
How to write a Reflection on Group Work Essay
Here are the exact steps you need to follow for a reflection on group work essay.
- Explain what Reflection Is
- Explore the benefits of group work
- Explore the challenges group
- Give examples of the benefits and challenges your group faced
- Discuss how your group handled your challenges
- Discuss what you will do differently next time
Do you have to reflect on how your group work project went?
This is a super common essay that teachers assign. So, let’s have a look at how you can go about writing a superb reflection on your group work project that should get great grades.
The essay structure I outline below takes the funnel approach to essay writing: it starts broad and general, then zooms in on your specific group’s situation.

Disclaimer: Make sure you check with your teacher to see if this is a good style to use for your essay. Take a draft to your teacher to get their feedback on whether it’s what they’re looking for!
This is a 6-step essay (the 7 th step is editing!). Here’s a general rule for how much depth to go into depending on your word count:
- 1500 word essay – one paragraph for each step, plus a paragraph each for the introduction and conclusion ;
- 3000 word essay – two paragraphs for each step, plus a paragraph each for the introduction and conclusion;
- 300 – 500 word essay – one or two sentences for each step.
Adjust this essay plan depending on your teacher’s requirements and remember to always ask your teacher, a classmate or a professional tutor to review the piece before submitting.
Here’s the steps I’ll outline for you in this advice article:

Step 1. Explain what ‘Reflection’ Is
You might have heard that you need to define your terms in essays. Well, the most important term in this essay is ‘reflection’.
So, let’s have a look at what reflection is…
Reflection is the process of:
- Pausing and looking back at what has just happened; then
- Thinking about how you can get better next time.
Reflection is encouraged in most professions because it’s believed that reflection helps you to become better at your job – we could say ‘reflection makes you a better practitioner’.
Think about it: let’s say you did a speech in front of a crowd. Then, you looked at video footage of that speech and realised you said ‘um’ and ‘ah’ too many times. Next time, you’re going to focus on not saying ‘um’ so that you’ll do a better job next time, right?
Well, that’s reflection: thinking about what happened and how you can do better next time.
It’s really important that you do both of the above two points in your essay. You can’t just say what happened. You need to say how you will do better next time in order to get a top grade on this group work reflection essay.
Scholarly Sources to Cite for Step 1
Okay, so you have a good general idea of what reflection is. Now, what scholarly sources should you use when explaining reflection? Below, I’m going to give you two basic sources that would usually be enough for an undergraduate essay. I’ll also suggest two more sources for further reading if you really want to shine!
I recommend these two sources to cite when explaining what reflective practice is and how it occurs. They are two of the central sources on reflective practice:
- Describe what happened during the group work process
- Explain how you felt during the group work process
- Look at the good and bad aspects of the group work process
- What were some of the things that got in the way of success? What were some things that helped you succeed?
- What could you have done differently to improve the situation?
- Action plan. What are you going to do next time to make the group work process better?
- What? Explain what happened
- So What? Explain what you learned
- Now What? What can I do next time to make the group work process better?
Possible Sources:
Bassot, B. (2015). The reflective practice guide: An interdisciplinary approach to critical reflection . Routledge.
Brock, A. (2014). What is reflection and reflective practice?. In The Early Years Reflective Practice Handbook (pp. 25-39). Routledge.
Gibbs, G. (1988) Learning by Doing: A guide to teaching and learning methods . Further Education Unit, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford.
Rolfe, G., Freshwater, D., Jasper, M. (2001). Critical reflection in nursing and the helping professions: a user’s guide. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Extension Sources for Top Students
Now, if you want to go deeper and really show off your knowledge, have a look at these two scholars:
- John Dewey – the first major scholar to come up with the idea of reflective practice
- Donald Schön – technical rationality, reflection in action vs. reflection on action
Get a Pdf of this article for class
Enjoy subscriber-only access to this article’s pdf
Step 2. Explore the general benefits of group work for learning
Once you have given an explanation of what group work is (and hopefully cited Gibbs, Rolfe, Dewey or Schon), I recommend digging into the benefits of group work for your own learning.
The teacher gave you a group work task for a reason: what is that reason?
You’ll need to explain the reasons group work is beneficial for you. This will show your teacher that you understand what group work is supposed to achieve. Here’s some ideas:
- Multiple Perspectives. Group work helps you to see things from other people’s perspectives. If you did the task on your own, you might not have thought of some of the ideas that your team members contributed to the project.
- Contribution of Unique Skills. Each team member might have a different set of skills they can bring to the table. You can explain how groups can make the most of different team members’ strengths to make the final contribution as good as it can be. For example, one team member might be good at IT and might be able to put together a strong final presentation, while another member might be a pro at researching using google scholar so they got the task of doing the initial scholarly research.
- Improved Communication Skills. Group work projects help you to work on your communication skills. Communication skills required in group work projects include speaking in turn, speaking up when you have ideas, actively listening to other team members’ contributions, and crucially making compromises for the good of the team.
- Learn to Manage Workplace Conflict. Lastly, your teachers often assign you group work tasks so you can learn to manage conflict and disagreement. You’ll come across this a whole lot in the workplace, so your teachers want you to have some experience being professional while handling disagreements.
You might be able to add more ideas to this list, or you might just want to select one or two from that list to write about depending on the length requirements for the essay.
Scholarly Sources for Step 3
Make sure you provide citations for these points above. You might want to use google scholar or google books and type in ‘Benefits of group work’ to find some quality scholarly sources to cite.
Step 3. Explore the general challenges group work can cause
Step 3 is the mirror image of Step 2. For this step, explore the challenges posed by group work.
Students are usually pretty good at this step because you can usually think of some aspects of group work that made you anxious or frustrated. Here are a few common challenges that group work causes:
- Time Consuming. You need to organize meetups and often can’t move onto the next component of the project until everyone has agree to move on. When working on your own you can just crack on and get it done. So, team work often takes a lot of time and requires significant pre-planning so you don’t miss your submission deadlines!
- Learning Style Conflicts. Different people learn in different ways. Some of us like to get everything done at the last minute or are not very meticulous in our writing. Others of us are very organized and detailed and get anxious when things don’t go exactly how we expect. This leads to conflict and frustration in a group work setting.
- Free Loaders. Usually in a group work project there’s people who do more work than others. The issue of free loaders is always going to be a challenge in group work, and you can discuss in this section how ensuring individual accountability to the group is a common group work issue.
- Communication Breakdown. This is one especially for online students. It’s often the case that you email team members your ideas or to ask them to reply by a deadline and you don’t hear back from them. Regular communication is an important part of group work, yet sometimes your team members will let you down on this part.
As with Step 3, consider adding more points to this list if you need to, or selecting one or two if your essay is only a short one.
8 Pros And Cons Of Group Work At University
You’ll probably find you can cite the same scholarly sources for both steps 2 and 3 because if a source discusses the benefits of group work it’ll probably also discuss the challenges.
Step 4. Explore the specific benefits and challenges your group faced
Step 4 is where you zoom in on your group’s specific challenges. Have a think: what were the issues you really struggled with as a group?
- Was one team member absent for a few of the group meetings?
- Did the group have to change some deadlines due to lack of time?
- Were there any specific disagreements you had to work through?
- Did a group member drop out of the group part way through?
- Were there any communication break downs?
Feel free to also mention some things your group did really well. Have a think about these examples:
- Was one member of the group really good at organizing you all?
- Did you make some good professional relationships?
- Did a group member help you to see something from an entirely new perspective?
- Did working in a group help you to feel like you weren’t lost and alone in the process of completing the group work component of your course?
Here, because you’re talking about your own perspectives, it’s usually okay to use first person language (but check with your teacher). You are also talking about your own point of view so citations might not be quite as necessary, but it’s still a good idea to add in one or two citations – perhaps to the sources you cited in Steps 2 and 3?
Step 5. Discuss how your group managed your challenges
Step 5 is where you can explore how you worked to overcome some of the challenges you mentioned in Step 4.
So, have a think:
- Did your group make any changes part way through the project to address some challenges you faced?
- Did you set roles or delegate tasks to help ensure the group work process went smoothly?
- Did you contact your teacher at any point for advice on how to progress in the group work scenario?
- Did you use technology such as Google Docs or Facebook Messenger to help you to collaborate more effectively as a team?
In this step, you should be showing how your team was proactive in reflecting on your group work progress and making changes throughout the process to ensure it ran as smoothly as possible. This act of making little changes throughout the group work process is what’s called ‘Reflection in Action’ (Schön, 2017).
Scholarly Source for Step 5
Schön, D. A. (2017). The reflective practitioner: How professionals think in action . Routledge.
Step 6. Conclude by exploring what you will do differently next time
Step 6 is the most important step, and the one far too many students skip. For Step 6, you need to show how you not only reflected on what happened but also are able to use that reflection for personal growth into the future.
This is the heart and soul of your piece: here, you’re tying everything together and showing why reflection is so important!
This is the ‘action plan’ step in Gibbs’ cycle (you might want to cite Gibbs in this section!).
For Step 6, make some suggestions about how (based on your reflection) you now have some takeaway tips that you’ll bring forward to improve your group work skills next time. Here’s some ideas:
- Will you work harder next time to set deadlines in advance?
- Will you ensure you set clearer group roles next time to ensure the process runs more smoothly?
- Will you use a different type of technology (such as Google Docs) to ensure group communication goes more smoothly?
- Will you make sure you ask for help from your teacher earlier on in the process when you face challenges?
- Will you try harder to see things from everyone’s perspectives so there’s less conflict?
This step will be personalized based upon your own group work challenges and how you felt about the group work process. Even if you think your group worked really well together, I recommend you still come up with one or two ideas for continual improvement. Your teacher will want to see that you used reflection to strive for continual self-improvement.
Scholarly Source for Step 6
Step 7. edit.
Okay, you’ve got the nuts and bolts of the assessment put together now! Next, all you’ve got to do is write up the introduction and conclusion then edit the piece to make sure you keep growing your grades.
Here’s a few important suggestions for this last point:
- You should always write your introduction and conclusion last. They will be easier to write now that you’ve completed the main ‘body’ of the essay;
- Use my 5-step I.N.T.R.O method to write your introduction;
- Use my 5 C’s Conclusion method to write your conclusion;
- Use my 5 tips for editing an essay to edit it;
- Use the ProWritingAid app to get advice on how to improve your grammar and spelling. Make sure to also use the report on sentence length. It finds sentences that are too long and gives you advice on how to shorten them – such a good strategy for improving evaluative essay quality!
- Make sure you contact your teacher and ask for a one-to-one tutorial to go through the piece before submitting. This article only gives general advice, and you might need to make changes based upon the specific essay requirements that your teacher has provided.
That’s it! 7 steps to writing a quality group work reflection essay. I hope you found it useful. If you liked this post and want more clear and specific advice on writing great essays, I recommend signing up to my personal tutor mailing list.
Let’s sum up with those 7 steps one last time:
- Explain what ‘Reflection’ Is
- Explore the benefits of group work for learning
- Explore the challenges of group work for learning
- Explore the specific benefits and challenges your group faced
- Discuss how your group managed your challenges
- Conclude by exploring what you will do differently next time

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
2 thoughts on “How to write a Reflection on Group Work Essay”
Great instructions on writing a reflection essay. I would not change anything.

Thanks so much for your feedback! I really appreciate it. – Chris.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Group Writing
What this handout is about.
Whether in the academic world or the business world, all of us are likely to participate in some form of group writing—an undergraduate group project for a class, a collaborative research paper or grant proposal, or a report produced by a business team. Writing in a group can have many benefits: multiple brains are better than one, both for generating ideas and for getting a job done. However, working in a group can sometimes be stressful because there are various opinions and writing styles to incorporate into one final product that pleases everyone. This handout will offer an overview of the collaborative process, strategies for writing successfully together, and tips for avoiding common pitfalls. It will also include links to some other handouts that may be especially helpful as your group moves through the writing process.
Disclaimer and disclosure
As this is a group writing handout, several Writing Center coaches worked together to create it. No coaches were harmed in this process; however, we did experience both the pros and the cons of the collaborative process. We have personally tested the various methods for sharing files and scheduling meetings that are described here. However, these are only our suggestions; we do not advocate any particular service or site.
The spectrum of collaboration in group writing
All writing can be considered collaborative in a sense, though we often don’t think of it that way. It would be truly surprising to find an author whose writing, even if it was completed independently, had not been influenced at some point by discussions with friends or colleagues. The range of possible collaboration varies from a group of co-authors who go through each portion of the writing process together, writing as a group with one voice, to a group with a primary author who does the majority of the work and then receives comments or edits from the co-authors.
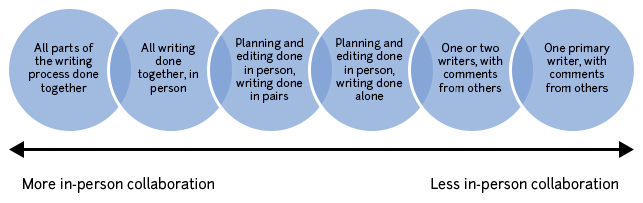
Group projects for classes should usually fall towards the middle to left side of this diagram, with group members contributing roughly equally. However, in collaborations on research projects, the level of involvement of the various group members may vary widely. The key to success in either case is to be clear about group member responsibilities and expectations and to give credit (authorship) to members who contribute an appropriate amount. It may be useful to credit each group member for their various contributions.
Overview of steps of the collaborative process
Here we outline the steps of the collaborative process. You can use these questions to focus your thinking at each stage.
- Share ideas and brainstorm together.
- Formulate a draft thesis or argument .
- Think about your assignment and the final product. What should it look like? What is its purpose? Who is the intended audience ?
- Decide together who will write which parts of the paper/project.
- What will the final product look like?
- Arrange meetings: How often will the group or subsets of the group meet? When and where will the group meet? If the group doesn’t meet in person, how will information be shared?
- Scheduling: What is the deadline for the final product? What are the deadlines for drafts?
- How will the group find appropriate sources (books, journal articles, newspaper articles, visual media, trustworthy websites, interviews)? If the group will be creating data by conducting research, how will that process work?
- Who will read and process the information found? This task again may be done by all members or divided up amongst members so that each person becomes the expert in one area and then teaches the rest of the group.
- Think critically about the sources and their contributions to your topic. Which evidence should you include or exclude? Do you need more sources?
- Analyze the data. How will you interpret your findings? What is the best way to present any relevant information to your readers-should you include pictures, graphs, tables, and charts, or just written text?
- Note that brainstorming the main points of your paper as a group is helpful, even if separate parts of the writing are assigned to individuals. You’ll want to be sure that everyone agrees on the central ideas.
- Where does your individual writing fit into the whole document?
- Writing together may not be feasible for longer assignments or papers with coauthors at different universities, and it can be time-consuming. However, writing together does ensure that the finished document has one cohesive voice.
- Talk about how the writing session should go BEFORE you get started. What goals do you have? How will you approach the writing task at hand?
- Many people find it helpful to get all of the ideas down on paper in a rough form before discussing exact phrasing.
- Remember that everyone has a different writing style! The most important thing is that your sentences be clear to readers.
- If your group has drafted parts of the document separately, merge your ideas together into a single document first, then focus on meshing the styles. The first concern is to create a coherent product with a logical flow of ideas. Then the stylistic differences of the individual portions must be smoothed over.
- Revise the ideas and structure of the paper before worrying about smaller, sentence-level errors (like problems with punctuation, grammar, or word choice). Is the argument clear? Is the evidence presented in a logical order? Do the transitions connect the ideas effectively?
- Proofreading: Check for typos, spelling errors, punctuation problems, formatting issues, and grammatical mistakes. Reading the paper aloud is a very helpful strategy at this point.
Helpful collaborative writing strategies
Attitude counts for a lot.
Group work can be challenging at times, but a little enthusiasm can go a long way to helping the momentum of the group. Keep in mind that working in a group provides a unique opportunity to see how other people write; as you learn about their writing processes and strategies, you can reflect on your own. Working in a group inherently involves some level of negotiation, which will also facilitate your ability to skillfully work with others in the future.
Remember that respect goes along way! Group members will bring different skill sets and various amounts and types of background knowledge to the table. Show your fellow writers respect by listening carefully, talking to share your ideas, showing up on time for meetings, sending out drafts on schedule, providing positive feedback, and taking responsibility for an appropriate share of the work.
Start early and allow plenty of time for revising
Getting started early is important in individual projects; however, it is absolutely essential in group work. Because of the multiple people involved in researching and writing the paper, there are aspects of group projects that take additional time, such as deciding and agreeing upon a topic. Group projects should be approached in a structured way because there is simply less scheduling flexibility than when you are working alone. The final product should reflect a unified, cohesive voice and argument, and the only way of accomplishing this is by producing multiple drafts and revising them multiple times.
Plan a strategy for scheduling
One of the difficult aspects of collaborative writing is finding times when everyone can meet. Much of the group’s work may be completed individually, but face-to-face meetings are useful for ensuring that everyone is on the same page. Doodle.com , whenisgood.net , and needtomeet.com are free websites that can make scheduling easier. Using these sites, an organizer suggests multiple dates and times for a meeting, and then each group member can indicate whether they are able to meet at the specified times.
It is very important to set deadlines for drafts; people are busy, and not everyone will have time to read and respond at the last minute. It may help to assign a group facilitator who can send out reminders of the deadlines. If the writing is for a co-authored research paper, the lead author can take responsibility for reminding others that comments on a given draft are due by a specific date.
Submitting drafts at least one day ahead of the meeting allows other authors the opportunity to read over them before the meeting and arrive ready for a productive discussion.
Find a convenient and effective way to share files
There are many different ways to share drafts, research materials, and other files. Here we describe a few of the potential options we have explored and found to be functional. We do not advocate any one option, and we realize there are other equally useful options—this list is just a possible starting point for you:
- Email attachments. People often share files by email; however, especially when there are many group members or there is a flurry of writing activity, this can lead to a deluge of emails in everyone’s inboxes and significant confusion about which file version is current.
- Google documents . Files can be shared between group members and are instantaneously updated, even if two members are working at once. Changes made by one member will automatically appear on the document seen by all members. However, to use this option, every group member must have a Gmail account (which is free), and there are often formatting issues when converting Google documents back to Microsoft Word.
- Dropbox . Dropbox.com is free to join. It allows you to share up to 2GB of files, which can then be synched and accessible from multiple computers. The downside of this approach is that everyone has to join, and someone must install the software on at least one personal computer. Dropbox can then be accessed from any computer online by logging onto the website.
- Common server space. If all group members have access to a shared server space, this is often an ideal solution. Members of a lab group or a lab course with available server space typically have these resources. Just be sure to make a folder for your project and clearly label your files.
Note that even when you are sharing or storing files for group writing projects in a common location, it is still essential to periodically make back-up copies and store them on your own computer! It is never fun to lose your (or your group’s) hard work.
Try separating the tasks of revising and editing/proofreading
It may be helpful to assign giving feedback on specific items to particular group members. First, group members should provide general feedback and comments on content. Only after revising and solidifying the main ideas and structure of the paper should you move on to editing and proofreading. After all, there is no point in spending your time making a certain sentence as beautiful and correct as possible when that sentence may later be cut out. When completing your final revisions, it may be helpful to assign various concerns (for example, grammar, organization, flow, transitions, and format) to individual group members to focus this process. This is an excellent time to let group members play to their strengths; if you know that you are good at transitions, offer to take care of that editing task.
Your group project is an opportunity to become experts on your topic. Go to the library (in actuality or online), collect relevant books, articles, and data sources, and consult a reference librarian if you have any issues. Talk to your professor or TA early in the process to ensure that the group is on the right track. Find experts in the field to interview if it is appropriate. If you have data to analyze, meet with a statistician. If you are having issues with the writing, use the online handouts at the Writing Center or come in for a face-to-face meeting: a coach can meet with you as a group or one-on-one.
Immediately dividing the writing into pieces
While this may initially seem to be the best way to approach a group writing process, it can also generate more work later on, when the parts written separately must be put together into a unified document. The different pieces must first be edited to generate a logical flow of ideas, without repetition. Once the pieces have been stuck together, the entire paper must be edited to eliminate differences in style and any inconsistencies between the individual authors’ various chunks. Thus, while it may take more time up-front to write together, in the end a closer collaboration can save you from the difficulties of combining pieces of writing and may create a stronger, more cohesive document.
Procrastination
Although this is solid advice for any project, it is even more essential to start working on group projects in a timely manner. In group writing, there are more people to help with the work-but there are also multiple schedules to juggle and more opinions to seek.
Being a solo group member
Not everyone enjoys working in groups. You may truly desire to go solo on this project, and you may even be capable of doing a great job on your own. However, if this is a group assignment, then the prompt is asking for everyone to participate. If you are feeling the need to take over everything, try discussing expectations with your fellow group members as well as the teaching assistant or professor. However, always address your concerns with group members first. Try to approach the group project as a learning experiment: you are learning not only about the project material but also about how to motivate others and work together.
Waiting for other group members to do all of the work
If this is a project for a class, you are leaving your grade in the control of others. Leaving the work to everyone else is not fair to your group mates. And in the end, if you do not contribute, then you are taking credit for work that you did not do; this is a form of academic dishonesty. To ensure that you can do your share, try to volunteer early for a portion of the work that you are interested in or feel you can manage.
Leaving all the end work to one person
It may be tempting to leave all merging, editing, and/or presentation work to one person. Be careful. There are several reasons why this may be ill-advised. 1) The editor/presenter may not completely understand every idea, sentence, or word that another author wrote, leading to ambiguity or even mistakes in the end paper or presentation. 2) Editing is tough, time-consuming work. The editor often finds himself or herself doing more work than was expected as they try to decipher and merge the original contributions under the time pressure of an approaching deadline. If you decide to follow this path and have one person combine the separate writings of many people, be sure to leave plenty of time for a final review by all of the writers. Ask the editor to send out the final draft of the completed work to each of the authors and let every contributor review and respond to the final product. Ideally, there should also be a test run of any live presentations that the group or a representative may make.
Entirely negative critiques
When giving feedback or commenting on the work of other group members, focusing only on “problems” can be overwhelming and put your colleagues on the defensive. Try to highlight the positive parts of the project in addition to pointing out things that need work. Remember that this is constructive feedback, so don’t forget to add concrete, specific suggestions on how to proceed. It can also be helpful to remind yourself that many of your comments are your own opinions or reactions, not absolute, unquestionable truths, and then phrase what you say accordingly. It is much easier and more helpful to hear “I had trouble understanding this paragraph because I couldn’t see how it tied back to our main argument” than to hear “this paragraph is unclear and irrelevant.”
Writing in a group can be challenging, but it is also a wonderful opportunity to learn about your topic, the writing process, and the best strategies for collaboration. We hope that our tips will help you and your group members have a great experience.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Cross, Geoffrey. 1994. Collaboration and Conflict: A Contextual Exploration of Group Writing and Positive Emphasis . Cresskill, NJ: Hampton Press.
Ede, Lisa S., and Andrea Lunsford. 1990. Singular Texts/Plural Authors: Perspectives on Collaborative Writing . Carbondale, IL: Southern Illinois University Press.
Speck, Bruce W. 2002. Facilitating Students’ Collaborative Writing . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Our Mission

Group Work That Works
Educators weigh in on solutions to the common pitfalls of group work.
Mention group work and you’re confronted with pointed questions and criticisms. The big problems, according to our audience: One or two students do all the work; it can be hard on introverts; and grading the group isn’t fair to the individuals.
But the research suggests that a certain amount of group work is beneficial.
“The most effective creative process alternates between time in groups, collaboration, interaction, and conversation... [and] times of solitude, where something different happens cognitively in your brain,” says Dr. Keith Sawyer, a researcher on creativity and collaboration, and author of Group Genius: The Creative Power of Collaboration .
So we looked through our archives and reached out to educators on Facebook to find out what solutions they’ve come up with for these common problems.
Making Sure Everyone Participates
“How many times have we put students in groups only to watch them interact with their laptops instead of each other? Or complain about a lazy teammate?” asks Mary Burns, a former French, Latin, and English middle and high school teacher who now offers professional development in technology integration.
Unequal participation is perhaps the most common complaint about group work. Still, a review of Edutopia’s archives—and the tens of thousands of insights we receive in comments and reactions to our articles—revealed a handful of practices that educators use to promote equal participation. These involve setting out clear expectations for group work, increasing accountability among participants, and nurturing a productive group work dynamic.
Norms: At Aptos Middle School in San Francisco, the first step for group work is establishing group norms. Taji Allen-Sanchez, a sixth- and seventh-grade science teacher, lists expectations on the whiteboard, such as “everyone contributes” and “help others do things for themselves.”
For ambitious projects, Mikel Grady Jones, a high school math teacher in Houston, takes it a step further, asking her students to sign a group contract in which they agree on how they’ll divide the tasks and on expectations like “we all promise to do our work on time.” Heather Wolpert-Gawron, an English middle school teacher in Los Angeles, suggests creating a classroom contract with your students at the start of the year, so that agreed-upon norms can be referenced each time a new group activity begins.
Group size: It’s a simple fix, but the size of the groups can help establish the right dynamics. Generally, smaller groups are better because students can’t get away with hiding while the work is completed by others.
“When there is less room to hide, nonparticipation is more difficult,” says Burns. She recommends groups of four to five students, while Brande Tucker Arthur, a 10th-grade biology teacher in Lynchburg, Virginia, recommends even smaller groups of two or three students.
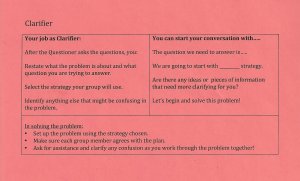
Meaningful roles: Roles can play an important part in keeping students accountable, but not all roles are helpful. A role like materials manager, for example, won’t actively engage a student in contributing to a group problem; the roles must be both meaningful and interdependent.
At University Park Campus School , a grade 7–12 school in Worcester, Massachusetts, students take on highly interdependent roles like summarizer, questioner, and clarifier. In an ongoing project, the questioner asks probing questions about the problem and suggests a few ideas on how to solve it, while the clarifier attempts to clear up any confusion, restates the problem, and selects a possible strategy the group will use as they move forward.
At Design 39, a K–8 school in San Diego, groups and roles are assigned randomly using Random Team Generator , but ClassDojo , Team Shake , and drawing students’ names from a container can also do the trick. In a practice called vertical learning, Design 39 students conduct group work publicly, writing out their thought processes on whiteboards to facilitate group feedback. The combination of randomizing teams and public sharing exposes students to a range of problem-solving approaches, gets them more comfortable with making mistakes, promotes teamwork, and allows kids to utilize different skill sets during each project.
Rich tasks: Making sure that a project is challenging and compelling is critical. A rich task is a problem that has multiple pathways to the solution and that one person would have difficulty solving on their own.
In an eighth-grade math class at Design 39, one recent rich task explored the concept of how monetary investments grow: Groups were tasked with solving exponential growth problems using simple and compound interest rates.
Rich tasks are not just for math class. When Dan St. Louis, the principal of University Park, was a teacher, he asked his English students to come up with a group definition of the word Orwellian . They did this through the jigsaw method, a type of grouping strategy that John Hattie’s study Visible Learning ranked as highly effective.
“Five groups of five students might each read a different news article about the modern world,” says St. Louis. “Then each student would join a new group of five where they need to explain their previous group’s article to each other and make connections to each. Using these connections, the group must then construct a definition of the word Orwellian .” For another example of the jigsaw approach, see this video from Cult of Pedagogy.
Supporting Introverts
Teachers worry about the impact of group work on introverts. Some of our educators suggest that giving introverts choice in who they’re grouped with can help them feel more comfortable.
“Even the quietest students are usually comfortable and confident when they are with peers with whom they connect,” says Shelly Kunkle, a veteran teacher at Wasawee Middle School in North Webster, Indiana. Wolpert-Gawron asks her students to list four peers they want to work with and then makes sure to pair them with one from their list.
Having defined roles within groups—like clarifier or questioner—also provides structure for students who may be less comfortable within complex social dynamics, and ensures that introverts don’t get overshadowed by their more extroverted peers.

Finally, be mindful that introverted students often simply need time to recharge. “Many introverts do not mind and even enjoy interacting in groups as long as they get some quiet time and solitude to recharge. It’s not about being shy or feeling unsafe in a large group,” says Barb Larochelle, a recently retired high school English teacher in Edmonton, Alberta, who taught for 29 years.
“I planned classes with some time to work quietly alone, some time to interact in smaller groups or as a whole class, and some time to get up and move around a little. A whole class of any one of those is going to be hard on one group, but a balance works well.”
Assessing Group Work
Grading group work is problematic. Often, you don’t have a clear understanding of what each student knows, and a single student’s lack of effort can torpedo the group grade. To some degree, strategies that assign meaningful roles or that require public presentations from groups provide a window in to each student’s knowledge and contributions.
But not all classwork needs to be graded. Suzanna Kruger, a high school science teacher in Seaside, Oregon, doesn’t grade group work—there are plenty of individual assignments that receive grades, and plenty of other opportunities for formative assessment.
John McCarthy, a former high school English and social studies teacher and current education consultant and adjunct professor at Madonna University for the graduate department for education, suggests using group presentations or group products as a non-graded review for a test. But if you want to grade group work, he recommends making all academic assessments within group work individual assessments. For example, instead of grading a group presentation, McCarthy grades each student on an essay, which the students then use to create their group presentation.

Laura Moffit, a fifth-grade teacher in Wilmington, North Carolina, uses self and peer evaluations to shed light on how each student is contributing to group work—starting with a lesson on how to do an objective evaluation. “Just have students circle :), :|, or :( on three to five statements about each partner, anonymously,” Moffit commented on Facebook. “Then give the evaluations back to each group member. Finding out what people really think of your performance is a wake-up call.”
And Ted Malefyt, a middle school science teacher in Hamilton, Michigan, carries a clipboard with the class list formatted in a spreadsheet and walks around checking in on students while they do group work.
“Using this spreadsheet, you have your own record of which student is meeting your expectations and who needs extra help,” explains Malefyt. “As formative assessment takes place, quickly document with simple checkmarks.”
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Over 170 Prompts to Inspire Writing and Discussion
Here are all of our Student Opinion questions from the 2020-21 school year. Each question is based on a different New York Times article, interactive feature or video.

By The Learning Network
Each school day we publish a new Student Opinion question, and students use these writing prompts to reflect on their experiences and identities and respond to current events unfolding around them. To introduce each question, we provide an excerpt from a related New York Times article or Opinion piece as well as a free link to the original article.
During the 2020-21 school year, we asked 176 questions, and you can find them all below or here as a PDF . The questions are divided into two categories — those that provide opportunities for debate and persuasive writing, and those that lend themselves to creative, personal or reflective writing.
Teachers can use these prompts to help students practice narrative and persuasive writing, start classroom debates and even spark conversation between students around the world via our comments section. For more ideas on how to use our Student Opinion questions, we offer a short tutorial along with a nine-minute video on how one high school English teacher and her students use this feature .
Questions for Debate and Persuasive Writing
1. Should Athletes Speak Out On Social and Political Issues? 2. Should All Young People Learn How to Invest in the Stock Market? 3. What Are the Greatest Songs of All Time? 4. Should There Be More Gender Options on Identification Documents? 5. Should We End the Practice of Tipping? 6. Should There Be Separate Social Media Apps for Children? 7. Do Marriage Proposals Still Have a Place in Today’s Society? 8. How Do You Feel About Cancel Culture? 9. Should the United States Decriminalize the Possession of Drugs? 10. Does Reality TV Deserve Its Bad Rap? 11. Should the Death Penalty Be Abolished? 12. How Should Parents Support a Student Who Has Fallen Behind in School? 13. When Is It OK to Be a Snitch? 14. Should People Be Required to Show Proof of Vaccination? 15. How Much Have You and Your Community Changed Since George Floyd’s Death? 16. Can Empathy Be Taught? Should Schools Try to Help Us Feel One Another’s Pain? 17. Should Schools or Employers Be Allowed to Tell People How They Should Wear Their Hair? 18. Is Your Generation Doing Its Part to Strengthen Our Democracy? 19. Should Corporations Take Political Stands? 20. Should We Rename Schools Named for Historical Figures With Ties to Racism, Sexism or Slavery? 21. How Should Schools Hold Students Accountable for Hurting Others? 22. What Ideas Do You Have to Improve Your Favorite Sport? 23. Are Presidential Debates Helpful to Voters? Or Should They Be Scrapped? 24. Is the Electoral College a Problem? Does It Need to Be Fixed? 25. Do You Care Who Sits on the Supreme Court? Should We Care? 26. Should Museums Return Looted Artifacts to Their Countries of Origin? 27. Should Schools Provide Free Pads and Tampons? 28. Should Teachers Be Allowed to Wear Political Symbols? 29. Do You Think People Have Gotten Too Relaxed About Covid? 30. Who Do You Think Should Be Person of the Year for 2020? 31. How Should Racial Slurs in Literature Be Handled in the Classroom? 32. Should There Still Be Snow Days? 33. What Are Your Reactions to the Storming of the Capitol by a Pro-Trump Mob? 34. What Do You Think of the Decision by Tech Companies to Block President Trump? 35. If You Were a Member of Congress, Would You Vote to Impeach President Trump? 36. What Would You Do First if You Were the New President? 37. Who Do You Hope Will Win the 2020 Presidential Election? 38. Should Media Literacy Be a Required Course in School? 39. What Are Your Reactions to the Results of Election 2020? Where Do We Go From Here? 40. How Should We Remember the Problematic Actions of the Nation’s Founders? 41. As Coronavirus Cases Surge, How Should Leaders Decide What Stays Open and What Closes? 42. What Is Your Reaction to the Inauguration of Joe Biden and Kamala Harris? 43. How Worried Should We Be About Screen Time During the Pandemic? 44. Should Schools Be Able to Discipline Students for What They Say on Social Media? 45. What Works of Art, Culture and Technology Flopped in 2020? 46. How Do You Feel About Censored Music? 47. Why Do You Think ‘Drivers License’ Became Such a Smash Hit? 48. Justice Ginsburg Fought for Gender Equality. How Close Are We to Achieving That Goal? 49. How Well Do You Think Our Leaders Have Responded to the Coronavirus Crisis? 50. To What Extent Is the Legacy of Slavery and Racism Still Present in America in 2020? 51. How Should We Reimagine Our Schools So That All Students Receive a Quality Education? 52. How Concerned Do You Think We Should Be About the Integrity of the 2020 Election? 53. What Issues in This Election Season Matter Most to You? 54. Is Summer School a Smart Way to Make Up for Learning Lost This School Year? 55. What Is Your Reaction to the Senate’s Acquittal of Former President Trump? 56. What Is the Worst Toy Ever? 57. How Should We Balance Safety and Urgency in Developing a Covid-19 Vaccine? 58. What Are Your Reactions to Oprah’s Interview With Harry and Meghan? 59. Should the Government Provide a Guaranteed Income for Families With Children? 60. Should There Be More Public Restrooms? 61. Should High School-Age Basketball Players Be Able to Get Paid? 62. Should Team Sports Happen This Year? 63. Who Are the Best Musical Artists of the Past Year? What Are the Best Songs? 64. Should We Cancel Student Debt? 65. How Closely Should Actors’ Identities Reflect the Roles They Play? 66. Should White Writers Translate a Black Author’s Work? 67. Would You Buy an NFT? 68. Should Kids Still Learn to Tell Time? 69. Should All Schools Teach Financial Literacy? 70. What Is Your Reaction to the Verdict in the Derek Chauvin Trial? 71. What Is the Best Way to Stop Abusive Language Online? 72. What Are the Underlying Systems That Hold a Society Together? 73. What Grade Would You Give President Biden on His First 100 Days? 74. Should High Schools Post Their Annual College Lists? 75. Are C.E.O.s Paid Too Much? 76. Should We Rethink Thanksgiving? 77. What Is the Best Way to Get Teenagers Vaccinated? 78. Do You Want Your Parents and Grandparents to Get the New Coronavirus Vaccine? 79. What Is Your Reaction to New Guidelines That Loosen Mask Requirements? 80. Who Should We Honor on Our Money? 81. Is Your School’s Dress Code Outdated? 82. Does Everyone Have a Responsibility to Vote? 83. How Is Your Generation Changing Politics?
Questions for Creative and Personal Writing
84. What Does Your Unique Style Say About You? 85. How Do You Spend Your Downtime? 86. Would You Want to Live to 200? 87. How Do You Connect to Your Heritage? 88. What Do You Think Are the Secrets to Happiness? 89. Are You a Sneakerhead? 90. What Role Have Mentors Played in Your Life? 91. If You Could Make Your Own Podcast, What Would It Be About? 92. Have You Ever Felt Pressure to ‘Sell Your Pain’? 93. Do You Think You Make Good Climate Choices? 94. What Does TikTok Mean to You? 95. Do Your Parents Overpraise You? 96. Do You Want to Travel in Space? 97. Do You Feel You’re Friends With Celebrities or Influencers You Follow Online? 98. Would You Eat Food Grown in a Lab? 99. What Makes You Cringe? 100. What Volunteer Work Would You Most Like to Do? 101. How Do You Respond When People Ask, ‘Where Are You From?’ 102. Has a School Assignment or Activity Ever Made You Uncomfortable? 103. How Does Your Identity Inform Your Political Beliefs and Values? 104. Are You an Orchid, a Tulip or a Dandelion? 105. Are You Having a Tough Time Maintaining Friendships These Days? 106. How Is Your Mental Health These Days? 107. Do You Love Writing or Receiving Letters? 108. What Has Television Taught You About Social Class? 109. Are You Easily Distracted? 110. What Objects Bring You Comfort? 111. What Is Your Favorite Memory of PBS? 112. Have You Ever Felt Embarrassed by Your Parents? 113. What Are You Doing to Combat Pandemic Fatigue? 114. Have You Ever Worried About Making a Good First Impression? 115. What Do You Want Your Parents to Know About What It’s Like to Be a Teenager During the Pandemic? 116. How Have You Collaborated From a Distance During the Pandemic? 117. How Important Is It to You to Have Similar Political Beliefs to Your Family and Friends? 118. How Are You Feeling About Winter This Year? 119. Which Celebrity Performer Would You Like to Challenge to a Friendly Battle? 120. How Mentally Tough Are You? 121. What Smells Trigger Powerful Memories for You? 122. What Are You Thankful for This Year? 123. Do You Miss Hugs? 124. Are You a Good Conversationalist? 125. What Habits Have You Started or Left Behind in 2020? 126. What Was the Best Art and Culture You Experienced in 2020? 127. What’s Your Relationship With Masks? 128. What Role Does Religion Play in Your Life? 129. How Will You Be Celebrating the Holidays This Year? 130. What Is Something Good That Happened in 2020? 131. What New Flavor Ideas Do You Have for Your Favorite Foods? 132. What Are Your Hopes and Concerns for the New School Year? 133. How Has 2020 Challenged or Changed You? 134. What Do You Hope for Most in 2021? 135. How Do You View Death? 136. What Is Your Favorite Fact You Learned in 2020? 137. What Are the Places in the World That You Love Most? 138. Have You Ever Experienced ‘Impostor Syndrome’? 139. How Well Do You Get Along With Your Siblings? 140. Do You Talk to Your Family About the Cost of College? 141. Do You Have a Healthy Diet? 142. How Do You Feel About Mask-Slipping? 143. Do You Believe in Manifesting? 144. How Do You Express Yourself Creatively? 145. What Are Your Family’s House Rules During the Covid Crisis? 146. What Online Communities Do You Participate In? 147. Have You Experienced Any Embarrassing Zoom Mishaps? 148. What Does Your Country’s National Anthem Mean to You? 149. Are Sports Just Not the Same Without Spectators in the Stands? 150. Would You Volunteer for a Covid-19 Vaccine Trial? 151. What ‘Old’ Technology Do You Think Is Cool? 152. Have You Ever Tried to Grow Something? 153. How Has the Pandemic Changed Your Relationship to Your Body? 154. How Do You Find New Books, Music, Movies or Television Shows? 155. Are You Nervous About Returning to Normal Life? 156. How Do You Celebrate Spring? 157. How Do You Talk With People Who Don’t Share Your Views? 158. Would You Want to Be a Teacher Someday? 159. What Would You Recommend That Is ‘Overlooked and Underappreciated’? 160. What Children’s Books Have Had the Biggest Impact on You? 161. What Is Your Gender Identity? 162. Have You Hit a Wall? 163. What Is the Code You Live By? 164. Do You Think You Have Experienced ‘Learning Loss’ During the Pandemic? 165. What Are the Most Memorable Things You’ve Seen or Experienced in Nature? 166. Do You Want to Have Children Someday? 167. What Have You Learned About Friendship This Year? 168. What Seemingly Mundane Feats Have You Accomplished? 169. Has a Celebrity Ever Convinced You to Do Something? 170. How Have You Commemorated Milestones During the Pandemic? 171. How Often Do You Read, Watch or Listen to Things Outside of Your Comfort Zone? 172. Do You Think You Live in a Political Bubble? 173. What Is Your Relationship With the Weight-Loss Industry? 174. What Have You Made This Year? 175. How Are You Right Now? 176. What Are You Grateful For?
Want more writing prompts?
You can find even more Student Opinion questions in our 300 Questions and Images to Inspire Argument Writing , 550 Prompts for Narrative and Personal Writing and 130 New Prompts for Argumentative Writing . We also publish daily Picture Prompts , which are image-centered posts that provide space for many different kinds of writing. You can find all of our writing prompts, added as they publish, here .

Working in Groups
Working in a group can be enjoyable or frustrating--sometimes both. The best way to ensure a good working experience in groups is to think hard about whether a project is best done in a group, and, if so, to have a clear set of expectations about group work.
Why Work in Groups?
You might choose to work or write a paper in a group rather than individually for many reasons. Some of the reasons include practical experience while others highlight why group work might provide a better learning experience:
- In group work, you can draw on each group member's knowledge and perspectives, frequently giving you a more well thought out paper at the end or a better understanding of the class material for exams, labs, etc.
- You can also draw on people's different strengths. For example, you might be a great proofreader while someone else is much better at organizing papers.
- Groups are great for motivation: they force you to be responsible to others and frequently, then, do more and better work on a project than you might when only responsible to yourself.
- Group work helps keep you on task. It's harder to procrastinate when working with others.
- Working in groups, especially writing texts together, mirrors working styles common outside school. In business, industry, and research organizations, collaborative work is the norm rather than the exception.
Writing Tasks Suited to Group Work
Although any piece of writing can be group-authored, some types of writing simply "make more sense" to be written in groups or are ideal for cutting down on certain aspects of the work load.
Whether you've chosen to do a group project or have been assigned to work together, any group works better if all members know the reason why more than one person is involved in writing the paper. Understanding what a group adds to the project helps alleviate some of the problems associated with group work, such as thinking you need to do it all yourself. While not exhaustive, the following are some of the types of papers that are typically better written when worked on in groups. To read more, choose any of the items below:
Papers Requiring "Original" Research
Whenever you have a paper that requires you to observe things, interview other experts, conduct surveys, or do any other kind of "field" research, having more than one person to divide these tasks among allows you to write a more thoroughly researched paper. Also, because these kinds of sources are frequently hard to "make sense" of, having more than one perspective on what you find is a great help in deciding how to use the information in a paper. For example, having more than one person observe the same thing frequently gives you two different perspectives on what happened.
Papers Requiring Library Research
Although most of us might be satisfied with two or three sources in a research paper using written sources, instructors usually expect more. Working with multiple people allows you to break up library tasks more easily and do a more thorough search for relevant material. For example, one person can check Internet sources, another might have to check a certain database in the library (like SAGE) while another works on a different database more specific to your topic (e.g. ERIC for education, MLA for literature, etc.). Also, the diversity of perspectives in a group helps you decide which sources are most relevant for your argument and audience.
Any Type of Argument
Arguments, by their very nature, involve having a good sense of audience, including audiences that may not agree with you. Imagining all the possible reactions to your audience is a difficult task with these types of papers. The diversity of perspectives and experiences of multiple people are a great advantage here. This is particularly true of "public" issues which affect many people because it is easy to assume your perspective on what the public thinks is "right" as opposed to being subject to your own, limited experience. This is equally true of more "academic" arguments because each member of a group might have a different sense, depending on their past course work and field experience, of what a disciplinary audience is expecting and what has already been said about a topic.
Interpretations
A paper that requires some type of interpretation--of literature, a design structure, a piece of art, etc.--always includes various perspectives, whether it be the historical perspective of the piece, the context of the city in which a landscape is designed, or the perspective of the interpreter. Given how important perspective is to this type of writing and thinking, reviewing or interpreting work from a variety of perspectives helps strengthen these papers. Such variety is a normal part of group work but much harder to get at individually.
Cultural Analyses
Any analysis of something cultural, whether it be from an anthropological perspective, a political science view of a public issue, or an analysis of a popular film, involves a "reading" or interpretation of the culture's context as well. However, context is never simply one thing and can be "read", much like a poem, in many ways. Having a variety of "eyes" to analyze a cultural scene, then, gives your group an advantage over single-authored papers that may be more limited.
Lab/Field Reports
Any type of experiment or field research involving observation and/or interpretation of data can benefit from multiple participants. More observers help lessen the work load and provide more data from a single observation which can lead to better, or even more objective, interpretations. For these reasons, much work in science is collaborative.
Any Type of Evaluation
An evaluation paper, such as reviews, critiques, or case reports, implies the ability to make and defend a judgment. judgments, as we all know, can be very idiosyncratic when only one person interprets the data or object at hand. As a result, performing an evaluation in a group allows you to gain multiple perspectives, challenge each other's ideas and assumptions, and thus defend a judgment that may not be as subject to bias.
Fact and Fiction: Common Fears about Group Work
Group work can be a frightening prospect for many people, especially in a school setting when so much of what we do is only "counted" (i.e. graded) if it's been completed individually. Some of these fears are fictions, but others are well founded and can be addressed by being careful about how group work is set up.
My individual ideas will be lost
Fact or Fiction? Both
In any group, no one's ideas count more than another's; as a result, you will not always get a given idea into a paper exactly as you originally thought it. However, getting your ideas challenged and changed is the very reason to do a group project. The key is to avoid losing your ideas entirely (i.e. being silenced in a group) without trying to control the group and silencing others.
Encourage Disagreement
It's okay to argue. Only through arguing with other members can you test the strength of not only others' ideas but also your own. Just be careful to keep the disagreement on the issue, not on personalities.
Encourage a Collaborative Attitude
No paper, even if you write it alone, is solely a reflection of your own ideas; the paper includes ideas you've gotten from class, from reading, from research. Think of your group members, and encourage them to think of you, as yet another source of knowledge.
Be Ready to Compromise
Look for ways in which differing ideas might be used to come up with a "new" idea that includes parts of both. It's okay to "stick to your guns," but remember everyone gives up a little in a group interaction. You must determine when you're willing to bend and when you're not.
Consider Including the Disagreement in the Paper
Depending on the type of paper you're writing, it's frequently okay to include more than one "right" answer by showing both are supportable with available evidence. In fact, papers which present disagreement without resolutions can sometimes be better than those that argue for only one solution or point of view.
I could write it better myself
Fact or Fiction? Usually both
Even if you are an excellent writer, collaboratively written papers are usually better than a single-authored one if for no other reason than the content is better: it is better researched, more well thought out, includes more perspectives, etc. The only time this is not true is if you've chosen to group-author a paper that does not need collaboration. However, writing a good final draft of a collaboratively written paper does take work that all group members should be prepared to do. To read more about collaborating successfully, choose any of the items below:
Divide the Writing Tasks
While everyone is not necessarily a great writer in all aspects, they usually know what they do well. Someone may be great at organizing but not be a good proofreader. Someone else might be great using vivid language, but lose their writing focus. Have group members write what they're best at and/or ask them to read the first draft for specific things they know well.
Leave Enough Time for Revising
First drafts of collaborative papers are frequently much worse than first drafts of individual papers because many disagreements are still being worked out when writing. Leave yourselves, then, a lot of time to critique the first draft and rewrite it.
Divide the Paper into Sections
People in your group may know a lot more about certain topics in the paper because they did the research for that section or may have more experience writing, say, a methods section than others. To get a good first draft going, divide tasks up according to what people feel the most comfortable with. Be sure, however, to do a lot of peer review as well.
Be Critical
One of the advantages of group work is you learn to read your own and others' writing more critically. Since this is your work too, don't be afraid to suggest and make changes on parts of the paper, even if you didn't write them in the drafting process. Every section, including yours, belongs to everyone in the group.
My grade will depend on what others do
Fact or Fiction? Fact
Although some instructors make provisions for individual grades even on a collaborative project, the fact remains that at least a part, if not the whole grade will depend on what others do. Although this may be frightening, the positive side to this is that it increases people's motivation and investment in the project. Of course, not everyone will care about grades as much as others. In this case, the group needs to make decisions early on for the "slacker" contingency. To read more about how to deal with unequal investments in the task, choose any of the items below:
Make Rules and Stick to Them
Before you even start work on a project, make rules about what will happen to those members not doing their part and outline the consequences. Here are some possible "consequences" other groups have used:
- If someone misses a meeting, or doesn't do a certain task, he/she has to type the final paper, buy pizza for the next meeting, etc.
- If more than one meeting is missed or a member consistently fails to do what she/he is supposed to, the group can decide not to include that name on the project. (Check this one with your instructor)
- In the same scenario, the group can decide to write a written evaluation of the member's work and pass it in to the instructor with the paper.
No one, usually, wants to anger their peers. When someone isn't doing his/her work, other group members need to tell that member. Many times people who end up doing more than their share do so because they don't complain.
Deal with It
This may sound harsh, but the reality of life outside of school is that some people do more work than others but are not necessarily penalized for it. You need to learn how to deal with these issues given that in the working world, you are frequently dependent on others you work with. Learning how to handle such situations now is a good learning experience in itself.
Group work will take more time than if I did it myself
There is no way around this, so be prepared. Even if you divide up many of the early tasks (research, etc.) which lessens the time you might put in individually, writing a collaborative paper takes a lot of time. It's time well spent as the final project is usually better than what any one individual could do, but don't fool yourself into thinking choosing a group option will mean less work. It hardly ever does.
My group members aren't as smart as I am
Fact or Fiction? Fiction
This is a dangerous attitude to bring into a group situation. If you honestly believe it's true, you should probably not choose group work if it's optional. If you don't have a choice, then consider the fact that other people might be thinking the same of you. To read about how your group can avoid this, choose any of the items below:
Discuss Member's Strengths and Weaknesses
At the first meeting, have each group member do a personal inventory covering a wide range of issues relevant to the work you'll do together. Remember that while one person may be good at ideas/course content, someone else may have strengths as a critical reader, researcher, or writer. Some questions might include: what do you know about our topic already? What experiences do you have that might be relevant? What have you done the best on in other parts of the course? What have you been complimented on about your writing in the past from teachers or peers? What kind of reader of other people's papers are you?
Practice Listening
It's too easy to judge someone based on personal assumptions. Assign someone each meeting to take careful notes on everything said, not just what that person thinks is relevant. Many good ideas are lost because we judge the person rather than what he/she says.
Think of your group members, and encourage them to think of you, as yet another source of knowledge just as you might a teacher, a book, or any other source you consult for a paper. Sometimes you can learn the most from someone you think is "wrong" because they can provide a perspective you've ignored.
We won't be able to agree
Group work is messy; you will disagree often. The best groups don't silence disagreement because it's usually in arguing that you can challenge each other to think more about the topic. However, groups that only disagree are no more functional than those that agree to everything. The key is balancing the two. To read more about how to handle disagreements, choose any of the items below:
Assign a Monitor/Mediator
For every meeting, ask someone to keep careful track of the differing opinions and reasons for them. At a certain point in the meeting (or for the next meeting), the mediator's job is to present all the views and try to reach a consensus which includes parts of them. To do this, the mediator must stay out of the arguments for that meeting only.
Decide Whether You Have to Agree
This won't work in every instance, but sometimes you might decide to include the disagreement in the paper itself. Presenting why two different sides of an issue are equally supportable can sometime strengthen the paper, rather than weaken it, depending on the purpose of the paper.
Make Discussion Rules
While arguing about ideas is good, personal attacks are not. Early on, decide as a group what is acceptable behavior toward each other and follow the rule: call someone on it when they go too far.
I don't have time to meet out of class
Fact or Fiction? Sometimes a Fact
Most of us, even if we're very busy, can find two hours to meet with a group. The key is having those two hours in common with other people, which is why, when forming a group, time in common is the first thing to consider. If you are assigned a group, however, this may not be possible. In this case, consider alternative ways of meeting: telephone, e-mail, meetings with some group members, etc. To read more about different alternatives, choose any of the items below:
Everyone on campus can get an e-mail account. You can work on much of the logistical (who needs to do what when) work of a group through e-mail communication. This is also a good way to exchange drafts of the paper, with each person making revisions when the draft gets to them. Or, it can serve as a way to send your "section" before you have a complete draft and/or to exchange research notes. It's not as useful for hashing out ideas or coming up with your thesis for the paper, however.
Talk to your instructor about setting up a chat room through the WWW. Although sometimes frustrating because you will be writing instead of talking, you can use a chat room to do much of the idea generation that e-mail isn't as useful for because of the time lag.
Partial Meetings
Meet in two different groups, with one person in common. Take good notes so that one person can communicate what you decided/talked about to the next group. This can work until the "final" decision stage of what the focus of the paper will be and the final changes to the draft. For these, you'll need probably to meet at least once (for the decision making) or pass the draft around continuously until everyone is ready to sign off on it.
Weekend Meetings
No one loves this option, but if you have no other free time together, you might be able to find a Sunday morning or Friday night when everyone can meet for the one or two meetings that seem as if they must be face-to-face.
I would learn more doing it on my own
While this may seem true because you'd have to do all the work, group work usually allows you to include more research than you could alone, exposes you to perspectives you wouldn't hear otherwise, and teaches you about your own writing strengths and weaknesses in ways writing alone and just getting a response never can. Thus, in group work, you learn more about writing itself, and, if done right, the topic as well.
I'll end up doing all the work
Unless you are unwilling to give up control or speak up for yourself, this shouldn't happen. Although the reality is that some people will try to get away with doing less, the chances of having a completely uncommitted group are rare. As a result, you simply have to watch for the tendency to think you "know better" than others and thus must do it all yourself and/or the attitude that your grade will suffer because everything isn't done the way you want it. To read about how not to do all the work, choose any of the items below:
- If you miss a meeting, or don't do a certain task, you have to type the final paper, buy pizza for the next meeting, etc.
- If more than one meeting is missed or a member consistently fails to do what she/he is supposed to, the group can decide not to include their name on the project. (Check this one with your instructor)
No one, usually, wants to anger his/her peers. When someone isn't doing their work, other group members need to tell them. Many times people who end up doing more than their share do so because they don't complain.
While everyone is not necessarily a great writer in all aspects, they usually know what they do well. Someone may be great at organizing but not be a good proofreader. Someone else might be great a vivid language, but lose their focus. Have group members write what they're best at and/or ask them to read the first draft for specific things they know well. Even if you're good at all aspects, this doesn't mean you can't draw on the others' strengths.
One of the advantages of group work is you learn to read your own and others' writing more critically. Since this is your work too, don't be afraid to suggest and make changes on parts of the paper, even if you didn't write them in the drafting process. Every section, including yours, belongs to everyone in the group. Thus, one way to get a better product without doing all the work yourself is to be a good reader.
What to Expect in Group Work
Several factors we may not always think about when working in a group are vital to a successful group project. You should always establish how your group will handle each of these. To learn more about these factors, choose any of the items below:
Although we might assume productive groups will always be in complete agreement and focused on task, the reality of groups, as we have probably all experienced, is much messier than this. "Ideal" productive groups do not exist. In fact, some of the most productive groups will disagree, spend a lot of time goofing around, and even follow many blind alleys before achieving consensus. It's important to be aware of the rather messy nature of group work.
Student groups will fight--in fact, they should fight, but only in particular ways. Research shows that "substantive" conflict, conflict directed toward the work at hand and issues pertaining to it, is highly productive and should be encouraged. "Personal" conflict, conflict directed toward group members' egos, however, is damaging and unproductive. The lesson is that students need to respect each other. Some groups decide to negotiate respect by making rules against inappropriate comments or personal attacks. When a damaging instance arises in a certain situation, any group member can immediately censor back the comment by saying "inappropriate comment."
Socializing
Of course, groups will not continually argue nor will they continually stay on task. Socializing, joking around, or telling stories are a natural part of group interaction and should be encouraged. It is primarily through "goofing off&qout; that group members learn about each other's personalities, communication styles, and senses of humor. Such knowledge builds trust and community among the members. Although groups should be counseled not to spend inappropriately long amounts of time simply gossiping or telling stories, they should also realize the importance and influence such interactions can have on achieving a group identity that all members come to share.
Wrong Decisions
Group members should be aware of and comfortable with the frequently frustrating reality of making the wrong decisions. Making mistakes, trying out options that don't work, and so on are not "a waste of time." In any creative situation, particularly in writing, trying out unsuccessful options is frequently the only way to discover what needs to be done. Although such frustrations take place even in individual contexts, they are particularly hard to negotiate in a group context because our immediate instinct is to blame another group member for a faulty suggestion. Students should be aware that all time spent on a task is productive even if it does not lead to any tangible product.
Unequal Commitments
In a perfect world, everyone would have as much time and desire in a group as others to create the best paper possible, but the reality is some people are procrastinators or care more about their grades in certain classes. Expect this and make contingencies for it by deciding early on what the "penalty" will be for those who miss meetings or fail to pull their weight.
Choosing Group Members
Sometimes in class assignments, you won't be able to choose your group, but if you have this option or are forming a group for your own purposes (e.g. study groups for exams), be careful of how you choose members. To read more about how to construct a group, choose any of the items below:
Time in Common to Meet
You'll want to have at least a two-hour chunk of time that everyone in the group can meet each week. While you'll probably not meet every week, everyone should be willing to keep this time free during the group project. If you plan to gather to write the text together, you'll need much larger chunks of time toward the end of the project.
Individual Strengths and Weaknesses
Any collaboratively written paper will include research, idea-generating, and writing abilities. For other groups, such as study groups, only idea-generating or understanding of class material may be relevant. As you ask people to join your group, have a specific reason why they would "add" to the group mix in terms of abilities. Choosing your friends is not always the best way to get a "balanced" group. For example, your friends might all be good at research but all lack writing skills.
If you're doing a group paper or studying together, including a diversity of people might be a real asset. For example, gender diversity may or may not be relevant depending on the topic. Past course work or job experience may or may not be relevant. Prepare a list of the types of diversity that may help strengthen your paper because of the different perspectives or types of expertise people can bring to the group.
Next to enough time to meet, this criterion is most important. Try to choose group members who have an equal investment in the project or study group as you do. It's unfair to invite someone because you think they'll do most of the work; it's equally unfair to you to invite someone you like but who will probably miss meetings or procrastinate.
Guidelines for Group Work
The members of student groups may benefit from keeping some common-sense rules and aphorisms in mind as they come to collaborate.
Collaboration teaches us what we know how to do , not just what we know. Collaboration teaches method. The activities of collaboration are as important as the material results.
Collaboration works best when it is apparent--when you know that you are collaborating. A certain amount of formality (e.g., established meeting times, a recorder to take minutes perhaps, a group monitor) is called for.
Collaboration succeeds when everybody succeeds--individual members as well as the group as a whole.
Collaboration is a key responsibility in the class experience--it means being involved in the teaching of the course.
No one ever knows how a collaborative activity will turn out.
Initial Decision-Making
This section provides suggestions about the types of decisions any group should make before getting into the work on a paper itself in order to prevent future problems.
Where many groups go wrong is not being clear about expectations from the onset. Problems are much easier to deal with when you discuses their possibility in the abstract rather than when they involve individual people and feelings. As such, making the following decisions early on can help deflect feelings of personal attack later and also help organize the group.
Agree on a Meeting Format
While many groups will (and should) spend time socializing, talking about class, etc., it's helpful to set up expectations for how much of this type of talk should/can occur during a meeting. Also, because of how much typically gets said during meetings, you need a way to keep track of what occurred and plan for the next meeting. For instance, you should:
- Appoint a secretary for each meeting
- Plan for the next meeting (set an agenda) at the end of each meeting
- Plan a short amount of time at the beginning of each meeting for chatting and appoint someone to get the group "started" after that time has passed

Construct Rules for Discussion
Although it usually seems unlikely in the beginning, a healthy disagreement can easily turn nasty when people are invested in a topic. Decide early on what will be considered inappropriate comments and make sure someone monitors these in later meetings. Here are some rules to consider:
- No personal attacks on a person's intelligence, background, way of speaking, etc.
- No yelling; all disagreements should be kept in a rational tone
- No name calling
- If a person objects to a comment directed at them, the conversation stops there, no matter anyone's opinion of the objection
- Out of Line Comments: "That's a dumb idea;" "You don't know what you're talking about;" "It figures a man/woman would say that"
Construct a Timeline
It's very easy to get lost in people's individual schedules week to week and put off certain tasks "just this time." Also, it's easy for a group project to seem "huge" until the tasks are broken down. For these reasons, it's useful to decide what tasks need to be done and when they need to be finished in order for the group to meet its final deadline.
Make a schedule and keep to it. This will also help group members monitor each other so that someone isn't stuck with all the work at the end. Consider the following:
- When will a final decision on the topic/focus be made?
- What kinds of research do we need to do? Who will do what? By when?
- When will people report back on research? What notes should they write up for others? By when?
- When must a final decision on the major point (thesis) of the paper be made?
- When will the paper be drafted initially?
- When will the comments/suggestions for revision be completed?
- When will the revisions be done by?
- When will the final proofreading occur?
Agree on Penalties for Missing Meetings or Deadlines
Although it would be great if this weren't true, the reality is some people are going to miss meetings and deadlines; some might even try to get others to do their work by not completing tasks. Groups need to be prepared for these contingencies by constructing rules and their consequences that can be applied later if individuals "drop the ball." Consider the following:
Discuss What Each Member Brings to the Group
While you might know your other group members as friends, you probably don't know as much about them as students as you might think. A very productive topic for the first meeting, after all the logistics have been worked out, is to discuss what individual members' strengths and weaknesses are. In short, have everyone conduct a "personal inventory" and share it with the other members on their experiences relevant to the collaborative assignment. Doing this also helps alleviate the feeling that some group members are "smarter" or "know more" than others. Everyone has strengths they bring to the group; we're simply not always aware of them. Consider the following:
- What's your previous experience with the topic?
- What do you understand best from class? What are you struggling with?
- Do you have any outside experience (job, internships, previous classes) relevant to the topic and/or class?
- What's your experience with the kind of research we're doing (field, library, etc.)
- What kinds of papers do you write best? What have teachers and others complimented you on?
- What problems do you have in writing?
Idea-Generating and Research Tasks
This section deals with the types of tasks that can and should occur before the group begins drafting the paper and provides suggestions on how to best distribute the work.
Although when we work on our own, all of us frequently deter from the model of "gather all your information, decide on a thesis, write and outline, and draft" typically recommended in writing text books. However, this is a useful order to try and follow in group work. Many times a group might work through this order recursively, researching, finding a topic, and then having to do more research, however breaking up these tasks initially helps lighten the workload later and helps you meet the final deadline.
Library Research
While it's a good idea to have everyone work on research, you don't want to end up finding the same sources. Consider breaking down the library research according to data bases. One person searches SAGE, another the New York Times, etc. Also construct a plan for how people will "report" back on research. Should they write a summary for everyone? Bring photocopies?
Field Research
Depending on the type of field research, you may break down what needs to be done individually or choose to send people out in pairs or groups. Pairs and groups, for example, work particularly well for observational projects where each person may observe something different. Also, construct a plan for how people will "report" back on research. Should they make a more extended copy of their notes? Should the group decide what's important to focus on and then ask each person to share that portion of their work? No matter what the decision, make sure each group member has the entire body of information to work from. Observations and interviews can't be used by everyone like a library source can unless the person doing them has a detailed, written record.
Evaluating Sources
The most difficult part of doing research individually or in pairs is deciding what's relevant or not to the group's project. It's useful, then, to either construct criteria for what makes a "good" source before the research begins, or to have people report back on everything they found, and decide a focus from there that can help you look more specifically for other sources. Developing a focus early on is especially important to field research as any surveys, observations, or interviews you do will only need to be redone if they don't elicit the information you later discover you need.
Deciding on a Focus
Depending on your topic, this may occur in different places in the process. For a library project, it's useful to have some idea of a focus before starting the research, then refining it according to what you find out. For observational research, it's useful to do a few observations without a sense of focus, and use what you see to determine what's most interesting to the group. In any type of research, however, a focus should be determined before the researching ends; otherwise, you may not end up with information you can use.
Coming to Consensus on the Main Point and Organization
Once you've gotten a focus and collected most of your data or sources, the group needs to conduct the most difficult task: decide upon the point of the paper. While in individual papers, many of us frequently "write to find a point," this is very difficult to do in a group. Before the writing starts, you want everyone to have the same conclusion or point in mind so that what they write will not lack coherence with other parts of the paper. For similar reasons, deciding on the organization of the paper beforehand, in some type of outline or list of sections, will make the writing much easier.
Writing the Paper Together
Depending on the purpose of the assignment, you can choose from a number of models for working in collaborative groups.
Determine what Final Paper Should 'Sound' Like
Before actually beginning to write, your group will need to make some decisions about the final draft, some of which may need to be checked with your instructor first. Consider the following:
- Is it okay to include disagreements? Should the paper argue for one point/interpretation/conclusion or present other possibilities that emerged in your discussions?
- Should the paper sound as if one person wrote it? Are different styles acceptable or will you have to revise for a similar style throughout?
- How will you refer to the author, as "we", as a group name, by last names? What's standard format for collaborative work in your discipline?
When you divide the writing tasks, each member does research and writes a portion of the document. The group then reconvenes to suggest revisions, smooth over transitions, and even edit style inconsistencies. This model is the most efficient and quickest for most groups that have not worked together in the past. Consider the following:
- This only works if you spend a lot of time discussing organization before writing; otherwise, sections tend to digress and/or repeat each others.
- Plan to write the introduction, conclusion, and transitions between sections together to help the text "flow."
- Edit/revise the draft for coherence; is it obvious how each section supports/leads to your main point? Skipping this stage could lead to an incomprehensible paper. People's ideas about the main point, no matter how much discussion, aren't always going to be the same.
Gather to Write Together
Writing together is efficient in that groups can sometimes make better decisions than individuals. Consequently, fewer drafts might be required. However, this kind of true collaborative writing, especially in larger groups, can be very difficult and time consuming. You may need to spend more time working together. Consider the following:
- How well this works depends a great deal on how comfortable you are with each other and if you're willing to correct and suggest in the middle of someone writing.
- Don't get caught up in arguments about sentence structure, word choice, etc. This is only a first draft and trying to be too "perfect" during the writing will increase the writing time exponentially.
- Plan more than one meeting for the drafting; writing like this cannot be done in one sitting.
- Leave time to critique the draft and make revisions. Writing together is not a substitute for revision.
Delegate Various Responsibilities
Members who might have excellent research skills might do most of the research; those who are excellent at writing correctly might do most of the editing and proofreading. This model requires a high degree of group coordination. For some groups--but definitely not all--this model is most efficient. For others, (in which no even split of skill levels exists) it will be the least efficient. Consider the following:
- Be sure everyone, not just the final editor, has approved what will be passed in. Everyone needs to read and critique each draft.
- Be sure tasks are broken down equally. Proofing the final copy is not equivalent to writing the first draft.
- For this method to work, those doing the research must keep detailed, accurate notes that others who might not have seen the original source can understand and use.
- "Planning" meetings are essential; the people drafting must have a clear idea of the point, organization, and what sources are relevant to what parts of the paper or else much time can be wasted.
Using Group Time Profitably
After making initial decisions about choice of topic and members' duties, a group will work best together if each member comes to meetings with at least some of his or her individual work and thinking already accomplished. Groups can then move directly to the more advanced writing process stages of organizing and negotiating between ideas or even of piecing together drafts. Various strategies help make group time as productive as possible:
Be Prepared
Come to the meeting with at least some of your individual work and thinking already accomplished. If you were assigned to write a portion of the draft, for example, have it done for the meeting and bring copies. If this is a planning meeting, think about the topic before hand and jot down some notes about what you think should be done.
Set an Agenda
Set aside time at the beginning of each meeting to run through (or create) the agenda and state aloud the goals for this meeting (i.e. what you want to accomplish). Save time at the end of each meeting to recap the events of the session, discuss plans for individual work, and set the agenda for the next meeting.
Appoint a Secretary
Group meetings can move very quickly with so many people talking. For each meeting appoint a scribe (a different one each time) to take down notes on the discussion and keep track of plans and decisions made. The scribe should provide each member with a copy of a particular meeting so everyone has the same sense of what happened and what was decided.
All committees need time for unfocused discussions that attempt to move the group toward consensus. More than a few group meetings may need to be devoted to what seems like unfocused talk. Allowing this to happen will make later sessions more productive since you've already explored many ideas about the topic; as a result, getting down to work will be easier.
Feel free to disagree. The best ideas come about when someone has the guts to question an idea or plan that seems to make sense to everyone else. Critiquing each other's work or ideas is essential to working together to create the best product. Don't hold to your individual ideas so strongly, however, that the group doesn't make any progress. Know when to compromise and when not to.
Be Strict about Deadlines
You expect all your other group members to complete the work they've committed themselves to; apply the same standard to yourself. Remember that you have a commitment to these people and failure to meet it will affect not only your grade but theirs as well.
Dealing With Problems in a Group
Group work is rarely flawless. Two methods for dealing with problems are monitoring the group and discussing the problems. If you agree ahead of time about how to resolve problems, you can avoid involving your instructor in the situation; however, if you can't resolve the problem it may be a good idea to ask for assistance.
Clarify Your Expectations Early
One way to avoid problems later is to make decisions about deadlines, meeting etiquette, and penalties for missed work before any of these occur. This way you can refer back to decisions already made and avoid the possibility that one member may feel like they're "being picked on" or meetings become so out of hand they can't be controlled.
Monitor the Group
One way to help alleviate some of the problems that may result from group interactions is to encourage the group to somehow monitor itself. To facilitate this monitoring, each group member can keep a journal in which she or he comments on each group meeting. The journal can become the place to express frustration, to analyze the nature of communication taking place in the group, and so on. Or the group may choose to divide up monitoring tasks. One group member might be put in charge of keeping track of turn-taking (i.e., who speaks and when; do all members have an equal opportunity to speak; are some members always silent?). Another member might watch for nonverbal cues about how members are reacting to what is being said, or to an individual speaker.
Discuss Problems
In any of these monitoring scenarios, group members should be encouraged to discuss with the entire group any problems they see arising so that the group might discuss certain aspects of the group's dynamic before they become problems. Sometimes, however, the group will not be able to solve their interaction problems on their own. When this occurs, they should be aware that they can discuss this--as a group preferably-- with the instructor.
Overall, groups should be left to negotiate their own agendas among themselves, but discussing possible problem areas may provide the ounce of prevention that prevents the need for a more painful cure.
LeCourt, Donna, & Dawn Kowalski. (1997). Working in Groups. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guides.cfm?guideid=42
Collaborative and Group Writing
Introduction
When it comes to collaborative writing, people often have diametrically opposed ideas. Academics in the sciences often write multi-authored articles that depend on sharing their expertise. Many thrive on the social interaction that collaborative writing enables. Composition scholars Lisa Ede and Andrea Lunsford enjoyed co-authoring so much that they devoted their career to studying it. For others, however, collaborative writing evokes the memories of group projects gone wrong and inequitable work distribution.
Whatever your prior opinions about collaborative writing, we’re here to tell you that this style of composition may benefit your writing process and may help you produce writing that is cogent and compelling. At its best, collaborative writing can help to slow down the writing process, since it necessitates conversation, planning with group members, and more deliberate revising. A study described in Helen Dale’s “The Influence of Coauthoring on the Writing Process” shows that less experienced writers behave more like experts when they engage in collaborative writing. Students working on collaborative writing projects have said that their collaborative writing process involved more brainstorming, discussion, and diverse opinions from group members. Some even said that collaborative writing entailed less of an individual time commitment than solo papers.
Although collaborative writing implies that every part of a collaborative writing project involves working cooperatively with co-author(s), in practice collaborative writing often includes individual work. In what follows, we’ll walk you through the collaborative writing process, which we’ve divided into three parts: planning, drafting, and revising. As you consider how you’ll structure the writing process for your particular project, think about the expertise and disposition of your co-author(s), your project’s due date, the amount of time that you can devote to the project, and any other relevant factors. For more information about the various types of co-authorship systems you might employ, see “Strategies for Effective Collaborative Manuscript Development in Interdisciplinary Science Teams,” which outlines five different “author-management systems.”
The Collaborative Writing Process
Planning includes everything that is done before writing. In collaborative writing, this is a particularly important step since it’s crucial that all members of a team agree about the basic elements of the project and the logistics that will govern the project’s completion.Collaborative writing—by its very definition—requires more communication than individual work since almost all co-authored projects oblige participants to come to an agreement about what should be written and how to do this writing. And careful communication at the planning stage is usually critical to the creation of a strong collaborative paper. We would recommend assigning team members roles. Ensure that you know who will be initially drafting each section, who will be revising and editing these sections, who will be responsible for confirming that all team members complete their jobs, and who will be submitting the finished project.
Drafting refers to the process of actually writing the paper. We’ve called this part of the process drafting instead of writing to highlight the recursive nature of crafting a compelling paper since strong writing projects are often the product of several rounds of drafts. At this point in the writing process, you’ll need to make a choice: will you write together, individually, or in some combination of these two modes?
Individually
Revising is the final stage in the writing process. It will occur after a draft (either of a particular section or the entire paper) has been written. Revising, for most writing projects, will need to go beyond making line-edits that revise at the sentence-level. Instead, you’ll want to thoroughly consider all aspects of the draft in order to create a version of it that satisfies each member of the team. For more information about revision, check out our Writer’s Handbook page about revising longer papers .Even if your team has drafted the paper individually, we would recommend coming together to discuss revisions. Revising together and making choices about how to improve the draft—either online or in-person— is a good way to build consensus among group members since you’ll all need to agree on the changes you make.After you’ve discussed the revisions as a group, you’ll need to how you want to complete these revisions. Just like in the drafting stage above, you can choose to write together or individually.
Person A writes a section Person B gives suggestions for revision on this section Person A edits the section based on these suggestions
Person A writes a section The entire team meets and gives suggestions for revision on this section Person B edits the section based on these suggestions
Think through the strengths of your co-authoring team and choose a system that will work for your needs.
Suggestions for Efficient and Harmonious Collaborative Writing
Establish ground rules.
Although it can be tempting to jump right into your project—especially when you have limited time—establishing ground rules right from the beginning will help your group navigate the writing process. Conflicts and issues will inevitably arise in during the course of many long-term project. Knowing how you’ll navigate issues before they appear will help to smooth out these wrinkles. For example, you may also want to establish who will be responsible for checking in with authors if they don’t seem to be completing tasks assigned to them by their due dates. You may also want to decide how you will adjudicate disagreements. Will the majority rule? Do you want to hold out for full consensus? Establishing some ground rules will ensure that expectations are clear and that all members of the team are involved in the decision-making process.
Respect your co-author(s)
Everyone has their strengths. If you can recognize this, you’ll be able to harness your co-author(s) assets to write the best paper possible. It can be easy to write someone off if they’re not initially pulling their weight, but this type of attitude can be cancerous to a positive group mindset. Instead, check in with your co-author(s) and figure out how each one can best contribute to the group’s effort.
Be willing to argue
Arguing (respectfully!) with the other members of your writing group is a good thing because it means that you are expressing your deeply held beliefs with your co-author(s). While you don’t need to fight your team members about every feeling you have (after all, group work has to involve compromise!), if there are ideas that you feel strongly about—communicate them and encourage other members of your group to do the same even if they conflict with others’ viewpoints.
Schedule synchronous meetings
While you may be tempted to figure out group work purely by email, there’s really no substitute for talking through ideas with your co-author(s) face-to-face—even if you’re looking at your teammates face through the computer. At the beginning of your project, get a few synchronous meetings on the books in advance of your deadlines so that you can make sure that you’re able to have clear lines of communication throughout the writing process.
Use word processing software that enables collaboration
Sending lots of Word document drafts back-and-forth over email can get tiring and chaotic. Instead, we would recommend using word processing software that allows online collaboration. Right now, we like Google Docs for this since it’s free, easy to use, allows many authors to edit the same document, and has robust collaboration tools like chat and commenting.
Dale, Helen. “The Influence of Coauthoring on the Writing Process.” Journal of Teaching Writing , vol. 15, no. 1, 1996, pp. 65-79.
Lunsford, Andrea A., and Lisa Ede. Writing Together: Collaboration in Theory and Practice . Bedford St. Martin, 2011.
Oliver, Samantha K., et al. “Strategies for Effective Collaborative Manuscript Development in Interdisciplinary Science Teams.” Ecosphere , vol. 9, no. 4, Apr. 2018, pp. 1–13., doi:10.1002/ecs2.2206.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper Introductions Paragraphing Developing Strategic Transitions Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Developing Strategic Transitions
Finishing your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
169 Teamwork Topics & Essay Examples
You’re better to check a teamwork essay example or two if you want to write a good paper on this subject. Good thing that here you will find great topics and samples collected by our experts.
✨ Top 12 Teamwork Topics to Explore
🏆 best teamwork topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good topics on teamwork, 📌 most interesting teamwork topics to write about, ❓ teamwork discussion questions.
- Leadership.
- Workplace Family.
- Team Games.
- Collaboration.
- Team-Building Activities.
- Personnel Selection.
- Importance of Individuality.
- Safety Training.
- Group Management.
- Teamwork Skills.
- Teamwork as Dream Work.
- An Analysis of the Experience of Teamwork I was also worried as I was not sure that I could be an effective member of the team for I had not had any experience in accreditation.
- Teamwork and Leadership From diversity to team hierarchy, many factors influence the eventual output of the team, affecting the leader, team members’ performance, and client’s satisfaction.
- Southwest Airlines: Organizational Behavior and Teamwork The company encourages self-actualization by motivating employees to be creative and innovative to be all they can, to improve effectiveness. Positive reinforcement is also used when employees contribute to increasing productivity and profit margins for […]
- Teamwork and Individual Work in Various Situations The challenges in the contemporary environment and the various situations that individuals have to encounter push people to think about how it is better and more effective to handle them.
- Team-Building Strategies of Apple The most judicious way to cultivate the Five Cs is by recruiting applicants that are team players and compatible with the company culture. Employees should be incentivized to participate through financial compensation and the offer […]
- Team Building Activity The team building activity included identifying the purpose of the team, the needs of the team, composition of team members, the time the team was likely to last, and the benefits to the designate individuals […]
- Watson Engine Company Organization Structure and Teamwork The organization structure of the company is old fashioned and hierarchical in nature that minimizes the influence of the employees in the running of the organization.
- Importance of Teamwork Skills One of the strategies I can utilize to improve my teamwork skills is to understand and contextualize my role within the group.
- Group Project Management and Teamwork Reflection The success of our group depended on the effectiveness of contribution to the project by each member of the group. The only mistake that the group made was it did not elect an interim leadership […]
- The Teamwork in Nursing Similarly, if the nurse manager or the physician blame the nurse for the error, it could affect trust within the team and create obstacles to teamwork in the future.
- Teamwork Concept in Nursing and Its Consequences Working in teams is crucial for nurses, and the concept of teamwork becomes central to the nursing practice. Teamwork is a positive concept, the occurrence of which results in desirable outcomes for all members and […]
- Significance of Teamwork in Schools However, teamwork in schools is initiated by the administration and embraced by teachers in their respective departments. Teamwork is important in ensuring the success of schools.
- Teamwork in organizations The practice of team work has been established in several workplaces and has proved to be not only effective in managing organisations but also a prudent measure of assessing the performance of employees and growth […]
- Communication and Teamwork in Providing Quality Healthcare In the quest for addressing the challenges of communication and teamwork at Quality Hospital’s ICU, this paper provides a breakdown of the formation of a task force that will help the ICU to address the […]
- Teamwork Issues Effects in Japanese Organisations The reason is that employees and management are in good terms and able to agree informally on various procedures and practices without compromising the quality of the organisational practices and objectives.
- Importance of teamwork, cohesiveness, consensus decision Teamwork is an initiative established by employers and employees to ensure people work together to achieve the objectives of their organizations.
- Teamwork as the Primary Determinant of Success Regardless of the size of an entity or the nature of activity which a group of individuals are involved in, teamwork is one of the primary determinant s of a group’s level of success.
- Team Building Issues The process of team building is not as easy as it may seem since there are factors to be considered if the goals of developing the team are to be achieved.
- Teamwork: Aspects of Problems and Solutions In this report, we present our findings on a group project in Team building with real-world simulation of soft skills necessary to build a high performance winning team. Learning about team building values which aid […]
- Proctor & Gamble Company’s Effective Team Building The purpose of this study was to examine the major strategies used by companies to build effective teams. The main purpose of the study was to identify evidence-based strategies that can be used to develop […]
- Teamwork Role in Patient Safety Promotion According to Manser, some of the most important considerations that either promote or hinder patient safety include the perceived quality of teamwork between professional groups, the quality of relational coordination and communication between team members, […]
- Motivational Strategies for Teamwork When members of a team desire to advance their skills and the team leader cannot offer the opportunities, the team members are likely to be less motivated and therefore perform poorly.
- The Discussion Feedback: Teamwork In the above reasoning, it is indicated that the team director is always nearby, but this is not the most effective way to save the team management. Perhaps his constant presence and dedication are not […]
- Nursing Leadership and Team Building Strategies A Doctor of Nursing Practice leader has a number of responsibilities, and one of them is to motivate a team and increase engagement toward a vision and goals.
- Teamwork in Business: Role and Impact on Work Environment In order to ensure and achieve a sufficient level of team cooperation, cohesiveness, and unity, the most critical qualities include trust, ownership, creativity, risk tolerance, effective conflict management, competence, open communication, and inclusiveness.
- Teamwork and Critical Thinking The analyst role is essential to team thinking in nursing practice because it enables the nurses to realize all the aspects of the situation, providing a wider view.
- Teamwork Experience and Recommendations Teamwork is a process in which each participant has equal rights and responsibilities, which are adjusted depending on the goals and objectives of the company.
- Teamwork Safety and Efficiency in Medical Emergencies: Rogers’s Theory In the third phase, the individual will consider the innovation’s pros and cons and weight change. The researcher will implement the innovation in the fourth stage and adjust the novelty to the state.
- Aspects of Teamwork in Healthcare It is essential in the United States to optimize the communication between all the employees of the organizational unit to provide medical aid according to the standards of care.
- Team Building: Understanding the Project’s Goals Being a supervisor of any project is a challenging task, requiring a creative and intelligent team and a lot of time and effort.
- Teamwork in Ireland’s Healthcare Organizations The team members understand that they have unique roles and positions in the group and do their best to support their teammates.
- Business Simulation Exercise’s Effect on Teamwork The aim of this paper is to describe the effects of the use of simulation exercises on teamwork. This section will undertake a detailed study of effective training in team building and contribution of simulation […]
- Team Building and Its Practical Benefits In business, it is imperative for all in the office or factory to work in sync with each other for a common goal to enhance productivity and profitability, which in turn leads to individual growth […]
- Teamwork in the Nursing Healthcare Environment The impact of organizational change is dependent on three factors; the stage of organizational development, the degree of flexibility, and the history of response to change.
- Biblical Foundation of Teamwork Teamwork and the team ministry started before the birth of Christ, and the bible encouraged people to work as a team.
- The Importance of Teamwork With Limited Resources The aviation industry on the other hand has been shown as one that has been facing teamwork problems since the beginning of the 21st century due to downsizing of the workers, resulting in a breach […]
- Emotional Intelligence’s Support for Teamwork and Teambuilding in Nursing In instances where a nurse lacks the luxury to pick a team with which to work, understanding others allows the individual to conduct amicable relations for the sake of proper execution of tasks, the health […]
- Teamwork Essay 100 Words The foundation of trust is likely to be beneficial because of the manner in which different interests are going to come together and be harmonized.
- Team Building and Teamwork Principles to the Areas of Health Care The literature shows that self-reflection and peer ratings are fantastic ways for small groups to gauge their level of functioning, cooperation and how to overcome interpersonal conflicts that may affect the outcome of group goals.
- Teamwork Dynamics, Motivation, Conflict Resolution, and Leadership In this scenario, such an approach is crucial, since the team is experiencing difficulties of the unclear origin and they can be identified and analyzed by engaging in the workflow.
- Communication and Teamwork in the Healthcare Facilities After picking the sample and identifying the patient by the bar code, I perform the test and report the results to the doctor.
- Teamwork Is Essential, but Impossible The challenge is the creation of real working teams, in a business situation where individuality is rewarded and team work ignored.
- Impact of Race, Age or Gender on Teamwork This is based on the difficulty of ascertaining in what way productivity is affected by a change in the age composition of the workforce.
- The Importance of Team Building in Companies In order to analyze the nature of the problem, it is necessary to inquire on whether the manager did everything possible to make the work knowledge and councils available.
- The Win-Win Approach: The Advantages and the Challenges of Teamwork The piece of the teamwork which we have fulfilled in a group of three has precisely demonstrated the advantages and challenges of any team activity described in numerous sources devoted to the team work.
- Teamwork Impact Within the TMC In this case, executives allow the employees to make decisions on what is to be manufactured; the intended quality and marketing procedures of the manufactured product; based on their talents and skills.
- Calling a Team: Successful Teamwork In particular, the authors emphasize that frequent meetings are necessary to set realistic goals and discuss the objectives of the teamwork.
- Lions Share Inc.’s Virtual Teamwork The team’s vision is to create a company that will provide new and unique products to the world, influence technology, and ensures that products’ quality is incomparable to that of other products, which will not […]
- Conflict Management: Teambuilding and Dynamics Each team has to perform the assigned task and in addition it must coordinate with other teams to ensure smooth progress in operations.
- Role of Communication and Teamwork in Improving Patient Safety In fact, research suggests the existence of communication difficulties between several departments and levels of hospital and healthcare settings including doctors, doctors and nurses, between nurses and between nurses and doctors, which have often resulted […]
- Organizational Behaviour: Teamwork in a Canadian Pub The main issues in the case are as follows: In the case, during the Brainiac game, a regular player Hannah suggested the other regulars to play cooperatively to improve the answering.
- Teamwork, Team Dynamics and Communication However, the success or otherwise of group dynamics is determined by many factors such as the large context of a country and its geographic features, the organization in which the group operates, the nature of […]
- Team Building and Role Assignment in Nursing When nurses engage their colleagues who have the requisite skills in community service and team building, they increase the scale of knowledge held by the new professionals in the team.
- Empowering People and Fostering Teamwork The strategy that I prefer to use to empower people in my team is different from the previous one when it comes to all-or-none situations that require taking well-considered decisions.
- The Secrets of Great Teamwork When all individuals in the team know the direction of the team and how they support the objective and target of the team, productivity improves.
- Mighty Tech Company’s Leadership and Teamwork For instance, Ben and Beatrice disagreed on the approach to follow in order to complete the job in time. Facilitation of the audit process also is constituted in the throughput since it is the organization […]
- Organizational Behavior: Teamwork and Leadership The attributes of a strong and successful group encompass effective communication, facilitated morale, excellent leadership, and the ability of the members to perceive themselves as valuable players.
- Leadership and Teamwork Experience Evaluation In order to record positive records, most of the members in the team focused on the targeted outcomes. Every member of the team was ready to engage in meaningful communication.
- Teamwork and Teambuilding The cons of this team are that work progress is hard to track and only depends on the honesty of team members, it is difficult to create a team culture since members are not close […]
- Group Conversations About Teamwork You have not provided the things that should be avoided when using your approaches to solve the conflict in the scenario.
- FireArts Company Teamwork Management Issues The key individuals in this case study are Erick Holt, FireArts new director of strategy, charged with the responsibility of putting together a team of top individuals within the organization, and Randy Louderback, the sales, […]
- Dysfunctional vs. Highly-Effective Teamwork The current essay aims to examine the experiences of the writer with a dysfunctional team and the factors that might have contributed to this.
- Team Building in the United Arab Emirates In this instance, volunteering not only contributes to the improvement of the team dynamics within the organization but also to the integration with the community and development of the positive brand image by taking responsibilities […]
- Team-Building Lessons from Chinese Restaurant Anina Blecher demonstrates many qualities that the Protagonist is expected to have. Her employees are friendly; everybody knows and promotes the values of the restaurant.
- Team Building Exercises in Project Management Through the use of metaphors below, I will demonstrate to the group members the importance of working in a group. The birds asked how they were going to help and the lizard suggested they bite […]
- Teamwork and Self-Awareness In order for a group of people to effectively collaborate and ensure long-term teamwork on a project, there must be a sense of self-awareness in each member.
- Effective Teambuilding for Childcare Center After pairing the teachers, the third stage will be used to guide and mentor the team. The fifth stage is to celebrate the functions and successes of the team.
- Healthcare: Collaborative Teamwork Evaluation The development of a stable leadership structure in the team is important because it can significantly lower the number of possible miscommunications and misunderstandings of the final goal.
- Hewlett Packard’s and Chartered Management Institute’s Teamwork At CMI, the idea of teamwork is taken seriously in an attempt to deliver positive results. Leaders should also be appointed and encouraged to meet the needs of different team members.
- Non-Profit Organisations and Team Building The authors of the article introduce the notion of feedback interventions, or FI, as a tool for managing the organizational performance, and provide a historical review and meta-analysis of the evidence for its efficiency and […]
- Motivational Aspects of Teamwork in Schools The problem that this paper is going to dwell on relates to the diverse impact of motivation on the eminence of teamwork in a school environment.
- Interdisciplinary Teamwork and Group Communication All group members should treat one another with respect, avoiding discrimination and conflicts; All group members should attend each meeting; In case of an emergency, the member should notify the rest of the group […]
- Fundamentals of Management: Leadership and Teambuilding They are also responsible for keeping the team on focus and functioning as a single unit. Interpersonal and communication are the life of a team.
- Proposal Preparation and Effective Teamwork One of the pillars of effective proposal preparation is the interaction with team members as it can ensure the effective functioning of the team.
- Teamwork for Organizational Efficiency In order to improve the efficiency of teams, it is important to enhance the effectiveness of teams. In Ruth Wageman, Heidi Garner, and Mark Mortensen’s article entitled Teams Have Changed: Catching Up to the Future, […]
- 1996 Mount Everest Disaster and Teamwork Factor The Everest case study illustrates some key problems that need to be addressed to avert the recurrence of errors or omissions that may have occasioned the deaths of the climbers.
- Teamwork Leads in Labor Force Improvement Teamwork plays an important role in the achievement of the positive results of the organization and promotes the maintenance of the competitive strengths of the company.
- Managerial Duties, Teamwork and Corporate Culture One of the most important duties of the contemporaneous manager is to assist the group affiliates in receiving new material, to give grounding in the best-known practice apprehensions, and to interfere in the work procedure […]
- Group Dynamics, Effective Teamwork and Technology Effective teams in an organisation are characterised by commitment between the members of the team. Understanding and support among team members are also important in determining the effectiveness of the team.
- Interprofessional Healthcare Teamwork By the end of the six-month period, the physical state of Carla will improve as cases of pneumonia will decrease by about 25%, as a result of the physical therapy, medication therapy, and changes in […]
- CMA Company’s Team-Building and Communication The focus on improving communication and promoting teamwork is crucial because of the lack of trust by which the relationships between the company members can be characterized. Therefore, it will be reasonable to focus on […]
- Multicultural Teamwork Approaches This was done to provide the team with the essential elements of the presentation in a shorter period and show an adequate level of collaboration.
- ABC Hospital’s Effective Team Building Building an effective team within a micro-system requires one to understand the mission of the micro-system and organization, and the goals that should be achieved by the team.
- Managers, Team Building and Results Orientation If a manager is in charge of a department, he or she should not try to win the false authority by being good.
- Diversity Consciousness in Team Rapport Building In regards to online communal, the designers’ key concentration is to generate the expertise that abide by the welfares, and the societal and basic requirements, of the online communal.
- Cognition and Emotions, Teamwork and Management The concepts of power and approach are used to organize the management process most efficiently. In any organization, power is the prerogative of the executive management and the managers of the middle level.
- Teamwork Management: Roles Identification and Ideas Transformation It is not only necessary to define the roles; it is more important to prove the importance of the identification process and the essence of each role in a team.
- Teamwork and Motivation Importance The motivation plan should outline steps that employees should take in order to guarantee realization of their mandate within the organization.
- DHL & Qantas Flight 32: Teamwork and Creative Approaches One of the most important aspects that need to be noted is that the crew that the issue that it was an uncontained failure of the engine at first, but smoke was noticed.
- Teamwork: Theory, Research and Practice Teamwork is one of the most imperative considerations not only in school but also in the current working environment because of the benefits acquired in the process of mixing and sharing with other people in […]
- Teamwork and Leadership: Overcoming Challenges Knowlton was the leader of the group, as he was arguably the one with the best leadership skills and had the best experience and knowledge regarding the project.
- The Company’s Teamwork Training Program One of the strategies that the manager intends to apply in achieving this goal is training employees on the significance of teamwork.
- Technology Support Team Building In a well orchestrated team the operation is so smooth it is difficult to recognize the role of the team leader. This can be taken to signify the absence of egocentric motives and personalities in […]
- Team Building: Good Planning of Participants Interaction Developing a team and being part of a team require first to understand the team dynamics and purpose of the group.
- Teamwork Behavior: Concept and Aspects An issue of immediate concern to these people is to understand the dynamics of team behavior and the factors that influence them.
- The Efficiency of the Teamwork The efficiency of the teamwork has to be profoundly analyzed since it defines the quality of the performance of the organization.
- Groupthink as the Curse of Teamwork Instead of members individually evaluating project alternatives, they just second ideas of group leaders or group members so as not to be seen to derail the team.
- WooWoo Company Management: Teamwork and Motivation The motivation plan of the company that manufactures ‘WooWoo’ would offer rewards to many employees of the company. The rewards would strive to meet the specific needs of the employees.
- Strategic Role of Human Resources and Promoting Effective Teamwork in the Workplace As the team leader, I had to ensure teamwork and cooperation among the players in order to enhance the team’s performance.
- Teams and Communication in Healthcare: Importance of Good Teamwork The article, titled “Importance of Good Teamwork in Urgent Care Services”, makes reference to a case study to investigate the topics of teamwork and communication in a London emergency department resuscitation unit, and also to […]
- Leadership, Teambuilding and Communication The task of building and managing diverse teams in an organization is similarly critical to the process of organizational leadership. Such barriers to communication affect the performance of the group and work teams in a […]
- Personal Development Plans: Teamwork and Culture Shock In an effort to achieve the desired level of personal development, it is important for one to take into account the concept of culture. The resultant effect is that the students are able to fit […]
- Personal Skills Development in the Teamwork In the team, the management ensured that organizational goals are achieved by modifying the tasks of individuals and the organization structure.
- Teamwork and Motivation: Woowooo Inc. With the entry of new workers, the next part of the motivation plan is to create a working schedule that will see the workers give the best output throughout the production and marketing process.
- The Concept of Organization Structure and Teamwork The amount of time team members commits to team assignment relates to team efforts and success of the team. The team members become more committed and extend their effort in ensuring a proactive achievement in […]
- Emotional Intelligence in Teamwork and Mutual Cooperation From this argument it is right to claim that the virtues of emotional intelligence contribute greatly to the aspects of personality and other individualistic provisions.
- Virtual Teams as Teamwork Efforts In this article the maturity and efficiency of virtual team is measured by a Virtual Team Operation Survey tool that assesses the indicators of virtual team performance.
- Conflict Resolution in a Team Building This would then be followed by drawing a scene in the office and each member of the team participating in the role that they had read in the card. In this activity, members of the […]
- The Role of Teamwork in Management Gupta is of the opinion that working as a team motivates individuals to be more risk taking in order to attain their goals.
- Teamwork, Decision-Making, and Strategy It is with the same intent that the manager intended to use the help of his team to launch a new division that manufactures liquid soap brands for the market by using the potential of […]
- Effective Team Building in Bell ExpressVu To organize an effective team-building event, the theme of the event should be exciting and inspiring to the employees. Such a theme helps to motivate and communicate effectively with the participants of team building.
- Teamwork and Communication Errors in Healthcare This paper states that medical errors have a number of underlying causes, including the fallibility of medical personnel, uncertainty of medical knowledge and imperfection of organizational systems, and pays special attention to the negative outcomes […]
- Team Building and Facilitation It further discusses group work in detail by focusing on concepts of team buildings, the life cycles of teams, types of teams, advantages of team focus in an organization, how to build effective teams and […]
- Leadership and Teambuilding The author classified important stages in the process of becoming a team as the following; Emergent themes The themes of “Speaking to” and “getting to know” were introduced at the beginning of project, a strategy […]
- Project Success and Team Building Overall, the development of these indicators is one of the first steps that managers should take prior to the start of any project.
- Teamwork’s Achievements and Challenges This difference can be attributed to the competence of the team members. These researchers found that poor communication is one of the major causes of misunderstanding and conflicts in a team.
- Effects of Generational Differences on Teamwork in Organisations in the UK However, in the UK, employees in most organisations belong to the Baby boomers generation, Generation X and Y. According to Lyons, Baby boomers prefer to work in teams because they are keen on learning new […]
- Teamwork Spirit Improvement The eventual beneficiaries of the project done by the group are the consumers of the company. This is a clear indication that the employees will find it unbearable to work one another and this will […]
- Corporate Team Building Strategies The choice of team designs range from self-directed teams, problem-solving teams, cross-functional teams and virtual teams. The type of design that firms adopt impact on the effectiveness of the teams and thus team building must […]
- Five Approaches to the Successful Team Building A team leader should consider explaining the mission of the team to the members because if he/she assumes that they understand it, he/she will be surprised later on because people understand things differently and this […]
- Teamwork and Collaboration First of all, one should speak about the role of “most responsible nurses” who had to care about a set of patients. The authors demonstrate that the partnership of nurses is critical for improving the […]
- Thinking Problem Solving and Team Building First and foremost, as a person endowed with the knowledge and a little bit of experience in offering engineering services for a range of pharmaceutical machines and equipments, it was my obligation to ensure that […]
- Challenges in Virtual Team Building On the other hand, a team is a group of individuals in the same region working together to achieve a common goal.
- When Collaboration Enhances Team Performance In addition, the background information on the nature and role of collaboration contributes positively towards the development of a logical argument.
- Teamwork and as an Important Part of Effective Performance The doubling of the number of calls at the call center is indicative of deterioration of customer service due to the above reasons.
- Teamwork Survey by Tuckman’s Model These scores show that the team is in the Performing stage, since the highest score is 38 and the highest possible points are 40.
- Team Building and Team Development The team has to attain the next stage of the development life cycle, which is the performing stage. At the initial stages of development, a team is expected to engage members to pursue goals or […]
- How Does Feedback Help Teamwork?
- How Does Effective Teamwork Look?
- How Do Teens Learn Teamwork: Agentic and Constructive Peer Processes?
- What Is the Power of Teamwork?
- How Idea Generators Juggle Between the Pros and Cons of Teamwork?
- Why Is Teamwork Essential in Life?
- What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Teamwork?
- What Skills Are Necessary for Teamwork?
- How Could Teamwork Leaders Cope With the Acceleration of Internationalization?
- Does Effective Teamwork Need Leadership and a Formal Structure This?
- How Can Teamwork Be Effective?
- What Makes Teamwork Efficient?
- Why Team and Teamwork Come Up With Better Solutions?
- What Are Three Essential Skills for Teamwork and Collaboration?
- What Does Teamwork Mean?
- What Is Teamwork Short Note?
- How Can Teamwork Damage Productivity?
- What Makes a Team Successful?
- What Are the Qualities of Good Teamwork?
- How Diversity and Teamwork of a Company?
- Can Teamwork Overcome the Negative Aspects Associated With Scientific Management Workplace Practices?
- What Are the Benefits of Teamwork?
- Why Is Teamwork Important in Life?
- Why Is Teamwork Essential in Research?
- How Do Teams and Teamwork Affect Individual Satisfaction?
- How Can Teamwork Improve Organizational Performance?
- Does Poor Supervisability Undermine Teamwork?
- Why Is Teamwork the Key to Success?
- What Does the Research Say About Teamwork?
- How Does Communication Affect Teamwork?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 1). 169 Teamwork Topics & Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/teamwork-essay-topics/
"169 Teamwork Topics & Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 1 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/teamwork-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '169 Teamwork Topics & Essay Examples'. 1 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "169 Teamwork Topics & Essay Examples." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/teamwork-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "169 Teamwork Topics & Essay Examples." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/teamwork-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "169 Teamwork Topics & Essay Examples." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/teamwork-essay-topics/.
- Team Management Paper Topics
- Social Work Essay Titles
- Social Networking Essay Ideas
- Time Management Essay Titles
- Team Leadership Research Ideas
- Conflict Resolution Essay Topics
- Leadership Essay Ideas
- Workplace Diversity Research Ideas
- Self-Reflection Research Topics
- Work-Life Balance Essay Titles
- Virtual Team Ideas
- Work Environment Research Topics
- Employee Engagement Essay Topics
- Talent Management Questions
- Mentorship Topics
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Business Teamwork
My Experience Working in a Group: a Reflection
Table of contents, challenges of group work, benefits and learning opportunities, lessons learned.
- Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. T. (2009). An educational psychology success story: Social interdependence theory and cooperative learning. Educational researcher, 38(5), 365-379.
- Belbin, R. M. (2012). Team roles at work. Taylor & Francis.
- Tuckman, B. W. (1965). Developmental sequence in small groups. Psychological Bulletin, 63(6), 384-399.
- Forsyth, D. R. (2014). Group dynamics (6th ed.). Cengage Learning.
- Katzenbach, J. R., & Smith, D. K. (2015). The wisdom of teams: Creating the high-performance organization. Harvard Business Review Press.
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Entrepreneurship
- Manufacturing
- Risk Assessment
- Company Analysis
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
The Confident Teacher is a blog by teacher and author, Alex Quigley ( @AlexJQuigley )
Top 10 Group Work Strategies
If I am continually vexed by any one question in education it is ‘ how can we enhance student motivation? ‘ Of course, I do not have the answer, and if there is one it is multi-faceted, complex and, frankly, not going to be solved in this blog post.
From my position as a classroom teacher, I am always on the look out for those strategies that create a state when students are motivated and in their element , where they work furiously without even realising they are doing so, without realising the clock is ticking down to the end of the lesson. There is no better compliment than when students question how long there is left and express genuine surprise at how fast time has passed, and that they have actually enjoyed that lesson.
My, admittedly non-scientific, observations are that many of the times students are in ‘ flow ‘, or their element, in my lessons is when they are collaborating in group work.
Why is this then? I believe that we are obviously social beings and we naturally learn in such groups (not always effectively it must be said), but that, more importantly, when working in a group we are able to correct, support, encourage, question and develop ideas much more effectively. The power of the group, guided by the expertise of the teacher, accelerates learning, makes it richer and demands a learning consensus that can push people beyond their habitual assumptions.
Don’t get me wrong, there are pitfalls and obstacles to group work. This constructivist approach should build upon expert teacher led pedagogy – ensuring that students have a good grounding in the relevant knowledge before undertaking in-depth group work. Group work can also be beset by issues in many nuanced forms: whether it is subtle intellectual bullying, where the student who shouts loudest prevails; or the encouragement of mediocrity and laziness, as students let others do all the work; or simply by poor, distracting behaviour.
Another issue is ‘group think’ miscomprehension – indeed, how does prejudice flourish if not in social groups? Yet, this failure is often great for learning as long as the teacher can illuminate the error of their ways. Of course, no teaching strategy is foolproof and plain good teaching should remedy many of the potential ills of group work, just as good teaching can make more traditional teacher-led ‘direct instruction’ wholly engaging and effective.
I am intrigued by the idea of ‘ social scaffolding ‘ (Vygotsky) – the concept that most of our learning is undertaken in group situations, where we learn through dialogue and debate with others, not simply by listening to that voice in our head! That being said, I am not talking teachers out of a classroom here.
The role of the teacher in devising and planning a successful group task takes skill, rigour and utter clarity and precision. Students need to be clear about a whole host of things: from their role, to the purpose of the task and the parameters of expected outcomes to name but a few. Teachers need to keep groups on track, intervene appropriately to improve learning and regularly regain student focus. Teachers have a pivotal role in guiding the group work at every stage.
Group work certainly isn’t the lazy option: it takes skill in the planning and the execution, and sometimes, despite our best laid plans, it still fails. That shouldn’t put us off – aren’t all teaching and learning strategies subject to such risks?
If I was to define a simple and straight-forward basis for the rules for group work it would be:
– Have clearly defined tasks, with sharp timings and with the appropriate tools organised – Have clearly defined group roles – Have clear ground rules for talk, listening and fair allocation of workload etc. – Target your support and interventions throughout the task, but make them interdependent of one another, not dependent upon you – Always be prepared to curtail group work if students don’t follow your high expectations.
So here it is, my entirely subjective top 10 strategies for group work that I believe to be effective (ideas for which I must thank a multitude of sources):
1. ‘Think-pair-share’ and ‘Think-pair-square’.
Well, no-one said this top ten had to be original! This strategy is one of those techniques that we employ so readily that we can almost forget about it, it is simply so automatic for most teachers; yet, because of that we can easily forget it in our planning. We need to use it regularly because it is the very best of scaffolded learning; it almost always facilitates better quality feedback by allowing proper thinking time and for students to sound out their ideas and receive instantaneous feedback from peers. ‘Think-pair-square’ adds a touch of added flavour, involving linking two pairs together (to form the ‘square’ to share their ideas before whole class feedback). I defer to this blog post by @headguruteacher for the skinny on ‘Think-pair-share’ here .
2. Snowballing or the Jigsaw method
Similar to the ‘square’ approach mentioned in ‘Think-Pair-Square’, the ‘snowballing’ activity is another simple but very effective way of building upon ideas by starting with small groups and expanding the groups in a structured way. As the metaphor of the snowball suggests, you can begin with an individual response to a question; followed by then pairing up students up; then creating a four and so on. It does allow for quick, flexible group work that doesn’t necessarily require much planning, but does keep shaping viewpoints and challenging ‘answers’ is a constructive fashion.
The ‘jigsaw method’ is slightly more intricate. David Didau describes here how it is the “ultimate teaching method”, but that it benefits greatly from careful planning. Put simply, when researching a topic, like the causes of the Second World War, each member of a group is allocated an area for which they need to become the ‘ expert ‘, such as ‘the impact of the Treaty of Versailles’, or ‘issues with the dissolution of Austria-Hungary’ for example. With five or six ‘ Home ‘ groups identified, the ‘ experts ‘ then leave that group to come together to pool their expertise on the one topic; they question one another and combine research, ideas and their knowledge. Then each ‘ expert ‘ returns to their ‘ home ‘ group to share their findings. It is a skilful way of varying group dynamics as well as scaffolding learning.
3. Debating (using clear rules)
As you probably know, our own inspiring leader, Michael Gove, was the President of the Oxford Union. Clearly, these ancient skills of rhetoric and debate have seen him rise to dizzying heights. Perhaps we need to teach debating with great skill if we are to produce citizens who can debate with the best of them…and with Michael Gove. The premise of a debate, and its value in enriching the learning of logic, developing understanding and the simultaneous sharpening and opening our minds, is quite obvious so I will not elaborate. If you are ever stuck for a debate topic then this website will be of great use: http://idebate.org/debatabase . The Oxford rules model is an essential model for the classroom in my view. It provides a clear structure and even a level of formality which is important, provide coherence and greater clarity to the debate. The rules, familiar steps though they are for many, are as follows:
Four speakers in each team (for and against the motion) First speaker introduces all the ideas that team has generated Second speaker outlines two or three more ideas in some depth Third speaker outlines two or three ideas in some depth Fourth speaker criticises the points made by the other team Each individual speaker has two minutes to speak (or more of course), with protected time of thirty seconds at the beginning or the end The rest of the team is the ‘ Floor ‘ and can interject at any time by calling out ‘ Point of Information ‘ and standing. The speaker can accept or reject an interjection.
You may wish to have the other groups work as feedback observers on the debate being undertaking (a little like Socratic circles – number 8 ). This has the benefit of keeping the whole class engaged and actively listening to the debate.
4. Project Based Learning/Problem Based Learning
I have to admit I have only ever undertaken project style work on a small scale, but in the last year I have been startled by the quality of work I have observed in project based learning across the world. The principals of Project Based Learning are key: such as identifying real audiences and purposes for student work (a key factor in enhancing motivation); promoting interdependent student work, often subtly guided by the teacher at most stages; letting students undertake roles and manage the attendant challenges that arise; learning is most often integrated and spans subject areas; and students constructing their own questions and knowledge. Truly the best guide is to survey these great examples:
The Innovation Unit has also produced this brilliant must-read guide to PBL in great depth here .
‘Problem based learning’ is clearly related to the project model, but it explicitly starts with a problem to be solved. It is based primarily upon the model from medicine – think Dr House (although he is hardly a team player!). David Didau sagely recommends that the teacher, or students in collaboration, find a specifically local problem – this raises the stakes of the task. Clearly, in Mathematics, real problem based learning can be a central way to approach mathematical challenges in a collaborative way; in Science or Philosophy, the options to tackle ethical and scientific problems are endless. There is criticism of this approach – that students struggle with the ‘ cognitive load’ without more of a working memory. Ideally, this learning approach follows some high quality direct instruction, and teacher led worked examples, to ensure that students have effective models to work from and some of the aforementioned working memory.
5. Group Presentations
I would ideally label this strategy: ‘ questions, questions, questions ‘ as it is all about creating, and modelling, a culture of enquiry by asking students questions about a given topic, rather than didactically telling them the answer – then helping shape their research. The teacher leads with a ‘ big question ‘; then it is taken on by groups who (given materials, such as books, magazines, essays, iPads, laptops, or access to the library or an ICT suite etc.) have to interrogate the question, forming their own sub-set of questions about the question/ topic. They then source and research the key information, before finally agreeing to the answers to the questions they had themselves formed. The crucial aspect about presentations is giving students enough time to make the presentation worthwhile, as well as allocating clear roles. High quality presentations take time to plan, research and execute.
Personally, I find the timekeeper role a waste of time (I can do that for free!), but other roles, such as leader, designer and scribe etc. have value. Also, the teaching needs to be carefully planned so the entire presentation is not reliant solely upon any one person or piece of technology. Developing a shared understanding of the outcome and the different parameters of the presentation is key: including features like banning text on PowerPoints; or making it an expectation that there is some element of audience participation; to agreeing what subject specific language should be included. The devil is in the detail!
6. ‘Devise the Display’
I have a troubled relationship with displays! I very rarely devise my own display as I think displays become wallpaper far too soon considering the effort taken to provide them – like newspapers, they become unused within days. I much prefer a ‘ working wall ‘, that can be constantly changed or updated (or a ‘learning continuum’ for an entire topic when can be periodically added to each lesson). That being said, I do think there is real high quality learning potential in the process of students devising and creating wall displays. It is great formative feedback to devise a wall display once you are well under way a topic. It makes the students identify and prioritise the key elements of their knowledge and the skills they are honing.
I find the most valuable learning is actually during the design ideas stage.You can ‘snowball’ design ideas with the students; beginning individually, before getting groups to decide collaboratively on their design; then having a whole class vote. I do include stipulations for what they must include, such as always including worked examples. Then, the sometimes chaotic, but enjoyable activity it to create the display. I always aim for the ‘ 60 Minute Makeover ‘ approach – quick and less painful (it also makes you less precious about the finer details)!
I think they also learn a whole host of valuable skills involving team work, empathy and not to annoy me by breaking our wall staplers! I think it is then important to not let any display fester and waste, but to pull it down and start afresh with a new topic. I know this strategy does put some people off, because it can be like organised chaos, but if everyone has a clear role and responsibility the results can be amazing. [Warning – some designs can look like they have been produced by Keith Richards on a spectacular acid trip!]
7. Gallery Critique
This stems from the outstanding work of on Berger. Both a teacher and a craftsman himself, Berger explains the value of critique as rich feedback in his brilliant book ‘ The Ethic of Excellence ‘. It can be used during the draft/main process or as a summative task. This strategy does have some specific protocols students should follow. The work of the whole group should be displayed in a gallery style for a short time. Students are expected to first undertake a short silent viewing (making notes to reflect is also useful here). The students make comments on the work – post it notes being ideal for this stage. Then the next step is a group discussion of ‘ what they noticed ‘ in particular, with debate and discussion encouraged – of course, the feedback should be both kind and constructive. The next step for discussion is talking about ‘ what they liked ‘, evaluating the work. The final stage has the teacher synthesise viewpoints and express their own; before ensuring students make notes and reflect upon useful observations for making improvements.
8. Socratic Talk
I have spoken about this strategy before here . What is key is that like the debating rules above, a clear and defined structure is in place, particularly with ‘ Socratic circles ‘ which embeds feedback and debate in a seamless way. It takes some skill in teaching students how to talk in this fashion, but once taught, it can become a crucial tool in the repertoire. In my experience, some of the most sensitive insights have emerged from this strategy and the listening skills encouraged are paramount and have an ongoing positive impact. It also allows for every student to have a role and quality feedback becomes an expectation.
9. Talking Triads
Another simple, but highly effective strategy. It is a strategy that gets people to explore a chosen topic, but with a really rigorous analysis of ideas and views. The triad comprises of a speaker , a questioner and a recorder/analyst . You can prepare questions, or you can get the questioner and the analyst to prepare questions whilst the speaker prepares or reflects upon potential answers. This can be done in front of the class as a gallery of sorts, or you can have all triads working simultaneously. If they do work simultaneously, then a nice addition is to raise your hand next to a particular triad, which signals for other groups to stop and listen whilst that specific triad continues, allowing for some quality listening opportunities.
10. Mastery Modelling
This involves a form of formative assessment from students, whereat the teacher gives a group a series of models, both exemplar models and lesser models, including some with common errors that students would likely identify. The students need to do a critical appraisal of the these models as a group and identify their summary assessment of the models first, before then devising and presenting a ‘mastery model’ that is a composite exemplar model of work. This strategy works in pretty much every subject, with the subject being either an essay, a piece of art, or a mathematical problem. This presentation should include an explicit focus upon the steps taken leading to create the ‘ mastery model ‘ during the feedback – this unveils the process required for mastery for the whole class.
Useful links:
A great research paper that analyses group work and its importance: ‘Toward a social pedagogy of classroom group work’ By Peter Blatchford, Peter Kutnick, Ed Baines, and Maurice Galton
An excellent National Strategies booklet from back in the day when the DfE was interested in pedagogy. I particularly like the ‘ different grouping criteria’/’size of grouping’ tables: Pedagogy and Practice: Teaching and Learning in Secondary Schools Unit 10: Group work
Nice step by step guide to the implementation and the delivery of group work ‘ Implementing Group Work in the Classroom ‘
11 thoughts on “Top 10 Group Work Strategies”
Pingback: Homepage
Pingback: Working SOLO in Group Work | meridianvale
Pingback: 4. Effective Group Work | Heathfield Community School
Pingback: Blog of the Week 3: Top Ten Group Work Strategies via HuntingEnglish | RGS Learning
Pingback: Group Work Skills | challengemyself
Great article. I’ve been successfully implementing primarily PBL in the undergrad classroom for years. I’m getting ready to launch the most ambitious group work project I’ve ever undertaken with my students – 130 students and 20 nonprofit organizations broken into collaborative teams to study each organization’s volunteer programs, to make recommendations for improving or refreshing them. I know so much about how to do this, and yet the project is so big and important that I am running around looking for affirmation that it’s ok to do this major thing. I am dragging in consultants and volunteer managers from local organizations as experts and creating an online professional learning community where everyone can bring their problems and discuss them and get help from the consultants. Thanks for the reassurance and the references!
Pingback: Hybrid Learning: A Complete List of Essential Resources | ViewSonic Library | Far World News
Pingback: Hybrid Learning: A Complete List of Essential Resources | ViewSonic Library - NWS100
Pingback: Hybrid Learning: A Complete List of Essential Resources | Education News – PePPer TV Cooking, Sport Health and Nutrition
Pingback: How to Improve Group Work | eCampus.com Blog
Pingback: Give two examples of individual strategies and two examples of group strategies a person could use to help quit smoking. – The Millennial Mirror
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Get the latest posts delivered to your mailbox:
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Self Reflection — Self-Reflection On My Experiences Working In A Group
A Reflection on My Experience Working in a Group
- Categories: Self Reflection
About this sample

Words: 464 |
Published: Nov 8, 2019
Words: 464 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Works Cited
- Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. T. (2009). An educational psychology success story: Social interdependence theory and cooperative learning. Educational researcher, 38(5), 365-379.
- Tuckman, B. W. (1965). Developmental sequence in small groups. Psychological bulletin, 63(6), 384-399.
- Katzenbach, J. R., & Smith, D. K. (2005). The wisdom of teams: Creating the high-performance organization. Harvard Business Review Press.
- Hackman, J. R. (2002). Leading teams: Setting the stage for great performances. Harvard Business Press.
- Lencioni, P. (2012). The advantage: Why organizational health trumps everything else in business. Jossey-Bass.
- Fisher, R., Ury, W., & Patton, B. (2011). Getting to yes: Negotiating agreement without giving in. Penguin.
- Belbin, R. M. (2012). Team roles at work. Routledge.
- Charkoudian, L., & Moore, W. (2017). Building a strong team culture in a healthcare setting. Journal of Healthcare Leadership , 9, 9-20.
- Belbin, M. (2016). Team Roles and Team Performance: Is there “really” a link?. International Journal of Management & Business Studies, 6(2), 47-58.
- Smith, G. D. (2018). Effective Teamwork: Practical Lessons from Organizational Research. John Wiley & Sons.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1105 words
4 pages / 1606 words
4 pages / 1682 words
1 pages / 514 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Self Reflection
Undertaking a journey of introspection and self-exploration inevitably leads to a captivating exploration of the myriad factors that have contributed to shaping my identity. This essay delves into the intricate web of influences [...]
The exploration of my identity reveals a multifaceted tapestry woven from cultural roots, passions, values, education, connections, and the willingness to embrace change. Just as every thread contributes to the beauty of a [...]
As I contemplate the journey of self-discovery and growth, it becomes evident that understanding what shaped me as a person is an intricate exploration. This essay delves into the factors and experiences that have played a [...]
The mentorship experience has been an integral chapter in my journey of growth and self-discovery. Through the guidance, encouragement, and insights of my mentor, I have navigated challenges, honed my skills, and gained a [...]
Culture is a compound term in itself to commence with; it takes decades to know about the metamorphosis of culture. Though, one can master it by reflecting into oneself; analyzing personal bias, introspecting one’s strengths and [...]
According to Dewey, 1933 reflection is a deliberate and active process about thinking to learn.The aim of this reflective journal is to analyse in the first part, my role, as an implementer, to plan a workable strategy and carry [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, what are the benefits of group work.
“More hands make for lighter work.” “Two heads are better than one.” “The more the merrier.”
These adages speak to the potential groups have to be more productive, creative, and motivated than individuals on their own.
Benefits for students
Group projects can help students develop a host of skills that are increasingly important in the professional world (Caruso & Woolley, 2008; Mannix & Neale, 2005). Positive group experiences, moreover, have been shown to contribute to student learning, retention and overall college success (Astin, 1997; Tinto, 1998; National Survey of Student Engagement, 2006).
Properly structured, group projects can reinforce skills that are relevant to both group and individual work, including the ability to:
- Break complex tasks into parts and steps
- Plan and manage time
- Refine understanding through discussion and explanation
- Give and receive feedback on performance
- Challenge assumptions
- Develop stronger communication skills.
Group projects can also help students develop skills specific to collaborative efforts, allowing students to...
- Tackle more complex problems than they could on their own.
- Delegate roles and responsibilities.
- Share diverse perspectives.
- Pool knowledge and skills.
- Hold one another (and be held) accountable.
- Receive social support and encouragement to take risks.
- Develop new approaches to resolving differences.
- Establish a shared identity with other group members.
- Find effective peers to emulate.
- Develop their own voice and perspectives in relation to peers.
While the potential learning benefits of group work are significant, simply assigning group work is no guarantee that these goals will be achieved. In fact, group projects can – and often do – backfire badly when they are not designed , supervised , and assessed in a way that promotes meaningful teamwork and deep collaboration.
Benefits for instructors
Faculty can often assign more complex, authentic problems to groups of students than they could to individuals. Group work also introduces more unpredictability in teaching, since groups may approach tasks and solve problems in novel, interesting ways. This can be refreshing for instructors. Additionally, group assignments can be useful when there are a limited number of viable project topics to distribute among students. And they can reduce the number of final products instructors have to grade.
Whatever the benefits in terms of teaching, instructors should take care only to assign as group work tasks that truly fulfill the learning objectives of the course and lend themselves to collaboration. Instructors should also be aware that group projects can add work for faculty at different points in the semester and introduce its own grading complexities .
Astin, A. (1993). What matters in college? Four critical years revisited. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Caruso, H.M., & Wooley, A.W. (2008). Harnessing the power of emergent interdependence to promote diverse team collaboration. Diversity and Groups. 11, 245-266.
Mannix, E., & Neale, M.A. (2005). What differences make a difference? The promise and reality of diverse teams in organizations. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 6(2), 31-55.
National Survey of Student Engagement Report. (2006). http://nsse.iub.edu/NSSE_2006_Annual_Report/docs/NSSE_2006_Annual_Report.pdf .
Tinto, V. (1987). Leaving college: Rethinking the causes and cures of student attrition. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.

Essay on Group Work
Students are often asked to write an essay on Group Work in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Group Work
What is group work.
Group work is when two or more people work together to achieve a common goal. This can happen in many places, like school, work, or even at home. People in a group have to communicate, cooperate, and share their ideas and skills. This way, they can solve problems and complete tasks faster and better.
Benefits of Group Work
Working in a group has many benefits. It helps people learn from each other, build teamwork skills, and understand different viewpoints. It also divides the workload, making it easier for everyone. Group work can also help improve communication and social skills.
Challenges in Group Work
Despite the benefits, group work can also have challenges. Sometimes, people may not agree with each other, leading to conflicts. Some group members may not contribute equally, causing frustration. It’s important to address these issues to make group work effective.
Effective Group Work
To make group work effective, everyone should have a clear role and understand the goal. Good communication and respect for each other’s ideas are also important. Everyone should contribute equally and help each other. This way, the group can achieve its goal effectively and efficiently.
In conclusion, group work is a powerful tool for learning and achieving goals. Despite its challenges, it offers many benefits. With good communication, respect, and equal contribution, group work can be very successful.
250 Words Essay on Group Work
Group work is when two or more people come together to do a task. It is like a team playing a game. Everyone has a role in the team, and they all work together to win the game. This is the same in group work. Everyone has a job to do, and they work together to finish the task.
Why is Group Work Important?
Group work is important for many reasons. First, it helps us learn from each other. We all have different skills and ideas. When we work in a group, we can share these skills and ideas. This helps us learn new things. Second, group work teaches us how to work with others. We learn how to listen, how to share, and how to solve problems together. These are important skills that we need in life.
Group work has many benefits. One benefit is that it can make a big task easier. If we have to do a big task by ourselves, it can be hard. But if we do it in a group, we can share the work. This makes the task easier and faster. Another benefit is that group work can help us make better decisions. When we make decisions in a group, we can hear many different ideas. This can help us make a better decision.
Challenges of Group Work
Group work also has some challenges. Sometimes, people in the group may not agree. This can cause problems. But if we learn how to listen and respect each other, we can solve these problems.
In conclusion, group work is a good way to learn and work. It has many benefits and can help us in many ways. But like all things, it also has challenges. We need to learn how to work in a group to make the most of it.
500 Words Essay on Group Work
Group work is when two or more people work together to achieve a common goal. It is often used in schools, colleges, and workplaces. The main idea behind group work is to encourage people to work together, share ideas, and learn from each other.
The Importance of Group Work
Group work is important for many reasons. First, it helps us to learn how to work with others. This is a skill that is very useful in real life, especially in jobs where teamwork is important. Second, group work can make difficult tasks easier. When we work in a group, we can share the workload and help each other. Third, group work can help us to learn new things. By working with others, we can learn from their experiences and knowledge.
There are many benefits of group work. One of the main benefits is that it can improve our problem-solving skills. When we work in a group, we need to solve problems together. This can help us to think in new ways and come up with creative solutions.
Another benefit of group work is that it can improve our communication skills. In a group, we need to listen to others and express our own ideas clearly. This can help us to become better communicators.
Finally, group work can also help us to develop our leadership skills. In a group, we often need to take turns leading the team. This can help us to learn how to lead others and make important decisions.
While group work has many benefits, it can also have some challenges. One of the main challenges is that it can sometimes be difficult to work with others. People have different ideas and ways of doing things, which can lead to disagreements.
Another challenge of group work is that it can be hard to coordinate tasks. In a group, everyone needs to know what they are supposed to do and when they need to do it. This can be difficult if the group is not well-organized.
In conclusion, group work is a very useful tool that can help us to learn new skills, solve problems, and work more efficiently. While it can have some challenges, the benefits of group work often outweigh the difficulties. By working together in a group, we can achieve more than we could on our own.
In the end, group work is not just about getting the job done. It’s also about learning to work with others, developing new skills, and growing as individuals. And these are things that can help us in many different areas of our lives.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Group Influence On Individual Behavior
- Essay on Growing Up In The 21st Century
- Essay on Growing Up On A Farm
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What Needs to Change About DEI — and What Doesn’t

As DEI faces social, political, and legal backlash, leaders need to take stock of their efforts.
As DEI work faces increasing scrutiny socially, politically, and legally, organizations are taking extra care to re-evaluate their DEI efforts. Leaders are right to consider change, not as a reaction to backlash, but to work toward a more accountable, transparent, and successful vision of what DEI could be. The author identifies three things that need to change: 1) Clumsy, jargon-heavy communication, 2) disconnected and decoupled DEI goals and programs, and 3) nonexistent or vanity DEI measurement. They also identify three things that should be maintained: 1) Responsiveness to broader society, 2) commitment to healthy organizations, and 3) the belief that we can be better.
Organizations and their leaders have endeavored to create more diverse, equitable, and inclusive organizations in one way or another since the mid-1960s , even as the sociopolitical climate around these efforts has fluctuated.
- Lily Zheng is a diversity, equity, and inclusion strategist, consultant, and speaker who works with organizations to achieve the DEI impact and outcomes they need. They are the author of DEI Deconstructed: Your No-Nonsense Guide to Doing the Work and Doing it Right.
Partner Center
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
What public k-12 teachers want americans to know about teaching.
Illustrations by Hokyoung Kim

At a time when most teachers are feeling stressed and overwhelmed in their jobs, we asked 2,531 public K-12 teachers this open-ended question:
If there’s one thing you’d want the public to know about teachers, what would it be?
We also asked Americans what they think about teachers to compare with teachers’ perceptions of how the public views them.
Related: What’s It Like To Be a Teacher in America Today?
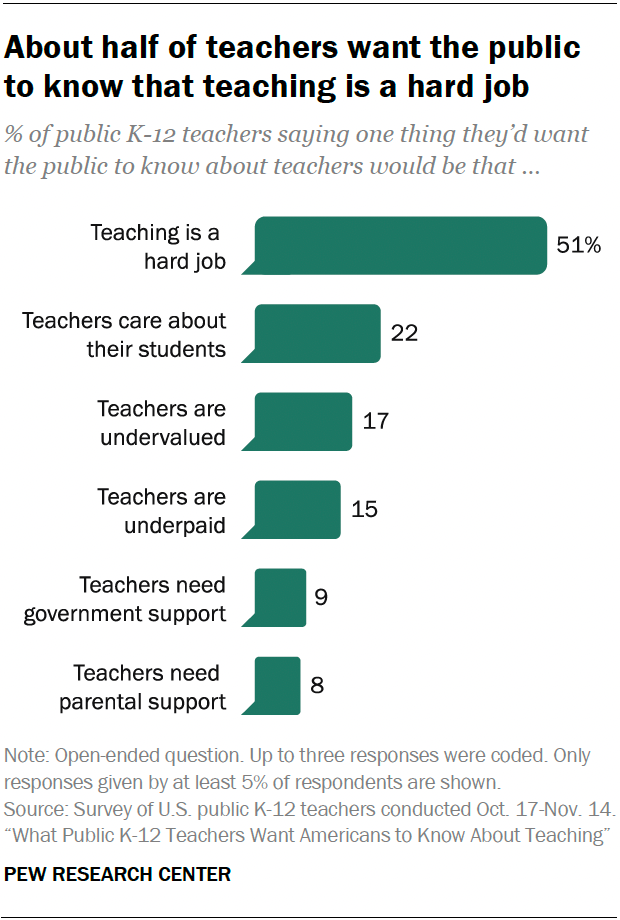
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to better understand what public K-12 teachers would like Americans to know about their profession. We also wanted to learn how the public thinks about teachers.
For the open-end question, we surveyed 2,531 U.S. public K-12 teachers from Oct. 17 to Nov. 14, 2023. The teachers surveyed are members of RAND’s American Teacher Panel, a nationally representative panel of public K-12 school teachers recruited through MDR Education. Survey data is weighted to state and national teacher characteristics to account for differences in sampling and response to ensure they are representative of the target population.
Overall, 96% of surveyed teachers provided an answer to the open-ended question. Center researchers developed a coding scheme categorizing the responses, coded all responses, and then grouped them into the six themes explored in the data essay.
For the questions for the general public, we surveyed 5,029 U.S. adults from Nov. 9 to Nov. 16, 2023. The adults surveyed are members of the Ipsos KnowledgePanel, a nationally representative online survey panel. Panel members are randomly recruited through probability-based sampling, and households are provided with access to the Internet and hardware if needed. To ensure that the results of this survey reflect a balanced cross section of the nation, the data is weighted to match the U.S. adult population by gender, age, education, race and ethnicity and other categories.
Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, the teacher survey methodology and the general public survey methodology .
Most of the responses to the open-ended question fell into one of these six themes:
Teaching is a hard job
About half of teachers (51%) said they want the public to know that teaching is a difficult job and that teachers are hardworking. Within this share, many mentioned that they have roles and responsibilities in the classroom besides teaching, which makes the job stressful. Many also talked about working long hours, beyond those they’re contracted for.
“Teachers serve multiple roles other than being responsible for teaching curriculum. We are counselors, behavioral specialists and parents for students who need us to fill those roles. We sacrifice a lot to give all of ourselves to the role as teacher.”
– Elementary school teacher
“The amount of extra hours that teachers have to put in beyond the contractual time is ridiculous. Arriving 30 minutes before and leaving an hour after is just the tip of the iceberg. … And as far as ‘having summers off,’ most of August is taken up with preparing materials for the upcoming school year or attending three, four, seven days’ worth of unpaid development training.”
– High school teacher
Teachers care about their students
The next most common theme: 22% of teachers brought up how fulfilling teaching is and how much teachers care about their students. Many gave examples of the hardships of teaching but reaffirmed that they do their job because they love the kids and helping them succeed.

“We are passionate about what we do. Every child we teach is important to us and we look out for them like they are our own.”
– Middle school teacher
“We are in it for the kids, and the most incredible moments are when children make connections with learning.”
Teachers are undervalued and disrespected
Some 17% of teachers want the public to know that they feel undervalued and disrespected, and that they need more public support. Some mentioned that they are well-educated professionals but are not treated as such. And many teachers in this category responded with a general plea for support from the public, which they don’t feel they’re getting now.
“We feel undervalued. The public and many parents of my students treat me and my peers as if we do not know as much as they do, as if we are uneducated.”
“The public attitudes toward teachers have been degrading, and it is making it impossible for well-qualified teachers to be found. People are simply not wanting to go into the profession because of public sentiments.”
Teachers are underpaid
A similar share of teachers (15%) want the public to know that teachers are underpaid. Many teachers said their salary doesn’t account for the effort and care they put into their students’ education and believe that their pay should reflect this.

“We are sorely underpaid for the amount of hours we work and the education level we have attained.”
Teachers need support and resources from government and administrators
About one-in-ten teachers (9%) said they need more support from the government, their administrators and other key stakeholders. Many mentioned working in understaffed schools, not having enough funding and paying for supplies out of pocket. Some teachers also expressed that they have little control over the curriculum that they teach.
“The world-class education we used to be proud of does not exist because of all the red tape we are constantly navigating. If you want to see real change in the classroom, advocate for smaller class sizes for your child, push your district to cap class sizes at a reasonable level and have real, authentic conversations with your child’s teacher about what is going on in the classroom if you’re curious.”
Teachers need more support from parents
Roughly the same share of teachers (8%) want the public to know that teachers need more support from parents, emphasizing that the parent-teacher relationship is strained. Many view parents as partners in their child’s education and believe that a strong relationship improves kids’ overall social and emotional development.

“Teachers help students to reach their potential. However, that job is near impossible if parents/guardians do not take an active part in their student’s education.”
How the U.S. public views teachers
While the top response from teachers in the open-ended question is that they want the public to know that teaching is a hard job, most Americans already see it that way. Two-thirds of U.S. adults say being a public K-12 teacher is harder than most other jobs, with 33% saying it’s a lot harder.
And about three-quarters of Americans (74%) say teachers should be paid more than they are now, including 39% who say teachers should be paid a lot more.
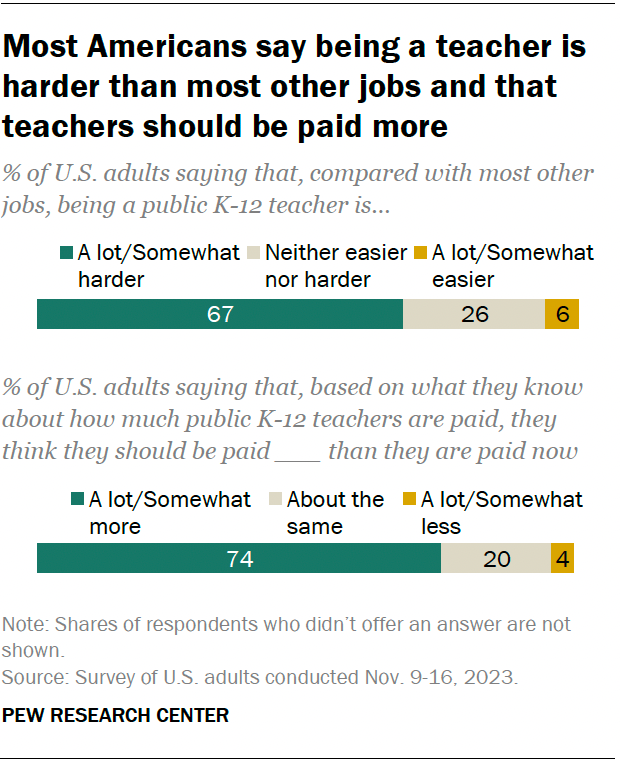
Americans are about evenly divided on whether the public generally looks up to (32%) or down on (30%) public K-12 teachers. Some 37% say Americans neither look up to or down on public K-12 teachers.
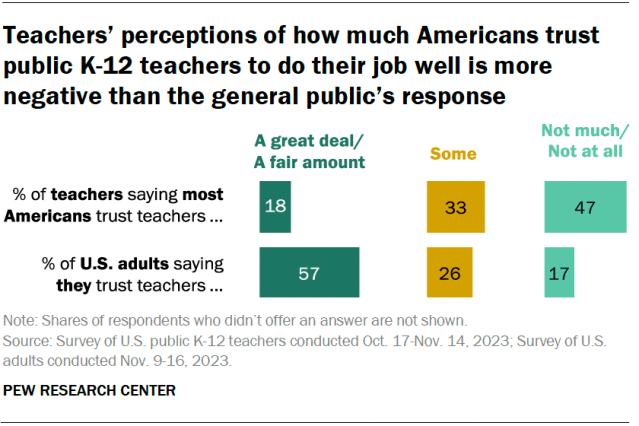
In addition to the open-ended question about what they want the public to know about them, we asked teachers how much they think most Americans trust public K-12 teachers to do their job well. We also asked the public how much they trust teachers. Answers differ considerably.
Nearly half of public K-12 teachers (47%) say most Americans don’t trust teachers much or at all. A third say most Americans trust teachers some, and 18% say the public trusts teachers a great deal or a fair amount.
In contrast, a majority of Americans (57%) say they do trust public K-12 teachers to do their job well a great deal or a fair amount. About a quarter (26%) say they trust teachers some, and 17% say they don’t trust teachers much or at all.
Related: About half of Americans say public K-12 education is going in the wrong direction
How the public’s views differ by party
There are sizable party differences in Americans’ views of teachers. In particular, Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents are more likely than Republicans and Republican leaners to say:
- They trust teachers to do their job well a great deal or a fair amount (70% vs. 44%)
- Teaching is a lot or somewhat harder when compared with most other jobs (77% vs. 59%)
- Teachers should be paid a lot or somewhat more than they are now (86% vs. 63%)
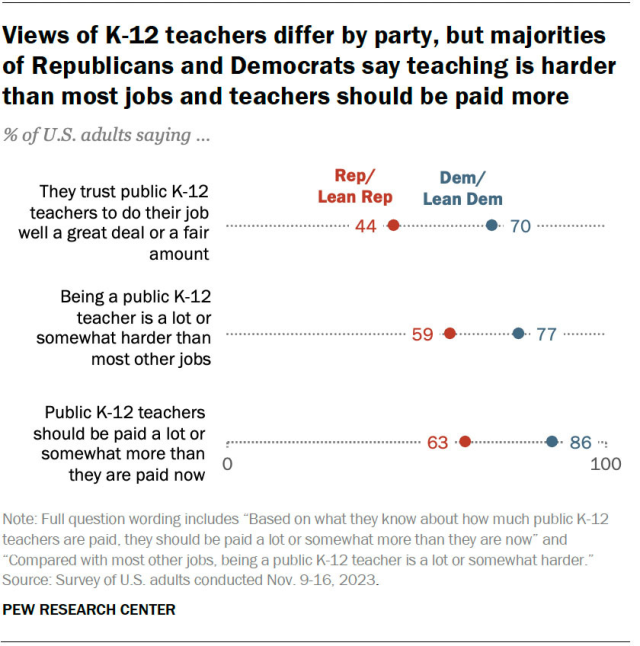
In their own words
Below, we have a selection of quotes that describe what teachers want the public to know about them and their profession.
Social Trends Monthly Newsletter
Sign up to to receive a monthly digest of the Center's latest research on the attitudes and behaviors of Americans in key realms of daily life
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share via E-mail
Former WA Gov. Dan Evans feted for energy, conservation work
The state’s other living three-term governor, 98, was recognized by the group that coordinates energy development in the Columbia Basin.
Venice Buhain

Former Governor Dan Evans, left, listens on stage next to John Carmichael, president of The Evergreen State College in Olympia, during an event on campus hosted by the Northwest Power and Conservation Council on April 9, 2024. Evans, 98, was Washington’s 16th governor, 1965-1977, and a U.S. senator 1983-1989. (David Ryder for Cascade PBS)
As regional leaders with the Northwest Power and Conservation Council grappled with the region’s rapidly growing energy needs , former Washington Gov. Daniel J. Evans, 98, was called on to impart some words of wisdom.
“I was very pleased that we ended up with a group on the first Council who got together who didn’t spend any time fighting, but an awful lot of time struggling with answers that no one knew at the time. And the end result was real progress, real progress that led to much more sensible leadership in our planning, and the end result was very successful for the Northwest,” Evans told the assembled crowd at The Evergreen State College’s longhouse, s'gʷi gʷi ʔ altxʷ (House of Welcome), on Tuesday.
Evans, a Republican – Washington’s other living three-term governor – was known for pushing for bipartisanship and setting political party affiliation aside to reach compromise. He has maintained that stance over the years since he left the governor’s mansion in 1977.
The event for Evans was part of the annual meeting of the Northwest Power and Conservation Council, a body that develops regional plans for the Columbia River Basin’s energy and natural resources. The Council, which consists of representatives from Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana, discussed the region’s future electricity needs as they relate to the Columbia River Basin, which crosses all four states.
The group met this week in Olympia at Evergreen – where Evans served as college president from 1977 to 1983 – as part of its annual regional rotation. While in Washington, the group took the opportunity to honor Evans, who sat on the inaugural Council from 1981 to 1983.
He was selected by then-Gov. John Spellman to represent Washington when the Council was launched by an act of Congress. Evans sat on the Council until Spellman asked him to fill the U.S. Senate seat vacated when Henry M. Jackson, D-WA, died in office in 1983.
Evans, who answered several questions about his tenure on the Council, said the group’s success was due to bringing together the various elements that had been fighting for resources and control to work with more unity.
“Never suggest that in every case, they will agree. But they will come closer. And I think that that's going to mean an awful lot for the success of the next approach to a major change in the power structure,” Evans said.

From left, Northwest Power and Conservation Council communications specialist Peter Jensen, former Governor Dan Evans, and Council member Les Purce chat during an event hosted by the Council at The Evergreen State College in Olympia on April 9, 2024. (David Ryder for Cascade PBS)
Evans, a Seattle native, became governor in 1964, defeating two-term Gov. Albert Rosellini, a Democrat. In the Washington House, Evans had represented the 43rd District in King County and served as the Republican floor leader.
During Evans’ time as governor, 1965 to 1977, Washington established the state community college system. He also bucked popular opinion at the time and welcomed Vietnamese refugees while other states, including California, were unwelcoming in the aftermath of the Vietnam War .
Gov. Evans was handily reelected twice, including defeating Rosellini again in 1972. While in office he was suggested as a possible running mate for both Richard Nixon and Gerald Ford. Evans was governor until 1977, after deciding not to run again. He became president of Evergreen, a four-year public college founded while he was governor.
However, he was called back into the political sphere by Spellman, first on the Northwest Power and Conservation Council and then in the Senate. During his time in the nation’s capital, he and Washington’s other senator, Democrat Brock Adams, pushed President Ronald Reagan to sign off on adding 1.7 million acres of Washington wildland to the National Parks system, including more than 875,000 acres in the Olympic National Park, now known as the Daniel J. Evans Wilderness . He decided not to run for reelection to the Senate in 1988, decrying the bureaucracy and politics that prevented decisions from being made.
Evans also has said in the past that Washington’s experience with the Washington Public Power Supply System, or WPPSS (pronounced “whoops”), influenced his time on the power planning council.
Throughout the 1950s through 1970s, Washington had tried to increase its power grid with five new nuclear power plants. Planning started in the late 1950s but delays, construction costs and rising interest rates through the 1960s and 1970s led to higher-than-planned expenses, as well as a growing mistrust of nuclear energy, eventually leading to the largest municipal bond default in history in 1982.
Congress created the Council in 1980 to help guide the development of hydroelectric power on the Columbia River and balance the region’s power needs with environmental considerations, as interest in developing hydropower as an alternative to nuclear power was growing.

Former Governor Dan Evans was honored for his conservation legacy at the event. (David Ryder for Cascade PBS)
Today, interest in green energy continues, as states like Washington push away from fossil fuels even as energy demands increase .
Evans wrote in his 2022 autobiography that regional planning, and the increased public outreach that the Council started with, might have averted the WPPSS boondoggle:
“My own culpability sprang from buying into the era’s conventional wisdom – namely the wildly inaccurate, survey-based energy demand forecasts from the mid-1960s,” he wrote. “‘Experts’ told us the Northwest would need 20 more nuclear power plants and two more coal-fired plants by the end of the century to meet residential and industrial energy demands.”
Evans also wrote in his autobiography that his involvement with the Council was “one of the most satisfying in my entire career.”
He praised the bipartisan collaboration at the time between the Democratic governors of Montana and Idaho, Ted Schwinden and John Victor Evans, and the Republican governors of Washington and Oregon, Spellman and Victor Atiyeh, as part of the Council’s success when he was on it.
“They did not allow their political affiliation to interfere with their effort to find the best solution to serve the entire region,” Evans wrote. “Their end result was a bipartisan plan for efficient energy use that produced huge savings for our citizens.”

Council member Les Purce chats with Evans during the event at The Evergreen State College. (David Ryder for Cascade PBS)
Please support independent local news for all.
We rely on donations from readers like you to sustain Crosscut's in-depth reporting on issues critical to the PNW.
About the Authors & Contributors

Venice Buhain is Cascade PBS' associate news editor. She previously covered education at Crosscut, and also worked for KING 5, The Seattle Globalist and TVW News. You can follow her on Twitter @venicebuhain or contact her at [email protected] .

Podcast | Watching "third places" disappear with Vanishing Seattle
We spoke with Cynthia Brothers, founder of the project that highlights disappearing institutions and cultures in the city, about losing public spaces.
- Maleeha Syed

COMMENTS
You might want to use google scholar or google books and type in 'Benefits of group work' to find some quality scholarly sources to cite. Step 3. Explore the general challenges group work can cause. Step 3 is the mirror image of Step 2. For this step, explore the challenges posed by group work.
Group Work That Really Works. A group essay writing activity pushes every student to contribute—and it can lead to real growth in writing ability. By Jori Krulder. July 6, 2018. ©Shutterstock/Lucky Business. Group work is a mode of learning I've struggled with for much of my teaching career. The concept of students working together to ...
Published: Mar 20, 2024. Table of contents. Group work is a common practice in academic settings, with many courses incorporating group projects and assignments as part of the curriculum. In this reflection paper, I will discuss my experiences with group work, the challenges I have faced, and the lessons I have learned from working in a team.
The range of possible collaboration varies from a group of co-authors who go through each portion of the writing process together, writing as a group with one voice, to a group with a primary author who does the majority of the work and then receives comments or edits from the co-authors. Group projects for classes should usually fall towards ...
At Design 39, a K-8 school in San Diego, groups and roles are assigned randomly using Random Team Generator, but ClassDojo, Team Shake, and drawing students' names from a container can also do the trick.In a practice called vertical learning, Design 39 students conduct group work publicly, writing out their thought processes on whiteboards to facilitate group feedback.
7. Be a good peer editor. Group writing assignments can be awkward for various reasons, but peer editing can be particularly uncomfortable. However, nailing this step is integral to the success of your group writing essay. As any editor will tell you, the line between constructive and destructive criticism can be a perilous one to walk.
During the 2020-21 school year, we asked 176 questions, and you can find them all below or here as a PDF. The questions are divided into two categories — those that provide opportunities for ...
2. Outline - Organize the ideas in a structured outline that could be used as a framework for the paper. Arrange the ideas in a way that addresses the prompt and the goal of the paper. 3. Research - Conduct any necessary research on the topic. For this step, dividing the work among group members would be beneficial. 4.
Group work helps keep you on task. It's harder to procrastinate when working with others. Working in groups, especially writing texts together, mirrors working styles common outside school. In business, industry, and research organizations, collaborative work is the norm rather than the exception.
Students working on collaborative writing projects have said that their collaborative writing process involved more brainstorming, discussion, and diverse opinions from group members. Some even said that collaborative writing entailed less of an individual time commitment than solo papers. Although collaborative writing implies that every part ...
Teamwork and Self-Awareness. In order for a group of people to effectively collaborate and ensure long-term teamwork on a project, there must be a sense of self-awareness in each member. Effective Teambuilding for Childcare Center. After pairing the teachers, the third stage will be used to guide and mentor the team.
In this essay will discuss the benefits of group work and how important is it. Secondly, it will move on to look at the obstacles and challenges in group work. Finally, it will argue that the factors that affect the success of groupwork and what skill can develop in group work. Group working is. 1083 Words.
Personal Examples of Prior Group Work. PAGES 2 WORDS 361. Group Work. The author of this response has been in a number of groups. Some of them have been good experiences while others have been controlled to complete chaos. Whether it be work or school groups, getting the wrong group of people together can cause issues.
Conclusion. In conclusion, the phrase "my experience working in a group" encapsulates a journey marked by challenges, benefits, and personal growth. While conflicts and differing opinions can pose hurdles, the advantages of. diverse perspectives, skill development, and life lessons make group work a worthwhile endeavor. As I reflect.
Psychologists have studied small groups for well over 60 years. Much of that research was initially conducted by social psychologists who were interested in how individual behavior was influenced by the group context and in factors that influenced interpersonal processes and group behavior (McGrath, 1964).For example, early work focused on power and social influence, social forces that bond ...
Group essays can work with just about any type of writing assignment, but I will give you specific examples that I've tried over the years. Literary Analysis Group Essay: Critical Lenses - Students analyze a text through critical lenses then either group with the same lens and write 3 individual perspectives or group with people of ...
Great article. I've been successfully implementing primarily PBL in the undergrad classroom for years. I'm getting ready to launch the most ambitious group work project I've ever undertaken with my students - 130 students and 20 nonprofit organizations broken into collaborative teams to study each organization's volunteer programs, to make recommendations for improving or refreshing ...
Group work refers to a collaborative effort of members towards a common goal. It involves sharing tasks, responsibilities, and support in achieving an objective. Members work together to build a consensus by sharing their expertise, experience, and ideas. Group work encourages communication, problem-solving, decision-making, and leadership ...
1071 Words. 5 Pages. Open Document. It's universally known that group assignments can be a headache to deal with. Working in a group can be very complicated whether they are at school or at work. However, group assignments do not have to be difficult. There are many ways one can make this situation more desirable.
Working in a group increases the productivity and improves once performance. This semester, I and other 4 of my classmates were assigned to make a group assignment with a topic of "Agencies that deals with emotional/physical disabilities". The purpose of this essay is to discuss my experience working in a group, and the lessons I have learnt.
Group work also introduces more unpredictability in teaching, since groups may approach tasks and solve problems in novel, interesting ways. This can be refreshing for instructors. Additionally, group assignments can be useful when there are a limited number of viable project topics to distribute among students. And they can reduce the number ...
Individual Reflective Report on Group Work. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Collaboration is a vital skill in today's workplace, and group work is a common way to develop it. However, working in a group can be challenging, with ...
500 Words Essay on Group Work What is Group Work? Group work is when two or more people work together to achieve a common goal. It is often used in schools, colleges, and workplaces. The main idea behind group work is to encourage people to work together, share ideas, and learn from each other.
Dan Richards is a serial founder, and as a former CEO, he led the turnaround of a public company in the financial industry. Today, he is an award-winning faculty member at the Rotman School of ...
Rebecca Knight is a journalist who writes about all things related to the changing nature of careers and the workplace. Her essays and reported stories have been featured in The Boston Globe ...
As DEI work faces increasing scrutiny socially, politically, and legally, organizations are taking extra care to re-evaluate their DEI efforts. Leaders are right to consider change, not as a ...
Most of the responses to the open-ended question fell into one of these six themes: Teaching is a hard job. About half of teachers (51%) said they want the public to know that teaching is a difficult job and that teachers are hardworking.
While in Washington, the group took the opportunity to honor Evans, who sat on the inaugural Council from 1981 to 1983. He was selected by then-Gov. John Spellman to represent Washington when the ...
and regional partners to work with farms to support the improvement of water quality across the state of Vermont through education and outreach, technical assistance, organizational capacity development, and conservation practice surveys. The eligible activity of organizational capacity development is related to partner organizations
How does DMC enrollment work? •Farmer signs up via Farm Service Agency and decides how to pay for premium - in full or via milk check deduction. Sign up process includes: •Selecting coverage level - $9.50 rate is highest coverage level and what is recommended •Premium calculated by coverage level - at $9.50 it is $0.15 per hundredweight