to a student, the student will struggle to keep up with the information and old information may fall away before it is secured into their memory.
- Less students will be left behind, confused and disillusioned in the classroom if they are given consolidation time.
- There is often not enough time in a crowded school curriculum to chunk information well enough.
- It is hard to tell how much is ‘too much’ information, and how long is long enough before knowledge is consolidated into memory.
Cognitive Overload Theory: If students are given too much information, their mind becomes ‘overloaded’ and they are unable to process more information. We only have a limited amount of working memory space in our minds. See: John Sweller’s cognitive overload theory .
- Only teach two or three key points per lesson.
- Provide a lot of discussion and practice time before moving on to presenting new information.
- Consistently use formative assessment and reflection in action during the lesson to see when is the ideal time to move on.
71. Snowball Discussions
Snowball discussions are another twist on the think-pair-share method. For snowball discussions, students start in pairs and share their thoughts and ideas together. Then, the pairs join up with another pair to create a group of four. These four people share thoughts together, compare notes, debate ideas, and come up with an agreed list of points on a topic.
Then, groups join up again to make groups of eight. The groups of eight compare points and perspectives, then join up to create groups of 16, etc. until it ends up being a whole class discussion.
- An effective strategy for promoting discussion between students. It can be useful for getting students to compare how different groups of students approach points from different perspectives.
- The class group needs to be large (20+) for enough rounds of this strategy to happen.
Sociocultural theory: social interaction helps students see perspectives that are not their own and challenge their own views. This helps them pick holes in their own points and improve their misconceptions.
72. Homework: Knowledge Consolidation
Yes, homework is a teaching strategy! A traditional approach to homework sees it as an opportunity for students to consolidate information that was taught in class. Studying for upcoming exams is often also an important part of homework.
Other homework strategies like flipped classroom are possible – see the flipped classroom discussion earlier in this article.
- Help students to consolidate information learned in class.
- Ensures students have an opportunity to keep information fresh in their minds and be reminded of information learned in previous months.
- Excessive homework can impede students’ rights to enjoyment, sports and extracurricular activities out of school.
- Students often do not have support at home if they get stuck.
Behaviorism: repetition over time helps memory retention.
73. Active Listening
Active listening involves using strategies to pay close attention to what someone is saying. Teachers can explicitly model active listening by giving students strategies like pointing their bodies at the speaker, keeping their eyes on the speaker, nodding when they agree, and putting hands up to ask questions or clarification.
- Active listening encourages respect in the classroom.
- It could help students to remember better because it minimizes distractions.
- Students may be more likely to contribute questions if they are paying more attention.
- Some students (such as students with autism) need stress balls, fidget toys, etc to help them concentrate.
Examples that show active listening include:
- Facing the speaker square-on
- Eye contact
- Asking questions
- Repeating, paraphrasing or summarizing the speaker’s statement.
74. Connect, Extend, Challenge
The “connect, extend, challenge” teaching strategy is a three-step strategy designed to get student thinking about how their knowledge is progressing.
In step 1, students ‘connect’ what they’re learning to their prior knowledge. In step 2, students think about how the new knowledge ‘extends’ what they already knew. In step 3, students reflect on what ‘challenges’ they still face: what is still confusing to them?
- This is a framework that gets students to explicitly think about how they are progressing in their learning.
- The clear steps give students guidelines to help them achieve success.
- Requires prompting and scaffolding
Social Constructivism: This strategy has implicit links to Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory. Students look at how their backgrounds impact their thinking, what level they are at, and what is still sitting in their ‘zone of proximal development’ (.e.g what they need to learn next).
- Split a piece of paper into three columns to help students in this task: one column for ‘connect’, one for ‘extend’, and one for ‘challenge’.
75. Create a Headline
While a seemingly simple activity, this instructional strategy gets students to refine the topic they’re exploring down to one simple sentence that catches the essence of the issue.
For this strategy, have students come up with a headline for the lesson as if they’re a journalist reporting on the issue at hand. Get them to think about how it can be catchy, explain the problem at hand, and provide an engaging ‘hook’ to draw readers in.
- Helps students identify the key point of a lesson, forcing them to think about what is really important in the lesson.
- Some issues are complex and refining it down to one sentence may risk simplification.
To extend this activity, have students write a journalistic piece to go under the headline.
76. Lesson Objective Transparency
Being transparent about a lesson objective is a teaching strategy designed to help students understand the purpose of the lesson. By knowing the objective from the outset, the students are less likely to get confused about the purpose and direction of their lesson.
- Students are aware of the purpose of the lesson, which may make it more relevant .
- Students can more objectively measure how successful they have been in the lesson.
- Lesson objectives are often worded for adults not children, so the wording may just confuse the students at times.
- Write your lesson objectives on the first slide of lecture slides if relevant.
77. Open-Ended Questioning
Open-ended questioning involves asking questions that require an elaboration in the response. In other words, it cannot be a question that can be answered with “yes” or “no”.
- Students are required to provide explanations and justifications for the points they make.
- Teachers get a more detailed appreciation of students’ levels of knowledge .
- Make a habit of using open ended questions when talking to students about their work.
- Write all assessment tasks with open ended questions.
- Pose open ended questions as stimulus prompts.
78. Fishbowl
The fishbowl strategy gets a small group of students to sit in a circle in the center if the classroom with the rest of the class sitting in a circle around the group.
The students in the middle of the circle complete a discussion or task as a demonstration for the students observing.
- Teachers can use advanced students in the middle of the group as a way of modeling skills or behaviors for the remainder of the class.
- More knowledgeable students can model behavior for less knowledgeable students.
- Students get a chance at performing in front of others.
- Many students will find doing a task I’m front of their peers intimidating.
Bandura’s observational learning : Bandura argues that students can learn from observing the modeling of others.
- Get older students from higher grades to sit in the middle of the fishbowl.
- Or, use the fishbowl as the “we do” step in the I do, we do, you do method.
79. Four corners
Use the four corners of the classroom as different stations for answering questions proposed by a teacher.
The stations may have answers like: strongly agree, agree, disagree, strongly disagree. Another example may be periods of time for a history exam: the 50s, 60s, 70s, 80s. Or, the corners may have specific answers in the corners related to the questions being asked.
- This activity may be appealing for kinesthetic learners who want to move about to stay engaged.
- Provides a visual comparison between different views of students in the class.
- When students head to the corners, the teacher needs to ask students to explain their decisions to ensure depth is achieved in the lesson.
Multiple Intelligences: The lesson can help students who are kinesthetic learners.
80. Give One, Get One
This strategy involves getting students to trade ideas with one another.
Students write down their answer or thoughts to a TEACHER’S question. Then, they pair up. The students give their answer to their partner and take their partner’s answer. They discuss the differences between and merits of each answer.
Students then split up and find a new partner to repeat the activity.
- Writing down an answer ensures all students participate and that all students provide an explicit response.
- Seeing other people’s answers helps students get a broader perspective on a topic.
- Pre-plan for what to do when you don’t have an even number of students in the class.
Sociocultural theory: students learn from their peers through discussion. Discussion can help broaden horizons and allows students to see multiple perspectives on an issue.
- Present a discussion topic or question to the class.
- Have each student write down 3 points on a piece of paper to answer the question.
- Pair students up to discuss their answers. Get them to consider similarities and differences as well as pros and cons of each answer.
- Have students break apart and trade answers in another pair.
81. Brainstorming
Brainstorming involves asking students to come up with their initial thoughts on an issue. The thoughts do not have to be refined or correct. Instead, the students should use the brainstorming time to get their mind flowing and discussion started. Usually, this activity takes place using flip chart / butcher’s paper.
- A good way to start discussion among students, especially if they don’t know each other well or are shy.
- The students may need to assign some roles to group members. Consider rotating the role of ‘writer’ between students (usually one person writes an idea for the whole group on the brainstorming paper).
- A good way of doing this activity is to place students in small groups and provide them a large sheet of paper to write down all their initial thoughts.
- Students can then report all their thoughts back to the class.
82. Expert Jigsaw
The expert jigsaw method teaching method involves having students split into groups of ‘experts’ and then ‘topics’.
First, each ‘expert’ group focuses on a sub-area of a topic to develop their ‘expertise’ as a group.
Once the initial group work discussion has concluded, the ‘expert groups’ split.
The teacher then forms new ‘topic groups’ with one student from each of the original expert groups in the new groups.
The idea is that each group in the second part of the lesson will have an ‘expert’ on a particular area of a topic. Every expert will be able to contribute their perspective to the group
For example, if the topic is dinosaurs, the initial ‘expert groups’ may get together to discuss separate issues: Group 1 will discuss extinction, Group 2 will discuss bones, Group 3 will discuss diets, and Group 4 will discuss geographical locations.
When the ‘topic groups’ converge, they should contain one expert on extinction, one expert on bones, one expert on diets and one expert on geographical locations. The topic group will therefore have a broad range of expert knowledge to discuss and share.
- Gives each student a sense that they have something meaningful to contribute because they will be an expert on something when converging in the ‘topic’ groups.
- Encourages collaboration and positive interdependence in group work.
- Requires forethought and organization by the teacher.
Social Constructivism: social interaction helps students construct ideas in their minds. Each student gets to hear the expert perspective of another student who is a ‘more knowledgeable other’, while also acting as the more knowledgeable other when it is their turn to share their expertise.
83. KWL Charts
A KWL chart is a type of graphic organizer that can be used throughout the course of a lesson to help students keep track of their learning.
The chart can be on a simple piece of paper split into three columns: (K) What I already know; (W) What I want to know in this lesson; (K) What I learned.
At the start of the lesson the students can fill out the first two columns. The first column will help the teacher assess prior knowledge. The second column will help the teacher and students guide the lesson by outlining what they want out of it.
At the end of the lesson, the third column can be filled-in: (L) What I learned in the lesson. This helps students reflect on the lesson to show them that they did actually learn something!
- Students can keep track of their own learning.
- There is physical evidence of what was learned that teachers can use in students’ final report card comments and teaching portfolios.
- It is a good structured tool to help guide a lesson.
- It would be good if there was a fourth column for ‘what I still want to know’ so student can leave the lesson with more questions that can be addressed in future classes.
- Students sometimes place topics in the (W) What I want to know column that are relevant but not covered in a pre-made lesson plan. This can require the student to get a bit creative in re-arranging their lesson on the fly.
84. SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis is a teaching tool used to help students identify their own Strengths , Weaknesses , Opportunities , and Threats .
It is often used at the beginning of a term or unit of work to help students self-identify how best to proceed in their studies.
A SWOT analysis starts with a piece of paper split into four quadrants. The top-left has ‘Strengths’, top-right has ‘Weaknesses’, bottom-left has ‘Opportunities’ and the bottom-right has ‘Threats’.
There are plenty of templates online you could download also.
Students then fill out the SWOT sheet, identifying their strengths and weaknesses (e.g. ‘I am organized’ or ‘I am time poor’) and opportunities and threats (e.g. ‘I have the opportunity to work with my peers to improve’ or ‘I have an upcoming swim meet that will take up more of my time’).
- Students are taught to self-assess and plan ahead to avoid upcoming challenges in their lives.
- Students can balance affirming statements about their own skills with honest recognition of their weaknesses.
- I often find students use generic phrases copied from their neighbors. It’s a good idea to insist on depth of engagement and thinking when doing this strategy .
85. Read Aloud
Read aloud is a strategy that involves the teacher reading a text out loud to students. The strategy relies on the teacher using strategic pauses, pitch and tone changes, pace and volume changes, and questioning and comments. These reading aloud strategies help students to become more engaged in a lesson and get more out of the reading experience.
- Can be more engaging than getting students to read to themselves.
- By using strategic pauses and asking questions of students, the text can both be read and analyzed at the same time. This may improve comprehension.
- I’ve found many pre-service teachers get nervous doing this task. Remember that people of all ages love being read to.
86. SIT: Surprising, Interesting, Troubling
A SIT analysis asks students to list aspects of a lesson that were surprising, interesting and troubling. It is useful following the viewing of a short film or reading a book about a topic that seems bizarre or a fact that is counterintuitive.
Like a KWL chart, you could do this task by splitting paper into three columns: one for ‘surprising’, one for ‘interesting’ and one for ‘troubling’.
- Gets students to take a critical stance and make judgements (particularly for ‘troubling’)
- Is a good way to take stock of students’ interests in order to create follow-up lessons based on topics the students have already demonstrated concern for.
- The ‘troubling’ part is often hard for students to complete – consider explicitly modeling a sample response before asking students to complete it alone.
Critical theory: students can use a SIT analysis to critique the justice or inequality issues presented in a text.
87. Higher Order Thinking
When writing a lesson plan, it’s often a very good idea to note any time you’re encouraging higher order thinking – especially if there’s a column in your lesson plan for ‘teaching strategies’. This help people reading the lesson plan to see that you’ve been intentional about promoting higher order thinking.
Following Bloom’s taxonomy, higher order thinking usually includes tasks that involve verbs like : Judge, Appraise, Evaluate, Compare, Criticize, Assess, Estimate, Deduce, Hypothesize and Generalize.
- Helps a teacher to be more explicit in their language and to ensure a lesson is challenging for students.
- Ensures students are practicing their critical thinking skills rather than just repeating a teacher’s ‘facts’.
- For higher order thinking tasks, it’s important that you don’t give students the answers. Instead, give them hints, pointers and resources that will help them to come up with the answers on their own.
Constructivism: Bloom was a constructivist who believed learning happens when students build knowledge in their mind rather than just copying facts from an authority figure in the classroom.
88. Debating
Getting students to debate an idea is a great way of getting them to build coherent and logical arguments in defence of a position. It requires them to gather, analyze and sort facts before they present them to an audience.
- Students learn to identify positive arguments on a topic even if they disagree with it, helping them to see things from multiple perspectives.
- Students may require resources to do background research to come up with strong points for or against a position.
- Split the class into two groups and assign each group a position for or against a statement.
- Give each group 15 minutes to come up with some arguments for their side of the argument. Each student in the group should have one argument to make for the team. The student writes their argument down on a piece of paper.
- Line the two groups of students up facing one another.
- Go down the lines getting each student to make their point for or against the position. Zig-zag from one group to the next as you go down the line
- Once the students have completed, do an anonymous poll of the class to find out which position is most convincing. For the poll, students do not have to vote for their team’s position.
89. Note Taking (Cornell Method)
Note taking involves getting students to actively listen out for key points in a speech or video and synthesize it into key points for remembering later.
A popular framework for not taking is the Cornell method. This involves splitting a page into two columns.
The column on the left is a ‘Cue’ column. In the cue column write key words, phrases or Quotes as if they were headings or headline points to remember.
The column on the right is the note taking column. This column is larger and allows space to add detail and diagrams explaining the ‘cues’ that were written on the left in more detail.
- Turns passive learning during a didactic explicit instruction lesson into a more active learning environment.
- Helps students organize and synthesize their thoughts.
- Helps with studying for exams later on.
- Teachers may talk too fast for students to take detailed notes. Remember to use strategic pauses and remind students at strategic times that they need to be taking notes.
- Feel free to download cornell method worksheets off the internet. Just look for them on your favorite search engine!
90. Lesson Recording
Recording a lesson involves using either video, audio or Screencast technology to save the lesson for revision later on.
- This method is very useful for students with learning disabilities who may require more time to process information. They can rewatch later on and make use of pause, rewind and slow functions during the revision.
- Great for when students miss a day so they can catch up.
- Whenever you work with technology, be prepared for issues to arise that may delay the lesson.
- Use Screencasts when teaching a lesson online.
- Screencasts can also save your work when writing on an Interactive Whitenoard. Revision at a later date will show the steps you took in doing the ‘working out’.
91. Word Wall
Word walls are sections on the walls of a classroom where teachers and students can record new vocabulary, quotes or key terms they encounter during a unit of work.
- Word walls can be visible evidence of progression through a unit.
- Students can refer to the word walls when trying to explain their points and ideas to the class.
- During exams, remember to cover the word walls so students can’t cheat by looking over at the answers.
- Word walls can be great props for refreshing students’ memories at the start of a lesson. Start the lesson by reviewing the vocabulary learned in the previous lesson.
92. Goal Setting
Goal setting involves explicitly instructing students on how to set short (within a lesson), medium (within a unit of work) and long term (through the year) personal targets for success.
The goals can be for a whole group or individual.
- Goal setting gives students something to strive toward.
- It is a way of gamifying education. Students can challenge themselves to reach their step by step goals.
- It helps students understand where they are headed and what the purpose of the lesson is.
- Ensure goals are achievable lo that students do not become disillusioned.
- Have students prepare their daily goals at the end of the previous day or start of the current day.
- Reflect on medium-term goals weekly.
93. Worked Examples
A worked example is a completed piece of work that students can look to as models for their own work.
A worked example could be a sample of a completed diagram our 3D model, a completed essay or anything else that is a finished product of something the students are about to attempt.
- Students feel more secure knowing what they are working toward.
- Students can get ideas from the worked sample that they can adapt for their Ken work.
- Sometimes students copy the sample too closely rather than using their own thinking. Consider using a sample that requires similar skills and processes but a different end product.
- Make sure you spend time discussing the steps it takes from going from nothing to the completed product.
- Provide students with past examples of creative writing pieces and discuss the strategies used by the authors.
- Show samples that are good and poor. Get students to discuss how the poorer samples could be improved.
94. Multiple Intelligences
Students have different learning styles (or more accurately, different learning preferences ).
One theory proposes that there are eight ‘intelligences’. A student may have one that is dominant and others that are weaker.
The eight intelligences are:
- Visual-Spatial : Prefers learning through images and visual arts. Uses diagrams to model relationships between concepts.
- Linguistic-Verbal : Prefers learning through storytelling, reading and writing.
- Interpersonal : Good at working in social situations, gets energy from social interaction, and can empathize with others easily. Enjoys group work.
- Intrapersonal : An introverted person who prefers learning alone. They do a lot of thinking and reading but mostly like to think through things in their own time (see: intrapersonal skills ).
- Logical-Mathematical : Sees patterns easily. Enjoys mathematical puzzles.
- Musical : Enjoys learning through music, songs and rhymes.
- Bodily-Kinesthetic : Learns through movement. Prefers lessons that require moving about.
- Naturalistic : Has an affinity with nature. Learns well in calm natural environments.
A teacher can integrate different activities into a lesson plan that appeal to different people’s learning preferences. In this way, they create a more inclusive classroom for multiple different types of learners.
- Inclusion: Teachers can use this theory to engage students who do not learn well in traditional lessons.
- Attempts to be student-centered and teach in ways that are appealing to students.
- In 2004, a detailed study in Scotland found no evidence or scientific toxic basis for the theory that different people have learning styles. Furthermore, it argued that the 8 styles in the multiple intelligences model were a arbitrarily contrived. Thus, learning styles may simply be learning preferences.
- It is unclear whether a teacher should create lessons catered to a student’s learning preference or help students strengthen their skills in areas students identify as their weaknesses.
- If students are not given a chance to practice all “styles” (not just their preferences) they may miss important skills, such as mathematical skills or literacy skills.
Howard Gardner: The theory of multiple intelligences was invented by Howard Gardner in the United States.
95. Non-Interventionism
Non-interventionism involves a teacher taking the role of ‘unobtrusive observer’ while students learn. The students are left to come to their own conclusions, face up to their own challenges, and ‘struggle’ through the lesson.
The teacher’s intervention may come through changing what they plan for the next lesson based on what they see, or lightly intervening after the students have struggled for some time.
Other reasons for intervention may be for safety or fairness reasons.
- Struggling to find an answer is Important for learning. Students can make mistakes and learn why the mistakes are wrong instead of just being told what us correct.
- Without a teacher imposing their views, students can come up with creative and thoughtful solutions to problems that the teacher dis not foresee.
- Students develop independent minds.
- Many parents and mentors watching your lesson may come away with a sense that you were lazy or did not do enough to help the students. This approach needs to be clearly explained and justified in lesson plans (I’d recommend referring to Montessori in your justification) and situations when you would go from observer to intervener should be spelled out in advance.
- If students are struggling too much, learning may not occur – there is a limit to this approach!
Montessori Classrooms: The role of the teacher as “unobtrusive observer” was pioneered by Maria Montessori.
Montessori argued that children learn best when placed in resource rich environments and left to explore. Our interventions may impede creativity, self-belief, autonomy and self-discovery.
96. Constructive Alignment
Constructive alignment involves explicitly linking the lesson assessment tasks to the compulsory learning outcomes in the curriculum.
This is an impressive thing to see in a lesson plan.
Use language (including verbs and nouns) from the learning outcome in the assessment task. Furthermore, make sure to provide a criteria for what constitutes pass or fail.
- Teachers can easily justify their lesson choices to their boss or assessor.
- The assessment tasks are always relevant and focused.
- Students can see the relevance of the assessment task to their learning goals.
- If the language of the curriculum objectives are complex or obtuse, it may just confuse students to use that language in their assessment task.
Biggs: Constructive alignment was invented by John Biggs who designed this method to ensure all lessons are relevant and move students a step closer to completing all learning outcomes.
97. Zone of Proximal Development
The ‘ zone of proximal development ‘ is a phrase used to explain the ideal difficulty level for a lesson.
A lesson that is too easy won’t help a student progress.
A lesson that is too hard will disengage a student who just won’t be able to do the task.
But a lesson that is difficult but achievable with effort will push a student forward. These lessons that are just hard enough but not too hard are lessons in the “zone of proximal development”.
- Students get lessons catered to their own needs.
- There is always catered support for any student in the class.
- By creating lessons that are always challenging, you are setting high expectations for all students.
- Differentiation like this can lead to bug Differences in ability levels across the whole class.
- You’re often under pressure to teach content that is too hard for students to meet standardized curriculum requirements
Sociocultural theory: Lev Vygotsky, one of the most famous educational psychologists, invented this approach to help teachers provide lessons that are at the right level for progressing a student’s learning.
- Weave the ZDP into a lesson plan by stating that you will assess a student’s current ability then teach them the thing that is the logical next.step.
- Another way to do this is create three student worksheets for three different ability levels. State in your lesson plan that you will assess each student’s ability and give them the appropriate worksheet. Each worksheet should build on the previous to help students move through their ZPD one step at a time.
98. Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement is the use of praise, stickers, candy or other rewards to show students that they have done a good job.
Teachers can stack positive reinforcements so students can take steps to get small, medium and large rewards to encourage students to keep on trying and working hard consistently.
- Students get clear signals to know when they have done well.
- Students get encouragement to keep going and keep trying in order to get the reward.
- Too much positive reinforcement can come across as insincere and lose students’ respect. Furthermore, students may become desensitized to praise if it occurs too much. Praise ‘scarcity’ makes occasional praise more valuable.
- Explicit reinforcements are extrinsic motivation . The best sort of motivation is intrinsic motivation (wanting to do something for the pleasure of doing it). For more, see my full guide on intrinsic vs extrinsic motivation .
Behaviorism: Positive reinforcement is believed to be beneficial for changing behavior over time. See: John Watson’s operant conditioning examples .
- Sticker charts
- A subtle nod or wink
- Certificates and awards
99. Negative Reinforcement
Negative reinforcement involves the removal of a privilege, points or tokens when a student gets an answer wrong.
This is often confused with punishments. For me, negative reinforcements should not punish but be used in limited learning scenarios as part of the learning ‘game’.
An example might be losing points in a gamified lesson so the student is less likely to win against their opponents. Students know it is part of the game and not a punishment designed to distress the student.
- Provides very clear messages to students about what is correct and incorrect, helping them to learn quickly.
- Parents often do not like any negative reinforces, so be very careful to set clear guidelines and use this strategy in limited circumstances.
- Be careful not to embarrass students in front of their classmates.
Behaviorism: Watson brought negative reinforcements into education, arguing that repeated use of them can change students’ behaviors.
- Losing points in a class contest.
- Failing a level in an educational computer game.
100. Drop Everything and Read
Drop everything and read (DEAR) involves getting students to stop what they are doing and read for 10 minutes.
It is a strategy that helps build students’ literacy skills (especially when students can choose their own book). However, it is also useful for helping students get more depth of knowledge on a topic being taught when you give them all an article or book to read to help them have more knowledge for subsequent parts of the lesson.
- An effective way of getting students to spend intense time learning about a topic.
- Helps integrate literacy into your daily activities.
- There will always be a small group of students who squirm and struggle when asked to read. Consider alternatives like the Read Aloud strategy or using videos instead if DEAR doesn’t work for your class.
- Make sure to follow up DEAR time with discussion and comprehension tasks.
- Introduce a topic with initial information to engage the class.
- Set a 10 minute silent reading task based on the topic.
- Discuss what was read with comprehension prompts.
101. Gallery Walk
A gallery walk involves a teacher placing stimulus questions on flip chart paper (butcher’s paper) around the walls of the classroom.
The charts the teacher has put up are stations that students will stop at during the activity.
The teacher places students into groups. If there are 5 stations around the room, the teacher will create 5 groups.
Students get a set amount of time at each station to read the prompt questions. The students can write on the chart paper with their group response and also respond to other groups who have already written their points.
Once all students have rotated through the stations, the students end up back at the station where they began. The teacher the. gives each group 3 minutes to present to the class a summary of the comments written on the paper at their station.
- Students get to learn from others and see other groups’ responses.
- The students are up and moving about which may help the concentration of bodily-kinesthetic learners.
- Some students may not participate fully. Consider getting students to rotate who writes on the paper at each station to mitigate this challenge a little.
102. Metacognition
Note whenever you would encourage metacognition in a lesson within your lesson plan. This will help anyone reading it know that you’ve thought about giving students strategies for “thinking about thinking”.
Metacogntion is about thinking about how you think. Strategies include:
- Thinking aloud
- Writing your steps to reach an answer
- Explaining your thought processes
- Reflecting on your learning and considering faster ur more efficient processes
- Helps students understand the processes required for thinking deeply about an issue.
- Gives students the strategies and skills to learn any task, not just the ones at hand.
- Metacognition is difficult because it requires explanation of your thinking. However, it is necessary if people want to know how to think .
103. Case Studies
Case studies are in-depth examples of an issue being examined. A case study should show how an issue or theory looks in real life. Teachers can present case studies through videos, newspaper articles, magazine articles, guests coming into the classroom, etc.
- Case studies help students to see how theories and ideas look in real life. This can also help a student understand the relevance of the topic being studied.
- A case study may help students make sense of a complex idea by putting it in real concrete terms.
- Case studies might not be representative of a generalized issue – they may be outliers or flukes. Pick your case study carefully and discuss whether it is a typical or outlier sample.
- A case study of city planning may be an innovative city that has recently been designed.
- A case study in mathematics may include looking at the mathematics underpinning a famous bridge’s construction.
- A case study during a unit of work on refugees might look at the experiences of one real-life refugee.
104. Mystery Making
Educators can create ‘mystery’ in their classroom by carefully structuring lessons that give ‘clues’ to a mystery that needs to be solved by the students. Ask the students to act as detectives and place clues around the classroom (like a gallery walk). Have students move around the classroom taking notes on the mystery which will reveal an answer after thorough investigation.
- Creates a sense of excitement in the classroom, helping students to engage.
- Forces students to use critical, logical and lateral thinking in order to find the answer.
- Ensure the mystery is not too far outside a student’s zone of proximal development so that the mystery can be solved.
105. Storytelling
Storytelling in the classroom involves teaching through narrative-style stories rather than telling (‘didactic learning’). Teachers can tell stories by reading books (see: Read Aloud strategy), turning a dry explanation into an allegorical story off the cuff, or bringing people into the classroom who have an engaging personal story to tell.
- Stories can draw students into a topic through the creation of a sense of excitement and entertainment.
Steiner-Waldorf Schools: Rudolf Steiner called the teacher the ‘chief storyteller’ whose role is to create a sense of enchantment around learning through stories.
- Invite guests into the classroom who have stories to tell.
- Use stories that have a moral of the the story, then analyze the moralistic message.
106. Newspaper Clippings
Use newspaper clippings to link topics and theories to current affairs. Teachers can bring in recent newspapers to let students search through them for relevant stories or use old newspapers to search for how a topic was discussed in the past. Alternatively, teachers can get students to search for newspaper articles online.
Teachers could also assign reading through newspapers and bringing newspapers to class as a part of their homework.
- Newspaper stories can show students how the topic being discussed plays out in real life.
- They also show students how the topic is relevant to the present-day lives of people in the community,
- Newspapers are increasingly uncommon – consider adjusting this to use online news sites and printing out articles from the web.
- Some topics won’t have relevant news articles associated with them. Do a search in newspapers and online yourself for articles before using this teaching strategy.
107. Self-Paced Learning
Self-paced learning involves.letting students progress from activity to activity in their own time. For this approach, a teacher lays out a list of 10 – 20 lessons that students can work on at their own pace. Students work on the activities while the teacher walks around and gives support.
- Students are encouraged to reflect on their own learning development and only move on when they are confident that they have consolidated the knowledge from an assessment.
- Less students will fall behind if the teacher doesn’t pressure them to move on.
- Teachers have time to work one-on-one with students while students work away at student-led tasks.
- Fast students will need extension tasks or personal projects to complete once they have finished and are waiting for slower students.
- There is often not enough time for slower students to finish.
These teaching strategy examples are clearly not the only ones out there – there are probably thousands! But, in my time teaching, these have been the most effective and common teaching strategies that I have come across. Use this teaching strategies list for your own lesson plans to demonstrate pedagogical knowledge and depth of understanding of how to educate a range of different learners.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
4 thoughts on “List of 107 Classroom Teaching Strategies (With Examples)”
this is valuable in my course production of Instructional materials in social studies. maraming Salamat!
Thank you very much for these valuable teaching strategies & techniques which can be used to enliven the classroom atmosphere, encourage students to do their tasks and learn more in the process. God bless!
As a student of Curriculum and Pedagogic Studies and also the Curriculum Lead in my school, this is best of resources I have had on the subject of teaching strategies. Thanks so much.
Thank you so much, these are very helpful and remind me that some of my teaching styles are already mentioned here.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Support our educational content for free when you buy through links on our site. Learn more
Teaching Strategies: 10 Effective Techniques for Classroom Success [2023]
- July 2, 2023
Classroom Management
Keywords: teaching strategy, classroom success, instructional strategies
Introduction: Teaching is an art, and every teacher knows the importance of implementing effective teaching strategies in the classroom. A well-planned and executed strategy can engage students, enhance learning, and contribute to overall classroom success. At Teacher Strategies™, we believe in providing educators with comprehensive strategies that promote student growth and achievement. In this article, we will explore 10 highly effective teaching strategies that are sure to bring success to your classroom. So let's dive in!
Table of Contents:
Differentiated Instruction
Active learning, cooperative learning, project-based learning, flipped classroom, technology integration, gamification, assessment for learning, culturally responsive teaching, quick tips and facts, useful links, reference links.
One size does not fit all in the classroom, and that's where differentiated instruction comes in. This teaching strategy aims to tailor instruction to meet the diverse needs of students. By catering to various learning styles, abilities, and interests, teachers can create a more inclusive and engaging learning environment. Here are some key principles of differentiated instruction:
- Flexible Content : Provide multiple options for content delivery, such as visual aids, audio recordings, or hands-on activities.
- Varied Process : Offer different pathways for students to acquire and demonstrate knowledge, such as group work, independent projects, or technology-based assignments.
- Diverse Products : Allow students to showcase their learning through various formats, such as presentations, written reports, or artistic creations.
✅ Benefits :
- Catering to different learning styles and needs improves student engagement and motivation.
- Students feel valued and acknowledged for their individual strengths.
❌ Challenges :
- Requires careful planning and organization to ensure that each student receives appropriate instruction.
- Meeting the needs of every student can be time-consuming.
Active learning goes beyond passive listening and classroom observation. It involves engaging students in the learning process through hands-on activities, discussions, and problem-solving. This teaching strategy encourages critical thinking, collaboration, and knowledge application. Here are some effective techniques for promoting active learning:
- Think-Pair-Share : Students reflect on a question individually, discuss their ideas with a partner, and then share their thoughts with the whole class.
- Jigsaw Method : Students become experts on a particular topic and teach their findings to their peers in small groups.
- Role-Playing : Students take on different roles to understand different perspectives and explore complex ideas.
- Promotes deeper understanding and retention of information.
- Enhances problem-solving and critical thinking skills.
- May take more time compared to traditional lecture-based instruction.
- Requires structured activities to avoid chaos and keep students focused.
Cooperative learning encourages students to work together in small groups to achieve a common goal. This strategy fosters collaboration, communication, and teamwork among students. By assigning roles and responsibilities within a group, teachers ensure that every student actively participates. Here are some popular cooperative learning techniques:
- Group Investigations : Students work collaboratively to explore a topic or solve a problem, sharing their findings with the whole class.
- Peer Tutoring : Students take turns teaching and supporting each other's learning.
- Group Projects : Students collaborate on a project, each contributing their unique skills and knowledge.
- Develops essential social and communication skills.
- Encourages accountability and shared responsibility.
- Requires effective group management to ensure equal participation.
- Conflict resolution skills may be necessary to address potential issues.
Project-Based Learning (PBL) immerses students in real-world problem-solving scenarios, allowing them to apply knowledge and skills in meaningful ways. This strategy encourages inquiry, critical thinking, and creativity. Teachers guide students through an extended project, which includes research, planning, and presentation phases. Key elements of PBL include:
- Authentic Problems : Students work on real or simulated challenges that have relevance to their lives or communities.
- Student Autonomy : Students take ownership of their learning, making decisions and solving problems independently or within a team.
- Presentation and Reflection : Students present their project to an authentic audience and reflect on their learning experience.
- Develops 21st-century skills, such as problem-solving, communication, and creativity.
- Increases engagement and motivation by making learning relevant and meaningful.
- Requires careful planning and scaffolding to ensure the success of the project.
- Time management skills may be necessary to complete projects within a designated timeline.
The flipped classroom model flips the traditional instructional approach. Instead of delivering new content during class time, teachers provide instructional materials, such as videos or readings, for students to access at home. Classroom time is then devoted to discussions, practice, and hands-on activities. Here's how the flipped classroom works:
- Pre-Class Assignments : Students review instructional materials independently before coming to class.
- Classroom Activities : Teachers facilitate discussions, group work, and individualized instruction to reinforce and apply the pre-class materials.
- Just-in-Time Support : Teachers provide immediate feedback and guidance during in-class activities.
- Maximizes valuable class time for active learning and higher-order thinking activities.
- Enables personalized support and differentiation based on students' needs.
- Requires effective communication with students and parents to ensure understanding of the flipped model.
- Technology-based resources and reliable internet access are necessary for students to access pre-class materials.

In today's digital age, integrating technology into the classroom is a must. Technology can enhance instruction, engage students, and provide access to a wealth of resources. When strategically incorporated, technology can transform the learning experience. Consider these ideas for technology integration:
- Interactive Whiteboards : Use interactive whiteboards to engage students in multimedia presentations, virtual field trips, and collaborative activities.
- Educational Apps : Explore educational apps that cater to different subject areas and learning objectives.
- Online Collaboration Tools : Utilize online platforms that allow students to collaborate on projects, share resources, and provide feedback to their peers.
- Enhances student engagement and motivation.
- Fosters digital literacy and prepares students for the future.
- Requires access to reliable technology and sufficient training for both teachers and students.
- Monitoring students' digital activities and ensuring online safety may be necessary.
Gamification infuses elements of games into the learning environment to increase engagement and motivation. By turning learning into a game-like experience, teachers can create a fun and interactive classroom atmosphere. Here's how to incorporate gamification:
- Points and Badges : Reward students with points or badges for completing tasks, participating, or demonstrating growth.
- Leaderboards : Display a leaderboard to track and recognize student progress throughout the learning process.
- Game-Inspired Challenges : Design challenges, quests, or escape rooms that require students to solve problems and demonstrate mastery.
- Increases student motivation and participation.
- Encourages healthy competition and fosters a growth mindset.
- Must strike a balance between game elements and meaningful learning objectives.
- Requires creativity and constant innovation to keep students engaged.
Assessment should not be limited to grading and evaluation. Assessment for learning focuses on gathering information about students' progress and using it to guide instruction and provide targeted feedback. Here are some assessment strategies that promote learning:
- Formative Assessment : Use ongoing, informal assessments to monitor student understanding and adjust instruction accordingly.
- Self-Assessment : Encourage students to reflect on their learning, identify strengths and weaknesses, and set goals for improvement.
- Peer Assessment : Provide opportunities for students to give constructive feedback to their peers.
- Helps teachers identify students' learning needs and adapt instruction accordingly.
- Empowers students to take ownership of their learning and develop metacognitive skills.
- Requires a balance between formative and summative assessment practices.
- Time-consuming when done in-depth, especially with large class sizes.
Effective classroom management is crucial for creating a positive learning environment where students can thrive. Teachers implement various strategies to establish routines, foster positive behavior, and maintain a productive atmosphere. Consider these classroom management techniques:
- Clear Expectations : Communicate classroom rules, procedures, and academic expectations to students.
- Positive Reinforcement : Recognize and reward desired behavior through praise, incentives, or a system of points.
- Consistent Consequences : Enforce fair and consistent consequences for inappropriate behavior.
- Creates a safe and conducive learning environment.
- Reduces disruptions and promotes a positive classroom culture.
- Requires strong classroom organization and proactive planning.
- Differentiated strategies may be necessary to address individual student needs.
Culturally responsive teaching acknowledges and values the diverse backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives of students. This teaching strategy promotes inclusivity, respect, and understanding among students. Here's how to implement culturally responsive teaching:
- Building Connections : Create opportunities for students to share their cultural traditions, stories, and experiences.
- Inclusive Curriculum : Select diverse and representative learning materials that reflect different cultures, identities, and perspectives.
- Open Dialogue : Encourage discussions about cultural diversity to promote understanding and empathy.
- Creates a supportive and accepting learning environment for all students.
- Enhances cultural competence and fosters a respect for diversity.
- Requires ongoing professional development for teachers to develop cultural competency.
- May need additional support and resources to address the needs of diverse students effectively.
What are the 5 instructional teaching strategies?
The 5 instructional teaching strategies:
- Differentiated Instruction : Tailoring instruction to meet the diverse needs of students.
- Active Learning : Engaging students in hands-on activities and critical thinking.
- Cooperative Learning : Encouraging collaboration and teamwork among students.
- Project-Based Learning : Allowing students to apply knowledge and skills in real-world contexts.
- Flipped Classroom : Flipping the traditional instructional approach by providing instructional materials outside class hours.
What is an example of a teaching strategy?
An example of a teaching strategy is the Jigsaw Method. In this strategy, students become experts on a particular topic and then teach their findings to their peers in small groups. This cooperative learning technique promotes research, collaboration, and knowledge sharing.
What is the best teaching strategy?
The "best" teaching strategy depends on various factors, such as the subject being taught, the learning needs of students, and the instructional goals. Differentiated instruction is often considered a highly effective strategy as it caters to the diverse learning needs of students. However, it is essential to use a combination of strategies to meet the unique needs of your students effectively.
What are the 3 approaches of teaching strategies?
The 3 approaches of teaching strategies can be categorized as follows:
- Direct Instruction : Traditional teacher-centered approach where the teacher leads the instruction.
- Constructivist Instruction : Facilitating learning through exploration, problem-solving, and group work.
- Inquiry-Based Instruction : Encouraging student-driven investigation, observation, questioning, and discovery.
- Incorporating a variety of teaching strategies helps reach students with different learning styles and needs.
- Effective teaching strategies promote student engagement, critical thinking, and meaningful learning experiences.
- Ongoing professional development and peer collaboration can enhance a teacher's repertoire of teaching strategies.
- Flexibility and adaptability are crucial when implementing teaching strategies to meet the ever-changing needs of students.
- The success of teaching strategies relies on building positive relationships and effectively managing the classroom.
- Teacher Strategies™
- Amazon – Teaching Strategies
- Walmart – Teaching Strategies
- Etsy – Teaching Strategies
- Book – "The Skillful Teacher: Building Your Teaching Skills"
- YouTube – Effective Teaching Strategies
- Differentiated Instruction: Maximizing the Learning of All Students
- The Power of Active Learning
- Cooperative Learning: Getting Started
- Project-Based Learning Explained
- Flipped Learning: A Guide for Higher Education Faculty
- Technology Integration in the Classroom: Challenging the Potential
- Why Gamification Works: How Manifold Benefits Translate to Success
- Formative Assessment: What Do Teachers Need to Know and Do?
- Classroom Management Strategies for Difficult Students
- Culturally Responsive Teaching: Theory, Research, and Practice
Meet Marti, a seasoned educator with a rich background in tutoring, communication, and social work, who contributes her invaluable insights and strategies to Teacher Strategies. Marti’s journey in the educational sector began during her university years, where she started as a tutor. This role not only fueled her passion for teaching but also provided her with an opportunity to develop and refine her educational techniques. Holding a degree in Communication, Marti excels in creating engaging and effective learning environments by utilizing clear, impactful communication strategies. Her ability to convey complex concepts in an understandable and relatable manner has made her a favorite among students and educators alike.
In addition to her prowess in communication, Marti also holds a degree in Social Work, which has endowed her with a deep understanding of the diverse backgrounds and challenges faced by students. This unique combination of skills allows her to approach teaching with empathy, patience, and an unwavering commitment to inclusivity. Marti believes that education should be accessible to all, and she incorporates principles of social work into her teaching to support and uplift students from all walks of life.
On Teacher Strategies, Marti shares her innovative approaches to education, drawing from her extensive experience in tutoring, her expertise in communication, and her background in social work. Her articles provide educators with practical tips and strategies to enhance their teaching methods, foster a positive and inclusive classroom environment, and effectively communicate with their students. Marti’s dedication to making a difference in the lives of students shines through in her contributions to the site, making her an invaluable resource for teachers looking to enrich their professional practice and impact their students’ lives positively.
Related Posts
What are the 6 management techniques that a teacher should develop [2023].
- November 24, 2023
[2023] 10 High Five Teaching Strategies for Success in the Classroom
- October 28, 2023

What are the 6 Key Teaching Strategies for 2023? [2023]
- September 5, 2023
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Add Comment *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment
Trending now
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Teaching Online: Effective Practices

If you’re teaching online for the first time or looking to hone your skills, you might ask yourself: What’s different about teaching online?
Online classes have the same rigor and expectations for students’ time and effort, and the same week-by-week teaching pace and regular interaction with students. You use many of the same evidence-based teaching strategies and frameworks, such as backward design, that you use in a physical classroom.
On the other hand, online classes often require additional time to design and build before they’re taught, have different needs for communicating expectations and instructions, and introduce different ways of thinking about and estimating credit hours and seat time. You’ll also need to use specific assignment approaches and teaching strategies proven to work well online.
Teaching effective online courses involves special considerations related to the course's format and administrative components, the technology you use (particularly CarmenCanvas ), and your choice of appropriate teaching methods.
Get started with this printable checklist of effective practices for online teaching , and refer back to it every time you teach online. Each item on the checklist is explained below.
Online Course Approvals
The university and individual colleges and departments have curricular and delivery standards related to accreditation, federal regulations, and student experience and access. For temporary remote approvals during the 2020-21 school year, the Office of Academic Affairs worked with each academic unit to create a common Course Assurance process , based on the effective practices on this page. Consult with your academic leaders and curriculum committee for approval processes and any additional requirements for your unit.
Format, Rigor, and Integrity
How can you ensure the quality and rigor of your course is equivalent to an in-person course? This section covers university policies and expectations for online courses, such as accreditation standards, attendance tracking for federal financial aid, and academic integrity considerations.
A number of federal and state regulations dictate requirements for the format and pacing of your online course.
- Students have opportunities for regular and substantive academic interactions with the instructor. These interactions must be initiated by you, regular and frequent, and meaningful or academic in nature. The myth that online learning is solitary comes from an earlier day when we knew far less about how students learn and succeed online. Your online course will only be successful if you establish a strong instructor presence and facilitate constructive interactions with your students.
- Students have a required participation activity at least once each week. This ensures that you can pinpoint when a student last participated and verify their “attendance,” which is an institutional requirement related to student financial aid. A few examples of participation activities are submitting an assignment, taking a quiz or exam, submitting a discussion post, or participating with you in an email exchange that is academic in nature.
- Learning outcomes and instruction time are equivalent to an in-person class of the same number of credit hours . Online courses must meet federal guidelines for equivalent “class time,” or direct instruction, and “out-of-class” time. Class time examples include lectures, discussions, and quizzes or exams, while out-of-class activities may include readings, study, or papers and projects.
- The syllabus provides clear expectations about any required synchronous, or live and scheduled, sessions. Students often expect online courses to be completely asynchronous, meaning that work can be done each week according to their own schedules. Make them explicitly aware of required synchronous sessions, ideally in both your syllabus and in the class schedule in BuckeyeLink.
Learn more about Online Instructor Presence , Attendance in Online Classes , and Policies for Online Teaching .
Academic integrity is a student’s commitment to abide by Ohio State’s code of academic conduct. It involves moral and ethical academic behavior, including adherence to course guidelines and avoidance of plagiarism or cheating. Online learning presents unique challenges to academic integrity since misconduct can arise from a lack of awareness or understanding due to unclear expectations and instructions.
How can you promote an environment of academic integrity in your online course?
- The course syllabus includes policies about academic integrity that are specific to online learning . Including this information—and discussing it openly with students—will help them understand your course's academic integrity expectations and guidelines for online courses at the university in general. Consider using the Online and Hybrid Course Syllabus Template, which includes online-specific language regarding academic integrity.
- Major assignments include specific academic integrity parameters in the directions . For example, students need to know if they are allowed to work in groups, use past work, use notes or the book for a quiz or exam, and so on.
- Course technologies, such as online proctoring or plagiarism detectors, or other strategies are in place to deter cheating . These tools help you monitor whether specific academic integrity criteria are met when students turn in assignments or take quizzes, midterms, or final exams. Learn more about Proctorio and Turnitin , an anti-plagiarism tool that integrates with Carmen.
Learn more in Strategies and Tools for Academic Integrity in Online Environments and A Positive Approach to Academic Integrity .
Technology and Materials
Students perform best in courses that are clear, navigable, welcoming, functional, and accessible. The structure you set up for your course using CarmenCanvas and other instructional technologies is central to creating a supportive online learning environment.
Follow these guidelines to ensure students can successfully access and navigate your materials, Carmen course, and chosen technologies.
For both ethical and legal reasons, all materials in your course must be accessible and meet copyright and fair use requirements.
- The documents, instructions, and materials in the course are in formats that are accessible for all students . When materials are " accessible, ” they can be used and navigated by students with vision, auditory, motor, or cognitive disabilities. Providing accessible materials gives all students the ability to access course content at the same time. It is easier to create your materials with accessibility in mind than to retroactively make them accessible—follow accessibility best practices from the get-go when building your course. Learn more about Digital Accessibility Services.
- Copyrighted materials are either provided to students securely through the library or a detailed fair use claim has been documented . Teaching online necessitates additional considerations around copyright law. If you show students a PowerPoint presentation or video clip in a face-to-face class, you aren’t giving them access to the material forever. But in an online environment, the works you share are easier for students to copy or distribute. Be sure to follow best practices when using licensed library materials and copyright exceptions, such as the TEACH Act or fair use. Learn more about Copyright Services at the University Libraries.
An organized and transparent Carmen course helps students navigate your content and learning activities with ease.
- Content and activities are organized into weekly modules or another clear navigation structure . Using Modules to house your content in Carmen provides a clear organization and structure, so students know how your course will run. The way you sequence your modules can show the “big picture” of your course, clarify the relationships between topics, and create a logical flow.
- Clear, consistent directions are included in Carmen about what students are expected to do with all materials and activities . Providing transparent instructions for new materials, assignments, and learning activities helps students contextualize them with your course content and goals.
- The course is built with an online-learning-specific Carmen course template . Using a consistent template for your course helps students easily navigate content and concentrate on learning rather than searching for files and directions. It also makes your course-building process more efficient and streamlined. Download the Carmen Course Template .
Learn more about Carmen Common Sense: Best Practices.
It’s easy to assume your online students are digital natives, but in fact, they come to your course with a range of technological experiences and skills. Students will benefit from guidance on the technology they need to access course materials and complete activities.
- The course syllabus lists all required technology, with instructions for how to access technical support for those technologies . Provide explicit instructions on how students can get technical support for tools used in your course, especially if they cannot get that assistance from the Ohio State IT Service Desk .
- The course syllabus includes accessibility, data privacy, and cost information for any non–Ohio State technologies . Share information on how students can get accessibility accommodations if required, how their data is used and stored, and any fees or costs beyond the cost of required textbook(s).
See the Online and Hybrid Syllabus Template Instructions .
Teaching Strategies
As with any class, you should employ evidence-based approaches to design and deliver your online course. Research repeatedly shows that four areas significantly impact online students’ learning, engagement, and satisfaction: instructor presence, student-student interaction, a variety of teaching methods , and student support and metacognition .
Several teaching methods are suggested below, but the list is not comprehensive. Successful courses need not employ all of these strategies and may incorporate additional approaches.
We know that students are more engaged when they perceive their instructor as a frequent and positive presence in the course. Some strategies for accomplishing this in your course include:
- Regular and planned instructor communications with the class via announcements or weekly check-ins
- Instructional content, such as video, audio, or interactive lessons, that is visibly created or mediated by the instructor
- Regular instructor participation in class discussion, either in Carmen Discussions or synchronous sessions
- Regular opportunities for students to receive personal instructor feedback on assignments
Learn more about Online Instructor Presence .
Students also engage more in courses when they have opportunities to interact with their peers and feel they are part of a community of learners. To foster peer connection in your course, it is important to provide:
- Opportunities for students to interact academically with classmates through regular class discussion or group assignments
- Opportunities for students to interact socially with classmates, such as through video conference sessions or a course Q&A forum
Learn more about Student Interaction Online .
Students understand and engage with your course material in a variety of ways. Overall, student success is maximized when you provide frequent and varied learning activities. You can accomplish this by including:
- Opportunities for students to receive course information through a variety of different sources, including indirect sources, such as textbooks and lectures, and direct sources, such as scholarly resources and field observation
- A variety of activity and assignment formats to provide students with multiple means of demonstrating learning
- Opportunities for students to apply course knowledge and skills to authentic, real-world tasks in assignments
Learn more about Creating and Adapting Assignments for Online Courses .
Students have successful, meaningful experiences when they understand how the components of a course connect, receive guidance on how to study, and are encouraged to take ownership of their learning. Consider including the following to support students in your course:
- Instructor explanations about the learning goals and overall design or organization of the course
- Context or rationale to explain the purpose and relevance of major tasks and assignments
- Guidance or resources for ancillary skills necessary to complete assignments, such as conducting library research or using technology tools
- Opportunities for students to take ownership or leadership in their learning, such as by choosing topics of interest for an assignment or leading a group discussion or meeting
- Opportunities for students to reflect on their learning process, including their goals, study strategies, and progress
- Opportunities for students to provide feedback on the course
Learn more about Supporting Student Learning and Metacognition.
- Effective Practices for Online Teaching (checklist)
- Online and Hybrid Course Syllabus Template
- Carmen Course Template
Learning Opportunities
Related teaching topics, carmen common sense: best practices, creating and adapting assignments for online courses, online instructor presence, policies for online teaching, student interaction online, related toolsets, carmencanvas, search for resources.

Teaching tips
Strategies for teaching online: the ultimate guide for educators.
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: March 1, 2022

With COVID-19 nearly overnight transforming our traditional classrooms into virtual ones, it can seem like distance learning has appeared out of nowhere. But, the truth is, education’s shift towards distance learning had been steadily growing long before this pandemic. And it’s here to stay.
What We Review
Why Distance Learning is Here to Stay
Nothing is perfect, and distance learning isn’t a solution to all a school’s problems. However, it does meet a variety of both students’ and school districts’ needs that traditional, brick-and-mortar classrooms can’t.
Fully virtual schools have been sprouting up across states for years, and only growing in popularity. While some families have realized that full-time distance learning doesn’t suit their personal lifestyles, for others it’s essential. Competitive student-athletes with rigorous training schedules, students with mental or physical ailments, and families who just want the flexibility in their day, to name a few.
Even traditional schools are utilizing fully virtual courses for their in-person populations. For example, say a district wants to offer a film studies course to their students but doesn’t have the funding or the student numbers to justify a full-time film teacher in every building. This district will instead hire one teacher to virtually run the course through an online Learning Management System, like Canvas or Moodle. Students across the district can now take this virtual course at any period of the day, in their school’s computer lab.
We see districts investing in virtual tools, digital subscriptions, practice software, and broadband. Digital citizenship courses are on the rise as a key component in school curricula.
For educators new to distance learning, it can be difficult to know what online teaching techniques work best, or even where to begin. In this comprehensive post, we detail effective online teaching strategies, easy-to-use tips, and provide a number of accessible resources.

The 3 Keys to Teaching Online Classes Effectively
While everyone’s teaching style is a bit different, successful educators all follow the same best practices in online teaching. These 5 simple principles are the framework for all of the top online learning strategies.
1. Clear communication with your students’ families.
Families want to hear from you often and regularly. It can be easy for students and parents to start to feel disconnected. Reassure them your “virtual door” is always open, and share your email and phone number early and often in multiple places. Clear, respectful communication is the key to building relationships and classroom community.
2. Vary your types of lessons.
Your teaching should be a blend of both synchronous (happening in real-time) and asynchronous (unscheduled and self-paced). Synchronous teaching through phone calls, video lessons, or live chats allows students to ask questions and build relationships with you and each other. Asynchronous activities, like discussion boards or recorded lectures, allow your students to complete assignments at their own time and pace. Both styles have their benefits and are necessary in their own ways.
3. Select the right tools for your class.
Your school’s Learning Management System or LMS will most likely be the primary tool you use for your direct communication and posting assignments. Familiarize yourself with it early, and don’t hesitate to reach out to your more tech-savvy coworkers with questions. You’ll also need a separate tool like Google Voice o r Zoom or phone calls, live lessons, and video chatting.
Beyond these basics, there are a huge variety of educational technology tools to transform your teaching and engage your students. This is the fun part! Use the tips and tricks provided later in this article for discovering, experimenting, and implementing new tools in your classroom.
Return to the Table of Contents
What are the Most Common Strategies of Distance Education?
Encouraging student engagement while ensuring they master their course content can be challenging in any setting. We provide vital online teaching ideas on how to make your lessons more interactive and foster active learning. We discuss these five most common strategies in distance education in more detail throughout this article:
1. Adapt your lessons to work online.
Revamp your in-person lessons to the online environment with engaging discussions, screen recordings, and interactive tech tools.
2. Set clear expectations with students and families.
Share your expectations and due dates early and often to prepare students and families for a successful year.
3. Build a strong online classroom community.
Classroom community is just as essential in the virtual environment and can be fostered with video chats, purposeful free time, and class message boards.
4. Connect with parents and keep them involved.
Keep parents involved consistently with frequent and engaging communications like weekly newsletters and personal phone calls throughout the school year.
5. Find and utilize the right EdTech for your needs.
Collaborate with fellow educators and identify specific needs to find and implement the best tools for your classroom.

Strategies for Teaching Online: How to Adapt Your Lesson Plans to Different Types of Learners
We know you’ve already put endless hours into your lessons plans, tweaking and perfecting them. Don’t feel like all that work has gone to waste! There are a bunch of different online learning strategies to adapt your in-person lesson plans to fit the virtual environment. It just takes a little creativity and the right tools.
1. Add discussions to increase engagement and comprehension.
An unbeatable tool for asynchronous discussions is Flipgrid . Instead of typing, students record themselves answering your posted questions. They can view and respond to each other’s videos, as well. This is a great option for reluctant writers, a strong way to boost engagement, and promote active learning.
For written discussions, Google Classroom is a great tool. You simply post the assignment instructions, let students post their answer, and then they can read and respond to others. Check out How to Teach From Home with Google Classroom and Albert for more tips.
For synchronous discussions, chat rooms like YO Teach allow students to message back and forth in real-time. Fair warning- these chatrooms require active monitoring from the teacher side.
2. Utilize screen recordings to pre-record yourself and your lessons.
For the Powerpoints you’ve already created, screen recording software like Loom or Screencastify allows you to record your presentation on-screen as you speak and click through your slides. It even has the option to include a little window with your face on the screen, so your students can still see you. These videos can be downloaded or shared via weblink.
Beyond just lessons, you can also record yourself explaining assignment directions, for those students who do better when verbally told what to do.
3. Make your lessons interactive and engaging.
Nearpod is one way to make online classes more interactive. It’s a dynamic tool that allows students to follow along and participate in your lessons on their own devices. First, you import your pre-existing lessons pdfs or Powerpoints. You then can add in places for student interaction: written responses, drawings, quizzes, polls, collaborate boards, and more. You can differentiate the type and difficulty of assignments for different student needs.
Strategies for Teaching Online: How to Set Clear Expectations with Students
Strong classroom management is as essential in the online environment as it is in the traditional one. Even though you won’t be physically seeing your students every day, read on for 5 effective online teaching strategies to hold them accountable.
1. Post behavior expectations in every live discussion.
Make your rules/expectations crystal clear from the outset, especially in live discussions. You’ll probably find even the quieter students feel more bold typing in the chat- which is great when it’s positive conversations, but not-so-great when it gets off-topic or inappropriate.
In your first synchronous lesson, spend time discussing with your students what you as a class want your “Online Classroom Norms” to be. Create a list of around 8-10 norms, including specific rules like “stay on topic,” “always be kind and respectful,” “raise your hand and wait to be called on before turning on your microphone.” After you create the norms, review and share the document before every live lesson.
2. Set and enforce consequences in live discussions.
The same in any classroom, it’s just as important to enforce your expectations as it is to create and share them. If a student is negatively participating, you can easily mute or remove him or her from the lesson. Then, follow up afterward with a phone call home to discuss the situation.
3. Find your positive reinforcement.
My students used to love cleaning the whiteboard, or getting small pieces of candy. But online, these rewards don’t translate. However, it’s still just as important to reward students to reinforce their positive behavior. Some ideas include:
- Public shoutouts : Recognize star students in your emails to the class, during synchronous lessons, or post them on a public board. A board like padlet can even let students post shoutouts recognizing each other.
- Private shoutouts : Send students and their families individual messages when they’ve done a great job.
- Student choice : Allowing students to make even seemingly small choices can be motivating. Let a student choose which song to play before the lesson starts or choose a fun image for your virtual Zoom background.
4. Set clear due dates.
Many students struggle with time management. Without a rigid school day schedule, it’s easy for students to lose track of time and fall behind on their work. Set due dates for everything, and send frequent reminders. By the way, check out our free teaching strategy discovery tool .
Where possible, chunk large assignments into smaller ones to help students keep on pace. For example, if assigning an essay, set a due date for the outline, the rough draft, and the final essay. This helps force the “wait til the last minute” folks to move forward at a steady pace.
5. Use acknowledgement forms.
In this online environment, you’ll find yourself inevitably wondering, “Does anyone even read my emails?” To guarantee your students read and understand any especially important communications, add a link to a quick Google Form where a student and/or parent will type their name to acknowledge they read and understood it.

Strategies for Teaching Online: How to Build Rapport and Community with Students
Without the natural opportunities to make connections in a traditional classroom, it’s important to create these spaces in the online setting. We share easy best practices in online teaching to build your classroom community:
1. Use interactive Flipgrid discussions.
With Flipgrid, you and your students can respond to topics you’ve posted with a selfie video. Students can view everyone’s responses and then post a video reply. Though these aren’t synchronous discussions, seeing and hearing you and their classmates helps to form a community bond.
2. Incorporate purposeful free time .
Allowing 10 minutes before a live lesson for students to enter early to chat with you and each other, is a great way to foster important, informal connections. If possible, host a half hour recess once a week, where students can log into a live meeting room just to hang out. If conversation lags or needs direction, you can facilitate topics with fun icebreakers and “would you rather” questions.
3. Have a regular show and tell .
The virtual classroom makes show and tell easier than ever! You set the topic (their pet, their favorite outfit, something from a fun vacation), and students can turn on their video cameras and microphones to share in a lesson. Alternatively, you can include your show and tell in the bottom of a weekly email update. Students can share videos or just pictures and a caption- whatever works best for you!
4. Utilize a class message board .
Padlet is a great tool for creating a collaborative class message board. Students can wish each other happy birthdays, share exciting events in their lives, or post shoutouts and encouragements to each other. You can adjust Padlet’s settings so that all messages have to be approved by you before posting.
5. Remember the value of a personal phone call.
Just reaching out and speaking with your student one-on-one builds an essential bond. It can be overwhelming if you have a large class, so set a goal to speak with a certain number of students each week to ensure you’re reaching everyone. If you don’t have a work phone, create a free Google Voice account so families don’t have access to your personal number.
Strategies for Teaching Online: How to Connect with Parents
We know that parent involvement strongly impacts student performance in school. Research shows the importance of teachers and parents developing relationships based on trust, respect, and solid communication.
In the online environment, parent involvement looks very different. As the person physically with the student, parents are now responsible for making sure their child is staying on-task and logging into the computer each day to complete assignments. It can take some parents a while to adjust to their new role. As the teachers, we must find ways to connect and support our parents, provide online learning strategies for students, and keep them involved throughout the school year.
1. Send frequent reminders with Remind 101 .
This is a great two-way communication tool, that allows you to send both mass and personalized text messages. Parents who aren’t fans of checking their email or logging into their LMS account every day benefit from receiving timely reminders like these directly to their phones:
- Class events, times, and locations
- Due dates for upcoming assignments or test days
- Links to resources, videos, and articles
2. Share out weekly newsletters.
Newsletter emails help keep families informed and involved with the happenings in your class and the school. We recommend including pictures and highlighting student achievements to keep parents engaged all school year. Lucidpress offers a number of different, free templates to choose from.
3. Be clear and consistent with your expectations.
Parents want to know what they can do to support their child’s learning, but don’t always know where to start. Having clear conversations about your goals and expectations for the school year helps. In the transition to online learning, we can discuss parent expectations like:
- Checking their child’s due dates and what they’ve submitted each day
- Checking the posted grades for each class
- Reading and responding to teacher emails and calls
- Reaching out with any questions or challenges

Strategies for Teaching Online: How to Find the Right EdTech Tools and Curricula Supports
With so many different tools out there, it can be overwhelming to find the one that’s best for you and your students. Our distance learning hub is a great place to start. You can also use these simple strategies to make your selection process easy and effective.
1. Utilize these 100+ Distance Learning Tools .
We provide a comprehensive guide of 100+ distance learning tools and strategies for effective student engagement. If you’re unsure where to begin, or just want to explore new technology, start with this list. It’s organized by both instructional need and content area.
2. Collaborate with colleagues.
Even though you’re not seeing your coworkers in the hallway every day, they’re still one of the most valuable resources you can find. It can be easy to feel isolated working home alone, but remember to reach out and ask what your fellow teachers are doing in their virtual classrooms. They’re all researching and testing out new strategies and tools just like you are, and sharing your mutual findings benefits everyone.
3. Supplement your Curricula Needs.
When you need to supplement your curriculum with ready-made online activities, Albert has engaging, standards-aligned resources across grade levels and subjects. While many resources are free, educators are encouraged to try Albert for free . Tips for teaching English online using Albert include varying our leveled readings in STEM and across topics to generate interest among different students.
4. EdTech Digital Promise Framework .
This process helps educational leaders select and run successful educational technology pilots in their schools. The steps include how to identify a need, discover and select a product, train staff, and much more.
5. Always do a test run before using a new tool in class.
After you’ve selected the new tool to try, create a mock class to assign work to. Log in and test out your activity as a student, so you can truly see if this will work for your class. Also, you’ll be able to help troubleshoot common problems that you might not have noticed from just your teacher log-in.
Common Mistakes Teachers Make When First Teaching Online
There’s a few common mistakes even the best veteran teachers make when first switching to the online environment. Keep in mind these strategies for teaching online when you get started:
1. Not setting boundaries with students and parents.
Working from home, it can be tough to disconnect from your work. It’s even tougher when you have students and families reaching out to you at all hours of the evening. It can be tempting to answer the phone or send a quick reply, but resist.
Share the hours you’re available with your families, and stick to them. Mimic your normal school day, like 7:30am to 3:30pm Monday to Friday. It’s important you give yourself the time to disconnect, and anything your student needs can wait until the next morning. Teacher burnout is real.
2. Not testing new tools a few times before rolling them out to your students.
We all know- technology is great… when it works. Inevitably, something won’t always go as planned. But, that’s okay! Just like in the traditional classroom, teachers adapt and move on if something goes wrong. It can be intimidating to try out a new tool for the first time, so we suggest setting up a mock class and using some willing colleagues or family members as your guinea pigs before rolling it out with students.
3. Rolling out too much too soon.
Be wary of assigning complex tasks and assignments without training your students on how to use the technology first. Families and students will be capable of handling this complexity at some point, if you build them up to it. You don’t want your student spending more time trying to decipher the instructions than learning the actual content.
When assigning a learning task using a new tech tool, consider that it may take your families an extra 30min to one hour to get the hang of using it. Provide clear instructions with common troubleshooting tips. Better yet, assign a “mock assignment” of something simple, before actually assigning a lesson. For example, if it’s a discussion board, have students’ first posts be about their family pet or what they did for fun that weekend.

Wrapping Things Up: Things to Remember When Teaching Online
We’ve covered a lot of online teaching ideas and strategies. To wrap things up, here are 3 key takeaways to carry into your virtual classroom:
1. Stay communicative :
Share your expectations for behavior early and often. Keep lines of communication open, using different tools like emails, Remind 101, phone calls, and class message boards. Weekly newsletters are a great way to build community with families.
2. Continuously adapt your classroom :
Use the lessons you’ve already created, and adapt them to the online environment with different ed tech tools. There’s no need to reinvent the wheel- take advantage of the great resources already out there. Albert has a huge library of standards aligned lessons and activities for all ages and subjects.
3. Keep activities interesting with students :
Use a variety of asynchronous and synchronous activities to keep your students engaged, and meet different learner needs. Build in purposeful community-building activities like Show and Tell and time for free chat to foster strong student relationships.
We hope you found this Ultimate Guide for Educators helpful. Remember, one of the strong resources educators have is each other! What are you doing in your online classroom? Share your favorite tips for teaching and online learning strategies for students in the comments below.
If you enjoyed this post, you may also like our post on 75 educational teacher websites , our viral post on distance learning tools here or our free 150+ teaching strategies discovery tool .
Interested in a school license?
10 thoughts on “strategies for teaching online: the ultimate guide for educators”.
I am thankful to this blog for giving unique and helpful knowledge; I read your blog and I have to say it shares some great information.
Glad you’re enjoying the blog!
Useful post. Thanks for sharing this informative post with us.
We’re happy to help, Rosie!
I find this post very informative and helpful. I must admit I learned so much from it.
Glad to know it was helpful!
I find this post very helpful. I must admit I learned so much from it.
Great to hear!
Glad you liked it!
Comments are closed.
Popular Posts

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score

Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.
Interested in a school license?

Bring Albert to your school and empower all teachers with the world's best question bank for: ➜ SAT® & ACT® ➜ AP® ➜ ELA, Math, Science, & Social Studies aligned to state standards ➜ State assessments Options for teachers, schools, and districts.
- Teaching Tips
17 Learning Strategies to Implement In Your Classroom
Learning strategies are a critical element in ensuring students grasp course concepts and are especially important in blended and online learning environments
Danielle Leboff
Learning strategies are methods used by instructors to initiate students into effective learning by using a variety of engaging learning techniques, activities and practices. These methods are all derived from years of meticulous research into how people learn best.
In any lesson plan, instructors can incorporate multiple learning strategies. By catering to different learning styles and varying your approach, you can better engage students while helping them master new concepts.
Top Hat’s 2021 Online Teaching Toolkit gives you easy-to-use teaching templates, active learning strategies and more to engage your students in an online or hybrid learning environment. Get free access today.
Why are learning strategies important?
Learning strategies are an essential component of creating an effective learning experience. They can help learners develop proficiency in various subject matter areas and develop new skill sets. They also help learners develop confidence in their own knowledge, proficiency and learning abilities.
The following describes some common strategies for achieving various learning outcomes, along with practical examples you can incorporate directly into your learning environment.
Think-pair-share
This active learning exercise is designed to activate any prior knowledge a student may have on a subject by having them share their thoughts and beliefs with their fellow learners.
A think-pair-share exercise is structured to help students first organize their thoughts, then share these with a partner followed by the broader class.
- Think : Students take a moment to contemplate the new concept or idea on their own. They can also write down their thoughts to help develop their note-taking skills.
- Pair : Students break off into pairs to share their thoughts and beliefs on the topic with another learner.
- Share : Students then share their takeaways from this conversation with one or more successively larger groups, up to and including the whole class.
Putting think-pair-share into action
To execute think-pair-share in your class, define the exercise for the group and display the prompts you’d like to pose for discussion. Once students have completed the exercise, you can then facilitate a larger class discussion.
Make a point of listening to student responses before offering your own ideas. You can also pose probing questions while encouraging other students to offer their own responses and reactions to each other’s ideas.
Tests and quizzes
There are several ways instructors can use tests and quizzes as effective strategies for learning.
Individual plus group quizzes : Have learners complete independent quizzes for grading. Following this, place learners into small groups and give them the same quiz as a form of cooperative learning. This time, allow the groups to discuss their answers and come up with an answer for each question. Then, grade the group as a whole on their collective performance.
Not every student likes group assignments, since this may raise concerns about their individual grades. To avoid penalizing more diligent learners, take an average of each student’s two scores if the group score is higher than their individual score. If the student’s individual score is higher than the group score, let that individual score stand as the average. This process encourages students to be accountable for their own learning while helping develop their test-taking and collaboration skills.
Tests and quizzes with distractors : Distractors are common preconceptions or misconceptions about a topic. Have students answer various questions and, then, discuss their answers with a fellow student. After this discussion, have each student answer the same question again and see if their answers are any different. To close off the activity, initiate a group discussion about why the correct answer is actually the correct one. This acts as a form of metacognition by encouraging students to think about their own learning.
Retrieval practice
The process of bringing information to mind, or retrieval practice, is an effective strategy in boosting learning. In these exercises, students put away all learning materials and answer questions or discuss a topic purely based on their own recall of the information. Students can then refer to learning to evaluate how accurately they conveyed the information. Retrieval practice exercises also work well using the think-pair-share format.
Elaboration
In elaboration, students demonstrate the depth of their knowledge of a given topic by describing and explaining as much as they know about it, including as many relevant details as they can call to mind. This strategy extends the concept of rote memorization by encouraging students to draw connections within the content and between the content and other knowledge they already possess.
Interleaving
Interleaving is the process by which students mix multiple subjects or topics while they study. This allows students the opportunity to practice different modes of thinking and problem-solving as opposed to ‘blocked practice,’ which involves studying one topic thoroughly before moving on to the next.
Interleaving has been shown to improve test scores in a number of studies. As a best practice, it is important to use interleaving for related topics. For example, interleaving works well when switching between different algebra problems but is not nearly as effective when switching between radically different subject matter areas, such as literature and math equations.
Muddiest point
This form of assessment helps educators understand which elements of their course pose difficulties that may impede student progress and performance.
In this exercise, instructors ask students to note the “muddiest points” of the lesson, or the most confusing or difficult to grasp. Have students rate their degree of understanding and capture where the difficulty lies.
While the exercise shouldn’t take more than a few minutes, it has additional benefits beyond helping the instructor understand where the obstacles are for students. It also helps students more effectively analyze their own learning and to zero in on the exact issue that may be holding them back.
Peer instruction
Also known as ‘reciprocal teaching,’ this structured teaching practice asks students to reflect on new concepts they may be confused about and then share their responses to those prompts with a small group. Each group then derives a consensus response to share collectively with the rest of the class.
Peer instruction offers a number of benefits, including:
- Increasing a student’s problem-solving skills and conceptual understanding abilities
- Deepening student understanding of a topic and encouraging greater knowledge retention
- Bolstering student engagement and raising student course satisfaction
Not only does this exercise call upon students to explain their thinking, it asks them to defend it against alternative arguments and modes. This helps reveal for students as much about how they think and process information as it does about the information itself.

Differentiated instruction
Not all students learn the same way. Differentiated instruction recognizes and accommodates for this by tailoring the learning process to individual needs. This is accomplished by altering the content, process, product or the learning environment itself.
With differentiated instruction, instructors consider the different learning styles of their students before devising their teaching strategies. That way, they can incorporate multiple modalities to allow all students to succeed equally in learning the material.
Some other ways to implement differentiated learning include:
- Grouping students together for assignments by shared topics, interests, learning abilities or styles
- Using formative assessment tools to assess individual student learning styles and progress and then adjusting lesson plans accordingly
- Using classroom management tools to create safe and supportive learning environments for all students
Gamification
Sometimes turning a lesson into a game can better engage students in learning and comprehending the material. Gamification essentially incorporates reward-based activities and teaching tools into the lesson plan. Examples of gamification include:
- Earning points for finishing tasks
- Competing against peers toward a goal
- Playing games that teach particular academic skills
Project-based learning
Through project-based learning, students work together on a project over an extended period, generally between one week and an entire semester. The project ideally involves solving a real-world problem or addressing a complex question. The finished product is a public presentation or product they can present to a live audience.
Problem-based learning
Problem-based learning involves incorporating real-world situations as a vehicle to help students apply course concepts in a practical application. This helps make learning more relevant by connecting concepts to the world outside the classroom and can add variety to the learning process itself.
Formative assessments
Formative assessments are designed to monitor learning and provide feedback on each student’s progress on an ongoing basis. The steady stream of feedback allows instructors to refine and improve their teaching strategies to keep the class on track. At the same time, students can practice their test-taking skills, improve information recall while honing in on their areas of strength and weakness.
Formative assessments are typically considered “low stakes.” The primary goal is not a letter grade but generating feedback for the instructor and the student. Examples of formative assessments include:
- Self-assessments
- Entry and exit slips
- Low-stakes polls and quizzes
- Exercises incorporating art or other visual representations of learning content
- Misconception and errors
- Interview assessments
Summative assessments
Instructors use summative assessments to evaluate how thoroughly students learned an area of study. Summative assessments usually come upon the completion of an instructional unit and compare student knowledge and achievement against a previously determined set of benchmarks.
Considered “high stakes,” summative assessments are commonly used to determine a student’s subsequent course work and educational progress. Examples of summative assessments include:
- Final projects
- Term papers
- Midterm, final or standardized exams
- Performance or recital
Educators may sometimes use summative assessments in a formative manner to guide student activities and efforts throughout their coursework.
Quick write
In this exercise, pose a prompt to the group to respond to in writing. Only allow five minutes for this exercise, so students can quickly reflect on their initial thoughts on a subject.
Uses and benefits of a quick write include helping to:
- Determine whether students completed their assigned homework
- Prime students to think about topics to be introduced or developed in the upcoming lesson
- Give students the chance to access previous knowledge they may have on a subject
- Instructors can opt to grade the quick write or simply collect it as a means of confirming attendance.
Pose a question to be answered or explained, and then take an anonymous poll to see how many students favor particular answers or explanations to the question.
Afterward, initiate a group discussion of the question and the poll’s results to see why students voted the way they did. Following the discussion, take the same poll again to gauge whether any students changed their answers and, if so, to what extent and why.
Hearing why students chose a particular explanation or answer helps the instructor understand how students think about that topic. It also helps them determine if additional explanation or clarification may be required before moving on in the lesson plan.
Turn and talk
In this exercise, instructors pose a question to the group, then instruct students to choose a partner to discuss their thoughts on the question with. This can create a comfortable atmosphere for sharing ideas before bringing ideas before the whole group.
Make sure the questions students are asked to discuss are clear and that the understanding of each participant is there in order to contribute to the conversation both as a speaker and listener.
This exercise is performed in small groups in which students read a preselected passage of course material. Students in each group divide up the material so that each member reads a portion of it silently and then shares what they’ve learned with the rest of the group.
Some questions participants can use as points of focus include:
- What’s the big idea here?
- What do you believe it means, and why does it matter?
- How can someone apply this idea to help understand a larger topic?
- What part(s) of the reading do you agree and/or disagree with?
- What questions does the reading raise for you?
Instructors can implement jigsaws in a number of ways. In an ‘expert and cooperative group’ format, assign different groups different pieces of the material to read individually and discuss. Each group then becomes the expert group on that portion of the material. Following this, groups are redivided so that each new cooperative group contains one or two representatives from each of the previous expert groups. Each cooperative group then reviews the material with the expert representative. The jigsaw method is a great way to get students up to speed quickly on material while honing their critical thinking and communication skills.
Learning strategies help you better engage students in active learning by using a variety of activities such as reading, writing, discussion or problem-solving. Easy to execute, these activities promote analysis, synthesis, and the evaluation of class content. Equally important, they provide students with opportunities for feedback on how well they understand course material, ensuring they are making meaningful progress toward achieving course objectives.
Recommended Readings

Educators In Conversation: How to Help Students ‘Do’ Sociology

A 6-Step Exercise for Discussing AI In Education
Subscribe to the top hat blog.
Join more than 10,000 educators. Get articles with higher ed trends, teaching tips and expert advice delivered straight to your inbox.
K-12 Resources By Teachers, For Teachers Provided by the K-12 Teachers Alliance
- Teaching Strategies
- Classroom Activities
- Classroom Management
- Technology in the Classroom
- Professional Development
- Lesson Plans
- Writing Prompts
- Graduate Programs
Differentiated Instruction Strategies: Tiered Assignments
Janelle cox.
- September 23, 2014

Many teachers use differentiated instruction strategies as a way to reach all learners and accommodate each student’s learning style. One very helpful tactic to employ differentiated instruction is called tiered assignments—a technique often used within flexible groups.
Much like flexible grouping—or differentiated instruction as a whole, really—tiered assignments do not lock students into ability boxes. Instead, particular student clusters are assigned specific tasks within each group according to their readiness and comprehension without making them feel completely compartmentalized away from peers at different achievement levels.
There are six main ways to structure tiered assignments: challenge level, complexity, outcome, process, product, or resources. It is your job, based upon the specific learning tasks you’re focused on, to determine the best approach. Here we will take a brief look at these techniques.
Ways to Structure Tiered Assignments
Challenge level.
Tiering can be based on challenge level where student groups will tackle different assignments. Teachers can use Bloom’s Taxonomy as a guide to help them develop tasks of structure or questions at various levels. For example:
- Group 1: Students who need content reinforcement or practice will complete one activity that helps build understanding.
- Group 2: Students who have a firm understanding will complete another activity that extends what they already know.
When you tier assignments by complexity, you are addressing the needs of students who are at different levels using the same assignment. The trick here is to vary the focus of the assignment based upon whether each group is ready for more advanced work or simply trying to wrap their head around the concept for the first time. You can direct your students to create a poster on a specific issue—recycling and environmental care, for instance—but one group will focus on a singular perspective, while the other will consider several points of view and present an argument for or against each angle.
Tiering assignments by differentiated outcome is vaguely similar to complexity—all of your students will use the same materials, but depending on their readiness levels will actually have a different outcome. It may sound strange at first, but this strategy is quite beneficial to help advanced students work on more progressive applications of their student learning.
This differentiated instruction strategy is exactly what it sounds like—student groups will use different processes to achieve similar outcomes based upon readiness.
Tiered assignments can also be differentiated based on product. Teachers can use the Howard Gardner’s multiple intelligences to form groups that will hone particular skills for particular learning styles . For example, one group would be bodily/kinesthetic, and their task is to create and act out a skit. Another group would be visual/spatial, and their task would be to illustrate.
Tiering resources means that you are matching project materials to student groups based on readiness or instructional need. One flexible group may use a magazine while another may use a traditional textbook. As a tip, you should assign resources based on knowledge and readiness, but also consider the group’s reading level and comprehension.
How to Make Tiering Invisible to Students
From time to time, students may question why they are working on different assignments, using varied materials, or coming to dissimilar outcomes altogether. This could be a blow to your classroom morale if you’re not tactful in making your tiers invisible.
Make it a point to tell students that each group is using different materials or completing different activities so they can share what they learned with the class. Be neutral when grouping students, use numbers or colors for group names, and be equally enthusiastic while explaining assignments to each cluster.
Also, it’s important to make each tiered assignment equally interesting, engaging, and fair in terms of student expectations. The more flexible groups and materials you use, the more students will accept that this is the norm.
Tiering assignments is a fair way to differentiate learning. It allows teachers to meet the needs of all students while using varying levels of tasks. It’s a concept that can be infused into homework assignments, small groups, or even learning centers. If done properly, it can be a very effective method to differentiate learning because it challenges all students.
- #DifferentiatedInstruction , #TieredAssignments
More in Teaching Strategies

Helping Students Improve Their Handwriting
Despite the widespread use of technology in the classroom, handwriting remains an essential…

Unleashing the Learning Potential of Classroom Focus Walls
Focus walls have emerged as an effective tool in today’s classrooms, and for…

Getting Older Students Excited About Science Class
As students move into middle and high school, it becomes increasingly challenging for…

AI-Powered Lesson Planning: Revolutionizing the Way Teachers Create Content
Traditional teaching methods are evolving since technology has been integrated into classrooms across…

Top 20 Effective Teaching Strategies in the Classroom
Effective teaching strategies are the backbone of any successful classroom. They not only help students learn better but also keep them engaged and interested in the learning process. We will explore the different types of teaching strategies, including traditional and modern approaches, active learning techniques, personalized learning, inquiry-based learning, and more. We will discuss how to integrate technology into your teaching strategies and how to manage your classroom effectively to promote a safe and supportive learning environment.
Effective teaching strategies in the classroom involve creating an engaging and inclusive learning environment, adapting to diverse learning styles, providing clear objectives, and using a mix of instructional techniques. These strategies include active learning, hands-on activities, multimedia resources, and regular feedback to promote critical thinking, collaboration, and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Importance of Teaching Strategies
Effective teaching strategies play a crucial role in enhancing student learning and understanding. By catering to individual student needs and learning styles, different teaching strategies promote active engagement and critical thinking. Research has shown that employing best practices in teaching strategies leads to improved student achievement.
Moreover, adapting teaching strategies to student learning needs fosters a positive classroom environment. Incorporating a variety of teaching strategies, such as group assignments and problem-solving activities, can be a great way to enhance the student experience and academic achievement.
The Role of Effective Teaching Strategies in Classrooms
Effective teaching strategies play a crucial role in facilitating student progress and academic performance. Well-implemented teaching strategies help students thrive. Using a variety of strategies is key to meeting the diverse learning needs of students, allowing them to learn at their own pace in different ways.
Furthermore, effective teaching strategies promote student engagement and motivation, enhancing the overall student experience. Incorporating formative assessment in teaching strategies further enhances student understanding and ensures continuous improvement in their academic achievement.
Different Types of Effective Teaching Strategies
Traditional teaching strategies, which involve direct instruction and whole-class activities, have long been used in classrooms. However, modern teaching approaches have shifted towards student-centered learning and individualized instruction.
These strategies focus on engaging students in the learning process and allowing them to progress at their own pace. Active learning strategies encourage student participation and collaboration, while visual aids like graphic organizers and charts are valuable teaching tools. Cooperative learning strategies foster peer interaction and cooperative problem-solving.
Educators can cater to different learning styles and enhance the overall student experience.
1. Traditional Teaching Strategies
Traditional teaching strategies in the classroom emphasize teacher-led instruction. This approach often involves lectures and class discussions to impart knowledge to students. Traditional teaching strategies provide structure and guidance to students. Direct instruction is a commonly used method within these strategies, relying on textbooks and worksheets for learning.
While traditional, this teaching style has its merits and can be a great way to introduce new information and concepts to students. It also allows for the implementation of tried-and-tested lesson plans that have been proven to enhance academic achievement. Additionally, traditional teaching strategies are often employed in large classes where it may not be feasible to adopt more modern teaching techniques.
2. Modern Teaching Strategies
Modern teaching strategies prioritize student-centered and active learning, fostering a dynamic and engaging environment for students. One effective approach is project-based learning, which encourages hands-on exploration and problem-solving. Integrating technology into the classroom enhances modern teaching strategies, providing access to a vast array of educational resources and facilitating interactive learning experiences.
Differentiated instruction is key to catering to individual student needs, allowing students to learn at their own pace and in ways that best suit them. Flipped classrooms and blended learning, where online and in-person instruction are combined, are also popular modern teaching approaches.
3. Active Learning Teaching Strategies
Active learning teaching strategies are a great way to promote student engagement and participation in the learning process. By incorporating group work and collaborative learning activities, students can interact with their peers and learn from each other.
Encouraging student discussions and debates further enhances active learning by allowing students to critically analyze and articulate their thoughts. Problem-solving and hands-on activities provide students with the opportunity to apply their knowledge in fostering active engagement in learning. Using real-life examples and case studies also helps students connect academic concepts to their own experiences.
4. Encouraging Student Participation and Interaction
Incorporating class discussions and debates fosters student participation and critical thinking. Providing platforms for students to share opinions and ideas promotes interaction. Peer-to-peer feedback and self-reflection enhance the learning experience. Small group activities and cooperative learning strategies engage students effectively. Creating a safe and inclusive environment encourages active student participation.
5. Promoting Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning strategies encourage teamwork and cooperation among students, fostering a sense of camaraderie in the classroom. Group projects and problem-solving activities provide opportunities for students to work together and learn from each other’s perspectives. Peer teaching and mentoring can further enhance collaborative learning, as students take on the role of educators and share their knowledge with their peers.
Using technology tools like online discussion boards can facilitate collaborative learning by allowing students to engage in virtual discussions and share ideas.
Top 15 effective teaching strategies in the classroom
Group discussions and brainstorming sessions also promote collaborative learning by encouraging active participation and diverse thinking. Now, let’s see the top 15 effective teaching strategies in the classroom in detail.
- Cooperative Learning skills
- Behavior learning management
- Blended Learning
- Differentiated Instruction
- Student Centered Inquiry
- Professional learning development
- Formative assessment
- Visualization learning
- Active Learning
- Personalized learning
- Experiential learning
- Technological skills
Formative Assessment
- Classroom management technology
- Student-centered learning
let’s see details about these strategies
1. Cooperative Learning skills
The emergence of virtual learning has helped educators recognize the significance of cooperation in the learning process. Cooperative learning is an instructional technique wherein a small group of students actively collaborate on a given assignment.
This assignment can range from solving a quiz to composing a story, encompassing both simple and complex tasks.
2. Behavior learning management
The implementation of behavior management strategies creates an environment of mutual respect, minimizes disruptive behavior, and guarantees that all students have an equitable chance to reach their full potential in the classroom. It is essential to create a positive and productive learning setting for them.
One way to achieve this is by introducing a reward system that utilizes an interactive chart, where students can progress or regress based on their performance and behavior in class.
3. Blended Learning
By implementing a blended learning approach, the use of technology is integrated into the traditional teaching method. This enables students to progress at their speed, explore their thoughts through research, and actively participate in lessons.
For instance, interactive tablets or whiteboards with captivating activities are provided, and classwork is made available online for convenient accessibility.
4. Differentiated Instruction
Differentiation is a teaching strategy that assigns tasks based on student’s abilities and needs. Effective classrooms are inclusive, teaching to a range of learning levels simultaneously. Examples include varying worksheet complexity or offering activity choices related to a lesson.
Ways to use differentiation:
- Provide materials at various reading levels.
- Generate personalized spelling lists for students with varying spelling abilities.
- Arrange intimate gatherings to offer personalized guidance to students.
- Provide individualized assistance to students facing difficulties after school.
5. Student-Centered Inquiry
Inquiry-based classrooms focus on the student’s role in learning. Students explore, make sense of concepts, share thoughts, and ideas, and ask questions instead of the teacher solely explaining concepts orally.
This strategy engages young learners and promotes curiosity. It encourages independent exploration, research, and reflection on information. It can also help to re-engage an inactive class.
6. Professional learning development
This can confuse students and frustration for teachers. Creating a clear understanding of expectations among students enhances their focus and engagement in lessons. Here are some suggestions for fostering a positive learning environment:
- Model ideal behavior: Provide a clear explanation of appropriate conduct and then adhere to it yourself.
- Encourage initiative: Encourage students to engage actively in the learning process by facilitating class discussions and providing exercises that promote the initiative.
- It is important to refrain from implementing collective punishment.: Although it may pose challenges, it is important to specifically address disruptive behaviors on an individual level rather than as a group.
7. Formative assessment
This assessments differ from summative assessments in that they occur while the teaching process is ongoing.
- Happens via chapter or unit
- Enhances the learning experience for students
- Covers small content areas
- Ensures the monitoring of students’ learning progress
- Centers on the procedure of students acquiring knowledge and skills
Summative Assessment
- Occurs at the end of the chapter or unit
- Assesses the knowledge acquired by students
- Includes comprehensive content across all areas
- Evaluates the comprehension of students by assigning a grade
8. Visualization learning
In the simplest terms, visualization refers to our capacity to generate mental images in response to spoken words or written text.
When effectively employed, this strategy can greatly enhance students’ ability to concentrate on the concept or subject matter being discussed. It can make concepts more vivid and prompt students to establish connections with the real world.
There are several approaches to incorporating this strategy into the classroom, such as:
- The utilization of audio-visual aids includes the use of photographs, videos, audio clips, songs, and other similar media.
- Illustrations, graphs, and conceptual diagrams
- Rephrased: Employing modeling techniques while teaching can be beneficial for visual learners who require visual representations to comprehend concepts, rather than relying solely on verbal explanations.
9. Active Learning
Active learning strategies place students as the focal point of the classroom, leading to heightened student participation in daily lessons. As per James Ballencia, a proponent of active learning, this approach can be equally beneficial for both teachers and students.
Some active learning strategies include:
- Reciprocal questioning: Encourage students to generate questions for the class regarding a recent lesson or concept.
- The pause procedure: To allow students the opportunity to engage in discussions, ask questions, or work on problem-solving, it is recommended that a break be taken every 10 to 15 minutes.
- Muddiest point: Instruct the students to jot down the part of the lesson that they find most difficult to understand.
10. Personalized learning
Personalized learning recognizes that every student is different and tailors the learning experience to cater to their specific abilities. A study conducted by the Gates Foundation suggests that incorporating personalized learning into math classes can lead to improved test scores.
Discover various possibilities for implementing personalized learning in your classroom, such as the utilization of teaching techniques and enhancing student engagement . To access a comprehensive compilation of suggestions, refer to the article “7 Personalized Learning Strategies and Examples.”
11. Experiential learning
Experiential learning is about learning by doing and using real-world experience. Unlike traditional lesson plans that focus on the teacher, this strategy encourages students to engage in activities that may not seem educational at first.
Experiential learning often involves games, experiments, and simulations. It can also include field trips that connect to the curriculum and provide practical lessons outside of the classroom.
12. Technological skills
Technology in the classroom keeps students engaged, especially with the rise of remote learning. Online interactive games encourage student participation and provide a fulfilling learning experience. These educational games allow children to learn through play.
13. Formative Assessment
Find educational games for math and ELA that make learning fun and engaging for your students.
- Enhances the learning experience for students by incorporating chapter or unit-based activities.
- Includes compact subject matter
- Monitors student learning
- Emphasizes the process of students’ acquisition of knowledge
14. Classroom management technology
Using technology in the classroom is an excellent method to enhance student engagement and generate excitement for learning. However, integrating technology seamlessly into lessons can pose a challenge. There are countless opportunities to incorporate technology effectively into teaching, such as:
- A virtual field trip: Use virtual rediscover popular landmarks and natural wonders through mobile applications. Embark on a journey to the Great Barrier Reef for an in-depth exploration of ecosystems, or join a Spanish class and experience a guided tour of Barcelona.
- Video mini-lessons: Teacher Tube provides an exclusive educational version of YouTube, featuring a wide range of videos covering various fundamental topics. This enhances the learning experience, particularly for individuals who learn best through visual stimuli.
15. Student-centered learning
Student-centered inquiry is an educational approach that emphasizes the active involvement of students in the learning process. Therefore, in a classroom that adopts inquiry-based learning, students would be observed engaging in activities such as exploring the subject matter or concept, comprehending it, exchanging thoughts and ideas, and inquiries instead of solely relying on the teacher’s verbal explanations.
Implementing this strategy is an effective method to pique the curiosity of young students and involve a class that lacks participation. Children have the opportunity to enhance their research abilities, make connections between different pieces of information, and contemplate their findings through independent exploration with the subject matter.
What are the 5 teaching strategies in early childhood education?
Early childhood education is a crucial phase in a child’s development, laying the foundation for lifelong learning. To ensure an engaging and effective learning experience, educators can employ unique teaching strategies that go beyond the conventional methods.
Here are five innovative teaching strategies for early childhood education:
1. Nature-Based Learning
Take the classroom outdoors and make nature the primary teacher. Children can learn about science, math, and the environment through hands-on experiences like planting gardens, observing wildlife, and exploring natural surroundings. This strategy not only fosters a love for the environment but also encourages curiosity and critical thinking.
2. Storytelling through Technology
Embrace the digital age by incorporating storytelling through technology. Use interactive apps and e-books that allow children to immerse themselves in the narrative. Technology-enhanced storytelling can make learning more engaging, stimulate creativity, and improve digital literacy.
3. Project-Based Learning
Encourage children to explore their interests and passions through project-based learning. Let them choose a topic they are curious about, and then guide them through the process of researching, and presenting their findings. This strategy promotes self-directed learning, problem-solving, and collaboration.
4. Art Integration
Go beyond traditional art classes by integrating art into every aspect of the curriculum. Art can be used to teach concepts in math, science, and social studies. This approach encourages creativity, expression, and a deeper understanding of academic content.
5. Mindfulness and Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
Incorporate mindfulness and SEL practices into the daily routine. Teach children to recognize and manage their emotions, develop empathy, and build positive relationships. Mindfulness exercises can help them focus and reduce stress. By prioritizing social and emotional development, educators prepare children not only academically but also for life’s challenges.
These unique teaching strategies aim to make early childhood education a dynamic and holistic experience. They empower young learners to think critically, express themselves creatively, and develop important life skills, setting them on a path of lifelong learning and personal growth.
Effective instructional strategies for the secondary classroom
Effective instructional strategies for the secondary classroom involve using a variety of teaching methods to engage students, fostering a dynamic and interactive learning environment.
These strategies can include differentiated instruction to cater to diverse learning styles, incorporating technology, encouraging critical thinking, and promoting student-led discussions and projects.
Establishing clear learning objectives, providing timely feedback, and building a positive and supportive classroom culture are also essential components of effective teaching at the secondary level.
How to Integrate Technology in Teaching Strategies?
Integrating technology in teaching strategies enhances student learning and engagement. Educational apps and online resources provide interactive learning experiences. Using digital tools for assessments and feedback streamlines teaching strategies.
Virtual simulations and multimedia resources enrich teaching and learning. Blended learning models combine traditional teaching strategies with online platforms.
Harnessing Digital Tools for Enhanced Education
Harnessing digital tools in the classroom revolutionizes education by providing diverse opportunities for enhanced learning. Online platforms and virtual classrooms foster distance learning, expanding educational reach. Multimedia presentations whiteboards engage students through immersive instruction.
Gasification and educational games make learning enjoyable and effective, promoting active participation. Online collaboration tools facilitate communication and teamwork in educational settings, encouraging collaborative problem-solving.
Personalized learning platforms adapt to individual student needs, promoting a tailored learning process. By integrating these digital tools, educators can create a dynamic and enriching student experience.
Utilizing Online Learning Platforms
Online learning platforms offer a wealth of educational resources, making them valuable tools for effective teaching strategies in the classroom.
The use of interactive multimedia content enhances engagement and understanding, while online forums and discussion boards promote collaboration and peer interaction. Real-time feedback and assessment tools allow teachers to monitor student progress and identify areas for improvement.
Personalized Learning as a Teaching Strategy
Personalized learning is a valuable teaching strategy that allows instructors to tailor instruction to meet the individual needs of students. By utilizing adaptive technology, targeted interventions and practice activities can be provided to address specific areas of improvement.
This approach is beneficial as it acknowledges the importance of student-driven goals and interests, increasing motivation and ownership of learning.
Top 7 Classroom management strategies for preschool teachers
Flexible pacing accommodates different learning styles, allowing students to progress at their own pace. Regular feedback supports students in taking ownership of their learning and continuously improving their academic achievement. See details about the classroom management strategies for preschool teachers.
1. Adapting to Individual Learning Styles
Recognizing and accommodating different learning styles enhances student understanding. Visual learners benefit from the use of graphic organizers and visual aids, while auditory learners thrive in discussions and lectures with audio cues.
Kinesthetic learners engage through hands-on activities and movement. Teachers can cater to the diverse learning preferences of their students. This approach allows for a more personalized learning experience, enabling students to grasp new concepts and information in their unique ways.
2. Differentiated Instruction for Diverse Learners
Differentiated instruction is a valuable teaching approach that addresses the unique needs of individual students. Teachers can provide varying levels of challenge based on student readiness. Flexible grouping strategies encourage collaboration and peer learning, fostering a supportive classroom Culture .
Teachers can also accommodate different learning preferences by using varied instructional materials. Continuous assessment plays a crucial role in informing differentiation and making necessary instructional adjustments. Overall, differentiated instruction is a powerful tool for promoting academic achievement and enhancing the student experience in diverse classrooms.
3. Inquiry-Based Learning Approach
Inquiry-based learning presents an opportunity for students to independently explore and discover knowledge. By posing open-ended questions, this approach promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Through research projects and investigations, students develop curiosity and gain a deeper understanding of concepts. Scaffold guidance is provided to support students in developing research and inquiry skills. Student-led discussions and reflections further enhance active learning and engagement, allowing students to take ownership of their learning process.
4. Encouraging Curiosity and Creativity in Students
Creating an environment in the classroom that nurtures curiosity is crucial for sparking student engagement. By encouraging divergent thinking perspectives, teachers can foster creativity among their students.
Open-ended projects and assignments provide opportunities for student exploration and innovation. Giving students choice and autonomy in learning tasks can spark intrinsic motivation.
Moreover, celebrating and valuing unique answers and approaches encourages risk-taking, ultimately leading to a more engaging and creative student experience.
5. Classroom Management Strategies
Establishing a positive and productive learning environment is crucial for effective classroom management. By setting clear expectations, teachers can promote order and minimize disruptions. Consistent behavior management strategies play a vital role in creating a safe and respectful classroom culture.
Building positive relationships with students enhances trust and cooperation, leading to a better learning experience. Proactive approaches like preventive discipline strategies can effectively prevent behavior issues. Implementing these strategies fosters an atmosphere where students can learn and thrive, ultimately contributing to their academic achievement and overall student experience.
6. Maintaining Discipline and Order in the Classroom
Establishing clear rules and consequences is key to maintaining discipline and order in the classroom. Non-verbal cues and proximity can be used to redirect off-task behavior , ensuring that students stay focused on the learning process . Implementing a behavior management system with rewards and incentives motivates students to follow the rules.
Modeling and reinforcing expected behavior through positive reinforcement creates a positive and supportive learning environment. Consistent communication and collaboration with parents are important in addressing behavior concerns a smooth school year. Teachers can create a structured and disciplined classroom where every student can learn at their own pace.
7. Creating a Safe and Supportive Learning Environment
Promoting student well-being and engagement is crucial in creating a safe and supportive learning environment. By incorporating team-building activities and class discussions, teachers can build a sense of community among students. Cultivating a positive classroom culture that values diversity and inclusivity further enhances the learning experience.
Providing emotional support through active listening helps students feel heard and understood. Additionally, creating welcoming and comfortable physical spaces fosters an environment conducive to learning. Teachers can ensure that their classrooms are safe, supportive, and empowering spaces for students to thrive.
The Role of Formative and Summative Assessments in Teaching Strategies
It provide ongoing feedback to inform instructional decisions, while summative assessments evaluate student mastery of content and skills. By using a combination of formative and summative assessments, teachers gain a comprehensive view of student progress.
This assessment data guides instructional planning and differentiation, allowing teachers to tailor their lesson plans to meet individual student needs. Furthermore, providing timely and constructive feedback supports student growth and improvement. Through these assessments, teachers can effectively gauge student understanding and make informed instructional choices to enhance the learning process.
Assessing Student Progress and Understanding
Throughout the learning process, teachers need to assess student progress and understanding. Formative assessments, such as using Venn diagrams or group assignments, offer valuable insights into individual and whole-class comprehension. They allow students to demonstrate their learning in different ways and at their own pace.
Teachers can guide students toward academic achievement. Additionally, summative assessments, like pie charts or academic concepts, evaluate overall student performance. Adjusting teaching strategies based on assessment results ensures that every student has the opportunity to succeed in their learning journey.
What Are the Challenges in Implementing Effective Teaching Strategies?
Implementing effective teaching strategies can be challenging due to various factors. Some teachers may resist change and stick to their established methods. Classroom size and student diversity can also pose difficulties.
Limited resources, such as time and funding, further hinder implementation. Schools must provide support and professional development for the successful adoption of these strategies.
Overcoming Obstacles in Teaching
Establishing a positive and inclusive classroom environment creates a learning process where students feel valued and engaged. Behavior management strategies are crucial for addressing disruptive behaviors and maintaining a focused learning environment . Cooperative learning and group work provide students with the opportunity to collaborate, problem-solve, and learn from each other. You have to know also the role of a teacher in the learning process.
Differentiating instruction caters to the individual needs of students, allowing them to learn at their own pace and in different ways. Incorporating active learning techniques such as hands-on activities, experiments, and discussions promotes critical thinking and inquiry.
The Future of Teaching Strategies
Embracing technology as a valuable tool for enhancing the learning experience, incorporating innovative teaching methods to cater to the needs of the 21st-century learner, and integrating interdisciplinary approaches to promote cross-curricular connections are some of the future directions in teaching strategies.
Utilizing data-driven insights to inform instructional decisions and personalize learning is another important aspect. Cultivating a growth mindset among students to foster a love for lifelong learning is crucial.
Educators can ensure that they are keeping up with the evolving needs and preferences of their students, ultimately leading to improved academic achievement and a more enriching student experience.
Evolving Teaching Strategies for the 21st Century Classroom
In the ever-evolving landscape of education, teachers must adapt their teaching strategies to meet the needs of 21st-century learners. One effective approach is incorporating project-based learning, which promotes the real-world application of knowledge.
Utilizing online platforms and resources supports blended learning environments, allowing students to learn at their own pace and in different ways. Encouraging student autonomy and self-directed learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving educational skills .
Integrating global perspectives and cultural diversity into the curriculum expands students’ horizons and enhances their learning experience.
People also ask
How can teachers continually improve their teaching strategies.
Teachers can continually improve their teaching strategies by engaging in ongoing professional development, reflecting on their practice and seeking feedback, collaborating with colleagues, incorporating research-based practices, and monitoring student achievement .
This continuous improvement ensures that teachers provide the best possible learning experiences for their students.
What are the five essential teaching strategies to deliver effective lessons?
Five essential teaching strategies for effective lessons are:
- Active Learning: Encourage student participation through discussions, group activities, and hands-on experiences.
- Differentiation: Tailor your teaching to meet individual student needs and learning styles.
- Clear Objectives: Set specific learning goals and communicate them clearly to students.
- Feedback: Provide timely and constructive feedback to help students improve.
- Engagement: Foster a positive and inclusive classroom environment to keep students motivated and interested in the subject matter.
What is the basic teaching model?
The Basic Teaching Model, developed by Robert Glaser in 1962, explains the relationship between teaching and learning.
To conclude, effective teaching strategies are crucial for creating engaging and impactful learning environments. By understanding different types of teaching strategies, such as traditional and modern approaches, active learning and questioning techniques , integrating technology, personalized learning, inquiry-based learning, and classroom management strategies, educators can cater to the diverse needs of students and promote their academic growth.
Utilizing formative and summative assessments helps in tracking student progress and identifying areas for improvement. However, it is essential for teachers to continually improve their teaching strategies by seeking professional development opportunities, staying updated with the latest educational trends, and adapting to the ever-evolving 21st-century classroom.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Course Development Institute
- Programmatic Assessment
- Instructional Technology
- Class Observations and Feedback
- Online Course Review and Feedback
- New Faculty Programs
- History of SoTL
- SOTL Resources
- IUB Database
- Featured SoTL Activity
- Intensive Writing
- Faculty Liaison
- Incorporating and Grading Writing
- Writing Tutorial Services
- Cel Conference
- CEL Course Development Institute
- ACE Program
- Community Partners
- CEL Course Designation
- CEL during COVID-19
- Annual AI Orientation
- Annual Classroom Climate Workshop
- GTAP Awardees
- Graduate Student Learning Communities
- Pedagogy Courses for Credit
- Diversity Statements
- Learning Communities
- Active Learning
- Frequent and Targeted Feedback
- Spaced Practice
- Transparency in Learning and Teaching
- Faculty Spotlights
- Preparing to Teach
- Decoding the Disciplines
- Backward Course Design
- Developing Learning Outcomes
- Syllabus Construction
- How to Productively Address AI-Generated Text in Your Classroom
- Accurate Attendance & Participation with Tophat
- Designing Assignments to Encourage Integrity
- Engaging Students with Mental Health Issues
- Inclusive and Equitable Syllabi
- Creating Accessible Classrooms
- Proctoring and Equity
- Equitable Assignment Design
- Making Teaching Transparent
- DEIJ Institute
- Sense of Belonging
- Trauma-Informed Teaching
- Managing Difficult Classroom Discussions
- Technology to Support Equitable and Inclusive Teaching
- Teaching during a Crisis
- Teaching for Equity
- Supporting Religious Observances
- DEIJ Resources
- Test Construction
- Summative and Formative Assessment
- Classroom Assessment Techniques
- Authentic Assessment
- Alternatives to Traditional Exams and Papers
- Assessment for General Education and Programmatic Review
- Rubric Creation and Use
- Google Suite
- Third Party Services: Legal, Privacy, and Instructional Concerns
- eTexts and Unizin Engage
- Next@IU Pilot Projects
- Web Conferencing
- Student Response Systems
- Mid-Semester Evaluations
- Teaching Statements & Philosophies
- Peer Review of Teaching
- Teaching Portfolios
- Administering and Interpreting Course Evaluations
- Temporary Online Teaching
- Attendance Policies and Student Engagement
- Teaching in the Face of Tragedy
- Application for an Active Learning Classroom
- Cedar Hall Classrooms
- Reflection in Service Learning
- Discussions
- Incorporating Writing
Team-Based Learning
- First Day Strategies
- Flipping the Class
- Holding Students Accountable
- Producing Video for Courses
- Effective Classroom Management
- Games for Learning
- Quick Guides
- Mosaic Initiative
- Kelley Office of Instructional Consulting and Assessment
Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning
- Teaching Resources
- Teaching Strategies
Organizing the Groups
Designating roles in groups, sharing group results.
Having students work in groups lets them practice the skills they are learning. Speaking in front of the whole class can be scary, and combined with the tension of speaking to the teacher, the situation can be downright terrifying to students. Breaking them up into groups not only develops social skills useful in the professional environment for which they are training, but gives them a chance to perform in a supportive environment before a test or even before having to do homework on the topic on their own.
Keep in mind the following elements of group work when selecting the appropriate type of group work for your class.
- Size : Two to six people in a group is ideal. The smaller the group, the more likely each student will be to contribute to the discussion. Groups of two or three students are sufficient for simple tasks for which consensus should be reached quickly. Groups of four to six are better for more complex tasks in which a greater number of ideas may improve the final results.
- Selection : You should either assign students randomly to groups or select students so that each group has an equal distribution of talents. Do not let students choose their own teams, for they may team up with friends or form cliques that can get off topic. Video on group formation (running time 4:57).
- Duration : Use the groups for a brief discussion in class or for all semester. Long-term groups work more substantively and less superficially.
To derive the greatest benefit from the group interaction, you should spend a few minutes clarifying the students’ roles and the expectations for the group’s work.
Groups that are created for in-class discussion can be easily organized around a four-person model based on roles. Each member of the group plays a specific role that supports the team’s collaborative effort. These roles include:
- Leader : Responsible for keeping the group on task, maintaining the schedule (meetings, deadlines), and maintaining contact information (phone numbers, emails).
- Encourager : Encourages conversation and inclusion of all opinions, and guides the discussion toward consensus.
- Prober : Ensures that the assumptions are correct and that there is sufficient evidence for the solution.
- Recorder : Writes down the group’s solution that will be submitted for the group grade.
While some people will tend to lead and some will tend to follow, everyone should be willing to compromise and modify their ideas in the interest of group unity. If the groups are going to be working together on a long-term project or multiple tasks, you may wish to modify these roles to emulate roles that one might encounter in your discipline. Ensure that the students rotate through these positions. Try to break a long project into at least as many tasks as there are people in each group and have the students rotate through the roles each time they start a new task.
Students should share the results of their group with the class at large. This holds them accountable to show their work. Having to show the other groups what they did can increase their motivation to produce higher level work. While in the past, instructors were used to having groups report out their work either verbally or on newsprint posted on walls along with a walk-around format, for long-term projects, many social pedagogies now exist that can be employed, such as Prezi presentations or having students create a Public Service Announcement (PSA), blog, or a web page of their results. Do not forget to debrief students about the lessons they might have learned from the group work.
Designing for Difficulty: Social Pedagogies as a Framework for Course Design
Discussion can motivate students, especially when the activity involves authentic learning—that is, real world and messy—allowing students to collaborate, reflect on, and synthesize their learning. When planning the structure for a discussion, look for one that will hold students accountable to their peers, not just the instructor, in a public way (Bass & Elmendorf, 2011).
IDEA Paper #49 Effective Classroom Discussion
This paper sets out basic principles to create the expectation for student discussion, as well as the role of the instructor in fostering discussion in class.
Team-Based Learning is an advanced form of group work in which content coverage is pushed outside of the class, with students using precious in-class time to take quizzes to show they have mastered the content and then practice the application of critical disciplinary skills such as problem-solving and argumentation. For more information, go the TBL website, which has many videos, including ones on forming groups, the difference between groups and teams, and peer evaluation of team members.
Who Is Doing This at IUB?
The National Study of Student Engagement data show that 68% of IUB seniors engage in class discussion. Many IUB professors commonly use various discussion techniques. Some specific examples are listed below:
Prof. Jill Robinson (Chemistry) uses small groups for problem solving and “clickers” to collect student responses to get students to think deeply about fundamental chemical principles that can influence our climate. She does so even though she is teaching a large class (140-student C118: Principles of Chemistry and Biochemistry) and often teaching in a challenging classroom space.
Biology Professor and Carnegie Scholar Whitney Schlegel leads students to learn with their peers by engaging in discussion, problem-solving, and inquiry by using team members as a resource in classes of over 100. She utilizes a high-tech classroom so that students can show the products of their group work during class.
For More Information or Help
To meet with a CITL consultant, contact us .
Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning social media channels
Useful indiana university information.
- Campus Policies
- Knowledge Base
- University Information Technology Services
- Office of the Vice Provost for Undergraduate Education
- Office of the Vice Provost for Faculty and Academic Affairs
- Faculty Academy on Excellence in Teaching
- Wells Library, 2nd Floor, East Tower 1320 East Tenth Street Bloomington, IN 47405
- Phone: 812-855-9023

Teaching and Learning Strategies: A classroom guide
January 4, 2022
Which classroom teaching and learning strategies are worth embedding in your school? Find out here.
Main, P (2022, January 04). Teaching and Learning Strategies: A classroom guide. Retrieved from https://www.structural-learning.com/post/teaching-and-learning-strategies-a-classroom-guide
What are the teaching and learning strategies?
Teaching strategies are the techniques and methods that a teacher applies to support student learning . A teacher selects the teaching strategy most suited to the current level of knowledge of the students, the concept being studied, and the stage in the learning journey of the students.
A learning strategy is a learner's way to organize and use a specific range of skills to learn curriculum content or complete other tasks more efficiently and effectively in a classroom setting as well as in non-academic settings.
An effective teacher applies the most innovative and creative teaching methods to teach academic concepts and meet the individual needs of students. However, the demands of ever-expanding curricular means that educators often stick to their favoured teaching methodology . We all have our preferred teaching methodology but it is important to explore evidence-informed pedagogical ideas that have the potential to expand our repertoire in the classroom .
What are some of the popular teaching and learning strategies?
It can be hard to know which teaching strategy will work the best with a particular student. So, below is a list of teaching strategies teachers can use to enhance their teaching methodologies:
- Visualization : Visualization is a useful technique to process or summarize the knowledge that has been instructed in class. When students receive the information through visual means , they are more able to retain both the previous learning and new information for a longer time. Visualization is also a helpful learning process for lower-attaining learners to receive the information in a simpler, clear and systematic way. Thus, an effective teacher would use visual tools such as flow charts, graphic organizers, concept maps and Venn diagrams, that allow students to grasp information more effectively through visual memory .

- Teamwork: Dividing the class into groups to complete a task is a teaching strategy that does wonders . It is recommended to encourage learners of mixed abilities to work with one another. By doing so, those who have more knowledge of the subject can share their knowledge and help their peers understand the topic better. Studies of classroom instruction show that the teachers can promote cooperative learning by splitting the class into small groups and dividing different tasks amongst students. For example, in Science class one student can experiment, another would read the instructions and someone else will write notes about the learning process. Previous studies reveal that group assignments improve teamwork and help students to succeed. For some educators, this is not a preference for teaching strategies. Group work needs to be well-managed and requires a level of independence.
- Inquiry-Based Teaching: Encouraging learners to ask a lot of questions is an effective teaching strategy that does not only motivate students to think more practically but also helps them to become independent learners . Inquiry-Based learning motivates students to ask questions and work with one another to solve any problem. Through this strategy, students tend to show more interest in the learning process such as formative assessments . Inquiry-based learning provides student experience of working with one another as a class and also allows students to revise previous learning and retain new learning in a better way.
- Student-led Classroom : Studies of classroom instruction reveal that giving more power to students allows them to become self-aware of their strengths . To facilitate Student-led instructions , teachers encourage learners to ask many questions and provide more frequent feedback . In a student-led classroom , teachers encourage students to perform their research online and bring their learning outcomes to the classroom. A student-led teaching strategy is widely used to build greater confidence in students. Previous studies show that this approach allows students to take more responsibility for their learning and bring long-term advantages such as higher levels of soft skills .

- Implementing Technology in the Classroom: The productive use of technological tools as active learning strategies i n educational institutions may develop a vibrant learning community, help educators prepare and improve their lesson plans . Using technology in the classroom is a valuable tool that prepares students to learn 21st-century skills. Use of PowerPoint presentations, videos, virtual classrooms, robots and augmented reality (AR) does not only add liveliness to the classroom but may also lead to a more inclusive and effective learning environment that improves inquisitiveness and collaboration between the students and allow educators to compile data on student performance. When classrooms around the world were forced to participate in online learning, schools had to re-examine their institutional teaching methods.
- Some of the student feedback surrounding the sudden use of technology was very positive. In certain parts of the world, student engagement increased. If however, your home did not have suitable technology, the student experience of home learning was not so positive .
Active Learning: Promoting Student Participation and Interaction
The integration of technology in today's classrooms has the potential to elevate education by fostering collaborative learning, enhancing oracy, and promoting dialogic teaching .
In this digital age, the myth of learning styles has been debunked , paving the way for a more holistic approach that accommodates the diverse range of cognitive thinking skills and multiple intelligences that students possess . Just as an orchestra harmoniously blends the unique sounds of various instruments, technology allows educators to embrace neurodiversity and orchestrate a cohesive learning experience for all.
However, it is essential for teachers to be mindful of the challenges that technology can present, such as social loafing , wherein some students may disengage from collaborative learning environments. To combat this issue, educators can employ digital tools that encourage active participation and foster a sense of accountability within group settings.
Research by Mercer (2008) and Dillenbourg (1999) highlights the power of dialogic teaching and collaborative learning in enhancing students' cognitive skills and overall academic performance.
By harnessing the capabilities of digital tools, teachers can create an inclusive and dynamic learning environment that caters to the diverse needs of their students, fostering a culture of collaboration, communication, and critical thinking that will prepare them for the challenges of the 21st century.
Learning strategies for students
Previous studies show that students depend upon their senses to process knowledge around them. Most of the successful learners tend to use one of their senses more frequently than the others. Over the last few years, the concept of ' Preferred Learning Styles ' has been heavily criticised. According to recent literature in the field of education, the idea that a child has a learning style preference is a myth. In some schools throughout the UK during the early 2000's, children were effectively labelled either a: Visual learners , auditory learners, social learners or even naturalist learners.
This practice was misinformed and sidetracked teachers from engaging with more evidence-informed ideas . If you were a teacher trained in the late 90s you may well have been on a workshop where you explored whether your class were verbal learners or tactile learners. It is widely agreed that there is limited evidence for the concept of preferred learning modes. This article is not advocating the idea of having a dominant learning style but it is worth exploring how the different senses play a part in the knowledge acquisition process.
- Visual Strategies: Pupils learn and retain the knowledge better when it is presented to them in a pictorial form , such as diagrams, charts, arrows and symbols. This approach has been refined through the research into dual coding . Using clear visuals of information hierarchy as an approach to teaching practices is an accessible way of giving access to complex regular content. To apply this approach into the classroom management strategy, teachers can apply the following in the classroom learning environment:
- Use a wide range of visual aids such as pictures, charts, graphs, and illustrations;
- Include handouts and outlines for teaching various academic concepts;
- Show pictures and explain ;
- Remove potential distractions;
- Leave some space in handouts where students can write notes;
- Show clear screens while using multimedia;
- Use colourful illustrations and presentations .

- Auditory strategies: Creating learning experiences that involve listening and talking. Successful teachers need to apply the following instructional methods in their classroom:
- Begin new topic with the background of what academic concepts are coming;
- Use activities such as discussion groups or brainstorming ;
- Ask the learners to read aloud the question;
- Have learners sit in groups where vocal collaboration is possible;
- Conclude by summarizing what was taught.
- Reading & Writing - Using more traditional instructional methods such as rewriting their notes, reading textbooks, and note-taking. They tend to learn better by applying the following in their classroom:
- They must be provided with the written information on worksheets, and other text-heavy resources;
- Ask students to rewrite notes;
- Using bullet point lists;
- Turning charts and diagrams into words.
- They must be asked to reference written text.
- Kinaesthetic Learning [or embodied cognition] is also referred to as tactile learning . Kinesthetic learning is the most physical of all the learning styles, as kinesthetic or tactile learners grasp information best through the instructional strategy that involves the practical strategy of motion, movement and touch. The word kinaesthetic learners indicate students' ability to sense movement and body position in the learning environment . Student understanding of Tactile learners is enhanced by the physical activity such as touching, feeling and moving things . In recent years, the field of embodied cognition has received a lot of interest. The work of Barbara Tversky has shown us that being referred to as a 'kinaesthetic learner' probably describes most of us. The following are a selection of strategies used to teach kinaesthetic learners (or anyone else for that matter!):
- Involve physical movement in the teaching methods;
- Provide hands-on experience to the learners;
- Use flashcards to teach;
- Engage students in classroom activities that involve physical materials .
- Ask students to draw images of information in the formative assessments .

Other teaching and learning strategies you should research
At Structural Learning , we have been trying to uncover classroom ideas that are both evidenced informed and easy to implement. Organisations such as the EEF condense the findings of studies of classroom instruction. We can use this extensive evidence to make better decisions about how we can teach our lessons. Focusing on the pedagogy is with the highest impact is a good starting point for any school.
The strategies listed within these journals help classroom practitioners widen their range of skills. If you are thinking about making some pedagogical changes across your school, you may want to explore some of the following topics:
- Integrating formative assessment strategies in your classroom.
- Advancing critical thinking skills by using graphic organisers to help students organise their thinking .
- Provide playful learning experiences that promote divergent thinking.
- Utilise dual coding methods to make curriculum content easier to understand.
- Integrate responsive teaching as a whole school philosophy.
- Build the pillars of teaching by embracing Rosenshine's principles of instruction .
- Provide insightful student feedback that moves their thinking forward.
- Promote critical thinking skills by using Oracy or dialogic teaching methods .
- Make abstract concepts in maths more concrete by using physical materials.
- Develop intervention lessons into engaging experiences by using different learning tools.
- Make your assessment strategy more creative by giving summative assessments less priority.
- Only embrace evidence-informed ideas that have a clear impact.

Integrating Technology: Harnessing Digital Tools for Enhanced Education
The integration of technology into the educational landscape has opened the door to a multitude of creative teaching strategies, enabling teachers to craft immersive and dynamic learning experiences for their students.
Just as a chameleon adapts to its surroundings, educators must harness digital tools to facilitate personalized learning , addressing the unique needs and abilities of each individual. Through platforms that support game-based learning and asynchronous learning, students can engage with the curriculum at their own pace, fostering a sense of autonomy and ownership in their educational journe y.
By drawing on Jerome Bruner's concepts of assimilation and accommodation , educators can use technology to enhance information-processing skills while also providing experiential learning opportunities.
This aligns with John Dewey's educational philosoph y, which emphasizes the importance of learning through experience and interaction with the environment. Technology-based learning tools act as a bridge between the abstract and the concrete, allowing students to actively engage with the subject matter and gain a deeper understanding of complex concepts .
In order to maximize the potential of technology for enhanced education, teachers should remain open to exploring new digital resources and incorporating them into their pedagogical approach.
Edutopia and the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE) offer a wealth of resources and strategies for effectively integrating technology into the classroom, empowering educators to elevate their teaching practice and unlock their students' full potential.

Final thoughts on learning and teaching strategies
The above discussion shows that students don't always have a unique learning style preference . It can be challenging to create learning solutions that are universally accessible for the whole class. E ducational researchers believe that using a mixture of active learning strategies may help to improve the learning outcomes of each student and may motivate students to show deeper understanding. Thus, the best instructional methods for a teacher are a mixture of teaching strategies that will help learners to learn quickly and retain more.
Enhance Learner Outcomes Across Your School
Download an Overview of our Support and Resources
We'll send it over now.
Please fill in the details so we can send over the resources.
What type of school are you?
We'll get you the right resource
Is your school involved in any staff development projects?
Are your colleagues running any research projects or courses?
Do you have any immediate school priorities?
Please check the ones that apply.
Download your resource
Thanks for taking the time to complete this form, submit the form to get the tool.
Classroom Practice
404 Not found
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
- Academic Leaders
- Faculty and Instructors
- Graduate Students and Postdocs
Center for Educational Innovation
- Campus and Collegiate Liaisons
- Pedagogical Innovations Journal Club
- Teaching Enrichment Series
- Recorded Webinars
- Video Series
- All Services
- Teaching Consultations
- Student Feedback Facilitation
- Instructional Media Production
- Curricular and Educational Initiative Consultations
- Educational Research and Evaluation
- Thank a Teacher
- All Teaching Resources
- Aligned Course Design
- Active Learning
- Team Projects
- Active Learning Classrooms
- Leveraging the Learning Sciences
- Inclusive Teaching at a Predominantly White Institution
- Assessments
- Online Teaching and Design
- AI and ChatGPT in Teaching
- Documenting Growth in Teaching
- Early Term Feedback
- Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
- Writing Your Teaching Philosophy
- All Programs
- Assessment Deep Dive
- Designing and Delivering Online Learning
- Early Career Teaching and Learning Program
- International Teaching Assistant (ITA) Program
- Preparing Future Faculty Program
- Teaching with Access and Inclusion Program
- Teaching for Student Well-Being Program
- Teaching Assistant and Postdoc Professional Development Program
Pedagogy - Diversifying Your Teaching Methods, Learning Activities, and Assignments
Definition of Pedagogy
In the most general sense, pedagogy is all the ways that instructors and students work with the course content. The fundamental learning goal for students is to be able to do “something meaningful” with the course content. Meaningful learning typically results in students working in the middle to upper levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy . We sometimes find that novice instructors conflate course content with pedagogy. This often results in “teaching as talking” where the presentation of content by the instructor is confused with the learning of content by the students. Think of your course content as clay and pedagogy as the ways you ask students to make “something meaningful” from that clay. Pedagogy is the combination of teaching methods (what instructors do), learning activities (what instructors ask their students to do), and learning assessments (the assignments, projects, or tasks that measure student learning).
Key Idea for Pedagogy
Diversify your pedagogy by varying your teaching methods, learning activities, and assignments. Critically assess your pedagogy through the lens of BIPOC students’ experiences at a PWI . We visualize these two related practices as a cycle because they are iterative and ongoing. Diversifying your pedagogy likely means shedding some typical ways of teaching in your discipline, or the teaching practices you inherited. It likely means doing more active learning and less traditional lecturing. Transforming good pedagogy into equitable pedagogy means rethinking your pedagogy in light of the PWI context and considering the ways your pedagogy may help or hinder learning for BIPOC students.
PWI Assumptions for Pedagogy
Understanding where students are on the spectrum of novice to expert learning in your discipline or course is a key challenge to implementing effective and inclusive pedagogy (National Research Council 2000). Instructors are typically so far removed from being a novice learner in their disciplines that they struggle to understand where students are on that spectrum. A key PWI assumption is that students understand how your disciplinary knowledge is organized and constructed . Students typically do not understand your discipline or the many other disciplines they are working in during their undergraduate years. Even graduate students may find it puzzling to explain the origins, methodologies, theories, logics, and assumptions of their disciplines. A second PWI assumption is that students are (or should be) academically prepared to learn your discipline . Students may be academically prepared for learning in some disciplines, but unless their high school experience was college preparatory and well supported, students (especially first-generation college students) are likely finding their way through a mysterious journey of different disciplinary conventions and modes of working and thinking (Nelson 1996).
A third PWI assumption is that instructors may confuse students’ academic underpreparation with their intelligence or capacity to learn . Academic preparation is typically a function of one’s high school experience including whether that high school was well resourced or under funded. Whether or not a student receives a quality high school education is usually a structural matter reflecting inequities in our K12 educational systems, not a reflection of an individual student’s ability to learn. A final PWI assumption is that students will learn well in the ways that the instructor learned well . Actually most instructors in higher education self-selected into disciplines that align with their interests, skills, academic preparation, and possibly family and community support. Our students have broader and different goals for seeking a college education and bring a range of skills to their coursework, which may or may not align with instructors’ expectations of how students learn. Inclusive teaching at a PWI means supporting the learning and career goals of our students.
Pedagogical Content Knowledge as a Core Concept
Kind and Chan (2019) propose that Pedagogical Content Knowledge (PCK) is the synthesis of Content Knowledge (expertise about a subject area) and Pedagogical Knowledge (expertise about teaching methods, assessment, classroom management, and how students learn). Content Knowledge (CK) without Pedagogical Knowledge (PK) limits instructors’ ability to teach effectively or inclusively. Novice instructors that rely on traditional lectures likely have limited Pedagogical Knowledge and may also be replicating their own inherited teaching practices. While Kind and Chan (2019) are writing from the perspective of science education, their concepts apply across disciplines. Moreover, Kind and Chan (2019) support van Driel et al.’s assertion that:
high-quality PCK is not characterized by knowing as many strategies as possible to teach a certain topic plus all the misconceptions students may have about it but by knowing when to apply a certain strategy in recognition of students’ actual learning needs and understanding why a certain teaching approach may be useful in one situation (quoted in Kind and Chan 2019, 975).
As we’ve stressed throughout this guide, the teaching context matters, and for inclusive pedagogy, special attention should be paid to the learning goals, instructor preparation, and students’ point of entry into course content. We also argue that the PWI context shapes what instructors might practice as CK, PK, and PCK. We recommend instructors become familiar with evidence-based pedagogy (or the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning , SoTL) in their fields. Moreover, we advise instructors to find and follow those instructors and scholars that specifically focus on inclusive teaching in their fields in order to develop an inclusive, flexible, and discipline-specific Pedagogical Content Knowledge.
Suggested Practices for Diversifying + Assessing Pedagogy
Although diversifying and critically assessing teaching methods, learning activities, and assignments will vary across disciplines, we offer a few key starting points. Diversifying your pedagogy is easier than critically assessing it through a PWI lens, but both steps are essential. In general, you can diversify your pedagogy by learning about active learning, peer learning, team-based learning, experiential learning, problem-based learning, and case-based learning, among others . There is extensive evidence-based pedagogical literature and practical guides readily available for these methods. And you can also find and follow scholars in your discipline that use these and other teaching methods.
Diversifying Your Pedagogy
Convert traditional lectures into interactive (or active) lectures.
For in-person or synchronous online courses, break a traditional lecture into “mini-lectures” of 10-15 minutes in length. After each mini-lecture, ask your students to process their learning using a discussion or problem prompt, a Classroom Assessment Technique (CAT), a Think-Pair-Share, or another brief learning activity. Read Lecturing from Center for Teaching , Vanderbilt University.
Structure small group discussions
Provide both a process and concrete questions or tasks to guide student learning (for example, provide a scenario with 3 focused tasks such as identify the problem, brainstorm possible solutions, and list the pros/cons for each solution). Read How to Hold a Better Class Discussion , The Chronicle of Higher Education .
Integrate active learning
Integrate active learning, especially into courses that are conceptual, theoretical, or otherwise historically challenging (for example, calculus, organic chemistry, statistics, philosophy). For gateway courses, draw upon the research of STEM and other education specialists on how active learning and peer learning improves student learning and reduces disparities. Read the Association of American Universities STEM Network Scholarship .
Include authentic learning
Include authentic learning, learning activities and assignments that mirror how students will work after graduation. What does it mean to think and work like an engineer? How do project teams work together? How does one present research in an educational social media campaign? Since most students seeking a college education will not become academic researchers or faculty, what kinds of things will they do in the “real world?” Help students practice and hone those skills as they learn the course content. Read Edutopia’s PBL: What Does It Take for a Project to Be Authentic?
Vary assignments and provide options
Graded assignments should range from low to high stakes. Low stakes assignments allow students to learn from their mistakes and receive timely feedback on their learning. Options for assignments allow students to demonstrate their learning, rather than demonstrate their skill at a particular type of assessment (such as a multiple choice exam or an academic research paper). Read our guide, Create Assessments That Promote Learning for All Students .
Critically Assess Your Pedagogy
Critically assessing your pedagogy through the PWI lens with attention to how your pedagogy may affect the learning of BIPOC students is more challenging and highly contextual. Instructors will want to review and apply the concepts and principles discussed in the earlier sections of this guide on Predominantly White Institutions (PWIs), PWI Assumptions, and Class Climate.
Reflect on patterns
Reflect on patterns of participation, progress in learning (grade distributions), and other course-related evidence. Look at your class sessions and assignments as experimental data. Who participated? What kinds of participation did you observe? Who didn’t participate? Why might that be? Are there a variety of ways for students to participate in the learning activities (individually, in groups, via discussion, via writing, synchronously/in-person, asynchronously/online)?
Respond to feedback on climate
Respond to feedback on climate from on-going check-ins and Critical Incident Questionnaires (CIQs) as discussed in the Climate Section (Ongoing Practices). Students will likely disengage from your requests for feedback if you do not respond to their feedback. Use this feedback to re-calibrate and re-think your pedagogy.
Seek feedback on student learning
Seek feedback on student learning in the form of Classroom Assessment Techniques (CATs), in-class polls, asynchronous forums, exam wrappers, and other methods. Demonstrate that you care about your students’ learning by responding to this feedback as well. Here’s how students in previous semesters learned this material … I’m scheduling a problem-solving review session in the next class in response to the results of the exam …
Be diplomatic but clear when correcting mistakes and misconceptions
First-generation college students, many of whom may also identify as BIPOC, have typically achieved a great deal with few resources and significant barriers (Yosso 2005). However, they may be more likely to internalize their learning mistakes as signs that they don’t belong at the university. When correcting, be sure to normalize mistakes as part of the learning process. The correct answer is X, but I can see why you thought it was Y. Many students think it is Y because … But the correct answer is X because … Thank you for helping us understand that misconception.
Allow time for students to think and prepare for participation in a non-stressful setting
This was already suggested in the Climate Section (Race Stressors), but it is worth repeating. BIPOC students and multilingual students may need more time to prepare, not because of their intellectual abilities, but because of the effects of race stressors and other stressors increasing their cognitive load. Providing discussion or problem prompts in advance will reduce this stress and make space for learning. Additionally both student populations may experience stereotype threat, so participation in the “public” aspects of the class session may be stressful in ways that are not true for the majority white and domestic students. If you cannot provide prompts in advance, be sure to allow ample individual “think time” during a synchronous class session.
Avoid consensus models or majority rules processes
This was stated in the Climate Section (Teaching Practices to Avoid), but it’s such an entrenched PWI practice that it needs to be spotlighted and challenged. If I am a numerical “minority” and I am asked to come to consensus or agreement with a numerical “majority,” it is highly likely that my perspective will be minimized or dismissed. Or, I will have to expend a lot of energy to persuade my group of the value of my perspective, which is highly stressful. This is an unacceptable burden to put on BIPOC students and also may result in BIPOC students being placed in the position of teaching white students about a particular perspective or experience. The resulting tensions may also damage BIPOC students’ positive relationships with white students and instructors. When suitable for your content, create a learning experience that promotes seeking multiple solutions to problems, cases, or prompts. Rather than asking students to converge on one best recommendation, why not ask students to log all possible solutions (without evaluation) and then to recommend at least two solutions that include a rationale? Moreover, for course content dealing with policies, the recommended solutions could be explained in terms of their possible effects on different communities. If we value diverse perspectives, we need to structure the consideration of those perspectives into our learning activities and assignments.
We recognize the challenges of assessing your pedagogy through the PWI lens and doing your best to assess the effects on BIPOC student learning. This is a complex undertaking. But we encourage you to invite feedback from your students as well as to seek the guidance of colleagues, including advisors and other student affairs professionals, to inform your ongoing practices of teaching inclusively at a PWI. In the next section, we complete our exploration of the Inclusive Teaching at a PWI Framework by exploring the importance of auditing, diversifying, and critically assessing course content.
Pedagogy References
Kind, Vanessa and Kennedy K.H. Chan. 2019. “Resolving the Amalgam: Connecting Pedagogical Content Knowledge, Content Knowledge and Pedagogical Knowledge.” International Journal of Science Education . 41(7): 964-978.
Howard, Jay. N.D. “How to Hold a Better Class Discussion: Advice Guide.” The Chronicle of Higher Education . https://www.chronicle.com/article/how-to-hold-a-better-class-discussion/#2
National Research Council. 2000. “How Experts Differ from Novices.” Chap 2 in How People Learn: Brain, Mind, Experience, and School: Expanded Edition . Washington D.C.: The National Academies Press. https://nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/9853/how-people-learn-brain-mind-experience-and-school-expanded-edition
Nelson, Craig E. 1996. “Student Diversity Requires Different Approaches to College Teaching, Even in Math and Science.” The American Behavioral Scientist . 40 (2): 165-175.
Sathy, Viji and Kelly A. Hogan. N.D. “How to Make Your Teaching More Inclusive: Advice Guide.” The Chronicle of Higher Education . https://www.chronicle.com/article/how-to-make-your-teaching-more-inclusive/?cid=gen_sign_in
Yosso, Tara J. 2005. “Whose Culture Has Capital? A Critical Race Theory Discussion of Community Cultural Wealth.” Race, Ethnicity and Education . 8 (1): 69-91.
- Research and Resources
- Why Use Active Learning?
- Successful Active Learning Implementation
- Addressing Active Learning Challenges
- Why Use Team Projects?
- Project Description Examples
- Project Description for Students
- Team Projects and Student Development Outcomes
- Forming Teams
- Team Output
- Individual Contributions to the Team
- Individual Student Understanding
- Supporting Students
- Wrapping up the Project
- Addressing Challenges
- Course Planning
- Working memory
- Retrieval of information
- Spaced practice
- Active learning
- Metacognition
- Definitions and PWI Focus
- A Flexible Framework
- Class Climate
- Course Content
- An Ongoing Endeavor
- Align Assessments
- Multiple Low Stakes Assessments
- Authentic Assessments
- Formative and Summative Assessments
- Varied Forms of Assessments
- Cumulative Assessments
- Equitable Assessments
- Essay Exams
- Multiple Choice Exams and Quizzes
- Academic Paper
- Skill Observation
- Alternative Assessments
- Assessment Plan
- Grade Assessments
- Prepare Students
- Reduce Student Anxiety
- SRT Scores: Interpreting & Responding
- Student Feedback Question Prompts
- Research Questions and Design
- Gathering data
- Publication
- GRAD 8101: Teaching in Higher Education
- Finding a Practicum Mentor
- GRAD 8200: Teaching for Learning
- Proficiency Rating & TA Eligibility
- Schedule a SETTA
- TAPD Webinars

- Teaching & learning
- The Complete List of Teaching Methods and Strategies

Apply as a tutor to teach students online from anywhere in the world.
The complete list of teaching methods and strategies.
- Chloe Daniel
- Published On: September 11 ,2021

Teachers are the main asset of a country because they are nation builders. Teachers and education systems play a vital role in building an individual’s character, and great teachers have set examples of changing their student’s lives. Therefore, one country should invest more in its educational institutes and teachers to succeed. You can find an endless amount of stories about how appropriate teaching methods and strategies have brought remarkable changes in a student’s life. The art of teaching matters a lot. To be a successful teacher, one should know all the possible teaching methods and strategies and use them correctly because students learn better when their teacher knows which teaching method will engage the students more.
Bertrand Russell has summed up the whole process in his quote as:
‘More important than the curriculum is the question of the methods of teaching and the spirit in which the teaching is given.’
After reading this blog, you will understand the difference between teaching methods and strategies, different teaching methodologies and strategies, their advantages and disadvantages, and how a teacher should prepare himself before the class lecture.
So let’s get started.
Difference between teaching methods and strategies
Methods and strategies are two different terms, but both are essential to make a class full of students of different caliber and understand the same subject. The method is a process, procedure, or way something is done or implementing a plan. While on the other hand, strategy is the goal, set of actions, or plans to achieve one aim or something. Let me clarify it with an example: strategy is how a teacher makes a whole year’s plan to complete a specific book or syllabus, and the method is how that teacher delivered the lecture or which way the teacher selects to do a task.
And there is a list of teaching methods and strategies acquired by the teachers or instructors that you will read below. The ideal teaching method is the one in which the learning of students occurs the most. Teaching and learning are considered the two sides of a coin, and for completing the teaching side, teachers should consider all the teaching strategies and methods.
Related Read: Hacks to Help Students Beat Procrastination
Types of teaching methods
The way of teaching is categorized into different types of teaching methods adopted by the teachers, and most of them are mentioned below:
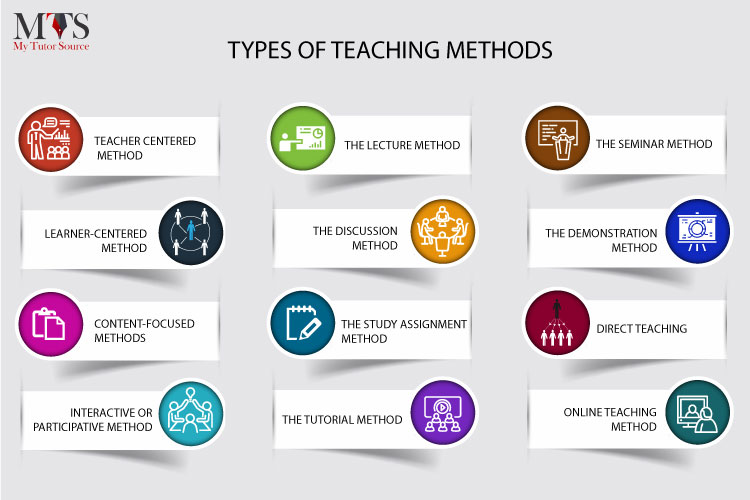
Teacher centered method
It is the method where the teacher is the only expert or an authority figure for the learners or students. They rely on the expert and receive knowledge to achieve positive grades in the end exams or assessments. The lecture method is used in the teacher-centered method, and it requires very little involvement of students or learners during the teaching process. It is also called a closed-ended method if the involvement of learners or students is zero.
Learner-centered method
In this teaching method, the teachers play a dual role. They act as learners and teachers; they learn new things every day while delivering the lecture. The learner-centered method is beneficial for both teacher and the student. The best way to implement this method is to follow the class’s discussion, inquiry-based, or discovery strategies.
Content-focused methods
Among different teaching methodologies, the teacher can use the content-focused method when the content, set of information, or skill taught by the teachers or experts cannot be changed or altered. It means the content to be taught is so important or unimpeachable that both the learner and the teacher have to fit in the subject without being critical about the content.
Interactive or participative method
It is the type of learning method that is considered beneficial for both the learners and the teachers. The teacher’s responsibility is to explain the key points or the importance of following the interactive or participating method during class in general so that students may not resist following it. Many strategies are used in this teaching method like writing exercises, think-pair-share, debate, problem-based learning, or situation analysis.
The lecture method
One of the most commonly used formal or semiformal teaching methods is the lecture method. Teachers mostly use this method for a large class. In this method, the teachers pick a topic and explain its basic definitions, facts, events, principles and clarify the whole point of the subject or topic with relevant examples and problems. The students are allowed to take notes and ask questions at the end of a lecture, and the master of the subject has to answer them all. Thus, in this method, a teacher is the main role model for the large class, and it has a strong mastery of that specific subject.
The discussion method
The discussion method can only be followed when the teacher is highly skilled and disciplined. Because in this two-way communication method, students are prepared to listen to their fellow’s point of view and exchange ideas. The role of a teacher is to introduce disciplined group discussion techniques among students and clear the concept of the topic meanwhile. This method is mainly used to utilize the knowledge, experience, and creativity of each student. When the whole discussion ends, the teacher corrects the mistakes and clears the debatable concepts.
The study assignment method
It is one of those teaching methods that promote active learning. In this method, the teacher or an instructor assigns a task to students before the class. It can be a book or research paper reading, project analysis, or any relevant material review. This method enhances the research skill abilities of students, and the discussion part in class makes the teacher and students know different points of view of each other.
The tutorial method
It is a teaching method that can only be used when a teacher or an instructor teaches one student and works directly. This method is also known as online tutoring , and it demands more money and time, unlike other teaching methods. Those who follow such methods know the safety and active participation of both learner and the reader. The tutorial teaching methods are user-friendly. The students can skip or restart the lesson any time, leave the tutorial in between, or get access to it when they feel like learning or motivated. Mostly these are the recorded lectures.
The seminar method
The seminar method is one of the costly teaching methods used by the experts or teachers to guide or educate the students about a certain topic or project. In this method, the instructors make groups of students work on their projects and then ask them to exchange the information or techniques used while completing the project. Highly professional; or competent teachers must arrange a seminar method and then evaluate the study, research paper, or project.
The demonstration method
The demonstration method is the kind of teaching method in which the teacher has to perform something or an operation to make its learner understand deeply and clearly. It can be the functioning of a tool or equipment, teaching troubleshooting, performing a certain job or an operation or anything. This teaching method can only be proposed when the instructor explains the why, how, where, what, and when. If the highly competent teacher will choose the method and rehearse well before teaching, it will save time, and the clarity of operation will help the students perform right. The demonstration teaching method is mostly used in laboratories.
Direct teaching
The direct teaching method is commonly used in all institutions as it makes the teacher or an instructor directly communicate with their student within the school or institution premises. This method lessens the communication barrier between students and the teacher. It focuses on the immediate teaching process, and the students are allowed to ask questions or give suggestions in between, with certain time limitations.
Online teaching method
One of the most flexible teaching methods is the online teaching method. The teacher and the learner can offer a flexible timescale, which is unrestricted to time and place. Both can communicate with each other via email or any other digital support. The access to recorded lectures after the online session helps the students to listen to them later and understand better. The advancement of technology has turned learners into online learning in the last few decades.
Online and private tutors have their way of teaching concepts within a certain time limit. Students with jobs mostly use this teaching method to learn during their free time and achieve their desired goals without moving places.
Independent study or practice
Some teachers or an instructor follow the independent study or practice teaching method because this improves the self-learning or self-study abilities of the students. In such methods, teachers mostly assign the same task to each student to practice or study it from home on their own, and then the other day, teachers evaluate the task and solve the students’ queries.
Types of teaching strategies
Before moving to the teaching strategies, I would like to add a quote from Benjamin Franklin, which says:
‘Tell me and I forgot. Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn.’
And this is how the teaching strategies work on students.

Classroom management
The very first strategy to engage all the students of a class is its management. The etiquette of a class is matters, and so does the management of the whole class. If you start listing down the classroom management strategies, the list will go on because it has its own set of techniques and different strategies to keep the class managed. Before moving to the teaching method, the teacher or an instructor should acknowledge the whole class management rules in dos and don’ts.
Develop an atmosphere of learning
The atmosphere of learning matters the most because no matter how well the teacher or an instructor delivers the lecture, it’s futile if the atmosphere does not support that all students are willing to learn or excited to start the new chapter or topic. So, to develop a learning atmosphere, the expert should get the whole class’s attention and inform them of the facts and purpose of reading the lecture. The more they will show interest in learning a subject, the more they will learn.
Celebrate achievements
Teachers should assign certain achievement levels with a reward to keep the whole class motivated to learn and do better. And the reward could be anything like the winning student will display their work in the school assembly or get to read the whole chapter and get candy from their teacher in return. The celebration can be small or big, it doesn’t matter, but the outcomes of celebrating success will make huge positive differences in a student’s life.
This teaching strategy is mostly used by the primary or secondary level student teachers to motivate and build students’ confidence. Teachers who make use of this strategy more often prepare the future winners. There is no failure. Only feedback. – Robert Allen
Flexible seating
The appropriate seating in the classroom that keeps the students comfortable is the utmost teaching strategy. Here the flexible seating of both the teacher and the learner matters. Institutions of all levels should follow many flexible seating ideas . Because if the students are sitting uncomfortably, then they will not be able to focus on the lecture.
It is more of an institution’s duty to take care of students’ sitting comfort and posture because students spend a lot of their day at schools or colleges.
Active learning
Active learning strategy is one of those strategies that not only help the students but the teachers too. The discussion break between the lecture and asking students to submit the clearest point after the lecture keeps the whole class attentive, and it’s called active learning. Their participation makes the teacher understand which part of the lecture has gotten more attention. Such smart tactics or quick questions in between lectures make the student learn better and faster.
Focus on student’s interests
When teachers focus on a student’s interests, it helps them understand the nature of their students way better, and ultimately, they follow the teaching method that can be more effective. And the constructive feedback on what students have done and what they have not mastered helped them determine how they could improve that mastery. This strategy makes the bond of student and teacher strong and improves the learning environment.
‘There is no failure. Only feedback. ’–Robert Allen
Differentiated instruction
One of the most useful teaching strategies is differentiated instruction. In this strategy, the teacher assigns tasks to each student based on abilities and interests. Doing so the students who are struggling will get the proper support or help, and the students with academic skills or capabilities will be assigned tasks that match their caliber. It ensures the dedicated behavior of teachers after knowing everyone’s learning gaps, and no student remains left behind.
Personalized learning
Teachers should focus on personalized learning strategy a bit too much. Students should review their content once learned. Sometimes, students’ queries remain unanswered and make all the students master their studies. Teachers should assign tasks to each individual according to their learning capability and style. This teaching strategy will help students develop reliability, motivation, self-learning, self-advocacy, and self-reflective abilities.
Peer teaching method
The teacher should follow the peer teaching strategy sometimes. It is being said that ‘to teach is to learn twice,’ which is the same case with this strategy. Peer teaching has its advantages and disadvantages, but it is worth pursuing a disciplined class atmosphere as it grows the student’s confidence and enhances communication skills.
“The best answer to the question, ‘what is the most effective teaching method?’ depends on the goal, the student, the content, and the teacher. But the next best answer is, ‘Students teaching other students’.” Wilbert J. MacKeachie
Response to intervention RTI
RTI, or Response to intervention, is one of the general teaching strategies that should be considered from day one of teaching. This strategy is to find out the learning and behavior needs of the students. Teachers should start the intervention process early in each class because the earlier the teacher understands the RTI strategies, the easier it will be to follow a better teaching method.
Project-based learning
Experienced teachers agree on the importance of getting students to recap the information learned during the lesson. And when it comes to project-based learning, it is important to educate students about what they need to learn to complete the assigned project. It is also crucial to get them to engage with the content actively. So, to foster their engagement, it is important to promote project-based learning in groups. Teachers should make the groups of students quite carefully and selectively as each student’s learning style and ability vary.
Classroom technology
Classroom technology is the best teaching strategy a teacher can use to keep the whole class engaged. This strategy can be used at any level or year of education because students get excited when they have to experience something new for the first time. Video lessons, virtual trips in geography or history class, animations to help kids learn basic skills, and many more adapt to this teaching strategy. Moreover, smart whiteboards, projectors should be used in classrooms.
Blended teaching and learning
In this modern era, teachers should go for a blended teaching strategy. It is a blend of online and offline teaching and uses digital strategies. Some students hesitate to speak up in the class, so blended learning works best for them. They contribute to an online class. Teachers like the blended teaching and learning strategy because it ensures that all voices are heard.
Humor in class
The use of humor should be one of the important teaching strategies, as dry lectures make the students feel bored and tiring and ultimately makes them lose interest. In such cases, a pinch of humor will not harm anyone. But teachers should be smart enough to quickly change the atmosphere of class back to lessons from fun. A comfortable and cozy class environment captures learners’ attention and results in better understanding and active learning.
Inquiry-based teaching
Interactive teaching enables students to be instructed by actively involving them in their learning process through regular teacher-student interaction, student-student interaction. And taking some time out of the class for inquiry-based questions helps improve students’ life skills like communication and problem-solving. The quality of questions matters a lot, and a teacher should ask the students to inquire with subject-based questions or other appropriate questions. However, the inquiry-based teaching strategy has guided inquiry, structured inquiry, open inquiry, and confirmation inquiry. These all promote the use of long-term memory of both teachers and learners.
Class gamification
It is observed that lessons learned while playing stays long in the student’s mind. This teaching strategy keeps the students more engaged and active in the class. Play and learn techniques should be in each teacher’s teaching method list. Age requirement shouldn’t be the barrier because class Gamification builds and improves the essential skills. A teacher can play any games to teach the basics like mind games, math multiplication games, problem-solving games, language learning games like ESL games , and many more.
Gamification has a future in education, and teachers or instructors should effectively use this strategy.
Convergent and divergent thinking
One of the main teaching strategies that all teachers should be aware of is two thinking methods: convergent thinking methods and divergent thinking methods. Teachers should educate their students about its difference as convergent thinking means there are multiple ways to reach one solution. On the other hand, the divergent teaching method makes the students learn and understand the base concepts to solve the given question or problem.
If the teachers and students know these differences, learning will be easier and better.
Problem-based learning
One of the essential teaching strategies a teacher or an instructor should follow is problem-based learning. They should prepare a list of problem-based open-ended questions before a class and ask the class to solve them in groups or teams. This technique helps in developing and improving the transferable and teamwork skills of students, respectively.
Media literacy
Students need to be educated about all the things happening around them. Like nowadays, students are very active on social media and get influenced quite easily. It’s the responsibility of the teachers to guide their students and understand what they are consuming from these platforms. Media literacy lets the students critically think and talk about the changes and innovations. Teachers should follow media literacy activities to bring out the creative side of students.
Visualization
Introducing visualization in class is the most advanced teaching strategy that institutions and teachers can use to make the students understand the textbook content with visuals and the real world. It lets the students experience the world while sitting in their classrooms. But again, it is just another strategy to keep the class engaged. The teacher has to play the main role, Bill Gates has said it too:
“Technology is just a tool. In terms of getting the kids to work together and motivating them, the teacher is the most important.”
Cooperative learning
Teachers should work on cooperative learning strategies in class, once a week at least. There are many ways to follow this strategy, such as solving mathematical puzzles, quick fraction questions, performing science experiments, short drama sketches, group presentations, or frequently asked question-answer sessions among students of the same class. This teaching strategy improves the verbal skills of students.
Behaviour management
Just like teaching methods, teachers should be acknowledged properly about the behavior management teaching strategy. Mutual respect of teachers and students is important to keep the class’s productive learning and disciplined environment. Institutions or teachers should reward students based on their behavior during class and overall interaction with their teachers and fellow mates. Teachers should be strict with this strategy because a noisy, disturbed, or undisciplined class cannot promote productive learning.
Professional development
Undoubtedly, teaching is a challenging job because you have to deliver the same knowledge to students with different mindsets and caliber simultaneously. It gets exhausting sometimes. To keep the teachers motivated and engaged, they should attend professional development seminars and people in the same field. These will keep the teachers updated about the new teaching tools, technologies, methods, and strategies.
How teacher should prepare for a lecture
Even after understanding the teaching strategies and teaching methods, teachers should prepare themselves before delivering a lecture. Just like a student rehearsing before giving a presentation. Because teachers too are presenting themselves and it is their job to keep the attention of the whole class throughout the lecture. So, to make the lecture qualitative, teachers should keep in mind that the lecture should not be too long as it exhausted the students and lost their attention. The whole theme and the purpose of studying certain topics should be explained before teaching, the teachers should use maximum examples or illustrations to make it easy to understand, usages of approaches and fluency of lecture should match with the student’s existing knowledge, so they relate to it and understand more clearly.
Other than considering these points, the teacher should make notes and rehearse the follow of lecture in advance, checklist the important points, keep all the relevant textbooks, tools, or other things prepared which need to be utilized during the lecture, pick the teaching strategy or teaching method that will go with the topic. Meanwhile, the teacher should also ensure that if all the students can see or hear him clearly, he should use the entire why, how, tell, and show techniques to explain the lecture or the assigned topic.
Lastly, class discipline matters a lot, and teachers should already tell the students to write down the question if any crosses their mind during the lecture, and in the last 15 minutes of discussion, they can ask freely one by one. And it is how the discipline of class and the flow of the lecture will not be disturbed. And if all the students have not got their answers due to a shortage of time or any other reason, it’s the teacher’s responsibility first to solve the queries the other day and then teach a new topic. That’s the complete preparation process of a teacher before delivering a qualitative lecture.
Here we summed up the difference between teaching strategies and teaching methods that all teachers should know. Knowing these teaching methodologies and strategies will make the classrooms a more creative and dynamic place for students to get qualitative education; furthermore, if you are a teacher and learning new teaching strategies or methods from this page, then make sure to use them in your classroom.
In this rapidly changing world, teachers should be given proper guidelines to transform the smart, creative, and tech knowledge into their students. And the personality of the teacher should inspire the students to learn from them and be a better addition to this world. The truth is teaching is the profession that teaches all the other professions, so educational institutions should invest in providing proper guidelines on types of teaching methods and teaching strategies from time to time to keep their teachers updated to the modern world.
Education is our passport to the future, for tomorrow belongs to the people who prepare for it today. Malcolm X
Find Top Tutors in Your Area

LATEST POST

- How Can Students Deal With Exam Stress?
March 21 ,2024
- The Importance of Moral Education For Students
March 19 ,2024
- How to Develop and Sharpen Your Mathematical Skills?
March 08 ,2024

- IGCSE vs GCSE Critical Facts & Guidance for Students

- English Greetings for English Learners
December 14 ,2023

- Find the Best Way to Learn English | 12 Amazing Ways
December 13 ,2023

- List of 5-Letter Words Starting with “P”
May 12 ,2023

- 5-letter words starting with G - Every Student Should Know!
April 03 ,2023

- Fill Your Vocabulary List with These Amazing 5-Letter R-Words!
March 13 ,2023

- The Ultimate List of 5-letter Words Starting with “T”
February 20 ,2023
Recent post.
- Communication
Offer Ends in
Hire an Expert Tutor in Just $9.8/hr
Form Submitted Successfully
No, I Don't Want to Avail This Offer
Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
4 Effective Instructional Strategies That Work for Math, Writing, and More

- Share article
What teacher isn’t on the lookout for new and effective instructional strategies?
In this multipart series, educators will share their “nominations” for those teaching strategies that can be effective in all content areas.
My personal choice is inductive teaching, which you can learn more about here .
Here are what today’s guests suggest ...
‘Thinking Routines’
Abeer Ramadan-Shinnawi, M.Ed., is a veteran social studies educator, school leader, teacher coach, and now program director for Re-Imagining Migration. She is also an educational consultant that focuses on the needs of Arab and Muslim youth:
Tapping into students’ social-emotional learning can be a difficult task when creating lessons. Many times teachers have created a lesson that is very engaging, crosses all the checks for a high-level lesson, but then falls short of knowing how to tie all of the learning together. That is not uncommon for educators, especially when they are always looking for new ways to engage their students.
One instructional strategy that has saved me a lot of time and effort that I have used and still use today that can be applied across multiple content areas is Harvard’s Project Zero Thinking Routines . These routines are backed by research, can be used across multiple content areas, and create depth to any classroom activity along with creating space for students to focus on their emotions to provide navigation into a discussed topic. The Thinking Routines are divided into types of thinking categories, which makes finding the right type of routine to fit your activity easy to manage. The Thinking Routines can be used in a group setting, individual work, or as an exit ticket. There is no limit as to how to implement the various routines, but here are two of the best that I would recommend:
1. The 3 Whys - This routine helps center the topic into the student’s world. Students, especially younger students may have a difficult time connecting with the content so using this routine would allow students to dig deep to find the connection. The 3 Whys are: Why might this [topic, question] matter to me? Why might it matter to people around me [family, friends, city, nation]? Why might it matter to the world?
2. See-Feel-Think-Wonder - Social-emotional learning can take place in many forms. Using this routine will help students build the bridge of empathy but also understanding why curiosity is important to learning. This routine has students break down their own perceptions from what is being taught and also allows them space to ponder other feelings, ideas, or thoughts that may surface. It also uses the following as a strategy to reach that depth in a student’s own understanding: See What do you see? Feel What feelings emerge for you as you look at this piece? Think What does this piece make you think about? Wonder What do you wonder about this piece?
These are just two of the many routines that can be utilized in many classrooms across many contents. As an educator, my advice would be to find a few routines that you enjoy teaching, perfect them, then move on to more. There is no shortage of finding an engaging method to help your students learn, so why not work smarter and not harder by using Project Zero Thinking Routines into your next class session.

Graphic Organizers
After teaching English for over 20 years, Donna L. Shrum is now teaching ancient history to freshmen in the Shenandoah Valley of Virginia. She remains active in the Shenandoah Valley Writing Project and freelance writing for education and history magazines:
Envision a small stone cottage from 16th-century France tucked away in the corner of a field with bees buzzing the lavender at the door. You walk inside and bemoan all the cleaning and the stones that have tumbled to the ground, letting in chinks of light.
With some sturdy scaffolding, you build it back to serviceability, leading to many lazy afternoons in the pleasure of its company. This is how I see the learning of my freshmen students arriving at my door after the wreckage of middle school. I call them my “COVID babies.” The cliche “learning loss” irritates me because they didn’t lose learning. They couldn’t lose something they never had. Like the cottage, they have gaps to fill and rooms to sweep, but the prior years haven’t been a total loss, and this year has been one for repairs. Having taught English for over 20 years before returning to history, I know the power of graphic organizers and that they can be used in every subject area (yes, math, even you).
The lovely thing about all types of graphic organizers is that they are freely available all over the internet. Our county has focused on writing across the curriculum this year. For years, I have remediated students who are struggling with writing, even up until their graduation day. The special education teachers in my early years confirmed graphic organizers are life rafts for students. These days, we need to use all the wisdom we can get from the special ed. teachers to help our struggling students.
To incorporate writing into my history curriculum, I provided graphic organizers at every step. When the time came to write an essay, I handed out a graphic organizer with more than five areas to fill because I never want students to think the five-paragraph essay is a natural, organic entity. Above each area of the organizer was a guiding question they could answer to formulate the paragraph. A 2020 study shows that doing it by hand rather than on the keyboard will light up more neurons (Askvik, van der Weel, van der Meer), so this organizer was on paper. (One caveat is to tell them to photograph the organizer at the end of each workshop because my “COVID babies” lost papers like the little flower girl leading the wedding procession.)
Some students freely wrote with a glance at the organizer and some organized on the computer. The majority used the organizer and were surprised at how easy it was to express their thoughts when they organized them. They had told me that eliminating accountability for state writing tests in middle school had led to less writing instruction, which I’d expected, so the last time they’d made a concerted effort to organize essay-length writing was in elementary school.
As the semester ends, and I look back with utter mental exhaustion, as always, I question if everything I’ve done is meaningful and helpful. Last week, I met a parent for an IEP meeting who said, “I’ve been letting my daughter’s English teacher for next semester know that the graphic organizers you provided for writing the essays in history class made her successful for the first time in writing an essay.” This easily provided scaffolding made all the difference.
In high school, we may sometimes regard graphic organizers as too basic or something they’ve shed on their path to high school and no longer need. Especially since they’ve emerged from the recent academic tunnel, graphic organizers are the scaffolds all our “COVID babies” need to rebuild with the intellectual blocks they’ve salvaged from the storm. The pieces of treasure they’ve gathered may have suffered a sea-change, but, if we can help them organize, those building blocks are waiting to coalesce into something rich and strange.

‘Turn, Talk, and Share’
Kanako Suwa (she/her) is a queer, multilingual TCK (Third Culture Kid)turned international educator, currently working at Chiang Mai International School as the EAL coordinator. You can follow her on Twitter at @kanakosuwa:
As an English-as a second language specialist, the strategy that I use the most frequently and with success is “Turn, Talk, and Share.” This is an extension of the well-known “Turn & Talk” strategy that adds an element of active listening and peer check-in. This strategy can be used in any content at all age groups, whether in a Grade 1 science lesson or a Grade 11 AP seminar, and is really simple to implement. After explaining instructions for an activity or introducing a new concept, ask students to turn to a classmate and take turns talking about what they heard and understood.
The traditional “Turn & Talk” ends here, but I challenge you to add on the “Share” aspect. This can be done in two levels. One: Have students share with the class what they said to their partner. Two: Have students share what their partner said to them. With level one, you are inviting students to share their own understanding, which may be helpful for everyone in the class to listen to. Especially in the case of EAL students, the same concept explained in multiple different ways, which can be considered to be a part of “multiple exposure,” can help solidify understanding.
Level two requires more effort from the students. This involves teachers asking students to share what their partner said, either verbatim or as a summary. This gives partners the chance to share, negotiate, and solidify their understanding—sometimes, partners listening will notice that there is a misunderstanding and will correct the other. Both partners may admit to not understanding and will be able to discuss without feeling like they are the only one who didn’t understand. And by discussing and co-constructing meaning before they share with the rest of the classroom, you can ensure that students have adequate understanding before you move on.
In addition to checking for understanding, Turn, Talk, and Share helps students build foundational skills for learning—active listening, negotiation of meaning, collaboration, and summarizing, to name a few. For example, while summarizing is generally considered to be a literacy skill, students should also be practicing the skill of summarizing by listening and summarizing lab findings from a science class. Providing transdisciplinary opportunities to practice critical skills is crucial in helping students apply these skills beyond one content area.
Finally, by having students talk to each other and collaboratively create meaning, you, as the teacher, can ensure that there is a shared understanding of concepts and activities in your classroom!

‘Preassessment’
Cindy Garcia has been a bilingual educator for 18 years and is currently a districtwide specialist for bilingual/ESL mathematics. She is active on X @CindyGarciaTX and on her blog:
The best instructional strategy that I have used is preassessment. During my first 1.5 years as a teacher, I found myself running out of time. I didn’t have enough time to facilitate all of the lessons that I had planned for a unit before needing to move on to the next unit. I found myself cutting important tasks and activities from the end of my units. I noticed that my instruction was surface level and we were not going deep enough. I was spending most of the time on prerequisite skills or skills from the previous grade level rather than on grade-level content.
For example, a 3rd grade math standard was telling time to one minute. I wanted to make sure that my students had a solid foundation. I spent too long on making sure my students knew the parts of a clock, telling time to the hour, telling time to the half-hour, and telling time to the five minutes. Once I started preassessing my students, I had a lot more time to spend on rigorous grade-level content.
My preassessments were very informal. Before starting each unit, I would show a picture or sample problem from the previous grade level that was aligned to the current topic. Students would solve the problem or create a web explaining everything they knew. I analyzed the student work and I was able to glean a lot of important information. I learned what vocabulary they had internalized. I learned what strategy or tools they were familiar with. I learned what they already knew and what gaps they might have.
Preassessments gave me the evidence I needed to not start each unit focusing on prerequisite skills. Most of the time I was able to get started further along in the unit. I was also able to be proactive because I had a better idea of where students might get stuck. I had just in time supports such as manipulatives, graphic organizers, visuals, and sentence frames ready for my students.

Thanks to Abeer, Donna, Kanako, and Cindy for contributing their thoughts.
They answered this question of the week:
What is the best instructional strategy that you have used that can be applied across multiple content areas?
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email . And if you missed any of the highlights from the first 12 years of this blog, you can see a categorized list here .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Book Bracket Template. For March and Beyond!
21 Essential Strategies in Teaching Math
Even veteran teachers need to read these.

We all want our kids to succeed in math. In most districts, standardized tests measure students’ understanding, yet nobody wants to teach to the test. Over-reliance on test prep materials and “drill and kill” worksheets steal instructional time while also harming learning and motivation. But sound instruction and good test scores aren’t mutually exclusive. Being intentional and using creative approaches to your instruction can get students excited about math. These essential strategies in teaching mathematics can make this your class’s best math year ever!
1. Raise the bar for all

WeAreTeachers
For math strategies to be effective, teachers must first get students to believe that they can be great mathematicians. Holding high expectations for all students encourages growth. As early as second grade, girls have internalized the idea that math is not for them . It can be a challenge to overcome the socially acceptable thought, I’m not good at math , says Sarah Bax, a math teacher at Hardy Middle School in Washington, D.C.
Rather than success being a function of how much math talent they’re born with, kids need to hear from teachers that anyone who works hard can succeed. “It’s about helping kids have a growth mindset ,” says Bax. “Practice and persistence make you good at math.” Build math equity and tell students about the power and importance of math with enthusiasm and high expectations.
(Psst … you can snag our growth mindset posters for your math classroom here. )
2. Don’t wait—act now!
Look ahead to the specific concepts students need to master for annual end-of-year tests, and pace instruction accordingly. Think about foundational skills they will need in the year ahead.
“You don’t want to be caught off guard come March thinking that students need to know X for the tests the next month,” says Skip Fennell, project director of Elementary Mathematics Specialists and Teacher Leaders Project and professor emeritus at McDaniel College in Westminster, Maryland. Know the specific standards and back-map your teaching from the fall so students are ready, and plan to use effective math strategies accordingly.
[contextly_auto_sidebar]
3. Create a testing pathway
You may not even see the results of standardized tests until next school year, but you have to prepare students for it now. Use formative assessments to ensure that students understand the concepts. What you learn can guide your instruction and determine the next steps, says Fennell. “I changed the wording because I didn’t want to suggest that we are in favor of ‘teaching to the test.'”
Testing is not something separate from your instruction. It should be integrated into your planning. Instead of a quick exit question or card, give a five-minute quiz, an open-ended question, or a meaningful homework assignment to confirm students have mastered the math skill covered in the day’s lesson. Additionally, asking students to explain their thinking orally or in writing is a great way to determine their level of understanding. A capable digital resource, designed to monitor your students in real-time, can also be an invaluable tool, providing actionable data to inform your instruction along the way.
4. Observe, modify, and reevaluate
Sometimes we get stuck in a mindset of “a lesson a day” in order to get through the content. However, we should keep our pacing flexible, or kids can fall behind. Walk through your classroom as students work on problems and observe the dynamics. Talk with students individually and include “hinge questions” in your lesson plans to gauge understanding before continuing, suggests Fennell. In response, make decisions to go faster or slower or put students in groups.
5. Read, read, read!

Although we don’t often think of reading as a math strategy, there’s almost nothing better to get students ready to learn a new concept than a great read-aloud. Kids love to be read to, and the more we show students how math is connected to the world around us, the more invested they become. Reading books with math connections helps children see how abstract concepts connect to their lives.
6. Personalize and offer choice
When students are given the opportunity to choose how they learn and demonstrate their understanding of a concept, their buy-in and motivation increase. It gives them the chance to understand their preferred learning style, provides agency over their own learning, and allows for the space to practice different strategies to solve math problems. Give students a variety of options, such as timed exercises, projects, or different materials , to show that they’ve mastered foundational skills. As students show what they’ve learned, teachers can track understanding, figure out where students need additional scaffolding or other assistance, and tailor lessons accordingly.
7. Plant the seeds!
Leave no child inside! A school garden is a great way to apply math concepts in a fun way while instilling a sense of purpose in your students. Measurement, geometry, and data analysis are obvious topics that can be addressed through garden activities, but also consider using the garden to teach operations, fractions, and decimals. Additionally, garden activities can help promote character education goals like cooperation, respect for the earth, and, if the crops are donated to organizations that serve those in need, the value of giving to others.
8. Add apps appropriately
The number of apps (interactive software used on touch-screen devices) available to support math instruction has increased rapidly in recent years. Kids who are reluctant to practice math facts with traditional pencil-and-paper resources will gladly do essentially the same work as long as it’s done on a touch screen. Many apps focus on practice via games, but there are some that encourage children to explore the content at a conceptual level.
9. Encourage math talk

Communicating about math helps students process new learning and build on their thinking. Engage students during conversations and have them describe why they solved a problem in a certain way. “My goal is to get information about what students are thinking and use that to guide my instruction, as opposed to just telling them information and asking them to parrot things back,” says Delise Andrews, who taught math (K–8) and is now a grade 3–5 math coordinator in the Lincoln Public Schools in Nebraska.
Instead of seeking a specific answer, Andrews wants to have deeper discussions to figure out what a student knows and understands. “True learning happens a lot around talking and doing math—not just drilling,” she says. Of course, this math strategy not only requires students to feel comfortable expressing their mathematical thinking, but also assumes that they have been trained to listen respectfully to the reasoning of their classmates.
Learn more: Free Let’s Talk Math Poster
10. The art of math
Almost all kids love art, and visual learners need a math strategy that works for them too, so consider integrating art and math instruction for one of the easiest strategies in teaching mathematics. Many concepts in geometry, such as shapes, symmetry, and transformations (slides, flips, and turns), can be applied in a fun art project. Also consider using art projects to teach concepts like measurement, ratios, and arrays (multiplication/division).
11. Seek to develop understanding
Meaningful math education goes beyond memorizing formulas and procedures. Memorization does not foster understanding. Set high goals, create space for exploration, and work with the students to develop a strong foundation. “Treat the kids like mathematicians,” says Andrews. Present a broad topic, review various strategies for solving a problem, and then elicit a formula or idea from the kids rather than starting with the formula. This creates a stronger conceptual understanding and mental connections with the material for the student.
12. Give students time to reflect
Sometimes teachers get so caught up in meeting the demands of the curriculum and the pressure to “get it all done” that they don’t give students the time to reflect on their learning. Students can be asked to reflect in writing at the end of an assignment or lesson, via class or small group discussion, or in interviews with the teacher. It’s important to give students the time to think about and articulate the meaning of what they’ve learned, what they still don’t understand, and what they want to learn more about. This provides useful information for the teacher and helps the student monitor their own progress and think strategically about how they approach mathematics.
13. Allow for productive struggle
When giving students an authentic problem, ask a big question and let them struggle to figure out several ways to solve it, suggests Andrews. “Your job as a teacher is to make it engaging by asking the right questions at the right time. So you don’t take away their thinking, but you help them move forward to a solution,” she says.
Provide as little information as possible but enough so students can be productive. Effective math teaching supports students as they grapple with mathematical ideas and relationships. Allow them to discover what works and experience setbacks along the way as they adopt a growth mindset about mathematics.
14. Emphasize hands-on learning

WeAreTeachers; Teacher Created Resources
In math, there’s so much that’s abstract. Hands-on learning is a strategy that helps make the conceptual concrete. Consider incorporating math manipulatives whenever possible. For example, you can use LEGO bricks to teach a variety of math skills, including finding area and perimeter and understanding multiplication.
15. Build excitement by rewarding progress
Students—especially those who haven’t experienced success—can have negative attitudes about math. Consider having students earn points and receive certificates, stickers, badges, or trophies as they progress. Weekly announcements and assemblies that celebrate the top players and teams can be really inspiring for students. “Having that recognition and moment is powerful,” says Bax. “Through repeated practice, they get better, and they are motivated.” Through building excitement, this allows for one of the best strategies in teaching mathematics to come to fruition.
16. Choose meaningful tasks
Kids get excited about math when they have to solve real-life problems. For instance, when teaching sixth graders how to determine area, present tasks related to a house redesign, suggests Fennell. Provide them with the dimensions of the walls and the size of the windows and have them determine how much space is left for the wallpaper. Or ask them to consider how many tiles they would need to fill a deck. You can absolutely introduce problem-based learning, even in a virtual world.
17. Play math games

Life Between Summers/Shape Guess Who via lifebetweensummers.com; 123 Homeschool 4 Me/Tic-Tac-Toe Math Game via 123homeschool4me.com; WeAreTeachers
Student engagement and participation can be a challenge, especially if you’re relying heavily on worksheets. Games, like these first grade math games , are an excellent way to make the learning more fun while simultaneously promoting strategic mathematical thinking, computational fluency , and understanding of operations. Games are especially good for kinesthetic learners and foster a home-school connection when they’re sent home for extra practice.
18. Set up effective math routines
Students generally feel confident and competent in the classroom when they know what to do and why they’re doing it. Establishing routines in your math class and training kids to use them can make math class efficient, effective, and fun! For example, consider starting your class with a number sense routine . Rich, productive small group math discussions don’t happen by themselves, so make sure your students know the “rules of the road” for contributing their ideas and respectfully critiquing the ideas of others.
19. Encourage teacher teamwork and reflection
You can’t teach in a vacuum. Collaborate with other teachers to improve your math instruction skills. Start by discussing the goal for the math lesson and what it will look like, and plan as a team to use the most effective math strategies. “Together, think through the tasks and possible student responses you might encounter,” says Andrews. Reflect on what did and didn’t work to improve your practice.

Learn With Play at Home/Plastic Bottle Number Bowling via learnwithplayathome.com; Math Geek Mama/Skip-Counting Hopscotch via mathgeekmama.com; WeAreTeachers
Adding movement and physical activity to your instruction might seem counterintuitive as a math strategy, but asking kids to get out of their seats can increase their motivation and interest. For example, you could ask students to:
- Make angles with their arms
- Create a square dance that demonstrates different types of patterns
- Complete a shape scavenger hunt in the classroom
- Run or complete other exercises periodically and graph the results
The possibilities of these strategies in teaching mathematics are limited only by your imagination and the math concepts you need to cover. Check out these active math games .
21. Be a lifelong learner
Generally, students will become excited about a subject if their teacher is excited about it. However, it’s hard to be excited about teaching math if your understanding hasn’t changed since you learned it in elementary school. For example, if you teach how to divide fractions by fractions and your understanding is limited to following the “invert and multiply” rule, take the time to understand why the rule works and how it applies to the real world. When you have confidence in your own mathematical expertise, then you can teach math confidently and joyfully to best apply strategies in teaching mathematics.
What do you feel are the most important strategies in teaching mathematics? Share in the comments below.
Want more articles like this be sure to subscribe to our newsletters ., learn why it’s important to honor all math strategies in teaching math . plus, check out the best math websites for teachers ..

You Might Also Like

24 Creative Ways to Use Math Manipulatives in Your Classroom
Students learn better when they’re engaged, and manipulatives in the classroom make it easy for kids to get excited. We Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Teaching Strategies Examples (List) 1. Flipped Instruction. Description. Flipped classrooms involve asking students to complete the reading, preparation and introductory work at home. Then, during class time, the students do practice questions that they would traditionally do for homework.
The 5 instructional teaching strategies: Differentiated Instruction: Tailoring instruction to meet the diverse needs of students. Active Learning: Engaging students in hands-on activities and critical thinking. Cooperative Learning: Encouraging collaboration and teamwork among students.
Problem-Solving. In this indirect learning method, students work their way through a problem to find a solution. Along the way, they must develop the knowledge to understand the problem and use creative thinking to solve it. STEM challenges are terrific examples of problem-solving instructional strategies.
4.2. Flipped classrooms. Regardless of where you teach, flipping your classroom is one of the most popular forms of active learning and among the most well-known instructional strategies. Instead of using classroom time for lecturing, educators provide students with a pre-recorded lecture to watch prior to class.
Using the Transparency in Learning and Teaching (TILT) framework to plan assignments that involve generative AI can help you clarify expectations for students and take a more intentional, productive, and ethical approach to AI use in your course. Step 1: Define your purpose.
Strategies for practicing new learning include visualization, mnemonics, quick writes, and effective questioning. Finally, tips for homework completion are provided for both teachers and parents. It is important to make sure that all students understand the content that has been taught. Practice and homework are effective instructional ...
3. Work as a team. Splitting the class up into different teams to complete an assignment is a teaching strategy that works wonders, especially at age groups where students insist on always working with their tight-knit circle of friends. Group assignments encourage teamwork and help your class to succeed.
Strategy instruction is a teaching practice that shows students how to learn the content or skills they need to acquire. It provides students with clear strategies (such as note-taking or thinking aloud) to help them process, remember, and express the information they learn. Think back to the last time you made a checklist for yourself, took ...
You'll also need to use specific assignment approaches and teaching strategies proven to work well online. Teaching effective online courses involves special considerations related to the course's format and administrative components, the technology you use (particularly CarmenCanvas), and your choice of appropriate teaching methods.
We discuss these five most common strategies in distance education in more detail throughout this article: 1. Adapt your lessons to work online. Revamp your in-person lessons to the online environment with engaging discussions, screen recordings, and interactive tech tools. 2.
Grouping students together for assignments by shared topics, interests, learning abilities or styles ... The steady stream of feedback allows instructors to refine and improve their teaching strategies to keep the class on track. At the same time, students can practice their test-taking skills, improve information recall while honing in on ...
Tiered assignments can also be differentiated based on product. Teachers can use the Howard Gardner's multiple intelligences to form groups that will hone particular skills for particular learning styles. For example, one group would be bodily/kinesthetic, and their task is to create and act out a skit. Another group would be visual/spatial ...
5. Promoting Collaborative Learning. Collaborative learning strategies encourage teamwork and cooperation among students, fostering a sense of camaraderie in the classroom. Group projects and problem-solving activities provide opportunities for students to work together and learn from each other's perspectives.
Teaching strategies are broken down into two major categories. ... Assignment. The assignment method of teaching is the most popular form of student-centered instruction. Assignments may include ...
She does so even though she is teaching a large class (140-student C118: Principles of Chemistry and Biochemistry) and often teaching in a challenging classroom space. Biology Professor and Carnegie Scholar Whitney Schlegel leads students to learn with their peers by engaging in discussion, problem-solving, and inquiry by using team members as ...
Teaching strategies are the techniques and methods that a teacher applies to support student learning. A teacher selects the teaching strategy most suited to the current level of knowledge of the students, the concept being studied, and the stage in the learning journey of the students. A learning strategy is a learner's way to organize and use ...
The Four Square is a graphic organizer that students can make themselves when given a blank sheet of paper. They fold it into four squares and draw a box in the middle of the page. The genius of ...
By the time one assignment is completed, it's far further possibly that the entire class will be ready to move the to the next concept or skill. And since degrees have already been given, it reduces after-class scoring time for teachers. ... Teaching strategies examples for advanced students 7.1. Curriculum compacting.
Pedagogy is the combination of teaching methods (what instructors do), learning activities (what instructors ask their students to do), and learning assessments (the assignments, projects, or tasks that measure student learning). Key Idea for Pedagogy. Diversify your pedagogy by varying your teaching methods, learning activities, and assignments.
5. Differentiation. Differentiation is a teaching strategy that lets you assign tasks to students based on their specific academic abilities and their learning needs. Effective classrooms are often inclusive settings so it's important to teach to a range of learning levels simultaneously.
The study assignment method. It is one of those teaching methods that promote active learning. In this method, the teacher or an instructor assigns a task to students before the class. It can be a book or research paper reading, project analysis, or any relevant material review. ... One of the essential teaching strategies a teacher or an ...
Graphic Organizers. After teaching English for over 20 years, Donna L. Shrum is now teaching ancient history to freshmen in the Shenandoah Valley of Virginia.
It involves the implementation of a variety of teaching techniques, from flexible grouping and tiered assignments to the integration of technology. This blog post will delve into 10 effective strategies for differentiated instruction, providing educators with the tools to create an engaging, inclusive, and dynamic learning environment.
These essential strategies in teaching mathematics can make this your class's best math year ever! 1. Raise the bar for all. ... Instead of a quick exit question or card, give a five-minute quiz, an open-ended question, or a meaningful homework assignment to confirm students have mastered the math skill covered in the day's lesson ...