myCBSEguide
- Business Studies
- Class 11 Business Studies...

Class 11 Business Studies Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Case Study Questions are available on myCBSEguide App . You can also download them from our student dashboard .
For students appearing for grade 11 CBSE exams from the Commerce stream, Business Studies is a fundamental subject. Business Studies is considered to be quite interesting as well as an occupying subject as compared to all other core subjects of the CBSE class 11 commerce stream. To ace this CBSE exam, students are not only required to work hard but they ought to learn to do smart work too.
Among all the other core subjects of the Commerce stream i.e accountancy, economics and business studies, Business Studies is the one that is purely theoretical. It is termed to be comparatively easier and more scoring than the other mandatory subjects of the commerce stream. Many students who opt for the commerce stream after their 10-grade exams desire to learn in-depth about the business organizations and their work, for them the subject is of utmost importance. Business Studies is an essential component of the class 11 commerce stream curriculum.
In order to ace the subject the student needs to have conceptual clarity. CBSE has designed the syllabus for class 11 Business Studies so as to provide students with a basic understanding of the various principles prevalent in the Business organizations as well as their interaction with their corresponding environment.
Case Study Questions in class 11 (Business Studies)
Case-based questions have always been an integral part of the Business Studies question paper for many years in the past. The case studies have always been considered to be challenging for the students, for such questions demand the application of their knowledge of the fundamental business concepts and principles. Last year i.e- 2021 CBSE introduced a few changes in the Business Studies question paper pattern to enhance and develop analytical and reasoning skills among students.
It was decided that the questions would be based on real-life scenarios encountered by the students.CBSE not only changed the way case-based questions were formulated but also incremented their weightage in the Business Studies question paper. The sole purpose of increasing the weightage of case-based questions in the class 11 curriculum by CBSE was to drift from rote learning to competency and situation-based learning.
What is a case study question? (Business Studies)
In Business Studies, a case study is more like a real-world test of how the implementation works. It is majorly a report of an organization’s implementation of anything, such as a practice,a product, a system, or a service. The questions would be based on the NCERT textbook for class 11 Business Studies. Case-based questions will definitely carry a substantial weightage in the class 11 Business Studies question paper. questions.
A hypothetical text will be provided on the basis of which the student is expected to solve the given case-based question asked in the Business Studies class 11 exam. Initially, the newly introduced case-based questions appeared to be confusing for both the students and the teachers. Perhaps, they were reluctant to experiment with something new but now a lot more clarity is there that has made the question paper quite student-friendly.
Case study questions could be based on any chapter or concept present in the NCERT textbook. Thus, it is expected from the students to thoroughly revise and memorize the key business fundamentals.
Business Studies syllabus of class 11 CBSE
The entire Business Studies course is divided into 2 parts:
- Part A, Foundation of Business
- Part B, Finance and Trade
The class 11 Business Studies exam is for a total of 100 marks, 80 marks are for the theory and the remaining 20 for the project. Most of the questions are based on the exercises from the NCERT textbook. It is recommended to rigorously go through the contents of the book. A single textbook has been published by NCERT for Class 11 Business studies. There are a total of 10 chapters in this book divided into 2 parts.
CBSE Class – 11
Business Studies (Code No. 054)
Theory: 80 Marks Time: 3 Hours Project: 20 Marks
Case Study Passage (Business Studies class)
As part of these questions, the students would be provided with a hypothetical situation or text, based on which analytical questions will have to be answered by them. It is a must for the students to read the passage in depth before attempting the questions. In the coming examination cycle (2022-23), case-based questions have a weightage of around 30%. These questions can be based on each chapter in the NCERT book for Business Studies, grade 11.
Students must prepare well for the case-based questions before appearing for their Business Studies exam as these questions demand complete knowledge of the various concepts in their syllabus. CBSE plans to increase the weightage of such questions in the upcoming years.
Sample case-based Questions in Business Studies
Business Studies as a subject provides a way of perceiving and interacting with the business ecosystem. It is a core subject of the commerce stream that is purely theoretical and relevantly easier than the other compulsory subjects of the stream. Class 11 Business Studies syllabus is closely related to trade and commerce. The subject cannot be ignored as it is the foundation of many concepts and theories which are studied at an advanced level in class 12.
The case-based questions asked in the CBSE Business Studies question paper for class 11 are of two types:
As per the latest circular issued by CBSE on Assessment and Evaluation practices of the board for the session 2022-23, CBSE has clearly mentioned that competency-based questions including case studies will be different from subjective questions.
The questions can also be categorized on their difficulty level:
- Direct: such questions can be easily solved. Their answer is visible in the given passage itself.
- Indirect/ Analytical: such questions are confusing and tricky. These can be solved by the application of the theory or principle that is highlighted in the provided text.
How To Prepare For Case-based Questions? (Business Studies grade 11)
Students need to prepare well for the case-based questions before appearing for their class 11 Business Studies exam. Here are some tips which will help the student to solve the case-based questions at ease:
- Read the provided text carefully
- Try to comprehend the situation and focus on the question asked
- Analyze and carefully answer the question asked
- In general, the passage given would be lengthy in Business Studies case-based questions but their solutions are comparatively short and simple
- One can significantly save time if they follow a reversal pattern, that is going through the questions before reading the comprehensive case study passage.
- Answer in a concise manner
- One should concentrate on solidifying key fundamental principles/theories
- Go through the NCERT textbook in depth. The language used is crisp and simple.
- While providing solutions to the case-based question, pick the keyword/keyline based on which you are driving insights.
In order to excel in the Business Studies class 11 exam, one needs to ignore the shortcut techniques and get to read the NCERT textbook rigorously. Case studies can be easily solved if your key fundamentals are strong and clear. The best part of having these questions is that the asked question itself projects a hint of its answer. These simple points if kept in mind will definitely help the students to fetch good marks in case study questions, class 11 Business Studies.
Case study question examples in Business Studies
Here a re some given case study questions for CBSE class 11 Business Studies. If you wish to get more case study questions and other study material, download the myCBSEguide app now. You can also access it through our student dashboard.
Business Studies Case Study 1
Read the hypothetical text given and answer the following questions:
Manish, Rahul and Madhav live in the same locality. They used to meet and discuss their ideas. After discussing the recent fire breakout in their area, they decided to take fire insurance for their house or work area. Manish gets his house insured against fire for ₹1 lakh and during the policy period, his house gets damaged due to fire and the actual loss amounts to ₹2.5 lakh. The insurance company acquired the burning material and approved his claim. Rahul gets his godown insured against fire for ₹1 lakh but does not take enough precautions to minimize the chances of fire like installing fire extinguishers in the factory. During the policy, a fire takes place in his godown and he does not take any preventive steps like throwing water and calling the employees from the fire fighting department to control the fire. He suffered a loss of ₹1,20,000. Madhav took a fire insurance policy of ₹20 lakh for his factory at an annual payment of ₹24,000. In order to reduce the annual premium, he did not disclose that highly explosive chemicals are being manufactured in his factory. Due to a fire, his factory gets severely damaged. The insurance company refused to make payment for the claim as it became aware of the highly explosive chemicals.
How much can Manish claim from the insurance company?
- None of the above
How much compensation can Rahul get from the insurance company?
Which principle is violated in the case of Rahul?
- Insurable Interest
- Utmost Good Faith
How much amount is the insurance company liable to pay to Madhav if he files a case against it?
- Insufficient information
Which principle of Insurance is violated by Madhav?
- Insurable interest
- Subrogation
- Proximate Cause
The insurance company acquired the burnt material and approved his claim. Which principle of Insurance is highlighted in the given statement.
- (a) Mitigation
- (a) Utmost Good Faith
- (d) Subrogation
Business Studies Case Study 2
Sarthak Electronics Ltd. has a loss of Rs 15,00,000 to pay. They are short of funds so they are trying to find means to arrange funds. Their manager suggested a claim from the insurance company against stock lost due to fire in the warehouse. He actually meant that they can put their warehouse on fire and claim from insurance companies against stock insured. They will use the claim money to pay the loan.
- Will the company receive a claim if the surveyor from the insurance company comes to know the real cause of fire?
- Write any two Values which the company ignores while planning to arrange money from false claims.
- State any three elements of fire insurance
Business Studies Case Study 3
OLX and qickr are examples of well-known websites used to conduct business. Tarasha’s sofa set got spoiled in the rain. Her friend suggested that she should change the fabric so that it looks new and put it for sale on Olx. Tarasha followed her friend’s advice and got her sofa repaired so that it looked better and uploaded nicely clicked pictures on the website without disclosing the fact that it was damaged from the inside. She found a buyer and sold it for Rs 10,000. After five days the buyer found the real state of the sofa set and called Tarasha but she did not answer any of the calls.
- identify the type of business highlighted in the above case.
- Identify any two values which are overlooked by Tarasha.
- Explain any two benefits and limitations of e-business.
Advantages of case study questions in Business Studies
Class 11 Business Studies syllabus is not very vast but has to be focussed upon as it forms the base for your 12th grade Business Studies syllabus. Students are supposed to prepare themselves thoroughly from the NCERT textbook. The Case-based questions prominently focus on the real and current scenarios of the Business world. Approximately 30% of the question paper will comprise case study questions that demand high-order thinking and reasoning skills from the students. The students ought to practice class 11 Business Studies case-based questions from the various options available to them, so as to excel in the subject.
- Enhance the qualitative and quantitative analysis skills of students
- Provides an in-depth understanding of the key Business theories/concepts
- Inculcate intellectual capabilities in students
- Help students retain knowledge for a longer period of time
- The questions would help to discard the concept of rote learning
- Case studies promote and strengthen practical learning.
“Failure is success if you learn from it”
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Class 11th Business Studies - Internal Trade Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Business Studies Subject - Internal Trade, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Internal trade case study questions with answer key.
11th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Business Studies
Vishal Mega Mart is India's largest Fashion-led hypermarket chain with a footprint of over 204 stores, cumulative trading area in excess of 3 million square feet, in over 110 cities and towns across India. Vishal is sharply focused at the needs of consumers in Apparel, General Merchandise, Grocery and Personal Care in Tier-L, Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities and towns and is dedicated to offer the best value and choice to its millions of customers. Vishal offers clearly differentiated value to customers in the following product categories for which it has three departments. (a) Fashion: Fresh, trendy and affordable fashion comprising latest Apparel, Footwear & Lifestyle accessories collection across Men's, Women's & Kid's. (b) General Merchandise: Catering to all the household needs such as Kitchen-ware, Home Furnishings, Luggage & Travel Accessories, HomelKitchen Appliances, Toys & Sports etc. at best prices (c) Grocery and Household Needs: Catering to all daily needs with an extensive Grocery & Staples, Packed Food, Branded Personal Care and Household Needs products. Which type of large scale retail trade is being referred to here? How many departments are there? Mention two merits of the type of large scale retail trade identified in part I. Mention two demerits of the type of large scale retail trade identified in part I.
The retail sector of Indian economy is categorized into two segments such as organized retail sector and unorganized retail sector. The latter holds larger share of the retail market. The key drives of the growth in retail consumption in India are basically (i) Clothes, Textile & Fashion Accessories (ii) Food, Grocery & General Merchandise The top 10 companies which have the most shares in organized retail market of India are:
Organized retail that has arrived in different formats as follows; Organized retail that has arrived in different formats as follows; (a) Hyper markets (b) Cash and Carry (c) Supermarkets (d) Discount Stores (e) Department Stores (f) Convenience Stores (g) Neighborhood stores (h) MBO (Multi-Brand Outlets) Organized retailing in India has been largely explored in urban or in metro cities. It's largely successful in NCR and Mumbai Region and major parts of southern portion of India. The entry of Malls, the largest form of organized retailing, which are located mainly in metro cities, in proximity to urban outskirts turned out to be a catalyst for Organized retailing. Source: https:/ / dartconsulting.cco.in/market- new/stop-10 retail-chains-in-India-success-stories-of-organized-retailing-and-stories-of-organised-retail-failure-in-india/. Which type of large scale retail trade reliance fresh is engaged in? Give three features of this type of organization. Identify two values that these large scale retail organizations communicate to the society.
Delhi Consumer's Cooperative Wholesale Store Ltd is a registered society under Delhi Cooperative Societies Act. It was registered in the year 1962. It was set up for supplying Consumer goods to its affiliated various Primary Consumer cooperative Stores functioning in various parts of the metropolis. The need for establishment of this society arose during the post China aggression period when the prices of the essential commodities went sky-high in the market due to over-all shortages of consumer goods created by the traders by hoarding stocks for profiteering. The society was required to make bulk procurement of essential consumer goods from the sources and supply the same to the affiliated Primary stores & to public at large on reasonable prices, to enable those stores to sell the consumer goods to the public at lower prices than those prevailing in the open market. The main objective of the Store is:- (a) To supply consumer goods to the public at reasonable rates through its Primary Consumer's Cooperative Stores and public through retail outlets of Apna Bazar functioning in the length and breadth of the Metropolis; (b) To supply stationery items and other general goods at competitive prices to the Govt. Schools, Govt. Offices, Para Military Forces and other officials and non-officials Organizations; (c) Functioning as nominated agency of the government for the sale of liquor through its 75 retail outlets set up in various parts of the city; (d) Tq.assist government in distribution of scares items of consumer goods during the period of temporary shortage to overcome the difficulties of the general consumers and (e) to supply dietary items to those Government Department like Social Welfare DepartmentJNGOs which are engaged in the service of down-trodden, handicapped, old and destitute on reasonable rates. 1.Give three features of consumer cooperative society. 2.Which principle is followed by it in decision making? 3.How does it utilize its profits? 4.Identity two values that cooperative society communicates to the society.
Super markets are large retailing business units selling variety of consumer goods under one roof. They operated on low margin and have self-service facility. Generally these are located in shopping centers. Goods are kept in such a way that consumer can see all that is available and choose what he wants. They take a trolley, pick up what they like, put it in the trolley, go to cash counter, pay, and take their goods after showing bill to the guard. These generally operate like departmental stores but unlike departmental stores, they do not provide services like free home delivery, credit facilities, etc. they generally also not hire any sales staff to promote sales. 1. Discuss three features of super markets. 2. Differentiate between super market and departmental store.
Sanjeev and Rajeev are two friends. They are arguing on channel of distribution. Sanjeev claims that wholesalers are of no use and must be eliminated from chain of distribution. But Rajeev opines that wholesalers playa significant role in distribution. He claims that wholesaler provides many facilities to manufacturers and retailers. Rajeev is not convinced. He feels that middlemen only add to cost and hence goods should reach from manufacturer t final consumer directly. 1.Who of the two is right in your opinion and why? 2. Mention two services that wholesalers provide to manufacturers. 3. Mention two services that wholesalers provide to manufacturers.
*****************************************
Related 11th standard cbse business studies materials, other 11th standard cbse materials.

CBSE 11th Physics Motion in a Straight Line Chapter Case Study Questions with Answers
Cbse 11th physics units and measurements chapter case study questions with answers.

CBSE 11th Chemistry Structure Of Atom Chapter Case Study Question with Answers
Cbse 11th chemistry some basic concept of chemistry chapter case study questions with answers.

11th Biology Biological Classification Chapter Case Study Question with Answers CBSE
11th biology the living world chapter case study question with answers cbse.

Class 11th Applied Mathematics - Coordinate Geometry Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
Class 11th applied mathematics - basics of financial mathematics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - descriptive statistics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - probability case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - calculus case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - mathematical reasoning case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - algebra case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - numbers, quantification and numerical applications case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th biology - chemical coordination and integration case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, tamilnadu stateboard 11th standard cbse study materials.

Tamilnadu Stateboard 11th Standard CBSE Subjects


Unseen Passage
For Class 4 to Class 12
- Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 11
Business Trade and Commerce Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions
Please refer to Business Trade and Commerce Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions with answers below. These solved questions for Chapter 1 Business Trade and Commerce in NCERT Book for Class 11 Business Studies have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these solved problems properly as these will help them to get better marks in your class tests and examinations. You will also be able to understand how to write answers properly. Revise these questions and answers regularly. We have provided Notes for Class 11 Business Studies for all chapters in your textbooks.
Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Business Trade and Commerce
All Business Trade and Commerce Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of Standard 11 Business Studies. Please learn them and let us know if you have any questions.
Short Answer Type Questions
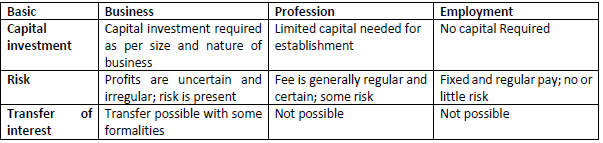
Question. Compare between Business, profession & Employment on the basis of the following: a) Capital Investment b) Risk c) Transfer of interest
Question. Explain any four objectives of business Answer : Objectives of Business are as follows: 1. Earning Profits: Business has to earn reasonable profit so as to sustain its growth and survive in the market 2. Market Standing: Business should have a better position in the market in relation to its competitors 3. Innovation: Business should come up with new ideas, inventions and new methods for sustainable growth and survival 4. Productivity: Productivity is ascertained by comparing the value of output with the value of input. Business must work efficiently and effectively so as to enhance its productivity.
Question. Distinguish between primary & secondary industry Give examples. Answer :

Question. Write difference among industry, commerce and trade on any five basis. Answer :
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. What provides the necessary link between producers & consumers with all those activities which are necessary for maintaining a free flow of goods & services? Discuss all those activities. OR In business activities, there are some activities that are involved in the removal of hindrances in process of exchange i.e. from the producer to the consumer Identify them. Also classify the activities which help in removing the following hindrances: (i)Hindrance of place ( ii)Hindrance of risk (iii)Hindrance of time (iv)Hindrance of finance (v)Hindrance of information OR Tea is mainly produced in Assam, while cotton in Gujrat & Maharastra but they are required for consumption in different parts of the country. How can this hindrance of place be removed? Also under what business activity will it be categorised. OR Commerce is the sum total of activities that remove hindrances in the free flow of goods from producers to consumers. Explain. OR How do trader remove the hindrance of person? Answer : Commerce refers to all those activities which are concerned with the transfer of goods and services from the producers to the consumers. It embraces all those activities which are necessary for maintaining a free flow of goods and services. The functions of commerce are as follows.

1. Removing the hindrance of person by marking goods available to consumers from the producers through trade. 2. Transportation removes hindrance of place by moving goods from the place of production to the markets for sale. 3. Storage and warehousing activities remove the hindrance of time by facilitating holding of stock of goods to be sold as and when required. 4. Insurance removes hindrance of risk of loss or damage of goods due to theft, fire, accidents etc. 5. Banking removes hindrance of finance-by providing funds to a businessman for acquiring assets, purchasing raw materials and meeting other expenses. 6. Advertising removes hindrance of information-by informing consumers about the goods and services available in the market.
Question. Profit maximization cannot be the sole objective of a business. Explain. OR “Profit is not an objective but a requirement of business.” Do you agree with the statement? Support your answers with reasons OR “Overemphasis on objective to earn profit may exploit the business”. What does a business should do to enable itself to bring the balance? Answer : Business is established for the purpose of earning profit. Profit plays a very important role in business for survival, growth, expansion but profit maximization is not the sole objective of business Business is an integral part of society. It makes use of resources of society. It earns profit by selling its products or services to members of society. So it becomes obligatory on the part of the businessman to do something for the society. The important social objective of business are as follows: 1. Quality goods and services at Fair Price: The first social objective of business is to provide better quality product at reasonable rice and in proper quantity on continuous basis to consumers 2. Avoidance of Anti-Social and Unfair trade practices: Anti-Social practices include hoarding, black marketing and adulteration. Making false claims in advertisements to mislead and exploit people is an example of unfair trade practice. Business should not indulge in such practices. 3. Generation of Employment: Now a days, employment is the biggest problem of society. Business should provide employment to more and more people living in the country. 4. Employee Welfare: Employees are a valuable asset and they make significant contributions towards the success of business. Another social objective of business, therefore, is to ensure welfare of employees by providing good working conditions, fair wages and facilities such as housing, medical and entertainment etc. such welfare facilities help to improve physical and mental health of employees. 5. Community service: Business should contribute something to the society where it is established and operated Library, dispensary, educational institutions etc. are certain contributions which a business can make and help in the development of community.
Question. JawaharLal prepares ‘Ghujiya’ for customers during Holi season every year. He prepared more ‘Ghujiya’ than he could sell this year. He employed women and children also and paid them less salary manufacturing on the packages. This way he generated profit for himself. (a)Do you think he is fulfilling all the objectives of business? (b) If not which aspects of this objective are not being fulfilled? (c)Write any two values lacking in JawaharLal. Answer : a) No, he is not fulfilling all the objectives of the business. Business is concentrating on the objective of profit earning. Business is an integral part of society. It makes use of resources of society. It earns profit by selling its products or services to members of society. So it becomes obligatory on the part of the businessman to do something for the society. b) Social objectives of business are not fulfilled. Business has two aspect of objectives. One is economic which means profit earning, productivity, innovation, market standing etc. Other aspect is social objective which consist of Quality goods, avoid unfair trade practices, employee welfare, community service, generation of employment etc. c) Two values lacking in Jawaharlal are as follows: 1 . Ethical practices: Jawarharlal has appointed women and children for manufacturing to generate profit. This behavior is unethical as Child labour is unethical practice in India. Business should not indulge in unfair, unethical trade practices. Anti-Social practices include hoarding, black marketing and adulteration. Making false claims in advertisements to mislead and exploit people is an example of unfair trade practice 2. Employee welfare: Employees are a valuable asset and they make significant contributions towards the success of business. Objective of business is to ensure welfare of employees by providing good working conditions, fair wages and facilities such as housing, medical and entertainment etc. such welfare facilities help to improve physical and mental health of employees. Jawaharlal paid less wages to manufacture ghujiya. Fair wages are not paid so, employee welfare objective is not met.
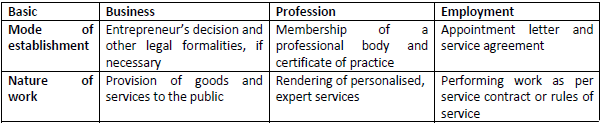
Question. Dr. Sanvi is an orthopedic surgeon in AIIMS Hospital and Dr Maruti, her friend is a Pediatrician who has set his own clinic. Dr Maruti’s wife, Ms. Aditi operates her Cosmetic store. Compare &differentiate the nature of tasks undertaken by them. Answer : Dr. Sanvi , an orthopedic surgeon in AIIMS Hospital is on employment whereas Dr Maruti , pediatrician having own clinic is following his profession and his wife Aditi owns Cosmetic store which is a business. Difference in the nature of tasks undertaken by them are given below:
Question. Zainab, Shelly &Ravina are friends. They have just completed a fashion designing course. They wish to start a business together. They have Rs.10,00,000 savings put together and are planning to take a bank loan of additional _ 10 lakhs. They have found a prime location in KarolBagh where they can set their boutique. They decide that they will initially not take very big orders. Based on this information, quote the lines associated with factors affecting the decision to start a business and classify them. Answer : 1. Selection of line of Business: They selected to start a boutique in Karol Bagh 2. Size of Firm : They wanted to start business on small scale. Therefore the risk factor is less and capital requirement can also be met. 3. Choice of form of ownership: The choice of the suitable form of ownership will depend on such factors as the line of business, capital requirements, liability of owners, division of profit, legal formalities, continuity of business etc. Here choice of form of ownership is partnership. They have to decide about the liability, division pf profit. They need to sign partnership deed 4. Location: Choice of location should be done based on the availability of raw material and labour, transportation and communication. Karol Bagh is the prime location as well as wholesale market. So, the choice of place is correct. 5. Finance: As they are bringing Rs 10 lac into business and taking an equal amount of loan to run the business. 6. Physical Facilities: They need to buy machine, equipment to start the business. 7. Layout: They need to draw a layout plan showing the arrangement of the facilities, so, as to haveefficient use of resources 8. Competent Workforrce: They need to have competent and committed workforce to perform the activities so that desired output is achieved. 9. Tax Planning: There are number of Tax laws which need to be taken into consideration before starting a business. 10. Start up: Now after taken into consideration the above point and checking the feasiability of the project, they can start with the launch of the boutique.
Related Posts
Internal trade class 11 business studies important questions, permutations and combinations class 11 mathematics important questions, class 11 mathematics important questions answers.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 – Business, Trade and Commerce
Home » CBSE » Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 – Business, Trade and Commerce

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 – Business, Trade, and Commerce
The Business Studies curriculum teaches students how to analyse, manage, assess, and respond to changes in the Business world. It gives you a new way to look at and interact with the Business world. Business, Trade and Commerce is the first chapter, and it lays the foundation for Business Studies. This chapter covers concepts such as the contribution of business activities in growth, concepts and objectives of a business, and categories and classification of businesses, and it carries significant weightage in the Business Studies syllabus. Students can easily access all concepts, important questions, and CBSE revision notes along with CBSE sample papers on the Extramarks website.
Quick Links
For Business Studies, students must read through chapters continuously to get good grades. Extramarks recognises the value of solving questions. Therefore, we’ve compiled them from various sources, including the NCERT Textbook, NCERT Exemplar, other reference books, previous exam papers, and so on. Our Business Studies experts have created step-by-step solutions to help students better comprehend the topics. Students can quickly register on the Extramarks website and access Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1.
Apart from Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1, Extramarks houses tons of material like CBSE previous year question papers, CBSE syllabus , CBSE extra questions, formulas, and so much more that the students can access and improve their understanding.
Get Access to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions 2022-23 with Solutions
Sign Up and get complete access to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions for other chapters too:
Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 1 Important Questions and Answers
The Extramarks team has compiled a thorough list of Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 from various sources. The questions comprise a wide variety of topics, including the contribution of business activities in growth, concepts and objectives of a business, categories, and classification of businesses and so on. These questions and their solutions help students better comprehend Business, Trade and Commerce.
Mentioned below are a few Chapters 1 Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions and their Solutions:
Q1. State the meaning of business.
Answer: The term ‘Business’ is derived from the term ‘busy.’ As a result, running business demands being busy. In a more exact sense, business refers to an occupation in which individuals regularly participate in purchasing, manufacturing, and selling products and services to make money. Production or acquisition of commodities for resale, as well as the exchange of goods or the supply of services to meet the needs of others, might all be part of this process.
Q2. State the objectives of business.
Answer: The following are some business objectives:
- Innovation: Every Business must develop novel ideas and innovations and apply them to stay afloat and develop.
- Productivity: When the value of the output is compared to the value of the input, productivity is established.
- Earning Profits: Any business entity open for business must make a decent profit to survive and develop.
Q3. State the different types of economic activities.
Answer: The following are some examples of economic activities:
- Profession: These tasks need specialised knowledge and abilities, and those participating are professionals.
- Employment: It is an economic activity in which individuals are paid for their services and are referred to as employees.
- Business: Business is an economic activity involving the trade of products and services for profit.
Q4. Which form of public sector was brought into existence by a special act of the parliament?
Answer: Statutory corporations are public format enterprises that were brought into existence by a Special Act of the Parliament. The act establishes the company’s functions, powers, rules and regulations, and relationships with other government agencies. As a result, they have government power and a significant level of private-sector operating flexibility.
Q5. Discuss the development of the indigenous banking system in the Indian subcontinent.
Answer: With the use of currency and subsequently with letters of credit, the indigenous banking system played a significant role in lending money and financing local and foreign trade. People began depositing precious metals with persons known as Seths as the banking system grew. Money became a tool for manufacturers to increase their output. Later, papers like Hundi and Chitti were used to conduct financial transactions. In ancient India, intermediaries played an essential role in commerce promotion. They were able to take chances in overseas trade because of the financial stability they provided. During the Mughal era and subsequently, the East India Company era, organisations like Jagat Seth had significant power. The expansion of commercial businesses was helped by the availability of loans and increased credit transactions.
India’s trade balance was excellent, with exports outnumbering imports by a wide margin. Manufacturers, traders, and merchants could obtain financing for expansion and development thanks to this system. Industrial and commercial banks grew into finance trade and commerce, and agriculture banks that gave farmers short- and long-term loans.
Q6. Explain the notion of business risk and any three sources of risks in light of this statement.
Answer: There is no way for a business to succeed without taking risks, as there is always the prospect of low earnings or even losses. In addition, changes in demand, technology, government legislation, and other factors place businesses at risk of profit unpredictability.
Uncertainties or unexpected developments in the business world can result in insufficient earnings or losses. The following are the three sources of company risk:
- Natural causes: These are caused by natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, and other natural disasters. These factors are beyond the control of most people, if not all.
- Human causes: Unexpected occurrences produced by man, such as employee carelessness, power outages, employee or customer dishonesty, and so on, are among these reasons.
- Economic causes: Economic reasons include changes and variations in the economy, such as uncertainty resulting from changes in technology and manufacturing methods, political upheavals, pricing fluctuations, and tax rates, among others.
Q7. Explain two business activities which auxiliaries to trade are.
Answer: The following are two examples of trade-related business activities:
- Transport and Communication: Most things are made in specific regions. Tea is grown predominantly in Assam; cotton is grown mainly in Gujarat and Maharashtra; jute is grown primarily in West Bengal and Odisha; sugar is mainly grown in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Maharashtra, and so on. On the other hand, these things are necessary for consumption in diverse parts of the country. The geographical barrier is broken down by transportation, whether by road, rail, or coastal ships. Raw materials are transported to manufacturing facilities, while finished commodities are transported from producers to consumers. Communication infrastructure is necessary in addition to transportation so that producers, traders, and consumers may communicate information. As a result, postal and phone services might be thought of as ancillary to economic activities.
- Banking and Finance: Financial resources are required to carry out business activities, including the acquisition of assets, the purchase of raw materials, and other expenses. A bank can provide the finances needed for a business. Consequently, banking helps firms overcome their financial difficulties. Commercial banks lend money through overdraft and cash credit facilities, loans, and advances. On behalf of traders, banks manage check collecting, payment transfer to other locations, and bill discounting. In international trade, commercial banks help exporters in collecting money from importers. Commercial banks also help entrepreneurs raise funding from the public.
Q8. “Profit is not an objective, but a requirement of business”. Do you agree with this argument? Give justifications for your answers.
Answer: Profit is, without a doubt, a necessary component of every business. The following are the reasons:
- Growth: Profits are required for corporate development, diversification, and expansion. Such growth tactics cannot be implemented by a company with little or little profit.
- Long-term survival: Only through making profit can a company thrive in the market in the long run. This is because the company requires money in all operations and domains. Finance is needed for everything from day-to-day spending to corporate development. As a result, if a company does not make a profit, it will be unable to pay its bills, develop, or survive in the market, eventually leading to its closure.
- Fulfill social objectives: The company’s other aims can only be met if it makes a substantial profit. If a company does not make enough money, it will not be able to meet social demands or contribute to society.
- Efficient performance: Profits serve as a motivator for both the owners and the staff. Greater earnings increase employee efficiency and productivity, resulting in higher quality performance.
- Reputation: Good profit margins allow the company to pay its costs on time, such as salaries, wages, dividends, and rentals. As a result, all stakeholders and stockholders are happy and satisfied with the company, resulting in a strong reputation and goodwill in the market.
- The reward for taking risks: A business takes many chances to keep operations running, and earnings are the payoff for taking those risks.
- Innovation: Nature’s law of change is unavoidable. As a result, to keep up with the changing and demanding environment, an organisation must continually evolve and invent. However, innovation necessitates highly trained personnel, extensive research, and cutting-edge technology, all of which are only achievable if the company is profitable.
Q9. Define Business. Describe its essential characteristics.
Answer: ‘Business’ is derived from the term ‘busy.’ As a result, running a business necessitates a high activity level. In a more exact sense, the industry refers to an occupation where individuals regularly participate in activities related to acquiring, manufacturing, and selling products and services to make money. Production or acquisition of commodities for resale, as well as the exchange of goods or the supply of services to suit the needs of others, might all be part of the activity.
- Production or procurement of goods and services: Before commodities may be sold to the public, businesses must either manufacture or purchase them. As a result, every business enterprise makes or acquires things from producers to resell to consumers or users. Consumable products, such as sugar, ghee, pens, notebooks, and so on, are examples of goods, as are capital goods, such as equipment, furniture, and so on. Services supplied to customers, corporations, and organisations include transportation, banking, energy, and other services.
- Exchange or sale of goods and services: Whether directly or indirectly, business involves transferring or exchanging goods and services for a monetary value. If something is made for personal consumption rather than for sale, it cannot be considered a commercial activity. For example, cooking meals at home for the family is not a business but cooking meals at a restaurant and selling them to others is. As a result, the sale or exchange of products or services between the seller and the consumer is one of the most significant elements of a business.
- Dealing with goods and services regularly: Trading commodities or services regularly is a necessary aspect of running a business. As a result, a single sale or purchase does not qualify as a business transaction. For example, if a person sells their household radio set for a profit, it is not considered a business activity. However, radio of sale sets regularly, whether in a store or from one’s house, is regarded as a commercial activity.
- Earning profit: Profit generation is one of a company’s primary objectives. No business can survive for long without making a profit. As a result, companies try to maximise profits through increased sales volume or cost reduction.
- Returns uncertain: Uncertainty of return refers to a lack of understanding about the quantity of money that a business will create over a specific time. To generate a profit, every business spends money on its operations. Therefore, it is impossible to estimate the amount of money that will be made. Furthermore, despite the company’s best efforts, there is always the possibility of losses.
- Element of risk: Risk is the degree of uncertainty associated with a loss of exposure. A bad or unfavourable event triggers it. Risk considerations include changes in customer taste and fashion, manufacturing processes, workplace strikes or lockouts, increased market rivalry, fire, theft, accidents, natural disasters, and so on. Risks are often seen as an inherent component of doing business.
Q10. The insurance sector is referred to as the tertiary industry. Explain.
Answer: Insurance serves both the primary and secondary sectors as a support service.
The tertiary industry is the part of the economy that provides services to clients, and it includes a wide range of enterprises, including schools, financial institutions, and restaurants. The tertiary sector, or service industry/sector, is another name.
Q11. What are the various types of industries?
Answer. The following are the various kinds of industries:
- Primary: All activities involving the extraction and production of natural resources, as well as the reproduction and growth of living beings, plants, and other living things, are included in this category.
- Secondary: These are related to the utilisation of materials that have been extracted in their natural state. These companies employ these materials to make items for end customers or for further processing by other companies.
- Tertiary: These oversee supporting primary and secondary industries and trade-related businesses.
Q12. How can a trader get rid of a person’s stumbling block?
Answer. The following are ways for a trader to get of a person’s hindrance:
- Getting rid of a person’s obstacle by making goods available to clients via trade from producers.
- Transportation removes a location’s barrier by delivering goods from their producing area to the marketplace for sale.
- However, insurance eliminates the risk of goods being lost or damaged due to disasters, theft, or accidents, among other things.
- Advertising eliminates the data barrier by keeping clients informed about the products and services available in the marketplace.
Q13. Define industry. Explain various types of industries giving examples.
Answer: The economic activities that result in converting resources into valuable items are referred to as an industry. Machines and technological abilities are employed in the production of a variety of things and the rearing of animals. There are three categories of industries:
Primary industry: These industries deal with items derived from natural resources. The primary goal of such sectors is to transform raw materials into consumable forms. Agriculture, hunting, mining, and fishing are examples of such businesses. Primary industries may be divided into two groups based on the actions done.
- Extractive industries: These industries deal with items that need to be polished before they can be utilised in other fields. Mining and fishing are two examples.
- Genetic industries: These businesses deal with breeding plants and animals and repurposing them.
Secondary industry: These industries deal with product manufacture, acquiring raw resources and converting them into things that may be further valued. These industries can be classified as follows:
- Manufacturing industries: Here, basic materials such as petroleum and wax derived from mineral oil are turned into final goods that are readily usable.
- Synthetic industries: These are essential components combined to create a new product. The cosmetics business is one example.
- Processing industries: The raw material is treated and refined before being turned into a finished product. The paper and sugar industries are two examples.
- Assembling industries: Assembling industries specialise in putting together numerous components to create the final product. Electronics, automobiles, and construction companies are just a few examples.
Tertiary industry: These industries act as intermediaries between primary and secondary industries. Baking and transportation are two examples of sectors that provide services to other industries.
Q14. What is commerce, and what role does it play in modern life?
Answer: The control of business among economic agents is referred to as commerce. It usually refers to exchanging goods, services, or other valuable objects between organisations or entities.
The following are the benefits of commerce:
- Between producers and customers, commerce serves as a catalyst.
- It creates chances for employment.
- It promotes trade on a worldwide scale.
- Assists in the development of new industries.
- Helps in times of need, such as natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, and droughts.
Q15. What factors are to be considered while starting a business? Explain.
Answer: The following are some considerations to make while starting a business:
- Selection of the line of business: The first considerations an entrepreneur must make are the kind and type of business to pursue. They will undoubtedly want to explore the sector of business and industry that gives the most profit possibilities. In addition, market client needs, the entrepreneur’s technical expertise, and excitement for producing a specific product will influence the selection.
- Size of the company: Another essential decision to make at the start of a firm is the company’s size or scope of activities. Some components favour a wide range of activities, while others want to keep it to a minimum. The enterprise will be started on a vast scale if the entrepreneur is certain that demand for the intended product will be substantial over time and that they can acquire the required finance. On the other hand, if market conditions are unknown and risks are considerable, a small business might be a preferable option.
- Ownership structure choice: In terms of ownership, the company might be a single proprietorship, a partnership, or a joint-stock corporation. Each kind has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Considerations such as the type of business, capital requirements, owner responsibility, profit split, legal formalities, company continuity, and interest transferability, among others, will decide the suitable form of ownership.
- Location of the business: When founding a business, the company’s headquarters is a crucial factor to consider. Any miscalculation here might lead to high production expenses, inconvenient access to the proper manufacturing inputs, or a failure to give clients the most excellent possible service. Likewise, when picking a site, raw materials and labour availability, as well as electricity and services like banking, transportation, communication, and warehousing, are all essential factors to consider.
- Obtaining funds: Financing is concerned with providing the required money for the start-up and continuance of a potential firm. Fixed assets like land, buildings, machinery, and equipment, as well as current assets like raw materials, books, debts, completed goods stock, and so on, require capital.
- Physical facilities: When launching a business, the availability of physical infrastructures such as machinery and equipment, as well as a building and accompanying services, is crucial. This decision will be influenced by the kind and scope of the firm, the availability of capital, and the production process.
- The layout of the plan: Once the necessity for physical facilities has been recognised; the entrepreneur should draft a layout plan explaining how they will organise them. Design refers to the physical arrangement of machinery and equipment needed to manufacture a product.
- Dedicated workforce: Every company needs qualified and devoted employees to do various duties to turn physical and financial resources into desired outputs. Because no single entrepreneur can do it all, they must assess the demand for skilled and unskilled labour and administrative staff. There should also be plans for how employees will be taught and encouraged to perform at their best.
- Tax preparation: Due to the country’s complex tax regulations, which touch almost every aspect of contemporary corporate operations, tax planning has become increasingly important in recent years. The tax responsibilities under various tax legislation and their influence on company actions must be evaluated by the business’s founder in advance.
- The beginning of a new business: Following the decisions mentioned above, the entrepreneur may go on with the actual business launch, which includes mobilizing various resources, completing the legal procedures, starting the manufacturing process, and initiating a sales advertising campaign.
Q16. Explain any five objectives of the business.
Answer: The following are the business’s objectives:
- Market standing refers to a company’s position in the market relative to its rivals. A company should improve its position by supplying consumers with competitive products and meeting their demands.
- Innovation: Innovation is the introduction of new ideas or techniques into how something is done or generated. Product or service innovation and product and service supply chain innovation in various skills and activities are two forms of innovation in any company. No company can thrive in a competitive climate without innovation. As a result, innovation has become a top priority.
- Productivity: To determine productivity, the value of output is compared to the value of inputs. It’s a measure used to assess efficiency. Every firm must aim for higher productivity by making the most effective use of available resources to secure long-term survival and profitability.
- Financial and physical resources: Any company must have material resources, such as plants, machinery, and offices, and financial resources, such as capital, to create and sell goods and services to its customers. The business enterprise’s purpose should be to acquire these resources and put them to good use in line with their demands.
- Profits: Businesses are operated to make a profit on the money invested. When we talk about profitability, we’re talking about profit as a percentage of invested capital. Every firm must produce a decent profit to secure its existence and growth.
Q17. A company’s primary goal cannot be only profit maximisation. Explain.
Answer: The primary goal of a business is to make money. Hence profit maximisation is the primary goal. However, because business exists in society and consumes society’s resources, it is not its sole goal.
As a result, it has various societal goals that could be pursued to protect the balance, as follows:
- Supply of desired services and goods: Businesses must provide high-quality goods and services with the necessary certifications. Customer pleasure must be the goal.
- Social and fair trade activities: Businesses must avoid black marketing, stockpiling, and lowering product quality or safety. Businesses must contribute to the betterment of society.
- Job possibilities: Businesses must generate employment opportunities for society, particularly for the less fortunate.
- Employee welfare: Businesses must promote employee growth and development, such as social and personal skill training and a pleasant working environment. Employees have a direct impact on productivity and profitability.
- Social welfare: Businesses must use their revenues to benefit society by establishing schools, charitable hospitals, and other vital institutions for society’s progress.
Key Topics Covered in Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Important Questions
Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 1 Important Questions covers the following key topics:
Classification of Activities
- Economic activities: Economic activities are any actions that are carried out to make money or provide a means of subsistence. A manufacturing worker, for example, or a schoolteacher, for example. It is mainly divided into three categories: employment, business, and profession.
- Non-economic activities: non-economic activities are those carried out for reasons other than profit, such as love, affection, sympathy, and so on—for instance, social work, religious activity, and so forth.
Role of Business in the Development of Economy
Since the beginning of time, people have been conducting business. As a result, there was a flow of products within and beyond the country, and the profits from such economic operations were utilised to fund more investments.
As an example, consider the following:
Hundi- It is a kind of trade employed in the past and consists of a contract that guarantees the payment of money, an unconditional promise or order, and the ability to swap it through proper discussion.
Patliputra, Peshawar, Taxila, Indraprastha, Mithila, Maduram, Surat, and other historic commercial centres emerged to import and export products.
A business is an economic activity carried out regularly and continuously to meet social demands while also earning profit by selling and acquiring products and services.
The following are the characteristics of business activities:
- Regularity in dealings
- An economic activity
- Exchange of goods and services creating value
- Profit earning
- Procuring goods and services
- Uncertainty of return
- Taking risks
Profession
A profession is any economic activity carried out by a person with specialised knowledge and abilities to benefit society.
Employment refers to any economic activity that involves doing labour for someone else in exchange for money.
Classification of Business activities
The following are the main categories of business activities:
It is primarily focused on the commercial production of products and services. It is then subdivided into the following groups: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
Primary industry: It encompasses all actions related to the extraction and production of natural resources and plant development. It is then subdivided into two sections:
- Extractive industries: These businesses offer specific essential raw resources, which are generally natural items. Farming, mining, and other activities are included.
- Genetic industries: These businesses specialise in breeding plants and animals for reproduction. Cattle breeding and poultry farming are two examples.
Secondary industry: These businesses are responsible for further processing the raw materials extracted in the primary sector to turn them into a completed product. Take, for example, iron ore mining.
It is then subdivided into two sections: manufacturing industries and the construction industry.
Manufacturing industry – These businesses process raw materials and create utilities to produce commodities. It’s further broken down into four sections:
- Analytical industry: Analytical industries separate and bifurcate distinct components from the source material to create various by-products from the same element. Petrol, diesel, and other fuels, for example, are all generated from the same raw material: crude oil.
- Synthetical industries: These businesses blend materials and components from several sources to create a new product. Consider the cement business.
- Processing industry: The processing industry is concerned with the extraction and processing of resources and raw materials to generate semi-finished or completed goods. The sugar industry, for example, the paper industry, the textile industry, and so on.
- Assembling industry: Assembling industries combine diverse components from many companies to create a new product. For example, various elements from many sectors are brought together to make and turn them into a television, computer, or automobile.
Construction industry – These businesses operate in the construction industry, which includes constructing dams, bridges, and buildings, among other things.
These businesses provide support services to primary and secondary sectors, allowing them to complete their tasks without interruption—for instance, in the banking, transportation, and communication industries.
All actions necessary for exchanging commodities and services are included in commerce. It also encompasses many activities that aid in eliminating obstacles like people, place, time, money, risk, and information that may arise during the exchange of products and services.
There are two sorts of activities in this category: trade and auxiliaries to trade.
Objectives of Business
- Market standing
- Earning profit
- Productivity
- Social responsibility
- Physical and financial resources
Business risks
Business risk is the risk of insufficient profits or losses due to uncertainty or unexpected events.
Nature of Business risks:
- Risk is a necessary component of every business. Therefore, it can only be decreased, not wholly abolished.
- It emerges because of unavoidable uncertainties such as natural disasters such as earthquakes and floods.
- The risk a company faces is determined by its type and size.
- Every firm should follow the rule of ‘no risk, no reward.’ As a result, profit is the incentive for taking risks.
Causes of Business Risks
- Natural causes: Natural disasters like floods and earthquakes are to blame. These factors are beyond the control of most people, if not all.
- Human causes: unexpected occurrences produced by man, such as employee carelessness, power outages, employee or customer dishonesty, and so on, are among these reasons.
- Other causes: Other reasons include anything that isn’t covered by the preceding categories, such as exchange rate changes and so on.
Factors for starting a business:
- Selection of the line of business
- Size of the company
- Choice of ownership structure
- Location of the Business
- Obtaining funds
- Physical facilities
- The layout of the plan
- Dedicated workforce
- Tax preparation
- The beginning of a new business
The briefly described topics in the sections given above are covered in the Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Important Questions.
Benefits of Solving Business Trade and Commerce Class 11 Important Questions
Business Studies requires a lot of constant reading and revision. Class 11 teaches the fundamentals of the subject and prepares the base for Class 12. We advise students to access Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1. Students will acquire confidence by solving important questions from the chapter by routinely solving problems and looking over our solutions.
Mentioned below are some benefits of solving Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1:
- The questions covered in Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 are based entirely on the chapter- Business, Trade, and Commerce.
- These essential questions are prepared by following the exam writing pattern. Therefore, going through these will help students prepare for exams too.
- Students can entirely rely upon these crucial questions as these are made following all the guidelines laid by CBSE and can help students for Chapter 1 Class 11 Business Studies important questions.
Extramarks provides comprehensive learning solutions for students from Class 1 to Class 12. We have abundant resources available on our website, along with essential questions and answers. Students can click on the links given below to access some of these resources:
- NCERT books
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE previous year question papers
- Important formulas
- CBSE extra questions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 Rita had a match stick factory in Nepal which got destructed by the recent earthquake. Highlight the risk.
A. Natural Causes
B. Human Causes
C. Economic Causes
D. Other Causes
Marks: 1 Ans
Natural Causes
Q.2 _______________is the bustling emporium that was even visited by Chinese ships to acquire items such as frankincense and myrrh.
C. Bangalore
D. Hyderabad
Q.3 Woolsworth was the Australias most valuable retail brand. The learning from Woolworths’ collapse was clear no business was too big, too old, or too close to the hearts of the British public to fail. Woolsworth shut down made its staff wept and the nation mourned. People of the High Street say that retail chains come, and retail chains go, but Woolworth’s was different. How important do you think it is to anticipate the failures also
Marks: 3 Ans
There is some amount of risk involved in every business. These can be minimised but not eliminated altogether. There are some of the causes of business risk that are beyond the control of humans. Causes can be natural, human or economic. Anticipating and providing for such risks is important to stop businesses from failing and leading to shutdown.
Q.4 Fresh Bakery Ltd. produces bread and cakes for sale in its 25 retail shops located across Southern part. The bakery needs goods and services from primary, secondary and tertiary sectors to make the bread and cakes and to sell the goods to customers.
a. Explain the interdependence of primary, secondary and tertiary sectors by using two examples.
b. Give one example of business in the primary sector that Fresh Bakery Ltd. might trade with. (1 marks)
c. Give two examples of businesses in the tertiary sector that Fresh Bakery Ltd. might trade with. (2 marks)
Marks: 5 Ans
a) Interdependence of primary, secondary and tertiary sector means that the sectors of industry are dependent upon each other and cannot work in isolation or without each other.
- Ingredients from the primary sector are used in the production of bread and cakes in the secondary sector.
- Fresh Bakery will have to buy insurance from the tertiary sector for the premises and employees.
- Fresh Bakery Ltd will have a bank account and a bank loan from the tertiary sector.
- Fresh Bakery Ltd may use the services of an advertising agency from the tertiary sector to design an advertising campaign for the company.
b) Example of business in the primary sector that Fresh Bakery Ltd. might trade with could include:
Farmer who produces flour, eggs, butter, milk.
c) Two examples of businesses in the tertiary sector that Fresh Bakery Ltd might trade with could include:
- Bank for finance and banking services (loan, financial advice)
- Transport for carrying in bulk: sugar, icing sugar, baking powder, salt, etc.
- An advertising agency for an advertising campaign.
Q.5 Mohan is a farmer who produces wheat to serve only his family. He does not generate any additional wheat for commercial sale purposes. To buy seeds and machinery, he has taken a loan from bank. Due to excessive rainfall, there was sever damage to wheat and it was all destroyed, which led to Mohan start working as a security guard for a business firm.
(i) In context to above case, state the economic activity that Mohan is engaged in.
(ii) Due to which cause of risk Mohan suffered damage
(iii) Can Mohan be considered as a businessman State your views in support of your answer.
Marks: 4 Ans
(i) In context to above case, state the economic activity that Mohan is engaged in is Employment.
Employment refers to the occupation in which people work for others and get remuneration or salary in return.
(ii) Due to natural cause of risk, Mohan suffered damage.
Natural causes of risk involve natural calamities resulting in heavy loss of life, property and income in business.
(iii) No, Mohan is not a businessman as he produces wheat for his family to eat and not for any commercial sale in the market.
Please register to view this section
Cbse class 11 business studies important questions, chapter 2 - forms of business organisation.

Chapter 3 - Private, Public and Global Enterprises
Chapter 4 - business services, chapter 5 - emerging modes of business, chapter 6 - social responsibilities of business and business ethics, chapter 7 - formation of a company, chapter 8 - sources of business finance, chapter 9 - small business, chapter 10 - internal trade, chapter 11 - international business, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. how to quickly grasp all the concepts of chapter 1 of class 11 business studies.
Constantly keeping in touch with the chapter is one way to understand the chapter. But referring to Extramarks Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 is the easiest way to comprehend this chapter thoroughly.
2. Can you suggest how to get above 90% in class 11?
Revising regularly is the key to success. Going through Extramarks Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 helps you comprehend the chapter entirely. Later you can make your notes or refer to notes made by subject matter experts on the Extramarks website. This will ensure your percentage goes up significantly.
3. Is Chapter 1 of Business Studies for Class 11 simple?
As it is the first time the students are introduced to this subject, Chapter 1 of Class 11 Business Studies may appear challenging. However, to avoid trouble with Business Studies, they must pay more attention and put in extra effort to grasp it. Students will better understand the chapter through regular study and practice, and they will lay the groundwork for the Class 12 board examinations.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.

NCERT Solutions for Class 11th: Ch 1 Business, Trade and Commerce
Ncert solutions for class 11th: ch 1 business, trade and commerce business studies, contact form.
- Commerce Important Questions
- Class 11 Business Studies
Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies
Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies are outlined by the subject matter experts from the latest edition of CBSE books. It is recommended for the students to practise the given Class 11 Business Studies chapter wise important questions with the answers. Learning these would definitely help the students in scoring good marks in the board examinations.
Chapter wise Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies
Important Questions for other Commerce Subjects:
- Important Questions for Class 11 Economics
- Important Questions for Class 11 Accountancy
- Important Questions for Class 11 Statistics
- Business Studies MCQs
Stay tuned to BYJU’S for more CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions, question papers, sample papers, syllabus and Commerce notifications.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
It is so nice study platform
- Share Share

Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

DK Goel Solutions
- Exam Questions
- Exam Questions Class 11
Business Studies Class 11 Exam Questions
Please refer to Business Studies Class 11 Exam Questions with solutions below. These important exams solved questions have been prepared based on the latest books and syllabus issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Our team of expert teachers of Class 11 Business Studies has designed these based on the latest examination guidelines and the type of questions expected to come in the examinations.
Exam Questions Class 11 Business Studies
We have provided exam questions with solutions for all chapters in Standard 11 Business Studies. You should learn these before the examinations as the answers have been designed to help you get better marks. You can click on the chapter-wise links below to access all problems and solutions for free. These will also help you to clear all concepts and improve your understanding of Business Studies in Class 11.
Chapterwise Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies

It is important for students to prepare for Class 11 Business Studies exams properly and practice questions and answers which have been designed based on the latest guidelines on the type of questions to be asked in the upcoming class 11 Economics examination. We have also provided MCQ Questions for Class 11 Business Studies which will be very useful for students. This year more MCQ-based questions and Case study-based questions are expected in examinations. We have provided all the latest questions which are expected to come in exams on our website. Students in Class 11 should download these questions in Pdf and share with teachers and friends.
Related Posts
Exam question for class 11 business studies chapter 10 internal trade, exam question for class 11 business studies chapter 1 business trade and commerce.

Exam Question for Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Business Trade And Commerce
Class 11 business studies chapter 1 business trade and commerce.
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Business Trade And Commerce, (Business Studies) exam are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions withinside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck withinside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students solve all of the questions and maintain their studies with out a doubt, we have provided step by step NCERT Solutions for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated Solutions as a way to similarly assist the students and answering the questions right.
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Business, Trade And Commerce
Class 11 business studies chapter 1 business, trade and commerce.
Short Questions
1. List any five major commercial cities of ancient India?
Commercial cities of Ancient India are:
1. Pataliputra
3. Indraprastha
4. Mohenjodaro
2. What is Hundi?
Hundi is a financial instrument that was developed in Medieval India to carry out transactions related to trade and credit. It is an unconditional order in writing made by a person directing another to pay a certain sum of money to a person named in the order. It is capable of being changed through transfer by valid negotiation.
3. List the major exports and imports in ancient India.
Exports items of India are -spices, wheat, sugar, indigo, opium, cotton, parrot, sesame oil, live animals and animal products such as hides, skin, horns, furs, tortoise shells, sapphires, pearls, quartz, crystal, lapis, granites, lazuli, turquoise and copper etc.
Imports items consisted of horses, animal products, Chinese silk, flax and linen, wine, glass, gold, silver, tin, lead, copper, rubies, coral, amber, etc.
4. What were the different types of Hundi in use by traders in ancient times?
Types of hundi are:
1. Shah Jog Hundi: Payable to a respectable man
2. Jokhmi Hundi: It is a type of hundi which is applicable on goods transported by ship
3. Nam Jog Hundi: Payable to the named party or his order
4. Dhani Hundi: Payable to owner of hundi
5. Jawabi Hundi: A type of hundi that resembles a money order.
6. Darshani Hundi: Payable on sight
7. Miadi Hundi or Muddati Hundi: Hundi that is payable after a specified period of time.
5. What do you understand by maritime trade?
A kind of trade that involves transportation of goods through sea using ships as the primary medium is called maritime trade. There are specific regulations for this kind of trade as there is risk involved in transporting goods through sea.
6. State the different types of economic activities.
Various economic activities are:
1. Profession: These are activities that requires specialised skills and knowledge and people involved in this are known as professionals
2. Employment: It is the type of economic activity where people get paid for the service they provide and are known as employees.
3. Business: It is the economic activity that deals with trading of goods and services with a motive to earn profit.
7. Why business is considered an economic activity?
Business is said to be an economic activity as the sole purpose of starting a business is to earn livelihood and also make profit from the activity. Hence, it is considered to be an economic activity.
8. State the meaning of business.
Business is the occupation where people engage themselves in activities that are related to purchase or production and sale of goods and services with the sole purpose of earning profit, and therefore produce or sell goods and services that are in demand.
9. How would you classify business activities?
Business activity can be classified as:
1. Industry
2. Commerce
Industry: It involves activities that are concerned with processing of raw materials to shape it into final product. The role of an industry is to provide value to the raw material so that it can be consumed by the end users (consumers). Industries are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary based on the function they perform.
Commerce: It is mainly concerned with trading and the related activities. It includes the exchange of goods and services. Commerce deals with two types of activities: trade and auxiliaries to trade. When goods are bought and sold, it is referred to as trade and auxiliaries to trade involved activities that include banking, transportation, advertising, communication. Commerce provides the necessary link that needs to exist between producers and consumers.
10. What are the various types of industries?
Industries can be broadly categorized into three types:
1. Primary Industries: These type of industries focus on getting raw material and the examples are mining, fishing and farming.
2. Secondary Industries: Such industries are mainly involved with manufacturing goods from raw materials and includes car, steel and electronics industry.
3. Tertiary Industries: These industries provide services and support to primary and secondary industries and with activities related to trade.
11. Explain any two business activities which are auxiliaries to trade.
Activities that facilitate exchange of goods and services are referred to as auxiliaries to trade. Two examples are:
1. Banking and Finance: Funds are necessary for acquiring assets, purchasing raw materials and also to meet other expenses. These funds can be obtained from a bank. Therefore, banking helps business activities to meet the required funds.
2. Advertising: It is an important component of marketing that involves promotion of products, and accurate promotion only help reach potential viewers that will result in sales.
12. What is the role of profit in business?
Profit is the only purpose for which business is done. Without profit a business will not sustain for long time. For a business to operate on a regular basis, a part of profit needs to be reinvested. It helps in growth of business. Role of profit in a business is that it is necessary for expansion of the business.
13. What is business risk? What is its nature?
Business risk, this term is referred to as the possibility of earning inadequate profits or losses due to unforeseen or unexpected circumstances. It can happen when demand for a particular product declines due to increased competition or change in customer preferences.
Nature of business risks are:
1. Profit related to risk: Profit is obtained as a reward for the risk taken in business.
2. Degree of risk taken depends upon the scale of operation of business
3. Risk is an essential part of any business.
4. Business risk arises due to uncertainties in business.
Long Questions answers
1. Discuss the development of indigenous banking system in Indian subcontinent.
Indigenous banking system played a prominent role in lending money and also in financing domestic and international trade with help of currency and later with the letter of credit. As the banking system developed, people began depositing precious metals with individuals who were known as Seths. Money became the means which manufacturers can use to produce more goods. Later, documents in the form of Hundi and Chitti were used for carrying out monetary transaction. In ancient India, for trade promotion, the intermediaries played a prominent role. The financial security offered by them helped in taking risks in foreign trade. The institutions such as of Jagat Seth also exercised great influence during the period of Mughals and later in the time of East India Company. The availability of loans and rise in credit transactions helped in growth of commercial establishments.
India enjoyed a great balance of trade with exports held the upper hand in comparison to imports. This system helped manufacturers, traders and merchants in getting funds for expansion and development. Industrial and Commercial banks evolved to become finance trade and commerce, agriculture banks which provided short and long term loans to finance those involved in agriculture activities.
2. Define business. Describe its important characteristics.
Characteristics of business are:
1. Business is considered to be an economic activity as the sole purpose of starting a business is for earning profit.
2. Business deals with procuring of raw materials and converting them into finished products and selling to consumers
3. Sustainability and the future growth of business is determined by the profit it is earning.
4. Business involves exchange of goods and service using a common medium i.e money.
5. Any business whether small or big will face business risks
6. There will be uncertainty of returns as the business may incur loss or gain profits
3. Compare business with profession and employment.
4. Define industry. Explain various types of industries giving examples.
Industry is referred to the economic activities that result in converting resources into useful goods. The use of machines and technical skills are involved which is used for producing variety of goods, breeding animals. There are three types of industries:
1. Primary Industries: These type of industries deal with products that are obtained from natural sources. The main purpose of such industries is to convert raw material into a form that can be consumable. Examples of such industries are farming, hunting, mining, fishing industries. Primary industries can be classified into two types based on the activities performed.
a. Extractive Industries: These industries deal with products that needs to be refined so that it can be used in some other industries. The examples are mining and fisheries.
b. Genetic Industries: These industries deal with breeding plants and animals and using them for further use.
2. Secondary Industries: These industries deal with manufacturing of products, they acquire raw materials and convert them into goods to which further value can be added. Such type of industries can be categorised as:
a. Manufacturing Industries: Here the raw materials gets converted into finished products to become readily usable such as petroleum, wax which is obtained from mineral oil etc.
b. Synthetic Industries: These combine raw materials to form a new product. Examples are cosmetic industry.
c. Processing Industries: Here the raw material is processed and purified in order to arrive at a final product. Examples are paper and sugar industries.
d. Assembling Industries: Combining various components in order to arrive at the final product is the speciality of assembling industries. Examples are electronics industry or automobile company or Construction Company.
3. Tertiary Industries: These industries serve as the facilitator of primary and secondary industries. These industries are mainly involved in providing service to the industries, Examples are baking, transportation.
5. Describe the activities relating to commerce.
There are two types of activities in commerce namely 1. Trade and 2. Auxiliaries to trade.
Buying and selling of goods is called trade whereas auxiliaries to trade involves activities such as banking, communication, transportation and advertising. Commerce enhances the link between consumers and producers.
1. Banking and Finance: It is one of the most important requirement to run any business. Without finance the free movement of goods is restricted. A banking arrangement helps in availability of credit to traders thus acting as an auxiliary to trade.
2. Warehousing: It refers to storing of goods till the time it is ready to be transported. Warehousing ensures proper storage and facilitates easy availability of goods.
3. Transportation: It helps producer in purchasing of goods and other necessary items from different places and also sell it in different areas. It helps in buying and selling of goods.
4. Advertising: Advertisements through various channels such as radio, TV helps in reaching the information to the audience and increase sale
5. Insurance: There will be risks in business and to cover against, you need to get insured.
6. Explain any five objectives of business
Business objectives can be discussed as follows:
1. Maximum Profit: The only motive of doing business is to earn profit. Growth prospects can be determined by the capacity to earn profits. The profit earned can be reinvested to earn higher growth.
2. Market Share: A business will have competition and by staying ahead of competitors a business develops a market share. Maximum market share can be captured by providing quality products at reasonable price.
3. Worker performance: A business will be performing at its best if the workers are motivated and satisfied. It requires a healthy working environment for the workers for making a great contribution.
4. Innovation: Innovation is the key to cutting down costs while improving performance, and by doing this a business can stay ahead of its competitors.
5. Social Responsibility: A business has certain responsibilities towards the society and these include removing poverty, unemployment and pollution etc. Fulfilling those responsibilities a business earns the goodwill.
7. Explain the concept of business risk and its causes.
Business risk, this term is referred to as the possibility of earning inadequate profits or losses due to unforeseen or unexpected circumstances. It can happen when demand for a particular product declines due to increased competition or change in customer preferences. It is very difficult to determine customer preferences as it is subject to change.
Business risk is of two types namely pure business risk and speculative business risk.
a. Pure Business Risk: In this type of risk, there is chance of losses or no loss whatsoever. Such risks can be associated with theft, various natural calamities and fire.
b. Speculative Business Risk: In this type of risk there is an equal chance of earning profit or incurring loss, such type of risk arises due to changes in government policy, competitor’s policy, price change or a change in consumer preferences.
Business risk is caused due to the following as discussed below:
1. Economic Causes: These types of business risk arises due to uncertainty surrounding the changes in policy of competitors, price change or changes in preference of consumer.
2. Natural causes: Natural calamities such as flood, earthquake and famine can cause extensive loss to a business. Such risks are beyond control.
3. Human causes: These are caused by negligence on part of humans like carelessness, riots, strikes are some examples.
4. Other causes: There are some events that are unpredictable such as political disturbances, interest and exchange rate fluctuations.
8. What factors are to be considered while starting a business? Explain.
It is common for a business to check all the aspects before starting the operations. Here are some of the important points to consider:
1. Line of Business: This helps in a determining the line of business as it will help boost confidence.
2. Scale of business: This determines the scale on which the business will be run.
3. Location: A location for setting up a business requires considering the following factors such as cheap labour, availability of raw material, good transportation facilities, sufficient power and infrastructural facilities.
4. Finance: Business is impacted in every step by finance, starting from purchasing raw materials to machinery and then the further investments needed for growth. Therefore, raising funds is necessary for business.
5. Efficiency of Workforce: A trained workforce is a pre-requisite to carry different business activities, therefore identifying skilled workforce is a must before starting a business.
6. Physical requirements of business: These include the tools, machinery and technology that increases the business efficiency. So it should be chosen as per the nature and scale of business.
Benefits of NCERT Solutions
NCERT’s Class 11 solution contains extremely important points, and for each chapter, each concept has been simplified to make it easier to remember and increase your chances of achieving excellent exam results. Exam Preparation References Here are some tips on how these solutions can help you prepare for the exam.
- This helps students solve many of the problems in each chapter and encourages them to make their concepts more meaningful.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 solutions encourage you to update your knowledge and refine your concepts so that you can get good results in the exam.
- These solutions are the best exam materials, allowing you to learn more about your week and your strengths. To get good results in the exam, it is important to overcome your weaknesses.
- Most of the questions in the exam are formulated in a similar way to NCERT textbooks. Therefore, students should review the solutions in each chapter in order to better understand the topic.
- It is free of cost.
Tips & Strategies for Class 11 Exam Preparation
- Plan your course and syllabus and make time for revision
- Please refer to the NCERT solution available on the cbsestudyguru website to clarify your concepts every time you prepare for the exam.
- Use the cbsestudyguru learning app to start learning to successfully pass the exam. Provide complete teaching materials, including resolved and unresolved tasks.
- It is important to clear all your doubts before the exam with your teachers or Alex (an Al study Bot).
- When you read or study a chapter, write down algorithm formulas, theorems, etc., and review them quickly before the exam.
- Practice an ample number of question papers to make your concepts stronger.
- Take rest and a proper meal. Don’t stress too much.
Why opt for cbsestudyguru NCERT Solutions for Class 11 ?
- cbsestudyguru provide NCERT Solutions for all subjects at your fingertips.
- These solutions are designed by subject matter experts and provide solutions to every NCERT textbook questions.
- cbsestudyguru especially focuses on making learning interactive, effective and for all classes.
- We provide free NCERT Solutions for class 11 and all other classes.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 10 - Internal Trade

CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter-10 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of Important Questions with Answers for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 10 - Internal Trade prepared by expert Business Studies teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books. Register for Online tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in CBSE examination.
Study Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter-10 Internal Trade
Very short answer questions (1 or 2 marks).
1. Differentiate between street trader and street shops
Ans: The differences between street trader and street shops are as follows:
2. What do you mean by a Cheap jack type of retail trade?
Ans: Retailers who operate temporary independent stores and continually move their firm from one location to the next, depending on the area's potential. They sell consumer goods as well as services such as watches, shoes, and bucket repair.
3. State any two advantages of supermarkets.
Ans: Two advantages of supermarkets are-
Keep a large variety of goods in various patterns, colors, and sizes so that purchasers can make better choices.
All sales are made in cash, and thus no bad debts exist.
4. Define Internal Trade
Ans: Internal trade refers to the buying and selling of goods and services within a country's borders. Internal Trade has the following characteristics such as:
Buying and selling takes occur in the home country,
Payments made or received in the home country
Only a few formalities for traders to complete.
5. List the two broad categories of trade.
Ans: Internal trade can be divided into two distinct categories:
Wholesale trade
Retail trade.
6. Which shops deal in specific line products?
Ans: Specialized stores deal in specific line products. Rather than selling a variety of products from multiple categories, these retail shops focus on selling a certain line of a product. Specialty stores are typically located in a central location where a big number of clients can be drawn, and they offer a diverse assortment of goods to customers.
7. Give two examples of chain stores
Ans: Walmart and Body Shop.
8. Mail order Houses provide a lot of convenience to the customers, yet they are not very popular. Why? Give one reason.
Ans: Ordering via mail Houses offer a lot of convenience to customers, but they aren't extremely popular because they need a lot of money to spend on product promotion, moreover due to chances of fraud by traders, the consumers are apprehensive regarding this method.
9. What are Vending Machines? Which type of goods are suitable for vending machines?
Ans: In many nations, coin-operated vending machines are handy for selling a variety of things such as hot beverages, platform tickets, milk, soft drinks, chocolates, newspapers, and so on. Vending machines are excellent for selling pre-packaged brands of low-cost products with high turnover and consistent size and weight. The initial cost of installing a vending machine, as well as the ongoing costs of maintenance and repair, are, nevertheless, rather significant.
10. Distinguish between a wholesaler and retailer. Give only one point of difference
Ans: The point of difference between wholesaler and retailer is given below:
Short Answer Questions (3 or 4 Marks)
11. Sandeep& Sons, Delhi orders pearl jewellery from Nasir Bros, Hyderabad. They enter into a contract and make certain that the payment will be made only on receiving the goods at Delhi in their Shop. Identify the term of trade in the above example
Ans: This example is a Cash-On-Delivery (COD) type of trade.
12. Discuss services of retailers to manufacturers and wholesalers.
Ans: The services of retailers to manufacturers and wholesalers are:
Help in the distribution of goods: Retailers assist in the dissemination of manufacturers products by making them available to end-users who may be dispersed across a vast geographic area. As a result, they supply place utility.
Personal selling: Retailers relieve producers of this work and considerably assist them in the process of actualizing product sales by engaging in personal selling efforts.
Enabling large-scale operations: Allows them to function at a somewhat large scale, allowing them to focus totally on their other tasks.
Collecting market information: Retailers are a significant source of market data about customer tastes, interests, and attitudes, which can help marketers make critical marketing decisions.
Help in promotion: Manufacturers and distributors must engage in a variety of promotional activities in order to improve product sales. Retailers take part in these activities and encourage product sales.
13. Identify the type of itinerant trader from the following:
a) Traders who open their shop on a fixed day.
Ans: Market vendors/traders: Small retailers that open their stores at different locations on specific days or dates are known as market vendors/traders. They primarily serve people from lower socioeconomic backgrounds and specialize in low-cost consumer goods.
b) Petty retailers who have temporary independent shops.
Ans: Cheap Jacks : Retailers with temporary independent businesses in a business district are known as cheap jacks. They continually move from one location to the next, depending on the area's potential. They sell consumer goods as well as services such as a watch, shoe, and bucket repair.
c) Traders commonly found in populated areas.
Ans: Street Traders: Street traders are the ones who sell consumer items of everyday utility, such as stationery, eatables, readymade clothing, newspapers, and magazines, and are usually found in places where a large floating population congregate, such as around railway stations and bus stops.
14. Jyoti has shifted residence to a new settlement colony. There are no retail shops nearby. What difficulties will Jyoti face in the above case?
Ans: Jyoti's challenges in the aforesaid circumstances are listed below:
She will be deprived of the convenience of having items available whenever she needs them.
She will not be informed about new products that are introduced to the market.
She will have to hoard goods, sometimes at higher prices in the absence of retail shops.
She will face inconvenience because she would have to travel a long distance for everything.
She’ll not be able to take advantage of the credit facility, as generally retail shops provide such facilities.
She will not have access to a wide range of products under one roof.
She will not be able to take advantage of after-sale services such as home delivery.
15. Identify the types of retailers in the following statements:
(a) Rohan displays his goods on bus-stands or pavements.
Ans: Street traders: They are the retailers who sell consumer items of everyday utility, such as stationery, eatables, readymade clothing, newspapers, and magazines, and are usually found in places where a large floating population congregate, such as around railway stations and bus stops.
(b) Mangal sells goods from one street to another, from one locality to another.
Ans: Peddlers and hawkers: They are little producers or petty traders that sell their items at consumers' doorsteps while travelling from place to place on a bicycle, a hand cart, a cycle-rickshaw, or on their heads. They primarily trade in uncommon and low-value items.
(c) Rajkumar sells only school uniforms.
Ans: Specialty stores: These retail establishments specialize in the sale of a specific line of a product rather than selling a variety of products of various categories. Specialty stores are typically located at a central location where a big number of clients can be drawn, and they offer a diverse assortment of goods to customers.
(d) Deepanshu deals only in second-hand books.
Ans: Second-hand goods stores: These stores sell used or second-hand goods such as books, clothes, autos, furniture, and other household items. These shops selling used goods may be in the form of a stall with very little structure like a table or a temporary platform to display the books or they may have reasonably good infrastructure, as in the case of those selling furniture, used cars, scooters, or motorcycles, which are located at street crossings or in busy streets.
16. A manufacturing Co. opens shops at different locations in India. He sells goods on cash only. The shops have identical decorations. The prices of goods are fixed. In this way they eliminate unnecessary middlemen thus benefiting the consumers.
(a) Identify the type of shop referred to.
Ans: Multiple store or a chain store. There are a lot of chain stores with comparable appearances that have sprouted up in various locations across the country. These various stores usually sell standardized and branded consumer goods with a high turnover of sales. These stores are owned by the same company and use the same merchandising tactics, as well as the same products and displays.
(b) Elaborate characteristics of such shops
Ans: The following are the characteristics of chain stores:
The goods are dispatched to each of these shops from the head office, which is located in a reasonably populous area where a significant number of clients may be approached.
The shop is under the direct supervision of a Branch Manager, who is responsible for its day-to-day management.
The head office is in charge of creating policies and ensuring that they are executed.
The prices of goods in such shops are fixed, and all sales are conducted in cash.
17. Vishal buys goods in larger quantities and sells them to small businessmen.
(a) Which type of trader is Vishal?
Ans: Vishal works as a wholesaler. A wholesaler buys the product in bulk from the manufacturer and sell it to the retailer/businessman. Because it acts as an intermediary between manufacturers and retailers, the wholesaler is an important link in the distribution network. The retail stage of distribution is where items are transmitted from the hands of small businessmen to the hands of consumers.
(b) State services to consumers of Retailers.
Ans: Services to consumers are as follows:
Regular availability of products: Maintain consistent availability of numerous products from various manufacturers. This allows buyers to purchase things as and when they are required.
New product information: Retailers convey crucial information to customers about the arrival, distinctive characteristics, and other aspects of new products by arranging for effective product display and through their personal selling efforts.
Convenience in buying: They offer tiny quantities of goods in close proximity to residential areas and are open for long periods of time. Hence, the customers appreciate the ease and convenience with which they can purchase things.
Wide selection: Maintain a diverse inventory of products from various producers. Customers can choose from a large range of products with varied styles, colors and designs as a result of this.
After-sales services: Provides after-sales services such as home delivery, spare part supply, and customer assistance.
Provide credit facilities: Allow regular customers to apply for credit. As a result, the latter can increase their consumption.
18. Mention differences between departmental store and multiple shops.
Ans: The differences between departmental store and multiple shops are:
19. Explain the features of Departmental store
Ans: The features of a departmental store are:
Type of Customers: Provide the best possible service to consumers in the upper section of society for whom pricing is secondary.
Location: In the heart of a city, in a central location that caters to a big number of customers.
Organization: Due to the vast size of these establishments, they are usually organized as a joint-stock company with a board of directors.
Services: A departmental store incorporates both retail and warehouse services.
Purchase and sale mechanism: They have centralized purchasing systems and sales are decentralized in several departments.
20. Enumerate the limitation of Multiple shops.
Ans: Limitations of Multiple shops are:
Limited choice: They do not sell products made by other companies. As a result, consumers have a limited choice of goods.
Heavy reliance on top level management: They have to rely on the top level for all advice, which takes away their ability to use their creative abilities to satisfy customers.
Lack of effort: Employees' lack of effort can often lead to indifference and a lack of personal touch.
Losses: Because of enormous stocks sitting unsold at the central depot, management may have to bear significant losses.
21. Explain two features, merits, and limitations of supermarket
Ans: Features
Generally carries a full range of food and grocery items, as well as non-food convenience items.
Under one roof, they may find a variety of things to meet their needs.
Merits
There are no bad debts because sales are made on a cash basis.
The advantages of large-scale buying and selling include decreased operating costs.
Limitations
Because the principle of self-service is followed, purchasers' purchasing power is limited.
As a result, they do not receive any personal attention.
Long Answer Questions (5 or 6 Marks)
22. Discuss the services of a wholesaler to the manufacturer and retailer.
Ans: Services to Manufacturers
Large-scale production facilitation: Wholesalers receive modest orders from a variety of shops and pass them on to manufacturers.
Taking chances: Wholesale merchants deal in commodities in their own name, take delivery, and store goods purchased in huge amounts in their warehouses; they face a variety of dangers, including price drops, theft, pilferage, spoilage, and fire.
Assistance with finances: They almost always pay in cash for the products they acquire. Sometimes they also advance money to the producers for large orders, so the manufacturers do not need to keep their capital in stockpiles.
Expert advice: Because wholesalers have direct contact with retailers, they may provide expert advice to manufacturers on a variety of topics, including customer tastes and preferences, market conditions, competitive activity, and the features that buyers like.
Assistance with the marketing function: Wholesalers relieves manufacturers of many marketing responsibilities, allowing them to focus on their core business. They handle the distribution of commodities to a number of retailers, who then sell them to a huge number of customers dispersed over the country.
Facilitate production continuity: Wholesalers ensure production continuity by purchasing items as they are produced and holding them until they are needed by retailers or customers.
Storage: Wholesalers receive items when they are manufactured in factories and store them in their godowns/warehouses, thus saving time.
Services to Retailers
Availability of goods: Relieves retailers of the effort of collecting goods from numerous manufacturers and keeping large inventories of the same
Marketing support : The wholesalers aid the retailers by performing various marketing duties and providing support. The retailers earn good profit since it helps them increase demand for various new products.
Credit: Wholesaler credit is usually extended to their frequent customers. As a result, retailers can run their businesses with a modest amount of operating capital.
Specialized knowledge: Wholesalers specialize in a single product line and are well-versed in the industry; they pass on the benefits of their specialized knowledge to retailers.
Risk sharing: By purchasing items in smaller quantities, businesses can minimize risks such as storage, pilferage, obsolescence, price reductions, and demand variations.
23. Why are consumer cooperative stores considered to be less expensive? What are their relative advantages over other large scale retailers?
Ans: A consumer cooperative store is a business that is owned, operated, and controlled entirely by consumers. The goal of such stores is to reduce the number of intermediaries who raise the cost of production and, as a result, provide better service to members.
Cooperative stores typically purchase large quantities of goods directly from manufacturers or wholesalers and resell them to consumers at low costs. The profits made by consumer cooperative stores over the course of a year are used to pay out bonuses to members and to build up general reserves and general welfare funds or similar funds for the members' social and educational benefits. This is why consumer cooperative stores are thought to be a good idea, and are less expensive.
The following are some of the benefits of consumer cooperative stores versus large-scale retailers:
Simple and easy to form: A consumer cooperative society is simple to create, and members' liability in a cooperative store is limited to the amount of capital they invest.
Assists the retailers: Relieves retailers of the effort of collecting goods from numerous manufacturers and keeping large inventories of the same.
Democratic formation: It is run democratically. Each member has one vote, regardless of how many shares he or she owns.
No middlemen: The elimination of middlemen leads to cheaper prices for members' consumption items.
Cash sales: The majority of items sold in consumer cooperative stores are paid for in cash.
Convenient location: Consumer cooperative stores are typically located in public settings where members and others can easily purchase the goods.
24. Discuss the features of fixed shop retailers? Explain different types of fixed shop small retailers?
Ans : Fixed shop retailers are retail stores that have a constant location where they offer their products. As a result, they do not relocate from one location to another to service their consumers.
Characteristics:
More resources and the ability to operate on a wide scale.
Deal with a variety of items, including both consumer durables and nondurables.
High customer trust exists.
There are four types of Fixed Shop Small Retailers:
General stores
These stores stock a wide range of products necessary to meet the day-to-day needs of customers in the surrounding areas. They stay open for long periods of time at convenient times and frequently offer credit to some of their regular customers.
Specialty store
Shops that specialize These retail establishments specialize in the sale of a specific line of a product rather than selling a variety of products of various categories. Specialty stores are typically located in a central location where a big number of clients can be drawn, and they offer a diverse assortment of goods to customers.
Street stall holders
Vendors on the street. They cater to roving clients and specialize in low-cost items such as hosiery, toys, cigarettes, soft drinks, and so on. They receive their goods from both local and wholesale sources. Because a stall's total size is so small, it can only hold a minimal amount of merchandise.
Second-hand good shops
A store that sells used products These stores sell used or used items such as books, clothing, autos, furniture, and other household items. Second-hand stores may be set up in the form of a stand with very little structure, a table or a makeshift structure, near street crossings or in busy streets.
25. Discuss the features of Mail order houses? State their merits and limitations?
Ans: Mail order houses are retail establishments that sell their merchandise via mail. In this sort of trading, there is usually no direct personal contact between customers and sellers.
Reaching the potential customers : To obtain orders, potential consumers are contacted by newspaper or magazine advertisements, circulars, catalogs, samples and bills, and price lists mailed to them.
Careful Inspection: When the orders are received, they are carefully inspected for compliance with the purchasers' specifications, which are carried out through the post office.
Payment options: There may be a variety of payment options available, such as cash payment, demand draft etc.
Suitability: Only goods that can be:
graded and standardized,
easily transported at a low cost,
have ready market demand,
available in large quantities throughout the year,
involve the least amount of market competition,
described through pictures and other means are suitable for this type of trading.
Merits of Mail order House
Less finances required: It may be established with a small amount of money.
Eliminates middlemen: It eliminates the need for unnecessary middlemen between buyers and sellers.
No bad debts : They do not provide credit to its consumers, thus there is no risk of bad debt.
Market potential: Big market potential because mail can reach a large number of people across the country.
Delivery: The goods are delivered at the customer’s place, and hence the customers need not go out to purchase the goods
Limitations of Mail order House
No personal contact: There is no personal contact between buyers and sellers under the mail order selling system, which increases the chances of misunderstanding and mistrust
Investment on product promotion: There is a lot of money spent on product promotion.
Services: There is no after-sales service, which is crucial for customer satisfaction
No credit facility: They don't provide credit facilities that discourage the customers from buying goods through this medium.
Chances of fraud: The chances of fraud exists in such a medium. At times dishonest traders defraud customers by making false claims about products or failing to honour commitments.
26. Uma, a village girl, comes to Delhi to visit her relatives. She goes with her cousin to a shop, which is centrally located. She becomes astonished by the varieties of goods which are sold here.
(a) Identify this type of shop.
Ans: A departmental store is a large store that sells a wide range of products organized into well-defined sections, to meet almost every customer's demand under one roof. It is divided into several departments, each of which focuses on a single type of product.
(b) Quoting lines from the above paragraph describe two characteristics of the shop.
Ans: The following are the characteristics of departmental stores:
Central Location: These are located at a central place in the heart of a city which caters to a large number of customers.
Quotation: “She goes with her cousin to a shop, which is centrally located.”
Wide range of products under one roof: Departmental stores are known for multifarious products and services with varied styles, colours, designs all available under one roof.
Quotation: “She becomes astonished by the varieties of goods which are sold here.”
(c) Explain advantages of such shops.
Ans: The following are some of the benefits of department stores:
They draw a huge number of clients due to their central location.
Provides a vast range of items under one roof
Aims to provide maximum services to clients
Organized on a very big scale, allowing them to reap the benefits of large-scale operations, notably in terms of purchasing goods
They spend a lot of money on advertising and other promotional efforts to assist them to increase their sales.
27. Nirmala orders a mixer on the basis of an advertisement in a newspaper specifying the features, price, delivery terms. It specified that the terms of payment will be VPP only.
(i) Identify this type of retail business.
Ans : Mail order houses are retail establishments that offer their wares via mail. In this sort of business, there is usually no direct human contact between the buyers and sellers. Potential consumers are approached for orders through newspaper or magazine advertisements, circulars, catalogs, samples and bills, and price lists mailed to them. When the orders arrive, they are thoroughly inspected for compliance with the purchasers' demands, which are then carried out through the post office. The goods could be sent using Value Paid Post (VPP). The goods are shipped via post and are only delivered to customers on making this agreement.
(ii) Explain two advantages and two limitations of them
Ans: Advantages
Disadvantages:
28. A London based manufacturing co. manufacturing washing machines wish to add 2 new products in India namely AC’s and Refrigerators. Out of a lot of 10 applicants the co. chose two wholesale firms (headed by females) whose proposals were very competitive and attractive. The wholesaler firm of AC’s hired the services of a (differently able retailer) Hari at competitive prices to sell AC’s in Delhi, Hari informs his wholesaler firm's head that the consumers of Delhi wish that their houses are cold when they reach their homes in the scorching heat of Delhi.
(a) Explain three services rendered by retailers to wholesalers or manufacturers.
Ans: Three services rendered by retailers to wholesalers or manufacturers are as follows:
Help in the distribution of goods
Assist in the dissemination of their products by making them available to end-users who may be dispersed across a vast geographic area. As a result, they supply place usefulness.
Personal selling
Retailers relieve producers of this work and considerably assist them in the process of actualizing product sales by engaging in personal selling efforts.
Enabling large scale operations
Allows them to function at a somewhat large scale, allowing them to focus totally on their other tasks.
(b) Identify two values which are being adhered to in the above paragraph
Ans: The following are the values that are upheld:
Women's Empowerment: The company chose two wholesale enterprises (both led by women) whose proposals were extremely competitive and appealing, resulting in women's empowerment.
Social Concern: The AC wholesaler firm enlisted the help of Hari, a (differently able retailer).
29. Briefly explain the role of Chamber of Commerce and Industry in promoting internal trade?
Ans: Role of Chamber of Commerce in promoting internal trade is as follows:
Interstate movement of goods
The Chambers of Commerce and Industry assist in a variety of operations related to the interstate movement of products, including car registration, surface transportation policies, and highway and road building.
Octroi and other local levies
These are collected from people entering the state or municipal bonds. The Chambers of Commerce make every effort to ensure that their regulations do not obstruct smooth transportation or local trade.
Harmonization of sales tax structure and Value Added Tax
The sales tax is a significant source of revenue for the state. For promoting trade balance, a sensible sales tax structure and uniform rates among states are critical.
Weights and Measures and prevention of duplication brands
Weights and measures laws, as well as brand protection laws, are required to defend the interests of both consumers and traders. These must be carefully enforced.
Promotion of Agro based products
The chamber of commerce frequently interacts with various agro based associations, consumer cooperatives, farming associations etc., and assists them in selling and promoting their products.
Excise duty
The central government's primary source of revenue is the excise tax, which is levied throughout all states. The excise policy has a significant impact on the pricing system.
Promoting sound infrastructure
The Chambers of Commerce and Industry meet with government departments to discuss infrastructure investments.
Labour legislation
Labor policy that is straightforward and flexible is beneficial to industries that want to maximize productivity and create jobs. The government and the Chambers of Commerce and Industry are continually focusing on such issues.

CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Business, Trade and Commerce. Answers of all short and long answers in proper explanation are given here on this webpage. Completely solved chapter end exercise and extra question answers are also included for practice. Important Questions for viva and practical are also given to revise this chapter.
Download Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Study Material in Hindi and English
- Study Material in English Medium
- Study Material in Hindi Medium
11th Business Studies Chapter 1 Short Answer Questions
List any five major commercial cities of ancient india.
Five major commercial cities of ancient India are: Patliputra : Major centre of export of stones. Taxila : City of financial and commercial banks. Indraprastha : Commercial junction for roads. Mathura : Emporium of trade and commerce. Varanasi : Major centre for textile industry and gained fame for the gold silk cloth.
What is Hundi?
It is a document which is used for carrying out transactions in which money is passed from one hand to another hand. Hundi is a tool of exchange, which was well-known in the subcontinent. It involved a contract which: (i) licence or warrant the payment of money, the promise or order which is unconditional (ii) capable of change through transfer by valid negotiation.
List the major exports and imports in ancient India.
Major exports and imports in ancient India are as follows: Imports: Copper, lead, animal products, horses, gold silver, coral, glass, tin etc. Exports: Sugar, indigo, cotton, spices, opium, wheat, sesame oil, crystal, granites, copper etc.
What were the different types of Hundi in use by traders in ancient times?
The different types of Hundi used by traders are as follows:
- Dhani-jog : This type of Hundi is payable to any person without putting any liability on the person who receives the payment.
- Sah-jog : This is payable to a specific person, someone who is deemed as respectable while putting a liability on the person who receives the payment..
- Firman-jog : This Hundi is payable on order.
- Dekhan-har : This is payable to the presenter or the bearer.
- Dhani-jog : This is payable to a person (called Dhani, who purchases it) without putting any liability over who receives the payment. However, the payment is done over a fixed time period.
- Firman-jog : This type of Hundi is payable to order following a fixed term..
- Jokhmi : This type of Hundi is drawn against dispatched goods. Herein, in case the goods are lost during the transit, then the drawer bears all the costs without putting any liability on the Drawee.
11th Business Studies Chapter 1 Important Questions
What do you understand by maritime trade.
Maritime trade or marine trade was an important branch of worldwide or global trade network. The Malabar Coast, on which Muzir is situated, has a fairly long history of International maritime trade going back to the era of the Roman Empire. Pepper was mainly valued in the Roman Empire and was known as Black Gold . For centuries, it remained the reason for opposition and conflict between various empires and trade powers to dictate the route for this trade. It was in the search for an alternate route to India for spices that led to the discovery of America by Columbus in the closing years of 15th century and also brought Vasco- da- Gama to the shores of Malabar in 1498.
State the different types of economic activities.
Economic activities involve production, distribution, exchange and consumption of services and goods to consumers. Our livelihoods depend on these activities. The different types of economic activities are as follows: Business : It refers to all those activities which involve production, purchase, sale and supply of goods and services on a regular basis. The main motive of any business is to earn maximum amount of profit. Profession : A profession is an occupation where individuals with an expertise or specialized knowledge and qualification provide specialised services in the relevant field to the masses to earn a living. Each profession is distinct from the other. Employment : People are hired to work regularly by different organisations. Salaries or wages are paid to employees in exchange for the working hours which they provide to a company.
Why business is considered an economic activity?
Any activity which has its main goal of earning profit is called an economic activity. However, there are certain other objectives which a business would like to attain along with earning profit such as increasing market share, improvement in productivity, employee satisfaction, consumer satisfaction, social objectives, but the core and basic objective of a business is to make profits. Therefore, it is called economic activity.
State the meaning of business.
Human beings, for earning a living, involve themselves in various economic activities. Business, an economic activity, is all about production, purchase, sale and supply of goods and services. The main motive behind engaging in a business is to earn adequate amount of profit. A businessman produces goods and services which are in demand so that he/she can earn maximum amount of profit.
How would you classify business activities?
Business activities are categorised as follows:
- Industry : It refers to the economic activities that involve the constituent of production where raw materials undergo change and get converted to finished products. It results in utility as the raw materials are converted into useful finished products. It is also the group of firms that are producing the same type of goods. For example, the sugar industry comprises of all the firms producing sugar. Industries are again classified into three categories-primary, secondary and tertiary.
- Commerce : After manufacturing and production, is the task of distributing goods. Activities that fall under the category of commerce involve helping directly or indirectly in the distribution of goods and services from the producers to the users or final consumers. Sometimes, goods that are high in demand , are produced at one place and need to be circulated and dispersed to consumers living at different places. In such situations, commerce or commercial activities take a lead in distributing and delivering the goods. Thus, the major commercial activities are transport, advertisement, packaging, warehousing, banking and communication. Hence, the gap between producers and consumers is removed by commerce. Commerce can then be further classified into¬ trade and auxiliaries to trade.
11th Business Studies Chapter 1 Important Questions Set 1
What are the various types of industries.
Different types of industries are as follows: 1. Primary industries: These include all those activities which are concerned with the extraction and production of natural resources. 2. Secondary industries: These are concerned with using the materials which have already been extracted at the primary stage. 3. Tertiary industries: These are concerned with providing support services to primary and secondary industries as well as activities relating to trade. These industries provide service facilities.
Explain any two business activities which are auxiliaries to trade.
Two business activities which are auxiliary to trade are explained below: 1. Transport and communication: Transport resolves the problem of movement of goods from the place of production of goods to the place where these are demanded in different parts of the country. The hindrance of place is eliminated by transport- road, rail or coastal shipping. Along with transport, communication is helps in exchange of information between producers, consumers and traders. 2. Advertising: Advertising is one of the most important methods of promoting the sale of products, particularly
What is the role of profit in business?
Profits play a vital role in any business. Earning of profits is essential for any business because of the following reasons given below: (a) Means of Livelihood: It is the most important source of income and provides livelihood for the businessman. Everyone has to satisfy his basic needs of food and shelter. (b) Rewards for taking risks: Profit is as reward earned by taking risk associated with the business. The profit element keeps the zeal alive in a business. (c) Funds for Growth: Profit is the source of finance for expansion and diversification of business activities. A business should not be restricted; rather it should be expanded whenever possible. (d) Symbolic of efficiency and efficacy: Profits symbolize that management is efficient and business is operating in a healthy manner. (e) Enhancement in goodwill: Profit help in building the reputation or goodwill of the business firms. With profit increasing over time, a business enterprise gains reputation in the market.
What is business risk? What is its nature?
Business Risk refers to the possible situation of inadequate profits or losses occurring due to uncertainties or unexpected events in the business. For example, the demand for a particular product may decline due to change customer mindset, tastes or preferences. Fall in demand will result in lesser sales and thereby lesser profits. These are of two types-speculative and pure. Nature of Business Risks
- Natural calamities, change in demand and prices, change in technology etc. are some of the examples of uncertainty which create risks.
- Business risk is unavoidable. Risk can be minimised but cannot be eliminated.
- Degree of risk depends mainly upon the nature and size of business: For small scale business it is less and for large scale business it is more.
- An entrepreneur takes risks and in consideration he gets rewarded with profit. Greater the risk higher is the chance of profit.
11th Business Studies Chapter 1 Long Answer Questions
Discuss the development of indigenous banking system in indian subcontinent..
Indigenous banking system is a banking system that was developed in the ancient times wherein individuals or private firms (also known as indigenous bankers) performed different functions like accepting deposits, lending money by way of currency or letter of credit etc. As the economic life progressed, metals began to complement other merchandise as money because of its sturdiness and divisibility. Money served as a medium of exchange and the introduction of metallic money and its use accelerated the economic activities. Documents such as Hundi and Chitti were in use for carrying out trade transactions in which money passed from hand to hand. Hundi was an instrument of exchange, which was prominent in the subcontinent. It involved a contract which(i) warrant the payment of money, the promise or order which is unconditional (ii) capable of change through transfer by valid negotiation. Indigenous banking system played an important role in lending money and financing domestic and foreign trade with currency and letter of credit. With the expansion of banking, people started depositing the precious metals with lending individuals carrying out banking as bankers or Seths, and money became an instrument for supplying the manufacturers with a means of producing more goods. Agriculture and the domestication of animals were important mechanism of the economic life of ancient people. Due to the favourable climatic conditions, they were able to grow two or sometimes three crops in a year. In addition to this, by doing weaving of cotton, dyeing fabrics, making clay pots, utensils, and handicrafts, sculpting, cottage industries, masonry, manufacturing, transports (i.e., carts, boats and ships), they were able to produce surplus and save for further investment. Workshops (Karkhana) were well-known for there skilled artisans who worked and converted raw materials into finished goods which were high in demand. Family-based apprenticeship system was in practice and was duly followed within the family in acquiring trade-specific skills. The artisans, craftsmen and skilled labourers of different kinds learnt and developed skills and knowledge, which were passed on from generation to generation.
Define Business. Describe characteristics of business.
Human beings, in order to earn a living were involved in various economic activities. Business, being an economic activity, is all about production, purchase, sale and supply of goods and services. The principle motive behind engaging in a business is to earn adequate amount of profit. A businessman produces goods and services which are in demand so that he/she can earn maximum amount of profit. The characteristics of business are as follows: 1. Economic activity: Business is conducted by entrepreneurs to earn an adequate amount of profit and not to fulfil psychological needs. Thus, we can conclude that it is an economic activity. 2. Production or procurement of goods and services: Business involves procurement of raw materials and semi-finished goods and services. It either manufactures the goods or acquires them from producers and then sells to the final consumers at higher prices. 3. Profit earning: Profit is the main purpose of business. A business can continue and grow only if it is earning a good amount of profit. If the profit motive is missing in a business, then it cannot be considered a business activity. 4. Sale or exchange of goods and services: Business involves the sale or exchange of goods and services between the seller and buyer (producer and consumer) for value. Thus, production of goods for self-consumption will not be considered business, but if production of goods is for sale in the market, then it will be called business. 5. Dealings in goods and services regularly: Business involves an exchange of goods and services done on a regular basis. One single transaction of sale does not constitute a business. Business transactions regularly are a must for the business to survive. 6. Risk element: Business risk may be defined as the possibility of incidence of losses or insufficient profits because of various unexpected events which cannot be controlled by business. Every type of business faces risk although the degree of risk may be different from business to business. A business risk can be reduced but cannot be eliminated. 7. Uncertainty of return: Uncertainty of return means lack of knowledge regarding the returns on investment. That is, a businessman does not know the amount of profit which he is going to earn in the future.
11th Business Studies Chapter 1 Important Questions Set 2
Define industry. explain with examples the various types of industries..
4 Following are the various types of industries: Primary industry : Under these industries, activities related to extraction and production of natural resources and reproduction and development of living species are involved. Farming, mining, lumbering, hunting, fishing operations, breeding farms and poultry farms are examples of primary industries. These industries are classified into extractive industries and genetic industries. Extractive industries : Products are extracted (taken out) from the natural resources such as soil and water. Then the manufacturing industries convert the products of these industries into useful goods or finished products. Examples: Farming, mining, lumbering, hunting and fishing operations Genetic industries : They include breeding and reproduction of plants and animals. Examples: Cattle breeding farms, poultry farms, fishing hatcheries Secondary industries : The final products of primary industries are processed and changed to final goods by secondary industries. Iron mining belongs to the primary industries, whereas manufacturing of steel comes under secondary industries. Secondary industries are further classified as manufacturing industries and construction industries. Manufacturing industries : These industries convert raw materials or semi-finished products into finished products. For example, sugarcane is converted to sugar. These industries are divided into the following categories. 1. Analytical industry: A raw material is analysed and separated into different products. Example: Oil refinery. 2. Synthetic industry: Different raw materials are combined to produce a new product. Examples: Cement industry, cosmetic industry. 3. Processing industry: This industry involves successive stages in order to produce the product. Examples: Sugar industry, paper industry. 4. Assembling industry: different parts are assembled to make a new product. Examples: Television, car, washing machine, computer. Construction industries : These industries are engaged in construction of buildings, dams, roads and bridges. These industries require engineering and architectural skills. Tertiary industries : These industries are the service providers for the primary and secondary industries and for trade-related activities. Examples: Transport, banking, insurance, warehousing, advertising
Describe the activities relating to commerce.
Activities that are related to commerce are¬ -trade and auxiliaries to trade. Trade means buying and selling of goods and services. It is only through trade that goods are made available to the consumers from manufacturers end. Trade can be classified into two types: Internal trade : When the trade occurs within the geographical boundaries of the country (within the country), it is called internal/home/domestic trade. It is further classified into wholesale and retail trade. i. Wholesale trade: It deals with buying and selling of goods on a large scale. ii. Retail trade: It deals with buying and selling of goods in smaller quantities. External trade : When trade occurs beyond the geographical boundaries of the country between people and organisations (with other countries), it is called external trade. External trade can be classified into import, export and entrepôt. i. Import trade: Goods purchased from foreign countries come under import trade. ii. Export trade: Goods sold to foreign countries fall under export trade. iii. Entrepôt trade: Importing goods for exporting them to the other country again is termed entrepôt trade.
Auxiliaries to trade : It refers to those activities which support the activities of trade. These activities are also called services as they eliminate various obstacles which take place while the goods are being produced and distributed. The following are the auxiliaries to trade. Transport and Communication : Production and consumption of goods take place at different places. Thus, it is essential to move goods from the place of production to the place of consumption. Transport facilitates this movement and transfers raw materials to the place of production. In addition to transport facility, communication is required so that information can be exchanged between producers, traders and consumers. Banking and Finance : A business cannot be get going unless it has funds and investments available for its expenses like purchasing raw materials and meeting day-to-day expenses. It can obtain funds from banks and financial institutions by taking loans, and thus, banks overcome the business’ problem of funds. Banks help businessmen in both internal and external trade. Insurance : Every business involves different types of risks such as risk of loss due to fire, theft and damage and risk of accident. To be safe from such risks, a business can opt for insurance. Insurance provides protection from all kinds of risks and in return charges fees (which is called premium). Warehousing : Production and consumption of goods does not take place simultaneously. There is a time gap between them. Hence, some place is needed for storing the goods before supplying them to the ultimate consumers. Advertising : It is a tool for promoting a product. Promotion of the product increases its sales. It is a way of letting the customers know about the features of a product to convince them to buy it.
Explain any five objectives of business.
Objectives are the end product of a business towards which all the business activities are directed. Although the main objective of every business is to earn maximum amount of profit, with growing competition and multiplicity, manifold objectives have been put in place. All the efforts of a business are inclined to achieve those objectives. Keeping the prime objective in mind, a business strives to achieve the following objectives:
- Market standing : It means the position of the firm in a market. A firm can hold a strong position in the market by providing a good quality product to its customers and offering product-related benefits.
- Innovation : It means the development or invention of new ideas, techniques and methods to meet the new and upcoming demands of the flourishing business and competitive market. It is one of the important objectives as no business can survive in the market without innovation or new ideas.
- Productivity : It is calculated by making a comparison between the output and input. Competence and efficiencyare measured through productivity. To survive and grow, it is essential for the organisation to be productive.
- Maximum profit : Profit is the excess of revenue over cost. The purpose of every business is to earn adequate amount of profit. A business can sustain and grow only if it is earning a good amount of profit.
- Physical and financial resources : Physical resources such as plants, machines, furniture and office and financial resources ( funds) are required by every business organisation to run the organisation.
11th Business Studies Chapter 1 Important Questions Set 3
Explain the concept of business risk and its causes..
Business risk may be defined in terms of the possibility of occurrence of losses or insufficient profits because of various unexpected events which cannot be controlled by business. For example, customer preferences for a certain product declines after a certain period because of some competitors’ policies or change in taste; in such cases, it is extremely difficult for a businessperson to correctly anticipate consumer preferences, as a result of which he or she always faces the risk of unforeseen fluctuations in demand. This results in the business going for a loss because of the fall in demand. Two types of business risks are speculative risk and pure risk. Speculative risk : Risks taken on the basis of forecasts and guesses can be termed speculative risk. It involves an equal possibility of earning gains or incurring losses. It arises because of change in market conditions like changes in government policies and fluctuation in demand and supply. Pure risk : Risks which cannot be predicted precisely is pure risk. A firm can incur only losses or incur no loss at all. Pure risk can be the risk associated with theft, fire and various natural calamities. Causes of business risk : Natural causes : The one thing which humans have no control over is nature. So, when unforeseen natural calamities occur, it causes heavy and irreplaceable losses to life, property and income. Economic causes : Price fluctuations and change in government policies, preferences, taste and demand of consumers are some of the economic causes which will cause the downfall of a business. Human causes: One of the common causes of business loss is humans. For example, dishonest behaviour of employees, carelessness of employees and strikes. Other causes : Political disturbances, exchange-rate and interest-rate fluctuations, budget amendments, physical or technical disabilities and mechanical failures can be some other causes which may result in a business risk.
What factors to be considered while starting a business? Explain.
Factors to be considered while starting a business: 1. Selecting a business line: The basic decision which needs to be taken at the start is choosing a line of business. This decision is dependent on many factors such as demand of consumers, interest area of entrepreneur and profit margin in the production of a particular product. Besides these, technical knowledge which an entrepreneur has for the production of a particular product influences the selection of a line of business. 2. Size of the business: The size of the business, i.e. whether to operate on a large scale or small scale, is also one of the important decisions to be considered while starting a business. A business can be operated on a large scale if the entrepreneur is confident regarding the demand for the product and the capital can be easily arranged. On the contrary, operations will be started on a small scale if the risk is high; there is difficulty in arranging large amount of capital and market conditions are unstable. 3. Location: The choice regarding the place of starting a business depends on the following factors. a) Availability of raw materials and labour b) Power supply c) Services such as banking, transport, communication and warehousing 4. Venturing into a business started at a wrong location will result in high cost of production, inconvenience in getting the right kind of raw materials and low demand. 5. Financial requirement: Finance is required at every stage of a business from the start point of business and purchase of fixed assets to continuous investment in the business. In this regard, a proper financial analysis helps determine the required capital amount, capital sources and the best ways to use capital. 6. Tax planning: Tax laws influence the profit margin and working of the business. Hence, it becomes essential for the business to do tax planning well in advance. 7. Physical facilities: Before starting a business, physical facilities such as machines, equipment, building and other important physical resources should be carefully considered. This is because physical resources add to the efficiency of a business. This decision is based on the nature, size and production process of the business as well as the availability of funds.
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

- Bihar Board
SRM University
Bseb 12th result.
- Bihar Board Result 2024
- UP Board Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Business, Trade and Commerce: Based on Revised CBSE Syllabus 2023-2024
Mcqs for class 11 business studies: multiple-choice questions for class 11 business studies chapter 1, business, trade and commerce are presented here. also, find attached links to important resources for the preparation of the cbse board examinations 2024..

MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1: Multiple-Choice Questions(MCQs) have been included as an essential part of the upcoming CBSE Board Exam, as per the latest CBSE Sample Paper. Here, we have brought to you important MCQ-type questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1, Business, Trade and Commerce. We have also attached links to some important resources to assist you in your preparation for the upcoming CBSE Board Examinations 2024.
MCQs are questions with multiple options and one correct answer among them. These are designed to enhance a student’s thinking capabilities, brainstorming capacity, and understanding. It has now been included in schools as an essential part of chapter-end exercises to ensure that students understand the concepts instead of mugging them up.
For appropriate preparation for examinations, it is important that a student is aware of resources to be adhered to while preparing. Here, we have attached a few throughout this article for your reference.
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Revised Syllabus 2023-2024 (PDF)
MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Business, Trade, and Commerce
Find the list of MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Business, Trade, and Commerce. A PDF download link for the same has also been attached below. Use the link to save the MCQs for future use.
1) Which of the following is/are treated as Auxiliaries to Trade?
( a ) Banking Industry
( b ) Insurance Industry
( c ) Transportation Industry
( d ) All of the above
Answer. d) All of the above
2)The reward of risk is:
(a) Success
(b) Failure
Answer. c) Profit
3)Name the two broad categories of business activities.
(a) Trade and commerce
(b) trade and industry
(c) industry and commerce
(d) none of these
Answer. c) Industry and Commerce
4)Assertion (A) Business represents the exchange of Goods and Services.
Reason (R) Risk and Uncertainties are always there in any form of business
(a) Both A and R are true. R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct, but R is incorrect
(d) A is incorrect, but R is correct
Answer. b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
5)Which of the following does not characterize business activity :
(a) Production of goods and services
(b) Presence of risk
(c) Sale or Exchange of goods and services
(d) Salary or wages
Answer. d) Salary of wages
6)“Amrut” is an NGO operating in the district of Rajkot since 2005. It deals in providing medicines and other medical facilities to the rural, backward, and below-poverty-line people in the district. In case of need, arrangements are made by the NGO to shift critical patients to referred hospitals. Name the type of human activities performed by the NGO “Amrut”.
(a) Economic Activities
(b) Non-Economic Activities
(c) Spiritual Activities
(d) None of the above
Answer. b) Non-Economic Activities
7)Maninder, Surinder and Balbinder and Harinder pursued their Master's Degrees in Business Management from a reputed institute in Delhi. After completion of their studies, all of them got engaged in different fields. Maninder got a job at an Oil Refinery Industry as a Junior Executive in Finance. Surinder joined his family business in Textile Industry in Jalandhar, Punjab. Balbinder opened his own Dairy Firm and Harinder join the construction business. Identify the type of industry Mr. Surinder worked with as highlighted in the above case.
(a) Analytical Industry
(b) Synthetic Industry
(c) Processing Industry
(d) Assembly Industry
Answer. c) Processing Industry
8)Which of the following cannot be classified as an auxiliary to trade?
(b) Insurance
(c) Warehousing
(d) Transport
Answer. a) Mining
9)Ruchi is a practicing Chartered Accountant. She has her C.A. Firm in Hyderabad, Telangana. She deals in providing Income Tax and GST-related services to her clients against very reasonable consultancy fees. She has her own professional coaching classes for C.A. Enrolled Students. Identify the types of economic activities performed by Ruchi as referred to in the above case.
(a) Business
(b) Profession
(c) Employment
Answer. b) Profession
10)Which of the broad categories of industries covers oil refineries and sugar mills?
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) None of these
Answer. b) Secondary
11)Assertion (A) Earning Livelihood is the main aim of Economic activities.
Reason (R) It helps people in earning their bread and butter by performing several activities.
Answer. a) Both A and R are true. R is the correct explanation of A
12)Nutan General Store is a big businessman who deals in selling Nestle products in his locality. He purchased products of Nestle directly from the State Distributor in bulk quantities and sold them in the market. Small shopkeepers from different corners of the city. Identify the type of trade followed by Nutan General Store.
(a) Wholesale Trade
(b) Retail Trade
(c) International Trade
(d) Entrepot Trade
Answer. a) Wholesale Trade
13)Business risk is not likely to arise due to:
(a) Change in govt, policy
(b) Good management
(c) Employee dishonesty
(d) Power failure
Answer. b) Good Management
14)Sankalp is a successful entrepreneur dealing in the Automobile sector, especially with Two Wheelers in Ahmedabad. He has been constantly earning good profits from his business and investing surplus towards the expansion of his business. All the latest Two-Wheeler models are available at his showroom. His marketing and sales teams are managed to create new customers from time to time. His unique style of business management has brought him success. Name the type of Business activity in which Sankalp is involved.
(a) Tertiary industries
(b) Secondary industries
(d) Auxiliaries to trade
Answer. c) Trade
15)Dell Inc is a company involved in the manufacturing of computers and related items. It’s a very popular name among the computer-savvy youth in India. There are different models of Desktop, Laptop, Tabs, Gaming and Workstations manufactured and sold by the company in the Indian market. Which type of Industry is highlighted in the above case?
(a) Genetic Industry
(b) Extractive Industry
Answer. d) Assembly Industry
We hope this article proves to be helpful and useful to you. This will provide you with an idea of solving the MCQs and understanding the pattern.
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2023-24 (All Subjects)
CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers 2023-24 (All Subjects)
NCERT Books for Class 12 (All Subjects)
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- AP TET Results 2024
- SSC GD Re-exam Date 2024
- Bihar Board 12th Result 2024
- JKPSC Mains Exam Date 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Important Diagrams
- NIACL Assistant Result 2024
- Bihar Lekhpal Sahayak Recruitment 2024
- Bihar Sakshamta Pariskha Answer Key 2024
- PNB SO Admit Card 2024
- MPNRC Result 2024
Trending Categories
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 11 Study Material
Latest Education News
Holika Dahan 2024: Know Date, Time, Significance and Story Behind Choli Holi
Bihar Board 12th Result 2024 Date Live: BSEB Inter Results Likely to be Declared by 23 March, Know How to Check by Roll Number
Only 1% With Sharp Vision Can Spot An Envelope And A Comb In This Classroom In 12 Seconds!
Bihar Board Result 2024 Class 12 LIVE: कल बिहार दिवस के मौके पर जारी हो सकता है इंटर का रिजल्ट, जानें क्या है लेटेस्ट न्यूज
WBPSC Food SI Answer Key 2024 OUT at psc.wb.gov.in: Download Shift 1 2 3 Keys Here
Naval Dockyard Mumbai Recruitment 2024 for 301 Apprentice Posts, Apply Online @indiannavy.nic.in
Optical Illusion: Find a tomato among the strawberries in 5 seconds!
BSEB 12th Result 2024 Date and Time Expected Tomorrow, How to Check Online Link
Seek and Find: Test your eye power by finding a horse in the picture in 5 seconds!
IPL 2024: हिंदी हो या भोजपुरी इन चर्चित कमेंटेटरों के साथ आईपीएल का लें लुफ्त
UP Metro Salary 2024: जानें कितनी मिलती है यूपी मेट्रो में सैलरी?
Personality Test: Your Arms Crossing Style Reveals Your True Personality Traits
MCQs for CBSE Class 12 Accountancy: As per Revised CBSE Syllabus
CBSE Class 12th Accountancy Revision Notes Download PDF
Simple and Beautiful Holi Drawing Ideas For Students with Images
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy (2023 - 2024) All Chapters, PDF Download
CBSE Class 12 Accountancy Deleted Syllabus 2023-24: Complete List of Topics Removed
BSEB Bihar Board 12th Result 2024: Check Inter Bihar Board Result Online at biharboardonline.bihar.gov.in, Download your scorecard
Easy Holi Poster and Banner Ideas for Students
Manabadi APTET Results 2024 Official Update Released, Check Here
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students
MCQ Questions for Class 11 Business Studies with Answers PDF Download Chapter Wise
Here you will find Chapter Wise NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Business Studies with Answers PDF Free Download based on the important concepts and topics given in the textbook. Answers of all CBSE Class 11 Business Studies MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers provided here with detailed solutions so that you can easily understand the logic behind each answer.
Class 11 Business Studies MCQs Questions with Answers Chapter Wise PDF Download
Practicing these CBSE NCERT Objective MCQ Questions of Class 11 Business Studies with Answers Pdf will guide students to do a quick revision for all the concepts present in each chapter and prepare for final exams.
- Nature and Purpose of Business Class 11 MCQ Questions
- Forms of Business Organisation Class 11 MCQ Questions
- Private, Public and Global Enterprises Class 11 MCQ Questions
- Business Services Class 11 MCQ Questions
- Emerging Modes of Business Class 11 MCQ Questions
- Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Class 11 MCQ Questions
- Formation of a Company Class 11 MCQ Questions
- Sources of Business Finance Class 11 MCQ Questions
- Small Business Class 11 MCQ Questions
- Internal Trade Class 11 MCQ Questions
- International Business Class 11 MCQ Questions
Students can also Check below CS Executive Business Important Questions and Answers
CS Executive MCQ & Important Questions and Answers
- CS Executive Jurisprudence, Interpretation & General Laws Important Questions
- CS Executive Company Law Important Questions
- CS Executive Economic, Business and Commercial Laws Important Questions
- CS Executive Setting Up of Business Entities and Closure Important Questions
- CS Executive Securities Laws and Capital Markets Important Questions
- CS Executive Tax Laws MCQ
- CS Executive Corporate and Management Accounting MCQ
- CS Executive Financial and Strategic Management MCQ
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Business Studies PDF Free Download will definitely yield fruitful results. If you have any queries related to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop your questions below and will get back to you in no time.

COMMENTS
Class 11 Business Studies syllabus is closely related to trade and commerce. The subject cannot be ignored as it is the foundation of many concepts and theories which are studied at an advanced level in class 12. ... These simple points if kept in mind will definitely help the students to fetch good marks in case study questions, class 11 ...
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Business Studies Subject - Business, Trade and Commerce, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
Element of Risk: Business is associated with a certain amount of risk as there is possibility of inadequate profits or losses due to change in tastes and preferences of customers, change in technology, fire theft, natural calamities, etc. 8. Write differences among industry, commerce and trade on any five bases.
Question 2. Name one economic pursuit, in which expertise is required. Answer: Profession is an economic pursuit, in which expertise is required. Question 3. Name the industries that furnish support to other fellow industries. Answer: Tertiary industries are involved in furnishing support to all the primary and secondary industries.
Here, we have discussed the units in a brief. 1. Unit 7: Financial Source of Business. The first unit of class 11 business studies part B has three chapters. The chapters are the concept of Finance in business, the concept of different business materials: owners' funds, shares, receipts, the concept of borrowed funds.
Mention two demerits of the type of large scale retail trade identified in part I. 5. (a) The retail sector of Indian economy is categorized into two segments such as organized retail sector and unorganized retail sector. The latter holds larger share of the retail market. The key drives of the growth in retail consumption in India are basically.
This study resource contains in-depth knowledge, and the Solutions collated by the subject matter experts are no different. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 - Business, Trade And Commerce briefly introduces the basic concepts in Business Studies. Download PDF Of Ncert Solution for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 ...
Earning Profits: Business has to earn reasonable profit so as to sustain its growth and survive in the. 2. Market Standing: Business should have a better position in the market in relation to its competitors. 3. Innovation: Business should come up with new ideas, inventions and new methods for sustainable.
Maximum CBSE Class 11 Business Studies students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams. Get the free view of Chapter 1, Business, Trade and Commerce Class 11 Business Studies additional questions for Mathematics Class 11 Business Studies CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
Business in Class 11 commerce is divided into two parts. The first part is based on the history of commerce and trade in India and the second part is about nature and the concept of business. Therefore, in Class 11 commerce students will study the different features of a business. Many other important topics are taught in Class 11 Commerce.
These questions and their solutions help students better comprehend Business, Trade and Commerce. Mentioned below are a few Chapters 1 Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions and their Solutions: Q1. State the meaning of business. Answer: The term 'Business' is derived from the term 'busy.'.
Business is considered to be an economic activity because it is undertaken with the object of earning money or livelihood and not because of love, affection, sympathy or any other sentimental reason. 8. State the meaning of business. Answer. The term 'business' has been derived from the word 'busy'.
Check important questions and answers for Class 11 Business Studies (Chapter 1 Business, Trade & Commerce). These NCERT based questions are frequently asked in annual exams CBSE Schools.
What Is Sole Proprietorship. Statement Of Retained Earnings. Fiscal Deficit. Business Environment. Great Depression. Intermediate Goods. Sandeep Garg Macroeconomics Class 12. Foreign Trade In India. Get the important questions (Chapterwise) with answers for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies.
Chapterwise Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies. Chapter 1 Business Trade and Commerce. Chapter 2 Forms of Business Organisation. Chapter 3 Private Public and Global Enterprises. Chapter 4 Business Services. Chapter 5 Emerging Modes of Business. Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics.
Chapter 1 Nature and Purpose of Business Class 11 Important Questions. Chapter 2 Forms of Business Organisation Class 11 Important Questions. Chapter 3 Private, Public and Global Enterprises Class 11 Important Questions. Chapter 4 Business Services Class 11 Important Questions. Chapter 5 Emerging Modes of Business Class 11 Important Questions.
Now you will see the exercise questions answers of Business, Trade and Commerce and download pdf link on it. Click the Download PDF link to obtain the Business, Trade and Commerce questions with answers document. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies . There are more chapters to study besides Business, Trade and Commerce in this subject.
There are two types of activities in commerce namely 1. Trade and 2. Auxiliaries to trade. Buying and selling of goods is called trade whereas auxiliaries to trade involves activities such as banking, communication, transportation and advertising. Commerce enhances the link between consumers and producers.
Short Answer Questions (3 or 4 Marks) 11. Sandeep& Sons, Delhi orders pearl jewellery from Nasir Bros, Hyderabad. They enter into a contract and make certain that the payment will be made only on receiving the goods at Delhi in their Shop. Identify the term of trade in the above example.
on January 27, 2022, 9:59 AM. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1 Business, Trade and Commerce. Answers of all short and long answers in proper explanation are given here on this webpage. Completely solved chapter end exercise and extra question answers are also included for practice.
By Tanisha Agarwal. Dec 22, 2023, 18:17 IST. Download MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1. MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1: Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) have ...
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions - Free PDF Download. Chapter 1 - Business, Trade and Commerce. Chapter 2 - Forms of Business Organisation. Chapter 3 - Private, Public and Global Enterprises. Chapter 4 - Business Services. Chapter 5 - Emerging Modes of Business. Chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and ...
Here you will find Chapter Wise NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Business Studies with Answers PDF Free Download based on the important concepts and topics given in the textbook. Answers of all CBSE Class 11 Business Studies MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers provided here with detailed solutions so that you can easily understand the logic behind each answer.