
Distribution Company Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Distribution Company Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Distribution Company business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Distribution Companies.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Distribution Company business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
KitchenWare Distributors is a startup distribution company located in Long Beach, California. The company was founded by Nelson Fuller, a former senior executive in a kitchenware company based in Chicago, Illinois. Nelson made over ten million dollars in kitchenware sales during the past two years for his former company, and felt the time was now right to start his own company in California. Because Long Beach is a leading port for ships bringing goods into the U.S. from China and other Asian countries, Nelson believes the greatest kitchen product range and highest dollar value can be amassed via the Long Beach import area.
KitchenWare Distributors specializes in selling kitchen products, including tabletop, tableware, cookware, and cutlery, to independent retailers, retail chains, and e-commerce platforms. Nelson recruited his wife, Jamie Fuller, to join him in the new startup, as her former position was a marketing manager for a small kitchen appliance company. Her new role will be as the Executive Manager of tabletop and cookware products.
Product Offering
The following are the services that KitchenWare Distributors will provide:
- Large-volume sales to kitchen product companies, including brick-and-mortar and ecommerce
- 24/7 customer service representative support
- Competitive pricing
- Diverse product selection
- Free transport from Long Beach to customer location
- Package pricing based on company loyalty programs
- Tiered products based on customer’s target audience
Customer Focus
KitchenWare Distributors will target retail companies, retail chains, and kitchenware stores. KitchenWare Distributors will also target e-commerce platform companies that specialize in kitchen product sales. KitchenWare Distributors will target industrial restaurant and kitchen supply companies. KitchenWare Distributors will target state and federal government cooking and kitchen supply sites.
Success Factors
KitchenWare Distributors will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Friendly, knowledgeable, and highly-qualified team at KitchenWare Distributors.
- Customer service representatives with 24/7 service for clients.
- Free transport from Long Beach to customer distribution centers or retail stores.
- Unique logistical software program designed for kitchen product retailers.
- KitchenWare Distributors offers reasonable pricing with free transportation included; both excellent savings.
Financial Highlights
KitchenWare Distributors is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its kitchen product line of goods. The funding will be dedicated toward securing the office space and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated toward three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the marketing costs. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Office space build-out: $20,000
- Office equipment, supplies, and materials: $10,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $10,000
- Working capital: $10,000
The following graph outlines the financial projections for KitchenWare Distributors.
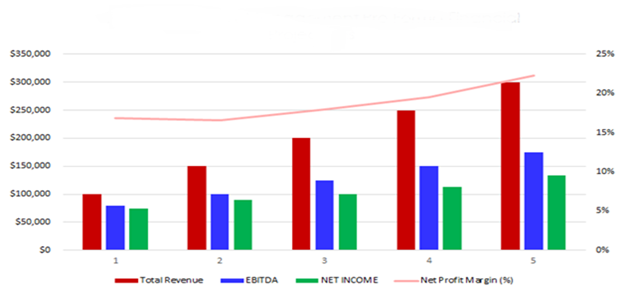
Company Overview
Who is kitchenware distributors.
KitchenWare Distributors is a newly established full-service distribution company based in Long Beach, California. KitchenWare Distributors is committed to becoming the most reliable, cost-effective, and efficient choice for retail chains, retailers and kitchenware supply stores in the U.S. KitchenWare Distributors will provide a comprehensive menu of customer support services for any client to utilize. Their full-service approach includes free transportation from the dock at Long Beach to the city of the client distribution center or retail store.
KitchenWare Distributors will present and sell through a vast array of kitchen products, including tabletop, kitchenware, cookware, serveware, and cutlery. The team of professionals are highly qualified and experienced in distribution and negotiations. KitchenWare Distributors removes all headaches and issues of the process of buying and transporting inventory for retail stores by taking excellent care of the inventory items and stock and ensuring that all issues are taken care of expeditiously while delivering the best customer service.
KitchenWare Distributors History
KitchenWare Distributors is owned and operated by Nelson and Jamie Fuller, both former executives working within the kitchen products industry in a kitchenware company based in Chicago, Illinois. Nelson made over ten million dollars in kitchenware sales during the past two years for his former company, and felt the time was now right to start his own company in California. Because Long Beach is a leading port for ships bringing goods into the U.S. from China and other Asian countries, Nelson believes the greatest kitchen product range and highest dollar value can be amassed via the Long Beach import area.
Since incorporation, KitchenWare Distributors has achieved the following milestones:
- Registered KitchenWare Distributors, LLC to transact business in the state of California.
- Has a contract in place at one of the office buildings, where the marketing department and administrative group will set up their 10,000 square foot office space.
- Reached out to numerous former clients and contacts to include KitchenWare Distributors as a distribution vendor.
- Began recruiting a staff of fifteen customer service representatives and five office personnel to work at KitchenWare Distributors.
KitchenWare Distributors Services
The following will be the services KitchenWare Distributors will provide:
Industry Analysis
The kitchen products industry is expected to grow during the next five years to over $44 billion. The growth will be driven by the consumer interest in premium kitchen countertop appliances that perform with precision. The growth will also be driven by smart kitchen appliances (remote turn on/turn off capabilities). The growth will be driven by color palette changes in 2027-28. Technological advances will drive the U.S. market growth. The growth will also be driven by eco-friendly, and sustainable tableware products. Costs will likely be reduced as kitchenware categories within lifestyle choices are discounted. Costs will likely be reduced as consumers turn to e-commerce for tableware and cookware choices, which reduces shipping costs overall.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
KitchenWare Distributors will target retail chains, retail stores, kitchenware stores, and government contract customers within California and the U.S. population. .
Customer Segmentation
KitchenWare Distributors will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Retail chains
- Retail stores, specifically kitchen product stores
- Ecommerce kitchen product companies
- State and government contractors for kitchen products
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
KitchenWare Distributors will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Strategic Distribution Group
The Strategic Distribution Group is located in New Jersey, near Ports America, Inc. The company receives goods via ship transport initiated in Shenzhen, China and directed to retail chains and kitchen stores throughout the U.S. The company was started by a partnership between Hershel Barts and Mark Tokien, formerly kitchen product managers for a major kitchen appliance manufacturer.
The Strategic Distribution Group offers limited discounts on product assortment groups or packages; however, shipping from the port to the retail chain market is provided at no cost. The strength of the company lies in the experience of the partners and the sales history in this industry sector they represent.
Cooking & Eating, Inc.
Cooking & Eating, Inc., headquartered in Scottsdale, Arizona, is a large retail chain that offers a distribution service to clients and guests who want shipment and associated logistics packaged together by Cooking & Eating, Inc. The company was founded in 2014 by Eddy Walker, who found the distribution ties were weak in the Southwest portion of the U.S. and wanted to improve the strength of the industry while also owning a cooking video company that could capitalize on the location and new product introduction.
Currently, Cooking & Eating, Inc. is focused on cooking videos for a YouTube audience of 1.5 million viewers and video reels for TikTok which demonstrate cooking and eating in comedic fashion. The owner of the company, Eddy, enjoys appearing and leading the conversational topics on the show, as well as introducing his company once again to the final outcomes of this year.
Retread Distributors & More
Retread Distributors & More specializes in closeout lots, damaged inventory, returned products and “scratch & dent” appliance units. Their clients include major resellers, such as Overstock.com, and other secondary markets who purchase lots at greatly discounted prices and then hope to sell those lots at a miniscule profit. Retread Distributors & More is owned by Dottie Masters, a woman who has been a leader in the reselling industry for over forty years. The company is one of several owned by Dottie, and as such, it presents a “bargain basement” type of atmosphere, albeit one with excellent pricing and values that can be very profitable for retailers should they choose to sell such inventory items.
Competitive Advantage
KitchenWare Distributors will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
- KitchenWare Distributors offers reasonable pricing with free transportation included; both advantageous savings.
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
KitchenWare Distributors will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Highly-qualified team of skilled employees who are able to provide comprehensive customer service support.
- Free shipping from Long Beach port to client retail location.
- Unbeatable 24/7 customer service for clients.
- Tiered discounts geared to assist all clients in savings
- Pricing packages that are advantageous for clients
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for KitchenWare Distributors is as follows:
Word of Mouth/Referrals
KitchenWare Distributors has built up an extensive list of contacts over the years by providing exceptional service and expertise to the former clients of Jamie Miller. Former clients have already committed to follow both new co-owners to the KitchenWare Distributors company and refer the new company to their associates.
Professional Associations and Networking
Both Nelson and Jamie Miller are members of national trade associations and both will continue to network and offer services to other members. The company may also choose to sponsor activities during trade shows that will highlight the new company.
Website/SEO Marketing
KitchenWare Distributors will extensively utilize their website. The website will be well organized, informative, and list all the services that KitchenWare Distributors provides. The website will also direct interested buyers to several pages of product inventory, including pricing and available quantities of each. Customers can buy online using the “Buy” page on the website. The website will list the contact number of their customer service representative and introduce them both via the Chat Box on the website. KitchenWare Distributors’s website presence will focus on SEO marketing tactics so that anytime someone types in the Google or Bing search engine “kitchen products company” or “kitchen supplies near me”, KitchenWare Distributors will be listed at the top of the search results.
The pricing of KitchenWare Distributors will be moderate and on par with competitors so customers feel they receive excellent value when purchasing their services.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for KitchenWare Distributors. Operation Functions:
- Nelson Miller will be the co-owner and president of the company. He will oversee all staff and manage client relations.
- Jamie Miller will be the Executive Manager of the tabletop and cookware divisions.
- Ken Stevens will be the Marketing Manager who will provide all marketing for KitchenWare Distributors.
Milestones:
KitchenWare Distributors will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
- 5/1/202X – Finalize contract to lease office space
- 5/15/202X – Finalize personnel and staff employment contracts for the KitchenWare Distributors
- 6/1/202X – Finalize contracts for KitchenWare Distributors clients
- 6/15/202X – Begin networking at industry events
- 6/22/202X – Begin moving into KitchenWare Distributors office
- 7/1/202X – KitchenWare Distributors opens its office for business
Management Team
Financial plan, key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for KitchenWare Distributors are the fees they will charge to the clients for their products and services.
The cost drivers will be the overhead costs required in order to staff KitchenWare Distributors. The expenses will be the payroll cost, rent, utilities, office supplies, and marketing materials.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
KitchenWare Distributors is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its distribution company. The funding will be dedicated toward securing the office space and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated toward three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the print ads and association memberships. The breakout of the funding is below:
Key Assumptions
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and in order to pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of Client Purchases Per Month: 63
- Average Revenue per Month: $616,000
- Office Lease per Year: $100,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, distribution company business plan faqs, what is a distribution company business plan.
A distribution company business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your distribution company business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Distribution Company business plan using our Distribution Company Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Distribution Company Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of distribution company businesses , some examples include: Exclusive Distribution Business, Direct Distribution Business, Selective Distribution Business, and Intensive Distribution Business.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Distribution Company Business Plan?
Distribution Company businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Distribution Company Business?
Starting a distribution company business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Distribution Company Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed distribution company business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your distribution company business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your distribution company business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Distribution Company Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your distribution company business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your distribution company business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Distribution Company Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your distribution company business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your distribution company business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.

Distribution Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Distribution Company Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their distribution businesses.
If you’re unfamiliar with creating a distribution company business plan, you may think creating one will be a time-consuming and frustrating process. For most entrepreneurs it is, but for you, it won’t be since we’re here to help. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a great business plan.
In this article, you will learn some background information on why business planning is important. Then, you will learn how to easily write a distribution company business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your distribution company as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan
If you’re looking to start a distribution business or grow your existing distribution company, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your distribution company to improve your chances of success. Your distribution company business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Distribution Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a distribution business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. When it comes to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to ensure that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for distribution businesses.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a distribution company.
If you want to start a distribution company or expand your current one, you need a business plan. The guide below details the necessary information for how to easily write each essential component of your distribution company business plan.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the kind of distribution business you are running and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a distribution company that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of distribution businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan.
- Give a brief overview of the distribution industry.
- Discuss the type of distribution business you are operating.
- Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers.
- Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
- Offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Overview
In your company overview, you will detail the type of distribution business you are operating.
For example, you might specialize in one of the following types of distribution businesses:
- Exclusive Distribution Business: Operates as the sole distributor for its client in a specified region.
- Direct Distribution Business: Sells products directly to retail stores.
- Selective Distribution Business: Typically operates in niche industries with limited retailers.
- Intensive Distribution Business: Provides distribution services to a high number of retailers.
In addition to explaining the type of distribution company you will operate, the company overview needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of clients served, the number of retailers secured, reaching $X amount in revenue, etc.
- Your legal business structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the distribution industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the distribution industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your marketing strategy, particularly if your analysis identifies market trends.
The third reason is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your distribution company business plan:
- How big is the distribution industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential target market for your distribution business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your distribution company business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: individuals, schools, organizations, government, and corporations.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of distribution business you operate. Clearly, schools would respond to different marketing promotions than corporations, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the potential customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can recognize and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Distribution Company Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other distribution businesses.
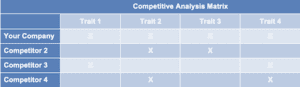
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What type of distribution business are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you offer products or services that your competition doesn’t?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a distribution company business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of distribution company that you documented in your company overview. Then, detail the specific products or services you will be offering. For example, will you provide exclusive distribution services, selective distribution services, intensive distribution services, or direct distribution services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of yo ur plan, yo u are presenting the products and/or services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the site of your distribution company. Document where your company is situated and mention how the site will impact your success. For example, is your distribution business located in a busy retail district, a business district, or a standalone office or warehouse? Discuss how your site might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your distribution company marketing plan is where you will document how you will drive potential customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertise in local papers, radio stations and/or magazines
- Reach out to websites
- Distribute flyers
- Engage in email marketing
- Advertise on social media platforms
- Improve the SEO (search engine optimization) on your website for targeted keywords
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your distribution business, including answering calls, scheduling shipments, billing clients and collecting payments, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to acquire your Xth client, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your distribution business to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your distribution company’s’ potential to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing distribution businesses. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing a distribution company.
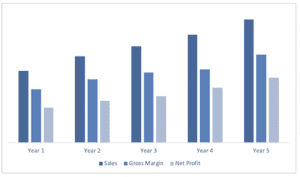
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance s heet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your distribution business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a lender writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and ensure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a distribution company:
- Cost of equipment and office supplies
- Cost of rent or mortgage on a facility
- Cost of purchasing and maintaining trucks/trailers
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Other start-up expenses (if you’re a new business) like legal expenses, permits, computer software, and equipment
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your office location lease or a copy of the wholesaler and auto insurance policies you’ve purchased.
Writing a business plan for your distribution company is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will understand the distribution industry, your competition, and your customers. You will develop a marketing strategy and will understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful distribution company.
Distribution Company Business Plan Template FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my distribution company business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily write your distribution company business plan.
How Do You Start a Distribution Company Business?
Starting a distribution company business is easy with these 14 steps:
- Choose the Name for Your Distribution Company Business
- Create Your Distribution Company Business Plan
- Choose the Legal Structure for Your Distribution Company Business
- Secure Startup Funding for Your Distribution Company Business (If Needed)
- Secure a Location for Your Business
- Register Your Distribution Company Business with the IRS
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
- Get Business Insurance for Your Distribution Company Business
- Buy or Lease the Right Distribution Company Business Equipment
- Develop Your Distribution Company Business Marketing Materials
- Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your Distribution Company Business
- Open for Business
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Distribution Company business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s business plan services can give you a winning business plan.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Wholesale & Distributor Business Plans
Coffee distribution business plan.
The Coffee Warehouse is a new business providing full service distribution of coffee and supplies to coffee houses and espresso stands throughout the Spokane and Northern Idaho market.
Farm Machinery Manufacturer Business Plan
Kouros Brothers Ltd. is an established manufacturer and retailer of agricultural planting and harvesting machinery on the island of Cyprus.
Fire Rescue E-commerce Business Plan
FireRescue Depot is a start-up showroom and Internet e-commerce business supplying fire and emergency rescue departments with specialized, heavy-duty, hydraulic rescue tools.
Wholesale Bicycle Distributor Business Plan
Wheelie Deals is a wholesale distributor of bicycles and bicycle parts, focusing on closeouts, discontinued models, seconds, etc.
Before you write a business plan, do your homework. These sample business plans for wholesale and distribution businesses will give you the head start you need to get your own business plan done.
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- Subscribers For Subscribers
- ELN Write for Entrepreneur
- Store Entrepreneur Store
- Spotlight Spotlight
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
How to Start a Wholesale Distribution Business Buy low, sell high: A background in sales and a keen eye for popular merchandise are the keys to success as a wholesale distributor.
Editor's note: This article was excerpted from our Wholesale Business Distribution start-up guide , available from Entrepreneur Bookstore.
So you want to start a wholesale distributorship. Whether you're currently a white-collar professional, a manager worried about being downsized, or bored with your current job, this may be the right business for you. Much like the merchant traders of the 18th century, you'll be trading goods for profit. And while the romantic notion of standing on a dock in the dead of night haggling over a tea shipment may be a bit far-fetched, the modern-day wholesale distributor evolved from those hardy traders who bought and sold goods hundreds of years ago.
The Distributor's Role
According to U.S. Industry and Trade Outlook, published by The McGraw-Hill Companies and the U.S. Department of Commerce/International Trade Administration, wholesale trade includes establishments that sell products to retailers, merchants, contractors and/or industrial, institutional and commercial users. Wholesale distribution firms, which sell both durable goods (furniture, office equipment, industrial supplies and other goods that can be used repeatedly) and nondurable goods (printing and writing paper, groceries, chemicals and periodicals), don't sell to ultimate household consumers.
Three types of operations can perform the functions of wholesale trade: wholesale distributors; manufacturers' sales branches and offices; and agents, brokers and commission agents. As a wholesale distributor, you will probably run an independently owned and operated firm that buys and sells products of which you have taken ownership. Generally, such operations are run from one or more warehouses where inventory goods are received and later shipped to customers.
Put simply, as the owner of a wholesale distributorship, you will be buying goods to sell at a profit, much like a retailer would. The only difference is that you'll be working in a business-to-business realm by selling to retail companies and other wholesale firms like your own, and not to the buying public. This is, however, somewhat of a traditional definition. For example, companies like Sam's Club and BJ's Warehouse have been using warehouse membership clubs, where consumers are able to buy at what appear to be wholesale prices, for some time now, thus blurring the lines. However, the traditional wholesale distributor is still the one who buys "from the source" and sells to a reseller.
Getting Into the Game
The field of wholesale distribution is a true buying and selling game-one that requires good negotiation skills, a nose for sniffing out the next "hot" item in your particular category, and keen salesmanship. The idea is to buy the product at a low price, then make a profit by tacking on a dollar amount that still makes the deal attractive to your customer.
Experts agree that to succeed in the wholesale distribution business, an individual should possess a varied job background. Most experts feel a sales background is necessary, as are the "people skills" that go with being an outside salesperson who hits the streets and/or picks up the phone and goes on a cold-calling spree to search for new customers.
In addition to sales skills, the owner of a new wholesale distribution company will need the operational skills necessary for running such a company. For example, finance and business management skills and experience are necessary, as is the ability to handle the "back end" (those activities that go on behind the scenes, like warehouse setup and organization, shipping and receiving, customer service, etc.). Of course, these back-end functions can also be handled by employees with experience in these areas if your budget allows.
"Operating very efficiently and turning your inventory over quickly are the keys to making money," says Adam Fein, president of Pembroke Consulting Inc., a Philadelphia strategic consulting firm. "It's a service business that deals with business customers, as opposed to general consumers. The startup entrepreneur must be able to understand customer needs and learn how to serve them well."
According to Fein, hundreds of new wholesale distribution businesses are started every year, typically by ex-salespeople from larger distributors who break out on their own with a few clients in tow. "Whether they can grow the firm and really become a long-term entity is the much more difficult guess," says Fein. "Success in wholesale distribution involves moving from a customer service/sales orientation to the operational process of managing a very complex business."
Setting Up Shop
According to Fein, wholesale distribution companies are frequently started in areas where land is not too expensive and where buying or renting warehouse space is affordable. "Generally, wholesale distributors are not located in downtown shopping areas, but off the beaten path," says Fein. "If, for example, you're serving building or electrical contractors, you'll need to choose a location in close proximity to them in order to be accessible as they go about their jobs."
State of the Industry
And that's not all: Every year, U.S. retail cash registers and online merchants ring up about $3.6 trillion in sales, and of that, about a quarter comes from general merchandise, apparel and furniture sales (GAF). This is a positive for wholesale distributors, who rely heavily on retailers as customers. To measure the scope of GAF, try to imagine every consumer item sold, then remove the cars, building materials and food. The rest, including computers, clothing, sports equipment and other items, fall into the GAF total. Such goods come directly from manufacturers or through wholesalers and brokers. Then they are sold in department, high-volume and specialty stores-all of which will make up your client base once you open the doors of your wholesale distribution firm.
All this is good news for the startup entrepreneur looking to launch a wholesale distribution company. However, there are a few dangers that you should be aware of. For starters, consolidation is rampant in this industry. Some sectors are contracting more quickly than others. For example, pharmaceutical wholesaling has consolidated more than just about any other sector, according to Fein. Since 1975, mergers and acquisitions have reduced the number of U.S. companies in that sector from 200 to about 50. And the largest four companies control more than 80 percent of the distribution market.
To combat the consolidation trend, many independent distributors are turning to the specialty market. "Many entrepreneurs are finding success by picking up the golden crumbs that are left on the table by the national companies," Fein says. "As distribution has evolved from a local to a regional to a national business, the national companies [can't or don't want to] cost-effectively service certain types of customers. Often, small customers get left behind or are just not [profitable] for the large distributors to serve."
Starting Out
For entrepreneurs looking to start their own wholesale distributorship, there are basically three avenues to choose from: buy an existing business, start from scratch or buy into a business opportunity. Buying an existing business can be costly and may even be risky, depending on the level of success and reputation of the distributorship you want to buy. The positive side of buying a business is that you can probably tap into the seller's knowledge bank, and you may even inherit his or her existing client base, which could prove extremely valuable.
The second option, starting from scratch, can also be costly, but it allows for a true "make or break it yourself" scenario that is guaranteed not to be preceded by an existing owner's reputation. On the downside, you will be building a reputation from scratch, which means lots of sales and marketing for at least the first two years or until your client base is large enough to reach critical mass.
The last option is perhaps the most risky, as all business opportunities must be thoroughly explored before any money or precious time is invested. However, the right opportunity can mean support, training and quick success if the originating company has already proven itself to be profitable, reputable and durable.
During the startup process, you'll also need to assess your own financial situation and decide if you're going to start your business on a full- or part-time basis. A full-time commitment probably means quicker success, mainly because you will be devoting all your time to the new company's success.
Because the amount of startup capital necessary will be highly dependent on what you choose to sell, the numbers vary. For instance, an Ohio-based wholesale distributor of men's ties and belts started his company with $700 worth of closeout ties bought from the manufacturer and a few basic pieces of office equipment. At the higher end of the spectrum, a Virginia-based distributor of fine wines started with $1.5 million used mainly for inventory, a large warehouse, internal necessities (pallet racking, pallets, forklift), and a few Chevrolet Astro vans for delivery.
Like most startups, the average wholesale distributor will need to be in business two to five years to be profitable. There are exceptions, of course. Take, for example, the ambitious entrepreneur who sets up his garage as a warehouse to stock full of small hand tools. Using his own vehicle and relying on the low overhead that his home provides, he could conceivably start making money within six to 12 months.
"Wholesale distribution is a very large segment of the economy and constitutes about 7 percent of the nation's GDP," says Pembroke Consulting Inc.'s Fein. "That said, there are many different subsegments and industries within the realm of wholesale distribution, and some offer much greater opportunities than others."
Among those subsegments are wholesale distributors that specialize in a unique niche (e.g., the distributor that sells specialty foods to grocery stores), larger distributors that sell everything from soup to nuts (e.g., the distributor with warehouses nationwide and a large stock of various, unrelated closeout items), and midsized distributors who choose an industry (hand tools, for example) and offer a variety of products to myriad customers.
The cornerstone of every distribution cycle, however, is the basic flow of product from manufacturer to distributor to customer. As a wholesale distributor, your position on that supply chain (a supply chain is a set of resources and processes that begins with the sourcing of raw material and extends through the delivery of items to the final consumer) will involve matching up the manufacturer and customer by obtaining quality products at a reasonable price and then selling them to the companies that need them.
In its simplest form, distribution means purchasing a product from a source-usually a manufacturer, but sometimes another distributor-and selling it to your customer. As a wholesale distributor, you will specialize in selling to customers-and even other distributors-who are in the business of selling to end users (usually the general public). It's one of the purest examples of the business-to-business function, as opposed to a business-to-consumer function, in which companies sell to the general public.
Weighing It Out: Operating Costs
Regardless of where a distributor sets up shop, some basic operating costs apply across the board. For starters, necessities like office space, a telephone, fax machine and personal computer will make up the core of your business. This means an office rental fee if you're working from anywhere but home, a telephone bill and ISP fees for getting on the internet.
No matter what type of products you plan to carry, you'll need some type of warehouse or storage space in which to store them; this means a leasing fee. Remember that if you lease a warehouse that has room for office space, you can combine both on one bill. If you're delivering locally, you'll also need an adequate vehicle to get around in. If your customer base is located further than 40 miles from your home base, then you'll also need to set up a working relationship with one or more shipping companies like UPS, FedEx or the U.S. Postal Service. Most distributors serve a mixed client base; some of the merchandise you move can be delivered via truck, while some will require shipping services
While they may sound a bit overwhelming, the above necessities don't always have to be expensive-especially not during the startup phase. For example, Keith Schwartz, owner of On Target Promotions, started his wholesale tie and belt distributorship from the corner of his living room. With no equipment other than a phone, fax machine and computer, he grew his company from the living room to the basement to the garage and then into a shared warehouse space (the entire process took five years). Today, the firm operates from a 50,000-square-foot distribution center in Warrensville Heights, Ohio. According to Schwartz, the firm has grown into a designer and importer of men's ties, belts, socks, wallets, photo frames and more.
To avoid liability early on in his entrepreneurial venture, Schwartz rented pallet space in someone else's warehouse, where he stored his closeout ties and belts. This meant lower overhead for the entrepreneur, along with no utility bills, leases or costly insurance policies in his name. In fact, it wasn't until he penned a deal with a Michigan distributor for a large project that he had to store product and relabel the closeout ties with his firm's own insignia. As a result, he finally rented a 1,000-square-foot warehouse space. But even that was shared, this time with another Ohio distributor. "I don't believe in having any liability if I don't have to have it," he says. "A warehouse is a liability."
The Day-to-Day Routine
"One reason that wholesale distributors have increased their share of total wholesale sales is that they can perform these functions more effectively and efficiently than manufacturers or customers," comments Fein.
To handle all these tasks and whatever else may come their way during the course of the day, most distributors rely on specialized software packages that tackle such functions as inventory control, shipping and receiving, accounting, client management, and bar-coding (the application of computerized UPC codes to track inventory).
And while not every distributor has adopted the high-tech way of doing business, those who have are reaping the rewards of their investments. Redondo Beach, California-based yoga and fitness distributor YogaFit Inc., for example, has been slowly tweaking its automation strategy over the past few years, according to Beth Shaw, founder and president. Shaw says the 25-employee company sells through a website that tracks orders and manages inventory, and the company also makes use of networking among its various computers and a database management program to maintain and update client information. In business since 1994, Shaw says technology has helped increase productivity while cutting down on the amount of time spent on repetitive activities, such as entering addresses used to create mailing labels for catalogs and individual orders. Adds Shaw, "It's imperative that any new distributor realize from day one that technology will make their lives much, much easier."
Who Are Your Customers?
Because every company relies on a pool of customers to sell its products and/or services to, the next logical step in the startup process involves defining exactly who will be included in that pool. Defining this group early on will allow you to develop business strategies, define your mission or answer the question "why am I in business?" and tailor your operations to meet the needs of your customer base.
As a wholesale distributor, your choice of customers includes:
Retail businesses: This includes establishments like grocery stores, independent retail stores, large department stores and power retailers like Wal-Mart and Target.
Retail distributors: This includes the distributors who sell to those retailers that you may find impenetrable on your own. For example, if you can't "get in" at a power retailer like Wal-Mart, you may be able to sell to one of its distributors.
Exporters: These are companies that collect United States-manufactured goods and ship them overseas.
Other wholesale distributors: It's always best to buy from the source, but that isn't always possible, due to exclusive contracts and issues like one-time needs (e.g., a distributor who needs 10 hard hats for a customer who is particular about buying one brand). For this reason, wholesale distributors often find themselves selling to other distributors.
The federal government: Uncle Sam is always looking for items that wholesale distributors sell. In fact, for wholesale distributors, selling to the government presents a great opportunity. For the most part, it's a matter of filling out the appropriate forms and getting on a "bid list." After you become an official government supplier, the various buying agencies will either fax or e-mail you requests for bids for materials needed by schools, various agencies, shipyards and other facilities.
For a small wholesale distributor, there are some great advantages to selling to the government, but the process can also be challenging in that such orders often require a lengthy bidding process before any contracts are awarded. Since opening her Redondo Beach, California, distributorship in 1994, Beth Shaw of YogaFit Inc. says she's made several successful sales to the government. Currently, the firm sells its exercise education programs and several styles of yoga mats to Army bases and other entities. Calling government sales "a good avenue" for wholesale distributors, Shaw says it's also one that's often overlooked, "especially by small businesses."
Finding a Profitable Niche
In other words, what matters is not so much what you sell, but how you sell it. There are profitable opportunities in every industry-from beauty supplies to hand tools, beverages to snack foods. No matter what they're selling, wholesale distributors are discovering ways to reaffirm their value to suppliers and customers by revealing the superior service they have to offer, as well as the cost-saving efficiencies created by those services. This mind-set opens up a wealth of opportunities to provide greater attention to the individual needs of customers, a chance to develop margin growth, and greater flexibility in product offerings and diversification of the business.
The whole trick, of course, is to find that niche and make it work for you. In wholesale distribution, a niche is a particular area where your company can most excel and prosper-be it selling tie-dyed T-shirts, roller bearings or sneakers. While some entrepreneurs may find their niche in a diverse area (for example, closeout goods purchased from manufacturers), others may wish to specialize (unique barstools that will be sold to regional bars and pubs).
On the other side of the coin, too much product and geographical specialization can hamper success. Take the barstool example. Let's say you were going to go with this idea but that in six months you'd already sold as many barstools as you could to the customer base within a 50-mile radius of your location. At that point, you would want to diversify your offerings, perhaps adding other bar-related items like dartboards, pool cues and other types of chairs.
The decision is yours: You can go into the wholesale distribution arena with a full menu of goods or a limited selection. Usually, that decision will be based on your finances, the amount of time you'll be able to devote to the business, and the resources available to you. Regardless of the choices you make, remember that market research provides critical information that enables a business to successfully go to market, and wholesale distributors should do as much as they can-on an ongoing basis. It is better to do simple research routinely than to shell out a lot of money once on a big research information project that may quickly become outdated.
Pinpointing a Startup Number
While entrepreneurs in some industries seem to be able to raise money with a snap of their fingers, most have to take a more detailed approach to the process. Perhaps the best starting point is to figure out just how much you need.
In the wholesale distribution sector, startup numbers vary widely, depending on what type of company you're starting, how much inventory will be necessary and what type of delivery systems you'll be using. For example, Keith Schwartz, who got his start selling belts and ties from his basement in Warrensville Heights, Ohio, started On Target Promotions with $700, while Don Mikovch, president of the wine distributor Borvin Beverage in Alexandria, Virginia, required $1.5 million. While Schwartz worked from a desk and only needed a small area in which to store his goods, Mikovch required a large amount of specialized storage space for his wines-and a safe method of transporting the bottles to his retailers.
The basic equipment needed for your wholesale distributorship will be highly dependent on what you choose to sell. If you plan to stock heavy items, then you should invest in a forklift (some run on fuel or propane, others are man-powered) to save yourself some strain. Pallets are useful for stocking and pallet racking is used to store the pallets and keep them in order for inventory purposes.
For distributors who are sourcing, storing and selling bulky goods (such as floor tile, for example), a warehouse of sufficient size (based on the size of products you're selling and the amount of inventory you'll be stocking) is a necessity. To ensure that the distribution process operates smoothly, select a location that allows you to move around efficiently and that includes the necessary storage equipment (such as pallet racking, on which you can store pallets). Don't forget to leave room for a forklift to be able to maneuver between racks of pallets and shelves stored in the warehouse.
As a startup distributor, your initial inventory investment will depend on what you're selling. Expect to carry some inventory, no matter what the product is, but also understand that your choice of goods will have some effect on how much you'll need to shell out upfront. Schwartz was buying surplus apparel, so $700 gave him plenty to work with for the first few months. When Garth Gordon and Vivienne Bramwell-Gordon, president and vice president, respectively, of Tampa, Florida-based Phones Etc., founded their company, they invested about $2,400 to purchase a shipment of high-end telephones. They quickly turned them around for a 300-percent profit and have been in the business of distributing refurbished Avaya telecom equipment to small companies and nonprofit groups ever since. Today, Phones Etc. carries about $600,000 in inventory at any given time.
Bill Green, managing partner at WSG Partners LLC in Cherry Hill, New Jersey, says the best way to determine inventory needs is to look at your customers' needs. If they're the type who "need everything yesterday" (contractors working on job sites would fall into this category), then your inventory will need to be ample enough to meet those last-minute requests. However, if there's usually a three-to-four-day span between order-taking and delivery, then you may be able to skimp a bit on inventory and instead focus on forming solid, reliable relationships with vendors who can help you meet those timelines.
"The most successful distributorships are the ones [whose owners] are working as close to their customers as possible and who can predict their needs and be there to provide value-along with the products," says Green. "That doesn't necessarily mean you need a huge warehouse and inventory, but you will need to find vendors who will 'hold' that inventory for you until your own customers ask for it."
Inventory Matters
There are caveats to both strategies. For starters, when a company chooses not to stock up, it runs the risk of being out of an item when the customer comes calling. At the same time, the distributors who overstock can find themselves in a real pickle if they can't get rid of merchandise they thought they could unload easily.
Being a distributor is all about "turning" inventory (selling everything you have in stock and then replenishing it)-the more times you can turn your inventory in a year, the more money you will make. Get the most turns by avoiding stocking items that may end up sitting in your warehouse for more than 90 days.
Stocking Up.Or Not?
On the other hand, if you are servicing a varied customer base located in different geographic areas, you may need to stock a little more than the entrepreneur in the previous example. Because you probably won't be visiting those customers at their locations, it may take a few months before you can determine just how much product they will be buying from you on a regular basis. Of course, you must also leave some breathing room for the "occasional" customer-the one who buys from you once a year and who will probably always catch you off guard. The good news is that having relationships with vendors can help fill those occasional needs quickly, even overnight or on the same day, if necessary.
"The biggest mistake companies make is developing an inventory load that is larger than what they really need," says Rich Sloan, co-founder of small-business consultancy StartupNation.com in Birmingham, Michigan. "The investment winds up sitting out in the warehouse when it could be put to much better use." Sloan says companies also jump into inventory purchases too quickly, without factoring in their customers' wants and needs-yet another way to wrap up too much investment in items that will be slow to move. "The trick is to keep it as lean as possible. That's a very smart, lower-risk way to go."
At Keith Schwartz's wholesale belt and tie distributorship in Warrensville Heights, Ohio, all it took was a $700 investment in closeout ties to get started. He resold them to a drugstore, pocketed the profits and reinvested the money in more inventory. It's a simple formula and one that works well for the small startup entrepreneur who is operating with low overhead.
The distributor who has already invested in a location, vehicles and other necessities should also factor product life cycle into the inventory equation. Those with longer life cycles (hand tools, for example) are usually less risky to stock, while those with shorter life cycles (food, for example, usually has a short life cycle) can become a liability if there are too many of them on the shelf. The shorter the life cycle, the less product you'll want to have on hand. Ultimately, your goal will be to sell the product before having to pay for it. In other words, if you are buying computers, and if the manufacturer offers you 30-day payment terms, then you'll want to have less than 30 days' worth of inventory on the shelf. That way, you never end up "owning" the inventory and instead serve as a middleman between the company that's manufacturing and/or selling the product and the one that's buying it.
To sum up the tricks to stocking a wholesale distributorship:
- Don't overdo it when it comes to buying inventory.
- Try to get a grasp on your customers' needs before you invest in inventory.
- If you can get away with doing it cheaply at first (especially those with low overhead), then go for it.
- Be wary of investing too much in short- life-cycle products, which you may get stuck with if they don't sell right away.
- Stock up to a level where you can sell the product before you have to pay for it.
For distributors, the biggest challenge is running your business on low operating profit margins. Adam Fein of Philadelphia-based Pembroke Consulting Inc. suggests making your operations as efficient as possible and turning inventory around as quickly as possible. "These are the keys to making money as a wholesale distributor," he says.
And while the operating profit margins may be low for distributors, Fein says the projected growth of the industry is quite optimistic. In 2004, total sales of wholesaler-distributors reached $3.2 trillion, and for 2005 Fein expects revenue growth to continue to outpace the growth of the economy overall, growing an estimated 7.7 percent (vs. projected gross domestic product growth of 3.5 percent).
Playing the Markup Game
Distributors can use the following formula when it comes to markup: If it costs the manufacturer $5 to produce the product and they have a 100 percent markup, then you (the distributor) buy it for $10. Following the same formula, the wholesaler would double the cost and sell it for $20. Thus, there is a 400 percent markup from manufactured price to the wholesaler's customer.
Wholesale Distribution Business Resources Associations and Professional Organizations
- Alabama Wholesale Distributors Association, (205) 823-8544
- American Wholesale Marketers Association
- California Distributors Association, (916) 446-7841
- Colorado Association of Distributors, (303) 690-8505
- General Merchandise Distributors Council, (719) 576-4260
- Idaho Wholesale Marketers Association, (208) 342-8900
- Industrial Supply Association
- Mississippi Wholesale Distributors Association, (601) 605-1482
- National Association of Wholesaler-Distributors
- North Carolina Wholesalers Association, (919) 271-2140
- Southern Association of Wholesale Distributors
- Texas Association of Wholesale Distributors, (512) 346-6912
- Virginia Wholesalers & Distributor Association, (804) 254-9170
- West Virginia Wholesalers Association, (304) 342-1081
- Integrated Distribution Management: Competing on Customer Service, Time and Cost by Christopher Gopal and Harold Cypress (Business One Irwin)
- Facing the Forces of Change: The Road to Opportunity by Pembroke Consulting ( www.pembroke_consulting.com )
- Managing Channels of Distribution by Kenneth Rolnicki (Amacom Books)
- The Complete Distribution Handbook by Timothy Van Mieghem (Prentice Hall)
- Wholesale Distribution Channels: New Insights and Perspectives by Bert Rosenbloom (Haworth Press)
Publications
- Electronic Distribution Today
- Industrial Distribution
- Modern Distribution Management

Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- 'The IRS is Coming in Hot': Jason Tartick Says All Business Owners Should Do This 1 Thing Before Filing Taxes — Or Risk a Potentially Pricey Audit
- Lock What Is a 'Dry Promotion' — and Has It Happened to You? Employees in This Specific Group May Be the Most Likely Victims .
- I Was a 25-Year-Old Nurse When I Started a Side Hustle to Combat Anxiety. It Made $1 Million in 7 Months — Then Sold for a Life-Changing Amount.
- Lock 2 Phrases I Learned From a Senior CIA Officer That Changed My Leadership Style
- The U.S. Justice Department Is Suing Apple in a Groundbreaking iPhone Monopoly Lawsuit — Here's Why
- Lock I Built My Company to 23 Profitable Stores. Here's My Advice to Small Business Owners Who Want to Grow Their Retail Presence.

Most Popular Red Arrow
Why dei still matters for small businesses and startups.
DEI shouldn't be just a buzzword.
Mark Zuckerberg Told Meta Engineers to 'Figure Out' Snapchat's Privacy Protections: 'We Have No Analytics on Them'
Recently unsealed court documents detail "Project Ghostbusters," Meta's project to work around Snapchat's end-to-end encryption to intercept data.
Save $240 on a Lifetime Subscription That Provides More Than 1,500 Book Summaries
With Headway Premium, you can gain knowledge at a rapid rate.
Sam Bankman-Fried Sentenced to 25 Years in Prison for Multibillion-Dollar Crypto Fraud
Southern District of New York Judge Lewis Kaplan said that the loss amount to the victims of Bankman-Fried's crimes surpassed $550 million.
The Brand Whiz Behind Sun Bum Is Famous For Making Boring Products Fun. Then, This One Stumped Him.
Everything Tom Rinks touched turned to gold until he took on a brand launch at Target that fizzled. Then, he found a creepy doll on Ebay, and he saw a way forward.
How To Improve Your Soft Skills and Emotional Intelligence in 7 Easy Steps
Using these simple but effective approaches will help a person in their business, life and relationships.
Successfully copied link
How to write a business plan for a distribution company?

Writing a business plan for a distribution company is essential in order to get your business off the ground, improve profitability or raise financing.
Whether you are starting up a new distribution company or looking to grow an existing one, having an effective and comprehensive business plan is key.
This guide will provide detailed information on why writing a business plan for your distribution company is important, what information it should contain, and what tools can be used to write your own.
With this guide as your reference, you will have all the knowledge needed to create an effective and successful business plan for your distribution company.
In this guide:
Why write a business plan for a distribution company?
What information is needed to create a business plan for a distribution company, how do i build a financial forecast for a distribution company, the written part of a distribution business plan, what tool should i use to write my distribution business plan.
There are several reasons to write a distribution business plan. Below, we cover some of the most important ones!
To set a clear roadmap
Writing a business plan for a distribution company is an important step for entrepreneurs to ensure the long-term success of their venture.
It requires you to think strategically and set objectives that will guide your decisions over the next 3-5 years.
This is especially critical for startups who need to consider all aspects of their business idea and ensure it can be viable before investing time and money, but also beneficial for established distribution companies looking to expand or improve operations in the coming years.
By having a clear roadmap laid out before them, you can have a better understanding of what needs to be done in order to reach your business objectives.
Planning ahead also helps you anticipate any potential obstacles that may stand in the way of success, allowing you to take proactive measures and adjust your plans accordingly.
To get clarity on your cash flow
One of the most important benefits of having a business plan is that it allows you to regularly compare your financial performance against what was planned and make necessary adjustments in order to keep your forecast accurate.
By doing this regularly, you can identify potential financial issues (such as an unexpected cash shortfall) early on and take corrective action before they become serious problems. This also enables you to seize opportunities that may arise along the way in order to maximise profits or grow faster.
To secure financing
Having a comprehensive distribution company business plan is also essential for getting financing from banks or investors.
Banks use the business plan to assess your borrowing capacity, identify potential collateral, and decide whether they think you will be able to repay the funds they lend your company.
Similarly, creating a business plan for your distribution company is also an essential step when looking to secure financing from equity investors.
Investors will carefully review the business plan to ensure that their investment in your distribution company can generate good returns. As such, they will want to see evidence of healthy growth and profitability as well as strong cash flows in your business plan.
With a comprehensive and well-thought-out business plan, you can be confident that you are presenting potential lenders or investors with all the information they need to make an informed decision about financing your company.
Now that we understand why it is important to write a business plan for your distribution company, let's look into what information is needed in order to create one.
Create your distribution business plan online!
Think your distribution business could be profitable? Find out how with a business plan!

Writing a distribution business plan requires research so that you can project sales, investments and cost accurately in your financial forecast.
In this section, we cover three key pieces of information you should gather before drafting your plan!
Carrying out market research for a distribution company
Carrying out market research prior to writing a business plan for your distribution company is essential in order to get an accurate understanding of your target market and competitive landscape
This information is invaluable when it comes to forecasting revenues and creating realistic projections in the business plan. But also in order to convince and demonstrate to the reader that there is a real opportunity to be seized on the target market.
Developing the marketing plan for a distribution company
Getting a clear picture of the road to market for your distribution company is also a prerequisite for writing the actual business plan itself.
This will be key when it comes to both forecasting sales and marketing expenditures in the financial forecast, and communicating your strategy effectively in your business plan.
The staffing and equipment needs of a distribution company
Distribution companies require serious capital expenditures - from fleets of trucks and warehouses to highly specialised packing equipment - and a significant workforce.
It is essential to think through the recruitment plan, financial investments, and any other costs (and associated timings) that may be associated with the business before you start drafting the document.
Once you've gathered the information mentioned above, it will be time to start working on the financial forecast for your distribution company. Let’s see what this entails
The objective of the financial forecast for a distribution company is to obtain 4 key financial tables: the Profit & Loss (P&L) statement, the balance sheet, cash flow forecast and a sources and uses table.
Let’s have a look at each of these in a bit more detail.
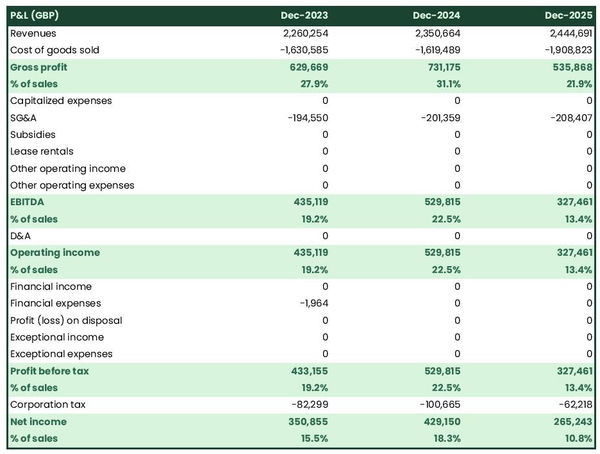
The projected P&L statement
The projected P&L statement of a distribution company shows us how much money the company will make and how much it is expected to grow in the future.
The projected balance sheet of your distribution company
The balance sheet for a distribution company is a financial document that provides an overview of the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
This statement serves as a snapshot of the business's financial health and can be used to determine the company’s ability to repay its debt in the short term (liquidity) and medium term (solvency).
Assets are items of value that your company holds, such as cash, inventory, accounts receivable and property; liabilities are the money owed to creditors or other businesses; and equity is what remains after liabilities have been subtracted from assets (and can be used as a proxy for shareholder value).
By looking at a company’s balance sheet, lenders, investors, and the business owner can gain insight into the financial health of the company.
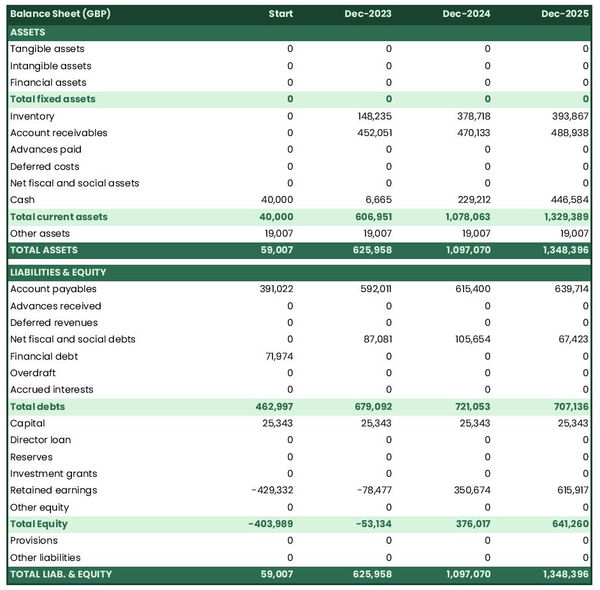
A balance sheet is a valuable tool for assessing how the company is doing financially, and ultimately its ability to remain sustainable and profitable over time.
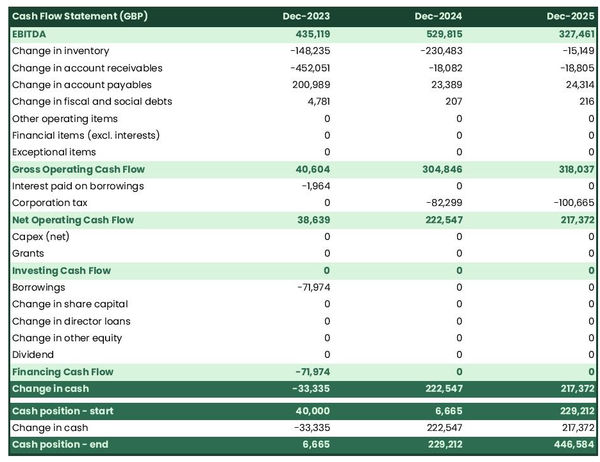
The projected cash flow statement
A projected cash flow statement is a helpful tool for a distribution company. It shows how much money the company will have coming in and going out over a certain period of time.
This helps you plan and ensure the business has enough capital for growth and investments.
The initial financing plan
The initial financing plan (also called the sources and uses table) shows the sums that the company needs to start and how they will be used.
It is important to have this so that you know how much capital is needed to deliver the business plan and what it will be used for.
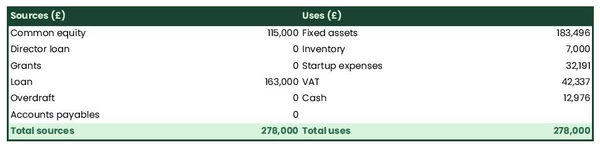
The sources show where the money comes from, such as investors or loans. The uses show what the money will be used for, like buying equipment or working capital. By having a source and use table, you can make sure that your business has enough money to get started!
Now that you understand what the financial forecast is made of, it's time to move on to another key part of the business plan - the written section.
The written section is an important component, as it provides the context needed to understand and interpret financial figures.
Let's dive in and take a closer look at this essential piece of your distribution company’s business plan.
A comprehensive business plan for your distribution company contains seven key sections: executive summary, presentation of the company, products and services section, market analysis, strategy section, operations section and financial plan.
1. The executive summary
The executive summary of a distribution company plan should start with a concise overview of your business.
This section should then include an overview of the market, highlighting any competitive advantages that your company has.
You should also include key financials such as expected revenues, costs, and profit margins.
Finally, this section should include a clear and concise explanation of the ask that your company is making to potential investors or lenders. This could include an overview of the funding required, and what it will be used for.
The executive summary should succinctly capture all of these important details in order to convince stakeholders to read the rest of your business plan.
2. The presentation of the company
When writing the presentation of a distribution company for a business plan, it is important to focus on three key elements: structure and ownership, location and management team.
Starting with the structure and ownership, it is important to provide an accurate description of the legal framework of the company. This includes information about the type of business entity the company is operating under, the ownership structure and whether any external investors are involved.
Additionally, investors may be interested in understanding any equity or debt held by the company and how the capital has been allocated.
The location of a distribution business is also critical for success. Any information about where the warehouse facilities are located as well as how many and what size they are should be included in the business plan.
This information should also include geographic reach and any serviceable areas where the company has a particularly strong presence.
Finally, a complete description of the management team is essential for investors. The management team’s expertise and experience in the industry must be highlighted, including information about their roles and qualifications.
3. The products and services section
When writing the products and services section of a business plan for a distribution company, it’s important to include detailed information about what your company actually does.
You should start with an overview of the types of services offered - such as transportation, storage, packaging, click and collect, etc. - and then move on to specifics like which modes of transport are used (airfreight, sea-freight) or what type of packaging is available (pharmaceutical goods, food and beverage, standard good parcels, etc.).
It’s also important to provide details on any additional value-added services provided by the company; these could include things like custom labelling and product assembly.
Additionally, mention if there are any special certifications or accreditations that make your business stand out from competitors in terms of quality control and safety standards. Ultimately these factors will be key in convincing potential investors that this is a viable business opportunity worth investing in.

4. The market analysis
When presenting the conclusion of your market analysis in your distribution company's business plan, it is important to include information about demographics and segmentation, target market, competition, barriers at entry, and regulation.
This will ensure that the reader of the business plan - whether they be a bank or an investor - has all the necessary information to make an informed decision with regard to the size of the opportunity in the target market.
Demographics and segmentation should cover the target market size as well as any other pertinent data points such as verticals served. Understanding these details will help provide insight into which segments are viable targets for the company’s products and services.
Additionally, understanding who your competitors are within those segments is key to assessing whether the company is well-positioned to capture the opportunity
It is also important for the reader to understand any potential barriers at entry that could limit your ability to enter certain market segments; this could include regulations from governmental agencies or clients being locked in existing long-term contracts with other distributors.
5. The strategy section
When writing the strategy section of a business plan for your distribution company, it is essential to include information about your competitive edge, pricing strategy, marketing plan, milestones and risks and mitigants.
The competitive edge should be outlined in detail; this includes any unique features or services that set your company apart from competitors.
Additionally, the pricing strategy must be included to demonstrate how you intend to remain profitable while still offering competitive prices in order to attract customers.
A comprehensive sales & marketing plan should also be included, this outlines how you intend to reach out and acquire new customers as well as retain existing ones with loyalty programs or special offers.
It’s also important to include specific milestones along with dates so that everyone involved has clear expectations of progress being made over time and what the next sets of goals are.
Finally, identifying potential risks early on and providing mitigating factors is essential in order for investors or lenders to feel secure in investing their money into your venture.
6. The operations section
In order to present the operations of your distribution company in a business plan, it is important to provide detailed information about the staffing team, roles of staff members, and recruitment plan.
This should include job descriptions for each role, details on how they will be compensated, and an outline of the recruitment and training processes.
Other key elements of a distribution company’s operations that need to be addressed in the business plan include any assets and intellectual property owned by the business.
This includes physical items such as warehouses (whether owned or leased), trucks, and equipment needed for daily operations.
Additionally, any relevant intellectual property such as brand names, logos and copyrights should be clearly stated in the plan.
Finally, it is important to outline the suppliers that a distribution company plans to work with. This should include information about contractual arrangements and payment terms for each supplier.
With this information included in the business plan, potential investors or lenders will have a better understanding of the operations that are required to run a successful distribution business.
7. The presentation of the financial plan
The financial plan section is where we will include the financial forecast we talked about earlier in this guide.
Now that we have discussed the content of a distribution company business plan, let us look at some of the tools available to help you create one.
In this section, we will review the three main solutions for creating a business plan for your distribution company: using Word and Excel, hiring a consultant, and using online business plan software.
Create your distribution company's business plan using Word and Excel
Using Microsoft Office’s Word and Excel applications for writing a business plan for a distribution company may seem like a cost-effective solution for business owners.
While this is true in terms of cost, there are also some drawbacks to this approach that should be considered when making the decision to use Word and Excel.
Creating an accurate financial forecast for a distribution company in Excel can be extremely challenging and time-consuming unless one is an expert accountant and financial modeller. Additionally, financiers may not view such an analysis as reliable since it was created by someone other than a professional.
Furthermore, once created it can be difficult to keep a financial forecast up-to-date.
Writing the actual business plan in Word is also inefficient as it requires the business owner to start from scratch and spend hours formatting the document afterwards.
Hire a consultant to write your distribution company's business plan
Outsourcing a distribution company plan to a consultant or accountant can be a viable solution for business owners looking to present their plan to investors or banks.
Consultants and accountants are both well-equipped to write business plans and create financial forecasts.
However, there are some drawbacks to outsourcing a business plan. For one, accountants may lack the industry expertise to accurately forecast sales.
Additionally, hiring consultants or accountants will be costly and there is potential for unexpected extra costs if modifications or updates need to be made to the plan.
Furthermore, entrepreneurs who outsource their distribution company's plan have less control over the outcome of the project than if they had written it themselves.
Finally, not all consultants have experience with business planning related to distribution companies and may not possess the same level of expertise as an entrepreneur who is very familiar with their industry.
Use an online business plan software for your distribution company's business plan
Another alternative is to use online business plan software . There are several advantages to using specialised software:
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can be inspired by already written business plan templates
- You can easily make your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you, without error
- You get a professional document, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank
- You can easily update your financial forecast and track it against actual financial performance to see where the business stands
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try our software for free by signing up here .
We hope that this article has helped you to better understand how to write the business plan for a distribution company. Do not hesitate to contact us if you still have questions!
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- Do I need a business plan? Your questions answered
- Business Model vs. Business Plan
- How to write the business plan for a grant application?
Know someone in the distribution industry? Share this article with them!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here
- Business Ideas
- Registered Agents
How to Start a Distribution Business in 14 Steps (In-Depth Guide)
Updated: March 1, 2024
BusinessGuru.co is reader-supported. When you buy through links on my site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more
Global distribution is on the rise, with more than $7 trillion earned in 2022 . With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5%, the market could hit 11.93 trillion in 2032. That’s a huge motivator for entrepreneurs looking to get started in the distribution industry.
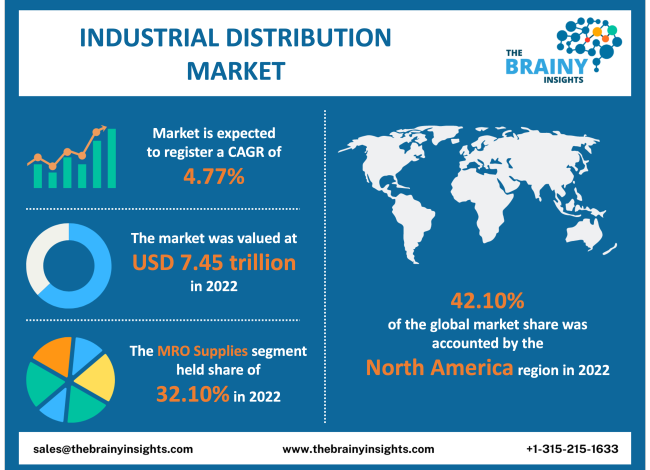
This article will walk you through the key steps for how to start a distribution business. We’ll cover everything from market research and registering an EIN, to opening a business bank account and compiling competitive analysis to build a better distribution business plan. Whether you want to focus on retail distribution, wholesale distribution, or e-commerce order fulfillment, you’ll find the essential advice to launch and grow a successful venture.
1. Conduct Distribution Market Research
Market research is essential to any wholesale distribution business. It offers insight into your target market, market saturation, supply chain trends, and other important elements of a successful wholesale distribution business.
Some details you might learn through market research include:
- Within wholesale distribution, the largest sectors are electronics, food service, and automotive parts.
- For retail distribution, e-commerce is fueling immense growth.
- Major retailers like Amazon and Walmart are building more warehouses and fulfillment centers.
- Beyond physical products, the distribution of digital goods like software, games, and apps is surging.
- Video games alone require distributing nearly 200 GB per title.
- Fast, reliable networks are essential.
The distribution sector provides immense opportunities across wholesale, retail, digital goods, and e-commerce order fulfillment. With strong inventory management, logistics networks, and customer service, new distribution companies can capture significant market share.
2. Analyze the Competition
Competitive analysis tells you a lot about the local distribution business market. Learning about other distribution businesses helps you better understand pricing, the best local retailers and inventory management products, and more.
Some ways to get to know about wholesale distribution company competitors include:
- Identify direct competitors in your geographic area or niche by searching industry databases.
- Drive by brick-and-mortar stores and assess the location, branding, customer traffic, and facilities.
- Research competitors online too. Check if they offer import/export services as well.
- Google their company and brand names to find their websites.
- Review their product catalog, messaging, offers, and site functionality.
- Check Alexa rankings and traffic estimates.
- Monitor their social media for customer engagement levels.
- Search their name on review platforms.
- Look for negative reviews that present opportunities to differentiate your business.
- Regularly check job sites like Indeed for openings that may indicate growth plans or challenges in retaining talent.
- Track press releases and news mentioning your rivals.
By thoroughly evaluating competitors across all channels, you can craft a distribution business positioned for success. Tailor your offerings, marketing, and operations to your target customers’ needs.
3. Costs to Start a Distribution Business
When starting a distribution company, your initial costs will vary based on your business model and scale. Let’s take a closer look at the expenses you’ll encounter as a wholesale distributor.
Start-up Costs
- Business registration and licensing – $500-$2,000 to form an LLC or corporation and obtain required state and local licenses. The cost rises if you need transport permits.
- Warehouse space – $2-$20 per sq. ft monthly, so a 5,000 sq. ft warehouse would run $10,000-$100,000 per month. Leasing provides more flexibility than buying commercial property.
- Racking and storage – $3,000-$10,000 for a basic pallet rack system for a small to mid-sized operation. Expandable as inventory grows.
- Trucks and vehicles – Used box trucks start around $20,000. Leasing trucks is often better financially than purchasing. Fuel costs must also be budgeted.
- Equipment – Pallet jacks ($250+ each), forklifts ($5,000+), conveyors, scales, and barcode scanners ($1,500+) are common distribution equipment costs.
- Technology – Warehouse Management System (WMS) software costs around $5,000 for an entry-level package. Must also budget for inventory, order, POS, and accounting software based on needs.
- Insurance – General liability insurance averages $1,000-$2,000/year. Commercial auto insurance for vehicles can run $5,000-$20,000 annually depending on fleet size.
- Initial inventory – Plan $10,000-$100,000+ to purchase your first product inventory stock, depending on supplier costs and diversity of SKUs.
- Staff – Warehouse workers average $15/hour. Delivery drivers often start around $18/hour. Will need 1-2 office staff in addition to variable warehouse headcount.
- Professional services – $1,000-$5,000 for legal, accounting, and business consulting services to start.
- Marketing – $2,000-$5,000 to build a basic website, branding, and promotional materials to launch.
Ongoing Costs
- Facility fees – Mortgage or continuing warehouse lease costs.
- Payroll – Salaries and hourly wages for all staff plus taxes and benefits management fees.
- New inventory – Replenishing stock as products sell through. Can range from thousands to millions based on sales.
- Software/technology – Monthly fees for business systems like WMS.
- Gas, oil, maintenance – For company vehicles, averaging 10-20 cents per mile.
- Utilities – Electric, gas, water, etc. for warehouse. May be included in the lease.
- Insurance – Monthly premiums for policies.
- Security – Alarm fees, video monitoring, etc. if not included in the lease.
- Taxes – Income, payroll, property, etc. Complex, so engage accounting professionals.
- Marketing – SEO services, PPC ads, trade shows, and other promotions to attract business. Budget $5,000-$50,000 based on marketing activities.
- Vehicle registration/inspection – For company trucks and fleets.
By planning for these costs and budgeting accordingly, you can launch a distribution startup while managing expenses wisely as you scale. Adjust costs for your specific needs and location.
4. Form a Legal Business Entity
When starting a distribution business, choosing the right legal structure is key. The main options each have pros and cons:
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the simplest structure. You alone own and operate the company directly. This gives total control and avoids corporate taxes. However, you assume unlimited personal liability for debts and legal issues.
Partnership
Partnerships let multiple owners share control and liability risk. A distribution partnership could combine experience in sales, operations, and finance. However, partnerships can get complicated if disputes arise between partners. Dissolving one also requires legal filings.
Corporation
A corporation offers limited liability for shareholders but requires extensive recordkeeping and corporate taxes. The board structure facilitates raising investment capital which distribution startups may need to expand. However, maintaining compliance as a C corporation has recurring costs.
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
For distribution, a limited liability company (LLC) offers the best of all worlds. As the name implies, your assets are protected from business debts and lawsuits. You get pass-through taxation to avoid corporate taxes. LLCs are relatively quick and affordable to establish and operate. You can still attract investors by issuing ownership units.
5. Register Your Business For Taxes
Before launching your distribution company, a key legal step is obtaining an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS. This unique 9-digit number identifies your business for tax purposes.
It’s easy to apply online at IRS.gov. Just follow these steps:
- Go to the EIN Assistant page: Apply for an EIN Online
- Answer a few questions about your business structure and details.
- When prompted, provide your personal identifying information for security purposes.
- Select a “responsible party” for your business, usually the owner.
- Review your information to ensure accuracy.
- Print the confirmation page with your new EIN for your records.
The entire process usually takes less than 10 minutes to complete and receive your EIN. This number will be used on your tax returns, applications, and other required IRS filings. There is no filing fee.
You’ll also need to contact your state’s revenue or taxation department to register for sales tax collection. This enables charging sales tax on purchases. Filing requirements and fees vary by state. This establishes your business as a lawful tax collector. Failure to register can lead to penalties.
Obtaining your federal EIN and registering for state sales tax collection are vital steps to operating legally as a distribution company. With these numbers, you can open business bank accounts, apply for licenses, hire employees, and collect and remit sales taxes. Taking these actions upfront will save hassle as your customer transactions grow.
6. Setup Your Accounting
Maintaining accurate financial records is critical for distribution companies. With frequent inventory purchases and sales transactions, keeping your books in order can get complex.
Accounting Software
Using small business accounting software like QuickBooks is highly recommended. The system can sync with your business bank accounts and credit cards to automatically import and categorize transactions. Features like invoicing, billing, and reporting make managing finances much easier.
Hire an Accountant
Hiring an accountant provides expert assistance. They can handle essential tasks like:
- Bookkeeping – Recording income and expenses in your accounting system.
- Payroll – Calculating taxes and preparing paychecks for employees.
- Cash flow analysis – Reviewing income and outflows to improve financial planning.
- Tax preparation – Filing quarterly estimated payments and annual tax returns.
Expect to pay $200-$500 monthly for ongoing bookkeeping and $2,000-$5,000 for annual tax preparation. Worth the investment for proper compliance and financial health monitoring.
Open a Business Bank Account
Keeping business and personal finances separate is also key. Open dedicated checking/savings accounts and apply for a business credit card. Business cards require your company’s information and focus on assessing potential based on factors like time in business, industry, and estimated revenue.
7. Obtain Licenses and Permits
Before launching your distribution startup, taking the time to get the right licenses and permits is crucial. Find federal license information through the U.S. Small Business Administration . The SBA also offers a local search tool for state and city requirements.
Some of the key licenses and permits for distribution companies include:
- Transportation permits – If providing delivery services, you likely need permits from the Department of Transportation for both the state you are based in as well as any states you will drive through.
- Business license – Most cities and counties require any business operating in their jurisdiction to be registered and licensed.
- Seller’s permit – If selling products wholesale or retail, you need a state seller’s permit to collect sales tax. You must file regular returns to remit taxes collected.
- Food handling permit – If distributing food or beverages, local health department permitting is required. This verifies safe food handling practices are in place.
- Alcohol distribution permit – For companies distributing alcohol, licensing with the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) is mandatory.
Failing to secure necessary permits and licenses right away can sink a distribution startup quickly. Work with local business attorneys and government agencies to determine which ones your business model requires before operations begin.
8. Get Business Insurance
Carrying adequate insurance is crucial to protect a distribution business from unexpected disasters and lawsuits. Without proper coverage, a single incident could destroy everything you’ve built.
For example, you could face major costs from:
- A burst pipe that floods your warehouse, damaging inventory. Without insurance, you’d pay for repairs and replaced stock out of pocket.
- A delivery truck accident that injures other drivers. You’d be liable for their medical bills without commercial auto insurance.
- An employee injury on-site led to a lawsuit. General liability coverage helps pay their claim so your assets are not at risk.
To get insured, first determine your risks. Consider property, general liability, commercial auto, workers comp, etc. Then shop quotes from providers like Hiscox , Next , and Progressive . Compare coverage options and pricing.
Apply by submitting details on your business operations and history. Policies can range from $500-$5,000+ annually depending on the level of protection.
Being underinsured can sink everything. With the right policies, you can rest easier knowing your distribution business is protected if the worst happens.
9. Create an Office Space
Having a dedicated office provides a professional home base for your distribution startup. It’s useful for tasks like payroll, accounting, sales calls, and meetings. Options range from working at home to leasing commercial space.
Home Office
A spare room can be converted into a home office cheaply. Provides flexibility and no commute. However, having staff onsite regularly could violate zoning laws. Isolation can also limit productivity. Expect costs of $100-$500 for basic furnishings and supplies.
Coworking Office
Coworking spaces like WeWork offer affordable shared offices on flexible terms. Great for solopreneurs. Access to amenities like lounges, conference rooms, and printing kiosks for around $300-$800 monthly. But noise and distractions could impact focus.
Retail Office
Retail space gives distribution companies a small storefront if direct-to-consumer sales are part of the model. Ranging from strip malls to standalone buildings, lease rates average $15-$30 per square foot. Benefits onsite visibility but requires manning the location.
Commercial Office
Commercial office leases provide dedicated space with privacy. Standalone small offices rent for approximately $800-$1,500 monthly. Multi-office suites in larger buildings average $1,000-$2,500 monthly. Ideal for stability but requires longer lease terms.
10. Source Your Equipment
Launching a distribution operation requires outfitting your warehouse, fleet, and teams with the right gear. From pallet racks to forklifts, various options exist to procure necessary supplies and equipment:
Major retailers like Costco , Sam’s Club , and BJ’s Wholesale sell a wide range of new equipment and bulk materials ideal for distribution. Products like pallet jacks, shelving, boxes, and labels are competitively priced. The downside is no chance to save on used items.
Buying Used
Check industry classifieds like BizBuySell to find listings for quality used warehouse and delivery equipment near you. Facebook Marketplace and Craigslist are other sources. Can get substantial savings over new. Ensure proper inspection and maintenance.
Equipment rental companies like United Rentals allow flexible access to equipment as needed. Pallet jacks rent for $25+/day and 4,000 lb. forklifts around $150+/day. No large upfront costs but expenses add up with ongoing frequent use.
Leasing equipment from companies provides long-term access to gear like conveyors, lifts, and racking without a huge initial investment. However, hiring general contractors can lock you into set monthly payments. Some flexibility on lease terms.
11. Establish Your Brand Assets
Creating a strong brand is crucial for distribution companies to stand out and be remembered. Your brand identity should be professional, and consistent, and convey your offerings.

Get a Business Phone Number
Getting a unique business phone number from providers like RingCentral shows customers you are legitimate. Dedicated numbers with custom greetings and voicemail boost credibility over using personal devices.
Design a Logo
Your logo is a pivotal part of your brand. Consider an icon, monogram, or abstract mark. Simple designs are memorable and scalable. Services like Looka offer affordable logo design and branding packages to fit your needs.
Print Business Cards
Business cards featuring your logo let sales reps seamlessly share your brand when networking. Signage and vehicle wraps should use your branding too. Vistaprint provides custom cards, banners, decals, and more to unify your visual identity.
Buy a Domain Name
Secure the ideal .com domain for your company quickly before someone else does through registrars like Namecheap . Make it easy to remember – similar to your name is best.
Design a Website
Building a modern, responsive website is a must through platforms like Wix or hiring a web developer from marketplaces like Fiverr . Showcase your capabilities and make it easy for prospects to learn about and contact your company.
12. Join Associations and Groups
Joining relevant local organizations and online communities provides invaluable connections and insights for distribution companies. Surrounding yourself with others in your industry helps you continuously learn and grow.

Local Associations
Search for associations like local chambers of commerce or industry-specific groups like the National Association of Wholesaler-Distributors . Meeting fellow business owners creates referral opportunities and mentorship. Attend association events whenever possible through organizers like NAW and the Houston Northwest Chamber .
Local Meetups
Regularly participating in local meetups and trade shows also expands your network. Sites like Meetup help find upcoming events near you. Bring plenty of business cards and product samples to share. Exchanging ideas in person fosters relationships.
Facebook Groups
Join industry-related Facebook Groups to tap into broader communities. The Wholesale Suppliers & Distributors in the US -SourceSupreme and Rellers / Dealers / Distributors / Manufacturers / Factory Price groups have thousands of members and discussions. Share your challenges and solutions while learning from experienced peers.
13. How to Market a Distribution Business
Implementing an effective marketing strategy is essential for distribution companies to attract new customers and expand. While referrals from your network provide a strong start, you’ll need diverse tactics to increase awareness and sales on an ongoing basis.
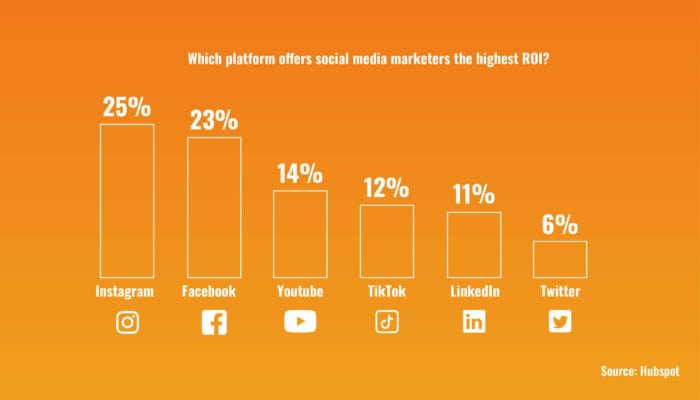
Personal Networking
Use your network to begin marketing your brand. Your friends, relatives, and past coworkers can assist with word-of-mouth marketing, passing out business cards, distributing fliers, and more.
Digital Marketing
Leveraging digital channels offers targeted, measurable promotion. Useful online marketing approaches include:
- Google Ads – PPC ads placed on Google Search alongside organic results based on keywords. Costs accrue when ads are clicked.
- Facebook Ads – Highly targeted ads within Facebook and Instagram based on detailed audience parameters to reach your ideal customers.
- SEO – Organic search optimization through keyword research, site optimization, content creation, and link building to rank highly in search engines.
- Email Marketing – Building an email subscriber list to promote services and offers through regular campaigns with a provider like Mailchimp.
- Social Media – Establishing accounts on platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and TikTok to interact with followers and share content.
- YouTube Channel – Creating video tutorials, testimonials, and other branded video content viewable on the world’s second-largest search engine.
Traditional Marketing
Traditional approaches still have value for raising local visibility:
- Printed Flyers – Inexpensive to design flyers highlighting your services and contact info to share around your region.
- Newspaper Ads – Local papers remain widely read and provide an established channel to reach nearby customers.
- Radio Spots – Short audio ads during talk radio shows related to business and entrepreneurship can boost brand awareness.
- Direct Mail – Targeted postcard and letter campaigns to businesses in your area that may need your distribution services.
With the right mix of digital marketing and selective traditional promotion, distribution companies can continually attract new accounts and grow revenue. Track results and iterate on what works best.
14. Focus on the Customer
Providing exceptional customer service is pivotal for distribution companies to retain accounts and drive referrals. How you support customers directly impacts your reputation and bottom line.
- Be responsive to inquiries with quick callbacks and emails, even when simply acknowledging requests.
- Set clear expectations for order fulfillment times and meet or beat them.
- Follow up post-delivery to resolve any issues immediately.
- Going above and beyond on service creates memorable experiences.
- For instance, directly assisting a retailer with setting up an initial product display and training staff on features builds lasting goodwill.
- Following up with customers routinely also opens the door for reorder reminders and sharing new offerings.
- Send occasional surveys to monitor satisfaction and identify areas for improvement.
- With the rise of review sites like Yelp, one bad customer experience with retail distributors can significantly damage their brand when shared publicly.
By making customer service a priority, distribution companies demonstrate reliability and value. This establishes trust that leads to repeat business and referrals that fuel sustainable growth.
You Might Also Like
January 15, 2024
0 comments
How to Start a General Contractor Business in 14 Steps (In-Depth Guide)
The construction industry is booming, with the overall market expected to reach $12.7 trillion ...
January 11, 2024
How to Start a Parking Lot Business in 14 Steps (In-Depth Guide)
The parking lot industry is a major market in the United States. As urban ...
November 13, 2023
Global distribution is on the rise, with more than $7 trillion earned in 2022. ...
October 19, 2023
How to Start a Recycling Business in 14 Steps (In-Depth Guide)
The global recycling industry makes more money than some people realize. The future is ...
Check Out Our Latest Articles
How to start a headstone cleaning business in 14 steps (in-depth guide), how to start a steam cleaning business in 14 steps (in-depth guide), how to start a dryer vent cleaning business in 14 steps (in-depth guide), how to start a yard cleaning business in 14 steps (in-depth guide).

COMMENTS
Business Overview. KitchenWare Distributors is a startup distribution company located in Long Beach, California. The company was founded by Nelson Fuller, a former senior executive in a kitchenware company based in Chicago, Illinois. Nelson made over ten million dollars in kitchenware sales during the past two years for his former company, and ...
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a distribution company business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of distribution company that you documented in your company overview.
Wheelie Deals is a wholesale distributor of bicycles and bicycle parts, focusing on closeouts, discontinued models, seconds, etc. Before you write a business plan, do your homework. These sample business plans for wholesale and distribution businesses will give you the head start you need to get your own business plan done.
In its most basic form, wholesale distribution is all about the "spread," or profit margin, between what you bought the product for and what you sold it for. The bigger the spread, the bigger the ...
A comprehensive business plan for your distribution company contains seven key sections: executive summary, presentation of the company, products and services section, market analysis, strategy section, operations section and financial plan. 1. The executive summary. The executive summary of a distribution company plan should start with a ...
Before launching your distribution company, a key legal step is obtaining an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS. This unique 9-digit number identifies your business for tax purposes. It’s easy to apply online at IRS.gov. Just follow these steps: Go to the EIN Assistant page: Apply for an EIN Online.