Using Graphic Organizers for Writing Essays, Summaries and Research
Ask any student – essay writing is one of the most despised tasks of their educational career. Perhaps there is so much displeasure associated with the task because it’s perceived as too linear – there isn’t enough visual and creative appeal. But if you use graphic organizer for writing essays then you can make writing enjoyable – or at least less terrible.
Not only enjoyable but graphic organizers (or diagrams) can make the writing process a snap. They’ll help you think outside the box, draw conclusions you wouldn’t normally observe, and make the entire process faster and more efficient.

Why Use Graphic Organizers for Writing
The phrase “graphic organizer” is just a fancy way of saying “diagram” or “visual aid.” Basically, they are a visual representation of the information you’ve acquired in the research process. There are quite a few reasons why you should use them when writing essays or summaries.
- Helps you visualize your research and how elements connect with each other
- Enhance your essays, summaries and research papers with visual elements
- Track correlations between your thoughts, observations, facts or general ideas
When it comes to essay writing, the most common graphic organizers are webs, mind maps, and concept maps .
Using Webs for Brainstorming
Webbing is a great way to see how various topics are interrelated. This graphic organizer is particularly useful during the brainstorming step of the writing process.
A web can sometimes get a bit messy. Usually, there are lots of arrows to connect overlapping ideas. However, even with lines crisscrossing every which way, it is still a great way to visualize your thoughts. If you’re using an online diagramming software like Creately you can overcome some of this because we automatically arrange the object for you.
Once you’ve created a map to document all your ideas and establish connections, you can easily transition to other forms of diagramming to better organize the information.
For example if you’re writing a research paper about the food web of the Australian bushes you can start creating a food web diagram similar to the one below. This way you can easily visualize the web while writing the paper. This is a simple example but graphic organizers become even more important when the subject gets complex.
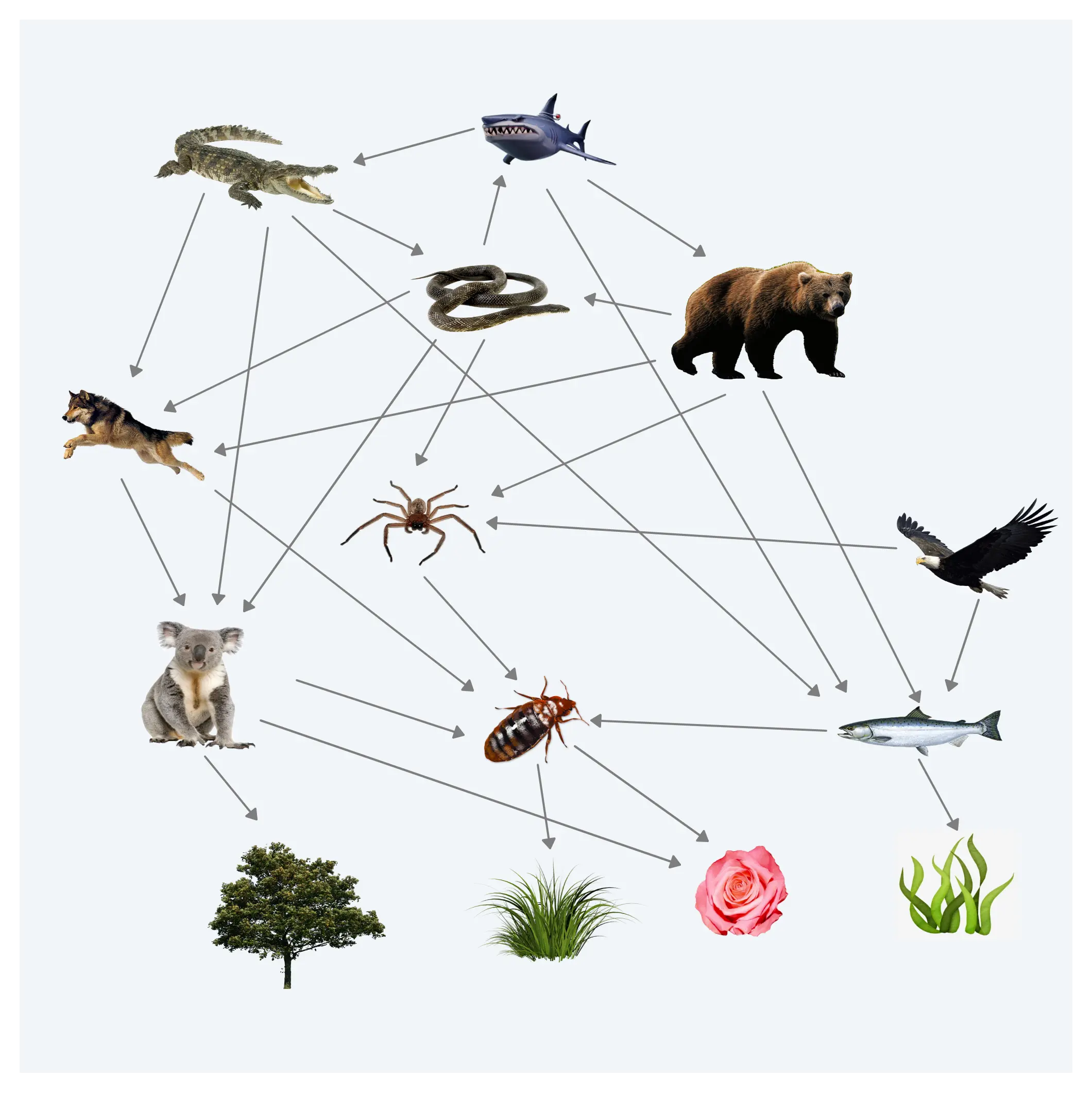
Although simple this example shows the importance of using graphic organizers for writing summaries. A comprehensive diagram pretty much does the summation for you.
Using Mind Maps as Graphic Organizers
Mind maps are a great way to depict a hierarchy. What is hierarchical organization ? The concept is simple: a singular topic dominates with each subsequent idea decreasing in importance.
Usually, the mind map starts with the thesis (or main idea) at the center. From there, you can branch out with your supporting evidence.
Use this process to replace your traditional note taking technique – note cards, outlines, whatever. You’ll quickly realize a mind map is a great way to formulate the structure of your essay. The thing to note here is that the nature of the mind maps force you think about sub topics and how to organize your ideas. And once the ideas are organized writing the essay become very easy.
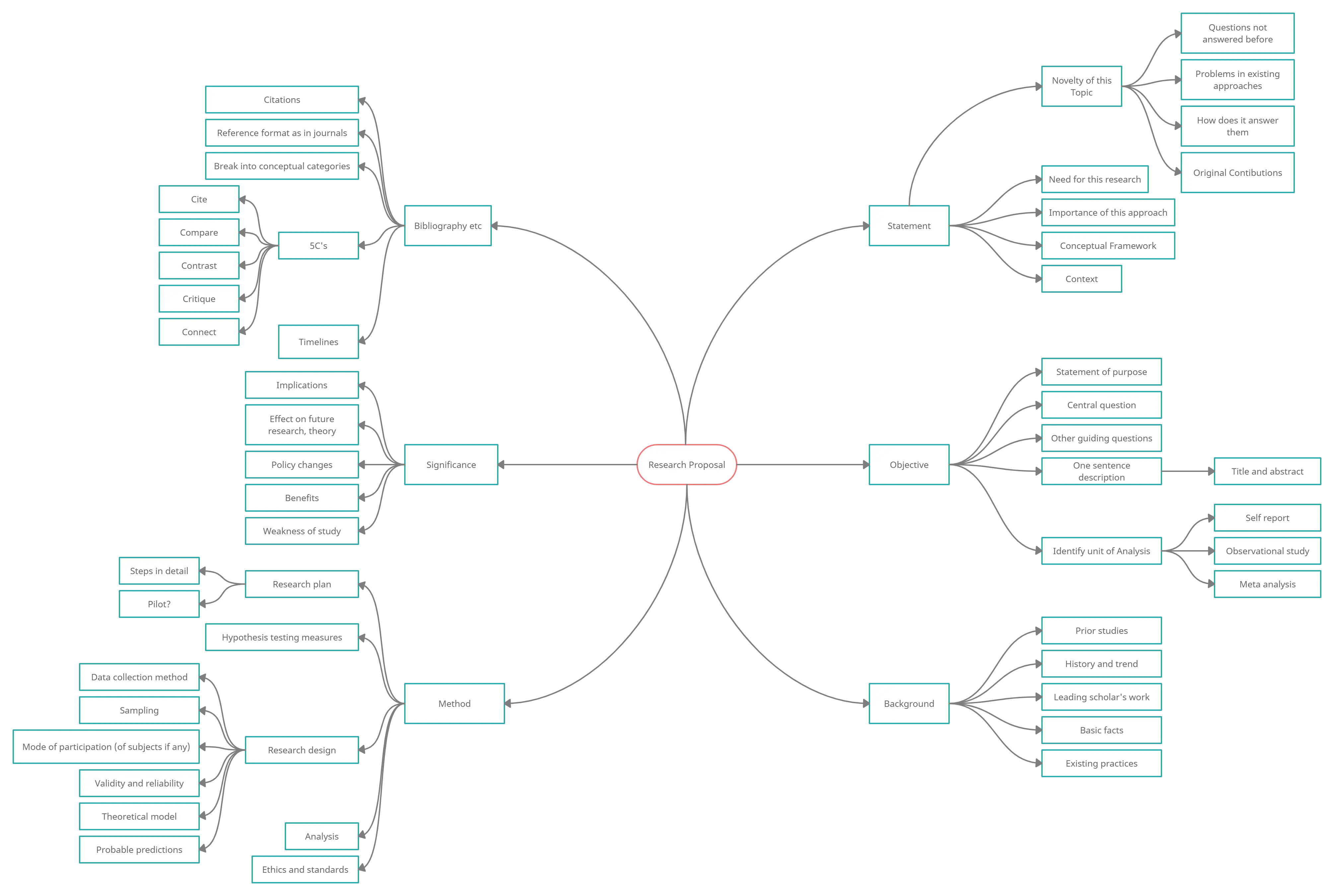
Above is a mind map of a research proposal. Click on it to see the full image or you can see the fully editable template via this link . As you can see in this mind map the difference areas of the research proposal is highlighted. Similarly when your writing the research paper you can use a mind map to break it down to sub topics. We have more mind map templates for you to get started.
Concept Maps
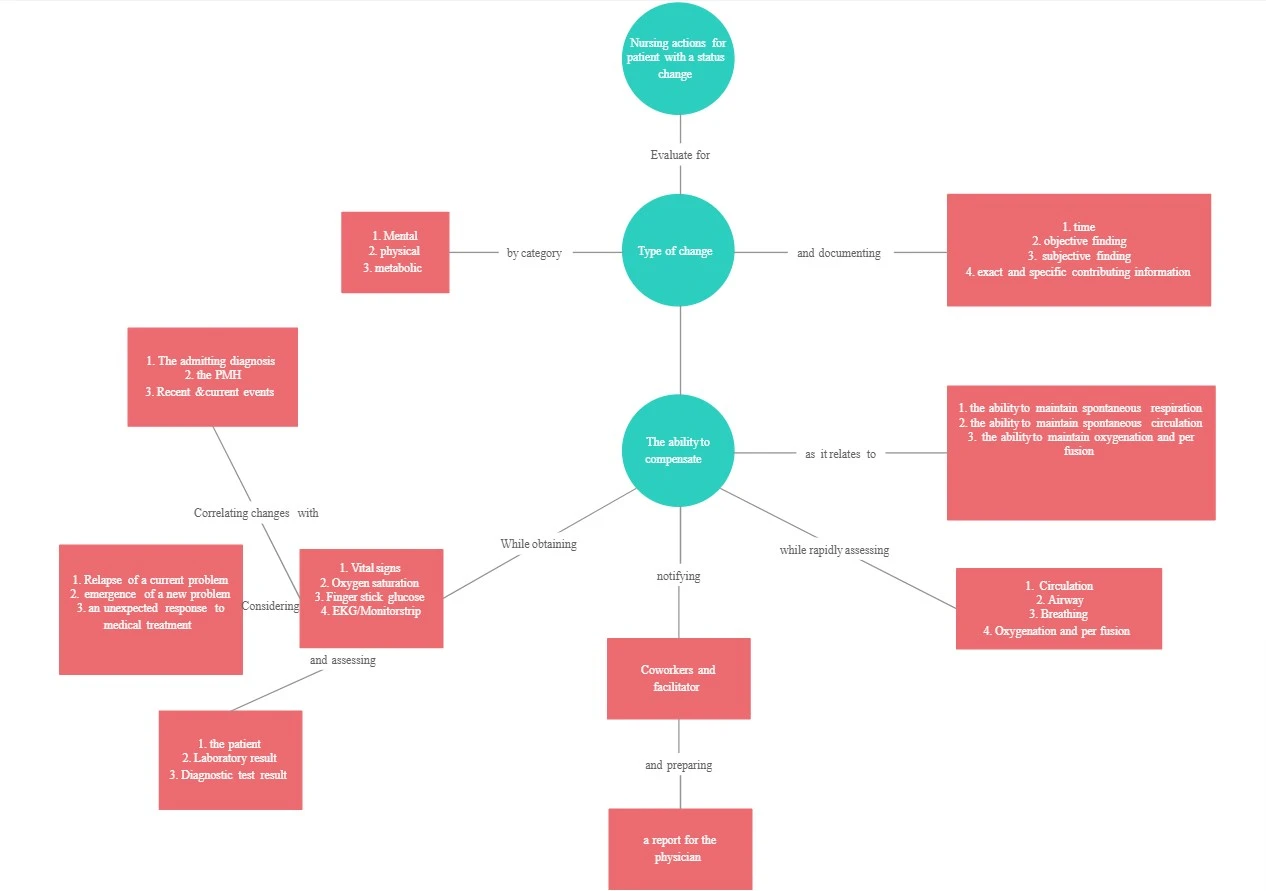
A concept map will help you visualize the connection between ideas. You can easily see cause and effect – how one concept leads to another. Often times, concept mapping includes the use of short words or phrases to depict the budding relationship between these concepts.
If you look closely you can see that its very similar to a mind map. But a concept maps gives more of a free reign compares to the rigid topic structure of a mind map. I’d say it’s the perfect graphic organizer for writing research papers where you have the license to explore.
By creating a concept map , you can also see how a broad subject can be narrowed down into specific ideas. This is a great way to counter writers block. Often, we look at the big picture and fail to see the specifics that lead to it. Identifying contributing factors and supporting evidence is difficult. But with a concept map, you can easily see how the smaller parts add up to the whole.
Why Bother With Graphic Organizers?
If you already detest the writing process, adding another step might seem insane. However, there really are several advantages of using them. If you haven’t already accepted the benefits of each individual diagram style, here are some more perks of graphic organizers in general:
- Quality essays are based on detail. No one is going to accept your opinions and reasoning just because you say so. You’ll need proof. And organizing that proof will require attention to detail. Graphic organizers can help you see that detail and how it contributes to the overall concept.
- Graphic organizers are flexible. You don’t need one of those giant pink erasers. You don’t need to restructure your outline. All you have to do is draw a few arrows and bam – the relationship has totally changed.
- No matter what you are writing about, a graphic organizer can help. They can be used to structure an essay on the Great Wall, theoretical physics, or Spanish speaking countries.
- If you write an outline, can you easily see how point A influences point X? Probably not. But if little thought bubble A is sitting out there all by itself, you can visualize the way it ties into point R, T and X.
- Some of us find it difficult to put our opinions, thoughts, and ideas into writing. However, communicating our feelings with little doodles and sketches is far less threatening.
- As a writer, our brain often feels like a 2-year-old’s toy box – a big jumbled mess. Taking that mess and putting it onto paper with some semblance of organization is challenging. Rather than trying to take your thoughts from total chaos to a perfectly structured list, just try to get them out of your brain and onto paper in the form of a diagram.
- A graphic organizer helps you establish validity and relevance. You can easily nix the ideas that don’t support or enhance your thesis.
The next time you are faced with a writing project, take a few minutes to explore the efficiency of graphic organizers. You can find a wealth of templates here.
Have you ever used a graphic organizer to structure an essay? How did it go? Do you have a diagram suggestion for the writing process that wasn’t mentioned here? Let us know!
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
These are awesome guest posts contributed by our users and technology enthusiasts. Do you have something interesting to share? Want to get exposed to a massive tech audience? Check out our Guest Posting Guidelines to how to proceed.

Formatting Graphics and Visuals in APA Style
Statistics and results from data analysis are often best presented in the form of a table, and a theoretical model or pages of information are often best presented in a well-designed visual such as a chart or graph. The American Psychological Association (APA) distinguishes between two types of visuals: tables and figures. Both are used to provide a large amount of information concisely and to promote greater understanding of a text. This article explains how to format tables and figures according to APA Style 7th Edition.
Tables in APA Style (7th ed.)
Tables are organized in a row and column format and provide information that is not already given in the text. Tables should also be able to stand alone and be understandable without the accompanying text. Therefore, having a descriptive title for the table is important and so is using a “note” to explain any symbols, abbreviations, or asterisks used in the table.
When inserting a table in your work, include the following information (also exemplified by Table 1):
- Table number , aligned left, bolded, and presented in sequence: Table 1 , Table 2 , etc.
- Table title , aligned left, italicized, and offering a brief description the table: Title of Table
- The table itself , without shading or vertical borders; use horizontal boarders only for clarity such as a top and bottom border or to separate a row containing the sums of column data. Tables are double spaced unless one or one and a half spacing would enable the table to be displayed on a single page.
- Table note , double-spaced below the table, after the label “note” in italics: Note .
Use a callout such as “See Table 1” in the paragraph before the table to point the reader to it.

Table Notes
Table notes are only used when needed, and there can be up to three notes per table, ordered by type:
- General Note : General notes are given first. Table 1 in this article has a general note. General notes provide definitions, keys, and copyright statements for any information that came from a source.
- Specific Note : Specific notes provide information about individual columns or rows. If, for example, a specific column or cell’s data needed explanation, a superscript letter such as “a” would be placed by the data, e.g. Xa, and the same superscript letter would be placed before the note about it.
- Probability Note : Probability notes explain asterisks (*) or other symbols that provide probability values used in statistical hypothesis testing used for ruling out something occurring due to chance alone.
- In statistical testing, researchers use a probability level between 0 to 1 to describe the chance of an event occurring, with 0 meaning the event will never occur and 1 meaning the event will always occur. In a table or figure, probability levels are assigned asterisks to indicate a range in probability such as p < .05 and * p < .01, and ***p < .001 (APA, 2020). The fewest number of asterisks indicates the largest probability and the greatest number of asterisks indicates the smallest probability level.
- Plus (+) and minus (-) signs are also used in probability notes to show confidence intervals. For example, the results of an opinion poll may show 56% of the respondents prefer candidate A. If the confidence interval is +/-3, then 53%-59% of the population agrees with those sampled.
- Probability notes may also provide confidence levels to indicate how certain the researcher is that the general population will agree with the poll respondents. For example, if the confidence level is 95%, then there is a 95% certainty that 53% to 59% of the population agrees with those polled. Researchers typically use a 95% confidence level.
Example of a general note, specific note, and probability note:
Note . The poll revealed that respondents prefer candidate A. YA = ages 18-30. A = ages 31-43. Adapted from “Title of Article,” by A. Author, Copyright Year, Publication Title, vol(issue) page-page. (URL). Copyright year by Copyright holder or Copyright License or In the public domain.
Data are for all genders.
p < .05. * p < .01.
In the example above, the notes are to be double spaced as shown in Table 1, and each type of note begins on a new line with the first note providing general information about the table including a copyright note for the data used in the table. The second note gives specific information about the data in the rows, and the third note provides the probability (p) values.
Reference Entries for Table Data
A reference entry would also be included for any source of information used in the table and noted in the table note. The reference entry goes on a reference list at the end of the paper.
Table Checklist
- Is the table necessary?
- Is the table mentioned in the text?
- Is the table inserted under the paragraph where it is first mentioned?
- Is the title brief but explanatory and one double-spaced line below the table number?
- Are all vertical borders in the table eliminated?
- Does every column have a heading including?
- Are the notes in the following order: general note, specific note, probability note?
- Are the notes double spaced?
- Are all abbreviations, symbols, and special uses of dashes, italics, or boldface explained in a note?
- If the table is for statistical testing, are probability levels identified?
- If more than one table is used, are probability level asterisks consistent from table to table?
- With statistical testing data, are confidence intervals reported and consistent for all tables?
- If all or part of a copyrighted table is reproduced or adapted, does the general table note give full credit to the copyright owner and have a corresponding reference entry?

Figures in APA Style (7th ed.)
Figures include visuals such as charts graphs, pictures, maps, etc. When inserting a figure in your work, include the following information (also exemplified in Figure 1):
- Figure # , aligned left, bolded, and in sequence: Figure 1 , Figure 2 , etc.
- Figure title , aligned left, italicized, and offering a brief description the table: Figure Title
- The figure itself
- Figure note , double-spaced below the table after the label “note” in italics: Note .
Use a callout such as “See Figure 1” in the paragraph before the figure to point the reader to it.

The Chart tool in Microsoft Word and Microsoft PowerPoint provides options for various types of graphs and charts. With so many types to choose from, it’s important to carefully consider which type will best present the information. For example,
• a column chart displays categories of variables; • a bar chart demonstrates comparisons between single items; • a pie chart shows percentages; • a scatter plot illustrates correlations; and • a line graph demonstrates relationships.
The Microsoft Office Support webpage provides examples of these types of charts and more.
Figure Notes
As with tables, there can be up to three notes under the figure, ordered by type: (a) general information about the figure including a copyright statement for compiled data or images from the Internet, (b) specific information about individual sections, bars, graphs, or other elements of the figure, and (c)) probability explanations as discussed in the section on tables.
Copyright Statements for Compiled Data
When you use data and information in your table or figure that was compiled from research, the figure must contain a general note with a copyright statement identifying the copyright holder of that information. Because you are using this information for an academic purpose that is not for profit, you will not need to also acquire permission from the copyholder. It is considered “fair use” for students and scholars to use information that has been previously published if the information is attributed to the copyright holder with proper documentation.
Use the following copyright statement template in a note for data or information that came from a journal or book:
Journal : Note . From [or Adapted from] “Title of Article,” by A. A. Author, year, Journal Title, Volume (Issue), p. xx (DOI or URL). Copyright year by Name of Copyright Holder or In the public domain or Copyright License such as CC BY-NC .
Book : Note . From [or Adapted from] Title of Book (p. xx), by A. A. Author, year, Publisher (DOI or URL). Copyright year by Name of Copyright Holder or In the public domain or CC BY-NC .
Copyright Statements for Images
Images are different than compiled data. Depending on where the image is from, it may or may not require a copyright statement in a note under the image.
Copyrighted images : To use a copyrighted photograph, permission from the copyright holder is needed. It is an act of plagiarism to use a copyrighted image without permission.
Copyright statement template for copyrighted image that you have permission to use:
From [or Adapted from]. Title of Work [Photograph], by A. A. Author, year of publication, Site Name (URL). Copyright year by Name of Copyright holder. Reprinted or Adapted with permission.
Creative Commons licensed images : Photographs with Creative Commons licenses may be used without permission, but each type of Creative Commons license has different stipulations. You can read about each here: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/ . The licenses generally all require attribution to the source or creator of the image. (See Figure 2).
Copyright statement for Creative Commons image:
From [or Adapted from]. Title of Work [Photograph], by A. A. Author, year of publication, Site Name (URL). License such as CC BY-NC .
Photograph With a Creative Commons License for Reproduction With Attribution

Note . From Lilies After Rain [Photograph], by C. Cairns, 2015, Flicker. (https://flic.kr/p/vDHife) . CC BY 2.0 .
Public Domain images : Public domain works are not protected by copyright law or they have expired copyrights such as works published before January 1, 1924. In APA Style, works in the public domain are credited in a copyright statement in the note. (See Figure 3).
Copyright statement for image in the public domain:
From [or Adapted from]. Title of Work [Photograph], by A. A. Author, year of publication, Site Name (URL). In the public domain.
Photograph in the Public Domain

Note . From Study for The Cellist [Photograph], by A. Modigliani, 1909, Abcgallery (http://www.abcgallery.com/M/modigliani/modigliani12.html) . In the public domain.
Free Photos Online: Some photo sites allow for reproduction of images without attribution to the source or creator of that image. Sites such as Pixabay , Pexels , and Unsplash , for example, provide images that do not require attribution. A copyright statement is not needed for these images.
Reference Entries for Figures
In addition to a copyright attribution, include a reference entry for any source credited in a figure note. Below is the APA Style (7th ed.) reference entry template for a photograph:
Author last name, First initial. Middle initial. (year). Title of photograph [Photograph]. Site or Source Name. URL
Figure Checklist
- Is the figure necessary?
- Is the resolution of the image clear enough to be read and understood?
- Is the figure mentioned in the paper’s text?
- Is the figure inserted under the paragraph where it is first mentioned?
- Does the text explain how the figure is relevant to the discussion in the paper without repeating all the information from the figure in the text?
- Does the figure title provide a brief explanation?
- Are all elements of the figure clearly labeled?
- Are all figures numbered consecutively?
- Is proper credit given to the source of the figure in the figure note?
- Has a reference entry been provided for the source of the figure?
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association: The official guide to APA style (7th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
© 2020 by Purdue Global Academic Success Center and Writing Center
Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
3 Responses
- Pingbacks 0
What size should the visual be in the actual paper? I have students ask this, and frequently their visuals cover half an entire page, but I cannot find the answer.
Hi Leslie, the American Psychological Association (APA) does not specify the size of visuals used, but does state that tables and figures should fit on one page. The publication manual of APA (2020) also states that tables and figures “should not be used for mere decoration in an academic paper. Instead, every table and figure should serve a purpose” (p. 195). It may be helpful to direct students with questions to review the sample tables and figures available here: https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/tables-figures
I”ve learned a lot from reading this.. I have never an apa paper before
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed

COMMENTS
Graphic Organizers for Research Papers, Spring 2023. 1 of 6 Graphic Organizers for Research Papers A graphic organizer (also referred to as a research matrix) is a useful tool for compiling detailed notes during the research process. These types of note-taking systems can take a long time to
Helps you visualize your research and how elements connect with each other. Enhance your essays, summaries and research papers with visual elements. Track correlations between your thoughts, observations, facts or general ideas. When it comes to essay writing, the most common graphic organizers are webs, mind maps, and concept maps.
The publication manual of APA (2020) also states that tables and figures “should not be used for mere decoration in an academic paper. Instead, every table and figure should serve a purpose” (p. 195).